테마플록사신
Temafloxacin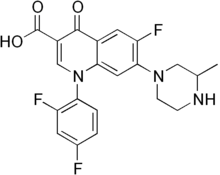 | |
| 임상자료 | |
|---|---|
| 상명 | 옴니플록스 |
| 경로: 행정 | 구강 |
| ATC 코드 | |
| 법적현황 | |
| 법적현황 |
|
| 식별자 | |
| |
| CAS 번호 | |
| 펍켐 CID | |
| 드러그뱅크 | |
| 켐스파이더 | |
| 유니 | |
| 케그 | |
| 체비 | |
| 켐벨 | |
| CompTox 대시보드 (EPA) | |
| 화학 및 물리적 데이터 | |
| 공식 | C21H18F3N3O3 |
| 어금질량 | 417.388 g·1998−1 |
| 3D 모델(JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
테마플록사신(Abbott Laboratories에서 옴니플록스로 판매)은 플루오로퀴놀론 항생제로, 1992년 승인 직후 미국에서 판매에서 회수되어 3명이 사망하였다.[1][2]그것은 유럽에서는 판매되지 않는다.null
역사
옴니플록스는 1992년 1월 미국 식품의약국(FDA)으로부터 하부 호흡기 감염, 생식기 및 요로 감염, 전립선염과 같은 피부 감염을 치료하도록 승인받았다.알레르기 반응과 용혈성 빈혈 등 심각한 부작용은 사용 후 4개월 동안 100명 이상의 환자에게서 발생하여 3명의 환자가 사망하였다.[3]애보트는 1992년 6월 이 약을 판매에서 철수시켰다.null
약동학
구강 투여 후 그 화합물은 위장관에서 잘 흡수된다.구강 생체이용률은 90% 이상이다.테마플록사신은 특히 호흡기 조직, 비강 분비물, 편도선, 전립선, 뼈 등 다양한 생물학적 액체와 조직에 잘 침투한다.[4]이 지역들에서 달성된 농도는 혈청 농도와 동일하거나 더 높다.[5]플루오로퀴놀론은 7~8시간 반의 수명을 가지고 있다.[6]중추신경계(CNS)로의 침투는 덜 뚜렷하다.[6]신체의 배설은 주로 신장에 있는 글로머 여과 때문이다.[7][8][9]null
임상용도
이 화합물은 하부 호흡기 감염(커뮤니티-취득 폐렴, 만성 기관지염의 악화), 생식기 및 요로 감염(프로스타트염, 임질, 비곤occal 요도염, 자궁경부염), 피부 및 연조직 감염을 치료하기 위해 표시되었다.[6][10][11][12]null
참고 항목
참조
- ^ "Recalling the Omniflox (Temafloxacin) Tablets" (pdf). Food and Drug Administration. 1992-06-05. Retrieved 2014-10-15.
- ^ "ABBOTT WITHDRAWS TEMAFLOXACIN - Pharmaceutical industry news". The Pharmaletter. 1992-06-15. Retrieved 2014-10-16.
- ^ Rubinstein, E. "History of quinolones and their side effects". Chemotherapy. 47 Suppl 3: 3–8, discussion 44–8. doi:10.1159/000057838. PMID 11549783.
- ^ Sorgel F, Naber KG, Kinzig M, Mahr G, Muth P (December 1991). "Comparative pharmacokinetics of ciprofloxacin and temafloxacin in humans: a review". Am. J. Med. 91 (6A): 51S–66S. doi:10.1016/0002-9343(91)90312-L. PMID 1662896.
- ^ Sörgel F (1992). "Penetration of temafloxacin into body tissues and fluids". Clin Pharmacokinet. 22 Suppl 1: 57–63. doi:10.2165/00003088-199200221-00010. PMID 1319872.
- ^ a b c Pankey GA (December 1991). "Temafloxacin: an overview". Am. J. Med. 91 (6A): 166S–172S. doi:10.1016/0002-9343(91)90332-r. PMID 1662889.
- ^ Granneman GR, Carpentier P, Morrison PJ, Pernet AG (February 1992). "Pharmacokinetics of temafloxacin in humans after multiple oral doses". Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 36 (2): 378–86. doi:10.1128/aac.36.2.378. PMC 188445. PMID 1318680.
- ^ Granneman GR, Braeckman R, Kraut J, Shupien S, Craft JC (November 1991). "Temafloxacin pharmacokinetics in subjects with normal and impaired renal function". Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 35 (11): 2345–51. doi:10.1128/aac.35.11.2345. PMC 245383. PMID 1666497.
- ^ Dudley MN (December 1991). "A review of the pharmacokinetic profile of temafloxacin". J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 28 Suppl C: 55–64. doi:10.1093/jac/28.suppl_c.55. PMID 1664830. Retrieved 2014-10-17.
- ^ Gentry LO (December 1991). "Review of quinolones in the treatment of infections of the skin and skin structure". J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 28 Suppl C: 97–110. doi:10.1093/jac/28.suppl_C.97. PMID 1787128. Retrieved 2014-10-17.
- ^ Wise R (December 1991). "Comparative penetration of selected fluoroquinolones into respiratory tract fluids and tissues". Am. J. Med. 91 (6A): 67S–70S. doi:10.1016/0002-9343(91)90313-M. PMID 1662897.
- ^ Symonds WT, Nix DE (September 1992). "Lomefloxacin and temafloxacin: two new fluoroquinolone antimicrobials". Clin Pharm. 11 (9): 753–66. PMID 1325892.
외부 링크
- 1992년 6월 5일 FDA 보도 자료


