JP2008275524A - Battery pack and residual capacity computing method - Google Patents
Battery pack and residual capacity computing method Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2008275524A JP2008275524A JP2007121348A JP2007121348A JP2008275524A JP 2008275524 A JP2008275524 A JP 2008275524A JP 2007121348 A JP2007121348 A JP 2007121348A JP 2007121348 A JP2007121348 A JP 2007121348A JP 2008275524 A JP2008275524 A JP 2008275524A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- current
- detection resistor
- current detection
- switch
- voltage
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02E—REDUCTION OF GREENHOUSE GAS [GHG] EMISSIONS, RELATED TO ENERGY GENERATION, TRANSMISSION OR DISTRIBUTION
- Y02E60/00—Enabling technologies; Technologies with a potential or indirect contribution to GHG emissions mitigation
- Y02E60/10—Energy storage using batteries
Landscapes
- Tests Of Electric Status Of Batteries (AREA)
- Charge And Discharge Circuits For Batteries Or The Like (AREA)
- Secondary Cells (AREA)
Abstract
Description
この発明は、二次電池の電池パックおよび電池パックの残容量算出方法に関する。 The present invention relates to a battery pack for a secondary battery and a battery pack remaining capacity calculation method.
近年、ノート型PC(Personal Computer)やPDA(Personal Digital Assistant)などの携帯型電子機器では、その電源として二次電池の電池パックが広く使用されている。このような電子機器では、機能の多様化が進み、最近では、例えば、PCとテレビジョン放送が受信可能な受信装置とが一体化されたテレビ機能付きPCなど、一つの電子機器に複数の異なるデバイスの機能を備え、目的に応じてデバイスを切り替えて使用することができる。 In recent years, in portable electronic devices such as notebook PCs (Personal Computers) and PDAs (Personal Digital Assistants), secondary battery packs are widely used as power sources. In such electronic devices, functions have been diversified, and recently, for example, a plurality of different electronic devices such as a PC with a TV function in which a PC and a receiving device capable of receiving television broadcasting are integrated. It has device functions and can be used by switching devices according to the purpose.
複数の異なるデバイスの機能を有する電子機器において、それぞれのデバイスの機能を用いた場合には、消費電流がそれぞれ異なることがある。また、同一のデバイスを使用するときにおいて、デバイスが起動している通常状態と低消費電力モードなどの待機状態とでは、消費電流に大きな差が生じる。 In an electronic apparatus having a plurality of different device functions, when the functions of the respective devices are used, current consumption may be different. Further, when using the same device, there is a large difference in current consumption between a normal state in which the device is activated and a standby state such as a low power consumption mode.
具体的には、例えば、上述のテレビ機能付きPCにおいて、PCを使用している場合やテレビジョン放送を視聴している通常状態の場合と、PCおよびテレビの電源がOFFであっても、ユーザがリモートコントロールコマンダー(以下、リモコンと適宜称する)などを操作することによりテレビの電源がONとされるのを待機している待機状態とでは、消費電流の大きさが異なる。例えば、PCが起動しているような通常状態における消費電流は、1[A]程度である。また、ユーザによるリモコンの操作をテレビが待機しているような待機状態における消費電流は、5[mA]程度である。 Specifically, for example, in the above-described PC with a TV function, even when the PC is used or in a normal state where a television broadcast is viewed, and even when the PC and the TV are turned off, the user However, the amount of current consumption differs from the standby state in which the television is turned on by operating a remote control commander (hereinafter referred to as a remote controller as appropriate). For example, the current consumption in a normal state where the PC is activated is about 1 [A]. Further, the current consumption in a standby state in which the television is waiting for the user's operation of the remote control is about 5 [mA].
通常、電子機器の電源がOFFとなっている場合には、電力がほとんど消費されることはないが、待機状態である場合には、微小電流が流れることにより、僅かながら電力が消費される。そのため、実際に電子機器を使用する際には、電池パックの電池残容量が減少してしまっていることが考えられる。 Normally, when the power of the electronic device is OFF, almost no power is consumed. However, when the electronic device is in a standby state, a small amount of power is consumed due to the flow of a minute current. Therefore, when actually using an electronic device, it is possible that the battery remaining capacity of the battery pack has decreased.
そこで、例えば下記の特許文献1に記載されているように、電池パックを使用する電子機器が待機状態であるか否かを検出し、検出結果に基づき待機中である場合には、消費電流を抑える技術が提案されている。
Therefore, for example, as described in
ところで、ノート型PCなどの携帯型電子機器では、電池残容量が不足して、電源が突然シャットダウンしてしまうと、使用中のデータが破損するおそれがあるなどの影響があるため、使用中の電池パックの電池残容量がどの程度残っているかを認識できることが非常に重要である。そのため、従来の電池パックでは、電池パック内で電池残容量の算出を行い、算出した電池残容量を電子機器の表示部等に表示できるようにされている。 By the way, in a portable electronic device such as a notebook PC, if the remaining battery capacity is insufficient and the power supply is suddenly shut down, there is a possibility that data in use may be damaged. It is very important to be able to recognize how much remaining battery capacity of the battery pack remains. Therefore, in the conventional battery pack, the remaining battery capacity is calculated in the battery pack, and the calculated remaining battery capacity can be displayed on the display unit or the like of the electronic device.
従来の電池パック100は、図5に示すように、電池セル110、制御部111、スイッチ回路112、電圧検出部113、電流検出部114、電流検出抵抗115、通信端子102aおよび102bで構成され、正極端子103および負極端子104がそれぞれ電子機器または充電器の正極端子および負極端子に接続され、充放電が行われる。
As shown in FIG. 5, the
電圧検出部113は、例えば、1または複数の二次電池を直列に接続した電池セル110の電圧を検出し、制御部111に検出結果を供給する。電流検出部114は、電流検出抵抗115を使用して電流の大きさおよび向きを検出し、制御部111に検出結果を供給する。
For example, the
スイッチ回路112は、充電制御FET(Field Effect Transistor)121と、放電制御FET122とから構成されている。電池電圧が過充電検出電圧となった場合には、制御部111からの制御信号により充電制御FET121をOFFとし、寄生ダイオード121aを介することによって放電のみが可能となる。また、電池電圧が過放電検出電圧となった場合には、制御部111からの制御信号により放電制御FET122をOFFとし、寄生ダイオード122aを介することによって充電のみが可能となる。
The
制御部111は、電圧検出部113からの検出結果に基づき、電池セル110の電圧が過充電検出電圧になった場合や、過放電検出電圧以下になった場合に、スイッチ回路112を制御して過充電、過放電を防止する。
Based on the detection result from the
また、制御部111は、電圧検出部113および電流検出部114から供給された検出結果に基づき、電圧値の測定や電流値の積算を行い、電池残容量の算出を行う。そして、通信端子102aおよび102bを介して、電池残容量に関する情報を機器に送信し、この情報を受け取った電子機器側に設けられた液晶等の表示部に残容量率、残り使用可能時間等が表示される。
In addition, the
電池パックの電池残容量を算出する方法の一例としては、電流積算法が挙げられる。電流積算法では、電流検出抵抗115に流れる電流を所定時間毎に測定して積算し、電池パックの放電電流量と積算された電流量との割合から電池パックの電池残容量を算出する。
An example of a method for calculating the remaining battery capacity of the battery pack is a current integration method. In the current integration method, the current flowing through the
しかしながら、従来の電流検出抵抗115を用いて電池残容量を算出した場合、電流検出抵抗115による電流の測定精度が低く、待機状態の際に流れる微小電流を正確に検出することができないため、積算された電流量に誤差が生じてしまう。したがって、電池残容量を正確に算出することができない。そのため、従来は、例えば、電子機器を起動した直後には、電池残容量が100%と表示されているにもかかわらず、実際の電池残容量は、50%程度であるといった、電池残容量の算出結果と実際の電池残容量とのずれが発生していた。
However, when the remaining battery capacity is calculated using the conventional
このように、従来の電池パックでは、待機状態における電池パックの消費電流を正確に検出することができず、正確な電池残容量の算出が困難であるという問題点があった。 As described above, the conventional battery pack cannot accurately detect the current consumption of the battery pack in the standby state, and it is difficult to accurately calculate the remaining battery capacity.
したがって、この発明の目的は、待機状態における消費電流を検出し、より正確に電池残容量を算出することができる電池パック、および電池パックの残容量算出方法を提供することにある。 Accordingly, an object of the present invention is to provide a battery pack capable of detecting current consumption in a standby state and calculating the remaining battery capacity more accurately, and a battery pack remaining capacity calculating method.
上述した課題を解決するために、第1の発明は、二次電池の電池パックであって、電流経路に設けられた第1の電流検出抵抗と、第1の電流検出抵抗に対して直列に接続され、第1の電流検出抵抗よりも抵抗値の大きい第2の電流検出抵抗と、第2の電流検出抵抗に対して並列に接続されたスイッチと、外部の機器から受け取った動作状態を示す情報に基づいて、外部の機器が通常状態である場合には、スイッチをONとして第2の電流検出抵抗をバイパスさせ、外部の機器が待機状態である場合には、スイッチをOFFとするように、スイッチを制御する動作検出部と、スイッチがONである場合に、第1の電流検出抵抗に流れる電流を検出する第1の検出部と、スイッチがOFFである場合に、第2の電流検出抵抗に流れる電流を検出する第2の検出部と、第1の検出部および第2の検出部によって検出された電流に基づき残容量を算出する演算部とを有することを特徴とする電池パックである。 In order to solve the above-described problem, a first invention is a battery pack of a secondary battery, wherein the first current detection resistor provided in the current path and the first current detection resistor are connected in series. A second current detection resistor connected and having a resistance value larger than that of the first current detection resistor, a switch connected in parallel to the second current detection resistor, and an operating state received from an external device are shown. Based on the information, when the external device is in a normal state, the switch is turned on to bypass the second current detection resistor, and when the external device is in a standby state, the switch is turned off. , An operation detection unit that controls the switch, a first detection unit that detects a current flowing through the first current detection resistor when the switch is ON, and a second current detection when the switch is OFF Detect the current flowing through the resistor A second detection unit, a battery pack and having a computing unit that calculates a remaining capacity based on the detected current by the first detector and the second detector.
また、第2の発明は、外部の機器から受け取った動作状態を示す情報に基づいて、外部の機器が通常状態である場合には、電流経路に設けられた第1の電流検出抵抗に対して直列に接続され、第1の電流検出抵抗よりも抵抗値の大きい第2の電流検出抵抗第2の電流検出抵抗に対して並列に接続されたスイッチをONとして第2の電流検出抵抗をバイパスさせ、外部の機器が待機状態である場合には、スイッチをOFFとするように、スイッチを制御する動作検出ステップと、スイッチがONである場合に、第1の電流検出抵抗に流れる電流を検出する第1の検出ステップと、スイッチがOFFである場合に、第2の電流検出抵抗に流れる電流を検出する第2の検出ステップと、第1の検出ステップおよび第2の検出ステップによって検出された電流に基づき残容量を算出する演算ステップとを有することを特徴とする残容量算出方法である。 Further, the second invention is based on the information indicating the operating state received from the external device, and the external device is in a normal state with respect to the first current detection resistor provided in the current path. A second current detection resistor connected in series and having a resistance value greater than that of the first current detection resistor is set to ON to bypass the second current detection resistor by turning on a switch connected in parallel to the second current detection resistor. When the external device is in a standby state, an operation detection step for controlling the switch so that the switch is turned OFF, and when the switch is ON, the current flowing through the first current detection resistor is detected. Detected by the first detection step, the second detection step for detecting the current flowing through the second current detection resistor when the switch is OFF, the first detection step, and the second detection step. A remaining capacity calculating method characterized by having a calculation step of calculating a remaining capacity based on current was.
上述したように、第1および第2の発明では、外部の機器から受け取った動作状態を示す情報に基づいて、外部の機器が通常状態である場合には、電流経路に設けられた第1の電流検出抵抗に対して直列に接続され、第1の電流検出抵抗よりも抵抗値の大きい第2の電流検出抵抗第2の電流検出抵抗に対して並列に接続されたスイッチをONとして第2の電流検出抵抗をバイパスさせ、外部の機器が待機状態である場合には、スイッチをOFFとするように、スイッチを制御しているため、通常状態である場合には、第1の電流検出抵抗に流れる電流を検出し、待機状態である場合に、第2の電流検出抵抗に流れる電流を検出することができる。 As described above, in the first and second inventions, when the external device is in the normal state based on the information indicating the operation state received from the external device, the first provided in the current path A second current detection resistor connected in series to the current detection resistor and having a resistance value larger than that of the first current detection resistor is set to ON by setting a switch connected in parallel to the second current detection resistor. Since the switch is controlled so that the current detection resistor is bypassed and the switch is turned off when the external device is in the standby state, the first current detection resistor is set in the normal state. The current flowing through the second current detection resistor can be detected when the flowing current is detected and in the standby state.
この発明は、待機状態である場合に、通常状態で用いられている第1の電流検出抵抗よりも抵抗値の大きい第2の電流検出抵抗に流れる電流を検出するようにしているため、より正確に電池残容量を算出することができるという効果がある。 In the present invention, the current flowing through the second current detection resistor having a resistance value larger than that of the first current detection resistor used in the normal state is detected in the standby state. The remaining battery capacity can be calculated.
また、この発明は、第1の電流検出抵抗と第2の電流検出抵抗とを直列に接続し、第2の電流検出抵抗に対してスイッチを並列に接続するようにしているため、電流検出抵抗を切り替えた際に電流経路が遮断してしまうことがないという効果がある。 In the present invention, the first current detection resistor and the second current detection resistor are connected in series, and the switch is connected in parallel to the second current detection resistor. There is an effect that the current path is not interrupted when switching between.
以下、この発明の実施の一形態について、図面を参照して説明する。この発明の実施の一形態による電池パックでは、接続された電子機器の動作状態を検出し、動作状態に応じて電流が流れる電流検出抵抗を切り替えることにより、待機している場合に流れる微小な消費電流を正確に測定するようにしている。なお、以下では、電子機器が起動し、様々な処理が行われている状態を通常状態と称し、処理は行われていないが外部から電源をONとする命令などを待機している状態を待機状態と称して説明する。 Hereinafter, an embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. In the battery pack according to one embodiment of the present invention, the operation state of the connected electronic device is detected, and the current consumption is changed according to the operation state. The current is measured accurately. In the following, the state in which the electronic device is activated and various processes are performed is referred to as a normal state, and the state in which the process is not performed but a command to turn on the power from outside is awaited. This will be described as a state.
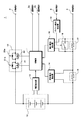
電池パック1は、図1に示すように、電子機器使用時には正極端子3および負極端子4がそれぞれ電子機器の正極端子および負極端子に接続され、放電が行われる。また、充電時には充電器に装着され、電気機器使用時と同様に、正極端子3および負極端子4がそれぞれ充電器の正極端子および負極端子に接続され、充電が行われる。
As shown in FIG. 1, in the
電池パック1は主に、電池セル10、演算部としての制御部11、スイッチ回路12、電圧検出部13、第1の検出部としての通常電流検出部14、第1の電流検出抵抗としての通常電流検出抵抗15、第2の検出部としての微小電流検出部16、第2の電流検出抵抗としての微小電流検出抵抗17、スイッチ18、デバイス動作検出部19、検出端子5、通信端子2aおよび2bで構成されている。電池セル10は、例えば、リチウムイオン電池の二次電池であり、1または複数の二次電池を直列に接続したものである。
The
電圧検出部13は、電池セル10の電圧を検出し、制御部11に検出結果を供給する。通常電流検出部14は、通常電流検出抵抗15を使用して電流の大きさおよび向きを検出し、制御部11に検出結果を供給する。通常電流検出抵抗15としては、電圧降下による電力損失を小さく抑えるようにするため、例えば、5[mΩ]程度の抵抗が用いられる。
The
微小電流検出部16は、微小電流検出抵抗17を使用して電流の大きさおよび向きを検出し、制御部11に検出結果を送る。微小電流検出抵抗17は、通常電流検出抵抗15に対して直列に接続されており、通常電流検出抵抗15よりも小さい抵抗値のものが用いられる。具体的には、例えば、20[mΩ]程度かそれ以上の抵抗が用いられる。
The minute current detection unit 16 detects the magnitude and direction of the current using the minute
スイッチ18は、微小電流検出抵抗17に対して並列に設けられ、後述するデバイス動作検出部19の制御に基づき、スイッチのON/OFFを行う。スイッチ18がONとなった場合には、微小電流検出抵抗17がバイパスされ、電流がスイッチ18を介して流れ、微小電流検出抵抗17に電流が流れないようにされている。デバイス動作検出部19は、検出端子5を介して電子機器から動作状態を示す情報を受け取り、受け取った動作状態を示す情報に基づきスイッチ18を制御し、電流経路の切り替えを行う。例えば、電子機器が起動している状態などの通常状態である場合には、スイッチ18をONとし、消費電流が小さい待機状態である場合には、スイッチ18をOFFとするように制御する。
The
スイッチ回路12は、充電制御FET(Field Effect Transistor)21と、放電制御FET22とから構成されている。電池電圧が過充電検出電圧となった場合には、制御部11からの制御信号により充電制御FET21をOFFとし、充電電流が流れないように制御される。なお、充電制御FET21のOFF後は、寄生ダイオード21aを介することによって放電のみが可能となる。また、電池電圧が過放電検出電圧となった場合には、制御部11からの制御信号により放電制御FET22をOFFとし、放電電流が流れないように制御される。なお、放電制御FET22のOFF後は、寄生ダイオード22aを介することによって充電のみが可能となる。
The
制御部11は、電圧検出部13からの検出結果に基づき、電池セル10の電圧が過充電検出電圧になった場合や、電池セル10の電圧が過放電検出電圧以下になった場合に、スイッチ回路12に制御信号を送ることにより、過充電、過放電を防止する。また、制御部11は、例えば、その内部にA/D(Analog / Digital)変換器を備え、電圧検出部13、通常電流検出部14および微小電流検出部16から供給された検出結果をディジタル信号に変換する。そして、ディジタル信号に変換された検出結果に基づき、電圧値の測定や電流値の積算を行い、電池残容量の算出を行う。なお、電池残容量の算出方法については後述する。
Based on the detection result from the
電圧検出部13、通常電流検出部14および微小電流検出部16で検出された検出結果等は、例えば、図示されないEEPROM(Electrically Erasable and Programmable Read Only Memory)などの不揮発性メモリに保存される。不揮発性メモリは、例えば制御部11に内蔵されていてもよいし、外部に設けられるようにしてもよい。
The detection results detected by the
通信端子2aおよび2bは、電子機器に装着された際に、所定の通信プロトコルを用いて電池残容量に関する情報を機器に送信する。この情報を受け取った電子機器側では、液晶等の表示部に残容量率、残り使用可能時間等を表示する。電子機器との通信としては、例えば、SMバス(System Management Bus)を用いることができる。
When the
次に、電池残容量の算出方法について説明する。電池パックの電池残容量の算出方法としては、例えば、電池セル10の電圧に基づく電圧法と、電池セル10の電圧および電流の積算値に基づく積算法とが挙げられる。電圧法は、電池セル10の電圧を測定し、二次電池の電圧と電池容量(残容量率)との相関性に基づき電池残容量を算出する。こうすることにより、例えば、リチウムイオン電池の場合は電池電圧が4.2V/セルで満充電、2.4V/セルになると過放電状態であると判別することができ、測定が容易である。
Next, a method for calculating the remaining battery capacity will be described. Examples of a method for calculating the remaining battery capacity of the battery pack include a voltage method based on the voltage of the
積算法は、さらに電流積算法と電力積算法とに分類できる。電流積算法は、電流を測定し、一定時間毎に積算することにより放電電流量を算出し、電池の持つ使用可能な電流量との割合から電池パックの電池残容量を算出する。電力積算法は、電圧と電流を測定し、これらを掛け合わせることで電力量を算出し、さらに一定時間毎に電力量を積算することにより放電電力量を算出し、電池の持つ使用可能な電力量との割合から電池パックの電池残容量を算出する。こうすることにより、電池パックの電圧の変動に左右されることなく、安定した残容量検出が可能となる。 The integration method can be further classified into a current integration method and a power integration method. In the current integration method, the amount of discharge current is calculated by measuring the current and integrating the current every predetermined time, and the remaining battery capacity of the battery pack is calculated from the ratio to the available current amount of the battery. The power integration method measures the voltage and current, calculates the amount of power by multiplying them, calculates the amount of discharge power by integrating the amount of power every fixed time, and the usable power of the battery The remaining battery capacity of the battery pack is calculated from the ratio with the amount. By doing so, stable remaining capacity detection can be performed without being affected by fluctuations in the voltage of the battery pack.
ノート型PCなどの携帯型電子機器に用いられる電池パックでは、正確な電池残容量の表示が求められるため、通常は、電流積算法を用いた電池残容量の算出方法が用いられる。この発明の実施の一形態では、電流積算法を用いた場合を例にとって、電池残容量の算出方法について説明する。 In battery packs used in portable electronic devices such as notebook PCs, an accurate display of remaining battery capacity is required, and therefore, a remaining battery capacity calculation method using a current integration method is usually used. In the embodiment of the present invention, a method for calculating the remaining battery capacity will be described by taking the case of using the current integration method as an example.
電流積算法を用いて電池残容量を算出する場合には、通常状態における通常電流検出抵抗15の電圧に基づく電流を算出するとともに、待機状態における微小電流検出抵抗17の電圧に基づく電流を算出する。そして、算出したそれぞれの電流を積算し、電池パックの持つ使用可能な電流量との割合に基づき電池残容量を算出する。なお、以下では、通常状態において通常電流検出抵抗15に流れる電流を通常電流と称し、待機状態において微小電流検出抵抗17に流れる電流を微小電流と称して説明する。
When calculating the remaining battery capacity using the current integration method, the current based on the voltage of the normal
電子機器が通常状態である場合、デバイス動作検出部19はスイッチ18をONとし、微小電流検出抵抗17をバイパスして通常電流が流れないようにする。こうすることにより、通常電流が微小電流検出抵抗17に流れることによって生じる電力損失によって発熱し、破損や発火してしまうのを防ぐことができる。通常電流検出部14は、通常電流検出抵抗15の電圧を測定する。制御部11は、内蔵されたA/D変換器を用いて、通常電流検出抵抗15の電圧に対してA/D変換を行い、アナログ電圧をディジタル電圧に変換する。そして、ディジタル電圧と通常電流検出抵抗15とに基づき通常電流を算出し、所定時間毎に算出した通常電流を積算する。
When the electronic device is in a normal state, the device
また、電子機器が待機状態である場合、デバイス動作検出部19は、スイッチ18をOFFとし、微小電流検出抵抗17に微小電流が流れるようにする。微小電流検出部16は、微小電流検出抵抗17の電圧を測定する。制御部11は、A/D変換器を用いて、微小電流検出抵抗17の電圧に対してA/D変換を行い、アナログ電圧をディジタル電圧に変換する。そして、ディジタル電圧と微小電流検出抵抗17とに基づき微小電流を算出し、所定時間毎に算出した微小電流を積算する。
When the electronic device is in a standby state, the device
制御部11は、このようにして積算された通常電流および微小電流をそれぞれ加算し、加算した電流と電池パックの持つ使用可能な電流量との割合に基づき、電池残容量を算出する。
The
なお、待機状態においては、微小電流検出抵抗17だけでなく通常電流検出抵抗15にも電流が流れるため、通常電流検出抵抗15による電圧降下も生じてしまうが、通常電流検出抵抗15の電圧は測定しないものとすると好ましい。このように、制御部11は、電子機器の動作状態に応じて通常電流検出部14および微小電流検出部16における電流検出の動作を制御する必要があるが、そのためには、例えば、電子機器から動作状態を示す情報を直接受け取るようにしてもよいし、デバイス動作検出部19を介して受け取るようにしてもよい。
In the standby state, since the current flows not only through the minute
ところで、上述のようにしてA/D変換器を用いてアナログ電圧をディジタル電圧に変換し、変換されたディジタル電圧から電流を算出する場合、抵抗値に応じて1ビットあたりの電流範囲が異なり、電流の測定精度に影響を与えてしまう。 By the way, when an analog voltage is converted into a digital voltage using an A / D converter as described above, and a current is calculated from the converted digital voltage, the current range per bit differs depending on the resistance value, This will affect the current measurement accuracy.
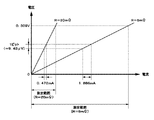
ここで、一例として、ビット数が15[bit]、リファレンス電圧が0.309[V]であるA/D変換器を用いて、アナログ電圧から電流を算出する場合について考える。この場合、1ビットの重みである1ビットあたりの電圧範囲は、ビット数による分割数が215であることから、数式(1)に基づき算出される。
1ビットあたりの電圧範囲=リファレンス電圧/分割数
=0.309[V]/215=9.43[μV] ・・・(1)
Here, as an example, consider a case where a current is calculated from an analog voltage using an A / D converter having a bit number of 15 [bit] and a reference voltage of 0.309 [V]. In this case, the voltage range per bit is the weight of one bit, the number of division by the number of bits from the range of 2 15, is calculated based on equation (1).
Voltage range per bit = reference voltage / number of divisions
= 0.309 [V] / 2 15 = 9.43 [μV] (1)
これにより、1ビットあたりの電流範囲は、電流検出抵抗をR[Ω]とすると、オームの法則により、数式(2)に基づき算出される。
1ビットあたりの電流範囲=1ビットあたりの電圧範囲/電流検出抵抗
=9.43[μV]/R[Ω] ・・・(2)
As a result, the current range per bit is calculated based on Equation (2) according to Ohm's law, where R [Ω] is the current detection resistor.
Current range per bit = Voltage range per bit / Current detection resistor
= 9.43 [μV] / R [Ω] (2)
したがって、電流検出抵抗が5[mΩ]である場合の1ビットあたりの電流範囲は、上述の数式(2)に基づき、図2に示すように、9.43[μV]/5[mΩ]=1.886[mA]となる。一方、電流検出抵抗が20[mΩ]の場合の1ビットあたりの電流範囲は、図2に示すように、9.43[μV]/20[mΩ]=0.472[mA]となる。 Therefore, the current range per bit when the current detection resistance is 5 [mΩ] is 9.43 [μV] / 5 [mΩ] = as shown in FIG. 2 based on the above equation (2). It becomes 1.886 [mA]. On the other hand, the current range per bit when the current detection resistance is 20 [mΩ] is 9.43 [μV] / 20 [mΩ] = 0.472 [mA] as shown in FIG.
このように、1ビットあたりの電圧範囲は、A/D変換器のリファレンス電圧およびビット数によって決定されるため、1ビットあたりの電流範囲は、電流検出抵抗によって変化する。そして、この1ビットあたりの電流範囲の大きさが電流の測定誤差となる。すなわち、電流検出抵抗の値を大きくすることにより、電流全体の測定範囲が狭くなり、最大測定電流が小さくなるが、1ビットあたりの電流範囲が小さくなることによって測定誤差を少なくすることができる。したがって、待機状態における微小電流を検出する場合には、通常状態において用いられる電流検出抵抗よりも大きい値の電流検出抵抗を用いることで、高い精度で電流を測定することができる。 Thus, since the voltage range per bit is determined by the reference voltage and the number of bits of the A / D converter, the current range per bit varies depending on the current detection resistor. The size of the current range per bit is a current measurement error. That is, by increasing the value of the current detection resistor, the measurement range of the entire current is narrowed and the maximum measurement current is reduced. However, the measurement error can be reduced by reducing the current range per bit. Therefore, when detecting a minute current in the standby state, the current can be measured with high accuracy by using a current detection resistor having a larger value than the current detection resistor used in the normal state.
次に、動作状態を示す情報について説明する。デバイス動作検出部19は、電子機器から動作状態を示す情報を受け取り、この情報に基づきスイッチ18のON/OFFを制御して電流経路の切り替えを行うが、電子機器から供給される動作状態を示す情報としては、例えば、電子機器の消費電流を示す情報が挙げられる。具体的には、例えば、電子機器は、消費電流を示す情報を出力し、デバイス動作検出部19は、この消費電流を示す情報を検出端子5を介して受け取る。そして、待機状態における消費電流が5[mA]程度であるとすると、実際の消費電流が例えば5[mA]以下である場合に、デバイス動作検出部19は、消費電流を示す情報に基づき電子機器が待機状態であると判断し、消費電流が5[mA]を超える場合には、電子機器が通常状態であると判断する。
Next, information indicating an operation state will be described. The device
また、動作状態を示す別の情報としては、例えば、PCやテレビなどの電子機器の電源をON/OFF状態を示す情報が挙げられる。例えば、電子機器の電源をONとした場合に立ち上がる信号を検出し、この信号が“H(ハイ)”である場合には、デバイス動作検出部19は、通常状態であると判断する。一方、電子機器の電源をOFFとした場合に、信号が“L(ロー)”である場合には、待機状態であると判断する。
Further, as another information indicating the operation state, for example, information indicating the ON / OFF state of the power supply of an electronic device such as a PC or a television can be cited. For example, a signal that rises when the power of the electronic device is turned on is detected, and when this signal is “H (high)”, the device
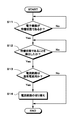
次に、デバイス動作検出部19による電流経路の切り替え方法について説明する。先ず、電子機器の動作状態が通常状態から待機状態に切り替わった場合の、電流経路の切り替え処理の流れについて、図3に示すフローチャートを参照して説明する。なお、特別な記載がない限り、以下の処理は、デバイス動作検出部19の制御の下で行われるものとする。
Next, a method for switching the current path by the device
ステップS11において、電子機器の動作状態が待機状態となり、消費電流が低消費電流になった場合には、処理がステップS12に移行する。一方、電子機器の動作状態が待機状態でない場合には、動作状態が待機状態となるまで処理がステップS11に戻る。 In step S11, when the operation state of the electronic device is in the standby state and the current consumption is low, the process proceeds to step S12. On the other hand, when the operation state of the electronic device is not the standby state, the process returns to step S11 until the operation state becomes the standby state.
ステップS12では、デバイス動作検出部19が検出端子5を介して電子機器から動作状態を示す情報を受け取り、受け取った情報に基づき電子機器の動作状態が判断される。電子機器の動作状態が待機状態であると判断された場合には、処理がステップS13に移行する。一方、電子機器の動作状態が通常状態であると判断された場合には、処理がステップS12に戻り、電子機器の動作状態の判断が再度行われる。
In step S12, the device
ステップS13では、スイッチ18のON/OFF状態に基づき、電流経路が通常電流用であるか否かが判断される。スイッチ18がONである場合には、通常電流用の電流経路であると判断し、処理がステップS14に移行し、スイッチ18をOFFにして微小電流用の電流経路に切り替え、微小電流検出抵抗17に電流が流れるようにして、一連の処理が終了する。
In step S13, based on the ON / OFF state of the
一方、ステップS13において、スイッチ18がOFFである場合には、微小電流用の電流経路であると判断し、一連の処理が終了する。
On the other hand, if the
このように、電流経路に微小電流が流れる待機状態の場合には、スイッチ18をOFFとすることにより電流経路を切り替え、微小電流検出抵抗17に電流を流すようにする。こうすることにより、微小電流検出抵抗17によって微小電流が測定され、正確に電池容量を検出することができる。
As described above, in a standby state in which a minute current flows through the current path, the current path is switched by turning off the
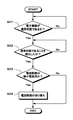
次に、電子機器の動作状態が待機状態から通常状態に切り替わった場合の、電流経路の切り替え処理の流れについて、図4に示すフローチャートを参照して説明する。ステップS21において、電子機器の動作が通常状態となり、消費電流が多くなった場合には、処理がステップS22に移行する。一方、電子機器の動作状態が待機状態である場合には、動作状態が通常状態となるまで処理がステップS21に戻る。 Next, the flow of the current path switching process when the operation state of the electronic device is switched from the standby state to the normal state will be described with reference to the flowchart shown in FIG. In step S21, when the operation of the electronic device is in a normal state and the current consumption increases, the process proceeds to step S22. On the other hand, when the operation state of the electronic device is the standby state, the process returns to step S21 until the operation state becomes the normal state.
ステップS22では、動作状態を示す情報に基づき電子機器の動作状態が判断される。電子機器の動作状態が通常状態であると判断された場合には、処理がステップS23に移行する。一方、電子機器の動作状態が待機状態であると判断された場合には、処理がステップS22に戻り、電子機器の動作状態の判断が再度行われる。 In step S22, the operating state of the electronic device is determined based on the information indicating the operating state. If it is determined that the operation state of the electronic device is the normal state, the process proceeds to step S23. On the other hand, when it is determined that the operation state of the electronic device is the standby state, the process returns to step S22, and the determination of the operation state of the electronic device is performed again.
ステップS23では、スイッチ18のON/OFF状態に基づき、電流経路が微小電流用であるか否かが判断される。スイッチ18がOFFである場合には、微小電流用の電流経路であると判断し、処理がステップS24に移行し、スイッチ18をONにして通常電流用の電流経路に切り替え、微小電流検出抵抗17をバイパスさせて電流が流れないようにし、一連の処理が終了する。
In step S23, based on the ON / OFF state of the
一方、ステップS23において、スイッチ18がONである場合には、通常電流用の電流経路であると判断し、一連の処理が終了する。
On the other hand, if the
このように、電流経路に通常電流が流れる通常状態の場合には、スイッチ18をONとすることにより電流経路を切り替え、微小電流検出抵抗17をバイパスさせて電流が流れないようにする。そして、通常電流検出抵抗15によって通常電流が測定され、正確に電池容量を検出することができる。
Thus, in the normal state where the normal current flows through the current path, the current path is switched by turning on the
この発明の実施の一形態では、電子機器の動作状態に応じて電流検出抵抗を切り替えるようにし、待機状態である場合には、通常電流検出抵抗よりも抵抗値の大きい微小電流検出抵抗に流れる電流を検出することができるようにしているため、より正確に電池残容量を算出することができる。また、通常状態の場合には、微小電流検出抵抗をバイパスさせて電流が流れないようにしているため、微小電流検出抵抗の発熱による破損や発火を防ぐことができる。 In one embodiment of the present invention, the current detection resistor is switched according to the operating state of the electronic device, and when in the standby state, the current flowing through the minute current detection resistor having a resistance value larger than that of the normal current detection resistor. Therefore, the remaining battery capacity can be calculated more accurately. Further, in the normal state, the minute current detection resistor is bypassed so that no current flows, so that the minute current detection resistor can be prevented from being damaged or ignited by heat generation.
さらに、微小電流検出抵抗が通常電流検出抵抗に対して直列に接続されていることにより、電子機器の動作状態に応じて電流経路を切り替えた際に、電流経路が遮断されてしまうのを防ぐことができる。 Furthermore, since the minute current detection resistor is connected in series with the normal current detection resistor, the current path is prevented from being interrupted when the current path is switched according to the operation state of the electronic device. Can do.
以上、この発明の実施の一形態について説明したが、この発明は、上述したこの発明の実施の一形態に限定されるものではなく、この発明の要旨を逸脱しない範囲内で様々な変形や応用が可能である。例えば、電池パック1では、電子機器に接続され、電子機器に対して電流が流れている場合の電極端子間の電圧(閉路電圧;Closed Circuit Voltage)と、電子機器に接続されていない、または、電子機器に接続されているが電子機器の電源がOFFとされているなどの電流が流れていない場合の電極端子間の電圧(開路電圧;Open Circuit Voltage)とが異なることが知られている。そこで、例えば、デバイス動作検出部19は、電極端子間の電圧に基づき、閉路電圧および開路電圧と比較を行うことにより電子機器の動作状態を判断してスイッチ18のON/OFFを制御するようにしてもよい。
The embodiment of the present invention has been described above. However, the present invention is not limited to the embodiment of the present invention described above, and various modifications and applications can be made without departing from the gist of the present invention. Is possible. For example, in the
1 電池パック
2a、2b 通信端子
3 正極端子
4 負極端子
5 検出端子
10 電池セル
11 制御部
12 スイッチ回路
13 電圧検出部
14 通常電流検出部
15 通常電流検出抵抗
16 微小電流検出部
17 微小電流検出抵抗
18 スイッチ
19 デバイス動作検出部
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (6)
電流経路に設けられた第1の電流検出抵抗と、
上記第1の電流検出抵抗に対して直列に接続され、上記第1の電流検出抵抗よりも抵抗値の大きい第2の電流検出抵抗と、
上記第2の電流検出抵抗に対して並列に接続されたスイッチと、
外部の機器から受け取った動作状態を示す情報に基づいて、上記外部の機器が通常状態である場合には、上記スイッチをONとして上記第2の電流検出抵抗をバイパスさせ、上記外部の機器が待機状態である場合には、上記スイッチをOFFとするように、上記スイッチを制御する動作検出部と、
上記スイッチがONである場合に、上記第1の電流検出抵抗に流れる電流を検出する第1の検出部と、
上記スイッチがOFFである場合に、上記第2の電流検出抵抗に流れる電流を検出する第2の検出部と、
上記第1の検出部および上記第2の検出部によって検出された電流に基づき残容量を算出する演算部と
を有することを特徴とする電池パック。 A secondary battery pack,
A first current detection resistor provided in the current path;
A second current detection resistor connected in series to the first current detection resistor and having a resistance value larger than that of the first current detection resistor;
A switch connected in parallel to the second current detection resistor;
When the external device is in a normal state based on the information indicating the operating state received from the external device, the second current detection resistor is bypassed by turning on the switch, and the external device is on standby. If it is in a state, an operation detection unit that controls the switch so as to turn off the switch;
A first detector that detects a current flowing through the first current detection resistor when the switch is ON;
A second detector for detecting a current flowing through the second current detection resistor when the switch is OFF;
A battery pack comprising: a calculation unit that calculates a remaining capacity based on the current detected by the first detection unit and the second detection unit.
上記第2の電流検出抵抗は、抵抗値が20mΩ以上である
ことを特徴とする電池パック。 The battery pack according to claim 1,
The battery pack according to claim 2, wherein the second current detection resistor has a resistance value of 20 mΩ or more.
上記動作状態を示す情報は、上記外部の機器の消費電流を示す情報である
ことを特徴とする電池パック。 The battery pack according to claim 1,
The battery pack according to claim 1, wherein the information indicating the operation state is information indicating a current consumption of the external device.
上記動作状態を示す情報は、消費電流が5mA以下である場合に、待機状態であることを示す
ことを特徴とする電池パック。 The battery pack according to claim 3,
The information indicating the operation state indicates that the battery pack is in a standby state when the current consumption is 5 mA or less.
上記動作状態を示す情報は、上記外部の機器の電源のON/OFFを示す情報である
ことを特徴とする電池パック。 The battery pack according to claim 1,
The battery pack characterized in that the information indicating the operation state is information indicating ON / OFF of the power supply of the external device.
上記スイッチがONである場合に、上記第1の電流検出抵抗に流れる電流を検出する第1の検出ステップと、
上記スイッチがOFFである場合に、上記第2の電流検出抵抗に流れる電流を検出する第2の検出ステップと、
上記第1の検出ステップおよび上記第2の検出ステップによって検出された電流に基づき残容量を算出する演算ステップと
を有することを特徴とする残容量算出方法。 Based on the information indicating the operating state received from the external device, when the external device is in a normal state, the external device is connected in series with the first current detection resistor provided in the current path, and A second current detection resistor having a resistance value larger than that of the first current detection resistor, a switch connected in parallel to the second current detection resistor is turned on to bypass the second current detection resistor, and the external device Is in a standby state, an operation detecting step for controlling the switch so as to turn off the switch;
A first detection step of detecting a current flowing through the first current detection resistor when the switch is ON;
A second detection step of detecting a current flowing through the second current detection resistor when the switch is OFF;
A remaining capacity calculation method comprising: a calculation step of calculating a remaining capacity based on the current detected by the first detection step and the second detection step.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007121348A JP2008275524A (en) | 2007-05-02 | 2007-05-02 | Battery pack and residual capacity computing method |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007121348A JP2008275524A (en) | 2007-05-02 | 2007-05-02 | Battery pack and residual capacity computing method |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2008275524A true JP2008275524A (en) | 2008-11-13 |
Family
ID=40053642
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007121348A Pending JP2008275524A (en) | 2007-05-02 | 2007-05-02 | Battery pack and residual capacity computing method |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2008275524A (en) |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013031302A (en) * | 2011-07-28 | 2013-02-07 | Sanyo Electric Co Ltd | Battery pack, battery-driven apparatus, and non-contact charging method of battery pack |
| US9944218B1 (en) | 2017-03-21 | 2018-04-17 | Hyundai Motor Company | Current control apparatus and vehicle having the same |
| JP2018152285A (en) * | 2017-03-14 | 2018-09-27 | 株式会社東芝 | Storage battery pack |
| CN110168841A (en) * | 2016-12-29 | 2019-08-23 | 威拓股份有限公司 | Hybrid battery charger/tester |
| CN113557440A (en) * | 2020-02-17 | 2021-10-26 | 株式会社Lg新能源 | Battery device and current sensor diagnostic method |
-
2007
- 2007-05-02 JP JP2007121348A patent/JP2008275524A/en active Pending
Cited By (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013031302A (en) * | 2011-07-28 | 2013-02-07 | Sanyo Electric Co Ltd | Battery pack, battery-driven apparatus, and non-contact charging method of battery pack |
| CN110168841A (en) * | 2016-12-29 | 2019-08-23 | 威拓股份有限公司 | Hybrid battery charger/tester |
| JP2020504994A (en) * | 2016-12-29 | 2020-02-13 | ヴィート エヌブイ | Hybrid battery charger / tester |
| JP2018152285A (en) * | 2017-03-14 | 2018-09-27 | 株式会社東芝 | Storage battery pack |
| US10673255B2 (en) | 2017-03-14 | 2020-06-02 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Battery pack and computer-implement battery pack control method |
| JP2020096529A (en) * | 2017-03-14 | 2020-06-18 | 株式会社東芝 | Storage battery pack |
| JP7074788B2 (en) | 2017-03-14 | 2022-05-24 | 株式会社東芝 | Battery pack |
| US9944218B1 (en) | 2017-03-21 | 2018-04-17 | Hyundai Motor Company | Current control apparatus and vehicle having the same |
| CN113557440A (en) * | 2020-02-17 | 2021-10-26 | 株式会社Lg新能源 | Battery device and current sensor diagnostic method |
| CN113557440B (en) * | 2020-02-17 | 2023-08-29 | 株式会社Lg新能源 | Battery device and current sensor diagnosis method |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4668957B2 (en) | Charge control method and electronic device | |
| KR100987606B1 (en) | Apparatus and method for correcting measurements of remaining capacity of battery pack | |
| KR101222409B1 (en) | System of charge and discharge for secondary battery and method of controlling charge and discharge for secondary battery | |
| JP5114884B2 (en) | Battery pack and detection method | |
| JP2008054494A (en) | Hybrid battery and its full-charge-capacity calculation method | |
| CN101807802A (en) | Battery pack and battery capacity calculating method | |
| JP2010124640A5 (en) | ||
| CN113196610A (en) | Method and apparatus for controlling charging current in battery pack containing different types of cells | |
| US20140203781A1 (en) | Battery pack and charging method thereof | |
| JP2010028876A (en) | Charging/discharging system and portable computer | |
| US9372238B2 (en) | Battery management system with over-discharge detection and warning, battery pack comprising the same, and method for protecting a battery from over-discharge | |
| JP5544922B2 (en) | Protection circuit and electronic equipment | |
| JP2009097954A (en) | Battery pack and residual capacity correction method of secondary battery | |
| JP4886530B2 (en) | Electronic device system and battery pack | |
| JP3925507B2 (en) | Secondary battery charging method and battery pack | |
| JP4086008B2 (en) | Secondary battery remaining capacity ratio calculation method and battery pack | |
| JP2008275524A (en) | Battery pack and residual capacity computing method | |
| JP3405525B2 (en) | Battery pack control device | |
| WO2011004788A1 (en) | Cell pack, semiconductor device, portable apparatus, and full charge reporting method | |
| KR20130061019A (en) | Battery pack | |
| JP4846755B2 (en) | Portable electronic devices | |
| KR20140025652A (en) | Battery pack and controlling method of the same | |
| US8937461B2 (en) | System for controlling charging of battery and battery pack comprising the same | |
| US8786258B2 (en) | Battery pack and method of controlling the battery pack | |
| JP5084117B2 (en) | Pack batteries and electrical equipment |