WO2020151605A1 - 氘代苯甲氨嘧啶二酮衍生物及其用途 - Google Patents
氘代苯甲氨嘧啶二酮衍生物及其用途 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2020151605A1 WO2020151605A1 PCT/CN2020/072904 CN2020072904W WO2020151605A1 WO 2020151605 A1 WO2020151605 A1 WO 2020151605A1 CN 2020072904 W CN2020072904 W CN 2020072904W WO 2020151605 A1 WO2020151605 A1 WO 2020151605A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- group
- atoms
- independently
- alkyl
- butyl
- Prior art date
Links
- 0 C[C@@](c1ccccc1)NC(NC(N1C(*)*)=O)=CC1=O Chemical compound C[C@@](c1ccccc1)NC(NC(N1C(*)*)=O)=CC1=O 0.000 description 1
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D239/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-diazine or hydrogenated 1,3-diazine rings
- C07D239/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-diazine or hydrogenated 1,3-diazine rings not condensed with other rings
- C07D239/24—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-diazine or hydrogenated 1,3-diazine rings not condensed with other rings having three or more double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D239/28—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-diazine or hydrogenated 1,3-diazine rings not condensed with other rings having three or more double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members with hetero atoms or with carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most one bond to halogen, directly attached to ring carbon atoms
- C07D239/46—Two or more oxygen, sulphur or nitrogen atoms
- C07D239/52—Two oxygen atoms
- C07D239/54—Two oxygen atoms as doubly bound oxygen atoms or as unsubstituted hydroxy radicals
- C07D239/545—Two oxygen atoms as doubly bound oxygen atoms or as unsubstituted hydroxy radicals with other hetero atoms or with carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most one bond to halogen, directly attached to ring carbon atoms
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/395—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins
- A61K31/495—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having six-membered rings with two or more nitrogen atoms as the only ring heteroatoms, e.g. piperazine or tetrazines
- A61K31/505—Pyrimidines; Hydrogenated pyrimidines, e.g. trimethoprim
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/395—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins
- A61K31/495—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having six-membered rings with two or more nitrogen atoms as the only ring heteroatoms, e.g. piperazine or tetrazines
- A61K31/505—Pyrimidines; Hydrogenated pyrimidines, e.g. trimethoprim
- A61K31/506—Pyrimidines; Hydrogenated pyrimidines, e.g. trimethoprim not condensed and containing further heterocyclic rings
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/395—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins
- A61K31/495—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having six-membered rings with two or more nitrogen atoms as the only ring heteroatoms, e.g. piperazine or tetrazines
- A61K31/505—Pyrimidines; Hydrogenated pyrimidines, e.g. trimethoprim
- A61K31/513—Pyrimidines; Hydrogenated pyrimidines, e.g. trimethoprim having oxo groups directly attached to the heterocyclic ring, e.g. cytosine
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P9/00—Drugs for disorders of the cardiovascular system
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P9/00—Drugs for disorders of the cardiovascular system
- A61P9/04—Inotropic agents, i.e. stimulants of cardiac contraction; Drugs for heart failure
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P9/00—Drugs for disorders of the cardiovascular system
- A61P9/10—Drugs for disorders of the cardiovascular system for treating ischaemic or atherosclerotic diseases, e.g. antianginal drugs, coronary vasodilators, drugs for myocardial infarction, retinopathy, cerebrovascula insufficiency, renal arteriosclerosis
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D239/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-diazine or hydrogenated 1,3-diazine rings
- C07D239/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-diazine or hydrogenated 1,3-diazine rings not condensed with other rings
- C07D239/24—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-diazine or hydrogenated 1,3-diazine rings not condensed with other rings having three or more double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D239/28—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-diazine or hydrogenated 1,3-diazine rings not condensed with other rings having three or more double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members with hetero atoms or with carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most one bond to halogen, directly attached to ring carbon atoms
- C07D239/46—Two or more oxygen, sulphur or nitrogen atoms
- C07D239/52—Two oxygen atoms
- C07D239/54—Two oxygen atoms as doubly bound oxygen atoms or as unsubstituted hydroxy radicals
- C07D239/545—Two oxygen atoms as doubly bound oxygen atoms or as unsubstituted hydroxy radicals with other hetero atoms or with carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most one bond to halogen, directly attached to ring carbon atoms
- C07D239/553—Two oxygen atoms as doubly bound oxygen atoms or as unsubstituted hydroxy radicals with other hetero atoms or with carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most one bond to halogen, directly attached to ring carbon atoms with halogen atoms or nitro radicals directly attached to ring carbon atoms, e.g. fluorouracil
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D401/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with only one nitrogen atom
- C07D401/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with only one nitrogen atom containing two hetero rings
- C07D401/04—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with only one nitrogen atom containing two hetero rings directly linked by a ring-member-to-ring-member bond
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D401/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with only one nitrogen atom
- C07D401/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with only one nitrogen atom containing two hetero rings
- C07D401/12—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with only one nitrogen atom containing two hetero rings linked by a chain containing hetero atoms as chain links
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D403/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, not provided for by group C07D401/00
- C07D403/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, not provided for by group C07D401/00 containing two hetero rings
- C07D403/04—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, not provided for by group C07D401/00 containing two hetero rings directly linked by a ring-member-to-ring-member bond
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D403/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, not provided for by group C07D401/00
- C07D403/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, not provided for by group C07D401/00 containing two hetero rings
- C07D403/12—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, not provided for by group C07D401/00 containing two hetero rings linked by a chain containing hetero atoms as chain links
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D405/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing both one or more hetero rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, and one or more rings having nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom
- C07D405/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing both one or more hetero rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, and one or more rings having nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom containing two hetero rings
- C07D405/04—Heterocyclic compounds containing both one or more hetero rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, and one or more rings having nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom containing two hetero rings directly linked by a ring-member-to-ring-member bond
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D405/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing both one or more hetero rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, and one or more rings having nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom
- C07D405/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing both one or more hetero rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, and one or more rings having nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom containing two hetero rings
- C07D405/12—Heterocyclic compounds containing both one or more hetero rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, and one or more rings having nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom containing two hetero rings linked by a chain containing hetero atoms as chain links
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D413/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having nitrogen and oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms
- C07D413/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having nitrogen and oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms containing two hetero rings
- C07D413/04—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having nitrogen and oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms containing two hetero rings directly linked by a ring-member-to-ring-member bond
Definitions
- the invention belongs to the technical field of medicines, and specifically relates to a compound and a pharmaceutical composition for treating hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and related heart disease, as well as methods and uses thereof.
- the present invention is a deuterium-containing benzylaminopyrimidinedione derivative that can be used as a myosin inhibitor.
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is a hereditary cardiomyopathy characterized by ventricular hypertrophy, ventricular cavity reduction, and decreased left ventricular diastolic compliance.
- the thickness of the ventricular septum or left ventricular wall measured by two-dimensional echocardiography is ⁇ 15mm, or the thickness of those with a clear family history is ⁇ 13mm, usually not accompanied by enlargement of the left ventricular cavity.
- Increased load such as hypertension and aortic stenosis should be excluded
- congenital aortic subvalvular septum caused by left ventricular wall thickening Most of them are asymptomatic.
- the main clinical manifestations are dyspnea and angina-like attacks. Obstructive patients have dizziness, near syncope, and have a tendency to sudden death.
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is dominated by myocardial hypertrophy, and heart weight increases. Cardiomyocytes are extremely hypertrophy, disorderly arrangement, nucleus malformation, muscle bundle structure destruction and spiral; with the development of the disease, the components of myocardial fibrosis gradually increase, and the coronary artery wall may become thicker and the lumen may become smaller.
- hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is mainly to use ⁇ -blockers (propranolol, metoprolol), calcium channel blockers (verapamil, diltiazem) ), IA antiarrhythmic drugs (disopyramide), etc. None of the above drugs are labeled for the treatment of HCM, and there is basically no rigorous clinical trial evidence to guide clinical use. There is no marketed drug for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
- Myosin is a superfamily of motor proteins. It is a long asymmetric molecule with a shape like "Y" and a length of about 160nm. Myosin is a highly asymmetric hexamer composed of two heavy chains (Myosin heavy chain, MHC), two essential light chains (ELC) and two regulatory light chains (RLC). Body is the main component of thick filaments. Myosin is not only an important structural protein and contractile protein of the heart muscle, but also has adenosine triphosphate (ATPase) activity, so it is usually called myosin ATPase. The direct energy source for muscle contraction is the hydrolysis of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) by myosin.
- ATP adenosine triphosphate
- Cardiac myosin has become a new strategy for the treatment of heart failure and cardiomyopathy. Cardiac myosin is the most downstream target that regulates myocardial contraction. Drugs acting on this target do not affect the intracellular calcium ion concentration, and can effectively increase or decrease myocardial contractility and avoid adverse reactions such as arrhythmia. Inhibitors targeting cardiac myosin will be an important new method for the treatment of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Most research data consistently show that mutations in cardiac myosin can lead to an increase in cardiac sarcomere contractile activity.
- small molecule inhibitors of sarcomere can improve the disease from its source and may eliminate the characteristics of HCM, such as hypertrophy, cell disorder, and cardiac fibrosis.
- the purpose of the present invention is to provide novel compounds as myosin inhibitors, thereby addressing the long-term demand for improved treatment of HCM and related heart diseases.
- the present invention relates to a new type of deuterium-containing benzalkonium pyrimidinedione derivatives, which can effectively inhibit the activity of myosin, so that they can be used to prepare medicines for the treatment of heart failure and cardiomyopathy, especially for the preparation of treatments for hypertrophy Types of cardiomyopathy and related heart disease drugs.
- the compound of the present invention has stable properties, good safety, pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetic advantages, such as good bioavailability or good metabolic stability, etc., so it has a good clinical application prospect.
- the present invention also provides methods for preparing such compounds and pharmaceutical compositions containing such compounds.
- the present invention relates to a compound, which is a compound represented by formula (I) or a stereoisomer, geometric isomer, tautomer, nitrogen oxide, hydrated compound represented by formula (I) Substance, solvate, metabolite, pharmaceutically acceptable salt or its prodrug,
- R 1 , R 2 , R 3 , R 4 , R 5 , R 6 and R 7 have the meanings as described in the present invention.
- R 1 is a C 1-6 alkyl group, a C 3-8 cycloalkyl group, a 3-8 atom heterocyclic group, a C 6-10 aryl group, or a 5-10 atom heterocyclic group.
- Aryl wherein the C 1-6 alkyl group, C 3-8 cycloalkyl group, heterocyclic group composed of 3-8 atoms, C 6-10 aryl group and heteroaryl group composed of 5-10 atoms
- Each is independently unsubstituted or substituted with 1, 2, 3 or 4 R x ; wherein R x has the meaning as described in the present invention.
- R 2 is a C 1-6 alkyl group, a C 3-8 cycloalkyl group, a 3-8 atom heterocyclic group, a C 6-10 aryl group, or a 5-10 atom heterocyclic group.
- Aryl wherein the C 1-6 alkyl group, C 3-8 cycloalkyl group, heterocyclic group composed of 3-8 atoms, C 6-10 aryl group and heteroaryl group composed of 5-10 atoms
- Each is independently unsubstituted or substituted with 1, 2, 3 or 4 R y ; wherein R y has the meaning as described in the present invention.
- R 7 is H, D, F, Cl, Br, I, C 1-6 alkyl, or C 1-6 haloalkyl.
- each R a and R b is independently H, C 1-6 alkyl, or C 1-6 haloalkyl.
- each R 0 is independently a C 3-8 cycloalkyl group, a 3-8 atom heterocyclic group, a C 6-10 aryl group, or a 5-10 atom heteroaryl group.
- each R c , R e , R f , R h , R i and R j is independently H, D, C 1-6 alkyl, C 1-6 haloalkyl, C 3-8 ring Alkyl group, heterocyclic group composed of 3-8 atoms, C 6-10 aryl group or heteroaryl group composed of 5-10 atoms; or, R e , R f and the nitrogen atom to which they are connected together form a 3- 8-atom heterocyclic group or 5-10 atom heteroaryl group.
- each R d and R g is independently H, OH, NH 2 , C 1-6 alkyl, C 1-6 haloalkyl, C 1-6 alkylamino, C 1-6 alkoxy , C 3-8 cycloalkyl, 3-8 heterocyclic group, C 6-10 aryl or 5-10 heteroaryl.
- each n is independently 1, 2, 3, or 4.
- the compound of the present invention is a compound represented by formula (II) or a stereoisomer, geometric isomer, tautomer, nitrogen oxide, Hydrate, solvate, metabolite, pharmaceutically acceptable salt or its prodrug,
- R 1 , R 2 , R 3 , R 4 , R 5 , R 6 and R 7 have the meanings as described in the present invention.
- R 1 is C 1-4 alkyl, C 3-6 cycloalkyl, 3-6 heterocyclic group, phenyl, or 5-6 heteroaryl;
- the C 1-4 alkyl group, C 3-6 cycloalkyl group, heterocyclic group composed of 3-6 atoms, phenyl group and heteroaryl group composed of 5-6 atoms are each independently unsubstituted or Substituted by 1, 2, 3 or 4 R x ; wherein R x has the meaning as described in the present invention.
- R 7 is H, D, F, Cl, Br, I, C 1-4 alkyl or C 1-4 haloalkyl.
- R 2 is C 1-4 alkyl, C 3-6 cycloalkyl, 3-6 heterocyclic group, phenyl, or 5-6 heteroaryl; Wherein, the C 1-4 alkyl group, C 3-6 cycloalkyl group, heterocyclic group composed of 3-6 atoms, phenyl group and heteroaryl group composed of 5-6 atoms are each independently unsubstituted or It is substituted by 1, 2, 3 or 4 R y ; wherein, R y has the meaning as described in the present invention.
- R 1 is methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl, n-butyl, tert-butyl, cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl, cyclohexyl, ethylene oxide Group, azetidinyl, oxetanyl, tetrahydrofuranyl, tetrahydrothienyl, tetrahydropyranyl, pyrrolidinyl, pyrazolidinyl, imidazolidinyl, piperidinyl, morpholinyl, piper Azinyl, phenyl, pyrrolyl, pyrazolyl, thienyl, thiazolyl, furyl, imidazolyl, oxazolyl, triazolyl, tetrazolyl, isoxazolyl, pyridyl, pyrimidinyl, pyrazine
- R 7 is H, D, F, Cl, Br, methyl, ethyl, or propyl.
- R 2 is methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl, n-butyl, 1-methylpropyl, tert-butyl, cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl , Cyclohexyl, oxirane, azetidinyl, oxetanyl, tetrahydrofuranyl, tetrahydrothienyl, tetrahydropyranyl, pyrrolidinyl, pyrazolidinyl, imidazolidinyl, piperidine Group, morpholinyl, piperazinyl, phenyl, pyrrolyl, pyrazolyl, thienyl, thiazolyl, furyl, imidazolyl, oxazolyl, triazolyl, tetrazolyl, isoxazolyl, pyridine Group, pyrimidinyl, pyra
- R a and R b are each independently H, C 1-4 alkyl or C 1-4 haloalkyl.
- each R 0 is independently a C 3-6 cycloalkyl group, a 3-6 atom heterocyclic group, a phenyl group, or a 5-6 atom heteroaryl group.
- each of R c , R e , R f , R h , R i and R j is independently H, D, C 1-4 alkyl, C 1-4 haloalkyl, C 3 -6 cycloalkyl, 3-6 heterocyclic group, phenyl or 5-6 heteroaryl; or, R e , R f and the nitrogen atom to which they are connected together form 3-6 A heterocyclic group consisting of three atoms or a heteroaryl group consisting of 5-6 atoms.
- each R d and R g are independently H, OH, NH 2 , C 1-4 alkyl, C 1-4 haloalkyl, C 1-4 alkylamino, C 1-4 Alkoxy group, C 3-6 cycloalkyl group, heterocyclic group composed of 3-6 atoms, phenyl group or heteroaryl group composed of 5-6 atoms.
- each of R x , R y and R z is independently D, F, Cl, Br, I, CN, NO 2 , OH, NH 2 , -SH, methyl, ethyl, N-propyl, isopropyl, n-butyl, tert-butyl, trifluoromethyl, difluoromethyl, methylamino, dimethylamino, cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl, cyclohexyl, epoxy Ethyl, azetidinyl, oxetanyl, tetrahydrofuranyl, tetrahydrothienyl, tetrahydropyranyl, pyrrolidinyl, pyrazolidinyl, imidazolidinyl, piperidinyl, morpholinyl, Piperazinyl, phenyl, pyrrolyl, pyrazolyl,
- R a and R b are each independently H, methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl, n-butyl, tert-butyl or trifluoromethyl.
- each R 0 is independently cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl, cyclohexyl, epoxyethyl, azetidinyl, oxetanyl, tetrahydrofuranyl, Tetrahydrothienyl, tetrahydropyranyl, pyrrolidinyl, pyrazolidinyl, imidazolidinyl, piperidinyl, morpholinyl, piperazinyl, phenyl, pyrrolyl, pyrazolyl, thienyl, thiazole Group, furyl, imidazolyl, oxazolyl, triazolyl, tetrazolyl, isoxazolyl, pyridyl, pyrimidinyl, pyrazinyl or pyridazinyl.
- each of R c, R e, R f , R h, R i and R j are independently H, D, methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl, n-butyl Base, tert-butyl, trifluoromethyl, difluoromethyl, cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl, cyclohexyl, epoxyethyl, azetidinyl, oxetanyl, tetrahydrofuranyl , Tetrahydrothienyl, tetrahydropyranyl, pyrrolidinyl, pyrazolidinyl, imidazolidinyl, piperidinyl, morpholinyl, piperazinyl, phenyl, pyrrolyl, pyrazolyl, thienyl, Thiazolyl, furanyl, imidazolyl, ox
- each R d and R g are independently H, OH, NH 2 , methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl, n-butyl, tert-butyl, trifluoromethyl Group, difluoromethyl, methylamino, dimethylamino, methoxy, ethoxy, cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl, cyclohexyl, epoxyethyl, azetidinyl, oxa Cyclobutyl, tetrahydrofuranyl, tetrahydrothienyl, tetrahydropyranyl, pyrrolidinyl, pyrazolidinyl, imidazolidinyl, piperidinyl, morpholinyl, piperazinyl, phenyl, pyrrolyl, pyrrolidinyl Azolyl, thienyl,
- the compound of the present invention is a compound having one of the following structures or a stereoisomer, geometric isomer, tautomer, nitroxide of a compound having one of the following structures Substance, hydrate, solvate, metabolite, pharmaceutically acceptable salt or its prodrug:
- the present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition
- a pharmaceutical composition comprising the compound disclosed in the present invention.
- the pharmaceutical composition of the present invention further comprises a pharmaceutically acceptable excipient, carrier, adjuvant or any combination thereof.
- the present invention relates to the use of the compound or pharmaceutical composition disclosed in the present invention in the preparation of a medicament for the prevention, treatment or alleviation of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy or the heart with pathophysiological characteristics related to hypertrophic cardiomyopathy disease.
- the present invention relates to the use of the compound or pharmaceutical composition disclosed in the present invention in the preparation of a medicine for preventing, treating or reducing diastolic heart failure, ischemic heart disease, and angina pectoris with preserved ejection fraction Or restrictive cardiomyopathy.
- the present invention relates to the use of the compound or pharmaceutical composition disclosed in the present invention in the preparation of a medicament for inhibiting myosin.
- the present invention relates to methods for the preparation, separation and purification of compounds represented by formula (I) or formula (II).
- any embodiment of any aspect of the present invention can be combined with other embodiments as long as they do not appear contradictory.
- any technical feature can be applied to the technical feature in other embodiments, as long as they do not conflict.
- the articles “a”, “an” and “said” used in the present invention are intended to include “at least one” or “one or more”. Therefore, these articles used in the present invention refer to articles of one or more than one (ie, at least one) object.
- a component refers to one or more components, that is, there may be more than one component considered to be adopted or used in the embodiment of the described embodiment.
- patient used in the present invention refers to humans (including adults and children) or other animals. In some embodiments, “patient” refers to a human.
- stereoisomers refers to compounds that have the same chemical structure, but differ in the arrangement of the atoms or groups in space. Stereoisomers include enantiomers, diastereomers, conformational isomers (rottamers), geometric (cis/trans) isomers, atropisomers, and the like.
- tautomer or "tautomeric form” refers to structural isomers with different energies that can be converted into each other through a low energy barrier. If tautomerism is possible (as in solution), the chemical equilibrium of tautomers can be reached.
- proton tautomers also called prototropic tautomers
- proton migration such as keto-enol isomerization and imine-ene Amine isomerization.
- “Pharmaceutically acceptable” refers to such compounds, raw materials, compositions and/or dosage forms, which are within the scope of reasonable medical judgment and are suitable for contact with patient tissues without excessive toxicity, irritation, allergic reactions or reasonable The benefit/risk ratio is commensurate with other problems and complications, and is effectively used for the intended purpose.
- substituted means that one or more hydrogen atoms in a given structure are replaced by a specific substituent. Unless otherwise indicated, an optional substituent group can be substituted at each substitutable position of the group.
- optional substituent group can be substituted at each substitutable position of the group.
- optional substituent group can be used interchangeably with the term “unsubstituted or replaced by", that is, the structure is unsubstituted or substituted by one or more of the present invention Group substitution, wherein the “plurality” refers to 1, 2, 3, 4 or more, but not exceeding the number of positions where the structure may be substituted.
- the multiple substituents may be the same or different substituent groups.
- C 1 -C 6 alkyl refers particularly to the disclosure independently methyl, ethyl, C 3 alkyl, C 4 alkyl, C 5 alkyl, and C 6 alkyl.
- linking substituents are described.
- the Markush variables listed for the group should be understood as the linking group.
- the Markush group definition of the variable lists “alkyl” or “aryl” it should be understood that the “alkyl” or “aryl” respectively represents the attached Alkylene group or arylene group.
- halogen and “halo” are used interchangeably in the present invention and refer to fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), or iodine (I).
- alkyl or “alkyl group” used in the present invention means a saturated linear or branched monovalent hydrocarbon group containing 1-20 carbon atoms, wherein the alkyl group may optionally Ground is substituted with one or more substituents described in this invention.
- the alkyl group contains 1-6 carbon atoms; in other embodiments, the alkyl group contains 1-4 carbon atoms; in some embodiments, the alkyl group contains 1 -3 carbon atoms.
- alkyl groups include, but are not limited to, methyl (Me, -CH 3 ), ethyl (Et, -CH 2 CH 3 ), n-propyl (n-Pr, -CH 2 CH 2 CH 3 ), isopropyl (i-Pr, -CH(CH 3 ) 2 ), n-butyl (n-Bu, -CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 3 ), isobutyl (i-Bu, -CH 2 CH (CH 3 ) 2 ), sec-butyl (s-Bu, -CH(CH 3 )CH 2 CH 3 ), tert-butyl (t-Bu, -C(CH 3 ) 3 ), etc.
- alkoxy means that the alkyl group is connected to the rest of the molecule through an oxygen atom, wherein the alkyl group has the meaning as described in the present invention. Unless otherwise specified, the alkoxy group contains 1-12 carbon atoms. In some embodiments, the alkoxy group contains 1-6 carbon atoms; in other embodiments, the alkoxy group contains 1-4 carbon atoms; in still other embodiments, the alkoxy group The group contains 1-3 carbon atoms. The alkoxy group may be optionally substituted with one or more substituents described in this invention.
- alkoxy groups include, but are not limited to, methoxy (MeO, -OCH 3 ), ethoxy (EtO, -OCH 2 CH 3 ), 1-propoxy (n-PrO, n- Propoxy, -OCH 2 CH 2 CH 3 ), 2-propoxy (i-PrO, i-propoxy, -OCH(CH 3 ) 2 ), 1-butoxy (n-BuO, n- Butoxy, -OCH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 3 ), 2-methyl-l-propoxy (i-BuO, i-butoxy, -OCH 2 CH(CH 3 ) 2 ), 2-but Oxygen (s-BuO, s-butoxy, -OCH(CH 3 )CH 2 CH 3 ), 2-methyl-2-propoxy (t-BuO, t-butoxy, -OC(CH 3 ) 3 ), etc.
- alkylamino or “alkylamino” includes “N-alkylamino” and “N,N-dialkylamino” refers to an amino group independently substituted with one or two alkyl groups, respectively , Wherein the alkyl group has the meaning as described in the present invention.
- Suitable alkylamino groups can be monoalkylamino or dialkylamino. Examples of such include, but are not limited to, N-methylamino, N-ethylamino, N,N-dimethylamino, N,N -Diethylamino and so on.
- the alkylamino group is optionally substituted with one or more substituents described in this invention.
- haloalkyl or haloalkoxy means that an alkyl or alkoxy group is substituted by one or more halogen atoms, wherein the alkyl and alkoxy groups have the meanings as described in the present invention, such Examples include, but are not limited to, trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, and the like.
- the C 1 -C 6 haloalkyl group comprises a fluorine-substituted C 1 -C 6 alkyl group; in other embodiments, the C 1 -C 4 haloalkyl group comprises a fluorine-substituted C 1 -C 4 alkyl group ; In still other embodiments, the C 1 -C 2 haloalkyl group comprises a fluorine-substituted C 1 -C 2 alkyl group.
- cycloalkyl refers to a monovalent or multivalent non-aromatic saturated monocyclic, bicyclic or tricyclic ring system containing 3-12 carbon atoms.
- the cycloalkyl group contains 3-12 carbon atoms; in other embodiments, the cycloalkyl group contains 3-8 carbon atoms; in still other embodiments, the cycloalkyl group contains 3-6 carbon atoms. carbon atom.
- Examples of cycloalkyl groups include, but are not limited to, cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl, cyclohexyl, and the like.
- the cycloalkyl group is optionally substituted with one or more substituents described in this invention.
- heterocycle refers to a monovalent or multivalent monocyclic, bicyclic or tricyclic ring system containing 3-14 ring atoms, wherein One or more atoms in the ring are independently replaced by heteroatoms, and the heteroatoms have the meaning as described in the present invention.
- the ring may be fully saturated or contain one or more degrees of unsaturation, but an aromatic ring is not allowed.
- a “heterocyclic”, “heterocyclyl” or “heterocyclic” group is a 3-8 membered monocyclic ring consisting of 3-8 atoms (2-7 carbon atoms and selected from 1-3 heteroatoms of N, O, P, S, where S or P is optionally substituted by one or more oxygen atoms to obtain groups like SO, SO 2 , PO, PO 2 ), or 7 -12-membered bicyclic ring (4-9 carbon atoms and 1-3 heteroatoms selected from N, O, P, S, where S or P is optionally substituted by one or more oxygen atoms to form SO , SO 2 , PO, PO 2 groups).
- the heterocyclyl group is optionally substituted with one or more substituents described in the present invention.
- the nitrogen atom of the ring can be optionally oxidized to an N-oxygen compound.
- heterocyclic groups include, but are not limited to, oxiranyl, azetidinyl, oxetanyl, thietanyl, pyrrolidinyl, 2-pyrrolinyl, 3-pyrrolinyl , Pyrazolinyl, pyrazolidinyl, imidazolinyl, imidazolidinyl, tetrahydrofuranyl, dihydrofuranyl, tetrahydrothienyl, dihydrothienyl, 1,3-dioxanyl, disulfide ring Pentyl, tetrahydropyranyl, dihydropyranyl, tetrahydrothiopyranyl, piperidinyl, morpholinyl, thiomorpholinyl, piperazinyl, dioxanyl, dithianyl, thio Oxalanyl, homopiperazinyl, homopiperidinyl, oxepanyl, etc.
- Examples in which the sulfur atom in the heterocyclic group is oxidized include, but are not limited to, sulfolane, thiomorpholinyl 1,1-dioxide, and the like.
- the heterocyclyl group is optionally substituted with one or more substituents described in the present invention.
- aryl means a monocyclic, bicyclic and tricyclic carbocyclic ring system containing 6-14 ring atoms, or 6-12 ring atoms, or 6-10 ring atoms, wherein at least one ring system is aromatic Family, where each ring system contains a ring composed of 3-7 atoms, and there are one or more attachment points connected to the rest of the molecule.
- aryl can be used interchangeably with the term “aromatic ring”. Examples of aryl groups may include phenyl, naphthyl, and anthracenyl. The aryl group is optionally substituted with one or more substituents described in the present invention.
- heteroaryl or “heteroaromatic ring” means a monovalent or multivalent monocyclic, bicyclic or tricyclic ring containing 5-14 ring atoms, or 5-10 ring atoms, or 5-6 ring atoms A system in which at least one ring is aromatic and at least one ring contains one or more heteroatoms.
- the heteroaryl group is usually, but not necessarily, connected to the parent molecule through the aromatic ring of the heteroaryl group.
- heteroaryl can be used interchangeably with the terms “heteroaromatic ring” or “heteroaromatic compound”.
- the heteroaryl group is optionally substituted with one or more substituents described in the present invention.
- the 5-10 atom heteroaryl group contains 1, 2, 3, or 4 heteroatoms independently selected from O, S, and N; in other embodiments, 5-6 atoms
- the heteroaryl group of is a single ring system and contains 1, 2, 3 or 4 heteroatoms independently selected from O, S and N.
- heteroaryl groups include, but are not limited to, pyrrolyl, pyrazolyl, thienyl, thiazolyl, furyl, imidazolyl, oxazolyl, triazolyl, tetrazolyl, isoxazolyl, Pyridyl, pyrimidinyl, pyrazinyl or pyridazinyl; also includes the following bicyclic rings, but not limited to these bicyclic rings: benzimidazolyl, benzofuranyl, benzothienyl, indolyl, quinolinyl, Isoquinolinyl, etc.
- j-atoms typically describes the number of atoms forming a ring in a molecule, and the number of atoms forming a ring in the molecule is j.
- piperidinyl is a 6-atom heterocyclic ring or 6-membered heterocyclic ring
- cyclohexyl is a 6-atom cycloalkyl or 6-membered cycloalkyl group.
- unsaturated means that the group contains one or more degrees of unsaturation.
- heteroatom refers to O, S, N, P and Si, including any oxidation state of N, S, and P; primary, secondary, tertiary amine and quaternary ammonium salt forms; or on the nitrogen atom in the heterocycle
- the form in which hydrogen is substituted for example, N (like N in 3,4-dihydro-2H-pyrrolyl), NH (like NH in pyrrolidinyl), or NR (like N-substituted pyrrolidinyl) NR and R are the substituents described in the present invention).
- prodrug represents the conversion of a compound into a compound represented by formula (I) or formula (II) in vivo. Such conversion is affected by the hydrolysis of the prodrug in the blood or the enzymatic conversion of the prodrug into the maternal structure in the blood or tissue.
- the prodrug compounds of the present invention can be esters.
- esters can be used as prodrugs include phenyl esters, aliphatic (C 1-24 ) esters, acyloxymethyl esters, and carbonates. , Carbamates and amino acid esters.
- a compound in the present invention contains a hydroxyl group, which can be acylated to obtain a compound in the form of a prodrug.
- Other prodrug forms include phosphate esters. For example, these phosphate ester compounds are obtained by phosphorylation of the parent hydroxyl group.
- Metal refers to the product obtained by the metabolism of a specific compound or its salt in the body.
- the metabolites of a compound can be identified by techniques well known in the art, and its activity can be characterized by experimental methods as described in the present invention. Such products can be obtained by oxidizing, reducing, hydrolyzing, amidating, deamidating, esterifying, degreasing, enzymatic cleavage, etc. of the administered compound.
- the present invention includes the metabolites of the compound, including the metabolites produced by fully contacting the compound of the present invention with a mammal for a period of time.
- “Pharmaceutically acceptable salt” used in the present invention refers to the organic and inorganic salts of the compound of the present invention.
- Pharmaceutically acceptable salts are well known to us in the field, as described in the literature: SMBerge et al., describe pharmaceutically acceptable salts in detail in J. Pharmaceutical Sciences, 1977, 66:1-19.
- Pharmaceutically acceptable non-toxic acid salts include, but are not limited to, inorganic acid salts formed by reaction with amino groups include hydrochloride, hydrobromide, phosphate, sulfate, perchlorate, And organic acid salts such as acetate, oxalate, maleate, tartrate, citrate, succinate, malonate, or other methods described in books and literature such as ion exchange These salts.
- the present invention also contemplates the quaternary ammonium salt formed by any compound containing the N group.
- Water-soluble or oil-soluble or dispersed products can be obtained by quaternization.
- Pharmaceutically acceptable salts further include appropriate, non-toxic ammonium, quaternary ammonium salts, and amine cations that resist counterion formation, such as halides, hydroxides, carboxylates, sulfates, phosphates, nitrates, and C 1 -C 8 sulfonate and aromatic sulfonate.
- solvate of the present invention refers to an association formed by one or more solvent molecules and the compound of the present invention.
- Solvents that form solvates include, but are not limited to, water, isopropanol, ethanol, methanol, dimethyl sulfoxide, ethyl acetate, acetic acid, ethanolamine or mixtures thereof.
- hydrate refers to the association formed by the solvent molecule being water.
- treating any disease or condition as used in the present invention, in some embodiments refers to ameliorating the disease or condition (ie slowing down or preventing or reducing the development of the disease or at least one of its clinical symptoms). In other embodiments, “treatment” refers to alleviating or improving at least one physical parameter, including physical parameters that may not be perceived by the patient. In other embodiments, “treatment” refers to the regulation of the disease or condition physically (for example, stabilizing the perceptible symptoms) or physiologically (for example, stabilizing the parameters of the body) or both. In other embodiments, “treating” refers to preventing or delaying the onset, occurrence, or worsening of a disease or condition.
- terapéuticaally effective amount means that when administered to a subject to treat a disease, the amount of the compound is sufficient for the treatment of the disease.
- the “therapeutically effective amount” can vary with the compound, the disease and severity, and the condition, age, weight, gender, etc. of the subject to be treated.
- the compounds of the present invention, their pharmaceutically acceptable salts, pharmaceutical preparations and their compositions can be used as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, and have potential for the treatment of human central nervous system dysfunction, especially affective disorders
- the affective disorder includes, but is not limited to, depression, anxiety, social phobia, obsessive-compulsive disorder, panic attack, specific phobia, agoraphobia, mania, panic disorder and post-traumatic stress disorder.
- the compounds of the present invention may exist in the form of salts.
- the salt refers to a pharmaceutically acceptable salt.
- pharmaceutically acceptable means that the substance or composition must be chemically and/or toxicologically compatible with the other ingredients comprising the formulation and/or the mammal to be treated with it.
- the salt is not necessarily a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, and may be an intermediate for preparing and/or purifying the compound of the present invention and/or for separating the enantiomers of the compound of the present invention.
- any structural formula given in the present invention is also intended to represent the non-isotopically enriched forms and isotopically enriched forms of these compounds.
- the isotope-enriched compound has the structure described by the general formula given in the present invention, except that one or more atoms are replaced by atoms having the selected atomic weight or mass number.
- Exemplary isotopes that can be introduced into the compounds of the present invention include isotopes of hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, sulfur, fluorine, and chlorine, such as 2 H, 3 H, 11 C, 13 C, 14 C, 15 N, 17 O , 18 O, 18 F, 31 P, 32 P, 35 S, 36 Cl and 125 I.
- the present invention relates to intermediates for preparing compounds represented by formula (I) or formula (II).
- the present invention provides a pharmaceutical composition
- a pharmaceutical composition comprising a compound represented by formula (I) or formula (II) or its individual stereoisomers, racemic or non-racemic mixtures of isomers or pharmaceutically acceptable The salt or solvate.
- the pharmaceutical composition further comprises at least one pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, adjuvant or excipient, and optionally, other therapeutic and/or preventive components.
- Suitable carriers, adjuvants and excipients are well-known to those skilled in the art and are described in detail in, for example, Ansel HCet al., Ansel's Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms and Drug Delivery Systems (2004) Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia; Gennaro ARet al. ., Remington: The Science and Practice of Pharmacy (2000) Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia; and Rowe RC, Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients (2005) Pharmaceutical Press, Chicago.
- compositions of the present invention may exist in free form or, if appropriate, in the form of pharmaceutically acceptable derivatives thereof.
- pharmaceutically acceptable derivatives include pharmaceutically acceptable prodrugs, salts, esters, and salts of these esters, or can directly or indirectly provide the present invention when administered to patients in need Any additional adducts or derivatives of the compound or its metabolites or residues.
- Suitable pharmaceutically acceptable excipients will vary depending on the specific dosage form selected.
- pharmaceutically acceptable excipients can be selected according to their specific functions in the composition.
- Suitable pharmaceutically acceptable excipients include the following types of excipients: diluents, fillers, binders, disintegrants, lubricants, glidants, granulating agents, coating agents, wetting agents , Solvents, co-solvents, suspending agents, emulsifiers, sweeteners, flavoring agents, taste masking agents, coloring agents, anti-caking agents, humectants, chelating agents, plasticizers, tackifiers, antioxidants, Preservatives, stabilizers, surfactants and buffers.
- certain pharmaceutically acceptable excipients can provide more than one function and provide alternative functions, depending on how many of these excipients are present in the formulation and what other excipients are present in the formulation Agent.
- composition disclosed in the present invention is prepared using techniques and methods known to those skilled in the art. For descriptions of some commonly used methods in this field, please refer to Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences (Mack Publishing Company).
- the present invention relates to a process for preparing a pharmaceutical composition, the pharmaceutical composition comprising a compound disclosed in the present invention and a pharmaceutically acceptable excipient, carrier, adjuvant, vehicle or a combination thereof, the process comprising Mix various ingredients.
- the pharmaceutical composition containing the compound disclosed in the present invention can be prepared by mixing at, for example, ambient temperature and atmospheric pressure.
- dosage forms include those suitable for the following routes of administration: (1) Oral administration, such as tablets, capsules, caplets, pills, lozenges, powders, syrups, elixirs, suspensions, Solutions, emulsions, sachets and cachets; (2) Parenteral administration, such as sterile solutions, suspensions and reconstituted powders; (3) Transdermal administration, such as transdermal patches ; (4) rectal administration, such as suppositories; (5) inhalation, such as aerosols, solutions and dry powders; and (6) topical administration, such as creams, ointments, lotions, solutions, pastes , Sprays, foams and gels.
- Oral administration such as tablets, capsules, caplets, pills, lozenges, powders, syrups, elixirs, suspensions, Solutions, emulsions, sachets and cachets
- Parenteral administration such as sterile solutions, suspensions and reconstituted powders
- Transdermal administration such
- the compounds disclosed herein can be formulated into oral dosage forms. In other embodiments, the compounds disclosed in the present invention can be formulated into inhaled dosage forms. In other embodiments, the compounds disclosed in the present invention can be formulated for nasal administration. In still other embodiments, the compounds disclosed in the present invention can be formulated for transdermal administration. In still some embodiments, the compounds disclosed in the present invention can be formulated for topical administration.
- the pharmaceutical composition provided by the present invention can be provided as compressed tablets, developed tablets, chewable lozenges, instant tablets, multiple compressed tablets, or enteric-coated tablets, sugar-coated or film-coated tablets.
- the pharmaceutical composition provided by the present invention can be provided in a soft capsule or a hard capsule, which can be prepared from gelatin, methylcellulose, starch or calcium alginate.
- the pharmaceutical composition provided by the present invention can be administered parenterally by injection, infusion or implantation for local or systemic administration.
- Parenteral administration as used in the present invention includes intravenous, intraarterial, intraperitoneal, intrathecal, intraventricular, intraurethral, intrasternal, intracranial, intramuscular, intrasynovial and subcutaneous administration.
- the pharmaceutical composition provided by the present invention can be formulated into any dosage form suitable for parenteral administration, including solutions, suspensions, emulsions, micelles, liposomes, microspheres, nanosystems, and suitable for being in liquid before injection. Make a solid form of a solution or suspension.
- dosage forms can be prepared according to conventional methods known to those skilled in the field of pharmaceutical science (see Remington: The Science and Practice of Pharmacy, ibid.).
- the compound of the present invention or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof can be administered in the following ways: oral, parenteral (for example, intramuscular, intraperitoneal, intravenous, ICV, Intracistern injection or infusion, subcutaneous injection or implantation), implantation (for example, when the compound or pharmaceutical salt is connected to the stent device), inhalation spray, nasal, vaginal, rectal, sublingual or topical administration , And can be formulated separately or together in an appropriate dosage unit formulation containing conventional non-toxic pharmaceutical carriers, excipients and vehicles suitable for each route of administration.
- an appropriate dosage level will usually be about 0.001 to 100 mg/kg patient body weight/day, which can be administered in a single dose or in multiple doses.
- the dosage level will be about 0.01 to about 25 mg/kg/day; in some embodiments, about 0.05 to about 10 mg/kg/day.
- a suitable dosage level may be about 0.01 to 25 mg/kg/day, about 0.05 to 10 mg/kg/day, or about 0.1 to 5 mg/kg/day. Within this range, the dosage may be 0.005 to 0.05, 0.05 to 0.5, or 0.5 to 5.0 mg/kg/day.
- the composition for oral administration, is provided in the following tablet form: containing 1.0 to 1000 mg of active ingredient, specifically containing 1.0, 5.0, 10.0, 15.0, 20.0, 25.0, 50.0, 75.0, 100.0, 150.0, 200.0, 250.0, 300.0, 400.0, 500.0, 600.0, 750.0, 800.0, 900.0, and 1000.0 mg of active ingredients are used to adjust the treatment given to the patient to be treated for symptoms.
- the compound or pharmaceutically acceptable salt may be administered in a regimen of 1 to 4 times a day, and in some embodiments, may be administered in a regimen of one or two times a day.
- the compound or pharmaceutical composition disclosed in the present invention can be administered simultaneously with, or before or after, one or more other therapeutic agents.
- the compound or pharmaceutical composition of the present invention and other therapeutic agents can be administered separately through the same or different administration routes, or they can be administered in the same pharmaceutical composition form.
- the pharmaceutical compositions provided by the present invention include those pharmaceutical compositions that contain one or more other active ingredients or therapeutic drugs in addition to the compounds or pharmaceutical compositions provided by the present invention.
- Appropriate other active drugs include: drugs that slow the progression of heart failure and try to prevent heart remodeling by down-regulating neurohormonal stimulation of the heart (for example, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers (ARB), blockers , Aldosterone receptor antagonists or neuroendopeptidase inhibitors); drugs that improve cardiac function by stimulating cardiac contractility (for example, inotropic drugs such as adrenergic agonists dobutamine or phosphodiesterase inhibitors) Milrinone); and drugs that reduce cardiac preload (for example, diuretics such as furosemide) or drugs that reduce cardiac afterload (any type of vasodilator, including but not limited to calcium channel blockers, phosphodiester Enzyme inhibitors, endothelin receptor antagonists, renin inhibitors or smooth muscle myosin modulators).
- the weight ratio of the compound provided by the present invention to the second active ingredient is variable and will depend on the effective dose of each ingredient. Generally, an effective dose of each ingredient will be used.
- the compounds provided by the present invention or their pharmaceutically acceptable salts and pharmaceutical compositions can be used to prepare drugs for preventing, treating or alleviating heart diseases in mammals, including humans, and can also be used to prepare drugs for inhibiting myosin. drug.
- the compound of the present invention or the pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof and the amount of the compound in the pharmaceutical composition can effectively and detectably selectively inhibit myosin, especially myocardial myosin.
- the compound of the present invention or its pharmaceutically acceptable salt and pharmaceutical composition can be used as a medicine for the treatment of human heart failure and cardiomyopathy, especially hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and heart diseases with pathophysiological characteristics related to hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
- the compound of the present invention or its pharmaceutically acceptable salt and pharmaceutical composition can be applied to, but is not limited to, the effective amount of the compound of the present invention or its pharmaceutically acceptable salt or the pharmaceutical composition is administered to a patient.
- the compound of the present invention or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof is also used to treat diastolic heart failure, ischemic heart disease, angina pectoris or restrictive cardiomyopathy with preserved ejection fraction.
- the compound of the present invention or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof can also promote beneficial ventricular remodeling of left ventricular hypertrophy caused by volume or pressure overload; such as chronic mitral regurgitation, chronic aortic stenosis, or chronic systemic hypertension
- the compound or its pharmaceutically acceptable salt is intended to correct or reduce the main cause of volume or pressure overload (valve repair/replacement, effective antihypertensive therapy).
- the compound of the present invention or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof can reduce the risk of pulmonary edema and respiratory failure; reducing or eliminating functional mitral regurgitation and/or reducing left atrial pressure can reduce suddenness Or the risk of persistent atrial fibrillation, and it reduces the concomitant risk of arterial thromboembolic complications including but not limited to cerebral artery embolic stroke; reducing or eliminating dynamic and/or static left ventricular outflow tract obstruction can reduce the need for separation The possibility of ablation treatment (surgical or percutaneous) and the concomitant risk of short- and long-term complications.
- the compound of the present invention or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof can reduce the severity of chronic ischemic states associated with HCM, and thereby reduce the need for implantable cardioversion devices-defibrillators (frequent and/or repeated ICDs). Discharge) the risk of sudden cardiac death (SCD) or its equivalent disease and/or reduce the need for potentially toxic antiarrhythmic drugs.
- the compounds of the present invention or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof may be valuable in reducing or eliminating the need for concurrent drugs (with their attendant potential toxicity, drug-drug interactions, and/or side effects).
- the compound of the present invention or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof can reduce interstitial myocardial fibrosis and/or slow the progression of left ventricular hypertrophy, prevent or reverse left ventricular hypertrophy.
- the compound and pharmaceutical composition of the present invention can also be applied to veterinary treatment of pets, introduced species of animals, and mammals in farm animals. Other examples of animals include horses, dogs, and cats.
- the compound of the present invention includes its pharmaceutically acceptable derivatives.
- the compounds of the present invention can be prepared by the methods described in the present invention, unless otherwise specified, wherein the definition of substituents is as shown in formula (I) or formula (II).
- the following reaction schemes and examples are used to further illustrate the content of the present invention.
- Anhydrous tetrahydrofuran, dioxane, toluene and ether are obtained by refluxing and drying with sodium metal.
- Anhydrous dichloromethane and chloroform are obtained by refluxing and drying with calcium hydride.
- Ethyl acetate, petroleum ether, n-hexane, N,N-dimethylacetamide and N,N-dimethylformamide are dried in advance with anhydrous sodium sulfate.
- reaction flask is plugged with a suitable rubber stopper, and the substrate is injected through a syringe.
- the glassware is all dried.
- the chromatographic column is a silica gel column.
- Silica gel 300-400 mesh was purchased from Qingdao Ocean Chemical Plant.
- 1 H NMR spectra were recorded using a Bruker 400MHz or 600MHz nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer.
- the 1 H NMR spectrum uses CDC1 3 , DMSO-d 6 , CD 3 OD or acetone-d 6 as the solvent (in ppm), and uses TMS (0 ppm) or chloroform (7.26 ppm) as the reference standard.
- the intermediate compound 1e can be prepared by the method described in the synthesis scheme 1.
- the specific synthesis process is as follows:
- Compound 1b can be obtained by reacting compound 1a with isocyanate in a solvent.
- the solvent used includes but is not limited to methylene chloride and the like.
- Compound 1d can be obtained by ring closure of compound 1b in alcohol with malonate 1c substituted with different R 7 and a base (including but not limited to sodium methoxide).
- the alcohol used includes but is not limited to methanol.
- Compound 1e can be obtained by reacting compound 1d with phosphorus oxychloride in the presence of a phase transfer catalyst (including but not limited to triethylbenzylammonium chloride, etc.).
- a phase transfer catalyst including but not limited to triethylbenzylammonium chloride, etc.
- Compound 2b can be obtained by reacting compound 2a with 2-methyl-2-propane sulfenamide and copper salt (including but not limited to anhydrous copper sulfate, etc.) in a solvent.
- the solvent used includes but is not limited to methylene chloride and the like.
- Compound 2c can be obtained by addition reaction of compound 2b with Grignard reagents substituted with different R 1 .
- the solvent used includes but is not limited to tetrahydrofuran and the like.
- Compound 2d can be obtained by stirring compound 2c in an organic solution of hydrogen chloride (including but not limited to 1,4-dioxane solution, etc.).
- the solvent used includes but is not limited to methanol and the like.
- Compound (I) can be obtained by substitution reaction of compound 2d and compound 1e in a solvent.
- the solvent used includes but is not limited to 1,4-dioxane and the like.
- the reaction solution was cooled with an ice bath, slowly dripped into saturated ammonium chloride solution to quench the reaction, separated, the aqueous phase was extracted with ethyl acetate (50mL ⁇ 2), the organic phases were combined, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, filtered, and concentrated.
- EE value is 96.3%
- detection conditions Chiralpak IC, 250mm ⁇ 4.6mm ⁇ 5 ⁇ m
- the reaction solution was cooled in an ice bath, slowly dripped into saturated ammonium chloride solution to quench the reaction, separated, the aqueous phase was extracted with ethyl acetate (20mL ⁇ 2), the organic phases were combined, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, filtered, and concentrated.
- the third step 6-chloro-3-(3,5-difluorophenyl)pyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione
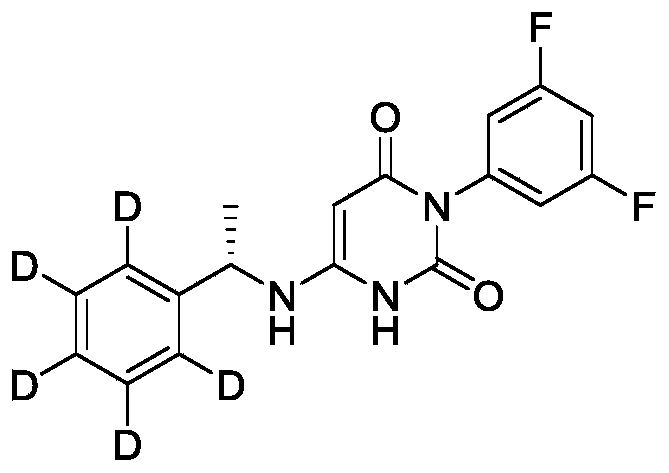
- Step 2 1-(Propan-2-yl-1,1,1,3,3,3-d6)pyrimidine-2,4,6(1H,3H,5H)-trione
- the third step 6-chloro-3-(propan-2-yl-1,1,1,3,3,3-d6)pyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione
- the first step 1-(sec-butyl)urea
- Trimethylsilyl isocyanate (9.25g, 68.36mmol) was slowly dropped into a solution of butyl-2-amine (5g, 68.36mmol) in dichloromethane (100mL) at room temperature, and the resulting reaction solution was stirred overnight at room temperature.
- the reaction solution was cooled to 0°C, and methanol (40 mL) was slowly added dropwise to quench the reaction.
- the resulting reaction solution was warmed to room temperature and stirred for 1 hour, then concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue obtained was stirred overnight with methanol/ether at room temperature and filtered to obtain a white solid
- the title compound is 5.5 g, and the yield is 69.2%.
- the third step 3-(sec-butyl)-6-chloropyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione
- the fourth step 3-(sec-butyl)-6-(((S)-1-(phenyl-d5)ethyl)amino)pyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione
- the ester (30 mL ⁇ 2) was extracted, the organic phases were combined, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, filtered, and concentrated to obtain 10 g of the crude title compound as a yellow solid with a yield of 96%, which was directly put into the next step.
- the third step 6-chloro-3-cyclobutylpyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione
- Bovine cardiac myosin has ATPase activity. During the reaction, it consumes ATP to produce adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and release free phosphorus ions. In the presence of phosphorus ions, purine nucleotide phosphorylase (PNP) catalyzes 2-amino-6-mercapto-7-methylpurine nucleoside (MESG) into 2-amino-6-mercapto-7-methylpurine , And can detect absorbance changes at 355nm.
- PNP purine nucleotide phosphorylase
- bovine myosin reaction system (0.0075mg/mL bovine myosin, 0.25mg/mL bovine myocardial thin filament complex, 0.6 ⁇ M ATP, 1X 2-amino-6-mercapto-7 -Methyl purine nucleoside, 1X purine nucleotide phosphorylase).
- the test compound is incubated with the above-mentioned bovine myosin reaction mixture for 30 minutes at room temperature. After 30 minutes, 120 ⁇ M CaCl 2 was added to start the reaction and detection was performed with EnSpire (OD355nM, 25°C), and read every 30 seconds for a total of 40 minutes.
- EnSpire ODA355nM, 25°C
- the compound of the present invention has a high inhibitory rate on bovine cardiac myosin, indicating that the compound of the present invention can effectively inhibit myosin.
- mice 4 healthy adult male SD rats (purchased from Hunan Slack Jingda Experimental Animal Co., Ltd.) were divided into two groups, one group was administered intravenously, and a group of three was administered orally. Stomach administration.
- composition Weigh a certain amount of the compound of the present invention or MYK461, add 10% DMSO, 10% Kolliphor HS15 and 80% saline to prepare a compound solution of the target concentration.
- the pharmacokinetic properties of the compound of the present invention are tested by the above test.
- the test results show that the compound of the present invention exhibits excellent pharmacokinetic characteristics in rats after intravenous injection or oral administration, that is, the compound of the present invention has excellent pharmacokinetic properties, specifically, intravenous
- the pharmacokinetic parameters in rats after injection are shown in Table 2.
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Cardiology (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Vascular Medicine (AREA)
- Urology & Nephrology (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Hospice & Palliative Care (AREA)
- Pharmaceuticals Containing Other Organic And Inorganic Compounds (AREA)
- Plural Heterocyclic Compounds (AREA)
Abstract
本发明公开了氘代苯甲氨嘧啶二酮衍生物及其用途,以及包含这类化合物的药物组合物,它们可用于抑制肌球蛋白的活性。本发明还涉及制备这类化合物和药物组合物的方法,以及它们在治疗肥厚型心肌病和相关心脏病中的用途。
Description
本发明属于药物技术领域,具体涉及用于治疗肥厚型心肌病和相关心脏病的化合物和药物组合物,及其使用方法和用途。特别地,本发明所述的是可以作为肌球蛋白抑制剂的含氘的苯甲氨嘧啶二酮衍生物。
肥厚型心肌病(Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy,HCM)是一种以心室肌肥厚、心室腔变小,左心室舒张期顺应性下降为特征的遗传性心肌疾病。用二维超声心动图测量的室间隔或左心室壁厚度≥15mm,或者有明确家族史者厚度≥13mm,通常不伴有左心室腔的扩大,需排除负荷增加如高血压、主动脉瓣狭窄和先天性主动脉瓣下隔膜等引起的左心室壁增厚。大部分无症状,主要临床表现为呼吸困难和类似心绞痛发作,梗阻性者有头晕、近似晕厥,有猝死倾向。
肥厚型心肌病病变以心肌肥厚为主,心脏重量增加。心肌细胞极度肥大、排列紊乱,细胞核畸形,肌束结构破坏呈螺旋状;随病情发展,心肌纤维化成分逐渐增多,并可有冠状动脉壁增厚、管腔变小。
肥厚型心肌病的治疗主要是使用β受体阻滞剂(普萘洛尔、美托洛尔)、钙通道阻滞剂(维拉帕米、地尔硫
)、IA类抗心律失常药(丙吡胺)等,以上药物都没有被标示用于治疗HCM,且基本上没有严格的临床试验证据可用于指导临床使用。目前尚无针对肥厚型心肌病的上市药物。
肌球蛋白是一种超家族的马达蛋白(motor protein),是长形不对称分子,形状如“Y”字,长约160nm。肌球蛋白是由两条重链(Myosin heavy chain,MHC)、两条必需轻链(Essential light chain,ELC)和两条调节轻链(Regulatory light chain,RLC)组成的高度不对称的六聚体,是粗肌丝的主要成分。肌球蛋白不仅是心肌重要的结构蛋白和收缩蛋白,而且还有三磷酸腺苷酶(ATP酶)活性,故通常也称之为肌球蛋白ATP酶。肌肉收缩的直接能量来源是肌球蛋白对三磷酸腺苷(ATP)的水解。
心肌肌球蛋白已成为治疗心力衰竭和心肌病的新策略。心肌肌球蛋白是调控心肌收缩的最下游靶点,作用于该靶点的药物可不影响细胞内钙离子浓度,可以有效的增加或减少心肌收缩力,避免心率失常等不良反应。以心肌肌球蛋白为靶点的抑制剂将是一种重要的治疗肥厚型心肌病的新方法。大多研究数据一致表明心肌肌球蛋白突变会导致心脏肌节收缩活性的增加。如果过度的肌节收缩是肥厚型心肌病的主要缺陷,则肌节的小分子抑制剂可从其来源改善疾病,并可能消除HCM的特征,如肥大、细胞混乱和心肌纤维化等。
本发明的目的是提供作为肌球蛋白抑制剂的新型化合物,从而解决对HCM和相关心脏病的改善治疗的长久需求。
发明内容
以下仅概括说明本发明的一些方面,并不局限于此。这些方面和其他部分在后面有更完整的说明。本说明书中的所有参考文献通过整体引用于此。当本说明书的公开内容与引用文献有差异时,以本说明书的公开内容为准。
本发明涉及一类新颖的含氘的苯甲氨嘧啶二酮衍生物,其可以有效抑制肌球蛋白的活性,从而可以用于制备治疗心力衰竭和心肌病的药物,特别是用于制备治疗肥厚型心肌病和相关心脏病的药物。
本发明化合物性质稳定,安全性良好,具有药效学和药代动力学优势,例如良好的生物利用度或良好的代谢稳定性等,因此具备较好的临床应用前景。
本发明还提供制备这类化合物的方法以及含有此类化合物的药物组合物。
一方面,本发明涉及一种化合物,其为式(I)所示的化合物或式(I)所示化合物的立体异构体、几何异构体、互变异构体、氮氧化物、水合物、溶剂化物、代谢产物、药学上可接受的盐或它的前药,
其中,R
1、R
2、R
3、R
4、R
5、R
6和R
7具有如本发明所述的含义。
在一些实施方案中,R
1为C
1-6烷基、C
3-8环烷基、3-8个原子组成的杂环基、C
6-10芳基或5-10个原子组成的杂芳基;其中,所述C
1-6烷基、C
3-8环烷基、3-8个原子组成的杂环基、C
6-10芳基和5-10个原子组成的杂芳基各自独立地未被取代或被1、2、3或4个R
x所取代;其中,R
x具有如本发明所述的含义。
在一些实施方案中,R
2为C
1-6烷基、C
3-8环烷基、3-8个原子组成的杂环基、C
6-10芳基或5-10个原子组成的杂芳基;其中,所述C
1-6烷基、C
3-8环烷基、3-8个原子组成的杂环基、C
6-10芳基和5-10个原子组成的杂芳基各自独立地未被取代或被1、2、3或4个R
y所取代;其中,R
y具有如本发明所述的含义。
在一些实施方案中,各R
3、R
4、R
5和R
6独立地为H、D、F、Cl、Br、I、CN、NO
2、OH、NH
2、SH、C
1-6烷基、C
1-6卤代烷基、C
1-6卤代烷氧基、C
1-6烷氨基、C
1-6烷氧基、-C(=O)R
g、-C(=O)OR
h、-S(=O)
2R
g、-C(=O)NR
iR
j、-S(=O)
2NR
iR
j、C
3-8环烷基、3-8个原子组成的杂环基、C
6-10芳基或5-10个原子组成的杂芳基;其中,OH、NH
2、SH、C
1-6烷基、C
1-6卤代烷基、C
1-6卤代烷氧基、C
1-6烷氨基、C
1-6烷氧基、C
3-8环烷基、3-8个原子组成的杂环基、C
6-10芳基和5-10个原子组成的杂芳基各自独立地未被取代或被1、2、3或4个R
z所取代;其中,R
g、R
h、R
i、R
j和R
z具有如本发明所述的含义。
在一些实施方案中,R
7为H、D、F、Cl、Br、I、C
1-6烷基或C
1-6卤代烷基。
在一些实施方案中,各R
x、R
y和R
z独立地为D、F、Cl、Br、I、CN、NO
2、OH、NH
2、-SH、C
1-6烷基、C
1-6卤代烷基、C
1-6烷氨基、C
3-8环烷基、3-8个原子组成的杂环基、C
6-10芳基、5-10个原子组成的杂芳基、-(CR
aR
b)
nR
0、-OR
c、-C(=O)R
d、-C(=O)OR
c、-S(=O)
2R
d、-C(=O)NR
eR
f或-S(=O)
2NR
eR
f;其中,R
0、R
a、R
b、R
c、R
d、R
e、R
f和n具有如本发明所述的含义。
在一些实施方案中,各R
a和R
b独立地为H、C
1-6烷基或C
1-6卤代烷基。
在一些实施方案中,各R
0独立地为C
3-8环烷基、3-8个原子组成的杂环基、C
6-10芳基或5-10个原子组成的杂芳基。
在一些实施方案中,各R
c、R
e、R
f、R
h、R
i和R
j独立地为H、D、C
1-6烷基、C
1-6卤代烷基、C
3-8环烷基、3-8个原子组成的杂环基、C
6-10芳基或5-10个原子组成的杂芳基;或者,R
e、R
f和与它们相连的氮原子一起形成3-8个原子组成的杂环基或5-10个原子组成的杂芳基。
在一些实施方案中,各R
d和R
g独立地为H、OH、NH
2、C
1-6烷基、C
1-6卤代烷基、C
1-6烷氨基、C
1-6烷氧基、C
3-8环烷基、3-8个原子组成的杂环基、C
6-10芳基或5-10个原子组成的杂芳基。
在一些实施方案中,各n独立地为1、2、3或4。
在一些实施方案中,本发明所述的化合物为式(II)所示的化合物或式(II)所示化合物的立体异构体、几何异构体、互变异构体、氮氧化物、水合物、溶剂化物、代谢产物、药学上可接受的盐或它的前药,
其中,R
1、R
2、R
3、R
4、R
5、R
6和R
7具有如本发明所述的含义。
在另一些实施方案中,R
1为C
1-4烷基、C
3-6环烷基、3-6个原子组成的杂环基、苯基或5-6个原子组成的杂芳基;其中,所述C
1-4烷基、C
3-6环烷基、3-6个原子组成的杂环基、苯基和5-6个原子组成的杂芳基各自独立地未被取代或被1、2、3或4个R
x所取代;其中,R
x具有如本发明所述的含义。
在另一些实施方案中,各R
3、R
4、R
5和R
6独立地为H、D、F、Cl、Br、I、CN、NO
2、OH、NH
2、SH、C
1-4烷基、C
1-4卤代烷基、C
1-4卤代烷氧基、C
1-4烷氨基、C
1-4烷氧基、-C(=O)R
g、-C(=O)OR
h、-S(=O)
2R
g、-C(=O)NR
iR
j、-S(=O)
2NR
iR
j、C
3-6环烷基、3-6个原子组成的杂环基、C
6-10芳基或5-6个原子组成的杂芳基;其中,OH、NH
2、SH、C
1-4烷基、C
1-4卤代烷基、C
1-4卤代烷氧基、C
1-4烷氨基、C
1-4烷氧基、C
3-6环烷基、3-6个原子组成的杂环基、C
6-10芳基和5-6个原子组成的杂芳基各自独立地未被取代或被1、2、3或4个R
z所取代;其中,R
g、R
h、R
i、R
j和R
z具有如本发明所述的含义。
在另一些实施方案中,R
7为H、D、F、Cl、Br、I、C
1-4烷基或C
1-4卤代烷基。
在另一些实施方案中,R
2为C
1-4烷基、C
3-6环烷基、3-6个原子组成的杂环基、苯基或5-6个原子组成的杂芳基;其中,所述C
1-4烷基、C
3-6环烷基、3-6个原子组成的杂环基、苯基和5-6个原子组成的杂芳基各自独立地未被取代或被1、2、3或4个R
y所取代;其中,R
y具有如本发明所述的含义。
在还一些实施方案中,R
1为甲基、乙基、正丙基、异丙基、正丁基、叔丁基、环丙基、环丁基、环戊基、环己基、环氧乙基、氮杂环丁基、氧杂环丁基、四氢呋喃基、四氢噻吩基、四氢吡喃基、吡咯烷基、吡唑烷基、咪唑烷基、哌啶基、吗啉基、哌嗪基、苯基、吡咯基、吡唑基、噻吩基、噻唑基、呋喃基、咪唑基、恶唑基、三唑基、四唑基、异恶唑基、吡啶基、嘧啶基、吡嗪基或哒嗪基;其中,甲基、乙基、正丙基、异丙基、正丁基、叔丁基、环丙基、环丁基、环戊基、环己基、环氧乙基、氮杂环丁基、氧杂环丁基、四氢呋喃基、四氢噻吩基、四氢吡喃基、吡咯烷基、吡唑烷基、咪唑烷基、哌啶基、吗啉基、哌嗪基、苯基、吡咯基、吡唑基、噻吩基、噻唑基、呋喃基、咪唑基、恶唑基、三唑基、四唑基、异恶唑基、吡啶基、嘧啶基、吡嗪基和哒嗪基各自独立地未被取代或被1、2、3或4个R
x所取代;其中,R
x具有如本发明所述的含义。
在还一些实施方案中,各R
3、R
4、R
5和R
6独立地为H、D、F、Cl、Br、I、CN、NO
2、OH、NH
2、SH、甲基、乙基、正丙基、异丙基、正丁基、叔丁基、三氟甲基、三氟甲氧基、甲氨基、二甲氨基、甲氧基、乙氧基、-C(=O)R
g、-C(=O)OR
h、-S(=O)
2R
g、-C(=O)NR
iR
j、-S(=O)
2NR
iR
j、环丙基、环丁基、环戊基、环己基、环氧乙基、氮杂环丁基、氧杂环丁基、四氢呋喃基、四氢噻吩基、四氢吡喃基、吡咯烷基、吡唑烷基、咪唑烷基、哌啶基、吗啉基、哌嗪基、苯基、吡咯基、吡唑基、噻吩基、噻唑基、呋喃基、咪唑基、恶唑基、三唑基、四唑基、异恶唑基、吡啶基、嘧啶基、吡嗪基或哒嗪基;其中,OH、NH
2、SH、甲基、乙基、正丙基、异丙基、正丁基、叔丁基、甲氨基、二甲氨基、甲氧基、乙氧基、环丙基、环丁基、环戊基、环己基、环氧乙基、氮杂环丁基、氧杂环丁基、四氢呋喃基、四氢噻吩基、四氢吡喃基、吡咯烷基、吡唑烷基、咪唑烷基、哌啶基、吗啉基、哌嗪基、苯基、吡咯基、吡唑基、噻吩基、噻唑基、呋喃基、咪唑基、恶唑基、三唑基、四唑基、异恶唑基、吡啶基、嘧啶基、吡嗪基和哒嗪基各自独立地未被取代或被1、2、3或4个R
z所取代;其中,R
g、R
h、R
i、R
j和R
z具有如本发明所述的含义。
在还一些实施方案中,R
7为H、D、F、Cl、Br、甲基、乙基或丙基。
在还一些实施方案中,R
2为甲基、乙基、正丙基、异丙基、正丁基、1-甲基丙基、叔丁基、环丙基、环丁基、环戊基、环己基、环氧乙基、氮杂环丁基、氧杂环丁基、四氢呋喃基、四氢噻吩基、四氢吡喃基、吡咯烷基、吡唑烷基、咪唑烷基、哌啶基、吗啉基、哌嗪基、苯基、吡咯基、吡唑基、噻吩基、噻唑基、呋喃基、咪唑基、恶唑基、三唑基、四唑基、异恶唑基、吡啶基、嘧啶基、吡嗪基或哒嗪基;其中,所述甲基、乙基、正丙基、异丙基、正丁基、叔丁基、环丙基、环丁基、环戊基、环己基、环氧乙基、氮杂环丁基、氧杂环丁基、四氢呋喃基、四氢噻吩基、四氢吡喃基、吡咯烷基、吡唑烷基、咪唑烷基、哌啶基、吗啉基、哌嗪基、苯基、吡咯基、吡唑基、噻吩基、噻唑基、呋喃基、咪唑基、恶唑基、三唑基、四唑基、异恶唑基、吡啶基、嘧啶基、吡嗪基和哒嗪基各自独立地未被取代或被1、2、3或4个R
y所取代;其中,R
y具有如本发明所述的含义。
在另一些实施方案中,其中,各R
x、R
y和R
z独立地为D、F、Cl、Br、I、CN、NO
2、OH、NH
2、-SH、C
1-4烷基、C
1-4卤代烷基、C
1-4烷氨基、C
3-6环烷基、3-6个原子组成的杂环基、苯基、5-6个原子组成的杂芳基、-(CR
aR
b)
nR
0、-OR
c、-C(=O)R
d、-C(=O)OR
c、-S(=O)
2R
d、-C(=O)NR
eR
f或-S(=O)
2NR
eR
f;其中,R
0、R
a、R
b、R
c、R
d、R
e、R
f和n具有如本发明所述的含义。
在另一些实施方案中,其中,各R
a和R
b独立地为H、C
1-4烷基或C
1-4卤代烷基。
在另一些实施方案中,其中,各R
0独立地为C
3-6环烷基、3-6个原子组成的杂环基、苯基或5-6个原子组成的杂芳基。
在另一些实施方案中,其中,各R
c、R
e、R
f、R
h、R
i和R
j独立地为H、D、C
1-4烷基、C
1-4卤代烷基、C
3-6环烷基、3-6个原子组成的杂环基、苯基或5-6个原子组成的杂芳基;或者,R
e、R
f和与它们相连的氮原子一起形成3-6个原子组成的杂环基或5-6个原子组成的杂芳基。
在另一些实施方案中,其中,各R
d和R
g独立地为H、OH、NH
2、C
1-4烷基、C
1-4卤代烷基、C
1-4烷氨基、C
1-4烷氧基、C
3-6环烷基、3-6个原子组成的杂环基、苯基或5-6个原子组成的杂芳基。
在还一些实施方案中,其中,各R
x、R
y和R
z独立地为D、F、Cl、Br、I、CN、NO
2、OH、NH
2、-SH、甲基、乙基、正丙基、异丙基、正丁基、叔丁基、三氟甲基、二氟甲基、甲氨基、二甲氨基、环丙基、环丁基、环戊基、环己基、环氧乙基、氮杂环丁基、氧杂环丁基、四氢呋喃基、四氢噻吩基、四氢吡喃基、吡咯烷基、吡唑烷基、咪唑烷基、哌啶基、吗啉基、哌嗪基、苯基、吡咯基、吡唑基、噻吩基、噻唑基、呋喃基、咪唑基、恶唑基、三唑基、四唑基、异恶唑基、吡啶基、嘧啶基、吡嗪基或哒嗪基、-(CR
aR
b)
nR
0、-OR
c、-C(=O)R
d、-C(=O)OR
c、-S(=O)
2R
d、-C(=O)NR
eR
f或-S(=O)
2NR
eR
f;其中,R
0、R
a、R
b、R
c、R
d、R
e、R
f和n具有如本发明所述的含义。
在还一些实施方案中,其中,各R
a和R
b独立地为H、甲基、乙基、正丙基、异丙基、正丁基、叔丁基或三氟甲基。
在还一些实施方案中,其中,各R
0独立地为环丙基、环丁基、环戊基、环己基、环氧乙基、氮杂环丁基、氧杂环丁基、四氢呋喃基、四氢噻吩基、四氢吡喃基、吡咯烷基、吡唑烷基、咪唑烷基、哌啶基、吗啉基、哌嗪基、苯基、吡咯基、吡唑基、噻吩基、噻唑基、呋喃基、咪唑基、恶唑基、三唑基、四唑基、异恶唑基、吡啶基、嘧啶基、吡嗪基或哒嗪基。
在还一些实施方案中,其中,各R
c、R
e、R
f、R
h、R
i和R
j独立地为H、D、甲基、乙基、正丙基、异丙基、正丁基、叔丁基、三氟甲基、二氟甲基、环丙基、环丁基、环戊基、环己基、环氧乙基、氮杂环丁基、氧杂环丁基、四氢呋喃基、四氢噻吩基、四氢吡喃基、吡咯烷基、吡唑烷基、咪唑烷基、哌啶基、吗啉基、哌嗪基、苯基、吡咯基、吡唑基、噻吩基、噻唑基、呋喃基、咪唑基、恶唑基、三唑基、四唑基、异恶唑基、吡啶基、嘧啶基、吡嗪基或哒嗪基;或者,R
e、R
f和与它们相连的氮原子一起形成3-6个原子 组成的杂环基或5-6个原子组成的杂芳基。
在还一些实施方案中,其中,各R
d和R
g独立地为H、OH、NH
2、甲基、乙基、正丙基、异丙基、正丁基、叔丁基、三氟甲基、二氟甲基、甲氨基、二甲氨基、甲氧基、乙氧基、环丙基、环丁基、环戊基、环己基、环氧乙基、氮杂环丁基、氧杂环丁基、四氢呋喃基、四氢噻吩基、四氢吡喃基、吡咯烷基、吡唑烷基、咪唑烷基、哌啶基、吗啉基、哌嗪基、苯基、吡咯基、吡唑基、噻吩基、噻唑基、呋喃基、咪唑基、恶唑基、三唑基、四唑基、异恶唑基、吡啶基、嘧啶基、吡嗪基或哒嗪基。
在另一些实施方案中,本发明所述的化合物,其为具有下列之一结构的化合物或具有下列之一结构的化合物的立体异构体、几何异构体、互变异构体、氮氧化物、水合物、溶剂化物、代谢产物、药学上可接受的盐或它的前药:
另一方面,本发明涉及一种药物组合物,所述药物组合物包含本发明公开的化合物。在一些实施方案中,本发明涉及的药物组合物,进一步包含药学上可接受的赋形剂、载体、佐剂或它们的任意组合。
一方面,本发明涉及本发明公开的化合物或药物组合物在制备药物中的用途,所述药物用于预防、治疗或减轻肥厚性心肌病或具有与肥厚性心肌病相关的病理生理学特征的心脏疾病。
另一方面,本发明涉及本发明公开的化合物或药物组合物在制备药物中的用途,所述药物用于预防、治疗或减轻射血分数保留的舒张性心力衰竭、缺血性心脏病、心绞痛或限制性心肌病。
另一方面,本发明涉及本发明公开的化合物或药物组合物在制备药物中的用途,所述药物用于抑制肌 球蛋白。
另一方面,本发明涉及式(I)或式(II)所示化合物的制备、分离和纯化的方法。
生物试验结果表明,本发明化合物对肌球蛋白、特别是心肌肌球蛋白具有较好的抑制作用,因此本发明提供的化合物可作为较好的肌球蛋白抑制剂。
本发明的任一方面的任一实施方案,可以与其它实施方案进行组合,只要它们不会出现矛盾。此外,在本发明任一方面的任一实施方案中,任一技术特征可以适用于其它实施方案中的该技术特征,只要它们不会出现矛盾。
前面所述内容只概述了本发明的某些方面,但并不限于这些方面。这些方面及其他方面的内容将在下面作更加具体完整的描述。
定义和一般术语
现在详细描述本发明的某些实施方案,其实例由随附的结构式和化学式说明。本发明意图涵盖所有的替代、修改和等同技术方案,它们均包括在如权利要求定义的本发明范围内。本领域技术人员应认识到,许多与本发明所述类似或等同的方法和材料能够用于实践本发明。本发明绝不限于本发明所述的方法和材料。在所结合的文献、专利和类似材料的一篇或多篇与本申请不同或相矛盾的情况下(包括但不限于所定义的术语、术语应用、所描述的技术,等等),以本申请为准。
应进一步认识到,本发明的某些特征,为清楚可见,在多个独立的实施方案中进行了描述,但也可以在单个实施例中以组合形式提供。反之,本发明的各种特征,为简洁起见,在单个实施方案中进行了描述,但也可以单独或以任意适合的子组合提供。
除非另外说明,应当应用本发明所使用的下列定义。出于本发明的目的,化学元素与元素周期表CAS版,和《化学和物理手册》,第75版,1994一致。此外,有机化学一般原理可参考“Organic Chemistry”,Thomas Sorrell,University Science Books,Sausalito:1999,和“March's Advanced Organic Chemistry”by Michael B.Smith and Jerry March,John Wiley&Sons,New York:2007中的描述,其全部内容通过引用并入本发明。
除非另有说明或者上下文中有明显的冲突,本发明所使用的冠词“一”、“一个(种)”和“所述”旨在包括“至少一个”或“一个或多个”。因此,本发明所使用的这些冠词是指一个或多于一个(即至少一个)宾语的冠词。例如,“一组分”指一个或多个组分,即可能有多于一个的组分被考虑在所述实施方案的实施方式中采用或使用。
本发明所使用的术语“患者”是指人(包括成人和儿童)或者其他动物。在一些实施方案中,“患者”是指人。
术语“立体异构体”是指具有相同化学构造,但原子或基团在空间上排列方式不同的化合物。立体异构体包括对映异构体、非对映异构体、构象异构体(旋转异构体)、几何(顺/反)异构体、阻转异构体,等等。
术语“互变异构体”或“互变异构形式”是指具有不同能量的可通过低能垒(low energy barrier)互相转化的结构异构体。若互变异构是可能的(如在溶液中),则可以达到互变异构体的化学平衡。例如,质子互变异构体(protontautomer)(也称为质子转移互变异构体(prototropic tautomer))包括通过质子迁移来进行的互相转化,如酮-烯醇异构化和亚胺-烯胺异构化。
“药学上可接受的”是指这样一些化合物、原料、组合物和/或剂型,它们在合理医学判断的范围内,适用于与患者组织接触而无过度毒性、刺激性、变态反应或与合理的利益/风险比相对称的其他问题和并发症,并有效用于既定用途。
术语“取代的”表示所给结构中的一个或多个氢原子被具体取代基所取代。除非其他方面表明,一个任 选的取代基团可以在基团各个可取代的位置进行取代。术语“任选地被…….所取代”,可以与术语“未取代或被…..所取代”交换使用,即所述结构是未取代的或者被一个或多个本发明所述的取代基取代,其中所述“多个”是指1个、2个、3个、4个或更多,但不超过所述结构可能被取代的位点的个数。当所述结构被多个取代基取代时,所述多个取代基可以是相同或不同的取代基基团。具体地,本发明所述的取代基包括,但不限于D,F,Cl,Br,I,N
3,-CN,-NO
2,-NH
2,-OH,-SH,-COOH,-CONH
2,-C(=O)NHCH
3,-C(=O)N(CH
3)
2,-C(=O)-烷基,-C(=O)-烷氧基,烷基,烷氧基,烷硫基,烷氨基,烯基,炔基,卤代烷基,卤代烷氧基,羟基取代的烷基,环烷基,杂环基,芳基,杂芳基等等。
在本说明书的各部分,本发明公开化合物的取代基按照基团种类或范围公开。特别指出,本发明包括这些基团种类和范围的各个成员的每一个独立的次级组合。例如,术语“C
1-C
6烷基”特别指独立公开的甲基、乙基、C
3烷基、C
4烷基、C
5烷基和C
6烷基。
在本发明的各部分,描述了连接取代基。当该结构清楚地需要连接基团时,针对该基团所列举的马库什变量应理解为连接基团。例如,如果该结构需要连接基团并且针对该变量的马库什基团定义列举了“烷基”或“芳基”,则应该理解,该“烷基”或“芳基”分别代表连接的亚烷基基团或亚芳基基团。
术语“卤素”和“卤代”在本发明中可互换使用,是指氟(F)、氯(Cl)、溴(Br)或碘(I)。
本发明使用的术语“烷基”或“烷基基团”,表示含有1-20个碳原子、饱和的直链或支链一价烃基基团,其中,所述烷基基团可以任选地被一个或多个本发明描述的取代基所取代。在一些实施方案中,烷基基团含有1-6个碳原子;在另一些实施方案中,烷基基团含有1-4个碳原子;还在一些实施方案中,烷基基团含有1-3个碳原子。烷基基团的实例包含,但并不限于,甲基(Me、-CH
3),乙基(Et、-CH
2CH
3),正丙基(n-Pr、-CH
2CH
2CH
3),异丙基(i-Pr、-CH(CH
3)
2),正丁基(n-Bu、-CH
2CH
2CH
2CH
3),异丁基(i-Bu、-CH
2CH(CH
3)
2),仲丁基(s-Bu、-CH(CH
3)CH
2CH
3),叔丁基(t-Bu、-C(CH
3)
3),等等。
术语“烷氧基”表示烷基基团通过氧原子与分子其余部分相连,其中烷基基团具有如本发明所述的含义。除非另外详细说明,所述烷氧基基团含有1-12个碳原子。在一些实施方案中,烷氧基基团含有1-6个碳原子;在另一些实施方案中,烷氧基基团含有1-4个碳原子;在又一些实施方案中,烷氧基基团含有1-3个碳原子。所述烷氧基基团可以任选地被一个或多个本发明描述的取代基所取代。
烷氧基基团的实例包括,但并不限于,甲氧基(MeO、-OCH
3),乙氧基(EtO、-OCH
2CH
3),1-丙氧基(n-PrO、n-丙氧基、-OCH
2CH
2CH
3),2-丙氧基(i-PrO、i-丙氧基、-OCH(CH
3)
2),1-丁氧基(n-BuO、n-丁氧基、-OCH
2CH
2CH
2CH
3),2-甲基-l-丙氧基(i-BuO、i-丁氧基、-OCH
2CH(CH
3)
2),2-丁氧基(s-BuO、s-丁氧基、-OCH(CH
3)CH
2CH
3),2-甲基-2-丙氧基(t-BuO、t-丁氧基、-OC(CH
3)
3),等等。
术语“烷氨基”或“烷基氨基”包括“N-烷基氨基”和“N,N-二烷基氨基”是指分别独立地被一个或两个烷基基团所取代的氨基基团,其中烷基基团具有如本发明所述的含义。合适的烷基氨基基团可以是单烷基氨基或二烷基氨基,这样的实例包括,但并不限于,N-甲氨基,N-乙氨基,N,N-二甲氨基,N,N-二乙氨基等等。所述烷氨基基团任选地被一个或多个本发明所描述的取代基所取代。
术语“卤代烷基”或“卤代烷氧基”表示烷基或烷氧基基团被一个或多个卤素原子所取代,其中烷基和烷氧基基团具有如本发明所述的含义,这样的实例包含,但并不限于,三氟甲基、三氟甲氧基等。在一些实施方案中,C
1-C
6卤代烷基包含氟取代的C
1-C
6烷基;在另一些实施方案中,C
1-C
4卤代烷基包含氟取代的C
1-C
4烷基;在又一些实施方案中,C
1-C
2卤代烷基包含氟取代的C
1-C
2烷基。
术语“环烷基”表示含有3-12个碳原子的,单价或多价的非芳香性的饱和单环、双环或三环体系。在一些实施方案中,环烷基包含3-12个碳原子;在另一些实施方案中,环烷基包含3-8个碳原子;在又一些实施方案中,环烷基包含3-6个碳原子。环烷基基团的实例包括,但并不限于,环丙基、环丁基、环戊基、环己基,等等。所述环烷基基团任选地被一个或多个本发明所描述的取代基所取代。
术语“杂环”、“杂环基”或“杂环的”在此处可交换使用,是指包含3-14个环原子的,单价或多价的单环、双环或者三环体系,其中环上一个或多个原子独立地被杂原子所替换,所述杂原子具有如本发明所述的含义,环可以是完全饱和的或包含一个或多个不饱和度,但一个芳香性环都不能有。在一些实施方案中,“杂环”,“杂环基”或“杂环的”基团是由3-8个原子组成的3-8元的单环(2-7个碳原子和选自N,O,P,S的1-3个杂原子,在此S或P任选地被一个或多个氧原子所取代得到像SO,SO
2,PO,PO
2的基团),或7-12元的双环(4-9个碳原子和选自N,O,P,S的1-3个杂原子,在此S或P任选地被一个或多个氧原子所取代得到像SO,SO
2,PO,PO
2的基团)。所述杂环基基团任选地被一个或多个本发明所描述的取代基所取代。杂环基可以是碳基或杂原子基;其中,环的-CH
2-基团可以任选地被-C(=O)-替代,环的硫原子可以任选地被氧化成S-氧化物,环的氮原子可以任选地被氧化成N-氧化合物。杂环基的实例包括,但不限于,环氧乙烷基、氮杂环丁基,氧杂环丁基,硫杂环丁基,吡咯烷基,2-吡咯啉基,3-吡咯啉基,吡唑啉基,吡唑烷基,咪唑啉基,咪唑烷基,四氢呋喃基,二氢呋喃基,四氢噻吩基,二氢噻吩基,1,3-二氧环戊基,二硫环戊基,四氢吡喃基,二氢吡喃基,四氢噻喃基,哌啶基,吗啉基,硫代吗啉基,哌嗪基,二噁烷基,二噻烷基,噻噁烷基,高哌嗪基,高哌啶基,氧杂环庚烷基,等等。杂环基中-CH
2-基团被-C(=O)-替代的实例包括,但不限于,2-氧代吡咯烷基、氧代-1,3-噻唑烷基、2-哌啶酮基、3,5-二氧代哌啶基、嘧啶二酮基,等等。杂环基中硫原子被氧化的实例包括,但不限于,环丁砜基、硫代吗啉基1,1-二氧化物,等等。所述杂环基基团任选地被一个或多个本发明所描述的取代基所取代。
术语“芳基”表示含有6-14个环原子,或6-12个环原子,或6-10个环原子的单环、双环和三环的碳环体系,其中,至少一个环体系是芳香族的,其中每一个环体系包含3-7个原子组成的环,且有一个或多个附着点与分子的其余部分相连。术语“芳基”可以和术语“芳香环”交换使用。芳基基团的实例可以包括苯基、萘基和蒽基。所述芳基基团任选地被一个或多个本发明所描述的取代基所取代。
术语“杂芳基”或“杂芳环”表示含有5-14个环原子,或5-10个环原子,或5-6个环原子的,单价或多价的单环、双环或三环体系,其中至少一个环是芳香族的,且至少一个环包含一个或多个杂原子。杂芳基基团通常,但不必须地通过杂芳基基团的芳香性环与母体分子连接。术语“杂芳基”可以与术语“杂芳环”或“杂芳族化合物”交换使用。所述杂芳基基团任选地被一个或多个本发明所描述的取代基所取代。在一些实施方案中,5-10个原子组成的杂芳基包含1、2、3或4个独立选自O、S和N的杂原子;在另一些实施方案中,5-6个原子组成的杂芳基为单环体系且包含1、2、3或4个独立选自O、S和N的杂原子。杂芳基基团的实例包括,但并不限于,吡咯基、吡唑基、噻吩基、噻唑基、呋喃基、咪唑基、恶唑基、三唑基、四唑基、异恶唑基、吡啶基、嘧啶基、吡嗪基或哒嗪基;也包括以下的双环,但绝不限于这些双环:苯并咪唑基、苯并呋喃基、苯并噻吩基、吲哚基、喹啉基、异喹啉基,等等。
术语“j个原子组成的”或“j元”,其中j是整数,典型地描述分子中组成环的原子的数目,在所述分子中成环的原子的数目是j。例如,哌啶基是6个原子组成的杂环或6元杂环,而环己基是6个原子组成的环烷基或6元环烷基。
在本发明中所使用的术语“不饱和的”表示基团中含有一个或多个不饱和度。
术语“杂原子”是指O、S、N、P和Si,包括N、S和P任何氧化态的形式;伯、仲、叔胺和季铵盐的形式;或者杂环中氮原子上的氢被取代的形式,例如,N(像3,4-二氢-2H-吡咯基中的N),NH(像吡咯烷基中的NH)或NR(像N-取代的吡咯烷基中的NR,R为本发明所述的取代基)。
本发明所使用的术语“前药”,代表一个化合物在体内转化为式(I)或式(II)所示的化合物。这样的转化受前体药物在血液中水解或在血液或组织中经酶转化为母体结构的影响。本发明前体药物类化合物可以是酯,在现有的发明中酯可以作为前体药物的有苯酯类,脂肪族(C
1-24)酯类,酰氧基甲基酯类,碳酸酯,氨基甲酸酯类和氨基酸酯类。例如本发明里的一个化合物包含羟基,即可以将其酰化得到前体药物形式的 化合物。其他的前体药物形式包括磷酸酯,如这些磷酸酯类化合物是经母体上的羟基磷酸化得到的。
“代谢产物”是指具体的化合物或其盐在体内通过代谢作用所得到的产物。一个化合物的代谢产物可以通过所属领域公知的技术来进行鉴定,其活性可以通过如本发明所描述的那样采用试验的方法进行表征。这样的产物可以是通过给药化合物经过氧化,还原,水解,酰氨化,脱酰氨作用,酯化,脱脂作用,酶裂解等等方法得到。相应地,本发明包括化合物的代谢产物,包括将本发明的化合物与哺乳动物充分接触一段时间所产生的代谢产物。
本发明所使用的“药学上可接受的盐”是指本发明的化合物的有机盐和无机盐。药学上可接受的盐在所属领域是为我们所熟知的,如文献:S.M.Berge et al.,describe pharmaceutically acceptable salts in detail in J.Pharmaceutical Sciences,1977,66:1-19.所记载的。药学上可接受的无毒的酸形成的盐包括,但并不限于,与氨基基团反应形成的无机酸盐有盐酸盐,氢溴酸盐,磷酸盐,硫酸盐,高氯酸盐,和有机酸盐如乙酸盐,草酸盐,马来酸盐,酒石酸盐,柠檬酸盐,琥珀酸盐,丙二酸盐,或通过书籍文献上所记载的其他方法如离子交换法来得到这些盐。本发明也拟构思了任何所包含N的基团的化合物所形成的季铵盐。水溶性或油溶性或分散产物可以通过季铵化作用得到。药学上可接受的盐进一步包括适当的、无毒的铵,季铵盐和抗平衡离子形成的胺阳离子,如卤化物,氢氧化物,羧化物,硫酸化物,磷酸化物,硝酸化物,C
1-C
8磺酸化物和芳香磺酸化物。
本发明的“溶剂化物”是指一个或多个溶剂分子与本发明的化合物所形成的缔合物。形成溶剂化物的溶剂包括,但并不限于,水,异丙醇,乙醇,甲醇,二甲亚砜,乙酸乙酯,乙酸、乙醇胺或其混合物。术语“水合物”是指溶剂分子是水所形成的缔合物。
如本发明所使用的术语“治疗”任何疾病或病症,在其中一些实施方案中指改善疾病或病症(即减缓或阻止或减轻疾病或其至少一种临床症状的发展)。在另一些实施方案中,“治疗”指缓和或改善至少一种身体参数,包括可能不为患者所察觉的身体参数。在另一些实施方案中,“治疗”指从身体上(例如稳定可察觉的症状)或生理学上(例如稳定身体的参数)或上述两方面调节疾病或病症。在另一些实施方案中,“治疗”指预防或延迟疾病或病症的发作、发生或恶化。
术语“治疗有效量”是指当给药于主体来治疗疾病时,化合物的分量足够对这种疾病的治疗起效。“治疗有效量”可以随着化合物,疾病和严重程度,以及有待治疗的主体的条件,年龄,体重,性别等而改变。
本发明涉及的化合物,其药学上可接受的盐,药物制剂及其组合物,可以用作选择性5-羟色胺再摄取抑制剂,对人类中枢神经系统功能障碍,特别是情感障碍的治疗有潜在的用途,所述情感障碍包括但并不限于,抑郁症、焦虑症、社交恐惧症、强迫症、惊恐发作、特定恐惧症、广场恐惧、躁狂症、惊恐障碍和创伤后应激障碍。
除非另作说明,本发明的化合物所有合适的同位素变化、立体异构体、互变异构体、溶剂化物、代谢产物、盐和药学上可接受的前药都包含在本发明范围内。
在本发明公开的结构中,当任意特定的手性原子的立体化学未指明时,则该结构的所有立体异构体都考虑在本发明之内,并且作为本发明公开化合物包括在本发明中。当立体化学被表示特定构型的实楔形线(solid wedge)或虚线指明时,则该结构的立体异构体就此明确和定义。
本发明化合物可以以盐的形式存在。在一些实施方案中,所述盐是指药学上可接受的盐。术语“药学上可接受的”是指物质或组合物必须与包含制剂的其它成分和/或用其治疗的哺乳动物化学上和/或毒理学上相容。在另一些实施方案中,所述盐不一定是药学上可接受的盐,可以是用于制备和/或提纯本发明化合物和/或用于分离本发明化合物的对映体的中间体。
本发明给出的任何结构式也意欲表示这些化合物未被同位素富集的形式以及同位素富集的形式。同位素富集的化合物具有本发明给出的通式描绘的结构,除了一个或多个原子被具有所选择原子量或质量数的 原子替换。可引入本发明化合物中的示例性同位素包括氢、碳、氮、氧、磷、硫、氟和氯的同位素,如
2H、
3H、
11C、
13C、
14C、
15N、
17O、
18O、
18F、
31P、
32P、
35S、
36Cl和
125I。
另一方面,本发明涉及制备式(I)或式(II)所示化合物的中间体。
本发明化合物的药物组合物、制剂和给药
本发明提供一种药物组合物,包括式(I)或式(II)所示化合物或其单独的立体异构体,异构体的外消旋或非外消旋混合物或其药学上可接受的盐或溶剂化物。在本发明的一些实施方式中,所述药物组合物进一步包含至少一种药学上可接受的载体、辅剂或赋形剂,以及任选地,其它的治疗和/或预防成分。
合适的载体、辅剂和赋形剂对于本领域技术人员是熟知的并且详细描述于例如Ansel H.C.et al.,Ansel’s Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms and Drug Delivery Systems(2004)Lippincott,Williams&Wilkins,Philadelphia;Gennaro A.R.et al.,Remington:The Science and Practice of Pharmacy(2000)Lippincott,Williams&Wilkins,Philadelphia;和Rowe R.C.,Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients(2005)Pharmaceutical Press,Chicago中。
也应认识到,在用于治疗时,本发明的某些化合物可以以游离形式存在,或者如果适当可以以其药学上可接受的衍生物的形式存在。药学上可接受衍生物的一些非限制性的实施方案包括药学上可接受的前药,盐,酯,这些酯的盐,或者对有需要的患者给药时能直接或间接提供本发明所述化合物或其代谢产物或残留物的任何另外的加合物或衍生物。
合适的药学上可接受的赋形剂会依所选具体剂型而不同。此外,可根据它们在组合物中的特定功能来选择药学上可接受的赋形剂。合适的药学上可接受的赋形剂包括以下类型的赋形剂:稀释剂、填充剂、粘合剂、崩解剂、润滑剂、助流剂、造粒剂、包衣剂、润湿剂、溶剂、共溶剂、助悬剂、乳化剂、甜味剂、矫味剂、掩味剂、着色剂、防结块剂、保湿剂、螯合剂、塑化剂、增粘剂、抗氧化剂、防腐剂、稳定剂、表面活性剂和缓冲剂。技术人员可认识到,某些药学上可接受的赋形剂可提供不止一种功能,并提供可供选择的功能,这取决于制剂中存在多少该赋形剂和制剂中存在哪些其他赋形剂。
本发明公开的药物组合物使用本领域技术人员已知的技术和方法来制备。本领域一些常用方法的描述可参见Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences(Mack Publishing Company)。
因此,另一方面,本发明涉及制备药物组合物的工艺,所述药物组合物包含本发明公开化合物和药学上可接受的赋形剂,载体,辅剂,溶媒或它们的组合,该工艺包括混合各种成分。包含本发明公开化合物的药物组合物,可以在例如环境温度和大气压下混合来制备。
本发明公开的化合物通常被配制成适合于通过所需途径对患者给药的剂型。例如,剂型包括那些适合于以下给药途径的剂型:(1)口服给药,例如片剂、胶囊剂、囊片剂、丸剂、含片剂、粉剂、糖浆剂、酏剂、混悬剂、溶液剂、乳剂、香包剂和扁囊剂;(2)胃肠外给药,例如无菌溶液剂、混悬剂和复溶粉末;(3)透皮给药,例如透皮贴片剂;(4)直肠给药,例如栓剂;(5)吸入,例如气雾剂、溶液剂和干粉剂;和(6)局部给药,例如乳膏剂、油膏剂、洗剂、溶液剂、糊剂、喷雾剂、泡沫剂和凝胶剂。
在一些实施方案中,本发明公开的化合物可以配制成口服剂型。在另一些实施方案中,本发明公开的化合物可以配制成吸入剂型。在另一些实施方案中,本发明公开的化合物可以配制成经鼻给药剂型。在又一些实施方案中,本发明公开的化合物可以配制成透皮给药剂型。还在一些实施方案中,本发明公开的化合物可以配制成局部给药剂型。
本发明提供的药物组合物可以以压制片、研制片、可咀嚼锭剂、速溶片、复压片、或肠溶片、糖衣或薄膜衣片来提供。
本发明提供的药物组合物可以以软胶囊或硬胶囊来提供,其可以由明胶、甲基纤维素、淀粉或海藻酸钙来制备。
本发明提供的药物组合物可以通过注射、输注或植入肠胃外给药,用于局部或全身给药。如本发明使用的肠胃外给药包括静脉内、动脉内、腹膜内、鞘内、心室内、尿道内、胸骨内、颅内、肌内、滑膜内和皮下给药。
本发明提供的药物组合物可以配制成适于肠胃外给药的任何剂型,包括溶液、混悬剂、乳剂、胶束、脂质体、微球、纳米体系和适于在注射前在液体中制成溶液或混悬液的固体形式。这样的剂型可以根据药物科学领域的技术人员已知的常规方法来制备(参见Remington:The Science和Practice of Pharmacy,同上)。
根据待治疗的疾病及受试者的状态,本发明所述化合物或其药学上可接受的盐可通过如下方式给药:经口服、肠胃外(例如肌内、腹膜内、静脉内、ICV、池内注射或输注、皮下注射或植入)、经植入(例如在该化合物或药用盐连接于支架装置时)、经吸入喷雾、鼻部、阴道、直肠、舌下或局部途径给药,且可单独或在适于每种给药途径的适当的含有常规无毒的药用载体、辅料和媒介物的剂量单位制剂中一起配制。
在治疗或预防在舒张期内需要改善的心室舒张的病症中,适当的剂量水平将通常为约0.001至100mg/kg患者体重/天,其可以单一剂量或多个剂量给予。在一些实施方案中,剂量水平将为约0.01至约25mg/kg/天;在一些实施方案中为约0.05至约10mg/kg/天。适当的剂量水平可为约0.01至25mg/kg/天、约0.05至10mg/kg/天或约0.1至5mg/kg/天。在该范围内,剂量可为0.005至0.05、0.05至0.5或0.5至5.0mg/kg/天。在一些实施方案中,对于口服给药,在以下片剂形式中提供该组合物:含有1.0至1000毫克的活性成分,具体地含有1.0、5.0、10.0、15.0、20.0、25.0、50.0、75.0、100.0、150.0、200.0、250.0、300.0、400.0、500.0、600.0、750.0、800.0、900.0和1000.0毫克的活性成分,以用于针对症状调整对待治疗的患者所给予的治疗。该化合物或药学上可接受的盐可在每天1至4次的方案中给予,在一些实施方案中,可在每天一或两次的方案中给予。
本发明公开化合物或药物组合物可以与一种或多种其它治疗剂同时,或在其之前或之后给药。本发明化合物或药物组合物可以与其他治疗剂通过相同或不同给药途径分别给药,或与之以同一药物组合物形式给药。当本发明提供的化合物或药物组合物与一种或多种其它治疗剂同时使用时,优选的是含有除本发明提供的化合物或药物组合物之外的所述其它药物的药物组合物。因此,本发明提供的药物组合物包括那些除了本发明提供的化合物或药物组合物之外还含有一种或多种其它活性成分或治疗药物的药物组合物。适当的其它活性药物包括:通过下调心脏的神经激素刺激来延缓心力衰竭的进展并尝试防止心脏重塑的药物(例如,ACE抑制剂、血管紧张素受体阻断剂(ARB)、阻断剂、醛固酮受体拮抗剂或神经内肽酶抑制剂);通过刺激心脏收缩性来改善心脏功能的药物(例如正性肌力药诸如肾上腺素能激动剂多巴酚丁胺或磷酸二酯酶抑制剂米力农);及降低心脏前负荷的药物(例如利尿剂诸如呋塞米)或降低心脏后负荷的药物(任何类别的血管舒张剂,包括但不限于钙通道阻断剂、磷酸二酯酶抑制剂、内皮素受体拮抗剂、肾素抑制剂或平滑肌肌球蛋白调节剂)。本发明提供的化合物与第二活性成分的重量比是可变化的且将取决于每种成分的有效剂量。一般来说,将使用每种成分的有效剂量。
本发明化合物和药物组合物的用途
本发明提供的化合物或其药学上可接受的盐和药物组合物可用于制备用于预防、治疗或减轻哺乳动物,包括人类的心脏疾病的药品,也可以用于制备用于抑制肌球蛋白的药品。
具体而言,本发明的化合物或其药学上可接受的盐和药物组合物中化合物的量可以有效地可探测地选择性地抑制肌球蛋白,特别是心肌肌球蛋白。本发明的化合物或其药学上可接受的盐和药物组合物可以作为治疗人类心力衰竭和心肌病,特别是肥厚型心肌病和具有与肥厚性心肌病相关的病理生理学特征的心脏疾病的药物。
本发明的化合物或其药学上可接受的盐和药物组合物可以应用于,但绝不限于,使用本发明的化合物或其药学上可接受的盐或所述药物组合物的有效量对患者给药来预防、治疗或减轻肥厚型心肌病和具有与肥厚性心肌病相关的病理生理学特征的心脏疾病。
本发明化合物或其药学上可接受的盐也用于治疗射血分数保留的舒张性心力衰竭、缺血性心脏病、心绞痛或限制性心肌病。本发明化合物或其药学上可接受的盐也可促进由于容量或压力过度负荷造成的左心室肥大的有益心室重构;例如慢性二尖瓣返流、慢性主动脉瓣狭窄或慢性系统性高血压;所述化合物或其药学上可接受的盐旨在纠正或减轻容量或压力过度负荷的主要原因的疗法(瓣修复/替换、有效的抗高血压疗法)。通过降低左心室充盈压,本发明化合物或其药学上可接受的盐可降低肺水肿和呼吸衰竭的风险;降低或消除功能性二尖瓣返流和/或降低左心房压力可降低突发性或持久性心房纤颤的风险,且其降低了动脉血栓栓塞性并发症包括但不限于脑动脉栓塞性中风的伴随性风险;降低或消除动态和/或静态左心室流出道阻塞可减少需要间隔消融治疗(手术或经皮)的可能性及其短期和长期并发症的伴随性风险。本发明化合物或其药学上可接受的盐可降低与HCM相关的慢性局部缺血状态的严重性,且由此降低具有可植入的复律器-除颤器(频繁和/或重复的ICD放电)的患者中的心脏性猝死(SCD)或其等同疾病的风险和/或降低对于可能有毒的抗心律不齐药物的需求。本发明化合物或其药学上可接受的盐可在降低或消除对于并行药物(具有其伴随的潜在毒性、药物-药物相互作用和/或副作用)的需求方面是有价值的。本发明化合物或其药学上可接受的盐可降低间质性心肌纤维化和/或减缓左心室肥大的进展、阻止或逆转左心室肥大。
本发明的化合物及药物组合物除了对人类治疗有益以外,还可应用于兽医治疗宠物、引进品种的动物和农场的动物中的哺乳动物。另外一些动物的实例包括马、狗和猫。在此,本发明的化合物包括其药学上可接受的衍生物。
一般合成步骤
为描述本发明,以下列出了实施例。但需要理解,本发明不限于这些实施例,只是提供实践本发明的方法。
一般地,本发明的化合物可以通过本发明所描述的方法制备得到,除非有进一步的说明,其中取代基的定义如式(I)或式(II)所示。下面的反应方案和实施例用于进一步举例说明本发明的内容。
所属领域的专业人员将认识到:本发明所描述的化学反应可以用来合适地制备许多本发明的其他化合物,且用于制备本发明的化合物的其它方法都被认为是在本发明的范围之内。例如,根据本发明那些非例证的化合物的合成可以成功地被所属领域的技术人员通过修饰方法完成,如适当的保护干扰基团,通过利用其他已知的试剂除了本发明所描述的,或将反应条件做一些常规的修改。另外,本发明所公开的反应或已知的反应条件也公认地适用于本发明其他化合物的制备。
下面所描述的实施例,除非其他方面表明所有的温度定为摄氏度。试剂购买于商品供应商如Aldrich Chemical Company,Arco Chemical Company and Alfa Chemical Company,使用时都没有经过进一步纯化,除非其他方面表明。一般的试剂从汕头西陇化工厂,广东光华化学试剂厂,广州化学试剂厂,天津好寓宇化学品有限公司,天津市福晨化学试剂厂,武汉鑫华远科技发展有限公司,青岛腾龙化学试剂有限公司,和青岛海洋化工厂购买得到。
无水四氢呋喃,二氧六环,甲苯,乙醚是经过金属钠回流干燥得到。无水二氯甲烷和氯仿是经过氢化钙回流干燥得到。乙酸乙酯,石油醚,正己烷,N,N-二甲基乙酰胺和N,N-二甲基甲酰胺是经无水硫酸钠事先干燥使用。
以下反应一般是在氮气或氩气正压下或在无水溶剂上套一干燥管(除非其他方面表明),反应瓶都塞上合适的橡皮塞,底物通过注射器打入。玻璃器皿都是干燥过的。
色谱柱是使用硅胶柱。硅胶(300-400目)购于青岛海洋化工厂。
1H NMR谱使用Bruker 400MHz或600MHz核磁共振谱仪记录。
1H NMR谱以CDC1
3、DMSO-d
6、CD
3OD或丙酮-d
6为溶剂(以ppm为单位),用TMS(0ppm)或氯仿(7.26ppm)作为参照标准。当出现多重峰的时候,将使用下面的缩写:s(singlet,单峰)、d(doublet,双峰)、t(triplet,三重峰)、m(multiplet,多重峰)、br(broadened,宽峰)、brs(broadened singlet,宽的单峰)、dd(doublet of doublets,双二重峰)、dt(doublet of triplets,双三重峰)。偶合常数J,用赫兹(Hz)表示。
下面简写词的使用贯穿本发明:
下列合成方案描述了制备本发明公开化合物的步骤,除非另外说明,其中各R
1、R
2、R
3、R
4、R
5、R
6和R
7具有本发明所述的定义,M为C
1-4烷基。
合成方案1
中间体化合物1e可以通过合成方案1所描述的方法制备得到,具体合成过程如下:
化合物1b可通过化合物1a在溶剂中与异氰酸酯反应得到。在反应中,所用的溶剂包括但不限于二氯甲烷等。
化合物1d可通过化合物1b在醇中与不同R
7取代的丙二酸酯1c和碱(包括但不限于甲醇钠)存在的条件下关环得到。在反应中,所用的醇包括但不限于甲醇。
化合物1e可通过化合物1d在相转移催化剂(包括但不限于三乙基苄基氯化胺等)存在下与三氯氧磷反应得到。
合成方案2
化合物(I)可以通过合成方案2所描述的方法制备得到,其具体合成过程如下:
化合物2b可通过化合物2a在溶剂中与2-甲基-2-丙烷亚磺酰胺和铜盐(包括但不限于无水硫酸铜等)反应得到。在反应中,所用的溶剂包括但不限于二氯甲烷等。
化合物2c可通过化合物2b与不同R
1取代的格式试剂进行加成反应得到。在反应中,所用的溶剂包括但不限于四氢呋喃等。
化合物2d可通过化合物2c在氯化氢的有机溶液(包括但不限于1,4-二氧六环溶液等)中搅拌得到。在反应中,所用的溶剂包括但不限于甲醇等。
化合物(I)可通过化合物2d与化合物1e在溶剂中进行取代反应得到。在反应中,所用的溶剂包括但不限于1,4-二氧六环等。
以下结合实施例对本发明提供的化合物、药物组合物及其应用进行进一步说明。
实施例1 (S)-3-异丙基-6-((1-(苯基-d5)乙基)氨基)嘧啶-2,4(1H,3H)-二酮
第一步:(R)-2-甲基-N-((苯基-d5)亚甲基)丙烷-2-亚磺酰胺
氮气保护下,于(R)-2-甲基丙烷-2-亚磺酰胺(4.91g,40.48mmol)、PPTS(339.12mg,1.35mmol)和硫酸镁(16.24g,134.95mmol)的二氯甲烷(200mL)混合体系中加入苯甲醛-2,3,4,5,6-d5(3g,26.99mmol),室温搅拌过夜,TLC监测反应完毕,过滤除去不溶物,滤饼用二氯甲烷洗涤(50mL),滤液浓缩,所得残留物经硅胶柱色谱纯化(PE/EA(v/v)=20/1),得到淡黄色固体标题化合物3g,收率51.8%。
第二步:(R)-2-甲基-N-((S)-1-(苯基-d5)乙基)丙烷-2-亚磺酰胺
氮气保护下,将(R)-2-甲基-N-((苯基-d5)亚甲基)丙烷-2-亚磺酰胺(3g,14mmol)溶于无水四氢呋喃(50mL)中,所得反应液降至-50℃,缓慢滴入甲基溴化镁(28mL,28mmol,1M)溶液,滴毕,缓慢升至室温继续搅拌过夜。反应液用冰浴冷却,缓慢滴入饱和氯化铵溶液淬灭反应,分液,水相再用乙酸乙酯萃取(50mL×2),合并有机相,无水硫酸钠干燥,过滤,浓缩,所得残留物经硅胶柱色谱纯化(PE/EA(v/v)=2/1),得到黄色油状标题化合物1.4g,收率43.4%。
第三步:(S)-1-(苯基-d5)乙烷-1-胺盐酸盐
于(R)-2-甲基-N-((S)-1-(苯基-d5)乙基)丙烷-2-亚磺酰胺(1.4g,6.08mmol)的甲醇(20mL)溶液中加入氯化氢的1,4-二氧六环溶液(3.04mL,12.16mmol),室温搅拌1小时,减压除去大部分溶剂,残留物用甲醇(3mL)溶解,然后加入乙醚(100mL),所得体系继续搅拌过夜,析出大量白色固体,过滤,滤饼用乙醚(20mL)洗涤,减压干燥,得到白色固体标题化合物800mg,收率81%。
第四步:(S)-3-异丙基-6-((1-(苯基-d5)乙基)氨基)嘧啶-2,4(1H,3H)-二酮
将(S)-1-(苯基-d5)乙烷-1-胺盐酸盐(388.1mg,2.39mmol)中加入20mL氢氧化钠溶液(1M)并搅拌30min,乙酸乙酯(50mL×2)萃取,无水硫酸钠干燥,过滤,减压浓缩。所得残留物加入6-氯-3-异丙基嘧啶-2,4(1H,3H)-二酮(300mg,1.59mmol)(参考CN105473576A,化合物1.3的合成路线)和1,4-二氧六环(10mL)溶液中,反应体系升温至100℃下搅拌过夜。停止反应,反应体系自然降至室温后,减压浓缩,所得残留物经硅胶柱色谱纯化(PE/EA(v/v)=1/1),得到白色固体标题化合物48mg,收率10.8%。
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z:279.2[M+1]
+;
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d
6)δ9.80(s,1H),6.53(d,J=6.0Hz,1H),4.96–4.84(m,1H),4.54–4.45(m,1H),4.34(s,1H),1.40(d,J=6.7Hz,3H),1.27(d,J=6.8Hz,6H).
EE值为96.3%,检测条件:手性色谱柱Chiralpak IC、250mm×4.6mm×5μm,洗脱剂为13%乙醇和87%正己烷的混合溶液,流速1.0mL/min,Rt=8.807min,266nm。
实施例2 (S)-3-异丙基-6-((1-(苯基-4-d)乙基)氨基)嘧啶-2,4(1H,3H)-二酮
第一步:(R)-2-甲基-N-((苯基-4-d)亚甲基)丙烷-2-亚磺酰胺
氮气保护下,将苯甲醛-4-d(0.7g,6.53mmol),(R)-2-甲基丙烷-2-亚磺酰胺(1.58g,13.07mmol)和无水硫酸铜(3.13g,19.60mmol)的二氯甲烷(200mL)溶液室温搅拌过夜,硅藻土过滤除去不溶物,滤饼用二氯甲烷洗涤(50mL),滤液浓缩,所得残留物经硅胶柱色谱纯化(PE/EA(v/v)=20/1),得到淡黄色固体标题化合物0.8g,收率58.4%。
第二步:(R)-2-甲基-N-((S)-1-(苯基-4-d)乙基)丙烷-2-亚磺酰胺
氮气保护下,将(R)-2-甲基-N-((苯基-4-d)亚甲基)丙烷-2-亚磺酰胺(0.8g,3.8mmol)溶于无水二氯甲烷(20mL)中,所得反应液降至-60℃,缓慢滴入甲基溴化镁(7.6mL,7.6mmol,1M)溶液,滴毕,缓慢升至室温继续搅拌过夜。反应液用冰浴冷却,缓慢滴入饱和氯化铵溶液淬灭反应,分液,水相再用乙酸乙酯萃取(20mL×2),合并有机相,无水硫酸钠干燥,过滤,浓缩,所得残留物经硅胶柱色谱纯化(PE/EA(v/v)=2/1),得到白色固体标题化合物0.8g,收率92.9%。
第三步:(S)-1-(苯基-4-d)乙基-1-胺盐酸盐
于(R)-2-甲基-N-((S)-1-(苯基-4-d)乙基)丙烷-2-亚磺酰胺(0.8g,3.5mmol)的甲醇(20mL)溶液中加入氯化氢的1,4-二氧六环溶液(1.9mL,7.6mmol),室温搅拌1小时,减压除去大部分溶剂,残留物用甲醇(1mL)溶解,然后加入乙醚(50mL),所得体系继续搅拌过夜,析出大量白色固体,过滤,滤饼用乙醚(20mL)洗涤,减压干燥,得到白色固体标题化合物500mg,收率90%。
第四步:(S)-3-异丙基-6-((1-(苯基-4-d)乙基)氨基)嘧啶-2,4(1H,3H)-二酮
将(S)-1-(苯基-4-d)乙基-1-胺盐酸盐(403.7mg,2.54mmol)中加入20mL氢氧化钠溶液(1M)并搅拌30min,乙酸乙酯(50mL×2)萃取,无水硫酸钠干燥,过滤,减压浓缩。所得残留物加入6-氯-3-异丙基 嘧啶-2,4(1H,3H)-二酮(400mg,2.12mmol)和1,4-二氧六环(10mL)溶液中,反应体系升温至100℃下搅拌过夜。停止反应,反应体系自然降至室温后,减压浓缩,所得残留物经硅胶柱色谱纯化(PE/EA(v/v)=1/1),得到淡黄色固体标题化合物81mg,收率13.9%。
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z:275.3[M+1]
+;
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d
6)δ9.79(s,1H),7.38–7.32(m,4H),6.52(d,J=6.4Hz,1H),4.97–4.84(m,1H),4.55–4.44(m,1H),4.34(s,1H),1.40(d,J=6.7Hz,3H),1.27(d,J=6.9Hz,6H)。
实施例3 (S)-3-(3,5-二氟苯基)-6-((1-(苯基-d5)乙基)氨基)嘧啶-2,4(1H,3H)-二酮
第一步:1-(3,5-二氟苯基)脲
室温下于3,5-二氟苯胺(5g,38.73mmol)的二氯甲烷(100mL)溶液中缓慢滴入异氰酸三甲基硅酯(4.45g,38.73mmol),所得反应液室温搅拌过夜。反应液降温至0℃,缓慢滴入甲醇(40mL)淬灭反应,所得反应液升至室温后继续搅拌1小时,减压浓缩,所得残留物用甲醇/乙醚室温搅拌过夜,过滤,得黄色固体标题化合物3.2g,收率48%。
第二步:1-(3,5-二氟苯基)嘧啶-2,4,6(1H,3H,5H)-三酮
室温下,于1-(3,5-二氟苯基)脲(2.3g,13.36mmol)的甲醇(40mL)溶液中加入甲醇钠的甲醇溶液(8.02mL,40.08mmol)和丙酸二甲酯(1.77g,13.36mmol),所得反应液升温至65℃搅拌过夜,自然冷却至室温后,加水淬灭反应,所得反应液减压出去大部分甲醇,水相用1M的盐酸调节至酸性(pH=2),乙酸乙酯(30mL×2)萃取,合并有机相,无水硫酸钠干燥,过滤,浓缩,所得残留物经硅胶柱色谱纯化(PE/EA(v/v)=2/1),得到白色固体标题化合物1.2g,收率37.4%。
第三步:6-氯-3-(3,5-二氟苯基)嘧啶-2,4(1H,3H)-二酮
于1-(3,5-二氟苯基)嘧啶-2,4,6(1H,3H,5H)-三酮(1.2g,5mmol)和三乙基苄基氯化铵(1.1g,5mmol)中加入三氯氧磷(10mL),所得反应液于50℃反应3小时,然后减压浓缩,残留物倒入冰水中,剧烈搅拌30分钟后,乙酸乙酯(30mL×2)萃取,合并有机相,无水硫酸钠干燥,过滤,浓缩,所得残留物经硅胶柱色谱纯化(PE/EA(v/v)=2/1),得到白色固体标题化合物700mg,收率54.2%。
第四步:(S)-3-(3,5-二氟苯基)-6-((1-(苯基-d5)乙基)氨基)嘧啶-2,4(1H,3H)-二酮
将(S)-1-(苯基-d5)乙烷-1-胺盐酸盐(301.93mg,1.86mmol)中加入20mL氢氧化钠溶液(1M)并搅拌30min,乙酸乙酯(30mL×2)萃取,无水硫酸钠干燥,过滤,减压浓缩。所得残留物加入6-氯-3-(3,5-二氟苯基)嘧啶-2,4(1H,3H)-二酮(400mg,1.55mmol)和1,4-二氧六环(10mL)溶液中,反应体系升温至100℃下搅拌过夜。停止反应,反应体系自然降至室温后,减压浓缩,所得残留物经硅胶柱色谱纯化(PE/EA(v/v)=1/1),得到白色固体标题化合物50mg,收率9.3%。
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z:349.2[M+1]
+;
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d
6)δ10.28(s,1H),7.26(t,J=9.4Hz,1H),7.08-6.99(m,2H),6.78(d,J=6.3Hz,1H),4.67-4.56(m,1H),4.53(s,1H),1.45(d,J=6.7Hz,3H)。
实施例4 (S)-6-((1-(苯基-d5)乙基)氨基)-3-(四氢-2H-吡喃-4-基)嘧啶-2,4(1H,3H)-二酮
将(S)-1-(苯基-d5)乙烷-1-胺盐酸盐(338.53mg,2.08mmol)中加入20mL氢氧化钠溶液(1M)并搅拌30min,乙酸乙酯(30mL×2)萃取,无水硫酸钠干燥,过滤,减压浓缩。所得残留物加入6-氯-3-(四氢-2H-吡喃-4-基)嘧啶-2,4(1H,3H)-二酮(400mg,1.73mmol)(参考CN105473576A,化合物9.3的合成路线)和1,4-二氧六环(10mL)溶液中,反应体系升温至100℃下搅拌过夜。停止反应,反应体系自然降至室温后,减压浓缩,所得残留物经硅胶柱色谱纯化(PE/EA(v/v)=1/1),得到白色固体标题化合物70mg,收率12.6%。
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z:321.2[M+1]
+;
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d
6)δ9.89(s,1H),6.59(s,1H),4.83-4.69(m,1H),4.57-4.47(m,1H),4.38(s,1H),3.97-3.80(m,2H),3.28(t,J=12.1Hz,2H),2.59-2.51(m,2H),1.40(d,J=6.7Hz,3H),1.31(d,J=11.6Hz,2H)。
实施例5 (S)-6-((1-苯基乙基)氨基)-3-(丙烷-2-基-1,1,1,3,3,3-d6)嘧啶-2,4(1H,3H)-二酮
第一步:1-(丙烷-2-基-1,1,1,3,3,3-d6)脲
氮气保护下,于丙烷-1,1,1,3,3,3-d6-2-胺盐酸盐(1g,9.84mmol)和三乙胺(1.37mL,9.84mmol)的二氯甲烷(20mL)溶液中缓慢滴入异氰酸三甲基硅酯(1.25g,10.83mmol),所得反应液室温搅拌过夜。反应液降温至0℃,缓慢滴入甲醇(10mL)淬灭反应,所得反应液升至室温后继续搅拌1小时,减压浓缩,所得残留物用甲醇/乙醚(1:40)打浆,过滤,得白色固体标题化合物1g,收率94.4%。
第二步:1-(丙烷-2-基-1,1,1,3,3,3-d6)嘧啶-2,4,6(1H,3H,5H)-三酮
室温下,于1-(丙烷-2-基-1,1,1,3,3,3-d6)脲(1g,9.24mmol)的甲醇(30mL)溶液中加入甲醇钠的甲醇溶液(4.62mL,23.11mmol)和丙二酸二甲酯(1.28g,9.71mmol),所得反应液升温至65℃搅拌过夜,自然冷却至室温后,加水淬灭反应,所得反应液减压出去大部分甲醇,水相用1M的盐酸调节至酸性(pH=2),乙酸乙酯(30mL×2)萃取,合并有机相,无水硫酸钠干燥,过滤,浓缩,得到白色固体标题化合物1.0g,收率61.3%。
第三步:6-氯-3-(丙烷-2-基-1,1,1,3,3,3-d6)嘧啶-2,4(1H,3H)-二酮
于1-(丙烷-2-基-1,1,1,3,3,3-d6)嘧啶-2,4,6(1H,3H,5H)-三酮(1.0g,5.68mmol)和三乙基苄基氯化铵(1.29g,5.68mmol)中加入三氯氧磷(10mL),所得反应液于50℃反应3小时,然后减压浓缩,残留物倒入冰水中,剧烈搅拌30分钟后,乙酸乙酯(30mL×2)萃取,合并有机相,无水硫酸钠干燥,过滤,浓缩,所得残留物经硅胶柱色谱纯化(PE/EA(v/v)=2/1),得到淡黄色固体标题化合物300mg,收率27.3%。
第四步:(S)-6-((1-苯基乙基)氨基)-3-(丙烷-2-基-1,1,1,3,3,3-d6)嘧啶-2,4(1H,3H)-二酮
(S)-1-苯基乙烷-1-胺(373.55mg,3.08mmol)与6-氯-3-(丙烷-2-基-1,1,1,3,3,3-d6)嘧啶-2,4(1H,3H)-二酮(300mg,1.54mmol)的1,4-二氧六环(10mL)溶液中,反应体系升温至100℃下搅拌过夜。停止反应, 反应体系自然降至室温后,减压浓缩,所得残留物经硅胶柱色谱纯化(PE/EA(v/v)=1/1),得到白色固体标题化合物45mg,收率10.4%。
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z:280.2[M+1]
+;
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d
6)δ9.78(s,1H),7.39–7.32(m,4H),7.26(t,J=6.6Hz,1H),6.51(d,J=6.6Hz,1H),4.87(s,1H)4.55-4.44(m,1H),4.34(s,1H),1.40(d,J=6.7Hz,3H)。
实施例6 3-(仲丁基)-6-(((S)-1-(苯基-d5)乙基)氨基)嘧啶-2,4(1H,3H)-二酮
第一步:1-(仲丁基)脲
室温下于丁基-2-胺(5g,68.36mmol)的二氯甲烷(100mL)溶液中缓慢滴入异氰酸三甲基硅酯(9.25g,68.36mmol),所得反应液室温搅拌过夜。反应液降温至0℃,缓慢滴入甲醇(40mL)淬灭反应,所得反应液升至室温后继续搅拌1小时,减压浓缩,所得残留物用甲醇/乙醚室温搅拌过夜,过滤,得白色固体标题化合物5.5g,收率69.2%。
第二步:1-(仲丁基)嘧啶-2,4,6(1H,3H,5H)-三酮
室温下,于1-(仲丁基)脲(5.5g,47.35mmol)的甲醇(40mL)溶液中加入甲醇钠的甲醇溶液(28.41mL,142.04mmol)和丙二酸二甲酯(5.41mL,47.35mmol),所得反应液升温至65℃搅拌过夜,自然冷却至室温后,加水淬灭反应,所得反应液减压出去大部分甲醇,水相用1M的盐酸调节至酸性(pH=2),乙酸乙酯(30mL×2)萃取,合并有机相,无水硫酸钠干燥,过滤,浓缩,得到黄色固体标题化合物粗品8.4g,收率96.3%,直接投入下一步。
第三步:3-(仲丁基)-6-氯嘧啶-2,4(1H,3H)-二酮
于1-(仲丁基)嘧啶-2,4,6(1H,3H,5H)-三酮(8.4g,45.6mmol)和三乙基苄基氯化铵(14.54g,63.85mmol)中加入三氯氧磷(50mL),所得反应液于50℃反应3小时,然后减压浓缩,残留物倒入冰水中,剧烈搅拌30分钟后,乙酸乙酯(30mL×2)萃取,合并有机相,无水硫酸钠干燥,过滤,浓缩,所得残留物经硅胶柱色谱纯化(PE/EA(v/v)=2/1),得到白色固体标题化合物2.8g,收率30.3%。
第四步:3-(仲丁基)-6-(((S)-1-(苯基-d5)乙基)氨基)嘧啶-2,4(1H,3H)-二酮
将(S)-1-(苯基-d5)乙烷-1-胺盐酸盐(361.25mg,2.22mmol)中加入20mL氢氧化钠溶液(1M)并搅拌30min,乙酸乙酯(30mL×2)萃取,无水硫酸钠干燥,过滤,减压浓缩。所得残留物加入3-(仲丁基)-6-氯嘧啶-2,4(1H,3H)-二酮(300mg,1.48mmol)和1,4-二氧六环(10mL)溶液中,反应体系升温至100℃下搅拌过夜。停止反应,反应体系自然降至室温后,减压浓缩,所得残留物经硅胶柱色谱纯化(PE/EA(v/v)=1/1),得到淡黄色固体标题化合物77mg,收率17.78%。
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z:293.2[M+1]
+;
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d
6)δ9.79(s,1H),6.53(s,1H),4.66(s,1H),4.55–4.44(m,1H),4.34(s,1H),1.97–1.85(m,1H),1.65–1.54(m,1H),1.40(d,J=6.7Hz,3H),1.24(d,J=6.8Hz,3H),0.75–0.65(m,3H)。
实施例7 (S)-3-环丁基-6-((1-(苯基-d5)乙基)氨基)嘧啶-2,4(1H,3H)-二酮
第一步:1-环丁基脲
室温下将环丁胺(5g,70.3mmol)溶于二氯甲烷(100mL)中,缓慢滴入异氰酸三甲基硅酯(9.52g,70.3mmol),所得反应液室温搅拌过夜。反应液降温至0℃,缓慢滴入甲醇(40mL)淬灭反应,所得反应液升至室温后继续搅拌1小时,减压浓缩,所得残留物用甲醇/乙醚室温搅拌过夜,过滤,得白色固体标题化合物6.5g,收率81%。
第二步:1-(环丁基)嘧啶-2,4,6(1H,3H,5H)-三酮
室温下,于1-环丁基脲(6.5g,56.94mmol)的甲醇(40mL)溶液中加入甲醇钠的甲醇溶液(28.47mL,142.36mmol)和丙二酸二甲酯(6.83mL,59.79mmol),所得反应液升温至65℃搅拌过夜,自然冷却至室温后,加水淬灭反应,所得反应液减压出去大部分甲醇,水相用1M的盐酸调节至酸性(pH=2),乙酸乙酯(30mL×2)萃取,合并有机相,无水硫酸钠干燥,过滤,浓缩,得到黄色固体标题化合物粗品10g,收率96%,直接投入下一步。
第三步:6-氯-3-环丁基嘧啶-2,4(1H,3H)-二酮
于1-环丁基嘧啶-2,4,6(1H,3H,5H)-三酮(10g,54.89mmol)和三乙基苄基氯化铵(17.5g,76.84mmol)中加入三氯氧磷(50mL),所得反应液于50℃反应3小时,然后减压浓缩,残留物倒入冰水中,剧烈搅拌30分钟后,乙酸乙酯(30mL×2)萃取,合并有机相,无水硫酸钠干燥,过滤,浓缩,所得残留物经硅胶柱色谱纯化(PE/EA(v/v)=2/1),得到黄色固体标题化合物0.8g,收率7.2%。
第四步:(S)-3-环丁基-6-((1-(苯基-d5)乙基)氨基)嘧啶-2,4(1H,3H)-二酮
将(S)-1-(苯基-d5)乙烷-1-胺盐酸盐(300mg,1.84mmol)中加入20mL氢氧化钠溶液(1M)并搅拌30min,乙酸乙酯(30mL×2)萃取,无水硫酸钠干燥,过滤,减压浓缩。所得残留物加入6-氯-3-环丁基嘧啶-2,4(1H,3H)-二酮(444mg,2.21mmol)和1,4-二氧六环(10mL)溶液中,反应体系升温至100℃下搅拌过夜。停止反应,反应体系自然降至室温后,减压浓缩,所得残留物经硅胶柱色谱纯化(PE/EA(v/v)=1/1),得到淡黄色固体标题化合物66mg,收率12.3%。
MS(ESI,pos.ion)m/z:291.2[M+1]
+;
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d
6)δ9.87(s,1H),6.55(d,J=6.4Hz,1H),5.17–5.03(m,1H),4.57–4.44(m,1H),4.34(s,1H),2.90–2.79(m,2H),2.01–1.93(m,2H),1.76–1.65(m,1H),1.65–1.53(m,1H),1.40(d,J=6.7Hz,3H)。
生物试验
实施例A:肌球蛋白抑制测定
试验方法及步骤
牛心肌肌球蛋白具有ATP酶活性,在发生反应过程中,会消耗ATP产生二磷酸腺苷(ADP)并且释放出游离的磷离子。磷离子存在条件下,嘌呤核苷酸磷酸化酶(PNP)将2-氨基-6-巯基-7-甲基嘌呤核苷(MESG)催化成2-氨基-6-巯基-7-甲基嘌呤,并且能够在355nm检测吸光度变化。
在室温条件下,配制牛心肌肌球蛋白反应体系(0.0075mg/mL牛心肌肌球蛋白,0.25mg/mL牛心肌细肌丝复合体,0.6μM ATP,1X 2-氨基-6-巯基-7-甲基嘌呤核苷,1X嘌呤核苷酸磷酸化酶)。待测化合物与上述牛肌球蛋白反应混合液,室温孵育30分钟。30分钟后,加入120μM CaCl
2起始反应使用EnSpire (OD355nM,25℃)进行检测,每间隔30秒读取一次,共40分钟。使用Prism program(GraphPad)进行数据分析。
将本发明化合物按照上述方法进行测试,实验结果如表1所示。
表1本发明化合物对肌球蛋白抑制活性
| 化合物 | 2.5uM(抑制率) | 0.5uM(抑制率) |
| 实施例1 | 48% | 9% |
结论:本发明化合物对牛心肌肌球蛋白的抑制率较高,表明本发明化合物可以有效的抑制肌球蛋白。实施例B药代动力学测试
1.试验方法
实验动物:健康成年雄性SD大鼠(购自湖南斯莱克景达实验动物有限公司)4只,分成两组,一组1只,进行静脉静注给药,一组3只,进行经口灌胃给药。
药物配置:称取一定量的本发明化合物或MYK461,加入10%DMSO,10%Kolliphor HS15和80%saline配置成目标浓度的化合物溶液。
给药与样品采集:动物给药前禁食12h,给药后3h进食,分别通过SD大鼠后肢脚静脉静注给药(IV,1mg/kg)和经口灌胃给药(PO,5mg/kg)。然后分别在时间点0、0.083、0.25、0.5、1、2、4、6、8、24h在大鼠尾静脉采血,采血量约200-400μL/时间点。每个时间点采集全血后,置K
2EDTA抗凝试管中,放于加冰袋的保温箱中保存。所有样品在15min内,于4600r/min,4℃,离心5min,分离得到血浆,使用LC/MS/MS法测定不同化合物给药后大鼠血浆中的浓度,根据药物浓度-时间曲线计算药动学参数。
本发明化合物的药代动力学性质通过以上试验测试。试验结果显示,本发明化合物经静脉注射给药或口服给药后在大鼠体内均表现出优良的药代动力学特征,即本发明化合物具有优良的药代动力学性质,具体地,经静脉注射给药后大鼠体内的药代动力学参数见表2。
2.试验结果
表2本发明化合物的药代动力学活性
结论:由表2可见,与MYK461相比,本发明化合物通过静脉给药后大鼠体内Cmax、AUC
INF及AUC
last水平更高,清除率Cl更低,半衰期T
1/2更长,具有优良的药代动力学特征。
在本说明书的描述中,参考术语“一个实施例”、“一实施方案”、“一些实施例”、“示例”、“具体示例”或“一些示例”等的描述意指结合该实施例、实施方案或示例描述的具体特征、结构、材料或者特点包含于本发明的至少一个实施例、实施方案或示例中。在本说明书中,对上述术语的示意性表述不必须针对的是相同的实施例、实施方案或示例。而且,描述的具体特征、结构、材料或者特点可以在任一个或多个实施例、实施方案或示例中以合适的方式结合。此外,在不相互矛盾的情况下,本领域的技术人员可以将本说明书中描述的不同实施例、实施方案或示例以及不同实施例、实施方案或示例的特征进行结合和组合。
尽管上面已经示出和描述了本发明的实施例,可以理解的是,上述实施例是示例性的,不能理解为对本发明的限制,本领域的普通技术人员在本发明的范围内可以对上述实施例进行变化、修改、替换和变型。
Claims (12)
- 一种化合物,其为式(I)所示的化合物或式(I)所示化合物的立体异构体、几何异构体、互变异构体、氮氧化物、水合物、溶剂化物、代谢产物、药学上可接受的盐或它的前药,其中:R 1为C 1-6烷基、C 3-8环烷基、3-8个原子组成的杂环基、C 6-10芳基或5-10个原子组成的杂芳基;其中,所述C 1-6烷基、C 3-8环烷基、3-8个原子组成的杂环基、C 6-10芳基和5-10个原子组成的杂芳基各自独立地未被取代或被1、2、3或4个R x所取代;R 2为C 1-6烷基、C 3-8环烷基、3-8个原子组成的杂环基、C 6-10芳基或5-10个原子组成的杂芳基;其中,所述C 1-6烷基、C 3-8环烷基、3-8个原子组成的杂环基、C 6-10芳基和5-10个原子组成的杂芳基各自独立地未被取代或被1、2、3或4个R y所取代;各R 3、R 4、R 5和R 6独立地为H、D、F、Cl、Br、I、CN、NO 2、OH、NH 2、SH、C 1-6烷基、C 1-6卤代烷基、C 1-6卤代烷氧基、C 1-6烷氨基、C 1-6烷氧基、-C(=O)R g、-C(=O)OR h、-S(=O) 2R g、-C(=O)NR iR j、-S(=O) 2NR iR j、C 3-8环烷基、3-8个原子组成的杂环基、C 6-10芳基或5-10个原子组成的杂芳基;其中,OH、NH 2、SH、C 1-6烷基、C 1-6卤代烷基、C 1-6卤代烷氧基、C 1-6烷氨基、C 1-6烷氧基、C 3-8环烷基、3-8个原子组成的杂环基、C 6-10芳基和5-10个原子组成的杂芳基各自独立地未被取代或被1、2、3或4个R z所取代;R 7为H、D、F、Cl、Br、I、C 1-6烷基或C 1-6卤代烷基;各R x、R y和R z独立地为D、F、Cl、Br、I、CN、NO 2、OH、NH 2、SH、C 1-6烷基、C 1-6卤代烷基、C 1-6烷氨基、C 3-8环烷基、3-8个原子组成的杂环基、C 6-10芳基、5-10个原子组成的杂芳基、-(CR aR b) nR 0、-OR c、-C(=O)R d、-C(=O)OR c、-S(=O) 2R d、-C(=O)NR eR f或-S(=O) 2NR eR f;各R a和R b独立地为H、C 1-6烷基或C 1-6卤代烷基;各R 0独立地为C 3-8环烷基、3-8个原子组成的杂环基、C 6-10芳基或5-10个原子组成的杂芳基;各R c、R e、R f、R h、R i和R j独立地为H、D、C 1-6烷基、C 1-6卤代烷基、C 3-8环烷基、3-8个原子组成的杂环基、C 6-10芳基或5-10个原子组成的杂芳基;或者,R e、R f和与它们相连的氮原子一起形成3-8个原子组成的杂环基或5-10个原子组成的杂芳基;各R d和R g独立地为H、OH、NH 2、C 1-6烷基、C 1-6卤代烷基、C 1-6烷氨基、C 1-6烷氧基、C 3-8环烷基、3-8个原子组成的杂环基、C 6-10芳基或5-10个原子组成的杂芳基;各n独立地为1、2、3或4。
- 根据权利要求1或2所述的化合物,其中,R 1为C 1-4烷基、C 3-6环烷基、3-6个原子组成的杂环基、苯基或5-6个原子组成的杂芳基;其中,所述C 1-4烷基、C 3-6环烷基、3-6个原子组成的杂环基、苯基和5-6个原子组成的杂芳基各自独立地未被取代或被1、2、3或4个R x所取代;各R 3、R 4、R 5和R 6独立地为H、D、F、Cl、Br、I、CN、NO 2、OH、NH 2、SH、C 1-4烷基、C 1-4卤代烷基、C 1-4卤代烷氧基、C 1-4烷氨基、C 1-4烷氧基、-C(=O)R g、-C(=O)OR h、-S(=O) 2R g、-C(=O)NR iR j、-S(=O) 2NR iR j、C 3-6环烷基、3-6个原子组成的杂环基、C 6-10芳基或5-6个原子组成的杂芳基;其中,OH、NH 2、SH、C 1-4烷基、C 1-4卤代烷基、C 1-4卤代烷氧基、C 1-4烷氨基、C 1-4烷氧基、C 3-6环烷基、3-6个原子组成的杂环基、C 6-10芳基和5-6个原子组成的杂芳基各自独立地未被取代或被1、2、3或4个R z所取代;R 7为H、D、F、Cl、Br、I、C 1-4烷基或C 1-4卤代烷基。
- 根据权利要求1-3任意一项所述的化合物,其中,R 2为C 1-4烷基、C 3-6环烷基、3-6个原子组成的杂环基、苯基或5-6个原子组成的杂芳基;其中,所述C 1-4烷基、C 3-6环烷基、3-6个原子组成的杂环基、苯基和5-6个原子组成的杂芳基各自独立地未被取代或被1、2、3或4个R y所取代。
- 根据权利要求1-4任意一项所述的化合物,其中,R 1为甲基、乙基、正丙基、异丙基、正丁基、叔丁基、环丙基、环丁基、环戊基、环己基、环氧乙基、氮杂环丁基、氧杂环丁基、四氢呋喃基、四氢噻吩基、四氢吡喃基、吡咯烷基、吡唑烷基、咪唑烷基、哌啶基、吗啉基、哌嗪基、苯基、吡咯基、吡唑基、噻吩基、噻唑基、呋喃基、咪唑基、恶唑基、三唑基、四唑基、异恶唑基、吡啶基、嘧啶基、吡嗪基或哒嗪基;其中,甲基、乙基、正丙基、异丙基、正丁基、叔丁基、环丙基、环丁基、环戊基、环己基、环氧乙基、氮杂环丁基、氧杂环丁基、四氢呋喃基、四氢噻吩基、四氢吡喃基、吡咯烷基、吡唑烷基、咪唑烷基、哌啶基、吗啉基、哌嗪基、苯基、吡咯基、吡唑基、噻吩基、噻唑基、呋喃基、咪唑基、恶唑基、三唑基、四唑基、异恶唑基、吡啶基、嘧啶基、吡嗪基和哒嗪基各自独立地未被取代或被1、2、3或4个R x所取代;各R 3、R 4、R 5和R 6独立地为H、D、F、Cl、Br、I、CN、NO 2、OH、NH 2、SH、甲基、乙基、正丙基、异丙基、正丁基、叔丁基、三氟甲基、三氟甲氧基、甲氨基、二甲氨基、甲氧基、乙氧基、-C(=O)R g、-C(=O)OR h、-S(=O) 2R g、-C(=O)NR iR j、-S(=O) 2NR iR j、环丙基、环丁基、环戊基、环己基、环氧乙基、氮杂环丁基、氧杂环丁基、四氢呋喃基、四氢噻吩基、四氢吡喃基、吡咯烷基、吡唑烷基、咪唑烷基、哌啶基、吗啉基、哌嗪基、苯基、吡咯基、吡唑基、噻吩基、噻唑基、呋喃基、咪唑基、恶唑基、三唑基、四唑基、异恶唑基、吡啶基、嘧啶基、吡嗪基或哒嗪基;其中,OH、NH 2、SH、甲基、乙基、正丙基、异丙基、正丁基、叔丁基、甲氨基、二甲氨基、甲氧基、乙氧基、环丙基、环丁基、环戊基、环己基、环氧乙基、氮杂环丁基、氧杂环丁基、四氢呋喃基、四氢噻吩基、四氢吡喃基、吡咯烷基、吡唑烷基、咪唑烷基、哌啶基、吗啉基、哌嗪基、苯基、吡咯基、吡唑基、噻吩基、噻唑基、呋喃基、咪唑基、恶唑基、三唑基、四唑基、异恶唑基、吡啶基、嘧啶基、吡嗪基和哒嗪基各自独立地未被取代或被1、2、3或4个R z所取代;R 7为H、D、F、Cl或Br。
- 根据权利要求1-5任意一项所述的化合物,其中,R 2为甲基、乙基、正丙基、异丙基、正丁基、1- 甲基丙基、叔丁基、环丙基、环丁基、环戊基、环己基、环氧乙基、氮杂环丁基、氧杂环丁基、四氢呋喃基、四氢噻吩基、四氢吡喃基、吡咯烷基、吡唑烷基、咪唑烷基、哌啶基、吗啉基、哌嗪基、苯基、吡咯基、吡唑基、噻吩基、噻唑基、呋喃基、咪唑基、恶唑基、三唑基、四唑基、异恶唑基、吡啶基、嘧啶基、吡嗪基或哒嗪基;其中,所述甲基、乙基、正丙基、异丙基、正丁基、叔丁基、环丙基、环丁基、环戊基、环己基、环氧乙基、氮杂环丁基、氧杂环丁基、四氢呋喃基、四氢噻吩基、四氢吡喃基、吡咯烷基、吡唑烷基、咪唑烷基、哌啶基、吗啉基、哌嗪基、苯基、吡咯基、吡唑基、噻吩基、噻唑基、呋喃基、咪唑基、恶唑基、三唑基、四唑基、异恶唑基、吡啶基、嘧啶基、吡嗪基和哒嗪基各自独立地未被取代或被1、2、3或4个R y所取代。
- 根据权利要求1-6任意一项所述的化合物,其中,各R x、R y和R z独立地为D、F、Cl、Br、I、CN、NO 2、OH、NH 2、-SH、C 1-4烷基、C 1-4卤代烷基、C 1-4烷氨基、C 3-6环烷基、3-6个原子组成的杂环基、苯基、5-6个原子组成的杂芳基、-(CR aR b) nR 0、-OR c、-C(=O)R d、-C(=O)OR c、-S(=O) 2R d、-C(=O)NR eR f或-S(=O) 2NR eR f;各R a和R b独立地为H、C 1-4烷基或C 1-4卤代烷基;各R 0独立地为C 3-6环烷基、3-6个原子组成的杂环基、苯基或5-6个原子组成的杂芳基;各R c、R e、R f、R h、R i和R j独立地为H、D、C 1-4烷基、C 1-4卤代烷基、C 3-6环烷基、3-6个原子组成的杂环基、苯基或5-6个原子组成的杂芳基;或者,R e、R f和与它们相连的氮原子一起形成3-6个原子组成的杂环基或5-6个原子组成的杂芳基;各R d和R g独立地为H、OH、NH 2、C 1-4烷基、C 1-4卤代烷基、C 1-4烷氨基、C 1-4烷氧基、C 3-6环烷基、3-6个原子组成的杂环基、苯基或5-6个原子组成的杂芳基;各n独立地为1、2、3或4。
- 根据权利要求1-7任意一项所述的化合物,其中,各R x、R y和R z独立地为D、F、Cl、Br、I、CN、NO 2、OH、NH 2、-SH、甲基、乙基、正丙基、异丙基、正丁基、叔丁基、三氟甲基、二氟甲基、甲氨基、二甲氨基、环丙基、环丁基、环戊基、环己基、环氧乙基、氮杂环丁基、氧杂环丁基、四氢呋喃基、四氢噻吩基、四氢吡喃基、吡咯烷基、吡唑烷基、咪唑烷基、哌啶基、吗啉基、哌嗪基、苯基、吡咯基、吡唑基、噻吩基、噻唑基、呋喃基、咪唑基、恶唑基、三唑基、四唑基、异恶唑基、吡啶基、嘧啶基、吡嗪基或哒嗪基、-(CR aR b) nR 0、-OR c、-C(=O)R d、-C(=O)OR c、-S(=O) 2R d、-C(=O)NR eR f或-S(=O) 2NR eR f;各R a和R b独立地为H、甲基、乙基、正丙基、异丙基、正丁基、叔丁基或三氟甲基;各R 0独立地为环丙基、环丁基、环戊基、环己基、环氧乙基、氮杂环丁基、氧杂环丁基、四氢呋喃基、四氢噻吩基、四氢吡喃基、吡咯烷基、吡唑烷基、咪唑烷基、哌啶基、吗啉基、哌嗪基、苯基、吡咯基、吡唑基、噻吩基、噻唑基、呋喃基、咪唑基、恶唑基、三唑基、四唑基、异恶唑基、吡啶基、嘧啶基、吡嗪基或哒嗪基;各R c、R e、R f、R h、R i和R j独立地为H、D、甲基、乙基、正丙基、异丙基、正丁基、叔丁基、三氟甲基、二氟甲基、环丙基、环丁基、环戊基、环己基、环氧乙基、氮杂环丁基、氧杂环丁基、四氢呋喃基、四氢噻吩基、四氢吡喃基、吡咯烷基、吡唑烷基、咪唑烷基、哌啶基、吗啉基、哌嗪基、苯基、吡咯基、吡唑基、噻吩基、噻唑基、呋喃基、咪唑基、恶唑基、三唑基、四唑基、异恶唑基、吡啶基、嘧啶基、吡嗪基或哒嗪基;或者,R e、R f和与它们相连的氮原子一起形成3-6个原子组成的杂环基或5-6个原子组成的杂芳基;各R d和R g独立地为H、OH、NH 2、甲基、乙基、正丙基、异丙基、正丁基、叔丁基、三氟甲基、二氟甲基、甲氨基、二甲氨基、甲氧基、乙氧基、环丙基、环丁基、环戊基、环己基、环氧乙基、氮杂环丁基、氧杂环丁基、四氢呋喃基、四氢噻吩基、四氢吡喃基、吡咯烷基、吡唑烷基、咪唑烷基、哌啶基、吗 啉基、哌嗪基、苯基、吡咯基、吡唑基、噻吩基、噻唑基、呋喃基、咪唑基、恶唑基、三唑基、四唑基、异恶唑基、吡啶基、嘧啶基、吡嗪基或哒嗪基;各n独立地为1、2、3或4。
- 一种药物组合物,包含权利要求1-9任意一项所述的化合物,和药学上可接受的赋形剂、载体、佐剂或它们的任意组合。
- 权利要求1-9任意一项所述的化合物或权利要求10所述的药物组合物在制备药物中的用途,其中,所述药物用于预防、治疗或减轻肥厚性心肌病或具有与肥厚性心肌病相关的病理生理学特征的心脏疾病。
- 权利要求1-9任意一项所述的化合物或权利要求10所述的药物组合物在制备药物中的用途,其中,所述药物用于预防、治疗或减轻射血分数保留的舒张性心力衰竭、缺血性心脏病、心绞痛或限制性心肌病。
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US17/425,408 US11851409B2 (en) | 2019-01-25 | 2020-01-19 | Deuterated benzylaminopyrimidinedione derivatives and use thereof |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201910070397 | 2019-01-25 | ||
| CN201910070397.4 | 2019-01-25 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2020151605A1 true WO2020151605A1 (zh) | 2020-07-30 |
Family
ID=70489718
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/CN2020/072904 WO2020151605A1 (zh) | 2019-01-25 | 2020-01-19 | 氘代苯甲氨嘧啶二酮衍生物及其用途 |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US11851409B2 (zh) |
| CN (1) | CN111116492B (zh) |
| WO (1) | WO2020151605A1 (zh) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2022047004A1 (en) * | 2020-08-28 | 2022-03-03 | MyoKardia, Inc. | Methods of treatment with myosin modulator |
| WO2023199258A1 (en) * | 2022-04-13 | 2023-10-19 | Teva Pharmaceuticals International Gmbh | Solid state forms of mavacamten and process for preparation thereof |
Families Citing this family (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TW202227420A (zh) * | 2020-11-20 | 2022-07-16 | 大陸商江蘇恆瑞醫藥股份有限公司 | 三嗪二酮類衍生物、其製備方法及其在醫藥上的應用 |
| CN114539229B (zh) * | 2020-11-24 | 2024-10-22 | 江苏恒瑞医药股份有限公司 | 嘧啶二酮类衍生物、其制备方法及其在医药上的应用 |
| TW202227402A (zh) * | 2020-11-24 | 2022-07-16 | 大陸商江蘇恆瑞醫藥股份有限公司 | 嘧啶二酮類衍生物、其製備方法及其在醫藥上的應用 |
| US20240262804A1 (en) * | 2021-03-17 | 2024-08-08 | Hansoh Bio Llc | Nitrogen-containing heterocyclic ketones, preparation methods and medicinal uses thereof |
| CN118591527A (zh) * | 2022-01-27 | 2024-09-03 | 深圳市康哲生物科技有限公司 | 7-氮杂螺[4,5]癸烷-6,10-二酮类化合物的晶型及其制备方法 |
| WO2024056096A1 (zh) * | 2022-09-16 | 2024-03-21 | 江苏豪森药业集团有限公司 | 一种含氮杂环酮化合物的晶型及其制备方法 |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0369627B1 (en) * | 1988-10-29 | 1994-12-21 | MITSUI TOATSU CHEMICALS, Inc. | Pyrimidinedione derivative compounds, method of producing the same and antiarrythmic agents containing the same |
| WO2004014868A2 (en) * | 2002-08-13 | 2004-02-19 | Warner-Lambert Company Llc | Pyrimidine-2,4-dione derivatives as matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors |
| CN105473576A (zh) * | 2013-06-21 | 2016-04-06 | 迈奥卡迪亚公司 | 针对心脏病症的嘧啶二酮化合物 |
Family Cites Families (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6221335B1 (en) * | 1994-03-25 | 2001-04-24 | Isotechnika, Inc. | Method of using deuterated calcium channel blockers |
| US6440710B1 (en) * | 1998-12-10 | 2002-08-27 | The Scripps Research Institute | Antibody-catalyzed deuteration, tritiation, dedeuteration or detritiation of carbonyl compounds |
| DK1104760T3 (da) * | 1999-12-03 | 2003-06-30 | Pfizer Prod Inc | Sulfamoylheteroarylpyrazolforbindelser som anti-inflammatoriske/analgetiske midler |
| DE10155018A1 (de) * | 2001-11-07 | 2003-07-10 | Berolina Drug Dev Ab Svedala | Deuterierte Pyrazolopyrimidinone sowie diese Verbindungen enthaltende Arzneimittel |
| TW200413273A (en) * | 2002-11-15 | 2004-08-01 | Wako Pure Chem Ind Ltd | Heavy hydrogenation method of heterocyclic rings |
| WO2005028467A1 (en) * | 2003-09-15 | 2005-03-31 | Anadys Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Antibacterial 3,5-diaminopiperidine-substitute aromatic and heteroaromatic compounds |
| JP2009511481A (ja) * | 2005-10-06 | 2009-03-19 | オースペックス・ファーマシューティカルズ・インコーポレイテッド | 増強された治療特性を持つ、胃H+,K+−ATPaseの重水素化阻害剤 |
| US7750168B2 (en) * | 2006-02-10 | 2010-07-06 | Sigma-Aldrich Co. | Stabilized deuteroborane-tetrahydrofuran complex |
| CN103965114B (zh) * | 2013-01-28 | 2016-01-06 | 苏州泽璟生物制药有限公司 | 氘代的苯基氨基嘧啶化合物以及包含该化合物的药物组合物 |
| CN104109149B (zh) * | 2013-04-22 | 2018-09-28 | 苏州泽璟生物制药有限公司 | 氘代的二氨基嘧啶化合物以及包含该化合物的药物组合物 |
| CN105254694B (zh) * | 2014-07-14 | 2018-11-27 | 正大天晴药业集团股份有限公司 | 氘代核苷衍生物 |
| CN108129400B (zh) * | 2017-12-29 | 2021-10-15 | 安帝康(无锡)生物科技有限公司 | 氘代噁拉戈利衍生物及其用途 |
-
2020
- 2020-01-19 US US17/425,408 patent/US11851409B2/en active Active
- 2020-01-19 WO PCT/CN2020/072904 patent/WO2020151605A1/zh active Application Filing
- 2020-01-19 CN CN202010057050.9A patent/CN111116492B/zh active Active
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0369627B1 (en) * | 1988-10-29 | 1994-12-21 | MITSUI TOATSU CHEMICALS, Inc. | Pyrimidinedione derivative compounds, method of producing the same and antiarrythmic agents containing the same |
| WO2004014868A2 (en) * | 2002-08-13 | 2004-02-19 | Warner-Lambert Company Llc | Pyrimidine-2,4-dione derivatives as matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors |
| CN105473576A (zh) * | 2013-06-21 | 2016-04-06 | 迈奥卡迪亚公司 | 针对心脏病症的嘧啶二酮化合物 |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2022047004A1 (en) * | 2020-08-28 | 2022-03-03 | MyoKardia, Inc. | Methods of treatment with myosin modulator |
| WO2023199258A1 (en) * | 2022-04-13 | 2023-10-19 | Teva Pharmaceuticals International Gmbh | Solid state forms of mavacamten and process for preparation thereof |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN111116492A (zh) | 2020-05-08 |
| CN111116492B (zh) | 2021-07-09 |
| US20220089551A1 (en) | 2022-03-24 |
| US11851409B2 (en) | 2023-12-26 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2020151605A1 (zh) | 氘代苯甲氨嘧啶二酮衍生物及其用途 | |
| AU2018256624B2 (en) | JAK2 and ALK2 inhibitors and methods for their use | |
| CA2808959C (en) | Quinoline and quinoxaline derivatives as kinase inhibitors | |
| CA3213029A1 (en) | Parp inhibitor containing piperazine structure, preparation method therefor and pharmaceutical use thereof | |
| EP3720858B1 (en) | Modulators of the beta-3 adrenergic receptor useful for the treatment or prevention of heart failure and disorders related thereto | |
| JP2011526294A (ja) | ホスホジエステラーゼ10阻害剤としての二置換フェニル化合物 | |
| JP2018528182A (ja) | 6−(アリールまたはヘテロアリール)−1,3,5−トリアジン−2,4−ジオール及び6−(アリールまたはヘテロアリール)−1,3,5−トリアジン−2,4−ジアミンを調製する方法 | |
| JP2013520407A (ja) | Nadphオキシダーゼ阻害剤としてのピラゾロピペリジン誘導体 | |
| JP2013519724A (ja) | Nadphオキシダーゼ阻害剤としてのピラゾロピペリジン誘導体 | |
| JPWO2004043936A1 (ja) | Plk阻害剤 | |
| CA3228411A1 (en) | Sulfonamide derivative, preparation method therefor and medical use thereof | |
| CN110240557B (zh) | 吡咯烷酰胺衍生物及其用途 | |
| WO2021227895A1 (zh) | 一种一氧化氮供体型ripasudil衍生物及其制备方法和用途 | |
| CN112142757B (zh) | 五元含氮杂芳基取代的嘧啶二酮类化合物及其用途 | |
| CN108299437B (zh) | 八氢吡咯并[3,4-c]吡咯衍生物及其用途 | |
| WO2020172565A1 (en) | Methods and materials for increasing or maintaining nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyl transferase-2 (nmnat2) polypeptide levels | |
| CN118339149A (zh) | 用于治疗与lpa受体活性相关的病症的化合物和组合物 | |
| US20230312481A1 (en) | Substituted (phthalazin-1-ylmethyl)ureas, substituted n-(phthalazin-1-ylmethyl)amides, and analogues thereof | |
| CN112300165B (zh) | 8-取代的苯乙烯基黄嘌呤衍生物及其用途 | |
| IL314473A (en) | An amide compound as a controller of potassium channels, its preparation and uses | |
| CN116438181A (zh) | 磺酰胺基取代的杂芳基嘧啶二酮类化合物及其用途 | |
| CN111072676A (zh) | 含氮稠合三环衍生物及其用途 | |
| WO2021097781A1 (zh) | 吡啶亚甲基哌啶衍生物及其用途 | |
| CN111018856A (zh) | 8-取代的苯乙烯基黄嘌呤衍生物及其用途 | |
| CN118217290B (zh) | 可溶性鸟苷酸环化酶刺激剂在防治高原肺水肿中的用途 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 20744757 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 20744757 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 20744757 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |