- Automation
- Home
- /
- Learning Hub
- /
- Selenium Tutorial
- -
- December 19 2023
What is Selenium? A Complete Guide on Selenium Testing
Explore our comprehensive guide on Selenium testing. Learn what is Selenium, its architecture, benefits, and how to automate web browsers with this open-source suite.
OVERVIEW
Selenium is a comprehensive suite offering various tools and libraries to automate web browser interactions. It includes features that mimic how users interact with browsers, and a server to manage browser usage across different platforms. It supports the W3C WebDriver standard that helps testers write code to make it work across all the major web browsers.
With Selenium, developers and testers can automate website testing, including functional testing, regression testing, and end-to-end testing. It supports a wide range of programming languages, including Java, JavaScript, C#, PHP, Python, and Ruby.
In this guide on what is Selenium, we'll cover everything you need to know to get started with the Selenium framework.
What is Selenium?
Selenium is an open-source suite of tools and libraries that automates the testing of websites and web applications. Its versatility in testing across different environments is attributed to its cross-browser, cross-language, and cross-platform capabilities. Selenium seamlessly integrates with existing development workflows and supports programming languages such as Java, JavaScript, C#, PHP, Python, and Ruby.
Moreover, Selenium offers extensive browser compatibility with major web browsers like Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge, and Opera to ensure comprehensive browser coverage. Its flexibility is further enhanced by its compatibility with different automation testing frameworks like TestNG, JUnit, MSTest, pytest, WebdriverIO, and more.
Selenium suite comprises three primary components: Selenium WebDriver, Selenium Grid, and Selenium IDE.
Who Uses Selenium?
Selenium, a powerful open-source tool, has gained immense popularity in the field of automated testing due to its flexibility and versatility. But who exactly uses Selenium? Let's delve into the primary users of this automation testing framework.
Software Testers and QA Professionals
The most obvious users of Selenium are software testers and Quality Assurance (QA) professionals. They leverage Selenium's capabilities to automate web browsers and validate the functionality of web applications across different browsers and platforms. With Selenium, testers can execute repetitive test cases, perform regression testing, and ensure the reliability and performance of web applications.
Developers
Developers also use Selenium to implement and validate the functionality of web features during the development phase. By automating browser actions and interactions, developers can identify and fix issues early in the development cycle, leading to faster delivery of high-quality software.
DevOps Engineers
In the DevOps culture, continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) are crucial. DevOps engineers use Selenium to automate the testing process as part of the CI/CD pipeline. Selenium can be integrated with various DevOps tools to automate the deployment of web applications and ensure that new changes do not introduce regressions or break existing functionalities.
Automation Engineers
Automation engineers specialize in creating robust and maintainable test automation frameworks. They utilize Selenium to design and implement scalable automation solutions that can handle complex test scenarios and provide accurate test results. Selenium's extensive support for multiple programming languages and its compatibility with various browsers and operating systems make it a preferred choice for automation engineers.
Freelancers and Consultants
Freelancers and independent consultants who offer software testing and automation services also utilize Selenium. Its open-source nature and wide community support make it accessible and cost-effective, allowing freelancers to deliver high-quality testing solutions to clients without significant investments in proprietary tools.
Educational Institutions and Students
Last but not least, educational institutions and students use Selenium for teaching and learning purposes. Many universities and training institutes include Selenium in their curriculum to equip students with practical skills in automated testing. Additionally, aspiring QA professionals and developers often use Selenium to enhance their technical proficiency and gain hands-on experience in automation testing.
Why Use Selenium for Automation Testing?
Automation testing with Selenium involves using the Selenium suite of tools to automate web browsers for testing web applications. It enables developers and testers to write test scripts in various programming languages, run tests across multiple browsers and platforms, and ensure accuracy and efficiency in their testing processes.
Here are some of the major reasons for choosing Selenium for automation testing.
Open-Source
Selenium is a free and open-source suite of tools, making it a cost-effective solution for web automation testing.
Multilingual Support
It supports a wide range of programming languages, including Java, Python, PHP, C#, Ruby, and JavaScript. This flexibility allows testers to work with their preferred programming languages.
Cross-Platform Compatibility
Selenium can be used on multiple operating systems, including Windows, macOS, and Linux, enabling testers to run tests on different platforms while ensuring consistent results across environments.
Cross Browser Testing
Selenium supports automated testing on a variety of web browsers, including Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and more. This comprehensive coverage helps ensure that web applications function seamlessly across different browsers.
Framework Integration
It can be integrated with various testing frameworks offered by Selenium-supported languages, such as TestNG, JUnit, TestCafe, and others. This integration streamlines the automation testing process by leveraging different capabilities of a framework.
Parallel Testing
Parallel testing with Selenium involves executing multiple test suites or test cases simultaneously to reduce the overall testing time. You can perform parallel testing either locally or on a cloud-based grid, effectively reducing your software release cycles.
With its grid, you can run Selenium test scripts both on the local and cloud grid. Cloud testing facilitates the communication between the client (test script) and the remote browser instances, ensuring seamless execution of test commands on the desired browsers.
Mouse and Keyboard Simulation
With Selenium, you can simulate real user interactions by replicating mouse behaviors and keyboard events. This is particularly useful for testing complex user interactions and scenarios such as automated interaction with webpages having dynamically loaded content, Single Page Applications (SPAs), and drag-and-drop interactions.
Headless Browser Testing
Headless browser testing with Selenium lets you achieve faster test execution, optimize resource utilization, and enhance testing scalability. Headless browser testing is particularly well-suited for end-to-end testing, regression testing, performance testing, visual regression testing, and data extraction (web scraping).
Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD)
Whether tests are run locally or on a cloud grid, with Selenium, testers can easily trigger continuous tests in a CI pipeline by leveraging popular CI/CD tools like Jenkins, CircleCI, and Travis CI.
Comprehensive Reporting and Documentation
Selenium provides detailed test execution logs and reports, making it easier for teams to track test results and pinpoint areas that require attention. This robust documentation ensures transparency and accountability throughout the testing process, facilitating better communication and collaboration among team members.
Community Support
Selenium has a large and active community that provides extensive support and resources. This community-driven approach ensures that Selenium remains up-to-date and adapts to evolving web technologies. The popularity of Selenium among developers is evident from its impressive GitHub statistics of over 29.2k Stars and 7.9k Forks (as of April 2024).
As per another Survey, 81% of the respondents chose Selenium as the preferred framework for test automation.

Even though Selenium is a widely used framework for automation testing, there are other frameworks in the market as well, such as Playwright and Cypress. However, using these frameworks can vary based on specific web project needs. Check out the detailed comparison of Selenium vs Playwright vs Cypress that can help you select the framework based on your requirements.
Note : Automate your Selenium testing on 3000+ desktop browsers. Try LambdaTest Now!
What Types of Testing Can Selenium Automate?
Selenium can help you with browser automation with various types of testing. Below are some of them.
Functional Testing
In functional testing, Selenium is used to validate if the website functions according to the specified requirements. It automates the execution of tests that check specific functionalities, simulating user interactions like clicking, typing, and navigation. Since Selenium can interact with web elements and verify their responses, it is an ideal framework for testing the functional aspects of a website, including forms, dialogs, and other interactive features.
Regression Testing
Regression testing with Selenium involves re-running existing tests to ensure that new changes have not impacted the existing functionalities. This type of testing is crucial for continuous development environments where frequent changes are made to the website or web application. Selenium automates these tests, providing quick feedback on the impact of recent code updates and helps maintain the stability of the website over time.
Visual Testing
Visual testing using Selenium automates the testing of verifying that a website or web application looks and behaves as intended and there are no unintended visual appearance or functionality changes. In this process, a baseline version of a website or web application is compared with a current version to identify visual deviations.
Smoke Testing
Smoke testing with Selenium runs basic tests that validate the functions of websites. This is a quick testing phase that checks the health of the website after a new build or update goes live.
Cross Browser Testing
Selenium excels in cross browser testing by running tests across multiple browsers, ensuring the website's behavior and appearance are consistent. This type of testing is important for web applications that target a broad user base, as it verifies compatibility with different browsers and their versions.
Data-Driven Testing
In data-driven testing, Selenium is integrated with data handling tools to test websites under various data conditions. It processes multiple sets of input data, validating the website’s behavior in each scenario. This approach not only enhances test coverage but also ensures the robustness of the website across different data-driven use cases.
UI Testing
UI testing validates the visual elements of a web application. Automated UI testing with Selenium tests the UI components like buttons, text fields, and menus, ensuring they are not only present and visible but also functional and responsive. This testing verifies the usability and aesthetic aspects of the website.
Monkey Testing
It involves breaking the system by giving a random input to the system. The input could be anything from an end-user’s perspective. It could be a click, scroll, or a dummy text string. Using Selenium, you can generate test scripts to automate monkey testing.
History of Selenium
The history of Selenium began in 2004 at Thoughtworks in Chicago. Jason Huggins at Thoughtworks developed the core mode known as JavaScriptTestRunner, a simple tool for internal testing. However, its potential quickly resonated with others, particularly Paul Hammant.

Meanwhile, others outside Thoughtworks were also nurturing Selenium. Dan Fabulich and Nelson Sproul from Bea increased its flexibility with Selenium Remote Control, while Pat Lightbody's Hosted QA project ensured it could handle large-scale testing effectively.
In 2007, Google came into the picture, with Jason Huggins joining their internal team and bringing their internal testing tools. Simon Stewart at Thoughtworks also contributed to his WebDriver project, which eventually merged with Selenium.
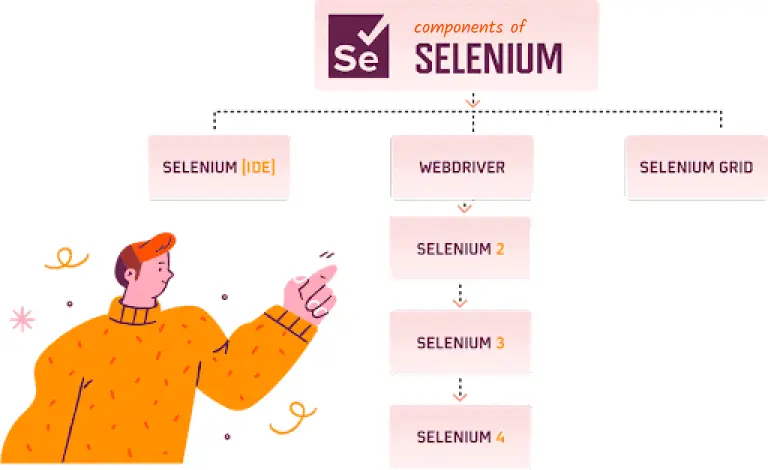
Components of Selenium
Selenium is a suite of tools widely used for automating web browsers. It provides a range of components, each designed to cater to different aspects of web application testing. Here are the primary components of Selenium, along with their technical functionalities.
- Selenium WebDriver
- Selenium Grid
- Selenium IDE
Selenium WebDriver
Selenium WebDriver is a component of the Selenium suite for automating web application testing. It provides an interface for developers and testers to create and run test scripts, which simulate user interactions with web browsers. This includes actions like clicking on links, filling out forms, and fetching web page data. All of these actions can be done either on local machines or remotely.
But when running Selenium tests on a remote (cloud) grid, there comes Selenium RemoteWebDriver that allows for running browser automation tests on a machine hosted on the cloud. Basically, it's a version of the WebDriver but runs on a remote server. Specific browser drivers, such as FirefoxDriver, ChromeDriver, and InternetExplorerDriver, are all built on top of the RemoteWebDriver class. This means they share its capabilities but are tailored to their respective browsers.
With Selenium’s version 4.6.0, Selenium Manager was launched, which handles the browser drivers under the hood, so you don’t have to worry about the browser drivers. It streamlines the setup process for Selenium users. This means that you no longer need to manually download, set up, or update browser drivers for different browsers like Chrome, Firefox, or Edge. Instead, Selenium Manager takes care of these aspects, ensuring that the appropriate browser drivers are always in use and up to date.
It supports all major browsers like Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge, and Internet Explorer. Selenium WebDriver is the language bindings and implementations of specific browser-controlling codes. In June 2018, WebDriver received a significant endorsement as it became a W3C WebDriver Protocol.
Architecture of Selenium WebDriver
Initially, Selenium was developed with two different components: WebDriver and RC. These were merged into a single, powerful unit called Selenium 2, also known as Selenium WebDriver 2. It also marked the beginning of a continuous evolution, with Selenium steadily adding features and functionalities. This led to the upgrade to Selenium 3, which relied on the JSON Wire Protocol for communication between test scripts and web browsers.
However, Selenium 4 brought a major shift. It replaced JSON Wire with the W3C protocol, eliminating the need for encoding and decoding test case requests. You can watch the below video to learn more about what’s new in Selenium 4.
Selenium WebDriver 4 Architecture
In Selenium 3, communication relied on the JSON Wire Protocol over HTTP, where language bindings (like C#, Java, Ruby, and Python) communicated directly with the browser driver. The protocol acted as a bridge, as the server only understood these protocols, not the programming languages. This led to slower test execution, more errors, and unstable tests.
Selenium WebDriver 3 use of the JSON Wire Protocol required encoding instructions into JSON and decoding responses, leading to inefficiencies, slower tests, and more errors. The shift to the W3C WebDriver protocol in modern browsers streamlined this process by standardizing commands and optimizing data handling, resulting in faster, more reliable automated testing.
However, Selenium WebDriver 4 introduced the W3C-compliant protocol, replacing the older JSON Wire Protocol. This shift means commands and API requests no longer require encoding and decoding.
In Selenium 4, the architecture of Selenium WebDriver is built around these four key components:
- Selenium Client Libraries
- WebDriver W3C Protocol
- Browser Drivers
- Real Web Browsers

Selenium Client Libraries
These are libraries or bindings that allow automation scripts to interact with Selenium WebDriver in various programming languages like Ruby, Java, C#, Python, and JavaScript. Each Selenium Client Library is a collection of methods and classes required to create automation scripts.
They are easy to install with language-specific package installers and can be downloaded from the UI test plan. To interact with the Selenium Server (Remote WebDriver) or to develop local Selenium WebDriver scripts, it's necessary to use client drivers specific to the programming language being used.
WebDriver W3C Protocol
This protocol allows for direct communication between the server and the client, eliminating the need for the JSON Wire Protocol. Since both Selenium WebDriver and modern web browsers utilize the same protocol, it ensures more consistent test execution across different browsers in automated Selenium testing.
Since Selenium WebDriver and web browsers now use the same protocol, there are less flaky Selenium tests. This means developers and testers don't have to modify their scripts for other browsers, leading to more consistent and stable testing in Selenium 4.
Before Selenium 4, the JSON Wire Protocol facilitated communication between the local machine and the web browser. The Selenium Client Libraries, using the JSON protocol, and the web browser, operating on the W3C protocol, was involved in the active encoding and decoding of APIs throughout the process.
Browser Drivers
In Selenium, browser drivers act as intermediaries between your Selenium tests (written in languages like Java, Python, etc.) and the web browser. Each major web browser has a specific driver, which allows Selenium to control the browser by translating commands from your test script into actions that the browser can understand and execute.
Real Web Browsers
These are the standard web browsers like Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Microsoft Edge, and Apple Safari, where the automated tests are performed. The Selenium WebDriver interacts with these browsers, executing commands and automated actions as directed by the test scripts.
Selenium WebDriver 3 Architecture
In Selenium 3, the primary mode of communication between a user's test script and the browser is through the JSON Wire Protocol. This protocol functions as a RESTful web service that transmits data in JSON format over HTTP. The architecture of Selenium WebDriver in this version is built around four key components.
- Selenium Client Libraries
- WebDriver W3C Protocol
- Browser Drivers
- Real Web Browsers
Here, the components in Selenium WebDriver 3 are similar to those in Selenium 4, with a notable change: the old JSON Wire Protocol is in place of the new WebDriver W3C Protocol.

Advantages of Selenium WebDriver
The following are the benefits of Selenium WebDriver:
Native Browser Interaction
WebDriver interacts with browsers using browser drivers as a real user would, whether on local or remote machines, providing realistic testing scenarios.
Cross Browser Compatibility
A browser engine renders your website differently from other browser engines. If your code isn't compatible with a specific browser rendering engine, you might encounter various rendering issues. Selenium WebDriver supports all major browsers like Firefox, Safari, Edge, Chrome, and Internet Explorer, enabling tests to be uniform across different browser environments.
W3C Standardization
As WebDriver is W3C compliant, it ensures more uniform behavior across different browsers, contributing to the stability of your automation scripts.
Support for Multiple Programming Languages
Selenium WebDriver allows using various programming languages for test script development, including Java, Python, C#, Ruby, and JavaScript, catering to diverse developer preferences. Language bindings for Selenium WebDriver can be downloaded from the Selenium Download page.
Integrations
Selenium WebDriver integrates with various Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) tools. This allows you to automate your testing process and ensure that your code is always of high quality.
Shortcomings of Selenium
Though Selenium has numerous advantages, it has a few downsides.
- Doesn't Automate Web Services: Selenium isn't suitable for automating web services like SOAP or REST.
- No Built-in Object Repository: Unlike some tools, Selenium doesn’t have a built-in feature for centralized object management.
- Lacks Built-in Reporting: Selenium has no default reporting capability. Therefore, integration with other tools is needed for using the reporting feature.
- No IDE for Script Creation/Execution: Selenium requires external IDEs like Eclipse or IntelliJ for creating and executing scripts.
- Customer-Supported Capabilities: Due to its open-source nature, Selenium lacks dedicated customer support services. Testers using Selenium typically rely on various forums and online videos to find answers to their queries.
Selenium Grid
Selenium Grid is a part of the Selenium suite for the running of multiple test scripts across different browsers, operating systems, and machines simultaneously. It uses a hub-and-node architecture, where the hub acts as a central point to control the network of test machines (nodes).
This setup enables distributed testing, significantly reducing the time for cross-browser and cross-platform testing. Grid facilitates parallel execution of tests, enhancing testing efficiency and coverage. It is particularly useful for large-scale test environments and continuous integration pipelines.
The stable release of Selenium 4, released in October 2021, brings major updates from its predecessor, Selenium 3. A key feature in Selenium 4 is the adoption of the W3C WebDriver Protocol, which replaces the JSON Wire Protocol used in Selenium 3. In this new version, the tester does not need to initiate Hub and Node separately to perform automation testing. Instead, Selenium 4 integrates the Hub and Node into a single jar file.
The architecture of Selenium Grid 4 supports four main processes: Session Map, Node, Router, and Distributor. Additionally, the Selenium 4 WebDriver hierarchy offers several enhanced features, including an improved graphical user interface and built-in Docker support, further augmenting its capabilities for automation testing.
Architecture of Selenium Grid 4
Selenium Grid 4, unlike its Selenium Grid 3, eliminates the traditional Hub structure and adopts a more complex architecture that enhances scalability.

Its components include:
- Router: It is the initial point of contact for client requests. The Router directs new session requests to the Session Queue and routes requests for existing sessions to the Session Map, which then assigns a node ID and directs the session to the appropriate node. Its primary role is to balance the load on the grid.
- Distributor: This component is responsible for registering and tracking the capabilities of all Nodes within the grid model. It queries the Session Queue to allocate new session requests to the most suitable node. Upon creation of a session at a node, the distributor updates the Session Map with the Session ID and Node ID.
- Session Map: This functions as a storage system, maintaining the association between session IDs and their corresponding Nodes. It helps the Router direct session requests to the correct Node based on the Session ID.
- Session Queue: Working on a FIFO (First In, First Out) basis, this component holds details about incoming new session requests. Both the Distributor and Router utilize this queue to allocate Nodes for these requests.
- Event Bus: The Event Bus facilitates interactions among Nodes, the Distributor, the Session Queue, and the Session Map.
- Nodes: These are the execution points where request commands are carried out on various browser drivers.
Architecture of Selenium Grid 3
The Selenium Grid 3 architecture is primarily built around two key components:

- Hub: This component acts as a central server that receives access requests from the WebDriver client. It directs the JSON test commands to the remote drivers located on various nodes. The Hub processes instructions from the client and simultaneously executes them across multiple nodes.
- Node: A Node is a remote machine with its own operating system and a remote WebDriver. It functions by accepting requests sent from the Hub, which are in the form of JSON test commands. These commands are then executed by the Node using its WebDriver.
Selenium IDE
Selenium IDE is an extension for Chrome, Firefox, and Edge that streamlines the task of recording and executing tests directly within the browser. With its intuitive interface and pre-built functionality, it enables testers to create reliable tests without any additional setup requirements quickly.
Moreover, it offers advanced debugging capabilities such as breakpoints and exception pausing, making the troubleshooting process more efficient. Another advantage of using Selenium IDE is its support for automated cross browser testing. This means you can run your tests on different browsers and operating systems using the Command-line Runner.
Architecture of Selenium IDE
Selenium IDE architecture consists of 3 components:

- Selenium Core: This is the core engine driving the IDE, responsible for executing test scripts. It manages the interaction with browsers and provides feedback on the test results.
- Browser Extension: Originally developed as an extension for Firefox, Selenium IDE later expanded its support to other browsers, such as Chrome, facilitating seamless integration with these browsers. However, it does not support Safari Browser.
- Selenium IDE User Interface: The IDE has a user-friendly interface, which simplifies the process of creating, modifying, and executing tests for users.
Working Principle of Selenium IDE
The functioning of Selenium IDE is centered around three primary actions, described as follows:
- Record: Using a browser extension, Selenium IDE allows users to capture their interactions within a web application. This feature logs user activities like clicking buttons, entering text, and navigating through pages.
- Playback: After creating the test script, the recorded script can be replayed to automate testing. During this phase, Selenium IDE runs the script, engaging with the browser to replicate the recorded user actions.
- Save: The test script that has been recorded can be stored for later usage. These test case scripts are saved with the .side file extension, ensuring they can be reused for future test runs.
What is the Difference Between Selenium 3 and Selenium 4?
Testers and developers must stay updated with Selenium's versions for automation testing. Selenium 3, released in 2016, focused on stability and bug fixes, removing Selenium RC Code and maintaining compatibility with older versions. Selenium 4, introduced in 2021, is the latest major release, featuring significant enhancements to the framework, addressing limitations of previous versions and improving the user experience for testing.
Upgrading from Selenium 3 to Selenium 4 offers several enhancements:
- Enhanced Performance: Faster test execution with improved browser interactions due to the new WebDriver W3C Protocol.
- Native File Upload Support: Simplifies file upload processes in tests, eliminating the need for workarounds.
- Relative Locators: Adds flexibility in identifying web elements based on their spatial relationships.
- Unified Selenium DevTools API: Direct access to Chrome DevTools from automated tests.
- Improved Selenium IDE: Supports multiple languages, with a more user-friendly interface and a scalable Selenium Grid 4 architecture.
- Window Mechanisms: Enhanced control over browser windows and tabs.
- Time Duration: Improved handling of time-related functions like timeouts and waits.
- Capabilities: Expanded and refined options for browser configurations and settings in automated tests.
To know more about the differences between Selenium 4 and Selenium 3, we recommend checking this article on Selenium 4 vs Selenium 3.
Popular Frameworks for Selenium Testing
Selecting a test automation framework is an important decision in the automation testing process. The right framework should match the team's expertise and be evaluated based on ease of use, scalability, and ability to manage complex test cases.
| Selenium Supported Language | Framework/Library |
|---|---|
| Selenium Java | Selenide, Gauge, TestNG, Geb, JUnit, Cucumber, Serenity BDD |
| Selenium Python | unittest, pytest, Behave, Robot, Lettuce |
| Selenium JavaScript | WebdriverIO, Nightwatch.js, Mocha, Jest, AngularJS, Cucumber, Jasmine, Karma, TestCafe, Nemo.js, Protractor |
| Selenium C# | SpecFlow, MSTest, NUnit |
| Selenium Ruby | RSpec, Cucumber, test-unit, Capybara |
| Selenium PHP | Laravel, Codeception, PHPUnit, Behat |
Here are some of the popular test automation frameworks for the widely used Selenium-supported programming languages:
Getting Started with Selenium Testing
Selenium enables automated test execution across various programming languages. Depending on the language chosen for the test script, such as Java or JavaScript, there are some prerequisites, setup, and execution processes you need to follow.
If you are using a local or cloud grid, you don't need to download browser drivers manually. Selenium WebDriverManager, a library automates the management of the binary drivers (like ChromeDriver for Google Chrome, GeckoDriver for Mozilla Firefox, etc.) required by Selenium WebDriver to interact with the browsers.
Prerequisites
Here are some high-level prerequisites you can follow when implementing test automation with Selenium.
- Select a Programming Language: Choose a programming language such as Java, Python, JavaScript, or C# for writing Selenium test scripts.
- Install Development Environment: Set up the development environment and install the necessary tools for the chosen programming language.
- Download and Install an IDE: Select and install an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) for managing Selenium test scripts. Popular choices are Eclipse, IntelliJ, and Visual Studio.
- Download and Install Selenium Language Bindings: Install and configure Selenium WebDriver language bindings for the selected programming language.
- Download and Configure Browser Drivers: Install the necessary browser drivers supported by Selenium.
- Chrome: ChromeDriver
- Firefox: GeckoDriver
- Microsoft Edge: Edge WebDriver
- Internet Explorer: Internet Explorer Driver
- Opera: Opera WebDriver
- Browser Versions: If you are using the local grid, ensure you have installed versions of Chrome, Firefox, and Edge that are compatible with their respective browser drivers.
- Configure Dependencies and Libraries: Install required libraries or packages, such as JUnit, TestNG, NUnit, or other utility libraries.
- Build and Dependency Management Tools: Using tools like Maven, Gradle, or npm is recommended for managing project dependencies and build configurations. These tools automate the process of downloading libraries and setting up your project.
In Selenium testing, you can choose between two approaches. The first is using a local Selenium WebDriver, which relies on a local Selenium Grid or infrastructure for cross browser testing. The alternative and more scalable and reliable option involves using a cloud grid for Selenium automation testing. This method allows for browser compatibility testing across a diverse range of web browsers and operating systems, offering more extensive testing capabilities.
Selenium Testing on Local Grid
Using Selenium for automation testing with a local infrastructure is a good starting point for browser compatibility checks. The adequacy of automated browser testing with a local Selenium Grid depends on the project's scale and complexity, and it might not always provide comprehensive test coverage.
Here, we will use the Java programming language and TestNG framework to run the test on the local grid. The tests will be run on the Chrome browser.
- Use Chrome WebDriver to navigate to the LambdaTest Sample ToDo App.
- Check off the first two items from the ToDo list displayed on the app.
- Enter the text - Yey, Let’s add it to list into the text box.
- Click the Add button to ensure the new item is successfully appended to the list.
package RelativeLocators;
import io.github.bonigarcia.wdm.WebDriverManager;
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebElement;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.firefox.FirefoxDriver;
import org.testng.annotations.AfterClass;
import org.testng.annotations.BeforeClass;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
import static org.openqa.selenium.support.locators.RelativeLocator.withTagName;
import static org.testng.Assert.assertEquals;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class TestNGToDo_local {
private WebDriver driver;
boolean status = false;
@BeforeClass
public void setUp(){
//System.setProperty("webdriver.chrome.driver","C:\Setup-Folder\chromedriver.exe");
driver = new FirefoxDriver();
driver.get("https://lambdatest.github.io/sample-todo-app/");
driver.manage().window().maximize();
driver.manage().timeouts().implicitlyWait(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
@AfterClass
public void tearDown() throws Exception {
if (driver != null) {
driver.quit();
}
}
@Test
public void test_login_using_relative_locators_1(){
//Change it to production page
driver.get("https://lambdatest.github.io/sample-todo-app/");
//Let's mark done first two items in the list.
driver.findElement(By.name("li1")).click();
driver.findElement(By.name("li2")).click();
// Let's add an item in the list.
driver.findElement(By.id("sampletodotext")).sendKeys("Yey, Let's add it to list");
driver.findElement(By.id("addbutton")).click();
// Let's check that the item we added is added in the list.
String enteredText = driver.findElement(By.xpath("/html/body/div/div/div/ul/li[6]/span")).getText();
if (enteredText.equals("Yey, Let's add it to list")) {
status = true;
}
driver.manage().timeouts().implicitlyWait(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
}
In the above test script, the setup() method is placed within the @BeforeClass annotation, while the teardown() method is encapsulated in the @AfterClass annotation. The primary test logic is executed within the scope of the @Test annotation.
Shown below is the output from Eclipse IDE, which confirms the successful execution of the test on the local grid.
Selenium Testing on Cloud Grid
Selenium testing on the local grid is adequate if you need limited test coverage. However, it falls short of extensive browser coverage. In such scenarios, performing Selenium automation testing on a cloud Selenium Grid is beneficial, as it improves test and browser coverage by allowing testing against various browser and OS combinations.
AI-powered test orchestration and execution platform like LambdaTest is more scalable and cost-effective than setting up an in-house Selenium Grid, as it offers an online browser farm of over 3000 combinations of browsers and operating systems for automation testing. To migrate from local to LambdaTest's cloud Selenium Grid, you'll need to update the infrastructure-related code in your test scripts.
To get started with Selenium testing on a cloud grid like LambdaTest, you need to set up an account.
After logging into your LambdaTest account, head to your LambdaTest Profile to get your authentication credentials (LambdaTest Username and Access Key) and set them as your environment variables.
To showcase Selenium automation testing on the LambdaTest grid, we will replicate the same test case previously executed using the local Selenium WebDriver.
We will use Java programming language and TestNG framework to run tests on the Chrome browser. However, LambdaTest also offers testing different Selenium-supported programming languages and automation frameworks to help you get started. Check out the documentation - Selenium testing on LambdaTest.
You can use LambdaTest Automation Capabilities Generator to generate browser and operating system capabilities on which automation testing has to be performed.
To demonstrate Selenium testing using Java and TestNG framework, we use the remote Selenium WebDriver to access the online Selenium Grid on LambdaTest. Tests implemented under the @Test annotation will take the parameters returned by the dataProvider method. A getData() method is defined with the data provider annotation, where the combination of browsers, browser versions, and operating systems is mentioned.
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.JavascriptExecutor;
import org.openqa.selenium.Keys;
import org.openqa.selenium.Platform;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebElement;
import org.openqa.selenium.remote.DesiredCapabilities;
import org.openqa.selenium.remote.RemoteWebDriver;
import org.testng.annotations.AfterTest;
import org.testng.Assert;
import org.testng.annotations.DataProvider;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
import org.testng.annotations.AfterClass;
import org.testng.annotations.AfterMethod;
import org.testng.annotations.BeforeMethod;
import org.testng.annotations.Parameters;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class TestNGToDo {
public static final String username= "user-name";
public static final String auth_key = "access-key";
public RemoteWebDriver driver;
public static final String URL= "@hub.lambdatest.com/wd/hub";
boolean status = false;
@Test(dataProvider= "Set_Environment")
public void login(/* Platform platform_used */ String platform_used, String browser_Name, String browser_Version)
{
ChromeOptions browserOptions = new ChromeOptions();
browserOptions.setPlatformName("Windows 11");
browserOptions.setBrowserVersion("121.0");
HashMap<String, Object> ltOptions = new HashMap<String, Object>();
ltOptions.put("username", "LT_USERNAME");
ltOptions.put("accessKey", "LT_ACCESS_KEY");
ltOptions.put("project", "Untitled");
ltOptions.put("selenium_version", "4.0.0");
ltOptions.put("w3c", true);
browserOptions.setCapability("LT:Options", ltOptions);
try
{
driver = new RemoteWebDriver(new URL("https://" + username + ":" + auth_key + URL), capability);
/* driver.set(new RemoteWebDriver(new URL("https://" + username + ":" + auth_key + URL), capability)); */
}
catch (Exception e)
{
System.out.println("Invalid grid URL" + e.getMessage());
}
try
{
driver.manage().timeouts().implicitlyWait(10,TimeUnit.SECONDS);
driver.get("https://lambdatest.github.io/sample-todo-app/");
driver.findElement(By.name("li1")).click();
driver.findElement(By.name("li2")).click();
WebElement element = driver.findElement(By.id("sampletodotext"));
element.sendKeys("Yey, Let's add it to list
");
Assert.assertEquals(driver.getTitle(), "Sample page - lambdatest.com");
status = true;
}
catch (Exception e)
{
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
@DataProvider(name="Set_Environment", parallel=true)
public static Object[][] getData()
{
Object[][] Browser_Property = new Object[][]
{
{"Windows 11", "Chrome", "121.0"},
};
return Browser_Property;
}
@AfterTest
public void tearDown()
{
if (driver != null) {
((JavascriptExecutor) driver).executeScript("lambda-status=" + status);
driver.quit();
}
}
}
Parallel execution is enabled by setting the attribute parallel=true in the @DataProvider, which is responsible for defining the getData() method.
Now, visit your LambdaTest Web Automation Dashboard to view your test results.
Parallel Testing in Selenium
Parallel testing with Selenium lets you execute numerous tests across different browsers, devices, and environments—this method greatly reduces the overall testing time, accelerating your software release cycles by multiple folds.
For instance, consider a scenario where you're testing a signup form across 60 different browser and OS combinations, with each test taking 2 minutes. Sequentially, this would total 120 minutes or 2 hours. This time frame becomes even more significant when testing additional components like pricing pages or contact forms.

However, by running three parallel tests at once in this scenario, the total execution time drops from 120 minutes to just 40 minutes.
Similarly, with four parallel tests, it would reduce further to 30 minutes, demonstrating how parallel testing can vastly expedite the testing process.

Automated testing on a local Selenium Grid can be challenging due to managing and setting up multiple machines. Parallel testing locally may face scalability issues, especially in covering a wide range of browsers, their various versions, and different operating systems.
Therefore, using a cloud-based Selenium Grid, like LambdaTest, eliminates the hassle of setting up an in-house grid for parallel testing. LambdaTest online Selenium Grid allows you to run parallel tests on over 3000 real browsers and their numerous versions, significantly reducing the costs and time associated with establishing a local testing infrastructure. This approach frees up resources so that you can focus on more critical tasks.
Test Reporting in Selenium
In Selenium testing, using a reporting tool can significantly enhance the effectiveness of your test process. These tools create detailed test reports, providing comprehensive insights into the testing process and the status of various test scenarios.
In scenarios where quick access to test reports is necessary, whether for presentation purposes or other reasons, the reporting tools for Selenium can be used to generate concise and clear reports. These reports are designed to be easily understood, enabling team members to quickly comprehend the testing results.
Since Selenium offers client APIs for various languages like Java, C#, Python, and more, it's crucial to pick a reporting tool for Selenium that not only aligns with your preferred programming language but also meets your specific requirements.
The test reports generated by Selenium should contain all the necessary information for team members to track the progress effectively. We recommend you check this article on the best reporting tools for Selenium to help you choose a tool based on factors like ease of setup, support report formats (HTML, XML), and the crispiness of content.
Best Practices for Using Selenium
While there aren't strict guidelines for creating scalable automation tests, certain key principles should be adhered to when developing tests with the Selenium framework. These principles are often referred to as Selenium best practices.
Create Cross Browser Compatibility Matrix
Cross browser testing can be tricky because you have to decide which browser and operating system combinations to test. When you consider different versions of browsers, the number of possibilities can become quite large. So, it's important to create a formal list of combinations involving the browser, operating system, and device. This list helps you prioritize which combinations to focus on for cross browser testing. This organized list is sometimes called the browser matrix or browser compatibility matrix.
This browser matrix comes from analyzing product data, geolocation, and detailed insights about how your audience uses different browsers. It also involves looking at statistics, such as the number of users on each browser, and analyzing your competitors. By using the browser matrix, you can make sure you cover all the browsers that matter for your product, which, in turn, can save you time and effort in development and testing.
Avoid Blocking Sleep Calls
In Selenium testing, it's recommended to avoid using blocking sleep calls like Thread.sleep or time.sleep. These calls stop the test thread, potentially delaying the test execution and not always guaranteeing effective timing due to external factors like network speed and server load. Instead, Selenium Implicit and Explicit waits are more efficient.
Implicit wait sets a default wait time for all elements through the test execution cycles. Explicit wait, using WebDriverWait and ExpectedConditions, pauses the script execution based on specific conditions, offering more flexibility and efficiency in handling delays. Execution continues once the specified condition is satisfied or a time out or exception occurs.
Cloud-based testing platforms like LambdaTest offer SmartWait feature to help you overcome synchronization issues in Selenium, enhancing the efficiency and accuracy of automated test execution by conducting actionability checks before interacting with webpage elements.
It leverages an intelligent algorithm that delays actions until the element is ready for interaction. If the element does not meet the required conditions within a set timeframe, SmartWait provides a relevant Selenium error message, ensuring smoother and more reliable test runs.
Maximize the Web Browser Window
Capturing screenshots in Selenium is a common step in test automation for debugging and monitoring product development. However, Selenium doesn't open browsers in maximized mode by default, which can impact the screenshots attached to test reports.
Ensuring the browser window is maximized after loading the test URL is crucial for obtaining full-page screenshots. This practice is recommended for Selenium testing across different browsers.
Use Design Patterns in Selenium
When writing Selenium test automation scripts, it’s crucial to ensure they are maintainable and scalable. Ideally, UI changes on the web page should require minimal adjustments to the test scripts. However, if scripts aren’t well-maintained, and multiple scripts reference the same web element, any element change necessitates updates in several script locations.
The Page Object Model (POM) addresses this by creating a centralized repository for web page controls, with each page represented as a separate class. This structure simplifies maintenance, as scripts interact with web elements through a middle layer of page classes or objects, enhancing maintainability and reducing code duplication across multiple Selenium scripts.
Choose the Right Web Locator
One of the challenges in Selenium test automation is the need to modify automation tests when there are changes in the locators used in the test code. Various web locators, such as ID, Name, LinkText, XPath, CSS Selector, and DOM Locator, are commonly used in Selenium WebDriver.
To minimize the impact of UI changes on tests, it's crucial to choose the right locator in Selenium. LinkText is preferred in dynamic situations, while ID, Class, and Name locators are easier to use and less prone to breaking.
XPath in Selenium is sometimes the only option. Still, it can vary between browsers, and using it in Internet Explorer may require a JavaScript XPath Query Engine, which can be slower. XPath is also more fragile, as page element reordering or new elements can disrupt existing XPath implementations.
For internationalized applications, LinkText or partialLinkText may not be suitable if anchor tags lack IDs or classes. In such cases, using partial href is recommended to maintain consistency even when the site's language changes.
The ideal order for web selectors is ID > Name > CSS Selector > XPath.
Besides the above-discussed best practices, there are a few more best practices that you can follow for Selenium testing. To know more, refer to this article - 16 Selenium Best Practices for Effective Test Automation.
Parallel Test Execution With SIDE Runner
Unlike the older version of Selenium IDE, which was limited to executing test cases or test suites sequentially, the latest Selenium IDE offers the capability for parallel testing. This feature is crucial in automated browser testing as it significantly speeds up the testing process.
With the updated Selenium IDE, you can configure test suites to run tests in parallel by adjusting the appropriate settings within the IDE. Moreover, the SIDE runner enhances this functionality, allowing for easy execution of tests in parallel. You can specify the number of parallel processes you want to run simply by using the -w option, which controls the parallel running processes. This enhancement streamlines the testing workflow, leading to more efficient and faster test execution.
Future of Selenium Testing
As technology landscapes continue to evolve, the future of Selenium testing appears promising with several anticipated trends and advancements. Here's a closer look at what the future might hold for Selenium testing:
- Integration of AI and Machine Learning
- Shift Towards Headless and Mobile Testing
- Enhanced Browser and OS Support
- Better Integration with DevOps and CI/CD
- Advancements in Parallel and Distributed Testing
- Improved Reporting and Visualization
- Incorporation of User Experience (UX) Testing
- Increased Focus on Security Testing
The integration of AI and machine learning is set to revolutionize Selenium testing. These technologies can significantly enhance test generation, data analysis, and test optimization processes. AI-powered algorithms can identify patterns in test failures, recommend improvements, and even automatically adjust test scripts based on application changes. This advancement promises to make Selenium testing more efficient and adaptive to changing application requirements.
With the rising significance of headless browsers and mobile applications, Selenium testing is expected to shift its focus towards automating tests for these environments. Headless browser testing offers faster execution times and enables the testing of scenarios that are difficult to replicate in graphical environments. As mobile and headless browsing become more prevalent, Selenium's capabilities in these areas will become increasingly important.
Selenium WebDriver is poised to continue expanding its support for new browser versions, as well as emerging browsers and operating systems. Maintaining compatibility with evolving browser technologies is crucial to address the changing landscape of web development practices. Selenium's commitment to supporting a wide range of browsers and operating systems ensures its relevance and applicability in modern web development projects.
Selenium testing will remain a cornerstone of DevOps and CI/CD pipelines, with more streamlined integration and faster test execution. Automation frameworks will likely offer easier ways to integrate Selenium tests with popular CI/CD tools and environments, facilitating smoother and more efficient development workflows.
Selenium Grid and other parallel testing solutions are expected to become more sophisticated, efficient, and user-friendly. Cloud-based solutions may also emerge as scalable and cost-effective options for running tests across various configurations, further enhancing Selenium's capabilities in parallel and distributed testing scenarios.
The future of Selenium testing will likely see enhancements in test reporting and visualization tools, providing more actionable insights into test results. These improvements will make it easier for teams to identify trends, failures, and areas for improvement, thereby optimizing the testing process and enhancing application quality.
Selenium testing may evolve to include more UX-related testing, ensuring that applications not only function correctly but also deliver a seamless and intuitive user experience. By incorporating UX testing into Selenium's capabilities, organizations can ensure that their applications meet user expectations and provide a positive user experience across all devices and platforms.
Security testing is expected to become a more integral part of Selenium testing, with specialized tools and libraries to automate security-related tests. As cybersecurity threats continue to evolve, incorporating robust security testing into Selenium's capabilities will be essential to safeguard applications and protect sensitive data.
Learning Resources for Selenium
Here, you can learn how to use Selenium for automation testing, its history, and components, like Selenium WebDriver, Selenium Grid, and Selenium IDE. You can refer to the resources mentioned below to boost your further learning.
Articles
Selenium Java
- What Is Selenium Java: Tutorial With Best Practices
- Selenium WebDriver Java Tutorial – Guide for Beginners
- Complete Guide on Automation Testing using Java
- Browser Automation With Selenium and Java
- Local Website Testing Using Selenium And Java
- Using Selenium WebDriver For Full Page Screenshots
- Selenium Java Tutorial – How To Test Login Process?
- How to Automate Registration Page Using Selenium And Java
- How to Handle Auto Suggestions in Selenium Java
- How To Perform Web Scraping with Selenium Java
- How To Handle Login Pop-up In Selenium WebDriver Using Java?
- How to Use @FindBy Annotation in Selenium Java
- How to Fix NoSuchElementException in Selenium
- Page Object Model Design Pattern in Selenium Java
Selenium TestNG
- TestNG Framework Tutorial: A Comprehensive Guide
- Create TestNG Project In Eclipse & Run Selenium Test Script
- Complete Guide For Your First TestNG Automation Script
- How To Automate Using TestNG In Selenium?
- TestNG Annotations Tutorial With Examples
- How To Use Assertions In TestNG With Selenium
- Automation Testing With Selenium, Cucumber & TestNG
- How To Perform Parallel Test Execution In TestNG
- How To Use TestNG Reporter Log In Selenium
- 90+ TestNG Interview Questions for 2023
Selenium JUnit
- JUnit Tutorial: A Comprehensive Guide to JUnit Testing
- JUnit Automation Testing With Selenium
- Tutorial On JUnit Annotations In Selenium With Examples
- JUnit Asserts With Examples
- How to run JUnit Selenium Tests using TestNG
- How To Run JUnit Tests In Jupiter? [JUnit Jupiter Tutorial]
- How to execute JUnit 4 tests with JUnit 5 [Tutorial]
- How to Use JUnit ErrorCollector [With Examples]
- Parallel Testing With JUnit 5 And Selenium [Tutorial]
- JUnit Parameterized Test Using Selenium: With Examples
- JUnit 5 vs. TestNG: Choosing The Right Framework
Selenium Selenide
Selenium Gauge
Selenium Python
- Why Python Is A Preferred Language For Test Automation?
- 7 Best Python Testing Frameworks
- Selenium 4 With Python: All You Need To Know
- How to Set Up Selenium With Python for Modern Web Automation
- Using Selenium and Python Hypothesis for Automation Testing
- Selenium Python Tutorial: Getting Started With BDD In Behave
- Getting Started With Selenium Python [Tutorial]
- Automated Browser Testing with Opera and Selenium in Python
- How To Take A Screenshot Using Python & Selenium?
- How To Drag And Drop In Selenium With Python?
- How To Switch Tabs In A Browser Using Selenium Python?
- How To Get Page Source In Selenium Using Python?
- How To Handle Dropdowns In Selenium WebDriver Using Python?
- Page Object Model (POM) In Selenium Python
- How To Read Configuration Files in Python Using Selenium
- How To Create an Automated Web Bot With Selenium in Python?
- How To Perform Web Scraping Using Selenium and Python?
- Adding Firefox Extensions With Selenium in Python
- How to Handle JavaScript Alert in Selenium WebDriver Using Python?
- Use Selenium Wait for Page to Load With Python
- Selenium Python Cheat Sheet for Test Automation
Selenium pytest
- Selenium Python Tutorial: Getting Started With pytest
- Running Python Selenium Test in Parallel With pytest
- How To Do Parameterization In pytest With Selenium?
- End To End Tutorial For pytest Fixtures With Examples
- Test Automation Using pytest and Selenium WebDriver
- Selenium pytest Tutorial: A Comprehensive Guide
- pytest Report Generation For Selenium Automation Scripts
- What Is pytest: Complete Guide With Best Practices
- pytest Tutorial – Python Selenium Test in Parallel
- Debugging Selenium pytest Failures
- 35 Commonly Asked Pytest Interview Questions in 2023
Selenium Robot
- Robot Framework Tutorial with Selenium and Python
- How To Use For Loop In Robot Framework: A Detailed Guide
- How To Use Robot Framework For Parallel Test Execution
- Top 30 Robot Framework: Interview Q&A
Selenium unittest
Selenium JavaScript
- What Is Selenium JavaScript: With Best Practices
- How To Implement Drag And Drop In JavaScript Using Selenium?
- Automation Testing with Selenium JavaScript [Tutorial]
- Best 9 JavaScript Testing Frameworks
- How To Use JavaScript Wait Function In Selenium WebDriver
- How To Get Data Of Attributes In JavaScript With Selenium
- How To Take Screenshots In Selenium WebDriver Using JavaScript
- How To Use Strings In JavaScript With Selenium WebDriver
- How To Use JavaScript Wait Function In Selenium WebDriver
- Guide To Web Scraping With JavaScript And Selenium
Selenium Jest
- Jest Tutorial: Complete Guide to Jest Testing
- Jest Testing with Selenium and JavaScript: Beginner’s Guide
- Jest vs. Mocha vs. Jasmine
- Unit Testing With Jest
Selenium Mocha
- Mocha Tutorial – A Detailed Guide On Mocha Testing
- Mocha JavaScript Tutorial With Examples For Selenium Testing
- Complete Guide on how to run Mocha npm Testing with Node.js
- How To Generate Mocha Reports With Mochawesome?
Selenium Jasmine
- Automated Testing with Jasmine Framework & Selenium
- Introduction to Jasmine Unit Testing: A Complete Tutorial
- Angular Testing With Jasmine And Karma Using Selenium
- How To Run Jasmine Integration Tests [Jasmine JS Tutorial]
- Most Asked Jasmine Interview Questions
- Automated Testing with Jasmine Framework & Selenium
Selenium WebdriverIO
- How To Generate HTML Reports With WebdriverIO?
- How To Use Deep Selectors In Selenium WebdriverIO
- Cross Browser Testing With WebDriverIO [Tutorial]
- How To Speed Up JavaScript Testing With Selenium and WebdriverIO?
- WebdriverIO Tutorial: Handling Alerts & Overlay In Selenium
- WebdriverIO Tutorial: Run Your First Automation Script
- WebdriverIO Tutorial For Handling Dropdown In Selenium
- WebdriverIO Tutorial: Browser Commands for Selenium Testing
- Automated Monkey Testing with Selenium & WebdriverIO (Examples)
- Selenium WebdriverIO Tutorial
- How To Use Strings In JavaScript With Selenium WebDriver?
Selenium Nightwatch.js
- How To Perform Automation Testing With Cucumber And Nightwatch.js?
- E2E Headless Browser Testing Using Nightwatch.js
- Nightwatch Vs. Protractor: Which Testing Framework Is Right For You?
- Running Your First Test With NightWatch.js
- Introduction To Nightwatch.js For Selenium Testing
- Nightwatch.js Tutorial For Test Automation Beginners – With Examples
Selenium Cucumber.js
- Configure Cucumber Setup In Eclipse And IntelliJ [Tutorial]
- Cucumber.js Tutorial with Examples For Selenium JavaScript
- How To Use Annotations In Cucumber Framework [Tutorial]
- How To Perform Automation Testing With Cucumber And Nightwatch.js?
- Automation Testing With Selenium, Cucumber & TestNG
- How To Integrate Cucumber With Jenkins?
- Top 5 Cucumber Best Practices For Selenium Automation
Selenium TestCafe
- Modern Web Testing With TestCafe Using JavaScript And Selenium
- TestCafe Tutorial: Complete Guide to TestCafe Framework
- Getting Started With TestCafe: Examples And Best Practices
- TestCafe Tutorial: How To Select Page Elements Using TestCafe Selectors
Selenium Protractor
- Selenium Protractor Tutorial: Examples and Best Practices
- Cross Browser Testing With Protractor & Selenium
- Protractor Tutorial: End To End Testing For AngularJS
- Complete Guide To Selenium Locators In Protractor
- How To Debug Protractor Tests for Selenium
- Protractor Tutorial: Handle Frames & iFrames in Selenium
- 50+ Protractor Interview Questions
- Protractor Tutorial: Handling Timeouts With Selenium
- Protractor Tutorial: Handle Mouse Actions & Keyboard Events
Selenium C#
- Selenium C# Tutorial: Setting Up Selenium In Visual Studio
- Selenium C# Tutorial: Using Implicit Wait in Selenium
- Selenium C# Tutorial: Using Explicit and Fluent Wait in Selenium
- Selenium C# Tutorial: Handling Alert Windows
- Selenium C# Tutorial: Handling Multiple Browser Windows
- Selenium C# Tutorial: Handling Frames & iFrames With Examples
- Selenium C#: Page Object Model Tutorial With Examples
- How to Find Element by Text in Selenium C#
Selenium NUnit
- NUnit Tutorial: Setting Up NUnit Environment With Visual Studio
- NUnit Tutorial: A Complete Guide With Examples and Best Practices
- NUnit Tutorial: Parameterized Tests With Examples
- NUnit Test Automation Using Selenium C#
- NUnit Annotations For Selenium Automation Testing
- How to Run Multiple NUnit Test Cases
- How To Use Asserts In NUnit Using Selenium?
- Top 28 Selenium WebDriver Commands in NUnit For Test Automation
Selenium xUnit
- Guide On xUnit Framework For Unit Testing With Selenium C#
- Selenium xUnit Tutorial: Setup Selenium WebDriver For xUnit Framework In C#
- NUnit vs. XUnit vs. MSTest: Comparing Unit Testing Frameworks In C#
- XUnit Tutorial: Parameterized Tests For Selenium Testing
- xUnit Testing Tutorial: Environment Setup For Selenium Testing
Selenium MSTest
- MSTest Setup Environment Tutorial: In 3 Easy Steps
- Most Complete MSTest Framework Tutorial Using .Net Core
- MSTest Tutorial: Running First Selenium Automation Script
- Selenium MSTest Tutorial: Setup Selenium WebDriver For MSTest Framework In C#
- MSTest Tutorial: Parameterized Tests For Selenium Testing
Selenium SpecFlow
- SpecFlow Tutorial: A Guide to Automation Testing with C# and Selenium
- Getting Started with SpecFlow Actions [SpecFlow Automation Tutorial]
- Top 60+ SpecFlow: Interview Questions and Answers
- Understanding SpecFlow Framework and Running Tests on Cloud Selenium Grid
- How To Easily Perform Specflow Parallel Execution With NUnit
Selenium Ruby
Selenium RSpec
Selenium Cucumber
Selenium Locators
- Complete Guide To Selenium Locators In Protractor (Examples)
- Locators In Selenium WebDriver With Examples
- Using Name Locator In Selenium Automation Testing
- Using ID Locator In Selenium Automation Testing
- Using TagName Locator In Selenium
- Using Class Name Locator In Selenium Automation Testing
- Using Link Text & Partial Link Text In Selenium
- How Selenium 4 Relative Locator Can Change The Way You Test?
- How WebdriverIO Uses Selenium Locators in a Unique Way
- Using CSS Selectors In Selenium Automation Testing
- Guide For Using XPath In Selenium With Examples
- Maven Tutorial For Selenium Test Automation
Use Cases of Selenium
- How To Automate Calendar Using Selenium WebDriver For Testing?
- How To Handle Web Table in Selenium WebDriver?
- How To Use Breakpoints For Debugging In Selenium WebDriver
- How To Create Data Driven Framework In Selenium
- How To Handle Cookies in Selenium WebDriver
- How to Handle JavaScript Alert in Selenium WebDriver Using Python?
- How To Scroll a Page Using Selenium WebDriver?
- How to use Assert and Verify in Selenium WebDriver
- How to perform Mouse Actions in Selenium WebDriver
- Tutorial On Handling Keyboard Actions In Selenium WebDriver
- How To Find Broken Images Using Selenium WebDriver?
- How To Find Broken Links Using Selenium WebDriver?
- How To Get Attribute Value In Selenium WebDriver?
- Auto Healing in Selenium Automation Testing
- Visual Regression Testing With Selenium
Miscellaneous:
- Geolocation Testing With Selenium Using Examples
- Selenium Firefox Driver: Automate Testing With Firefox Browsers
- What is Selenium WebDriver: Tutorial With Examples
- Why Selenium WebDriver Should Be Your First Choice for Automation Testing
- Selenium WebDriver Tutorial for Cross Browser Testing
- What is Selenium IDE? Why Is It Must For Every QA?
- How To Run Selenium IDE Test Over Online Selenium Grid?
- How To Speed Up Selenium Test Cases Execution?
- How To Perform Localization Testing Using Selenium WebDriver?
- How To Handle Internationalization In Selenium WebDriver?
- Complete Selenium WebDriver Tutorial with Examples
- Desired Capabilities in Selenium WebDriver
- How To Use JavaScriptExecutor in Selenium WebDriver?
Videos
Selenium Java
- Selenium 4 Tutorial
- Selenium WebDriver Tutorial
- Selenium Java Tutorial - Learn Selenium 4 with Java
- TestNG Framework Tutorial | Complete Step-by-Step Tutorials
- JUnit Tutorial For Beginners | JUnit Basics With Selenium
- Selenium JUnit 5 | Complete Tutorial | LambdaTest
Selenium Python
- pytest Tutorial | Selenium Tutorial For pytest
- Robot Tutorial | Selenium Tutorial using Python and Robot
Selenium JavaScript
- Selenium JavaScript | Complete Tutorial | LambdaTest
- WebdriverIO Tutorial | Complete Step-by-Step Tutorials
Selenium C#
- NUnit Tutorial | Selenium With C# | LambdaTest
- xUnit Tutorial | Complete Tutorial with Selenium C#
- MSTest Tutorial | Selenium C# With MSTest
- Specflow Tutorial | Specflow Selenium C# Tutorial
Certifications
Apart from the above learning resources, it is also important take your Selenium expertise to the next levels. And this is where LambdaTest Certifications in Selenium offers you an excellent opportunity to validate and showcase your skills.
Following are the Selenium certifications that LambdaTest offers:
On this page
- Overview
- What is Selenium?
- Who Uses Selenium?
- Why Use Selenium for Automation Testing?
- What Types of Testing Can Selenium Automate?
- History of Selenium
- Components of Selenium
- What is the Difference Between Selenium 3 and Selenium 4?
- Popular Frameworks for Selenium Testing
- Getting Started with Selenium Testing
- Parallel Testing in Selenium
- Test Reporting in Selenium
- Best Practices for Using Selenium
- Future of Selenium Testing
- Learning Resources for Selenium
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Frequently asked questions
- General →
Did you find this page helpful?
More Hubs
Try LambdaTest Now !!
Get 100 minutes of automation test minutes FREE!!