KR20130038603A - Method of manufacturing a magnetic memory device - Google Patents
Method of manufacturing a magnetic memory device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR20130038603A KR20130038603A KR1020110103048A KR20110103048A KR20130038603A KR 20130038603 A KR20130038603 A KR 20130038603A KR 1020110103048 A KR1020110103048 A KR 1020110103048A KR 20110103048 A KR20110103048 A KR 20110103048A KR 20130038603 A KR20130038603 A KR 20130038603A
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- layer
- pattern
- sacrificial layer
- magnetic
- main
- Prior art date
Links
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 21
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 81
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 20
- 238000005530 etching Methods 0.000 claims description 91
- RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Titanium Chemical compound [Ti] RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 14
- 229910052715 tantalum Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 14
- GUVRBAGPIYLISA-UHFFFAOYSA-N tantalum atom Chemical compound [Ta] GUVRBAGPIYLISA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 14
- 239000010936 titanium Substances 0.000 claims description 14
- 229910052719 titanium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 14
- WFKWXMTUELFFGS-UHFFFAOYSA-N tungsten Chemical compound [W] WFKWXMTUELFFGS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 14
- 229910052721 tungsten Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 14
- 239000010937 tungsten Substances 0.000 claims description 14
- NRTOMJZYCJJWKI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Titanium nitride Chemical compound [Ti]#N NRTOMJZYCJJWKI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 13
- 238000001039 wet etching Methods 0.000 claims description 13
- 238000000059 patterning Methods 0.000 claims description 12
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 11
- 238000010884 ion-beam technique Methods 0.000 claims description 11
- 229910052814 silicon oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 11
- MZLGASXMSKOWSE-UHFFFAOYSA-N tantalum nitride Chemical compound [Ta]#N MZLGASXMSKOWSE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 11
- KRHYYFGTRYWZRS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Fluorane Chemical compound F KRHYYFGTRYWZRS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 10
- 229910052581 Si3N4 Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 10
- HQVNEWCFYHHQES-UHFFFAOYSA-N silicon nitride Chemical compound N12[Si]34N5[Si]62N3[Si]51N64 HQVNEWCFYHHQES-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 10
- 230000003071 parasitic effect Effects 0.000 claims description 6
- PXGOKWXKJXAPGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Fluorine Chemical compound FF PXGOKWXKJXAPGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000011737 fluorine Substances 0.000 claims description 5
- 229910052731 fluorine Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000012528 membrane Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 238000010790 dilution Methods 0.000 claims 1
- 239000012895 dilution Substances 0.000 claims 1
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 description 278
- 239000011229 interlayer Substances 0.000 description 18
- 238000005229 chemical vapour deposition Methods 0.000 description 14
- KJTLSVCANCCWHF-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ruthenium Chemical compound [Ru] KJTLSVCANCCWHF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 13
- 229910052707 ruthenium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 13
- 229910001260 Pt alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 12
- 238000000231 atomic layer deposition Methods 0.000 description 12
- BASFCYQUMIYNBI-UHFFFAOYSA-N platinum Chemical compound [Pt] BASFCYQUMIYNBI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 11
- KDLHZDBZIXYQEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Palladium Chemical compound [Pd] KDLHZDBZIXYQEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 9
- 229910045601 alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 9
- 239000000956 alloy Substances 0.000 description 9
- 239000004020 conductor Substances 0.000 description 7
- 239000012535 impurity Substances 0.000 description 7
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 7
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 7
- 239000011651 chromium Substances 0.000 description 6
- 239000010949 copper Substances 0.000 description 6
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 description 6
- 239000010931 gold Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000002955 isolation Methods 0.000 description 4
- CPLXHLVBOLITMK-UHFFFAOYSA-N magnesium oxide Inorganic materials [Mg]=O CPLXHLVBOLITMK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 239000000395 magnesium oxide Substances 0.000 description 4
- AXZKOIWUVFPNLO-UHFFFAOYSA-N magnesium;oxygen(2-) Chemical compound [O-2].[Mg+2] AXZKOIWUVFPNLO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 229910052763 palladium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 229910052697 platinum Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 229910021420 polycrystalline silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 229920005591 polysilicon Polymers 0.000 description 4
- VYZAMTAEIAYCRO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Chromium Chemical compound [Cr] VYZAMTAEIAYCRO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Copper Chemical compound [Cu] RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 229910020708 Co—Pd Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 229910020707 Co—Pt Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 229910001252 Pd alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 229910052804 chromium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 239000000696 magnetic material Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229910000510 noble metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 238000001020 plasma etching Methods 0.000 description 3
- 125000006850 spacer group Chemical group 0.000 description 3
- 229910018072 Al 2 O 3 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 229910000521 B alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- ZOXJGFHDIHLPTG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Boron Chemical compound [B] ZOXJGFHDIHLPTG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Carbon Chemical compound [C] OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910004298 SiO 2 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 229910000577 Silicon-germanium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- BQCADISMDOOEFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silver Chemical compound [Ag] BQCADISMDOOEFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910008423 Si—B Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229910052796 boron Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 229910052799 carbon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- JKWMSGQKBLHBQQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N diboron trioxide Chemical compound O=BOB=O JKWMSGQKBLHBQQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000003085 diluting agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N gold Chemical compound [Au] PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910052737 gold Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 238000005468 ion implantation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000003475 lamination Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000005415 magnetization Effects 0.000 description 2
- TWNQGVIAIRXVLR-UHFFFAOYSA-N oxo(oxoalumanyloxy)alumane Chemical compound O=[Al]O[Al]=O TWNQGVIAIRXVLR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910052709 silver Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000004332 silver Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910020598 Co Fe Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910002519 Co-Fe Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910019236 CoFeB Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N Iron Chemical compound [Fe] XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910003271 Ni-Fe Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical compound [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LEVVHYCKPQWKOP-UHFFFAOYSA-N [Si].[Ge] Chemical compound [Si].[Ge] LEVVHYCKPQWKOP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000006227 byproduct Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910017052 cobalt Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010941 cobalt Substances 0.000 description 1
- GUTLYIVDDKVIGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N cobalt atom Chemical compound [Co] GUTLYIVDDKVIGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052732 germanium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- GNPVGFCGXDBREM-UHFFFAOYSA-N germanium atom Chemical compound [Ge] GNPVGFCGXDBREM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000009413 insulation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012212 insulator Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000010354 integration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910044991 metal oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000004706 metal oxides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000000206 photolithography Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229920002120 photoresistant polymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 238000007517 polishing process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002356 single layer Substances 0.000 description 1
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10N—ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10N50/00—Galvanomagnetic devices
- H10N50/10—Magnetoresistive devices
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G11—INFORMATION STORAGE
- G11C—STATIC STORES
- G11C13/00—Digital stores characterised by the use of storage elements not covered by groups G11C11/00, G11C23/00, or G11C25/00
- G11C13/0002—Digital stores characterised by the use of storage elements not covered by groups G11C11/00, G11C23/00, or G11C25/00 using resistive RAM [RRAM] elements
- G11C13/0004—Digital stores characterised by the use of storage elements not covered by groups G11C11/00, G11C23/00, or G11C25/00 using resistive RAM [RRAM] elements comprising amorphous/crystalline phase transition cells
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10B—ELECTRONIC MEMORY DEVICES
- H10B61/00—Magnetic memory devices, e.g. magnetoresistive RAM [MRAM] devices
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10N—ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10N50/00—Galvanomagnetic devices
- H10N50/01—Manufacture or treatment
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Crystallography & Structural Chemistry (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Hall/Mr Elements (AREA)
- Mram Or Spin Memory Techniques (AREA)
Abstract
Description
본 발명은 자기 메모리 소자의 제조 방법에 관한 것으로서, 더욱 상세하게는, 자기 저항을 이용하는 자기 메모리 소자의 제조 방법에 관한 것이다.The present invention relates to a method of manufacturing a magnetic memory device, and more particularly, to a method of manufacturing a magnetic memory device using a magnetoresistance.
자기 메모리 소자는 두 개의 자성체와 그 사이에 개재된 절연막을 포함하는 자기 터널 접합 패턴(magnetic tunnel junction pattern)을 사용하여 데이터를 읽고 쓰는 불휘발성 메모리 장치이다. 두 자성체의 자화(magnetization) 방향에 따라 상기 자기 터널 접합 패턴의 저항값이 달라질 수 있는데, 이러한 저항값의 차이를 이용하여 데이터를 프로그래밍 또는 제거할 수 있다. 그 중, 스핀 트랜스퍼 토크(spin transfer torque: STT) 현상을 이용한 자기 메모리 소자는 한쪽 방향으로 스핀(spin)이 분극화(polarized)된 전류를 흘려줄 때, 전자의 스핀 전달에 의해 자성체의 자화 방향이 달라지는 방식을 이용한다. STT 현상을 이용한 자기 메모리 소자의 경우 셀의 크기가 작아질수록 요구되는 전류가 작아지므로 고집적화에 유리한 장점을 갖는다. 그러나, 셀의 크기가 작아질수록 상기 자기 터널 접합 패턴의 패터닝이 어려운 문제점이 있다. 예를 들어, 자성체의 패터닝에 의한 식각 잔류물들이 자기 터널 접합 패턴의 측벽 상에 재증착되어 전기적 단락 등이 발생하는 문제점이 있다.The magnetic memory device is a nonvolatile memory device that reads and writes data using a magnetic tunnel junction pattern including two magnetic bodies and an insulating layer interposed therebetween. The resistance value of the magnetic tunnel junction pattern may vary depending on the magnetization direction of the two magnetic materials. The data may be programmed or removed using the difference in the resistance values. Among them, in the magnetic memory device using spin transfer torque (STT) phenomenon, the magnetization direction of the magnetic material is changed by the spin transfer of electrons when a current in which the spin is polarized flows in one direction. Use a different way. In the case of the magnetic memory device using the STT phenomenon, the smaller the size of the cell, the smaller the required current, which has the advantage of high integration. However, the smaller the cell size is, the more difficult the patterning of the magnetic tunnel junction pattern is. For example, the etching residues due to the patterning of the magnetic material are redeposited on the sidewall of the magnetic tunnel junction pattern, thereby causing an electrical short.
본 발명이 이루고자 하는 기술적 과제는, 패터닝시 전기적 단락을 방지하는 자기 메모리 소자의 제조 방법을 제공하는 것이다.SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION The present invention has been made in an effort to provide a method of manufacturing a magnetic memory device that prevents an electrical short during patterning.
상기 기술적 과제를 달성하기 위한 본 발명에 따른 자기 메모리 소자의 제조 방법에서, 기판 상에 하부 자성층 및 절연층을 순차적으로 형성한다. 상기 절연층 상에 상부 자성 패턴을 형성한다. 상기 상부 자성 패턴의 측벽 상에 주희생막을 형성한다. 상기 상부 자성 패턴 및 상기 주희생막을 식각 마스크로 사용하여 상기 절연층 및 상기 하부 자성층을 패터닝하여 절연 패턴 및 하부 자성 패턴을 형성한다. 상기 주희생막을 제거한다.In the method of manufacturing a magnetic memory device according to the present invention for achieving the above technical problem, a lower magnetic layer and an insulating layer are sequentially formed on a substrate. An upper magnetic pattern is formed on the insulating layer. A main sacrificial layer is formed on the sidewalls of the upper magnetic pattern. The insulating layer and the lower magnetic layer are patterned by using the upper magnetic pattern and the main sacrificial film as an etching mask to form an insulating pattern and a lower magnetic pattern. Remove the main diluent.
예시적인 실시예들에 있어서, 상기 주희생막이 제거될 때, 상기 주희생막의 측벽 상에 재증착되는 상기 하부 자성층의 식각 잔류물이 함께 제거될 수 있다.In example embodiments, when the main sacrificial layer is removed, an etch residue of the lower magnetic layer redeposited on the sidewall of the main sacrificial layer may be removed together.
예시적인 실시예들에 있어서, 상기 주희생막은 20Å 이하의 두께를 가질 수 있다.In example embodiments, the main sacrificial film may have a thickness of 20 μs or less.
예시적인 실시예들에 있어서, 상기 상부 자성 패턴을 형성할 때, 상기 상부 자성층 상에 상부 전극을 형성하고, 상기 상부 전극의 측벽 상에 부희생막을 형성하며, 상기 상부 전극 및 상기 부희생막을 식각 마스크로 사용하여 상기 상부 자성층을 패터닝함으로써 상기 절연층 상에 상기 상부 자성 패턴을 형성하고, 상기 부희생막을 제거할 수 있다.In example embodiments, when the upper magnetic pattern is formed, an upper electrode is formed on the upper magnetic layer, an auxiliary sacrificial layer is formed on sidewalls of the upper electrode, and the upper electrode and the auxiliary sacrificial layer are etched. The upper magnetic layer may be patterned using a mask to form the upper magnetic pattern on the insulating layer, and the side layer may be removed.
예시적인 실시예들에 있어서, 상기 부희생막이 제거될 때, 상기 부희생막의 측벽 상에 재증착되는 상기 상부 자성층의 식각 잔류물이 함께 제거될 수 있다.In example embodiments, when the parasitic layer is removed, an etching residue of the upper magnetic layer which is redeposited on the sidewall of the parasitic layer may be removed together.
예시적인 실시예들에 있어서, 상기 부희생막은 20Å 이하의 두께를 가질 수 있다.In example embodiments, the para sacrificial layer may have a thickness of 20 μs or less.
예시적인 실시예들에 있어서, 상기 주희생막 및 부희생막은 각각 실리콘 산화물, 실리콘 질화물, 티타늄, 탄탈륨, 티타늄 질화물, 탄탈륨 질화물 또는 텅스텐을 사용하여 형성될 수 있다. In example embodiments, the main sacrificial layer and the para sacrificial layer may be formed using silicon oxide, silicon nitride, titanium, tantalum, titanium nitride, tantalum nitride, or tungsten, respectively.
예시적인 실시예들에 있어서, 이온 빔 에칭(ion beam etching) 공정 또는 습식 식각(wet etching) 공정을 사용하여 상기 주희생막이 제거될 수 있다.In example embodiments, the main sacrificial layer may be removed using an ion beam etching process or a wet etching process.
예시적인 실시예들에 있어서, 불산 등 플루오르를 함유하는 식각액을 사용한 습식 식각 공정을 사용하여 상기 주희생막이 제거될 수 있다.In example embodiments, the main sacrificial layer may be removed using a wet etching process using an etchant containing fluorine such as hydrofluoric acid.
상기 기술적 과제를 달성하기 위한 본 발명에 따른 자기 메모리 소자의 제조 방법에서, 기판 상에 하부 자성층, 절연층 및 상부 자성층을 순차적으로 형성한다. 상기 상부 자성층 상에 상부 전극을 형성한다. 상기 상부 전극의 측벽 상에 부희생막을 형성한다. 상기 상부 전극 및 상기 부희생막을 식각 마스크로 사용하여 상기 상부 자성층을 식각함으로써 상부 자성 패턴을 형성한다. 상기 부희생막을 제거한다. 상기 상부 전극 및 상기 상부 자성 패턴의 측벽들 상에 주희생막을 형성한다. 상기 상부 전극, 상기 상부 자성 패턴 및 상기 주희생막을 식각 마스크로 사용하여 상기 절연층 및 상기 하부 자성층을 순차적으로 식각함으로써 절연 패턴 및 하부 자성 패턴을 형성한다. 상기 주희생막을 제거한다.In the method of manufacturing a magnetic memory device according to the present invention for achieving the above technical problem, a lower magnetic layer, an insulating layer and an upper magnetic layer are sequentially formed on a substrate. An upper electrode is formed on the upper magnetic layer. An auxiliary sacrificial layer is formed on the sidewall of the upper electrode. An upper magnetic pattern is formed by etching the upper magnetic layer using the upper electrode and the auxiliary sacrificial layer as an etching mask. The parasitic membrane is removed. A main sacrificial layer is formed on sidewalls of the upper electrode and the upper magnetic pattern. The insulating layer and the lower magnetic pattern are sequentially formed by etching the insulating layer and the lower magnetic layer using the upper electrode, the upper magnetic pattern, and the main sacrificial layer as an etching mask. Remove the main diluent.
본 발명에 따른 자기 메모리 소자의 제조 방법은, 상부 자성 패턴 형성시 부희생막 측벽 상에 식각 잔류물들이 재증착됨에 따라 상기 식각 잔류물들의 제거가 용이하다. 또한, 하부 자성 패턴 형성시 주희생막 측벽에 식각 잔류물들이 재증착됨에 따라 상기 식각 잔류물들의 제거가 용이하다. 따라서, 상기 식각 잔류물들이 상부 자성 패턴 및 하부 자성 패턴 측벽들 상에 재증착됨에 따라 발생하는 상기 자기 메모리 소자의 전기적 단락을 방지할 수 있다.In the method of manufacturing the magnetic memory device according to the present invention, as the etching residues are redeposited on the sidewalls of the sacrificial layer during the formation of the upper magnetic pattern, the etching residues are easily removed. In addition, as the etching residues are redeposited on the sidewalls of the main sacrificial layer during the formation of the lower magnetic pattern, the etching residues are easily removed. Thus, an electrical short circuit of the magnetic memory device may be prevented as the etch residues are redeposited on the upper magnetic pattern and the lower magnetic pattern sidewalls.
도 1 내지 도 7은 예시적인 실시예들에 따른 자기 메모리 소자의 제조 방법을 설명하기 위한 단면도들이다.
도 8 내지 도 12는 예시적인 실시예들에 따른 자기 메모리 소자의 제조 방법을 나타내는 단면도들이다.
도 13 내지 도 21은 예시적인 실시예들에 따른 반도체 장치의 제조 방법을 설명하기 위한 단면도들이다.1 to 7 are cross-sectional views illustrating a method of manufacturing a magnetic memory device in accordance with example embodiments.
8 through 12 are cross-sectional views illustrating a method of manufacturing a magnetic memory device in accordance with example embodiments.
13 to 21 are cross-sectional views illustrating a method of manufacturing a semiconductor device in accordance with example embodiments.
이하, 첨부된 도면을 참조하여 본 발명의 바람직한 실시예를 상세히 설명하기로 한다.Hereinafter, exemplary embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings.
본 발명의 실시예들은 당해 기술 분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자에게 본 발명을 더욱 완전하게 설명하기 위하여 제공되는 것이며, 하기 실시예는 여러 가지 다른 형태로 변형될 수 있으며, 본 발명의 범위가 하기 실시예에 한정되는 것은 아니다. 오히려 이들 실시예들은 본 개시를 더욱 충실하고 완전하게 하고, 당업자에게 본 발명의 사상을 완전하게 전달하기 위하여 제공되는 것이다. 또한, 도면에서 각 층의 두께나 크기는 설명의 편의 및 명확성을 위하여 과장된 것이다.The embodiments of the present invention are described in order to more fully explain the present invention to those skilled in the art, and the following embodiments may be modified into various other forms, It is not limited to the embodiment. Rather, these embodiments are provided so that this disclosure will be thorough and complete, and will fully convey the scope of the invention to those skilled in the art. In addition, the thickness or size of each layer in the drawings is exaggerated for convenience and clarity of description.
도 1 내지 도 7은 본 발명의 예시적인 실시예들에 따른 자기 메모리 소자의 제조 방법을 나타내는 단면도이다.1 to 7 are cross-sectional views illustrating a method of manufacturing a magnetic memory device according to exemplary embodiments of the present invention.
도 1을 참조하면, 기판(100) 상에 하부 전극막(110), 하부 자성층(120), 절연층(130), 상부 자성층(140) 및 상부 전극막(150)을 순차적으로 형성한다.Referring to FIG. 1, the
기판(100)은 실리콘(Si) 기판, 게르마늄(Ge) 기판, 실리콘-게르마늄(SiGe) 기판, 실리콘-온-인슐레이터 (silicon-on-insulator: SOI) 기판 등의 반도체 기판을 포함할 수 있다.The
하부전극막(110)은 티타늄, 탄탈륨, 루테늄, 티타늄 질화물, 탄탈륨 질화물, 텅스텐 등 도전성 물질을 사용하여 원자층 적층 공정, 화학 기상 증착 공정 등에 의해 형성될 수 있다. 예를 들어, 하부 전극막(110)은 루테늄/티타늄, 루테늄/탄탈륨, 루테늄/티타늄 질화물, 루테늄/탄탈륨 질화물, 티타늄 질화물/텅스텐 등의 이중막 구조를 가질 수 있다. The
하부 자성층(120)은 하부 전극막(110) 상에 형성된다. 예시적인 실시예들에 있어서, 하부 자성층(120)은 Fe-Pt 합금, Fe-Pd 합금, Co-Pd 합금, Co-Pt 합금, Fe-Ni-Pt 합금, Co-Fe-Pt 합금, 및 Co-Ni-Pt 합금 등을 사용하여 원자층 적층 공정, 화학 기상 증착 공정 등에 의해 형성될 수 있다. 다른 실시예들에 있어서, 하부 자성층(120)은 붕소(B), 탄소(C), 구리(Cu), 은(Ag), 금(Au) 및 크롬(Cr) 중 적어도 어느 하나를 더 포함할 수 있다. The lower
절연층(130)은 하부 자성층(120) 상에 형성된다. 예시적인 실시예들에 있어서, 절연층(130)은 붕소 산화물(B2O3), 실리콘 산화물(SiO2), 마그네슘 산화물(MgO), 알루미늄 산화물(Al2O3) 등을 사용하여 원자층 적층 공정, 화학 기상 증착 공정 등에 의해 형성될 수 있다. The
상부 자성층(140)은 절연층(130) 상에 형성된다. 상부 자성층(140)은 복수의 자성층들과 적어도 하나 이상의 중간층들이 순차적으로 적층된 다층막 구조로 형성될 수 있다. 예시적인 실시예들에 따르면, 상부 자성층(140)은 제1 자성층, 제1 중간층, 제2 자성층, 제2 중간층 및 제3 자성층이 순차적으로 적층된 다층막 구조로 형성할 수 있다. 제1 자성층은 Fe-Pt 합금, Fe-Pd 합금, Co-Pd 합금, Co-Pt 합금, Fe-Ni-Pt 합금, Co-Fe-Pt 합금, Co-Ni-Pt 합금, Ni-Fe 합금, Co-Fe 합금, Ni-Fe-B 합금, Co-Fe-B 합금, Ni-Fe-Si-B 합금 또는 Co-Fe-Si-B 등을 사용하여 형성할 수 있다. 제2 및 제3 자성층들은 코발트(Co), 철(Fe), 백금(Pt), 팔라듐(Pd) 등의 단일막, 또는 이들의 다중막을 사용하여 형성할 수 있고, 상기 중간층은 루테늄(Ru), 탄탄륨(Ta), 크롬(Cr), 구리(Cu) 등을 사용하여 형성할 수 있다. 예를 들면, 상부 자성층(140)은 CoFeB/Ta/(Co/Pt)n/Ru/(Co/Pt)m의 다층 구조를 가질 수 있다. 상부 자성층(140)은 화학 기상 증착 공정, 원자층 적층 공정 등을 사용하여 형성될 수 있다.The upper
상부 전극막(150)은 상부 자성층(140) 상에 형성된다. 예시적인 실시예들에 있어서, 상부 전극막(150)은 티타늄, 탄탈륨, 루테늄, 티타늄 질화물, 탄탈륨 질화물, 텅스텐 등 도전성 물질을 사용하여 화학 기상 증착 공정, 원자층 적층 공정 등을 사용하여 형성될 수 있다. 예를 들어, 상부 전극막(150)은 루테늄/티타늄, 루테늄/탄탈륨, 루테늄/티타늄 질화물, 루테늄/탄탈륨 질화물, 티타늄 질화물/텅스텐 등의 이중막 구조를 갖도록 형성될 수 있다.The
도 2를 참조하면, 상부 전극막(150) 상에 마스크 패턴(160)을 형성한다. 예시적인 실시예들에 따르면, 마스크 패턴(160)은 포토레지스트 패턴일 수 있고, 실리콘 산화물, 실리콘 질화물 등을 포함하는 하드 마스크 패턴일 수 있다. Referring to FIG. 2, a
마스크 패턴(160)을 식각 마스크로 사용하여 상부 전극막(150)을 패터닝함으로써 상부 자성층(140) 상에 상부 전극(155)을 형성한다.The
이후, 마스크 패턴(160) 및 상부 전극(155)의 측벽들 상에 부희생막(170)을 형성한다. 예시적인 실시예들에 따르면, 마스크 패턴(160) 및 상부 전극(155)을 덮는 예비 부희생막(도시되지 않음)을 상부 자성층(140) 상에 형성하고, 상기 예비 부희생막에 이방성 식각 공정을 수행함으로써 마스크 패턴(160) 및 상부 전극(155)의 측벽들 상에 부희생막(170)을 형성한다. 상기 예비 부희생막은 실리콘 산화물, 실리콘 질화물, 텅스텐, 티타늄, 티타늄 질화물, 탄탈륨, 탄탈륨 질화물 등을 사용하여 원자층 적층 공정, 화학 기상 증착 공정 등에 의해 형성할 수 있다. 이외에도, 상기 예비 부희생막은 상부 자성층(140)과 식각 선택비를 갖는 물질을 사용하여 형성될 수 있다. 상기 예비 부희생막은 약 20Å 이하의 두께를 갖도록 형성될 수 있다. 부희생막(170)은 마스크 패턴(160) 및 상부 전극(155)의 측벽 상에 균일한 두께로 형성된다.Subsequently, the para
도 3을 참조하면, 마스크 패턴(160) 및 부희생막(170)을 식각 마스크로 사용하여 절연층(130) 상면이 노출될 때까지 상부 자성층(140)을 식각함으로써 절연층(130) 상에 상부 자성 패턴(145)을 형성한다. 예시적인 실시예들에 따르면, 상부 자성층(140)은 반응성 이온 식각(reactive ion etching) 공정 등을 수행함으로써 패터닝될 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 3, the upper
한편, 식각 공정에서 상부 자성층(140)의 식각 잔류물들(180)이 부희생막(170) 측벽들 상에 재증착(redeposition)될 수 있다. 상부 자성층(140)이 백금, 팔라듐 등의 귀금속을 포함하는 경우, 식각 잔류물들(180)은 주로 불휘발성이며, 패터닝된 영역에 인접한 부위에 재증착되므로 효율적으로 패터닝하기 어려운 문제가 있다. 또한, 식각 잔류물들(180)이 도전성 물질을 포함하므로, 상부 자성 패턴(145) 및 후속 공정에서 형성될 하부 자성 패턴 사이에 전기적 단락이 발생할 수도 있다. 본 실시예에서는 상부 전극(155) 측벽 상에 부희생막(170)이 형성되므로, 상부 전극(155)에 식각 잔류물들(180)이 재증착되는 대신, 부희생막(170) 측벽에 식각 잔류물들(180)이 재증착된다.Meanwhile, in the etching process, the
도 4를 참조하면, 부희생막(170) 및 식각 잔류물들(180)이 제거된다. 예시적인 실시예들에 따르면, 부희생막(170)은 이온 빔 에칭(ion beam etching) 공정, 습식 식각 공정 등을 사용하여 제거될 수 있다. 예를 들면, 경사를 갖는 이온 빔 에칭(tilted ion beam etching) 공정 등을 사용하여 상부 전극(155) 및 마스크 패턴(160) 측벽에 형성된 부희생막(170)을 제거할 수 있다. 또한, 불산 등 플루오르를 포함하는 식각액을 사용한 습식 식각 공정을 수행함으로써 부희생막(170)을 제거할 수도 있다. 한편, 부희생막(170)이 제거될 때, 부희생막(170) 측벽에 증착된 식각 잔류물들(180)이 함께 제거될 수 있다. 한편, 부희생막(170)이 제거된 후, 패터닝된 상부 자성 패턴(145) 및 상부 전극(155) 사이에는 단차가 발생하게 된다. 예를 들어, 약 20Å 이하의 부희생막(170)이 상부 전극(155)과 함께 식각 마스크로 사용되므로, 부희생막(170)이 제거된 후, 상부 자성 패턴(145)의 폭은 부희생막(170)의 두께만큼 상부 전극(155)보다 넓은 폭을 가질 수 있다. Referring to FIG. 4, the para
도 5를 참조하면, 마스크 패턴(160), 상부 전극(155) 및 상부 자성 패턴(145)의 측벽들 상에 주희생막(190)을 형성한다. 예시적인 실시예들에 따르면, 마스크 패턴(160), 상부 전극(155) 및 상부 자성 패턴(145)을 덮는 예비 주희생막(도시되지 않음)을 절연층(130) 상에 형성하고, 상기 예비 주희생막에 이방성 식각 공정을 수행함으로써 마스크 패턴(160), 상부 전극(155) 및 상부 자성 패턴(145)의 측벽들 상에 주희생막(190)을 형성할 수 있다. 상기 예비 주희생막은 실리콘 산화물, 실리콘 질화물, 텅스텐, 티타늄, 티타늄 질화물, 탄탈륨, 탄탈륨 질화물 등을 사용하여 원자층 적층 공정, 화학 기상 증착 공정 등에 의해 형성할 수 있다. 상기 예비 주희생막은 약 20Å 이하의 두께를 갖도록 형성될 수 있다. 주희생막(190)은 마스크 패턴(160), 상부 전극(155) 및 상부 자성 패턴(145)의 측벽들 상에 컨포멀(conformal)하게 형성될 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 5, a main
도 6을 참조하면, 마스크 패턴(160) 및 주희생막(190)을 식각 마스크로 사용하여 절연층(130), 하부 자성층(120) 및 하부 전극막(110)을 순차적으로 패터닝함으로써 절연 패턴(135), 하부 자성 패턴(125) 및 하부 전극(115)을 형성한다. 예시적인 실시예들에 따르면, 절연층(130), 하부 자성층(120) 및 하부 전극막(110)은 반응성 이온 식각 공정 등을 통해 패터닝될 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 6, the insulating
한편, 식각 공정에서 하부 자성층(120)의 식각 잔류물들(200)이 주희생막(190) 측벽들 상에 재증착(redeposition)될 수 있다. 하부 자성층(120)이 백금, 팔라듐 등의 귀금속을 포함하는 경우, 식각 잔류물들(200)은 주로 불휘발성이며, 패터닝된 영역에 인접한 부위에 재증착되므로 효율적으로 패터닝하기 어려운 문제가 있다. 또한, 식각 잔류물들(200)이 도전성 물질을 포함하므로, 상부 자성 패턴(145) 및 하부 자성 패턴(125) 사이에 전기적 단락이 발생할 수도 있다. 본 실시예에서는 상부 자성 패턴(145) 측벽 상에 주희생막(190)이 형성되므로, 상부 자성 패턴(145)에 식각 잔류물들(200)이 재증착되는 대신, 주희생막(190) 측벽에 식각 잔류물들(200)이 재증착된다.Meanwhile, in the etching process, the
도 7을 참조하면, 주희생막(190) 및 식각 잔류물들(200)이 제거된다. 예시적인 실시예들에 따르면, 주희생막(190)은 이온 빔 에칭(ion beam etching) 공정, 습식 식각 공정 등을 사용하여 제거될 수 있다. 예를 들면, 경사를 갖는 이온 빔 에칭(tilted ion beam etching) 공정 등을 사용하여 상부 자성 패턴(145), 상부 전극(155) 및 마스크 패턴(160) 측벽들 상에 형성된 주희생막(190)을 제거할 수 있다. 또한, 불산, 플루오르 등을 포함하는 식각액을 사용한 습식 식각 공정을 수행함으로써 주희생막(190)을 제거할 수도 있다. 한편, 주희생막(190)이 제거될 때, 주희생막(190) 측벽에 증착된 식각 잔류물들(200)이 함께 제거될 수 있다. 한편, 주희생막(190)이 제거된 후, 패터닝된 하부 자성 패턴(125) 및 상부 자성 패턴(145) 사이에는 단차가 발생하게 된다. 예를 들어, 약 20Å 이하의 주희생막(190)이 상부 자성 패턴(145)과 함께 식각 마스크로 사용되므로, 주희생막(190)이 제거된 후, 하부 자성 패턴(125)의 폭은 상부 자성 패턴(145) 보다 주희생막(190)의 두께만큼 넓은 폭을 가질 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 7, the main
이후, 마스크 패턴(160)이 제거될 수 있다.Thereafter, the
본 발명에 따른 자기 메모리 소자의 제조 방법은, 상부 자성 패턴(145) 형성시 부희생막(170) 측벽 상에 식각 잔류물(180)이 재증착됨에 따라 식각 잔류물들(180)의 제거가 용이하다. 또한, 하부 자성 패턴(125) 형성시 주희생막(190) 측벽에 식각 잔류물들(200)이 재증착됨에 따라 식각 잔류물들(200)의 제거가 용이하다. 따라서, 식각 잔류물들(180, 200)이 상부 자성 패턴(145) 및 하부 자성 패턴(125) 측벽들 상에 재증착됨에 따라 발생하는 전기적 단락을 방지할 수 있다. In the method of manufacturing the magnetic memory device according to the embodiment of the present invention, the
도 8 내지 도 12는 예시적인 실시예들에 따른 자기 메모리 소자의 제조 방법을 나타내는 단면도들이다. 상기 제조 방법은 부희생막이 형성되지 않는 점을 제외하면 도 1 내지 도 7을 참조로 설명한 자기 메모리 소자의 제조 방법과 유사하므로, 전술한 차이점을 중심으로 설명한다. 8 through 12 are cross-sectional views illustrating a method of manufacturing a magnetic memory device in accordance with example embodiments. Since the fabrication method is similar to the fabrication method of the magnetic memory device described with reference to FIGS. 1 to 7 except that no side layer is formed, the following description will focus on the above-described differences.
도 8을 참조하면, 기판(100) 상에 하부 전극막(110), 하부 자성층(120), 절연층(130), 상부 자성층(140) 및 상부 전극막(150)을 순차적으로 형성한다.Referring to FIG. 8, the
이후, 상부 전극막(150) 상에 마스크 패턴(160)을 형성한다.Thereafter, a
도 9를 참조하면, 마스크 패턴(160)을 식각 마스크로 사용하여 상부 전극막(150)을 패터닝함으로써 상부 자성층(140) 상에 상부 전극(155)을 형성한다.Referring to FIG. 9, the
이후, 마스크 패턴(160) 및 상부 전극(155)을 식각 마스크로 사용하여 상부 자성층(140)을 패터닝함으로써 상부 자성 패턴(145)을 형성한다.Subsequently, the upper
한편, 상부 자성 패턴(145) 형성시 식각 잔류물들(180)이 마스크 패턴(160) 및 상부 전극(155)의 측벽들 상에 재증착될 수 있다.Meanwhile, when the upper
도 10을 참조하면, 마스크 패턴(160) 및 상부 전극(155) 측벽에 재증착된 식각 잔류물들(180)을 제거할 수 있다. 예시적인 실시예들에 따르면, 경사를 갖는 이온 빔 에칭(tilted ion beam etching) 공정을 사용하여 마스크 패턴(160) 및 상부 전극(155)의 측벽들 상에 마스크 패턴(160) 및 상부 전극(155)의 측벽들 상에 재증착된 식각 잔류물들(180)을 제거할 수 있다. 다른 실시예들에 따르면, 습식 식각 공정을 수행하여 마스크 패턴 한편, 상기 에칭 공정에서 절연층(130)이 식각 정지막 역할을 할 수 있으므로, 식각 잔류물들(180)의 선택적 제거가 가능하다. Referring to FIG. 10, the
이후, 마스크 패턴(160), 상부 전극(155) 및 상부 자성 패턴(145)의 측벽들 상에 주희생막(190)을 형성한다. 예시적인 실시예들에 따르면, 마스크 패턴(160), 상부 전극(155) 및 상부 자성 패턴(145)을 덮는 예비 주희생막(도시되지 않음)을 절연층(130) 상에 형성하고, 상기 예비 주희생막에 이방성 식각 공정을 수행함으로써 마스크 패턴(160), 상부 전극(155) 및 상부 자성 패턴(145)의 측벽들 상에 주희생막(190)을 형성할 수 있다. 상기 예비 주희생막은 실리콘 산화물, 실리콘 질화물, 텅스텐, 티타늄, 탄탈륨 등의 금속을 사용하여 원자층 적층 공정, 화학 기상 증착 공정 등에 의해 형성할 수 있다. 상기 예비 주희생막은 약 20Å 이하의 두께를 갖도록 형성될 수 있다. 주희생막(190)은 마스크 패턴(160), 상부 전극(155) 및 상부 자성 패턴(145)의 측벽들 상에 컨포멀(conformal)하게 형성될 수 있다.Thereafter, the main
도 11을 참조하면, 마스크 패턴(160) 및 희생막(190)을 식각 마스크로 사용하여 절연층(130), 하부 자성층(120) 및 하부 전극막(110)을 순차적으로 패터닝함으로써 절연 패턴(135), 하부 자성 패턴(125) 및 하부 전극(115)을 형성한다. 예시적인 실시예들에 따르면, 절연층(130), 하부 자성층(120) 및 하부 전극막(110)은 반응성 이온 식각 공정 등을 통해 패터닝될 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 11, an insulating
한편, 식각 공정에서 하부 자성층(120)의 식각 잔류물들(200)이 주희생막(190) 측벽들 상에 재증착(redeposition)될 수 있다. 하부 자성층(120)이 백금, 팔라듐 등의 귀금속을 포함하는 경우, 식각 잔류물들(200)은 주로 불휘발성이며, 패터닝된 영역에 인접한 부위에 재증착되므로 효율적으로 패터닝하기 어려운 문제가 있다. 또한, 식각 잔류물들(200)이 도전성 물질을 포함하므로, 상부 자성 패턴(145) 및 하부 자성 패턴(125) 사이에 전기적 단락이 발생할 수도 있다. 본 실시예에서는 상부 자성 패턴(145) 측벽 상에 주희생막(190)이 형성되므로, 상부 자성 패턴(145)에 식각 잔류물들(200)이 재증착되는 대신, 주희생막(190) 측벽에 식각 잔류물들(200)이 재증착된다.Meanwhile, in the etching process, the
도 12를 참조하면, 주희생막(190) 및 식각 잔류물들(200)이 제거된다. 예시적인 실시예들에 따르면, 주희생막(190)은 이온 빔 에칭(ion beam etching) 공정, 습식 식각 공정 등을 사용하여 제거될 수 있다. 예를 들면, 경사를 갖는 이온 빔 에칭(tilted ion beam etching) 공정 등을 사용하여 상부 자성 패턴(145), 상부 전극(155) 및 마스크 패턴(160) 측벽들 상에 형성된 주희생막(190)을 제거할 수 있다. 또한, 불산 등 플루오르를 포함하는 식각액을 사용한 습식 식각 공정을 수행함으로써 주희생막(190)을 제거할 수도 있다. 한편, 주희생막(190)이 제거될 때, 주희생막(190) 측벽에 증착된 식각 잔류물들(200)이 함께 제거될 수 있다. 한편, 주희생막(190)이 제거된 후, 패터닝된 하부 자성 패턴(125) 및 상부 자성 패턴(145) 사이에는 단차가 발생하게 된다. 예를 들어, 약 20Å 이하의 주희생막(190)이 상부 자성 패턴(145)과 함께 식각 마스크로 사용되므로, 주희생막(190)이 제거된 후, 하부 자성 패턴(125)의 폭은 상부 자성 패턴(145) 보다 주희생막(190)의 두께만큼 넓은 폭을 가질 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 12, the main
이후, 마스크 패턴(160)이 제거될 수 있다.Thereafter, the
본 발명의 자기 메모리 소자의 제조 방법은, 하부 자성 패턴(125) 형성시 주희생막(190) 측벽에 식각 잔류물들(200)이 재증착됨에 따라 식각 잔류물들(200)의 제거가 용이하다. 따라서, 식각 잔류물들(200)이 상부 자성 패턴(145) 및 하부 자성 패턴(125) 측벽들 상에 재증착됨에 따라 발생하는 전기적 단락을 방지할 수 있다. In the method of manufacturing the magnetic memory device of the present invention, as the
도 13 내지 도 21은 예시적인 실시예들에 따른 반도체 장치의 제조 방법을 설명하기 위한 단면도들이다. 상기 반도체 장치는 도 1 내지 도 7을 참조로 설명한 자기 메모리 소자를 포함하므로, 차이점을 중심으로 설명한다.13 to 21 are cross-sectional views illustrating a method of manufacturing a semiconductor device in accordance with example embodiments. Since the semiconductor device includes the magnetic memory device described with reference to FIGS. 1 to 7, the description will be mainly given of differences.
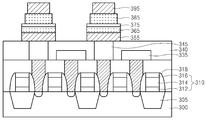
도 13을 참조하면, 기판(300)에 소자 분리막(305)을 형성한다. 예시적인 실시예들에 따르면, 소자 분리막(305)은 얕은 트렌치 소자 분리(STI) 공정을 통해 형성될 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 13, an
기판(300) 상에 게이트 절연막, 게이트 전극막 및 게이트 마스크막을 순차적으로 형성하고, 사진 식각 공정을 통해 이들을 패터닝하여, 기판(300) 상에 순차적으로 적층된 게이트 절연막 패턴(312), 게이트 전극(314) 및 게이트 마스크(316)를 각각 포함하는 복수 개의 게이트 구조물들(310)을 형성한다. 상기 게이트 절연막은 실리콘 산화물 혹은 금속 산화물을 사용하여 형성될 수 있다. 상기 게이트 전극막은 도핑된 폴리실리콘 혹은 금속을 사용하여 형성될 수 있다. 상기 게이트 마스크막은 실리콘 질화물을 사용하여 형성될 수 있다. A gate insulating film, a gate electrode film, and a gate mask film are sequentially formed on the
이후, 게이트 구조물들(310)을 이온 주입 마스크로 사용하는 이온 주입 공정을 통해, 게이트 구조물들(310)에 인접한 기판(300) 상부에 제1 및 제2 불순물 영역들(301, 303)을 형성한다. 제1 및 제2 불순물 영역들(301, 303)은 트랜지스터의 소스/드레인 영역으로 기능할 수 있다. Thereafter, first and
게이트 구조물(310) 및 불순물 영역들(301, 303)은 상기 트랜지스터를 형성할 수 있다. 한편, 게이트 구조물들(310)의 측벽들에는 실리콘 질화물을 사용하여 스페이서들(318)을 형성할 수 있다.The
게이트 구조물들(310) 및 스페이서들(318)을 커버하는 제1 층간 절연막(320)을 기판(300) 상에 형성한다. 제1 층간 절연막(320)을 부분적으로 식각하여 불순물 영역들(301, 303)을 노출시키는 제1 홀들(도시하지 않음)을 형성한다. 예시적인 실시예들에 따르면, 상기 제1 홀들은 게이트 구조물들(310) 및 스페이서들(318)에 자기 정렬될 수 있다.A first interlayer insulating layer 320 covering the
이후, 상기 제1 홀들을 매립하는 제1 도전막을 제1 층간 절연막(320) 상에 형성하고, 기계 화학적 연마 공정 및/또는 에치 백 공정을 통해 제1 층간 절연막(320)이 노출될 때까지 상기 제1 도전막 상부를 제거함으로써, 상기 제1 홀들 내에 형성된 제1 플러그(321) 및 제2 플러그(323)를 형성한다. 제1 플러그(321)는 제1 불순물 영역(301)에 접촉할 수 있고, 제2 플러그(323)는 제2 불순물 영역(303)에 접촉할 수 있다. 상기 제1 도전막은 도핑된 폴리실리콘, 금속 등을 사용하여 형성될 수 있다. 제1 플러그(321)는 소스 라인 콘택으로 기능할 수 있다. Thereafter, a first conductive layer filling the first holes is formed on the first interlayer insulating layer 320, and the first interlayer insulating layer 320 is exposed through a mechanical chemical polishing process and / or an etch back process. By removing the upper portion of the first conductive layer, the
제1 플러그(321)에 접촉하는 제2 도전막(도시하지 않음)을 제1 층간 절연막(320) 상에 형성하고 이를 패터닝함으로써 소스 라인(335)을 형성한다. 상기 제2 도전막은 도핑된 폴리실리콘, 금속 등을 사용하여 형성될 수 있다. 이후, 상기 비트 라인을 커버하는 제2 층간 절연막(340)을 제1 층간 절연막(320) 상에 형성한다. 제2 층간 절연막(340)을 부분적으로 식각하여 제2 플러그(323)를 노출시키는 제2 홀들(도시하지 않음)을 형성하고, 상기 제2 홀들을 매립하는 제3 도전막을 제2 플러그(323) 및 제2 층간 절연막(340) 상에 형성한다. 기계 화학적 연마(chemical mechanical polish) 공정 및/또는 에치 백(etch-back) 공정을 통해 제2 층간 절연막(340)이 노출될 때까지 상기 제3 도전막 상부를 제거함으로써, 상기 제2 홀들 내에 형성된 하부 콘택(345)을 형성한다. 상기 제3 도전막은 티타늄, 티타늄 질화물, 탄탈륨, 탄탈륨 질화물, 텅스텐, 도핑된 폴리실리콘 등을 사용하여 형성될 수 있다.A
도 14를 참조하면, 제2 층간 절연막(340) 및 하부 콘택(345) 상에 하부 전극막(350), 하부 자성층(360), 절연층(370), 상부 자성층(380) 및 상부 전극막(390)이 순차적으로 형성된다.Referring to FIG. 14, a
하부 전극막(350)은 제2 층간 절연막(340) 및 하부 콘택(345) 상에 형성될 수 있다. 예시적인 실시예들에 있어서, 하부 전극막(350)은 티타늄, 탄탈륨, 루테늄, 티타늄 질화물, 탄탈륨 질화물, 텅스텐 등 도전성 물질을 사용하여 원자층 적층 공정, 화학 기상 증착 공정 등에 의해 형성될 수 있다.The
하부 자성층(360)은 하부 전극막(350) 상에 형성된다. 예시적인 실시예들에 있어서, 하부 자성층(360)은 Fe-Pt 합금, Fe-Pd 합금, Co-Pd 합금, Co-Pt 합금, Fe-Ni-Pt 합금, Co-Fe-Pt 합금, 및 Co-Ni-Pt 합금 등을 사용하여 원자층 적층 공정, 화학 기상 증착 공정 등에 의해 형성될 수 있다. 다른 실시예들에 있어서, 하부 자성층(360)은 붕소(B), 탄소(C), 구리(Cu), 은(Ag), 금(Au) 및 크롬(Cr) 중 적어도 어느 하나를 더 포함할 수 있다.The lower
절연층(370)은 하부 자성층(360) 상에 형성된다. 예시적인 실시예들에 있어서, 절연층(370)은 붕소 산화물(B2O3), 실리콘 산화물(SiO2), 마그네슘 산화물(MgO), 알루미늄 산화물(Al2O3) 등을 사용하여 원자층 적층 공정, 화학 기상 증착 공정 등에 의해 형성될 수 있다.The insulating
상부 자성층(380)은 절연층(370) 상에 형성된다. 상부 자성층(380)은 복수의 자성층들과 적어도 하나 이상의 중간층들이 순차적으로 적층된 다층막 구조로 형성될 수 있다. 예시적인 실시예들에 따르면, 상부 자성층(380)은 제1 자성층, 제1 중간층, 제2 자성층, 제2 중간층 및 제3 자성층이 순차적으로 적층된 다층막 구조로 형성할 수 있다.The upper
상부 전극막(390)은 상부 자성층(380) 상에 형성된다. 예시적인 실시예들에 있어서, 상부 전극막(390)은 티타늄, 탄탈륨, 루테늄, 티타늄 질화물, 탄탈륨 질화물, 텅스텐 등 도전성 물질을 사용하여 원자층 적층 공정, 화학 기상 증착 공정 등에 의해 형성될 수 있다.The
도 15를 참조하면, 마스크 패턴(400)은 상부 전극막(390) 상에 형성된다. Referring to FIG. 15, a
이후, 마스크 패턴(400)을 식각 마스크로 사용하여 상부 전극막(390)을 패터닝함으로써 상부 전극(395)을 형성한다.Subsequently, the
마스크 패턴(400) 및 상부 전극(395)의 측벽들 상에 부희생막(410)을 형성한다. 부희생막(410)은 실리콘 산화물, 실리콘 질화물, 텅스텐, 티타늄, 탄탈륨 등의 금속을 사용하여 원자층 적층 공정, 화학 기상 증착 공정 등에 의해 형성할 수 있다. 부희생막(410)은 약 20Å 이하의 두께를 갖도록 형성될 수 있다.The para
도 16을 참조하면, 마스크 패턴(400) 및 부희생막(410)을 식각 마스크로 사용하여 상부 자성층(380)을 패터닝함으로써 상부 자성 패턴(385)을 형성한다. 한편, 식각 공정에서 상부 자성층(380)의 식각 잔류물들(420)이 부희생막(410) 측벽에 재증착될 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 16, the upper
도 17을 참조하면, 부희생막(410) 및 식각 잔류물들(420)이 제거된다. 예시적인 실시예들에 따르면, 부희생막(410)은 이온 빔 에칭(ion beam etching) 공정, 습식 식각 공정 등을 사용하여 제거될 수 있다. 한편, 부희생막(410)이 제거될 때, 부희생막(410) 측벽에 증착된 식각 잔류물들(420)이 함께 제거될 수 있다. 한편, 부희생막(170)이 제거된 후, 패터닝된 상부 자성 패턴(145) 및 상부 전극(155) 사이에는 단차가 발생하게 된다. 예를 들어, 약 20Å 이하의 부희생막(170)이 상부 전극(155)과 함께 식각 마스크로 사용되므로, 부희생막(170)이 제거된 후, 상부 자성 패턴(145)의 폭은 부희생막(170)의 두께만큼 상부 전극(155)보다 넓은 폭을 가질 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 17, the para
도 18을 참조하면, 마스크 패턴(400), 상부 전극(395) 및 상부 자성 패턴(385)의 측벽들 상에 주희생막(430)을 형성한다. 주희생막(430)은 실리콘 산화물, 실리콘 질화물, 텅스텐, 티타늄, 탄탈륨 등의 금속을 사용하여 원자층 적층 공정, 화학 기상 증착 공정 등에 의해 형성할 수 있다. 주희생막(430)은 약 20Å 이하의 두께를 갖도록 형성될 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 18, a main
도 19를 참조하면, 마스크 패턴(400) 및 주희생막(430)을 식각 마스크로 사용하여 절연층(370), 하부 자성층(360) 및 하부 전극막(350)을 순차적으로 패터닝함으로써 절연 패턴(375), 하부 자성 패턴(365) 및 하부 전극(355)을 형성한다. 한편, 식각 공정에서 하부 자성층(360)의 식각 잔류물들(440)이 주희생막(430) 측벽들 상에 재증착(redeposition)될 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 19, the insulating
도 20을 참조하면, 주희생막(430) 및 식각 잔류물들(440)이 제거된다. 예시적인 실시예들에 따르면, 주희생막(430)은 이온 빔 에칭(ion beam etching) 공정, 습식 식각 공정 등을 사용하여 제거될 수 있다. 한편, 주희생막(430)이 제거될 때, 주희생막(430) 측벽에 증착된 식각 잔류물들(440)이 함께 제거될 수 있다. 한편, 주희생막(190)이 제거된 후, 패터닝된 하부 자성 패턴(125) 및 상부 자성 패턴(145) 사이에는 단차가 발생하게 된다. 예를 들어, 약 20Å 이하의 주희생막(190)이 상부 자성 패턴(145)과 함께 식각 마스크로 사용되므로, 주희생막(190)이 제거된 후, 하부 자성 패턴(125)의 폭은 상부 자성 패턴(145) 보다 주희생막(190)의 두께만큼 넓은 폭을 가질 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 20, the main
이후, 마스크 패턴(400)이 제거될 수 있다.Thereafter, the
도 21을 참조하면, 제2 층간 절연막(340) 상에 하부 전극(355), 하부 자성 패턴(365), 절연 패턴(375), 상부 자성 패턴(385) 및 상부 전극(395)을 덮는 절연막(도시되지 않음)을 형성한 후, 상부 전극(395)의 상면이 노출될 때까지 상기 절연막을 평탄화함으로써 제3 층간 절연막(450)을 형성한다. Referring to FIG. 21, an insulating film covering the
제3 층간 절연막(450) 상에 제4 층간 절연막(460)을 형성한다. 이후, 상부 전극(395)의 상면을 노출하는 개구(도시되지 않음)를 형성하고, 상기 개구를 채우는 도전막(도시되지 않음)을 형성한다. 제4 층간 절연막(460)의 상면이 노출될 때까지 상기 도전막을 평탄화함으로써 상부 전극(395)에 전기적으로 연결되는 상부 콘택(465)을 형성한다.The fourth
상부 콘택(465) 상에 비트 라인(470)을 형성한다.The
전술한 공정을 수행하여 상기 반도체 장치가 완성된다. The semiconductor device is completed by performing the above-described process.
본 발명에 따른 반도체 장치의 제조 방법은, 상부 자성 패턴(395) 형성시 부희생막(410) 측벽 상에 식각 잔류물(420)이 재증착됨에 따라 식각 잔류물들(420)의 제거가 용이하다. 또한, 하부 자성 패턴(365) 형성시 주희생막(430) 측벽에 식각 잔류물들(440)이 재증착됨에 따라 식각 잔류물들(440)의 제거가 용이하다. 따라서, 식각 잔류물들(420, 440)이 상부 자성 패턴(395) 및 하부 자성 패턴(365) 측벽들 상에 재증착됨에 따라 발생하는 전기적 단락을 방지할 수 있다. In the method of manufacturing a semiconductor device according to the embodiment of the present invention, as the
이상에서 설명한 본 발명이 전술한 실시예 및 첨부된 도면에 한정되지 않으며, 본 발명의 기술적 사상을 벗어나지 않는 범위 내에서 여러 가지 치환, 변형 및 변경이 가능하다는 것은, 본 발명이 속하는 기술분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자에게 있어 명백할 것이다.It will be apparent to those skilled in the art that various modifications and variations can be made in the present invention without departing from the spirit or scope of the invention. Will be clear to those who have knowledge of.
100, 300: 기판 110, 350: 하부 전극막
115, 355: 하부 전극 120, 360: 하부 자성층
125, 365: 하부 자성 패턴 130, 370: 절연층
135, 375: 절연 패턴 140, 380: 상부 자성층
145, 385: 상부 자성 패턴 150, 390: 상부 전극막
155, 395: 상부 전극 160, 400: 마스크 패턴
170, 410: 부희생막 180, 200, 420, 440: 식각 잔류물
190, 430: 주희생막 301, 303: 불순물 영역
305: 소자 분리막 310: 게이트 구조물
320, 340, 450, 460: 층간 절연막
321, 323: 플러그 335: 소스 라인
345: 하부 콘택 465: 상부 콘택
470: 비트 라인100, 300:
115, 355:
125 and 365: lower
135, 375:
145 and 385: Upper
155 and 395:
170, 410:
190, 430:
305: device isolation layer 310: gate structure
320, 340, 450, 460: interlayer insulating film
321, 323: Plug 335: Source line
345: lower contact 465: upper contact
470: bit line
Claims (10)
상기 절연층 상에 상부 자성 패턴을 형성하는 단계;
상기 상부 자성 패턴의 측벽 상에 주희생막을 형성하는 단계;
상기 상부 자성 패턴 및 상기 주희생막을 식각 마스크로 사용하여 상기 절연층 및 상기 하부 자성층을 패터닝하여 절연 패턴 및 하부 자성 패턴을 형성하는 단계; 및
상기 주희생막을 제거하는 단계를 포함하는 자기 메모리 소자의 제조 방법.Sequentially forming a lower magnetic layer and an insulating layer on the substrate;
Forming an upper magnetic pattern on the insulating layer;
Forming a main sacrificial film on sidewalls of the upper magnetic pattern;
Patterning the insulating layer and the lower magnetic layer by using the upper magnetic pattern and the main sacrificial film as an etching mask to form an insulating pattern and a lower magnetic pattern; And
And removing the main sacrificial layer.
상기 상부 자성층 상에 상부 전극을 형성하는 단계;
상기 상부 전극의 측벽 상에 부희생막을 형성하는 단계;
상기 상부 전극 및 상기 부희생막을 식각 마스크로 사용하여 상기 상부 자성층을 패터닝함으로써 상기 절연층 상에 상기 상부 자성 패턴을 형성하는 단계; 및
상기 부희생막을 제거하는 단계를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 자기 메모리 소자의 제조 방법.The method of claim 1, wherein the forming of the upper magnetic pattern comprises:
Forming an upper electrode on the upper magnetic layer;
Forming an auxiliary sacrificial layer on sidewalls of the upper electrode;
Forming the upper magnetic pattern on the insulating layer by patterning the upper magnetic layer by using the upper electrode and the para sacrificial layer as an etching mask; And
And removing the parasitic layer.
상기 상부 자성층 상에 상부 전극을 형성하는 단계;
상기 상부 전극의 측벽 상에 부희생막을 형성하는 단계;
상기 상부 전극 및 상기 부희생막을 식각 마스크로 사용하여 상기 상부 자성층을 식각함으로써 상부 자성 패턴을 형성하는 단계;
상기 부희생막을 제거하는 단계;
상기 상부 전극 및 상기 상부 자성 패턴의 측벽들 상에 주희생막을 형성하는 단계;
상기 상부 전극, 상기 상부 자성 패턴 및 상기 주희생막을 식각 마스크로 사용하여 상기 절연층 및 상기 하부 자성층을 순차적으로 식각함으로써 절연 패턴 및 하부 자성 패턴을 형성하는 단계; 및
상기 주희생막을 제거하는 단계를 포함하는 자기 메모리 소자의 제조 방법.Sequentially forming a lower magnetic layer, an insulating layer, and an upper magnetic layer on the substrate;
Forming an upper electrode on the upper magnetic layer;
Forming an auxiliary sacrificial layer on sidewalls of the upper electrode;
Forming an upper magnetic pattern by etching the upper magnetic layer using the upper electrode and the auxiliary sacrificial layer as an etching mask;
Removing the parasitic membrane;
Forming a main sacrificial layer on sidewalls of the upper electrode and the upper magnetic pattern;
Forming an insulating pattern and a lower magnetic pattern by sequentially etching the insulating layer and the lower magnetic layer using the upper electrode, the upper magnetic pattern, and the main sacrificial layer as an etching mask; And
And removing the main sacrificial layer.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020110103048A KR20130038603A (en) | 2011-10-10 | 2011-10-10 | Method of manufacturing a magnetic memory device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020110103048A KR20130038603A (en) | 2011-10-10 | 2011-10-10 | Method of manufacturing a magnetic memory device |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20130038603A true KR20130038603A (en) | 2013-04-18 |
Family
ID=48439091
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020110103048A KR20130038603A (en) | 2011-10-10 | 2011-10-10 | Method of manufacturing a magnetic memory device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR20130038603A (en) |
Cited By (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20150051795A (en) * | 2013-11-05 | 2015-05-13 | 삼성전자주식회사 | semiconductor device |
| KR20150111529A (en) * | 2014-03-25 | 2015-10-06 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Cleaning composition applied to semiconductor device |
| KR20160015507A (en) * | 2014-07-30 | 2016-02-15 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Memory device and forming the same |
| US9577183B2 (en) | 2014-04-03 | 2017-02-21 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Methods of manufacturing a magnetoresistive random access memory device |
| KR20170038491A (en) * | 2015-09-30 | 2017-04-07 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Magneto-resistance random access memory device and method of fabricating the same |
| CN107785483A (en) * | 2016-08-25 | 2018-03-09 | 中电海康集团有限公司 | A kind of preparation method of magnetic RAM |
| US10529919B2 (en) | 2017-09-20 | 2020-01-07 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Method of manufacturing a magnetoresistive random access memory device using hard masks and spacers |
| CN118678695A (en) * | 2024-08-26 | 2024-09-20 | 青岛海存微电子有限公司 | Semiconductor memory device and method of forming the same |
-
2011
- 2011-10-10 KR KR1020110103048A patent/KR20130038603A/en not_active Application Discontinuation
Cited By (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20150051795A (en) * | 2013-11-05 | 2015-05-13 | 삼성전자주식회사 | semiconductor device |
| US9806027B2 (en) | 2013-11-05 | 2017-10-31 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Semiconductor device |
| KR20150111529A (en) * | 2014-03-25 | 2015-10-06 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Cleaning composition applied to semiconductor device |
| US9577183B2 (en) | 2014-04-03 | 2017-02-21 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Methods of manufacturing a magnetoresistive random access memory device |
| KR20160015507A (en) * | 2014-07-30 | 2016-02-15 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Memory device and forming the same |
| KR20170038491A (en) * | 2015-09-30 | 2017-04-07 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Magneto-resistance random access memory device and method of fabricating the same |
| CN107785483A (en) * | 2016-08-25 | 2018-03-09 | 中电海康集团有限公司 | A kind of preparation method of magnetic RAM |
| US10529919B2 (en) | 2017-09-20 | 2020-01-07 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Method of manufacturing a magnetoresistive random access memory device using hard masks and spacers |
| CN118678695A (en) * | 2024-08-26 | 2024-09-20 | 青岛海存微电子有限公司 | Semiconductor memory device and method of forming the same |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR20130038603A (en) | Method of manufacturing a magnetic memory device | |
| KR101865566B1 (en) | Methods of manufacturing a vertical memory device | |
| US10283698B2 (en) | Semiconductor devices and methods of fabricating the same | |
| KR102316317B1 (en) | Semiconductor devices and methods of manufacturing the same | |
| US9306156B2 (en) | Methods of manufacturing a magnetoresistive random access memory device | |
| JP5660651B2 (en) | Semiconductor structure and static random access memory (SRAM) cell comprising a plurality of parallel conductive material containing structures and method of forming a semiconductor structure | |
| KR101718794B1 (en) | Method of manufacturing a semiconductor device | |
| US8415750B2 (en) | Semiconductor device and method of fabricating the same | |
| TW201725682A (en) | Integrated circuits | |
| KR102101407B1 (en) | Magnetoresistive random access device and method of manufacturing the same | |
| KR100615598B1 (en) | Semiconductor Devices Having A Planarization Isolating Layer And Methods Of Forming The Same | |
| US10008409B2 (en) | Method for fabricating a semiconductor device | |
| JP2014011230A (en) | Semiconductor memory device and method of manufacturing the same | |
| KR101087880B1 (en) | Method for manufacturing semiconductor device | |
| US10163703B2 (en) | Method for forming self-aligned contact | |
| KR20170082732A (en) | Semiconductor devices and methods of manufacturing the same | |
| JP2011023498A (en) | Semiconductor device, and method of manufacturing the same | |
| TWI651764B (en) | Devices and methods for forming cross coupled contacts | |
| CN110890326B (en) | Method for producing gate cut structure on semiconductor fin array | |
| US12087619B2 (en) | Semiconductor device and method of fabricating the same | |
| TW200818409A (en) | Method for fabricating storage node contact in semiconductor device | |
| CN108123035B (en) | Phase change memory | |
| TWI752377B (en) | Semiconductor device and method of fabricating the same | |
| WO2024066384A1 (en) | Spin-orbit-torque (sot) mram with doubled layer of sot metal | |
| CN118265438A (en) | Method for manufacturing magnetic memory cell |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| WITN | Application deemed withdrawn, e.g. because no request for examination was filed or no examination fee was paid |