Spacing in math mode
This article explains how to insert spaces of different widths in math mode.
Introduction
Adjusting (La)TeX's default math mode spacing can be useful in certain situations; let's see an example:
\documentclass{article}
\usepackage{amssymb}
\begin{document}
Assume we have the next sets
\[
S = \{ z \in \mathbb{C}\, |\, |z| < 1 \} \quad \textrm{and} \quad S_2=\partial{S}
\]
\end{document}
This example produces the following output:
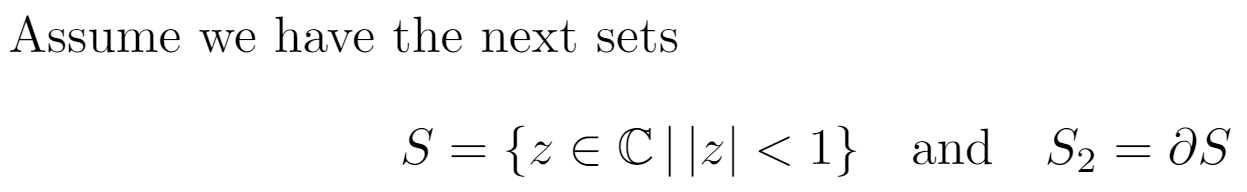
As you see in this example, a mathematical text can be explicitly spaced by means of some special commands.
Spaces
The example below contains a complete list of spaces inserted using various commands and demonstrates their effect on the typeset math.
\documentclass{article}
\usepackage{amsmath}
\begin{document}
Spaces in mathematical mode.
\begin{align*}
f(x) &= x^2\! +3x\! +2 \\
f(x) &= x^2+3x+2 \\
f(x) &= x^2\, +3x\, +2 \\
f(x) &= x^2\: +3x\: +2 \\
f(x) &= x^2\; +3x\; +2 \\
f(x) &= x^2\ +3x\ +2 \\
f(x) &= x^2\quad +3x\quad +2 \\
f(x) &= x^2\qquad +3x\qquad +2
\end{align*}
\end{document}
This example produces the following output:

Check the reference guide for a description of the commands.
Note: to see a description of the align* environment see Aligning equations with amsmath
Operators spacing
Spacing around operators and relations in math mode are governed by specific skip widths:
\thinmuskip(by default it is equal to 3 mu)\medmuskip(by default it is equal to 4 mu)\thickmuskip(by default it is equal to 5 mu)
\begin{align*}
3ax+4by=5cz\\
3ax<4by+5cz
\end{align*}
This example produces the following output:

For relational operators, such as \(<\), \(>\) and \(=\), LaTeX establishes \thickmuskip space. But for binary operators such as \(+\), \(-\) and \(\times\), the \medmuskip space is set. The difference is almost unnoticeable.
User-defined binary and relational operators
You can force the spacing used in binary or relational operators, so you can define your own.
\begin{align*}
34x^2a \mathbin{\#} 13bc \\
34x^2a \mathrel{\#} 13bc
\end{align*}
This example produces the following output:
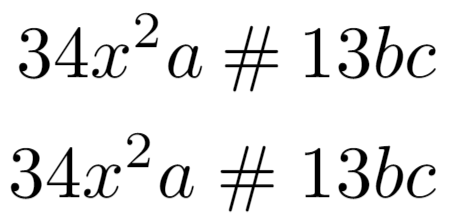
The previous example sets a particular spacing before and after # by using \mathrel (relational) and \mathbin (binary) commands.
Reference guide
Description of spacing commands
| LaTeX code | Description |
|---|---|
\quad |
space equal to the current font size (= 18 mu) |
\, |
3/18 of \quad (= 3 mu)
|
\: |
4/18 of \quad (= 4 mu)
|
\; |
5/18 of \quad (= 5 mu)
|
\! |
-3/18 of \quad (= -3 mu)
|
\ (space after backslash!) |
equivalent of space in normal text |
\qquad |
twice of \quad (= 36 mu)
|
Further reading
For more information see
Overleaf guides
- Creating a document in Overleaf
- Uploading a project
- Copying a project
- Creating a project from a template
- Using the Overleaf project menu
- Including images in Overleaf
- Exporting your work from Overleaf
- Working offline in Overleaf
- Using Track Changes in Overleaf
- Using bibliographies in Overleaf
- Sharing your work with others
- Using the History feature
- Debugging Compilation timeout errors
- How-to guides
- Guide to Overleaf’s premium features
LaTeX Basics
- Creating your first LaTeX document
- Choosing a LaTeX Compiler
- Paragraphs and new lines
- Bold, italics and underlining
- Lists
- Errors
Mathematics
- Mathematical expressions
- Subscripts and superscripts
- Brackets and Parentheses
- Matrices
- Fractions and Binomials
- Aligning equations
- Operators
- Spacing in math mode
- Integrals, sums and limits
- Display style in math mode
- List of Greek letters and math symbols
- Mathematical fonts
- Using the Symbol Palette in Overleaf
Figures and tables
- Inserting Images
- Tables
- Positioning Images and Tables
- Lists of Tables and Figures
- Drawing Diagrams Directly in LaTeX
- TikZ package
References and Citations
- Bibliography management with bibtex
- Bibliography management with natbib
- Bibliography management with biblatex
- Bibtex bibliography styles
- Natbib bibliography styles
- Natbib citation styles
- Biblatex bibliography styles
- Biblatex citation styles
Languages
- Multilingual typesetting on Overleaf using polyglossia and fontspec
- Multilingual typesetting on Overleaf using babel and fontspec
- International language support
- Quotations and quotation marks
- Arabic
- Chinese
- French
- German
- Greek
- Italian
- Japanese
- Korean
- Portuguese
- Russian
- Spanish
Document structure
- Sections and chapters
- Table of contents
- Cross referencing sections, equations and floats
- Indices
- Glossaries
- Nomenclatures
- Management in a large project
- Multi-file LaTeX projects
- Hyperlinks
Formatting
- Lengths in LaTeX
- Headers and footers
- Page numbering
- Paragraph formatting
- Line breaks and blank spaces
- Text alignment
- Page size and margins
- Single sided and double sided documents
- Multiple columns
- Counters
- Code listing
- Code Highlighting with minted
- Using colours in LaTeX
- Footnotes
- Margin notes
Fonts
Presentations
Commands
Field specific
- Theorems and proofs
- Chemistry formulae
- Feynman diagrams
- Molecular orbital diagrams
- Chess notation
- Knitting patterns
- CircuiTikz package
- Pgfplots package
- Typesetting exams in LaTeX
- Knitr
- Attribute Value Matrices
Class files
- Understanding packages and class files
- List of packages and class files
- Writing your own package
- Writing your own class