anaphase
Also found in: Thesaurus, Medical, Encyclopedia, Wikipedia.
Related to anaphase: anaphase lag
an·a·phase
(ăn′ə-fāz′)n.
The stage of mitosis and meiosis in which the chromosomes move to opposite ends of the nuclear spindle.
American Heritage® Dictionary of the English Language, Fifth Edition. Copyright © 2016 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
anaphase
(ˈænəˌfeɪz)n
1. (Biology) the third stage of mitosis, during which the chromatids separate and migrate towards opposite ends of the spindle. See also prophase, metaphase, telophase
2. (Biology) the corresponding stage of the first division of meiosis
[C19: from ana- + phase]
Collins English Dictionary – Complete and Unabridged, 12th Edition 2014 © HarperCollins Publishers 1991, 1994, 1998, 2000, 2003, 2006, 2007, 2009, 2011, 2014
an•a•phase
(ˈæn əˌfeɪz)n.
the stage in mitosis or meiosis following metaphase in which the chromosomes move away from each other to opposite ends of the cell.
[1885–90]
an`a•pha′sic, adj.
Random House Kernerman Webster's College Dictionary, © 2010 K Dictionaries Ltd. Copyright 2005, 1997, 1991 by Random House, Inc. All rights reserved.
an·a·phase
(ăn′ə-fāz′)The American Heritage® Student Science Dictionary, Second Edition. Copyright © 2014 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
ThesaurusAntonymsRelated WordsSynonymsLegend:
Switch to new thesaurus
| Noun | 1. | 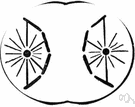 anaphase - the stage of meiosis or mitosis when chromosomes move toward opposite ends of the nuclear spindle anaphase - the stage of meiosis or mitosis when chromosomes move toward opposite ends of the nuclear spindlemeiosis, miosis, reduction division - (genetics) cell division that produces reproductive cells in sexually reproducing organisms; the nucleus divides into four nuclei each containing half the chromosome number (leading to gametes in animals and spores in plants) phase of cell division - a stage in meiosis or mitosis |
Based on WordNet 3.0, Farlex clipart collection. © 2003-2012 Princeton University, Farlex Inc.
Translations
an·a·phase
n. anafase, etapa de la división celular.
English-Spanish Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012