WO2015163195A1 - レジスト下層膜形成組成物及びそれを用いたレジストパターンの形成方法 - Google Patents
レジスト下層膜形成組成物及びそれを用いたレジストパターンの形成方法 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2015163195A1 WO2015163195A1 PCT/JP2015/061467 JP2015061467W WO2015163195A1 WO 2015163195 A1 WO2015163195 A1 WO 2015163195A1 JP 2015061467 W JP2015061467 W JP 2015061467W WO 2015163195 A1 WO2015163195 A1 WO 2015163195A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- group
- underlayer film
- formula
- resist underlayer
- carbon atoms
- Prior art date
Links
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 75
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims description 15
- 229920000642 polymer Polymers 0.000 claims abstract description 91
- 238000001459 lithography Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 50
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 claims abstract description 31
- 239000003960 organic solvent Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 19
- 125000005843 halogen group Chemical group 0.000 claims abstract description 14
- 125000003118 aryl group Chemical group 0.000 claims abstract description 13
- 125000004435 hydrogen atom Chemical group [H]* 0.000 claims abstract description 13
- 125000002887 hydroxy group Chemical group [H]O* 0.000 claims abstract description 13
- 125000000962 organic group Chemical group 0.000 claims abstract description 13
- 239000003431 cross linking reagent Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 12
- 125000004185 ester group Chemical group 0.000 claims abstract description 3
- 125000001997 phenyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C([H])=C(*)C([H])=C1[H] 0.000 claims abstract description 3
- 125000004076 pyridyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims abstract description 3
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 39
- 125000004432 carbon atom Chemical group C* 0.000 claims description 36
- ARXJGSRGQADJSQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-methoxypropan-2-ol Chemical compound COCC(C)O ARXJGSRGQADJSQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 31
- 125000001424 substituent group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 24
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims description 24
- 125000000217 alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 19
- 238000004132 cross linking Methods 0.000 claims description 15
- LZCLXQDLBQLTDK-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 2-hydroxypropanoate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C(C)O LZCLXQDLBQLTDK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 14
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 claims description 11
- 239000000178 monomer Substances 0.000 claims description 10
- LLHKCFNBLRBOGN-UHFFFAOYSA-N propylene glycol methyl ether acetate Chemical compound COCC(C)OC(C)=O LLHKCFNBLRBOGN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 9
- 239000002253 acid Substances 0.000 claims description 6
- JHIVVAPYMSGYDF-UHFFFAOYSA-N cyclohexanone Chemical compound O=C1CCCCC1 JHIVVAPYMSGYDF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- 238000010894 electron beam technology Methods 0.000 claims description 5
- 229940116333 ethyl lactate Drugs 0.000 claims description 5
- 125000003903 2-propenyl group Chemical group [H]C([*])([H])C([H])=C([H])[H] 0.000 claims description 4
- MRABAEUHTLLEML-UHFFFAOYSA-N Butyl lactate Chemical compound CCCCOC(=O)C(C)O MRABAEUHTLLEML-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000001191 butyl (2R)-2-hydroxypropanoate Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 125000004433 nitrogen atom Chemical group N* 0.000 claims description 4
- JOLQKTGDSGKSKJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-ethoxypropan-2-ol Chemical compound CCOCC(C)O JOLQKTGDSGKSKJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- 125000000623 heterocyclic group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000002994 raw material Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 125000002947 alkylene group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000006615 aromatic heterocyclic group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000007795 chemical reaction product Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 230000001737 promoting effect Effects 0.000 claims description 2
- 230000005855 radiation Effects 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000000547 substituted alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000001183 hydrocarbyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims 3
- 125000004169 (C1-C6) alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 abstract 4
- 239000010408 film Substances 0.000 description 99
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 45
- 238000003786 synthesis reaction Methods 0.000 description 42
- 239000000243 solution Substances 0.000 description 39
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 25
- IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N Atomic nitrogen Chemical compound N#N IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 24
- -1 nitrogen-containing compound Chemical class 0.000 description 24
- YCLSOMLVSHPPFV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-(2-carboxyethyldisulfanyl)propanoic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)CCSSCCC(O)=O YCLSOMLVSHPPFV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 16
- 238000005227 gel permeation chromatography Methods 0.000 description 16
- 150000002430 hydrocarbons Chemical group 0.000 description 16
- 230000000052 comparative effect Effects 0.000 description 15
- XGQJGMGAMHFMAO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,3,4,6-tetrakis(methoxymethyl)-3a,6a-dihydroimidazo[4,5-d]imidazole-2,5-dione Chemical compound COCN1C(=O)N(COC)C2C1N(COC)C(=O)N2COC XGQJGMGAMHFMAO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 14
- YCPXWRQRBFJBPZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-sulfosalicylic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C1=CC(S(O)(=O)=O)=CC=C1O YCPXWRQRBFJBPZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 13
- 239000004793 Polystyrene Substances 0.000 description 13
- 229910052757 nitrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 13
- 229920002223 polystyrene Polymers 0.000 description 13
- 238000004458 analytical method Methods 0.000 description 12
- 239000007864 aqueous solution Substances 0.000 description 12
- JHYNXXDQQHTCHJ-UHFFFAOYSA-M ethyl(triphenyl)phosphanium;bromide Chemical compound [Br-].C=1C=CC=CC=1[P+](C=1C=CC=CC=1)(CC)C1=CC=CC=C1 JHYNXXDQQHTCHJ-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 12
- 239000004094 surface-active agent Substances 0.000 description 12
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical compound [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 10
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 10
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 description 10
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 10
- KQEJGXLRINKCST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-methyl-3,5-bis(oxiran-2-ylmethyl)-1,3,5-triazinane-2,4,6-trione Chemical compound O=C1N(CC2OC2)C(=O)N(C)C(=O)N1CC1CO1 KQEJGXLRINKCST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 9
- 125000002723 alicyclic group Chemical group 0.000 description 7
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 7
- XEKOWRVHYACXOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethyl acetate Chemical compound CCOC(C)=O XEKOWRVHYACXOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- DNIAPMSPPWPWGF-UHFFFAOYSA-N Propylene glycol Chemical compound CC(O)CO DNIAPMSPPWPWGF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 238000011161 development Methods 0.000 description 6
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 6
- 239000002904 solvent Substances 0.000 description 6
- DKPFZGUDAPQIHT-UHFFFAOYSA-N Butyl acetate Natural products CCCCOC(C)=O DKPFZGUDAPQIHT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 239000004698 Polyethylene Substances 0.000 description 5
- YXFVVABEGXRONW-UHFFFAOYSA-N Toluene Chemical compound CC1=CC=CC=C1 YXFVVABEGXRONW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- FUZZWVXGSFPDMH-UHFFFAOYSA-N hexanoic acid Chemical compound CCCCCC(O)=O FUZZWVXGSFPDMH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 229920002120 photoresistant polymer Polymers 0.000 description 5
- 229920000573 polyethylene Polymers 0.000 description 5
- 239000011148 porous material Substances 0.000 description 5
- DIZBQMTZXOUFTD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(furan-2-yl)-3h-benzimidazole-5-carboxylic acid Chemical compound N1C2=CC(C(=O)O)=CC=C2N=C1C1=CC=CO1 DIZBQMTZXOUFTD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- XNWFRZJHXBZDAG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-METHOXYETHANOL Chemical compound COCCO XNWFRZJHXBZDAG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- AJBWNNKDUMXZLM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-methylsulfonylbenzoic acid Chemical compound CS(=O)(=O)C1=CC=C(C(O)=O)C=C1 AJBWNNKDUMXZLM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- FTOAOBMCPZCFFF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5,5-diethylbarbituric acid Chemical compound CCC1(CC)C(=O)NC(=O)NC1=O FTOAOBMCPZCFFF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- ZMXDDKWLCZADIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N N,N-Dimethylformamide Chemical compound CN(C)C=O ZMXDDKWLCZADIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 229920003171 Poly (ethylene oxide) Polymers 0.000 description 4
- WPYMKLBDIGXBTP-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzoic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 WPYMKLBDIGXBTP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- HTZCNXWZYVXIMZ-UHFFFAOYSA-M benzyl(triethyl)azanium;chloride Chemical compound [Cl-].CC[N+](CC)(CC)CC1=CC=CC=C1 HTZCNXWZYVXIMZ-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 4
- 238000006116 polymerization reaction Methods 0.000 description 4
- 125000004805 propylene group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([*:1])C([H])([H])[*:2] 0.000 description 4
- YGSDEFSMJLZEOE-UHFFFAOYSA-N salicylic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1O YGSDEFSMJLZEOE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 238000012360 testing method Methods 0.000 description 4
- WGTYBPLFGIVFAS-UHFFFAOYSA-M tetramethylammonium hydroxide Chemical compound [OH-].C[N+](C)(C)C WGTYBPLFGIVFAS-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 4
- ZWEHNKRNPOVVGH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-Butanone Chemical compound CCC(C)=O ZWEHNKRNPOVVGH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetic acid Chemical compound CC(O)=O QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- UHOVQNZJYSORNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N Benzene Chemical compound C1=CC=CC=C1 UHOVQNZJYSORNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- KFZMGEQAYNKOFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Isopropanol Chemical compound CC(C)O KFZMGEQAYNKOFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- KWYUFKZDYYNOTN-UHFFFAOYSA-M Potassium hydroxide Chemical compound [OH-].[K+] KWYUFKZDYYNOTN-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 3
- XBDQKXXYIPTUBI-UHFFFAOYSA-M Propionate Chemical compound CCC([O-])=O XBDQKXXYIPTUBI-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 3
- HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M Sodium hydroxide Chemical compound [OH-].[Na+] HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 3
- ZMANZCXQSJIPKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Triethylamine Chemical compound CCN(CC)CC ZMANZCXQSJIPKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000000654 additive Substances 0.000 description 3
- KRKNYBCHXYNGOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N citric acid Chemical compound OC(=O)CC(O)(C(O)=O)CC(O)=O KRKNYBCHXYNGOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000011248 coating agent Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000001312 dry etching Methods 0.000 description 3
- WJRBRSLFGCUECM-UHFFFAOYSA-N hydantoin Chemical compound O=C1CNC(=O)N1 WJRBRSLFGCUECM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- RAXXELZNTBOGNW-UHFFFAOYSA-N imidazole Natural products C1=CNC=N1 RAXXELZNTBOGNW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000002736 nonionic surfactant Substances 0.000 description 3
- FJKROLUGYXJWQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N papa-hydroxy-benzoic acid Natural products OC(=O)C1=CC=C(O)C=C1 FJKROLUGYXJWQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000002685 polymerization catalyst Substances 0.000 description 3
- QQONPFPTGQHPMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N propylene Natural products CC=C QQONPFPTGQHPMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000010409 thin film Substances 0.000 description 3
- BJFHJALOWQJJSQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N (3-methoxy-3-methylpentyl) acetate Chemical compound CCC(C)(OC)CCOC(C)=O BJFHJALOWQJJSQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- DMFAHCVITRDZQB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-propoxypropan-2-yl acetate Chemical compound CCCOCC(C)OC(C)=O DMFAHCVITRDZQB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- SVONRAPFKPVNKG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-ethoxyethyl acetate Chemical compound CCOCCOC(C)=O SVONRAPFKPVNKG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- XLLIQLLCWZCATF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-methoxyethyl acetate Chemical compound COCCOC(C)=O XLLIQLLCWZCATF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- YEJRWHAVMIAJKC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-Butyrolactone Chemical compound O=C1CCCO1 YEJRWHAVMIAJKC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- QNVNLUSHGRBCLO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-hydroxybenzene-1,3-dicarboxylic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C1=CC(O)=CC(C(O)=O)=C1 QNVNLUSHGRBCLO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000005711 Benzoic acid Substances 0.000 description 2
- 0 CCC(C)CC(CN(C(N(C)C(N1CC(C*C)O)=O)=O)C1=O)O Chemical compound CCC(C)CC(CN(C(N(C)C(N1CC(C*C)O)=O)=O)C1=O)O 0.000 description 2
- XXRCUYVCPSWGCC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethyl pyruvate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C(C)=O XXRCUYVCPSWGCC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- QUSNBJAOOMFDIB-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethylamine Chemical compound CCN QUSNBJAOOMFDIB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- YCKRFDGAMUMZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-N Fluorine atom Chemical compound [F] YCKRFDGAMUMZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- SECXISVLQFMRJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-Methylpyrrolidone Chemical compound CN1CCCC1=O SECXISVLQFMRJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- UFWIBTONFRDIAS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Naphthalene Chemical compound C1=CC=CC2=CC=CC=C21 UFWIBTONFRDIAS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- NQRYJNQNLNOLGT-UHFFFAOYSA-N Piperidine Chemical compound C1CCNCC1 NQRYJNQNLNOLGT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229920001214 Polysorbate 60 Polymers 0.000 description 2
- JUJWROOIHBZHMG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Pyridine Chemical compound C1=CC=NC=C1 JUJWROOIHBZHMG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- KAESVJOAVNADME-UHFFFAOYSA-N Pyrrole Chemical compound C=1C=CNC=1 KAESVJOAVNADME-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910052581 Si3N4 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- CDBYLPFSWZWCQE-UHFFFAOYSA-L Sodium Carbonate Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[O-]C([O-])=O CDBYLPFSWZWCQE-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 2
- 239000004115 Sodium Silicate Substances 0.000 description 2
- IYFATESGLOUGBX-YVNJGZBMSA-N Sorbitan monopalmitate Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)OC[C@@H](O)[C@H]1OC[C@H](O)[C@H]1O IYFATESGLOUGBX-YVNJGZBMSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000004147 Sorbitan trioleate Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000003513 alkali Substances 0.000 description 2
- MWPLVEDNUUSJAV-UHFFFAOYSA-N anthracene Chemical compound C1=CC=CC2=CC3=CC=CC=C3C=C21 MWPLVEDNUUSJAV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 235000010233 benzoic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 229920001400 block copolymer Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 229940043232 butyl acetate Drugs 0.000 description 2
- NMJJFJNHVMGPGM-UHFFFAOYSA-N butyl formate Chemical compound CCCCOC=O NMJJFJNHVMGPGM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 125000000484 butyl group Chemical group [H]C([*])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 2
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 description 2
- BGTOWKSIORTVQH-UHFFFAOYSA-N cyclopentanone Chemical compound O=C1CCCC1 BGTOWKSIORTVQH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- JQVDAXLFBXTEQA-UHFFFAOYSA-N dibutylamine Chemical compound CCCCNCCCC JQVDAXLFBXTEQA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 235000014113 dietary fatty acids Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 125000003700 epoxy group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- CKSRFHWWBKRUKA-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 2-ethoxyacetate Chemical compound CCOCC(=O)OCC CKSRFHWWBKRUKA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- BHXIWUJLHYHGSJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 3-ethoxypropanoate Chemical compound CCOCCC(=O)OCC BHXIWUJLHYHGSJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229940093499 ethyl acetate Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 125000001495 ethyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 2
- FKRCODPIKNYEAC-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl propionate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)CC FKRCODPIKNYEAC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229940117360 ethyl pyruvate Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 238000011156 evaluation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000000194 fatty acid Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229930195729 fatty acid Natural products 0.000 description 2
- 239000011737 fluorine Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052731 fluorine Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 125000004051 hexyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 2
- 229940091173 hydantoin Drugs 0.000 description 2
- MLFHJEHSLIIPHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N isoamyl acetate Chemical compound CC(C)CCOC(C)=O MLFHJEHSLIIPHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- ZFSLODLOARCGLH-UHFFFAOYSA-N isocyanuric acid Chemical compound OC1=NC(O)=NC(O)=N1 ZFSLODLOARCGLH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 125000001449 isopropyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])(*)C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 2
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 2
- LPEKGGXMPWTOCB-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 2-hydroxypropionate Chemical compound COC(=O)C(C)O LPEKGGXMPWTOCB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- BDJSOPWXYLFTNW-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 3-methoxypropanoate Chemical compound COCCC(=O)OC BDJSOPWXYLFTNW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- TZIHFWKZFHZASV-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl formate Chemical compound COC=O TZIHFWKZFHZASV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 125000002496 methyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 2
- CWKLZLBVOJRSOM-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl pyruvate Chemical compound COC(=O)C(C)=O CWKLZLBVOJRSOM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 125000001147 pentyl group Chemical group C(CCCC)* 0.000 description 2
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 2
- 125000001436 propyl group Chemical group [H]C([*])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 2
- WGYKZJWCGVVSQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N propylamine Chemical compound CCCN WGYKZJWCGVVSQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 150000003242 quaternary ammonium salts Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 229960004889 salicylic acid Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 125000002914 sec-butyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])(*)C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 2
- HQVNEWCFYHHQES-UHFFFAOYSA-N silicon nitride Chemical compound N12[Si]34N5[Si]62N3[Si]51N64 HQVNEWCFYHHQES-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- NTHWMYGWWRZVTN-UHFFFAOYSA-N sodium silicate Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[O-][Si]([O-])=O NTHWMYGWWRZVTN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910052911 sodium silicate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000001570 sorbitan monopalmitate Substances 0.000 description 2
- 235000011071 sorbitan monopalmitate Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 229940031953 sorbitan monopalmitate Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 235000019337 sorbitan trioleate Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 229960000391 sorbitan trioleate Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 125000000472 sulfonyl group Chemical group *S(*)(=O)=O 0.000 description 2
- 125000000999 tert-butyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C(*)(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 2
- JOXIMZWYDAKGHI-UHFFFAOYSA-N toluene-4-sulfonic acid Chemical compound CC1=CC=C(S(O)(=O)=O)C=C1 JOXIMZWYDAKGHI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- WCRJSEARWSNVQQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N (3-methoxy-2-methylpentyl) acetate Chemical compound CCC(OC)C(C)COC(C)=O WCRJSEARWSNVQQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RYNQKSJRFHJZTK-UHFFFAOYSA-N (3-methoxy-3-methylbutyl) acetate Chemical compound COC(C)(C)CCOC(C)=O RYNQKSJRFHJZTK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XJBWZINBJGQQQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N (4-methoxy-3-methylpentyl) acetate Chemical compound COC(C)C(C)CCOC(C)=O XJBWZINBJGQQQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QAVJODPBTLNBSW-UHFFFAOYSA-N (4-methoxy-4-methylpentyl) acetate Chemical compound COC(C)(C)CCCOC(C)=O QAVJODPBTLNBSW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MIOPJNTWMNEORI-GMSGAONNSA-N (S)-camphorsulfonic acid Chemical compound C1C[C@@]2(CS(O)(=O)=O)C(=O)C[C@@H]1C2(C)C MIOPJNTWMNEORI-GMSGAONNSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FFJCNSLCJOQHKM-CLFAGFIQSA-N (z)-1-[(z)-octadec-9-enoxy]octadec-9-ene Chemical compound CCCCCCCC\C=C/CCCCCCCCOCCCCCCCC\C=C/CCCCCCCC FFJCNSLCJOQHKM-CLFAGFIQSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MCEKOERWHIKDFW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,1,3,3-tetrakis(butoxymethyl)urea Chemical compound CCCCOCN(COCCCC)C(=O)N(COCCCC)COCCCC MCEKOERWHIKDFW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GQNTZAWVZSKJKE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,1,3,3-tetrakis(methoxymethyl)urea Chemical compound COCN(COC)C(=O)N(COC)COC GQNTZAWVZSKJKE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZORQXIQZAOLNGE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,1-difluorocyclohexane Chemical compound FC1(F)CCCCC1 ZORQXIQZAOLNGE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JYEUMXHLPRZUAT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,2,3-triazine Chemical compound C1=CN=NN=C1 JYEUMXHLPRZUAT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WFCOXVISFBRIKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,3-bis(oxiran-2-ylmethyl)-1,3,5-triazinane-2,4,6-trione Chemical compound O=C1N(CC2OC2)C(=O)NC(=O)N1CC1CO1 WFCOXVISFBRIKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LIPRQQHINVWJCH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-ethoxypropan-2-yl acetate Chemical compound CCOCC(C)OC(C)=O LIPRQQHINVWJCH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CSZZMFWKAQEMPB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-methoxybutan-2-ol Chemical compound CCC(O)COC CSZZMFWKAQEMPB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FPZWZCWUIYYYBU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(2-ethoxyethoxy)ethyl acetate Chemical compound CCOCCOCCOC(C)=O FPZWZCWUIYYYBU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- SBASXUCJHJRPEV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(2-methoxyethoxy)ethanol Chemical compound COCCOCCO SBASXUCJHJRPEV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BJINVQNEBGOMCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(2-methoxyethoxy)ethyl acetate Chemical compound COCCOCCOC(C)=O BJINVQNEBGOMCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FMRPQUDARIAGBM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(2-phenoxyethoxy)ethyl acetate Chemical compound CC(=O)OCCOCCOC1=CC=CC=C1 FMRPQUDARIAGBM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GWQAFGZJIHVLGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(2-propoxyethoxy)ethyl acetate Chemical compound CCCOCCOCCOC(C)=O GWQAFGZJIHVLGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- UHOPWFKONJYLCF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(2-sulfanylethyl)isoindole-1,3-dione Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C(=O)N(CCS)C(=O)C2=C1 UHOPWFKONJYLCF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NQBXSWAWVZHKBZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-butoxyethyl acetate Chemical compound CCCCOCCOC(C)=O NQBXSWAWVZHKBZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- IELTYWXGBMOKQF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-ethoxybutyl acetate Chemical compound CCOC(CC)COC(C)=O IELTYWXGBMOKQF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZNQVEEAIQZEUHB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-ethoxyethanol Chemical compound CCOCCO ZNQVEEAIQZEUHB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- IPUDBCXGMBSQGH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-methoxybutan-1-ol Chemical compound CCC(CO)OC IPUDBCXGMBSQGH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CUAXPJTWOJMABP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-methoxypentyl acetate Chemical compound CCCC(OC)COC(C)=O CUAXPJTWOJMABP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BNCADMBVWNPPIZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-n,2-n,4-n,4-n,6-n,6-n-hexakis(methoxymethyl)-1,3,5-triazine-2,4,6-triamine Chemical compound COCN(COC)C1=NC(N(COC)COC)=NC(N(COC)COC)=N1 BNCADMBVWNPPIZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WHFKYDMBUMLWDA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-phenoxyethyl acetate Chemical compound CC(=O)OCCOC1=CC=CC=C1 WHFKYDMBUMLWDA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QMAQLCVJIYANPZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-propoxyethyl acetate Chemical compound CCCOCCOC(C)=O QMAQLCVJIYANPZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VYNUATGQEAAPAQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-sulfonylacetic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C=S(=O)=O VYNUATGQEAAPAQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MFKRHJVUCZRDTF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-methoxy-3-methylbutan-1-ol Chemical compound COC(C)(C)CCO MFKRHJVUCZRDTF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QMYGFTJCQFEDST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-methoxybutyl acetate Chemical compound COC(C)CCOC(C)=O QMYGFTJCQFEDST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NMUMFCGQLRQGCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-methoxypentyl acetate Chemical compound CCC(OC)CCOC(C)=O NMUMFCGQLRQGCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LDMRLRNXHLPZJN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-propoxypropan-1-ol Chemical compound CCCOCCCO LDMRLRNXHLPZJN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VPWNQTHUCYMVMZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4,4'-sulfonyldiphenol Chemical compound C1=CC(O)=CC=C1S(=O)(=O)C1=CC=C(O)C=C1 VPWNQTHUCYMVMZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RJWBTWIBUIGANW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-chlorobenzenesulfonic acid Chemical compound OS(=O)(=O)C1=CC=C(Cl)C=C1 RJWBTWIBUIGANW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VBWLLBDCDDWTBV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-ethoxybutyl acetate Chemical compound CCOCCCCOC(C)=O VBWLLBDCDDWTBV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LMLBDDCTBHGHEO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-methoxybutyl acetate Chemical compound COCCCCOC(C)=O LMLBDDCTBHGHEO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GQILQHFLUYJMSM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-methoxypentyl acetate Chemical compound COC(C)CCCOC(C)=O GQILQHFLUYJMSM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WVYWICLMDOOCFB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-methyl-2-pentanol Chemical compound CC(C)CC(C)O WVYWICLMDOOCFB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XGBAEJOFXMSUPI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-propoxybutyl acetate Chemical compound CCCOCCCCOC(C)=O XGBAEJOFXMSUPI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XZIIFPSPUDAGJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 6-chloro-2-n,2-n-diethylpyrimidine-2,4-diamine Chemical compound CCN(CC)C1=NC(N)=CC(Cl)=N1 XZIIFPSPUDAGJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VHUUQVKOLVNVRT-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ammonium hydroxide Chemical compound [NH4+].[OH-] VHUUQVKOLVNVRT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FERIUCNNQQJTOY-UHFFFAOYSA-M Butyrate Chemical compound CCCC([O-])=O FERIUCNNQQJTOY-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- CZFMWFUVKUTLNW-UHFFFAOYSA-N C(C)(=O)OCC(CC)OC.C(C)(=O)OCCOCCOCCCC Chemical compound C(C)(=O)OCC(CC)OC.C(C)(=O)OCCOCCOCCCC CZFMWFUVKUTLNW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethanol Chemical compound CCO LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- IJMWOMHMDSDKGK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Isopropyl propionate Chemical compound CCC(=O)OC(C)C IJMWOMHMDSDKGK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RJUFJBKOKNCXHH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methyl propionate Chemical compound CCC(=O)OC RJUFJBKOKNCXHH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XYVQFUJDGOBPQI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methyl-2-hydoxyisobutyric acid Chemical compound COC(=O)C(C)(C)O XYVQFUJDGOBPQI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WRQNANDWMGAFTP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methylacetoacetic acid Chemical group COC(=O)CC(C)=O WRQNANDWMGAFTP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 101100078144 Mus musculus Msrb1 gene Proteins 0.000 description 1
- UEEJHVSXFDXPFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-dimethylaminoethanol Chemical compound CN(C)CCO UEEJHVSXFDXPFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CTQNGGLPUBDAKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N O-Xylene Chemical compound CC1=CC=CC=C1C CTQNGGLPUBDAKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920001213 Polysorbate 20 Polymers 0.000 description 1
- CZPWVGJYEJSRLH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Pyrimidine Chemical compound C1=CN=CN=C1 CZPWVGJYEJSRLH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- HVUMOYIDDBPOLL-XWVZOOPGSA-N Sorbitan monostearate Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)OC[C@@H](O)[C@H]1OC[C@H](O)[C@H]1O HVUMOYIDDBPOLL-XWVZOOPGSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PRXRUNOAOLTIEF-ADSICKODSA-N Sorbitan trioleate Chemical compound CCCCCCCC\C=C/CCCCCCCC(=O)OC[C@@H](OC(=O)CCCCCCC\C=C/CCCCCCCC)[C@H]1OC[C@H](O)[C@H]1OC(=O)CCCCCCC\C=C/CCCCCCCC PRXRUNOAOLTIEF-ADSICKODSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GSEJCLTVZPLZKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Triethanolamine Chemical compound OCCN(CCO)CCO GSEJCLTVZPLZKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- IJCWFDPJFXGQBN-RYNSOKOISA-N [(2R)-2-[(2R,3R,4S)-4-hydroxy-3-octadecanoyloxyoxolan-2-yl]-2-octadecanoyloxyethyl] octadecanoate Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)OC[C@@H](OC(=O)CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC)[C@H]1OC[C@H](O)[C@H]1OC(=O)CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC IJCWFDPJFXGQBN-RYNSOKOISA-N 0.000 description 1
- KXKVLQRXCPHEJC-UHFFFAOYSA-N acetic acid trimethyl ester Natural products COC(C)=O KXKVLQRXCPHEJC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000000996 additive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004220 aggregation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002776 aggregation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 125000003545 alkoxy group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 150000001346 alkyl aryl ethers Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000005215 alkyl ethers Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229920005603 alternating copolymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N ammonia Natural products N QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229940072049 amyl acetate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- PGMYKACGEOXYJE-UHFFFAOYSA-N anhydrous amyl acetate Natural products CCCCCOC(C)=O PGMYKACGEOXYJE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000006117 anti-reflective coating Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000004429 atom Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- HNYOPLTXPVRDBG-UHFFFAOYSA-N barbituric acid Chemical compound O=C1CC(=O)NC(=O)N1 HNYOPLTXPVRDBG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MIAUJDCQDVWHEV-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzene-1,2-disulfonic acid Chemical compound OS(=O)(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1S(O)(=O)=O MIAUJDCQDVWHEV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NEPKLUNSRVEBIX-UHFFFAOYSA-N bis(oxiran-2-ylmethyl) benzene-1,4-dicarboxylate Chemical compound C=1C=C(C(=O)OCC2OC2)C=CC=1C(=O)OCC1CO1 NEPKLUNSRVEBIX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000001246 bromo group Chemical group Br* 0.000 description 1
- 238000012662 bulk polymerization Methods 0.000 description 1
- ZAZUOXBHFXAWMD-UHFFFAOYSA-N butyl 2-oxopropanoate Chemical compound CCCCOC(=O)C(C)=O ZAZUOXBHFXAWMD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- DFFDSQBEGQFJJU-UHFFFAOYSA-M butyl carbonate Chemical compound CCCCOC([O-])=O DFFDSQBEGQFJJU-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 229910052799 carbon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 125000003178 carboxy group Chemical group [H]OC(*)=O 0.000 description 1
- 125000001309 chloro group Chemical group Cl* 0.000 description 1
- OEYIOHPDSNJKLS-UHFFFAOYSA-N choline Chemical compound C[N+](C)(C)CCO OEYIOHPDSNJKLS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960001231 choline Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229920006037 cross link polymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 125000004976 cyclobutylene group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000004956 cyclohexylene group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000004979 cyclopentylene group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 229960002887 deanol Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 125000002704 decyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- 230000007547 defect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 1
- HPNMFZURTQLUMO-UHFFFAOYSA-N diethylamine Chemical compound CCNCC HPNMFZURTQLUMO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XXJWXESWEXIICW-UHFFFAOYSA-N diethylene glycol monoethyl ether Chemical compound CCOCCOCCO XXJWXESWEXIICW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229940075557 diethylene glycol monoethyl ether Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000012972 dimethylethanolamine Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000003438 dodecyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- 238000001035 drying Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000012776 electronic material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010828 elution Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000007720 emulsion polymerization reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005530 etching Methods 0.000 description 1
- 125000001301 ethoxy group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])O* 0.000 description 1
- GFUIDHWFLMPAGY-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 2-hydroxy-2-methylpropanoate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C(C)(C)O GFUIDHWFLMPAGY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZANNOFHADGWOLI-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 2-hydroxyacetate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)CO ZANNOFHADGWOLI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JLEKJZUYWFJPMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 2-methoxyacetate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)COC JLEKJZUYWFJPMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- IJUHLFUALMUWOM-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 3-methoxypropanoate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)CCOC IJUHLFUALMUWOM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XYIBRDXRRQCHLP-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl acetoacetate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)CC(C)=O XYIBRDXRRQCHLP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000000816 ethylene group Chemical group [H]C([H])([*:1])C([H])([H])[*:2] 0.000 description 1
- 125000001153 fluoro group Chemical group F* 0.000 description 1
- WBJINCZRORDGAQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N formic acid ethyl ester Natural products CCOC=O WBJINCZRORDGAQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000010528 free radical solution polymerization reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 125000000524 functional group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 238000007429 general method Methods 0.000 description 1
- VPVSTMAPERLKKM-UHFFFAOYSA-N glycoluril Chemical compound N1C(=O)NC2NC(=O)NC21 VPVSTMAPERLKKM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920000578 graft copolymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- MNWFXJYAOYHMED-UHFFFAOYSA-M heptanoate Chemical compound CCCCCCC([O-])=O MNWFXJYAOYHMED-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- YAMHXTCMCPHKLN-UHFFFAOYSA-N imidazolidin-2-one Chemical compound O=C1NCCN1 YAMHXTCMCPHKLN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000001771 impaired effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 125000002346 iodo group Chemical group I* 0.000 description 1
- 229940117955 isoamyl acetate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- JMMWKPVZQRWMSS-UHFFFAOYSA-N isopropanol acetate Natural products CC(C)OC(C)=O JMMWKPVZQRWMSS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229940011051 isopropyl acetate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- GWYFCOCPABKNJV-UHFFFAOYSA-N isovaleric acid Chemical compound CC(C)CC(O)=O GWYFCOCPABKNJV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LVWZTYCIRDMTEY-UHFFFAOYSA-N metamizole Chemical compound O=C1C(N(CS(O)(=O)=O)C)=C(C)N(C)N1C1=CC=CC=C1 LVWZTYCIRDMTEY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000000956 methoxy group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])O* 0.000 description 1
- 125000004184 methoxymethyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])OC([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- YSGBMDFJWFIEDF-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 2-hydroxy-3-methylbutanoate Chemical compound COC(=O)C(O)C(C)C YSGBMDFJWFIEDF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- HSDFKDZBJMDHFF-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 3-ethoxypropanoate Chemical compound CCOCCC(=O)OC HSDFKDZBJMDHFF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229940017219 methyl propionate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 125000001570 methylene group Chemical group [H]C([H])([*:1])[*:2] 0.000 description 1
- 125000004170 methylsulfonyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])S(*)(=O)=O 0.000 description 1
- CQDGTJPVBWZJAZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N monoethyl carbonate Chemical compound CCOC(O)=O CQDGTJPVBWZJAZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GNVRJGIVDSQCOP-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-ethyl-n-methylethanamine Chemical compound CCN(C)CC GNVRJGIVDSQCOP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PSZYNBSKGUBXEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N naphthalene-1-sulfonic acid Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C(S(=O)(=O)O)=CC=CC2=C1 PSZYNBSKGUBXEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000001400 nonyl group Chemical group [H]C([*])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- 229920002114 octoxynol-9 Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 125000002347 octyl group Chemical group [H]C([*])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- 125000005375 organosiloxane group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000004430 oxygen atom Chemical group O* 0.000 description 1
- QUBQYFYWUJJAAK-UHFFFAOYSA-N oxymethurea Chemical compound OCNC(=O)NCO QUBQYFYWUJJAAK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920000259 polyoxyethylene lauryl ether Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000000256 polyoxyethylene sorbitan monolaurate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000010486 polyoxyethylene sorbitan monolaurate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000001818 polyoxyethylene sorbitan monostearate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000010989 polyoxyethylene sorbitan monostearate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000001816 polyoxyethylene sorbitan tristearate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000010988 polyoxyethylene sorbitan tristearate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229920001451 polypropylene glycol Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 150000003141 primary amines Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000003672 processing method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 125000002572 propoxy group Chemical group [*]OC([H])([H])C(C([H])([H])[H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- ILVGAIQLOCKNQA-UHFFFAOYSA-N propyl 2-hydroxypropanoate Chemical compound CCCOC(=O)C(C)O ILVGAIQLOCKNQA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ILPVOWZUBFRIAX-UHFFFAOYSA-N propyl 2-oxopropanoate Chemical compound CCCOC(=O)C(C)=O ILPVOWZUBFRIAX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JCMFJIHDWDKYIL-UHFFFAOYSA-N propyl 3-methoxypropanoate Chemical compound CCCOC(=O)CCOC JCMFJIHDWDKYIL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FOWDZVNRQHPXDO-UHFFFAOYSA-N propyl hydrogen carbonate Chemical compound CCCOC(O)=O FOWDZVNRQHPXDO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000001681 protective effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- UMJSCPRVCHMLSP-UHFFFAOYSA-N pyridine Natural products COC1=CC=CN=C1 UMJSCPRVCHMLSP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZDYVRSLAEXCVBX-UHFFFAOYSA-N pyridinium p-toluenesulfonate Chemical compound C1=CC=[NH+]C=C1.CC1=CC=C(S([O-])(=O)=O)C=C1 ZDYVRSLAEXCVBX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000010453 quartz Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920005604 random copolymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 230000035484 reaction time Effects 0.000 description 1
- 150000003335 secondary amines Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229910052814 silicon oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910000029 sodium carbonate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 235000019795 sodium metasilicate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229940035044 sorbitan monolaurate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000001593 sorbitan monooleate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000011069 sorbitan monooleate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229940035049 sorbitan monooleate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000001587 sorbitan monostearate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000011076 sorbitan monostearate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229940035048 sorbitan monostearate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000001589 sorbitan tristearate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000011078 sorbitan tristearate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229960004129 sorbitan tristearate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 150000003460 sulfonic acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229910052717 sulfur Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 125000004434 sulfur atom Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 238000010557 suspension polymerization reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000003512 tertiary amines Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229940073455 tetraethylammonium hydroxide Drugs 0.000 description 1
- LRGJRHZIDJQFCL-UHFFFAOYSA-M tetraethylazanium;hydroxide Chemical compound [OH-].CC[N+](CC)(CC)CC LRGJRHZIDJQFCL-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- ITMCEJHCFYSIIV-UHFFFAOYSA-N triflic acid Chemical compound OS(=O)(=O)C(F)(F)F ITMCEJHCFYSIIV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000002948 undecyl group Chemical group [H]C([*])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- 239000008096 xylene Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G03—PHOTOGRAPHY; CINEMATOGRAPHY; ANALOGOUS TECHNIQUES USING WAVES OTHER THAN OPTICAL WAVES; ELECTROGRAPHY; HOLOGRAPHY
- G03F—PHOTOMECHANICAL PRODUCTION OF TEXTURED OR PATTERNED SURFACES, e.g. FOR PRINTING, FOR PROCESSING OF SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; MATERIALS THEREFOR; ORIGINALS THEREFOR; APPARATUS SPECIALLY ADAPTED THEREFOR
- G03F7/00—Photomechanical, e.g. photolithographic, production of textured or patterned surfaces, e.g. printing surfaces; Materials therefor, e.g. comprising photoresists; Apparatus specially adapted therefor
- G03F7/004—Photosensitive materials
- G03F7/09—Photosensitive materials characterised by structural details, e.g. supports, auxiliary layers
- G03F7/11—Photosensitive materials characterised by structural details, e.g. supports, auxiliary layers having cover layers or intermediate layers, e.g. subbing layers
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08G—MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS OBTAINED OTHERWISE THAN BY REACTIONS ONLY INVOLVING UNSATURATED CARBON-TO-CARBON BONDS
- C08G73/00—Macromolecular compounds obtained by reactions forming a linkage containing nitrogen with or without oxygen or carbon in the main chain of the macromolecule, not provided for in groups C08G12/00 - C08G71/00
- C08G73/06—Polycondensates having nitrogen-containing heterocyclic rings in the main chain of the macromolecule
- C08G73/0605—Polycondensates containing five-membered rings, not condensed with other rings, with nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms
- C08G73/0616—Polycondensates containing five-membered rings, not condensed with other rings, with nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms with only two nitrogen atoms in the ring
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08G—MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS OBTAINED OTHERWISE THAN BY REACTIONS ONLY INVOLVING UNSATURATED CARBON-TO-CARBON BONDS
- C08G73/00—Macromolecular compounds obtained by reactions forming a linkage containing nitrogen with or without oxygen or carbon in the main chain of the macromolecule, not provided for in groups C08G12/00 - C08G71/00
- C08G73/06—Polycondensates having nitrogen-containing heterocyclic rings in the main chain of the macromolecule
- C08G73/0622—Polycondensates containing six-membered rings, not condensed with other rings, with nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms
- C08G73/0633—Polycondensates containing six-membered rings, not condensed with other rings, with nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms with only two nitrogen atoms in the ring
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08G—MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS OBTAINED OTHERWISE THAN BY REACTIONS ONLY INVOLVING UNSATURATED CARBON-TO-CARBON BONDS
- C08G73/00—Macromolecular compounds obtained by reactions forming a linkage containing nitrogen with or without oxygen or carbon in the main chain of the macromolecule, not provided for in groups C08G12/00 - C08G71/00
- C08G73/06—Polycondensates having nitrogen-containing heterocyclic rings in the main chain of the macromolecule
- C08G73/0622—Polycondensates containing six-membered rings, not condensed with other rings, with nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms
- C08G73/0638—Polycondensates containing six-membered rings, not condensed with other rings, with nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms with at least three nitrogen atoms in the ring
- C08G73/0644—Poly(1,3,5)triazines
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08G—MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS OBTAINED OTHERWISE THAN BY REACTIONS ONLY INVOLVING UNSATURATED CARBON-TO-CARBON BONDS
- C08G73/00—Macromolecular compounds obtained by reactions forming a linkage containing nitrogen with or without oxygen or carbon in the main chain of the macromolecule, not provided for in groups C08G12/00 - C08G71/00
- C08G73/06—Polycondensates having nitrogen-containing heterocyclic rings in the main chain of the macromolecule
- C08G73/0622—Polycondensates containing six-membered rings, not condensed with other rings, with nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms
- C08G73/0638—Polycondensates containing six-membered rings, not condensed with other rings, with nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms with at least three nitrogen atoms in the ring
- C08G73/065—Preparatory processes
- C08G73/0655—Preparatory processes from polycyanurates
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09D—COATING COMPOSITIONS, e.g. PAINTS, VARNISHES OR LACQUERS; FILLING PASTES; CHEMICAL PAINT OR INK REMOVERS; INKS; CORRECTING FLUIDS; WOODSTAINS; PASTES OR SOLIDS FOR COLOURING OR PRINTING; USE OF MATERIALS THEREFOR
- C09D179/00—Coating compositions based on macromolecular compounds obtained by reactions forming in the main chain of the macromolecule a linkage containing nitrogen, with or without oxygen, or carbon only, not provided for in groups C09D161/00 - C09D177/00
- C09D179/04—Polycondensates having nitrogen-containing heterocyclic rings in the main chain; Polyhydrazides; Polyamide acids or similar polyimide precursors
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09D—COATING COMPOSITIONS, e.g. PAINTS, VARNISHES OR LACQUERS; FILLING PASTES; CHEMICAL PAINT OR INK REMOVERS; INKS; CORRECTING FLUIDS; WOODSTAINS; PASTES OR SOLIDS FOR COLOURING OR PRINTING; USE OF MATERIALS THEREFOR
- C09D179/00—Coating compositions based on macromolecular compounds obtained by reactions forming in the main chain of the macromolecule a linkage containing nitrogen, with or without oxygen, or carbon only, not provided for in groups C09D161/00 - C09D177/00
- C09D179/04—Polycondensates having nitrogen-containing heterocyclic rings in the main chain; Polyhydrazides; Polyamide acids or similar polyimide precursors
- C09D179/08—Polyimides; Polyester-imides; Polyamide-imides; Polyamide acids or similar polyimide precursors
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G03—PHOTOGRAPHY; CINEMATOGRAPHY; ANALOGOUS TECHNIQUES USING WAVES OTHER THAN OPTICAL WAVES; ELECTROGRAPHY; HOLOGRAPHY
- G03F—PHOTOMECHANICAL PRODUCTION OF TEXTURED OR PATTERNED SURFACES, e.g. FOR PRINTING, FOR PROCESSING OF SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; MATERIALS THEREFOR; ORIGINALS THEREFOR; APPARATUS SPECIALLY ADAPTED THEREFOR
- G03F7/00—Photomechanical, e.g. photolithographic, production of textured or patterned surfaces, e.g. printing surfaces; Materials therefor, e.g. comprising photoresists; Apparatus specially adapted therefor
- G03F7/004—Photosensitive materials
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G03—PHOTOGRAPHY; CINEMATOGRAPHY; ANALOGOUS TECHNIQUES USING WAVES OTHER THAN OPTICAL WAVES; ELECTROGRAPHY; HOLOGRAPHY
- G03F—PHOTOMECHANICAL PRODUCTION OF TEXTURED OR PATTERNED SURFACES, e.g. FOR PRINTING, FOR PROCESSING OF SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; MATERIALS THEREFOR; ORIGINALS THEREFOR; APPARATUS SPECIALLY ADAPTED THEREFOR
- G03F7/00—Photomechanical, e.g. photolithographic, production of textured or patterned surfaces, e.g. printing surfaces; Materials therefor, e.g. comprising photoresists; Apparatus specially adapted therefor
- G03F7/004—Photosensitive materials
- G03F7/0045—Photosensitive materials with organic non-macromolecular light-sensitive compounds not otherwise provided for, e.g. dissolution inhibitors
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G03—PHOTOGRAPHY; CINEMATOGRAPHY; ANALOGOUS TECHNIQUES USING WAVES OTHER THAN OPTICAL WAVES; ELECTROGRAPHY; HOLOGRAPHY
- G03F—PHOTOMECHANICAL PRODUCTION OF TEXTURED OR PATTERNED SURFACES, e.g. FOR PRINTING, FOR PROCESSING OF SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; MATERIALS THEREFOR; ORIGINALS THEREFOR; APPARATUS SPECIALLY ADAPTED THEREFOR
- G03F7/00—Photomechanical, e.g. photolithographic, production of textured or patterned surfaces, e.g. printing surfaces; Materials therefor, e.g. comprising photoresists; Apparatus specially adapted therefor
- G03F7/004—Photosensitive materials
- G03F7/09—Photosensitive materials characterised by structural details, e.g. supports, auxiliary layers
- G03F7/094—Multilayer resist systems, e.g. planarising layers
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G03—PHOTOGRAPHY; CINEMATOGRAPHY; ANALOGOUS TECHNIQUES USING WAVES OTHER THAN OPTICAL WAVES; ELECTROGRAPHY; HOLOGRAPHY
- G03F—PHOTOMECHANICAL PRODUCTION OF TEXTURED OR PATTERNED SURFACES, e.g. FOR PRINTING, FOR PROCESSING OF SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; MATERIALS THEREFOR; ORIGINALS THEREFOR; APPARATUS SPECIALLY ADAPTED THEREFOR
- G03F7/00—Photomechanical, e.g. photolithographic, production of textured or patterned surfaces, e.g. printing surfaces; Materials therefor, e.g. comprising photoresists; Apparatus specially adapted therefor
- G03F7/16—Coating processes; Apparatus therefor
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G03—PHOTOGRAPHY; CINEMATOGRAPHY; ANALOGOUS TECHNIQUES USING WAVES OTHER THAN OPTICAL WAVES; ELECTROGRAPHY; HOLOGRAPHY
- G03F—PHOTOMECHANICAL PRODUCTION OF TEXTURED OR PATTERNED SURFACES, e.g. FOR PRINTING, FOR PROCESSING OF SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; MATERIALS THEREFOR; ORIGINALS THEREFOR; APPARATUS SPECIALLY ADAPTED THEREFOR
- G03F7/00—Photomechanical, e.g. photolithographic, production of textured or patterned surfaces, e.g. printing surfaces; Materials therefor, e.g. comprising photoresists; Apparatus specially adapted therefor
- G03F7/16—Coating processes; Apparatus therefor
- G03F7/162—Coating on a rotating support, e.g. using a whirler or a spinner
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G03—PHOTOGRAPHY; CINEMATOGRAPHY; ANALOGOUS TECHNIQUES USING WAVES OTHER THAN OPTICAL WAVES; ELECTROGRAPHY; HOLOGRAPHY
- G03F—PHOTOMECHANICAL PRODUCTION OF TEXTURED OR PATTERNED SURFACES, e.g. FOR PRINTING, FOR PROCESSING OF SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; MATERIALS THEREFOR; ORIGINALS THEREFOR; APPARATUS SPECIALLY ADAPTED THEREFOR
- G03F7/00—Photomechanical, e.g. photolithographic, production of textured or patterned surfaces, e.g. printing surfaces; Materials therefor, e.g. comprising photoresists; Apparatus specially adapted therefor
- G03F7/16—Coating processes; Apparatus therefor
- G03F7/168—Finishing the coated layer, e.g. drying, baking, soaking
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G03—PHOTOGRAPHY; CINEMATOGRAPHY; ANALOGOUS TECHNIQUES USING WAVES OTHER THAN OPTICAL WAVES; ELECTROGRAPHY; HOLOGRAPHY
- G03F—PHOTOMECHANICAL PRODUCTION OF TEXTURED OR PATTERNED SURFACES, e.g. FOR PRINTING, FOR PROCESSING OF SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; MATERIALS THEREFOR; ORIGINALS THEREFOR; APPARATUS SPECIALLY ADAPTED THEREFOR
- G03F7/00—Photomechanical, e.g. photolithographic, production of textured or patterned surfaces, e.g. printing surfaces; Materials therefor, e.g. comprising photoresists; Apparatus specially adapted therefor
- G03F7/20—Exposure; Apparatus therefor
- G03F7/2002—Exposure; Apparatus therefor with visible light or UV light, through an original having an opaque pattern on a transparent support, e.g. film printing, projection printing; by reflection of visible or UV light from an original such as a printed image
- G03F7/2004—Exposure; Apparatus therefor with visible light or UV light, through an original having an opaque pattern on a transparent support, e.g. film printing, projection printing; by reflection of visible or UV light from an original such as a printed image characterised by the use of a particular light source, e.g. fluorescent lamps or deep UV light
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G03—PHOTOGRAPHY; CINEMATOGRAPHY; ANALOGOUS TECHNIQUES USING WAVES OTHER THAN OPTICAL WAVES; ELECTROGRAPHY; HOLOGRAPHY
- G03F—PHOTOMECHANICAL PRODUCTION OF TEXTURED OR PATTERNED SURFACES, e.g. FOR PRINTING, FOR PROCESSING OF SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; MATERIALS THEREFOR; ORIGINALS THEREFOR; APPARATUS SPECIALLY ADAPTED THEREFOR
- G03F7/00—Photomechanical, e.g. photolithographic, production of textured or patterned surfaces, e.g. printing surfaces; Materials therefor, e.g. comprising photoresists; Apparatus specially adapted therefor
- G03F7/20—Exposure; Apparatus therefor
- G03F7/2002—Exposure; Apparatus therefor with visible light or UV light, through an original having an opaque pattern on a transparent support, e.g. film printing, projection printing; by reflection of visible or UV light from an original such as a printed image
- G03F7/2004—Exposure; Apparatus therefor with visible light or UV light, through an original having an opaque pattern on a transparent support, e.g. film printing, projection printing; by reflection of visible or UV light from an original such as a printed image characterised by the use of a particular light source, e.g. fluorescent lamps or deep UV light
- G03F7/2006—Exposure; Apparatus therefor with visible light or UV light, through an original having an opaque pattern on a transparent support, e.g. film printing, projection printing; by reflection of visible or UV light from an original such as a printed image characterised by the use of a particular light source, e.g. fluorescent lamps or deep UV light using coherent light; using polarised light
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G03—PHOTOGRAPHY; CINEMATOGRAPHY; ANALOGOUS TECHNIQUES USING WAVES OTHER THAN OPTICAL WAVES; ELECTROGRAPHY; HOLOGRAPHY
- G03F—PHOTOMECHANICAL PRODUCTION OF TEXTURED OR PATTERNED SURFACES, e.g. FOR PRINTING, FOR PROCESSING OF SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; MATERIALS THEREFOR; ORIGINALS THEREFOR; APPARATUS SPECIALLY ADAPTED THEREFOR
- G03F7/00—Photomechanical, e.g. photolithographic, production of textured or patterned surfaces, e.g. printing surfaces; Materials therefor, e.g. comprising photoresists; Apparatus specially adapted therefor
- G03F7/20—Exposure; Apparatus therefor
- G03F7/2037—Exposure with X-ray radiation or corpuscular radiation, through a mask with a pattern opaque to that radiation
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G03—PHOTOGRAPHY; CINEMATOGRAPHY; ANALOGOUS TECHNIQUES USING WAVES OTHER THAN OPTICAL WAVES; ELECTROGRAPHY; HOLOGRAPHY
- G03F—PHOTOMECHANICAL PRODUCTION OF TEXTURED OR PATTERNED SURFACES, e.g. FOR PRINTING, FOR PROCESSING OF SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; MATERIALS THEREFOR; ORIGINALS THEREFOR; APPARATUS SPECIALLY ADAPTED THEREFOR
- G03F7/00—Photomechanical, e.g. photolithographic, production of textured or patterned surfaces, e.g. printing surfaces; Materials therefor, e.g. comprising photoresists; Apparatus specially adapted therefor
- G03F7/20—Exposure; Apparatus therefor
- G03F7/2051—Exposure without an original mask, e.g. using a programmed deflection of a point source, by scanning, by drawing with a light beam, using an addressed light or corpuscular source
- G03F7/2053—Exposure without an original mask, e.g. using a programmed deflection of a point source, by scanning, by drawing with a light beam, using an addressed light or corpuscular source using a laser
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G03—PHOTOGRAPHY; CINEMATOGRAPHY; ANALOGOUS TECHNIQUES USING WAVES OTHER THAN OPTICAL WAVES; ELECTROGRAPHY; HOLOGRAPHY
- G03F—PHOTOMECHANICAL PRODUCTION OF TEXTURED OR PATTERNED SURFACES, e.g. FOR PRINTING, FOR PROCESSING OF SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; MATERIALS THEREFOR; ORIGINALS THEREFOR; APPARATUS SPECIALLY ADAPTED THEREFOR
- G03F7/00—Photomechanical, e.g. photolithographic, production of textured or patterned surfaces, e.g. printing surfaces; Materials therefor, e.g. comprising photoresists; Apparatus specially adapted therefor
- G03F7/26—Processing photosensitive materials; Apparatus therefor
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/04—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer
- H01L21/18—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer the devices having semiconductor bodies comprising elements of Group IV of the Periodic Table or AIIIBV compounds with or without impurities, e.g. doping materials
- H01L21/30—Treatment of semiconductor bodies using processes or apparatus not provided for in groups H01L21/20 - H01L21/26
- H01L21/302—Treatment of semiconductor bodies using processes or apparatus not provided for in groups H01L21/20 - H01L21/26 to change their surface-physical characteristics or shape, e.g. etching, polishing, cutting
- H01L21/306—Chemical or electrical treatment, e.g. electrolytic etching
- H01L21/308—Chemical or electrical treatment, e.g. electrolytic etching using masks
- H01L21/3081—Chemical or electrical treatment, e.g. electrolytic etching using masks characterised by their composition, e.g. multilayer masks, materials
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/04—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer
- H01L21/18—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer the devices having semiconductor bodies comprising elements of Group IV of the Periodic Table or AIIIBV compounds with or without impurities, e.g. doping materials
- H01L21/30—Treatment of semiconductor bodies using processes or apparatus not provided for in groups H01L21/20 - H01L21/26
- H01L21/302—Treatment of semiconductor bodies using processes or apparatus not provided for in groups H01L21/20 - H01L21/26 to change their surface-physical characteristics or shape, e.g. etching, polishing, cutting
- H01L21/306—Chemical or electrical treatment, e.g. electrolytic etching
- H01L21/308—Chemical or electrical treatment, e.g. electrolytic etching using masks
- H01L21/3083—Chemical or electrical treatment, e.g. electrolytic etching using masks characterised by their size, orientation, disposition, behaviour, shape, in horizontal or vertical plane
- H01L21/3086—Chemical or electrical treatment, e.g. electrolytic etching using masks characterised by their size, orientation, disposition, behaviour, shape, in horizontal or vertical plane characterised by the process involved to create the mask, e.g. lift-off masks, sidewalls, or to modify the mask, e.g. pre-treatment, post-treatment
Definitions
- the present invention is excellent in solubility in an organic solvent of a solid content, has good coating properties on a substrate, and aims at improving the line width variation of the resist pattern to be formed and the adhesion of the resist pattern.
- the present invention relates to a resist underlayer film forming composition for lithography and a resist pattern forming method using the resist underlayer film forming composition.
- the microfabrication forms a thin film of a photoresist composition on a semiconductor substrate such as a silicon wafer, and irradiates with an actinic ray such as ultraviolet rays through a mask pattern on which a device pattern is drawn, and develops it.
- This is a processing method for forming fine irregularities corresponding to the pattern on the substrate surface by etching the substrate using the obtained photoresist pattern as a protective film.
- Patent Documents 1 to 3 there is no intermixing with the photoresist film formed on the upper layer, and when exposure is performed using an ArF excimer laser, desired optical parameters (k value, n value) are obtained, and A resist underlayer film (antireflection film) capable of obtaining a desired dry etching rate is disclosed.
- the characteristics required for the resist lower layer film include, for example, that no intermixing with the resist film formed in the upper layer occurs (insoluble in the resist solvent), and a higher dry etching rate than the resist film. Is mentioned.
- the line width of the resist pattern to be formed is 32 nm or less, and the resist underlayer film for EUV exposure is used with a thinner film thickness than in the past.
- the resist underlayer film for EUV exposure is used with a thinner film thickness than in the past.
- An object of this invention is to obtain the composition for forming a resist underlayer film which can form a desired resist pattern by solving the said subject.
- the inventors of the present invention have found that the above problem can be solved by using a resist underlayer film forming composition containing a polymer having a sulfonyl group introduced at a terminal site in a lithography process.
- the first aspect of the present invention is a lithography comprising a polymer having a structure represented by the following formula (1) or (2) at the end of a polymer chain, a crosslinking agent, a compound for promoting a crosslinking reaction, and an organic solvent.
- the present invention relates to a resist underlayer film forming composition.
- R 1 represents an alkyl group having 1 to 6 carbon atoms which may have a substituent, a phenyl group, a pyridyl group, a halogeno group or a hydroxy group
- R 2 represents a hydrogen atom, 1 to 1 carbon atoms
- 6 represents an alkyl group, a hydroxy group, a halogeno group or an ester group represented by —C ( ⁇ O) OX, wherein X represents an optionally substituted alkyl group having 1 to 6 carbon atoms.
- R 3 represents a hydrogen atom, an alkyl group having 1 to 6 carbon atoms, a hydroxy group or a halogeno group
- R 4 represents a direct bond, or a divalent organic group having 1 to 8 carbon atoms
- R 5 represents Represents a divalent organic group having 1 to 8 carbon atoms
- A represents an aromatic ring or an aromatic heterocyclic ring
- t represents 0 or 1
- u represents 1 or 2.
- X represents an alkyl group having a substituent
- substituent include an alkoxy group having 1 to 3 carbon atoms such as a methoxy group, an ethoxy group, and a propoxy group.
- the divalent organic group may have one or more atoms selected from a nitrogen atom, an oxygen atom, and a sulfur atom.
- halogeno group and the halogeno group described later in this specification include a fluoro group, a chloro group, a bromo group, and an iodo group.
- a resist underlayer film forming composition for lithography of the present invention is applied on a semiconductor substrate and baked to form a resist underlayer film.
- a resist solution is used on the resist underlayer film.
- a step of forming a film a step of exposing the semiconductor substrate coated with the resist underlayer film and the resist film with radiation selected from the group consisting of KrF excimer laser, ArF excimer laser, extreme ultraviolet (EUV), and electron beam, And a method of forming a resist pattern including a step of developing after exposure.
- the polymer terminal contained in the resist underlayer film forming composition is capped with a structure represented by the formula (1) or formula (2).
- a composition comprising such a polymer, a crosslinking agent, a compound that promotes a crosslinking reaction, and an organic solvent.
- FIG. 1 is a diagram showing an upper surface and a cross-section of a substrate on which a pattern is used, which is used in an applicability test.
- the polymer contained in the resist underlayer film forming composition for lithography of the present invention has a structure represented by the above formula (1) or (2) at the end of the polymer chain.
- the polymer is a compound represented by the following formula (1a), a compound represented by the following formula (2a), or both a compound represented by the following formula (1b) and a compound represented by the following formula (3).
- the reaction product of the raw material monomer containing. wherein R 1 , R 2 , R 3 , R 4 , R 5 , X, A, t, and u are R 1 , R 2 , (It has the same definition as R 3 , R 4 , R 5 , X, A, t and u.)
- alkyl group having 1 to 6 carbon atoms as described above and later in the specification include, for example, methyl group, ethyl group, propyl group, isopropyl group, butyl group, sec-butyl group, tert-butyl group, pentyl group and hexyl.
- the group can be mentioned.
- Examples of the aromatic ring described above and later in the specification include benzene, naphthalene, and anthracene.
- Examples of the aromatic heterocycle include triazine, pyrimidine, imidazole, and pyridine.
- the polymer has, for example, a structural unit represented by the following formula (4) and a structural unit represented by the following formula (5).
- Q 1 and Q 2 are each independently a divalent organic group having a hydrocarbon group having 1 to 13 carbon atoms which may have a substituent, or a divalent organic group having an aromatic ring. Or a divalent organic group having a heterocyclic ring containing 1 to 3 nitrogen atoms.
- the hydrocarbon group having 1 to 13 carbon atoms represents, for example, a linear or branched alkyl group having 1 to 13 carbon atoms, and is a tert-butyl group, a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, or an isopropyl group. Butyl group, sec-butyl group, pentyl group, hexyl group, octyl group, nonyl group, decyl group, undecyl group and dodecyl group.
- examples of the substituent include a halogeno group.
- the hydrocarbon group is a linear or branched hydrocarbon group, an alicyclic hydrocarbon group, or a combination of a linear or branched hydrocarbon group and an alicyclic hydrocarbon group.
- the alicyclic hydrocarbon group include a cyclobutylene group, a cyclopentylene group, and a cyclohexylene group.
- the heterocyclic ring containing 1 to 3 nitrogen atoms include triazine trione, pyrimidine trione, imidazolidinedione, imidazolidone and pyridone.
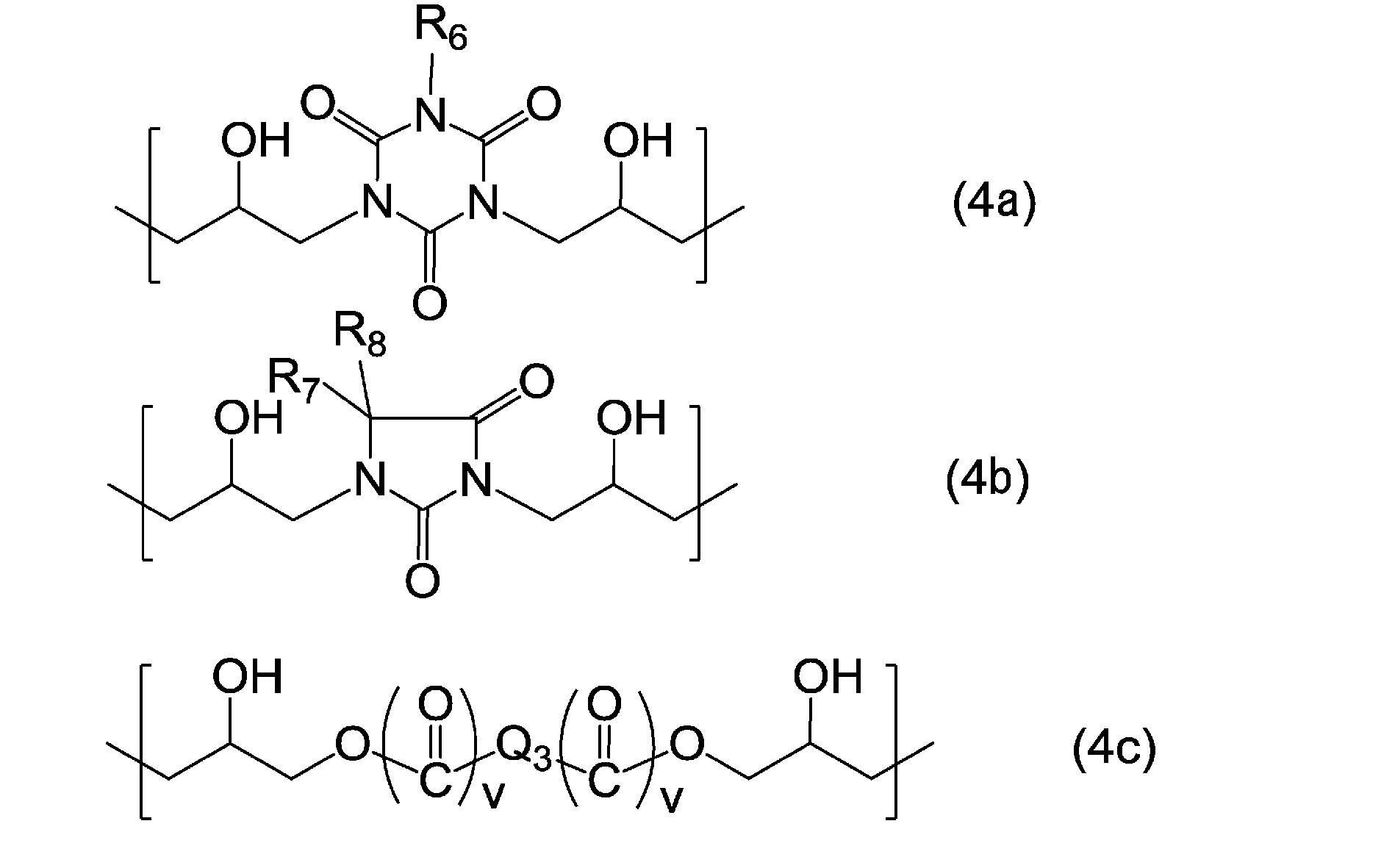
- the structural unit represented by the formula (4) is, for example, a structural unit represented by the following formula (4a), formula (4b), or formula (4c).
- R 6 represents a hydrogen atom, an alkyl group having 1 to 6 carbon atoms, or an allyl group
- R 7 and R 8 each independently represents a hydrogen atom or an alkyl group having 1 to 6 carbon atoms
- Q 3 represents a hydrocarbon group having 1 to 13 carbon atoms which may have a substituent, or an aromatic ring which may have a substituent
- two v's independently represent 0 or 1.
- examples of the substituent include a halogeno group.
- the hydrocarbon group is a linear or branched hydrocarbon group, an alicyclic hydrocarbon group, or a combination of a linear or branched hydrocarbon group and an alicyclic hydrocarbon group.
- examples of the substituent include an alkyl group having 1 to 6 carbon atoms.
- Q 3 represents a group represented by the following formula, for example.
- the structural unit represented by the formula (5) is, for example, a structural unit represented by the following formula (5a), formula (5b), formula (5c), or formula (5d).
- R 9 and R 10 each independently represents a hydrogen atom, an alkyl group having 1 to 6 carbon atoms or an aromatic ring
- R 11 represents an alkyl group having 1 to 6 carbon atoms, or an allyl group
- R 12 and R 13 each independently represents an alkylene group having 1 to 3 carbon atoms, such as a methylene group, an ethylene group, or a propylene group
- Q 4 is a carbon atom having 1 to 13 carbon atoms that may have a substituent.
- Q 4 is a carbon atom having 1 to 13 carbon atoms that may have a substituent.
- examples of the substituent include a hydroxy group and a halogeno group.
- the hydrocarbon group is a linear or branched hydrocarbon group, an alicyclic hydrocarbon group, or a combination of a linear or branched hydrocarbon group and an alicyclic hydrocarbon group.
- the linear or branched hydrocarbon group may have a double bond between two carbon atoms.
- examples of the substituent include an alkyl group having 1 to 6 carbon atoms and a hydroxy group.
- Q 4 represents, for example, a group represented by the following formula.
- Examples of the compound represented by the formula (1a) include compounds represented by the following formulas (1a-1) to (1a-89).
- Examples of the compound represented by the formula (2a) include compounds represented by the following formulas (2a-1) to (2a-18).
- Examples of the compound represented by the formula (1b) include compounds represented by the following formulas (1b-1) to (1b-20).
- Examples of the compound represented by the formula (3) include propylene glycol monomethyl ether and 4-methyl-2-pentanol, but are not limited thereto.
- Examples of the monomer that forms the structural unit represented by the formula (4) include compounds having two epoxy groups represented by the following formulas (4-1) to (4-16). it can.
- Examples of the monomer that forms the structural unit represented by the formula (5) include compounds represented by the following formulas (5-1) to (5-12).
- the polymer contained in the resist underlayer film forming composition for lithography of the present invention is, for example, a polymer represented by the following formula (6) or formula (7).
- R 1 , R 2 , R 3 , R 4 , R 5 , A, t, and u are R 1 , R 2 , R 3 , and the structure represented by the formula (1) or (2), R 4, R 5, X, a, has the same meaning as defined in t and u
- Y is a polymer chain having a structural unit represented by the formula (4) and a structural unit formula represented (5) To express.
- the compound represented by the formula (1a), the compound represented by the formula (2a), or the formula ( Both the compound represented by 1b) and the compound represented by the formula (3) include a monomer that forms the structural unit represented by the formula (4) and the structural unit represented by the formula (5).
- the total amount of monomers to be formed is 100% by mass, it is, for example, 1% by mass to 30% by mass (in terms of monomer charge ratio), and preferably 2% by mass to 20% by mass.
- the polymer contained in the resist underlayer film forming composition for lithography of the present invention may be any of a random copolymer, a block copolymer, an alternating copolymer, and a graft copolymer.
- a polymer polymerization method various methods such as solution polymerization, suspension polymerization, emulsion polymerization, and bulk polymerization are possible, and a polymerization catalyst or the like may be appropriately used.
- the monomer that forms the structural unit represented by the formula (4) and the monomer that forms the structural unit represented by the formula (5) are represented by the formula (1a).
- a compound represented by the formula (2a) and a polymerization catalyst can be added to carry out heat polymerization to synthesize.
- the organic solvent used here can be suitably selected from the preferable examples as the organic solvent contained in the resist underlayer film forming composition for lithography of the present invention described later.
- the polymerization catalyst include benzyltriethylammonium chloride and ethyltriphenylphosphonium bromide.
- the polymerization can be performed by heating to 50 ° C to 160 ° C, preferably 70 ° C to 130 ° C.
- the reaction time is, for example, 1 hour to 50 hours, preferably 2 hours to 12 hours.
- the weight average molecular weight of the polymer is, for example, 800 to 100,000, preferably 800 to 10,000. When the value of this weight average molecular weight is too high, the applicability of the resist underlayer film forming composition for lithography of the present invention deteriorates.
- the resist underlayer film forming composition for lithography of the present invention is 100% by mass, the polymer contained in the composition is, for example, 0.01% by mass to 3% by mass, preferably 0.1% by mass to 2% by mass. It is.
- the resist underlayer film forming composition for lithography of the present invention further contains a crosslinking agent.
- a crosslinking agent there is no restriction
- crosslinking formation substituents for example, a methylol group, a methoxymethyl group, a butoxymethyl group is used preferably.
- crosslinking agent examples include hexamethoxymethyl melamine, tetramethoxymethyl benguanamine, 1,3,4,6-tetrakis (methoxymethyl) glycoluril, 1,3,4,6-tetrakis (butoxymethyl) glycoluril. 1,3,4,6-tetrakis (hydroxymethyl) glycoluril, 1,3-bis (hydroxymethyl) urea, 1,1,3,3-tetrakis (butoxymethyl) urea, 1,1,3,3 -Tetrakis (methoxymethyl) urea.
- the crosslinking agent contained in the resist underlayer film forming composition for lithography of the present invention is, for example, 1% by mass to 100% by mass, preferably 10% by mass to 50% by mass, when the polymer in the composition is 100% by mass. It is.
- These crosslinking agents include a structural unit represented by the formula (4) that reacts with the polymer, particularly a crosslinking agent to form a crosslinking, and a crosslinking functional group (hydroxy group) in the structural unit represented by the formula (5). A crosslinking reaction can occur.
- the resist underlayer film forming composition for lithography of the present invention further contains a compound that promotes the crosslinking reaction.
- a compound that promotes the crosslinking reaction examples include p-toluenesulfonic acid, trifluoromethanesulfonic acid, pyridinium-p-toluenesulfonate, salicylic acid, camphorsulfonic acid, 5-sulfosalicylic acid, 4-chlorobenzenesulfonic acid, 4-hydroxybenzenesulfone.
- Acid benzenedisulfonic acid, 1-naphthalenesulfonic acid, citric acid, benzoic acid, hydroxybenzoic acid and other sulfonic acid compounds and carboxylic acid compounds can be used. These compounds that accelerate the crosslinking reaction can be used alone or in combination of two or more.
- the compound that promotes the crosslinking reaction contained in the resist underlayer film forming composition for lithography of the present invention is, for example, 0.1% by mass to 25% by mass, preferably 1%, assuming that the polymer in the composition is 100% by mass. Mass% to 10 mass%.
- the resist underlayer film forming composition for lithography of the present invention further contains an organic solvent.
- the organic solvent used in the present invention is not particularly limited as long as it can dissolve the aforementioned polymer.
- the organic solvent contained in the resist underlayer film forming composition for lithography of the present invention is, for example, 90% by mass to 99.99% by mass, preferably 98% by mass to 99.9% by mass, assuming that the composition is 100% by mass. %.
- excluding the organic solvent from the resist underlayer film forming composition is expressed as solid content.
- the resist underlayer film forming composition for lithography of the present invention may further contain an acid generator.
- an acid generator include bis (4-hydroxyphenyl) sulfone.
- the resist underlayer film forming composition for lithography of the present invention contains the acid generator, for example, 0.1% by mass to 5% by mass, preferably 0.2% by mass, when the polymer in the composition is 100% by mass. % To 3% by mass.
- the composition for forming a resist underlayer film for lithography of the present invention may further contain various additives such as a surfactant as necessary as long as the effects of the present invention are not impaired.
- the surfactant is an additive for improving the applicability of the composition to the substrate.
- Known surfactants such as nonionic surfactants and fluorine-based surfactants can be used.
- the surfactant include, for example, polyoxyethylene lauryl ether, polyoxyethylene stearyl ether, polyoxyethylene cetyl ether, polyoxyethylene alkyl ethers such as polyoxyethylene oleyl ether, and polyoxyethylene octylphenyl ether.
- Polyoxyethylene alkylaryl ethers such as polyoxyethylene nonylphenyl ether, polyoxyethylene / polyoxypropylene block copolymers, sorbitan monolaurate, sorbitan monopalmitate, sorbitan monostearate, sorbitan monooleate, sorbitan trioleate Sorbitan fatty acid esters such as sorbitan tristearate, polyoxyethylene sorbitan monolaurate, polyoxy Nonionic surfactants such as polyoxyethylene sorbitan fatty acid esters such as tylene sorbitan monopalmitate, polyoxyethylene sorbitan monostearate, polyoxyethylene sorbitan trioleate, polyoxyethylene sorbitan tristearate, Ftop [registered trademark] EF301, EF303, EF352 (Mitsubishi Materials Electronics Chemical Co., Ltd.), MegaFac [registered trademark] F171, F173, R-30, R-40, R-40-LM (DIC Corporation) )),
- the resist underlayer film forming composition for lithography of the present invention contains the above surfactant, for example, when the polymer in the composition is 100% by mass, it is 0.1% by mass to 5% by mass, preferably 0.8%. 2 to 3% by mass is contained.
- a substrate used in the manufacture of a precision integrated circuit element for example, a semiconductor substrate such as a silicon wafer coated with a silicon oxide film, a silicon nitride film or a silicon oxynitride film, a silicon nitride substrate, a quartz substrate, a glass substrate (no (Including alkali glass, low alkali glass, crystallized glass), glass substrate on which an ITO film is formed]
- the resist underlayer film forming composition for lithography of the present invention is applied on a glass substrate on which an ITO film is formed by an appropriate application method such as a spinner or coater. Thereafter, the resist underlayer film is produced by baking and curing using a heating means such as a hot plate.
- the conditions for baking after coating are appropriately selected from the range of, for example, a baking temperature of 80 to 250 ° C. and a baking time of 0.3 to 60 minutes, and preferably 150 to 250 ° C. and 0.5 to 5 minutes. It is.
- a crosslinking structure such as a hydroxyl group in the structural unit of the polymer reacts with a crosslinking agent to form a crosslinked structure.
- the crosslinking density of the crosslinked polymer can be increased by crosslinking the polymer contained in the resist underlayer film forming composition for lithography of the present invention.
- the thickness of the resist underlayer film is, for example, 0.001 ⁇ m (1 nm) to 0.2 ⁇ m (200 nm), and preferably 0.003 ⁇ m (3 nm) to 0.1 ⁇ m (100 nm).
- the resist film is formed by a general method, that is, by applying a resist solution onto the resist underlayer film and baking.
- the resist solution to be applied is not particularly limited as long as it is sensitive to, for example, KrF excimer laser, ArF excimer laser, EUV, or electron beam, and either negative type or positive type can be used.
- Usable resist solutions include, for example, Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd .; trade names PAR710, PAR855, JSR Corporation; trade names AR2772JN, Shin-Etsu Chemical Co., Ltd .; trade names SEPR 430, Dow Chemical Company ( Manufactured by former ROHM & Haas Electronic Materials); trade name APEX-X.
- the resist film formed on the upper layer of the resist lower layer film is exposed through a predetermined mask (reticle).
- a predetermined mask for the exposure, for example, a KrF excimer laser, an ArF excimer laser, or EUV can be used. However, in the case of electron beam exposure, a mask (reticle) is not required.
- post-exposure heating PEB: Post Exposure Bake
- the conditions for the post-exposure heating are appropriately selected from the range of a heating temperature of 80 ° C. to 150 ° C. and a heating time of 0.3 minutes to 60 minutes.
- a good resist pattern is obtained by developing, rinsing and drying after exposure.
- an alkaline aqueous solution or an organic solvent can be used as the developer for the resist film.
- alkaline aqueous solutions include aqueous solutions of inorganic alkalis such as sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, sodium carbonate, sodium silicate, sodium metasilicate, and aqueous ammonia, and primary amines such as ethylamine and n-propylamine.
- Aqueous solutions aqueous solutions of secondary amines such as diethylamine and di-n-butylamine, aqueous solutions of tertiary amines such as triethylamine and methyldiethylamine, aqueous solutions of alcoholamines such as dimethylethanolamine and triethanolamine, Examples include aqueous solutions of quaternary ammonium salts such as tetramethylammonium hydroxide, tetraethylammonium hydroxide, choline, and aqueous solutions of cyclic amines such as pyrrole and piperidine.
- an appropriate amount of an alcohol such as isopropyl alcohol or a nonionic surfactant may be added to the alkaline aqueous solution.
- a preferred developer is an aqueous solution of a quaternary ammonium salt, more preferably an aqueous solution of tetramethylammonium hydroxide.
- organic solvent used as the developer examples include methyl acetate, butyl acetate, ethyl acetate, isopropyl acetate, amyl acetate, isoamyl acetate, ethyl methoxyacetate, ethyl ethoxy acetate, propylene glycol monomethyl ether acetate, ethylene glycol monoethyl ether Acetate, ethylene glycol monopropyl ether acetate, ethylene glycol monobutyl ether acetate, ethylene glycol monophenyl ether acetate, diethylene glycol monomethyl ether acetate, diethylene glycol monopropyl ether acetate, diethylene glycol monoethyl ether acetate, diethylene glycol monophenyl ether acetate, diethylene glycol monobutyl ether acetate 2-methoxybutyl acetate, 3-methoxybutyl acetate, 4-methoxybutyl acetate, 3-methyl-3-
- the resist underlayer film exposed by developing and removing the resist film in the above-described step is removed by dry etching, and a desired pattern can be formed on the substrate.
- the weight average molecular weights shown in the following Synthesis Examples 1 to 10, Comparative Synthesis Example 1 and Comparative Synthesis Example 2 are measurement results by gel permeation chromatography (hereinafter abbreviated as GPC in this specification).
- GPC gel permeation chromatography
- a GPC device manufactured by Tosoh Corporation was used, and the measurement conditions were as follows. Further, the dispersity shown in the following synthesis examples of the present specification is calculated from the measured weight average molecular weight and number average molecular weight.
- the reaction vessel was purged with nitrogen and reacted at 135 ° C. for 4 hours to obtain a polymer solution.
- the polymer solution does not cause white turbidity or the like even when cooled to room temperature, and has good solubility in propylene glycol monomethyl ether.
- the polymer in the obtained solution had a weight average molecular weight of 2600 and a dispersity of 3.448 in terms of standard polystyrene.
- the polymer obtained in this synthesis example has structural units represented by the following formulas (4a-1) and (5a-1), and has a structure represented by the following formula (1-1) at the terminal. .
- the polymer solution does not cause white turbidity or the like even when cooled to room temperature, and has good solubility in propylene glycol monomethyl ether.
- the polymer in the obtained solution had a weight average molecular weight of 2590 and a dispersity of 2.77 in terms of standard polystyrene.
- the polymer obtained in this synthesis example has structural units represented by the following formulas (4b-1) and (5a-1), and has a structure represented by the following formula (1-1) at the terminal. .
- the polymer solution does not cause white turbidity or the like even when cooled to room temperature, and has good solubility in propylene glycol monomethyl ether.
- the polymer in the obtained solution had a weight average molecular weight of 3240 and a dispersity of 2.265 in terms of standard polystyrene.
- the polymer obtained in this synthesis example has structural units represented by the following formulas (4b-1) and (5b-1), and has a structure represented by the following formula (1-1) at the terminal. .
- the polymer obtained in this synthesis example has structural units represented by the following formulas (4a-2) and (5c-1), and has a structure represented by the following formula (1-2) at the terminal. . It is believed that the epoxy group of monomethyldiglycidyl isocyanuric acid reacts preferentially with the carboxyl group over the hydroxy group of 5-sulfosalicylic acid.
- the polymer obtained in this synthesis example has structural units represented by the following formulas (4a-2) and (5c-1), and has a structure represented by the following formula (1-2) at the terminal. .
- the polymer obtained in this synthesis example has structural units represented by the following formulas (4a-2) and (5c-1), and has a structure represented by the following formula (1-2) at the terminal. .
- monomethyldiglycidyl isocyanuric acid manufactured by Shikoku Kasei Kogyo Co., Ltd., solid content 50% by mass
- 4.18 g of 3,3′-dithiodipropionic acid manufactured by Sakai Chemical Industry Co., Ltd.
- the reaction vessel was purged with nitrogen and reacted at 105 ° C. for 24 hours to obtain a polymer solution.
- the weight average molecular weight was 2500 in terms of standard polystyrene.
- the polymer obtained in this synthesis example has structural units represented by the following formulas (4a-2) and (5c-1), and has a structure represented by the following formula (1-1) at the terminal. .
- the reaction vessel was purged with nitrogen and reacted at 105 ° C. for 24 hours to obtain a polymer solution.
- GPC analysis was performed, it was weight average molecular weight 1650 in standard polystyrene conversion.
- the polymer obtained in this synthesis example has structural units represented by the following formulas (4a-2) and (5c-1), and has a structure represented by the following formula (1-1) at the terminal. .
- the reaction vessel was purged with nitrogen and reacted at 105 ° C. for 24 hours to obtain a polymer solution.
- GPC analysis was performed, it was weight average molecular weight 3300 in standard polystyrene conversion.
- the polymer obtained in this synthesis example has structural units represented by the following formulas (4a-2) and (5c-1), and has a structure represented by the following formula (2-1) at the terminal. .
- the reaction vessel was purged with nitrogen and reacted at 105 ° C. for 24 hours to obtain a polymer solution.
- GPC analysis was performed, it was weight average molecular weight 2600 in standard polystyrene conversion.
- the polymer obtained in this synthesis example has structural units represented by the following formulas (4a-2) and (5c-1), and has a structure represented by the following formula (2-1) at the terminal. .
- the polymer solution does not cause white turbidity or the like even when cooled to room temperature, and has good solubility in propylene glycol monomethyl ether.
- the polymer in the obtained solution had a weight average molecular weight of 15700 in terms of standard polystyrene and a dispersity of 3.39.
- the polymer obtained in this synthesis example has structural units represented by the following formulas (4c-1) and (5d-1).
- the polymer is represented by the above formula (1) or formula (2). There is no structure at the end.
- the polymer obtained in this synthesis example has structural units represented by the following formulas (4a-2) and (5c-1), and the polymer is represented by the above formula (1) or formula (2). There is no structure at the end.
- Example 1 To 4.82 g of the polymer solution containing 0.63 g of the polymer obtained in Synthesis Example 1, 0.1563 g of tetramethoxymethyl glycoluril (manufactured by Nippon Cytec Industries, Ltd., trade name: POWDERLINK [registered trademark] 1174) and 0.0016 g of p-phenolsulfonic acid (manufactured by Tokyo Chemical Industry Co., Ltd.) and 0.0031 g of a surfactant (manufactured by DIC Corporation, trade name: Megafac [registered trademark] R-40) were mixed with propylene.
- POWDERLINK tetramethoxymethyl glycoluril
- a surfactant manufactured by DIC Corporation, trade name: Megafac [registered trademark] R-40
- Example 3 To 1.73 g of the polymer solution containing 0.23 g of the polymer obtained in Synthesis Example 3, 0.059 g of tetramethoxymethylglycoluril (manufactured by Nippon Cytec Industries, Inc., trade name: POWDERLINK [registered trademark] 1174) and 0.0059 g of p-phenol sulfonic acid (manufactured by Tokyo Chemical Industry Co., Ltd.) and 0.0011 g of a surfactant (manufactured by DIC Corporation, trade name: MegaFace [registered trademark] R-40) were mixed, and propylene was mixed.
- tetramethoxymethylglycoluril manufactured by Nippon Cytec Industries, Inc., trade name: POWDERLINK [registered trademark] 1174
- p-phenol sulfonic acid manufactured by Tokyo Chemical Industry Co., Ltd.
- a surfactant manufactured by DIC Corporation, trade name: MegaFace [registered trademark] R-40
- Example 4 To 1.14 g of the polymer solution obtained in Synthesis Example 4 above, 0.059 g of tetramethoxymethylglycoluril (manufactured by Nippon Cytec Industries, Inc., trade name: POWDERLINK [registered trademark] 1174) and 5-sulfosalicylic acid (Tokyo Kasei) Industrial Co., Ltd. (0.0059 g) was mixed, and 27.68 g of propylene glycol monomethyl ether was added and dissolved to obtain a resist underlayer film forming composition for lithography.
- POWDERLINK registered trademark
- Example 5 To 1.10 g of the polymer solution obtained in Synthesis Example 5, 0.059 g of tetramethoxymethylglycoluril (manufactured by Nippon Cytec Industries, Inc., trade name: POWDERLINK [registered trademark] 1174) and 5-sulfosalicylic acid (Tokyo Kasei) 0.0059 g of Kogyo Co., Ltd.) was mixed, and 27.73 g of propylene glycol monomethyl ether was added and dissolved to obtain a resist underlayer film forming composition for lithography.
- POWDERLINK registered trademark
- Example 7 To 1.47 g of the polymer solution obtained in Synthesis Example 7, 0.059 g of tetramethoxymethylglycoluril (manufactured by Nippon Cytec Industries, Inc., trade name: POWDERLINK [registered trademark] 1174) and 5-sulfosalicylic acid (Tokyo Chemical Industry) Industrial Co., Ltd. (0.0059 g) was mixed, and 27.35 g of propylene glycol monomethyl ether was added and dissolved to obtain a resist underlayer film forming composition for lithography.
- POWDERLINK Registered trademark
- Example 8> To 1.58 g of the polymer solution obtained in Synthesis Example 8 above, 0.059 g of tetramethoxymethylglycoluril (manufactured by Nippon Cytec Industries, Ltd., trade name: POWDERLINK [registered trademark] 1174) and 5-sulfosalicylic acid (Tokyo Kasei) Industrial Co., Ltd. (0.0059 g) was mixed, and 27.24 g of propylene glycol monomethyl ether was added and dissolved to obtain a resist underlayer film forming composition for lithography.
- POWDERLINK registered trademark
- Example 9 To 1.46 g of the polymer solution obtained in Synthesis Example 9 above, 0.059 g of tetramethoxymethylglycoluril (manufactured by Nippon Cytec Industries, Ltd., trade name: POWDERLINK [registered trademark] 1174) and 5-sulfosalicylic acid (Tokyo Kasei) 0.0059 g of Kogyo Co., Ltd.) was mixed and 22.07 g of propylene glycol monomethyl ether was added and dissolved to obtain a resist underlayer film forming composition for lithography.
- POWDERLINK registered trademark
- Each of the resist underlayer film forming compositions of Examples 1 to 3 and Comparative Example 1 has a structure having a top surface and a cross section shown in FIG.
- the film was coated with a film thickness of 5 nm on a silicon wafer on which a cross-shaped pattern of 14 ⁇ m, 14 ⁇ m in width, and 230 nm in height was formed, and the coating property was confirmed with a dark field of an optical microscope (manufactured by Olympus Corporation, MX61L). Good coatability was confirmed only when the resist underlayer film forming compositions of Examples 1 to 3 were applied.
- the resist underlayer film forming composition of Comparative Example 1 was applied, application unevenness was observed, and thus the applicability was confirmed to be poor.
- the minimum line width where no resist pattern collapse is observed is defined as the minimum dimension before collapse (nm).
- the index of the pattern collapse resistance is shown in Table 1.
- the minimum dimension before collapse is shown in Table 1.
- the pattern collapse resistance is determined as “good” when the minimum dimension before collapse is 50 nm or less, and as “bad” when it exceeds 50 nm. did.
- the resist underlayer film forming composition of Example 1, Example 2 and Comparative Example 1 of the present invention was spin-coated, and heated at 205 ° C. for 1 minute to form a resist underlayer film.
- PEB post-exposure heating
- the substrate was cooled to room temperature on a cooling plate, developed and rinsed, and a resist pattern was formed on the silicon wafer.
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Polymers & Plastics (AREA)
- Architecture (AREA)
- Structural Engineering (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
- Wood Science & Technology (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Optics & Photonics (AREA)
- Spectroscopy & Molecular Physics (AREA)
- Materials For Photolithography (AREA)
- Exposure And Positioning Against Photoresist Photosensitive Materials (AREA)
- Polyoxymethylene Polymers And Polymers With Carbon-To-Carbon Bonds (AREA)
- Exposure Of Semiconductors, Excluding Electron Or Ion Beam Exposure (AREA)
Abstract
Description
(式中、R1は置換基を有してもよい炭素原子数1乃至6のアルキル基、フェニル基、ピリジル基、ハロゲノ基又はヒドロキシ基を表し、R2は水素原子、炭素原子数1乃至6のアルキル基、ヒドロキシ基、ハロゲノ基又は-C(=O)O-Xで表されるエステル基を表し、Xは置換基を有してもよい炭素原子数1乃至6のアルキル基を表し、R3は水素原子、炭素原子数1乃至6のアルキル基、ヒドロキシ基又はハロゲノ基を表し、R4は直接結合、又は炭素原子数1乃至8の二価の有機基を表し、R5は炭素原子数1乃至8の二価の有機基を表し、Aは芳香族環又は芳香族複素環を表し、tは0又は1を表し、uは1又は2を表す。
本発明のリソグラフィー用レジスト下層膜形成組成物に含まれるポリマーは、前記式(1)又は式(2)で表される構造をポリマー鎖の末端に有する。
(式中、R1、R2、R3、R4、R5、X、A、t及びuは、前記式(1)又は式(2)で表される構造のR1、R2、R3、R4、R5、X、A、t及びuの定義と同義である。)
上記及び本明細書で後述する炭素原子数1ないし6のアルキル基として、例えば、メチル基、エチル基、プロピル基、イソプロピル基、ブチル基、sec-ブチル基、tert-ブチル基、ペンチル基及びヘキシル基を挙げることができる。上記及び本明細書で後述する芳香族環として、例えば、ベンゼン、ナフタレン、アントラセンを挙げることができる。上記芳香族複素環として、例えば、トリアジン、ピリミジン、イミダゾール及びピリジンを挙げることができる。
(式中、Q1及びQ2はそれぞれ独立に、置換基を有してもよい炭素原子数1乃至13の炭化水素基を有する二価の有機基、芳香族環を有する二価の有機基、又は窒素原子を1乃至3つ含む複素環を有する二価の有機基を表す。)
上記炭化水素基が置換基を有する場合、その置換基として、例えばハロゲノ基が挙げられる。上記炭化水素基は、直鎖状若しくは分岐鎖状の炭化水素基、脂環式炭化水素基、又は直鎖状若しくは分岐鎖状の炭化水素基と脂環式炭化水素基との組み合わせである。該脂環式炭化水素基として、例えば、シクロブチレン基、シクロペンチレン基及びシクロヘキシレン基を挙げることができる。
上記窒素原子を1乃至3つ含む複素環として、例えばトリアジントリオン、ピリミジントリオン、イミダゾリジンジオン、イミダゾリドン及びピリドンを挙げることができる。
(式中、R6は水素原子、炭素原子数1乃至6のアルキル基、又はアリル基を表し、R7及びR8はそれぞれ独立に水素原子又は炭素原子数1乃至6のアルキル基を表し、Q3は置換基を有してもよい炭素原子数1乃至13の炭化水素基、又は置換基を有してもよい芳香族環を表し、2つのvはそれぞれ独立に0又は1を表す。)
前記Q3は例えば、下記式で表される基を表す。
(式中、R9及びR10それぞれ独立に水素原子、炭素原子数1乃至6のアルキル基又は芳香族環を表し、R11は炭素原子数1乃至6のアルキル基、又はアリル基を表し、R12及びR13はそれぞれ独立に炭素原子数1乃至3のアルキレン基、例えばメチレン基、エチレン基、プロピレン基を表し、Q4は置換基を有してもよい炭素原子数1乃至13の炭化水素基、又は置換基を有してもよい芳香族環を表し、2つのwはそれぞれ独立に0又は1を表す。)
(式中、R1、R2、R3、R4、R5、A、t及びuは前記式(1)又は式(2)で表される構造のR1、R2、R3、R4、R5、X、A、t及びuの定義と同義であり、Yは前記式(4)で表される構造単位及び前記式(5)で表される構造単位を有するポリマー鎖を表す。)
本発明のリソグラフィー用レジスト下層膜形成組成物は、さらに架橋剤を含む。その架橋剤として、特に制限はないが、少なくとも二つの架橋形成置換基(例えば、メチロール基、メトキシメチル基、ブトキシメチル基)を有する含窒素化合物が好ましく用いられる。
架橋反応を促進させるために、本発明のリソグラフィー用レジスト下層膜形成組成物は、さらに架橋反応を促進させる化合物を含む。そのような化合物としては、例えば、p-トルエンスルホン酸、トリフルオロメタンスルホン酸、ピリジニウム-p-トルエンスルホナート、サリチル酸、カンファースルホン酸、5-スルホサリチル酸、4-クロロベンゼンスルホン酸、4-ヒドロキシベンゼンスルホン酸、ベンゼンジスルホン酸、1-ナフタレンスルホン酸、クエン酸、安息香酸、ヒドロキシ安息香酸等のスルホン酸化合物及びカルボン酸化合物を使用できる。これら架橋反応を促進させる化合物は、一種のみを使用することができ、また、二種以上を組み合わせて用いることもできる。本発明のリソグラフィー用レジスト下層膜形成組成物に含まれる上記架橋反応を促進させる化合物は、当該組成物中のポリマーを100質量%とすると、例えば0.1質量%乃至25質量%、好ましくは1質量%乃至10質量%である。
本発明のリソグラフィー用レジスト下層膜形成組成物はさらに有機溶媒を含む。本発明において使用される有機溶媒としては、前述のポリマーを溶解することができれば特に制限されず、例えば、エチレングリコールモノメチルエーテル、エチレングリコールモノエチルエーテル、メチルセロソルブアセテート、エチルセロソルブアセテート、ジエチレングリコールモノメチルエーテル、ジエチレングリコールモノエチルエーテル、プロピレングリコール、プロピレングリコールモノメチルエーテル、プロピレングリコールモノプロピルエーテル、1-エトキシ-2-プロパノール、プロピレングリコールモノメチルエーテルアセテート、プロピレングリコールプロピルエーテルアセテート、1-メトキシ-2-ブタノール、2-メトキシ-1-ブタノール、3-メトキシ-3-メチルブタノール、3-メトキシ-1-ブタノール、トルエン、キシレン、メチルエチルケトン、シクロペンタノン、シクロヘキサノン、γ-ブチロラクトン、N-メチル-2-ピロリドン、2-ヒドロキシイソ酪酸メチル、2-ヒドロキシプロピオン酸エチル、2-ヒドロキシ-2-メチルプロピオン酸エチル、エトキシ酢酸エチル、ヒドロキシ酢酸エチル、2-ヒドロキシ-3-メチルブタン酸メチル、3-メトキシプロピオン酸メチル、3-メトキシプロピオン酸エチル、3-エトキシプロピオン酸エチル、3-エトキシプロピオン酸メチル、ピルビン酸メチル、ピルビン酸エチル、酢酸エチル、酢酸ブチル、乳酸エチル、乳酸ブチルを用いることができる。これらの有機溶剤は単独で、又は2種以上の組合せで使用される。
本発明のリソグラフィー用レジスト下層膜形成組成物はさらに酸発生剤を含んでいてもよい。そのような酸発生剤としては、例えば、ビス(4-ヒドロキシフェニル)スルホンが挙げられる。本発明のリソグラフィー用レジスト下層膜形成組成物が上記酸発生剤を含む場合、当該組成物中のポリマーを100質量%とすると、例えば0.1質量%乃至5質量%、好ましくは0.2質量%乃至3質量%含む。
本発明のリソグラフィー用レジスト下層膜形成組成物には、必要に応じて界面活性剤等の各種添加剤を、本発明の効果を損なわない限りにおいてさらに含んでもよい。界面活性剤は、基板に対する当該組成物の塗布性を向上させるための添加物である。ノニオン系界面活性剤、フッ素系界面活性剤のような公知の界面活性剤を用いることができる。
GPCカラム:Shodex〔登録商標〕・Asahipak〔登録商標〕(昭和電工(株))
カラム温度:40℃
溶媒:N,N-ジメチルホルムアミド(DMF)
流量:0.6ml/分
標準試料:ポリスチレン(東ソー(株)製)
ディテクター:RIディテクター(東ソー(株)製、RI-8020)
モノアリルジグリシジルイソシアヌル酸(四国化成工業(株)製)7.00g、5,5-ジエチルバルビツール酸(八代製薬(株)製)3.93g、4-(メチルスルホニル)安息香酸(東京化成工業(株)製)1.51g及びエチルトリフェニルホスホニウムブロミド(Sigma-Aldrich社製)0.47gを、反応容器中のプロピレングリコールモノメチルエーテル73.14gに加え溶解させた。その反応容器を窒素置換後、135℃で4時間反応させ、ポリマー溶液を得た。当該ポリマー溶液は、室温に冷却しても白濁等を生じることはなく、プロピレングリコールモノメチルエーテルに対する溶解性は良好である。GPC分析を行ったところ、得られた溶液中のポリマーは、標準ポリスチレン換算にて重量平均分子量2600、分散度3.448はであった。本合成例で得られたポリマーは、下記式(4a-1)及び式(5a-1)で表される構造単位を有すると共に、下記式(1-1)で表される構造を末端に有する。
ヒダントインジグリシジル(四国化成工業(株)製)7.42g、5,5-ジエチルバルビツール酸(八代製薬(株)製)4.83g、4-(メチルスルホニル)安息香酸(東京化成工業(株)製)1.85g及びエチルトリフェニルホスホニウムブロミド(Sigma-Aldrich社製)0.57gを、反応容器中のプロピレングリコールモノメチルエーテル83.21gに加え溶解させた。その反応容器を窒素置換後、135℃で4時間反応させ、ポリマー溶液を得た。当該ポリマー溶液は、室温に冷却しても白濁等を生じることはなく、プロピレングリコールモノメチルエーテルに対する溶解性は良好である。GPC分析を行ったところ、得られた溶液中のポリマーは、標準ポリスチレン換算にて重量平均分子量2590、分散度2.77はであった。本合成例で得られたポリマーは、下記式(4b-1)及び式(5a-1)で表される構造単位を有すると共に、下記式(1-1)で表される構造を末端に有する。
ヒダントインジグリシジル(四国化成工業(株)製)10.06g、モノアリルシアヌル酸(四国化成工業(株)製)6.01g、4-(メチルスルホニル)安息香酸(東京化成工業(株)製)2.51g及びエチルトリフェニルホスホニウムブロミド(Sigma-Aldrich社製)0.78gを、反応容器中のプロピレングリコールモノメチルエーテル109.73gに加え溶解させた。その反応容器を窒素置換後、135℃で4時間反応させ、ポリマー溶液を得た。当該ポリマー溶液は、室温に冷却しても白濁等を生じることはなく、プロピレングリコールモノメチルエーテルに対する溶解性は良好である。GPC分析を行ったところ、得られた溶液中のポリマーは、標準ポリスチレン換算にて重量平均分子量3240、分散度2.265はであった。本合成例で得られたポリマーは、下記式(4b-1)及び式(5b-1)で表される構造単位を有すると共に、下記式(1-1)で表される構造を末端に有する。
モノメチルジグリシジルイソシアヌル酸(四国化成工業(株)製、固形分48.7質量%)10g、3,3’-ジチオジプロピオン酸(堺化学工業(株)製)、4.18g、5-スルホサリチル酸(東京化成工業(株)製)0.65g及びエチルトリフェニルホスホニウムブロミド0.37gを、反応容器中のプロピレングリコールモノメチルエーテル35gに加え溶解させた。その反応容器を窒素置換後105℃で24時間反応させポリマー溶液を得た。GPC分析を行ったところ標準ポリスチレン換算にて重量平均分子量1100であった。本合成例で得られたポリマーは、下記式(4a-2)及び式(5c-1)で表される構造単位を有すると共に、下記式(1-2)で表される構造を末端に有する。モノメチルジグリシジルイソシアヌル酸のエポキシ基は、5-スルホサリチル酸のヒドロキシ基よりもカルボキシル基と優先的に反応すると考えられる。
モノメチルジグリシジルイソシアヌル酸(四国化成工業(株)製、固形分48.7質量%)10g、3,3’-ジチオジプロピオン酸(堺化学工業(株)製)4.18g、5-スルホサリチル酸(東京化成工業(株)製)0.87g及びエチルトリフェニルホスホニウムブロミド0.37gを、反応容器中のプロピレングリコールモノメチルエーテル36gに加え溶解させた。その反応容器を窒素置換後105℃で24時間反応させポリマー溶液を得た。GPC分析を行ったところ標準ポリスチレン換算にて重量平均分子量910であった。本合成例で得られたポリマーは、下記式(4a-2)及び式(5c-1)で表される構造単位を有すると共に、下記式(1-2)で表される構造を末端に有する。
モノメチルジグリシジルイソシアヌル酸(四国化成工業(株)製、固形分50質量%)10g、3,3’-ジチオジプロピオン酸(堺化学工業(株)製)4.18g、5-スルホサリチル酸(東京化成工業(株)製)1.3g及びエチルトリフェニルホスホニウムブロミド0.37gを、反応容器中のプロピレングリコールモノメチルエーテル38.4gに加え溶解させた。その反応容器を窒素置換後105℃で24時間反応させポリマー溶液を得た。GPC分析を行ったところ標準ポリスチレン換算にて重量平均分子量890であった。本合成例で得られたポリマーは、下記式(4a-2)及び式(5c-1)で表される構造単位を有すると共に、下記式(1-2)で表される構造を末端に有する。
モノメチルジグリシジルイソシアヌル酸(四国化成工業(株)製、固形分50質量%)10g、3,3’-ジチオジプロピオン酸(堺化学工業(株)製)4.18g、4-(メチルスルホニル)安息香酸(東京化成工業(株)製)0.80g及びエチルトリフェニルホスホニウムブロミド0.37gを、反応容器中のプロピレングリコールモノメチルエーテル36.38gに加え溶解させた。その反応容器を窒素置換後105℃で24時間反応させポリマー溶液を得た。GPC分析を行ったところ標準ポリスチレン換算にて重量平均分子量2500であった。本合成例で得られたポリマーは、下記式(4a-2)及び式(5c-1)で表される構造単位を有すると共に、下記式(1-1)で表される構造を末端に有する。
モノメチルジグリシジルイソシアヌル酸(四国化成工業(株)製、固形分50質量%)10g、3,3’-ジチオジプロピオン酸(堺化学工業(株)製)4.18g、4-(メチルスルホニル)安息香酸(東京化成工業(株)製)1.19g及びエチルトリフェニルホスホニウムブロミド0.37gを、反応容器中のプロピレングリコールモノメチルエーテル37.98gに加え溶解させた。その反応容器を窒素置換後105℃で24時間反応させポリマー溶液を得た。GPC分析を行ったところ標準ポリスチレン換算にて重量平均分子量1650であった。本合成例で得られたポリマーは、下記式(4a-2)及び式(5c-1)で表される構造単位を有すると共に、下記式(1-1)で表される構造を末端に有する。
モノメチルジグリシジルイソシアヌル酸(四国化成工業(株)製、固形分50質量%)10g、3,3’-ジチオジプロピオン酸(堺化学工業(株)製)4.18g、2-(p-トルエンスルホニル)酢酸(東京化成工業(株)製)0.85g及びエチルトリフェニルホスホニウムブロミド0.37gを、反応容器中のプロピレングリコールモノメチルエーテル36.61gに加え溶解させた。その反応容器を窒素置換後105℃で24時間反応させポリマー溶液を得た。GPC分析を行ったところ標準ポリスチレン換算にて重量平均分子量3300であった。本合成例で得られたポリマーは、下記式(4a-2)及び式(5c-1)で表される構造単位を有すると共に、下記式(2-1)で表される構造を末端に有する。
モノメチルジグリシジルイソシアヌル酸(四国化成工業(株)製、固形分50質量%)10g、3,3’-ジチオジプロピオン酸(堺化学工業(株)製)4.18g、2-(p-トルエンスルホニル)酢酸(東京化成工業(株)製)1.28g及びエチルトリフェニルホスホニウムブロミド0.37gを、反応容器中のプロピレングリコールモノメチルエーテル38.31gに加え溶解させた。その反応容器を窒素置換後105℃で24時間反応させポリマー溶液を得た。GPC分析を行ったところ標準ポリスチレン換算にて重量平均分子量2600であった。本合成例で得られたポリマーは、下記式(4a-2)及び式(5c-1)で表される構造単位を有すると共に、下記式(2-1)で表される構造を末端に有する。
テレフタル酸ジグリシジルエステル(ナガセケムテックス(株)製、商品名:デナコール〔登録商標〕EX711)5.00g、5-ヒドロキシイソフタル酸(東京化成工業(株)製)3.15g及びベンジルトリエチルアンモニウムクロリド(東京化成工業(株)製)0.20gを、反応容器中のプロピレングリコールモノメチルエーテル35.60gに加え溶解させた。その反応容器を窒素置換後、135℃で4時間反応させ、ポリマー溶液を得た。当該ポリマー溶液は、室温に冷却しても白濁等を生じることはなく、プロピレングリコールモノメチルエーテルに対する溶解性は良好である。GPC分析を行ったところ、得られた溶液中のポリマーは、標準ポリスチレン換算にて重量平均分子量15700、分散度は3.39であった。本合成例で得られたポリマーは、下記式(4c-1)及び式(5d-1)で表される構造単位を有するが、そのポリマーは上記式(1)又は式(2)で表される構造を末端に有さない。
モノメチルジグリシジルイソシアヌル酸(四国化成工業(株)製、固形分50質量%)10g、3,3’-ジチオジプロピオン酸(堺化学工業(株)製)4.18g及びエチルトリフェニルホスホニウムブロミド0.36gを、反応容器中のプロピレングリコールモノメチルエーテル33gに加え溶解させた。その反応容器を窒素置換後105℃で24時間反応させポリマー溶液を得た。GPC分析を行ったところ標準ポリスチレン換算にて重量平均分子量2500であった。本合成例で得られたポリマーは、下記式(4a-2)及び式(5c-1)で表される構造単位を有するが、そのポリマーは上記式(1)又は式(2)で表される構造を末端に有さない。
上記合成例1で得られた、ポリマー0.63gを含むポリマー溶液4.82gに、テトラメトキシメチルグリコールウリル(日本サイテックインダストリーズ(株)製、商品名:POWDERLINK〔登録商標〕1174)0.1563gとp-フェノールスルホン酸(東京化成工業(株)製)0.0016g、及び界面活性剤(DIC(株)製、商品名:メガファック〔登録商標〕R-40)0.0031gを混合し、プロピレングリコールモノメチルエーテル67.00g及びプロピレングリコールモノメチルエーテルアセテート7.92gを加え溶解させた。その後孔径0.05μmのポリエチレン製ミクロフィルターを用いてろ過して、リソグラフィー用レジスト下層膜形成組成物とした。
上記合成例2で得られた、ポリマー0.63gを含むポリマー溶液4.91gに、テトラメトキシメチルグリコールウリル(日本サイテックインダストリーズ(株)製、商品名:POWDERLINK〔登録商標〕1174)0.1563gとp-フェノールスルホン酸(東京化成工業(株)製)0.0016g、及び界面活性剤(DIC(株)製、商品名:メガファック〔登録商標〕R-40)0.0031gを混合し、プロピレングリコールモノメチルエーテル67.00g及びプロピレングリコールモノメチルエーテルアセテート7.92gを加え溶解させた。その後孔径0.05μmのポリエチレン製ミクロフィルターを用いてろ過して、リソグラフィー用レジスト下層膜形成組成物とした。
上記合成例3で得られた、ポリマー0.23gを含むポリマー溶液1.73gに、テトラメトキシメチルグリコールウリル(日本サイテックインダストリーズ(株)製、商品名:POWDERLINK〔登録商標〕1174)0.059gとp-フェノールスルホン酸(東京化成工業(株)製)0.0059g、及び界面活性剤(DIC(株)製、商品名:メガファック〔登録商標〕R-40)0.0011gを混合し、プロピレングリコールモノメチルエーテル25.29g及びプロピレングリコールモノメチルエーテルアセテート2.97gを加え溶解させた。その後孔径0.05μmのポリエチレン製ミクロフィルターを用いてろ過して、リソグラフィー用レジスト下層膜形成組成物とした。
上記合成例4で得られたポリマー溶液1.14gに、テトラメトキシメチルグリコールウリル(日本サイテックインダストリーズ(株)製、商品名:POWDERLINK〔登録商標〕1174)0.059gと5-スルホサリチル酸(東京化成工業(株)製)0.0059gを混合し、プロピレングリコールモノメチルエーテル27.68gを加え溶解させ、リソグラフィー用レジスト下層膜形成組成物とした。
上記合成例5で得られたポリマー溶液1.10gに、テトラメトキシメチルグリコールウリル(日本サイテックインダストリーズ(株)製、商品名:POWDERLINK〔登録商標〕1174)0.059gと5-スルホサリチル酸(東京化成工業(株)製)0.0059gを混合し、プロピレングリコールモノメチルエーテル27.73gを加え溶解させ、リソグラフィー用レジスト下層膜形成組成物とした。
上記合成例6で得られたポリマー溶液1.32gに、テトラメトキシメチルグリコールウリル(日本サイテックインダストリーズ(株)製、商品名:POWDERLINK〔登録商標〕1174)0.071gと5-スルホサリチル酸(東京化成工業(株)製)0.0071gを混合し、プロピレングリコールモノメチルエーテル27.27gを加え溶解させ、リソグラフィー用レジスト下層膜形成組成物とした。
上記合成例7で得られたポリマー溶液1.47gに、テトラメトキシメチルグリコールウリル(日本サイテックインダストリーズ(株)製、商品名:POWDERLINK〔登録商標〕1174)0.059gと5-スルホサリチル酸(東京化成工業(株)製)0.0059gを混合し、プロピレングリコールモノメチルエーテル27.35gを加え溶解させ、リソグラフィー用レジスト下層膜形成組成物とした。
上記合成例8で得られたポリマー溶液1.58gに、テトラメトキシメチルグリコールウリル(日本サイテックインダストリーズ(株)製、商品名:POWDERLINK〔登録商標〕1174)0.059gと5-スルホサリチル酸(東京化成工業(株)製)0.0059gを混合し、プロピレングリコールモノメチルエーテル27.24gを加え溶解させ、リソグラフィー用レジスト下層膜形成組成物とした。
上記合成例9で得られたポリマー溶液1.46gに、テトラメトキシメチルグリコールウリル(日本サイテックインダストリーズ(株)製、商品名:POWDERLINK〔登録商標〕1174)0.059gと5-スルホサリチル酸(東京化成工業(株)製)0.0059gを混合し、プロピレングリコールモノメチルエーテル22.07gを加え溶解させ、リソグラフィー用レジスト下層膜形成組成物とした。
上記合成例10で得られたポリマー溶液1.49gに、テトラメトキシメチルグリコールウリル(日本サイテックインダストリーズ(株)製、商品名:POWDERLINK〔登録商標〕1174)0.059gと5-スルホサリチル酸(東京化成工業(株)製)0.0059gを混合し、プロピレングリコールモノメチルエーテル22.04gを加え溶解させ、リソグラフィー用レジスト下層膜形成組成物とした。
上記比較合成例1で得られた、ポリマー0.23gを含むポリマー溶液1.31gに、テトラメトキシメチルグリコールウリル(日本サイテックインダストリーズ(株)製、商品名:POWDERLINK〔登録商標〕1174)0.059g及び5-スルホサリチル酸0.0058gを混合し、プロピレングリコールモノメチルエーテル21.27g及びプロピレングリコールモノメチルエーテルアセテート8.91gを加え溶解させた。その後孔径0.05μmのポリエチレン製ミクロフィルターを用いてろ過して、リソグラフィー用レジスト下層膜形成組成物とした。
前記特許文献1に記載の合成例1により得られた、下記式(4a-1)及び式(5a-1)で表される構造単位を有するポリマー0.94gを含むポリマー溶液5.16gに、テトラメトキシメチルグリコールウリル(日本サイテックインダストリーズ(株)製、商品名:POWDERLINK〔登録商標〕1174)0.23gとp-フェノールスルホン酸(東京化成工業(株)製)0.023g、及び界面活性剤(DIC(株)製、商品名:メガファック〔登録商標〕R-40)0.0046gを混合し、プロピレングリコールモノメチルエーテル50.93g及びプロピレングリコールモノメチルエーテルアセテート23.64gを加え溶解させた。その後孔径0.05μmのポリエチレン製ミクロフィルターを用いてろ過して、リソグラフィー用レジスト下層膜形成組成物とした。
上記比較合成例2で得られたポリマー溶液1.38gに、テトラメトキシメチルグリコールウリル(日本サイテックインダストリーズ(株)製、商品名:POWDERLINK〔登録商標〕1174)0.055gと5-スルホサリチル酸(東京化成工業(株)製)0.0055gを混合し、プロピレングリコールモノメチルエーテル27.52gを加え溶解させ、リソグラフィー用レジスト下層膜形成組成物とした。
実施例1乃至実施例10、及び比較例1乃至比較例3のレジスト下層膜形成組成物を、それぞれ、スピナーにより、半導体基板であるシリコンウェハー上に塗布した。そのシリコンウェハーをホットプレート上に配置し、205℃で1分間ベークし、レジスト下層膜(膜厚0.05μm)を形成した。これらのレジスト下層膜をフォトレジストに使用する溶剤である乳酸エチル及びプロピレングリコールモノメチルエーテルに浸漬し、それらの溶剤に不溶であることを確認した。
実施例1乃至実施例3、及び比較例1のレジスト下層膜形成組成物を、それぞれ、図1に上面及び断面を示す構造の、縦13μm、横13μm、高さ230nmの正方形のパターン、及び縦14μm、横14μm、高さ230nmの十字形のパターンが形成されたシリコンウェハー上に5nmの膜厚で塗布し、光学顕微鏡(オリンパス(株)製、MX61L)のダークフィールドで塗布性を確認した。実施例1乃至実施例3のレジスト下層膜形成組成物を塗布した場合のみ、良好な塗布性を確認できた。一方、比較例1のレジスト下層膜形成組成物を塗布した場合は、塗布ムラが見られるため、塗布性が不良であることが確認された。
実施例4乃至実施例10及び比較例3のレジスト下層膜形成組成物を、スピナーを用いてシリコンウェハー上にそれぞれ塗布した。そのシリコンウェハーを、ホットプレート上で、205℃で60秒間ベークし、膜厚28nmのレジスト下層膜を得た。そのレジスト下層膜上に、ArFエキシマレーザー用ポジ型レジスト溶液をスピンコートし、80℃で60秒間加熱し、ArFレジスト膜を形成した。そのレジスト膜に対し、ArFエキシマレーザー用露光装置((株)ニコン製、NSR S307R)を用い、所定の条件で露光した。露光後、95℃で60秒間ベーク(PEB)を行い、クーリングプレート上で室温まで冷却し、酢酸ブチルで現像した後、酢酸ブチルでリンス処理をし、62nmライン/124nmピッチのレジストパターンを形成した。レジストパターンの測長には走査型電子顕微鏡((株)日立ハイテクノロジーズ製、S-9380)を用いた。上記レジストパターンの形成において、62nmライン/124nmピッチ(ラインアンドスペース(L/S=1/1)を形成した露光量を最適露光量とした。この最適露光量よりも段階的に露光量を小さくすると、得られるパターンの線幅は次第に細くなり最終的にレジストパターンの倒壊が観察される。そこで、レジストパターンの倒壊が認められない最小の線幅を最小倒壊前寸法(nm)と定義してパターン倒れ耐性の指標とした。表1にこの最小倒壊前寸法の値を示す。パターン倒れ耐性は、最小倒壊前寸法が50nm以下の場合は「良好」、50nmを超える場合は「不良」と判断した。
シリコンウェハー上に、本発明の実施例1、実施例2及び比較例1のレジスト下層膜形成組成物をスピンコートし、205℃で1分間加熱することにより、レジスト下層膜を形成した。そのレジスト下層膜上に、EUV用レジスト溶液をスピンコートし加熱を行い、EUV露光装置(ASML社製、NXE3100)を用い、NA=0.25Dipoleの条件で露光した。露光後、PEB(露光後加熱)を行い、クーリングプレート上で室温まで冷却し、現像及びリンス処理を行い、シリコンウェハー上にレジストパターンを形成した。評価は、25nmのラインアンドスペース(L/S)の形成可否、形成されたラインパターン上面からの観察による当該ラインパターンのライン幅のラフネス(LWR)の大小、及びレジストパターンの倒壊が認められない最小の線幅である最小倒壊前寸法により行った。表2に評価の結果を示す。ラインアンドスペースが形成された場合を「良好」とした。また、LWRについて、形成されたラインパターンの線幅のバラツキの大きさをnmで示した。最小倒壊前寸法及びLWRは小さい値ほど好ましいことから、実施例1及び実施例2は比較例1と比べて、良好な最小倒壊前寸法及びLWRを示した。
Claims (10)
- 下記式(1)又は式(2)で表される構造をポリマー鎖の末端に有するポリマー、架橋剤、架橋反応を促進させる化合物及び有機溶媒を含むリソグラフィー用レジスト下層膜形成組成物。
(式中、R1は置換基を有してもよい炭素原子数1乃至6のアルキル基、フェニル基、ピリジル基、ハロゲノ基又はヒドロキシ基を表し、R2は水素原子、炭素原子数1乃至6のアルキル基、ヒドロキシ基、ハロゲノ基又は-C(=O)O-Xで表されるエステル基を表し、Xは置換基を有してもよい炭素原子数1乃至6のアルキル基を表し、R3は水素原子、炭素原子数1乃至6のアルキル基、ヒドロキシ基又はハロゲノ基を表し、R4は直接結合、又は炭素原子数1乃至8の二価の有機基を表し、R5は炭素原子数1乃至8の二価の有機基を表し、Aは芳香族環又は芳香族複素環を表し、tは0又は1を表し、uは1又は2を表す。) - 前記ポリマーの重量平均分子量は800乃至100000である請求項1乃至請求項6のいずれか一項に記載のリソグラフィー用レジスト下層膜形成組成物。
- 前記有機溶媒は、プロピレングリコールモノメチルエーテル、プロピレングリコールモノメチルエーテルアセテート、1-エトキシ-2-プロパノール、乳酸エチル、乳酸ブチル、及びシクロヘキサノンからなる群から選択される1種、又は2種以上の組み合わせである請求項1乃至請求項7のいずれか一項に記載のリソグラフィー用レジスト下層膜形成組成物。
- 更に酸発生剤を含むものである請求項1乃至請求項8のいずれか一項に記載のリソグラフィー用レジスト下層膜形成組成物。
- 請求項1乃至請求項9のいずれか一項に記載のリソグラフィー用レジスト下層膜形成組成物を半導体基板上に塗布しベークしてレジスト下層膜を形成する工程、前記レジスト下層膜上にレジスト溶液を用いてレジスト膜を形成する工程、フォトマスクを介して前記レジスト下層膜と前記レジスト膜で被覆された半導体基板をKrFエキシマレーザー、ArFエキシマレーザー、極端紫外線及び電子線からなる群から選択される放射線により露光する工程、及び露光後に現像する工程を含む、レジストパターンの形成方法。
Priority Applications (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201580021424.9A CN106233207B (zh) | 2014-04-25 | 2015-04-14 | 抗蚀剂下层膜形成用组合物以及使用该组合物的抗蚀剂图案的形成方法 |
| KR1020167027963A KR102156732B1 (ko) | 2014-04-25 | 2015-04-14 | 레지스트 하층막 형성 조성물 및 이것을 이용한 레지스트 패턴의 형성방법 |
| US15/305,793 US9910354B2 (en) | 2014-04-25 | 2015-04-14 | Resist underlayer film-forming composition and method for forming resist pattern using the same |
| JP2016514876A JP6493695B2 (ja) | 2014-04-25 | 2015-04-14 | レジスト下層膜形成組成物及びそれを用いたレジストパターンの形成方法 |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014091782 | 2014-04-25 | ||
| JP2014-091782 | 2014-04-25 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2015163195A1 true WO2015163195A1 (ja) | 2015-10-29 |
Family
ID=54332362
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2015/061467 WO2015163195A1 (ja) | 2014-04-25 | 2015-04-14 | レジスト下層膜形成組成物及びそれを用いたレジストパターンの形成方法 |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US9910354B2 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP6493695B2 (ja) |
| KR (1) | KR102156732B1 (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN106233207B (ja) |
| TW (1) | TWI652304B (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2015163195A1 (ja) |
Cited By (14)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2018008341A1 (ja) * | 2016-07-07 | 2018-01-11 | 日産化学工業株式会社 | ヒダントイン環を有する化合物の製造方法 |
| KR20190004259A (ko) * | 2016-04-28 | 2019-01-11 | 닛산 가가쿠 가부시키가이샤 | 레지스트 하층막 형성 조성물 |
| CN109313389A (zh) * | 2016-03-30 | 2019-02-05 | 日产化学株式会社 | 包含具有甘脲骨架的化合物作为添加剂的抗蚀剂下层膜形成组合物 |
| CN109416512A (zh) * | 2016-07-15 | 2019-03-01 | 日产化学株式会社 | 包含具有乙内酰脲环的化合物的抗蚀剂下层膜形成用组合物 |
| JP2019094314A (ja) * | 2017-11-28 | 2019-06-20 | 日産化学株式会社 | トリアジン−2,4−ジオン誘導体及びその製造方法 |
| WO2019138823A1 (ja) * | 2018-01-09 | 2019-07-18 | Jsr株式会社 | パターニングされた基板の製造方法 |
| WO2020022086A1 (ja) * | 2018-07-24 | 2020-01-30 | 日産化学株式会社 | ヘテロ原子をポリマー主鎖中に含むレジスト下層膜形成組成物 |
| KR20200107198A (ko) * | 2019-03-06 | 2020-09-16 | 삼성에스디아이 주식회사 | 레지스트 하층막용 조성물 및 이를 이용한 패턴 형성 방법 |
| WO2021111976A1 (ja) * | 2019-12-04 | 2021-06-10 | 日産化学株式会社 | ポリマーの製造方法 |
| KR20210071980A (ko) | 2018-10-05 | 2021-06-16 | 닛산 가가쿠 가부시키가이샤 | 레지스트 하층막 형성 조성물 및 그것을 이용한 레지스트패턴의 형성방법 |
| WO2022025090A1 (ja) * | 2020-07-29 | 2022-02-03 | 日産化学株式会社 | ヒダントイン化合物の反応生成物を含むレジスト下層膜形成組成物 |
| JP2022519360A (ja) * | 2019-03-29 | 2022-03-23 | サムスン エスディアイ カンパニー,リミテッド | レジスト下層膜用組成物およびこれを用いたパターン形成方法 |
| WO2022196606A1 (ja) * | 2021-03-15 | 2022-09-22 | 日産化学株式会社 | 酸触媒担持型ポリマーを含むレジスト下層膜形成組成物 |
| KR20230024916A (ko) * | 2020-06-12 | 2023-02-21 | 닛산 가가쿠 가부시키가이샤 | 디올구조를 포함하는 레지스트 하층막 형성용 조성물 |
Families Citing this family (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TWI689988B (zh) * | 2016-07-21 | 2020-04-01 | 日商東京威力科創股份有限公司 | 半導體裝置之製造方法、真空處理裝置及基板處理裝置 |
| WO2018143359A1 (ja) * | 2017-02-03 | 2018-08-09 | 日産化学工業株式会社 | ウレア結合を有する構造単位を有するポリマーを含むレジスト下層膜形成組成物 |
| JP6809315B2 (ja) * | 2017-03-15 | 2021-01-06 | 東京エレクトロン株式会社 | 半導体装置の製造方法及び真空処理装置 |
| CN112166379A (zh) * | 2018-05-25 | 2021-01-01 | 日产化学株式会社 | 使用了环式羰基化合物的抗蚀剂下层膜形成用组合物 |
| US11965059B2 (en) * | 2019-04-11 | 2024-04-23 | Nissan Chemical Corporation | Chemical-resistant protective film forming composition containing hydroxyaryl-terminated polymer |
| KR102448568B1 (ko) | 2020-01-17 | 2022-09-27 | 삼성에스디아이 주식회사 | 레지스트 하층막용 조성물 및 이를 이용한 패턴형성방법 |
Citations (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO1996033233A1 (fr) * | 1995-04-19 | 1996-10-24 | Kazunori Kataoka | Copolymeres en blocs heterotelecheliques et procede de production |
| JP2004250377A (ja) * | 2003-02-20 | 2004-09-09 | Maruzen Petrochem Co Ltd | チオール化合物、共重合体及び共重合体の製造方法 |
| WO2006040922A1 (ja) * | 2004-10-14 | 2006-04-20 | Nissan Chemical Industries, Ltd. | 芳香族スルホン酸エステル化合物及び光酸発生剤を含む下層反射防止膜形成組成物 |
| WO2006040921A1 (ja) * | 2004-10-12 | 2006-04-20 | Nissan Chemical Industries, Ltd. | 硫黄原子を含むリソグラフィー用反射防止膜形成組成物 |
| WO2006049045A1 (ja) * | 2004-11-01 | 2006-05-11 | Nissan Chemical Industries, Ltd. | スルホン酸エステルを含有するリソグラフィー用反射防止膜形成組成物 |
| JP2008015223A (ja) * | 2006-07-06 | 2008-01-24 | Nissan Chem Ind Ltd | スルホンを含有するレジスト下層膜形成組成物 |
| JP2010134437A (ja) * | 2008-10-28 | 2010-06-17 | Shin-Etsu Chemical Co Ltd | フォトレジスト下層膜形成材料及びパターン形成方法 |
| WO2012124597A1 (ja) * | 2011-03-15 | 2012-09-20 | 日産化学工業株式会社 | レジスト下層膜形成組成物及びそれを用いたレジストパターンの形成方法 |
| WO2012157607A1 (ja) * | 2011-05-17 | 2012-11-22 | 日産化学工業株式会社 | ビスフェノールs含有ポリマーを含むレジスト下層膜形成組成物 |
| WO2013133088A1 (ja) * | 2012-03-08 | 2013-09-12 | 日産化学工業株式会社 | 高密着性レジスト下層膜形成用組成物 |
| WO2013141015A1 (ja) * | 2012-03-23 | 2013-09-26 | 日産化学工業株式会社 | Euvリソグラフィー用レジスト下層膜形成組成物 |
| WO2013168610A1 (ja) * | 2012-05-07 | 2013-11-14 | 日産化学工業株式会社 | レジスト下層膜形成組成物 |
Family Cites Families (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4703102A (en) * | 1984-07-19 | 1987-10-27 | Asahi Kasei Kogyo Kabushiki Kaisha | Aromatic polyether ketones |
| JPH06104722B2 (ja) * | 1992-03-04 | 1994-12-21 | 旭化成工業株式会社 | 末端封止型芳香族ポリエーテルケトン及びその製造法 |
| WO2003034152A1 (fr) * | 2001-10-10 | 2003-04-24 | Nissan Chemical Industries, Ltd. | Composition de formation d'un film antireflet pour lithographie |
| JP4252872B2 (ja) * | 2003-10-06 | 2009-04-08 | 信越化学工業株式会社 | レジスト下層膜材料およびパターン形成方法 |
| WO2005098542A1 (ja) | 2004-04-09 | 2005-10-20 | Nissan Chemical Industries, Ltd. | 縮合系ポリマーを有する半導体用反射防止膜 |
| WO2009096340A1 (ja) | 2008-01-30 | 2009-08-06 | Nissan Chemical Industries, Ltd. | 硫黄原子を含有するレジスト下層膜形成用組成物及びレジストパターンの形成方法 |
| WO2009104685A1 (ja) | 2008-02-21 | 2009-08-27 | 日産化学工業株式会社 | レジスト下層膜形成組成物及びそれを用いたレジストパターンの形成方法 |
| KR101766796B1 (ko) | 2008-11-27 | 2017-08-09 | 닛산 가가쿠 고교 가부시키 가이샤 | 아웃가스 발생이 저감된 레지스트 하층막 형성 조성물 |
| JP5516200B2 (ja) * | 2009-08-05 | 2014-06-11 | 信越化学工業株式会社 | パターン形成方法、化学増幅ポジ型レジスト材料、及び、レジスト変性用組成物 |
| KR101682919B1 (ko) * | 2010-11-17 | 2016-12-06 | 닛산 가가쿠 고교 가부시키 가이샤 | 레지스트 하층막 형성 조성물 및 이를 이용한 레지스트 패턴의 형성방법 |
| JP5723648B2 (ja) * | 2011-03-25 | 2015-05-27 | 東京応化工業株式会社 | レジスト組成物、レジストパターン形成方法 |
-
2015
- 2015-04-14 US US15/305,793 patent/US9910354B2/en active Active
- 2015-04-14 CN CN201580021424.9A patent/CN106233207B/zh active Active
- 2015-04-14 JP JP2016514876A patent/JP6493695B2/ja active Active
- 2015-04-14 WO PCT/JP2015/061467 patent/WO2015163195A1/ja active Application Filing
- 2015-04-14 KR KR1020167027963A patent/KR102156732B1/ko active IP Right Grant
- 2015-04-22 TW TW104112863A patent/TWI652304B/zh active
Patent Citations (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO1996033233A1 (fr) * | 1995-04-19 | 1996-10-24 | Kazunori Kataoka | Copolymeres en blocs heterotelecheliques et procede de production |
| JP2004250377A (ja) * | 2003-02-20 | 2004-09-09 | Maruzen Petrochem Co Ltd | チオール化合物、共重合体及び共重合体の製造方法 |
| WO2006040921A1 (ja) * | 2004-10-12 | 2006-04-20 | Nissan Chemical Industries, Ltd. | 硫黄原子を含むリソグラフィー用反射防止膜形成組成物 |
| WO2006040922A1 (ja) * | 2004-10-14 | 2006-04-20 | Nissan Chemical Industries, Ltd. | 芳香族スルホン酸エステル化合物及び光酸発生剤を含む下層反射防止膜形成組成物 |
| WO2006049045A1 (ja) * | 2004-11-01 | 2006-05-11 | Nissan Chemical Industries, Ltd. | スルホン酸エステルを含有するリソグラフィー用反射防止膜形成組成物 |
| JP2008015223A (ja) * | 2006-07-06 | 2008-01-24 | Nissan Chem Ind Ltd | スルホンを含有するレジスト下層膜形成組成物 |
| JP2010134437A (ja) * | 2008-10-28 | 2010-06-17 | Shin-Etsu Chemical Co Ltd | フォトレジスト下層膜形成材料及びパターン形成方法 |
| WO2012124597A1 (ja) * | 2011-03-15 | 2012-09-20 | 日産化学工業株式会社 | レジスト下層膜形成組成物及びそれを用いたレジストパターンの形成方法 |
| WO2012157607A1 (ja) * | 2011-05-17 | 2012-11-22 | 日産化学工業株式会社 | ビスフェノールs含有ポリマーを含むレジスト下層膜形成組成物 |
| WO2013133088A1 (ja) * | 2012-03-08 | 2013-09-12 | 日産化学工業株式会社 | 高密着性レジスト下層膜形成用組成物 |
| WO2013141015A1 (ja) * | 2012-03-23 | 2013-09-26 | 日産化学工業株式会社 | Euvリソグラフィー用レジスト下層膜形成組成物 |
| WO2013168610A1 (ja) * | 2012-05-07 | 2013-11-14 | 日産化学工業株式会社 | レジスト下層膜形成組成物 |
Cited By (26)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN109313389A (zh) * | 2016-03-30 | 2019-02-05 | 日产化学株式会社 | 包含具有甘脲骨架的化合物作为添加剂的抗蚀剂下层膜形成组合物 |
| CN109313389B (zh) * | 2016-03-30 | 2020-07-14 | 日产化学株式会社 | 包含具有甘脲骨架的化合物作为添加剂的抗蚀剂下层膜形成组合物 |
| KR102328436B1 (ko) | 2016-04-28 | 2021-11-18 | 닛산 가가쿠 가부시키가이샤 | 레지스트 하층막 형성 조성물 |
| KR20190004259A (ko) * | 2016-04-28 | 2019-01-11 | 닛산 가가쿠 가부시키가이샤 | 레지스트 하층막 형성 조성물 |
| CN109415350A (zh) * | 2016-07-07 | 2019-03-01 | 日产化学株式会社 | 具有乙内酰脲环的化合物的制造方法 |
| WO2018008341A1 (ja) * | 2016-07-07 | 2018-01-11 | 日産化学工業株式会社 | ヒダントイン環を有する化合物の製造方法 |
| CN109416512A (zh) * | 2016-07-15 | 2019-03-01 | 日产化学株式会社 | 包含具有乙内酰脲环的化合物的抗蚀剂下层膜形成用组合物 |
| JP2019094314A (ja) * | 2017-11-28 | 2019-06-20 | 日産化学株式会社 | トリアジン−2,4−ジオン誘導体及びその製造方法 |
| JP7116356B2 (ja) | 2017-11-28 | 2022-08-10 | 日産化学株式会社 | トリアジン-2,4-ジオン誘導体及びその製造方法 |
| WO2019138823A1 (ja) * | 2018-01-09 | 2019-07-18 | Jsr株式会社 | パターニングされた基板の製造方法 |
| JP7375757B2 (ja) | 2018-07-24 | 2023-11-08 | 日産化学株式会社 | ヘテロ原子をポリマー主鎖中に含むレジスト下層膜形成組成物 |
| JPWO2020022086A1 (ja) * | 2018-07-24 | 2021-09-09 | 日産化学株式会社 | ヘテロ原子をポリマー主鎖中に含むレジスト下層膜形成組成物 |
| WO2020022086A1 (ja) * | 2018-07-24 | 2020-01-30 | 日産化学株式会社 | ヘテロ原子をポリマー主鎖中に含むレジスト下層膜形成組成物 |
| KR20210071980A (ko) | 2018-10-05 | 2021-06-16 | 닛산 가가쿠 가부시키가이샤 | 레지스트 하층막 형성 조성물 및 그것을 이용한 레지스트패턴의 형성방법 |
| US12072631B2 (en) | 2018-10-05 | 2024-08-27 | Nissan Chemical Corporation | Resist underlayer film-forming composition and method for forming resist pattern using the same |
| US11249396B2 (en) | 2019-03-06 | 2022-02-15 | Samsung Sdi Co., Ltd. | Resist underlayer composition, and method of forming patterns using the composition |
| KR102348675B1 (ko) | 2019-03-06 | 2022-01-06 | 삼성에스디아이 주식회사 | 레지스트 하층막용 조성물 및 이를 이용한 패턴 형성 방법 |
| KR20200107198A (ko) * | 2019-03-06 | 2020-09-16 | 삼성에스디아이 주식회사 | 레지스트 하층막용 조성물 및 이를 이용한 패턴 형성 방법 |
| JP2022519360A (ja) * | 2019-03-29 | 2022-03-23 | サムスン エスディアイ カンパニー,リミテッド | レジスト下層膜用組成物およびこれを用いたパターン形成方法 |
| JP7244659B2 (ja) | 2019-03-29 | 2023-03-22 | サムスン エスディアイ カンパニー,リミテッド | レジスト下層膜用組成物およびこれを用いたパターン形成方法 |
| US12130552B2 (en) | 2019-03-29 | 2024-10-29 | Samsung Sdi Co., Ltd. | Composition for resist underlayer, and pattern forming method using same |
| WO2021111976A1 (ja) * | 2019-12-04 | 2021-06-10 | 日産化学株式会社 | ポリマーの製造方法 |
| KR20230024916A (ko) * | 2020-06-12 | 2023-02-21 | 닛산 가가쿠 가부시키가이샤 | 디올구조를 포함하는 레지스트 하층막 형성용 조성물 |
| KR102665285B1 (ko) | 2020-06-12 | 2024-05-13 | 닛산 가가쿠 가부시키가이샤 | 디올구조를 포함하는 레지스트 하층막 형성용 조성물 |
| WO2022025090A1 (ja) * | 2020-07-29 | 2022-02-03 | 日産化学株式会社 | ヒダントイン化合物の反応生成物を含むレジスト下層膜形成組成物 |
| WO2022196606A1 (ja) * | 2021-03-15 | 2022-09-22 | 日産化学株式会社 | 酸触媒担持型ポリマーを含むレジスト下層膜形成組成物 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN106233207B (zh) | 2020-04-10 |
| KR102156732B1 (ko) | 2020-09-16 |
| JP6493695B2 (ja) | 2019-04-03 |
| JPWO2015163195A1 (ja) | 2017-04-13 |
| KR20160146691A (ko) | 2016-12-21 |
| CN106233207A (zh) | 2016-12-14 |
| US20170045820A1 (en) | 2017-02-16 |
| TWI652304B (zh) | 2019-03-01 |
| TW201605966A (zh) | 2016-02-16 |
| US9910354B2 (en) | 2018-03-06 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6493695B2 (ja) | レジスト下層膜形成組成物及びそれを用いたレジストパターンの形成方法 | |
| JP5888523B2 (ja) | レジスト下層膜形成組成物及びそれを用いたレジストパターンの形成方法 | |
| JP6458952B2 (ja) | レジスト下層膜形成組成物及びそれを用いたレジストパターンの形成方法 | |
| JP6497535B2 (ja) | レジスト下層膜形成組成物用添加剤及び該添加剤を含むレジスト下層膜形成組成物 | |
| JP5382321B2 (ja) | レジスト下層膜形成組成物及びそれを用いたレジストパターンの形成方法 | |
| WO2014171326A1 (ja) | レジスト下層膜形成組成物 | |
| JP5737526B2 (ja) | レジスト下層膜形成組成物及びそれを用いたレジストパターンの形成方法 | |
| WO2012105648A1 (ja) | 非感光性レジスト下層膜形成組成物 | |
| JP2015145944A (ja) | レジスト下層膜形成組成物及びそれを用いたレジストパターンの形成方法 | |
| WO2012081619A1 (ja) | レジスト下層膜形成組成物及びそれを用いたレジストパターンの形成方法 | |
| JPWO2019039355A1 (ja) | レジスト下層膜形成組成物 | |
| JP2017203941A (ja) | 添加剤を含むリソグラフィー用レジスト下層膜形成組成物 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 15783727 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2016514876 Country of ref document: JP Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 20167027963 Country of ref document: KR Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 15305793 Country of ref document: US |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 15783727 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |