Brackets and Parentheses
Introduction
Parentheses and brackets are very common in mathematical formulas. You can easily control the size and style of brackets in LaTeX; this article explains how.
Here's an table of listing some common math braces and parentheses used in LaTeX:
| Type | LaTeX markup | Renders as |
|---|---|---|
| Parentheses; round brackets | (x+y)
|
\((x+y)\) |
| Brackets; square brackets | [x+y]
|
\([x+y]\) |
| Braces; curly brackets | \{ x+y \}
|
\(\{ x+y \}\) |
| Angle brackets | \langle x+y \rangle
|
\(\langle x+y\rangle\) |
| Pipes; vertical bars | |x+y|
|
\(\displaystyle| x+y |\) |
| Double pipes | \|x+y\|
|
\(\| x+y \|\) |
Some examples
The size of brackets and parentheses can be manually set, or they can be resized dynamically in your document, as shown in the next example:
\[
F = G \left( \frac{m_1 m_2}{r^2} \right)
\]
Open this LaTeX fragment in Overleaf
The above example produces the following output:
\[
F = G \left( \frac{m_1 m_2}{r^2} \right)
\]
Notice that to insert the parentheses or brackets, the \left and \right commands are used. Even if you are using only one bracket, both commands are mandatory. \left and \right can dynamically adjust the size, as shown by the next example:
\[
\left[ \frac{ N } { \left( \frac{L}{p} \right) - (m+n) } \right]
\]
Open this LaTeX fragment in Overleaf
The above example produces the following output:
\[\left[ \frac{ N } { \left( \frac{L}{p} \right) - (m+n) } \right]\]
When writing multi-line equations with the align, align* or aligned environments, the \left and \right commands must be balanced on each line and on the same side of &. Therefore the following code snippet will fail with errors:
\begin{align*}
y = 1 + & \left( \frac{1}{x} + \frac{1}{x^2} + \frac{1}{x^3} + \ldots \\
& \quad + \frac{1}{x^{n-1}} + \frac{1}{x^n} \right)
\end{align*}
Open this LaTeX fragment in Overleaf (with errors)
The solution is to use "invisible" brackets to balance things out, i.e. adding a \right. at the end of the first line, and a \left. at the start of the second line after &:
\begin{align*}
y = 1 + & \left( \frac{1}{x} + \frac{1}{x^2} + \frac{1}{x^3} + \ldots \right. \\
&\left. \quad + \frac{1}{x^{n-1}} + \frac{1}{x^n} \right)
\end{align*}
Open this LaTeX fragment in Overleaf
The above example produces the following output:
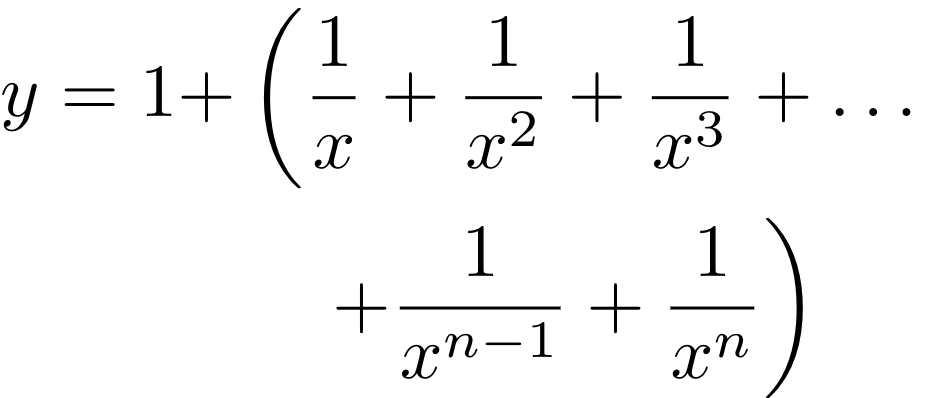
Controlling types and sizes
The size of the brackets can be controlled explicitly, as shown in this LaTeX code fragment:
\[
\Biggl \langle 3x+7 \biggr \rangle
\]
Open this LaTeX fragment in Overleaf
The above example produces the following output:
\[\Biggl \langle 3x+7 \biggr \rangle\]
The commands \Biggl and \biggr establish the size of the delimiters < and > respectively, with the l or r indicating whether it's the left or the right parenthesis. For a complete list of parentheses and sizes see the reference guide.
Reference guide
| LaTeX markup | Renders as |
|---|---|
\bigl( \Bigl( \biggl( \Biggl(
|
|
\bigr] \Bigr] \biggr] \Biggr]
|
|
\bigl\{ \Bigl\{ \biggl\{ \Biggl\{
|
|
\bigl \langle \Bigl \langle \biggl \langle \Biggl \langle
|
|
\bigr \rangle \Bigr \rangle \biggr \rangle \Biggr \rangle
|
|
\big| \Big| \bigg| \Bigg|
|
\(\displaystyle\big| \; \Big| \; \bigg| \; \Bigg|\) |
\big\| \Big\| \bigg\| \Bigg\|
|
\(\displaystyle\big\| \; \Big\| \; \bigg\| \; \Bigg\|\) |
\bigl \lceil \Bigl \lceil \biggl \lceil \Biggl \lceil
|
\(\displaystyle\big \lceil \Big \lceil \bigg \lceil \Bigg \lceil\) |
\bigr \rceil \Bigr \rceil \biggr \rceil \Biggr \rceil
|
\(\displaystyle\big \rceil \Big \rceil \bigg \rceil \Bigg \rceil\) |
\bigl \lfloor \Bigl \lfloor \biggl \lfloor \Biggl \lfloor
|
\(\displaystyle\big \lfloor \Big \lfloor \bigg \lfloor \Bigg \lfloor\) |
\bigr \rfloor \Bigr \rfloor \biggr \rfloor \Biggr \rfloor
|
\(\displaystyle\big \rfloor \Big \rfloor \bigg \rfloor \Bigg \rfloor\) |
Further reading
Overleaf guides
- Creating a document in Overleaf
- Uploading a project
- Copying a project
- Creating a project from a template
- Using the Overleaf project menu
- Including images in Overleaf
- Exporting your work from Overleaf
- Working offline in Overleaf
- Using Track Changes in Overleaf
- Using bibliographies in Overleaf
- Sharing your work with others
- Using the History feature
- Debugging Compilation timeout errors
- How-to guides
- Guide to Overleaf’s premium features
LaTeX Basics
- Creating your first LaTeX document
- Choosing a LaTeX Compiler
- Paragraphs and new lines
- Bold, italics and underlining
- Lists
- Errors
Mathematics
- Mathematical expressions
- Subscripts and superscripts
- Brackets and Parentheses
- Matrices
- Fractions and Binomials
- Aligning equations
- Operators
- Spacing in math mode
- Integrals, sums and limits
- Display style in math mode
- List of Greek letters and math symbols
- Mathematical fonts
- Using the Symbol Palette in Overleaf
Figures and tables
- Inserting Images
- Tables
- Positioning Images and Tables
- Lists of Tables and Figures
- Drawing Diagrams Directly in LaTeX
- TikZ package
References and Citations
- Bibliography management with bibtex
- Bibliography management with natbib
- Bibliography management with biblatex
- Bibtex bibliography styles
- Natbib bibliography styles
- Natbib citation styles
- Biblatex bibliography styles
- Biblatex citation styles
Languages
- Multilingual typesetting on Overleaf using polyglossia and fontspec
- Multilingual typesetting on Overleaf using babel and fontspec
- International language support
- Quotations and quotation marks
- Arabic
- Chinese
- French
- German
- Greek
- Italian
- Japanese
- Korean
- Portuguese
- Russian
- Spanish
Document structure
- Sections and chapters
- Table of contents
- Cross referencing sections, equations and floats
- Indices
- Glossaries
- Nomenclatures
- Management in a large project
- Multi-file LaTeX projects
- Hyperlinks
Formatting
- Lengths in LaTeX
- Headers and footers
- Page numbering
- Paragraph formatting
- Line breaks and blank spaces
- Text alignment
- Page size and margins
- Single sided and double sided documents
- Multiple columns
- Counters
- Code listing
- Code Highlighting with minted
- Using colours in LaTeX
- Footnotes
- Margin notes
Fonts
Presentations
Commands
Field specific
- Theorems and proofs
- Chemistry formulae
- Feynman diagrams
- Molecular orbital diagrams
- Chess notation
- Knitting patterns
- CircuiTikz package
- Pgfplots package
- Typesetting exams in LaTeX
- Knitr
- Attribute Value Matrices
Class files
- Understanding packages and class files
- List of packages and class files
- Writing your own package
- Writing your own class

![{\displaystyle {\big ]}{\Big ]}{\bigg ]}{\Bigg ]}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/7aec0f2dd592401b2f08fe01f8908e45955784aa)


