JP6178682B2 - Plasma arc welding system - Google Patents
Plasma arc welding system Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6178682B2 JP6178682B2 JP2013197038A JP2013197038A JP6178682B2 JP 6178682 B2 JP6178682 B2 JP 6178682B2 JP 2013197038 A JP2013197038 A JP 2013197038A JP 2013197038 A JP2013197038 A JP 2013197038A JP 6178682 B2 JP6178682 B2 JP 6178682B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- value
- arc
- pilot arc
- current
- pilot
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000003466 welding Methods 0.000 title claims description 59
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 claims description 53
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims description 29
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 29
- 230000001174 ascending effect Effects 0.000 claims description 6
- 230000007547 defect Effects 0.000 description 11
- 101100452236 Caenorhabditis elegans inf-1 gene Proteins 0.000 description 10
- NCGICGYLBXGBGN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-morpholin-4-yl-1-oxa-3-azonia-2-azanidacyclopent-3-en-5-imine;hydrochloride Chemical compound Cl.[N-]1OC(=N)C=[N+]1N1CCOCC1 NCGICGYLBXGBGN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 5
- 230000003247 decreasing effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000002950 deficient Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 2
- WFKWXMTUELFFGS-UHFFFAOYSA-N tungsten Chemical compound [W] WFKWXMTUELFFGS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910052721 tungsten Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000010937 tungsten Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010304 firing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000010365 information processing Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000007257 malfunction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000000630 rising effect Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Arc Welding In General (AREA)
- Arc Welding Control (AREA)
Description
本発明は、プラズマアーク溶接システムに関する。 The present invention relates to a plasma arc welding system.
従来から、プラズマアーク溶接方法が知られている。プラズマアーク溶接方法では、電極とプラズマノズルとの間にパイロットアークが発生している状態で、電極と母材との間にメインアークを点弧させる。メインアークは、パイロットアークに誘発されることにより、点弧する。そして、メインアークが発生している状態で母材の定常溶接を行う。プラズマアーク溶接方法は、たとえば、特許文献1や特許文献2に開示されている。
Conventionally, plasma arc welding methods are known. In the plasma arc welding method, a main arc is ignited between an electrode and a base material in a state where a pilot arc is generated between the electrode and a plasma nozzle. The main arc is ignited by being induced by the pilot arc. Then, steady welding of the base material is performed in a state where the main arc is generated. The plasma arc welding method is disclosed in
このようなプラズマアーク溶接方法において、メインアークを確実に点弧できなくなることがあった。このようなことでは、作業効率の悪化を招いてしまう。 In such a plasma arc welding method, the main arc may not be reliably ignited. In such a case, work efficiency is deteriorated.
本発明は、上記した事情のもとで考え出されたものであって、メインアークをより確実に点弧することのできるプラズマアーク溶接システムを提供することをその主たる課題とする。 The present invention has been conceived under the circumstances described above, and its main object is to provide a plasma arc welding system capable of firing a main arc more reliably.
本発明の第1の側面によると、非消耗電極および前記非消耗電極を囲むプラズマノズルを含むトーチを用いる、プラズマアーク溶接方法のためのプラズマアーク溶接システムであって、前記非消耗電極および前記プラズマノズルの間にパイロットアーク電流を流すパイロットアーク電源回路と、前記非消耗電極および前記プラズマノズルとの間に発生しているパイロットアークの状態を示すアーク状態反映値を検出する検出回路と、を備え、前記パイロットアーク電源回路は、前記検出回路によって検出されたアーク状態反映値に基づき、電源出力値を上昇させ、前記アーク状態反映値は、前記非消耗電極および前記プラズマノズルの間のパイロットアーク電圧の電圧値と、前記非消耗電極および前記プラズマノズルの間に流れるパイロットアーク電流の電流値と、のいずれか一方であり、前記電源出力値は、前記パイロットアーク電圧の電圧値と、前記パイロットアーク電流の電流値と、の他方である、プラズマアーク溶接システムが提供される。 According to a first aspect of the present invention, there is provided a plasma arc welding system for a plasma arc welding method using a torch including a non-consumable electrode and a plasma nozzle surrounding the non-consumable electrode, the non-consumable electrode and the plasma A pilot arc power supply circuit for passing a pilot arc current between the nozzles, and a detection circuit for detecting an arc state reflection value indicating a state of the pilot arc generated between the non-consumable electrode and the plasma nozzle. The pilot arc power circuit increases a power output value based on the arc state reflected value detected by the detection circuit, and the arc state reflected value is a pilot arc voltage between the non-consumable electrode and the plasma nozzle. And the pilot value that flows between the non-consumable electrode and the plasma nozzle A plasma arc welding system, wherein the power output value is the other of the pilot arc voltage value and the pilot arc current value. Is done.
好ましくは、第1基準値を記憶する第1基準値記憶部を更に備え、前記パイロットアーク電源回路は、前記アーク状態反映値が前記第1基準値を下回ると、前記電源出力値を上昇させる第1上昇処理を行う。 Preferably, the pilot arc power supply circuit further includes a first reference value storage unit that stores the first reference value, and the pilot arc power supply circuit increases the power supply output value when the arc state reflected value falls below the first reference value. 1 Ascending processing is performed.
好ましくは、第2基準値を記憶する第2基準値記憶部を更に備え、前記パイロットアーク電源回路は、前記第1上昇処理を終えた後に、前記アーク状態反映値が第2基準値を下回る場合、前記電源出力値を上昇させる第2上昇処理を行う。 Preferably, the apparatus further includes a second reference value storage unit that stores a second reference value, and the pilot arc power supply circuit has a case where the arc state reflected value is lower than the second reference value after finishing the first ascent process. Then, a second increase process for increasing the power output value is performed.
好ましくは、前記パイロットアーク電源回路は、前記第1上昇処理を終えた後、前記アーク状態反映値が第2基準値以上である場合、前記電源出力値を上昇させない。 Preferably, the pilot arc power supply circuit does not increase the power supply output value when the arc state reflected value is equal to or greater than a second reference value after finishing the first increase process.
好ましくは、前記電源出力値の上限値を記憶する上限値記憶部を更に備え、前記パイロットアーク電源回路は、前記上限値に基づいて、前記パイロットアーク電源回路の出力状態を決定する。 Preferably, an upper limit storage unit for storing an upper limit value of the power supply output value is further provided, and the pilot arc power supply circuit determines an output state of the pilot arc power supply circuit based on the upper limit value.
好ましくは、前記パイロットアーク電源回路は、前記電源出力値が、前記上限値以上である場合、前記パイロットアーク電源回路の出力を停止する。 Preferably, the pilot arc power supply circuit stops the output of the pilot arc power supply circuit when the power supply output value is equal to or greater than the upper limit value.
好ましくは、前記パイロットアーク電源回路は、前記電源出力値が前記上限値を下回っている場合であり、且つ、前記第1上昇処理を終えた後に、前記アーク状態反映値が第2基準値を下回る場合、前記第2上昇処理を行う。 Preferably, the pilot arc power supply circuit is a case where the power supply output value is lower than the upper limit value, and the arc state reflected value is lower than a second reference value after finishing the first increasing process. In the case, the second ascent process is performed.
好ましくは、第1基準値を記憶する第1基準値記憶部と、報知部と、を更に備え、前記報知部は、前記アーク状態反映値が前記第1基準値を下回ると、前記パイロットアークが不具合状態であることを示す不具合情報を報知する。 Preferably, the information processing apparatus further includes a first reference value storage unit that stores a first reference value, and a notification unit, wherein the notification unit is configured to cause the pilot arc to be generated when the arc state reflected value falls below the first reference value. The trouble information indicating the trouble state is notified.
好ましくは、前記電源出力値の上限値を記憶する上限値記憶部と、報知部と、を更に備え、前記報知部は、前記電源出力値が、前記上限値以上である場合、前記プラズマノズルが高温であることを示す高温警報を報知する。 Preferably, an upper limit storage unit that stores an upper limit value of the power supply output value, and a notification unit, wherein the notification unit, when the power supply output value is greater than or equal to the upper limit value, A high temperature alarm indicating that the temperature is high is notified.
好ましくは、前記パイロットアーク電源回路は、前記非消耗電極および母材の間にメインアークが発生していない場合にのみ、前記電源出力値を上昇させる。 Preferably, the pilot arc power supply circuit increases the power supply output value only when a main arc is not generated between the non-consumable electrode and the base material.
好ましくは、前記非消耗電極と母材との間にメインアーク電流を流すメインアーク電源回路を更に備える。 Preferably, a main arc power supply circuit for supplying a main arc current between the non-consumable electrode and the base material is further provided.
好ましくは、前記非消耗電極と前記プラズマノズルとの間にプラズマガスを流すプラズマガス供給装置を更に備える。 Preferably, the apparatus further includes a plasma gas supply device for flowing a plasma gas between the non-consumable electrode and the plasma nozzle.
本発明のその他の特徴および利点は、添付図面を参照して以下に行う詳細な説明によって、より明らかとなろう。 Other features and advantages of the present invention will become more apparent from the detailed description given below with reference to the accompanying drawings.
以下、本発明の実施の形態につき、図面を参照して具体的に説明する。 Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be specifically described with reference to the drawings.
<第1実施形態>
図1〜図5を用いて、本発明の第1実施形態について説明する。
<First Embodiment>
1st Embodiment of this invention is described using FIGS.
図1は、本発明の第1実施形態にかかるプラズマアーク溶接システムのブロック図である。 FIG. 1 is a block diagram of a plasma arc welding system according to a first embodiment of the present invention.
同図に示すプラズマアーク溶接システムB1は、溶接ロボット1と、動作制御回路2と、パイロットアーク用回路3と、メインアーク用回路4と、プラズマガス流量制御回路491と、シールドガス流量制御回路492と、プラズマガス供給装置81と、シールドガス供給装置82と、報知部85と、を備える。
The plasma arc welding system B1 shown in the figure includes a
溶接ロボット1は、母材Wに対してプラズマアーク溶接を自動で行うものである。溶接ロボット1は、マニピュレータ11と、トーチ12と、を含む。
The
マニピュレータ11は、たとえば多関節ロボットである。トーチ12は、マニピュレータ11の駆動により、上下前後左右に自在に移動できる。
The manipulator 11 is, for example, an articulated robot. The
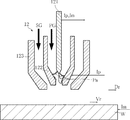
図2によく表れているように、トーチ12は、非消耗電極121と、プラズマノズル122と、シールドガスノズル123とを有する。
As clearly shown in FIG. 2, the
非消耗電極121は、たとえばタングステンからなる金属棒である。プラズマノズル122は筒状の部材である。プラズマノズル122は非消耗電極121を囲んでいる。プラズマノズル122は、非消耗電極121の先端の位置する側とは反対側に開放している。
Non-consumable
プラズマノズル122内をプラズマガスPGが流れる。プラズマガスPGを媒体として、プラズマノズル122と非消耗電極121との間にパイロットアークPaが発生する。パイロットアークPaが発生している際、プラズマノズル122と非消耗電極121との間には、パイロットアーク電流Ipが流れる。なお、パイロットアーク電流Ipの電流値とは、特に断りのない限り、パイロットアーク電流Ipの電流値の絶対値の時間平均値のことを意味する。なお、プラズマノズル122は、冷却手段(図示略)によって、適宜冷却される。
Plasma gas PG flows in the
非消耗電極121と母材Wとの間には、メインアークMaが発生する。メインアークMaは、プラズマノズル122のノズル開口に拘束される。メインアークMaが発生している際、非消耗電極121と母材Wとの間には、メインアーク電流Imが流れる。メインアーク電流Imは、母材Wの材質に応じて、直流もしくは交流いずれかが選択される。メインアーク電流Imは、直流のパルス電流である場合もあるし、交流のパルス電流である場合もある。なお、メインアーク電流Imの電流値とは、特に断りのない限り、メインアーク電流Imの電流値の絶対値の時間平均値のことを意味する。メインアークMaが発生している際、非消耗電極121と母材Wとの間には、メインアーク電圧Vmが印加される。
A main arc Ma is generated between the
シールドガスノズル123は筒状の部材である。シールドガスノズル123はプラズマノズル122を囲んでいる。シールドガスノズル123とプラズマノズル122との間を、シールドガスSGが流れる。本実施形態とは異なり、トーチ12がシールドガスノズル123を含んでいなくてもよい。
The
動作制御回路2は、マイクロコンピュータおよびメモリ(ともに図示略)を有している。このメモリには、溶接ロボット1の各種の動作が設定された作業プログラムが記憶されている。動作制御回路2はロボット移動速度Vrを制御する。ロボット移動速度Vrは、母材Wに沿った溶接進行方向Drにおける、母材Wに対する非消耗電極121の速度である。動作制御回路2は、上記作業プログラム、溶接ロボット1におけるエンコーダからの座標情報、およびロボット移動速度Vr等に基づき、溶接ロボット1に対して動作制御信号Msを送る。溶接ロボット1は動作制御信号Msを受け、マニピュレータ11を駆動させ、トーチ12が、母材Wにおける所定の溶接開始位置に移動したり、母材Wの面内方向に沿って移動したりする。
The operation control circuit 2 has a microcomputer and a memory (both not shown). The memory stores a work program in which various operations of the
パイロットアーク用回路3は、非消耗電極121とプラズマノズル122との間にパイロットアーク電流Ipを流す。本実施形態では、パイロットアーク用回路3は、パイロットアーク電流Ipの電流値を、設定された値となるように制御する。すなわち、パイロットアーク用回路3は、定電流制御を行う。本実施形態とは異なり、パイロットアーク用回路3は、定電圧制御を行なってもよい。パイロットアーク用回路3が定電圧制御を行う場合、パイロットアーク用回路3は、パイロットアーク電圧Vpの電圧値を設定された値となるように制御する。
The
パイロットアーク用回路3は、パイロットアーク電源回路31と、パイロットアーク電流検出回路33と、パイロットアーク電圧検出回路36と、第1基準値記憶部391と、第2基準値記憶部392と、上限値記憶部393と、を含む。
The
第1基準値記憶部391には第1基準値vp1が記憶されており、第2基準値記憶部392には第2基準値vp2が記憶されており、上限値記憶部393には上限値ip1が記憶されている。第2基準値vp2は第1基準値vp1よりも大きい値である。第1基準値記憶部391と、第2基準値記憶部392と、上限値記憶部393とは、パイロットアーク電源回路31に接続している。
The first reference
パイロットアーク電源回路31は、たとえば200V等の商用電源を整流し抵抗器を直列に挿入した回路を含む。これにより、パイロットアーク電源回路31は、非消耗電極121およびプラズマノズル122の間にパイロットアーク電流Ipを流す。パイロットアーク電源回路31は、パイロットアーク電流Ipの電流値を、設定された値となるように制御する。
Pilot arc
パイロットアーク電源回路31のその他の説明については、パイロットアーク電流検出回路33およびパイロットアーク電圧検出回路36の説明の後に記載する。
The other description of the pilot arc
パイロットアーク電流検出回路33は、非消耗電極121とプラズマノズル122との間に流れるパイロットアーク電流Ipの電流値を検出するためのものである。パイロットアーク電流検出回路33は、パイロットアーク電流Ipの電流値に対応するパイロットアーク電流検出信号Idpを送る。パイロットアーク電流検出信号Idpは、パイロットアーク電源回路31に送られる。
The pilot arc
パイロットアーク電圧検出回路36は、非消耗電極121とプラズマノズル122との間のパイロットアーク電圧Vpの電圧値を検出するためのものである。パイロットアーク電圧検出回路36は、パイロットアーク電圧Vpの電圧値に対応するパイロットアーク電圧検出信号Vdpを送る。パイロットアーク電圧検出信号Vdpは、パイロットアーク電源回路31に送られる。なお、本実施形態では、パイロットアーク電圧検出回路36は、本発明の検出回路の一例に相当する。
The pilot arc
パイロットアーク電源回路31は、パイロットアーク電圧検出回路36(検出回路)によって検出されたアーク状態反映値に基づき、電源出力値を上昇させる。アーク状態反映値とは、非消耗電極121およびプラズマノズル122との間に発生しているパイロットアークPaの状態を示すものである。そして、アーク状態反映値は、非消耗電極121およびプラズマノズル122の間のパイロットアーク電圧Vpの電圧値と、非消耗電極121およびプラズマノズル122の間に流れるパイロットアーク電流Ipの電流値と、のいずれか一方である。電源出力値は、パイロットアーク電圧Vpの電圧値、および、パイロットアーク電流Ipの電流値の他方である。そして、本実施形態では、パイロットアーク用回路3(パイロットアーク電源回路31)では定電流制御がなされている。そのため、パイロットアーク電流Ipの電流値は、パイロットアークPaの状態に依って変化せず、パイロットアーク電圧Vpの電圧値がパイロットアークPaの状態を反映した値となる。すなわち、本実施形態では、アーク状態反映値は、パイロットアーク電圧Vpの電圧値である。電源出力値は、パイロットアーク電流Ipの電流値である。
The pilot arc
本実施形態とは異なり、パイロットアーク電源回路31が定電圧制御されている場合、パイロットアーク電圧Vpの電圧値は、パイロットアークPaの状態に依って変化せず、パイロットアーク電流Ipの電流値がパイロットアークPaの状態を反映した値となる。この場合、アーク状態反映値は、パイロットアーク電流Ipの電流値であり、電源出力値は、パイロットアーク電圧Vpの電圧値である。
Unlike the present embodiment, when the pilot arc
パイロットアーク電源回路31は、パイロットアーク電流検出信号Idpと、パイロットアーク電圧検出信号Vdpと、メインアーク電流通電検出信号Dim(後述)と、を受ける。また、パイロットアーク電源回路31は、報知指示信号SIn1および報知指示信号SIn2を報知部85に送る。
Pilot arc
メインアーク用回路4は、非消耗電極121と母材Wとの間にメインアーク電流Imを流す。本実施形態では、メインアーク用回路4は、メインアーク電流Imの電流値を、設定された値となるように制御する。すなわち、メインアーク用回路4は、定電流制御を行う。
The
メインアーク用回路4は、メインアーク電源回路41と、メインアーク電流検出回路43と、メインアーク電流通電検出回路45と、を含む。
The
メインアーク電源回路41は、たとえば3相200V等の商用電源を入力として、インバータ制御、サイリスタ位相制御等の出力制御を行う。これにより、メインアーク電源回路41は、非消耗電極121および母材Wの間にメインアーク電流Imを流す。メインアーク電源回路41は、メインアーク電流Imの電流値を、設定された値となるように制御する。
The main arc
メインアーク電流検出回路43は、非消耗電極121と母材Wとの間に流れるメインアーク電流Imの電流値を検出するためのものである。メインアーク電流検出回路43は、メインアーク電流Imの電流値に対応するメインアーク電流検出信号Idmを送る。
The main arc
メインアーク電流通電検出回路45はメインアーク電流検出信号Idmを受ける。メインアーク電流通電検出回路45は、メインアーク電流Imの通電を検出するためのものである。メインアーク電流通電検出回路45は、メインアーク電流Imの通電を検出すると、メインアーク電流通電検出信号Dimをパイロットアーク電源回路31に送る。メインアーク電流通電検出回路45は、メインアーク電流Imの通電を、たとえば、メインアーク電流Imの電流値とあるしきい値とを比較することにより、検出する。なお、メインアーク電流通電検出回路45は、メインアーク電流Imの通電を検出している間は常に、メインアーク電流通電検出信号Dimを送り続ける。
Main arc current
プラズマガス流量制御回路491は、プラズマガスPGの流量を制御するためのものである。プラズマガス流量制御回路491は、プラズマガスPGの流量を指示するためのプラズマガス流量制御信号Spgを送る。
The plasma gas flow
シールドガス流量制御回路492は、シールドガスSGの流量を制御するためのものである。シールドガス流量制御回路492は、シールドガスSGの流量を指示するためのシールドガス流量制御信号Ssgを送る。
The shield gas flow
プラズマガス供給装置81は、プラズマガスPGをプラズマノズル122の内部に供給するためのものである。プラズマガス供給装置81は、プラズマガス流量制御回路491から受けたプラズマガス流量制御信号Spgに基づき、プラズマガスPGを供給する。
The plasma
シールドガス供給装置82は、シールドガスSGをプラズマノズル122とシールドガスノズル123との間に供給するためのものである。シールドガス供給装置82は、シールドガス流量制御回路492から受けたシールドガス流量制御信号Ssgに基づき、シールドガスSGを供給する。
The shield
報知部85は、たとえば、ブザーや警告灯や表示装置である。報知部85は、報知指示信号SIn1を受けると、不具合情報Inf1を報知する。不具合情報Inf1は、パイロットアークが不具合状態であることを示す情報である。不具合情報Inf1は、たとえばブザー音やアラーム音やライトの点灯やパイロットアークPaに不具合が生じた旨の表示である。報知部85は、報知指示信号SIn2を受けると、高温警報Inf2を報知する。高温警報Inf2は、プラズマノズル122が高温であることを示す警報である。高温警報Inf2は、たとえばブザー音やアラーム音や、ライトの点灯や、プラズマノズル122が高温となっている旨の表示である。
The
次に、図3を更に用いて、プラズマアーク溶接システムB1を用いたアーク溶接方法について説明する。 Next, the arc welding method using plasma arc welding system B1 is demonstrated further using FIG.
図3は、プラズマアーク溶接システムB1を用いたプラズマアーク溶接方法における各信号等のタイミングチャートである。同図では、(a)はパイロットアーク電流Ipの電流値、(b)はメインアーク電流Imの電流値、(c)は高温警報Inf2、(d)はロボット移動速度Vr、(e)はパイロットアーク電圧Vpの電圧値、(f)はメインアーク電圧Vmの電圧値、(g)はプラズマガスPGの流量、(h)不具合情報Inf1のそれぞれの変化状態を示す。 FIG. 3 is a timing chart of signals and the like in the plasma arc welding method using the plasma arc welding system B1. In this figure, (a) is the current value of the pilot arc current Ip, (b) is the current value of the main arc current Im, (c) is the high temperature alarm Inf2, (d) is the robot moving speed Vr, and (e) is the pilot. The voltage value of the arc voltage Vp, (f) indicates the voltage value of the main arc voltage Vm, (g) indicates the flow rate of the plasma gas PG, and (h) the change state of the defect information Inf1.
<時刻t11以前>
時刻t11以前において、非消耗電極121と母材Wとの間にメインアークMaが発生した状態で、定常溶接が行われている。
<Before time t11>
Prior to time t11, steady welding is performed in a state where the main arc Ma is generated between the
<時刻t11〜時刻t12>
時刻t11〜時刻t12の間も定常溶接が行われている。同図(b)に示すように、時刻t11〜時刻t12の間、メインアーク電流Imが流れている。時刻t11〜時刻t12のメインアーク電流Imの電流値は、たとえば、20〜350Aである。同図(f)に示すように、時刻t11〜時刻t12の間、非消耗電極121と母材Wとの間には、メインアーク電圧Vmが印加されている。時刻t11〜時刻t12のメインアーク電圧Vmの電圧値は、たとえば、10〜30Vである。同図(d)に示すように、時刻t11〜時刻t12の間、ロボット移動速度Vrが予め定められた値(0より大きい)となっている。すなわち、溶接進行方向Drに、非消耗電極121が母材Wに対して移動している。同図(g)に示すように、時刻t11〜時刻t12の間、プラズマガスPGが、非消耗電極121とプラズマノズル122との間に流れている。時刻t11〜時刻t12の間のプラズマガスPGのガス流量は、たとえば、0.3〜1.0L/minである。
<Time t11 to Time t12>
Steady welding is also performed between time t11 and time t12. As shown in FIG. 5B, the main arc current Im flows between time t11 and time t12. The current value of the main arc current Im from time t11 to time t12 is, for example, 20 to 350A. As shown in FIG. 5F, the main arc voltage Vm is applied between the
また、本実施形態では、定常溶接の間、非消耗電極121とプラズマノズル122との間にパイロットアークPaが発生したままとなっている。そのため、同図(a)に示すように、時刻t11〜時刻t12の間、パイロットアーク電流Ipが流れている。時刻t11〜時刻t12のパイロットアーク電流Ipの電流値は、たとえば、5〜15Aである。同図(e)に示すように、時刻t11〜時刻t12の間、非消耗電極121とプラズマノズル122との間には、パイロットアーク電圧Vpが印加されている。時刻t11〜時刻t12のパイロットアーク電圧Vpの電圧値は、たとえば、15〜17Vである。なお、本実施形態とは異なり、定常溶接の間、非消耗電極121とプラズマノズル122との間にパイロットアークPaを発生させていなくてもよい。
In the present embodiment, the pilot arc Pa remains generated between the
<時刻t12〜時刻t13>
時刻t12において、定常溶接終了信号(図示略)が、メインアーク電源回路41および動作制御回路2に送られる。メインアーク電源回路41は、定常溶接終了信号を受けると、出力を停止し、メインアークMaを消弧させる。これにより、同図(b)に示すように、時刻t12において、メインアーク電流Imは0になる。また、同図(f)に示すように、時刻t12において、メインアーク電圧Vmは0になる。同図(d)に示すように、動作制御回路2は、定常溶接終了信号を受けると、ロボット移動速度Vrを0とするための動作制御信号Msを溶接ロボット1に送る。これにより、時刻t12において、溶接進行方向Drにおける、非消耗電極121の母材Wに対する移動が停止する。
<Time t12 to Time t13>
At time t12, a steady welding end signal (not shown) is sent to the main arc
時刻t12においても、パイロットアーク電源回路31は定電流制御を行っているため、パイロットアーク電流Ipの電流値は変化しない。時刻t12において、メインアークMaが消弧すると、同図(e)に示すように、パイロットアーク電圧Vpの電圧値が増加する。これは、パイロットアーク電流Ipが、メインアークMaを経由して流れることができなくなるためである。時刻t12〜時刻t13にて上昇後のパイロットアーク電圧Vpの電圧値は、たとえば、24〜28Vである。図2に示すように、時刻t12直後のパイロットアークPaは、母材Wにより近接する位置まで発生している。
Even at time t12, the pilot arc
時刻t13直前には、パイロットアークPaがより弱くなる。図4には、時刻t13におけるパイロットアークPaを示している。パイロットアークPaが弱くなるにつれ、同図(e)に示すように、パイロットアーク電圧Vpの電圧値が減少してゆく。 Immediately before time t13, the pilot arc Pa becomes weaker. FIG. 4 shows the pilot arc Pa at time t13. As the pilot arc Pa becomes weaker, the voltage value of the pilot arc voltage Vp decreases as shown in FIG.
パイロットアークPaが弱くなるにつれ、パイロットアーク電圧Vpの電圧値が減少してゆく原因としては、たとえば、次の理由が考えられる。まず、プラズマノズル122の内面に酸化物が付着する。このような酸化物は、非消耗電極121を構成する材料(タングステン)の酸化物である可能性がある。プラズマノズル122の内面に酸化物が付着すると、非消耗電極121とプラズマノズル122との間に、酸化物を経由した電流経路が形成され、パイロットアークPaのうちプラズマノズル122の開口から出ている部分が少なくなる。また、非消耗電極121とプラズマノズル122との間に、酸化物を経由した電流経路が形成されると、非消耗電極121とプラズマノズル122との間の抵抗値が小さくなる。非消耗電極121とプラズマノズル122との間の抵抗値が小さくなると、パイロットアーク電圧Vpが減少していく。
As the pilot arc Pa becomes weaker, for example, the following reasons can be considered as the cause of the decrease in the pilot arc voltage Vp. First, oxide adheres to the inner surface of the
<時刻t13〜時刻t14>
時刻t13において、パイロットアーク電圧Vpの電圧値が、第1基準値記憶部391に記憶された第1基準値vp1を下回る。また、時刻t13においてはメインアークMaが消弧しているため、メインアーク電流Imは流れていない。そのため、パイロットアーク電源回路31は、メインアーク電流通電検出信号Dimを受けていない。すなわち、本実施形態では、パイロットアーク電源回路31がメインアーク電流通電検出信号Dimを受けていない場合に、パイロットアーク電圧Vpの値が第1基準値記憶部391に記憶された第1基準値vp1を下回っている。この場合、パイロットアーク電源回路31は、パイロットアークPaに不具合が発生したと判断し、報知部85に報知指示信号SIn1を送る。図3(h)に示すように、報知部85は、報知指示信号SIn1を受けると、不具合情報Inf1を報知する。不具合情報Inf1は、パイロットアークPaが不具合状態であることを示す情報である。不具合情報Inf1は、たとえばブザー音やアラーム音やライトの点灯やパイロットアークPaに不具合が生じた旨の表示である。
<Time t13 to Time t14>
At time t <b> 13, the voltage value of the pilot arc voltage Vp is lower than the first reference value vp <b> 1 stored in the first reference
報知部85によって、不具合情報Inf1が報知されると、ユーザは、パイロットアークPaの状態が悪いことを知る。
When the failure information Inf1 is notified by the
<時刻t14〜時刻t15>
パイロットアーク電源回路31は、パイロットアーク電圧検出回路36によって検出されたパイロットアーク電圧Vpの電圧値に基づき、パイロットアーク電流Ipの電流値を上昇させる(時刻t14以降参照)。なお、本実施形態では、大幅にパイロットアーク電流Ipを上昇させずに、徐々にパイロットアーク電流Ipを上昇させる。プラズマノズル122が過度に高温となることを防止するためである。
<Time t14 to Time t15>
The pilot arc
具体的には、パイロットアーク電源回路31は、パイロットアーク電圧Vpの電圧値が、第1基準値記憶部391に記憶された第1基準値vp1を下回ると、パイロットアーク電流Ipの電流値を上昇させる第1上昇処理を行う。また、パイロットアーク電源回路31は、パイロットアーク電流Ipの電流値が上限値ip1を下回る場合にのみ、上記第1上昇処理を行うことが好ましい。本実施形態では、図3(e)に示すように、時刻t13にて、パイロットアーク電圧Vpの電圧値が、第1基準値記憶部391に記憶された第1基準値vp1を下回っている。また、同図(a)に示すように、時刻t13にて、パイロットアーク電流Ipの電流値が上限値ip1を下回っている。そのため、同図(a)に示すように、時刻t14にて、パイロットアーク電源回路31は、パイロットアーク電流Ipの電流値を上昇させている。パイロットアーク電流Ipの電流値を上昇させると、同図(e)に示すように、パイロットアーク電圧Vpの電圧値も上昇する。なお、第1基準値vp1は、たとえば、17〜18Vである。また、時刻t14にてパイロットアーク電流Ipは、たとえば、3〜5A上昇する。時刻t14〜時刻t15は、たとえば、5〜45secである。
Specifically, the pilot arc
本実施形態では、時刻t13〜時刻t14は、たとえば、0.5〜5minである。本実施形態とは異なり、時刻t13〜時刻t14が比較的短くてもよく、たとえば、1〜10secであってもよい。 In the present embodiment, the time t13 to the time t14 is, for example, 0.5 to 5 minutes. Unlike this embodiment, time t13 to time t14 may be relatively short, for example, 1 to 10 sec.
<時刻t15〜時刻t16>
パイロットアーク電源回路31は、時刻t14の第1上昇処理を終えた後に、パイロットアーク電圧Vpの電圧値が、第2基準値vp2を下回っている場合、パイロットアーク電流Ipの電流値を上昇させる第2上昇処理を行う。また、パイロットアーク電源回路31は、パイロットアーク電流Ipの電流値が上限値ip1を下回る場合にのみ、上記第2上昇処理を行うことが好ましい。本実施形態では、図3(e)に示すように、時刻t15直前にて、パイロットアーク電圧Vpの電圧値が第2基準値vp2を下回っている。また、同図(a)に示すように、時刻t15直前にて、パイロットアーク電流Ipの電流値が上限値ip1を下回っている。そのため、同図(a)に示すように、時刻t15にて、パイロットアーク電源回路31は、パイロットアーク電流Ipの電流値を上昇させる。パイロットアーク電流Ipの電流値を上昇させると、同図(e)に示すように、パイロットアーク電圧Vpの電圧値も上昇する。また、時刻t15にてパイロットアーク電流Ipは、たとえば、3〜5A上昇する。時刻t15〜時刻t16は、たとえば、5〜45secである。なお、第2基準値vp2は、たとえば、18〜22Vである。上限値ip1は、たとえば、24〜26Aである。
<Time t15 to Time t16>
The pilot
<時刻t16〜時刻t17>
図3(e)に示すように、時刻t16直前にて、パイロットアーク電圧Vpの電圧値が第2基準値vp2を下回っている。また、同図(a)に示すように、時刻t16直前にて、パイロットアーク電流Ipの電流値が上限値ip1を下回っている。そのため、パイロットアーク電源回路31は、時刻t16にて再び第2上昇処理を行う。具体的には、同図(a)に示すように、時刻t16にて、パイロットアーク電源回路31は、パイロットアーク電流Ipの電流値を上昇させる。パイロットアーク電流Ipの電流値を上昇させると、同図(e)に示すように、パイロットアーク電圧Vpの電圧値も上昇する。このときのパイロットアーク電流Ipの電流値の上昇値も、たとえば3〜5Aである。
<Time t16 to Time t17>
As shown in FIG. 3E, the voltage value of the pilot arc voltage Vp is lower than the second reference value vp2 immediately before time t16. Further, as shown in FIG. 5A, immediately before time t16, the current value of pilot arc current Ip is lower than upper limit value ip1. Therefore, pilot arc
パイロットアーク電源回路31は、パイロットアーク電流Ipの電流値を上昇させた後、パイロットアーク電圧Vpの電圧値が、第2基準値vp2以上である場合、パイロットアーク電流Ipの電流値を維持する。また、パイロットアーク電源回路31は、パイロットアーク電流Ipの電流値が上限値ip1を下回る場合にのみ、パイロットアーク電流Ipの電流値を維持する。本実施形態では、図3(e)に示すように、時刻t16にてパイロットアーク電流Ipを上昇させた後、パイロットアーク電圧Vpの電圧値が第2基準値vp2以上となっている。また、同図(a)に示すように、時刻t16にてパイロットアーク電流Ipを上昇させた後、パイロットアーク電流Ipの電流値が上限値ip1を下回っている。よって、時刻t16以降、パイロットアーク電源回路31は、パイロットアーク電流Ipの電流値を維持する。このとき、パイロットアークPaは通常の強さに戻っている。
After increasing the pilot arc current Ip current value, the pilot arc
<時刻t17〜時刻t18>
そして、時刻t17において、溶接開始指示信号(図示略)が動作制御回路2やメインアーク用回路4に送られる。これにより、図3(f)に示すように、非消耗電極121と母材Wとの間に、メインアーク電圧Vmが印加され、非消耗電極121と母材Wとの間にメインアークMaが発生する。メインアークMaが発生すると、図3(b)に示すように、メインアーク電流Imが流れ始める。メインアーク電流Imが流れ始めると、メインアーク電流通電検出回路45からメインアーク電流通電検出信号Dimが、パイロットアーク電源回路31に送られる。メインアーク電流Imが流れている間は常に、メインアーク電流通電検出信号Dimは送られる。
<Time t17 to Time t18>
At time t17, a welding start instruction signal (not shown) is sent to the operation control circuit 2 and the
同図(e)に示すように、メインアークMaが発生すると、パイロットアーク電圧Vpが低下する。これは、パイロットアーク電流Ipの一部がメインアークMaを経由して流れる結果、非消耗電極121とプラズマノズル122との間の抵抗が低下するためである。
As shown in FIG. 5E, when the main arc Ma is generated, the pilot arc voltage Vp is decreased. This is because a part of the pilot arc current Ip flows through the main arc Ma, and as a result, the resistance between the
パイロットアーク電源回路31は、メインアーク電流通電検出信号Dimを受けている場合に、パイロットアーク電圧Vpの電圧値が第1基準値vp1を下回ったとしても、パイロットアーク電流Ipの電流値を上昇させる上述の第1上昇処理を行わない。すなわち、パイロットアーク電源回路31は、メインアークMaが発生している場合には、パイロットアーク電圧Vpの電圧値が第1基準値vp1を下回ったとしても、パイロットアーク電流Ipの電流値を上昇させる上述の第1上昇処理を行わない。
When receiving the main arc current energization detection signal Dim, the pilot arc
<時刻t18以降>
同図(d)に示すように、時刻t18において、プラズマノズル122が母材Wに対して移動し始め(ロボット移動速度Vrが0より大きい値となり)、定常溶接が開始される。そして、時刻t18以降のいずれかの時点において、パイロットアーク電流Ipの電流値が時刻t14以前の値まで減少させられる。その後は、上述の時刻t11からの工程が繰り返される。なお、メインアークMaが発生した後は、メインアークMaの熱等によって非消耗電極121やプラズマノズル122に付着した酸化物が除去される。
<After time t18>
As shown in FIG. 4D, at time t18, the
図3では、パイロットアーク電流Ipが上限値ip1を超えない場合を示したが、図5に示すように、パイロットアーク電流Ipが上限値ip1を超えてしまう場合もある。パイロットアーク電流Ipが上限値ip1を超えた場合について、図5を用いて説明する。 Although FIG. 3 shows the case where the pilot arc current Ip does not exceed the upper limit value ip1, as shown in FIG. 5, the pilot arc current Ip may exceed the upper limit value ip1. A case where pilot arc current Ip exceeds upper limit ip1 will be described with reference to FIG.
<時刻t16〜時刻t17> <Time t16 to Time t17>
図5(a)に示すように、図3と同様に時刻t16にてパイロットアーク電流Ipの電流値を上昇させると、パイロットアーク電流Ipの電流値が上限値ip1以上となっている。この場合、パイロットアーク電源回路31は、プラズマノズル122が高温になるおそれがあると判断し、報知指示信号SIn2を報知部85に送る。報知部85は、報知指示信号SIn2を受けると、図5(c)に示すように、時刻t17にて高温警報Inf2を報知する。高温警報Inf2は、プラズマノズル122が高温であることを示す警報である。高温警報Inf2は、たとえばブザー音やアラーム音や、ライトの点灯や、プラズマノズル122が高温となっている旨の表示である。
As shown in FIG. 5A, when the current value of pilot arc current Ip is increased at time t16 as in FIG. 3, the current value of pilot arc current Ip becomes equal to or greater than upper limit value ip1. In this case, the pilot arc
また、パイロットアーク電流Ipの電流値が上限値ip1以上となっている場合、パイロットアーク電源回路31は、出力を停止し、パイロットアークPaを消弧する。これにより、同図(a)に示すように、時刻t18において、パイロットアーク電流Ipが0となり、同図(e)に示すように、パイロットアーク電圧Vpが0となる。
When the current value of pilot arc current Ip is equal to or higher than upper limit value ip1, pilot arc
次に、本実施形態の作用効果について説明する。 Next, the effect of this embodiment is demonstrated.
本実施形態においては、パイロットアーク電源回路31は、パイロットアーク電圧検出回路36によって検出されたパイロットアーク電圧Vpの電圧値に基づき、パイロットアーク電流Ipの電流値を上昇させる。このような構成によると、パイロットアーク電流Ipの電流値(電源出力値)とともに、パイロットアーク電圧Vpの電圧値(アーク状態反映値)が上昇し、パイロットアークPaがより強くなる。これにより、より確実にメインアークMaを点弧させることができる。
In the present embodiment, the pilot arc
本実施形態においては、第1基準値vp1および第2基準値vp2を用いているため、パイロットアークPaが弱くなったことを検出する基準値と、パイロットアークPaが適正になったことを検出する基準値と、を異ならせることができる。これにより、パイロットアークPaをより適正な強さまで戻すことができる。そのため、より確実にメインアークMaを点弧させることができる。 In the present embodiment, since the first reference value vp1 and the second reference value vp2 are used, a reference value for detecting that the pilot arc Pa has become weak and that the pilot arc Pa has become appropriate are detected. The reference value can be made different. Thereby, the pilot arc Pa can be returned to a more appropriate strength. Therefore, the main arc Ma can be fired more reliably.
本実施形態においては、パイロットアーク電流Ipの電流値の上限値ip1を記憶する上限値記憶部393を更に備える。パイロットアーク電源回路31は、上限値ip1に基づいて、パイロットアーク電源回路31の出力状態を決定する。このような構成によると、プラズマノズル122が過度に高温となることを抑制できる。
In the present embodiment, an upper
本実施形態においては、パイロットアーク電源回路31は、パイロットアーク電流Ipの電流値の値が、上限値ip1以上である場合、パイロットアーク電源回路31の出力を停止する。このような構成は、プラズマノズル122が過度に高温となることを抑制するのに適する。
In the present embodiment, the pilot arc
本実施形態においては、報知部85は、パイロットアーク電圧Vpの電圧値の値が第1基準値vp1を下回ると、パイロットアークPaが不具合状態であることを示す不具合情報Inf1を報知する。このような構成によると、プラズマアーク溶接システムB1のユーザが、パイロットアークPaが不具合であることを、知ることができる。
In the present embodiment, when the value of the pilot arc voltage Vp falls below the first reference value vp1, the
本実施形態においては、報知部85は、パイロットアーク電流Ipの電流値が、上限値ip1以上である場合、プラズマノズル122が高温であることを示す高温警報Inf2を報知する。このような構成によると、プラズマアーク溶接システムB1のユーザが、プラズマノズル122が高温となっている可能性があることを知ることができる。
In the present embodiment, when the current value of the pilot arc current Ip is equal to or higher than the upper limit value ip1, the
本実施形態においては、パイロットアーク電源回路31は、非消耗電極121および母材Wの間にメインアークMaが発生していない場合にのみ、パイロットアーク電流Ipを上昇させる。このような構成によると、正常にメインアークMaが点弧した場合に、パイロットアークPaが不具合であると判断される不具合を回避できる。
In the present embodiment, the pilot
本発明は、上述した実施形態に限定されるものではない。本発明の各部の具体的な構成は、種々に設計変更自在である。 The present invention is not limited to the embodiment described above. The specific configuration of each part of the present invention can be changed in various ways.
1 溶接ロボット
11 マニピュレータ
12 トーチ
121 非消耗電極
122 プラズマノズル
123 シールドガスノズル
2 動作制御回路
3 パイロットアーク用回路
31 パイロットアーク電源回路
33 パイロットアーク電流検出回路
36 パイロットアーク電圧検出回路
391 第1基準値記憶部
392 第2基準値記憶部
393 上限値記憶部
4 メインアーク用回路
41 メインアーク電源回路
43 メインアーク電流検出回路
45 メインアーク電流通電検出回路
491 プラズマガス流量制御回路
492 シールドガス流量制御回路
81 プラズマガス供給装置
82 シールドガス供給装置
85 報知部
B1 プラズマアーク溶接システム
Dim メインアーク電流通電検出信号
Dr 溶接進行方向
Idm メインアーク電流検出信号
Idp パイロットアーク電流検出信号
Im メインアーク電流
Inf1 不具合情報
Inf2 高温警報
Ip パイロットアーク電流
ip1 上限値
Ma メインアーク
Ms 動作制御信号
Pa パイロットアーク
PG プラズマガス
SG シールドガス
SIn1 報知指示信号
SIn2 報知指示信号
Spg プラズマガス流量制御信号
Ssg シールドガス流量制御信号
t11,t12,t13,t14,t15,t16,t17,t18 時刻
Vdp パイロットアーク電圧検出信号
Vm メインアーク電圧
Vp パイロットアーク電圧
vp1 第1基準値
vp2 第2基準値
Vr ロボット移動速度
W 母材
1 welding robot 11
Claims (7)
前記非消耗電極および前記プラズマノズルの間にパイロットアーク電流を流すパイロットアーク電源回路と、
前記非消耗電極および前記プラズマノズルとの間に発生しているパイロットアークの状態を示すアーク状態反映値を検出する検出回路と、を備え、
前記パイロットアーク電源回路は、前記検出回路によって検出されたアーク状態反映値に基づき、電源出力値を上昇させ、
前記アーク状態反映値は、前記非消耗電極および前記プラズマノズルの間のパイロットアーク電圧の電圧値と、前記非消耗電極および前記プラズマノズルの間に流れるパイロットアーク電流の電流値と、のいずれか一方であり、
前記電源出力値は、前記パイロットアーク電圧の電圧値と、前記パイロットアーク電流の電流値と、の他方であり、
第1基準値を記憶する第1基準値記憶部と、前記第1基準値よりも大きい第2基準値を記憶する第2基準値記憶部と、を備え、
前記パイロットアーク電源回路は、前記アーク状態反映値が前記第1基準値を下回ると、前記電源出力値を上昇させる第1上昇処理を行い、
前記パイロットアーク電源回路は、前記第1上昇処理を終えた後に、前記アーク状態反映値が第2基準値を下回る場合、前記電源出力値を上昇させる第2上昇処理を行う、プラズマアーク溶接システム。 A plasma arc welding system for a plasma arc welding method using a torch including a non-consumable electrode and a plasma nozzle surrounding the non-consumable electrode,
A pilot arc power supply circuit for passing a pilot arc current between the non-consumable electrode and the plasma nozzle;
A detection circuit that detects an arc state reflection value indicating a state of a pilot arc generated between the non-consumable electrode and the plasma nozzle;
The pilot arc power circuit increases the power output value based on the arc state reflected value detected by the detection circuit,
The arc state reflected value is either a voltage value of a pilot arc voltage between the non-consumable electrode and the plasma nozzle, or a current value of a pilot arc current flowing between the non-consumable electrode and the plasma nozzle. And
The power output value, the voltage value of the pilot arc voltage, the current value of the pilot arc current, the other der of is,
A first reference value storage unit that stores a first reference value; and a second reference value storage unit that stores a second reference value larger than the first reference value;
The pilot arc power supply circuit performs a first increase process for increasing the power output value when the arc state reflected value is lower than the first reference value,
The plasma arc welding system , wherein the pilot arc power supply circuit performs a second ascending process for increasing the power output value when the arc state reflected value is lower than a second reference value after finishing the first ascending process .
前記パイロットアーク電源回路は、前記メインアークが再点弧した後に、前記電源出力値を減少させる、請求項2に記載のプラズマアーク溶接システム。 Removing the oxide by a re-ignited main arc between the non-consumable electrode and the base material;
The plasma arc welding system according to claim 2, wherein the pilot arc power circuit reduces the power output value after the main arc is re-ignited .
前記パイロットアーク電源回路は、前記上限値に基づいて、前記パイロットアーク電源回路の出力状態を決定する、請求項1または請求項4に記載のプラズマアーク溶接システム。 An upper limit storage unit for storing an upper limit value of the power output value;
The plasma arc welding system according to claim 1 or 4, wherein the pilot arc power circuit determines an output state of the pilot arc power circuit based on the upper limit value.
前記電源出力値が前記上限値を下回っている場合であり、且つ、
前記第1上昇処理を終えた後に、前記アーク状態反映値が第2基準値を下回る場合、
前記第2上昇処理を行う、請求項5または請求項6に記載のプラズマアーク溶接システム。 The pilot arc power circuit is
The power output value is below the upper limit, and
When the arc state reflected value is lower than the second reference value after finishing the first ascent process,
The plasma arc welding system according to claim 5 or 6, wherein the second ascending process is performed.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013197038A JP6178682B2 (en) | 2013-09-24 | 2013-09-24 | Plasma arc welding system |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013197038A JP6178682B2 (en) | 2013-09-24 | 2013-09-24 | Plasma arc welding system |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2015062912A JP2015062912A (en) | 2015-04-09 |
| JP6178682B2 true JP6178682B2 (en) | 2017-08-09 |
Family
ID=52831274
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013197038A Active JP6178682B2 (en) | 2013-09-24 | 2013-09-24 | Plasma arc welding system |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6178682B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017205770A (en) * | 2016-05-16 | 2017-11-24 | 株式会社ダイヘン | Plasma welding equipment |
| GB2579835A (en) * | 2018-12-17 | 2020-07-08 | Linde Ag | Intelligent preflow-plasma gas control |
Family Cites Families (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH03142075A (en) * | 1989-10-26 | 1991-06-17 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Plasma arc machine |
| JP4509252B2 (en) * | 1999-07-05 | 2010-07-21 | パナソニック株式会社 | Plasma welding equipment |
| JP2008212969A (en) * | 2007-03-02 | 2008-09-18 | Nippon Steel & Sumikin Welding Co Ltd | Plasma torch |
-
2013
- 2013-09-24 JP JP2013197038A patent/JP6178682B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2015062912A (en) | 2015-04-09 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6596669B2 (en) | Control method of arc welding | |
| JP4422729B2 (en) | How to control the welding process | |
| JP2018118315A (en) | Device and method for welding with ac waveform | |
| JP2018118316A (en) | Apparatus and method for welding with ac waveform | |
| JPWO2019202854A1 (en) | Welding torch and arc welding equipment using it | |
| JP2018118317A (en) | Device and method for welding with ac waveform | |
| JP6178682B2 (en) | Plasma arc welding system | |
| JP5596394B2 (en) | Arc welding method | |
| TWI516331B (en) | Arc welding method and arc welding system | |
| WO2015186474A1 (en) | Arc start control method for consumable electrode type arc welding, and welding device | |
| JP7303383B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for welding weld seams | |
| JP5937323B2 (en) | Plasma keyhole welding method and plasma keyhole welding system | |
| JP6174959B2 (en) | Plasma arc welding system | |
| JP2010214399A (en) | Arc welding method | |
| JP5545996B2 (en) | Constriction detection control method for consumable electrode arc welding | |
| JP4490011B2 (en) | Arc start control method | |
| JP6356990B2 (en) | Industrial product manufacturing method, spot welding system | |
| JP4780146B2 (en) | Welding end control method | |
| US20220097161A1 (en) | Systems and methods to control a wire electrode at the end of a weld | |
| JP6077833B2 (en) | Welding apparatus and arc welding system | |
| JP5986469B2 (en) | Plasma arc welding system | |
| JPH05261535A (en) | Method for controlling consumable electrode ac arc welding machine | |
| JP2011200867A (en) | Arc welding equipment | |
| JP5977553B2 (en) | Plasma arc welding method and plasma arc welding system | |
| JP2010284665A (en) | Plasma key hole welding method |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20160824 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20170412 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20170502 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20170531 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20170711 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20170714 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 6178682 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |