KR102103307B1 - AGM battery manufacturing method using electrolytic solution containing colloidal silica in a container formation process and AGM battery - Google Patents
AGM battery manufacturing method using electrolytic solution containing colloidal silica in a container formation process and AGM battery Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR102103307B1 KR102103307B1 KR1020180126015A KR20180126015A KR102103307B1 KR 102103307 B1 KR102103307 B1 KR 102103307B1 KR 1020180126015 A KR1020180126015 A KR 1020180126015A KR 20180126015 A KR20180126015 A KR 20180126015A KR 102103307 B1 KR102103307 B1 KR 102103307B1
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- electrolyte
- silica
- agm battery
- electrolytic solution
- colloidal silica
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M10/00—Secondary cells; Manufacture thereof
- H01M10/06—Lead-acid accumulators
- H01M10/12—Construction or manufacture
- H01M10/128—Processes for forming or storing electrodes in the battery container
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M10/00—Secondary cells; Manufacture thereof
- H01M10/06—Lead-acid accumulators
- H01M10/08—Selection of materials as electrolytes
- H01M10/10—Immobilising of electrolyte
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M10/00—Secondary cells; Manufacture thereof
- H01M10/42—Methods or arrangements for servicing or maintenance of secondary cells or secondary half-cells
- H01M10/4235—Safety or regulating additives or arrangements in electrodes, separators or electrolyte
-
- H01M2/1613—
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M50/00—Constructional details or processes of manufacture of the non-active parts of electrochemical cells other than fuel cells, e.g. hybrid cells
- H01M50/40—Separators; Membranes; Diaphragms; Spacing elements inside cells
- H01M50/409—Separators, membranes or diaphragms characterised by the material
- H01M50/431—Inorganic material
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M2300/00—Electrolytes
- H01M2300/0085—Immobilising or gelification of electrolyte
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02E—REDUCTION OF GREENHOUSE GAS [GHG] EMISSIONS, RELATED TO ENERGY GENERATION, TRANSMISSION OR DISTRIBUTION
- Y02E60/00—Enabling technologies; Technologies with a potential or indirect contribution to GHG emissions mitigation
- Y02E60/10—Energy storage using batteries
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02P—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES IN THE PRODUCTION OR PROCESSING OF GOODS
- Y02P70/00—Climate change mitigation technologies in the production process for final industrial or consumer products
- Y02P70/50—Manufacturing or production processes characterised by the final manufactured product
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Electrochemistry (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Inorganic Chemistry (AREA)
- Secondary Cells (AREA)
- Filling, Topping-Up Batteries (AREA)
Abstract
Description
본 발명은 컨테이너 포메이션 공정에서의 콜로이다 실리카가 포함된 전해액을 적용한 AGM 배터리 제조 방법 및 AGM 배터리에 관한 것으로서, 더욱 상세하게는 Gel화 되지 않는 수준으로 Silica 함량을 조절하고, 전해액 주액기에 Gel화된 전해액이 잔존하지 않도록 전해액 주액기와 Silica 첨가 설비인 디스펜서 펌프를 분리하여 전해액 주액 후에 Silica를 AGM 배터리에 첨가하는 컨테이너 포메이션 공정에서의 콜로이다 실리카가 포함된 전해액을 적용한 AGM 배터리 제조 방법 및 AGM 배터리에 관한 것이다.The present invention relates to an AGM battery manufacturing method and an AGM battery to which an electrolytic solution containing colloidal silica is applied in a container formation process, and more specifically, to control the Silica content to a level that does not gel, and gelled into an electrolyte injector. Colloidal in a container formation process that separates the electrolyte injector and the dispenser pump, which is a silica addition facility, so that the electrolyte does not remain, and then adds the silica to the AGM battery after the electrolyte injection, to the AGM battery manufacturing method and the AGM battery using an electrolyte containing silica. It is about.
일반적으로 자동차 등에 사용되는 납축전지는 충전과 방전이 가능한 2차 전지이다. In general, lead acid batteries used in automobiles and the like are secondary batteries capable of charging and discharging.
납축전지의 기판은 활물질을 지지할 뿐 아니라, 전류의 이동 통로 역할도 같이 한다. The substrate of the lead acid battery not only supports the active material, but also serves as a passage for electric current.
이 중에서 에이지엠 배터리(AGM battery)는 유리섬유매트(Absorptive Glass Mat)에 전해액을 흡수시켜 전해액 유동을 방지한 배터리로서 익스펜디드공법으로 제작된 기판이 사용된다.Among them, the AGM battery is a battery that absorbs an electrolyte solution in an absorptive glass mat and prevents the flow of the electrolyte solution, and a substrate manufactured by an expanded method is used.
특히, 납축전지 중 본 발명과 관련된 AGM 배터리를 고전압 환경에서 과충전이 진행될 경우, 배터리 내의 전해액 감소가 빠르게 일어나며, 특히 AGM 배터리는 셀 안의 전해액 량이 적기 때문에 과충전을 방지하여 전해액을 유지하는 것이 내구성 향상에 중요한 요인이다. Particularly, when the overcharging of the AGM battery related to the present invention among the lead-acid batteries proceeds in a high voltage environment, the electrolyte decreases rapidly in the battery, and in particular, the AGM battery has a small amount of electrolyte in the cell, thus preventing overcharging to maintain the electrolyte to improve durability. It is an important factor.
전해액에 Silica가 첨가되면 과충전을 억제하는데 도움이 되나, Container Formation 공정에서 Silica를 첨가하여 AGM 배터리를 제조할 경우, 화성 중 전해액 Gel화로 인해 격리판 외부에 고형화되어 AGM 격리판 내부에 함습되는 전해액이 부족하게 된다. When Silica is added to the electrolyte solution, it helps to suppress overcharging.However, in the case of manufacturing AGM battery by adding Silica in the Container Formation process, the electrolyte solution solidified outside the separator due to gelation of the electrolyte during chemical conversion and wetted inside the AGM separator Will run out.
또한, 주액 전에 전해액과 Silica를 혼합하면 주액 설비에 Gel화된 전해액이 조금씩 잔존하게 되어 설비 부품 교환 주기가 빨라지게 된다.In addition, when the electrolyte and Silica are mixed before the injection, the gelated electrolyte remains in the injection equipment little by little, thereby speeding up the replacement cycle of equipment parts.
따라서, 화성 중 전해액 Gel화로 인해 격리판 외부에 고형화되어 AGM 격리판 내부에 함습되는 전해액이 부족하게 되는 현상을 방지할 수 있으며, 주액 전에 전해액과 Silica를 혼합하면 주액 설비에 Gel화된 전해액이 조금씩 잔존하게 되어 설비 부품 교환 주기가 빨라지게 되는 문제점을 개선할 수 있는 기술이 필요하게 되었다.Therefore, it is possible to prevent the phenomenon that the electrolyte is solidified on the outside of the separator due to gelation of the electrolyte during chemical conversion, and the electrolyte that is wetted inside the AGM separator becomes insufficient. When the electrolyte and Silica are mixed before the injection, the gelled electrolyte is gradually left in the injection equipment. As a result, there is a need for a technology capable of improving the problem that the replacement cycle of equipment parts becomes faster.
따라서, 본 발명은 상기 종래의 문제점을 해소하기 위해 안출된 것으로,Therefore, the present invention has been devised to solve the conventional problems,
Gel화 되지 않는 수준으로 Silica 함량을 조절하고, 전해액 주액기에 Gel화된 전해액이 잔존하지 않도록 전해액 주액기와 Silica 첨가 설비인 디스펜서 펌프를 분리하여 전해액 주액 후에 Silica를 AGM 배터리에 첨가하는 제조 방법을 제공하고자 한다.Provides a manufacturing method of controlling the silica content to a level that does not gel, and separating the electrolyte injector and the dispenser pump, which is a facility for adding silica, to prevent the gelated electrolyte from remaining in the electrolyte injector, and adding the silica to the AGM battery after the electrolyte is injected. I want to.
본 발명이 해결하고자 하는 과제를 달성하기 위하여, 본 발명의 일실시예에 따른 컨테이너 포메이션 공정에서의 콜로이다 실리카가 포함된 전해액을 적용한 AGM 배터리 제조 방법은,In order to achieve the object to be solved by the present invention, a method for manufacturing an AGM battery using an electrolytic solution containing colloidal silica in a container formation process according to an embodiment of the present invention,
AGM 배터리에 전해액 주액기로 전해액을 주액하는 전해액주액단계(S100);와Electrolyte injecting step (S100) to inject the electrolytic solution into the AGM battery with the electrolyte injector; and
디스펜서 펌프를 통해 설정된 양만큼 실리카를 상기 전해액 주액된 AGM 배터리에 첨가하는 실리카첨가단계(S200);를 포함함으로써, 본 발명의 과제를 해결하게 된다.Including the silica addition step (S200) of adding the amount of silica to the AGM battery injected with the electrolyte through a dispenser pump, solves the problem of the present invention.
이때, 상기 설정된 양은,At this time, the set amount,
전해액 100 중량부 대비 실리카 1 중량부인 것을 특징으로 함으로써, 본 발명의 과제를 해결하게 된다.The problem of the present invention is solved by characterizing 1 part by weight of silica compared to 100 parts by weight of the electrolytic solution.
이때, 컨테이너 포메이션 공정에서의 콜로이다 실리카가 포함된 전해액을 적용한 AGM 배터리 제조 방법은 AGM 배터리 완제품 기준 총 전해액량이 7,070 중량부일 경우, 전해액 7,000 중량부, 실리카 70 중량부인 것을 특징으로 한다.At this time, the AGM battery manufacturing method using the electrolytic solution containing colloidal silica in the container formation process is characterized in that when the total amount of electrolyte based on the finished AGM battery is 7,070 parts by weight, 7,000 parts by weight of the electrolyte solution and 70 parts by weight of silica.
본 발명인 컨테이너 포메이션 공정에서의 콜로이다 실리카가 포함된 전해액을 적용한 AGM 배터리 제조 방법 및 AGM 배터리를 통해, Gel화 되지 않는 수준으로 Silica 함량을 조절하고, 전해액 주액기에 Gel화된 전해액이 잔존하지 않도록 전해액 주액기와 Silica 첨가 설비인 디스펜서 펌프를 분리하여 전해액 주액 후에 Silica를 AGM 배터리에 첨가함으로써, AGM 배터리의 셀 안의 전해액 량을 일정하게 유지시키는 효과와, 과충전 방지에 따른 내구성 향상을 제공하게 된다.In the container formation process of the present inventor, a method for manufacturing an AGM battery using an electrolytic solution containing colloidal silica and an AGM battery to control the Silica content to a level that does not gel, and to prevent the gelated electrolyte from remaining in the electrolyte injector By separating the main unit and the dispenser pump, which is a Silica addition facility, after adding the electrolyte, Silica is added to the AGM battery, thereby providing the effect of maintaining the amount of the electrolyte in the cell of the AGM battery constant and improving durability due to overcharge prevention.
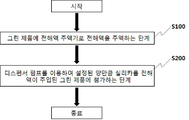
도 1은 본 발명의 일실시예에 따른 컨테이너 포메이션 공정에서의 콜로이다 실리카가 포함된 전해액을 적용한 AGM 배터리 제조 방법의 공정도이다.
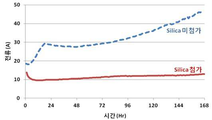
도 2의 그래프는 전해액에 실리카를 포함한 본 발명과, 포함하지 않은 종래 기술을 통해 제조된 800Ah 제품을 2.6V 168시간 정전압 충전하여 그에 따른 충전 전류를 측정한 결과 그래프이다.1 is a process diagram of an AGM battery manufacturing method using an electrolytic solution containing colloidal silica in a container formation process according to an embodiment of the present invention.
The graph of FIG. 2 is a graph showing a result of measuring a charging current according to the present invention including silica in an electrolytic solution and a 800Ah product manufactured through a conventional technique that does not include a constant voltage of 2.6V for 168 hours.
본 발명의 일실시예에 따른 컨테이너 포메이션 공정에서의 콜로이다 실리카가 포함된 전해액을 적용한 AGM 배터리 제조 방법은,A method for manufacturing an AGM battery using an electrolytic solution containing colloidal silica in a container formation process according to an embodiment of the present invention,
AGM 배터리에 전해액 주액기로 전해액을 주액하는 전해액주액단계(S100);와Electrolyte injecting step (S100) to inject the electrolytic solution into the AGM battery with the electrolyte injector; and
디스펜서 펌프를 통해 설정된 양만큼 실리카를 상기 전해액 주액된 AGM 배터리에 첨가하는 실리카첨가단계(S200);를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 한다.It characterized in that it comprises a; silica addition step (S200) of adding the amount of silica to the AGM battery injected with the electrolyte through a dispenser pump.
이때, 상기 실리카는,At this time, the silica,
콜로이다 실리카(Colloidal Silica)인 것을 특징으로 한다.It is characterized by being colloidal silica.
이때, 상기 설정된 양은,At this time, the set amount,
전해액 100 중량부 대비 실리카 1 중량부인 것을 특징으로 한다.Characterized in that 1 part by weight of silica compared to 100 parts by weight of the electrolyte.
또한, AGM 배터리 완제품 기준 총 전해액량이 7,070 중량부일 경우, 전해액 7,000 중량부, 실리카 70 중량부인 것을 특징으로 한다.In addition, when the total amount of electrolyte based on the AGM battery finished product is 7,070 parts by weight, it is characterized in that 7,000 parts by weight of electrolyte and 70 parts by weight of silica.
이때, 상기 콜로이다 실리카(Colloidal Silica)는,At this time, the colloidal silica (Colloidal Silica),
물 70 중량부, 실리카 30 중량부를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 한다.Characterized in that it comprises 70 parts by weight of water and 30 parts by weight of silica.
이때, 본 발명인 콜로이다 실리카가 포함된 전해액을 적용한 AGM 배터리 제조 방법은,At this time, the method of manufacturing an AGM battery using an electrolytic solution containing colloidal silica according to the present invention,
전해액 주액기와 디스펜서 펌프를 동시에 동작시키지 않고, 전해액 주액 후, 실리카를 첨가함으로써, 겔화를 방지하는 것을 특징으로 한다.It is characterized in that gelation is prevented by adding silica after the electrolyte injection, without simultaneously operating the electrolyte injection machine and the dispenser pump.
구체적으로, 상기 콜로이다 실리카가 포함된 전해액을 적용한 AGM 배터리 제조 방법은,Specifically, the method of manufacturing an AGM battery to which an electrolytic solution containing colloidal silica is applied,
AGM 배터리에 전해액 주액을 완료한 후, 실리카를 첨가하여 AGM 배터리 내부에서 실리카와 전해액이 혼합되도록 함으로써, 전해액 주액기에 겔화된 전해액이 잔존하는 것을 방지하는 것을 특징으로 한다.After completing the electrolyte injection into the AGM battery, silica is added to allow the silica and the electrolyte to mix inside the AGM battery, thereby preventing the gelled electrolyte from remaining in the electrolyte injection machine.
이때, 상기 제조 방법에 의해 제조된 콜로이다 실리카가 포함된 전해액을 포함하고 있는 AGM 배터리를 제공하게 된다.At this time, an AGM battery including an electrolytic solution containing colloidal silica prepared by the above manufacturing method is provided.
이하, 본 발명에 의한 컨테이너 포메이션 공정에서의 콜로이다 실리카가 포함된 전해액을 적용한 AGM 배터리 제조 방법 및 AGM 배터리의 실시예를 통해 상세히 설명하도록 한다.Hereinafter, a method for manufacturing an AGM battery to which an electrolytic solution containing colloidal silica in a container formation process according to the present invention is applied and an embodiment of an AGM battery will be described in detail.
도 1은 본 발명의 일실시예에 따른 컨테이너 포메이션 공정에서의 콜로이다 실리카가 포함된 전해액을 적용한 AGM 배터리 제조 방법의 공정도이다.1 is a process diagram of an AGM battery manufacturing method using an electrolytic solution containing colloidal silica in a container formation process according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 1에 도시한 바와 같이, 본 발명인 컨테이너 포메이션 공정에서의 콜로이다 실리카가 포함된 전해액을 적용한 AGM 배터리 제조 방법은, AGM 배터리에 전해액 주액기로 전해액을 주액하는 전해액주액단계(S100);와As shown in Figure 1, the method of manufacturing an AGM battery to which an electrolytic solution containing colloidal silica in a container formation process according to the present invention is applied, an electrolytic solution injecting step (S100) of injecting an electrolytic solution into an AGM battery using an electrolyte injector; and
디스펜서 펌프를 통해 설정된 양만큼 실리카를 상기 전해액 주액된 AGM 배터리에 첨가하는 실리카첨가단계(S200);를 포함하게 된다.It includes; a silica addition step (S200) of adding the amount of silica to the AGM battery injected with the electrolyte through a dispenser pump.
상기한 바와 같이, 전해액주액단계(S100)를 통해 AGM 배터리에 전해액 주액기로 전해액을 주액하게 된다.As described above, the electrolyte is injected into the AGM battery through the electrolyte injector through the electrolyte injecting step (S100).
이후, 실리카첨가단계(S200)를 통해 디스펜서 펌프를 통해 설정된 양만큼 실리카를 상기 전해액 주액된 AGM 배터리에 첨가하게 된다.Thereafter, silica is added to the AGM battery injected with the electrolyte in a predetermined amount through a dispenser pump through the silica addition step (S200).
즉, 전해액 주액 단계와 실리카 첨가 단계를 동시에 혼합하여 제공하지 않고, 분리하여 각각 AGM 배터리에 제공하는 것이다.That is, the electrolyte injection step and the silica addition step are not mixed and provided at the same time, but separately provided to each AGM battery.
구체적으로 그 이유를 설명하자면, 고전압 환경에서 과충전이 진행될 경우, 배터리 내의 전해액 감소가 빠르게 일어나며, 특히 AGM 배터리는 셀 안의 전해액 량이 적기 때문에 과충전을 방지하여 전해액을 유지하는 것이 내구성 향상에 중요한 요인이 된다.Specifically, to explain the reason, when overcharging proceeds in a high voltage environment, the electrolyte decreases rapidly in the battery, and in particular, since the amount of the electrolyte in the cell is small, it is important to prevent overcharging and maintain the electrolyte to maintain durability. .
이때, 전해액에 실리카(Silica)가 첨가되면 과충전을 억제하는데 도움이 되나, 컨테이너 포메이션(Container Formation) 공정에서 Silica를 첨가하여 AGM 배터리를 제조할 경우에 화성 중 전해액 겔(Gel) 화로 인해 격리판 외부에 고형화되어 AGM 격리판 내부에 함습되는 전해액이 부족하게 된다. At this time, when silica is added to the electrolyte solution, it is helpful to suppress overcharging, but when adding the silica in the container formation process to manufacture the AGM battery, the electrolyte outside of the separator due to the gelation of the electrolyte during chemical conversion And solidified in the AGM separator, resulting in insufficient electrolyte.
또한, 주액 전에 전해액과 Silica를 혼합하면 주액 설비인 전해액 주액기에 Gel 화된 전해액이 조금씩 잔존하게 되어 설비 부품 교환 주기가 빨라지게 된다.In addition, when the electrolyte and Silica are mixed before the injection, the gelated electrolyte remains in the electrolyte injection machine, which is the injection equipment, little by little, and the replacement cycle of equipment parts becomes faster.
따라서, 생산성 및 유지 보수의 어려움이 발생하게 되었다.Therefore, difficulties in productivity and maintenance have occurred.
이는 본 발명의 동기가 되어 어떻게 하면 겔화를 방지할 수 있을 것인가로부터 도출한 발명인 것이다.This is an invention derived from how to prevent gelation in the motive of the present invention.
이때, 본 발명의 실리카는,At this time, the silica of the present invention,
콜로이다 실리카(Colloidal Silica)인 것을 특징으로 한다.It is characterized by being colloidal silica.
그리고, 상기 설정된 양은,And, the set amount,
전해액 100 중량부 대비 실리카 1 중량부인 것을 특징으로 한다.Characterized in that 1 part by weight of silica compared to 100 parts by weight of the electrolyte.
또한, 상기 콜로이다 실리카(Colloidal Silica)는,In addition, the colloidal silica (Colloidal Silica),
물 70 중량부, 실리카 30 중량부를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 한다.Characterized in that it comprises 70 parts by weight of water and 30 parts by weight of silica.
도 2를 참조하여 구체적으로 설명하자면, 본 발명에서는, 겔(Gel) 화 되지 않는 수준으로 Silica 함량을 조절하고, 전해액 주액 설비인 전해액 주액기에 Gel 화된 전해액이 잔존하지 않도록 전해액 주액기와 Silica 첨가 설비인 디스펜서 펌프를 분리하여 전해액 주액 후에 Silica를 제품에 첨가하였다. Referring to Figure 2 in detail, in the present invention, the amount of the silica (Gel) is adjusted to a level of Silica, and the electrolyte injector and Silica are added so that the gelled electrolyte does not remain in the electrolyte injector, which is an electrolyte injector. Silica was added to the product after the electrolyte was dispensed by separating the equipment dispenser pump.
분말 Silica는 혼합 공정이 추가로 필요하므로, 전해액에 실리카를 첨가할 경우에 전해액에 완전한 분산이 가능하도록 예를 들어, 에스켐텍의 SS-Sol 30E(물 : 70wt%, Silica : 30wt%) Coloidal Silica를 사용하여 실험을 진행하였다.Powder Silica requires an additional mixing process, so when adding silica to the electrolyte, it is possible to completely disperse it in the electrolyte, for example, SS-Sol 30E (water: 70wt%, Silica: 30wt%) Coloidal Silica The experiment was conducted using.
도 2의 그래프는 2V 800Ah 제품을 2.6V 168시간 정전압 충전하여 그에 따른 충전 전류를 측정한 결과이다. The graph of FIG. 2 is a result of measuring a charging current by charging a 2V 800Ah product with a constant voltage of 2.6V for 168 hours.
Coloidal Silica는 Silica 함량이 1.0wt%가 되도록 전해액에 첨가하였다.Coloidal Silica was added to the electrolyte so that the Silica content was 1.0 wt%.
즉, 전해액 100 중량부 대비 실리카 1 중량부를 첨가한 것이다.That is, 1 part by weight of silica is added to 100 parts by weight of the electrolyte.
그 결과, 종래 기술의 경우, 24시간까지 급격하게 충전 전류가 상승하고, 24시간 이후 시간이 지날수록 완만한 상승을 가지게 되었지만, 실리카를 전해액에 첨가하게 되면 24시간이 지나도 일정한 충전 전류를 유지하고 있음을 확인할 수 있었다.As a result, in the case of the prior art, the charging current rapidly rises up to 24 hours, and after 24 hours, the charging current gradually increases, but when silica is added to the electrolyte, the constant charging current is maintained even after 24 hours. It was confirmed that there was.
따라서, 전해액에 실리카를 첨가하여 과충전을 방지하여 전해액을 일정량 유지함으로써, AGM 배터리의 내구성이 향상될 수 있게 되는 것이다.Therefore, by adding silica to the electrolytic solution to prevent overcharging to maintain a certain amount of the electrolytic solution, the durability of the AGM battery can be improved.
또한, 실험 결과, Silica는 전해액에 첨가되는 양에 따라 Gel 화가 진행되는데, 배터리 전해액 비중 1.280 ~ 1.300 수준에서 Silica 함량이 5 wt% 정도가 되면 Gel 화 되어 고체 상태로 변한다. In addition, as a result of the experiment, the gelation proceeds according to the amount added to the electrolytic solution. When the silica content is about 5 wt% at the specific gravity of 1.280 to 1.300, the gel is converted into a solid state.
그리고, Gel 화가 되는 시간은 온도가 높을수록 빨라지는데, 배터리 화성(Container Formation) 중 전해액 온도는 60 ~ 70℃까지 상승하게 되어 Gel 화 속도가 빨라지고, Silica 함량 2 ~ 3 wt% 정도만 첨가하여도 일부 전해액이 Gel로 변환되는 것을 확인하였다.In addition, the time for gelation increases as the temperature increases, but the electrolyte temperature rises to 60 to 70 ° C during battery formation, resulting in a faster gelation rate, and adding some silica content of 2 to 3 wt% It was confirmed that the electrolytic solution was converted to Gel.
AGM 배터리의 전해액이 화성 중 Gel 화가 되면 격리판 외부에 Gel 화 된 상태로 고형화되어 Gel 상태로 변화한 전해액만큼 격리판 내부의 전해액이 부족하게 되고, Dendrite short가 발생할 가능성이 높아진다. When the electrolyte of the AGM battery becomes gelated during formation, the electrolyte inside the separator becomes insufficient as much as the electrolyte changed to a gel state after being solidified in a gelled state outside the separator, and the possibility of Dendrite short increases.
때문에 전해액이 Gel 화 되지 않을 만큼 Silica가 첨가되어야 하고, 실험 결과, 전해액 량 대비 Silica 함량이 1.0 wt%에서는 화성 중에 온도가 많이 상승하여도 전해액이 Gel 화 되지 않음을 확인할 수 있었다.Therefore, the silica should be added so that the electrolyte does not gel, and as a result of the experiment, it was confirmed that the electrolyte does not gel when the silica content is 1.0 wt% compared to the amount of the electrolyte, even if the temperature rises significantly during chemical conversion.
따라서, 설정된 양은,Therefore, the set amount is
전해액 100 중량부 대비 실리카 1 중량부로 결정하게 된 것이다.It was decided to be 1 part by weight of silica compared to 100 parts by weight of the electrolyte.
예를 들어, 전해액 100 wt% 대비 Silica 1.0 wt%를 전해액에 첨가하게 되는 것이다.For example, 1.0 wt% of Silica compared to 100 wt% of the electrolyte is added to the electrolyte.
본 발명의 도 2의 시험에 사용한 2V 800Ah 제품은 Silica를 제외하고 7000g/cell의(완제품 기준) 전해액이 필요하다. The 2V 800Ah product used in the test of FIG. 2 of the present invention requires an electrolyte of 7000 g / cell (based on the finished product) excluding Silica.
시험에 사용한 Colloidal Silica는 물 70 중량부, 실리카 30 중량부로 구성되어 있고, Colloidal Silica에 포함된 물과 전해액이 합쳐 AGM 배터리의 경우, 7000g이 되도록 비율을 설정해야 하므로, 완제품 기준으로 전해액 6835g이 되도록 화성 전해액 량을 조정하고, 화성 전 Colloidal Silica 235g(물 165g + Silica 70g)을 첨가하였다. Colloidal Silica used for the test is composed of 70 parts by weight of water and 30 parts by weight of silica, and the ratio of water and electrolyte contained in Colloidal Silica should be set to be 7000 g in the case of AGM battery, so that the electrolyte solution becomes 6835 g The amount of chemical conversion solution was adjusted, and 235 g of Colloidal Silica (165 g of water + 70 g of Silica) was added before chemical conversion.
그리하여 완제품 기준 총 전해액량 7070g으로(전해액 7000g, Silica 70g) Silica 함량을 1 wt%가 되도록 설정하였다.Thus, the total amount of electrolyte based on the finished product was 7070 g (electrolyte 7000 g, Silica 70 g), and the Silica content was set to be 1 wt%.
Container Formation 공정에서 일반적인 Silica 첨가 방법은 Silica와 전해액을 혼합 후 배터리에 넣는다. In the general method of adding silica in the container formation process, the silica and the electrolyte are mixed and put into a battery.
하지만, Silica와 전해액이 혼합하는 순간부터 Gel 화가 진행되며, Silica 함량을 아무리 낮춘다 하여도 전해액 주액 설비인 전해액 주액기에 전해액과 혼합된 Silica가 조금씩 남게 된다. However, gelation proceeds from the moment the Silica and the electrolyte are mixed, and no matter how much the Silica content is lowered, the Silica mixed with the electrolyte is gradually left in the electrolyte injector, the electrolyte injector equipment.
이 공정을 장기간 사용하게 된다면 전해액 주액기에 Gel 화 된 Silica가 쌓여 설비 노후가 빠르게 진행된다. If this process is to be used for a long time, the gelated Silica accumulates in the electrolyte injector, and the equipment ages rapidly.
이러한 현상을 막기 위해 배터리에 전해액 주액을 완료한 이후 Silica를 첨가하여 배터리 내부에서 Silica와 전해액이 혼합되도록 하였고, Silica와 전해액의 혼합이 간단하게 이루어지도록 Colloidal Silica를 사용하였다. To prevent this phenomenon, after completing the electrolyte injection to the battery, Silica was added to mix the Silica and the electrolyte inside the battery, and Colloidal Silica was used to simplify mixing of the Silica and the electrolyte.
Colloidal Silica는 물에 나노 사이즈의 Silica가 완벽하게 분산되어 있는 상태로, 이것을 전해액에 넣을 경우, 추가적인 혼합 공정 없이도 배터리 화성 중에 Silica가 전해액에 완벽하게 분산되는 효과를 얻을 수 있다. Colloidal Silica is a nano-sized Silica completely dispersed in water, and when it is added to the electrolyte, Silica can be perfectly dispersed in the electrolyte during battery formation without additional mixing.
따라서, 실리카 중에서 Colloidal Silica를 선정하게 된 것이다.Therefore, Colloidal Silica was selected from among silica.
Colloidal Silica를 넣는 순서는 전해액 주액기 옆에 디스펜서 펌프를 설치하고 배터리에 전해액 주액이 완료되면 디스펜서 펌프로 설정한 량만큼 Colloildal Silica를 첨가한다. The order of adding colloidal silica is to install the dispenser pump next to the electrolyte injector, and when the electrolyte injection is completed in the battery, add the colloildal silica to the amount set by the dispenser pump.
예를 들어, 전해액 100 중량부 대비 Colloildal Silica 1 중량부를 첨가하는 것이다.For example, it is to add 1 part by weight of Colloildal Silica to 100 parts by weight of the electrolyte.
첨가는 예를 들어, 디스펜서 펌프를 이용함으로써, 계량 및 주액을 동시에 진행하기 때문에 설비를 단순화시킬 수 있고, Silica 혼합을 설비가 아닌 배터리 내부에서 진행하므로 혼합 설비가 필요치 않으므로 초기 설비 설치 비용을 줄일 수 있다.Addition, for example, by using a dispenser pump, simplifies the equipment because the metering and pouring are performed simultaneously, and the mixing of Silica is performed inside the battery, not the equipment, so no mixing equipment is required, reducing the initial installation cost. have.
요약하자면, 본 발명인 콜로이다 실리카가 포함된 전해액을 적용한 AGM 배터리 제조 방법은,In summary, the method of manufacturing an AGM battery using an electrolytic solution containing colloidal silica according to the present invention,
전해액 주액기와 디스펜서 펌프를 동시에 동작시키지 않고, 전해액 주액 후, 실리카를 첨가함으로써, 겔 화를 방지하게 되는 것이다.It is to prevent gelation by adding silica after the electrolyte injection, without simultaneously operating the electrolyte injection machine and the dispenser pump.
이는 단순할 수도 있으나, 수회 반복되는 실험과 구조 변경을 통해 최적화된 공정을 완성하게 된 것이다.This may be simple, but the process is optimized through repeated experiments and structural changes.
또한, 본 발명인 콜로이다 실리카가 포함된 전해액을 적용한 AGM 배터리 제조 방법은,In addition, the method of manufacturing an AGM battery using an electrolytic solution containing colloidal silica according to the present invention,
AGM 배터리에 전해액 주액을 완료한 후, 실리카를 첨가하여 AGM 배터리 내부에서 실리카와 전해액이 혼합되도록 함으로써, 전해액 주액기에 겔화된 전해액이 잔존하는 것을 방지하는 것을 특징으로 한다.After completing the electrolyte injection into the AGM battery, silica is added to allow the silica and the electrolyte to mix inside the AGM battery, thereby preventing the gelled electrolyte from remaining in the electrolyte injection machine.
즉, 전해액 주액과 실리카를 동시에 AGM 배터리에 투입하여 혼합하는 방식이 아닌, 전해액 주액을 AGM 배터리에 먼저 실행한 후, 디스펜서 펌프를 이용하여 개량 및 실리카 투입을 실시하게 됨으로써, AGM 배터리 내부에서 실리카와 전해액이 혼합되어 전해액 주액기에 겔 화된 전해액이 잔존하는 것을 방지할 수 있었던 것이다.In other words, instead of mixing the electrolyte solution and silica into the AGM battery at the same time, the electrolyte solution is first run into the AGM battery, and then improved and injected with silica using a dispenser pump. It was possible to prevent the electrolytic solution from being mixed and the gelled electrolyte remaining in the electrolytic solution injector.
본 발명을 통해, Gel화 되지 않는 수준으로 Silica 함량을 조절하고, 전해액 주액기에 Gel화된 전해액이 잔존하지 않도록 전해액 주액기와 Silica 첨가 설비인 디스펜서 펌프를 분리하여 전해액 주액 후에 Silica를 AGM 배터리에 첨가함으로써, AGM 배터리의 셀 안의 전해액 량을 일정하게 유지시키는 효과와, 과충전 방지에 따른 내구성 향상을 제공하게 된다.Through the present invention, the silica content is adjusted to a level that does not gel, and the electrolyte main machine and the dispenser pump, which is a facility for adding silica, are separated from the electrolyte main body so that the gel main body does not remain in the electrolyte main body. By doing so, it is possible to provide an effect of keeping the amount of electrolyte in the cell of the AGM battery constant, and improving durability due to overcharge prevention.
상기와 같은 내용의 본 발명이 속하는 기술분야의 당업자는 본 발명의 기술적 사상이나 필수적 특징을 변경하지 않고서 다른 구체적인 형태로 실시될 수 있다는 것을 이해할 수 있을 것이다. 그러므로 이상에서 기술한 실시 예들은 모든 면에서 예시된 것이며 한정적인 것이 아닌 것으로서 이해해야만 한다. Those of ordinary skill in the art to which the present invention pertains to the above contents can understand that the present invention can be implemented in other specific forms without changing the technical spirit or essential features of the present invention. Therefore, the embodiments described above are exemplified in all respects and should be understood as non-limiting.
S100 : 전해액주액단계
S200 : 실리카첨가단계S100: electrolyte injection step
S200: silica addition step
Claims (8)
AGM 배터리에 전해액 주액기로 전해액을 주액하는 전해액주액단계(S100);와
디스펜서 펌프를 통해 설정된 양만큼 실리카를 상기 전해액 주액된 AGM 배터리에 첨가하는 실리카첨가단계(S200);를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 컨테이너 포메이션 공정에서의 콜로이다 실리카가 포함된 전해액을 적용한 AGM 배터리 제조 방법.
In the method of manufacturing an AGM battery using an electrolytic solution containing colloidal silica in a container formation process,
Electrolyte injecting step (S100) to inject the electrolytic solution into the AGM battery with the electrolyte injector; and
Silica addition step (S200) of adding silica to the electrolyte-injected AGM battery in a predetermined amount through a dispenser pump; a method for manufacturing an AGM battery using an electrolytic solution containing colloidal silica in a container formation process comprising the steps of: .
상기 실리카는,
콜로이다 실리카(Colloidal Silica)인 것을 특징으로 하는 컨테이너 포메이션 공정에서의 콜로이다 실리카가 포함된 전해액을 적용한 AGM 배터리 제조 방법.
According to claim 1,
The silica,
A method for manufacturing an AGM battery using an electrolytic solution containing colloidal silica in a container formation process, characterized in that it is colloidal silica.
상기 설정된 양은,
전해액 100 중량부 대비 실리카 1 중량부인 것을 특징으로 하는 컨테이너 포메이션 공정에서의 콜로이다 실리카가 포함된 전해액을 적용한 AGM 배터리 제조 방법.
According to claim 1,
The set amount,
A method for manufacturing an AGM battery using an electrolytic solution containing colloidal silica in a container formation process, characterized in that it is 1 part by weight of silica compared to 100 parts by weight of the electrolytic solution.
AGM 배터리 완제품 기준 총 전해액량이 7,070 중량부일 경우, 전해액 7,000 중량부, 실리카 70 중량부인 것을 특징으로 하는 컨테이너 포메이션 공정에서의 콜로이다 실리카가 포함된 전해액을 적용한 AGM 배터리 제조 방법.
According to claim 1,
AGM battery AGM battery manufacturing method using an electrolytic solution containing colloidal silica in a container formation process, characterized in that the total amount of electrolyte based on the finished product is 7,070 parts by weight, 7,000 parts by weight of electrolyte, and 70 parts by weight of silica.
상기 콜로이다 실리카(Colloidal Silica)는,
물 70 중량부, 실리카 30 중량부를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 컨테이너 포메이션 공정에서의 콜로이다 실리카가 포함된 전해액을 적용한 AGM 배터리 제조 방법.
According to claim 2,
The colloidal silica (Colloidal Silica),
AGM battery manufacturing method using an electrolytic solution containing colloidal silica in a container formation process comprising 70 parts by weight of water and 30 parts by weight of silica.
상기 콜로이다 실리카가 포함된 전해액을 적용한 AGM 배터리 제조 방법은,
전해액 주액기와 디스펜서 펌프를 동시에 동작시키지 않고, 전해액 주액 후, 실리카를 첨가함으로써, 겔화를 방지하는 것을 특징으로 하는 컨테이너 포메이션 공정에서의 콜로이다 실리카가 포함된 전해액을 적용한 AGM 배터리 제조 방법.
According to claim 1,
The method of manufacturing an AGM battery to which an electrolytic solution containing colloidal silica is applied,
A method of manufacturing an AGM battery using an electrolytic solution containing colloidal silica in a container formation process in which gelation is prevented by adding silica after the electrolyte injection, without simultaneously operating the electrolyte injection machine and the dispenser pump.
상기 콜로이다 실리카가 포함된 전해액을 적용한 AGM 배터리 제조 방법은,
AGM 배터리에 전해액 주액을 완료한 후, 실리카를 첨가하여 AGM 배터리 내부에서 실리카와 전해액이 혼합되도록 함으로써, 전해액 주액기에 겔화된 전해액이 잔존하는 것을 방지하는 것을 특징으로 하는 컨테이너 포메이션 공정에서의 콜로이다 실리카가 포함된 전해액을 적용한 AGM 배터리 제조 방법.
According to claim 1,
The method of manufacturing an AGM battery to which an electrolytic solution containing colloidal silica is applied,
After completing the electrolyte injection into the AGM battery, silica is added to allow the silica and the electrolyte to mix inside the AGM battery, thereby preventing coexistence of the gelled electrolyte in the electrolyte injection machine. AGM battery manufacturing method using silica-containing electrolyte.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020180126015A KR102103307B1 (en) | 2018-10-22 | 2018-10-22 | AGM battery manufacturing method using electrolytic solution containing colloidal silica in a container formation process and AGM battery |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020180126015A KR102103307B1 (en) | 2018-10-22 | 2018-10-22 | AGM battery manufacturing method using electrolytic solution containing colloidal silica in a container formation process and AGM battery |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR102103307B1 true KR102103307B1 (en) | 2020-04-23 |
Family
ID=70472314
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020180126015A KR102103307B1 (en) | 2018-10-22 | 2018-10-22 | AGM battery manufacturing method using electrolytic solution containing colloidal silica in a container formation process and AGM battery |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR102103307B1 (en) |
Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH0883622A (en) * | 1994-09-09 | 1996-03-26 | Shin Kobe Electric Mach Co Ltd | Sealed lead-acid battery |
| JP2847761B2 (en) * | 1989-06-12 | 1999-01-20 | 株式会社ユアサコーポレーション | Sealed lead-acid battery and method of manufacturing the same |
| JP3042027B2 (en) * | 1991-06-13 | 2000-05-15 | 松下電器産業株式会社 | Sealed lead-acid battery |
| JP3055937B2 (en) * | 1990-04-25 | 2000-06-26 | ホリングスワース アンド ヴォーズ コムパニー | Glass fiber separator and method for producing the same |
| KR20100096232A (en) * | 2007-12-11 | 2010-09-01 | 피. 에이치. 글랫펠터 컴퍼니 | Battery separator structures |
| KR20130107550A (en) * | 2012-03-22 | 2013-10-02 | 삼성에스디아이 주식회사 | Separator and lithium secondary battery |
| KR20180040850A (en) | 2016-10-13 | 2018-04-23 | 주식회사 엘지화학 | Electrolyte comprising hollow silica and vanadium redox flow battery comprising the same |
-
2018
- 2018-10-22 KR KR1020180126015A patent/KR102103307B1/en active IP Right Grant
Patent Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2847761B2 (en) * | 1989-06-12 | 1999-01-20 | 株式会社ユアサコーポレーション | Sealed lead-acid battery and method of manufacturing the same |
| JP3055937B2 (en) * | 1990-04-25 | 2000-06-26 | ホリングスワース アンド ヴォーズ コムパニー | Glass fiber separator and method for producing the same |
| JP3042027B2 (en) * | 1991-06-13 | 2000-05-15 | 松下電器産業株式会社 | Sealed lead-acid battery |
| JPH0883622A (en) * | 1994-09-09 | 1996-03-26 | Shin Kobe Electric Mach Co Ltd | Sealed lead-acid battery |
| KR20100096232A (en) * | 2007-12-11 | 2010-09-01 | 피. 에이치. 글랫펠터 컴퍼니 | Battery separator structures |
| KR20130107550A (en) * | 2012-03-22 | 2013-10-02 | 삼성에스디아이 주식회사 | Separator and lithium secondary battery |
| KR20180040850A (en) | 2016-10-13 | 2018-04-23 | 주식회사 엘지화학 | Electrolyte comprising hollow silica and vanadium redox flow battery comprising the same |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN102368567B (en) | Formation method for dynamic lead-acid cell jar formation | |
| CN102201563A (en) | Method of injecting electrolyte into a lithium ion battery, and lithium ion battery prepared by the same | |
| CN101540389B (en) | Method for injecting colloid electrolyte into lead-acid battery | |
| CN103943893A (en) | Lead-acid battery container formation technology | |
| CN107978790A (en) | A kind of battery mends lithium method and apparatus | |
| CN103931043A (en) | Lead storage cell | |
| CN106786877A (en) | The method and device charged to high power battery | |
| CN101257129B (en) | Valve-regulated lead-acid battery and production method thereof | |
| CN111697271A (en) | Lithium ion battery formation and capacity-dividing method | |
| KR102103307B1 (en) | AGM battery manufacturing method using electrolytic solution containing colloidal silica in a container formation process and AGM battery | |
| CN106876813A (en) | A kind of method for pre-charging lithium ion batteries | |
| CN105140474A (en) | Anode lead paste for power lead-acid storage battery and preparation method of anode lead paste | |
| CN101958417A (en) | Anode additive of lead acid storage battery | |
| CN101630752B (en) | Lead-acid accumulator colloid additive | |
| CN101702451B (en) | Gradual storage battery colloid, preparation method and gel-filling technology of storage battery | |
| JPS6322027B2 (en) | ||
| CN107123835B (en) | A kind of electrochemical method and system of lead-acid accumulator desulfurization | |
| CN110993897A (en) | Positive electrode additive for prolonging service life of valve-controlled sealed lead-acid battery and application thereof | |
| KR102098510B1 (en) | Rapid formation of electrodes | |
| JPH0696793A (en) | Manufacture of sealed lead-acid battery | |
| US1802818A (en) | Treating storage-battery plates | |
| CN104073683B (en) | A kind of low temperature deeper cavity positive grid alloy and preparation method thereof | |
| KR100531450B1 (en) | Lead storage battery comprising gel electrolyte coated with silica powder | |
| CN102163751B (en) | Preparation method of gel electrolyte for lead-acid battery | |
| US2101326A (en) | Storage battery separator containing a compound of mercury |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right | ||
| GRNT | Written decision to grant |