핀1
PIN1펩티딜 프롤릴 cis-trans isomerase NIMA-interaction 1은 인간에서 PIN1 유전자에 의해 인코딩되는 효소다.[5][6]
핀 1 또는 펩티딜 프롤릴 시스/트랜스 이소머라아제(PPI아제)는 인광-세린/트레오닌-프로라인 모티브만 이소머화한다.효소는 단백질의 서브셋에 결합되어 단백질 기능을 조절하는 사후 인산화 조절의 역할을 한다.핀1 규제 완화가 각종 질병에 중추적인 역할을 할 수 있다는 연구결과가 나왔다.특히 핀1의 상향 조정은 특정 암에, 하향 조정된 핀1은 알츠하이머병과 관련이 있다.핀1의 억제제는 암과[7][8] 면역 장애에 치료적 영향을 미칠 수 있다.[9]
디스커버리
핀1 유전자 부호화는 1996년 유사 조절에 관련된 단백질의 유전자/생물화학 스크린의 결과로 확인되었다.그것은 몇몇 유기체들의 세포분열을 위해 필수적인 것으로 밝혀졌다.그러나 1999년에 이르러 핀1 녹아웃 생쥐는 놀랄 만큼 가벼운 표현형을 가지고 있다는 것이 명백해졌고, 이는 세포분할에 효소가 필요하지 않다는 것을 보여준다.이후 추가 연구 결과 마우스 표시장치에서 핀1 손실은 뉴런 퇴행성 표현형일 뿐만 아니라 사이클린 D1-null 생쥐와 유사한 몇 가지 이상이라는 사실이 밝혀져 핀1에 의해 매개되는 순응 변화가 세포 정상 기능에 매우 중요할 수 있음을 시사했다.
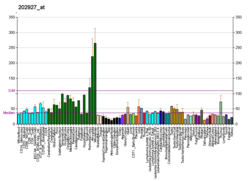
활성화
Pin1로 인식하려면 기판 내 Ser/Thr-Pro 모티브의 인산화 작업이 필요하다.핀은 18kDa의 작은 단백질로 핵 국산화나 수출 신호가 없다.그러나 2009년, 루페이 외 연구진은 핀1이 배치적인 참신한 핵 국산화 신호(NLS), 핀1은 수입 α5(KPNA1)와 상호작용을 한다고 보고했다.[10]기질 상호작용과 WW영역은 세포하 분포를 결정한다.표현은 E2F 전사 인자의 성장 신호에 의해 유도된다.발현 수준은 정상에서는 변동하지만 암세포에서는 변동하지 않는다.표현은 종종 세포 증식과 관련이 있다.Ser16의 인산화 같은 후분해적 수정은 Pin1의 기질 결합 능력을 억제하며, 이러한 억제 과정은 종양 발생 시 변경될 수 있다.Pin1도 단백질 분해 경로에 의해 규제될 수 있다는 가설이 있지만 입증되지는 않았다.
함수
핀1 활동은 프로라인 방향 키나아제(예: MAPK, CDK 또는 GSK3) 신호 전달의 결과를 조절하고 결과적으로 세포 증식(부분적으로는 사이클린 D1 수준과 안정성의 제어를 통한)과 세포 생존을 조절한다.핀1의 정확한 효과는 시스템에 따라 달라진다.핀1은 Cdc25와 타우의 탈인산화를 가속화하지만, 편재와 프로테롤리시스로부터 인산화 사이클린 D를 보호한다.최근의 데이터는 또한 핀1이 면역 반응에서 중요한 역할을 하고 있으며, 적어도 부분적으로는 그들이 결합하는 단백질 복합체에 영향을 줌으로써 사이토카인 mRNA의 안정성을 증가시킴으로써 핀1이 면역 반응에 중요한 역할을 하고 있다는 것을 보여준다.핀1은 분자 타이머 역할을 하도록 가설되었다.[11]
억제
PIN1은 유방암, 자궁경부암, 난소암, 자궁내막암 등 [12][13]암세포선 억제에 대한 흥미로운 분자 대상으로 널리 연구되어 왔다.[14]비타민 A에서 추출한 천연 화합물인 올트랜트 레티노산(ATRA)이 PIN1 억제와 관련이 있다는 연구결과가 나왔다.[15]게다가 ATRA는 또한 Pin1을 줄이고 암 성장을 억제하는 소라페니브의 능력을 시너지 효과를 높인 것으로 보고되었다.[16]일부 전기산 유도체들은 또한 PIN1에 대한 억제 활성을 가지고 보고되었다.[17] 또한 몇몇 계산적 증거들은 넴의 일부 트라이터페노이드가 또한 전기산 유도체들과[12] 유사한 방식으로 PIN1을 억제할 수 있다는 것을 증명했다.
상호작용
PIN1은 다음과 상호 작용하는 것으로 나타났다.
참조
- ^ a b c GRCh38: 앙상블 릴리스 89: ENSG00000127445 - 앙상블, 2017년 5월
- ^ a b c GRCm38: 앙상블 릴리스 89: ENSMUSG000032171 - 앙상블, 2017년 5월
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Lu KP, Hanes SD, Hunter T (Apr 1996). "A human peptidyl-prolyl isomerase essential for regulation of mitosis". Nature. 380 (6574): 544–7. doi:10.1038/380544a0. PMID 8606777. S2CID 4258406.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: PIN1 Protein (peptidylprolyl cis/trans isomerase) NIMA-interacting 1".
- ^ da Costa, Kauê Santana; Galúcio, João Marcos; de Jesus, Deivid Almeida; Gomes, Guelber Cardoso; Lima e Lima, Anderson Henrique; Taube, Paulo Sérgio; dos Santos, Alberto Monteiro; Lameira, Jerônimo (2019-10-25). "Targeting Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase NIMA-interacting 1: A Structure-based Virtual Screening Approach to Find Novel Inhibitors". Current Computer-Aided Drug Design. 15 (5): 605–617. doi:10.2174/1573409915666191025114009. PMID 31654518. S2CID 204907887.
- ^ Campaner, Elena; Rustighi, Alessandra; Zannini, Alessandro; Cristiani, Alberto; Piazza, Silvano; Ciani, Yari; Kalid, Ori; Golan, Gali; Baloglu, Erkan; Shacham, Sharon; Valsasina, Barbara (August 2017). "A covalent PIN1 inhibitor selectively targets cancer cells by a dual mechanism of action". Nature Communications. 8 (1): 15772. doi:10.1038/ncomms15772. ISSN 2041-1723. PMC 5472749. PMID 28598431.
- ^ Rudrabhatla, P.; Albers, W.; Pant, H. C. (2009-11-25). "Peptidyl-Prolyl Isomerase 1 Regulates Protein Phosphatase 2A-Mediated Topographic Phosphorylation of Neurofilament Proteins". Journal of Neuroscience. 29 (47): 14869–14880. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4469-09.2009. ISSN 0270-6474. PMC 3849796. PMID 19940183.
- ^ Lufei C, Cao X (2009). "Nuclear import of Pin1 is mediated by a novel sequence in the PPIase domain". FEBS Letters. 583 (2): 271–276. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2008.12.011. PMID 19084525. S2CID 23995242.
- ^ Lu KP, Finn G, Lee TH, Nicholson LK (Oct 2007). "Prolyl cis-trans isomerization as a molecular timer". Nature Chemical Biology. 3 (10): 619–29. doi:10.1038/nchembio.2007.35. PMID 17876319.
- ^ a b da Costa KS, Galúcio JM, de Jesus DA, Gomes GC, Lima E, Lima AH, et al. (2020-11-09). "Targeting Peptidyl-prolyl Cis-trans Isomerase NIMA-interacting 1: A Structure-based Virtual Screening Approach to Find Novel Inhibitors". Current Computer-Aided Drug Design. 16 (5): 605–617. doi:10.2174/1573409915666191025114009. PMID 31654518. S2CID 204907887.
- ^ Russo Spena C, De Stefano L, Poli G, Granchi C, El Boustani M, Ecca F, et al. (January 2019). "Virtual screening identifies a PIN1 inhibitor with possible antiovarian cancer effects". Journal of Cellular Physiology. 234 (9): 15708–15716. doi:10.1002/jcp.28224. PMID 30697729. S2CID 59412053.
- ^ Kim G, Bhattarai PY, Choi HS (February 2019). "Peptidyl-prolyl cis/trans isomerase NIMA-interacting 1 as a molecular target in breast cancer: a therapeutic perspective of gynecological cancer". Archives of Pharmacal Research. 42 (2): 128–139. doi:10.1007/s12272-019-01122-3. PMID 30684192. S2CID 59274466.
- ^ Wei S, Kozono S, Kats L, Nechama M, Li W, Guarnerio J, et al. (May 2015). "Active Pin1 is a key target of all-trans retinoic acid in acute promyelocytic leukemia and breast cancer". Nature Medicine. 21 (5): 457–66. doi:10.1038/nm.3839. PMC 4425616. PMID 25849135.
- ^ Zheng M, Xu H, Liao XH, Chen CP, Zhang AL, Lu W, et al. (May 2017). "Inhibition of the prolyl isomerase Pin1 enhances the ability of sorafenib to induce cell death and inhibit tumor growth in hepatocellular carcinoma". Oncotarget. 8 (18): 29771–29784. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.15967. PMC 5444702. PMID 28404959.
- ^ Li X, Li L, Zhou Q, Zhang N, Zhang S, Zhao R, et al. (December 2014). "Synthesis of the novel elemonic acid derivatives as Pin1 inhibitors". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 24 (24): 5612–5615. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2014.10.087. PMID 25466185.
- ^ Wulf GM, Ryo A, Wulf GG, Lee SW, Niu T, Petkova V, Lu KP (Jul 2001). "Pin1 is overexpressed in breast cancer and cooperates with Ras signaling in increasing the transcriptional activity of c-Jun towards cyclin D1". The EMBO Journal. 20 (13): 3459–72. doi:10.1093/emboj/20.13.3459. PMC 125530. PMID 11432833.
- ^ a b c d e Shen M, Stukenberg PT, Kirschner MW, Lu KP (Mar 1998). "The essential mitotic peptidyl-prolyl isomerase Pin1 binds and regulates mitosis-specific phosphoproteins". Genes & Development. 12 (5): 706–20. doi:10.1101/gad.12.5.706. PMC 316589. PMID 9499405.
- ^ Goldstrohm AC, Albrecht TR, Suñé C, Bedford MT, Garcia-Blanco MA (Nov 2001). "The transcription elongation factor CA150 interacts with RNA polymerase II and the pre-mRNA splicing factor SF1". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 21 (22): 7617–28. doi:10.1128/MCB.21.22.7617-7628.2001. PMC 99933. PMID 11604498.
- ^ a b c Lu PJ, Zhou XZ, Shen M, Lu KP (Feb 1999). "Function of WW domains as phosphoserine- or phosphothreonine-binding modules". Science. 283 (5406): 1325–8. doi:10.1126/science.283.5406.1325. PMID 10037602.
- ^ a b Messenger MM, Saulnier RB, Gilchrist AD, Diamond P, Gorbsky GJ, Litchfield DW (Jun 2002). "Interactions between protein kinase CK2 and Pin1. Evidence for phosphorylation-dependent interactions". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 277 (25): 23054–64. doi:10.1074/jbc.M200111200. PMID 11940573.
- ^ He J, Xu J, Xu XX, Hall RA (Jul 2003). "Cell cycle-dependent phosphorylation of Disabled-2 by cdc2". Oncogene. 22 (29): 4524–30. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1206767. PMID 12881709.
- ^ Ruan L, Torres CM, Qian J, Chen F, Mintz JD, Stepp DW, Fulton D, Venema RC (Feb 2011). "Pin1 prolyl isomerase regulates endothelial nitric oxide synthase". Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology. 31 (2): 392–8. doi:10.1161/ATVBAHA.110.213181. PMC 3075952. PMID 21051667.
- ^ Brenkman AB, de Keizer PL, van den Broek NJ, van der Groep P, van Diest PJ, van der Horst A, Smits AM, Burgering BM (Sep 2008). "The peptidyl-isomerase Pin1 regulates p27kip1 expression through inhibition of Forkhead box O tumor suppressors". Cancer Research. 68 (18): 7597–605. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-1059. PMID 18794148.
- ^ Kamimoto T, Zama T, Aoki R, Muro Y, Hagiwara M (Oct 2001). "Identification of a novel kinesin-related protein, KRMP1, as a target for mitotic peptidyl-prolyl isomerase Pin1". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 276 (40): 37520–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.M106207200. PMID 11470801.
- ^ Wells NJ, Watanabe N, Tokusumi T, Jiang W, Verdecia MA, Hunter T (Oct 1999). "The C-terminal domain of the Cdc2 inhibitory kinase Myt1 interacts with Cdc2 complexes and is required for inhibition of G(2)/M progression". Journal of Cell Science. 112 (19): 3361–71. doi:10.1242/jcs.112.19.3361. PMID 10504341.
- ^ a b Nakano A, Koinuma D, Miyazawa K, Uchida T, Saitoh M, Kawabata M, Hanai J, Akiyama H, Abe M, Miyazono K, Matsumoto T, Imamura T (Mar 2009). "Pin1 down-regulates transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) signaling by inducing degradation of Smad proteins". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 284 (10): 6109–15. doi:10.1074/jbc.M804659200. PMID 19122240.
- ^ Wulf GM, Liou YC, Ryo A, Lee SW, Lu KP (Dec 2002). "Role of Pin1 in the regulation of p53 stability and p21 transactivation, and cell cycle checkpoints in response to DNA damage". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 277 (50): 47976–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.C200538200. PMID 12388558.
- ^ Zacchi P, Gostissa M, Uchida T, Salvagno C, Avolio F, Volinia S, Ronai Z, Blandino G, Schneider C, Del Sal G (Oct 2002). "The prolyl isomerase Pin1 reveals a mechanism to control p53 functions after genotoxic insults". Nature. 419 (6909): 853–7. doi:10.1038/nature01120. PMID 12397362. S2CID 4311658.
- ^ Lavoie SB, Albert AL, Handa H, Vincent M, Bensaude O (Sep 2001). "The peptidyl-prolyl isomerase Pin1 interacts with hSpt5 phosphorylated by Cdk9". Journal of Molecular Biology. 312 (4): 675–85. doi:10.1006/jmbi.2001.4991. PMID 11575923.
추가 읽기
- Lu KP, Liou YC, Zhou XZ (Apr 2002). "Pinning down proline-directed phosphorylation signaling". Trends in Cell Biology. 12 (4): 164–72. doi:10.1016/S0962-8924(02)02253-5. PMID 11978535.
- Wulf G, Finn G, Suizu F, Lu KP (May 2005). "Phosphorylation-specific prolyl isomerization: is there an underlying theme?". Nature Cell Biology. 7 (5): 435–41. doi:10.1038/ncb0505-435. PMID 15867923. S2CID 180385.
- Etzkorn FA (May 2006). "Pin1 flips Alzheimer's switch". ACS Chemical Biology. 1 (4): 214–6. doi:10.1021/cb600171g. PMID 17163675.
- Balastik M, Lim J, Pastorino L, Lu KP (Apr 2007). "Pin1 in Alzheimer's disease: multiple substrates, one regulatory mechanism?". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease. 1772 (4): 422–9. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2007.01.006. PMC 1868500. PMID 17317113.
- Maleszka R, Hanes SD, Hackett RL, de Couet HG, Miklos GL (Jan 1996). "The Drosophila melanogaster dodo (dod) gene, conserved in humans, is functionally interchangeable with the ESS1 cell division gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 93 (1): 447–51. doi:10.1073/pnas.93.1.447. PMC 40255. PMID 8552658.
- Ranganathan R, Lu KP, Hunter T, Noel JP (Jun 1997). "Structural and functional analysis of the mitotic rotamase Pin1 suggests substrate recognition is phosphorylation dependent". Cell. 89 (6): 875–86. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80273-1. PMID 9200606. S2CID 16219532.
- Campbell HD, Webb GC, Fountain S, Young IG (Sep 1997). "The human PIN1 peptidyl-prolyl cis/trans isomerase gene maps to human chromosome 19p13 and the closely related PIN1L gene to 1p31". Genomics. 44 (2): 157–62. doi:10.1006/geno.1997.4854. PMID 9299231.
- Crenshaw DG, Yang J, Means AR, Kornbluth S (Aug 1998). "The mitotic peptidyl-prolyl isomerase, Pin1, interacts with Cdc25 and Plx1". The EMBO Journal. 17 (5): 1315–27. doi:10.1093/emboj/17.5.1315. PMC 1170480. PMID 9482729.
- Shen M, Stukenberg PT, Kirschner MW, Lu KP (Mar 1998). "The essential mitotic peptidyl-prolyl isomerase Pin1 binds and regulates mitosis-specific phosphoproteins". Genes & Development. 12 (5): 706–20. doi:10.1101/gad.12.5.706. PMC 316589. PMID 9499405.
- Lu PJ, Zhou XZ, Shen M, Lu KP (Feb 1999). "Function of WW domains as phosphoserine- or phosphothreonine-binding modules". Science. 283 (5406): 1325–8. doi:10.1126/science.283.5406.1325. PMID 10037602.
- Lu PJ, Wulf G, Zhou XZ, Davies P, Lu KP (Jun 1999). "The prolyl isomerase Pin1 restores the function of Alzheimer-associated phosphorylated tau protein". Nature. 399 (6738): 784–8. doi:10.1038/21650. PMID 10391244. S2CID 4373905.
- Albert A, Lavoie S, Vincent M (Aug 1999). "A hyperphosphorylated form of RNA polymerase II is the major interphase antigen of the phosphoprotein antibody MPM-2 and interacts with the peptidyl-prolyl isomerase Pin1". Journal of Cell Science. 112. 112 (15): 2493–500. doi:10.1242/jcs.112.15.2493. PMID 10393805.
- Wells NJ, Watanabe N, Tokusumi T, Jiang W, Verdecia MA, Hunter T (Oct 1999). "The C-terminal domain of the Cdc2 inhibitory kinase Myt1 interacts with Cdc2 complexes and is required for inhibition of G(2)/M progression". Journal of Cell Science. 112. 112 (19): 3361–71. doi:10.1242/jcs.112.19.3361. PMID 10504341.
- Gerez L, Mohrmann K, van Raak M, Jongeneelen M, Zhou XZ, Lu KP, van Der Sluijs P (Jul 2000). "Accumulation of rab4GTP in the cytoplasm and association with the peptidyl-prolyl isomerase pin1 during mitosis". Molecular Biology of the Cell. 11 (7): 2201–11. doi:10.1091/mbc.11.7.2201. PMC 14913. PMID 10888662.
- Verdecia MA, Bowman ME, Lu KP, Hunter T, Noel JP (Aug 2000). "Structural basis for phosphoserine-proline recognition by group IV WW domains". Nature Structural Biology. 7 (8): 639–43. doi:10.1038/77929. PMID 10932246. S2CID 20088089.
- Rippmann JF, Hobbie S, Daiber C, Guilliard B, Bauer M, Birk J, Nar H, Garin-Chesa P, Rettig WJ, Schnapp A (Jul 2000). "Phosphorylation-dependent proline isomerization catalyzed by Pin1 is essential for tumor cell survival and entry into mitosis". Cell Growth & Differentiation. 11 (7): 409–16. PMID 10939594.
- Liu W, Youn HD, Zhou XZ, Lu KP, Liu JO (May 2001). "Binding and regulation of the transcription factor NFAT by the peptidyl prolyl cis-trans isomerase Pin1". FEBS Letters. 496 (2–3): 105–8. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(01)02411-5. PMID 11356192. S2CID 7707812.
- Wulf GM, Ryo A, Wulf GG, Lee SW, Niu T, Petkova V, Lu KP (Jul 2001). "Pin1 is overexpressed in breast cancer and cooperates with Ras signaling in increasing the transcriptional activity of c-Jun towards cyclin D1". The EMBO Journal. 20 (13): 3459–72. doi:10.1093/emboj/20.13.3459. PMC 125530. PMID 11432833.
- Kamimoto T, Zama T, Aoki R, Muro Y, Hagiwara M (Oct 2001). "Identification of a novel kinesin-related protein, KRMP1, as a target for mitotic peptidyl-prolyl isomerase Pin1". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 276 (40): 37520–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.M106207200. PMID 11470801.