US2366109A - Wall and partition for buildings - Google Patents
Wall and partition for buildings Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- US2366109A US2366109A US463789A US46378942A US2366109A US 2366109 A US2366109 A US 2366109A US 463789 A US463789 A US 463789A US 46378942 A US46378942 A US 46378942A US 2366109 A US2366109 A US 2366109A
- Authority
- US
- United States
- Prior art keywords
- slabs
- wall
- vertical
- grooves
- partition
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E04—BUILDING
- E04B—GENERAL BUILDING CONSTRUCTIONS; WALLS, e.g. PARTITIONS; ROOFS; FLOORS; CEILINGS; INSULATION OR OTHER PROTECTION OF BUILDINGS
- E04B2/00—Walls, e.g. partitions, for buildings; Wall construction with regard to insulation; Connections specially adapted to walls
- E04B2/56—Load-bearing walls of framework or pillarwork; Walls incorporating load-bearing elongated members
- E04B2/70—Load-bearing walls of framework or pillarwork; Walls incorporating load-bearing elongated members with elongated members of wood
- E04B2/706—Load-bearing walls of framework or pillarwork; Walls incorporating load-bearing elongated members with elongated members of wood with supporting function
- E04B2/707—Load-bearing walls of framework or pillarwork; Walls incorporating load-bearing elongated members with elongated members of wood with supporting function obturation by means of panels
Definitions
- This invention relates to walls and partitions for buildings and is directed towards the construction of walls and partitions for buildings at low cost and greater speed than is possible in building by traditional methods.
- the primary object of this invention is to provide wallsand partitions between posts or other frame members having holes in the faces therein at intervals by the use of slabs having grooves at both sides, dowel bars being arranged in the grooves between adjacent slabs and projecting into the holes in the frame members.
- Another object is to provide such dowel bars aforesaid slightly longer than the distances between the faces of frame members so that they be inserted in position by deflecting them and snapping the ends into the holes in the frame members.
- the partitions may be in the form of vertical partitions to form rooms or horizontal partitions such as floors or ceilings.
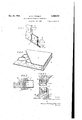
- Fig. 1 shows in perspective a portion of an external wall of a building constructed in one manner according to the invention
- Fig. 2 shows in perspective a portion of an internal partition
- Fig. 3 shows in vertical section the connection of a partition to a door frame
- Fig. 4 shows a broken vertical section through an internal partition
- Fig. 5 shows an elevation, viewed from inside the building, of an external slab wall with separate internal and external slabs
- Fig. 6 is a sectional plan view of the structure shown in Fig. 5.
- Fig. 7 is part of a vertical section, to enlarged scale taken upon the line XX of Fig. 6.
- the wall consists of hollow slabs A arranged between vertical frame members or posts 3.
- the slabs consist of inner and outer sheets 0, D respectively 1 of suitable material such as asbestos cement for the sheets C and plaster board for the sheets D connected to timber frame members E grooved at top and bottom. 7
- the posts B have shallow blind holes F in the sides thereof at spaced intervals.
- Dowel rods G- are housed in the grooves in the members E of the slabs A. These dowel rods G areslightly longer than the distance between the posts a and are u' 2 Claims. (Cl. 20-4) of timber or like material which can be bent sufficiently to enable them to be snapped into the blind holes F in the posts 3 or to be inserted in any other manner.
- the bottom slabs rest upon a timber plate H resting upon the floor or concrete surface.
- the internal partitions consist of plaster board sheets K secured to timber grooved frame members E and] stiffened by rings L made from waste'wood veneer.
- the frame members E of the slabs A present grooves on all four sides respectively of the slabs so that dowel rods G can be used for vertical connection to door frames M Fig. 3 and also to vertical post members as previously described for the external wall.
- Fig. 3 shows cover slips J for the joints between the slabs and door frames.
- Fig. 4 shows a bottom plate H, a corresponding top plate N, a cornice P and skirtings Q, R.
- the outer wall slabs are clamped between intermediate vertical members 21 of asbestos cement and vertical posts I by rods 28. These rods 28 extend through the members 21 and the timber and tubular steel cores 3 of post I. The rods 28 are also disposed in grooves in contiguous slabs. Clamping nuts 35 on the ends of the rods 28 bear on the posts I to hold the rods and slabs in place. Asbestos cement strips 29 are interposed between posts I and the members 26 of adjacent slabs.
- the inner wall is constructed of slabs 3
- the sheets 32 are secured to grooved frames 33 of wood.
- Dowel rods G of wood or other material pass through vertical timber battens 30 secured at intervals to the frame members 26 of the outer slabs.
- the rods G extend through slot shaped holes 34 in the battens 80. These holes enable the slabs-to be'ioggled in place since the holes provide a certain amount of play. Thus the assembling of the slabs is facilitated.
- a panel wall for a building comprising posts having holes in the sides thereof. slabs horizontal frame member each having grooves in its upper and lower end surfaces respectively, each slab including inner and outer sheets in spaced relation to each other dowel bars extending through said holes in the posts and each disposed in the grooves in contiguous slabs, vertical battens, internal slabs each having grooves in its upper and lower end surfaces respectively, and additional dowel bars disposed in the grooves in the contiguous internal slabs and also extending through said battens.
- a building structure including vertical and arranged in rectanguouter and inner wall slabs each havlower end surfaces lar relation, ing grooves in its upper and respectively.
- outer battens arranged in spaced relation with respect to each other and with respect to the vertical frame members between the latter, said outer wall slabs being arranged in the spaces respectively defined by said frame and battens in contact therewith, rods extending through said vertical frame and battens and each rod also disposed in the grooves in contiguous slabs, inner vertical battens laid against said horizontal frame members and disposed between adjacent inner wall slabs, and additional rods disposed in the grooves in contiguous inner wall slabs and also extending through said inner slabs.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Architecture (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Electromagnetism (AREA)
- Civil Engineering (AREA)
- Structural Engineering (AREA)
- Load-Bearing And Curtain Walls (AREA)
Description
Dec. 26, 1944.
W. G. HITCHINS WALL AND PARTITION F OR BUILDINGS 2 Sheets-Sheet 1 Filed Oct. 29, 1942 W44, MW
7 Attorneys I Dec. 26, 1944.
w. G. HlTCHlNS 2,366,109
, WALL AND PARTITION FOR BUILDINGS Filed Oct; 29, 1942 2 Sheets-Sheet 2 J il/ 28 I nveritor v 7 William Georgeffiichine g v B ,M AW
ttomeys Patented Dec. 26, 1944 2.366.109 WALL AND PARTITION FOR BUILDINGS William George Hitchins, London, England Application October 29, 1942. Serial No. 463,789
In Great Britain October 22, 1941 This invention relates to walls and partitions for buildings and is directed towards the construction of walls and partitions for buildings at low cost and greater speed than is possible in building by traditional methods.
The primary object of this invention is to provide wallsand partitions between posts or other frame members having holes in the faces therein at intervals by the use of slabs having grooves at both sides, dowel bars being arranged in the grooves between adjacent slabs and projecting into the holes in the frame members.
Another object is to provide such dowel bars aforesaid slightly longer than the distances between the faces of frame members so that they be inserted in position by deflecting them and snapping the ends into the holes in the frame members.
The partitions may be in the form of vertical partitions to form rooms or horizontal partitions such as floors or ceilings.
With the above and other objects in view the invention consists in the novel combination and processes set out in the claims which follow.
In the accompanying drawings which illus-' trat the invention in a diagrammatic manner,
Fig. 1 shows in perspective a portion of an external wall of a building constructed in one manner according to the invention,
Fig. 2 shows in perspective a portion of an internal partition,
Fig. 3 shows in vertical section the connection of a partition to a door frame,
Fig. 4 shows a broken vertical section through an internal partition,
Fig. 5 shows an elevation, viewed from inside the building, of an external slab wall with separate internal and external slabs,
Fig. 6 is a sectional plan view of the structure shown in Fig. 5.
Fig. 7 is part of a vertical section, to enlarged scale taken upon the line XX of Fig. 6.
Referring first to Fig. 1 of the drawings the wall consists of hollow slabs A arranged between vertical frame members or posts 3. The slabs consist of inner and outer sheets 0, D respectively 1 of suitable material such as asbestos cement for the sheets C and plaster board for the sheets D connected to timber frame members E grooved at top and bottom. 7
The posts B have shallow blind holes F in the sides thereof at spaced intervals. Dowel rods G- are housed in the grooves in the members E of the slabs A. These dowel rods G areslightly longer than the distance between the posts a and are u' 2 Claims. (Cl. 20-4) of timber or like material which can be bent sufficiently to enable them to be snapped into the blind holes F in the posts 3 or to be inserted in any other manner.
The bottom slabs rest upon a timber plate H resting upon the floor or concrete surface.
The vertical joints between the slabs and posts and intermediate slabs are made weatherproof by cover fillets J.
Referring next to Figs. 2-4 the internal partitions consist of plaster board sheets K secured to timber grooved frame members E and] stiffened by rings L made from waste'wood veneer. The
rings L are arranged between the sheets K are secured thereto.
The frame members E of the slabs A present grooves on all four sides respectively of the slabs so that dowel rods G can be used for vertical connection to door frames M Fig. 3 and also to vertical post members as previously described for the external wall.
Fig. 3 shows cover slips J for the joints between the slabs and door frames.
Fig. 4 shows a bottom plate H, a corresponding top plate N, a cornice P and skirtings Q, R.
Referring now to Figs. 5 to '7, inclusive-it will beapparent the outer wall slabs each consist of inner and outer sheets 25 of asbestos cement secured to horizontal timber frame members 28.
and
The outer wall slabs are clamped between intermediate vertical members 21 of asbestos cement and vertical posts I by rods 28. These rods 28 extend through the members 21 and the timber and tubular steel cores 3 of post I. The rods 28 are also disposed in grooves in contiguous slabs. Clamping nuts 35 on the ends of the rods 28 bear on the posts I to hold the rods and slabs in place. Asbestos cement strips 29 are interposed between posts I and the members 26 of adjacent slabs.
The inner wall is constructed of slabs 3| having panels or sheets 32 of plaster board covered with finishing material, such as wood veneer for the inner surface. The sheets 32 are secured to grooved frames 33 of wood. Dowel rods G of wood or other material pass through vertical timber battens 30 secured at intervals to the frame members 26 of the outer slabs. The rods G extend through slot shaped holes 34 in the battens 80. These holes enable the slabs-to be'ioggled in place since the holes provide a certain amount of play. Thus the assembling of the slabs is facilitated. I
I claim:
1. A panel wall for a building comprising posts having holes in the sides thereof. slabs horizontal frame member each having grooves in its upper and lower end surfaces respectively, each slab including inner and outer sheets in spaced relation to each other dowel bars extending through said holes in the posts and each disposed in the grooves in contiguous slabs, vertical battens, internal slabs each having grooves in its upper and lower end surfaces respectively, and additional dowel bars disposed in the grooves in the contiguous internal slabs and also extending through said battens.
2. A building structure including vertical and arranged in rectanguouter and inner wall slabs each havlower end surfaces lar relation, ing grooves in its upper and respectively. outer battens arranged in spaced relation with respect to each other and with respect to the vertical frame members between the latter, said outer wall slabs being arranged in the spaces respectively defined by said frame and battens in contact therewith, rods extending through said vertical frame and battens and each rod also disposed in the grooves in contiguous slabs, inner vertical battens laid against said horizontal frame members and disposed between adjacent inner wall slabs, and additional rods disposed in the grooves in contiguous inner wall slabs and also extending through said inner slabs.
WILLIAM GEORGE HITCHINS.
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| GB2366109X | 1941-10-22 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| US2366109A true US2366109A (en) | 1944-12-26 |
Family
ID=10904840
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US463789A Expired - Lifetime US2366109A (en) | 1941-10-22 | 1942-10-29 | Wall and partition for buildings |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US2366109A (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE976077C (en) * | 1953-04-18 | 1963-02-14 | Willibald Hartlmaier | Spacer for tile components |
-
1942
- 1942-10-29 US US463789A patent/US2366109A/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE976077C (en) * | 1953-04-18 | 1963-02-14 | Willibald Hartlmaier | Spacer for tile components |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US3305982A (en) | Interlocking block building construction | |
| US3256652A (en) | Building of assembled box-shaped elements | |
| US3309826A (en) | Resiliently mounted dry wall partition for building structures | |
| US2191804A (en) | Building construction unit | |
| US2198466A (en) | Siding for buildings | |
| US3339327A (en) | Assembly with prefabricated wall elements | |
| US1785067A (en) | Building | |
| US2795305A (en) | Wall construction | |
| GB2172621A (en) | Supporting structure for cladding panels | |
| US3149437A (en) | Building construction | |
| DK165645C (en) | Vertical or horizontal wall (partition, outer wall, floor or ceiling) consisting of wall panels assembled with spring and groove and with galvanized sheet metal structural beams, and a method for making them | |
| US1963410A (en) | Building unit | |
| US1671505A (en) | Toy building | |
| US2134894A (en) | Wall construction | |
| US2366109A (en) | Wall and partition for buildings | |
| US1757763A (en) | Interlocking-unit construction | |
| US1899454A (en) | Building construction | |
| US1563598A (en) | Building construction | |
| US2148575A (en) | Prefabricated building and building construction | |
| US1284758A (en) | Metallic building construction. | |
| US2143420A (en) | Building construction | |
| US1715587A (en) | Building unit | |
| GB589804A (en) | New or improved fireproof floor, ceiling or wall construction | |
| ES489310A0 (en) | PROCEDURE TO BUILD BUILDINGS WITH FLOORS, TWO FORM BY BEAMS-PLATES. | |
| US1851452A (en) | Trellis for building construction |