가도다이아미드
Gadodiamide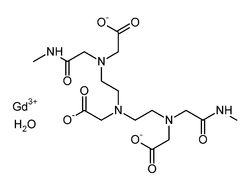 | |
| 임상자료 | |
|---|---|
| 상명 | 옴니스칸 |
| 기타 이름 | 2-[bis[2-(carboxylatomethyl-(methylcarbamoylmethyl)amino)]ethyl]acetate; gadolinium3) cation |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | 마이크로메덱스 상세 소비자 정보 |
| 라이센스 데이터 | |
| 경로: 행정 | 정맥주사 |
| ATC 코드 | |
| 법적현황 | |
| 법적현황 | |
| 약동학 데이터 | |
| 단백질 결합 | 무시할 만한 |
| 신진대사 | 대사되지 않은 |
| 제거 반감기 | 77.8분 |
| 배설 | 신장 |
| 식별자 | |
| |
| CAS 번호 |
|
| 펍켐 CID | |
| 드러그뱅크 | |
| 켐스파이더 | |
| 유니 | |
| 케그 | |
| 체비 | |
| 켐벨 | |
| CompTox 대시보드 (EPA) | |
| 화학 및 물리적 데이터 | |
| 공식 | C16H28GdN5O9 |
| 어금질량 | 591.68 g·190−1 |
| 3D 모델(JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
오미스칸이라는 상표명으로 판매되는 가도다이아미드는 자기공명영상(MRI) 시술에 쓰이는 가돌리늄 기반의 MRI 조영제(GBCA)로 혈관의 시각화를 돕는다.
의학적 용법
가도다이아미드는 정맥 투여 후 두개골 및 척추자기공명영상(MRI)과 신체의 일반 MRI에 사용되는 조영제다. 대조도 향상을 제공하고 중추신경계(CNS)를 포함한 신체의 여러 부분에서 비정상적인 구조나 병변의 시각화를 용이하게 한다. 혈액뇌장벽이 손상되지 않고 교차한다.[3]
역효과
이것은 신장 질환을 가진 일부 사람들에게서 발생하는 독성 반응인 신겐성 전신 섬유증(NSF)과 관련된 주요 GBCA 중 하나이다.[4] 신장 기능이 정상인 사람에게서 어떤 사례도 발견되지 않았다.[5]
2015년 한 연구는 가돌리늄을 받은 사람들의 뇌 조직에 축적된 가돌리늄을 발견했다.[6] 사후에 질량분석을 이용한 다른 연구에서는 대부분의 예탁금이 주사 후 최소 2년 이상 경과한 후 신장 질환이 없는 개인에게도 남아 있는 것으로 나타났다.
이탈리아의 한 대책위원회는 모유 수유 엄마들에게 신혈성 전신 섬유증과 관련된 가도디아미드 같은 조영제를 예방적으로 피하라고 권고했다.[8]
사회와 문화
가도다이아미드는 2017년 유럽의약품청으로부터 가도펜테틱산(마그네비스트)과 함께 중단됐다.[9]
참조
- ^ "Omniscan- gadodiamide injection". DailyMed. Retrieved 29 August 2021.
- ^ "Active substance: gadodiamide" (PDF). List of nationally authorised medicinal products. European Medicine Agency. 14 January 2021.
- ^ Rasschaert M, Weller RO, Schroeder JA, Brochhausen C, Idée JM (2020). "Retention of Gadolinium in Brain Parenchyma: Pathways for Speciation, Access, and Distribution. A Critical Review". Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging. 52 (5): 1293–1305. doi:10.1002/jmri.27124. PMC 7687192. PMID 32246802.
- ^ Ibrahim MA, Hazhirkarzar B, Dublin AB (January 2018). "Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), Gadolinium". StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. PMID 29494094.
- ^ Canavese C, Mereu MC, Aime S, Lazzarich E, Fenoglio R, Quaglia M, Stratta P (2008). "Gadolinium-associated nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: the need for nephrologists' awareness". Journal of Nephrology. 21 (3): 324–36. PMID 18587720.
- ^ Anderson P (26 March 2015). "Gadolinium Found in Brain Tissue". Medscape. Retrieved 14 April 2015.
- ^ Bower DV, Richter JK, von Tengg-Kobligk H, Heverhagen JT, Runge VM (August 2019). "Gadolinium-Based MRI Contrast Agents Induce Mitochondrial Toxicity and Cell Death in Human Neurons, and Toxicity Increases With Reduced Kinetic Stability of the Agent". Investigative Radiology. 54 (8): 453–463. doi:10.1097/RLI.0000000000000567. PMID 31265439. S2CID 164486744.
- ^ Cova MA, Stacul F, Quaranta R, Guastalla P, Salvatori G, Banderali G, et al. (August 2014). "Radiological contrast media in the breastfeeding woman: a position paper of the Italian Society of Radiology (SIRM), the Italian Society of Paediatrics (SIP), the Italian Society of Neonatology (SIN) and the Task Force on Breastfeeding, Ministry of Health, Italy". European Radiology. 24 (8): 2012–22. doi:10.1007/s00330-014-3198-6. PMID 24838733. S2CID 24502257.
- ^ "Gadolinium-containing contrast agents: removal of Omniscan and iv Magnevist, restrictions to the use of other linear agents". GOV.UK. 14 December 2017. Retrieved 29 August 2021.
외부 링크
- "Gadodiamide". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.



