KR102181434B1 - Laser device - Google Patents
Laser device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR102181434B1 KR102181434B1 KR1020167000913A KR20167000913A KR102181434B1 KR 102181434 B1 KR102181434 B1 KR 102181434B1 KR 1020167000913 A KR1020167000913 A KR 1020167000913A KR 20167000913 A KR20167000913 A KR 20167000913A KR 102181434 B1 KR102181434 B1 KR 102181434B1
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- light
- laser
- semiconductor laser
- prism
- optical system
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02B—OPTICAL ELEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS
- G02B27/00—Optical systems or apparatus not provided for by any of the groups G02B1/00 - G02B26/00, G02B30/00
- G02B27/10—Beam splitting or combining systems
- G02B27/12—Beam splitting or combining systems operating by refraction only
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02B—OPTICAL ELEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS
- G02B27/00—Optical systems or apparatus not provided for by any of the groups G02B1/00 - G02B26/00, G02B30/00
- G02B27/09—Beam shaping, e.g. changing the cross-sectional area, not otherwise provided for
- G02B27/0905—Dividing and/or superposing multiple light beams
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02B—OPTICAL ELEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS
- G02B27/00—Optical systems or apparatus not provided for by any of the groups G02B1/00 - G02B26/00, G02B30/00
- G02B27/10—Beam splitting or combining systems
- G02B27/106—Beam splitting or combining systems for splitting or combining a plurality of identical beams or images, e.g. image replication
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02B—OPTICAL ELEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS
- G02B5/00—Optical elements other than lenses
- G02B5/04—Prisms
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01S—DEVICES USING THE PROCESS OF LIGHT AMPLIFICATION BY STIMULATED EMISSION OF RADIATION [LASER] TO AMPLIFY OR GENERATE LIGHT; DEVICES USING STIMULATED EMISSION OF ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION IN WAVE RANGES OTHER THAN OPTICAL
- H01S5/00—Semiconductor lasers
- H01S5/005—Optical components external to the laser cavity, specially adapted therefor, e.g. for homogenisation or merging of the beams or for manipulating laser pulses, e.g. pulse shaping
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01S—DEVICES USING THE PROCESS OF LIGHT AMPLIFICATION BY STIMULATED EMISSION OF RADIATION [LASER] TO AMPLIFY OR GENERATE LIGHT; DEVICES USING STIMULATED EMISSION OF ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION IN WAVE RANGES OTHER THAN OPTICAL
- H01S5/00—Semiconductor lasers
- H01S5/40—Arrangement of two or more semiconductor lasers, not provided for in groups H01S5/02 - H01S5/30
- H01S5/4012—Beam combining, e.g. by the use of fibres, gratings, polarisers, prisms
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01S—DEVICES USING THE PROCESS OF LIGHT AMPLIFICATION BY STIMULATED EMISSION OF RADIATION [LASER] TO AMPLIFY OR GENERATE LIGHT; DEVICES USING STIMULATED EMISSION OF ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION IN WAVE RANGES OTHER THAN OPTICAL
- H01S5/00—Semiconductor lasers
- H01S5/40—Arrangement of two or more semiconductor lasers, not provided for in groups H01S5/02 - H01S5/30
- H01S5/4025—Array arrangements, e.g. constituted by discrete laser diodes or laser bar
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02B—OPTICAL ELEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS
- G02B19/00—Condensers, e.g. light collectors or similar non-imaging optics
- G02B19/0033—Condensers, e.g. light collectors or similar non-imaging optics characterised by the use
- G02B19/0047—Condensers, e.g. light collectors or similar non-imaging optics characterised by the use for use with a light source
- G02B19/0052—Condensers, e.g. light collectors or similar non-imaging optics characterised by the use for use with a light source the light source comprising a laser diode
- G02B19/0057—Condensers, e.g. light collectors or similar non-imaging optics characterised by the use for use with a light source the light source comprising a laser diode in the form of a laser diode array, e.g. laser diode bar
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02B—OPTICAL ELEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS
- G02B27/00—Optical systems or apparatus not provided for by any of the groups G02B1/00 - G02B26/00, G02B30/00
- G02B27/09—Beam shaping, e.g. changing the cross-sectional area, not otherwise provided for
- G02B27/0916—Adapting the beam shape of a semiconductor light source such as a laser diode or an LED, e.g. for efficiently coupling into optical fibers
- G02B27/0922—Adapting the beam shape of a semiconductor light source such as a laser diode or an LED, e.g. for efficiently coupling into optical fibers the semiconductor light source comprising an array of light emitters
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02B—OPTICAL ELEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS
- G02B27/00—Optical systems or apparatus not provided for by any of the groups G02B1/00 - G02B26/00, G02B30/00
- G02B27/10—Beam splitting or combining systems
- G02B27/1066—Beam splitting or combining systems for enhancing image performance, like resolution, pixel numbers, dual magnifications or dynamic range, by tiling, slicing or overlapping fields of view
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01S—DEVICES USING THE PROCESS OF LIGHT AMPLIFICATION BY STIMULATED EMISSION OF RADIATION [LASER] TO AMPLIFY OR GENERATE LIGHT; DEVICES USING STIMULATED EMISSION OF ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION IN WAVE RANGES OTHER THAN OPTICAL
- H01S5/00—Semiconductor lasers
- H01S5/40—Arrangement of two or more semiconductor lasers, not provided for in groups H01S5/02 - H01S5/30
- H01S5/4025—Array arrangements, e.g. constituted by discrete laser diodes or laser bar
- H01S5/4031—Edge-emitting structures
- H01S5/4043—Edge-emitting structures with vertically stacked active layers
- H01S5/405—Two-dimensional arrays
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Optics & Photonics (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- Electromagnetism (AREA)
- Semiconductor Lasers (AREA)
- Laser Beam Processing (AREA)
- Optical Elements Other Than Lenses (AREA)
Abstract
N개의 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택과, N개의 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택 각각으로부터 출력된 광속의 광축을 시프트하는 것에 의해 광속끼리의 간격을 축소하는 프리즘 광학계와, 광속을 광속마다 집광 및 편향하는 결상 광학계를 구비하며, 결상 광학계는, 소정 위치에서 광속이 서로 겹치도록 광속을 편향함과 아울러, 결상 광학계와 소정 위치와의 사이에 광속의 집광점을 생기게 하는, 레이저 장치.It is equipped with a prism optical system that reduces the spacing between the beams by shifting the optical axis of the beams output from each of the N semiconductor laser array stacks and the N semiconductor laser array stacks, and an imaging optical system that condenses and deflects the beams for each beam. , The imaging optical system deflects the light beams so that the beams overlap each other at a predetermined position, and creates a condensing point of the light beam between the imaging optical system and a predetermined position.
Description
본 발명의 일측면은, 레이저 장치에 관한 것이다. One aspect of the present invention relates to a laser device.
특허 문헌 1에는, 고체 레이저의 여기(勵起)에 이용되는 집광(集光) 장치에 관한 기술이 개시되어 있다. 도 9는, 특허 문헌 1에 개시된 집광 장치(100)의 구성을 나타내는 사시도이다. 도 9에 나타내어지는 바와 같이, 집광 장치(100)는, 2개의 광원(106)과, 2개의 광학계(112)와, 집광 렌즈(114)를 구비하고 있다. 광원(106)은, 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(stack)(102) 및 실린드리칼 렌즈 스택(104)을 가진다. 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(102)은, 복수의 발광 영역을 가지는 반도체 레이저 어레이(116)가 복수 적층되어 이루어진다. 실린드리칼 렌즈 스택(104)은, 반도체 레이저 어레이(116)와 동수(同數)의 실린드리칼 렌즈(118)가 적층 방향으로 배열되어 이루어지며, 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(102)의 복수의 발광 영역의 근방에 설치된다. 또, 광학계(112)는, 프리즘(108) 및 프리즘(110)을 가진다. 프리즘(108)은, 삼각기둥 모양의 직각 프리즘이며, 측면에는 전반사(全反射) 코팅이 실시되어 있다. 프리즘(110)은, 삼각기둥 모양의 직각 프리즘이며, 광 입사면에는 반사 방지 코팅이 실시되고, 전반사면에는 고반사 코팅이 실시되어 있다. 집광 렌즈(114)는, 집광 장치(100)의 여기 대상인 고체 레이저(120) 내에 초점을 가지고 있다.
이 집광 장치(100)에서는, 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(102)의 각 반도체 레이저 어레이(116)의 발광 영역으로부터 레이저 광(La1)이 출사된다. 이 레이저 광(La1)은, 실린드리칼 렌즈 스택(104)의 각 실린드리칼 렌즈(118)에 의해서 평행화 된 후, 프리즘(108)의 2개의 측면에서 반사되어, 광속 Lb1과, 광속 Lc1으로 분할된다. 광속 Lc1은, 프리즘(110)의 2개의 전반사면에서 반사된 후, 프리즘(108) 위를 통과하여, 광속 Lb1에 대해서 평행하게 인접한다. 그 후, 광속 Lb1 및 Lc1은, 필요에 따라서 반사 미러(122, 124)에 의해 광로가 변경된 후, 집광 렌즈(114)에 의해서 고체 레이저(120)의 내부에 집광된다. In this
대출력의 레이저 광원으로서, 발광 영역을 복수 가지는 반도체 레이저 어레이가 복수개 적층되어 이루어지는 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택이 이용되고 있다. 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택은, 예를 들면 레이저 매질을 가지는 고에너지 고체 레이저 장치의 여기 광원으로서 이용된다. 이러한 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택에서, 레이저 광량을 높이기 위해서는 발광 영역의 수를 증가시키거나, 즉 보다 많은 반도체 레이저 어레이를 적층하거나, 또는 보다 많은 발광 영역을 각 반도체 레이저 어레이에 마련할 수 있다. 그러나, 발광 영역의 수가 늘어나는 만큼 발열량도 늘어난다. 따라서, 냉각 장치의 대형화나 조립의 수율의 관점으로부터 보면, 하나의 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택을 대형화하는 것 보다도, 적당한 크기의 복수의 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택을 조합시키는 쪽이 바람직하다. As a high-power laser light source, a semiconductor laser array stack comprising a plurality of stacked semiconductor laser arrays having a plurality of light emitting regions is used. The semiconductor laser array stack is used, for example, as an excitation light source of a high energy solid state laser device having a laser medium. In such a semiconductor laser array stack, in order to increase the amount of laser light, the number of emission regions may be increased, that is, more semiconductor laser arrays may be stacked, or more emission regions may be provided in each semiconductor laser array. However, the amount of heat generated increases as the number of light-emitting regions increases. Therefore, from the viewpoint of increasing the size of the cooling device and the yield of assembly, it is more preferable to combine a plurality of semiconductor laser array stacks of appropriate sizes rather than increasing the size of one semiconductor laser array stack.
복수의 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택을 조합시키는 경우, 복수의 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택으로부터 출사되는 레이저 광속을 단일의 광속으로 모을 필요가 있다. 그러나, 복수의 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택끼리가 인접하면, 냉각이 불충분하게 되기 쉽고, 또 충분히 냉각하기 위해서 냉각 장치를 대형화하지 않을 수 없게 되어 버린다. 따라서, 복수의 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택끼리의 간격을 적당히 두고 배치하는 것이 바람직하다. 그 경우, 복수의 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택으로부터 각각 출사되는 복수의 레이저 광속을, 광학계를 이용하여 하나로 통합할 필요가 있다. 예를 들면 도 9에 나타내어진 집광 장치(100)에서도, 2개의 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(102)으로부터 출사된 레이저 광속이, 프리즘(108, 110)이나 반사 미러(122, 124)라고 하는 광학계를 이용하여 하나로 통합되어 있다.When combining a plurality of semiconductor laser array stacks, it is necessary to collect the laser beams emitted from the plurality of semiconductor laser array stacks into a single beam. However, when a plurality of semiconductor laser array stacks are adjacent to each other, cooling is likely to be insufficient, and in order to sufficiently cool, the cooling device must be enlarged. Therefore, it is desirable to arrange a plurality of semiconductor laser array stacks at appropriate intervals. In that case, it is necessary to integrate a plurality of laser beams each emitted from a plurality of semiconductor laser array stacks into one using an optical system. For example, even in the
그렇지만, 특허 문헌 1에 개시된 집광 장치(100)에서는, 복수의 레이저 광속이 광축을 일치시키면서, 단일의 집광 렌즈(114)에 입사하고 있다. 따라서, 예를 들면 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(102)의 일부에 열화(劣化)가 생기면, 조사 대상물인 고체 레이저(120)에서, 그 열화 부분에 대응하는 개소의 레이저 광량이 국소적으로 저하하여, 조사 대상물에서의 레이저 광량의 균일성을 해쳐 버린다. However, in the
본 발명의 일측면은, 이러한 문제점을 감안하여 이루어진 것이며, 복수의 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택끼리를 인접시킬 필요가 없고, 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택의 일부에 열화가 생긴 경우라도 조사 대상물에서의 레이저 광량의 균일성을 유지할 수 있는 레이저 장치를 제공하는 것을 목적으로 한다. One aspect of the present invention has been made in view of such a problem, and it is not necessary to make a plurality of semiconductor laser array stacks adjacent to each other, and even when deterioration occurs in a part of the semiconductor laser array stack, uniformity of the laser light quantity in the irradiated object An object of the present invention is to provide a laser device capable of maintaining
본 발명의 일측면에 관한 레이저 장치는, 소정 방향으로 배열된 2개 이상의 발광 영역으로부터 레이저 광을 출사하는 복수의 반도체 레이저 어레이가 출사 방향을 일치시켜 소정 방향 및 출사 방향과 교차하는 적층 방향으로 적층되어 이루어지며, 복수의 반도체 레이저 어레이로부터 출사되는 레이저 광을 하나의 광속(光束)으로서 각각 출력하는 N개(N은 2 이상의 정수(整數))의 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(stack)과, 광속에 포함되는 레이저 광의 속축(速軸) 방향의 평행화를 행하는 제1 콜리메이트부와, N개의 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택 각각으로부터 출력되어 제1 콜리메이트부를 거친 광속을 투과함과 아울러, 해당 광속의 광축을 해당 광축과 교차하는 방향으로 시프트하는 것에 의해 광속끼리의 간격을 축소하는 프리즘 광학계와, N개의 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택 각각으로부터 출력된 각 광속을, 지축(遲軸) 방향과 교차하는 면내에서 광속마다 집광함과 아울러, 해당 면내에서 각 광속의 광축을 광속마다 편향하는 결상 광학계를 구비하며, 결상 광학계는, 소정 위치에서 N개의 광속이 서로 겹치도록 각 광속을 편향함과 아울러, 결상 광학계와 소정 위치와의 사이에 각 광속의 집광점을 생기게 한다. In the laser device according to one aspect of the present invention, a plurality of semiconductor laser arrays that emit laser light from two or more light emitting regions arranged in a predetermined direction are stacked in a stacking direction crossing a predetermined direction and an emission direction by matching the emission direction. A stack of N semiconductor laser arrays (N is an integer greater than or equal to 2) each outputting laser light emitted from a plurality of semiconductor laser arrays as one beam of light, and included in the beam The first collimating unit that parallelizes the laser light to be parallelized in the direction of the speed axis, and the light beam that is output from each of the N semiconductor laser array stacks and passes through the first collimating unit, corresponds to the optical axis of the corresponding light beam. A prism optical system that reduces the spacing between the beams by shifting in the direction intersecting the optical axis, and each beam of light output from each of the N semiconductor laser array stacks is condensed for each beam in the plane intersecting the direction of the axis. In addition, an imaging optical system is provided for deflecting the optical axis of each beam in the corresponding plane for each beam, and the imaging optical system deflects each beam so that N beams overlap each other at a predetermined position. In between, there is a condensing point of each beam.
이 레이저 장치에서는, N개의 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택으로부터 출사된 광속의 광축이 프리즘 광학계에 의해서 시프트되는 것에 의해, 광속끼리의 간격이 축소된다. 여기서, 광속의 광축을 시프트한다는 것은, 예를 들면, 프리즘 광학계로부터 출사하는 광속의 광축을, 프리즘 광학계에 입사하는 광속의 광축에 대해 대략 평행하게 하면서, 해당 광축과 교차하는 방향으로 이동시키는 것을 말한다. 이러한 프리즘 광학계가 마련되는 것에 의해, 복수의 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택끼리를 인접시킬 필요가 없게 되어, 냉각을 충분히 할 수 있고, 또 냉각 장치의 대형화를 회피할 수 있다. In this laser device, when the optical axis of the light beam emitted from the N semiconductor laser array stack is shifted by the prism optical system, the interval between the light beams is reduced. Here, shifting the optical axis of the luminous flux means, for example, moving the optical axis of the luminous flux emitted from the prism optical system in a direction that intersects the optical axis while being approximately parallel to the optical axis of the luminous flux incident on the prism optical system. . By providing such a prism optical system, it is not necessary to make a plurality of semiconductor laser array stacks adjacent to each other, cooling can be sufficiently performed, and an increase in size of the cooling device can be avoided.
또, 이 레이저 장치에서는, 결상 광학계가, 결상 광학계와 소정 위치와의 사이에 각 광속의 집광점이 생기도록 각 광속을 광속마다 집광한다. 이것에 의해, 소정 위치에서의 레이저 광량의 균일성을 높일 수 있고, 예를 들면 소정 위치에 설치되는 조사 대상물에 균일한 광 강도의 레이저 광속을 부여할 수 있다. 게다가, 이 레이저 장치에서는, 결상 광학계가, 균일한 N개의 레이저 광속을 소정 위치에서 서로 겹치도록 광속마다 편향한다. 이것에 의해, 소정 위치에서 균일하게 퍼진 N개의 레이저 광속이 서로 겹치므로, 어느 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택의 일부에 열화가 생겨, 한 개의 레이저 광속에 그 영향이 생겼다고 해도, 다른 레이저 광속에 의해서 광량의 균일성을 유지할 수 있다. Moreover, in this laser device, the imaging optical system condenses each beam for each beam so that a condensing point of each beam is generated between the imaging optical system and a predetermined position. Thereby, the uniformity of the amount of laser light at a predetermined position can be improved, and for example, a laser beam of uniform light intensity can be applied to an irradiation object provided at a predetermined position. In addition, in this laser device, the imaging optical system deflects for each beam so that uniform N laser beams overlap each other at predetermined positions. As a result, since N laser beams uniformly spread at a predetermined position overlap each other, deterioration occurs in a part of a semiconductor laser array stack, and even if the effect occurs on one laser beam, the amount of light is uniform by the other laser beam. You can keep your castle.
또, 레이저 장치는, 결상 광학계가, N개의 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택 각각으로부터 출력된 각 광속을 광속마다 집광하는 N개의 결상 렌즈와, 각 광속의 광축을 광속마다 편향하는 N개의 편향 광학 소자를 포함해도 괜찮다. 이것에 의해, 상기의 결상 광학계를 실현할 수 있다. Further, the laser device may include N imaging lenses for condensing each beam of light output from each of the N semiconductor laser array stacks for each beam, and N deflection optical elements for deflecting the optical axis of each beam for each beam. Okay. Thereby, the above-described imaging optical system can be realized.
또, 레이저 장치는, N개의 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택이 적층 방향으로 늘어서 배치되어 있으며, 프리즘 광학계가, 광속의 광축을 적층 방향으로 시프트해도 괜찮다. 이러한 구성에 의해서, 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택의 적층 방향으로 적당한 간격을 두면서, N개의 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택을 배치할 수 있다. In addition, in the laser device, N semiconductor laser array stacks are arranged in a stacking direction, and the prism optical system may shift the optical axis of the light beam in the stacking direction. With this configuration, it is possible to arrange the N semiconductor laser array stacks with appropriate intervals in the stacking direction of the semiconductor laser array stack.
또, 레이저 장치는, 하나 또는 복수의 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택을 포함하는 제1 군(群)과, 하나 또는 복수의 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택을 포함하는 제2 군이 소정 방향으로 늘어서 배치되어 있으며, 프리즘 광학계는, 제1 군에 포함되는 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택으로부터 출사되는 광속과, 제2 군에 포함되는 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택으로부터 출사되는 광속과의 간격이 축소하도록, 소정 방향으로 해당 광속의 광축을 시프트해도 괜찮다. In addition, in the laser device, a first group including one or a plurality of semiconductor laser array stacks and a second group including one or more semiconductor laser array stacks are arranged in a predetermined direction, and a prism optical system May shift the optical axis of the light beam in a predetermined direction so that the distance between the light beam emitted from the semiconductor laser array stack included in the first group and the light beam emitted from the semiconductor laser array stack included in the second group is reduced. .
본 발명의 일측면에 관한 레이저 장치에 의하면, 복수의 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택끼리를 인접시킬 필요가 없고, 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택의 일부에 열화가 생긴 경우라도 조사 대상물에서의 레이저 광량의 균일성을 유지할 수 있다. According to the laser device according to one aspect of the present invention, it is not necessary to make a plurality of semiconductor laser array stacks adjacent to each other, and even when deterioration occurs in a part of the semiconductor laser array stack, the uniformity of the laser light quantity in the irradiated object can be maintained. have.
도 1은 제1 실시 형태에 관한 레이저 장치의 구성을 나타내는 평면도이다.
도 2는 레이저 장치가 구비하는 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택의 구성을 나타내는 사시도이다.
도 3은 제2 실시 형태에 관한 레이저 장치의 구성을 나타내는 평면도이다.
도 4는 도 3에 나타내어진 레이저 장치를 Y축 방향으로부터 본 측면도이다.
도 5는 도 3에 나타내어진 레이저 장치의 구성을 나타내는 사시도이다.
도 6은 제3 실시 형태에 관한 레이저 장치의 구성을 나타내는 평면도이다.
도 7은 도 6에 나타내어진 레이저 장치를 Y축 방향으로부터 본 측면도이다.
도 8은 도 6에 나타내어진 레이저 장치의 구성을 나타내는 사시도이다.
도 9는 특허 문헌 1에 개시된 집광 장치의 구성을 나타내는 사시도이다. 1 is a plan view showing a configuration of a laser device according to a first embodiment.
2 is a perspective view showing the configuration of a semiconductor laser array stack included in the laser device.
3 is a plan view showing a configuration of a laser device according to a second embodiment.
Fig. 4 is a side view of the laser device shown in Fig. 3 viewed from the Y-axis direction.
5 is a perspective view showing the configuration of the laser device shown in FIG. 3.
6 is a plan view showing a configuration of a laser device according to a third embodiment.
Fig. 7 is a side view of the laser device shown in Fig. 6 viewed from the Y-axis direction.
8 is a perspective view showing the configuration of the laser device shown in FIG. 6.
9 is a perspective view showing the configuration of a condensing device disclosed in
이하, 첨부 도면을 참조하면서 본 발명의 일측면에 관한 레이저 장치의 실시 형태를 상세하게 설명한다. 또, 도면의 설명에서 동일한 요소에는 동일한 부호를 부여하고, 중복하는 설명을 생략한다. Hereinafter, embodiments of a laser device according to an aspect of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings. In addition, in the description of the drawings, the same reference numerals are assigned to the same elements, and redundant descriptions are omitted.
(제1 실시 형태) (First embodiment)
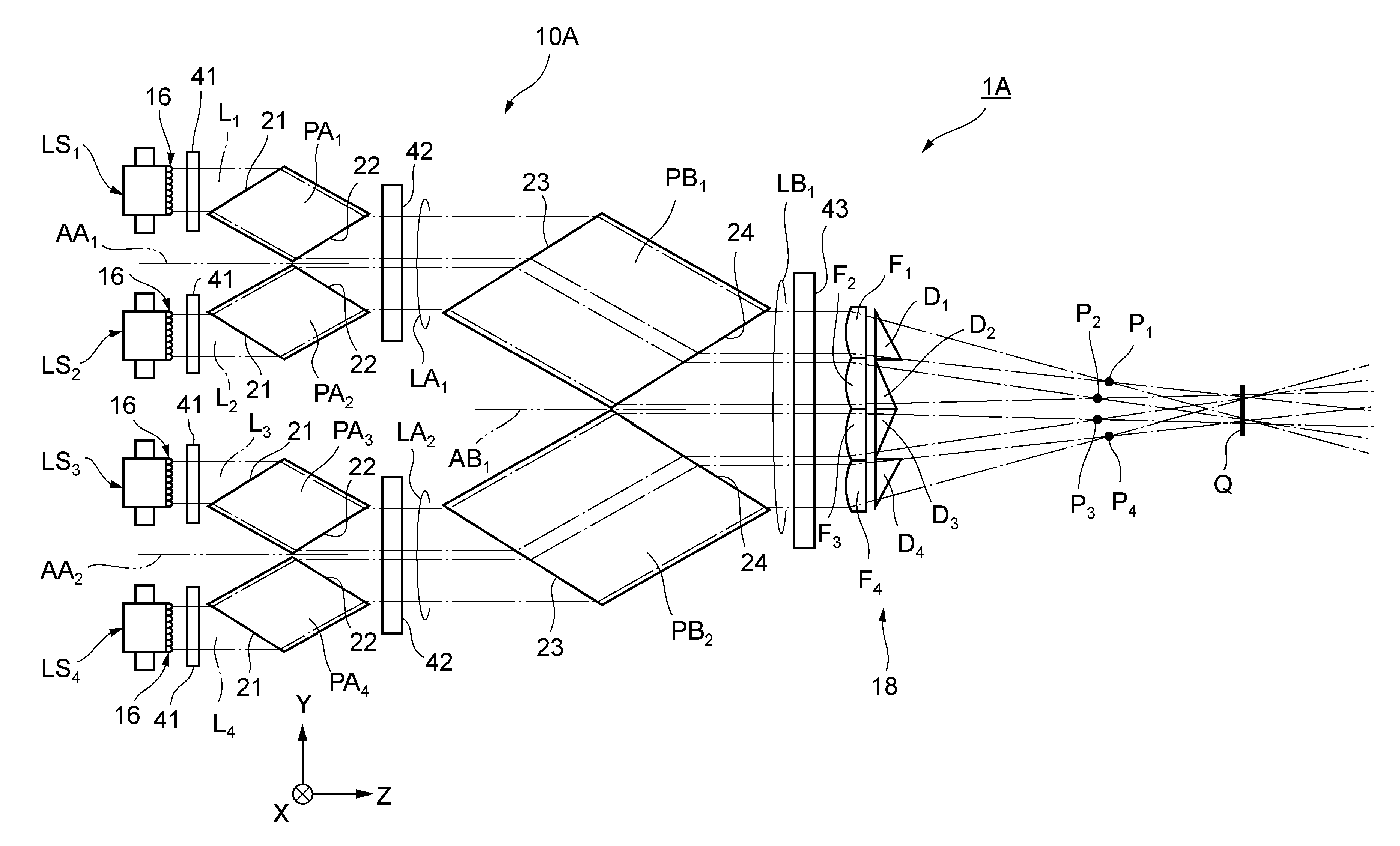
도 1은, 제1 실시 형태에 관한 레이저 장치(1A)의 구성을 나타내는 평면도이다. 또, 도 2는, 레이저 장치(1A)가 구비하는 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(stack)(LS1~LSN)의 구성을 나타내는 사시도이다. 또, 이해를 용이하게 하기 위해, 도 1 및 도 2에는 XYZ 직교좌표계가 나타내어져 있다. 1 is a plan view showing a configuration of a
도 1에 나타내어지는 바와 같이, 본 실시 형태의 레이저 장치(1A)는, N개(N은 2 이상의 정수(整數). 도면에서는 N=4인 경우를 예시)의 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(LS1~LSN)과, 프리즘 광학계(10A)를 구비하고 있다. 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(LS1~LSN)은, Y축 방향으로 서로 간격을 두고 늘어서 배치되어 있다. 프리즘 광학계(10A)는, 이들 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(LS1~LSN)에 일대일로 대응하여 마련된 N개의 제1 프리즘(PA1~PAN)과, 제2 프리즘(PB1~PBK)(단, K=N/2)을 가진다. 제1 프리즘(PA1~PAN) 및 제2 프리즘(PB1~PBK)도 또, 각각 Y축 방향으로 늘어서 배치되어 있다. As shown in Fig. 1, the
도 2에 나타내어지는 바와 같이, 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(LS1~LSN)은, 복수의 반도체 레이저 어레이(12)를 가진다. 이들 반도체 레이저 어레이(12)는, 소정 방향(본 실시 형태에서는 X축 방향)으로 배열된 2개 이상의 발광 영역(14)을 각각 가지고 있으며, 이들 발광 영역(14) 각각으로부터 혹은 광 출사 방향(본 실시 형태에서는 Z축 방향)을 향해서 레이저 광(La)이 출사된다. 레이저 광(La)의 속축(速軸) 방향은 Y축 방향을 따르고 있으며, 지축(遲軸) 방향은 X축 방향을 따르고 있다. 복수의 반도체 레이저 어레이(12)는, 광 출사 방향을 일치시켜 상기 소정 방향(X축 방향) 및 광 출사 방향(Z축 방향)과 교차하는 적층 방향(본 실시 형태에서는 Y축 방향)으로 적층되어 있다. 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(LS1~LSN)은, 복수의 반도체 레이저 어레이(12)로부터 출사되는 이들 레이저 광(La)을 하나의 광속(光束)으로서 각각 출력한다. As shown in FIG. 2, the semiconductor laser array stacks LS 1 to LS N have a plurality of
도 1을 다시 참조하면, 제n 번째 (n은 1 이상 N 이하의 정수)의 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(LSn)으로부터 출력된 레이저 광속(Ln)은, 콜리메이터 렌즈 스택(16)을 통과한다. 콜리메이터 렌즈 스택(16)은, 본 실시 형태에서의 제1 콜리메이트부 로서, 각 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(LS1~LSN)에 대응하여 배치되고, 각 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(LS1~LSN)의 발광 영역(14)에 대향하고 있다. 콜리메이터 렌즈 스택(16)은, X축 방향으로 연장하고 있으며 복수의 반도체 레이저 어레이(12)에 각각 대응하는 복수의 실린드리칼 렌즈를 가진다. 각 실린드리칼 렌즈는, 대응하는 반도체 레이저 어레이(12)로부터 출사된 레이저 광(La)의 속축 방향의 평행화를 행한다. Referring again to FIG. 1, the laser beam L n output from the n-th semiconductor laser array stack LS n (n is an integer of 1 or more and N or less) passes through the
콜리메이터 렌즈 스택(16)에 의해서 속축 방향의 평행화가 이루어진 레이저 광속(Ln)은, 대응하는 제n 번째의 제1 프리즘(PAn)의 광 입사면(21)에 입사한다. 제1 프리즘(PA1~PAN)은, 예를 들면 유리, 석영 등의 투명 재료로 이루어지는 프리즘으로서, 광 입사면(21) 및 광 출사면(22)을 가진다. 본 실시 형태의 제1 프리즘(PA1~PAN)은, YZ평면을 따른 단면(斷面)이 평행사변형(예를 들면 능형(菱形)) 등의 형상을 나타내며, 해당 평행사변형의 한 변이 광 입사면(21)으로 되어 있고, 해당 한 변과 평행한 다른 한 변이 광 출사면(22)으로 되어 있다. The laser beam L n , which has been parallelized in the speed axis direction by the
제n 번째의 제1 프리즘(PAn)은, 광 입사면(21)에 입사한 레이저 광속(Ln)을 투과하여, 광 출사면(22)으로부터 출사한다. 광 입사면(21)은 XZ평면에 대해서 경사져 있어, 레이저 광속(Ln)이 광 입사면(21)에 입사할 때, 레이저 광속(Ln)은 광 출사 방향(Z축 방향)에 대해서 소정 각도만큼 굴절한다. 또, 광 출사면(22)은 광 입사면(21)에 대해서 평행이어서, 레이저 광속(Ln)이 광 출사면(22)으로부터 출사할 때, 레이저 광속(Ln)은 앞의 굴절과는 반대 방향으로 상기 소정 각도만큼 다시 굴절하고, 다시 광 출사 방향(Z축 방향)을 따라서 진행한다. 이와 같이, 제1 프리즘(PAn)은, 레이저 광속(Ln)의 광축을, 해당 광축과 교차하는 방향(본 실시 형태에서는 Y축 방향)으로 시프트한다. 환언하면, 제1 프리즘(PAn)은, 광 출사면(22)으로부터 출사되는 레이저 광속(Ln)의 광축을, 광 입사면(21)에 입사하는 레이저 광속(Ln)의 광축에 대해 대략 평행하게 하면서, Y축 방향으로 이동시킨다. The n-th first prism PA n passes through the laser beam L n incident on the
또, 본 실시 형태에서는, (2k-1)번째 (단, k는 1 이상 K 이하의 정수)의 제1 프리즘(PA2k-1)과, 2k번째의 제1 프리즘(PA2k)이 Y축 방향에서 서로 인접하여 배치되어 있고, 제1 프리즘(PA2k-1)의 광 입사면(21) 및 광 출사면(22)과, 제1 프리즘(PA2k)의 광 입사면(21) 및 광 출사면(22)이, XZ평면을 따른 기준면(AAk)을 사이에 두고 대칭의 위치에 배치되어 있다. 그리고, 제1 프리즘(PA2k-1)의 광 입사면(21)에 입사한 레이저 광속(L2k-1)은, 서로 이웃하는 레이저 광속(L2k)에 가까워지는 방향으로 굴절하고, 또, 제1 프리즘(PA2k)의 광 입사면(21)에 입사한 레이저 광속(L2k)은, 서로 이웃하는 레이저 광속(L2k-1)에 가까워지는 방향으로 굴절한다. 이것에 의해, 이들 레이저 광속(L2k-1, L2k)이 광 출사면(22)으로부터 출사할 때에는, 레이저 광속(L2k-1, L2k)끼리의 간격이 축소되어, 한 쌍의 광속(L2k-1, L2k)으로 이루어지는 레이저 광속군(LAk)이 형성된다. 이 레이저 광속군(LAk)은, 원래의 광 출사 방향(Z축 방향)을 따라서 진행한다. 또, 본 실시 형태의 레이저 광속군(LAk)을 구성하는 레이저 광속(L2k-1, L2k)은, 서로 인접하여 진행되지만, 서로 겹치지 않고, 예를 들면 1mm 정도의 간격을 가진다. In addition, in this embodiment, the first prism PA 2k-1 of the (2k-1)th (where k is an integer of 1 or more and K or less) and the first prism PA 2k of the 2kth are the Y-axis Are disposed adjacent to each other in the direction, the
제2 프리즘(PB1~PBK)은, 예를 들면 유리, 석영 등의 투명 재료로 이루어지는 프리즘으로서, 광 입사면(23) 및 광 출사면(24)을 가진다. 본 실시 형태의 제2 프리즘(PB1~PBK)은, 제1 프리즘(PA1~PAN)과 마찬가지로, YZ평면을 따른 단면에서 평행사변형(예를 들면 능형) 등의 형상을 나타내며, 해당 평행사변형의 한 변이 광 입사면(23)으로 되어 있고, 해당 한 변과 평행한 다른 한 변이 광 출사면(24)으로 되어 있다. The second prisms PB 1 to PB K are prisms made of, for example, a transparent material such as glass and quartz, and have a
제1 프리즘(PA2k-1, PA2k)으로부터 출사된 레이저 광속(L2k-1, L2k)은, 레이저 광속군(LAk)으로서 제k 번째의 제2 프리즘(PBk)의 광 입사면(23)에 입사한다. 제2 프리즘(PBk)은, 광 입사면(23)에 입사한 레이저 광속군(LAk)을 투과하여, 광 출사면(24)으로부터 출사한다. 광 입사면(23)은 XZ평면에 대해서 경사져 있어, 레이저 광속군(LAk)이 광 입사면(23)에 입사할 때, 레이저 광속군(LAk)은 광 출사 방향(Z축 방향)에 대해서 소정 각도만큼 굴절한다. 또, 광 출사면(24)은 광 입사면(23)에 대해서 평행이어서, 레이저 광속군(LAk)이 광 출사면(24)으로부터 출사할 때, 레이저 광속군(LAk)은 앞의 굴절과는 반대 방향으로 상기 소정 각도만큼 다시 굴절하고, 다시 광 출사 방향(Z축 방향)을 따라서 진행한다. 이와 같이, 제2 프리즘(PBk)은, 레이저 광속군(LAk)의 광축을, 해당 광축과 교차하는 방향(본 실시 형태에서는 Y축 방향)으로 시프트한다. 환언하면, 제2 프리즘(PBk)은, 광 출사면(24)으로부터 출사되는 레이저 광속군(LAk)의 광축을, 광 입사면(23)에 입사하는 레이저 광속군(LAk)의 광축에 대해 대략 평행하게 하면서, Y축 방향으로 이동시킨다. The laser beams (L 2k-1 , L 2k ) emitted from the first prism (PA 2k-1 , PA 2k ) are the laser beam groups (LA k ) and are incident on the k-th second prism (PB k ). It enters the
또, 본 실시 형태에서는, (2m-1)번째 (단, m은 1 이상 M 이하의 정수. M=N/4)의 제2 프리즘(PB2m-1)과, (2m)번째의 제2 프리즘(PB2m)이 Y축 방향에서 서로 인접하여 배치되어 있고, 제2 프리즘(PB2m-1)의 광 입사면(23) 및 광 출사면(24)과, 제2 프리즘(PB2m)의 광 입사면(23) 및 광 출사면(24)이, XZ평면을 따른 기준면(ABm)을 사이에 두고 대칭의 위치에 배치되어 있다. 따라서, 제2 프리즘(PB2m-1)의 광 입사면(23)에 입사한 레이저 광속군(LA2m-1)은, 서로 이웃하는 레이저 광속군(LA2m)에 가까워지는 방향으로 굴절하고, 또, 제2 프리즘(PB2m)의 광 입사면(23)에 입사한 레이저 광속군(LA2m)은, 서로 이웃하는 레이저 광속군(LA2m-1)에 가까워지는 방향으로 굴절한다. 이것에 의해, 이들 레이저 광속군(LA2m-1, LA2m)이 광 출사면(24)으로부터 출사하는 때에는, 레이저 광속군(LA2m-1, LA2m)끼리의 간격이 축소되어, 한 쌍의 레이저 광속군(LA2m-1, LA2m)으로 이루어지는 레이저 광속군(LBm)이 형성된다. 이 레이저 광속군(LBm)은, 원래의 광 출사 방향(Z축 방향)을 따라서 진행한다. 또, 본 실시 형태의 레이저 광속군(LBm)을 구성하는 레이저 광속군(LA2m-1, LA2m)은, 서로 인접하여 진행되지만, 서로 겹치지 않고, 예를 들면 1mm 정도의 간격을 가져 겹치지 않는다. 즉, 1개의 레이저 광속군(LBm)에는 4개의 레이저 광속(Ln)이 포함되고, 또한, 이들 레이저 광속(Ln)은 Y축 방향으로 늘어서 있고, 서로 겹치지 않으며, 예를 들면 서로 이웃하는 레이저 광속의 사이에 1mm 정도의 간격을 가진다. In the present embodiment, the second prism PB 2m-1 of the (2m-1)th (where m is an integer of 1 or more and M=N/4) and the second prism of the (2m)th Prism (PB 2m ) is disposed adjacent to each other in the Y-axis direction, the
본 실시 형태의 레이저 장치(1A)는, 결상 광학계(18)를 더 구비하고 있다. 결상 광학계(18)는, 제1 프리즘(PA1~PAN) 및 제2 프리즘(PB1~PBK)을 투과한 각 레이저 광속(L1~LN)을, 지축 방향과 교차하는 면내(본 실시 형태에서는 YZ평면내)에서 레이저 광속마다 집광한다. 또, 결상 광학계(18)는, 해당 면내에서 각 레이저 광속(L1~LN)의 광축을 레이저 광속마다 편향한다. The
구체적으로는, 결상 광학계(18)는, N개의 결상 렌즈(F1~FN)와, N개의 편향 광학 소자(D1~DN)를 포함하여 구성되어 있다. 결상 렌즈(F1~FN)는, N개의 레이저 광속(L1~LN)에 일대일로 대응하여 마련되어 있고, 제n 번째의 결상 렌즈(FN)는, 대응하는 레이저 광속(Ln)을 YZ평면 내에서 집광한다. 또, 본 실시 형태에서는, 결상 렌즈(F1~FN)는 XZ평면 내에서는 집광 작용을 가지지 않아, 레이저 광속(L1~LN)은 XZ평면 내에서는 집광되지 않는다. Specifically, the imaging
또, 결상 렌즈(F1~FN)는, 결상 광학계(18)와 Z축 방향의 소정 위치 Q와의 사이에 각 레이저 광속(L1~LN)의 집광점(P1~PN)을 생기게 한다. 보다 상세하게는, 결상 렌즈(F1~FN)의 초점 거리는 결상 광학계(18)와 소정 위치 Q와의 거리 보다도 짧고, 레이저 광속(L1~LN)은 소정 위치 Q의 바로 앞에서 일단 수렴한 후, 다시 확대하면서 소정 위치 Q를 통과한다. In addition, the imaging lenses (F 1 to F N ), the condensing points (P 1 to P N ) of each laser beam (L 1 to L N ) between the imaging
편향 광학 소자(D1~DN)는, N개의 레이저 광속(L1~LN)에 일대일로 대응하여 마련되어 있고, 제n 번째의 편향 광학 소자(Dn)는, 대응하는 레이저 광속(Ln)을 YZ평면 내에서 편향한다. 여기서, 레이저 광속(Ln)을 편향한다는 것은, 레이저 광속(Ln)의 광축의 방향을 약간 변경하는 것을 말하며, 본 실시 형태에서는, 레이저 광속(Ln)의 광축이 Z축 방향을 기준으로 하여 Y축 방향으로 약간의 경사진다. The deflection optical elements D 1 to D N are provided in a one-to-one correspondence with N laser beams L 1 to L N , and the n-th deflection optical element D n is a corresponding laser beam L n ) deflects in the YZ plane. Here, a laser beam is that the deflecting (L n), the laser light beam the means to slightly change the direction of the optical axis (L n), the present embodiment, based on the laser beam optical axis in the Z-axis direction (L n) And slightly inclined in the Y-axis direction.
이러한 레이저 광속(Ln)의 편향은, Z축 방향의 소정 위치 Q에서 N개의 레이저 광속(L1~LN)이 서로 겹치도록 행해진다. 환언하면, X축 방향으로부터 본 레이저 광속(L1~LN)의 각 광축은, 편향 광학 소자(D1~DN)를 통과한 후, 소정 위치 Q에서 서로 겹친다. 이러한 작용을 가지는 편향 광학 소자(D1~DN)는, 예를 들면 웨지(wedge) 프리즘에 의해서 실현된다. 소정 위치 Q에는, 예를 들면 조사 대상물이 배치된다. 이 조사 대상물로서는, 예를 들면, 레이저 공진기의 공진 광로 상에 배치되며, 여기광(勵起光)이 공급됨으로써 방출광을 발생시키는 고체 레이저 매질을 들 수 있다. Such deflection of the laser beam L n is performed so that the N laser beams L 1 to L N overlap each other at a predetermined position Q in the Z-axis direction. In other words, the respective optical axes of the laser beams L 1 to L N viewed from the X-axis direction overlap each other at a predetermined position Q after passing through the deflection optical elements D 1 to D N. The deflection optical elements D 1 to D N having such an action are realized by, for example, a wedge prism. At the predetermined position Q, an object to be irradiated is disposed, for example. Examples of the irradiation target include a solid-state laser medium that is disposed on a resonant optical path of a laser resonator and generates emission light by supplying excitation light.
본 실시 형태의 레이저 장치(1A)는, 지축 콜리메이터 렌즈(41, 42, 및 43)를 더 구비하고 있다. 지축 콜리메이터 렌즈(41)는 본 실시 형태에서의 제2 콜리메이트부이며, 지축 콜리메이터 렌즈(43)는 본 실시 형태에서의 제3 콜리메이트부이다. 지축 콜리메이터 렌즈(41)는, 콜리메이터 렌즈 스택(16)과 제1 프리즘(PA1~PAN)과의 사이의 광축 상에 배치되며, 레이저 광속(Ln)에 포함되는 레이저 광(La)의 지축 방향(본 실시 형태에서는, X축 방향)의 평행화를 행한다. 지축 콜리메이터 렌즈(42)는, 제1 프리즘(PA1~PAN)과 제2 프리즘(PB1~PBK)과의 사이의 광축 상에 배치되며, 레이저 광속군(LAk)에 포함되는 레이저 광(La)의 지축 방향의 평행화를 행한다. 지축 콜리메이터 렌즈(43)는, 제2 프리즘(PB1~PBK)과 결상 광학계(18)와의 사이의 광축 상에 배치되며, 레이저 광속군(LBm)에 포함되는 레이저 광(La)의 지축 방향의 평행화를 행한다. The
이상의 구성을 구비하는 본 실시 형태의 레이저 장치(1A)에 의해서 얻어지는 효과에 대해 설명한다. 이 레이저 장치(1A)에서는, N개의 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(LS1~LSN)으로부터 출사된 레이저 광속(L1~LN)의 광축이 프리즘 광학계(10A)(제1 프리즘(PA1~PAN), 제2 프리즘(PB1~PBK))에 의해서 시프트되는 것에 의해, 레이저 광속(L1~LN)끼리의 간격이 축소된다. 이러한 프리즘 광학계(10A)가 마련되는 것에 의해, 복수의 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(LS1~LSN)끼리를 인접시킬 필요가 없게 되므로, 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(LS1~LSN)의 사이의 간극을 이용하여 냉각을 충분히 할 수 있고, 또 간소한 냉각 장치로 충분하기 때문에 냉각 장치의 대형화를 회피할 수 있다. 또, 프리즘 광학계(10A)와 같은 간이한 구성으로서 레이저 광속(L1~LN)을 모을 수 있으므로, 레이저 장치(1A)를 더 소형화할 수 있다. The effects obtained by the
또, 이 레이저 장치(1A)에 의하면, 프리즘 광학계(10A)를 이용하여 레이저 광속(L1~LN)을 전송하므로, 레이저 광속(L1~LN)을, 작은 스페이스에서, 저손실(예를 들면 수% 이하)로 장거리(예를 들면 1m 이상) 전송할 수 있다. 또, 임의의 위치 Q에서 균일성이 높은 공간 강도 분포를 가지고, 임의의 크기(예를 들면 1cm각(角))의 영역 내에 충분한 광 강도(예를 들면 수십 kW/cm2 이상)로 레이저 광속(L1~LN)을 수렴시킬 수 있다. In addition, according to this
또, 이 레이저 장치(1A)에서는, 결상 광학계(18)가, 각 레이저 광속(L1~LN)을 광속마다 집광하고, 결상 광학계(18)와 소정 위치 Q와의 사이에 각 레이저 광속(L1~LN)의 집광점(P1~PN)을 생기게 하고 있다. 이것에 의해, 소정 위치 Q에서의 레이저 광량의 균일성을 높일 수 있고, 예를 들면 소정 위치 Q에 설치되는 조사 대상물에 균일한 광 강도의 레이저 광속을 부여할 수 있다. 게다가, 이 레이저 장치(1A)에서는, 결상 광학계(18)가, 균일한 N개의 레이저 광속(L1~LN)을 소정 위치 Q에서 서로 겹치도록 광속마다 편향한다. 이것에 의해, 소정 위치 Q에서 균일한 N개의 레이저 광속(L1~LN)이 서로 겹치므로, 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(LS1~LSN) 중 어느 일부에 열화가 생겨, 하나의 레이저 광속(Ln)에 그 영향이 생겼다고 해도, 다른 레이저 광속에 의해서 레이저 광속군(LBm)의 광량의 균일성을 유지할 수 있다. Moreover, in this
예를 들면, 레이저 광원 장치가 고체 레이저 매질의 여기에 이용되는 경우, 여기광의 공간 패턴의 강도 변동은, 고체 레이저 매질의 출력 특성(에너지 안정성, 패턴의 균일성)에 크게 영향을 주고, 또, 광학 소자 등의 광 손상의 한 요인이 된다. 본 실시 형태의 레이저 장치(1A)에 의하면, 상술한 바와 같이 레이저 광속군(LBm)의 광량의 균일성을 유지할 수 있으므로, 고체 레이저 매질의 출력 특성을 안정시키고, 광학 소자 등의 광 손상을 저감하는 것이 가능해진다. For example, when a laser light source device is used for excitation of a solid laser medium, fluctuations in the intensity of the spatial pattern of the excitation light greatly affect the output characteristics (energy stability, pattern uniformity) of the solid laser medium, and It becomes a factor of optical damage to optical elements and the like. According to the
또, 이 레이저 장치(1A)에서는, 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(LS1~LSN)의 개수 N을 증감시키고 싶은 경우라도 대규모의 구조 변경을 필요로 하지 않고, 프리즘 광학계(10A)에 포함되는 제1 프리즘(PA1~PAN) 및 제2 프리즘(PB1~PBK), 및 결상 광학계(18)에 포함되는 결상 렌즈(F1~FN) 및 편향 광학 소자(D1~DN)의 개수를 증감하는 것만으로 된다. 따라서, 레이저 장치(1A)에 의하면, 조사 광량의 증감이 용이하고 확장성이 높은 레이저 장치(1A)를 제공할 수 있다. Further, in this
또, 본 실시 형태와 같이, N개의 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(LS1~LSN)이 적층 방향으로 늘어서 배치되어 있고, 프리즘 광학계(10A)가, 레이저 광속(L1~LN)의 광축을 적층 방향으로 시프트해도 괜찮다. 이러한 구성에 의해서, 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(LS1~LSN)의 적층 방향으로 적당한 간격을 두면서, N개의 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(LS1~LSN)을 배치할 수 있다. In addition, as in the present embodiment, N semiconductor laser array stacks LS 1 to LS N are arranged in a stacking direction, and the prism
또, 프리즘 광학계(10A)를 대신하여, 반사 미러를 이용하여 레이저 광속(L1~LN)을 시프트하는 것도 고려되어진다. 그렇지만, 반사 미러에서는, 레이저 광속의 입사각이 어떤 방향으로 변동하면 출사각이 반대의 방향으로 변동하므로, N개의 레이저 광속(L1~LN)의 광로의 어긋남이 크게 되어, 이들을 정밀도 좋게 늘어놓는 것이 어렵다고 하는 문제가 있다. 이것에 대해, 프리즘에서는, 레이저 광속의 입사각과 출사각은 동일 방향으로 변동하므로, N개의 레이저 광속(L1~LN)의 광로의 어긋남이 억제되고, N개의 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(LS1~LSN)을 설치할 때의 허용 오차를 크게 할 수 있다. Further, in place of the prism
(제2 실시 형태) (2nd embodiment)
도 3은, 제2 실시 형태에 관한 레이저 장치(1B)의 구성을 나타내는 평면도이다. 도 4는, 도 3에 나타내어진 레이저 장치(1B)를 Y축 방향으로부터 본 측면도이다. 도 5는, 도 3에 나타내어진 레이저 장치(1B)의 구성을 나타내는 사시도이다. 도 3~도 5에 나타내어지는 바와 같이, 본 실시 형태의 레이저 장치(1B)는, N개(N은 2 이상의 정수. 도면에서는 N=8인 경우를 예시)의 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(LS1~LSN)과, 프리즘 광학계(10B)와, 콜리메이터 렌즈 스택(16)과, 결상 광학계(18)를 구비하고 있다. 또, 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(LS1~LSN) 자체의 구성, 콜리메이터 렌즈 스택(16)의 배치 및 구성, 및 결상 광학계(18)의 구성은, 전술한 제1 실시 형태와 동일하기 때문에 상세한 설명을 생략한다. 3 is a plan view showing a configuration of a
N개의 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(LS1~LSN) 중, 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(LS1, LS3, …, LS2K-1)(단, K=N/2)은 제1 군(6a)을 구성하고 있고, 다른 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(LS2, LS4, …, LS2K)은 제2 군(6b)을 구성하고 있다. 제1 군(6a)과 제2 군(6b)은, 서로 소정 방향(X축 방향)으로 늘어서 배치되어 있다. 또, 제1 군(6a)에 포함되는 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(LS1, LS3, …, LS2K-1)은, Y축 방향으로 서로 간격을 두고 늘어서 배치되어 있다. 마찬가지로, 제2 군(6b)에 포함되는 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(LS2, LS4, …, LS2K)은, Y축 방향으로 서로 간격을 두고 늘어서 배치되어 있다. 게다가, X축 방향으로부터 보아, 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(LS1, LS3, …, LS2K-1)과 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(LS2, LS4, …, LS2K)이 교호(交互)가 되도록, 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(LS1~LSN)의 Y축 방향의 위치가 정해져 있다. Of the N semiconductor laser array stacks (LS 1 to LS N ), the semiconductor laser array stacks (LS 1 , LS 3 , …, LS 2K-1 ) (however, K=N/2) refers to the
프리즘 광학계(10B)는, 이들 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(LS1~LSN)에 일대일로 대응하여 마련된 N개의 프리즘(PC1~PCN)을 가진다. N개의 프리즘(PC1~PCN) 중, 프리즘(PC1, PC3, …, PC2K-1)은, 대응하는 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(LS1, LS3, …, LS2K-1)을 따라서 Y축 방향으로 늘어서 배치되어 있고, 프리즘(PC2, PC4, …, PC2K)은, 대응하는 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(LS2, LS4, …, LS2K)을 따라서 Y축 방향으로 늘어서 배치되어 있다. 또, 프리즘(PC1, PC3, …, PC2K-1)과 프리즘(PC2, PC4, …, PC2K)은, Y축 방향으로 교호로 늘어서 있다. The prism
제n 번째의 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(LSn)으로부터 출사된 레이저 광속(Ln)은, 콜리메이터 렌즈 스택(16)에 의해서 속축 방향의 평행화가 이루어진 후, 대응하는 제n 번째의 프리즘(PCn)의 광 입사면(25)(도 4를 참조)에 입사한다. 프리즘(PC1~PCN)은, 예를 들면 유리, 석영 등의 투명 재료로 이루어지는 프리즘으로서, 광 입사면(25) 및 광 출사면(26)(도 4를 참조)을 가진다. 본 실시 형태의 프리즘(PC1~PCN)은, XZ평면을 따른 단면이 평행사변형(예를 들면 능형) 등의 형상을 나타내며, 해당 평행사변형의 한 변이 광 입사면(25)으로 되어 있고, 해당 한 변과 평행한 다른 한 변이 광 출사면(26)으로 되어 있다. The laser beam L n emitted from the n-th semiconductor laser array stack LS n is parallelized in the speed axis direction by the
제n 번째의 프리즘(PCn)은, 광 입사면(25)에 입사한 레이저 광속(Ln)을 투과하여, 광 출사면(26)으로부터 출사한다. 광 입사면(25)은 YZ평면에 대해서 경사져 있고, 레이저 광속(Ln)이 광 입사면(25)에 입사할 때, 레이저 광속(Ln)은 광 출사 방향(Z축 방향)에 대해서 소정 각도만큼 굴절한다. 또, 광 출사면(26)은 광 입사면(25)에 대해서 평행이어서, 레이저 광속(Ln)이 광 출사면(26)으로부터 출사할 때, 레이저 광속(Ln)은 앞의 굴절과는 반대 방향으로 상기 소정 각도만큼 다시 굴절하고, 다시 광 출사 방향(Z축 방향)을 따라서 진행한다. 이와 같이, 프리즘(PCn)은, 레이저 광속(Ln)의 광축을, 해당 광축과 교차하는 방향(본 실시 형태에서는 X축 방향)으로 시프트한다. 환언하면, 프리즘(PCn)은, 광 출사면(26)으로부터 출사되는 레이저 광속(Ln)의 광축을, 광 입사면(25)에 입사하는 레이저 광속(Ln)의 광축에 대해 대략 평행하게 하면서, X축 방향으로 이동시킨다. The n-th prism PC n passes through the laser beam L n incident on the
또, 본 실시 형태에서는, 프리즘(PC1, PC3, …, PC2K-1)의 광 입사면(25)에 입사한 레이저 광속(L1, L3, …, L2K-1)은, Y축 방향으로부터 보아, 서로 이웃하는 레이저 광속(L2, L4, …, L2K)에 가까워지는 방향(예를 들면 X축 부(負)방향)으로 굴절하고, 또, 프리즘(PC2, PC4, …, PC2K)의 광 입사면(25)에 입사한 레이저 광속(L2, L4, …, L2K)은, Y축 방향으로부터 보아, 서로 이웃하는 레이저 광속(L1, L3, …, L2K-1)에 가까워지는 방향(예를 들면 X축 정(正)방향)으로 굴절한다. 이것에 의해, 이들 레이저 광속(L1, L2, …, L2K-1, L2K)이 광 출사면(26)으로부터 출사할 때에는, 레이저 광속(L1, L3, …, L2K-1)과 레이저 광속(L2, L4, …, L2K)과의 간격이 축소되어, 레이저 광속(L1, L2, …, L2K-1, L2K)으로 이루어지는 단일의 레이저 광속군(LC)이 형성된다. 이 레이저 광속군(LC)은, 원래의 광 출사 방향(Z축 방향)을 따라서 진행한다. 또, 본 실시 형태의 레이저 광속군(LC)을 구성하는 레이저 광속(L1, L2, …, L2K-1, L2K)은, 서로 인접하여 진행되지만, 서로 겹치지 않고, 예를 들면 1mm 정도의 간격을 가진다. In this embodiment, the prism (PC 1, PC 3, ... , PC 2K-1) the
본 실시 형태의 레이저 장치(1B)는, 지축 콜리메이터 렌즈(44, 45, 및 46)를 더 구비하고 있다. 지축 콜리메이터 렌즈(44)는 본 실시 형태에서의 제2 콜리메이트부이며, 지축 콜리메이터 렌즈(45)는 본 실시 형태에서의 제3 콜리메이트부이다. 지축 콜리메이터 렌즈(44)는, 콜리메이터 렌즈 스택(16)과 프리즘(PC1~PCN)과의 사이의 광축 상에 배치되고, 레이저 광속(Ln)에 포함되는 레이저 광(La)(도 2를 참조)의 지축 방향(본 실시 형태에서는, X축 방향)의 평행화를 행한다. 지축 콜리메이터 렌즈(45)는, 프리즘(PC1~PCN)과 결상 광학계(18)와의 사이의 광축 상에 배치되고, 레이저 광속군(LC)에 포함되는 레이저 광(La)의 지축 방향의 평행화를 행한다. 지축 콜리메이터 렌즈(46)는, 결상 광학계(18)와 집광점(P1~PN)과의 사이의 광축 상에 배치되고, 레이저 광속군(LC)에 포함되는 레이저 광(La)의 지축 방향의 평행화를 행한다. The
이상의 구성을 구비하는 본 실시 형태의 레이저 장치(1B)에서는, N개의 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(LS1~LSN)으로부터 출사된 레이저 광속(L1~LN)의 광축이 프리즘 광학계(10B)(프리즘(PC1~PCN))에 의해서 시프트되는 것에 의해, 레이저 광속(L1~LN)끼리의 간격이 축소된다. 이러한 프리즘 광학계(10B)가 마련되는 것에 의해, 복수의 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(LS1~LSN)끼리를 인접시킬 필요가 없게 되므로, 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(LS1~LSN)의 사이의 간극을 이용하여 냉각을 충분히 할 수 있고, 또 간소한 냉각 장치로 충분하기 때문에 냉각 장치의 대형화를 회피할 수 있다. 또, 프리즘 광학계(10B)와 같은 간이한 구성으로 레이저 광속(L1~LN)을 모을 수 있으므로, 레이저 장치(1B)를 더 소형화할 수 있다. In the
또, 이 레이저 장치(1B)는, 전술한 제1 실시 형태와 동일한 구성을 가지는 결상 광학계(18)를 구비하고 있다. 이것에 의해, 소정 위치 Q에서의 레이저 광량의 균일성을 높일 수 있고, 예를 들면 소정 위치 Q에 설치되는 조사 대상물에 균일한 광 강도의 레이저 광속을 부여할 수 있다. 또, 소정 위치 Q에서 균일한 N개의 레이저 광속(L1~LN)이 서로 겹치므로, 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(LS1~LSN) 중 어느 일부에 열화가 생겨, 하나의 레이저 광속(Ln)에 그 영향이 생겼다고 해도, 다른 레이저 광속에 의해서 레이저 광속군(LC)의 광량의 균일성을 유지할 수 있다. Moreover, this
(제3 실시 형태) (3rd embodiment)
도 6은, 제3 실시 형태에 관한 레이저 장치(1C)의 구성을 나타내는 평면도이다. 도 7은, 도 6에 나타내어진 레이저 장치(1C)를 Y축 방향으로부터 본 측면도이다. 도 8은, 레이저 장치(1C)의 구성을 나타내는 사시도이다. 또, 이해를 용이하게 하기 위해, 도 8에서는 레이저 광속의 도시를 생략하고 있다. 6 is a plan view showing a configuration of a
도 6~도 8에 나타내어지는 바와 같이, 본 실시 형태의 레이저 장치(1C)는, N개(N은 2 이상의 정수. 도면에서는 N=8인 경우를 예시)의 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(LS1~LSN)과, 프리즘 광학계(10C)과, 콜리메이터 렌즈 스택(16)과, 결상 광학계(18)를 구비하고 있다. 또, 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(LS1~LSN) 자체의 구성, 콜리메이터 렌즈 스택(16)의 배치 및 구성, 및 결상 광학계(18)의 구성은, 전술한 제1 실시 형태와 동일하기 때문에 상세한 설명을 생략한다. As shown in Figs. 6 to 8, the
N개의 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(LS1~LSN) 중, 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(LS1~LSJ)(단, J는 2개 이상 (N-1) 미만의 정수. 도면에서는 J=4인 경우를 예시)은, 제1 군(6c)을 구성하고 있다. 또, 다른 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(LSJ+1~LSn)은, 제2 군(6d)을 구성하고 있다. 제1 군(6c)과 제2 군(6d)은, 서로 소정 방향(X축 방향)으로 늘어서 배치되어 있다. 또, 제1 군(6c)에 포함되는 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(LS1~LSJ)은, Y축 방향으로 서로 간격을 두고 늘어서 배치되어 있다. 마찬가지로, 제2 군(6d)에 포함되는 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(LSJ+1~LSn)은, Y축 방향으로 서로 간격을 두고 늘어서 배치되어 있다. Of the N semiconductor laser array stacks (LS 1 to LS N ), the semiconductor laser array stacks (LS 1 to LS J ) (wherein J is an integer of 2 or more and less than (N-1). In the drawing, when J=4 Exemplarily) constitutes the
프리즘 광학계(10C)는, 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(LS1~LSN)에 일대일로 대응하여 마련된 N개의 제1 프리즘(PA1~PAN)과, 제2 프리즘(PB1~PBK)(단, K=N/2)과, 제3 프리즘(PD1~PDM)(단, M=N/4)을 가진다. N개의 제1 프리즘(PA1~PAN) 중, 제1 프리즘(PA1~PAJ)은 대응하는 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(LS1~LSJ)을 따라서 Y축 방향으로 늘어서 배치되어 있고, 제1 프리즘(PAJ+1~PAN)은, 대응하는 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(LSJ+1~LSn)을 따라서 Y축 방향으로 늘어서 배치되어 있다. 또, 제1 프리즘(PA1~PAJ)으로 이루어지는 프리즘열과, 제1 프리즘(PAJ+1~PAN)으로 이루어지는 프리즘열은, 서로 X축 방향으로 늘어서 배치되어 있다. The prism
제1 프리즘(PA1~PAN)은, 제1 실시 형태의 제1 프리즘(PA1~PAN)과 동일한 구성을 가진다. 즉, 제1 프리즘(PA1~PAN)은, 광 입사면(21) 및 광 출사면(22)을 가지는 평행사변형 모양을 나타내고 있고, 제n 번째의 제1 프리즘(PAn)은, 레이저 광속(Ln)의 광축을, 해당 광축과 교차하는 방향(본 실시 형태에서는 Y축 방향)으로 시프트한다. 또, (2k-1)번째의 제1 프리즘(PA2k-1)과, 2k번째의 제1 프리즘(PA2k)이 Y축 방향에서 서로 인접하여 배치되어 있고, 제1 프리즘(PA2k-1)의 광 입사면(21)에 입사한 레이저 광속(L2k-1)은, 서로 이웃하는 레이저 광속(L2k)에 가까워지는 방향으로 굴절하고, 또, 제1 프리즘(PA2k)의 광 입사면(21)에 입사한 레이저 광속(L2k)은, 서로 이웃하는 레이저 광속(L2k-1)에 가까워지는 방향으로 굴절한다. 이것에 의해, 이들 레이저 광속(L2k-1, L2k)이 광 출사면(22)으로부터 출사할 때에는, 레이저 광속(L2k-1, L2k)끼리의 간격이 축소되고, 한 쌍의 광속(L2k-1, L2k)으로 이루어지는 레이저 광속군(LAk)이 형성된다. 이 레이저 광속군(LAk)은, 원래의 광 출사 방향(Z축 방향)을 따라서 진행한다. The first prisms PA 1 to PA N have the same configuration as the first prisms PA 1 to PA N of the first embodiment. That is, the first prisms PA 1 to PA N have a parallelogram shape having a
제2 프리즘(PB1~PBK)도 또, 제1 실시 형태의 제2 프리즘(PB1~PBK)과 동일한 구성을 가진다. 즉, 제2 프리즘(PB1~PBK)은, 광 입사면(23) 및 광 출사면(24)을 가지는 평행사변형 모양을 나타내고 있고, 제k 번째의 제2 프리즘(PBk)은, 레이저 광속군(LAk)의 광축을, 해당 광축과 교차하는 방향(본 실시 형태에서는 Y축 방향)으로 시프트한다. 또, (2m-1)번째의 제2 프리즘(PB2m-1)과, 2m번째의 제2 프리즘(PB2m)이 Y축 방향에서 서로 인접하여 배치되어 있고, 제2 프리즘(PB2m-1)의 광 입사면(23)에 입사한 레이저 광속군(LA2m-1)은, 서로 이웃하는 레이저 광속군(LA2m)에 가까워지는 방향으로 굴절하고, 또, 제2 프리즘(PB2m)의 광 입사면(23)에 입사한 레이저 광속군(LA2m)은, 서로 이웃하는 레이저 광속군(LA2m-1)에 가까워지는 방향으로 굴절한다. 이것에 의해, 이들 레이저 광속군(LA2m-1, LA2m)이 광 출사면(24)으로부터 출사할 때에는, 레이저 광속군(LA2m-1, LA2m)끼리의 간격이 축소되어, 한 쌍의 레이저 광속군(LA2m-1, LA2m)으로 이루어지는 레이저 광속군(LBm)이 형성된다. 이 레이저 광속군(LBm)은, 원래의 광 출사 방향(Z축 방향)을 따라서 진행한다. The second prisms PB 1 to PB K also have the same configuration as the second prisms PB 1 to PB K of the first embodiment. That is, the second prism (PB 1 to PB K ) has a parallelogram shape having a
제3 프리즘(PD1~PDM)은, 예를 들면 유리, 석영 등의 투명 재료로 이루어지는 프리즘으로서, 광 입사면(27) 및 광 출사면(28)을 가진다. 본 실시 형태의 제3 프리즘(PD1~PDM)은, XZ평면을 따른 단면에서 평행사변형(예를 들면 능형) 등의 형상을 나타내며, 해당 평행사변형의 한 변이 광 입사면(27)으로 되어 있고, 해당 한 변과 평행한 다른 한 변이 광 출사면(28)으로 되어 있다. The third prisms PD 1 to PD M are prisms made of, for example, a transparent material such as glass and quartz, and have a light incident surface 27 and a light exit surface 28. The third prism (PD 1 to PD M ) of this embodiment exhibits a shape such as a parallelogram (e.g., a rhomboid shape) in a cross section along the XZ plane, and one side of the parallelogram becomes the light incident surface 27. And the other side parallel to the one side is the light exit surface 28.
제2 프리즘(PB2m-1, PB2m)으로부터 출사된 레이저 광속군(LBm)은, 제m 번째의 제3 프리즘(PDm)의 광 입사면(27)에 입사한다. 제3 프리즘(PDm)은, 광 입사면(27)에 입사한 레이저 광속군(LBm)을 투과하여, 광 출사면(28)으로부터 출사한다. 광 입사면(27)은 YZ평면에 대해서 경사져 있어, 레이저 광속군(LBm)이 광 입사면(27)에 입사할 때, 레이저 광속군(LBm)은 광 출사 방향(Z축 방향)에 대해서 상기 각도만큼 굴절한다. 또, 광 출사면(28)은 광 입사면(27)에 대해서 평행이어서, 레이저 광속군(LBm)이 광 출사면(28)으로부터 출사할 때, 레이저 광속군(LBm)은 앞의 굴절과는 반대 방향으로 상기 각도만큼 다시 굴절하고, 다시 광 출사 방향(Z축 방향)을 따라서 진행한다. 이와 같이, 제3 프리즘(PDm)은, 레이저 광속군(LBm)의 광축을, 해당 광축과 교차하는 방향(본 실시 형태에서는 X축 방향)으로 시프트한다. 환언하면, 제3 프리즘(PDm)은, 광 출사면(28)으로부터 출사되는 레이저 광속군(LBm)의 광축을, 광 입사면(27)에 입사하는 레이저 광속군(LBm)의 광축에 대해 대략 평행하게 하면서, X축 방향으로 이동시킨다. The laser beam group LB m emitted from the second prism PB 2m-1 and PB 2m enters the light incident surface 27 of the m-th third prism PD m . The third prism PD m passes through the laser beam group LB m incident on the light incidence surface 27, and is emitted from the light exit surface 28. The light incident surface 27 is inclined with respect to the YZ plane, and when the laser beam group LB m enters the light incident surface 27, the laser beam group LB m is in the light exit direction (Z axis direction). Is refracted by the above angle. In addition, the light exit surface 28 is parallel to the light incidence surface 27, so when the laser beam group LB m is emitted from the light exit surface 28, the laser beam group LB m is refracted from the front. Refracts again by the angle in the opposite direction to and proceeds again along the light exit direction (Z-axis direction). In this way, the third prism PD m shifts the optical axis of the laser beam group LB m in the direction intersecting the optical axis (in the present embodiment, the X-axis direction). In other words, the optical axis of the third prism (PD m), a laser beam group (LB m) that enters the optical axis of the laser beam groups (LB m) which is emitted from the light exit surface 28, to the light input surface 27 It moves in the X-axis direction while making it approximately parallel to.
또, 본 실시 형태에서는, (2i-1)번째(단, i는 1 이상 I 이하의 정수. I=N/8)의 제3 프리즘(PD2i-1)에 입사한 레이저 광속군(LB2i-1)은, 서로 이웃하는 레이저 광속군(LB2i)에 가까워지는 방향(예를 들면 X축 부방향)으로 굴절하고, (2i)번째의 제3 프리즘(PD2i)에 입사한 레이저 광속군(LB2i)은, 서로 이웃하는 레이저 광속군(LB2i-1)에 가까워지는 방향(예를 들면 X축 정방향)으로 굴절한다. 이것에 의해, 이들 레이저 광속군(LBm)이 광 출사면(28)으로부터 출사할 때에는, 레이저 광속군(LB2i-1)과 레이저 광속군(LB2i)과의 간격이 축소되어, 레이저 광속군(LB1~LBM)으로 이루어지는 단일의 레이저 광속군(LD)이 형성된다. In addition, in this embodiment, the laser beam group LB 2i incident on the third prism PD 2i-1 of the (2i-1)th (where i is an integer of 1 or more and I or less. I = N/8) -1 ) is a group of laser beams that are refracted in a direction closer to each other adjacent laser beam groups (LB 2i ) (for example, in the negative X-axis direction) and incident on the third prism (PD 2i ) of the (2i)-th (LB 2i ) refracts in a direction closer to each other adjacent laser beam group LB 2i-1 (for example, the X-axis positive direction). Thereby, when these laser beam groups LB m are emitted from the light exit surface 28, the distance between the laser beam group LB 2i-1 and the laser beam group LB 2i is reduced, and the laser beam beam A single laser beam group LD made of groups LB 1 to LB M is formed.
또, 본 실시 형태에서는, 제3 프리즘(PD1~PDM)이 결상 광학계(18)와 집광 위치(P1~PN)와의 사이에 배치되어 있지만, 제3 프리즘(PD1~PDM)은 제2 프리즘(PB1~PBK)과 결상 광학계(18)와의 사이에 배치되어도 괜찮다. Further, in the present embodiment, the third prism (PD 1 to PD M ) is disposed between the imaging
이상의 구성을 구비하는 본 실시 형태의 레이저 장치(1C)에서는, N개의 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(LS1~LSN)으로부터 출사된 레이저 광속(L1~LN)의 광축이 프리즘 광학계(10C)(제1 프리즘(PA1~PAN), 제2 프리즘(PB1~PBK), 제3 프리즘(PD1~PDM))에 의해서 시프트되는 것에 의해, 레이저 광속(L1~LN)끼리의 간격이 축소된다. 이러한 프리즘 광학계(10C)가 마련되는 것에 의해, 복수의 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(LS1~LSN)끼리를 인접시킬 필요가 없게 되므로, 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(LS1~LSN) 사이의 간극을 이용하여 냉각을 충분히 할 수 있고, 또 간소한 냉각 장치로 충분하기 때문에 냉각 장치의 대형화를 회피할 수 있다. 또, 프리즘 광학계(10C)와 같은 간이한 구성으로서 레이저 광속(L1~LN)을 모을 수 있으므로, 레이저 장치(1C)를 더 소형화할 수 있다. In the
또, 이 레이저 장치(1C)는, 전술한 제1 실시 형태와 동일한 구성을 가지는 결상 광학계(18)를 구비하고 있다. 이것에 의해, 소정 위치 Q에서의 레이저 광량의 균일성을 높일 수 있고, 예를 들면 소정 위치 Q에 설치되는 조사 대상물에 균일한 광 강도의 레이저 광속을 부여할 수 있다. 또, 소정 위치 Q에서 균일한 N개의 레이저 광속(L1~LN)이 서로 겹치므로, 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택(LS1~LSN) 중 어느 일부에 열화가 생겨, 하나의 레이저 광속(Ln)에 그 영향이 생겼다고 해도, 다른 레이저 광속에 의해서 레이저 광속군(LD)의 광량의 균일성을 유지할 수 있다. Moreover, this
본 발명의 일측면에 관한 레이저 장치는, 상술한 실시 형태에 한정되는 것이 아니고, 이외에 여러가지 변형이 가능하다. 예를 들면, 제1 실시 형태에서는 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택의 개수 N이 4인 경우를 나타내고, 제2 실시 형태 및 제3 실시 형태에서는 개수 N이 8인 경우를 나타냈지만, 본 발명의 일측면에 관한 레이저 장치에서는, 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택의 개수에 제한은 없고, 임의의 개수의 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택을 조합시킬 수 있다. The laser device according to one aspect of the present invention is not limited to the above-described embodiment, and various modifications are possible. For example, in the first embodiment, a case where the number N of the semiconductor laser array stack is 4 is shown, and in the second embodiment and the third embodiment, a case where the number N is 8 is shown, but in relation to one aspect of the present invention In the laser device, the number of semiconductor laser array stacks is not limited, and any number of semiconductor laser array stacks can be combined.
[산업상의 이용 가능성][Industrial availability]
본 발명의 일측면에 관한 레이저 장치에 의하면, 복수의 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택끼리를 인접시킬 필요가 없고, 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택의 일부에 열화가 생긴 경우라도 조사 대상물에서의 레이저 광량의 균일성을 유지할 수 있다. According to the laser device according to one aspect of the present invention, it is not necessary to make a plurality of semiconductor laser array stacks adjacent to each other, and even when deterioration occurs in a part of the semiconductor laser array stack, the uniformity of the laser light quantity in the irradiated object can be maintained. have.
1A, 1B, 1C - 레이저 장치 10A, 10B, 10C - 프리즘 광학계
12 - 반도체 레이저 어레이 14 - 발광 영역
16 - 콜리메이터 렌즈 스택 18 - 결상 광학계
21, 23, 25, 27 - 광 입사면 22, 24, 26, 28 - 광 출사면
41~46 - 지축 콜리메이터 렌즈 D1~DN - 편향 광학 소자
F1~FN - 결상 렌즈 L1~LN - 레이저 광속
La - 레이저 광 LA1~LAK - 레이저 광속군
LB1~LBM - 레이저 광속군 LC - 레이저 광속군
LD - 레이저 광속군
LS1~LSN - 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택
P1~PN - 집광점 PA1~PAN - 제1 프리즘
PB1~PBK - 제2 프리즘 PC1~PCN - 프리즘
PD1~PDM - 제3 프리즘 Q - 소정 위치1A, 1B, 1C-
12-Semiconductor laser array 14-Light emitting area
16-collimator lens stack 18-imaging optics
21, 23, 25, 27-
41~46-axis collimator lens D 1 ~D N -deflection optical element
F 1 to F N -imaging lens L 1 to L N -laser beam
La-laser light LA 1 ~LA K -laser beam group
LB 1 ~LB M -laser beam group LC-laser beam group
LD-laser beam group
LS 1 to LS N -semiconductor laser array stack
P 1 ~P N -Condensing point PA 1 ~PA N -1st prism
PB 1 ~PB K -2nd prism PC 1 ~PC N -Prism
PD 1 ~PD M -3rd prism Q-predetermined position
Claims (4)
상기 광속에 포함되는 상기 레이저 광의 속축(速軸) 방향의 평행화를 행하는 제1 콜리메이트부와,
상기 N개의 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택 각각으로부터 출력되어 상기 제1 콜리메이트부를 거친 상기 광속을 투과함과 아울러, 해당 광속의 광축을 해당 광축과 교차하는 방향으로 시프트하는 것에 의해 상기 광속끼리의 간격을 축소하는 프리즘 광학계와,
상기 N개의 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택 각각으로부터 출력된 각 광속을, 지축(遲軸) 방향과 교차하는 면내에서 광속마다 집광(集光)하는 N개의 결상 렌즈, 및 해당 면내에서 각 광속의 광축을 광속마다 편향하는 N개의 편향 광학 소자를 포함하는 결상(結像) 광학계를 구비하며,
상기 N개의 편향 광학 소자는, 소정 위치에서 N개의 상기 광속이 서로 겹치도록 각 광속을 편향하고,
상기 N개의 결상 렌즈는, 상기 결상 광학계와 상기 소정 위치와의 사이에 각 광속의 집광점을 생기게 하는, 레이저 장치.A plurality of semiconductor laser arrays that emit laser light from two or more light emitting regions arranged in a predetermined direction are stacked in the predetermined direction and in a stacking direction crossing the emission direction by matching the emission direction, and the plurality of semiconductor lasers A semiconductor laser array stack of N (N is an integer of 2 or more) each outputting the laser light emitted from the array as one beam of light,
A first collimating portion which parallelizes the laser beam included in the beam in a direction of a fast axis;
It transmits the light beam output from each of the N semiconductor laser array stacks and passes through the first collimating part, and reduces the interval between the light beams by shifting the optical axis of the light beam in a direction crossing the optical axis. With a prism optical system,
N imaging lenses that focus each light flux outputted from each of the N semiconductor laser array stacks for each light flux in a plane intersecting the support axis direction, and an optical axis of each light flux in the plane for each light flux It has an imaging optical system including N deflection optical elements to deflect,
The N deflection optical elements deflect each light beam so that the N light beams overlap each other at a predetermined position,
The N imaging lenses, the laser device for generating a condensing point of each light beam between the imaging optical system and the predetermined position.
상기 N개의 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택이 상기 적층 방향으로 늘어서 배치되어 있고,
상기 프리즘 광학계가, 상기 광속의 광축을 상기 적층 방향으로 시프트하는, 레이저 장치.The method according to claim 1,
The N semiconductor laser array stacks are arranged in a row in the stacking direction,
The laser device, wherein the prism optical system shifts the optical axis of the light beam in the lamination direction.
하나 또는 복수의 상기 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택을 포함하는 제1 군(群)과, 하나 또는 복수의 상기 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택을 포함하는 제2 군이 상기 소정 방향으로 늘어서 배치되어 있으며,
상기 프리즘 광학계는, 상기 제1 군에 포함되는 상기 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택으로부터 출사되는 상기 광속과, 상기 제2 군에 포함되는 상기 반도체 레이저 어레이 스택으로부터 출사되는 상기 광속과의 간격이 축소하도록, 상기 소정 방향으로 해당 광속의 광축을 시프트하는, 레이저 장치.The method according to claim 1,
A first group including one or more of the semiconductor laser array stacks and a second group including one or more of the semiconductor laser array stacks are arranged in the predetermined direction,
The prism optical system may be configured such that an interval between the light flux emitted from the semiconductor laser array stack included in the first group and the light flux emitted from the semiconductor laser array stack included in the second group is reduced. A laser device that shifts the optical axis of the light flux in the direction.
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013139993A JP6285650B2 (en) | 2013-07-03 | 2013-07-03 | Laser equipment |
| JPJP-P-2013-139993 | 2013-07-03 | ||
| PCT/JP2014/063720 WO2015001866A1 (en) | 2013-07-03 | 2014-05-23 | Laser device |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20160026988A KR20160026988A (en) | 2016-03-09 |
| KR102181434B1 true KR102181434B1 (en) | 2020-11-23 |
Family
ID=52143459
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020167000913A KR102181434B1 (en) | 2013-07-03 | 2014-05-23 | Laser device |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US10133079B2 (en) |
| EP (1) | EP3018776B1 (en) |
| JP (1) | JP6285650B2 (en) |
| KR (1) | KR102181434B1 (en) |
| CN (1) | CN105340140B (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2015001866A1 (en) |
Families Citing this family (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6761600B2 (en) * | 2017-01-05 | 2020-09-30 | 大日本印刷株式会社 | Lighting device |
| JP6536724B1 (en) * | 2018-07-04 | 2019-07-03 | ウシオ電機株式会社 | Light source device, projector |
| US10795172B1 (en) * | 2018-09-20 | 2020-10-06 | Casey LEWIS | Apparatus and method of combining multiple laser beams using a negative focal length radial gradient index rod lens |
| CN109581326B (en) * | 2018-11-16 | 2021-05-07 | 上海禾赛科技股份有限公司 | Optical device fixing structure for laser radar |
| CN109375337B (en) * | 2018-11-16 | 2021-10-08 | 上海禾赛科技有限公司 | Prism fixed knot constructs |
| CN113165115B (en) * | 2018-12-06 | 2023-07-18 | 新唐科技日本株式会社 | Light source unit, illumination device, processing device, and deflection element |
| JP7428140B2 (en) * | 2018-12-13 | 2024-02-06 | ソニーグループ株式会社 | Optical connectors, optical cables and electronic equipment |
| CN111722459B (en) * | 2019-03-19 | 2022-08-26 | 青岛海信激光显示股份有限公司 | Laser device assembly, laser light source and laser projection equipment |
| CN114296089B (en) * | 2022-03-03 | 2022-06-14 | 深圳市海创光学有限公司 | Optical system and laser radar |
| CN115128894B (en) * | 2022-07-29 | 2023-09-26 | 青岛海信激光显示股份有限公司 | Projection light source and projection device |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004096092A (en) * | 2002-07-10 | 2004-03-25 | Nippon Steel Corp | Semiconductor laser device and solid state laser device using the same |
| JP2008021900A (en) * | 2006-07-14 | 2008-01-31 | Jtekt Corp | Laser condensing device |
Family Cites Families (22)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS60108802A (en) * | 1983-11-18 | 1985-06-14 | Fuji Photo Film Co Ltd | Method and device for optical beam synthesis |
| DE4220705C2 (en) * | 1992-06-24 | 2003-03-13 | Lambda Physik Ag | Device for splitting a light beam into homogeneous partial beams |
| DE19915000C2 (en) * | 1999-04-01 | 2002-05-08 | Microlas Lasersystem Gmbh | Device and method for controlling the intensity distribution of a laser beam |
| JP4347467B2 (en) * | 1999-10-06 | 2009-10-21 | 浜松ホトニクス株式会社 | Concentrator |
| JP2002148562A (en) * | 2000-11-14 | 2002-05-22 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Semiconductor laser machining device |
| JP4059623B2 (en) * | 2000-12-15 | 2008-03-12 | 株式会社リコー | Illumination device and uniform illumination device |
| CN1313861C (en) | 2001-03-30 | 2007-05-02 | 新日本制铁株式会社 | Semiconductor laser device and solid laser device using same |
| JP2003103389A (en) * | 2001-09-27 | 2003-04-08 | Toyoda Mach Works Ltd | Converging device for semiconductor laser beam |
| FI116010B (en) * | 2002-05-22 | 2005-08-31 | Cavitar Oy | Method and laser device for producing high optical power density |
| US6993059B2 (en) * | 2003-06-11 | 2006-01-31 | Coherent, Inc. | Apparatus for reducing spacing of beams delivered by stacked diode-laser bars |
| US7230968B2 (en) | 2003-07-10 | 2007-06-12 | Nippon Steel Corporation | Semiconductor laser device and solid-state laser device using same |
| JP2005051135A (en) | 2003-07-31 | 2005-02-24 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Method for manufacturing semiconductor device |
| US7680170B2 (en) * | 2006-06-15 | 2010-03-16 | Oclaro Photonics, Inc. | Coupling devices and methods for stacked laser emitter arrays |
| JP5082316B2 (en) * | 2006-07-19 | 2012-11-28 | 株式会社ジェイテクト | Condensing block |
| US7639722B1 (en) * | 2007-10-29 | 2009-12-29 | The United States Of America As Represented By The Secretary Of The Air Force | Multifaceted prism to cause the overlap of beams from a stack of diode laser bars |
| US8804246B2 (en) * | 2008-05-08 | 2014-08-12 | Ii-Vi Laser Enterprise Gmbh | High brightness diode output methods and devices |
| JP5894529B2 (en) * | 2009-08-20 | 2016-03-30 | コーニンクレッカ フィリップス エヌ ヴェKoninklijke Philips N.V. | Laser device with brightness distribution that can be changed |
| WO2011109760A2 (en) * | 2010-03-05 | 2011-09-09 | TeraDiode, Inc. | Wavelength beam combining system and method |
| WO2011109763A2 (en) * | 2010-03-05 | 2011-09-09 | TeraDiode, Inc. | Selective repositioning and rotation wavelength beam combining system and method |
| US8602592B2 (en) * | 2011-04-07 | 2013-12-10 | Coherent, Inc. | Diode-laser illuminator with interchangeable modules for changing irradiance and beam dimensions |
| CN102722027B (en) | 2012-01-16 | 2014-10-01 | 深圳市光峰光电技术有限公司 | Light shaping apparatus and laser light source |
| CN202720390U (en) * | 2012-02-29 | 2013-02-06 | 南通傲迈光电科技有限公司 | Beam shaping structure of array semiconductor laser |
-
2013
- 2013-07-03 JP JP2013139993A patent/JP6285650B2/en active Active
-
2014
- 2014-05-23 EP EP14819679.3A patent/EP3018776B1/en active Active
- 2014-05-23 US US14/900,288 patent/US10133079B2/en active Active
- 2014-05-23 KR KR1020167000913A patent/KR102181434B1/en active IP Right Grant
- 2014-05-23 CN CN201480036662.2A patent/CN105340140B/en active Active
- 2014-05-23 WO PCT/JP2014/063720 patent/WO2015001866A1/en active Application Filing
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004096092A (en) * | 2002-07-10 | 2004-03-25 | Nippon Steel Corp | Semiconductor laser device and solid state laser device using the same |
| JP2008021900A (en) * | 2006-07-14 | 2008-01-31 | Jtekt Corp | Laser condensing device |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN105340140B (en) | 2019-04-30 |
| US10133079B2 (en) | 2018-11-20 |
| JP6285650B2 (en) | 2018-02-28 |
| JP2015015305A (en) | 2015-01-22 |
| EP3018776A4 (en) | 2017-05-03 |
| EP3018776A1 (en) | 2016-05-11 |
| KR20160026988A (en) | 2016-03-09 |
| CN105340140A (en) | 2016-02-17 |
| WO2015001866A1 (en) | 2015-01-08 |
| US20160370593A1 (en) | 2016-12-22 |
| EP3018776B1 (en) | 2019-05-22 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR102181434B1 (en) | Laser device | |
| US6700709B1 (en) | Configuration of and method for optical beam shaping of diode laser bars | |
| US7668214B2 (en) | Light source | |
| US7079566B2 (en) | Semiconductor laser apparatus capable of routing laser beams emitted from stacked-array laser diode to optical fiber with little loss | |
| KR101676499B1 (en) | Device and method for beam forming | |
| US7881355B2 (en) | System and method for generating intense laser light from laser diode arrays | |
| US6778732B1 (en) | Generation of high-power, high brightness optical beams by optical cutting and beam-shaping of diode lasers | |
| US7110183B2 (en) | Device for the optical beam transformation of a linear arrangement of several light sources | |
| US5877898A (en) | Arrangement for combining and shaping the radiation of a plurality of laser diode lines | |
| JP6157194B2 (en) | Laser apparatus and light beam wavelength coupling method | |
| US8842369B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for combining light sources | |
| US20050264893A1 (en) | Laser diode bar integrator/reimager | |
| CA2368958A1 (en) | Optical arrangement for symmetrizing the radiation of two-dimensional arrays of laser diodes | |
| US7773653B2 (en) | Diode laser arrangement and associated beam shaping unit | |
| CN102208753A (en) | External cavity semiconductor laser with multi-wavelength combination | |
| CN109073908B (en) | Parallel light generating device | |
| CN104678557B (en) | Wavelength stabilizing beam combiner | |
| US9513483B2 (en) | Beam shaper system for laser diode array | |
| JP2000098191A (en) | Semiconductor laser beam source device | |
| JP2011085916A (en) | Multibeam deflector, two dimensional scanner, and multibeam deflector module | |
| US7260131B2 (en) | Symmetrization device and laser diode system provided with the same | |
| US20190013650A1 (en) | Multiplexed laser light source | |
| US20170292679A1 (en) | Light-emitting device | |
| CA2492617C (en) | Symmetrization device and laser diode system provided with the same | |
| KR20220027876A (en) | Conversion device for laser radiation |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A201 | Request for examination | ||
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right | ||
| GRNT | Written decision to grant |