WO2018090598A1 - 变速箱油温度调节系统、热交换组件及阀组件 - Google Patents
变速箱油温度调节系统、热交换组件及阀组件 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2018090598A1 WO2018090598A1 PCT/CN2017/086525 CN2017086525W WO2018090598A1 WO 2018090598 A1 WO2018090598 A1 WO 2018090598A1 CN 2017086525 W CN2017086525 W CN 2017086525W WO 2018090598 A1 WO2018090598 A1 WO 2018090598A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- interface
- valve
- heat exchange
- passage
- notch
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F01—MACHINES OR ENGINES IN GENERAL; ENGINE PLANTS IN GENERAL; STEAM ENGINES
- F01M—LUBRICATING OF MACHINES OR ENGINES IN GENERAL; LUBRICATING INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES; CRANKCASE VENTILATING
- F01M5/00—Heating, cooling, or controlling temperature of lubricant; Lubrication means facilitating engine starting
- F01M5/002—Cooling
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F01—MACHINES OR ENGINES IN GENERAL; ENGINE PLANTS IN GENERAL; STEAM ENGINES
- F01M—LUBRICATING OF MACHINES OR ENGINES IN GENERAL; LUBRICATING INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES; CRANKCASE VENTILATING
- F01M5/00—Heating, cooling, or controlling temperature of lubricant; Lubrication means facilitating engine starting
- F01M5/005—Controlling temperature of lubricant
- F01M5/007—Thermostatic control
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16H—GEARING
- F16H57/00—General details of gearing
- F16H57/04—Features relating to lubrication or cooling or heating
- F16H57/0412—Cooling or heating; Control of temperature
- F16H57/0415—Air cooling or ventilation; Heat exchangers; Thermal insulations
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16K—VALVES; TAPS; COCKS; ACTUATING-FLOATS; DEVICES FOR VENTING OR AERATING
- F16K11/00—Multiple-way valves, e.g. mixing valves; Pipe fittings incorporating such valves
- F16K11/02—Multiple-way valves, e.g. mixing valves; Pipe fittings incorporating such valves with all movable sealing faces moving as one unit
- F16K11/06—Multiple-way valves, e.g. mixing valves; Pipe fittings incorporating such valves with all movable sealing faces moving as one unit comprising only sliding valves, i.e. sliding closure elements
- F16K11/065—Multiple-way valves, e.g. mixing valves; Pipe fittings incorporating such valves with all movable sealing faces moving as one unit comprising only sliding valves, i.e. sliding closure elements with linearly sliding closure members
- F16K11/07—Multiple-way valves, e.g. mixing valves; Pipe fittings incorporating such valves with all movable sealing faces moving as one unit comprising only sliding valves, i.e. sliding closure elements with linearly sliding closure members with cylindrical slides
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16K—VALVES; TAPS; COCKS; ACTUATING-FLOATS; DEVICES FOR VENTING OR AERATING
- F16K17/00—Safety valves; Equalising valves, e.g. pressure relief valves
- F16K17/02—Safety valves; Equalising valves, e.g. pressure relief valves opening on surplus pressure on one side; closing on insufficient pressure on one side
- F16K17/04—Safety valves; Equalising valves, e.g. pressure relief valves opening on surplus pressure on one side; closing on insufficient pressure on one side spring-loaded
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16K—VALVES; TAPS; COCKS; ACTUATING-FLOATS; DEVICES FOR VENTING OR AERATING
- F16K17/00—Safety valves; Equalising valves, e.g. pressure relief valves
- F16K17/02—Safety valves; Equalising valves, e.g. pressure relief valves opening on surplus pressure on one side; closing on insufficient pressure on one side
- F16K17/04—Safety valves; Equalising valves, e.g. pressure relief valves opening on surplus pressure on one side; closing on insufficient pressure on one side spring-loaded
- F16K17/048—Safety valves; Equalising valves, e.g. pressure relief valves opening on surplus pressure on one side; closing on insufficient pressure on one side spring-loaded combined with other safety valves, or with pressure control devices
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16K—VALVES; TAPS; COCKS; ACTUATING-FLOATS; DEVICES FOR VENTING OR AERATING
- F16K31/00—Actuating devices; Operating means; Releasing devices
- F16K31/002—Actuating devices; Operating means; Releasing devices actuated by temperature variation
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16K—VALVES; TAPS; COCKS; ACTUATING-FLOATS; DEVICES FOR VENTING OR AERATING
- F16K49/00—Means in or on valves for heating or cooling
- F16K49/005—Circulation means for a separate heat transfer fluid
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16L—PIPES; JOINTS OR FITTINGS FOR PIPES; SUPPORTS FOR PIPES, CABLES OR PROTECTIVE TUBING; MEANS FOR THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16L53/00—Heating of pipes or pipe systems; Cooling of pipes or pipe systems
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F28—HEAT EXCHANGE IN GENERAL
- F28D—HEAT-EXCHANGE APPARATUS, NOT PROVIDED FOR IN ANOTHER SUBCLASS, IN WHICH THE HEAT-EXCHANGE MEDIA DO NOT COME INTO DIRECT CONTACT
- F28D1/00—Heat-exchange apparatus having stationary conduit assemblies for one heat-exchange medium only, the media being in contact with different sides of the conduit wall, in which the other heat-exchange medium is a large body of fluid, e.g. domestic or motor car radiators
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F28—HEAT EXCHANGE IN GENERAL
- F28D—HEAT-EXCHANGE APPARATUS, NOT PROVIDED FOR IN ANOTHER SUBCLASS, IN WHICH THE HEAT-EXCHANGE MEDIA DO NOT COME INTO DIRECT CONTACT
- F28D9/00—Heat-exchange apparatus having stationary plate-like or laminated conduit assemblies for both heat-exchange media, the media being in contact with different sides of a conduit wall
- F28D9/0031—Heat-exchange apparatus having stationary plate-like or laminated conduit assemblies for both heat-exchange media, the media being in contact with different sides of a conduit wall the conduits for one heat-exchange medium being formed by paired plates touching each other
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F28—HEAT EXCHANGE IN GENERAL
- F28D—HEAT-EXCHANGE APPARATUS, NOT PROVIDED FOR IN ANOTHER SUBCLASS, IN WHICH THE HEAT-EXCHANGE MEDIA DO NOT COME INTO DIRECT CONTACT
- F28D9/00—Heat-exchange apparatus having stationary plate-like or laminated conduit assemblies for both heat-exchange media, the media being in contact with different sides of a conduit wall
- F28D9/0031—Heat-exchange apparatus having stationary plate-like or laminated conduit assemblies for both heat-exchange media, the media being in contact with different sides of a conduit wall the conduits for one heat-exchange medium being formed by paired plates touching each other
- F28D9/0043—Heat-exchange apparatus having stationary plate-like or laminated conduit assemblies for both heat-exchange media, the media being in contact with different sides of a conduit wall the conduits for one heat-exchange medium being formed by paired plates touching each other the plates having openings therein for circulation of at least one heat-exchange medium from one conduit to another
- F28D9/005—Heat-exchange apparatus having stationary plate-like or laminated conduit assemblies for both heat-exchange media, the media being in contact with different sides of a conduit wall the conduits for one heat-exchange medium being formed by paired plates touching each other the plates having openings therein for circulation of at least one heat-exchange medium from one conduit to another the plates having openings therein for both heat-exchange media
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F28—HEAT EXCHANGE IN GENERAL
- F28F—DETAILS OF HEAT-EXCHANGE AND HEAT-TRANSFER APPARATUS, OF GENERAL APPLICATION
- F28F27/00—Control arrangements or safety devices specially adapted for heat-exchange or heat-transfer apparatus
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F28—HEAT EXCHANGE IN GENERAL
- F28F—DETAILS OF HEAT-EXCHANGE AND HEAT-TRANSFER APPARATUS, OF GENERAL APPLICATION
- F28F27/00—Control arrangements or safety devices specially adapted for heat-exchange or heat-transfer apparatus
- F28F27/02—Control arrangements or safety devices specially adapted for heat-exchange or heat-transfer apparatus for controlling the distribution of heat-exchange media between different channels
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F28—HEAT EXCHANGE IN GENERAL
- F28F—DETAILS OF HEAT-EXCHANGE AND HEAT-TRANSFER APPARATUS, OF GENERAL APPLICATION
- F28F9/00—Casings; Header boxes; Auxiliary supports for elements; Auxiliary members within casings
- F28F9/02—Header boxes; End plates
- F28F9/0246—Arrangements for connecting header boxes with flow lines
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F28—HEAT EXCHANGE IN GENERAL
- F28F—DETAILS OF HEAT-EXCHANGE AND HEAT-TRANSFER APPARATUS, OF GENERAL APPLICATION
- F28F9/00—Casings; Header boxes; Auxiliary supports for elements; Auxiliary members within casings
- F28F9/02—Header boxes; End plates
- F28F9/04—Arrangements for sealing elements into header boxes or end plates
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G05—CONTROLLING; REGULATING
- G05D—SYSTEMS FOR CONTROLLING OR REGULATING NON-ELECTRIC VARIABLES
- G05D23/00—Control of temperature
- G05D23/01—Control of temperature without auxiliary power
- G05D23/02—Control of temperature without auxiliary power with sensing element expanding and contracting in response to changes of temperature
- G05D23/021—Control of temperature without auxiliary power with sensing element expanding and contracting in response to changes of temperature the sensing element being a non-metallic solid, e.g. elastomer, paste
- G05D23/022—Control of temperature without auxiliary power with sensing element expanding and contracting in response to changes of temperature the sensing element being a non-metallic solid, e.g. elastomer, paste the sensing element being placed within a regulating fluid flow
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G05—CONTROLLING; REGULATING
- G05D—SYSTEMS FOR CONTROLLING OR REGULATING NON-ELECTRIC VARIABLES
- G05D23/00—Control of temperature
- G05D23/01—Control of temperature without auxiliary power
- G05D23/02—Control of temperature without auxiliary power with sensing element expanding and contracting in response to changes of temperature
- G05D23/024—Control of temperature without auxiliary power with sensing element expanding and contracting in response to changes of temperature the sensing element being of the rod type, tube type, or of a similar type
- G05D23/025—Control of temperature without auxiliary power with sensing element expanding and contracting in response to changes of temperature the sensing element being of the rod type, tube type, or of a similar type the sensing element being placed within a regulating fluid flow
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16H—GEARING
- F16H2700/00—Transmission housings and mounting of transmission components therein; Cooling; Lubrication; Flexible suspensions, e.g. floating frames
- F16H2700/02—Transmissions, specially for working vehicles
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16H—GEARING
- F16H57/00—General details of gearing
- F16H57/04—Features relating to lubrication or cooling or heating
- F16H57/0412—Cooling or heating; Control of temperature
- F16H57/0413—Controlled cooling or heating of lubricant; Temperature control therefor
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16H—GEARING
- F16H57/00—General details of gearing
- F16H57/04—Features relating to lubrication or cooling or heating
- F16H57/0412—Cooling or heating; Control of temperature
- F16H57/0415—Air cooling or ventilation; Heat exchangers; Thermal insulations
- F16H57/0417—Heat exchangers adapted or integrated in the gearing
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F28—HEAT EXCHANGE IN GENERAL
- F28D—HEAT-EXCHANGE APPARATUS, NOT PROVIDED FOR IN ANOTHER SUBCLASS, IN WHICH THE HEAT-EXCHANGE MEDIA DO NOT COME INTO DIRECT CONTACT
- F28D21/00—Heat-exchange apparatus not covered by any of the groups F28D1/00 - F28D20/00
- F28D2021/0019—Other heat exchangers for particular applications; Heat exchange systems not otherwise provided for
- F28D2021/008—Other heat exchangers for particular applications; Heat exchange systems not otherwise provided for for vehicles
- F28D2021/0089—Oil coolers
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F28—HEAT EXCHANGE IN GENERAL
- F28F—DETAILS OF HEAT-EXCHANGE AND HEAT-TRANSFER APPARATUS, OF GENERAL APPLICATION
- F28F2230/00—Sealing means
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F28—HEAT EXCHANGE IN GENERAL
- F28F—DETAILS OF HEAT-EXCHANGE AND HEAT-TRANSFER APPARATUS, OF GENERAL APPLICATION
- F28F2250/00—Arrangements for modifying the flow of the heat exchange media, e.g. flow guiding means; Particular flow patterns
- F28F2250/06—Derivation channels, e.g. bypass
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F28—HEAT EXCHANGE IN GENERAL
- F28F—DETAILS OF HEAT-EXCHANGE AND HEAT-TRANSFER APPARATUS, OF GENERAL APPLICATION
- F28F9/00—Casings; Header boxes; Auxiliary supports for elements; Auxiliary members within casings
- F28F9/007—Auxiliary supports for elements
- F28F9/0075—Supports for plates or plate assemblies
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F28—HEAT EXCHANGE IN GENERAL
- F28F—DETAILS OF HEAT-EXCHANGE AND HEAT-TRANSFER APPARATUS, OF GENERAL APPLICATION
- F28F9/00—Casings; Header boxes; Auxiliary supports for elements; Auxiliary members within casings
- F28F9/02—Header boxes; End plates
- F28F9/0246—Arrangements for connecting header boxes with flow lines
- F28F9/0251—Massive connectors, e.g. blocks; Plate-like connectors
- F28F9/0253—Massive connectors, e.g. blocks; Plate-like connectors with multiple channels, e.g. with combined inflow and outflow channels
Definitions
- the invention relates to the field of fluid control, and in particular to a transmission oil temperature regulation system, a heat exchange assembly and a valve assembly.
- the parts of the car need to be lubricated with lubricating oil in time to ensure the normal operation of the car. If the lubricating oil is not well lubricated, it will affect the service life of the car.
- the lubricating properties of lubricating oils are strongly related to their own temperatures. When the lubricating oil temperature is too high or too low, the lubricating properties of the lubricating oil will be affected.
- Lubricating oil temperature is generally not too high during normal driving.
- the vehicle may drive under the transitional slip condition of the torque converter, which may cause the gearbox.
- the oil temperature is too high, thus losing lubrication.
- the existing transmission oil mainly realizes the temperature adjustment function through a cooling flow path composed of a temperature control valve and an external cooling device.
- the existing temperature regulating valve needs to be connected to the external cooling device through the pipeline, so that the arrangement of the components is complicated, the space is large, and the risk of leakage is also large.
- the present invention provides a heat exchange assembly including a heat exchange core, a mounting plate fixed to the heat exchange core, and the heat exchange assembly further includes An interface, a second interface, a third interface, and a fourth interface, the heat exchange core body includes an end plate, and the heat exchange core further includes a first flow path and a second flow path separated from each other, wherein the first The first channel is in communication with the first interface and the second interface, and the second channel is in communication with the third interface and the fourth interface, the second channel includes a first channel and a second channel,
- the heat exchange core further includes a through passage penetrating the heat exchange core, the mounting plate is provided with a connecting passage connecting the through passage and the fourth interface, and the second passage runs through The heat exchange core and one end of the second passage is in communication with the fourth interface;
- the heat exchange assembly further includes a valve assembly and an adapter, the adapter is provided with a cavity opposite to the second passage and a fifth interface communicating with the cavity, the adapter further Provided with a sixth interface in communication with the through passage, the valve assembly being disposed or partially disposed in the second passage, the valve assembly including a main valve body and a thermal component mounted in the main valve body One end of the main valve body is sealingly mounted with an inner wall of the fifth interface, and one end of the main valve body is sealingly mounted with an inner wall of the fourth interface or the second passage, the main valve body a side wall is provided with a first gap, a first valve port is disposed in the main valve body, and the first valve port is located between the first notch and the fourth interface, and is close to or through the thermal component Far from the first valve port, the first valve port is not connected or connected to the fourth interface;
- the third interface is sequentially connected to the fourth interface through the first passage, the second passage, the first notch and the first valve port;
- the third interface is in communication with the fifth interface through the first channel, the second channel and the first gap.
- the heat exchange assembly of the present invention integrates a valve assembly, so that the heat exchange assembly has both a heat exchange function and a fluid flow adjustment and switching function, and has a compact structure and a small volume, which can improve the miniaturization and integration of the transmission oil cooling system.
- Figure 1 is a perspective view showing the structure of a valve assembly in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 2 is a cross-sectional structural view of the valve assembly of FIG. 1 with the first valve port closed and the second valve port opened.
- FIG. 3 is a cross-sectional structural view of the valve assembly of FIG. 1 when the second valve port is closed and the first valve port is opened.
- FIG. 4 is a cross-sectional view showing the main valve body of the valve assembly shown in FIG. 1.
- Figure 5 is a perspective view of the upper valve sleeve of the valve assembly of Figure 1.
- Figure 6 is a perspective view showing the structure of the support cap of the valve assembly shown in Figure 1.
- Figure 7 is a perspective view of the lower valve sleeve of the valve assembly of Figure 1.
- Figure 8 is a schematic cross-sectional view of the lower valve sleeve of Figure 7.
- Figure 9 is a perspective view of an embodiment of a heat exchange assembly with a valve assembly of the present invention.
- Figure 10 is a cross-sectional view of Figure 9.
- Figure 11 is a partial enlarged view of the valve assembly portion of Figure 10.
- Figure 12 is a schematic illustration of the operation of a transmission oil temperature adjustment system having the heat exchange assembly of Figure 9 at low temperatures of the cooling oil.
- Figure 13 is a schematic illustration of the operation of a transmission oil temperature adjustment system having the heat exchange assembly of Figure 9 at a high temperature of the cooling oil.
- Figure 14 is a perspective schematic view of yet another embodiment of a heat exchange assembly of the present invention having a valve assembly mounted thereon.
- Figure 15 is a schematic illustration of the operation of a transmission oil temperature adjustment system having the heat exchange assembly of Figure 14 at low temperatures of the cooling oil.
- Figure 16 is a schematic illustration of the operation of a transmission oil temperature adjustment system having the heat exchange assembly of Figure 14 at a high temperature of the cooling oil.
- the initial deformation force described in this specification refers to the pressure generated when a spring in a compressed state when the product is not in use is deformed by an external force.
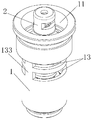
- the valve assembly includes a hollow main valve body 1 and a thermal element 6 mounted in the main valve body 1. Both ends of the main valve body 1 are opened, and an upper valve sleeve 2 and a lower valve sleeve 3 are fixedly attached to both ends of the main valve body 1 respectively.
- a first spring 4 and a second spring are also disposed in the main valve body 1.
- the spring 5 has one end of the first spring 4 abutting against the lower valve sleeve 3, the other end of the first spring 4 abutting one end of the thermal element 6, and one end of the second spring 5 abuts the other end of the thermal element 6.
- the other end of the second spring 5 abuts against the upper valve sleeve 2.
- the first spring 4 and the second spring 5 are in a compressed state, so that the thermal element 6 is fixed in the main valve body 1.
- the two ends of the main valve body 1 are respectively provided with a first opening 11 and a second opening 12, wherein the inner diameter of the first opening 11 is larger than the inner diameter of the second opening 12, and the inner wall of the second opening 12 is disposed inside. Thread.
- the main valve body 1 is further provided with a receiving cavity 15 between the first opening 11 and the second opening 12, the inner diameter of the receiving cavity 15 being smaller than the inner diameter of the first opening 11, in the first opening 11 and the receiving cavity 15 A step portion is formed therebetween, and an inner diameter of the second opening 12 is smaller than an inner diameter of the accommodating chamber 15, and a step portion is formed between the accommodating chamber 15 and the second opening 12.
- a first notch 13 is defined in a side wall of the main valve body 1 corresponding to the accommodating cavity 15, and the first notch 13 is located above the lower valve sleeve 3.
- the first notch 13 is adjacent to the first opening 11 and accommodates A step portion is formed between the cavities 15.
- the first notch 13 includes the first sub-gap 131 and the second sub-gap 132, and at the same time, the first sub-gap 131 and the second sub-gap
- a ring-shaped connecting portion 14 is provided between the notches 132, wherein the ring-shaped connecting portion 14 may be a part of a side wall of the main valve body 1.
- the ring-shaped connecting portion 14 is not provided, when the first notch 13 is large, the side wall of the main valve body 13 corresponding to the portion of the first notch 13 is the connecting post 133, so that the stability of the main valve body 1 is low.
- the stability of the main valve body 1 can be preferably improved.
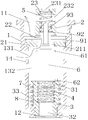
- the upper valve sleeve 2 has a cap-like structure, and the upper valve sleeve 2 includes a support portion 21 having a larger outer diameter and a main body portion 20 having a smaller outer diameter than the support portion 21, the outer wall of the main body portion A certain distance is maintained between the inner walls of the receiving chamber to form a fluid passage.
- a cavity is disposed in the main body portion 20, and the second spring 5 is received in the cavity of the main body portion 20.
- a support cap 93 is further disposed in the cavity of the main body portion 20. The support cap 93 is fixed by the second buckle 92.
- the support portion 21 is further provided with a second valve port 211, which is opposite to and communicates with the cavity of the main body portion 20, and the second valve port 211 may be a part of the cavity.
- the main body portion 20 is provided with a second notch 22 near the support portion 21, wherein the second notch 22 is located below the support cap 93, and the second notch 22 is in communication with the second valve port 211.
- the flow area of the second notch 22 is still not large enough, resulting in a large decrease in flow resistance.
- the flow area of the fluid flowing out of the upper valve sleeve is increased.
- at least one notch 932 may be opened in the extension portion 931 of the support cap 93. .
- a fluid passage is formed between the notch 932 and the inner wall of the upper valve sleeve 2.
- a third notch 232 may be formed in the upper end portion of the support cap 93 of the main body portion 20 of the upper valve sleeve 2, and a portion of the fluid can pass through the notch 932 and the inner wall of the upper valve sleeve 2 after passing through the second valve port 211. The fluid passage formed between them flows out of the upper valve sleeve 2 through the third gap 232.
- the stroke of the support cap 93 is prevented from intersecting with the third notch 232, and the third notch 232 may be located at the maximum stroke of the extension cap 931 when the support cap 93 compresses the movement of the second spring 5.
- a third opening 231 is further opened in the bottom portion 23 of the main body portion 20, so that the resistance of the fluid flowing out of the upper valve sleeve 2 is further lowered.
- the fluid can flow out of the upper valve sleeve 2 more smoothly, and the flow resistance of the fluid flowing out of the upper valve sleeve 2 can be reduced.
- the support portion 21 of the upper valve sleeve 2 is in contact with a step formed between the first opening 11 and the accommodating cavity 15, and the upper valve sleeve 2 can be fixed by the first buckle 91, and the support portion and the first portion A gap fits between the inner walls of an opening.
- the upper valve sleeve 2 can also be fixed by other means (for example, riveting, screwing, etc.).
- a seal ring may be provided between the support portion 21 and the inner wall of the accommodating chamber 15.
- the first notch 13 can communicate with the second notch, the third notch, and the third opening through the second valve port 211, respectively.
- a portion of the lower valve sleeve 3 is located in the receiving chamber 15, and another portion of the lower valve sleeve 3 is located in the second opening 12 and is threadedly coupled to the inner wall of the second opening 12.
- the lower valve sleeve 3 includes a valve seat portion 34, a spring support seat 33, a fitting portion 35, and a through hole 32 penetrating the lower valve sleeve 3, and the valve seat portion 34 is provided with a first valve penetrating the valve seat portion.
- the port 31, the first valve port 31 may be a part of the through hole 32, and the first valve port is relatively far from the first opening with respect to the first notch.
- the fitting portion 35 is provided with an external thread which can be engaged with the internal thread of the second opening 12 of the main valve body 1, so that the lower valve sleeve 3 is fixedly mounted.
- a recessed spring support is also provided.
- the concave portion 37 of the portion 33 may have a polygonal structure or a plurality of concave structures, and is not limited herein.
- a fourth notch 36 is further provided between the spring support portion 33 and the valve seat portion 34.
- the fourth notch 36 is in communication with the through hole 32 corresponding to the fitting portion 35, that is, the fluid passing through the fourth notch 36 can flow out of the lower valve sleeve 3 through the lower port of the through hole 32.
- the fitting portion 35 of the lower valve sleeve 3 is fixed to the second opening 12 of the main valve body 1 by screwing.
- One end of the first spring 4 abuts against the thermal element 6, and the other end abuts against the spring support seat 33.
- the outer diameter of the valve seat portion 34 is larger than the outer diameter of the other portion of the lower valve sleeve 3, and the outer diameter of the valve seat portion 34 is smaller than the inner diameter of the accommodating chamber 15, and the outer wall of the valve seat portion 34 and the inner wall corresponding to the accommodating chamber 15 A passage for fluid flow is formed.
- a pressure relief ring 7 and a third spring 8 are further disposed in the accommodating chamber 15, and the pressure relief ring is provided with a through hole through which the pressure relief ring is sleeved on the lower valve sleeve, The inner diameter of the through hole is smaller than the outer diameter of the valve seat portion, so that the pressure releasing ring 7 can abut against the valve seat portion 34, and the pressure releasing ring 7 is slidably engaged with the inner wall corresponding to the receiving chamber 15.
- One end of the third spring 8 abuts against the pressure relief ring 7, the other end abuts against the step formed between the accommodation chamber 15 and the second opening 12, and the third spring 8 is in a compressed state.
- the pressure relief ring 7 abuts against the valve seat portion 34 under the action of the third spring 8, and the passage for fluid flow formed between the outer wall of the valve seat portion 34 and the inner wall corresponding to the accommodating chamber 15 is vented.
- the pressure ring 7 is closed, and the passage for fluid flow formed between the outer wall of the valve seat portion 34 and the inner wall corresponding to the accommodating chamber 15 cannot communicate with the fourth gap 36.
- the thermal element 6 includes a first valve body 62 and a second valve core 61.
- the first valve core 62 corresponds to the first valve port 31, and can be opened and closed by the first valve core 62.
- a valve port 31, the second valve body 61 corresponds to the second valve port 211, and the second valve port 211 can be opened and closed by the second valve core 61.
- the initial elastic deformation force of the second spring 5 is greater than the elastic deformation force of the first spring when the first valve port 31 is closed, so that if the first valve opening 31 is closed, if the flow flows from the first notch 13
- the ejector rod of the thermal element 6 can start to move upward to compress the second spring 5, thereby preventing the heat-sensitive substance from over-expanding to make the kinetic element 6 damaged.
- the valve assembly of this embodiment includes at least two states: 1.
- the first valve port is open, the second valve port is closed, 2, the first valve port is closed, and the second valve port is open.
- the first valve body 62 of the thermal element 6 is away from the first valve port 31 by the restoring force of the first spring 4, at which time the first valve port 31 is opened.
- the second valve port 211 is closed, and after flowing in from the first notch 13, the fluid can flow out through the first valve port 31, the through hole 32 and the second opening 12 in sequence; when the temperature of the fluid flowing from the first notch 13 is high, The thermal element 6 is thermally expanded, the first spool 62 moves downward to compress the first spring 4 until the first valve port 31 is closed, and then if the thermodynamic element 6 continues to expand, the valve stem moves upward to compress the second spring 5,
- the first valve port is closed and the second valve port is opened, after the fluid flows in from the first notch 13, a part of the fluid can flow out through the second valve port 211, the second notch 22 and the first opening 11, and a part of the fluid can pass through the first step.
- the second valve port 211, the third notch 232, and the third opening 231 flow out.
- the second spring may not be provided. At this time, one end of the stem of the thermal element extending beyond the thermal element abuts or is fixed to the upper valve sleeve. In the present embodiment, the provision of the second spring can act as a buffer to prevent excessive expansion and damage of the thermal element.
- a pressure relief state is further included.
- the first valve port 31 is closed, if the external device or the pipeline after the fluid flows out of the valve assembly is blocked, the fluid cannot flow out of the valve assembly, so that the pressure of the fluid is greater than the third.
- the spring is initially elastically deformed, the pressure relief ring 7 moves downward, and the pressure relief ring 7 moves downward to compress the third spring 8, when the pressure relief ring 7 moves downward to intersect the fourth notch 36 or is located at the fourth notch 36.
- the fluid sequentially flows through the passage between the outer wall of the valve seat portion 34 and the inner wall corresponding to the accommodating chamber 15 to allow the fluid to flow, the fourth notch 36, the through hole 32, and the second opening 12.
- the lower valve sleeve 3 can be integrated with the main valve body 1 at this time, that is, the valve seat portion 34 and the spring support seat 33 in the lower valve sleeve 3 are part of the main valve body 1,
- the end of the second opening 12 corresponding to the step between the second opening 12 and the receiving cavity 15 may serve as a first valve port, and a spring support seat 33 may be disposed in the second opening 12.
- the heat exchange assembly includes a heat exchange core 10, a mounting plate 101 fixed to the heat exchange core, an adapter, and a One The interface 1041, the second interface 1042, the third interface 1011, and the fourth interface 1012.
- the heat exchange core 10 includes an end plate 102, and first and second flow paths that are isolated from each other, and the fluid flowing in the first flow path and the fluid flowing in the second flow path can be heat exchanged.
- the first flow channel is in communication with the first interface 1041 and the second interface 1042
- the second flow channel is in communication with the third interface 1011 and the fourth interface 1012.
- the first interface 1041 and the second interface 1042 are in communication with the external system in the form of a takeover.
- the third interface 1011 and the fourth interface 1012 are formed on the mounting board 101.
- the third interface 1011 and the fourth interface 1012 extend through the mounting board 101. This allows the mounting board to be directly fixed to the gearbox, which is convenient to install and has less risk of leakage.
- a seal ring 1013 and a seal ring 1014 are respectively disposed on the outer peripheral sides of the third port 1011 and the fourth port 1012 of the mounting plate 101.
- the second flow path includes a first channel 1051 and a second channel 1052.
- One end of the first channel 1051 is in communication with the third interface 1011, and the other end of the first channel 1051 is blocked by the end plate 102.
- One end of the second channel 1052 is The fourth interface 1012 is in communication, and the other end of the second channel 1052 is in communication with the adapter.
- the adapter includes a first adapter 1031 and a second adapter 1032.
- the first adapter 1031 includes a receiving cavity 1034 and a fifth interface 1033 that communicates with the receiving cavity 1034.
- the second adapter 1032 includes a seat body 1036.
- the seat body 1036 defines a cavity penetrating the seat body 1036.
- the inner wall of the seat body 1036 corresponding to the cavity of the seat body 1036 is formed with a step 1035.
- the second adapter 1032 is fixed to the end plate 102, for example, by welding, screwing or the like. Also, the cavity penetrating the seat body 1036 corresponds to the second passage 1052.
- the first adapter 1031 and the second adapter 1032 are fixed by screwing or the like, and the cavity of the through-body 1036 corresponds to the receiving cavity 1034, and the fifth interface 1033 can pass through the receiving cavity 1034 and the through-body 1036. At least a portion of the cavity is in communication.
- the first adapter and the second adapter are fixedly connected by screws.
- a sealing ring may be disposed between the sealing surfaces of the first adapter 1031 and the second adapter 1032.
- the valve assembly is disposed in the second passage 1052, and at least a portion of the valve assembly is located in the second passage 1052. In this embodiment, at least a portion is located within the adapter.
- the valve assembly is secured by providing a snap ring 1037 in the second adapter 1032 to limit axial displacement of the valve assembly.
- the main valve body 1 includes a first mating portion 161 whose outer diameter gradually decreases, and a second match.
- the first engaging portion 161 is clearance-fitted with the inner wall of the seat body 1036 corresponding to the cavity of the through-body 1036, and the step formed between the first mating portion 161 and the second mating portion 162 and the cavity of the through-body 1036 The step 1035 formed by the inner wall of the corresponding seat body 1036 abuts.
- the second mating portion 162 is also gap-fitted with the inner wall of the seat body 1036 corresponding to the cavity of the through-body 1036, and the second mating portion 162 can also be disposed between the inner wall of the seat body 1036 corresponding to the cavity of the through-body 1036. There are seals to improve sealing performance and reduce internal leakage.
- the problem that the fluid is not uniformly distributed by the valve assembly during the flow from the first passage 1051 to the second passage 1052 is prevented, and the second fitting portion 162 is away from the first transfer.
- the end face of the seat 1031 does not exceed the end plate 102, and the outer diameter of the third mating portion 163 is smaller than the inner diameter of the second passage 1052, so that when the fluid flows from the inter-plate passage into the second passage 1052, all the inter-plate passages are absolutely large.
- the end of the third engaging portion 163 remote from the first adapter seat 1031 is located below the second valve port 211, and the end portion is formed usefully.
- the shoulder of the support portion 21 of the upper valve sleeve 2 is supported.
- the flow guiding portion 164 is located between the third mating portion 163 and the fourth mating portion 165, and the flow guiding portion 164 is located in the second passage 1052.
- the outer diameter of the guiding portion 164 is smaller than the outer diameter of the third mating portion 163.
- the difference between the outer diameter of the flow guiding portion 164 and the inner diameter of the second passage 1052 is greater than the difference between the outer diameter of the third fitting portion 163 and the inner diameter of the second passage 1052.
- the first notch is located in the flow guiding portion 164 and can also facilitate fluid flow into the valve assembly.
- the fourth engaging portion 165 extends into the fourth interface 1012, and the fourth engaging portion 165 is clearance-fitted with the fourth interface 1012.
- the inner diameter of the fourth interface is smaller than the inner diameter of the second passage, and the flow guiding portion 164 and the fourth engaging portion 165
- the shoulder formed therebetween abuts or abuts the mounting plate.
- a sealing ring may be disposed between the fourth fitting portion 165 and the fourth interface 1012.
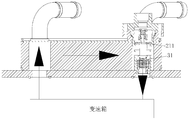
- FIG. 12 and 13 illustrate a transmission oil temperature adjustment system having the above described heat exchange assembly, the transmission oil temperature adjustment system including a transmission, a heat exchange assembly, an oil cooler, and an engine water tank (figure Not shown), wherein the first interface and the second interface of the heat exchange assembly are in communication with the engine water tank via a conduit, and the third interface and the fourth interface are in communication with the inlet and outlet of the transmission either directly or through a conduit.
- One of the flow passages of the oil cooler is in communication with the fifth port of the heat exchange assembly and the inlet of the transmission through the conduit, and the other flow passage of the oil cooler can be in communication with a refrigeration system (not shown).
- a valve port 31 is in an open state, and the second valve port 211 is in a closed state.
- the cooling oil can pass through the first valve port 31 and flow back to the gearbox through the fourth port and the inlet of the gearbox, thus completing one cycle.
- the cooling oil flows into the valve assembly through the first gap, and the thermal element is thermally expanded, and the thermal element moves downward.
- the high temperature cooling oil can utilize the pressure relief function of the valve assembly to enable the cooling oil to pass.
- a passage for fluid flow, a fourth port, and an inlet of the gearbox are formed between the outer wall of the valve seat portion 34 and the inner wall corresponding to the accommodating chamber 15 to flow back to the gearbox to prevent oil loss of the gearbox.
- FIG. 14 shows a heat exchange assembly according to still another embodiment of the present invention.
- the heat exchange assembly of the embodiment is different from the heat exchange assembly of the above embodiment in that a heat exchange core is further provided with a through passage communicating with the fourth interface 1012. 106, the through passage 106 penetrates the heat exchange core 105, and the through passage 106 is neither in communication with the first passage of the heat exchange core nor with the second passage.
- the second adapter 1032 is further provided with a sixth interface 1034, the sixth interface 1034 is disposed opposite the through passage 106 and the sixth interface 1034 is connected to the through passage 106. .
- the through passage 106 In order to prevent the through passage 106 from communicating with the first passage and the second passage, in the present embodiment, it is realized by providing a connecting pipe 1061 in the heat exchange core. Of course, it can also be realized by other means, for example, processing into a turn hole in a sheet constituting the heat exchange core, and stacking the turn in the stack The through passages 106 are formed together.
- the mounting plate 101 includes a first mounting plate 1015 and a second mounting plate 1016, wherein the second mounting plate 1016 and the heat exchange core The body is fixed by the welding phase, and the first mounting plate 1015 and the second mounting plate 1016 are fixed by welding.
- the second mounting plate 1016 is further provided with a connecting hole 1017 connected to the through hole 106.
- the first mounting plate 1015 is provided with a recess 1018, and the two ends of the recess 1018 communicate with the connecting hole 1017 and the fourth interface 1012, respectively.
- the 1018 cooperates with the second mounting plate 1015 to form a connecting passage connecting the through passage and the fourth interface.
- first mounting plate and the second mounting plate can also be combined into one mounting plate, and in this embodiment, the mounting plate is divided into two parts, and the processing technique is simple.
- FIG. 15 and FIG. 16 show a transmission oil temperature adjustment system including the heat exchange assembly of the present embodiment, and the present embodiment differs from the transmission oil temperature adjustment system shown in FIGS. 12 and 13 in that the heat exchange assembly is different.
- the heat exchange assembly is provided with a through passage 106, so that the outlet of the oil cooler can be directly communicated through the through passage 106 and the fourth interface 1012, so that the inlet of the transmission only needs to be connected with the fourth interface 1012.
- the integration is high, and it can further reduce the risk of leakage.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Thermal Sciences (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Fluid Mechanics (AREA)
- Automation & Control Theory (AREA)
- Valve Housings (AREA)
- Temperature-Responsive Valves (AREA)
- Multiple-Way Valves (AREA)
- General Details Of Gearings (AREA)
- Control Of Transmission Device (AREA)
- Heat-Exchange Devices With Radiators And Conduit Assemblies (AREA)
- Safety Valves (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Claims (15)
- 一种热交换组件,包括换热芯体、与所述换热芯体相固定的安装板,所述热交换组件还包括第一接口、第二接口、第三接口和第四接口,所述换热芯体包括端板,所述换热芯体还包括相互隔离的第一流道和第二流道,其中所述第一流道与所述第一接口和第二接口相连通,所述第二流道与所述第三接口和第四接口相连通,所述第二流道包括第一通道和第二通道,其特征在于,所述换热芯体还包括一贯穿所述换热芯体的贯通通道,所述安装板设置有一连通所述贯通通道和所述第四接口的连接通道,所述第二通道贯穿所述换热芯体并且所述第二通道的一端与所述第四接口相连通;所述热交换组件还包括一阀组件和一转接座,所述转接座设置有一与所述第二通道相对的腔以及与所述腔相连通的第五接口,所述转接座还设置有与所述贯通通道相连通的第六接口,所述阀组件设置于或者部分设置于所述第二通道,所述阀组件包括主阀体和安装在所述主阀体内的热动元件,所述主阀体的一端与所述第五接口的内壁密封配合安装,所述主阀体的一端与所述第四接口或者所述第二通道的内壁密封配合安装,所述主阀体的侧壁设置有第一缺口,所述主阀体内设置有第一阀口,所述第一阀口位于所述第一缺口和所述第四接口之间,通过所述热动元件靠近或者远离所述第一阀口,所述第一阀口与所述第四接口不连通或者连通;当所述第一阀口打开时,所述第三接口依次通过第一通道、第二通道、第一缺口和第一阀口与第四接口连通;当所述第一阀口关闭时,所述第三接口依次通过第一通道、第二通道和第一缺口与第五接口连通。
- 根据权利要求1所述的热交换组件,其特征在于,所述主阀体的一端与所述转接座内的腔所对应的内壁密封固定,所述主阀体的另一端与所述第四接口的内壁密封固定,所述主阀体还包括位于所述第二通道的导流部,所述第一缺口位于所述导流部,所述导流部的外径小于所述第二通道的内径。
- 根据权利要求2所述的热交换组件,其特征在于,所述主阀体的两端分别设置有第一开口和第二开口,所述主阀体包括容纳腔,所述容纳腔 位于第一开口和第二开口之间,在所述容纳腔对应的主阀体的侧壁开设有所述第一缺口,所述阀组件在所述第一开口或相对靠近第一开口处设置有上阀套,所述热动元件的另一端与所述上阀套相支撑,所述上阀套包括支撑部和主体部,所述第一开口的直径大于所述容纳腔的内径,所述第一开口和容纳腔之间形成有台阶部,通过设置第一卡扣,所述支撑部与所述第一开口和容纳腔之间的台阶部相抵接,所述支撑部与所述第一开口的内壁之间间隙配合,所述主体部与所述第一开口的内壁之间保持距离以形成有流道。
- 根据权利要求3所述的热交换组件,其特征在于,所述主阀体内还设置有第一弹簧和第二弹簧,所述第一弹簧和第二弹簧处于压缩状态,所述热动元件的两端分别与所述第一弹簧的一端和第二弹簧的一端与相抵接,所述第二弹簧的初始弹性形变力大于所述第一阀口关闭时所述第一弹簧的弹性形变力,所述主体部的腔内还设置有一支撑帽和第二卡扣,所述支撑帽通过所述第二卡扣固定,所述第二弹簧的一端与主体部的底部的内底面相抵接,所述第二弹簧的另一端与所述支撑帽相抵接,所述第二弹簧处于压缩状态,所述第二缺口位于所述支撑部与所述第二卡扣之间。
- 根据权利要求4所述的热交换组件,其特征在于,所述支撑帽包括外延部,所述外延部与所述主体部的腔的内壁间隙配合或者滑动配合,所述外延部开设有至少一个槽口,所述槽口与所述主体部的腔的内壁之间形成有供流体通过的通道;所述主体部的相对于支撑帽上端部分开设有第三缺口,所述第三缺口与所述槽口与所述主体部的腔的内壁之间形成的供流体通过的通道相连通。
- 根据权利要求5所述的热交换组件,其特征在于,所述支撑部还设置有第二阀口,通过所述热动元件远离靠近所述第二阀口来打开关闭所述第二阀口,当所述第一阀口关闭时,所述第二缺口通过所述第二阀口与所述第一缺口连通,所述第三缺口依次通过所述槽口与所述主体部的腔的内壁之间形成的供流体通过的通道和第二阀口与所述第一缺口连通,所述第三开口通过所述槽口与所述主体部的腔的内壁之间形成的供流体通过的通道和第二阀口与所述第一缺口连通;当所述第二阀口关闭时,所述第一阀口打开时,所述第三接口依次通过第一通道、第二通道、第一缺口和第一阀口与第四接口连通,所述第三接口与所述第五接口不连通;当所述第一阀口关闭时,所述第二阀口打开,所述第三接口依次通过第一通道、第二通道、第一缺口和第二阀口与第五接口连通,所述第三接口与所述第四接口不连通。
- 根据权利要求1至6任一项所述的热交换组件,其特征在于,所述安装板包括第一安装板和第二安装板,所述第二安装板还设置有与所述贯通孔相连接的连接孔,所述第一安装板设置有一凹槽,并且所述凹槽的两端分别连通所述连接孔和第四接口,所述凹槽与第二安装板配合形成连通贯通通道和第四接口的所述连接通道。
- 根据权利要求7所述的热交换组件,其特征在于,所述转接座包括第一转接座和第二转接座,所述第一转接座包括容纳腔、以及与所述容纳腔相连通的所述第五接口,所述第二转接座包括所述座体、所述贯穿座体的腔和所述第六接口,所述容纳腔与所述贯穿座体的腔相对应,所述第五接口通过所述容纳腔与所述贯穿座体的腔连通,所述第二转接座中还设置有一卡环,通过所述卡环固定所述阀组件并限制所述阀组件的轴线位移。
- 根据权利要求8所述的热交换组件,其特征在于,所述主阀体包括外径逐渐减小的第一配合部、第二配合部、第三配合部、导流部和第四配合部,所述第一配合部和第二配合部之间的形成的台阶与所述贯穿座体的腔所对应的所述座体的内壁形成的台阶相靠接,所述第一配合部和第二配合部与所述贯穿座体的腔所对应的所述座体的内壁间隙配合,所述第二配合部与贯穿座体的腔所对应的座体的内壁之间还置有密封圈,所述第三配合部和导流部位于所述第二通道中,并且所述第三配合部的外径小于所述第二通道的内径,第四配合部位于所述第四接口中,并且所述第四配合部与所述第四接口之间间隙配合,所述第四配合部与所述第四接口之间还设置有密封圈。
- 一种变速箱油温度调节系统,其特征在于,所述变速箱油温度调节系统包括变速箱、热交换组件和油冷器,所述热交换组件为权利要求1至9任一项所述的热交换组件,所述第三接口和第四接口直接或者通过管 路与变速箱的进出口相连通,所述油冷器的其中一条流道的出口通过管路与热交换组件的第六接口相连通,所述油冷器的流道的进口与所述第五接口相连通;当从变速箱出口出来的冷却油进入换热芯体进行热交换后的温度处于正常状态时,冷却油通过第一缺口进入阀组件,由于热动元件在第一弹簧的回复力作用下第一阀口处于开启状态,冷却油穿过所述第一阀口后通过第四接口和变速箱的进口流回变速箱;当从变速箱出口出来的冷却油进入换热芯体进行热交换后的温度较高时,冷却油通过第一缺口流入阀组件,此时热动元件受热膨胀关闭第一阀口,第一阀口处于关闭状态,冷却油通过第五接口流向油冷器,流出油冷器的冷却油通过贯通通道和第五接口后通过变速箱进口流回变速箱。
- 一种热交换组件,包括换热芯体、与所述换热芯体相固定的安装板,所述热交换组件还包括第一接口、第二接口、第三接口和第四接口,所述换热芯体包括端板,所述换热芯体还包括相互隔离的第一流道和第二流道,其中所述第一流道与所述第一接口和第二接口相连通,所述第二流道与所述第三接口和第四接口相连通,所述第二流道包括第一通道和第二通道,其特征在于,所述第一通道的一端与所述第三接口相连通,所述第一通道的另一端受到所述端板的阻挡,所述第二通道贯穿所述换热芯体并且所述第二通道的一端与所述第四接口相连通;所述热交换组件还包括一阀组件和一转接座,所述转接座设置有第五接口,所述阀组件设置于或者部分设置于所述第二通道,所述阀组件包括主阀体和安装在所述主阀体内的热动元件,所述主阀体包括容纳腔,所述主阀体的一端与所述第五接口的内壁密封配合安装,所述主阀体的一端与所述第四接口或者所述第二通道的内壁密封配合安装,所述主阀体的容纳腔所对应的侧壁设置有第一缺口,所述第一缺口与所述第二通道相连通,所述第一缺口与所述容纳腔相连通,所述第二通道通过所述第一缺口与所述容纳腔相连通。
- 根据权利要求1至9任一项所述的热交换组件,其特征在于,所述阀组件还包括下阀套,所述下阀套的一部分位于所述容纳腔,所述下阀套的另一部分位于所述第二开口并且与所述第二开口的内壁密封固定,所 述下阀套包括阀座部、弹簧支撑座、配合部和贯穿所述下阀套的贯通孔,所述第一阀口位于所述阀座部,所述第一阀口为所述贯通孔的一部分,所述配合部与所述第二开口的内壁之间密封固定,当所述第一阀口关闭时,所述第一缺口不与所述第二开口连通,所述弹簧支撑部与阀座部之间设置有第四缺口,所述第四缺口与配合部相对应的贯通孔部分相连通,所述第四缺口通过所述贯通孔与所述第二开口连通,所述阀座部的外径大于所述下阀套其它部分的外径,所述阀座部的外径小于所述容纳腔的内径,所述阀座部的外壁与所述容纳腔之间形成有供流体流动的通道,所述容纳腔内还设置有泄压环和第三弹簧,所述泄压环设置有通孔,通过所述通孔,所述泄压环套设于所述下阀套,所述通孔的内径小于所述阀座部的外径,所述泄压环与容纳腔所对应的内壁之间滑动配合,所述第三弹簧的一端与所述泄压环相抵接,所述第三弹簧的另一端与所述主阀体的内壁相抵接,通过所述第三弹簧,所述泄压环与所述阀座部相抵接;通过所述泄压环抵接或者远离所述阀座部,所述阀座部的外壁与所述容纳腔之间形成的供流体流动的通道与所述第四缺口不连通或者连通。
- 一种阀组件,包括主阀体和热动元件,所述阀组件还设置有第一弹簧,所述第一弹簧、热动元件位于所述主阀体内,所述第一弹簧处于压缩状态,所述第一弹簧的一端与所述热动元件相抵接,所述阀组件还设置有第一阀口,第一阀口在所述主阀体内,通过所述热动元件动作来打开关闭所述第一阀口或调节所述第一阀口的开度,所述主阀体的两端分别设置有第一开口和第二开口,所述主阀体包括容纳腔,所述容纳腔位于第一开口和第二开口之间,在所述容纳腔对应的主阀体的侧壁开设有第一缺口;所述阀组件在所述第一开口或相对靠近第一开口处设置有上阀套,所述热动元件的另一端与所述上阀套相支撑,所述上阀套包括支撑部和主体部,支撑部与所述主阀体相固定或限位,主体部相对支撑部外径较小,所述主体部开设有一腔,所述主体部设置有与所述主体部内的腔相连通的第二缺口;当所述第一阀口关闭时,所述第一缺口能够通过所述第二缺口与所述第一开口相连通。
- 一种热交换组件,包括换热芯体、与所述换热芯体相固定的安装 板,所述热交换组件还包括第一接口、第二接口、第三接口和第四接口,所述换热芯体包括端板,所述换热芯体还包括相互隔离的第一流道和第二流道,其中所述第一流道与所述第一接口和第二接口相连通,所述第二流道与所述第三接口和第四接口相连通,所述第二流道包括第一通道和第二通道,其特征在于,所述第二通道贯穿所述换热芯体并且所述第二通道的一端与所述第四接口相连通,所述热交换组件还包括一阀组件和一转接座,所述转接座设置有一腔和第五接口,所述第五接口与所述腔相连通,所述阀组件设置于所述第二通道或者部分位于第二通道,所述阀组件包括主阀体和安装在所述主阀体内的热动元件,所述主阀体内还设置有第一阀口,通过所述热动元件动作来打开关闭所述第一阀口,所述主阀体的两端分别设置有第一开口和第二开口,所述主阀体内包括一容纳腔,所述容纳腔位于第一开口和第二开口之间,所述容纳腔所述对应的主阀体的侧壁开设有第一缺口,所述第一缺口与所述第二通道相连通;在所述第一开口内设置有上阀套,所述热动元件的一端与所述上阀套相支撑或限位,所述主体部内开设有一腔,所述主体部设置有与所述主体部内的腔相连通的第二缺口,所述第二缺口与所述第五接口相连通;当所述第一阀口打开时,所述第三接口依次通过第一通道、第二通道、第一缺口和第一阀口与第四接口连通;当所述第一阀口关闭时,所述第三接口依次通过第一通道、第二通道、第一缺口和第二缺口与第五接口连通。
- 一种热交换组件,包括换热芯体、与所述换热芯体相固定的安装板,所述热交换组件还包括第一接口、第二接口、第三接口和第四接口,所述换热芯体包括端板,所述换热芯体还包括相互隔离的第一流道和第二流道,其中所述第一流道与所述第一接口和第二接口相连通,所述第二流道与所述第三接口和第四接口相连通,所述第二流道包括第一通道和第二通道,其特征在于,所述第一通道的一端与所述第三接口相连通,所述第一通道的另一端受到所述端板的阻挡,所述第二通道贯穿所述换热芯体并且所述第二通道的一端与所述第四接口相连通,所述热交换组件还包括一阀组件和一转接座,所述转接座设置有第五 接口,所述阀组件设置于或者部分设置于所述第二通道,所述阀组件包括主阀体和安装在所述主阀体内的热动元件,所述主阀体的一端与所述第五接口的内壁密封配合安装,所述主阀体的一端与所述第四接口或者所述第二通道的内壁密封配合安装,所述主阀体的侧壁设置有第一缺口,所述主阀体内设置有第一阀口,所述第一阀口位于所述第一缺口和所述第四接口之间,通过所述热动元件动作,所述第一阀口与所述第四接口不连通或者连通;当所述第一阀口打开时,所述第三接口依次通过第一通道、第二通道、第一缺口和第一阀口与第四接口连通;当所述第一阀口关闭时,所述第三接口依次通过第一通道、第二通道和第一缺口与第五接口连通。
Priority Applications (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US16/332,333 US11187464B2 (en) | 2016-11-21 | 2017-05-31 | System for adjusting temperature of transmission oil, heat exchange assembly and valve assembly |
| KR1020197010426A KR102288080B1 (ko) | 2016-11-21 | 2017-05-31 | 변속기 오일의 온도를 조정하기 위한 시스템, 열 교환 조립체 및 밸브 조립체 |
| JP2019515827A JP6851469B2 (ja) | 2016-11-21 | 2017-05-31 | トランスミッション油の温度調節システム、熱交換アセンブリ及びバルブアセンブリ |
| EP17871049.7A EP3543635B1 (en) | 2016-11-21 | 2017-05-31 | System for adjusting temperature of transmission oil, heat exchange assembly and valve assembly |
Applications Claiming Priority (8)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201611040875.X | 2016-11-21 | ||
| CN201611040046.1 | 2016-11-21 | ||
| CN201611040101.7 | 2016-11-21 | ||
| CN201611040875.XA CN108087532B (zh) | 2016-11-21 | 2016-11-21 | 热交换组件 |
| CN201611040046.1A CN108087530B (zh) | 2016-11-21 | 2016-11-21 | 热交换组件 |
| CN201611040101.7A CN108087531B (zh) | 2016-11-21 | 2016-11-21 | 热交换组件 |
| CN201611040514.5 | 2016-11-21 | ||
| CN201611040514.5A CN108087579B (zh) | 2016-11-21 | 2016-11-21 | 阀组件 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2018090598A1 true WO2018090598A1 (zh) | 2018-05-24 |
Family
ID=62145172
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/CN2017/086525 WO2018090598A1 (zh) | 2016-11-21 | 2017-05-31 | 变速箱油温度调节系统、热交换组件及阀组件 |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US11187464B2 (zh) |
| EP (1) | EP3543635B1 (zh) |
| JP (1) | JP6851469B2 (zh) |
| KR (1) | KR102288080B1 (zh) |
| WO (1) | WO2018090598A1 (zh) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN109163082A (zh) * | 2018-10-31 | 2019-01-08 | 东风富士汤姆森调温器有限公司 | 变速箱温控装置 |
| CN110553025A (zh) * | 2018-05-30 | 2019-12-10 | 浙江三花汽车零部件有限公司 | 一种调温阀及具有该调温阀的热管理系统 |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN109681617B (zh) * | 2017-10-18 | 2020-09-29 | 浙江三花汽车零部件有限公司 | 一种热交换装置 |
| KR102654462B1 (ko) | 2019-11-04 | 2024-04-03 | 현대자동차 주식회사 | 차량용 밸브 장치 |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101802469A (zh) * | 2007-07-26 | 2010-08-11 | 达纳加拿大公司 | 防泄漏的旁通阀 |
| US20110127458A1 (en) * | 2004-11-24 | 2011-06-02 | Mark Stephen Kozdras | By-Pass Valve for Heat Exchanger |
| KR101519961B1 (ko) * | 2014-09-05 | 2015-05-15 | 주식회사 코렌스 | 트랜스미션 오일 바이패스 조립체 |
| CN104806739A (zh) * | 2014-01-27 | 2015-07-29 | 福特全球技术公司 | 变速器系统及调温旁通阀 |
| CN105277013A (zh) * | 2014-06-23 | 2016-01-27 | 现代自动车株式会社 | 用于车辆的换热器 |
| CN205036847U (zh) * | 2015-08-24 | 2016-02-17 | 东风富士汤姆森调温器有限公司 | 一种通过冷却介质控制变速箱油温的温控装置 |
Family Cites Families (38)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3768731A (en) * | 1971-08-25 | 1973-10-30 | Altair Inc | Fail safe thermostatic switch |
| US4190198A (en) * | 1978-04-12 | 1980-02-26 | Lockhart Industries, Inc. | Oil cooler bypass valve actuating means |
| DE2932481A1 (de) * | 1979-08-10 | 1981-03-26 | Robert Bosch Gmbh, 70469 Stuttgart | Steuerventil |
| US4763834A (en) * | 1987-06-25 | 1988-08-16 | Standard-Thomson Corporation | Valve seat structure for automotive thermostatic fluid control valve device |
| IT1308829B1 (it) * | 1999-09-21 | 2002-01-11 | Gevipi Ag | Valvola automatica per la stabilizzazione di un dispositivomiscelatore termostatico. |
| JP2002168591A (ja) | 2000-11-29 | 2002-06-14 | Denso Corp | アルミニウム製熱交換器 |
| JP4077610B2 (ja) | 2001-03-16 | 2008-04-16 | カルソニックカンセイ株式会社 | ハウジングレス式オイルクーラ |
| DE102005046635A1 (de) * | 2005-09-29 | 2007-04-05 | Zf Friedrichshafen Ag | Einrichtung zum Abkoppeln des Öldurchflusses durch einen Kühler |
| DE102006039554A1 (de) * | 2006-08-23 | 2008-03-06 | Zf Friedrichshafen Ag | Bypassventil für einen einem Hydraulikaggregat nachgeordneten Kühler |
| DE102007010393B4 (de) * | 2007-03-03 | 2011-07-14 | Modine Manufacturing Co., Wis. | Wärmeübertrager |
| DK2166423T3 (en) * | 2008-09-19 | 2018-03-12 | Isomatic As | Balanced fluid valve |
| CN102575782B (zh) * | 2009-08-17 | 2014-04-09 | 盾安美斯泰克股份有限公司 | 微型机械装置和控制方法 |
| US20120097365A1 (en) * | 2010-10-22 | 2012-04-26 | Visteon Global Technologies, Inc. | Heat exchanger with an integrated temperature manipulation element |
| US9239195B2 (en) * | 2011-04-26 | 2016-01-19 | Hyundai Motor Company | Heat exchanger for vehicle |
| KR101283591B1 (ko) * | 2011-09-19 | 2013-07-05 | 현대자동차주식회사 | 차량용 열교환기 |
| KR101776718B1 (ko) * | 2011-11-22 | 2017-09-11 | 현대자동차 주식회사 | 차량용 열교환기 |
| KR101284337B1 (ko) * | 2011-11-25 | 2013-07-08 | 현대자동차주식회사 | 차량용 열교환기 |
| US20130133875A1 (en) * | 2011-11-25 | 2013-05-30 | Hyundai Motor Company | Heat exchanger for vehicle |
| KR101765582B1 (ko) * | 2011-12-06 | 2017-08-08 | 현대자동차 주식회사 | 차량용 열교환기 |
| US9464853B2 (en) | 2011-12-22 | 2016-10-11 | Dana Canada Corporation | Heat exchanger with integrated thermal bypass valve |
| WO2013177711A1 (en) * | 2012-05-31 | 2013-12-05 | Dana Canada Corporation | Heat exchanger assemblies with integrated valve |
| KR101339250B1 (ko) * | 2012-06-11 | 2013-12-09 | 현대자동차 주식회사 | 차량용 열교환기 |
| CN104822975B (zh) * | 2012-08-07 | 2017-12-29 | 浙江三花汽车零部件有限公司 | 一种调温器 |
| KR101405186B1 (ko) | 2012-10-26 | 2014-06-10 | 현대자동차 주식회사 | 차량용 열교환기 |
| KR101416388B1 (ko) | 2012-12-05 | 2014-07-08 | 현대자동차 주식회사 | 차량용 열교환기 |
| KR101575315B1 (ko) * | 2013-10-14 | 2015-12-07 | 현대자동차 주식회사 | 차량용 열교환기 |
| KR101499221B1 (ko) * | 2013-11-14 | 2015-03-05 | 현대자동차주식회사 | 밸브 액추에이터 내장형 배기열 회수장치 |
| KR101610099B1 (ko) * | 2014-04-30 | 2016-04-08 | 현대자동차 주식회사 | 캔형 열교환기 |
| IL233943B (en) * | 2014-08-04 | 2020-06-30 | Israel Aerospace Ind Ltd | Two-stage valve |
| US9829115B2 (en) * | 2014-10-08 | 2017-11-28 | Hyundai Motor Company | Valve |
| KR101683491B1 (ko) * | 2014-12-09 | 2016-12-07 | 현대자동차 주식회사 | 차량용 열교환기 |
| US10619530B2 (en) * | 2015-01-26 | 2020-04-14 | Modine Manufacturing Company | Thermal management unit for vehicle powertrain |
| US10087793B2 (en) | 2015-01-26 | 2018-10-02 | Modine Manufacturing Company | Thermal management unit for vehicle powertrain |
| KR101703603B1 (ko) * | 2015-06-15 | 2017-02-07 | 현대자동차 주식회사 | 캔형 열교환기 |
| EP3327397B1 (en) * | 2015-07-17 | 2022-09-07 | Zhejiang Sanhua Automotive Components Co., Ltd. | Heat exchange device |
| EP3124907B1 (en) * | 2015-07-29 | 2019-04-10 | Zhejiang Sanhua Automotive Components Co., Ltd. | Heat exchange device |
| DE102015216481A1 (de) * | 2015-08-28 | 2017-03-02 | Volkswagen Aktiengesellschaft | Wärmetauscher in Plattenbauweise mit Bypass sowie Verfahren zur Herstellung eines Wärmetauschers in Plattenbauweise mit Bypass |
| JP2017116135A (ja) * | 2015-12-22 | 2017-06-29 | 株式会社マーレ フィルターシステムズ | オイルクーラのオイルバイパス構造 |
-
2017
- 2017-05-31 WO PCT/CN2017/086525 patent/WO2018090598A1/zh active Application Filing
- 2017-05-31 KR KR1020197010426A patent/KR102288080B1/ko active IP Right Grant
- 2017-05-31 JP JP2019515827A patent/JP6851469B2/ja active Active
- 2017-05-31 US US16/332,333 patent/US11187464B2/en active Active
- 2017-05-31 EP EP17871049.7A patent/EP3543635B1/en active Active
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20110127458A1 (en) * | 2004-11-24 | 2011-06-02 | Mark Stephen Kozdras | By-Pass Valve for Heat Exchanger |
| CN101802469A (zh) * | 2007-07-26 | 2010-08-11 | 达纳加拿大公司 | 防泄漏的旁通阀 |
| CN104806739A (zh) * | 2014-01-27 | 2015-07-29 | 福特全球技术公司 | 变速器系统及调温旁通阀 |
| CN105277013A (zh) * | 2014-06-23 | 2016-01-27 | 现代自动车株式会社 | 用于车辆的换热器 |
| KR101519961B1 (ko) * | 2014-09-05 | 2015-05-15 | 주식회사 코렌스 | 트랜스미션 오일 바이패스 조립체 |
| CN205036847U (zh) * | 2015-08-24 | 2016-02-17 | 东风富士汤姆森调温器有限公司 | 一种通过冷却介质控制变速箱油温的温控装置 |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN110553025A (zh) * | 2018-05-30 | 2019-12-10 | 浙江三花汽车零部件有限公司 | 一种调温阀及具有该调温阀的热管理系统 |
| CN110553025B (zh) * | 2018-05-30 | 2023-06-27 | 浙江三花汽车零部件有限公司 | 一种调温阀及具有该调温阀的热管理系统 |
| CN109163082A (zh) * | 2018-10-31 | 2019-01-08 | 东风富士汤姆森调温器有限公司 | 变速箱温控装置 |
| CN109163082B (zh) * | 2018-10-31 | 2023-10-13 | 东风富士汤姆森调温器有限公司 | 变速箱温控装置 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP3543635A4 (en) | 2020-06-03 |
| JP2019537698A (ja) | 2019-12-26 |
| EP3543635B1 (en) | 2021-04-14 |
| JP6851469B2 (ja) | 2021-03-31 |
| US20190234507A1 (en) | 2019-08-01 |
| EP3543635A1 (en) | 2019-09-25 |
| KR20190047018A (ko) | 2019-05-07 |
| US11187464B2 (en) | 2021-11-30 |
| KR102288080B1 (ko) | 2021-08-12 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US9541211B2 (en) | Thermoregulator and thermoregulator component | |
| EP2884134B1 (en) | Thermoregulator | |
| WO2018090598A1 (zh) | 变速箱油温度调节系统、热交换组件及阀组件 | |
| US7735546B2 (en) | Heat exchanger bypass valve having temperature insensitive pressure bypass function | |
| KR102380176B1 (ko) | 밸브 조립체, 열교환 조립체, 및 기어박스용 오일온도조절 시스템 | |
| WO2017181869A1 (zh) | 一种调温器及一种温控系统 | |
| EP3467352B1 (en) | Temperature regulating valve | |
| CN108087530B (zh) | 热交换组件 | |
| WO2017185972A1 (zh) | 调温阀 | |
| CN106704685B (zh) | 温控阀及变速箱温控系统 | |
| CN108087531B (zh) | 热交换组件 | |
| CN108087532B (zh) | 热交换组件 | |
| CN109937317A (zh) | 一种调温阀、及具有该调温阀的热管理组件 | |
| CN108087579B (zh) | 阀组件 | |
| CN209743553U (zh) | 一种换热装置及热管理装置 | |
| CN108930777B (zh) | 调温阀 | |
| CN112747167B (zh) | 一种调温阀 | |
| KR20200065050A (ko) | 열교환기 | |
| CN114439908A (zh) | 换热组件 | |
| CN112747166A (zh) | 一种阀组件 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 17871049 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2019515827 Country of ref document: JP Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 20197010426 Country of ref document: KR Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2017871049 Country of ref document: EP |