KR101348742B1 - 반도체 장치 - Google Patents
반도체 장치 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR101348742B1 KR101348742B1 KR1020070011236A KR20070011236A KR101348742B1 KR 101348742 B1 KR101348742 B1 KR 101348742B1 KR 1020070011236 A KR1020070011236 A KR 1020070011236A KR 20070011236 A KR20070011236 A KR 20070011236A KR 101348742 B1 KR101348742 B1 KR 101348742B1
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- plate
- communication
- silicon interposer
- shaped member
- chip
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B17/00—Surgical instruments, devices or methods, e.g. tourniquets
- A61B17/30—Surgical pincettes without pivotal connections
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/73—Means for bonding being of different types provided for in two or more of groups H01L24/10, H01L24/18, H01L24/26, H01L24/34, H01L24/42, H01L24/50, H01L24/63, H01L24/71
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B17/00—Surgical instruments, devices or methods, e.g. tourniquets
- A61B17/04—Surgical instruments, devices or methods, e.g. tourniquets for suturing wounds; Holders or packages for needles or suture materials
- A61B17/0482—Needle or suture guides
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B17/00—Surgical instruments, devices or methods, e.g. tourniquets
- A61B17/04—Surgical instruments, devices or methods, e.g. tourniquets for suturing wounds; Holders or packages for needles or suture materials
- A61B17/06—Needles ; Sutures; Needle-suture combinations; Holders or packages for needles or suture materials
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F9/00—Methods or devices for treatment of the eyes; Devices for putting-in contact lenses; Devices to correct squinting; Apparatus to guide the blind; Protective devices for the eyes, carried on the body or in the hand
- A61F9/007—Methods or devices for eye surgery
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L23/00—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices
- H01L23/48—Arrangements for conducting electric current to or from the solid state body in operation, e.g. leads, terminal arrangements ; Selection of materials therefor
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L23/00—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices
- H01L23/52—Arrangements for conducting electric current within the device in operation from one component to another, i.e. interconnections, e.g. wires, lead frames
- H01L23/538—Arrangements for conducting electric current within the device in operation from one component to another, i.e. interconnections, e.g. wires, lead frames the interconnection structure between a plurality of semiconductor chips being formed on, or in, insulating substrates
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L23/00—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices
- H01L23/52—Arrangements for conducting electric current within the device in operation from one component to another, i.e. interconnections, e.g. wires, lead frames
- H01L23/538—Arrangements for conducting electric current within the device in operation from one component to another, i.e. interconnections, e.g. wires, lead frames the interconnection structure between a plurality of semiconductor chips being formed on, or in, insulating substrates
- H01L23/5385—Assembly of a plurality of insulating substrates
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L25/00—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof
- H01L25/03—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof all the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/00, or in a single subclass of H10K, H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes
- H01L25/04—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof all the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/00, or in a single subclass of H10K, H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes the devices not having separate containers
- H01L25/065—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof all the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/00, or in a single subclass of H10K, H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes the devices not having separate containers the devices being of a type provided for in group H01L27/00
- H01L25/0652—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof all the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/00, or in a single subclass of H10K, H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes the devices not having separate containers the devices being of a type provided for in group H01L27/00 the devices being arranged next and on each other, i.e. mixed assemblies
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L25/00—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof
- H01L25/03—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof all the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/00, or in a single subclass of H10K, H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes
- H01L25/04—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof all the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/00, or in a single subclass of H10K, H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes the devices not having separate containers
- H01L25/065—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof all the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/00, or in a single subclass of H10K, H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes the devices not having separate containers the devices being of a type provided for in group H01L27/00
- H01L25/0657—Stacked arrangements of devices
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B17/00—Surgical instruments, devices or methods, e.g. tourniquets
- A61B2017/00969—Surgical instruments, devices or methods, e.g. tourniquets used for transplantation
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/10—Bump connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/15—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/16—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process of an individual bump connector
- H01L2224/161—Disposition
- H01L2224/16151—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive
- H01L2224/16221—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked
- H01L2224/16225—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being non-metallic, e.g. insulating substrate with or without metallisation
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2225/00—Details relating to assemblies covered by the group H01L25/00 but not provided for in its subgroups
- H01L2225/03—All the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/648 and H10K99/00
- H01L2225/04—All the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/648 and H10K99/00 the devices not having separate containers
- H01L2225/065—All the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/648 and H10K99/00 the devices not having separate containers the devices being of a type provided for in group H01L27/00
- H01L2225/06503—Stacked arrangements of devices
- H01L2225/06517—Bump or bump-like direct electrical connections from device to substrate
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2225/00—Details relating to assemblies covered by the group H01L25/00 but not provided for in its subgroups
- H01L2225/03—All the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/648 and H10K99/00
- H01L2225/04—All the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/648 and H10K99/00 the devices not having separate containers
- H01L2225/065—All the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/648 and H10K99/00 the devices not having separate containers the devices being of a type provided for in group H01L27/00
- H01L2225/06503—Stacked arrangements of devices
- H01L2225/06527—Special adaptation of electrical connections, e.g. rewiring, engineering changes, pressure contacts, layout
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2225/00—Details relating to assemblies covered by the group H01L25/00 but not provided for in its subgroups
- H01L2225/03—All the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/648 and H10K99/00
- H01L2225/04—All the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/648 and H10K99/00 the devices not having separate containers
- H01L2225/065—All the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/648 and H10K99/00 the devices not having separate containers the devices being of a type provided for in group H01L27/00
- H01L2225/06503—Stacked arrangements of devices
- H01L2225/06572—Auxiliary carrier between devices, the carrier having an electrical connection structure
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L23/00—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices
- H01L23/28—Encapsulations, e.g. encapsulating layers, coatings, e.g. for protection
- H01L23/31—Encapsulations, e.g. encapsulating layers, coatings, e.g. for protection characterised by the arrangement or shape
- H01L23/3107—Encapsulations, e.g. encapsulating layers, coatings, e.g. for protection characterised by the arrangement or shape the device being completely enclosed
- H01L23/3121—Encapsulations, e.g. encapsulating layers, coatings, e.g. for protection characterised by the arrangement or shape the device being completely enclosed a substrate forming part of the encapsulation
- H01L23/3128—Encapsulations, e.g. encapsulating layers, coatings, e.g. for protection characterised by the arrangement or shape the device being completely enclosed a substrate forming part of the encapsulation the substrate having spherical bumps for external connection
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01005—Boron [B]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01006—Carbon [C]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01013—Aluminum [Al]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01019—Potassium [K]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01023—Vanadium [V]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01033—Arsenic [As]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01074—Tungsten [W]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01082—Lead [Pb]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/15—Details of package parts other than the semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/151—Die mounting substrate
- H01L2924/153—Connection portion
- H01L2924/1531—Connection portion the connection portion being formed only on the surface of the substrate opposite to the die mounting surface
- H01L2924/15311—Connection portion the connection portion being formed only on the surface of the substrate opposite to the die mounting surface being a ball array, e.g. BGA
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/15—Details of package parts other than the semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/151—Die mounting substrate
- H01L2924/156—Material
- H01L2924/157—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron [B], silicon [Si], germanium [Ge], arsenic [As], antimony [Sb], tellurium [Te] and polonium [Po], and alloys thereof
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/19—Details of hybrid assemblies other than the semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/191—Disposition
- H01L2924/19101—Disposition of discrete passive components
- H01L2924/19107—Disposition of discrete passive components off-chip wires
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Surgery (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Ophthalmology & Optometry (AREA)
- Vascular Medicine (AREA)
- Semiconductor Integrated Circuits (AREA)
- Die Bonding (AREA)
Abstract
간단하고 또한 싼 값(安價)으로 제조를 할 수 있으며, 적은 소비 전력(電力)으로 통신할 수 있는 반도체 장치를 실현하는 것을 과제로 한다.
본 발명에서는, 실리콘 인터포저(silicon interposer)(101)의 표면(102)에 통신 칩(105)과 평판(平板)(121-1)을 형성한다. 실리콘 인터포저(201)에도 마찬가지로, 그 표면(202)에 통신 칩(205)과 평판(221-1)을 형성한다. 2개의 실리콘 인터포저(101, 201)를, 이면(103, 203)이 대향하도록 해서 배치하고, 평판(121-1, 221-1)의 정전 유도(靜電誘導)에 의해, 통신 칩(105, 205) 사이에서 통신을 행한다.
실리콘 인터포저, 표면, 이면, 범프, 통신 칩, 전극.
Description
도 1은 종래의 멀티 칩 모듈의 구성을 도시하는 단면도,
도 2는 종래의 실리콘 인터포저 사이의 통신을 설명하는 도면,
도 3은 본 발명을 적용한 멀티 칩 모듈에 적용하는 실리콘 인터포저의 구성을 설명하는 측단면도,
도 4는 본 발명을 적용한 멀티 칩 모듈의 단면의 구성을 도시하는 측단면도,
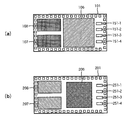
도 5는 실리콘 인터포저의 평면의 구성을 도시하는 평면도,
도 6은 통신 칩의 구성을 도시하는 평면도,
도 7은 통신 칩 부근의 구성을 도시하는 측단면도,
도 8은 실리콘 인터포저를 조합한 상태의 구성을 도시하는 측단면도,
도 9는 체적 저항율을 설명하는 도면,
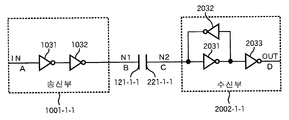
도 10은 통신부의 구성을 도시하는 회로도,
도 11은 도 10의 회로도의 동작을 설명하는 타이밍차트,
도 12는 다른 통신부의 구성을 도시하는 회로도,
도 13은 도 12의 통신부의 동작을 설명하는 타이밍차트,
도 14는 실리콘 인터포저의 평면의 구성을 도시하는 평면도,
도 15는 실리콘 인터포저를 조합한 상태를 설명하는 측단면도,
도 16은 실리콘 인터포저의 내부 구성을 도시하는 측단면도.
[부호의 설명]
101: 실리콘 인터포저, 102: 표면, 103: 이면, 104: 범프, 105: 통신 칩, 106, 107, 108: 칩, 201: 실리콘 인터포저, 202: 표면, 203: 이면, 204: 범프, 205: 통신 칩, 206, 207, 208: 칩, 301: 실리콘 인터포저, 302: 표면, 303: 이면, 304: 범프, 305: 통신 칩, 306, 307: 칩, 401: 실리콘 인터포저, 402: 표면, 403: 이면, 404: 범프, 405: 통신 칩, 406, 407: 칩.
본 발명은 반도체 장치에 관한 것으로서, 특히, 간단하고 또한 싼 값(安價)으로 제조할 수 있고, 적은 소비 전력(電力)으로 통신할 수 있도록 한 반도체 장치에 관한 것이다.
전자 기기(電子機器)의 보급에 따라서, 멀티 칩 모듈(MCM)을 적층(積層)한 멀티 칩 패키지, 혹은 시스템 인 패키지(SIP)를 저코스트로 실현하는 적층 기술, 칩간 배선 기술 등이 제안되고 있다.
도 1에는, 종래의 멀티 칩 모듈의 구조의 예를 도시하고 있다. 이 멀티 칩 모듈에서는, 실리콘 인터포저(silicon interposer)(1)와 실리콘 인터포저(21)가 조합(組合)되어 있다. 실리콘 인터포저(1)의 표면(2)에는, 칩(5)가 범프(4)를 거쳐서 장착(裝着; mount)되어 있다. 마찬가지로, 실리콘 인터포저(21)의 표면(22)에는, 칩(25)이 범프(24)를 거쳐서 장착되어 있다. 또, 실리콘 인터포저(1)의 표면(2)과 이면(3) 사이에는 관통 홀(6)이 형성되어 있고, 실리콘 인터포저(21)의 표면(22)과 이면(23) 사이에는 관통 홀(26)이 형성되어 있다. 그리고, 관통 홀(6)과 관통 홀(26)은, 범프(7)를 거쳐서 상호(相互) 접속되어 있다. 실리콘 인터포저(1) 위(上)의 칩(5)과, 실리콘 인터포저(21) 위의 칩(25)과의 사이의 통신은, 실리콘 인터포저(1) 위에 형성된 패턴, 실리콘 인터포저(1)의 관통 홀(6), 범프(7), 실리콘 인터포저(21)의 관통 홀(26)과, 실리콘 인터포저(21) 위의 패턴을 거쳐서 행해진다.
그렇지만, 관통 홀을 형성하려면 새로운 프로세스 개발이 필요하게 될 뿐만 아니라, 실리콘 인터포저의 이면에 전극 형성이 필요하게 되며, 또 미세(微細)한 관통 홀의 형성은 곤란하다는 등의 과제가 있다.
그래서, 예를 들면 도 2의 (a)에 도시되는 바와 같이, 정전 용량 결합(靜電容量結合)을 이용하여 통신을 행하는 것이 알려져 있다(예를 들면, 비특허 문헌 1). 도 2의 (a)의 예에서는, 실리콘 인터포저(1)의 표면(2)(칩(5)이 장착되어 있는 면(面))에 전극(41)이 형성되고, 마찬가지로 인터포저(21)의 표면(22)(칩(25)이 장착되어 있는 면)에 전극(51)이 형성되고, 전극(41)과 전극(51)이 대향하도록 실리콘 인터포저(1)의 표면(2)과 실리콘 인터포저(21)의 표면(22)이 배치되어 있다. 실리콘 인터포저(1)의 표면(2) 위의 칩(5)과 실리콘 인터포저(21)의 표면(22) 위의 칩(25)은 각각, 전극(41)과 전극(51)의 정전 유도(靜電誘導)를 이용한 통신로(通信路)를 거쳐서 통신을 행한다.
[비특허 문헌 1] 「닛케이 일렉트로닉스」 2005년 10월 10일 발행, p. 92-99
그렇지만, 도 2의 (a)에 도시되는 바와 같이, 전극(41, 51)을 대향해서 배치하여 무선(無線) 통신을 행하는 것이면, 예를 들면 도 2의 (b)에 도시되는 바와 같이, 실리콘 인터포저(1)의 표면(2)과 실리콘 인터포저(21)의 표면(22)과의 사이에 범프(61)를 배치하고, 이 범프(61)를 거쳐서 통신을 행하도록 한 쪽이, 보다 싼 값으로 제조가 용이하게 된다.
본 발명은, 이와 같은 상황을 감안해서 이루어진 것이며, 간단하고 또한 싼 값으로 제조할 수 있으며, 적은 소비 전력으로 통신할 수 있는 반도체 장치를 실현하는 것이다.
본 발명의 측면은, 고저항의 소재(素材)로 이루어지는 판모양 부재(板狀部材)로서, 한쪽 면에 회로가 형성된 제1 판모양 부재와, 고저항의 소재로 이루어지는 판모양 부재로서, 한쪽 면에 회로가 형성된 제2 판모양 부재와, 상기 제1 판모양 부재의 상기 회로가 형성된 면에 배치된 통신용 안테나로서의 복수(複數)의 제1 평판(平板)과, 상기 제1 판모양 부재의 상기 회로가 형성된 면에 배치된, 상기 제1 평판을 거쳐서 통신하는 제1 통신부와, 상기 제2 판모양 부재의 상기 회로가 형성된 면에 배치된 통신용 안테나로서의 복수의 제2 평판과, 상기 제2 판모양 부재의 상기 회로가 형성된 면에 배치된, 상기 제2 평판을 거쳐서 통신하는 제2 통신부를 구비하고, 상기 제1 판모양 부재와 상기 제2 판모양 부재가, 각각의 상기 회로가 형성되어 있지 않은 쪽의 면이 대향하도록 배치된 반도체 장치이다.
상기 제1 판모양 부재는, 전력의 공급을 받는 본딩 와이어를 가지고, 상기 제2 판모양 부재는, 전력의 공급을 받는 범프를 가질 수가 있다.
상기 제1 판모양 부재와 상기 제2 판모양 부재는, 실리콘 인터포저이며, 그 체적 저항(體積抵抗)은, 1㏀㎝ 이상으로 할 수가 있다.
상기 제1 판모양 부재와 상기 제2 판모양 부재로 이루어지는 조합을 적어도 2조(組; pair) 구비하고, 한쪽 조의 상기 제1 판모양 부재와 상기 제2 판모양 부재 중의 한쪽의 상기 회로가 형성된 면과, 다른쪽 조의 상기 제1 판모양 부재와 상기 제2 판모양 부재 중의 한쪽의 상기 회로가 형성된 면은, 상호 대향하도록 배치되고, 양자(兩者) 사이에는 통신용 범프와 전력 공급용 범프를 설치(設; provide)할 수가 있다.
본 발명의 측면에 있어서는, 회로가 형성된 면에 통신용 안테나로서의 복수의 제1 평판이 배치된 제1 판모양 부재와, 회로가 형성된 면에 통신용 안테나로서의 복수의 제2 평판이 배치된 제2 판모양 부재가, 각각의 회로가 형성되어 있지 않은 쪽의 면이 대향하도록 배치된다. 제1 판모양 부재와 제2 판모양 부재가 사이에 개재(介在; interpose)된 상태의 제1 평판과 제2 평판에 의한 정전 유도를 이용해서, 제1 판모양 부재의 제1 통신부와 제2 판모양 부재의 제2 통신부와의 사이에서 통신이 행해진다.
[발명을 실시하기 위한 최량의 형태]
이하에 본 발명의 실시형태를 설명하겠지만, 본 발명의 구성 요건과 명세서 또는 도면에 기재된 실시형태와의 대응 관계를 예시하면, 다음과 같이 된다. 이 기재는, 본 발명을 서포트하는 실시형태가, 명세서 또는 도면에 기재되어 있는 것을 확인하기 위한 것이다. 따라서, 명세서 또는 도면 중(中)에는 기재되어 있지만, 본 발명의 구성 요건에 대응하는 실시형태로서 여기에는 기재되어 있지 않은 실시형태가 있었다고 해도, 그것은, 그 실시형태가, 그 구성 요건에 대응하는 것이 아닌 것을 의미하는 것은 아니다. 역(逆)으로, 실시형태가 구성 요건에 대응하는 것으로서 여기에 기재되어 있었다고 해도, 그것은, 그 실시형태가, 그 구성 요건 이외의 구성 요건에는 대응하지 않는 것인 것을 의미하는 것도 아니다.
본 발명의 측면은, 고저항의 소재로 이루어지는 판모양 부재로서, 한쪽 면에 회로(예를 들면, 도 4의 칩(106, 107))가 형성된 제1 판모양 부재(예를 들면, 도 4의 실리콘 인터포저(101))와, 고저항의 소재로 이루어지는 판모양 부재로서, 한쪽 면에 회로(예를 들면, 도 4의 칩(206, 207))가 형성된 제2 판모양 부재(예를 들면, 도 4의 실리콘 인터포저(201))와, 상기 제1 판모양 부재의 상기 회로가 형성된 면(예를 들면, 도 4의 표면(102))에 배치된 통신용 안테나로서의 복수의 제1 평판(예 를 들면, 도 8의 평판(121-1))과, 상기 제1 판모양 부재의 상기 회로가 형성된 면에 배치된, 상기 제1 평판을 거쳐서 통신하는 제1 통신부(예를 들면, 도 10의 송신부(1001-1-1))와, 상기 제2 판모양 부재의 상기 회로가 형성된 면에 배치된 통신용 안테나로서의 복수의 제2 평판(예를 들면, 도 8의 평판(221-1))과, 상기 제2 판모양 부재의 상기 회로가 형성된 면에 배치된, 상기 제2 평판을 거쳐서 통신하는 제2 통신부(예를 들면, 도 10의 수신부(2002-1-1))를 구비하고, 상기 제1 판모양 부재와 상기 제2 판모양 부재가, 각각의 상기 회로가 형성되어 있지 않은 쪽의 면(예를 들면, 도 4의 이면(103, 203))이 대향하도록 배치된 반도체 장치이다.
상기 제1 판모양 부재는, 전력의 공급을 받는 본딩 와이어(예를 들면, 도 4의 본딩 와이어(504))를 가지고, 상기 제2 판모양 부재는, 전력의 공급을 받는 범프(예를 들면, 도 4의 범프(505))를 가질 수가 있다.
상기 제1 판모양 부재와 상기 제2 판모양 부재로 이루어지는 조합을 적어도 2조(예를 들면, 도 4의 실리콘 인터포저(101, 201)의 조와, 실리콘 인터포저 (301, 401)의 조) 구비하고, 한쪽 조(예를 들면, 도 4의 실리콘 인터포저(101, 201)의 조)의 상기 제1 판모양 부재와 상기 제2 판모양 부재 중의 한쪽의 상기 회로가 형성된 면(예를 들면, 도 4의 실리콘 인터포저(201)의 표면(202))과, 다른쪽 조(예를 들면, 도 4의 실리콘 인터포저(301, 401)의 조)의 상기 제1 판모양 부재와 상기 제2 판모양 부재 중의 한쪽의 상기 회로가 형성된 면(예를 들면, 도 4의 실리콘 인터포저(301)의 표면(302))은, 상호 대향하도록 배치되고, 양자 사이에는 통신용 범프와 전력 공급용 범프(예를 들면, 도 4의 범프(505))를 설치할 수가 있다.
이하, 도면을 참조하여 본 발명의 실시형태에 대해서 설명한다.
도 3에는, 본 발명이 적용되는 멀티 칩 모듈에 실장(組入; incorporate)되는 고저항의 소재로 이루어지는 판모양 부재로서의 실리콘 인터포저의 구성을 도시하고 있다. 실리콘 인터포저(101)에는, 그 표면(102)에 복수의 범프(104)를 거쳐서 통신 칩(105)이 배치되어 있음과 동시에, 칩(106, 107)이 배치되어 있다. 통신 칩(105)은, 그의 상세(詳細)는 도 6 내지 도 8을 참조하여 후술하겠지만, 다른(他) 실리콘 인터포저와의 사이에서의 통신을 행한다. 칩(106, 107)은, 예를 들면 CPU(Central Processing Unit), 혹은 메모리 등에 의해 구성되고, 각각 미리 정해진 소정(所定)의 기능에 관한 처리를 실행한다. 실리콘 인터포저(101)의 표면(102)에는, 도시(圖示)는 하지 않지만, 배선 패턴이 형성되어 있다. 이것에 대해서, 표면(102)의 반대측의 이면(103)에는, 칩은 배치되어 있지 않다.
실리콘 인터포저(201)도 마찬가지로, 표면(202)에 통신 칩(205), 칩(206, 207)이 복수의 범프(204)를 거쳐서 장착되어 있다. 실리콘 인터포저(201)의 이면(203)에는 칩은 장착되어 있지 않다.
실리콘 인터포저(301)의 표면(302)에는, 통신 칩(305), 칩(306, 307)이 복수의 범프(304)를 거쳐서 배치되어 있다. 실리콘 인터포저(301)의 이면(303)에는 칩은 배치되어 있지 않다.
마찬가지로, 실리콘 인터포저(401)의 표면(402)에는, 통신 칩(405), 칩(406, 407)이 복수의 범프(404)를 거쳐서 장착되어 있다. 실리콘 인터포저(401)의 이면(403)에는 칩은 장착되어 있지 않다.
칩(206, 207, 306, 307, 406, 407)도 칩(106, 107)과 마찬가지로, 통신 이외의 소정의 기능을 실행하는 칩이다.
도 4에는, 실리콘 인터포저(101 내지 401)를 조합해서 제조한 멀티 칩 모듈의 구성을 도시하고 있다. 이 멀티 칩 모듈(501)에서는, 실리콘 인터포저(101)와 실리콘 인터포저(201)가 조로 되고, 실리콘 인터포저(301)와 실리콘 인터포저(401)가 조로 되어 있다.
즉, 실리콘 인터포저(101)와 실리콘 인터포저(201)는, 각각 통신 칩(105)과 통신 칩(205)의 안테나로서의 평판(도 6을 참조하여 후술한다)이, 각각 대향하도록, 또한, 각각의 이면(103)과 이면(203)이 대향하도록 배치된다. 마찬가지로, 이 실리콘 인터포저(301)와 실리콘 인터포저(401)는, 각각의 이면(303)과 이면(403)이 대향하도록, 또한, 통신 칩(305)의 평판과 통신 칩(405)의 평판이, 각각 대향하도록 배치된다.
기판(502)의 표면(503)에는 배선 패턴이 형성되어 있음과 동시에, 필요에 따라서 각종 칩도 장착되어 있다(모두 도시하지 않음). 또, 표면(503)은, 본딩 와이어(506)를 거쳐서 실리콘 인터포저(301)의 표면(302)에 접속되어 있다. 실리콘 인터포저(101)의 표면(102)도, 본딩 와이어(504)를 거쳐서 기판(502)의 표면(503)과 접속되어 있다. 실리콘 인터포저(401)의 표면(402)은, 복수의 범프(404)를 거쳐서 기판(502)의 표면(503)에 접속되어 있다. 또, 실리콘 인터포저(301)의 표면(302)과 실리콘 인터포저(201)의 표면(202)은, 복수의 범프(505)에 의해 접속되어 있다.
이와 같이 구성함으로써, 기판(502)의 표면(503)에 형성되어 있는 배선 패턴 으로부터, 범프(404) 중의 소정의 것을 거쳐서 실리콘 인터포저(401)의 표면(402) 위에 배치되어 있는 통신 칩(405), 칩(406, 407)에 필요한 전력이 공급된다. 또 마찬가지로, 소정의 다른 범프(404)를 거쳐서, 기판(502)의 표면(503)에 형성된 소정의 배선 패턴과 실리콘 인터포저(401) 위의 통신 칩(405), 칩(406, 407)과의 사이에서 신호의 수수(授受; exchange)가 행해진다.
실리콘 인터포저(301) 위의 통신 칩(305), 칩(306, 307)에는, 기판(502)의 표면(503)의 배선 패턴으로부터 본딩 와이어(506)를 거쳐서 필요한 전력이 공급된다. 실리콘 인터포저(301) 위의 칩(306, 307)은, 통신 칩(305)과 통신 칩(405)을 거쳐서, 실리콘 인터포저(401) 위의 칩(406, 407)과 통신한다.
실리콘 인터포저(201) 위의 통신 칩(205), 칩(206, 207)에는, 기판(500) 표면(503)의 배선 패턴으로부터 본딩 와이어(506), 실리콘 인터포저(301) 위의 배선 패턴, 소정의 범프(505), 실리콘 인터포저(201)의 표면(202)의 배선 패턴, 소정의 범프(204)를 거쳐서 전력이 공급된다. 칩(206, 207)은, 소정의 범프(204), 실리콘 인터포저(201) 위의 배선 패턴, 소정의 범프(505), 실리콘 인터포저(301) 위의 배선 패턴, 소정의 범프(304)를 거쳐서 실리콘 인터포저(301) 위의 칩(306, 307)과 통신한다.
실리콘 인터포저(101)의 통신 칩(105), 칩(106, 107)에는, 기판(502)의 표면(503) 위의 배선 패턴으로부터 본딩 와이어(504), 실리콘 인터포저(101) 위의 배선 패턴, 소정의 범프(104)를 거쳐서 필요한 전력이 공급된다. 칩(106, 107)과 칩(206, 207)과의 사이의 통신은, 통신 칩(105, 205)을 거쳐서 행해진다.
직접 인접(隣接)해 있지 않은 실리콘 인터포저 사이의 통신은, 직접 인접하는 실리콘 인터포저 사이의 통신을 순차(順次) 거침으로써 행해진다. 예를 들면, 칩(106, 107)과 칩(306, 307)과의 사이의 통신은, 통신 칩(105), 통신 칩(205), 범프(505)를 거쳐서 행해진다. 또, 칩(106, 107)과 칩(406, 407)과의 사이의 통신은, 통신 칩(105), 통신 칩(205), 범프(505), 통신 칩(305), 통신 칩(405)을 거쳐서 행해진다. 칩(106, 107)과 기판(502)의 표면(503) 위의 도시되지 않은 칩과의 통신은, 통신 칩(105), 통신 칩(205), 범프(505), 통신 칩(305), 통신 칩(405), 범프(404)를 거쳐서 행해진다.
도 5에는, 실리콘 인터포저(101)와 실리콘 인터포저(201)의 평면적 구성을 도시하고 있다. 실리콘 인터포저(101)는, 도 5의 (a)에 도시되는 바와 같이, 칩(106)의 왼쪽 위(左上)에 칩(108)이 배치되고, 칩(106)의 왼쪽 아래(左下) 측에 칩(107)이 배치되어 있다. 칩(106)의 우측의 영역 Q에는 통신 영역(111)이 형성되어 있다. 이 통신 영역(111)에는, 또 통신 칩(105-1 내지 105-4)이 배치되어 있다.
마찬가지로, 도 5의 (b)에 도시되는 바와 같이, 실리콘 인터포저(201) 위에서는, 칩(206)의 왼쪽 아래 측에 칩(207)이 배치되고, 왼쪽 위 측에 칩(208)이 배치되어 있다. 칩(206)의 우측의 영역 Q에는 통신 영역(211)이 형성되어 있고, 통신 영역(211)에는, 또 통신 칩(205-1 내지 205-4)이 배치되어 있다.
도시는 생략하지만, 실리콘 인터포저 (301, 401)도 마찬가지로 구성되어 있다.
도 6에는, 통신 칩(105-1 내지 105-4)의 평면적 구성을 확대해서 도시하고 있다. 통신 칩(105-1)에는, 그의 상측에 알루미늄 등의 금속으로 구성되는 안테나로서의 평판(121-1-1, 122-1-1)이 형성되어 있다. 평판(121-1-1, 122-1-1)은, 조로 되어 송신 또는 수신의 통신이 행해진다. 마찬가지로, 통신 칩(105-1)은, 평판(121-1-1, 122-1-1)의 왼쪽에서 오른쪽으로 순번대로, 또 평판(121-1-2, 122-1-2 내지 121-1-8, 122-1-8)을 가지고 있다. 또는 마찬가지로, 하측에는 왼쪽에서 오른쪽으로 순번대로, 평판(121-1-9, 122-1-9 내지 121-1-16, 122-1-16)을 가지고 있다(번호의 도시는 일부 생략되어 있다).
마찬가지로, 통신 칩(105-2)은 평판(121-2-1,1 22-2-1 내지 121-2-16, 122-2-16)을 가지고, 통신 칩(105-3)은, 평판(121-3-1, 122-3-1 내지 121-3-16, 122-3-16)을 가지고, 통신 칩(105-4)은, 평판(121-4-1, 122-4-1 내지 121-4-16,1 22-4-16)을 가지고 있다.
도 7에는, 통신 칩(105-1)의 단면 구성을 확대해서 도시하고 있다. 같은 도면(同圖)에 도시되는 바와 같이, 통신 칩(105-1)의 도면중 우측과 좌측에는, 범프(104)를 거쳐서 평판(121-1, 121-9)이 배치되어 있다. 또, 통신 칩(105-1)은, 범프(104)를 거쳐서 실리콘 인터포저(101) 위의 패드(131)와 접속되어 있다. 이 패드(131)는 또, 도시하지 않은 배선 패턴과 접속되어 있다.
실리콘 인터포저(101)의 평판(121-1)((121-1-1내지121-1-16))과, 실리콘 인터포저(201)의 평판(221-1)((221-1-1내지221-1-16))은, 도 8에 도시되는 바와 같이, 대응하는 것이 대향하도록 배치된다. 그 결과, 대향해서 배치되는 평판(121-1)과 평판(221-1) 사이에, 고저항의 재료로 구성되는 실리콘 인터포저(101, 201)가 개재하게 된다. 실리콘 인터포저(101, 201)는, 고저항 실리콘 기판이기 때문에 유전율(誘電率)이 높고, 평판(121-1, 221-1)으로 구성되는 콘덴서의 용량이, 도 2의 (a)에 도시되는 바와 같이 전극(41, 51)을 단순히 공기를 거쳐서 대향 배치하는 경우에 비해서, 지극히 큰 값으로 할 수가 있다. 그 결과, 평판(121-1, 221-1)의 면적을 작게 했다고 해도, 충분히 큰 정전 결합을 실현하는 것이 가능하게 된다.
실리콘 인터포저(101 내지 401)의 체적 저항율은, 구체적으로는, 1㏀㎝ 이상의 값으로 된다. 체적 저항율은, 예를 들면 도 9에 도시되는 바와 같이, 폭(幅)W, 두께(厚) t, 길이(長) L의 물질 중에 전류 I를 흐르게 했을 때, 거리 L의 양단(兩端)에 발생하는 전위차(電位差) V를 측정하는 것에 의해, 다음 식으로부터 구할 수가 있다.
체적 저항율=(V/I)×(W/L)×t …(1)
고저항의 실리콘 인터포저는, 실리콘은 본래(本來) 비도전(非導電) 부재이기 때문에 불순물을 실리콘에 도프(doping)하지 않음으로써 실현할 수가 있다.
통신 칩(105, 205, 305, 405)은 각각, 각 평판에 대응해서 송신부 또는 수신부의 적어도 한쪽으로 이루어지는 통신부를 가지고 있다. 즉, 송신용 평판에 대해서는 송신부가, 수신용 평판에 대해서는 수신부가, 각각 설치되어 있다. 대응하는 평판이 송신과 수신의 양쪽(良方)을 행하는 경우에는, 송신부와 수신부의 양쪽이 설치되어 있다. 통신 칩(105)과 통신 칩(205)은, 각각 송신용 평판에 대해서 수신용 평판이 대향하도록 배치된다. 예를 들면, 송신용 평판(121-1-1, 122-1-1)에 대해서 수신용 평판(221-1-1, 222-1-1)이 대향하도록 배치된 경우, 송신용 평판(121- 1-1, 122-1-1)에 대응하는 송신부(1001-1-1)와, 수신용 평판(221-1-1, 222-1-1)에 대응하는 수신부(2002-1-1)가, 도 10에 도시되는 바와 같이 접속된다.
송신부(1001-1-1)는, 인버터(1011 내지 1014)에 의해 구성되어 있다. 단자 IN으로부터 입력된 신호는, 인버터(1011, 1012, 1013)를 거쳐서 단자 N1로부터 평판(121-1-1)에 공급됨과 동시에, 인버터(1011, 1014)를 거쳐서 단자 N2로부터 평판(122-1-1)에 공급된다.
수신부(2002-1-1)의 입력 단자 N3, N4에는, 평판(221-1-1, 222-1-1)이 각각 접속되어 있다. 입력 단자 N3, N4는, 증폭기(增幅器; amplifier)(2013)의 입력 단자에 접속되어 있다. 입력 단자 N3과 N4 사이에는, 저항(2011, 2012)이 접속되어 있다. 저항(2011)과 저항(2012) 사이에는, 기준 전압 VREF가 공급되고 있다. 증폭기(2013)의 출력은, 히스테리시스 콤퍼레이터(Hysteresis Comparator)(2014)의 비반전(非反轉) 입력 단자와, 히스테리시스 콤퍼레이터(2016)의 반전(反轉) 입력 단자에 공급되고 있다. 콤퍼레이터(2014)의 반전 입력 단자에는, 기준 전압 VR1이 공급되고, 콤퍼레이터(2016)의 비반전 입력 단자에는 기준 전압 VR2가 공급되고 있다.
콤퍼레이터(2014)의 출력(노드 N5)은, 인버터(2015)를 거쳐서, NAND 회로(2019)와 함께 크로스 래치 회로를 구성하는 NAND 회로(2018)의 한쪽의 입력에 접속되어 있다. 콤퍼레이터(2016)의 출력(노드 N6)은, 인버터(2017)를 거쳐서 NAND 회로(2019)의 한쪽의 입력에 접속되어 있다. NAND 회로(2018)의 출력은 NAND 회로(2019)의 다른쪽의 입력에 접속되고, NAND 회로(2019)의 출력은 NAND 회로(2018) 의 다른쪽의 입력에 접속되어 있다.
송신부(1001-1-1)의 단자 IN에 신호(도 11 A)가 입력되면, 단자 N1(평판(121-1-1))에는, 인버터(1011, 1012, 1013)를 거쳐서, 단자 N2(평판(122-1-1))에는, 인버터(1011, 1014)를 거쳐서, 각각 역위상(逆位相)의 전압(도 11의 (b)의 파선(破線)으로 나타내어지는 전압과 실선(實線)으로 나타내어지는 전압)이 발생한다. 정전 유도에 의해 수신측의 평판(221-1-1, 222-1-1)(입력 단자 N3, N4)에는, 역위상의 전압이 발생한다(도 11의 (c)의 파선으로 나타내어지는 전압과 실선으로 나타내어지는 전압). 증폭기(2013)는, 이 정전 유도에 의해 공급된 신호를 증폭하고, 노드 VA에 출력한다(도 11의 (d)).
콤퍼레이터(2014)는, 증폭기(2013)로부터 입력된 신호의 레벨을 기준 전압 VR1과 비교하고, 기준 전압 VR1보다 큰 경우에는, 노드 N5에 정(正)의 펄스를 출력한다(도 11의 (e)). 마찬가지로, 콤퍼레이터(2016)는, 증폭기(2013)로부터 출력된 신호의 레벨을 기준 전압 VR2와 비교하고, 기준 전압 VR2보다 작은 경우에는, 노드 N6에 정(正)의 펄스를 출력한다(도 11의 (f). 노드 N5, N6의 출력이 각각 인버터(2015, 2017)에 의해 반전되고, 부(負)의 펄스가 입력될 때마다 출력을 반전하는 크로스 래치 회로에 의해 래치되고, 출력된다(도 11의 (g)).
이상에서는, 2조의 평판에서 신호를 수수하도록 했지만, 충분한 레벨의 신호가 얻어지는 경우에는, 도 12에 도시되는 바와 같이, 1조의 평판(121-1-1, 122-1-1)에서 신호를 수수할 수도 있다. 이 경우, 송신부(1001-1-1)는, 인버터(1031, 1032)로 구성되고, 단자 IN에 입력된 신호가, 인버터(1031, 1032)를 거쳐서 단자 N1에 접속되어 있는 평판(121-1-1)에 공급된다.
수신부(2002-1-1)는, 인버터(2031, 2032, 2033)에 의해 구성되고, 단자 N2에 접속되어 있는 평판(221-1-1)으로부터의 신호는, 인버터(2031, 2032)를 거쳐서 단자 OUT로부터 출력된다. 또, 인버터(2031)의 출력은, 인버터(2032)를 거쳐서 인버터(2031)의 입력에 귀환(歸還)된다.
송신부(1001-1-1)의 단자 IN에 신호(도 13의 (a))가 입력되면, 단자 N1(평판(121-1-1))에는, 인버터(1031, 1032)를 거쳐서 전압(도 13의 (b))이 발생한다. 정전 유도에 의해 수신측의 평판(221-1-1)(입력 단자 N2)에도 전압이 발생한다(도 13의 (c)). 단자 N2의 전압이, 인버터(2031)의 임계값(threshold value) Vth보다 커지면, 인버터(2031)의 출력이 반전하고, 인버터(2032)의 출력도 반전해서, 인버터(2031)의 입력의 변화를 가속(加速)한다. 인버터(2031)의 출력은 또, 인버터(2033)에 의해 반전되고, 단자 OUT로부터 출력된다(도 13의 (d)).
이상에서는, 실리콘 인터포저(101 내지 401) 위에 통신 칩(105 내지 405), 칩(106 내지 406, 107 내지 407)을 각각 탑재(搭載; mount)함으로써, 대응하는 회로를 형성하도록 했지만, 각 실리콘 인터포저(101 내지 401) 위에 직접 실장함으로써 대응하는 회로를 형성하도록 해도 좋다.
도 14에 도시되는 실시형태에서는, 실리콘 인터포저(101) 위에 통신 회로(151-1 내지 151-4)가 직접 실장함으로써 형성되어 있다. 마찬가지로, 실리콘 인터포저(201) 위에서도 통신 회로(251-1 내지 251-4)가 직접 실장함으로써 형성되어 있다.
이 경우, 실리콘 인터포저(101)와 실리콘 인터포저(201)를 조합하면, 도 15에 도시되는 바와 같이 된다. 이 경우에 있어서는, 실리콘 인터포저(101)의 표면(102) 위에 통신 회로(151-1 내지 151-4)에 대응하는 CMOS(Complementary Mental-Oxide Semiconductor) 회로(161)가 형성되어 있다. 다만, 이 경우에 있어서도, 평판(121-1)은, 도 8에서의 경우와 마찬가지로 형성되어 있다.
또, 실리콘 인터포저(201) 위의 표면(202)에도 통신 회로(251-1 내지 251-4)에 대응하는 CMOS 회로(261)가 형성되어 있다. 이 경우에 있어서도, 평판(221-1)은, 도 8에서의 경우와 마찬가지로, 실리콘 인터포저(201)의 표면(202) 위에 형성되어 있다.
따라서, 이 경우에 있어서도, 도 8에서의 경우와 마찬가지로 통신 처리를 행하는 것이 가능하게 된다.
도 16에는, 실리콘 인터포저의 통신 영역(111)의 내부의 단면(斷面) 구성의 예를 도시하고 있다(도 14나 도 15에 도시되는 실시형태에서의 CMOS 구조는 도시하지 않는다). P형 실리콘 벌크(silicon bulk)(1511) 위에는, 필드 산화막(1512)이 형성되어 있다. 필드 산화막(1512) 위에는, 폴리사이드(1513)와, 폴리사이드(1513)로부터 소정의 간격을 두고 떨어져서 폴리사이드(1514)가 형성되어 있다. 폴리사이드(1513, 1514) 사이의 용량은 전원(電源)의 안정화에 이용된다. 폴리사이드(1513)는, 컨택트(1515)에 의해 금속층(1516)에 접속되어 있다.
금속층(1516)과, 그 위에 산화막(1518)을 거쳐서 형성되어 있는 금속층(1519)은, 비어(via; 관통구멍)(1517)에 의해 접속되어 있다. 금속층(1519)과 그 위에 산화막(1520)을 거쳐서 형성되어 있는 금속층(1521)과는, 비어(1522)로 접속되어 있다. 금속층(1521) 위에는 산화막(1523)이 형성되고, 또 그 위에는, 보호막(1524)이 형성되어 있다. 보호막(1524)과 산화막(1523)에는, PAD 개구(開口)(1525)가 형성되어 있다.
이상에서는, 본 발명을 멀티 칩 모듈에 적용한 경우를 예로서 설명했지만, 본 발명은 그 밖의 반도체 장치에 적용하는 것도 가능하다.
또한, 본 발명의 실시형태는, 상술한 실시형태에 한정되는 것은 아니며, 본 발명의 요지(要旨)를 일탈(逸脫)하지 않는 범위에서 여러 가지 변경이 가능하다.
이상과 같이, 본 발명의 측면에 따르면, 반도체 장치를 실현할 수가 있다. 특히, 간단하고 또한 싼 값으로 제조할 수 있고, 적은 소비 전력으로 통신할 수 있는 반도체 장치를 실현할 수가 있다.
Claims (4)
- 고저항의 소재(素材)로 이루어지는 판모양 부재(板狀部材)로서, 한쪽 면(面)에 회로가 형성된 제1 판모양 부재와,고저항의 소재로 이루어지는 판모양 부재로서, 한쪽 면에 회로가 형성된 제2 판모양 부재와,상기 제1 판모양 부재의 상기 회로가 형성된 면에 배치된 통신용 안테나로서의 복수(複數)의 제1 평판과,상기 제1 판모양 부재의 상기 회로가 형성된 면에 배치된, 상기 제1 평판을 거쳐서 통신하는 제1 통신부와,상기 제2 판모양 부재의 상기 회로가 형성된 면에 배치된 통신용 안테나로서의 복수의 제2 평판과,상기 제2 판모양 부재의 상기 회로가 형성된 면에 배치된, 상기 제2 평판을 거쳐서 통신하는 제2 통신부에 의해 구성되는 복합 부재로서,상기 제 1 판모양 부재와 상기 제 2 판모양 부재가, 각각의 상기 회로가 형성되어 있지 않은 쪽의 면이 대향하도록 배치되어 구성되는 상기 복합 부재를 적어도 2조(組; pair) 구비하고,상기 제 1 판모양 부재에는, 상기 제 1 통신부에 전력을 공급하기 위한 본딩 와이어가 설치되어 있고,상기 2 조의 한쪽 조에서의 상기 제 1 판모양 부재와 다른쪽 조에서의 상기 제 2 판모양 부재가, 각각의 상기 회로가 형성되어 있는 쪽의 면이 대향하도록 배치되고,한쪽 조에서의 상기 제1 판모양 부재와 다른쪽 조에서의 상기 제 2 판모양 부재가 대향하는 면 사이에는, 다른쪽 조에서의 상기 제 2 통신부의 통신에 이용하는 범프가 설치되어 있고,상기 범프는, 다른쪽 조에서의 상기 제 2 통신부에 전력도 공급하는반도체 장치.
- 삭제
- 제1항에 있어서,상기 제1 판모양 부재와 상기 제2 판모양 부재는, 실리콘 인터포저이고, 그 체적 저항(體積抵抗)은, 1㏀㎝ 이상인반도체 장치.
- 삭제
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006031271A JP4725346B2 (ja) | 2006-02-08 | 2006-02-08 | 半導体装置 |
| JPJP-P-2006-00031271 | 2006-02-08 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20070080828A KR20070080828A (ko) | 2007-08-13 |
| KR101348742B1 true KR101348742B1 (ko) | 2014-01-08 |
Family
ID=37966491
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020070011236A KR101348742B1 (ko) | 2006-02-08 | 2007-02-02 | 반도체 장치 |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (2) | US7351068B2 (ko) |
| EP (1) | EP1818986A3 (ko) |
| JP (1) | JP4725346B2 (ko) |
| KR (1) | KR101348742B1 (ko) |
| CN (1) | CN100511670C (ko) |
| TW (1) | TW200805617A (ko) |
Families Citing this family (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US7462038B2 (en) * | 2007-02-20 | 2008-12-09 | Qimonda Ag | Interconnection structure and method of manufacturing the same |
| JP5216532B2 (ja) * | 2008-10-30 | 2013-06-19 | 株式会社日立製作所 | 半導体集積回路 |
| US8344503B2 (en) | 2008-11-25 | 2013-01-01 | Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. | 3-D circuits with integrated passive devices |
| JP5578797B2 (ja) * | 2009-03-13 | 2014-08-27 | ルネサスエレクトロニクス株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| JP5801531B2 (ja) * | 2009-10-16 | 2015-10-28 | ルネサスエレクトロニクス株式会社 | 半導体パッケージ及びその製造方法 |
| US8592973B2 (en) * | 2009-10-16 | 2013-11-26 | Stats Chippac Ltd. | Integrated circuit packaging system with package-on-package stacking and method of manufacture thereof |
| US20110168785A1 (en) * | 2010-01-14 | 2011-07-14 | Rfmarq, Inc. | System and Method To Embed A Wireless Communication Device Into Semiconductor Packages |
| ITTO20100697A1 (it) * | 2010-08-13 | 2012-02-14 | St Microelectronics Srl | Dispositivo elettronico con isolamento galvanico e procedimento per la fabbricazione di un dispositivo elettronico |
| US8491315B1 (en) * | 2011-11-29 | 2013-07-23 | Plastronics Socket Partners, Ltd. | Micro via adapter socket |
| US9627357B2 (en) | 2011-12-02 | 2017-04-18 | Intel Corporation | Stacked memory allowing variance in device interconnects |
| KR20130071884A (ko) | 2011-12-21 | 2013-07-01 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 다이 패키지 및 이를 포함하는 시스템 |
| US12068231B2 (en) * | 2014-05-24 | 2024-08-20 | Broadpak Corporation | 3D integrations and methods of making thereof |
| KR102618460B1 (ko) | 2019-03-26 | 2023-12-29 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 반도체 패키지 및 그 제조 방법 |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH08274124A (ja) * | 1995-03-30 | 1996-10-18 | Sharp Corp | 樹脂封止型半導体装置 |
| JP2004186497A (ja) * | 2002-12-04 | 2004-07-02 | Sony Corp | 半導体装置および半導体装置の製造方法 |
| JP2005203657A (ja) * | 2004-01-19 | 2005-07-28 | Atsushi Iwata | 半導体装置 |
Family Cites Families (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5200631A (en) * | 1991-08-06 | 1993-04-06 | International Business Machines Corporation | High speed optical interconnect |
| US5786979A (en) * | 1995-12-18 | 1998-07-28 | Douglass; Barry G. | High density inter-chip connections by electromagnetic coupling |
| JPH10320519A (ja) * | 1997-05-19 | 1998-12-04 | Rohm Co Ltd | Icカード通信システムにおける応答器 |
| JP3939429B2 (ja) * | 1998-04-02 | 2007-07-04 | 沖電気工業株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| US6988312B2 (en) * | 2001-10-31 | 2006-01-24 | Shinko Electric Industries Co., Ltd. | Method for producing multilayer circuit board for semiconductor device |
| JP4389471B2 (ja) * | 2003-05-19 | 2009-12-24 | パナソニック株式会社 | 電子回路の接続構造とその接続方法 |
| US7173442B2 (en) * | 2003-08-25 | 2007-02-06 | Delaware Capital Formation, Inc. | Integrated printed circuit board and test contactor for high speed semiconductor testing |
| TW200520201A (en) * | 2003-10-08 | 2005-06-16 | Kyocera Corp | High-frequency module and communication apparatus |
| JP4285309B2 (ja) * | 2004-04-13 | 2009-06-24 | パナソニック株式会社 | 電子回路モジュールの製造方法と多層電子回路モジュールおよびその製造方法 |
| US7248036B2 (en) * | 2004-05-27 | 2007-07-24 | Intel Corporation | Method and apparatus to probe bus signals using repeaters |
| WO2006011960A1 (en) * | 2004-06-25 | 2006-02-02 | Sun Microsystems, Inc. | Integrated circuit chip that supports through-chip electromagnetic communication |
| JP4403090B2 (ja) * | 2005-03-02 | 2010-01-20 | 日東電工株式会社 | 配線回路基板 |
| US8190086B2 (en) * | 2005-09-02 | 2012-05-29 | Nec Corporation | Transmission method, interface circuit, semiconductor device, semiconductor package, semiconductor module and memory module |
-
2006
- 2006-02-08 JP JP2006031271A patent/JP4725346B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2007
- 2007-01-26 US US11/627,527 patent/US7351068B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2007-02-01 TW TW096103713A patent/TW200805617A/zh not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2007-02-02 KR KR1020070011236A patent/KR101348742B1/ko not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2007-02-05 EP EP07101732A patent/EP1818986A3/en not_active Withdrawn
- 2007-02-08 CN CNB2007100028492A patent/CN100511670C/zh not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2008
- 2008-04-01 US US12/060,490 patent/US7578676B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH08274124A (ja) * | 1995-03-30 | 1996-10-18 | Sharp Corp | 樹脂封止型半導体装置 |
| JP2004186497A (ja) * | 2002-12-04 | 2004-07-02 | Sony Corp | 半導体装置および半導体装置の製造方法 |
| JP2005203657A (ja) * | 2004-01-19 | 2005-07-28 | Atsushi Iwata | 半導体装置 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN101017813A (zh) | 2007-08-15 |
| US7578676B2 (en) | 2009-08-25 |
| US7351068B2 (en) | 2008-04-01 |
| US20080188096A1 (en) | 2008-08-07 |
| TW200805617A (en) | 2008-01-16 |
| TWI349359B (ko) | 2011-09-21 |
| US20070184677A1 (en) | 2007-08-09 |
| EP1818986A3 (en) | 2011-02-02 |
| CN100511670C (zh) | 2009-07-08 |
| JP2007214274A (ja) | 2007-08-23 |
| KR20070080828A (ko) | 2007-08-13 |
| EP1818986A2 (en) | 2007-08-15 |
| JP4725346B2 (ja) | 2011-07-13 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR101348742B1 (ko) | 반도체 장치 | |
| CN107732651B (zh) | 光发射器封装件 | |
| US10229900B2 (en) | Semiconductor memory device including stacked chips and memory module having the same | |
| KR101139396B1 (ko) | 반도체 장치 및 기판 | |
| KR101118711B1 (ko) | 중앙 콘택을 구비한 적층형 마이크로전자 조립체 | |
| US7576421B2 (en) | Semiconductor device having a multi-layered semiconductor substrate | |
| US20020036338A1 (en) | Stacked type semiconductor device | |
| JP2003124383A5 (ko) | ||
| US20080078571A1 (en) | Device mounting board and semiconductor module | |
| JP6449439B2 (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| US9252132B2 (en) | Semiconductor device and semiconductor module | |
| JP2003324183A (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| KR101169354B1 (ko) | 반도체 패키징을 위한 전력 증폭 회로 | |
| KR100605434B1 (ko) | 적층형 반도체 디바이스 | |
| JPS6188547A (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| CN103620776A (zh) | 半导体装置 | |
| JP2008147438A (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| KR20200090627A (ko) | 전지 시스템용 회로 캐리어 및 전지 시스템 | |
| CN218385228U (zh) | 电子器件 | |
| US20210242176A1 (en) | Semiconductor packages | |
| US20230244045A1 (en) | OPTO-Electronic Integrated Module | |
| KR20130068485A (ko) | 관통 전극을 구비하는 반도체 디바이스, 그것의 제조방법, 반도체 디바이스를 구비한 적층형 패키지 및 적층형 패키지의 제조방법 | |
| US20100117211A1 (en) | Integrated circuit package | |
| WO2008142764A1 (ja) | 積層型パッケージ、及び、積層型パッケージの形成方法 | |
| KR20130020528A (ko) | 반도체 패키징을 위한 전력 증폭 회로 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A201 | Request for examination | ||
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right | ||
| GRNT | Written decision to grant | ||
| LAPS | Lapse due to unpaid annual fee |