JP5495302B2 - Motor built-in roller - Google Patents
Motor built-in roller Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5495302B2 JP5495302B2 JP2009245362A JP2009245362A JP5495302B2 JP 5495302 B2 JP5495302 B2 JP 5495302B2 JP 2009245362 A JP2009245362 A JP 2009245362A JP 2009245362 A JP2009245362 A JP 2009245362A JP 5495302 B2 JP5495302 B2 JP 5495302B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- motor
- roller
- braking force
- magnet
- permanent magnet
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Rollers For Roller Conveyors For Transfer (AREA)
Description
本発明は、主としてコンベア等に用いられるモータ内蔵ローラ、並びにローラに関するものであり、さらに詳細には、高い精度で回転角度や回転方向を検出可能であり、且つモータ停止時にローラを停止するためのブレーキ機能を有するモータ内蔵ローラに関するものである。 The present invention relates to a roller with a built-in motor mainly used for a conveyor and the like, and more specifically, for detecting a rotation angle and a rotation direction with high accuracy and for stopping the roller when the motor is stopped. The present invention relates to a motor built-in roller having a brake function.
コンベア等に用いられるローラには、ローラの内部にモータを配し、該モータによって前記ローラを回転駆動させるモータ内蔵ローラが数多くある。ところで、モータの回転動作を制御する構成として、位置検出手段を用いてモータの回転角度を検出する構成が知られている。例えば、位置検出手段にホールICを用いてモータの回転角度を検知するモータ内蔵ローラを用いた搬送システムが特許文献1に開示されている。
Many rollers used in conveyors have a motor built-in roller in which a motor is arranged inside the roller and the roller is driven to rotate by the motor. By the way, as a configuration for controlling the rotation operation of the motor, a configuration for detecting the rotation angle of the motor using a position detection means is known. For example,
また、このようなモータ内蔵ローラでは、動作制御等のためにモータの外側に磁石を配置することにより制動装置とすることができる。具体的には、図7に示されるように、まずモータの回転軸を円筒型のケース部材の両端から突出させて、その片側に磁石102を取り付ける。さらに、ローラ本体内部の対向する内壁面に、それぞれ2つの磁石103を異なる磁極が向かい合うように取り付ける。そして、内壁面に設けた2つの磁石103の間にモータ外部の磁石102が位置するように配置する。そうすることにより、モータ外部に取り付けた磁石102の2つの磁極が、それぞれ内壁面に設けた2つの磁石103と引き合うことにより、モータの回転駆動を制動するというものである。
Moreover, in such a motor built-in roller, it can be set as a braking device by arrange | positioning a magnet outside a motor for operation control etc. Specifically, as shown in FIG. 7, first, the rotating shaft of the motor is projected from both ends of the cylindrical case member, and the
そこで本発明者らは、ローラの構成の効率化のため、制動装置の磁石を位置検出用の磁石として使用することを考えた。具体的には、モータの外部に設けた制動装置の磁石の側にホールICを設置して、制動装置の磁石の磁界を検知する構成である。
しかしながらこの方策では、ローラ本体内部の内周壁に設けた磁石103の磁界がホールICのホール素子に干渉してしまうため、モータの回転角度が正確に検出できなくなり、実施することができなかった。
Therefore, the present inventors considered using the magnet of the braking device as a position detection magnet in order to increase the efficiency of the roller configuration. Specifically, the Hall IC is installed on the magnet side of the braking device provided outside the motor to detect the magnetic field of the braking device magnet.
However, in this measure, since the magnetic field of the
この問題を解決する方法として、図8のように、磁界がホールIC101(ホール素子)に干渉しないように磁石を配置するという方法が考えられる。しかしながらこの方法では、モータの回転軸に対して垂直方向に働いていた磁力が斜め方向に働いてしまい、振動が発生してしまうという問題がある。また、磁力が斜め方向に働くことにより、制動する力が弱くなってしまうという問題もある。 As a method of solving this problem, as shown in FIG. 8, a method of arranging magnets so that the magnetic field does not interfere with the Hall IC 101 (Hall element) can be considered. However, with this method, there is a problem that the magnetic force acting in the direction perpendicular to the rotation axis of the motor acts in an oblique direction, causing vibration. There is also a problem that the braking force is weakened by the magnetic force acting in an oblique direction.
そこで本発明は、従来技術の上記した問題点に注目し、モータ外部に設けた位置検出のための磁石を制動装置の一部として使用しても、振動や制動力の低下が起きないことのできるモータ内蔵ローラを提供することを課題とするものである。 Therefore, the present invention pays attention to the above-mentioned problems of the prior art, and even if a position detecting magnet provided outside the motor is used as a part of the braking device, vibration and braking force do not decrease. An object of the present invention is to provide a roller with a built-in motor.
上記課題を解決するための請求項1に記載の発明は、ローラ本体内にモータが内蔵されたモータ内蔵ローラであって、前記モータの回転子と同期的に回転する制動力発生用永久磁石と、磁界を検知する検知手段とを有し、前記検知手段は制動力発生用永久磁石の近傍にあって前記制動力発生用永久磁石の発生させる磁界を検知してモータの回転情報を取得するものであり、制動力発生用永久磁石の近傍に一時磁石が配されており、前記一時磁石は鉄片であり、前記一時磁石は、制動力発生用永久磁石の周囲を不連続に囲むものであり、当該一時磁石と制動力発生用永久磁石との間の磁力によるブレーキ機能による回転子の制動力を発生させることを特徴とするモータ内蔵ローラである。
The invention according to
本発明のモータ内蔵ローラでは、制動力発生用永久磁石がモータの回転子と同期的に回転するので、制動力発生用永久磁石の発生させる磁界を検知することにより、モータの回転情報を検知することができる。そして本発明のモータ内蔵ローラでは、検知手段が制動力発生用永久磁石の近傍に配されるため、より正確に制動力発生用永久磁石の磁界を検知可能となっている。したがって、検知手段がモータ内部の回転子の磁界を検知する場合と比べて、より正確にモータの回転情報を検知することができる。
ここで、「回転情報」とはモータの回転方向や回転角度等モータの回転動作に係る情報のことである。
In the motor built-in roller of the present invention, the braking force generating permanent magnet rotates synchronously with the rotor of the motor, so that the rotation information of the motor is detected by detecting the magnetic field generated by the braking force generating permanent magnet. be able to. In the roller with a built-in motor according to the present invention, since the detecting means is arranged in the vicinity of the braking force generating permanent magnet, the magnetic field of the braking force generating permanent magnet can be detected more accurately. Therefore, the rotation information of the motor can be detected more accurately than when the detection means detects the magnetic field of the rotor inside the motor.
Here, “rotation information” refers to information related to the rotation operation of the motor, such as the rotation direction and rotation angle of the motor.
また、本発明のモータ内蔵ローラでは、制動力発生用永久磁石と一時磁石との間の磁力によって回転子の制動力を発生させる。即ち、制動力発生用永久磁石を、モータの回転情報の高精度な検知と、回転子の制動力の発生という二つの動作のために使用可能である。そのため、制動力を発生させる制動装置と、高精度なモータの回転情報の検知を行う検知装置とを個別に設ける場合と比べて、部品点数を減らすことができる。 In the motor built-in roller of the present invention, the braking force of the rotor is generated by the magnetic force between the braking force generating permanent magnet and the temporary magnet. That is, the braking force generating permanent magnet can be used for two operations of highly accurate detection of the rotation information of the motor and generation of the braking force of the rotor. Therefore, the number of parts can be reduced as compared with a case where a braking device that generates a braking force and a detection device that detects rotation information of the motor with high accuracy are individually provided.
ここで、一時磁石は自発的に磁界を発生させないので、検知手段の磁界の検知を阻害しない。そのため、本発明のモータ内蔵ローラでは、一時磁石と検知手段を共に制動力発生用永久磁石との近傍に配することができる。
したがって、検知手段を制動力発生用永久磁石の側に配置すると共に、一時磁石と制動力発生用永久磁石との間に発生する磁力の向きがモータの回転軸と垂直になるように、一時磁石を配置することができる。したがって、モータの回転情報を高精度に検知でき、且つ磁力の向きが回転軸に対して傾くことによるローラ本体の振動や、制動力の減少を抑制することができる。
加えて、本発明のモータ内蔵ローラでは、制動力を発生させる機構とモータの回転情報を検知する機構をまとめて同じ場所に配置できるので、モータ内部の空間を有効に活用することができる。
Here, since the temporary magnet does not spontaneously generate a magnetic field, it does not hinder the detection of the magnetic field of the detection means. Therefore, in the motor built-in roller of the present invention, both the temporary magnet and the detection means can be arranged in the vicinity of the braking force generating permanent magnet.
Therefore, the temporary magnet is arranged so that the detecting means is disposed on the side of the permanent magnet for generating the braking force and the direction of the magnetic force generated between the temporary magnet and the permanent magnet for generating the braking force is perpendicular to the rotation axis of the motor. Can be arranged. Therefore, the rotation information of the motor can be detected with high accuracy, and the vibration of the roller body and the decrease of the braking force due to the inclination of the direction of the magnetic force with respect to the rotation axis can be suppressed.
In addition, in the motor built-in roller of the present invention, the mechanism for generating the braking force and the mechanism for detecting the rotation information of the motor can be collectively arranged at the same place, so that the space inside the motor can be effectively utilized.
さらに本発明のモータ内蔵ローラでは、検知装置が磁界(磁気)を検知するものであるため、光学式の検知装置と比べて塵や埃、油等の汚れの影響を受けにくいという利点がある。 Furthermore, the roller with a built-in motor according to the present invention has an advantage that it is less affected by dirt such as dust, dust, and oil than the optical detection device because the detection device detects a magnetic field (magnetism).
請求項2に記載の発明は、ローラ本体内にモータが内蔵されたモータ内蔵ローラであって、前記モータの回転子と同期的に回転する制動力発生用永久磁石と、磁界を検知する検知手段とを有し、前記検知手段は前記制動力発生用永久磁石の発生させる磁界を検知してモータの回転情報を取得するものであり、制動力発生用永久磁石の近傍に一時磁石が配されており、前記一時磁石は鉄片であり、前記一時磁石は、制動力発生用永久磁石の周囲を不連続に囲むものであり、前記検知手段が当該一時磁石と接触し、前記一時磁石と制動力発生用永久磁石との間の磁力によるブレーキ機能による回転子の制動力を発生させることを特徴とするモータ内蔵ローラである。 According to a second aspect of the present invention, there is provided a motor built-in roller in which a motor is built in a roller body, the braking force generating permanent magnet rotating synchronously with the rotor of the motor, and a detecting means for detecting a magnetic field. The detecting means detects a magnetic field generated by the braking force generating permanent magnet and acquires rotation information of the motor, and a temporary magnet is disposed in the vicinity of the braking force generating permanent magnet. The temporary magnet is an iron piece, and the temporary magnet discontinuously surrounds a permanent magnet for generating a braking force, and the detecting means is in contact with the temporary magnet and generates the braking force with the temporary magnet. a motorized roller, characterized in that the braking force is generated in the rotor due to by that brake function the magnetic force between the use permanent magnets.
本発明のモータ内蔵ローラでは、一時磁石が自発的に磁界を発生させず、制動力発生用永久磁石の近傍に配され、また、検知手段が一時磁石と接触している。そのため、検知手段が一時磁石を介して制動力発生用永久磁石の磁界を検知することができる。そのことにより、検知手段と制動力発生用永久磁石が離れている状態でも、制動力発生用永久磁石が発する磁界の高精度の検知が可能になる。したがって、モータ内蔵ローラの本体内における部材の配置時の制約が少なくなり、ローラ本体内の多様な設計が可能となる。 In the roller with a built-in motor according to the present invention, the temporary magnet does not spontaneously generate a magnetic field, is disposed in the vicinity of the permanent magnet for generating the braking force, and the detection means is in contact with the temporary magnet. Therefore, the detection means can detect the magnetic field of the braking force generating permanent magnet via the temporary magnet. As a result, even when the detection means and the braking force generating permanent magnet are separated, the magnetic field generated by the braking force generating permanent magnet can be detected with high accuracy. Therefore, there are less restrictions on the arrangement of members in the main body of the motor built-in roller, and various designs in the roller main body are possible.
請求項3に記載の発明は、ローラ本体内にモータが内蔵されたモータ内蔵ローラであって、前記モータは、永久磁石又はコイルによって構成された回転子と、コイルによって構成された固定子と、回転子の回転姿勢を検知して固定子を流れる電流の向きを切り替えるための信号を発生させる検知手段とを備えたブラシレスモータであり、回転子と同期的に回転する制動力発生用永久磁石を有し、前記検知手段は磁界を検知するものであり、前記検知手段は制動力発生用永久磁石の近傍にあって、前記制動力発生用永久磁石の磁界を検知して固定子を流れる電流の向きを切り替えるための信号を発生させ、制動力発生用永久磁石の近傍に一時磁石が配されており、前記一時磁石は鉄片であり、前記一時磁石は、制動力発生用永久磁石の周囲を不連続に囲むものであり、当該一時磁石と制動力発生用永久磁石との間の磁力によるブレーキ機能による回転子の制動力を発生させることを特徴とするモータ内蔵ローラである。
The invention according to
本発明のモータ内蔵ローラでは、内蔵するモータにブラシレスモータを使用して、検知手段が検知した情報を基に、ブラシレスモータの固定子に流れる電流を切り替える信号を発生させることができる。つまり、ブラシレスモータの外部に設けた検知手段によりブラシレスモータの動作の制御を行うため、上記した利点に加えて、制御用のコンピュータシステム等にモータの動作制御を組み込み易いという利点がある。 In the roller with a built-in motor of the present invention, a brushless motor can be used as the built-in motor, and a signal for switching the current flowing through the stator of the brushless motor can be generated based on the information detected by the detecting means. That is, since the operation of the brushless motor is controlled by the detection means provided outside the brushless motor, in addition to the above-described advantages, there is an advantage that the motor operation control can be easily incorporated into a control computer system or the like.
請求項4に記載の発明は、前記検知手段がホールICであることを特徴とする請求項1乃至3のいずれかに記載のモータ内蔵ローラである。
The invention according to
本発明のモータ内蔵ローラでは検知手段にホールICを用いる。そのため、モータの回転量と回転方向を非接触の状態で検知可能である。そのため、接触型のセンサと比べて検知手段を長寿命化することができる。また、回路に組み込み易いという利点もある。 In the motor built-in roller of the present invention, a Hall IC is used as the detecting means. Therefore, the rotation amount and rotation direction of the motor can be detected in a non-contact state. Therefore, the life of the detection means can be extended compared to the contact type sensor. There is also an advantage that it can be easily incorporated into a circuit.
前記した請求項1乃至4のいずれかに記載のモータ内蔵ローラでは、前記一時磁石が鉄片であることを特徴としている。
In the motor built-in roller according to any one of
そのことにより、安価で安定した一時磁石を使用可能であるため、モータ内蔵ローラの製造コストを低減すると共に、安定した制動力を得ることができる。 This makes it possible to use an inexpensive and stable temporary magnet, thereby reducing the manufacturing cost of the motor built-in roller and obtaining a stable braking force.
請求項5に記載の発明は、ローラ本体内に制御基板が設けられていることを特徴とする請求項1乃至4のいずれかに記載のモータ内蔵ローラである。
また本発明に関連する発明は、ローラと同期的に回転する制動力発生用永久磁石と、磁界を検知する検知手段とを有し、前記検知手段は制動力発生用永久磁石の近傍にあって前記制動力発生用永久磁石の発生させる磁界を検知してローラの回転情報を取得するものであり、制動力発生用永久磁石の近傍に一時磁石が配されており、当該一時磁石と制動力発生用永久磁石との間の磁力によって回転子の制動力を発生させることを特徴とするローラである。
The invention described in
The invention related to the present invention further includes a braking force generating permanent magnet that rotates synchronously with the roller, and a detecting means for detecting a magnetic field, the detecting means being in the vicinity of the braking force generating permanent magnet. The rotation force of the roller is obtained by detecting the magnetic field generated by the permanent magnet for generating the braking force, and a temporary magnet is disposed in the vicinity of the permanent magnet for generating the braking force. This is a roller characterized in that the braking force of the rotor is generated by the magnetic force between the permanent magnet for use.
本発明のローラでは、制動力発生用永久磁石の磁界を検知してローラの回転情報を取得する検知手段を有し、制動力発生用永久磁石と一時磁石との間の磁力によってローラの制動力を発生させる。即ち、制動力発生用永久磁石は、ローラの回転情報の検知と、回転子の制動力の発生という二つの動作のために使用可能である。そのため、制動力を発生させる制動装置と、モータの回転情報の検知を行う検知装置とを個別に設ける場合と比べて、部品点数を減らすことが可能である。 The roller of the present invention has a detecting means for detecting the magnetic field of the permanent magnet for generating the braking force and acquiring the rotation information of the roller, and the braking force of the roller is generated by the magnetic force between the permanent magnet for generating the braking force and the temporary magnet. Is generated. In other words, the braking force generating permanent magnet can be used for two operations: detection of roller rotation information and generation of rotor braking force. Therefore, it is possible to reduce the number of parts compared to a case where a braking device that generates a braking force and a detection device that detects rotation information of the motor are provided separately.
ここで、一時磁石は自発的に磁界を発生させないので、検知手段の磁界の検知を阻害しない。そのため、本発明のローラでは、一時磁石と検知手段を共に制動力発生用永久磁石との近傍に配することができる。そのため、検知手段と制動力発生用永久磁石との距離を短くできるので、高精度の検知が可能となる。 Here, since the temporary magnet does not spontaneously generate a magnetic field, it does not hinder the detection of the magnetic field of the detection means. Therefore, in the roller of the present invention, both the temporary magnet and the detection means can be arranged in the vicinity of the braking force generating permanent magnet. As a result, the distance between the detection means and the braking force generating permanent magnet can be shortened, so that highly accurate detection is possible.
もう一つの関連発明は、ローラと同期的に回転する制動力発生用永久磁石と、磁界を検知する検知手段とを有し、前記検知手段は前記制動力発生用永久磁石の発生させる磁界を検知してローラの回転情報を取得するものであり、制動力発生用永久磁石の近傍に一時磁石が配されており、前記検知手段が当該一時磁石と接触し、前記一時磁石と前記制動力発生用永久磁石との間の磁力によって回転子の制動力を発生させることを特徴とするローラである。 Another related invention has a braking force generating permanent magnet that rotates synchronously with a roller and a detecting means for detecting a magnetic field, and the detecting means detects a magnetic field generated by the braking force generating permanent magnet. The rotation information of the roller is obtained, and a temporary magnet is disposed in the vicinity of the permanent magnet for generating a braking force, and the detection means is in contact with the temporary magnet, and the temporary magnet and the braking force are generated. The roller is characterized in that the braking force of the rotor is generated by the magnetic force between the permanent magnet.
本発明のローラでは、一時磁石が自発的に磁界を発生させず、制動力発生用永久磁石の近傍に配され、また、検知手段が一時磁石と接触している。そのため、検知手段が一時磁石を介して制動力発生用永久磁石の磁界を検知することができる。そのことにより、検知手段と制動力発生用永久磁石が離れている状態でも、制動力発生用永久磁石が発する磁界の高精度の検知が可能になる。したがって、ローラ本体内における部材の配置時の制約が少なくなり、ローラ本体内の多様な設計が可能となる。 In the roller of the present invention, the temporary magnet does not spontaneously generate a magnetic field, is disposed in the vicinity of the permanent magnet for generating braking force, and the detection means is in contact with the temporary magnet. Therefore, the detection means can detect the magnetic field of the braking force generating permanent magnet via the temporary magnet. As a result, even when the detection means and the braking force generating permanent magnet are separated, the magnetic field generated by the braking force generating permanent magnet can be detected with high accuracy. Therefore, there are fewer restrictions when arranging the members in the roller body, and various designs in the roller body are possible.
さらに関連発明は、前記検知手段がホールICである上記ローラである。 Further, the related invention is the above roller, wherein the detection means is a Hall IC.
さらに関連発明は、前記一時磁石が鉄片であることを特徴とする上記ローラである。 Further, the related invention is the above-described roller, wherein the temporary magnet is an iron piece.
本発明のローラは、上記したモータ内蔵ローラと同様の理由により、検知装置の長寿命化や製造コストを低減、及び安定した制動力の取得といった利点を有する。 The roller of the present invention has advantages such as extending the life of the detection device, reducing the manufacturing cost, and obtaining a stable braking force for the same reason as the above-described motor built-in roller.
本発明のモータ内蔵ローラでは、より正確にモータの回転角度を検知可能であると共に、回転駆動時のローラの振動や、制動動作時の制動力の減少を低減できる。また、従来の物に比べて部品点数を減らすことが可能であり、ローラ内部の空間を広く使用できる。 The roller with a built-in motor according to the present invention can detect the rotation angle of the motor more accurately, and can reduce the vibration of the roller during rotation driving and the decrease in braking force during braking operation. In addition, the number of parts can be reduced as compared with the conventional one, and the space inside the roller can be widely used.
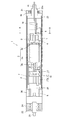
続いて、本発明の第一の実施形態に係る、モータ内蔵ローラ1について図面を参照しながら詳細に説明する。なお、図1は本実施形態のモータ内蔵ローラの断面図であるが、ハッチングは付さずに省略している。図1,2に示すように、本発明のモータ内蔵ローラ1は、内部に空間を有する略円柱状の部材であるローラ本体2の内部に、ローラ本体2と略同形状の筒体7が内蔵されている。筒体7の内部には駆動用モータ3(モータ)、制御基板18、減速機14が設けられている。また、筒体7の一端から出力部材8が突出して設けられている。そして、駆動用モータ3の動作に伴って、出力部材8が回転し、出力部材8の回転により、ローラ本体2が筒体7に対して相対的に回転するものである。以下具体的に説明する。
Next, the motor built-in
ローラ本体2は筒状の部材であり、両端に閉塞部材16、22がそれぞれ設けられている。閉塞部材16,22は、それぞれ形状の異なるローラ本体2の端部の開口を閉塞するキャップ状の部材である。具体的には、それぞれローラ本体2の端部の形状に沿う様な形状であり、ローラ本体2の端部に一体に固定することが可能である。
The
閉塞部材16は中心部分に貫通孔と段差を有している。段差には周知のボールベアリングであるボールベアリング21が嵌入可能となっており、貫通孔には後述する軸取り付け部材23の軸部分23aを挿入可能となっている。
The closing
閉塞部材22は中心部分に貫通孔を有しており、貫通孔近傍には周知のボールベアリングであるボールベアリング24が配置可能であり、固定軸29が挿通可能となっている。
The closing
筒体7は、ローラ本体2の内部に挿入可能な筒状の部材であり、端部の一方に軸取り付け部材23が一体に設けられている。軸取り付け部材23は、端部にフランジ状の部分を有する略円筒状部材の部材であり、中心部分にケーブル15(電気供給用電線)を挿通可能な貫通孔を有している。
The
駆動用モータ3は、公知のブラシレスモータが採用されており、モータ本体3aの内部に図示しない固定子と回転子を有し、半導体スイッチ及び外部からの信号等により固定子に流れる電流の向きを変更可能となっている。
本実施形態では、図1,3に示す様に、回転軸3bがモータ本体3aの両端部から突出し、その回転軸の一方の端部には、4極に着磁された回転磁石4(制動力発生用永久磁石)が配され、回転磁石4の周囲を囲むようにブレーキ片5(一時磁石)が配されている。即ち、ブレーキ片5は、回転磁石4の外側且つ筒体7の内側に配置されている。この構成により、駆動用モータ3の回転に対して抵抗を与える。即ち、回転磁石4及びブレーキ片5によって、ブレーキ機能を果たすコギングブレーキ機能が形成される。なお、ブレーキ片5は筒体7の内壁に固定されている。
また、回転磁石4が発生する磁界を、後述する2個のホールIC(検知手段)で検知することにより、駆動用モータの回転数をパルス信号として認識させることが可能となる。
The
In this embodiment, as shown in FIGS. 1 and 3, the
Further, by detecting the magnetic field generated by the
回転磁石4は、略円筒状であって中心部分に駆動用モータ3の回転軸を挿入可能な貫通孔を有している。また、回転磁石4は前述したように4極に着磁されている。具体的には図3に示されるように、異なる2つの磁極が隣り合わせた位置に着磁されており、2つの磁極を2つずつ有する。なお、回転磁石4には、磁界や電流の供給を受けることなく磁界を発生させる、アルニコ磁石、フェライト磁石、ネオジム磁石等の適宜なものが使用される。
The
ブレーキ片5は、図1,3に示されるように、断面が略U字状になるように曲げられた板状の部材であり、軟鉄により形成された鉄片である。なお、ブレーキ片5は自発的に磁界を発生させないため、後述するホールIC6が行う磁界の検知を阻害しない。
As shown in FIGS. 1 and 3, the
一方、駆動用モータ3のモータ本体3aから突出する、回転軸3bの他方の端部には、減速機14が配され、当該減速機14を介して出力部材8と接続されている。
減速機14は、周知の遊星歯車機構を有する遊星ギア部17で構成されており、遊星ギア部17の中心に接続された回転軸3bの回転を減速して出力部材8に伝達可能なものである。本実施形態のモータ内蔵ローラ1では、減速機14は略同じ構成を有した2つの遊星ギア部17と1つの遊星ギア部17aが3段に並んで配されている。これにより、駆動用モータ3の回転を減速させて、その回転を安定して出力部材8に伝導させることが可能となる。
On the other hand, a
The
出力部材8は、駆動用モータ3の回転力をローラ本体2に伝導するもので、出力部材8の一部(内筒配置部35)が筒体7内部に配され、残部(外筒装着部36)が筒体7の外部に位置されている。具体的には、内筒配置部35は筒体7と非接触で減速機14と接続されているため、減速機14の回転により出力部材8と共に筒体7が回転することはない。即ち、出力部材8は回転しても、筒体7は回転しない。
The
また、外筒装着部36は、筒体7より僅かに大きい外径を有しており、出力部材8がローラ本体2の内部に配置されると、外筒装着部36がローラ本体2の内部と嵌合状態となる。即ち、出力部材8と共にローラ本体2は回転する。従って、出力部材8に駆動用モータ3の減速された回転が伝導されることで、ローラ本体2がその減速された速度で回転を行う。
Further, the outer
制御基板18は、略長方形の板状で、制御ICが搭載されている。制御基板18は、筒体7の中心軸近傍に位置し、さらに駆動用モータ3を挟んで減速機14と対向する位置に配され、駆動用モータ3と共に回転しないように筒体7に固定されている。また、制御基板18には、外部電源と接続可能なケーブル15が接続されている。
The
また制御基板18は、回転磁石4に対向する位置に2個のホールIC6が設けられている。周知のホールICと同様であって、磁気センサであるホール素子とホール素子の出力信号をデジタル信号に変換するICが一体となっている素子である。
したがって、ホールIC6は、駆動用モータ3に取り付けられた回転磁石4の磁界を検知して、駆動用モータ3の回転数をパルス信号として後述する情報受信部25に送信可能なものである。これらを2個配することで位相が異なる2相のパルス信号が検知される。即ち、2個のホールIC6を設けることで、前記した回転磁石4の回転方向(正回転及び逆回転)を検知することが可能となる。従って、回転磁石4と2個のホールIC16により、駆動用モータ3の回転数と回転方向を検知することができる。
The
Therefore, the
そして、制御基板18はホールIC6が出力した情報を処理できる構成を有している。即ち、制御基板18は、図4に示す様に、ホールIC6が発信した信号を受信する情報受信部25と、情報受信部25で受信した回転情報(ホールIC6が発信した信号であり、回転数及び回転方向)を記憶する記憶部26と、情報受信部25で受信した回転情報と記憶部26で記憶された回転情報に対して比較や演算が可能な比較補正部27と、比較補正部27で比較された信号を受信して駆動用モータ3を制御するモータ制御部28とを有している。
And the
記憶部26は、情報受信部25が受信した回転情報(回転数及び回転方向)が記憶されるものである。即ち、情報受信部25が受信した情報から回転数を積算し、算出した回転数を回転方向と共に記憶することができる。
The
比較補正部27は、情報受信部25と記憶部26が接続されており、ホールICから受信した情報や記憶部26に記憶された情報を用いて演算を行う。そして、駆動用モータ3に特定の動作をさせる信号や、駆動用モータ3を停止させる信号を生成してモータ制御部28に送信する。
The
モータ制御部28は、情報受信部25,記憶部26並びに比較補正部27で処理された信号を受信して駆動用モータ3に指令を出す。
The
次に本実施形態のモータ内蔵ローラ1の組み立て構造について説明する。
Next, the assembly structure of the motor built-in
図1に示されるように、モータ内蔵ローラ1は、ローラ本体2に筒体7が内蔵されている。このとき、軸取り付け部材23の軸部分23aが、閉塞部材16の中心部分にある貫通孔に挿通されている。なお、閉塞部材16の貫通孔の周囲にはボールベアリング21が取り付けてあるので、軸部分23aはボールベアリング21の内側に配される。したがって、閉塞部材16は軸部分23aに対して相対的に回転可能になる。ここで、軸取り付け部材23は筒体7の端部に一体に取り付けられているので、閉塞部材16は筒体7及び軸取り付け部材23(軸部分23a)に対して相対的に回転可能な状態となっている。
また、軸部分23aの中心部分にある貫通孔にはケーブル15が挿通されており、ケーブル15は図示しない外部電源と制御基板18を接続している。
As shown in FIG. 1, the motor built-in
A
また、閉塞部材22の貫通孔付近にはボールベアリング24が取り付けられており、ボールベアリング24の内側に固定軸29が挿通されている。即ち、閉塞部材22の貫通孔にボールベアリング24を介して固定軸29が挿通されているので、閉塞部材22は固定軸29に対して相対的に回転可能に取り付けられている。
A
閉塞部材16,22は共にローラ本体2に一体に取り付けられている。また、軸部分23aと固定軸29はローラ本体2の両端部であって、ローラ本体2の中心軸上に配されている。そのため、ローラ本体2は軸部分23a及び固定軸29に対して相対的に回転可能となっている。
即ち、モータ内蔵ローラ1は、ローラ本体2が回転しても筒体7や軸部分23a及び固定軸29は回転しないように取り付けられている。
Both the blocking
In other words, the motor built-in
筒体7の内部においては、図1に示すように、閉塞部材22側から順番に出力部材8,減速機14,駆動用モータ3,回転磁石4及びブレーキ片5,制御基板18が配置されている。具体的に順を追って説明すると、出力部材8は閉塞部材22から任意の間隔を空けて配されている。出力部材8は、外筒装着部36がローラ本体2の所定の位置に装着されて配されており、内筒装着部35が筒体7の内部に非接触状態で位置して減速機14と接続されている。即ち、出力部材8は、ローラ本体2を一体的に回転させるものである。言い換えれば、出力部材8と筒体7は相対的に回転する。
As shown in FIG. 1, the
また、筒体7の軸上に回転軸3bが配され、回転軸3bの一方の端部が減速機14を介して出力部材8に接続されている。そして、他方の端部は駆動用モータ3を挟んで回転磁石4が配されている。そして回転磁石4は、2つのブレーキ片5により周囲を囲まれている。
A
回転磁石4の近傍から閉塞部材16方向に延伸した形状を有する制御基板18が配されている。なお、制御基板18は、筒体7の中心軸と平行な配置である。制御基板18は、回転磁石4側に2個のホールIC6が配されている。即ち、ホールIC6は回転磁石4に近い位置に配されており、回転磁石4から駆動用モータ3の回転に伴うパルス信号を受信できる。
A
そして、周知のコンベア装置等の固定用の部材に、上記したモータ内蔵ローラ1の軸部分23a及び固定軸29を挿通して使用するものである。
Then, the
以下、本実施形態のモータ内蔵ローラ1をコンベア装置等に用いた場合の動作について説明する。
Hereinafter, the operation when the roller with built-in
初めに駆動用モータ3を起動して、回転軸3bを回転させる。すると、回転軸3bの回転が減速機14を介して出力部材8に伝達され、軸部分23a、固定軸29及び筒体7に対してローラ本体2が相対回転を開始する。そして、回転磁石4も回転軸3bの回転によって、筒体7に対して相対回転を開始する。
First, the
このとき、回転磁石4近傍に設けられたホールIC6が、回転磁石4の回転情報(回転方向及び回転速度)を検知して制御基板18の情報受信部25へ送信を行う。このときホールICの近傍に配置させたブレーキ片5が自発的に磁気を発しないため、ホールIC6の回転磁石4の磁界の検知を阻害しない。そのため、ブレーキ片5が永久磁石である場合に比べて精度の高い検知を実行することができる。
At this time, the
そして、回転情報を受信した情報受信部25は、記憶部26に回転情報を送信し、記憶部26は、受信した情報に対して回転数の積算等の適宜な演算を必要に応じて行い、受信した情報、又は演算結果を記憶する。
Then, the
また比較補正部27は、情報受信部25や記憶部26から送信された回転情報を演算することで、予め決められた速度や方向に従ってローラ本体2が回転しているかどうかを判別する。そして、ローラ本体2が決められた動作をしていないと判別された場合、駆動用モータ3の回転を制御する命令をモータ制御部28に送信し、モータ制御部28が駆動用モータ3の回転速度を調整する。
The
そのことによりモータ内蔵ローラ1は、微細な調整を行いながら動作することで、精密な動作を継続して行うことができる。
As a result, the motor built-in
次に、モータ内蔵ローラ1の回転駆動を停止する場合について説明する。初めに駆動用モータ3を停止する。このとき、永久磁石4とブレーキ片5の間には引き合う方向に磁力が働いているため、永久磁石4から回転軸3bに対して回転を停止する方向に力が加わる。そのことにより、回転軸3bの回転が時間の経過と共に減速して、やがて停止する。それに伴い、減速装置14及び出力部材8の回転駆動も減速を続けて停止する。そして、出力部材8と連動するローラ本体2の回転も同様に停止する。
Next, a case where the rotational drive of the motor built-in
本実施形態では、ブレーキ片5に軟鉄の鉄片を用いたがブレーキ片5はこれに限るものではない。軟鉄でなく鉄でもよいし、ニッケル等の他の素材を用いて形成してもよい。また、電磁石のようにコイルを巻いたものを使用してもよい。
要は、ホールIC6(検知手段)の磁気の検知を阻害せず、回転磁石4との間に引き合う力が働けばよい。
In the present embodiment, a soft iron piece is used for the
In short, it is sufficient that the attractive force acts between the Hall IC 6 (detection means) and the
また、本実施形態ではブレーキ片5を円弧状に折り曲げているが、円弧状に限らず平板状でもよい。円弧状に折り曲げる際は、曲げ角度は適宜変更可能であるが、本実施形態のように回転磁石4を4極に着磁した場合、ブレーキ片5を約120度前後の開き角で折り曲げると制動力が強くなるので好ましい。
Moreover, in this embodiment, although the
本実施形態ではホールIC6を2つ設ける構成を示したが、本発明はこれに限定されるものではなく3個以上設けてもよいし、1個でもよい。また、検知手段はホールIC6に限るものではない、磁気を検知することで駆動用モータ3の回転情報を取得できればよい。
In the present embodiment, the configuration in which two
本実施形態では、回転磁石4が4極に着磁された構成を示したが、本発明はこれに限定されるものではない、例えば2極のように4極以下でもよいし、6極のように4極以上でもよい。
In the present embodiment, the configuration in which the
本実施形態では、ホールIC6が取得した回転情報によって駆動用モータ3の回転速度と回転方向を制御したが、制御基板18による回転情報を使用する制御はこれに限るものではない。
例えば、ブラシレスモータである駆動用モータの固定子に流れる電流の向きの変更を制御する構成にしてもよい。
In the present embodiment, the rotation speed and direction of the
For example, the configuration may be such that the change in the direction of the current flowing in the stator of the driving motor that is a brushless motor is controlled.
本実施形態では、駆動用モータ3のモータ本体3aから突出する回転軸3bは、同一の軸が異なる場所から突出しているものとしたが、異なる2つの軸が突出している構成にしてもよい。要は、突出している部分が回転時において同方向に同じ速さで回転すればよい。
In the present embodiment, the
本実施形態では、駆動用モータ3にブラシレスモータを使用したが、駆動用モータ3はこれに限るものではない。例えば、ブラシを有する直流モータを使用してもよい。
In the present embodiment, a brushless motor is used as the
続いて、本発明の第二の実施形態に係る、モータ内蔵ローラ40について図面を参照しながら説明する。なお、第一の実施形態におけるモータ内蔵ローラ1と同様の構造等、同様の説明については、同じ符号を付し、重複する説明は省略する。
Next, the motor built-in
本発明の第二の実施形態に係るモータ内蔵ローラ40は、図5に示されるように、ホールIC6をブレーキ片5と接触する位置に設けたものである。
As shown in FIG. 5, the motor built-in
本実施形態では、ブレーキ片5が自発的に磁界を発生することはなく、回転磁石4のみが自発的に磁界を発する。そのため、ブレーキ片5からの磁界の干渉を受けることなく、ホールIC6が回転磁石4の磁界を検知することができる。したがって、ホールIC6が回転磁石4から離れた位置にあっても回転磁石4の磁界を高精度に検知することができる。
In the present embodiment, the
次に参考発明に係る実施形態を説明する。第三の実施形態(参考発明)に係るローラ41は、図6に示されるように、モータを内蔵しないローラ41にブレーキ片と回転磁石を設けたものである。
Next, an embodiment according to the reference invention will be described. As shown in FIG. 6, the
ローラ41は所謂フリーローラであって、ホールIC6、ローラ本体43、蓋部材44、固定軸45、ブレーキ片46、回転磁石47から構成されている。
The
ローラ本体43は内部に空間を有する円筒状の部材である。
The
蓋部材44はフランジ部分を有する円板状の部材であって、貫通孔の内壁近傍に周知のベアリングが取り付けられている。
The
固定軸45は、断面が円形のパイプ状の部材である。
The fixed
ブレーキ片46は軟鉄で形成された一時磁石であって、中央部分に貫通孔を有するドーナツ状の部材である。
The
回転磁石47は、永久磁石であり、略「U」字状に曲げられた板状の部材である。
The rotating
そして、円筒状のローラ本体43の両端に、中心部分に貫通孔を有する蓋部材44が一体に取り付けられている。そして、それぞれの蓋部材44の貫通孔には固定軸45が挿通されている。つまり、蓋部材44を介して固定軸45に軸支されている。即ち、ローラ本体43は固定軸45と相対的に回転可能である。
A
また、固定軸45の一つは、ローラ本体43の内部側に位置する端部がブレーキ片46の貫通孔を挿通している。つまり、ブレーキ片46がローラ本体43の内部に位置する様に、固定軸45にブレーキ片46が一体に取り付けられている。そして、ブレーキ片46の周囲を囲むように回転磁石47が配されている。即ち、回転磁石47は、ブレーキ片46の外側且つローラ本体43の内側に配置されている。この構成により、ローラ41の回転に対して抵抗を与える。即ち、ブレーキ片46及び回転磁石47によって、ブレーキ機能を果たすコギングブレーキ機能が形成される。なお、回転磁石47はローラ本体43の内壁に固定されている。
Further, one of the fixed
そして、ブレーキ片46の外周にはホールIC6が一体に取り付けられており、ローラ本体43に設けられた回転磁石47の磁界を検知することで、ローラ41の回転方向や回転角度が検知可能となる。また、このホールIC6は固定軸45の内部に挿通された通信線を介して、外部の図示しない基板に対して検知した情報を送信可能になっている。
The
本実施形態によれば、フリーローラであるローラ41の回転方向や回転角度が検知可能となり、コンベア等において、モータを設けていないローラからも回転情報を取得できる。また、ローラ41にブレーキを掛けることが可能となり、コンベアを停止させた場合等において、慣性によって回り続けているローラの回転情報を取得してしまうといった誤検知の発生を減少させることができる。そのため、コンベアのより精密な搬送制御を行うことが可能となる。
According to the present embodiment, the rotation direction and rotation angle of the
上記した各実施形態では、本発明のモータ内蔵ローラ及びフリーローラ(参考発明)をコンベア用として用いた例を示したが、本発明のモータ内蔵ローラやローラはこれに限るものではない。例えば、カーテン巻上用ローラ、スクロール用モータ内蔵ローラとして本発明のモータ内蔵ローラやローラを使用してもよい。要は、円筒形の回転物が内部の駆動装置や外部からの力によって軸部分を中心に回転する構造であれば、本発明のモータ内蔵ローラ並びにローラを使用することができる。 In each of the above-described embodiments, an example in which the motor built-in roller and the free roller (reference invention) of the present invention are used for conveyors is shown, but the motor built-in roller and roller of the present invention are not limited thereto. For example, the motor built-in roller or roller of the present invention may be used as a curtain winding roller or scroll motor built-in roller. In short, the motor-equipped roller and the roller of the present invention can be used as long as the cylindrical rotating object is structured to rotate around the shaft portion by an internal driving device or external force.
1 モータ内蔵ローラ
2 ローラ本体
3 駆動用モータ
4 永久磁石(制動力発生用永久磁石)
5 ブレーキ片(一時磁石)
6 ホールIC(検知手段)
DESCRIPTION OF
5 Brake piece (temporary magnet)
6 Hall IC (detection means)
Claims (5)
前記モータの回転子と同期的に回転する制動力発生用永久磁石と、磁界を検知する検知手段とを有し、前記検知手段は制動力発生用永久磁石の近傍にあって前記制動力発生用永久磁石の発生させる磁界を検知してモータの回転情報を取得するものであり、制動力発生用永久磁石の近傍に一時磁石が配されており、前記一時磁石は鉄片であり、前記一時磁石は、制動力発生用永久磁石の周囲を不連続に囲むものであり、当該一時磁石と制動力発生用永久磁石との間の磁力によるブレーキ機能による回転子の制動力を発生させることを特徴とするモータ内蔵ローラ。 A motor built-in roller with a motor built in the roller body,
A braking force generating permanent magnet that rotates synchronously with the rotor of the motor; and a detecting means for detecting a magnetic field, the detecting means being in the vicinity of the braking force generating permanent magnet and for generating the braking force. Detecting the magnetic field generated by the permanent magnet to acquire the rotation information of the motor, a temporary magnet is disposed in the vicinity of the permanent magnet for generating the braking force, the temporary magnet is an iron piece, the temporary magnet is , which surrounds the braking force generating permanent magnets discontinuously, characterized in that the braking force is generated in the rotor due to by that brake function the magnetic force between the temporary magnet and the braking force generating permanent magnets Motor built-in roller.
前記モータの回転子と同期的に回転する制動力発生用永久磁石と、磁界を検知する検知手段とを有し、前記検知手段は前記制動力発生用永久磁石の発生させる磁界を検知してモータの回転情報を取得するものであり、制動力発生用永久磁石の近傍に一時磁石が配されており、前記一時磁石は鉄片であり、前記一時磁石は、制動力発生用永久磁石の周囲を不連続に囲むものであり、前記検知手段が当該一時磁石と接触し、前記一時磁石と制動力発生用永久磁石との間の磁力によるブレーキ機能による回転子の制動力を発生させることを特徴とするモータ内蔵ローラ。 A motor built-in roller with a motor built in the roller body,
A braking force generating permanent magnet that rotates synchronously with the rotor of the motor; and a detecting means for detecting a magnetic field, wherein the detecting means detects a magnetic field generated by the braking force generating permanent magnet. The temporary magnet is arranged in the vicinity of the braking force generating permanent magnet, the temporary magnet is an iron piece, and the temporary magnet does not surround the permanent magnet for generating the braking force. is intended to enclose the continuous, characterized in that said detecting means is in contact with the temporary magnet, to generate a braking force of the rotor by by that brake function the magnetic force between the braking force generating permanent magnet and the one o'clock magnet Motor built-in roller.
前記モータは、永久磁石又はコイルによって構成された回転子と、コイルによって構成された固定子と、回転子の回転姿勢を検知して固定子を流れる電流の向きを切り替えるための信号を発生させる検知手段とを備えたブラシレスモータであり、
回転子と同期的に回転する制動力発生用永久磁石を有し、前記検知手段は磁界を検知するものであり、前記検知手段は制動力発生用永久磁石の近傍にあって、前記制動力発生用永久磁石の磁界を検知して固定子を流れる電流の向きを切り替えるための信号を発生させ、制動力発生用永久磁石の近傍に一時磁石が配されており、前記一時磁石は鉄片であり、前記一時磁石は、制動力発生用永久磁石の周囲を不連続に囲むものであり、当該一時磁石と制動力発生用永久磁石との間の磁力によるブレーキ機能による回転子の制動力を発生させることを特徴とするモータ内蔵ローラ。 A motor built-in roller with a motor built in the roller body,
The motor detects a rotor configured by a permanent magnet or a coil, a stator configured by a coil, and a signal for switching a direction of a current flowing through the stator by detecting a rotational posture of the rotor. A brushless motor with means,
A permanent magnet for generating braking force that rotates synchronously with a rotor; and the detecting means detects a magnetic field, and the detecting means is in the vicinity of the permanent magnet for generating braking force, and generates the braking force. Detecting a magnetic field of the permanent magnet for generating a signal for switching the direction of the current flowing through the stator, a temporary magnet is disposed in the vicinity of the permanent magnet for generating the braking force, and the temporary magnet is an iron piece, wherein one o'clock magnet, which surrounds the braking force generating permanent magnets discontinuously, generating a braking force of the rotor by by that brake function the magnetic force between the braking force generating permanent magnets and the temporary magnet A roller with a built-in motor.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009245362A JP5495302B2 (en) | 2009-10-26 | 2009-10-26 | Motor built-in roller |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009245362A JP5495302B2 (en) | 2009-10-26 | 2009-10-26 | Motor built-in roller |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2011088733A JP2011088733A (en) | 2011-05-06 |
| JP5495302B2 true JP5495302B2 (en) | 2014-05-21 |
Family
ID=44107356
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009245362A Active JP5495302B2 (en) | 2009-10-26 | 2009-10-26 | Motor built-in roller |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5495302B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2014178399A1 (en) * | 2013-04-30 | 2014-11-06 | 伊東電機株式会社 | Roller conveyor device, controller, and mechanical device abnormality detection method |
| JP2016141566A (en) * | 2015-02-05 | 2016-08-08 | 株式会社三龍社 | Drive roller and roller conveyor |
| AT516925B1 (en) | 2015-03-12 | 2021-08-15 | Tgw Mechanics Gmbh | Conveyor device with improved wiring of the drive motor and brake of a conveyor roller and operating procedures for it |
| PL3390248T3 (en) * | 2016-08-05 | 2023-01-30 | Interroll Holding Ag | Motor-driven conveyor roller with bus control |
| DE102016114524B4 (en) * | 2016-08-05 | 2020-09-03 | Interroll Holding Ag | Drum motor with frequency converter and optional belt tension sensor |
Family Cites Families (16)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS5813381U (en) * | 1981-07-21 | 1983-01-27 | 芝浦メカトロニクス株式会社 | automatic door |
| JPS63196403A (en) * | 1987-02-09 | 1988-08-15 | Hakko Denki Seisakusho:Kk | Braking device for roller conveyer |
| JP2579293B2 (en) * | 1988-02-03 | 1997-02-05 | 日本電気精器株式会社 | Brushless DC motor with non-contact brake |
| JPH01120682U (en) * | 1988-02-05 | 1989-08-16 | ||
| US5467266A (en) * | 1991-09-03 | 1995-11-14 | Lutron Electronics Co., Inc. | Motor-operated window cover |
| JPH05146185A (en) * | 1991-11-20 | 1993-06-11 | Yaskawa Electric Corp | Braking method for permanent magnet synchronous motor |
| JPH08227466A (en) * | 1995-02-20 | 1996-09-03 | Nippon Signal Co Ltd:The | Automatic ticket examining machine |
| JP3424013B2 (en) * | 1999-04-21 | 2003-07-07 | 伊東電機株式会社 | Brushless motor drive and conveyor system |
| JP4187127B2 (en) * | 1999-05-25 | 2008-11-26 | オークラ輸送機株式会社 | Transport device |
| JP2001106330A (en) * | 1999-10-06 | 2001-04-17 | Ito Denki Kk | Belt driving motor pulley, belt conveyer apparatus, and motor roller |
| JP3637265B2 (en) * | 2000-06-14 | 2005-04-13 | 東京パーツ工業株式会社 | Position detection device and brushless motor equipped with the same |
| JP2002029625A (en) * | 2000-07-14 | 2002-01-29 | Ito Denki Kk | Control method for roller with built-in motor |
| JP2002145438A (en) * | 2000-11-13 | 2002-05-22 | Ito Denki Kk | Roller unit for motor built-in roller |
| JP2002186245A (en) * | 2000-12-12 | 2002-06-28 | Isuzu Motors Ltd | Eddy current speed reducer |
| JP2003134881A (en) * | 2001-10-26 | 2003-05-09 | Ito Denki Kk | Motor, and roller with built-in motor |
| JP2009240077A (en) * | 2008-03-27 | 2009-10-15 | Ito Denki Kk | Apparatus for controlling roller with built-in motor, roller with built-in motor and conveyor apparatus |
-
2009
- 2009-10-26 JP JP2009245362A patent/JP5495302B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2011088733A (en) | 2011-05-06 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US7042211B2 (en) | Multirotation type encoder | |
| US8159096B2 (en) | Apparatus for detecting position of rotation of motor | |
| JP5495302B2 (en) | Motor built-in roller | |
| EP2797210A1 (en) | Motor, motor system, and motor encoder | |
| WO2017002869A1 (en) | Brushless motor | |
| JP2007252097A (en) | Brushless motor | |
| CN114270673B (en) | Rotation detector and motor having the same | |
| JPWO2005040730A1 (en) | Rotation angle detector | |
| EP3553531B1 (en) | Speed detection device | |
| JP6914443B2 (en) | Motor and valve timing adjuster | |
| JP2009273292A (en) | Brushless motor | |
| JP6165480B2 (en) | PM stepping motor | |
| JP6965709B2 (en) | Electric actuator | |
| JP4690710B2 (en) | Electric motor with reduction mechanism | |
| JP2006230125A (en) | Rotary electric machine | |
| JP2001004403A (en) | Rotation detecting sensor and electric brake using the sensor | |
| JP2009261149A (en) | Brushless motor | |
| JP6965710B2 (en) | Electric actuator | |
| CN114039436A (en) | Rotor for rotating electric machine | |
| JP2016111889A (en) | Stepping motor | |
| JP4716901B2 (en) | Geared motor | |
| JP7389609B2 (en) | motor device | |
| JP4877599B2 (en) | SR motor rotation angle detection device | |
| JP2009033899A (en) | Motor | |
| JP4418045B2 (en) | Electric motor |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20111111 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20111209 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20130410 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20130418 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20130614 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20131212 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20140131 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20140227 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20140227 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5495302 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |