JPWO2005104248A1 - Semiconductor chip for driving light emitting element, light emitting device and lighting device - Google Patents
Semiconductor chip for driving light emitting element, light emitting device and lighting device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JPWO2005104248A1 JPWO2005104248A1 JP2006512534A JP2006512534A JPWO2005104248A1 JP WO2005104248 A1 JPWO2005104248 A1 JP WO2005104248A1 JP 2006512534 A JP2006512534 A JP 2006512534A JP 2006512534 A JP2006512534 A JP 2006512534A JP WO2005104248 A1 JPWO2005104248 A1 JP WO2005104248A1
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- light emitting
- light
- emitting element
- terminal
- emitting device
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Withdrawn
Links
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 78
- 238000009792 diffusion process Methods 0.000 claims description 16
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 12
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 claims description 12
- 230000001681 protective effect Effects 0.000 claims description 12
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 claims description 7
- 239000003086 colorant Substances 0.000 claims description 7
- 230000005611 electricity Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- 230000003068 static effect Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 238000003672 processing method Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 description 77
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 73
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium Chemical compound [Al] XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 73
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 57
- 239000003990 capacitor Substances 0.000 description 42
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 30
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 28
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 description 21
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 description 21
- 230000015556 catabolic process Effects 0.000 description 18
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 14
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical compound [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 11
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 11
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 description 11
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 8
- 239000004642 Polyimide Substances 0.000 description 6
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 6
- 229920001721 polyimide Polymers 0.000 description 6
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 230000004397 blinking Effects 0.000 description 4
- 239000004020 conductor Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000005286 illumination Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Copper Chemical compound [Cu] RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000004593 Epoxy Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910004298 SiO 2 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000011248 coating agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910052681 coesite Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000010949 copper Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052906 cristobalite Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N gold Chemical compound [Au] PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910052737 gold Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000010931 gold Substances 0.000 description 2
- 150000004767 nitrides Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 230000003071 parasitic effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229920000642 polymer Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000000377 silicon dioxide Substances 0.000 description 2
- 235000012239 silicon dioxide Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 229910052682 stishovite Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 229910052905 tridymite Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 238000007740 vapor deposition Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000012528 membrane Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05B—ELECTRIC HEATING; ELECTRIC LIGHT SOURCES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; CIRCUIT ARRANGEMENTS FOR ELECTRIC LIGHT SOURCES, IN GENERAL
- H05B45/00—Circuit arrangements for operating light-emitting diodes [LED]
- H05B45/40—Details of LED load circuits
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05B—ELECTRIC HEATING; ELECTRIC LIGHT SOURCES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; CIRCUIT ARRANGEMENTS FOR ELECTRIC LIGHT SOURCES, IN GENERAL
- H05B45/00—Circuit arrangements for operating light-emitting diodes [LED]
- H05B45/30—Driver circuits
- H05B45/345—Current stabilisation; Maintaining constant current
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05B—ELECTRIC HEATING; ELECTRIC LIGHT SOURCES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; CIRCUIT ARRANGEMENTS FOR ELECTRIC LIGHT SOURCES, IN GENERAL
- H05B45/00—Circuit arrangements for operating light-emitting diodes [LED]
- H05B45/30—Driver circuits
- H05B45/37—Converter circuits
- H05B45/3725—Switched mode power supply [SMPS]
- H05B45/38—Switched mode power supply [SMPS] using boost topology
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/02—Bonding areas; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/04—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/05—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process of an individual bonding area
- H01L2224/0554—External layer
- H01L2224/0555—Shape
- H01L2224/05552—Shape in top view
- H01L2224/05554—Shape in top view being square
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/47—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/48—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process of an individual wire connector
- H01L2224/481—Disposition
- H01L2224/48151—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive
- H01L2224/48221—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked
- H01L2224/48245—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being metallic
- H01L2224/48247—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being metallic connecting the wire to a bond pad of the item
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L25/00—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof
- H01L25/16—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof the devices being of types provided for in two or more different main groups of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/00, or in a single subclass of H10K, H10N, e.g. forming hybrid circuits
- H01L25/167—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof the devices being of types provided for in two or more different main groups of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/00, or in a single subclass of H10K, H10N, e.g. forming hybrid circuits comprising optoelectronic devices, e.g. LED, photodiodes
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/10—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/11—Device type
- H01L2924/12—Passive devices, e.g. 2 terminal devices
- H01L2924/1203—Rectifying Diode
- H01L2924/12032—Schottky diode
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/10—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/11—Device type
- H01L2924/13—Discrete devices, e.g. 3 terminal devices
- H01L2924/1304—Transistor
- H01L2924/1305—Bipolar Junction Transistor [BJT]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/10—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/11—Device type
- H01L2924/13—Discrete devices, e.g. 3 terminal devices
- H01L2924/1304—Transistor
- H01L2924/1306—Field-effect transistor [FET]
- H01L2924/13091—Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor [MOSFET]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L33/00—Semiconductor devices having potential barriers specially adapted for light emission; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof
- H01L33/48—Semiconductor devices having potential barriers specially adapted for light emission; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof characterised by the semiconductor body packages
- H01L33/52—Encapsulations
- H01L33/54—Encapsulations having a particular shape
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L33/00—Semiconductor devices having potential barriers specially adapted for light emission; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof
- H01L33/48—Semiconductor devices having potential barriers specially adapted for light emission; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof characterised by the semiconductor body packages
- H01L33/58—Optical field-shaping elements
- H01L33/60—Reflective elements
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05B—ELECTRIC HEATING; ELECTRIC LIGHT SOURCES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; CIRCUIT ARRANGEMENTS FOR ELECTRIC LIGHT SOURCES, IN GENERAL
- H05B45/00—Circuit arrangements for operating light-emitting diodes [LED]
- H05B45/30—Driver circuits
- H05B45/34—Voltage stabilisation; Maintaining constant voltage
Abstract
実装面積の小さい発光装置を提供する。 本発明の発光装置は、電気信号端子を備えてこの電気信号端子に外部から与えられる電気信号によって駆動され発光する発光素子と、電気信号を出力して電気信号端子に印加する発光素子駆動用回路を半導体を用いて形成した発光素子駆動用半導体チップと、を有し、発光素子を発光素子駆動用半導体チップの面上に装着すると共に、発光素子駆動用半導体チップの面上に複数個の発光素子を相互接続する導電経路を備える。A light-emitting device with a small mounting area is provided. A light emitting device of the present invention includes an electric signal terminal, a light emitting element that emits light by being driven by an electric signal applied to the electric signal terminal from the outside, and a light emitting element driving circuit that outputs the electric signal and applies the electric signal to the electric signal terminal A light emitting element driving semiconductor chip formed using a semiconductor, and mounting the light emitting element on the surface of the light emitting element driving semiconductor chip and a plurality of light emitting elements on the surface of the light emitting element driving semiconductor chip. Conductive paths interconnecting the elements are provided.
Description
本発明は、発光素子駆動用半導体チップ、発光装置及び照明装置に関する。 The present invention relates to a light emitting element driving semiconductor chip, a light emitting device, and an illumination device.
近年、携帯電話やデジタルカメラ等の電子機器において、可視発光ダイオード(可視光LED)等の発光素子を駆動する発光装置、及びその発光装置を複数個用いた照明装置が利用される機会が増えている。電子機器の高集積化に伴い、実装面積の小さい発光装置が市場より要求されている。可視発光ダイオード等の発光素子は静電破壊や耐圧破壊しやすいため、保護素子を必要とし、さらに発光素子を駆動するドライバICを必要とするため、発光装置の実装面積が大きくなるという問題があった。 In recent years, in electronic devices such as mobile phones and digital cameras, an opportunity to use a light emitting device that drives a light emitting element such as a visible light emitting diode (visible light LED) and a lighting device using a plurality of the light emitting devices has increased. Yes. As electronic devices are highly integrated, light-emitting devices with a small mounting area are required from the market. Since a light emitting element such as a visible light emitting diode is susceptible to electrostatic breakdown or breakdown withstand voltage, a protective element is required, and a driver IC for driving the light emitting element is required, which increases the mounting area of the light emitting device. It was.
特開2003−8075号公報(特許文献1)に、保護素子の上に発光素子を実装し、1つの発光モジュールとすることで発光装置の実装面積を削減する技術が開示されている。図12〜図14を用いて、特許文献1に記載された従来例の発光装置について説明する。図12は、従来例の発光装置の構成を示す平面図である。図13は、図12の破線A−A’の断面図である。図14は、図12及び図13に示す従来例の発光装置の回路図である。図12〜14において、同じ構成要素については、同じ符号を用いている。 Japanese Patent Laying-Open No. 2003-8075 (Patent Document 1) discloses a technique for reducing the mounting area of a light emitting device by mounting a light emitting element on a protective element to form a single light emitting module. A conventional light emitting device described in Patent Document 1 will be described with reference to FIGS. FIG. 12 is a plan view showing a configuration of a conventional light emitting device. FIG. 13 is a cross-sectional view taken along the broken line A-A ′ in FIG. 12. FIG. 14 is a circuit diagram of the conventional light emitting device shown in FIGS. 12-14, the same code | symbol is used about the same component.
まず、図12及び図13について説明する。従来例の発光装置は、基板1202上に基板配線1203(VCC配線及びGND配線を含む。)を形成し、基板配線1203上に発光モジュール1201と電源回路104とドライバIC1204とを実装している。発光モジュール1201、電源回路104、及びドライバIC1204を構成している内部回路の各素子は、基板配線1203により、それぞれ電気的に接続されている。 First, FIG. 12 and FIG. 13 will be described. In the conventional light emitting device, substrate wiring 1203 (including VCC wiring and GND wiring) is formed on a
電源回路104は、VCC配線とGND配線との間に接続された入力コンデンサ143と、VCC配線を介して入力コンデンサ143に接続されたコイル141と、基板配線1203によりコイル141に接続されたショットキーダイオード142と、一端を基板配線1203を介してショットキーダイオード142と電圧帰還端子125とに接続されて他端をGND配線に接続された出力コンデンサ144を有する。 The
発光モジュール1201の各構成要素について説明する。発光モジュール1201において、リードフレーム114は、基板1202の上方に実装されている。ツェナダイオード1213は、リードフレーム114上に固定される。ツェナダイオード1213の上面は、パッド孔113を除いて絶縁膜131で覆われている。 Each component of the
ツェナダイオード1213上の両端に近い部分を除くパッド孔113にはバンプ115が載せられ、バンプ115の上に発光素子111が実装されている。発光素子111は、可視発光ダイオード(LED)である。ツェナダイオード1213は、発光素子111を静電破壊及び高耐圧破壊から保護している。
図12及び図13において2個のツェナダイオード1213の上に、それぞれ1つずつ発光素子111が実装されている。従来例の発光装置は、発光素子111をツェナダイオード1213上に実装して一体化したモジュールとすることで、ツェナダイオード1213と発光素子111とを別々に実装する場合よりも、実装面積を小さくしている。 12 and 13, one
ツェナダイオード1213上の両端に近い部分のパッド孔113には、2つのボンディングワイヤ116のそれぞれの一端が接続されている。一方のボンディングワイヤ116の他端は、アノード側端子1253に接続され、もう一方のボンディングワイヤ116の他端は、カソード側端子1254に接続される。 One end of each of the two
発光素子111の上部に凸レンズ119が配置されている。凸レンズ119は、発光素子111の光を集光し、光の指向性を強くし、基板1202に垂直な方向の輝度を高める。 A convex
光透過性樹脂モールド117は、発光素子111、ツェナダイオード1213、リードフレーム114、及び凸レンズ119を含む全体を覆い、基板1202と一体に構成されている。光透過性樹脂モールド117の上半分は、パラボラ形状であって、光を実効的に全反射して集光する反射面を形成している。 The light
ドライバIC1204の各構成要素について説明する。ドライバIC1204において、リードフレーム114は、基板1202の上方に実装される。ドライバICチップ112は、リードフレーム114上に固定されている。ドライバICチップ112の上面は、パッド孔113を除いて絶縁膜131に覆われている。 Each component of the
6つのパッド孔には6つのボンディングワイヤ116の一端がそれぞれ接続され、各ボンディングワイヤ116の他端はそれぞれ外部接続端子(制御端子123、電圧帰還端子125、スイッチング端子124、電流帰還端子126、VCC端子121、GND端子122)に接続されている。このように複数のボンディングワイヤ116を通して、ドライバICチップ112は、外部接続端子に電気的に接続されている。 One end of each of the six
VCC端子121は、VCC配線に接続されている。GND端子122は、GND配線に接続されている。制御端子123は、ドライバIC1204のON/OFFの切替を行うための信号を入力される端子である。制御端子123に入力された入力電圧がHighの時には、ドライバICチップ112は動作して、発光素子111が連続発光する。入力電圧がLowの時には、ドライバICチップ112は動作を停止し、発光素子111の発光も停止する。制御端子123にパルス電圧を入力することで、発光素子111の点滅の動作を繰り返すこともできる。 The
スイッチング端子124は、基板配線1203によりショットキーダイオード142のアノード端子とコイル141とに接続している。電圧帰還端子125は、基板配線1203によって、ショットキーダイオード142のカソード端子、発光モジュール1201のアノード側端子1253、及び出力コンデンサ144と接続している。電流帰還端子126は、基板配線1203によって、発光モジュール1201のカソード側端子1254と接続している。 The
図14の従来例の発光装置の回路構成を説明する。図14に示すように、従来例の発光装置は、外部電源140の出力する電圧を昇圧する電源回路104と、外部接続端子(VCC端子121、スイッチング端子124、電圧帰還端子125)を介して電源回路104に接続されるドライバIC1204と、アノード側端子1253を介して電源回路104に接続されカソード側端子1254を介してドライバIC1204に接続される発光モジュール1201とを有する。 The circuit configuration of the conventional light emitting device of FIG. 14 will be described. As shown in FIG. 14, the light emitting device of the conventional example has a power supply via a
図14においてドライバIC1204の枠内に示す回路は、ドライバICチップ112に搭載される内部回路である。ドライバICチップ112は、電圧帰還端子125とGND端子122との間に接続された第1の保護回路501、VCC端子121とGND端子122との間に接続され、その中間接続点に電流帰還端子126を接続された第2の保護回路1401、電流帰還端子126と接地電位との間に接続された電流検出抵抗504、制御端子123と電圧帰還端子125と電流帰還端子126に接続された電圧検出回路503、及び制御端子123と電圧検出回路503とスイッチング端子124に接続された駆動回路502を有する。 In FIG. 14, the circuit shown in the frame of the
第1の保護回路501は、電圧帰還端子125へのサージ印加により、電圧検出回路503が静電破壊されることを防ぐもので、ツェナダイオード、MOSトランジスタ、又はバイポーラトランジスタ等で構成される。図14の第1の保護回路501は、ツェナダイオードである。 The
第2の保護回路1401は、電流帰還端子126へのサージ印加により、ドライバICチップ112の内部回路が静電破壊されることを防ぐ。図14において、第2の保護回路1401は、2個のダイオードの直列接続回路で構成している。 The
駆動回路502は、スイッチング端子124を介してコイル141とショットキーダイオード142を駆動し、外部電源140からの入力電圧を昇圧する。これにより、出力コンデンサ144には、入力電圧より高い電圧が出力電圧として印加される。出力コンデンサ144の電圧は、発光モジュール1201のアノード側端子1253を通して、発光素子111のアノード側に印加される。 The
発光モジュール1201において、ツェナダイオード1213と発光素子111は1対で並列接続されている。ツェナダイオード1213は、発光モジュール1201の実装時等にアノード側端子1253あるいはカソード側端子1254に印加されるサージから発光素子111を保護する。 In the
発光モジュール1201のカソード側端子1254は、ドライバICチップ112内部の電流検出抵抗504に接続された電流帰還端子126に接続される。電圧検出回路503は、電流検出抵抗504の端子電圧を一定に保つことにより、発光素子111に流れる電流を一定に保つ。電圧検出回路503は、電圧帰還端子125の電圧が規定値を超えないように、出力電圧の検出及び制御を行う。 The
従来例の駆動回路502及び電圧検出回路503は本発明と同じであるため、図14において内部の回路を省略又は簡略化して記載している。駆動回路502及び電圧検出回路503の内部回路の詳細は、本発明の実施の形態1で説明する。
上記のように構成された従来例の発光装置は、発光素子111を含む発光モジュール1201と、ドライバICチップ112を含むドライバIC1204とが別々のリードフレームに実装されているため、実装面積が大きくなるという問題があった。特に発光素子111が複数個使用される場合、ツェナダイオード1213の占めるスペースが大きくなり、問題となっていた。従来例の発光装置において、発光素子111の静電破壊や耐圧破壊を保護する保護素子1213と、発光素子111を駆動するドライバIC112とは必要であったため、実装面積を小さくするために取り除くことはできない。 The conventional light emitting device configured as described above has a large mounting area because the
本発明は、上記問題を解決するもので、実装面積の小さい発光装置を提供することを目的とする。
本発明は、任意の数の発光素子と組み合わせて使用できる安価な発光素子駆動用半導体チップを提供することを目的とする。
本発明は、安価な照明装置を提供することを目的とする。
本発明は、高輝度で小型の照明装置を提供することを目的とする。The present invention solves the above-described problems, and an object thereof is to provide a light-emitting device with a small mounting area.
An object of the present invention is to provide an inexpensive light emitting element driving semiconductor chip that can be used in combination with an arbitrary number of light emitting elements.
An object of the present invention is to provide an inexpensive lighting device.
An object of the present invention is to provide a small illuminating device with high luminance.
上記課題を解決するため、本発明は下記の構成を有する。
本発明の1つの観点による発光装置は、電気信号端子を備え、前記電気信号端子に外部から与えられる電気信号によって駆動され発光する発光素子と、前記電気信号を出力して前記電気信号端子に印加する発光素子駆動用回路を半導体を用いて形成した発光素子駆動用半導体チップと、を有し、前記発光素子を前記発光素子駆動用半導体チップの面上に装着する。In order to solve the above problems, the present invention has the following configuration.
A light emitting device according to one aspect of the present invention includes an electric signal terminal, a light emitting element that is driven by an electric signal supplied from the outside to the electric signal terminal, emits light, and outputs the electric signal to be applied to the electric signal terminal. A light emitting element driving semiconductor chip formed using a semiconductor, and the light emitting element is mounted on a surface of the light emitting element driving semiconductor chip.
この発明は、発光素子駆動用半導体チップ(ドライバICチップ)上に発光素子を実装することで、実装面積の小さい発光装置を実現できる。 According to the present invention, a light emitting device having a small mounting area can be realized by mounting a light emitting element on a light emitting element driving semiconductor chip (driver IC chip).
本発明の他の観点による上記の発光装置において、前記発光素子駆動用半導体チップは、前記発光素子又は前記発光素子駆動用回路を外部から印加される静電気や高電圧(以下、静電気や高電圧を「サージ電圧」と呼ぶ。)から保護する保護回路と、前記保護回路を外部と電気的に接続するための保護端子と、を備え、前記保護端子を前記発光素子の前記電気信号端子に接続する。 In the light emitting device according to another aspect of the present invention, the semiconductor chip for driving the light emitting element may be configured to apply static electricity or high voltage (hereinafter, static electricity or high voltage) applied to the light emitting element or the light emitting element driving circuit. A protection circuit for protecting from the surge voltage) and a protection terminal for electrically connecting the protection circuit to the outside, and connecting the protection terminal to the electrical signal terminal of the light emitting element. .
ドライバICチップの内部回路を保護するための保護回路を設ける工程で、発光素子の保護回路をドライバICチップ上に設けることにより、又はドライバICチップの内部回路の保護と発光素子の保護とを兼ねる保護回路を設けることによって、信頼性の高い発光装置を安価に実現できる。この発明によれば、発光素子を外部から印加されるサージ電圧から保護するためだけの従来のような第1の保護回路をドライバICチップの外部に設けないため、従来と比較して安価で実装面積の小さい発光装置を実現できる。 In the step of providing a protection circuit for protecting the internal circuit of the driver IC chip, the protection circuit of the light emitting element is provided on the driver IC chip, or the protection of the internal circuit of the driver IC chip and the protection of the light emitting element are combined. By providing the protection circuit, a highly reliable light-emitting device can be realized at low cost. According to the present invention, the conventional first protection circuit only for protecting the light emitting element from the surge voltage applied from the outside is not provided outside the driver IC chip. A light emitting device with a small area can be realized.
本発明の別の観点による上記の発光装置において、前記保護回路は、前記発光素子駆動用半導体チップの発光素子駆動用回路を形成する素子と同一の製法によって形成された、一若しくは複数個の素子を備える。 In the above light-emitting device according to another aspect of the present invention, the protection circuit is one or a plurality of elements formed by the same manufacturing method as the element forming the light-emitting element driving circuit of the light-emitting element driving semiconductor chip. Is provided.
例えば、保護回路は、PN接合のダイオード、バイポーラトランジスタ、MOSトランジスタの中の少なくとも1つを用いて形成される。この発明は、安価で信頼性が高く実装面積の小さい発光装置を実現できる。 For example, the protection circuit is formed using at least one of a PN junction diode, a bipolar transistor, and a MOS transistor. The present invention can realize a light-emitting device that is inexpensive, highly reliable, and has a small mounting area.
本発明の更に別の観点による上記の発光装置において、前記発光素子駆動用半導体チップの面上に、それぞれ別個のチップで構成された複数個の前記発光素子が装着されており、前記発光素子駆動用半導体チップは、前記発光素子を相互に接続する導電経路を設ける。 In the above light emitting device according to still another aspect of the present invention, a plurality of the light emitting elements each composed of a separate chip are mounted on the surface of the light emitting element driving semiconductor chip, and the light emitting element driving is performed. The semiconductor chip for use is provided with a conductive path for connecting the light emitting elements to each other.
ドライバICチップ上に複数の発光素子の相互接続のみのための導電経路を設けることにより、安価で実装面積の小さい発光装置を実現できる。
導電経路は、極めて低い抵抗値の導電体であっても良く、所定の抵抗値又は所定の電圧降下を生じる経路であっても良い。一般的には、導電経路は極めて低い抵抗値の導電体で形成されることが好ましい場合が多い。導電経路は、ドライバICチップの半導体基板自体に拡散層で形成されても良く、半導体基板の上に蒸着、接着、塗布等の任意の方法で形成されても良い。導電経路の材質は任意である。例えば、ドライバICチップ上に形成された拡散層、金属配線層、樹脂導電層等である。By providing a conductive path only for interconnection of a plurality of light emitting elements on the driver IC chip, a light emitting device that is inexpensive and has a small mounting area can be realized.
The conductive path may be a conductor having an extremely low resistance value, or may be a path that generates a predetermined resistance value or a predetermined voltage drop. In general, it is often preferable that the conductive path is formed of a conductor having an extremely low resistance value. The conductive path may be formed as a diffusion layer on the semiconductor substrate itself of the driver IC chip, or may be formed on the semiconductor substrate by any method such as vapor deposition, adhesion, and coating. The material of the conductive path is arbitrary. For example, a diffusion layer, a metal wiring layer, a resin conductive layer, or the like formed on the driver IC chip.
本発明の更に別の観点による上記の発光装置において、前記導電経路は、前記発光素子駆動用半導体チップにおいて前記発光素子駆動用回路を形成する拡散層又は金属配線層と同一処理方法によって形成された拡散層又は金属配線層によって形成される。 In the light emitting device according to still another aspect of the present invention, the conductive path is formed by the same processing method as a diffusion layer or a metal wiring layer forming the light emitting element driving circuit in the light emitting element driving semiconductor chip. It is formed by a diffusion layer or a metal wiring layer.
この発明により、安価で実装面積の小さい発光装置を実現できる。 According to the present invention, a light-emitting device that is inexpensive and has a small mounting area can be realized.
本発明の更に別の観点による上記の発光装置において、前記導電経路は、所定の値を有する抵抗を備える。 In the light emitting device according to another aspect of the present invention, the conductive path includes a resistor having a predetermined value.
この発明によれば、例えば導電経路の抵抗値の変化に基づいて発光素子近傍の温度を検出したり、導電経路の両端電圧に基づいて発光素子を流れる電流を検出したり、複数の発光素子を並列に接続した回路においてそれぞれの発光素子に抵抗値を有する導電経路を直列接続することにより各発光素子に流れる電流を均一化したりできる。 According to the present invention, for example, the temperature in the vicinity of the light emitting element is detected based on a change in the resistance value of the conductive path, the current flowing through the light emitting element is detected based on the voltage across the conductive path, or a plurality of light emitting elements are In a circuit connected in parallel, a current flowing through each light emitting element can be made uniform by connecting in series a conductive path having a resistance value to each light emitting element.
本発明の更に別の観点による上記の発光装置は、異なる波長で発光する複数個の可視発光素子を備える。 The light-emitting device according to still another aspect of the present invention includes a plurality of visible light-emitting elements that emit light at different wavelengths.
この発明によれば、発光色が異なる複数の発光素子を非常に近接した位置に配置できるので、例えば複数の発光素子を同時に点灯した場合、複数の発光素子は良く混色し、どの角度から見ても色ムラが生じにくい。 According to the present invention, since a plurality of light emitting elements having different emission colors can be arranged at very close positions, for example, when a plurality of light emitting elements are turned on at the same time, the plurality of light emitting elements are well mixed and viewed from any angle. Is less likely to cause color unevenness.
本発明の更に別の観点による上記の発光装置において、前記発光素子は、赤、緑、青の3原色でそれぞれ発光する複数の可視発光素子を含む。 In the above light-emitting device according to another aspect of the present invention, the light-emitting element includes a plurality of visible light-emitting elements that respectively emit light in three primary colors of red, green, and blue.
この発明の発光装置は、カラー表示が出来る。発光装置単体がドライバICチップを有する故に、周辺回路を削減でき、複数の発光装置を接続することは容易である。発光装置の実装面積が小さく、各発光装置の全体面積の中で発光面積が占める割合が大きいので、複数の発光装置を密集して並べると、従来よりはるかに高輝度の発光装置の表示装置(照明装置)を実現できる。例えば屋外用画像表示装置として有用である。 The light emitting device of the present invention can perform color display. Since a single light emitting device has a driver IC chip, peripheral circuits can be reduced and it is easy to connect a plurality of light emitting devices. Since the mounting area of the light emitting device is small, and the ratio of the light emitting area to the total area of each light emitting device is large, when a plurality of light emitting devices are arranged closely, a display device of a light emitting device with a much higher brightness than conventional ones ( Lighting device) can be realized. For example, it is useful as an outdoor image display device.
本発明の更に別の観点による上記の発光装置において、複数個の前記発光素子が、前記発光装置に一体で形成された一透過型集光レンズの焦点近傍に配置されている。 In the above light emitting device according to still another aspect of the present invention, the plurality of light emitting elements are disposed in the vicinity of a focal point of a single transmission type condensing lens formed integrally with the light emitting device.
発光素子を集光用光学系の焦点に配置することにより、発光素子が発する光を所定の方向に集中できる。発光素子を回路基板に取り付ける精度上の制約等により、回路基板上に複数の発光素子を配置した従来の発光装置においては、各発光素子をある程度の距離を置いて配置せざるを得なかった。それ故に、複数の発光素子は集光用光学系の焦点から少し離れた所に取り付けられた。例えば、複数の発光素子は、大きめのパラボラ型反射面の下にパラボラの焦点から少しずつずれた位置に配置され、パラボラの底で各発光素子の真上に個別の樹脂製の凸レンズが設けられていた。それ故に、発光素子が発した光の一部が所定の方向に向かわず、一定以上集光率を高められないという問題があった。この発明によれば、従来より高い集光率、強い指向性を有する発光装置を実現できる。 By arranging the light emitting element at the focal point of the condensing optical system, the light emitted from the light emitting element can be concentrated in a predetermined direction. In a conventional light-emitting device in which a plurality of light-emitting elements are arranged on a circuit board due to restrictions on the accuracy of attaching the light-emitting elements to the circuit board, each light-emitting element has to be arranged at a certain distance. Therefore, the plurality of light emitting elements were attached at a position slightly away from the focal point of the condensing optical system. For example, the plurality of light emitting elements are arranged at positions slightly shifted from the parabolic focus under the large parabolic reflecting surface, and individual resin convex lenses are provided at the bottom of the parabola directly above each light emitting element. It was. Therefore, there is a problem that a part of the light emitted from the light emitting element is not directed in a predetermined direction, and the light collection rate cannot be increased beyond a certain level. According to the present invention, it is possible to realize a light-emitting device having a higher light collection rate and stronger directivity than conventional ones.
本発明の更に別の観点による上記の発光装置において、複数個の前記発光素子は、前記発光装置に一体で形成された一反射面の焦点近傍に配置されている。 In the above light emitting device according to still another aspect of the present invention, the plurality of light emitting elements are arranged in the vicinity of a focal point of one reflecting surface formed integrally with the light emitting device.
反射面は、典型的には、内面で光が全反射するように形成された透明の樹脂の反射面である。この発明によれば、高い集光率、強い指向性を有する発光装置を実現できる。 The reflecting surface is typically a transparent resin reflecting surface formed so that light is totally reflected on the inner surface. According to the present invention, a light emitting device having a high light collection rate and strong directivity can be realized.
本発明の1つの観点による照明装置は、前記発光素子に所定の電流を印加する定電流回路又は前記発光素子に所定の電圧を印加する定電圧回路を有する前記発光素子駆動用半導体チップを備えた、上記の発光装置を複数個有する。 An illumination device according to one aspect of the present invention includes the light emitting element driving semiconductor chip including a constant current circuit that applies a predetermined current to the light emitting element or a constant voltage circuit that applies a predetermined voltage to the light emitting element. And a plurality of the above light emitting devices.
この発明により、発光装置の相互の配線を簡素化した安価な照明装置を実現できる。発光装置を密集して配置することにより、従来より高輝度の及び/又は小型の照明装置を実現できる。照明装置は、例えば通常の照明装置、大型の表示パネル、映像表示装置等を含む。 According to the present invention, it is possible to realize an inexpensive lighting device that simplifies the mutual wiring of the light emitting device. By arranging the light emitting devices densely, it is possible to realize a lighting device with higher brightness and / or smaller size than in the past. The lighting device includes, for example, a normal lighting device, a large display panel, a video display device, and the like.
本発明の1つの観点による発光素子駆動用半導体チップは、電気信号端子を備えて、前記電気信号端子に与えられる電気信号によって駆動され発光する、複数個の発光素子を装着する発光素子駆動用半導体チップであって、半導体を用いて形成され、前記電気信号を出力して前記電気信号端子に印加する発光素子駆動用回路と、前記複数個の発光素子の前記電気信号端子を相互に接続する導電経路と、を備える。 A light-emitting element driving semiconductor chip according to an aspect of the present invention includes a light-emitting element driving semiconductor having a plurality of light-emitting elements, each of which has an electric signal terminal and is driven by an electric signal applied to the electric signal terminal to emit light. A light emitting element driving circuit that is formed using a semiconductor and outputs the electric signal and applies the electric signal to the electric signal terminal; and a conductive element that interconnects the electric signal terminals of the plurality of light emitting elements. A route.
この発明によれば、発光素子駆動用半導体チップ(ドライバICチップ)上に、複数の発光素子の相互接続のみのための導電経路を設けることにより、安価で実装面積の小さい発光素子駆動用半導体チップを実現できる。 According to the present invention, a light-emitting element driving semiconductor chip that is inexpensive and has a small mounting area is provided on a light-emitting element driving semiconductor chip (driver IC chip) by providing a conductive path only for interconnection of a plurality of light-emitting elements. Can be realized.
本発明の他の観点による上記の発光素子駆動用半導体チップにおいて、それぞれ別個のチップで構成された個数P(Pは1以上の正整数)の前記発光素子と、前記発光素子駆動用半導体回路の回路素子は、前記導電経路に設けられたバンプを経由して相互に接続される。 In the semiconductor chip for driving a light emitting element according to another aspect of the present invention, the number P of light emitting elements (P is a positive integer of 1 or more) each formed by a separate chip, and the semiconductor circuit for driving the light emitting element The circuit elements are connected to each other via bumps provided in the conductive path.
この発明によれば、ワイヤボンディングが不要な安価で実装面積の小さい発光素子駆動用半導体チップを実現できる。 According to the present invention, a light-emitting element driving semiconductor chip that does not require wire bonding and has a small mounting area can be realized.
本発明の別の観点による上記の発光素子駆動用半導体チップにおいて、前記導電経路は、個数Pの前記発光素子に代えて、前記発光素子とほぼ同一形状の個数Q(QはPと異なる正整数)の発光素子を実装する導電経路形状を有する。 In the semiconductor chip for driving a light emitting element according to another aspect of the present invention, the conductive path has a number Q (Q is a positive integer different from P) having substantially the same shape as the light emitting element instead of the number P of the light emitting elements. ) Of the conductive path for mounting the light emitting element.
この発明により、1種類の導電経路パターン(例えばアルミ配線パターン)で、発光素子の搭載場所を変更することにより、異なる数の発光素子を有する複数の発光装置を作ることが出来る。この発明によれば、導電経路パターンを形成するマスクが1種類で済む。又、1種類のドライバICチップと、任意の発光素子とを組み合わせて、需要に応じた発光装置を製造できるので、LEDの材料としてのドライバICチップの在庫を少なくできる。この発明によれば、工場の管理コストを削減できる。 According to the present invention, a plurality of light emitting devices having different numbers of light emitting elements can be manufactured by changing the mounting location of the light emitting elements with one type of conductive path pattern (for example, an aluminum wiring pattern). According to the present invention, only one type of mask is necessary for forming the conductive path pattern. Further, since a light emitting device according to demand can be manufactured by combining one type of driver IC chip and an arbitrary light emitting element, the inventory of driver IC chips as LED materials can be reduced. According to this invention, the management cost of a factory can be reduced.
本発明の更に別の観点による上記の発光素子駆動用半導体チップは、前記発光素子を駆動する電流又は電圧値を可変とするための外部接続端子を有する。 The light emitting element driving semiconductor chip according to still another aspect of the present invention has an external connection terminal for making a current or voltage value for driving the light emitting element variable.
例えばドライバICチップが1個の発光素子を駆動する場合と、4個の発光素子を駆動する場合とでは、ドライバICチップの設定を変更する場合がある。この発明の発光素子駆動用半導体チップは、外部接続端子から発光素子に流す電流又は発光素子に印加する電圧を可変できるので、1種類のドライバICチップを用いて、多種類の発光装置を製造できる。 For example, the setting of the driver IC chip may be changed between when the driver IC chip drives one light emitting element and when the driver IC chip drives four light emitting elements. Since the semiconductor chip for driving a light emitting element of the present invention can vary the current flowing from the external connection terminal to the light emitting element or the voltage applied to the light emitting element, various types of light emitting devices can be manufactured using one type of driver IC chip. .
発明の新規な特徴は添付の請求の範囲に特に記載したものであるが、構成及び内容の双方に関して本発明は、他の目的や特徴と共に、図面と共同して理解されるところの以下の詳細な説明から、より良く理解され評価されるであろう。 The novel features of the invention are set forth with particularity in the appended claims, but the invention, both in terms of construction and content, together with other objects and features, the following details are to be understood in conjunction with the drawings. From this explanation, it will be better understood and appreciated.
図面の一部又は全部は、図示を目的とした概要的表現により描かれており、必ずしもそこに示された要素の実際の相対的大きさや位置を忠実に描写しているとは限らないことは考慮願いたい。 Part or all of the drawings are drawn in a schematic representation for illustration purposes and do not necessarily depict the actual relative sizes and positions of the elements shown there faithfully. Please consider.
本発明によれば、実装面積の小さい発光装置を実現できるという有利な効果が得られる。
本発明によれば、従来必要であったツェナダイオード等の保護素子をなくすことにより、安価で信頼性が高い発光装置を実現できるという有利な効果が得られる。
本発明によれば、発光モジュールの外部接続端子の静電破壊の耐圧を高くする発光装置を実現できるという有利な効果が得られる。
本発明の発光装置によれば、ドライバICチップ上に発光素子を搭載するため、従来と比較して基板配線の寄生抵抗、浮遊容量が減る。そのため、電流値を安定させる位相補償の設計が容易となり、発光の輝度が安定し発光のちらつきが無くなるという有利な効果が得られる。
本発明によれば、任意の数の発光素子と組み合わせて使用できる安価な発光素子駆動用半導体チップを実現できるという有利な効果が得られる。
本発明によれば、安価な照明装置を実現できるという有利な効果が得られる。
本発明によれば、高輝度で小型の照明装置を実現できるという有利な効果が得られる。According to the present invention, an advantageous effect that a light emitting device having a small mounting area can be realized.
According to the present invention, it is possible to obtain an advantageous effect that it is possible to realize an inexpensive and highly reliable light-emitting device by eliminating a protection element such as a Zener diode which has been conventionally required.
According to the present invention, it is possible to obtain an advantageous effect that it is possible to realize a light emitting device that can increase the withstand voltage of electrostatic breakdown of the external connection terminal of the light emitting module.
According to the light emitting device of the present invention, since the light emitting element is mounted on the driver IC chip, the parasitic resistance and the stray capacitance of the substrate wiring are reduced as compared with the conventional case. Therefore, it is easy to design a phase compensation that stabilizes the current value, and it is possible to obtain an advantageous effect that the luminance of light emission is stabilized and the flicker of light emission is eliminated.
According to the present invention, an advantageous effect that an inexpensive light emitting element driving semiconductor chip that can be used in combination with an arbitrary number of light emitting elements can be realized.
According to the present invention, an advantageous effect that an inexpensive lighting device can be realized is obtained.
According to the present invention, it is possible to obtain an advantageous effect that a small-sized lighting device with high luminance can be realized.
以下本発明の実施をするための最良の形態を具体的に示した実施の形態について、図面とともに記載する。 DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS Embodiments that specifically show the best mode for carrying out the present invention will be described below with reference to the drawings.
《実施の形態1》
図1〜5を用いて、本発明の実施の形態1の発光装置について説明する。図1は、本発明の実施の形態1における発光装置の平面図である。図2は、図1中の破線A−A’で切断した断面図である。図3は、ドライバICチップ112の部分拡大断面図である。図4は、LEDである発光素子111a、111bとドライバICチップ112との間を接続するアルミ配線の形状を示す平面図である。図5は、本発明の実施の形態1の発光装置の回路図である。図1〜5において、同じ構成要素については同じ符号を用いている。図1〜5において、従来例の図12〜14と同じ構成要素については同じ符号を用いている。Embodiment 1
The light-emitting device of Embodiment 1 of this invention is demonstrated using FIGS. FIG. 1 is a plan view of the light-emitting device according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention. 2 is a cross-sectional view taken along a broken line AA ′ in FIG. FIG. 3 is a partial enlarged cross-sectional view of the
図1及び図2を用いて、本発明の実施の形態1の発光装置について説明する。本発明の実施の形態1の発光装置は、基板102上に基板配線103(VCC配線及びGND配線を含む。)を形成し、基板配線103上に電源回路104と発光モジュール101とを実装する。発光モジュール101の内部回路の各素子と電源回路104の内部回路の各素子は、基板配線103により、それぞれ電気的に接続される。VCC配線は外部電源に接続され、GND配線は接地電位に接続される。 A light-emitting device according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention will be described with reference to FIGS. 1 and 2. In the light emitting device according to the first embodiment of the present invention, substrate wiring 103 (including VCC wiring and GND wiring) is formed on a
電源回路104は、VCC配線とGND配線との間に接続された入力コンデンサ143と、VCC配線を介して入力コンデンサ143に接続されたコイル141と、基板配線103によりコイル141に接続されたショットキーダイオード142と、一端を基板配線103を介してショットキーダイオード142に接続されて他端をGND配線に接続された出力コンデンサ144を有する。 The
発光モジュール101は、基板配線103により電源回路104に接続される外部接続端子(VCC端子121、GND端子122、制御端子123、スイッチング端子124、電圧帰還端子125)を有する。 The
VCC端子121は、VCC配線に接続されている。GND端子122は、GND配線に接続されている。制御端子123は、通常、マイクロコンピュータ等の制御回路の出力に接続され、発光素子111a、111bの発光/停止を切り替える信号を入力される。 The
スイッチング端子124は、基板配線103により、ショットキーダイオード142のアノード端子とコイル141とに接続している。電圧帰還端子125は、基板配線103により、ショットキーダイオード142のカソード端子と出力コンデンサ144とに接続している。 The switching
発光モジュール101を構成する各素子について更に説明する。本発明の実施の形態1の発光モジュール101において、リードフレーム114が基板102の上方に実装され、リードフレーム114上にドライバICチップ(発光素子駆動用半導体チップ)112が固定されている。ドライバICチップ112の上面は、パッド孔113を除いて、絶縁膜131で覆われている。パッド孔113は、ドライバICチップ112上において、絶縁膜131が存在しない部分である。両端に近い部分を除いて、パッド孔113にバンプ115が設けられ、発光素子111a、111bはバンプ115の上に実装される。 Each element constituting the
本発明の発光装置が従来例の発光装置と異なる特徴点は、発光モジュール101内にドライバICチップ112が内蔵されており、発光素子111a、111bがドライバICチップ112上に実装されていることである。そのため、本発明の基板102のサイズは、従来例の基板1202よりも小さい。本発明の発光装置は、発光素子111a、111bをドライバICチップ112上に実装するため、従来と比較して発光装置の実装面積を小さくすることができる。 The light emitting device of the present invention is different from the light emitting device of the conventional example in that the
発光素子111a、111b(両者をまとめて発光素子111と表示する。)は、それぞれ別個のチップで構成される。本発明の実施の形態1において、複数個の発光素子がドライバICチップ112上に実装される。図1〜5においては、2個の発光素子111a、111bが実装されている。 The
発光素子111a、111bは、可視発光ダイオード(LED)である。発光素子の色は所望のものを用いうる。実施の形態1においては、発光素子111a、111bは青色発光ダイオードであって、表面に白色の蛍光物質を塗布した透過型集光レンズ119を通して白色光を外部に放射する。本発明において、複数の発光素子がそれぞれ異なる波長で発光しても良い。発光素子111の上部に配置された凸レンズ119は、発光素子111の光を集光し、光の指向性を強くし、基板102に垂直な方向の輝度を高める。 The
光透過性樹脂モールド117は、発光素子111、ドライバICチップ112、リードフレーム114、及び凸レンズ119を含む全体を覆い、固定し保護している。光透過性樹脂モールド117は、発光素子111の光を集光し、輝度や光の指向性を調整する役割を果たしている。光透過性樹脂モールド117の上半分は、パラボラ形状であって、光を実効的に全反射して集光し、基板102に垂直な方向の輝度を高める反射面を形成している。 The light
実施の形態1において、光透過性樹脂モールド117及び凸レンズ119は、同一材質で一体に形成されている。複数の発光素子111a、111bが、発光装置に一体で形成された1個の表面に白色の蛍光物質を塗布した透過型集光レンズ119及び1個の反射面117の焦点近傍に配置される。 In the first embodiment, the light
図3は、ドライバICチップ112の上面の一部を拡大した図である。ドライバICチップ112の基板であるP型シリコン基板132は、上面を絶縁膜133aで覆われている。絶縁膜133aの上面は、導電経路であるアルミ配線118a、118b、118cの箇所を除いて、絶縁膜133bで覆われている。 FIG. 3 is an enlarged view of a part of the upper surface of the
実施の形態1において、絶縁膜133a及び絶縁膜133bは、酸化膜(SiO2)である。なお、絶縁膜133a、133bの材質は、酸化膜(SiO2)に限定されず、窒化膜(SiN)、高分子化合物(ポリイミド等)、樹脂(エポキシ等)等であっても良い。In the first embodiment, the insulating
絶縁膜133bと、アルミ配線118a、118b、118cの上面は、パッド孔113を除いて絶縁膜131で覆われている。パッド孔113は、ボンディングワイヤ116を接続するためと、バンプ115を載せるために設けられる。アルミ配線118a、118b、118c上のパッド孔113のある所定の位置に、バンプ115が設けられる。 The upper surfaces of the insulating
発光素子111a、111bは、バンプ115の上に実装される。発光素子111a、111bは、バンプ115を通じて、ドライバICチップ112上のアルミ配線118a、118b、118cに接続される。 The
図3の両端に近い部分に示すパッド孔113には、図1及び図2に示すようにボンディングワイヤ116が接続される。ドライバICチップ112は、ボンディングワイヤ116により、内部回路と外部接続端子(VCC端子121、GND端子122、制御端子123、スイッチング端子124、電圧帰還端子125)とを電気的に接続される。
図4のアルミ配線の形状及び図5の回路図に示すように、発光素子111bのアノード(電気信号端子)は、バンプ115及びアルミ配線118cを介してドライバICチップ112の内部回路素子及び電圧帰還端子(保護端子)125に接続される。発光素子111bのカソードは、バンプ115及びアルミ配線188bを介して発光素子111aのアノードに接続される。発光素子111aのカソードは、バンプ115及びアルミ配線118aを介してドライバICチップ112の内部回路素子(電流帰還用の抵抗素子504等)と接続される。発光素子111a、111bのアノード及びカソードは、電気信号端子である。 As shown in the shape of the aluminum wiring in FIG. 4 and the circuit diagram in FIG. 5, the anode (electric signal terminal) of the
アルミ配線118bは、発光素子111bのカソードと発光素子111aのアノードとを接続する役割のみを有し、ドライバICチップ112上に形成された回路素子と接続されない。 The
本発明の実施の形態1のアルミ配線118a、118b、118cに代えて、金属配線層又は拡散層等で形成された導電経路により、ドライバICチップ112及び複数の発光素子111a、111bを相互に接続しても良い。金属配線層は、例えばアルミ、金又は銅で形成される。 Instead of the
図5の実施の形態1の発光装置の回路図を説明する。図5に示すように、本発明の実施の形態1の発光装置は、外部電源140の出力する電圧を昇圧する電源回路104と、外部接続端子(VCC端子121、スイッチング端子124、電圧帰還端子125)を介して電源回路104に接続される発光モジュール101とを有する。 A circuit diagram of the light-emitting device of Embodiment 1 in FIG. 5 will be described. As shown in FIG. 5, the light emitting device according to the first embodiment of the present invention includes a
電源回路104において、外部電源140に入力コンデンサ143の一端が接続されている。入力コンデンサ143の他端は、接地電位に接続される。コイル141は、入力電源140とショットキーダイオード142のアノード端子とに接続される。ショットキーダイオード142のカソード端子は、出力コンデンサ144の一端に接続される。出力コンデンサの他端は接地電位に接続されている。 In the
図5に示す発光モジュール101の枠内に記載された第1の保護回路501、駆動回路502、電圧検出回路503、及び電流検出抵抗504は、ドライバICチップ112に搭載される発光素子駆動用回路である。ドライバICチップ112は、入力コンデンサ143とコイル141との間に接続されているVCC端子121から電源を供給されて駆動する。 The
電圧帰還端子125は、ショットキーダイオード142のカソード端子と出力コンデンサ144との間に接続されて、出力電圧を入力する。GND端子122は、接地電位に接続される。 The
電圧帰還端子125とGND端子122との間には、第1の保護回路501と、電圧検出回路503の第1の分圧抵抗521及び第2の分圧抵抗522とが並列に接続されている。 Between the
実施の形態1において、第1の保護回路501はツェナダイオードである。第1の保護回路501は、電圧帰還端子125にサージ電圧が印加されることにより、電圧検出回路503が静電破壊されることを防止する。 In Embodiment 1, the
電圧帰還端子125には、更に発光素子111bのアノードが接続されている。発光素子111bのカソードは、発光素子111aのアノードに接続されている。発光素子111aのカソードは、電流検出抵抗504を介して接地電位に接続されている。 The
発光素子111bのアノード側は、電圧帰還端子125を通して外部に電気的に露出している。実装工程などにおいて、電圧帰還端子125を通して発光素子111bのアノードに印加されるサージ電圧は、第1の保護回路501により吸収される。これにより、発光素子111a及び111bは、静電破壊から防止される。 The anode side of the
第1の保護回路501は、本来ドライバICチップ112の内部を保護するための回路であるが、発光素子111bと発光モジュール101内で接続されているため、発光素子111a及び111bの保護回路としても機能する。よって本発明の発光装置は、従来例の発光装置で必要であった図14のツェナダイオード1213を省略することができる。 The
発光素子111aのカソード側は、発光モジュール101内部で電流検出抵抗504に接続されているため、外部からのサージ電圧の印加を受けることがない。そのため、本発明の発光装置は、従来例の発光装置で必要であった第2の保護回路1401(図14)も不要となる。これにり、本発明は従来の発光装置と比較して、ドライバICチップ112の面積を削減できる。 Since the cathode side of the
発光素子111aと電流検出抵抗504との接続点は、誤差アンプ526の反転入力端子に接続されている。誤差アンプ526の非反転入力端子には、第1の基準電圧525の一端が接続されている。第1の基準電圧525の他端は接地電位に接続されている。誤差アンプ525の出力端子は、PWMコンパレータ528の非反転入力端子に接続されるとともに、コンデンサ及び抵抗を介して誤差アンプ525の非反転入力端子に接続されている。 A connection point between the light emitting
PWMコンパレータ528の反転入力端子には、制御端子123に一端を接続された鋸波発振器527の他端に接続されている。PWMコンパレータ528の出力端子は、駆動回路502内部ののAND回路511の入力端子に接続されている。 The inverting input terminal of the
上記のように電圧検出回路503の内部の各素子を相互に接続することにより、電流検出抵抗504の端子間電圧が誤差アンプ526の非反転入力端子に入力される第1の基準電圧525と等しくなるように、負帰還の動作を行う。こうして、電流検出抵抗504に流れる電流を一定にすることにより、発光素子111に流れる電流を一定に制御し、発光の明るさを一定に保つことができる。 By connecting the elements inside the
駆動回路502内部のAND回路511の入力端子には、更にコンパレータ524の出力端子が接続されている。コンパレータ524の反転入力端子には、第1の分圧回路521と第2の分圧回路522の接続点が接続されている。コンパレータ524の非反転入力端子には、第2の基準電圧523の一端が接続されている。第2の基準電圧523の他端は接地電位に接続されている。 The output terminal of the
上記のように接続された第1の分圧抵抗521、第2の分圧抵抗522、第2の基準電圧523、及びコンパレータ524は、出力コンデンサ144の出力電圧(電圧帰還端子125の電圧)が規定値を超えないように、出力電圧の検出及び制御を行うための保護回路である。 The first
駆動回路502において、AND回路511の出力端子は、アンプを介してNチャネルMOSトランジスタ512のゲートに接続されている。NチャネルMOSトランジスタ512のソースは接地電位に接続され、ドレインはスイッチング端子124に接続されている。 In the
駆動回路502は、AND回路511の出力により、Nチャネル型MOSトランジスタ512のオンオフのスイッチング動作を制御する。このスイッチング動作により、外部電源140の出力する入力電圧は昇圧され、出力コンデンサ144には入力電圧より高い電圧が印加される。 The
AND回路511の入力端子には、制御端子123が接続されている。制御端子123に入力される入力電圧がHighの時に、ドライバICチップ112は動作し、駆動回路502は発光素子111を連続発光させる。入力電圧がLowの時に、ドライバICチップ112は動作を停止し、駆動回路502は発光素子111の発光を停止させる。このように駆動回路502は、制御端子123に入力される入力電圧に基づいて発光素子111のON/OFFの切替を行う。制御端子123にパルス電圧を入力することで、発光素子111の点滅の動作を繰り返すこともできる。 A
上記のように構成された本発明の発光装置において、発光素子111a及び111bに定電流が供給される動作について説明する。発光素子111aと発光素子111bに流れる電流が増加すると、電流検出抵抗504の端子電圧は高くなる。電流検出抵抗504の端子電圧が第1の基準電圧525よりも高くなり、電流検出抵抗504の端子電圧と第1の基準電圧525との差が大きくなると、電圧検出回路503の誤差アンプ526の出力信号は低くなる。 An operation of supplying a constant current to the
誤差アンプ526の出力信号を非反転入力端子に入力され、発振器527の出力信号を反転入力端子に入力されるPWMコンパレータ528の出力信号は、誤差アンプ526の出力信号が低くなるにつれロー(Low)期間が長くなり、ハイ(High)期間が短くなる。PWMコンパレータ528の出力信号がハイの間、Nチャネル型MOSトランジスタ512はオンになる。オン時間が短くなるため、外部電源140から入力された電流をコイル141に蓄積する量が少なくなる。 The output signal of the
コイル141に蓄積される電流が少ないため、PWMコンパレータ528の出力信号がローになり、Nチャネル型MOSトランジスタ512がオフになったときに、出力コンデンサ144及び電圧帰還端子125に印加される電圧値は小さくなる。電圧帰還端子125から発光素子111a及び発光素子111bに流れる電流は少なくなる。すると、電流検出抵抗504の端子電圧が下がり、電流検出抵抗504の端子電圧と第1の基準電圧525との差が小さくなる。 Since the current accumulated in the
発光素子111a及び111bに流れる電流が少なくなったときの動作については、上記の動作と逆の動作を行う。上記のように、電圧検出回路503は電流検出抵抗504の端子電圧が第1の基準電圧525と等しくなるように、駆動回路502のNチャネル型MOSトランジスタ512のスイッチング動作を制御する。こうして、発光素子111に一定電流が流れる。 About the operation | movement when the electric current which flows into the
本発明の実施の形態1の発光装置においては、発光モジュール101に外部接続端子としての電流帰還端子126が設けられていない。従来例の発光装置においては、電流帰還端子126はドライバIC1204に設けられて、従来の発光モジュール1201のカソード側端子1254に接続していた。本発明の実施の形態1においては、発光モジュール101内に発光素子111とドライバICチップ112を搭載し、それぞれを接続する故、従来のような電流帰還端子126は不要である。 In the light emitting device according to the first embodiment of the present invention, the
本発明の実施の形態1のドライバICチップ112は、定電流回路であって、入力電圧を昇圧し、発光素子111a、111bに所定の電流を流すよう構成されていた。その構成に代えて、ドライバICチップ112は、定電圧回路であって、入力電圧を昇圧し、発光素子111a、111bに所定の電圧を印加するよう構成しても良い。 The
また別構成として、ドライバICチップ112は、入力電圧を一定電圧に昇圧する定電圧回路と、並列に接続された複数の発光素子のそれぞれに所定の電流を流す定電流回路とを有していても良い。ドライバICチップ112は、入力電圧を降圧し、発光素子111a、111bに所定の電流を流す定電流回路、又は発光素子111a、111bに所定の電圧を印加する定電圧回路であっても良い。 As another configuration, the
本発明の発光装置は、発光素子111をドライバICチップ112上に実装する構成である故、従来例の発光装置と比較して、大幅に実装面積を削減できることができる。 Since the light emitting device of the present invention has a configuration in which the
本発明によれば、従来のツェナダイオード等によるディスクリート保護素子による保護に比べて、ドライバICチップ112内において多種類の保護回路構成が可能となるため、発光モジュール101の外部接続端子の静電破壊の耐圧を高くすることができる。 According to the present invention, since various types of protection circuit configurations are possible in the
《実施の形態2》
図6を用いて、実施の形態2の発光装置を説明する。図6は、実施の形態2の発光装置を示す回路図である。図6において、図5と同一の素子には同一の符号を付している。実施の形態6の発光装置が実施の形態1の発光装置と異なる点は、発光素子111(111a、111b、111c、111d)を4つ直列接続していることである。それ以外の構成は、実施の形態1と同一である。それ故重複する説明を省略する。この実施の形態2においても要部の構成が同一である故、実施の形態1と同一の効果を有する。<< Embodiment 2 >>
The light-emitting device of Embodiment 2 is demonstrated using FIG. FIG. 6 is a circuit diagram showing the light emitting device of the second embodiment. 6, the same elements as those in FIG. 5 are denoted by the same reference numerals. The light emitting device of the sixth embodiment is different from the light emitting device of the first embodiment in that four light emitting elements 111 (111a, 111b, 111c, 111d) are connected in series. Other configurations are the same as those of the first embodiment. Therefore, the overlapping description is omitted. Also in the second embodiment, since the configuration of the main part is the same, the same effect as in the first embodiment is obtained.
なお、発光素子111の個数や接続は、実施の形態1及び実施の形態2に限定するものではなく、任意の所望の数の発光素子を接続することや、複数の発光素子と直列抵抗とを並列接続する実施の態様も本発明に含まれる。もちろん、発光素子が1つであっても構わない。 Note that the number and connection of the light-emitting
また、実施の形態1及び2では、発光素子111の上部に配置される凸レンズ119は一つであったが、発光素子の数に合わせて複数の凸レンズを配置することも可能である。例えば、発光素子1つに対して凸レンズ1つの組合せであっても良い。 In Embodiments 1 and 2, the number of the
《実施の形態3》
図7を用いて、実施の形態3の発光装置を説明する。実施の形態3の発光装置は、第1の保護回路501の構成のみが実施の形態1(図5)と異なる。図7は、実施の形態3の発光装置の保護回路の構成を示す回路図である。実施の形態3の第1の保護回路501は、ツェナダイオード711とダイオード712とを並列に接続した回路である。<< Embodiment 3 >>
The light-emitting device of Embodiment 3 is demonstrated using FIG. The light-emitting device of Embodiment 3 is different from Embodiment 1 (FIG. 5) only in the configuration of the
ダイオード712は、主にPN接合が用いられる。ツェナダイオード711及びダイオード712のカソードが実施の形態1の図5の電圧帰還端子125に接続される。ツェナダイオード711及びダイオード712のアノードは、図5のGND端子122に接続される。なお、第1の保護回路501は、ダイオード712のみであっても良い。 A PN junction is mainly used for the
実施の形態3において、第1の保護回路501の構成以外は実施の形態1と同一である。それ故重複する説明を省略する。この実施の形態3においても要部の構成が同一である故、実施の形態1と同一の効果を有する。本実施の形態においても、実施の形態1及び2と同様に、発光素子と凸レンズの数の組合せは任意である。 The third embodiment is the same as the first embodiment except for the configuration of the
《実施の形態4》
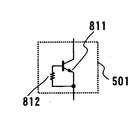
図8を用いて、実施の形態4の発光装置を説明する。実施の形態4の発光装置は、第1の保護回路501の構成のみが実施の形態1(図5)と異なる。図8は、実施の形態4の発光装置の保護回路の構成を示す回路図である。実施の形態4の第1の保護回路501は、NPN型バイポーラトランジスタ811のベース−エミッタ間に抵抗812を接続した構成である。<< Embodiment 4 >>
The light-emitting device of Embodiment 4 is demonstrated using FIG. The light-emitting device of Embodiment 4 is different from Embodiment 1 (FIG. 5) only in the configuration of the
NPN型バイポーラトランジスタ811のエミッタは、実施の形態1の図5のGND端子122に接続される。NPN型バイポーラトランジスタ811のコレクタは、実施の形態1の図5の電圧帰還端子125に接続される。実施の形態4の第1の保護回路501は、抵抗812の抵抗値を変化させることで耐圧を調整できる。バイポーラトランジスタ811を用いた保護回路は一般的に、ダイオードを用いた保護回路よりも小さい面積で実現できる。 The emitter of NPN-type
実施の形態4において、第1の保護回路501以外の構成は実施の形態1と同一である。それ故重複する説明を省略する。この実施の形態4においても要部の構成が同一である故、実施の形態1と同一の効果を有する。本実施の形態においても、実施の形態1及び2と同様に、発光素子と凸レンズの数の組合せは任意である。 In the fourth embodiment, the configuration other than the
《実施の形態5》
図9を用いて、実施の形態5の発光装置を説明する。実施の形態5の発光装置は、第1の保護回路501の構成のみが実施の形態1(図5)と異なる。図9は、実施の形態5の発光装置の保護回路の構成を示す回路図である。実施の形態5の第1の保護回路501は、Nチャネル型MOSトランジスタ911を用いる。<< Embodiment 5 >>
The light-emitting device of Embodiment 5 is demonstrated using FIG. The light-emitting device of Embodiment 5 is different from Embodiment 1 (FIG. 5) only in the configuration of the
Nチャネル型MOSトランジスタ911のゲート、バックゲート、ソース端子を共通にし、実施の形態1の図5のGND端子122に接続された構成である。Nチャネル型MOSトランジスタ911のドレインが実施の形態1の図5の電圧帰還端子125に接続される。Nチャネル型MOSトランジスタ911を用いた保護回路501は一般的に、ダイオードを用いた保護回路よりも小さい面積で実現できる。 The N
実施の形態5において、第1の保護回路501外の構成は実施の形態1と同一である。それ故重複する説明を省略する。この実施の形態5においても要部の構成が同一である故、実施の形態1と同一の効果を有する。本実施の形態においても、実施の形態1及び2と同様に、発光素子と凸レンズの数の組合せは任意である。 In the fifth embodiment, the configuration outside the
《実施の形態6》
図10を用いて、実施の形態6の発光装置を説明する。図10は、実施の形態6のドライバICチップ112の部分拡大断面図である。図10において、実施の形態1の図3と同一の構成要素には、同一の符号を付している。実施の形態6の発光装置が実施の形態1の発光装置と異なる点は、発光素子111aと発光素子111bの接続である。<< Embodiment 6 >>
The light-emitting device of Embodiment 6 is demonstrated using FIG. FIG. 10 is a partial enlarged cross-sectional view of the
実施の形態6の発光装置は、ドライバICチップ112の基板であるP型シリコン基板132の上部に、P型拡散抵抗1002を配置し、P型拡散抵抗1002の周囲をN型ウェル1001で覆っている。P型シリコン基板132の上面は、アルミ配線1018a、1018a’と絶縁膜133aで覆われている。更にその上は、絶縁膜133bとアルミ配線118a、1018b、1018b’、118cで覆われている。 In the light emitting device of the sixth embodiment, a P-type diffused
絶縁膜133bとアルミ配線118a、1018b、1018b’、118cの上は、パッド孔113を除いて絶縁膜131で覆われている。実施の形態6の絶縁膜131は、ポリイミドである。パッド孔113の所定の位置には、バンプ115が載せられ、その上に発光素子111a及び111bが実装される。発光素子111aは、バンプ115、アルミ配線1018b、アルミ配線1018a、P型拡散抵抗1002、アルミ配線1018a’、アルミ配線1018b’を介して、発光素子111bに、電気的に接続される。 The insulating
実施の形態6の発光装置において、その他の構成は実施の形態1と同一である。それ故重複する説明を省略する。この実施の形態6においても要部の構成が同一である故、実施の形態1の発光装置と同一の効果を有する。本実施の形態において、凸レンズの数を発光素子111a及び111bの数に合わせて2つにしても良い。 The other configurations of the light emitting device of the sixth embodiment are the same as those of the first embodiment. Therefore, the overlapping description is omitted. Since the configuration of the main part is the same in the sixth embodiment, the same effect as the light emitting device of the first embodiment is obtained. In the present embodiment, the number of convex lenses may be two according to the number of
《実施の形態7》
図11を用いて、実施の形態7の発光装置を説明する。図11は、ドライバICチップ112の部分拡大断面図である。図11において、実施の形態1の図3及び実施の形態6の図10と同一の構成要素には、同一の符号を付している。実施の形態3の発光装置が実施の形態1及び実施の形態6と異なる点は、複数の発光素子111の相互の接続の仕方である。<< Embodiment 7 >>
The light-emitting device of Embodiment 7 is demonstrated using FIG. FIG. 11 is a partial enlarged cross-sectional view of the
実施の形態7の発光装置は、ドライバICチップ112のP型シリコン基板132の上部に、P型拡散抵抗1002を配置し、P型拡散抵抗1002の周囲をN型ウェル1001で覆っている。P型シリコン基板132の上面は、4層の絶縁膜(下から133a、133b、133c、133d)と、4層のアルミ配線(1118aと1118a’、1118bと1118b’、1118cと1118c’、118aと1118dと1118d’)で覆われている。 In the light emitting device of the seventh embodiment, a P-type diffused
上層の絶縁膜133dとアルミ配線118a、1118d、1118d’の上には、更に絶縁膜131がパッド孔113を除いて形成されている。実施の形態7の絶縁膜131は、ポリイミドである。パッド孔113の所定の位置にはバンプ115が設けられ、その上に発光素子111a、111bが実装されている。発光素子111aと111bは互いに、バンプ115、4層のアルミ配線(1118a、1118a’、1118b、1118b’、1118c、1118c’、1118d、1118d’)、P型拡散抵抗1002を介して、電気的に接続される。 An insulating
実施の形態7の発光装置において、その他の構成は実施の形態1と同一である。それ故重複する説明を省略する。この実施の形態7においても要部の構成が同一である故、実施の形態1の発光装置と同一の効果を有する。本実施の形態において、凸レンズ119の数を発光素子111の数に合わせて複数個配置しても良い。 The other configurations of the light emitting device of the seventh embodiment are the same as those of the first embodiment. Therefore, the overlapping description is omitted. Since the configuration of the main part is the same in the seventh embodiment, the same effect as the light emitting device of the first embodiment is obtained. In the present embodiment, a plurality of
《実施の形態8》
図15を用いて、実施の形態8の発光装置を説明する。図15(a)は、実施の形態8の導電経路であるアルミ配線の形状を示す平面図である。図15(b)から図15(d)は、それぞれ2個、3個、4個の発光素子をアルミ配線1510上に搭載した図である。図15(a)から図15(d)のアルミ配線1510は、すべて同じ形状である。実施の形態8の発光装置のアルミ配線1510は、2個から4個の任意の数の発光素子を電気的に接続可能な形状を有する。<< Embodiment 8 >>
The light-emitting device of Embodiment 8 is demonstrated using FIG. FIG. 15A is a plan view showing the shape of the aluminum wiring that is the conductive path of the eighth embodiment. FIGS. 15B to 15D are diagrams in which two, three, and four light emitting elements are mounted on an
実施の形態8の発光装置は、複数のアルミ配線1510をドライバICチップ112上に実装している。図15(a)〜(d)において、アルミ配線1510上の白丸1511は、バンプの位置を示している。発光素子1501〜1509は、アルミ配線1510の上に設けられたバンプを介して、アルミ配線1510と電気的に接続される。実施の形態8の発光装置が実施の形態1と異なる点は、アルミ配線1510の形状のみである。図15(b)〜(c)において、各発光素子1501〜1509が接続しているバンプ1511とバンプ1511の間には、電流が流れる経路1512を示している。 In the light emitting device of the eighth embodiment, a plurality of
本発明の実施の形態8によれば、1種類の導電経路パターン(例えばアルミ配線1510のパターン)を用いて、発光素子1501〜1509の搭載場所を変更するだけで、異なる数の発光素子を有する複数の発光装置を作ることが出来る。本発明の実施の形態8によれば、導電経路パターンを形成するマスクが1種類で済む。また、1種類のドライバICチップと、任意の発光素子とを組み合わせて、需要に応じた発光装置を製造できるので、LEDの材料としてのドライバICチップの在庫を少なくできる。工場の管理コストを削減できる。 According to the eighth embodiment of the present invention, only one type of conductive path pattern (for example, a pattern of aluminum wiring 1510) is used to change the mounting location of the
実施の形態8の発光装置のドライバICチップ112は、発光素子に流す電流又は発光素子に印加する電圧を可変するための外部接続端子を有していても良い。 The
実施の形態8の発光装置において、導電経路であるアルミ配線の形状以外の構成は実施の形態1と同一である。それ故重複する説明を省略する。この実施の形態8においても要部の構成が同一である故、実施の形態1の発光装置と同一の効果を有する。本実施の形態において、凸レンズの数を発光素子の数に合わせて複数個配置しても良い。 In the light emitting device of the eighth embodiment, the configuration other than the shape of the aluminum wiring that is the conductive path is the same as that of the first embodiment. Therefore, the overlapping description is omitted. Since the configuration of the main part is the same in the eighth embodiment, it has the same effect as the light emitting device of the first embodiment. In the present embodiment, a plurality of convex lenses may be arranged in accordance with the number of light emitting elements.
上記の実施の形態1から実施の形態8の発光装置は、異なる波長で発光する複数の可視発光素子を有していても良い。上記の実施の形態1から実施の形態8の発光装置は、赤、緑、青の3原色でそれぞれ発光する複数の可視発光素子を有していても良い。上記の実施の形態1から実施の形態8の発光装置を複数個並列に接続した照明装置を作ることが出来る。 The light-emitting devices of Embodiments 1 to 8 may include a plurality of visible light-emitting elements that emit light at different wavelengths. The light-emitting devices of Embodiments 1 to 8 may include a plurality of visible light-emitting elements that emit light in the three primary colors of red, green, and blue. A lighting device in which a plurality of the light-emitting devices of Embodiments 1 to 8 are connected in parallel can be manufactured.
発明をある程度の詳細さをもって好適な形態について説明したが、この好適形態の現開示内容は構成の細部において変化してしかるべきものであり、各要素の組合せや順序の変化は請求された発明の範囲及び思想を逸脱することなく実現し得るものである。 Although the invention has been described in its preferred form with a certain degree of detail, the present disclosure of this preferred form should vary in the details of construction, and combinations of elements and changes in order may vary in the claimed invention. It can be realized without departing from the scope and spirit.
本発明は、発光素子駆動用半導体チップ、発光装置及び照明装置に有用である。 The present invention is useful for a semiconductor chip for driving a light emitting element, a light emitting device, and a lighting device.
本発明は、発光素子駆動用半導体チップ、発光装置及び照明装置に関する。 The present invention relates to a light emitting element driving semiconductor chip, a light emitting device, and an illumination device.
近年、携帯電話やデジタルカメラ等の電子機器において、可視発光ダイオード(可視光LED)等の発光素子を駆動する発光装置、及びその発光装置を複数個用いた照明装置が利用される機会が増えている。電子機器の高集積化に伴い、実装面積の小さい発光装置が市場より要求されている。可視発光ダイオード等の発光素子は静電破壊や耐圧破壊しやすいため、保護素子を必要とし、さらに発光素子を駆動するドライバICを必要とするため、発光装置の実装面積が大きくなるという問題があった。 In recent years, in electronic devices such as mobile phones and digital cameras, an opportunity to use a light emitting device that drives a light emitting element such as a visible light emitting diode (visible light LED) and a lighting device using a plurality of the light emitting devices has increased. Yes. As electronic devices are highly integrated, light-emitting devices with a small mounting area are required from the market. Since a light emitting element such as a visible light emitting diode is susceptible to electrostatic breakdown or breakdown withstand voltage, a protective element is required, and a driver IC for driving the light emitting element is required, which increases the mounting area of the light emitting device. It was.
特開2003−8075号公報(特許文献1)に、保護素子の上に発光素子を実装し、1つの発光モジュールとすることで発光装置の実装面積を削減する技術が開示されている。図12〜図14を用いて、特許文献1に記載された従来例の発光装置について説明する。図12は、従来例の発光装置の構成を示す平面図である。図13は、図12の破線A−A’の断面図である。図14は、図12及び図13に示す従来例の発光装置の回路図である。図12〜14において、同じ構成要素については、同じ符号を用いている。 Japanese Patent Laying-Open No. 2003-8075 (Patent Document 1) discloses a technique for reducing the mounting area of a light emitting device by mounting a light emitting element on a protective element to form a single light emitting module. A conventional light emitting device described in Patent Document 1 will be described with reference to FIGS. FIG. 12 is a plan view showing a configuration of a conventional light emitting device. FIG. 13 is a cross-sectional view taken along the broken line A-A ′ in FIG. 12. FIG. 14 is a circuit diagram of the conventional light emitting device shown in FIGS. 12-14, the same code | symbol is used about the same component.
まず、図12及び図13について説明する。従来例の発光装置は、基板1202上に基板配線1203(VCC配線及びGND配線を含む。)を形成し、基板配線1203上に発光モジュール1201と電源回路104とドライバIC1204とを実装している。発光モジュール1201、電源回路104、及びドライバIC1204を構成している内部回路の各素子は、基板配線1203により、それぞれ電気的に接続されている。
First, FIG. 12 and FIG. 13 will be described. In the conventional light emitting device, substrate wiring 1203 (including VCC wiring and GND wiring) is formed on a
電源回路104は、VCC配線とGND配線との間に接続された入力コンデンサ143と、VCC配線を介して入力コンデンサ143に接続されたコイル141と、基板配線1203によりコイル141に接続されたショットキーダイオード142と、一端を基板配線1203を介してショットキーダイオード142と電圧帰還端子125とに接続されて他端をGND配線に接続された出力コンデンサ144を有する。
The
発光モジュール1201の各構成要素について説明する。発光モジュール1201において、リードフレーム114は、基板1202の上方に実装されている。ツェナダイオード1213は、リードフレーム114上に固定される。ツェナダイオード1213の上面は、パッド孔113を除いて絶縁膜131で覆われている。
Each component of the
ツェナダイオード1213上の両端に近い部分を除くパッド孔113にはバンプ115が載せられ、バンプ115の上に発光素子111が実装されている。発光素子111は、可視発光ダイオード(LED)である。ツェナダイオード1213は、発光素子111を静電破壊及び高耐圧破壊から保護している。
図12及び図13において2個のツェナダイオード1213の上に、それぞれ1つずつ発光素子111が実装されている。従来例の発光装置は、発光素子111をツェナダイオード1213上に実装して一体化したモジュールとすることで、ツェナダイオード1213と発光素子111とを別々に実装する場合よりも、実装面積を小さくしている。
12 and 13, one
ツェナダイオード1213上の両端に近い部分のパッド孔113には、2つのボンディングワイヤ116のそれぞれの一端が接続されている。一方のボンディングワイヤ116の他端は、アノード側端子1253に接続され、もう一方のボンディングワイヤ116の他端は、カソード側端子1254に接続される。
One end of each of the two
発光素子111の上部に凸レンズ119が配置されている。凸レンズ119は、発光素子111の光を集光し、光の指向性を強くし、基板1202に垂直な方向の輝度を高める。
A
光透過性樹脂モールド117は、発光素子111、ツェナダイオード1213、リードフレーム114、及び凸レンズ119を含む全体を覆い、基板1202と一体に構成されている。光透過性樹脂モールド117の上半分は、パラボラ形状であって、光を実効的に全反射して集光する反射面を形成している。
The light
ドライバIC1204の各構成要素について説明する。ドライバIC1204において、リードフレーム114は、基板1202の上方に実装される。ドライバICチップ112は、リードフレーム114上に固定されている。ドライバICチップ112の上面は、パッド孔113を除いて絶縁膜131に覆われている。
Each component of the
6つのパッド孔には6つのボンディングワイヤ116の一端がそれぞれ接続され、各ボンディングワイヤ116の他端はそれぞれ外部接続端子(制御端子123、電圧帰還端子125、スイッチング端子124、電流帰還端子126、VCC端子121、GND端子122)に接続されている。このように複数のボンディングワイヤ116を通して、ドライバICチップ112は、外部接続端子に電気的に接続されている。
One end of each of the six
VCC端子121は、VCC配線に接続されている。GND端子122は、GND配線に接続されている。制御端子123は、ドライバIC1204のON/OFFの切替を行うための信号を入力される端子である。制御端子123に入力された入力電圧がHighの時には、ドライバICチップ112は動作して、発光素子111が連続発光する。入力電圧がLowの時には、ドライバICチップ112は動作を停止し、発光素子111の発光も停止する。制御端子123にパルス電圧を入力することで、発光素子111の点滅の動作を繰り返すこともできる。
The
スイッチング端子124は、基板配線1203によりショットキーダイオード142のアノード端子とコイル141とに接続している。電圧帰還端子125は、基板配線1203によって、ショットキーダイオード142のカソード端子、発光モジュール1201のアノード側端子1253、及び出力コンデンサ144と接続している。電流帰還端子126は、基板配線1203によって、発光モジュール1201のカソード側端子1254と接続している。
The switching
図14の従来例の発光装置の回路構成を説明する。図14に示すように、従来例の発光装置は、外部電源140の出力する電圧を昇圧する電源回路104と、外部接続端子(VCC端子121、スイッチング端子124、電圧帰還端子125)を介して電源回路104に接続されるドライバIC1204と、アノード側端子1253を介して電源回路104に接続されカソード側端子1254を介してドライバIC1204に接続される発光モジュール1201とを有する。
The circuit configuration of the conventional light emitting device of FIG. 14 will be described. As shown in FIG. 14, the light emitting device of the conventional example has a power supply via a
図14においてドライバIC1204の枠内に示す回路は、ドライバICチップ112に搭載される内部回路である。ドライバICチップ112は、電圧帰還端子125とGND端子122との間に接続された第1の保護回路501、VCC端子121とGND端子122との間に接続され、その中間接続点に電流帰還端子126を接続された第2の保護回路1401、電流帰還端子126と接地電位との間に接続された電流検出抵抗504、制御端子123と電圧帰還端子125と電流帰還端子126に接続された電圧検出回路503、及び制御端子123と電圧検出回路503とスイッチング端子124に接続された駆動回路502を有する。
In FIG. 14, the circuit shown in the frame of the
第1の保護回路501は、電圧帰還端子125へのサージ印加により、電圧検出回路503が静電破壊されることを防ぐもので、ツェナダイオード、MOSトランジスタ、又はバイポーラトランジスタ等で構成される。図14の第1の保護回路501は、ツェナダイオードである。
The
第2の保護回路1401は、電流帰還端子126へのサージ印加により、ドライバICチップ112の内部回路が静電破壊されることを防ぐ。図14において、第2の保護回路1401は、2個のダイオードの直列接続回路で構成している。
The
駆動回路502は、スイッチング端子124を介してコイル141とショットキーダイオード142を駆動し、外部電源140からの入力電圧を昇圧する。これにより、出力コンデンサ144には、入力電圧より高い電圧が出力電圧として印加される。出力コンデンサ144の電圧は、発光モジュール1201のアノード側端子1253を通して、発光素子111のアノード側に印加される。
The
発光モジュール1201において、ツェナダイオード1213と発光素子111は1対で並列接続されている。ツェナダイオード1213は、発光モジュール1201の実装時等にアノード側端子1253あるいはカソード側端子1254に印加されるサージから発光素子111を保護する。
In the
発光モジュール1201のカソード側端子1254は、ドライバICチップ112内部の電流検出抵抗504に接続された電流帰還端子126に接続される。電圧検出回路503は、電流検出抵抗504の端子電圧を一定に保つことにより、発光素子111に流れる電流を一定に保つ。電圧検出回路503は、電圧帰還端子125の電圧が規定値を超えないように、出力電圧の検出及び制御を行う。
The
従来例の駆動回路502及び電圧検出回路503は本発明と同じであるため、図14において内部の回路を省略又は簡略化して記載している。駆動回路502及び電圧検出回路503の内部回路の詳細は、本発明の実施の形態1で説明する。
上記のように構成された従来例の発光装置は、発光素子111を含む発光モジュール1201と、ドライバICチップ112を含むドライバIC1204とが別々のリードフレームに実装されているため、実装面積が大きくなるという問題があった。特に発光素子111が複数個使用される場合、ツェナダイオード1213の占めるスペースが大きくなり、問題となっていた。従来例の発光装置において、発光素子111の静電破壊や耐圧破壊を保護する保護素子1213と、発光素子111を駆動するドライバIC112とは必要であったため、実装面積を小さくするために取り除くことはできない。
The conventional light emitting device configured as described above has a large mounting area because the
本発明は、上記問題を解決するもので、実装面積の小さい発光装置を提供することを目的とする。
本発明は、任意の数の発光素子と組み合わせて使用できる安価な発光素子駆動用半導体チップを提供することを目的とする。
本発明は、安価な照明装置を提供することを目的とする。
本発明は、高輝度で小型の照明装置を提供することを目的とする。
The present invention solves the above-described problems, and an object thereof is to provide a light-emitting device with a small mounting area.
An object of the present invention is to provide an inexpensive light emitting element driving semiconductor chip that can be used in combination with an arbitrary number of light emitting elements.
An object of the present invention is to provide an inexpensive lighting device.
An object of the present invention is to provide a small illuminating device with high luminance.
上記課題を解決するため、本発明は下記の構成を有する。
本発明の1つの観点による発光装置は、電気信号端子を備え、前記電気信号端子に外部から与えられる電気信号によって駆動され発光する発光素子と、前記電気信号を出力して前記電気信号端子に印加する発光素子駆動用回路、及び外部と電気的に接続するための保護端子に接続された保護回路を半導体を用いて形成した発光素子駆動用半導体チップと、を有し、前記発光素子は、絶縁膜を介して前記発光素子駆動用半導体チップ上に配置され、前記絶縁膜を貫通する接続体によって前記発光素子駆動用半導体チップに接続され、前記発光素子及び前記発光素子駆動用回路のそれぞれは、前記保護端子を通して外部と接続される。
In order to solve the above problems, the present invention has the following configuration.
A light emitting device according to one aspect of the present invention includes an electric signal terminal, a light emitting element that is driven by an electric signal supplied from the outside to the electric signal terminal, emits light, and outputs the electric signal to be applied to the electric signal terminal. A light emitting element driving circuit , and a light emitting element driving semiconductor chip formed by using a semiconductor with a protective circuit connected to a protective terminal for electrical connection to the outside, and the light emitting element is insulated disposed in the light emitting element driving semiconductor chip on the flop through the membrane, which is connected to the light emitting element driving semiconductor chip by connection members passing through the insulating film, each of said light emitting element and the light emitting element driving circuit And connected to the outside through the protective terminal.
この発明は、発光素子駆動用半導体チップ(ドライバICチップ)上に発光素子を実装することで、実装面積の小さい発光装置を実現できる。 According to the present invention, a light emitting device having a small mounting area can be realized by mounting a light emitting element on a light emitting element driving semiconductor chip (driver IC chip).
保護回路は、発光素子又は発光素子駆動用回路を外部から印加される静電気や高電圧(以下、静電気や高電圧を「サージ電圧」と呼ぶ。)から保護する。 Protection circuitry is emitting light element or static electricity or high voltage applied to the light - emitting element driving circuit from the outside (hereinafter, a static electricity or high voltage is referred to as a "surge voltage".) That protects from.
ドライバICチップの内部回路を保護するための保護回路を設ける工程で、発光素子の保護回路をドライバICチップ上に設けることにより、又はドライバICチップの内部回路の保護と発光素子の保護とを兼ねる保護回路を設けることによって、信頼性の高い発光装置を安価に実現できる。この発明によれば、発光素子を外部から印加されるサージ電圧から保護するためだけの従来のような第1の保護回路をドライバICチップの外部に設けないため、従来と比較して安価で実装面積の小さい発光装置を実現できる。 In the step of providing a protection circuit for protecting the internal circuit of the driver IC chip, the protection circuit of the light emitting element is provided on the driver IC chip, or the protection of the internal circuit of the driver IC chip and the protection of the light emitting element are combined. By providing the protection circuit, a highly reliable light-emitting device can be realized at low cost. According to the present invention, the conventional first protection circuit only for protecting the light emitting element from the surge voltage applied from the outside is not provided outside the driver IC chip. A light emitting device with a small area can be realized.
本発明の別の観点による上記の発光装置において、前記保護回路は、前記発光素子駆動用半導体チップの発光素子駆動用回路を形成する素子と同一の製法によって形成された、一若しくは複数個の素子を備える。 In the above light-emitting device according to another aspect of the present invention, the protection circuit is one or a plurality of elements formed by the same manufacturing method as the element forming the light-emitting element driving circuit of the light-emitting element driving semiconductor chip. Is provided.
例えば、保護回路は、PN接合のダイオード、バイポーラトランジスタ、MOSトランジスタの中の少なくとも1つを用いて形成される。この発明は、安価で信頼性が高く実装面積の小さい発光装置を実現できる。 For example, the protection circuit is formed using at least one of a PN junction diode, a bipolar transistor, and a MOS transistor. The present invention can realize a light-emitting device that is inexpensive, highly reliable, and has a small mounting area.
本発明の更に別の観点による上記の発光装置において、前記発光素子駆動用半導体チップの面上に、それぞれ別個のチップで構成された複数個の前記発光素子が装着されており、前記発光素子駆動用半導体チップは、前記発光素子を相互に接続する導電経路を設ける。 In the above light emitting device according to still another aspect of the present invention, a plurality of the light emitting elements each composed of a separate chip are mounted on the surface of the light emitting element driving semiconductor chip, and the light emitting element driving is performed. The semiconductor chip for use is provided with a conductive path for connecting the light emitting elements to each other.
ドライバICチップ上に複数の発光素子の相互接続のみのための導電経路を設けることにより、安価で実装面積の小さい発光装置を実現できる。
導電経路は、極めて低い抵抗値の導電体であっても良く、所定の抵抗値又は所定の電圧降下を生じる経路であっても良い。一般的には、導電経路は極めて低い抵抗値の導電体で形成されることが好ましい場合が多い。導電経路は、ドライバICチップの半導体基板自体に拡散層で形成されても良く、半導体基板の上に蒸着、接着、塗布等の任意の方法で形成されても良い。導電経路の材質は任意である。例えば、ドライバICチップ上に形成された拡散層、金属配線層、樹脂導電層等である。
By providing a conductive path only for interconnection of a plurality of light emitting elements on the driver IC chip, a light emitting device that is inexpensive and has a small mounting area can be realized.
The conductive path may be a conductor having an extremely low resistance value, or may be a path that generates a predetermined resistance value or a predetermined voltage drop. In general, it is often preferable that the conductive path is formed of a conductor having an extremely low resistance value. The conductive path may be formed as a diffusion layer on the semiconductor substrate itself of the driver IC chip, or may be formed on the semiconductor substrate by any method such as vapor deposition, adhesion, and coating. The material of the conductive path is arbitrary. For example, a diffusion layer, a metal wiring layer, a resin conductive layer, or the like formed on the driver IC chip.
本発明の更に別の観点による上記の発光装置において、前記導電経路は、前記発光素子駆動用半導体チップにおいて前記発光素子駆動用回路を形成する拡散層又は金属配線層と同一処理方法によって形成された拡散層又は金属配線層によって形成される。 In the light emitting device according to still another aspect of the present invention, the conductive path is formed by the same processing method as a diffusion layer or a metal wiring layer forming the light emitting element driving circuit in the light emitting element driving semiconductor chip. It is formed by a diffusion layer or a metal wiring layer.
この発明により、安価で実装面積の小さい発光装置を実現できる。 According to the present invention, a light-emitting device that is inexpensive and has a small mounting area can be realized.
本発明の更に別の観点による上記の発光装置において、前記導電経路は、所定の値を有する抵抗を備える。 In the light emitting device according to another aspect of the present invention, the conductive path includes a resistor having a predetermined value.
この発明によれば、例えば導電経路の抵抗値の変化に基づいて発光素子近傍の温度を検出したり、導電経路の両端電圧に基づいて発光素子を流れる電流を検出したり、複数の発光素子を並列に接続した回路においてそれぞれの発光素子に抵抗値を有する導電経路を直列接続することにより各発光素子に流れる電流を均一化したりできる。 According to the present invention, for example, the temperature in the vicinity of the light emitting element is detected based on a change in the resistance value of the conductive path, the current flowing through the light emitting element is detected based on the voltage across the conductive path, or a plurality of light emitting elements are In a circuit connected in parallel, a current flowing through each light emitting element can be made uniform by connecting in series a conductive path having a resistance value to each light emitting element.
本発明の更に別の観点による上記の発光装置は、異なる波長で発光する複数個の可視発光素子を備える。 The light-emitting device according to still another aspect of the present invention includes a plurality of visible light-emitting elements that emit light at different wavelengths.
この発明によれば、発光色が異なる複数の発光素子を非常に近接した位置に配置できるので、例えば複数の発光素子を同時に点灯した場合、複数の発光素子は良く混色し、どの角度から見ても色ムラが生じにくい。 According to the present invention, since a plurality of light emitting elements having different emission colors can be arranged at very close positions, for example, when a plurality of light emitting elements are turned on at the same time, the plurality of light emitting elements are well mixed and viewed from any angle. Is less likely to cause color unevenness.
本発明の更に別の観点による上記の発光装置において、前記発光素子は、赤、緑、青の3原色でそれぞれ発光する複数の可視発光素子を含む。 In the above light-emitting device according to another aspect of the present invention, the light-emitting element includes a plurality of visible light-emitting elements that respectively emit light in three primary colors of red, green, and blue.
この発明の発光装置は、カラー表示が出来る。発光装置単体がドライバICチップを有する故に、周辺回路を削減でき、複数の発光装置を接続することは容易である。発光装置の実装面積が小さく、各発光装置の全体面積の中で発光面積が占める割合が大きいので、複数の発光装置を密集して並べると、従来よりはるかに高輝度の発光装置の表示装置(照明装置)を実現できる。例えば屋外用画像表示装置として有用である。 The light emitting device of the present invention can perform color display. Since a single light emitting device has a driver IC chip, peripheral circuits can be reduced and it is easy to connect a plurality of light emitting devices. Since the mounting area of the light emitting device is small, and the ratio of the light emitting area to the total area of each light emitting device is large, when a plurality of light emitting devices are arranged closely, a display device of a light emitting device with a much higher brightness than conventional ones ( Lighting device) can be realized. For example, it is useful as an outdoor image display device.
本発明の更に別の観点による上記の発光装置において、複数個の前記発光素子が、前記発光装置に一体で形成された一透過型集光レンズの焦点近傍に配置されている。 In the above light emitting device according to still another aspect of the present invention, the plurality of light emitting elements are disposed in the vicinity of a focal point of a single transmission type condensing lens formed integrally with the light emitting device.
発光素子を集光用光学系の焦点に配置することにより、発光素子が発する光を所定の方向に集中できる。発光素子を回路基板に取り付ける精度上の制約等により、回路基板上に複数の発光素子を配置した従来の発光装置においては、各発光素子をある程度の距離を置いて配置せざるを得なかった。それ故に、複数の発光素子は集光用光学系の焦点から少し離れた所に取り付けられた。例えば、複数の発光素子は、大きめのパラボラ型反射面の下にパラボラの焦点から少しずつずれた位置に配置され、パラボラの底で各発光素子の真上に個別の樹脂製の凸レンズが設けられていた。それ故に、発光素子が発した光の一部が所定の方向に向かわず、一定以上集光率を高められないという問題があった。この発明によれば、従来より高い集光率、強い指向性を有する発光装置を実現できる。 By arranging the light emitting element at the focal point of the condensing optical system, the light emitted from the light emitting element can be concentrated in a predetermined direction. In a conventional light-emitting device in which a plurality of light-emitting elements are arranged on a circuit board due to restrictions on the accuracy of attaching the light-emitting elements to the circuit board, each light-emitting element has to be arranged at a certain distance. Therefore, the plurality of light emitting elements were attached at a position slightly away from the focal point of the condensing optical system. For example, the plurality of light emitting elements are arranged at positions slightly shifted from the parabolic focus under the large parabolic reflecting surface, and individual resin convex lenses are provided at the bottom of the parabola directly above each light emitting element. It was. Therefore, there is a problem that a part of the light emitted from the light emitting element is not directed in a predetermined direction, and the light collection rate cannot be increased beyond a certain level. According to the present invention, it is possible to realize a light-emitting device having a higher light collection rate and stronger directivity than conventional ones.
本発明の更に別の観点による上記の発光装置において、複数個の前記発光素子は、前記発光装置に一体で形成された一反射面の焦点近傍に配置されている。 In the above light emitting device according to still another aspect of the present invention, the plurality of light emitting elements are arranged in the vicinity of a focal point of one reflecting surface formed integrally with the light emitting device.
反射面は、典型的には、内面で光が全反射するように形成された透明の樹脂の反射面である。この発明によれば、高い集光率、強い指向性を有する発光装置を実現できる。 The reflecting surface is typically a transparent resin reflecting surface formed so that light is totally reflected on the inner surface. According to the present invention, a light emitting device having a high light collection rate and strong directivity can be realized.
本発明の1つの観点による照明装置は、前記発光素子に所定の電流を印加する定電流回路又は前記発光素子に所定の電圧を印加する定電圧回路を有する前記発光素子駆動用半導体チップを備えた、上記の発光装置を複数個有する。 An illumination device according to one aspect of the present invention includes the light emitting element driving semiconductor chip including a constant current circuit that applies a predetermined current to the light emitting element or a constant voltage circuit that applies a predetermined voltage to the light emitting element. And a plurality of the above light emitting devices.
この発明により、発光装置の相互の配線を簡素化した安価な照明装置を実現できる。発光装置を密集して配置することにより、従来より高輝度の及び/又は小型の照明装置を実現できる。照明装置は、例えば通常の照明装置、大型の表示パネル、映像表示装置等を含む。 According to the present invention, it is possible to realize an inexpensive lighting device that simplifies the mutual wiring of the light emitting device. By arranging the light emitting devices densely, it is possible to realize a lighting device with higher brightness and / or smaller size than in the past. The lighting device includes, for example, a normal lighting device, a large display panel, a video display device, and the like.
本発明の1つの観点による発光素子駆動用半導体チップは、電気信号端子を備えて、前記電気信号端子に与えられる電気信号によって駆動され発光する、複数個の発光素子を装着する発光素子駆動用半導体チップであって、半導体を用いて形成され、前記電気信号を出力して前記電気信号端子に印加する発光素子駆動用回路と、前記複数個の発光素子の前記電気信号端子を相互に接続する導電経路と、を備える。 A light-emitting element driving semiconductor chip according to an aspect of the present invention includes a light-emitting element driving semiconductor having a plurality of light-emitting elements, each of which has an electric signal terminal and is driven by an electric signal applied to the electric signal terminal to emit light. A light emitting element driving circuit that is formed using a semiconductor and outputs the electric signal and applies the electric signal to the electric signal terminal; and a conductive element that interconnects the electric signal terminals of the plurality of light emitting elements. A route.
この発明によれば、発光素子駆動用半導体チップ(ドライバICチップ)上に、複数の発光素子の相互接続のみのための導電経路を設けることにより、安価で実装面積の小さい発光素子駆動用半導体チップを実現できる。 According to the present invention, a light-emitting element driving semiconductor chip that is inexpensive and has a small mounting area is provided on a light-emitting element driving semiconductor chip (driver IC chip) by providing a conductive path only for interconnection of a plurality of light-emitting elements. Can be realized.
本発明の他の観点による上記の発光素子駆動用半導体チップにおいて、それぞれ別個のチップで構成された個数P(Pは1以上の正整数)の前記発光素子と、前記発光素子駆動用回路の回路素子は、前記導電経路に設けられたバンプを経由して相互に接続される。 In another aspect of the above light-emitting element driving semiconductor chips of the present invention, each said light emitting element number configured in a separate chip P (P is one or more positive integer), the light-emitting element driving circuits The circuit elements are connected to each other via bumps provided in the conductive path.
この発明によれば、ワイヤボンディングが不要な安価で実装面積の小さい発光素子駆動用半導体チップを実現できる。 According to the present invention, a light-emitting element driving semiconductor chip that does not require wire bonding and has a small mounting area can be realized.
本発明の別の観点による上記の発光素子駆動用半導体チップにおいて、前記導電経路は、個数Pの前記発光素子に代えて、前記発光素子とほぼ同一形状の個数Q(QはPと異なる正整数)の発光素子を実装する導電経路形状を有する。 In the semiconductor chip for driving a light emitting element according to another aspect of the present invention, the conductive path has a number Q (Q is a positive integer different from P) having substantially the same shape as the light emitting element instead of the number P of the light emitting elements. ) Of the conductive path for mounting the light emitting element.
この発明により、1種類の導電経路パターン(例えばアルミ配線パターン)で、発光素子の搭載場所を変更することにより、異なる数の発光素子を有する複数の発光装置を作ることが出来る。この発明によれば、導電経路パターンを形成するマスクが1種類で済む。又、1種類のドライバICチップと、任意の発光素子とを組み合わせて、需要に応じた発光装置を製造できるので、LEDの材料としてのドライバICチップの在庫を少なくできる。この発明によれば、工場の管理コストを削減できる。 According to the present invention, a plurality of light emitting devices having different numbers of light emitting elements can be manufactured by changing the mounting location of the light emitting elements with one type of conductive path pattern (for example, an aluminum wiring pattern). According to the present invention, only one type of mask is necessary for forming the conductive path pattern. Further, since a light emitting device according to demand can be manufactured by combining one type of driver IC chip and an arbitrary light emitting element, the inventory of driver IC chips as LED materials can be reduced. According to this invention, the management cost of a factory can be reduced.
本発明の更に別の観点による上記の発光素子駆動用半導体チップは、前記発光素子を駆動する電流又は電圧値を可変とするための外部接続端子を有する。 The light emitting element driving semiconductor chip according to still another aspect of the present invention has an external connection terminal for making a current or voltage value for driving the light emitting element variable.
例えばドライバICチップが1個の発光素子を駆動する場合と、4個の発光素子を駆動する場合とでは、ドライバICチップの設定を変更する場合がある。この発明の発光素子駆動用半導体チップは、外部接続端子から発光素子に流す電流又は発光素子に印加する電圧を可変できるので、1種類のドライバICチップを用いて、多種類の発光装置を製造できる。 For example, the setting of the driver IC chip may be changed between when the driver IC chip drives one light emitting element and when the driver IC chip drives four light emitting elements. Since the semiconductor chip for driving a light emitting element of the present invention can vary the current flowing from the external connection terminal to the light emitting element or the voltage applied to the light emitting element, various types of light emitting devices can be manufactured using one type of driver IC chip. .
発明の新規な特徴は添付の請求の範囲に特に記載したものであるが、構成及び内容の双方に関して本発明は、他の目的や特徴と共に、図面と共同して理解されるところの以下の詳細な説明から、より良く理解され評価されるであろう。 The novel features of the invention are set forth with particularity in the appended claims, but the invention, both in terms of construction and content, together with other objects and features, the following details are to be understood in conjunction with the drawings. From this explanation, it will be better understood and appreciated.
本発明によれば、実装面積の小さい発光装置を実現できるという有利な効果が得られる。
本発明によれば、従来必要であったツェナダイオード等の保護素子をなくすことにより、安価で信頼性が高い発光装置を実現できるという有利な効果が得られる。
本発明によれば、発光モジュールの外部接続端子の静電破壊の耐圧を高くする発光装置を実現できるという有利な効果が得られる。
本発明の発光装置によれば、ドライバICチップ上に発光素子を搭載するため、従来と比較して基板配線の寄生抵抗、浮遊容量が減る。そのため、電流値を安定させる位相補償の設計が容易となり、発光の輝度が安定し発光のちらつきが無くなるという有利な効果が得られる。
本発明によれば、任意の数の発光素子と組み合わせて使用できる安価な発光素子駆動用半導体チップを実現できるという有利な効果が得られる。
本発明によれば、安価な照明装置を実現できるという有利な効果が得られる。
本発明によれば、高輝度で小型の照明装置を実現できるという有利な効果が得られる。
According to the present invention, an advantageous effect that a light emitting device having a small mounting area can be realized.
According to the present invention, it is possible to obtain an advantageous effect that it is possible to realize an inexpensive and highly reliable light-emitting device by eliminating a protection element such as a Zener diode which has been conventionally required.
According to the present invention, it is possible to obtain an advantageous effect that it is possible to realize a light emitting device that can increase the withstand voltage of electrostatic breakdown of the external connection terminal of the light emitting module.
According to the light emitting device of the present invention, since the light emitting element is mounted on the driver IC chip, the parasitic resistance and the stray capacitance of the substrate wiring are reduced as compared with the conventional case. Therefore, it is easy to design a phase compensation that stabilizes the current value, and it is possible to obtain an advantageous effect that the luminance of light emission is stabilized and the flicker of light emission is eliminated.
According to the present invention, an advantageous effect that an inexpensive light emitting element driving semiconductor chip that can be used in combination with an arbitrary number of light emitting elements can be realized.
According to the present invention, an advantageous effect that an inexpensive lighting device can be realized is obtained.
According to the present invention, it is possible to obtain an advantageous effect that a small-sized lighting device with high luminance can be realized.
以下本発明の実施をするための最良の形態を具体的に示した実施の形態について、図面とともに記載する。 DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS Embodiments that specifically show the best mode for carrying out the present invention will be described below with reference to the drawings.
《実施の形態1》
図1〜5を用いて、本発明の実施の形態1の発光装置について説明する。図1は、本発明の実施の形態1における発光装置の平面図である。図2は、図1中の破線A−A’で切断した断面図である。図3は、ドライバICチップ112の部分拡大断面図である。図4は、LEDである発光素子111a、111bとドライバICチップ112との間を接続するアルミ配線の形状を示す平面図である。図5は、本発明の実施の形態1の発光装置の回路図である。図1〜5において、同じ構成要素については同じ符号を用いている。図1〜5において、従来例の図12〜14と同じ構成要素については同じ符号を用いている。
Embodiment 1
The light-emitting device of Embodiment 1 of this invention is demonstrated using FIGS. FIG. 1 is a plan view of the light-emitting device according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention. 2 is a cross-sectional view taken along a broken line AA ′ in FIG. FIG. 3 is a partial enlarged cross-sectional view of the
図1及び図2を用いて、本発明の実施の形態1の発光装置について説明する。本発明の実施の形態1の発光装置は、基板102上に基板配線103(VCC配線及びGND配線を含む。)を形成し、基板配線103上に電源回路104と発光モジュール101とを実装する。発光モジュール101の内部回路の各素子と電源回路104の内部回路の各素子は、基板配線103により、それぞれ電気的に接続される。VCC配線は外部電源に接続され、GND配線は接地電位に接続される。
A light-emitting device according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention will be described with reference to FIGS. 1 and 2. In the light emitting device according to the first embodiment of the present invention, substrate wiring 103 (including VCC wiring and GND wiring) is formed on a
電源回路104は、VCC配線とGND配線との間に接続された入力コンデンサ143と、VCC配線を介して入力コンデンサ143に接続されたコイル141と、基板配線103によりコイル141に接続されたショットキーダイオード142と、一端を基板配線103を介してショットキーダイオード142に接続されて他端をGND配線に接続された出力コンデンサ144を有する。
The
発光モジュール101は、基板配線103により電源回路104に接続される外部接続端子(VCC端子121、GND端子122、制御端子123、スイッチング端子124、電圧帰還端子125)を有する。
The
VCC端子121は、VCC配線に接続されている。GND端子122は、GND配線に接続されている。制御端子123は、通常、マイクロコンピュータ等の制御回路の出力に接続され、発光素子111a、111bの発光/停止を切り替える信号を入力される。
The
スイッチング端子124は、基板配線103により、ショットキーダイオード142のアノード端子とコイル141とに接続している。電圧帰還端子125は、基板配線103により、ショットキーダイオード142のカソード端子と出力コンデンサ144とに接続している。
The switching
発光モジュール101を構成する各素子について更に説明する。本発明の実施の形態1の発光モジュール101において、リードフレーム114が基板102の上方に実装され、リードフレーム114上にドライバICチップ(発光素子駆動用半導体チップ)112が固定されている。ドライバICチップ112の上面は、パッド孔113を除いて、絶縁膜131で覆われている。パッド孔113は、ドライバICチップ112上において、絶縁膜131が存在しない部分である。両端に近い部分を除いて、パッド孔113にバンプ115が設けられ、発光素子111a、111bはバンプ115の上に実装される。
Each element constituting the
本発明の発光装置が従来例の発光装置と異なる特徴点は、発光モジュール101内にドライバICチップ112が内蔵されており、発光素子111a、111bがドライバICチップ112上に実装されていることである。そのため、本発明の基板102のサイズは、従来例の基板1202よりも小さい。本発明の発光装置は、発光素子111a、111bをドライバICチップ112上に実装するため、従来と比較して発光装置の実装面積を小さくすることができる。
The light emitting device of the present invention is different from the light emitting device of the conventional example in that the
発光素子111a、111b(両者をまとめて発光素子111と表示する。)は、それぞれ別個のチップで構成される。本発明の実施の形態1において、複数個の発光素子がドライバICチップ112上に実装される。図1〜5においては、2個の発光素子111a、111bが実装されている。
The
発光素子111a、111bは、可視発光ダイオード(LED)である。発光素子の色は所望のものを用いうる。実施の形態1においては、発光素子111a、111bは青色発光ダイオードであって、表面に白色の蛍光物質を塗布した透過型集光レンズ119を通して白色光を外部に放射する。本発明において、複数の発光素子がそれぞれ異なる波長で発光しても良い。発光素子111の上部に配置された凸レンズ119は、発光素子111の光を集光し、光の指向性を強くし、基板102に垂直な方向の輝度を高める。
The
光透過性樹脂モールド117は、発光素子111、ドライバICチップ112、リードフレーム114、及び凸レンズ119を含む全体を覆い、固定し保護している。光透過性樹脂モールド117は、発光素子111の光を集光し、輝度や光の指向性を調整する役割を果たしている。光透過性樹脂モールド117の上半分は、パラボラ形状であって、光を実効的に全反射して集光し、基板102に垂直な方向の輝度を高める反射面を形成している。
The light
実施の形態1において、光透過性樹脂モールド117及び凸レンズ119は、同一材質で一体に形成されている。複数の発光素子111a、111bが、発光装置に一体で形成された1個の表面に白色の蛍光物質を塗布した透過型集光レンズ119及び1個の反射面117の焦点近傍に配置される。
In the first embodiment, the light
図3は、ドライバICチップ112の上面の一部を拡大した図である。ドライバICチップ112の基板であるP型シリコン基板132は、上面を絶縁膜133aで覆われている。絶縁膜133aの上面は、導電経路であるアルミ配線118a、118b、118cの箇所を除いて、絶縁膜133bで覆われている。
FIG. 3 is an enlarged view of a part of the upper surface of the
実施の形態1において、絶縁膜133a及び絶縁膜133bは、酸化膜(SiO2)である。なお、絶縁膜133a、133bの材質は、酸化膜(SiO2)に限定されず、窒化膜(SiN)、高分子化合物(ポリイミド等)、樹脂(エポキシ等)等であっても良い。
In Embodiment 1, the insulating
絶縁膜133bと、アルミ配線118a、118b、118cの上面は、パッド孔113を除いて絶縁膜131で覆われている。パッド孔113は、ボンディングワイヤ116を接続するためと、バンプ115を載せるために設けられる。アルミ配線118a、118b、118c上のパッド孔113のある所定の位置に、バンプ115が設けられる。
The upper surfaces of the insulating
発光素子111a、111bは、バンプ115の上に実装される。発光素子111a、111bは、バンプ115を通じて、ドライバICチップ112上のアルミ配線118a、118b、118cに接続される。
The
図3の両端に近い部分に示すパッド孔113には、図1及び図2に示すようにボンディングワイヤ116が接続される。ドライバICチップ112は、ボンディングワイヤ116により、内部回路と外部接続端子(VCC端子121、GND端子122、制御端子123、スイッチング端子124、電圧帰還端子125)とを電気的に接続される。
図4のアルミ配線の形状及び図5の回路図に示すように、発光素子111bのアノード(電気信号端子)は、バンプ115及びアルミ配線118cを介してドライバICチップ112の内部回路素子及び電圧帰還端子(保護端子)125に接続される。発光素子111bのカソードは、バンプ115及びアルミ配線188bを介して発光素子111aのアノードに接続される。発光素子111aのカソードは、バンプ115及びアルミ配線118aを介してドライバICチップ112の内部回路素子(電流帰還用の抵抗素子504等)と接続される。発光素子111a、111bのアノード及びカソードは、電気信号端子である。
As shown in the shape of the aluminum wiring in FIG. 4 and the circuit diagram in FIG. 5, the anode (electric signal terminal) of the
アルミ配線118bは、発光素子111bのカソードと発光素子111aのアノードとを接続する役割のみを有し、ドライバICチップ112上に形成された回路素子と接続されない。
The
本発明の実施の形態1のアルミ配線118a、118b、118cに代えて、金属配線層又は拡散層等で形成された導電経路により、ドライバICチップ112及び複数の発光素子111a、111bを相互に接続しても良い。金属配線層は、例えばアルミ、金又は銅で形成される。
Instead of the
図5の実施の形態1の発光装置の回路図を説明する。図5に示すように、本発明の実施の形態1の発光装置は、外部電源140の出力する電圧を昇圧する電源回路104と、外部接続端子(VCC端子121、スイッチング端子124、電圧帰還端子125)を介して電源回路104に接続される発光モジュール101とを有する。
A circuit diagram of the light-emitting device of Embodiment 1 in FIG. 5 will be described. As shown in FIG. 5, the light emitting device according to the first embodiment of the present invention includes a
電源回路104において、外部電源140に入力コンデンサ143の一端が接続されている。入力コンデンサ143の他端は、接地電位に接続される。コイル141は、入力電源140とショットキーダイオード142のアノード端子とに接続される。ショットキーダイオード142のカソード端子は、出力コンデンサ144の一端に接続される。出力コンデンサの他端は接地電位に接続されている。
In the
図5に示す発光モジュール101の枠内に記載された駆動回路502、電圧検出回路503、及び電流検出抵抗504は、ドライバICチップ112に搭載される発光素子駆動用回路である。ドライバICチップ112は、入力コンデンサ143とコイル141との間に接続されているVCC端子121から電源を供給されて駆動する。
Drive moving
電圧帰還端子125は、ショットキーダイオード142のカソード端子と出力コンデンサ144との間に接続されて、出力電圧を入力する。GND端子122は、接地電位に接続される。
The
電圧帰還端子125とGND端子122との間には、第1の保護回路501と、電圧検出回路503の第1の分圧抵抗521及び第2の分圧抵抗522とが並列に接続されている。
Between the
実施の形態1において、第1の保護回路501はツェナダイオードである。第1の保護回路501は、電圧帰還端子125にサージ電圧が印加されることにより、電圧検出回路503が静電破壊されることを防止する。
In Embodiment 1, the
電圧帰還端子125には、更に発光素子111bのアノードが接続されている。発光素子111bのカソードは、発光素子111aのアノードに接続されている。発光素子111aのカソードは、電流検出抵抗504を介して接地電位に接続されている。
The
発光素子111bのアノード側は、電圧帰還端子125を通して外部に電気的に露出している。実装工程などにおいて、電圧帰還端子125を通して発光素子111bのアノードに印加されるサージ電圧は、第1の保護回路501により吸収される。これにより、発光素子111a及び111bは、静電破壊から防止される。
The anode side of the
第1の保護回路501は、本来ドライバICチップ112の内部を保護するための回路であるが、発光素子111bと発光モジュール101内で接続されているため、発光素子111a及び111bの保護回路としても機能する。よって本発明の発光装置は、従来例の発光装置で必要であった図14のツェナダイオード1213を省略することができる。
The
発光素子111aのカソード側は、発光モジュール101内部で電流検出抵抗504に接続されているため、外部からのサージ電圧の印加を受けることがない。そのため、本発明の発光装置は、従来例の発光装置で必要であった第2の保護回路1401(図14)も不要となる。これにり、本発明は従来の発光装置と比較して、ドライバICチップ112の面積を削減できる。
Since the cathode side of the
発光素子111aと電流検出抵抗504との接続点は、誤差アンプ526の反転入力端子に接続されている。誤差アンプ526の非反転入力端子には、第1の基準電圧525の一端が接続されている。第1の基準電圧525の他端は接地電位に接続されている。誤差アンプ526の出力端子は、PWMコンパレータ528の非反転入力端子に接続されるとともに、コンデンサ及び抵抗を介して誤差アンプ526の反転入力端子に接続されている。
A connection point between the light emitting
PWMコンパレータ528の反転入力端子には、制御端子123に一端を接続された鋸波発振器527の他端に接続されている。PWMコンパレータ528の出力端子は、駆動回路502内部のAND回路511の入力端子に接続されている。
The inverting input terminal of the
上記のように電圧検出回路503の内部の各素子を相互に接続することにより、電流検出抵抗504の端子間電圧が誤差アンプ526の非反転入力端子に入力される第1の基準電圧525と等しくなるように、負帰還の動作を行う。こうして、電流検出抵抗504に流れる電流を一定にすることにより、発光素子111に流れる電流を一定に制御し、発光の明るさを一定に保つことができる。
By connecting the elements inside the
駆動回路502内部のAND回路511の入力端子には、更にコンパレータ524の出力端子が接続されている。コンパレータ524の反転入力端子には、第1の分圧抵抗521と第2の分圧抵抗522の接続点が接続されている。コンパレータ524の非反転入力端子には、第2の基準電圧523の一端が接続されている。第2の基準電圧523の他端は接地電位に接続されている。
The output terminal of the
上記のように接続された第1の分圧抵抗521、第2の分圧抵抗522、第2の基準電圧523、及びコンパレータ524は、出力コンデンサ144の出力電圧(電圧帰還端子125の電圧)が規定値を超えないように、出力電圧の検出及び制御を行うための保護回路である。
The first
駆動回路502において、AND回路511の出力端子は、アンプを介してNチャネルMOSトランジスタ512のゲートに接続されている。NチャネルMOSトランジスタ512のソースは接地電位に接続され、ドレインはスイッチング端子124に接続されている。
In the
駆動回路502は、AND回路511の出力により、Nチャネル型MOSトランジスタ512のオンオフのスイッチング動作を制御する。このスイッチング動作により、外部電源140の出力する入力電圧は昇圧され、出力コンデンサ144には入力電圧より高い電圧が印加される。
The
AND回路511の入力端子には、制御端子123が接続されている。制御端子123に入力される入力電圧がHighの時に、ドライバICチップ112は動作し、駆動回路502は発光素子111を連続発光させる。入力電圧がLowの時に、ドライバICチップ112は動作を停止し、駆動回路502は発光素子111の発光を停止させる。このように駆動回路502は、制御端子123に入力される入力電圧に基づいて発光素子111のON/OFFの切替を行う。制御端子123にパルス電圧を入力することで、発光素子111の点滅の動作を繰り返すこともできる。
A
上記のように構成された本発明の発光装置において、発光素子111a及び111bに定電流が供給される動作について説明する。発光素子111aと発光素子111bに流れる電流が増加すると、電流検出抵抗504の端子電圧は高くなる。電流検出抵抗504の端子電圧が第1の基準電圧525よりも高くなり、電流検出抵抗504の端子電圧と第1の基準電圧525との差が大きくなると、電圧検出回路503の誤差アンプ526の出力信号は低くなる。
An operation of supplying a constant current to the
誤差アンプ526の出力信号を非反転入力端子に入力され、発振器527の出力信号を反転入力端子に入力されるPWMコンパレータ528の出力信号は、誤差アンプ526の出力信号が低くなるにつれロー(Low)期間が長くなり、ハイ(High)期間が短くなる。PWMコンパレータ528の出力信号がハイの間、Nチャネル型MOSトランジスタ512はオンになる。オン時間が短くなるため、外部電源140から入力された電流をコイル141に蓄積する量が少なくなる。
The output signal of the
コイル141に蓄積される電流が少ないため、PWMコンパレータ528の出力信号がローになり、Nチャネル型MOSトランジスタ512がオフになったときに、出力コンデンサ144及び電圧帰還端子125に印加される電圧値は小さくなる。電圧帰還端子125から発光素子111a及び発光素子111bに流れる電流は少なくなる。すると、電流検出抵抗504の端子電圧が下がり、電流検出抵抗504の端子電圧と第1の基準電圧525との差が小さくなる。
Since the current accumulated in the
発光素子111a及び111bに流れる電流が少なくなったときの動作については、上記の動作と逆の動作を行う。上記のように、電圧検出回路503は電流検出抵抗504の端子電圧が第1の基準電圧525と等しくなるように、駆動回路502のNチャネル型MOSトランジスタ512のスイッチング動作を制御する。こうして、発光素子111に一定電流が流れる。
About the operation | movement when the electric current which flows into the
本発明の実施の形態1の発光装置においては、発光モジュール101に外部接続端子としての電流帰還端子126が設けられていない。従来例の発光装置においては、電流帰還端子126はドライバIC1204に設けられて、従来の発光モジュール1201のカソード側端子1254に接続していた。本発明の実施の形態1においては、発光モジュール101内に発光素子111とドライバICチップ112を搭載し、それぞれを接続する故、従来のような電流帰還端子126は不要である。
In the light emitting device according to the first embodiment of the present invention, the
本発明の実施の形態1のドライバICチップ112は、定電流回路であって、入力電圧を昇圧し、発光素子111a、111bに所定の電流を流すよう構成されていた。その構成に代えて、ドライバICチップ112は、定電圧回路であって、入力電圧を昇圧し、発光素子111a、111bに所定の電圧を印加するよう構成しても良い。
The
また別構成として、ドライバICチップ112は、入力電圧を一定電圧に昇圧する定電圧回路と、並列に接続された複数の発光素子のそれぞれに所定の電流を流す定電流回路とを有していても良い。ドライバICチップ112は、入力電圧を降圧し、発光素子111a、111bに所定の電流を流す定電流回路、又は発光素子111a、111bに所定の電圧を印加する定電圧回路であっても良い。
As another configuration, the
本発明の発光装置は、発光素子111をドライバICチップ112上に実装する構成である故、従来例の発光装置と比較して、大幅に実装面積を削減できることができる。
Since the light emitting device of the present invention has a configuration in which the
本発明によれば、従来のツェナダイオード等によるディスクリート保護素子による保護に比べて、ドライバICチップ112内において多種類の保護回路構成が可能となるため、発光モジュール101の外部接続端子の静電破壊の耐圧を高くすることができる。
According to the present invention, since various types of protection circuit configurations are possible in the
《実施の形態2》
図6を用いて、実施の形態2の発光装置を説明する。図6は、実施の形態2の発光装置を示す回路図である。図6において、図5と同一の素子には同一の符号を付している。実施の形態6の発光装置が実施の形態1の発光装置と異なる点は、発光素子111(111a、111b、111c、111d)を4つ直列接続していることである。それ以外の構成は、実施の形態1と同一である。それ故重複する説明を省略する。この実施の形態2においても要部の構成が同一である故、実施の形態1と同一の効果を有する。
<< Embodiment 2 >>
The light-emitting device of Embodiment 2 is demonstrated using FIG. FIG. 6 is a circuit diagram showing the light emitting device of the second embodiment. 6, the same elements as those in FIG. 5 are denoted by the same reference numerals. The light emitting device of the sixth embodiment is different from the light emitting device of the first embodiment in that four light emitting elements 111 (111a, 111b, 111c, 111d) are connected in series. Other configurations are the same as those of the first embodiment. Therefore, the overlapping description is omitted. Also in the second embodiment, since the configuration of the main part is the same, the same effect as in the first embodiment is obtained.
なお、発光素子111の個数や接続は、実施の形態1及び実施の形態2に限定するものではなく、任意の所望の数の発光素子を接続することや、複数の発光素子と直列抵抗とを並列接続する実施の態様も本発明に含まれる。もちろん、発光素子が1つであっても構わない。
Note that the number and connection of the light-emitting
また、実施の形態1及び2では、発光素子111の上部に配置される凸レンズ119は一つであったが、発光素子の数に合わせて複数の凸レンズを配置することも可能である。例えば、発光素子1つに対して凸レンズ1つの組合せであっても良い。
In Embodiments 1 and 2, the number of the
《実施の形態3》
図7を用いて、実施の形態3の発光装置を説明する。実施の形態3の発光装置は、第1の保護回路501の構成のみが実施の形態1(図5)と異なる。図7は、実施の形態3の発光装置の保護回路の構成を示す回路図である。実施の形態3の第1の保護回路501は、ツェナダイオード711とダイオード712とを並列に接続した回路である。
<< Embodiment 3 >>
The light-emitting device of Embodiment 3 is demonstrated using FIG. The light-emitting device of Embodiment 3 is different from Embodiment 1 (FIG. 5) only in the configuration of the
ダイオード712は、主にPN接合が用いられる。ツェナダイオード711及びダイオード712のカソードが実施の形態1の図5の電圧帰還端子125に接続される。ツェナダイオード711及びダイオード712のアノードは、図5のGND端子122に接続される。なお、第1の保護回路501は、ダイオード712のみであっても良い。
A PN junction is mainly used for the
実施の形態3において、第1の保護回路501の構成以外は実施の形態1と同一である。それ故重複する説明を省略する。この実施の形態3においても要部の構成が同一である故、実施の形態1と同一の効果を有する。本実施の形態においても、実施の形態1及び2と同様に、発光素子と凸レンズの数の組合せは任意である。
The third embodiment is the same as the first embodiment except for the configuration of the
《実施の形態4》
図8を用いて、実施の形態4の発光装置を説明する。実施の形態4の発光装置は、第1の保護回路501の構成のみが実施の形態1(図5)と異なる。図8は、実施の形態4の発光装置の保護回路の構成を示す回路図である。実施の形態4の第1の保護回路501は、NPN型バイポーラトランジスタ811のベース−エミッタ間に抵抗812を接続した構成である。
<< Embodiment 4 >>
The light-emitting device of Embodiment 4 is demonstrated using FIG. The light-emitting device of Embodiment 4 is different from Embodiment 1 (FIG. 5) only in the configuration of the
NPN型バイポーラトランジスタ811のエミッタは、実施の形態1の図5のGND端子122に接続される。NPN型バイポーラトランジスタ811のコレクタは、実施の形態1の図5の電圧帰還端子125に接続される。実施の形態4の第1の保護回路501は、抵抗812の抵抗値を変化させることで耐圧を調整できる。バイポーラトランジスタ811を用いた保護回路は一般的に、ダイオードを用いた保護回路よりも小さい面積で実現できる。
The emitter of NPN-type
実施の形態4において、第1の保護回路501以外の構成は実施の形態1と同一である。それ故重複する説明を省略する。この実施の形態4においても要部の構成が同一である故、実施の形態1と同一の効果を有する。本実施の形態においても、実施の形態1及び2と同様に、発光素子と凸レンズの数の組合せは任意である。
In the fourth embodiment, the configuration other than the
《実施の形態5》
図9を用いて、実施の形態5の発光装置を説明する。実施の形態5の発光装置は、第1の保護回路501の構成のみが実施の形態1(図5)と異なる。図9は、実施の形態5の発光装置の保護回路の構成を示す回路図である。実施の形態5の第1の保護回路501は、Nチャネル型MOSトランジスタ911を用いる。
<< Embodiment 5 >>
The light-emitting device of Embodiment 5 is demonstrated using FIG. The light-emitting device of Embodiment 5 is different from Embodiment 1 (FIG. 5) only in the configuration of the
Nチャネル型MOSトランジスタ911のゲート、バックゲート、ソース端子を共通にし、実施の形態1の図5のGND端子122に接続された構成である。Nチャネル型MOSトランジスタ911のドレインが実施の形態1の図5の電圧帰還端子125に接続される。Nチャネル型MOSトランジスタ911を用いた保護回路501は一般的に、ダイオードを用いた保護回路よりも小さい面積で実現できる。
The N
実施の形態5において、第1の保護回路501外の構成は実施の形態1と同一である。それ故重複する説明を省略する。この実施の形態5においても要部の構成が同一である故、実施の形態1と同一の効果を有する。本実施の形態においても、実施の形態1及び2と同様に、発光素子と凸レンズの数の組合せは任意である。
In the fifth embodiment, the configuration outside the
《実施の形態6》
図10を用いて、実施の形態6の発光装置を説明する。図10は、実施の形態6のドライバICチップ112の部分拡大断面図である。図10において、実施の形態1の図3と同一の構成要素には、同一の符号を付している。実施の形態6の発光装置が実施の形態1の発光装置と異なる点は、発光素子111aと発光素子111bの接続である。
<< Embodiment 6 >>
The light-emitting device of Embodiment 6 is demonstrated using FIG. FIG. 10 is a partial enlarged cross-sectional view of the
実施の形態6の発光装置は、ドライバICチップ112の基板であるP型シリコン基板132の上部に、P型拡散抵抗1002を配置し、P型拡散抵抗1002の周囲をN型ウェル1001で覆っている。P型シリコン基板132の上面は、アルミ配線1018a、1018a’と絶縁膜133aで覆われている。更にその上は、絶縁膜133bとアルミ配線118a、1018b、1018b’、118cで覆われている。
In the light emitting device of the sixth embodiment, a P-type diffused
絶縁膜133bとアルミ配線118a、1018b、1018b’、118cの上は、パッド孔113を除いて絶縁膜131で覆われている。実施の形態6の絶縁膜131は、ポリイミドである。パッド孔113の所定の位置には、バンプ115が載せられ、その上に発光素子111a及び111bが実装される。発光素子111aは、バンプ115、アルミ配線1018b、アルミ配線1018a、P型拡散抵抗1002、アルミ配線1018a’、アルミ配線1018b’を介して、発光素子111bに、電気的に接続される。
The insulating
実施の形態6の発光装置において、その他の構成は実施の形態1と同一である。それ故重複する説明を省略する。この実施の形態6においても要部の構成が同一である故、実施の形態1の発光装置と同一の効果を有する。本実施の形態において、凸レンズの数を発光素子111a及び111bの数に合わせて2つにしても良い。
The other configurations of the light emitting device of the sixth embodiment are the same as those of the first embodiment. Therefore, the overlapping description is omitted. Since the configuration of the main part is the same in the sixth embodiment, the same effect as the light emitting device of the first embodiment is obtained. In the present embodiment, the number of convex lenses may be two according to the number of
《実施の形態7》
図11を用いて、実施の形態7の発光装置を説明する。図11は、ドライバICチップ112の部分拡大断面図である。図11において、実施の形態1の図3及び実施の形態6の図10と同一の構成要素には、同一の符号を付している。実施の形態3の発光装置が実施の形態1及び実施の形態6と異なる点は、複数の発光素子111の相互の接続の仕方である。
<< Embodiment 7 >>
The light-emitting device of Embodiment 7 is demonstrated using FIG. FIG. 11 is a partial enlarged cross-sectional view of the
実施の形態7の発光装置は、ドライバICチップ112のP型シリコン基板132の上部に、P型拡散抵抗1002を配置し、P型拡散抵抗1002の周囲をN型ウェル1001で覆っている。P型シリコン基板132の上面は、4層の絶縁膜(下から133a、133b、133c、133d)と、4層のアルミ配線(1118aと1118a’、1118bと1118b’、1118cと1118c’、118aと1118dと1118d’)で覆われている。
In the light emitting device of the seventh embodiment, a P-type diffused
上層の絶縁膜133dとアルミ配線118a、1118d、1118d’の上には、更に絶縁膜131がパッド孔113を除いて形成されている。実施の形態7の絶縁膜131は、ポリイミドである。パッド孔113の所定の位置にはバンプ115が設けられ、その上に発光素子111a、111bが実装されている。発光素子111aと111bは互いに、バンプ115、4層のアルミ配線(1118a、1118a’、1118b、1118b’、1118c、1118c’、1118d、1118d’)、P型拡散抵抗1002を介して、電気的に接続される。
An insulating
実施の形態7の発光装置において、その他の構成は実施の形態1と同一である。それ故重複する説明を省略する。この実施の形態7においても要部の構成が同一である故、実施の形態1の発光装置と同一の効果を有する。本実施の形態において、凸レンズ119の数を発光素子111の数に合わせて複数個配置しても良い。
In the light emitting device of the seventh embodiment, other configurations are the same as those of the first embodiment. Therefore, the overlapping description is omitted. Since the configuration of the main part is the same in the seventh embodiment, the same effect as the light emitting device of the first embodiment is obtained. In the present embodiment, a plurality of
《実施の形態8》
図15を用いて、実施の形態8の発光装置を説明する。図15(a)は、実施の形態8の導電経路であるアルミ配線の形状を示す平面図である。図15(b)から図15(d)は、それぞれ2個、3個、4個の発光素子をアルミ配線1510上に搭載した図である。図15(a)から図15(d)のアルミ配線1510は、すべて同じ形状である。実施の形態8の発光装置のアルミ配線1510は、2個から4個の任意の数の発光素子を電気的に接続可能な形状を有する。
<< Embodiment 8 >>
The light-emitting device of Embodiment 8 is demonstrated using FIG. FIG. 15A is a plan view showing the shape of the aluminum wiring that is the conductive path of the eighth embodiment. FIGS. 15B to 15D are diagrams in which two, three, and four light emitting elements are mounted on an
実施の形態8の発光装置は、複数のアルミ配線1510をドライバICチップ112上に実装している。図15(a)〜(d)において、アルミ配線1510上の白丸1511は、バンプの位置を示している。発光素子1501〜1509は、アルミ配線1510の上に設けられたバンプを介して、アルミ配線1510と電気的に接続される。実施の形態8の発光装置が実施の形態1と異なる点は、アルミ配線1510の形状のみである。図15(b)〜(c)において、各発光素子1501〜1509が接続しているバンプ1511とバンプ1511の間には、電流が流れる経路1512を示している。
In the light emitting device of the eighth embodiment, a plurality of
本発明の実施の形態8によれば、1種類の導電経路パターン(例えばアルミ配線1510のパターン)を用いて、発光素子1501〜1509の搭載場所を変更するだけで、異なる数の発光素子を有する複数の発光装置を作ることが出来る。本発明の実施の形態8によれば、導電経路パターンを形成するマスクが1種類で済む。また、1種類のドライバICチップと、任意の発光素子とを組み合わせて、需要に応じた発光装置を製造できるので、LEDの材料としてのドライバICチップの在庫を少なくできる。工場の管理コストを削減できる。
According to the eighth embodiment of the present invention, only one type of conductive path pattern (for example, a pattern of aluminum wiring 1510) is used to change the mounting location of the
実施の形態8の発光装置のドライバICチップ112は、発光素子に流す電流又は発光素子に印加する電圧を可変するための外部接続端子を有していても良い。
The
実施の形態8の発光装置において、導電経路であるアルミ配線の形状以外の構成は実施の形態1と同一である。それ故重複する説明を省略する。この実施の形態8においても要部の構成が同一である故、実施の形態1の発光装置と同一の効果を有する。本実施の形態において、凸レンズの数を発光素子の数に合わせて複数個配置しても良い。 In the light emitting device of the eighth embodiment, the configuration other than the shape of the aluminum wiring that is the conductive path is the same as that of the first embodiment. Therefore, the overlapping description is omitted. Since the configuration of the main part is the same in the eighth embodiment, it has the same effect as the light emitting device of the first embodiment. In the present embodiment, a plurality of convex lenses may be arranged in accordance with the number of light emitting elements.
上記の実施の形態1から実施の形態8の発光装置は、異なる波長で発光する複数の可視発光素子を有していても良い。上記の実施の形態1から実施の形態8の発光装置は、赤、緑、青の3原色でそれぞれ発光する複数の可視発光素子を有していても良い。上記の実施の形態1から実施の形態8の発光装置を複数個並列に接続した照明装置を作ることが出来る。 The light-emitting devices of Embodiments 1 to 8 may include a plurality of visible light-emitting elements that emit light at different wavelengths. The light-emitting devices of Embodiments 1 to 8 may include a plurality of visible light-emitting elements that emit light in the three primary colors of red, green, and blue. A lighting device in which a plurality of the light-emitting devices of Embodiments 1 to 8 are connected in parallel can be manufactured.
図面の一部又は全部は、図示を目的とした概要的表現により描かれており、必ずしもそこに示された要素の実際の相対的大きさや位置を忠実に描写しているとは限らないことは考慮願いたい。 Part or all of the drawings are drawn in a schematic representation for illustration purposes and do not necessarily depict the actual relative sizes and positions of the elements shown there faithfully. Please consider.
発明をある程度の詳細さをもって好適な形態について説明したが、この好適形態の現開示内容は構成の細部において変化してしかるべきものであり、各要素の組合せや順序の変化は請求された発明の範囲及び思想を逸脱することなく実現し得るものである。 Although the invention has been described in its preferred form with a certain degree of detail, the present disclosure of this preferred form should vary in the details of construction, and combinations of elements and changes in order may vary in the claimed invention. It can be realized without departing from the scope and spirit.
本発明は、発光素子駆動用半導体チップ、発光装置及び照明装置に有用である。 The present invention is useful for a semiconductor chip for driving a light emitting element, a light emitting device, and a lighting device.
101 発光モジュール 101 Light emitting module
102 基板 102 substrates
103 基板配線 103 Substrate wiring
111a、111b 発光素子 111a, 111b Light emitting element
112 ドライバICチップ 112 Driver IC chip
113 パッド孔 113 Pad hole
114 リードフレーム 114 lead frame
115 バンプ 115 Bump
116 ボンディングワイヤ 116 Bonding wire
117 光透過性樹脂モールド 117 Light transmissive resin mold
118a、118b、118c アルミ配線 118a, 118b, 118c Aluminum wiring
119 凸レンズ 119 Convex lens
121 VCC端子 121 VCC terminal
122 GND端子 122 GND terminal
123 制御端子 123 Control terminal
124 スイッチング端子 124 Switching terminal
125 電圧帰還端子 125 Voltage feedback terminal
126 電流帰還端子 126 Current feedback terminal
131 絶縁膜 131 Insulating film
132 P型シリコン基板 132 P-type silicon substrate
133a、133b、133c、133d 絶縁膜 133a, 133b, 133c, 133d insulating film
140 外部電源 140 External power supply
141 コイル 141 coil
142 ショットキーダイオード 142 Schottky diode
143 入力コンデンサ 143 Input capacitor
144 出力コンデンサ 144 Output capacitor
501 第1の保護回路 501 First protection circuit
502 駆動回路 502 Drive circuit
503 電圧検出回路 503 Voltage detection circuit
504 電流検出抵抗 504 Current detection resistor
1204 ドライバIC 1204 Driver IC
1213 ツェナダイオード 1213 Zener diode
1401 第2の保護回路 1401 Second protection circuit
Claims (15)
前記電気信号を出力して前記電気信号端子に印加する発光素子駆動用回路を半導体を用いて形成した発光素子駆動用半導体チップと、
を有し、
前記発光素子を前記発光素子駆動用半導体チップの面上に装着したことを特徴とする発光装置。A light-emitting element that includes an electric signal terminal and is driven by an electric signal applied to the electric signal terminal from the outside;
A light emitting element driving semiconductor chip formed by using a semiconductor light emitting element driving circuit for outputting the electric signal and applying the electric signal to the electric signal terminal;
Have
A light-emitting device, wherein the light-emitting element is mounted on a surface of the semiconductor chip for driving the light-emitting element.
前記発光素子又は前記発光素子駆動用回路を外部から印加される静電気や高電圧から保護する保護回路と、
前記保護回路を外部と電気的に接続するための保護端子と、
を備え、
前記保護端子を前記発光素子の前記電気信号端子に接続したことを特徴とする請求項1に記載の発光装置。The light emitting element driving semiconductor chip,
A protection circuit for protecting the light emitting element or the light emitting element driving circuit from static electricity or high voltage applied from the outside;
A protective terminal for electrically connecting the protective circuit to the outside;
With
The light emitting device according to claim 1, wherein the protective terminal is connected to the electric signal terminal of the light emitting element.
前記発光素子駆動用半導体チップが、前記発光素子を相互に接続する導電経路を設けたことを特徴とする請求項1に記載の発光装置。On the surface of the light emitting element driving semiconductor chip, a plurality of the light emitting elements each composed of a separate chip are mounted,
2. The light emitting device according to claim 1, wherein the light emitting element driving semiconductor chip is provided with a conductive path for connecting the light emitting elements to each other.
半導体を用いて形成され、前記電気信号を出力して前記電気信号端子に印加する発光素子駆動用回路と、
前記複数個の発光素子の前記電気信号端子を相互に接続する導電経路と、
を備えたことを特徴とする発光素子駆動用半導体チップ。A light-emitting element driving semiconductor chip having a plurality of light-emitting elements that includes an electric signal terminal and is driven by an electric signal applied to the electric signal terminal to emit light,
A light emitting element driving circuit that is formed using a semiconductor, outputs the electric signal, and applies the electric signal to the electric signal terminal;
A conductive path interconnecting the electrical signal terminals of the plurality of light emitting elements;
A semiconductor chip for driving a light emitting element.
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004123453 | 2004-04-19 | ||
| JP2004123453 | 2004-04-19 | ||
| PCT/JP2005/007412 WO2005104248A1 (en) | 2004-04-19 | 2005-04-18 | Semiconductor chip for driving light emitting element, light emitting device, and lighting device |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JPWO2005104248A1 true JPWO2005104248A1 (en) | 2007-08-30 |
Family
ID=35197282
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006512534A Withdrawn JPWO2005104248A1 (en) | 2004-04-19 | 2005-04-18 | Semiconductor chip for driving light emitting element, light emitting device and lighting device |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US20070257901A1 (en) |
| JP (1) | JPWO2005104248A1 (en) |
| CN (1) | CN1943049A (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2005104248A1 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPWO2012086517A1 (en) * | 2010-12-20 | 2014-05-22 | ローム株式会社 | Light emitting element unit and light emitting element package |
Families Citing this family (16)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US8076680B2 (en) | 2005-03-11 | 2011-12-13 | Seoul Semiconductor Co., Ltd. | LED package having an array of light emitting cells coupled in series |
| DE102007001706A1 (en) * | 2007-01-11 | 2008-07-17 | Osram Opto Semiconductors Gmbh | Housing for optoelectronic component and arrangement of an optoelectronic component in a housing |
| CN102308384B (en) * | 2009-02-05 | 2015-06-17 | 皇家飞利浦电子股份有限公司 | Improved packaging for LED combinations |
| DE102009022901A1 (en) * | 2009-05-27 | 2010-12-02 | Osram Opto Semiconductors Gmbh | Optoelectronic module and method for producing an optoelectronic module |
| US8573807B2 (en) * | 2009-06-26 | 2013-11-05 | Intel Corporation | Light devices having controllable light emitting elements |
| JP5091962B2 (en) * | 2010-03-03 | 2012-12-05 | 株式会社東芝 | Semiconductor device |
| KR101711961B1 (en) * | 2010-09-10 | 2017-03-03 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Light emitting device |
| US9070851B2 (en) | 2010-09-24 | 2015-06-30 | Seoul Semiconductor Co., Ltd. | Wafer-level light emitting diode package and method of fabricating the same |
| KR101766297B1 (en) | 2011-02-16 | 2017-08-08 | 삼성전자 주식회사 | Light emitting device package and method of fabricating the same |
| JP5962285B2 (en) * | 2012-07-19 | 2016-08-03 | 日亜化学工業株式会社 | Light emitting device and manufacturing method thereof |
| US20140167083A1 (en) * | 2012-12-19 | 2014-06-19 | Avago Technologies General Ip (Singapore) Pte. Ltd. | Led package with integrated reflective shield on zener diode |
| CN205944139U (en) | 2016-03-30 | 2017-02-08 | 首尔伟傲世有限公司 | Ultraviolet ray light -emitting diode spare and contain this emitting diode module |
| JP6414183B2 (en) * | 2016-11-16 | 2018-10-31 | 富士ゼロックス株式会社 | Light emitting element array and optical transmission device |
| EP3534404B1 (en) | 2017-09-26 | 2020-12-16 | LG Chem, Ltd. | Transparent light emitting device display |
| DE102018215951A1 (en) * | 2018-09-19 | 2020-03-19 | Osram Gmbh | LIGHT-EMITTING DEVICE AND METHOD FOR PRODUCING THE SAME |
| CN113990212A (en) * | 2020-07-27 | 2022-01-28 | 北京芯海视界三维科技有限公司 | Light-emitting module and display device |
Family Cites Families (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH03251467A (en) * | 1990-03-01 | 1991-11-08 | Nec Corp | Optical printing head |
| JPH0645654A (en) * | 1991-01-23 | 1994-02-18 | Eastman Kodak Japan Kk | Light emitting device |
| JPH0593058U (en) * | 1992-05-25 | 1993-12-17 | シャープ株式会社 | Light emitting diode with built-in driver |
| JPH06237016A (en) * | 1993-02-09 | 1994-08-23 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Optical fiber module and manufacture thereof |
| JPH11354829A (en) * | 1998-06-08 | 1999-12-24 | Yokogawa Electric Corp | Optical semiconductor element |
| JP3613328B2 (en) * | 2000-06-26 | 2005-01-26 | サンケン電気株式会社 | Semiconductor light emitting device |
| DE10216008A1 (en) * | 2001-04-12 | 2002-10-24 | Toyoda Gosei Kk | Led lamp |
| JP3771144B2 (en) * | 2001-06-27 | 2006-04-26 | 豊田合成株式会社 | LED lamp |
| JP2003030771A (en) * | 2001-07-18 | 2003-01-31 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Automatic inspection radio measuring device |
-
2005
- 2005-04-18 JP JP2006512534A patent/JPWO2005104248A1/en not_active Withdrawn
- 2005-04-18 CN CNA200580011789XA patent/CN1943049A/en active Pending
- 2005-04-18 WO PCT/JP2005/007412 patent/WO2005104248A1/en active Application Filing
- 2005-04-18 US US10/599,966 patent/US20070257901A1/en not_active Abandoned
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPWO2012086517A1 (en) * | 2010-12-20 | 2014-05-22 | ローム株式会社 | Light emitting element unit and light emitting element package |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US20070257901A1 (en) | 2007-11-08 |
| WO2005104248A1 (en) | 2005-11-03 |
| CN1943049A (en) | 2007-04-04 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JPWO2005104248A1 (en) | Semiconductor chip for driving light emitting element, light emitting device and lighting device | |
| JPWO2005104249A1 (en) | Semiconductor chip for driving light emitting element, light emitting device, and lighting device | |
| US9705059B2 (en) | Light emitting package having a guiding member guiding an optical member | |
| US8410514B2 (en) | Light emitting device | |
| US7655957B2 (en) | Submounts for semiconductor light emitting device packages and semiconductor light emitting device packages including the same | |
| US6646491B2 (en) | LED lamp package for packaging an LED driver with an LED | |
| US20080012125A1 (en) | Light Emitting Diode Package | |
| JP2007294953A (en) | High-efficiency light-emitting diode package | |
| JP2006019598A (en) | Light emitting diode | |
| US7402842B2 (en) | Light emitting diode package | |
| US9370063B2 (en) | LED driving device and lighting device | |
| US8492981B2 (en) | Lighting apparatus using PN junction light-emitting element | |
| US20050128767A1 (en) | Light source structure of light emitting diode | |
| JP2006339542A (en) | Chip led | |
| JP2013219263A (en) | Led module | |
| KR101237389B1 (en) | Led package and lighting device comprising the same | |
| US10964866B2 (en) | LED device, system, and method with adaptive patterns | |
| US20200313053A1 (en) | High power led assembly and method of forming a high power led assembly | |
| JP2006019594A (en) | Semiconductor wafer, method for manufacturing semiconductor device, and semiconductor device | |
| US8882312B2 (en) | Light emitting device with light emitting diodes fixed to printed circuit | |
| US11373985B2 (en) | Illumination device and illumination system | |
| KR20180012123A (en) | Illumination module and illumination apparatus including the same | |
| KR20060009684A (en) | Led package | |
| JP6568481B2 (en) | LED bulb |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A761 | Written withdrawal of application |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A761 Effective date: 20080702 |