WO2013189241A1 - 嘧啶二胺类衍生物、其制备方法及其在医药上的应用 - Google Patents
嘧啶二胺类衍生物、其制备方法及其在医药上的应用 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2013189241A1 WO2013189241A1 PCT/CN2013/076837 CN2013076837W WO2013189241A1 WO 2013189241 A1 WO2013189241 A1 WO 2013189241A1 CN 2013076837 W CN2013076837 W CN 2013076837W WO 2013189241 A1 WO2013189241 A1 WO 2013189241A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- group
- compound
- formula
- cycloalkyl
- aryl
- Prior art date
Links
- CDGVGXPLHABBHG-UHFFFAOYSA-N CC(C)(COc(cc1)c(N2)nc1Nc1nc(Cl)ncc1Cl)C2=O Chemical compound CC(C)(COc(cc1)c(N2)nc1Nc1nc(Cl)ncc1Cl)C2=O CDGVGXPLHABBHG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QSHLRLHDFDHQAI-UHFFFAOYSA-N CC(C)(COc(cc1)c(N2)nc1Nc1nc(Nc(cc3)cc(F)c3N3CCOCC3)ncc1F)C2=O Chemical compound CC(C)(COc(cc1)c(N2)nc1Nc1nc(Nc(cc3)cc(F)c3N3CCOCC3)ncc1F)C2=O QSHLRLHDFDHQAI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RJRLZHJKERDJKC-UHFFFAOYSA-N CC(C)(COc(cc1)c(N2)nc1Nc1nc(Nc(cc3OC)cc(OC)c3OC)ncc1C)C2=O Chemical compound CC(C)(COc(cc1)c(N2)nc1Nc1nc(Nc(cc3OC)cc(OC)c3OC)ncc1C)C2=O RJRLZHJKERDJKC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BQSHRABSHCAGTJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N CC(C)(COc(cc1)c(N2)nc1Nc1nc(Nc(cc3OC)cc(OC)c3OC)ncc1Cl)C2=O Chemical compound CC(C)(COc(cc1)c(N2)nc1Nc1nc(Nc(cc3OC)cc(OC)c3OC)ncc1Cl)C2=O BQSHRABSHCAGTJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GIKMWFAAEIACRF-UHFFFAOYSA-N Clc(cnc(Cl)n1)c1Cl Chemical compound Clc(cnc(Cl)n1)c1Cl GIKMWFAAEIACRF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FQGIBHQUVCGEAC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Nc(cc1)cc(F)c1N1CCOCC1 Chemical compound Nc(cc1)cc(F)c1N1CCOCC1 FQGIBHQUVCGEAC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D498/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing in the condensed system at least one hetero ring having nitrogen and oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms
- C07D498/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing in the condensed system at least one hetero ring having nitrogen and oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms in which the condensed system contains two hetero rings
- C07D498/04—Ortho-condensed systems
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P11/00—Drugs for disorders of the respiratory system
- A61P11/06—Antiasthmatics
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P17/00—Drugs for dermatological disorders
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P17/00—Drugs for dermatological disorders
- A61P17/06—Antipsoriatics
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P19/00—Drugs for skeletal disorders
- A61P19/02—Drugs for skeletal disorders for joint disorders, e.g. arthritis, arthrosis
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P21/00—Drugs for disorders of the muscular or neuromuscular system
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P29/00—Non-central analgesic, antipyretic or antiinflammatory agents, e.g. antirheumatic agents; Non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs [NSAID]
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P35/00—Antineoplastic agents
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P35/00—Antineoplastic agents
- A61P35/02—Antineoplastic agents specific for leukemia
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P37/00—Drugs for immunological or allergic disorders
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P37/00—Drugs for immunological or allergic disorders
- A61P37/02—Immunomodulators
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P37/00—Drugs for immunological or allergic disorders
- A61P37/08—Antiallergic agents
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D498/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing in the condensed system at least one hetero ring having nitrogen and oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms
- C07D498/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing in the condensed system at least one hetero ring having nitrogen and oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms in which the condensed system contains two hetero rings
- C07D498/10—Spiro-condensed systems
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a novel pyrimidinediamine derivative, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, or a pharmaceutical composition containing the same, and a process for the preparation thereof.
- the invention further relates to the use of said pyrimidinediamine derivatives, and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, or pharmaceutical compositions containing the same, in the preparation of a therapeutic, in particular a Syk inhibitor. Background technique
- Syk was originally cloned from the porcine spleen cDNA, which encodes a non-receptor tyrosine kinase and is called Spleen Tyrosine kinase (Syk).
- Syk with a molecular weight of about 72 kDa and Zap70 (C-chain-associated protein kinase of 70 kDa) belong to the ZAP70/Syk tyrosine kinase family.
- Syk is mainly expressed in blood cells, and is also expressed in vascular endothelial cells, fibroblasts, airway epithelial cells, hepatocytes, and osteoclasts.
- the Syk protein contains a relatively conserved protein tyrosine kinase domain and two tandem SH2 (Src homology 2) domains.
- SH2 mainly mediates the interconnection of various signal proteins in the cytoplasm to form protein heteromeric complexes, thereby regulating signal transduction in signal transduction pathways.
- the amino acid region (interdomain B) that links the SH2 domain and the kinase domain contains many tyrosine residues. When these tyrosine residues are phosphorylated, they can serve as anchor sites for a variety of proteins, and these proteins may be The substrate of Syk.
- BCRs B-cell receptors
- FcRs Fc Receptors, FcRs
- activated natural killer receptors activating natural killer receptors
- Syk mainly binds to the immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM) phosphorylated by the SH2 domain, and the downstream signaling cascade plays an important role, such as affecting B cells.
- ITAM immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif
- FcRs are one of the most active and active receptors on immune cells. Among them, FcyR and FcsR recognize the Fc segments of immunoglobulin IgG and IgE, respectively.
- Syk is an important signaling molecule in FcyR and FcsR signaling. Macrophages and neutrophils are activated by FcRs, and ITAMs are diphosphorylated by upstream Fc receptor-associated Src family kinases such as Lyn and Lck. Activation of FcRs results in the binding of Syk to the Fc of the Fc receptor ⁇ chain via its own SH2(N) domain and activation.
- Syk phosphorylates many downstream substrates such as Vav, LAT and SLP-76.
- the formation of signaling complexes also triggers activation of many downstream signaling pathways such as PLC subtype-mediated calcium mobilization and PKC activation.
- This also activates a variety of MAPKs such as JNK and ERK, resulting in the production of lipid mediators and cytokines.
- MAPKs such as JNK and ERK
- NFATcl also relies on RANKL to activate c-Fos and TRAF6.
- RANKL may also Promote efficient conduction of the ITAM signal.
- various downstream signaling molecules such as SLP-65 are phosphorylated, providing anchor sites for important proteins such as ⁇ , Vav, Cbl and Btk, which form signal complexes. , activate the downstream signal path.
- Syk is a key mediator of immunoreceptors expressed in inflammatory cells such as B cells, mast cells, macrophages, and receptors on these immune cells are closely related to allergic and antibody-mediated autoimmune diseases. Therefore, Syk is used as an intervention target, providing new treatments for refractory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, asthma, allergic rhinitis, lymphoma, leukemia, malignant epithelial tumors, and tumor metastasis.
- the object of the present invention is to provide a compound represented by the formula (I) or a tautomer, a mesogen, a racemate, an enantiomer, a diastereomer thereof, and Mixture form and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, as well as metabolites and metabolic precursors
- E is selected from S, 0 or C;
- Z is C(R 5 R 6 );
- Ring A, ring B is aryl or heteroaryl
- R 1 is selected from the group consisting of a hydrogen atom, a halogen, a hydroxyl group, a cyano group, a nitro group, an alkyl group, an alkoxy group, an alkenyl group, a aryl group, a cycloalkyl group, -C(0)NR 7 R 8 , -OR 9 , -C (0) OR 9 , aryl or heteroaryl;
- R 2 , R 3 or R 4 are each independently selected from the group consisting of a hydrogen atom, a halogen, a cyano group, a nitro group, a hydroxyl group, an alkyl group, an alkoxy group, a cycloalkyl group, a heterocyclic group, an aryl group, a heteroaryl group, -NR 7 R 8 , -C(0)NR 7 R 8 -NHS(0) m R 9 -OS(0) m R 9 -S(0) m R 9 -NHC(0)R 9 -OR 9 , -C (0) R 9 -OC(0)R 9 or -C(0)OR 9 , wherein the alkyl group, alkoxy group, cycloalkyl group, heterocyclic group, aryl group or heteroaryl group are each independently Further selected from one or more selected from the group consisting of hydroxyl, halogen, alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl, heteroaryl, -
- R 2 and R 3 form a cycloalkyl or heterocyclic group, wherein the heterocyclic group contains one or more selected a hetero atom of g N, O or S(0) m , and the heterocyclic group optionally further selected from one or more selected from the group consisting of alkyl, halogen, cyano, cycloalkyl, heterocyclic, aryl, hetero Aryl, -NR 7 R 8 , -C(0)NR 7 R 8 -NHS(0) m R 9 -S(0) m R 9 -NHC(0)R 9 -OR 9 , -C(0) Substituted by a substituent of R 9 -OC(0)R 9 or -C(0)OR 9 ;
- R 5 or R 6 are each independently selected from a hydrogen atom, a halogen, an alkyl group, a cycloalkyl group, a hydroxyl group, an alkoxy group, an aryl group or a heteroaryl group, wherein said alkyl group, cycloalkyl group, aryl group or hetero group
- the aryl groups are each independently optionally further selected from one or more selected from the group consisting of hydroxyl, halogen, alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl, heteroaryl, -NR 7 R 8 , -C(0)NR 7 R 8 , -NHS(0) m R 9 , -S(0) m R 9 , -NHC(0)R 9 , -OR 9 , -C(0)R 9 , -OC(0)R 9 or - Substituted by a substituent of C(0)OR 9 ;
- R 5 and R 6 together with the C atom to which they are attached form a cycloalkyl or heterocyclic group, each of which is optionally independently further selected from one or more selected from the group consisting of a hydroxyl group and a halogen. Substituted with a substituent of an alkyl group, an alkoxy group, a cycloalkyl group or a heterocyclic group;
- R 7 or R 8 are each independently selected from a hydrogen atom, an alkyl group, a cycloalkyl group, a heterocyclic group, an aryl group or a heteroaryl group, said hydrogen atom, an alkyl group, a cycloalkyl group, a heterocyclic group, an aryl group.
- the heteroaryl groups are each independently optionally further substituted with one or more substituents selected from hydroxy, halo, alkyl, alkoxy, cycloalkyl or heterocyclyl; or R 7 and R 8 are related thereto
- the linked N atoms together form a 3-8 membered heterocyclic group, wherein the 3 ⁇
- the 8-membered heterocyclic group contains one or more N, 0 or S(0) m heteroatoms, and the 3 to 8 membered heterocyclic group is optionally further selected from one or more selected from the group consisting of alkyl, halogen, hydroxy, Substituted with a substituent of an amino group, a cyano group, an alkoxy group, a cycloalkyl group, a heterocyclic group, an aryl group or a heteroaryl group;
- R 9 is selected from a hydrogen atom, an alkyl group, an amino group, a cycloalkyl group, a heterocyclic group, an aryl group or a heteroaryl group, and the alkyl group, the cycloalkyl group, the heterocyclic group, the aryl group or the heteroaryl group are each independently Optionally further substituted with one or more substituents selected from alkyl, halo, hydroxy, amino, cyano, alkoxy, cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl or heteroaryl;
- n 0, 1, or 2.
- the compound of the formula (I) or tautomerized thereof a form, a meso form, a racemate, an enantiomer, a diastereomer, a mixture thereof, and a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, wherein R 5 or R 6 are each independently selected from halogen Or an alkyl group.
- the compound of the formula (I) or a tautomer, a mesogen, a racemate, an enantiomer, a diastereomer thereof The construct, and mixtures thereof, and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, R 5 and R 6 together form a cycloalkyl group.
- the compound of the formula (I) or a tautomer, a mesogen, a racemate, an enantiomer, a diastereomer thereof The construct, and mixtures thereof, and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, R 5 and R 6 together form a cyclopropyl group.
- the compound of the formula (I) or a tautomer, a mesogen, a racemate, an enantiomer, a diastereomer thereof a form, a mixture thereof, and a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof wherein R 2 , R 3 or R 4 are each independently selected from the group consisting of a hydrogen atom, a halogen, a hydroxyl group, an alkyl group, an alkoxy group, a cycloalkyl group, and a heterocyclic ring.
- R 7 or R 8 are each independently selected from a hydrogen atom or an alkyl group
- R 9 is selected from a hydrogen atom, an alkyl group, an amino group, a cycloalkyl group, a heterocyclic group, an aryl group or a heteroaryl group, and the alkyl group, the cycloalkyl group, the heterocyclic group, the aryl group or the heteroaryl group are each independently Optionally further substituted with one or more substituents selected from alkyl, halo, hydroxy, amino, cyano, alkoxy, cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl or heteroaryl;
- n 0, 1, or 2.
- the compound of the formula (I) or a tautomer, a mesogen, a racemate, an enantiomer, a diastereomer thereof a form, a mixture thereof, and a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof are a compound of the formula ( ⁇ ) or a tautomer thereof, a mesogen and a racemate, an enantiomer, Diastereoisomers and mixtures thereof, and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof:
- Y is an N or C atom; and E, Z, and ring 8, Ri ⁇ R 4 are as defined in the formula (I).
- the compound of the formula (I) or a tautomer, a mesogen, a racemate, an enantiomer, a diastereomer thereof a form, a mixture thereof, and a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof are a compound of the formula ( ⁇ ) or a tautomer thereof, a mesogen and a racemate, an enantiomer, Diastereomeric salt:
- Typical compounds of the invention include, but are not limited to:
- the present invention also relates to a compound of the formula (IA) which can be used as a compound of the formula (I) or a tautomer thereof, a mesogen, a racemate, an enantiomer or a non- Intermediates in the form of enantiomers, and mixtures thereof:
- E is selected from S, 0 or C;
- Z is C(R 5 R 6 );
- Ring A is an aryl or heteroaryl group
- R 1 is selected from the group consisting of a hydrogen atom, a halogen, a hydroxyl group, a cyano group, a nitro group, an alkyl group, an alkoxy group, an alkenyl group, a block group, and a ring.
- Each of RRR 555 or or RRR 666 is independently selected from the group consisting of atomic protons derived from hydrogen hydrogen hydrogen hydrogenogen, halohalo halogen, and alkylene alkyl groups. ,, a cyclocycloalkylalkyl group, a hydroxyhydroxyl hydroxy group, an alkane alkoxyoxy group, an arylarylaryl group or an or a heteroaromatic aryl group Alkylalkyl group, a cyclocycloalkylalkylalkyl group, an aromatic arylalkyl group or or a mixture thereof as described in the above
- Each of the heteropolyaryl aryl groups is independently selected from the standpoint of being independently selected, step by step, being one by one, or more or more Each one selected from the group consisting of a hydroxyhydroxyl group, a halogen halide, an alkylene group, a cyclocycloalkylalkyl group, a heteroheterocycle Cycloringyl
- the RRR 555 and the AND and the RR 666 are formed together with the CCC original atomic sub-members connected to the other end of the connection, forming a one-to-one shape together a cyclocycloalkylalkylalkyl group or a or heteroheterocyclic ring-based group, a cyclocyclocycloalkylalkyl group or a hetero- or hetero-homocyclic group as described
- Each of the ring-ring-based groups is independently selected from the stand-alone basis, and is optionally selected one by one or one or more.
- XXX is for the departure of the base group, and the superior is preferably selected as the halohalogen. . .
- ⁇ E ⁇ , ⁇ Z ⁇ ,, XXX,, and RRR 111 are as defined in the general formula ((( ⁇ I ⁇ --- ⁇ A ⁇ )))) Described in the middle of China. . .
- the present invention has been developed in a step-by-step manner involving the general formula (((III)) involved in the preparation of various preparations as described in the preparation of the preparations.
- a compound of the compound shown in the above, or a chito-isomutation variant thereof, or a meso-endomer Body , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , ,
- XX is a leaving group, and preferably is halogen halide; wherein EE, ZZ, ring, ring ring ⁇ 11 ⁇ 11
- EE, ZZ, ring, ring ring ⁇ 11 ⁇ 11 The definition of 44 is as described in the general formula ((II)). .
- composition composition comprising a therapeutic agent An effective amount of the compound of the formula (II) shown in the above formula, or a tautomeric variant thereof, or Nene Eliminating cyclone body, outer and outer racemic body, pair of enantiomeric isomers, non-diastereomeric isomers, and mixtures thereof
- a pharmaceutical composition composition comprising a therapeutic agent
- An effective amount of the compound of the formula (II) shown in the above formula, or a tautomeric variant thereof, or Nene Eliminating cyclone body, outer and outer racemic body, pair of enantiomeric isomers, non-diastereomeric isomers, and mixtures thereof The form of the complex form, and the salt of the cocoa medicinal agent thereof, and the carrier carrier which is pharmaceutically acceptable.
- the chemical compound represented by the general formula ((II)) or the mutual variation thereof Constructor body, endogenous racemic body, outer and outer racemic body, pair of enantiomeric isomers, non-diastereomeric isomers And the mixed form of the mixed composition thereof, and the salt of the cocoa medicinal agent thereof, or the inclusion of the pharmaceutical composition composition containing the same
- the preparation of the egg white protein kinase inhibitor inhibiting preparation is preferably selected from the group consisting of SSyykk inhibitory preparations. .
- the protein kinase is selected from the group consisting of a receptor tyrosine kinase, a non-receptor tyrosine kinase or a serine-threonine kinase.
- the invention also relates to a compound of the formula (I) or a tautomer, a mesogen, a racemate, an enantiomer, a diastereomer thereof, And a mixture thereof, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, or a pharmaceutical composition comprising the same, which is a protein kinase inhibitor, preferably a Syk protein kinase inhibitor.
- the invention also relates to a compound of the formula (I) or a tautomer, a racemate, an enantiomer, a diastereomer thereof, and mixtures thereof, And use of a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, or a pharmaceutical composition comprising the same, for the manufacture of a medicament for treating a protein kinase-related disease.
- the protein kinase-related disease is a Syk protein kinase-related disease selected from the group consisting of a malignant lymphoma, an autoimmune disease, scarring, an allergic disease, a disease associated with tissue destruction, and inflammation associated with tissue. The disease.
- the autoimmune disease is selected from the group consisting of allograft rejection, Hashimoto's thyroiditis, autoimmune hemolytic anemia, atrophic gastritis of autoimmune pernicious anemia, autoimmune encephalomyelitis, autoimmune orchitis, Goodpas Hill disease, autoimmune thrombocytopenia, craniocerebral inflammation, muscle weakness, Graves' disease, primary biliary sclerosis, chronic aggressive hepatitis, membranous glomerular disease, and autoimmune diseases involving autoimmune disorders of body tissues.
- the autoimmune diseases involving autoimmune disorders of body tissues are preferably systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, Sjogren's syndrome, Reiter syndrome, polymyositis-dermatomyositis, body tissue sclerosis, multiple arteries Inflammation, multiple triangulation, large acne and psoriasis.
- the knot is selected from the group consisting of scleroderma, increased fibrosis, neoplasms, post-surgical scars, pulmonary fibrosis, vasospasm, migraine, reperfusion injury, and posterior myocardial infarction.
- the disease associated with tissue destruction is selected from the group consisting of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, cardiac bronchitis, and posterior myocardial infarction.
- the inflammation associated with tissue is selected from the group consisting of rheumatoid arthritis, allergic diseases, spastic colon and inflammatory colon diseases.
- the present invention relates to a method for treating or preventing a protein kinase-associated disease in a mammal, comprising administering to the mammal a therapeutically effective amount of a compound of the formula (I) of the present invention or A tautomer, a racemate, an enantiomer, a diastereomer, a mixture thereof, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, or a pharmaceutical composition comprising the same.
- the protein kinase-related disease is preferably a disease associated with Syk protein kinase selected from the group consisting of malignant lymphoma, autoimmune diseases, scarring, allergic diseases, diseases associated with tissue destruction, and inflammation associated with tissues. disease.
- the autoimmune diseases are preferably systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, Sjogren's syndrome, Reiter syndrome, polymyositis-dermatomyositis, body tissue sclerosis, polyarteritis, multiple triangulation, Large categories of acne and psoriasis.
- the allergic diseases are preferably conjunctivitis, rhinitis, asthma, atopic dermatitis and food allergy.
- the knot is selected from the group consisting of scleroderma, increased fibrosis, neoplasms, post-surgical scars, pulmonary fibrosis, vasospasm, migraine, reperfusion injury, and posterior myocardial infarction.
- the disease associated with tissue destruction is selected from the group consisting of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, cardiac bronchitis, and posterior myocardial infarction.
- the inflammation associated with tissue is selected from allergic diseases, spastic colon And inflammatory colon disease.
- the mammal is a human.
- Another aspect of the invention relates to a compound of the formula (I) or a tautomer, a racemate, an enantiomer, a diastereomer thereof, a mixture thereof, and A pharmaceutically acceptable salt, or a pharmaceutical composition comprising the same, as a medicament for treating a protein kinase-related disease.
- the protein kinase-associated disease described therein is preferably a disease associated with Syk protein kinase selected from the group consisting of malignant lymphoma, autoimmune disease, scarring, allergic diseases, diseases associated with tissue destruction, and inflammation associated with tissues. The disease.
- the autoimmune diseases are preferably systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, Sjogren's syndrome, Reiter syndrome, polymyositis-dermatomyositis, body tissue sclerosis, polyarteritis, multiple triangulation, Large categories of acne and psoriasis.
- the allergic diseases are preferably conjunctivitis, rhinitis, asthma, atopic dermatitis and food allergy.
- the knot is selected from the group consisting of scleroderma, increased fibrosis, neoplasms, post-surgical scars, pulmonary fibrosis, vasospasm, migraine, reperfusion injury, and posterior myocardial infarction.
- the disease associated with tissue destruction is selected from the group consisting of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, cardiac bronchitis, and posterior myocardial infarction.
- the association with tissue inflammation is selected from the group consisting of allergic diseases, sputum colon and inflammatory colon diseases.
- Another aspect of the invention relates to a method for inhibiting Fc receptor signal transduction cascades comprising an Fc receptor cell having a gamma homodimer, as in the formula for effectively inhibiting its signal transduction cascade a compound represented by (I) or a tautomer, a racemate, an enantiomer, a diastereomer thereof, a mixture thereof, and a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, or a compound thereof
- the step of contacting the pharmaceutical composition is selected from the group consisting of Fc a RI Fc y RI Fc ⁇ R III and Fc ⁇ RI.
- the present invention relates to a compound which discriminates the catalytic activity of a protein kinase, which contacts a cell expressing the protein kinase with a compound or salt of the present invention, and then detects the effect on the cell.
- the present invention also relates to a compound which discriminates the catalytic activity of a protein kinase by contacting an artificially recombinant synthetic kinase protein with a compound or salt of the present invention, and then detecting the effect on the kinase activity by the Elisa method.
- the pharmaceutical composition containing the active ingredient may be in a form suitable for oral administration, such as tablets, troches, lozenges, aqueous or oily suspensions, dispersible powders or granules, emulsions, hard or soft capsules, or syrups or Tincture.
- Oral compositions can be prepared according to any method known in the art for preparing a pharmaceutical composition, such compositions may contain one or more ingredients selected from the group consisting of sweeteners, flavoring agents, coloring agents, and preservatives, To provide a pleasing and tasty pharmaceutical preparation. Tablets contain the active ingredient and non-toxic pharmaceutically acceptable excipients suitable for the preparation of tablets for mixing.
- excipients may be inert excipients such as calcium carbonate, sodium carbonate, lactose, calcium phosphate or sodium phosphate; granulating agents and disintegrating agents such as microcrystalline cellulose, croscarmellose sodium, corn Starch or alginic acid; a binder such as starch, gelatin, polyvinylpyrrolidone or gum arabic; and a lubricant such as magnesium stearate, stearic acid or talc.
- These tablets may be uncoated or may be coated by a known technique which provides a sustained release effect over a long period of time by masking the taste of the drug or delaying disintegration and absorption in the gastrointestinal tract.
- water-soluble taste masking materials such as hydroxypropylmethylcellulose or hydroxypropylcellulose, or extended-time materials such as ethylcellulose, cellulose acetate butyrate may be used.
- hard gelatin capsules in which the active ingredient is mixed with an inert solid diluent such as calcium carbonate, calcium phosphate or kaolin, or the active ingredient with a water-soluble carrier such as polyethylene glycol or an oil vehicle such as peanut oil, Soft gelatin capsules mixed with liquid paraffin or olive oil provide oral preparations.
- an inert solid diluent such as calcium carbonate, calcium phosphate or kaolin
- a water-soluble carrier such as polyethylene glycol or an oil vehicle such as peanut oil
- Soft gelatin capsules mixed with liquid paraffin or olive oil provide oral preparations.
- the aqueous suspension contains the active substance and excipients suitable for the preparation of the aqueous suspension for mixing.
- excipients are suspending agents, such as sodium carboxymethylcellulose, methylcellulose, hydroxypropylmethylcellulose, sodium alginate, polyvinylpyrrolidone and gum arabic; dispersing or wetting agents can be naturally occurring a phospholipid such as lecithin, or a condensation product of an alkylene oxide with a fatty acid such as polyoxyethylene stearate, or a condensation product of ethylene oxide with a long chain fatty alcohol, such as heptadecyl ethyleneoxy cetyl alcohol (heptadecaethyleneoxy cetanol), or a condensation product of ethylene oxide with a partial ester derived from a fatty acid and a hexitol, such as polyethylene oxide sorbitan monooleate, or ethylene oxide with derivatives derived from fatty acids and hexitols
- the aqueous suspensions may also contain one or more preservatives such as ethylparaben or n-propylparaben, one or more coloring agents, one or more flavoring agents, and one or more sweetening agents.
- preservatives such as ethylparaben or n-propylparaben
- coloring agents such as ethylparaben or n-propylparaben
- flavoring agents such as sucrose, saccharin or aspartame.
- the oil suspension can be formulated by suspending the active ingredient in a vegetable oil such as peanut oil, olive oil, sesame oil or coconut oil, or a mineral oil such as liquid paraffin.
- the oil suspensions may contain a thickening agent, such as beeswax, hard paraffin or cetyl alcohol.
- the above sweeteners and flavoring agents may be added to provide a palatable preparation.
- These compositions can be preserved by the addition of an anti-oxidant such as butylated hydroxyanisole or (X-tocopherol).
- Dispersible powders and granules suitable for use in the preparation of aqueous suspensions may be employed in the preparation of aqueous dispersions in the presence of a dispersible or wetting agent, a suspending agent or one or more preservatives. Suitable dispersing or wetting agents and suspending agents can be used to illustrate the above examples. Other excipients such as sweetening, flavoring, and coloring agents can also be added. These compositions are preserved by the addition of an anti-oxidant such as ascorbic acid.
- the pharmaceutical compositions of the invention may also be in the form of an oil-in-water emulsion.
- the oil phase may be a vegetable oil such as olive oil or peanut oil, or a mineral oil such as liquid paraffin or a mixture thereof.
- Suitable emulsifiers may be naturally occurring phospholipids, such as soy lecithin and esters or partial esters derived from fatty acids and hexitol anhydrides such as sorbitan monooleate, and condensation products of the partial esters and ethylene oxide, For example, polyethylene oxide sorbitol monooleate.
- the emulsions may also contain sweeteners, flavoring agents, preservatives, and antioxidants.
- Syrups and elixirs may be formulated with sweetening agents such as glycerol, propylene glycol, sorbitol or sucrose. Such formulations may also contain a demulcent, a preservative, a colorant, and an antioxidant.
- sweetening agents such as glycerol, propylene glycol, sorbitol or sucrose.
- Such formulations may also contain a demulcent, a preservative, a colorant, and an antioxidant.
- the pharmaceutical composition may be in the form of a sterile injectable aqueous solution.
- acceptable vehicles and solvents that may be employed are water, Ringer's solution and isotonic sodium chloride solution.
- the sterile injectable preparation may be a sterile injectable oil-in-water microemulsion in which the active ingredient is dissolved in the oil phase.
- the active ingredient is dissolved in a mixture of soybean oil and lecithin.
- the oil solution is then added to a mixture of water and glycerin to form a microemulsion.
- the injection or microemulsion can be injected into the patient's bloodstream by local injection.
- the solution and microemulsion are preferably administered in a manner that maintains a constant circulating concentration of the compound of the invention.
- a continuous intravenous delivery device can be used.
- An example of such a device is the Deltec CADD-PLUS. TM. 5400 intravenous pump.
- the pharmaceutical composition may be in the form of a sterile injectable aqueous or oily suspension for intramuscular and subcutaneous administration.
- the suspension may be formulated according to known techniques using those suitable dispersing or wetting agents and suspending agents.
- the sterile injectable preparation may also be a sterile injection solution or a mixture prepared in a non-toxic parenterally acceptable diluent or solvent.
- a suspension such as a solution prepared in 1,3-butanediol.
- sterile fixed oils may be conveniently employed as a solvent or suspending medium. For this purpose, any blended fixed oil including synthetic mono- or diglycerides can be used.
- fatty acids such as oleic acid can also be prepared as an injection.
- the compounds of the invention may be administered in the form of a suppository for rectal administration.
- These pharmaceutical compositions can be prepared by mixing the drug with a suitable non-irritating excipient which is solid at ordinary temperatures but liquid in the rectum and thus dissolves in the rectum to release the drug.
- suitable non-irritating excipient include a mixture of cocoa butter, glycerin gelatin, hydrogenated vegetable oil, polyethylene glycols of various molecular weights, and fatty acid esters of polyethylene glycol.
- the dosage of the drug depends on a variety of factors including, but not limited to, the following factors: the activity of the particular compound used, the age of the patient, the weight of the patient, the health of the patient, the performance of the patient, the patient Diet, time of administration, mode of administration, rate of excretion, combination of drugs, etc.; alternatively, the preferred mode of treatment such as the mode of treatment, the daily amount of the compound of formula (I) or the type of pharmaceutically acceptable salt may be Validated according to traditional treatment protocols.
- the preferred mode of treatment such as the mode of treatment, the daily amount of the compound of formula (I) or the type of pharmaceutically acceptable salt may be Validated according to traditional treatment protocols.
- Alkyl means a saturated aliphatic hydrocarbon group including straight chain and branched chain groups of 1 to 20 carbon atoms. An alkyl group having 1 to 10 carbon atoms is preferred, and an alkyl group having 1 to 6 carbon atoms is more preferred.
- Non-limiting examples include methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl, n-butyl, isobutyl, tert-butyl, sec-butyl, n-pentyl, 1,1-dimethylpropyl, 1,2-dimethylpropyl, 2,2-dimethylpropyl, 1-ethylpropyl, 2-methylbutyl, 3-methylbutyl, n-hexyl, 1-ethyl-2 -methylpropyl, 1,1,2-trimethylpropyl, 1,1-dimethylbutyl, 1,2-dimethylbutyl, 2,2-dimethylbutyl, 1, 3-dimethylbutyl, 2-ethylbutyl, 2-methylpentyl, 3-methylpentyl, 4-methylpentyl, 2,3-dimethylbutyl, n-heptyl, 2-methylhexyl, 3-methylhexyl, 4-methylhexyl, 5-methylhexyl,
- lower alkyl groups having 1 to 6 carbon atoms More preferred are lower alkyl groups having 1 to 6 carbon atoms, and non-limiting examples include methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl, n-butyl, isobutyl, t-butyl, sec-butyl Base, n-pentyl, 1,1-dimethylpropyl, 1,2-dimethylpropyl, 2,2-dimethylpropyl, 1-ethylpropyl, 2-methylbutyl, 3-methylbutyl, n-hexyl, 1-ethyl-2-methylpropyl, 1,1,2-trimethylpropyl, 1,1-dimethylbutyl, 1,2-dimethyl Butyl, 2,2-dimethylbutyl, 1,3-dimethylbutyl, 2-ethylbutyl, 2-methylpentyl, 3-methylpentyl, 4-methylpentyl Base, 2,3-dimethylbutyl and the like.
- the alkyl group may be substituted or unsubstituted, and when substituted, the substituent may be substituted at any available point of attachment, preferably one or more of the following groups, independently selected from alkyl, alkenyl, Block, alkoxy, alkylthio, alkylamino, halogen, fluorenyl, hydroxy, nitro, cyano, cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl, heteroaryl, cycloalkoxy, Heterocycloalkoxy, cycloalkylthio, heterocycloalkylthio, oxo, -NR 7 R 8 , -C(O) NR 7 R 8 , -S(0) m R 9 -OR 9 , -C (0) R 9 , -OC(0)R 9 or -C(0)OR 9 .
- alkenyl refers to an alkyl group as defined above consisting of at least two carbon atoms and at least one carbon-carbon double bond. For example, vinyl, 1-propenyl, 2-propenyl, 1-, 2- or 3-butenyl, and the like.
- the alkenyl group may be substituted or unsubstituted, and when substituted, the substituent is preferably one or more of the following groups, independently selected from the group consisting of alkyl, alkoxy, halogen, hydroxy, nitro, cyano, and ring.
- Block group refers to an alkyl group as defined above consisting of at least two carbon atoms and at least one carbon-carbon triple bond. For example, an ethyl group, a 1-propyl block group, a 2-propyl block group, a 1-, 2- or 3-butyl block group, and the like.
- the block group may be substituted or unsubstituted, and when substituted, the substituent is preferably one or more of the following groups, independently selected from the group consisting of alkyl, alkoxy, halogen, hydroxy, nitro, cyano, ring.
- Cycloalkyl means a saturated or partially unsaturated monocyclic or polycyclic cyclic hydrocarbon substituent comprising from 3 to 20 carbon atoms, preferably from 3 to 12 carbon atoms, more preferably the cycloalkyl ring comprises from 3 to 10 One carbon atom.
- monocyclic cycloalkyl groups include cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl, cyclopentenyl, cyclohexyl, cyclohexenyl, cyclohexadienyl, cycloheptyl, cycloheptatriene Alkenyl, cyclooctyl and the like.
- Polycyclic cycloalkyl groups include spiro, fused, and bridged cycloalkyl groups.
- Spirocycloalkyl means a polycyclic group of 5 to 20 members which shares a carbon atom (referred to as a spiro atom) between the monocyclic rings. These may contain one or more double bonds, but none of the rings are fully conjugated. ⁇ electronic system. It is preferably 6 to 14 members, more preferably 7 to 10 members.
- the spirocycloalkyl group is classified into a monospirocycloalkyl group, a bispirocycloalkyl group or a polyspirocycloalkyl group, preferably a monospirocycloalkyl group and a bispirocycloalkyl group, depending on the number of common spiro atoms between the ring and the ring.
- “Fused cycloalkyl” means 5 to 20 members, each ring of the system sharing an adjacent carbon atom of an all-carbon polycyclic group with other rings in the system, wherein one or more rings may contain one or more Two double bonds, but none of the rings have a fully conjugated ⁇ -electron system. It is preferably 6 to 14 members, more preferably 7 to 10 members. According to the number of constituent rings, it may be classified into a bicyclic, tricyclic, tetracyclic or polycyclic fused ring alkyl group, preferably a bicyclic ring or a tricyclic ring.
- Bridge cycloalkyl refers to 5 to 20 yuan, any two rings share two carbon atoms that are not directly connected to the carbon Ring groups, these may contain one or more double bonds, but none of the rings have a fully conjugated ⁇ -electron system. It is preferably 6 to 14 members, more preferably 7 to 10 members. Depending on the number of constituent rings, it may be classified into a bicyclic, tricyclic, tetracyclic or polycyclic bridged cycloalkyl group, preferably a bicyclic ring, a tricyclic ring or a tetracyclic ring, and more preferably a bicyclic ring or a tricyclic ring. Unrestricted bridged cycloalkyl
- the cycloalkyl ring may be fused to an aryl, heteroaryl or heterocyclyl ring, wherein the ring to which the parent structure is attached is a cycloalkyl group, non-limiting examples include indanyl, tetrahydronaphthalene Base, benzocycloheptyl and the like.
- the cycloalkyl group may be optionally substituted or unsubstituted, and when substituted, the substituent is preferably one or more of the following groups independently selected from the group consisting of alkyl, alkenyl, block, alkoxy, alkylthio Base, alkylamino, thiol, decyl, hydroxy, nitro, cyano, cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl, heteroaryl, cycloalkoxy, heterocycloalkoxy, cycloalkylthio, Heterocycloalkylthio, oxo, -NR 7 R 8 , -C(0) NR 7 R 8 , -S(0) m R 9 , -OR 9 , -C(0)R 9 , -OC(0 ) R 9 or -C(0)OR 9 .
- Heterocyclyl means a saturated or partially unsaturated monocyclic or polycyclic cyclic hydrocarbon substituent comprising from 3 to 20 ring atoms wherein one or more of the ring atoms are selected from nitrogen, oxygen or S(0) m ( Wherein m is a hetero atom of the integer 0 to 2), but does not include a ring moiety of -0-0-, -0-S- or -SS-, and the remaining ring atoms are carbon. It preferably comprises from 3 to 12 ring atoms, wherein from 1 to 4 are heteroatoms, more preferably the cycloalkyl ring contains from 3 to 8 ring atoms.
- Non-limiting examples of monocyclic heterocyclic groups include pyrrolidinyl, piperidinyl, piperazinyl, morpholinyl, thiomorpholinyl, high
- the polycyclic heterocyclic group includes a spiro ring, a fused ring, and a heterocyclic group of a bridged ring.
- spiroheterocyclyl means a polycyclic heterocyclic group of 5 to 20 members in which one atom (referred to as a spiro atom) is shared between monocyclic rings, wherein one or more ring atoms are selected from nitrogen, oxygen or S(0) m
- a hetero atom (where m is an integer from 0 to 2), and the remaining ring atoms are carbon. These may contain one or more double bonds, but none of the rings have a fully conjugated pi-electron system. It is preferably 6 to 14 members, more preferably 7 to 10 members.
- the spirocycloalkyl group is classified into a monospiroheterocyclic group, a dispiroheterocyclic group or a polyspirocyclic group according to the number of common spiro atoms between the rings, preferably a monospirocycloalkyl group and a bispirocycloalkyl group. More preferably, it is 4 yuan / 4 yuan, 4 yuan / 5 yuan, 4 yuan / 6 yuan, 5 yuan / 5 yuan or 5 yuan / 6 yuan monospirocycloalkyl.
- Non-limiting examples of spirocycloalkyl groups include
- “Fused heterocyclic group” means 5 to 20 members, each ring in the system shares an adjacent pair of atomic polycyclic heterocyclic groups with other rings in the system, and one or more rings may contain one or more a bond, but none of the rings have a fully conjugated ⁇ -electron system in which one or more ring atoms are selected from nitrogen, oxygen or S(0) m (where m is an integer from 0 to 2), and the remaining ring atoms are carbon. It is preferably 6 to 14 members, more preferably 7 to 10 members.
- the bicyclic, tricyclic, tetracyclic or polycyclic fused heterocyclic group may be classified according to the number of constituent rings, preferably bicyclic or tricyclic, more preferably 5- to 5- or 5-membered/6-membered bicyclic fused heterocyclic group.
- fused heterocyclic groups include
- “Bridge heterocyclyl” refers to a polycyclic heterocyclic group of 5 to 14 members in which two rings share two atoms which are not directly bonded, and these may contain one or more double bonds, but none of the rings have a complete conjugation
- a ⁇ -electron system in which one or more ring atoms are selected from nitrogen, oxygen or S(0) m (where m is an integer from 0 to 2), and the remaining ring atoms are carbon. It is preferably 6 to 14 members, more preferably 7 to 10 members. 7 to 10 yuan.
- bridged cycloalkyl groups include:
- the heterocyclyl ring may be fused to an aryl, heteroaryl or cycloalkyl ring, wherein the ring to which the parent structure is attached is a heterocyclic group, and the examples include:
- the heterocyclic group may be optionally substituted or unsubstituted, and when substituted, the substituent is preferably one or more of the following groups, independently selected from the group consisting of alkyl, alkenyl, block, alkoxy, alkylthio Base, alkylamino, halogen, fluorenyl, hydroxy, nitro, cyano, cycloalkyl, heterocyclic, aryl, heteroaryl, cycloalkoxy, heterocyclomethoxy, cycloalkylthio, hetero Cycloalkylthio, -NR 7 R 8 , -C(0) NR 7 R 8 , -S(0) m R 9 , -OR 9 , -C(0)R 9 , -OC(0)R 9 or -C(0)OR 9 .
- the substituent is preferably one or more of the following groups, independently selected from the group consisting of alkyl, alkenyl, block, alkoxy, alkylthio Base, alkylamino,
- Aryl means a 6 to 14 membered all-carbon monocyclic or fused polycyclic ring (ie, a ring that shares a pair of adjacent carbon atoms) having a conjugated ⁇ -electron system, preferably 6 to 10 members, such as phenyl. And naphthyl.
- the aryl ring can Fused to a heteroaryl, heterocyclyl or cycloalkyl ring wherein the ring to which the parent structure is attached is an aryl ring, non-limiting examples comprising:
- the aryl group may be substituted or unsubstituted, and when substituted, the substituent is preferably one or more of the following groups, independently selected from the group consisting of alkyl, alkenyl, block, alkoxy, alkylthio, alkane.
- Heteroaryl means a heteroaromatic system containing from 1 to 4 heteroatoms, 5 to 14 ring atoms, wherein the heteroatoms include oxygen, sulfur and nitrogen. It is preferably 5 to 10 yuan.
- the heteroaryl group is preferably 5- or 6-membered, such as furyl, thienyl, pyridyl, pyrazolyl, pyrrolyl, N-alkylpyrrolyl, pyrimidinyl, pyrazinyl, imidazolyl, tetrazolyl, etc.
- the heteroaryl ring may be fused to an aryl, heterocyclic or cycloalkyl ring wherein the ring with the parent is a heteroaryl ring, non-limiting examples comprising:
- the heteroaryl group may be optionally substituted or unsubstituted, and when substituted, the substituent is preferably one or more of the following groups independently selected from the group consisting of alkyl, alkenyl, block, alkoxy, alkylthio Base, alkylamino, halogen, fluorenyl, hydroxy, nitro, cyano, cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl, heteroaryl, cycloalkoxy, heterocycloalkoxy, cycloalkylthio, hetero Cycloalkylthio, -NR 7 R 8 , -C(0) NR 7 R 8 , -S(0) m R 9 , -OR 9 , -C(0)R 9 , -OC(0)R 9 or -C(0)OR 9 .
- Alkoxy means -o-(fluorenyl) and -o-(unsubstituted cycloalkyl), wherein alkyl, cycloalkyl are as defined above. Non-limiting examples include methoxy, ethoxy, propoxy, butoxy, cyclopropoxy, cyclobutoxy, cyclopentyloxy, cyclohexyloxy and the like.
- the alkoxy group may be optionally substituted or unsubstituted, and when substituted, the substituent is preferably one or more of the following groups, independently selected from the group consisting of an alkyl group, an alkenyl group, a block group, an alkoxy group, and an alkane group.
- Haldroxy means an -OH group.
- Hydroalkyl means HO-(alkyl) and HO-(unsubstituted cycloalkyl), wherein alkyl, cycloalkyl are as defined above.
- Halogen means fluoro, chloro, bromo or iodo.
- Neitro means -N0 2 .
- Network group means -CH 2 -phenyl.
- Amino means -NH 2 .
- heterocyclic group optionally substituted by an alkyl group means that an alkyl group may be, but not necessarily, present, including the case where the heterocyclic group is substituted by an alkyl group and the case where the heterocyclic group is not substituted by an alkyl group.
- Substituted means one or more hydrogen atoms in the group, preferably up to 5, more preferably 1 to 3, hydrogen atoms are independently substituted with each other by a corresponding number of substituents. It goes without saying that the substituents are only in their possible chemical positions, and those skilled in the art will be able to determine (by experiment or theory) substitutions that may or may not be possible without undue effort. For example, an amino or hydroxyl group having a free hydrogen may be unstable when combined with a carbon atom having an unsaturated (e.g., olefinic) bond.
- “Pharmaceutical composition” means a mixture comprising one or more of the compounds described herein, or a physiological/pharmaceutically acceptable salt or prodrug thereof, and other chemical components, as well as other components such as physiological/pharmaceutically acceptable carriers and excipient.
- the purpose of the pharmaceutical composition is to promote the administration of the organism, which facilitates the absorption of the active ingredient and thereby the biological activity.
- the preparation method of the compound of the formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof of the present invention comprises the following steps:
- X is a leaving group, preferably a halogen or a sulfonyloxy group, more preferably a halogen; wherein E, Z, ring, B, Ri ⁇ R 4 are as defined in the formula (I).
- X is a leaving group, preferably a halogen or a sulfonyloxy group, more preferably a halogen;
- Y, ring B, Ri ⁇ R 4 are as defined in the formula ( ⁇ ).
- the nitro-substituted phenylpropionate ( ⁇ -1) compound is reduced to an amino-substituted phenylpropionate ( ⁇ -2) compound in a solution, and the compound of the formula ( ⁇ -2) is in a solvent.
- Forming a compound of the formula ( ⁇ -3) by sodium hydride; a compound of the formula ( ⁇ -3) in a solvent with a halogen-substituted pyrimidine, which gives a general formula ( ⁇ - ⁇ ) under heating a compound of the formula ( ⁇ ) and a compound of the formula (IB) are reacted in a solvent under microwave conditions under acidic conditions to obtain a compound of the formula ( ⁇ );
- X is a leaving group, preferably a halogen or a sulfonyloxy group, more preferably a halogen; wherein E, Z, and ring Ri to R 4 are as defined in the formula (III).
- the preparation method of the compound of the formula (IV) of the present invention or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof comprises the following steps:
- X is a leaving group, preferably a halogen or a sulfonyloxy group, more preferably a halogen; wherein E, Z, ring 8, Ri ⁇ R 4 are as defined in the formula (IV).
- the above reaction provides acidic conditions including organic acids and inorganic acids, including, but not limited to, hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, strong acid such as hydrochloric acid, preferably concentrated hydrochloric acid;
- Catalysts include, but are not limited to, tetra-triphenylphosphine palladium, triphenylphosphine, palladium dichloride, palladium acetate, 1,1 '-bis(dibenzylphosphine) dichlorodipentadium iron palladium, tris(dibenzylidene) Acetone) dipalladium, palladium/carbon or Raney nickel.
- Solvents used include, but are not limited to: acetic acid, methanol, ethanol, acetonitrile, tetrahydrofuran, dichloromethane, dimethyl sulfoxide, 1,4-dioxane, water, N, N-dimethylacetamide or N, N-dimethylformamide, preferably a polar solvent, more preferably ethanol;
- the microwave heating temperature is 140-180 ° C, and the preferred reaction conditions are 160 ° C. detailed description
- Example The structure of the compound is determined by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) or/and mass spectrometry (MS). NMR shifts ([delta]) are given in units of 10- 6 (ppm) a.
- the NMR was measured by a Bruker AVANCE-400 nuclear magnetic apparatus, and the solvent was deuterated dimethyl sulfoxide deuterated chloroform (CDC1 3 ), deuterated methanol (CD 3 OD), and internal standard was tetramethylsilane (CTMS).
- NMR nuclear magnetic resonance
- MS mass spectrometry
- the HPLC was measured using an Agilent 1200 DAD high pressure liquid chromatograph (Sunfire C18 150 x 4.6 mm column) and a Waters 2695-2996 high pressure liquid chromatograph (Gimini C18 150 x 4.6 mm column).
- the average inhibition rate of the kinase and the IC 5Q value were determined using a NovoStar plate reader (BMG, Germany).
- the silica gel plate used has a specification of 0.15 mm to 0.2 mm, and the thin layer chromatography separation and purification product has a specification of 0.4 mm to 0.5 mm.
- the known starting materials of the present invention may be synthesized by or according to methods known in the art, or may be purchased from ABCR GmbH & Co. KG, Acros Organics, Aldrich Chemical Company, Accela ChemBio Inc, Companies such as Dare Chemicals.
- reaction can be carried out under an argon atmosphere or a nitrogen atmosphere.
- An argon atmosphere or a nitrogen atmosphere means that the reaction flask is connected to an argon or nitrogen balloon having a volume of about 1 L.
- the hydrogen atmosphere means that the reaction flask is connected to a hydrogen balloon of about 1 L volume.
- the pressurized hydrogenation reaction uses a Parr 3916EKX hydrogenation apparatus and a clear blue QL-500 hydrogen generator or
- the hydrogenation reaction is usually evacuated, charged with hydrogen, and operated three times.
- the microwave reaction was carried out using a CEM Discover-S Model 908860 microwave reactor.
- the solution means an aqueous solution.
- reaction temperature is room temperature and is 20 ° C to 30 ° C.
- the progress of the reaction in the examples was monitored by thin layer chromatography (TLC).
- TLC thin layer chromatography
- the system used for the reaction was: A: dichloromethane and methanol system, B: n-hexane and ethyl acetate system, C: n-hexane , ethyl acetate and dichloromethane, D: acetone system, the volume ratio of the solvent is adjusted depending on the polarity of the compound.
- the system for the elution of the column chromatography and the developer system for the thin layer chromatography using the purified compound include: A: dichloromethane and methanol system, B: n-hexane and ethyl acetate system, C: n-hexane, acetic acid Ester and dichloromethane, D: Acetone system, the volume ratio of the solvent is adjusted according to the polarity of the compound, and may be adjusted by adding a small amount of an alkaline or acidic reagent such as triethylamine or acetic acid.
- A dichloromethane and methanol system
- B n-hexane and ethyl acetate system
- C n-hexane
- D Acetone system
- the volume ratio of the solvent is adjusted according to the polarity of the compound, and may be adjusted by adding a small amount of an alkaline or acidic reagent such as trie
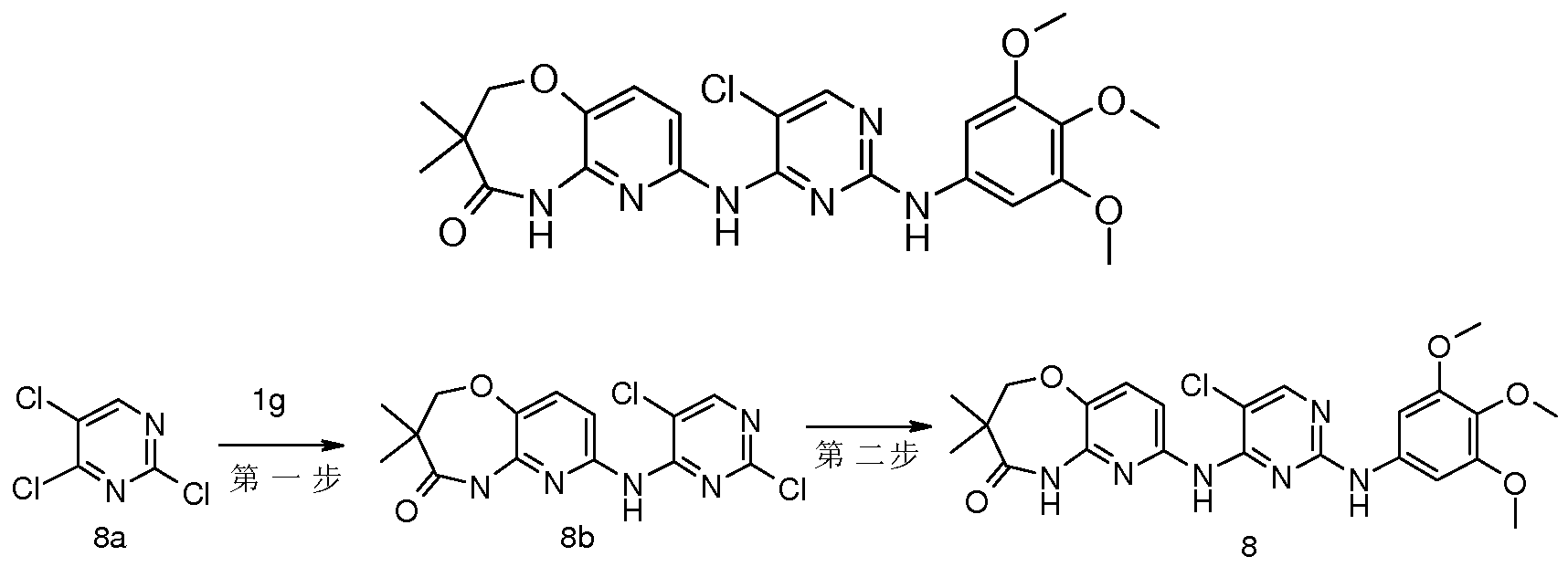
- the crude product is 7-P-chloro-5-fluoropyrimidin-4-ylamino)-3,3-dimethyl-2,3-dihydrobenzo[b][l,4]oxazepine-4 (5H ketone 5g (50 mg, 0.15 mmol) and 3,4,5-trimethoxyaniline (41 mg, 0.23 mmol) were dissolved in 1 mL of ethanol, and 1 drop of concentrated hydrochloric acid was added thereto, and the mixture was subjected to microwave reaction at 160 ° C for 1 hour.
- the obtained residue was purified to give crystalljjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjj
- N-H4-(3,3-dimethyl-4-carbonyl-2,3,4,5-tetrahydropyrido[3,2-b][l,4]oxazepin-7-yl Amino) 5-fluoropyrimidin-2-ylamino 5-methylphenyl 2-hydroxyacetamide 7-0 chloro-5-fluoro-pyrimidin-4-ylamino)-3,3-dimethyl-2 ,3-dihydropyrido[3,2-b][l,4]oxazepin-4(5H)-one 1h (50 mg, 0.15 mmol) and N-(3-amino-5- Phenylphenyl)-2-hydroxyacetamide llb (27 mg, 0.15 mmol) was dissolved in 2 mL of isopropanol, and 1 drop of trifluoroacetic acid was added thereto, and the mixture was subjected to microwave reaction at 180 ° C for 1 hour.
- Test Example 1 Determination of inhibition of Syk kinase activity by a compound of the present invention
- the in vitro kinase assay described below can determine the inhibitory activity of a test compound against Syk kinase (Invitrogen, PV3857).
- In vitro activity assays of Syk inhibitors were performed using the Invitrogen kit Z'-LYTE® Kinase Assay Kit- Tyrosine 2 Peptide (Invitrogen, PV3191).
- kit instructions configure the appropriate concentration of enzyme buffer (50 mM HEPES PH7.5, 0.01% BRIJ-35, 10 mM MgCl 2 , 4 mM MnCl 2 , 1 mM EGTA, 2 mMDTT), enzyme/substrate peptide
- enzyme buffer 50 mM HEPES PH7.5, 0.01% BRIJ-35, 10 mM MgCl 2 , 4 mM MnCl 2 , 1 mM EGTA, 2 mMDTT
- the solution, the ATP solution and the fully phosphorylated substrate peptide were gently mixed uniformly; the 4 X concentration of the test compound solution was prepared with distilled water and mixed well.
- the developing solution was prepared according to the corresponding ratio. After mixing, add 5 ⁇ L of each reaction well, and attach the sealing plate to the shaker for 30 seconds to mix the solutions uniformly, and incubate for 1 hour at room temperature. Add 5 stop solution to each well, mix well, and read fluorescence at 445 nm and 520 nm with 400 nm excitation.
- the biochemical activity of the compounds of the present invention was determined by the above test, and the IC 5 was measured. The values are shown in Table 1 below.
- Test Example 2 Determination of the inhibitory effect of the compound of the present invention on proliferation of SU-DHL-6 cells
- the in vitro cell assay described below can determine the inhibitory activity of the test compound on SU-DHL-6 immunocyte proliferation.
- RPMI-1640 RPMI-1640 medium (Hyclone, Cat# SH30809.01B , Lot#
- FBS calf serum (GIBCO, Lot# 8172881);
- PBS Phosphate-buffered saline
- SU-DHL-6 cells (ATCC, Cat. No. CRL-2959TM) were cultured in RPMI-1640 medium (10% FBS, 100 units/ml P/S), washed three times with PBS and resuspended in RPMI-1640 ( Add 2% FBS, 100 units/ml P/S) medium with a density of 2.5 X 10 5 cells/ml. Add 90 ⁇ l to each well in a 96-well plate.
- the drug was configured as a 20 mM stock solution, diluted to a 200 X concentration gradient with 100% DMSO (dimethyl sulfoxide), and then RPMI-1640 (2% FBS, 100 units/ml P/S) The medium was diluted 20-fold (to ensure that the DMSO concentration in each culture system was 0.5%). Add 10 ⁇ of drug to each well and mix gently by shaking. The group and the blank group contained only 100 ⁇ RPMI-1640 (2% FBS, 100 units/ml P/S), placed in a 37 ° C, 5% C0 2 incubator, and 72 hours later by the ATPliteTM kit. (PerkinElmer, Cat# 6016947) Detection.
- the biochemical activity of the compounds of the present invention was determined by the above test, and the measured IC 5Q values are shown in Table 2 below.
- Rats were used as test animals, and the compounds of Example 1, the compound of Example 5, the compound of Example 6, the compound of Example 7, the compound of Example 8, and the Example 12 were administered intragastrically by LC/MS/MS. The concentration of the drug in the plasma at different times after the compound. The pharmacokinetic behavior of the compounds of the invention in rats was investigated and their pharmacokinetic characteristics were evaluated.
- Example 1 compound Example 5 compound, Example 6 compound, Example 7 compound, Example 8 compound and Example 12 compound.
- the compound of Example 1, the compound of Example 5, the compound of Example 6, the compound of Example 7, the compound of Example 8, and the compound of Example 12 were administered by gavage in rats, 0.5, 1.0, 2.0 before and after administration. 3.0, 4.0, 6.0, 8.0, 11.0, 24.0 hours of blood sampling 0.1 ml, placed in heparinized tubes, centrifuged at 3500 rpm for 5 min, and stored at 20 ° C. Eat 2 hours after administration.
- the content of the test compound in the plasma of rats after intragastric administration of different concentrations of the compounds was determined by LC/MS/MS.
- the linear range of the method was 1.00 ⁇ 2000 ng/ml; plasma samples were analyzed by methanol precipitation protein analysis.
- the pharmacokinetic parameters of the compounds of the invention are as follows:
- the compound of the present invention has good pharmacological absorption and has obvious pharmacokinetic advantages.
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Immunology (AREA)
- Pulmonology (AREA)
- Rheumatology (AREA)
- Dermatology (AREA)
- Orthopedic Medicine & Surgery (AREA)
- Physical Education & Sports Medicine (AREA)
- Hematology (AREA)
- Oncology (AREA)
- Pain & Pain Management (AREA)
- Neurology (AREA)
- Pharmaceuticals Containing Other Organic And Inorganic Compounds (AREA)
Abstract
一种通式(I)所示的嘧啶二胺类衍生物及其可药用的盐、含有其的药物组合物、其制备方法及其在医药上的应用。该化合物及其可药用的盐或包含其的药物组合物可用于制备Syk蛋白酶抑制剂。
Description
嘧啶二胺类衍生物、 其制备方法及其在医药上的应用 技术领域
本发明涉及一种新的嘧啶二胺类衍生物及其可药用的盐或含有其的药物组合 物、 及其制备方法。 本发明进一步涉及所述嘧啶二胺衍生物及其可药用的盐或含 有其的药物组合物在制备治疗剂, 特别是 Syk抑制剂中的用途。 背景技术
Syk最初从猪脾 cDNA克隆出来, 其编码蛋白是一种非受体型酪氨酸激酶, 故 被称为脾酪氨酸激酶 (Spleen tyrosine kinase, Syk)。 分子量约 72kDa 的 Syk 与 Zap70(C-chain-associated protein kinase of 70kDa)同属于 ZAP70/Syk酪氨酸激酶家 族。 Syk主要表达于血液细胞中, 另外还表达于血管内皮细胞、 成纤维细胞、 呼吸 道上皮细胞、 肝细胞和破骨细胞等。
Syk 蛋白含有一个相对保守的蛋白酪氨酸激酶区和两个串联的 SH2 (Src homology 2)结构域。 SH2主要介导胞质内多种信号蛋白的相互连接, 形成蛋白质 异聚体复合物, 从而调节信号转导途径中的信号传递。 连接 SH2结构域和激酶结 构域的氨基酸区域 (interdomain B)含有许多酪氨酸残基, 当这些酪氨酸残基被磷酸 化后, 能够充当多种蛋白的锚定位点, 而这些蛋白可能是 Syk的作用底物。 在一 些典型的免疫受体包括 B细胞受体 (B-cell receptors, BCRs), FcRs (Fc Receptors, FcRs)和活化的自然杀伤细胞受体 (activating natural killer receptors)所引发的信号传 导过程中, Syk主要通过 SH2结构域与受体上磷酸化的免疫受体酪氨酸活化基序 (immunoreceptor tyrosine -based activation motif, ITAM)相结合,弓 I发下游信号级联, 发挥重要作用如影响 B细胞早期发育和活化, 肥大细胞脱颗粒, 中性粒细胞和巨 噬细胞的吞噬功能, 血小板活化。 这些细胞功能异常无不与自身免疫性疾病和过 敏性疾病相关。
FcRs (FcsRI, FcyRI, FcyRIIA, FcyRIIIA)是免疫细胞上常见的、 功能活跃的受 体之一。其中 FcyR和 FcsR分别能识别免疫球蛋白 IgG和 IgE的 Fc段。而 Syk是 FcyR和 FcsR信号传递中重要信号分子。巨噬细胞和中性粒细胞通过 FcRs被激活, ITAMs被上游的 Fc受体相关 Src家族激酶 (如 Lyn和 Lck)二磷酸化。 FcRs的活化 导致 Syk通过自身 SH2(N)结构域与 Fc受体 γ链的 ΙΤΑΜ结合并被激活。随后活化 的 Syk磷酸化许多下游底物如 Vav, LAT和 SLP-76。 信号复合体的形成还引发许 多下游信号通路的活化如 PLC亚型介导的钙动员和 PKC活化。 这也激活了多种 MAPKs如 JNK和 ERK, 从而导致脂类介质和细胞因子的产生。 在破骨细胞中, 免疫受体和 RANKL-RANK相互作用刺激 ITAM磷酸化,进而招募 Syk家族激酶, 激活 ΡΙ γ和钙信号, 这对 NFATcl的诱导至关重要。 同时, NFATcl的诱导也依 赖于 RANKL激活 c-Fos和 TRAF6。通过诱导免疫受体或其配体, RANKL亦可能
促使 ITAM信号的有效传导。 在 Β细胞中, 经 Β细胞受体激活 Syk后, 多种下游 信号分子如 SLP-65被磷酸化, 为一些重要蛋白质如 ΡΙ γ, Vav, Cbl和 Btk提供 锚定位点, 进而形成信号复合体, 激活下游信号通路。
Syk作为免疫受体的关键介质在炎性细胞如 B细胞、 肥大细胞、 巨噬细胞中 表达, 这些免疫细胞上的受体与过敏性和抗体介导的自身免疫性疾病密切相关。 因此将 Syk作为干预治疗靶点, 为一些常规方法来说难治的疾病, 包括风湿性关 节炎、 哮喘、 过敏性鼻炎、 淋巴瘤、 白血病、 恶性上皮肿瘤、 肿瘤转移等提供新 的治疗方法。
目前公开了一系列的 Syk 抑制剂的专利申请, 其中包括 WO03063794、 US20040198750、 WO2006078846或 WO2011014795等。
至今一些制药公司仍在研究抑 Syk蛋白激酶的新化合物, 以期待找到更安全 有效的新型药物化合物, 并通过单一用药或与其他药物联用来治疗癌症疾病。 本 发明设计具有通式(I )所示的结构的化合物, 并发现具有此类结构的化合物表现出 优异的效果和作用, 尤其是作为 Syk蛋白激酶抑制剂在医药上的应用。 发明内容
( I )
其巾:
E选自 S、 0或 C;
Z为 C(R5R6);
A环, B环为芳基或杂芳基;
R1选自氢原子、 卤素、 羟基、 氰基、 硝基、 烷基、 烷氧基、 烯基、 块基、 环 烷基、 -C(0)NR7R8、 -OR9、 -C(0)OR9、 芳基或杂芳基;
R2、 R3 或 R4各自独立地选自氢原子、 卤素、 氰基、 硝基、 羟基、 烷基、 烷氧 基、环烷基、杂环基、芳基、杂芳基、 -NR7R8、 -C(0)NR7R8 -NHS(0)mR9 -OS(0)mR9 -S(0)mR9 -NHC(0)R9 -OR9、 -C(0)R9 -OC(0)R9或 -C(0)OR9, 其中所述的烷基、 烷氧基、 环烷基、 杂环基、 芳基或杂芳基各自独立地任选进一步被一个或多个选 自羟基、 卤素、 烷基、 环烷基、 杂环基、 芳基、 杂芳基、 -NR7R8、 -C(0) NR7R -S(0)mR9 -C(0)R9 -OC(0)R9或 -C(0)OR9的取代基所取代;
或者, R2和 R3形成环烷基或杂环基, 其中所述的杂环基内含有一个或多个选
g N、 O或 S(0)m的杂原子, 并且所述杂环基任选进一步被一个或多个选自烷基、 卤素、氰基、环烷基、杂环基、芳基、杂芳基、 -NR7R8、 -C(0)NR7R8 -NHS(0)mR9 -S(0)mR9 -NHC(0)R9 -OR9、 -C(0)R9 -OC(0)R9或 -C(0)OR9的取代基所取代;
R5或 R6各自独立地选自氢原子、 卤素、 烷基、 环烷基、 羟基、 烷氧基、 芳基 或杂芳基, 其中所述的烷基、 环烷基、 芳基或杂芳基各自独立地任选进一步被一 个或多个选自羟基、 卤素、 烷基、 环烷基、 杂环基、 芳基、 杂芳基、 -NR7R8、 -C(0)NR7R8、 -NHS(0)mR9、 -S(0)mR9、 -NHC(0)R9、 -OR9、 -C(0)R9、 -OC(0)R9 或 -C(0)OR9的取代基所取代;
或者, R5和 R6与其相连接的 C原子一起形成一个环烷基或杂环基, 所述的环 烷基或杂环基各自独立地任选进一步被一个或多个选自羟基、 卤素、 烷基、 烷氧 基、 环烷基或杂环基的取代基所取代;
R7或 R8各自独立地选自氢原子、 烷基、 环烷基、 杂环基、 芳基或杂芳基, 所 述的氢原子、 烷基、 环烷基、 杂环基、 芳基或杂芳基各自独立地任选进一步被一 个或多个选自羟基、 卤素、 烷基、 烷氧基、 环烷基或杂环基的取代基所取代; 或者, R7和 R8与其相连接的 N原子一起形成一个 3〜8元杂环基,其中所述 3〜
8元杂环基内含有一个或多个 N、 0或 S(0)m杂原子, 并且所述 3〜8元杂环基任 选进一步被一个或多个选自烷基、 卤素、 羟基、 氨基、 氰基、 烷氧基、 环烷基、 杂环基、 芳基或杂芳基的取代基所取代;
R9选自氢原子、 烷基、 氨基、 环烷基、 杂环基、 芳基或杂芳基, 所述的烷基、 环烷基、 杂环基、 芳基或杂芳基各自独立地任选进一步被一个或多个选自烷基、 卤素、 羟基、 氨基、 氰基、 烷氧基、 环烷基、 杂环基、 芳基或杂芳基的取代基所 取代; 和
m为 0、 1或 2。
在本发明的一个实施方案中, 所述的通式(I )所示的化合物或其互变异构体、 内消旋体、 外消旋体、 对映异构体、 非对映异构体、 及其混合物形式、 及其可药 用的盐, 其中 E为氧原子。
在本发明的一个实施方案中, 所述的通式(I )所示的化合物或其互变异构体、 内消旋体、 外消旋体、 对映异构体、 非对映异构体、 及其混合物形式、 及其可药 用的盐, 其中环 B为芳基。
在本发明的一个实施方案中, 所述的通式(I )所示的化合物或其互变异构体、 内消旋体、 外消旋体、 对映异构体、 非对映异构体、 及其混合物形式、 及其可药 用的盐, 其中环 B为苯基。
在本发明的又一个实施方案中, 所述的通式( I )所示的化合物或其互变异构 体、 内消旋体、 外消旋体、 对映异构体、 非对映异构体、 及其混合物形式、 及其 可药用的盐, 其中环 R5、 R6为烷基。
在本发明的又一个实施方案中, 所述的通式( I )所示的化合物或其互变异构
体、 内消旋体、 外消旋体、 对映异构体、 非对映异构体、 及其混合物形式、 及其 可药用的盐, 其中 R5或 R6各自独立地选自卤素或烷基。
在本发明的又一个实施方案中, 所述的通式( I )所示的化合物或其互变异构 体、 内消旋体、 外消旋体、 对映异构体、 非对映异构体、 及其混合物形式、 及其 可药用的盐, 其中 R5或 R6各自独立为甲基。
在本发明的又一个实施方案中, 所述的通式( I )所示的化合物或其互变异构 体、 内消旋体、 外消旋体、 对映异构体、 非对映异构体、 及其混合物形式、 及其 可药用的盐, R5和 R6—起形成环烷基。
在本发明的又一个实施方案中, 所述的通式( I )所示的化合物或其互变异构 体、 内消旋体、 外消旋体、 对映异构体、 非对映异构体、 及其混合物形式、 及其 可药用的盐, R5和 R6—起形成环丙基。
在本发明的又一个实施方案中, 所述的通式( I )所示的化合物或其互变异构 体、 内消旋体、 外消旋体、 对映异构体、 非对映异构体、 及其混合物形式、 及其 可药用的盐, 其中 R1为卤素。
在本发明的又一个实施方案中, 所述的通式( I )所示的化合物或其互变异构 体、 内消旋体、 外消旋体、 对映异构体、 非对映异构体、 及其混合物形式、 及其 可药用的盐, 其中 R2、 R3 或 R4各自独立地选自氢原子、 卤素、 羟基、 烷基、 烷 氧基、环烷基、杂环基、芳基、杂芳基、 -NR7R8、 -C(0)NR7R8, -NHS(0)mR9 -S(0)mR9 -NHC(0)R9 -OR9、 -C(0)R9 -OC(0)R9或 -C(0)OR9, 其中所述的烷基、 烷氧基、 环烷基、 杂环基、 芳基或杂芳基各自独立地任选进一步被一个或多个选自羟基、 卤素、 烷基、 环烷基、 杂环基、 芳基、 杂芳基、 -NR7R8、 -C(0) NR7R8, -S(0)mR9 -C(0)R9 -OC(0)R9或 -C(0)OR9的取代基所取代;
R7或 R8各自独立地选自氢原子或烷基;
R9选自氢原子、 烷基、 氨基、 环烷基、 杂环基、 芳基或杂芳基, 所述的烷基、 环烷基、 杂环基、 芳基或杂芳基各自独立地任选进一步被一个或多个选自烷基、 卤素、 羟基、 氨基、 氰基、 烷氧基、 环烷基、 杂环基、 芳基或杂芳基的取代基所 取代; 和
m为 0、 1或 2。
在本发明的又一个实施方案中, 所述的通式( I )所示的化合物或其互变异构 体、 内消旋体、 外消旋体、 对映异构体、 非对映异构体、 及其混合物形式、 及其 可药用的盐, 为通式 (Π) 所示的化合物或其互变异构体、 内消旋体和外消旋体、对 映异构体、 非对映异构 及其混合物形式、 及其可药用的盐:
其中: Y为 N或 C原子; E、 Z、 环8、 Ri〜R4的定义如通式 (I) 中所定义。 在本发明的又一个实施方案中, 所述的通式( I )所示的化合物或其互变异构 体、 内消旋体、 外消旋体、 对映异构体、 非对映异构体、 及其混合物形式、 及其 可药用的盐, 为通式 (ΠΙ) 所示的化合物或其互变异构体、 内消旋体和外消旋体、 对映异构体、 非对映 盐:
在本发明的又一个实施方案中, 所 I )所示的化合物或其互变异构
工
体、 内消旋体、 外消旋体、 及其混合物形式、 及其 可药用的盐, 为通式 (IV) 所示的化合物或其互变异构体、 内消旋体和外消旋体、
工 z -π
对映异构体、 非对映 工工工 。。、 、
其中: E、 Z、 环8、 Ri〜R4的定义如通式 (I) 中所定义<
本发明的典型化合物包括, 但不限于:
实施例编号 化合物结构与命名
1
7-(5-氟 -2-(3,4,5-三甲氧基苯基氨基)嘧啶 -4-基氨基 )-3,3-二甲 基 -2,3-二氢吡啶并 [3,2 ][1,4]氧氮杂环庚 -4(5/ί)-酮
2
7-(5-氟 -2-(3-氟 -4-吗啉 -苯基氨基)嘧啶 -4-基氨基 )-3,3-二甲基 -2,3-二氢吡啶并 [3,2-b][l,4]氧氮杂环庚 -4(5H 酮
物形式、 及其可药用的盐。
本发明还涉及一种通式 (I-A)所示的化合物, 可作为合成通式 (I) 化合物或其 互变异构体、 内消旋体、 外消旋体、 对映异构体、 非对映异构体、 及其混合物形 式的中间体:
(I-A )
其中: E选自 S、 0或 C;
Z为 C(R5R6);
环 A为芳基或杂芳基;
R1选自氢原子、 卤素、 羟基、 氰基、 硝基、 烷基、 烷氧基、 烯基、 块基、 环
烷烷烷基基基、、、 ---CCC(((000)))NNNRRR777RRR888、、、 ---OOORRR999、、、 ---CCC(((000)))OOORRR999 芳芳芳基基基或或或杂杂杂芳芳芳基基基;;;
RRR555或或或 RRR666各各各自自自独独独立立立地地地选选选自自自氢氢氢原原原子子子、、、 卤卤卤素素素、、、 烷烷烷基基基、、、 环环环烷烷烷基基基、、、 羟羟羟基基基、、、 烷烷烷氧氧氧基基基、、、 芳芳芳基基基 或或或杂杂杂芳芳芳基基基,,, 其其其中中中所所所述述述的的的烷烷烷基基基、、、 环环环烷烷烷基基基、、、 芳芳芳基基基或或或杂杂杂芳芳芳基基基各各各自自自独独独立立立地地地任任任选选选进进进一一一步步步被被被一一一 个个个或或或多多多个个个选选选自自自羟羟羟基基基、、、 卤卤卤素素素、、、 烷烷烷基基基、、、 环环环烷烷烷基基基、、、 杂杂杂环环环基基基、、、 芳芳芳基基基、、、 杂杂杂芳芳芳基基基、、、 ---NNNRRR777RRR888、、、 ---CCC(((000)))NNNRRR777RRR888、、、 ---NNNHHHSSS(((000)))mmmRRR999、、、 ---SSS(((000)))mmmRRR999、、、 ---NNNHHHCCC(((000)))RRR999、、、 ---OOORRR999、、、 ---CCC(((000)))RRR999、、、 ---OOOCCC(((000)))RRR999 或或或 ---CCC(((000)))OOORRR999的的的取取取代代代基基基所所所取取取代代代;;;
或或或者者者,,, RRR555和和和 RRR666与与与其其其相相相连连连接接接的的的 CCC原原原子子子一一一起起起形形形成成成一一一个个个环环环烷烷烷基基基或或或杂杂杂环环环基基基,,, 所所所述述述的的的环环环 烷烷烷基基基或或或杂杂杂环环环基基基各各各自自自独独独立立立地地地任任任选选选进进进一一一步步步被被被一一一个个个或或或多多多个个个选选选自自自羟羟羟基基基、、、 卤卤卤素素素、、、 烷烷烷基基基、、、 烷烷烷氧氧氧 基基基、、、 环环环烷烷烷基基基或或或杂杂杂环环环基基基的的的取取取代代代基基基所所所取取取代代代;;; 和和和
XXX为为为离离离去去去基基基团团团,,, 优优优选选选为为为卤卤卤素素素。。。
在在在本本本发发发明明明的的的又又又一一一个个个实实实施施施方方方案案案中中中,,, 所所所述述述通通通式式式((( III---AAA )))所所所示示示的的的化化化合合合物物物及及及其其其可可可药药药用用用的的的盐盐盐 为为为通通通式式式 (((ΙΙΙΠΠΠ---ΑΑΑ)))及及及 (((IIIVVV---AAA)))所所所示示示的的的化化化合合合物物物及及及其其其可可可药药药用用用的的的盐盐盐:::
(((III NNN---AAA))) (((IIIVVV---AAA)))
其其其中中中::: ΕEΕ、、、 ΖZΖ、、、 XXX、、、 RRR111的的的定定定义义义如如如通通通式式式(((ΙIΙ---ΑAΑ )))中中中所所所述述述。。。
本本本发发发明明明进进进一一一步步步涉涉涉及及及一一一种种种制制制备备备所所所述述述的的的通通通式式式(((III )))所所所示示示的的的化化化合合合物物物或或或其其其互互互变变变异异异构构构体体体、、、 内内内 消消消旋旋旋体体体、、、 外外外消消消旋旋旋体体体、、、 对对对映映映异异异构构构体体体、、、 非非非对对对映映映异异异构构构体体体、、、 及及及其其其混混混合合合物物物形形形式式式、、、 及及及其其其可可可药药药用用用 的的的盐盐盐的的的
通通式式 ((II--AA))化化合合物物和和通通式式 ((II--BB))化化合合物物在在溶溶剂剂中中,, 酸酸性性条条件件下下加加热热进进行行反反应应,, 得得 到到通通式式((II ))化化合合物物;;
其其中中:: XX为为离离去去基基团团,, 优优选选为为卤卤素素;; 其其中中 EE、、 ZZ、、 环环 、、 环环^^ 11^^〜〜11 44的的定定义义 如如通通式式((II ))中中所所述述。。
在在本本发发明明的的另另一一个个方方面面,, 提提供供一一种种药药物物组组合合物物,, 所所述述药药物物组组合合物物含含有有治治疗疗有有 效效量量的的所所述述的的通通式式((II ))所所示示的的化化合合物物或或其其互互变变异异构构体体、、 内内消消旋旋体体、、 外外消消旋旋体体、、 对对映映 异异构构体体、、 非非对对映映异异构构体体、、 及及其其混混合合物物形形式式、、 及及其其可可药药用用的的盐盐及及药药学学上上可可接接受受的的载载 体体。。
在在本本发发明明的的另另一一个个方方面面,, 还还涉涉及及通通式式((II ))所所示示的的化化合合物物或或其其互互变变异异构构体体、、 内内消消 旋旋体体、、 外外消消旋旋体体、、 对对映映异异构构体体、、 非非对对映映异异构构体体、、 及及其其混混合合物物形形式式、、 及及其其可可药药用用的的 盐盐,, 或或包包含含其其的的药药物物组组合合物物在在制制备备蛋蛋白白激激酶酶抑抑制制剂剂,, 优优选选为为 SSyykk抑抑制制剂剂中中的的用用途途。。
在在本本发发明明的的另另一一个个方方面面,, 还还涉涉及及一一种种调调节节蛋蛋白白激激酶酶催催化化活活性性的的方方法法,, 其其中中包包
括将所述的蛋白激酶与通式(I )所示的化合物或其互变异构体、 外消旋体、 对映异 构体、 非对映异构体、 及其混合物形式、 及其可药用的盐, 或其药学上可接受的 盐, 或包含其的药物组合物接触的步骤。 优选的, 所述蛋白激酶选自受体酪氨酸 激酶、 非受体酪氨酸激酶或丝氨酸-苏氨酸激酶。
在本发明的另一个方面, 还涉及通式(I )所示的化合物或其互变异构体、 内消 旋体、 外消旋体、 对映异构体、 非对映异构体、 及其混合物形式、 及其可药用的 盐, 或包含其的药物组合物, 其作为蛋白激酶抑制剂, 优选为 Syk蛋白激酶抑制 剂。
在本发明的另一个方面, 还涉及通式(I )所示的化合物或其互变异构体、 外消 旋体、 对映异构体、 非对映异构体、 及其混合物形式、 及其可药用的盐, 或包含 其的药物组合物在制备治疗与蛋白激酶有关的疾病的药物中的用途。 优选的, 所 述的与蛋白激酶有关的疾病为 Syk蛋白激酶有关的疾病, 其选自恶性淋巴瘤、 自 身免疫性疾病、 结疤、 过敏性疾病、 与组织破坏有关的疾病和与组织发炎有关的 疾病。 所述的自身免疫性疾病选自同种异体移植排斥、 桥本甲状腺炎、 自免疫溶 血性贫血、 自免疫恶性贫血的萎縮性胃炎、 自免疫脑脊髓炎、 自免疫睾丸炎、 古 德帕斯丘病、 自免疫血小板减少症、 交叉神经眼炎、 肌肉衰弱症、 格雷夫斯疾病、 初级胆汁硬化、 慢性侵略性肝炎、 膜血管小球病和牵涉身体组织自免疫紊乱的自 免疫疾病。 所述牵涉身体组织自免疫紊乱的自免疫性疾病优选为全身红斑狼疮、 风湿性关节炎、 舍格伦综合症、 赖特尔综合症、 多肌炎-皮肌炎、 身体组织硬化、 多动脉炎、 多样三角化、 大类天疤疮和银屑病。 所述的结疤选自硬皮病、 增加纤 维化、 瘢瘤、 手术后疤痕、 肺纤维化、 血管痉挛、 偏头痛、 再灌流伤害和后心肌 梗塞。 所述的与组织破坏有关的疾病选自慢性阻塞性肺病、 心脏支气管炎和后心 肌梗塞。 所述的与组织发炎有关选自风湿性关节炎、 过敏疾病、 痉挛性结肠和炎 性结肠疾病。
在本发明的另一个方面, 还涉及一种治疗或预防哺乳动物与蛋白激酶有关的 疾病的方法, 包括对该哺乳动物施用治疗有效剂量的本发明的通式(I )所示的化合 物或其互变异构体、 外消旋体、 对映异构体、 非对映异构体、 及其混合物形式、 及其可药用的盐, 或包含其的药物组合物。 所述的与蛋白激酶有关的疾病优选为 与 Syk蛋白激酶有关的疾病, 其选自恶性淋巴瘤、 自身免疫性疾病、 结疤、 过敏 性疾病、 与组织破坏有关的疾病和与组织发炎有关的疾病。 所述的自身免疫性疾 病优选为全身红斑狼疮、 风湿性关节炎、 舍格伦综合症、 赖特尔综合症、 多肌炎- 皮肌炎、 身体组织硬化、 多动脉炎、 多样三角化、 大类天疤疮和银屑病。 所述的 过敏性疾病优选为结膜炎、 鼻炎、 哮喘、 特应性皮肤炎和食物过敏。 所述的结疤 选自硬皮病、 增加纤维化、 瘢瘤、 手术后疤痕、 肺纤维化、 血管痉挛、 偏头痛、 再灌流伤害和后心肌梗塞。 所述的与组织破坏有关的疾病选自慢性阻塞性肺病、 心脏支气管炎和后心肌梗塞。 所述的与组织发炎有关选自过敏疾病、 痉挛性结肠
和炎性结肠疾病。 优选的, 所述的哺乳动物是人。
本发明的另一方面涉及通式(I )所示的化合物或其互变异构体、 外消旋体、 对 映异构体、 非对映异构体、 及其混合物形式、 及其可药用的盐, 或包含其的药物 组合物, 其作为治疗与蛋白激酶有关的疾病的药物。 其中所述的与蛋白激酶有关 的疾病优选为与 Syk蛋白激酶有关的疾病, 其选自恶性淋巴瘤、 自身免疫性疾病、 结疤、 过敏性疾病、 与组织破坏有关的疾病和与组织发炎有关的疾病。 所述的自 身免疫性疾病优选为全身红斑狼疮、 风湿性关节炎、 舍格伦综合症、 赖特尔综合 症、 多肌炎-皮肌炎、 身体组织硬化、 多动脉炎、 多样三角化、 大类天疤疮和银屑 病。 所述的过敏性疾病优选为结膜炎、 鼻炎、 哮喘、 特应性皮肤炎和食物过敏。 所述的结疤选自硬皮病、 增加纤维化、 瘢瘤、 手术后疤痕、 肺纤维化、 血管痉挛、 偏头痛、 再灌流伤害和后心肌梗塞。 所述的与组织破坏有关的疾病选自慢性阻塞 性肺病、 心脏支气管炎和后心肌梗塞。 所述的与组织发炎有关选自过敏疾病、 痉 挛性结肠和炎性结肠疾病。
本发明的另一方面涉及一种抑制 Fc受体信号转导级联方法, 其包含将具有 γ 同型二聚体的 Fc受体细胞, 与有效抑制其信号转导级联的量的如通式( I )所示的 化合物或其互变异构体、 外消旋体、 对映异构体、 非对映异构体、 及其混合物形 式、 及其可药用的盐, 或包含其的药物组合物接触的步骤。所述的 Fc受体选自 Fc a RI Fc y RI Fc γ R III禾口 Fc ε RI。
本发明涉及鉴别蛋白激酶催化活性的化合物, 使表达该蛋白激酶的细胞与本 发明化合物或盐接触, 然后检测对细胞的效果。
本发明还涉及鉴别蛋白激酶催化活性的化合物, 使人工重组合成激酶蛋白与 本发明化合物或盐接触, 然后用 Elisa方法检测对激酶活性的影响。
含活性成分的药物组合物可以是适用于口服的形式, 例如片剂、 糖锭剂、 锭 剂、 水或油混悬液、 可分散粉末或颗粒、 乳液、 硬或软胶囊, 或糖浆剂或酏剂。 可按照本领域任何已知制备药用组合物的方法制备口服组合物, 此类组合物可含 有一种或多种选自以下的成分: 甜味剂、 矫味剂、 着色剂和防腐剂, 以提供悦目 和可口的药用制剂。 片剂含有活性成分和用于混合的适宜制备片剂的无毒的可药 用的赋形剂。 这些赋形剂可以是惰性赋形剂, 如碳酸钙、 碳酸钠、 乳糖、 磷酸钙 或磷酸钠; 造粒剂和崩解剂, 例如微晶纤维素、 交联羧甲基纤维素钠、 玉米淀粉 或藻酸; 粘合剂, 例如淀粉、 明胶、 聚乙烯吡咯烷酮或阿拉伯胶; 和润滑剂, 例 如硬脂酸镁、 硬脂酸或滑石粉。 这些片剂可以不包衣或可通过掩盖药物的味道或 在胃肠道中延迟崩解和吸收, 因而在较长时间内提供缓释作用的已知技术将其包 衣。 例如, 可使用水溶性味道掩蔽物质, 例如羟丙基甲基纤维素或羟丙基纤维素, 或延长时间物质例如乙基纤维素、 醋酸丁酸纤维素。
也可用其中活性成分与惰性固体稀释剂例如碳酸钙、 磷酸钙或高岭土混合的 硬明胶胶囊, 或其中活性成分与水溶性载体例如聚乙二醇或油溶媒例如花生油、
液体石蜡或橄榄油混合的软明胶胶囊提供口服制剂。
水悬浮液含有活性物质和用于混合的适宜制备水悬浮液的赋形剂。 此类赋形 剂是悬浮剂, 例如羧基甲基纤维素钠、 甲基纤维素、 羟丙基甲基纤维素、 藻酸钠、 聚乙烯吡咯烷酮和阿拉伯胶; 分散剂或湿润剂可以是天然产生的磷脂例如卵磷脂, 或烯化氧与脂肪酸的縮合产物例如聚氧乙烯硬脂酸酯, 或环氧乙烷与长链脂肪醇 的縮合产物, 例如十七碳亚乙基氧基鲸蜡醇 (heptadecaethyleneoxy cetanol), 或环氧 乙烷与由脂肪酸和己糖醇衍生的部分酯的縮合产物, 例如聚环氧乙烷山梨醇单油 酸酯, 或环氧乙烷与由脂肪酸和己糖醇酐衍生的偏酯的縮合产物, 例如聚环氧乙 烷脱水山梨醇单油酸酯。 水混悬液也可以含有一种或多种防腐剂例如尼泊金乙酯 或尼泊金正丙酯、 一种或多种着色剂、 一种或多种矫味剂和一种或多种甜味剂, 例如蔗糖、 糖精或阿司帕坦。
油混悬液可通过使活性成分悬浮于植物油如花生油、 橄榄油、 芝麻油或椰子 油, 或矿物油例如液体石蜡中配制而成。 油悬浮液可含有增稠剂, 例如蜂蜡、 硬 石蜡或鲸蜡醇。 可加入上述的甜味剂和矫味剂, 以提供可口的制剂。 可通过加入 抗氧化剂例如丁羟茴醚或 (X-生育酚保存这些组合物。
通过加入水可使适用于制备水混悬液的可分散粉末和颗粒提供活性成分和用 于混合的分散剂或湿润剂、 悬浮剂或一种或多种防腐剂。 适宜的分散剂或湿润剂 和悬浮剂可说明上述的例子。 也可加入其他赋形剂例如甜味剂、 矫味剂和着色剂。 通过加入抗氧化剂例如抗坏血酸保存这些组合物。
本发明的药物组合物也可以是水包油乳剂的形式。 油相可以是植物油例如橄 榄油或花生油, 或矿物油例如液体石蜡或其混合物。 适宜的乳化剂可以是天然产 生的磷脂, 例如大豆卵磷脂和由脂肪酸和己糖醇酐衍生的酯或偏酯例如山梨坦单 油酸酯, 和所述偏酯和环氧乙烷的縮合产物, 例如聚环氧乙烷山梨醇单油酸酯。 乳剂也可以含有甜味剂、 矫味剂、 防腐剂和抗氧剂。 可用甜味剂例如甘油、 丙二 醇、 山梨醇或蔗糖配制糖浆和酏剂。 此类制剂也可含有缓和剂、 防腐剂、 着色剂 和抗氧剂。
药物组合物可以是无菌注射水溶液形式。 可在使用的可接受的溶媒和溶剂中 有水、 林格氏液和等渗氯化钠溶液。 无菌注射制剂可以是其中活性成分溶于油相 的无菌注射水包油微乳。 例如将活性成分溶于大豆油和卵磷脂的混合物中。 然后 将油溶液加入水和甘油的混合物中处理形成微乳。 可通过局部大量注射, 将注射 液或微乳注入患者的血流中。 或者, 最好按可保持本发明化合物恒定循环浓度的 方式给予溶液和微乳。 为保持这种恒定浓度, 可使用连续静脉内递药装置。 这种 装置的实例是 Deltec CADD-PLUS. TM. 5400型静脉注射泵。
药物组合物可以是用于肌内和皮下给药的无菌注射水或油混悬液的形式。 可 按已知技术, 用上述那些适宜的分散剂或湿润剂和悬浮剂配制该混悬液。 无菌注 射制剂也可以是在无毒肠胃外可接受的稀释剂或溶剂中制备的无菌注射溶液或混
悬液, 例如 1,3-丁二醇中制备的溶液。此外, 可方便地用无菌固定油作为溶剂或悬 浮介质。 为此目的, 可使用包括合成甘油单或二酯在内的任何调和固定油。 此外, 脂肪酸例如油酸也可以制备注射剂。
可按用于直肠给药的栓剂形式给予本发明化合物。 可通过将药物与在普通温 度下为固体但在直肠中为液体, 因而在直肠中会溶化而释放药物的适宜的无刺激 性赋形剂混合来制备这些药物组合物。 此类物质包括可可脂、 甘油明胶、 氢化植 物油、 各种分子量的聚乙二醇和聚乙二醇的脂肪酸酯的混合物。
本领域技术人员所熟知的, 药物的给药剂量依赖于多种因素, 包括但并非限 定以下因素: 所用特定化合物的活性、 病人的年龄、 病人的体重、 病人的健康状 况、 病人的表现、 病人的饮食、 给药时间、 给药方式、 排泄的速率、 药物的组合 等; 另外, 最佳的治疗方式如治疗的模式、 通式化合物 (I)的日用量或可药用的盐 的种类可以根据传统的治疗方案来验证。 发明的详细说明
除非有相反陈述, 否则下列用在说明书和权利要求书中的术语具有下述含义。
"烷基 "指饱和的脂族烃基团, 包括 1至 20个碳原子的直链和支链基团。 优选 含有 1至 10个碳原子的烷基, 更优选含有 1至 6个碳原子的烷基。 非限制性实施 例包括甲基、 乙基、 正丙基、 异丙基、 正丁基、 异丁基、 叔丁基、 仲丁基、 正戊 基、 1,1-二甲基丙基、 1,2-二甲基丙基、 2,2-二甲基丙基、 1-乙基丙基、 2-甲基丁基、 3-甲基丁基、正己基、 1-乙基 -2-甲基丙基、 1,1,2-三甲基丙基、 1,1-二甲基丁基、 1,2- 二甲基丁基、 2,2-二甲基丁基、 1,3-二甲基丁基、 2-乙基丁基、 2-甲基戊基、 3-甲基 戊基、 4-甲基戊基、 2,3-二甲基丁基、 正庚基、 2-甲基己基、 3-甲基己基、 4-甲基己 基、 5-甲基己基、 2,3-二甲基戊基、 2,4-二甲基戊基、 2,2-二甲基戊基、 3,3-二甲基 戊基、 2-乙基戊基、 3-乙基戊基、 正辛基、 2,3-二甲基己基、 2,4-二甲基己基、 2,5- 二甲基己基、 2,2-二甲基己基、 3,3-二甲基己基、 4,4-二甲基己基、 2-乙基己基、 3- 乙基己基、 4-乙基己基、 2-甲基 -2-乙基戊基、 2-甲基 -3-乙基戊基、 正壬基、 2-甲基 -2-乙基己基、 2-甲基 -3-乙基己基、 2,2-二乙基戊基、 正癸基、 3,3-二乙基己基、 2,2- 二乙基己基, 及其各种支链异构体等。 更优选的是含有 1至 6个碳原子的低级烷 基, 非限制性实施例包括甲基、 乙基、 正丙基、 异丙基、 正丁基、 异丁基、 叔丁 基、 仲丁基、 正戊基、 1,1-二甲基丙基、 1,2-二甲基丙基、 2,2-二甲基丙基、 1-乙基 丙基、 2-甲基丁基、 3-甲基丁基、 正己基、 1-乙基 -2-甲基丙基、 1,1,2-三甲基丙基、 1,1-二甲基丁基、 1,2-二甲基丁基、 2,2-二甲基丁基、 1,3-二甲基丁基、 2-乙基丁基、 2-甲基戊基、 3-甲基戊基、 4-甲基戊基、 2,3-二甲基丁基等。 烷基可以是取代的或 未取代的, 当被取代时, 取代基可以在任何可使用的连接点上被取代, 优选为一 个或多个以下基团, 独立地选自烷基、 烯基、 块基、 烷氧基、 烷硫基、 烷基氨基、 卤素、 巯基、 羟基、 硝基、 氰基、 环烷基、 杂环基、 芳基、 杂芳基、 环烷氧基、
杂环烷氧基、 环烷硫基、 杂环烷硫基、 氧代、 -NR7R8、 -C(O) NR7R8、 -S(0)mR9 -OR9、 -C(0)R9、 -OC(0)R9或 -C(0)OR9。
"烯基 "指由至少两个碳原子和至少一个碳-碳双键组成的如上述定义的烷基。 例如乙烯基、 1-丙烯基、 2-丙烯基、 1-, 2-或 3-丁烯基等。 烯基可以是取代的或未 取代的, 当被取代时, 取代基优选为一个或多个以下基团, 独立地选自烷基、 烷 氧基、卤素、羟基、硝基、氰基、环烷基、杂环基、芳基、杂芳基、 -NR7R8、 -S(0)mR9, -S(0)m NR7R8、 -OR9、 -C(0)R9、 -OC(0)R9或 -C(0)OR9。
"块基"指至少两个碳原子和至少一个碳-碳三键组成的如上所定义的烷基。 例 如乙块基、 1-丙块基、 2-丙块基、 1-, 2-或 3-丁块基等。 块基可以是取代的或未取 代的, 当被取代时, 取代基优选为一个或多个以下基团, 独立地选自烷基、 烷氧 基、 卤素、 羟基、 硝基、 氰基、 环烷基、 杂环基、 芳基、 杂芳基、 -NR7R8、 -C(O) NR7R8、 -S(0)mR9、 -OR9、 -C(0)R9、 -OC(0)R9或 -C(0)OR9。
"环烷基"指饱和或部分不饱和单环或多环环状烃取代基, 其包括 3至 20个碳 原子, 优选包括 3至 12个碳原子, 更优选环烷基环包含 3至 10个碳原子。 单环 环烷基的非限制性实施例包含环丙基、 环丁基、 环戊基、 环戊烯基、 环己基、 环 己烯基、 环己二烯基、 环庚基、 环庚三烯基、 环辛基等。 多环环烷基包括螺环、 稠环和桥环的环烷基。
"螺环烷基"指 5至 20元, 单环之间共用一个碳原子 (称螺原子)的多环基团, 这些可以含有一个或多个双键, 但没有一个环具有完全共轭的 π 电子系统。 优选 为 6至 14元, 更优选为 7至 10元。 根据环与环之间共用螺原子的数目将螺环烷 基分为单螺环烷基、 双螺环烷基基或多螺环烷基, 优选为单螺环烷基和双螺环烷 基。 更优选为 4元 /4元、 4元 /5元、 4元 /6元、 5元 /5元或 5元 /6元单螺环烷基。 螺环烷基的非限制性
"稠环烷基"指 5至 20元, 系统中的每个环与体系中的其他环共享毗邻的一对 碳原子的全碳多环基团, 其中一个或多个环可以含有一个或多个双键, 但没有一 个环具有完全共轭的 π电子系统。 优选为 6至 14元, 更优选为 7至 10元。 根据 组成环的数目可以分为双环、 三环、 四环或多环稠环烷基, 优选为双环或三环,
"桥环烷基"指 5至 20元,任意两个环共用两个不直接连接的碳原子的全碳多
环基团, 这些可以含有一个或多个双键, 但没有一个环具有完全共轭的 π 电子系 统。 优选为 6至 14元, 更优选为 7至 10元。 根据组成环的数目可以分为双环、 三环、 四环或多环桥环烷基, 优选为双环、 三环或四环, 更有选为双环或三环。 桥环烷基的非限制
所述环烷基环可以稠合于芳基、 杂芳基或杂环基环上, 其中与母体结构连接在一 起的环为环烷基, 非限制性实施例包括茚满基、 四氢萘基、 苯并环庚烷基等。 环 烷基可以是任选取代的或未取代的, 当被取代时, 取代基优选为一个或多个以下 基团, 独立地选自烷基、 烯基、 块基、 烷氧基、 烷硫基、 烷基氨基、 ^素、 巯基、 羟基、 硝基、 氰基、 环烷基、 杂环基、 芳基、 杂芳基、 环烷氧基、 杂环烷氧基、 环烷硫基、 杂环烷硫基、 氧代、 -NR7R8、 -C(0) NR7R8、 -S(0)mR9、 -OR9、 -C(0)R9、 -OC(0)R9或 -C(0)OR9。
"杂环基"指饱和或部分不饱和单环或多环环状烃取代基,其包括 3至 20个环 原子,其中一个或多个环原子选自氮、氧或 S(0)m (其中 m是整数 0至 2)的杂原子, 但不包括 -0-0-、 -0-S-或 -S-S-的环部分, 其余环原子为碳。 优选包括 3至 12个环 原子, 其中 1〜4个是杂原子, 更优选环烷基环包含 3至 8个环原子。
多环杂环基包括螺环、 稠环和桥环的杂环基。 "螺杂环基"指 5至 20元, 单环 之间共用一个原子 (称螺原子)的多环杂环基团, 其中一个或多个环原子选自氮、氧 或 S(0)m (其中 m是整数 0至 2)的杂原子, 其余环原子为碳。 这些可以含有一个或 多个双键, 但没有一个环具有完全共轭的 π电子系统。 优选为 6至 14元, 更优选 为 7至 10元。 根据环与环之间共用螺原子的数目将螺环烷基分为单螺杂环基、 双 螺杂环基或多螺杂环基, 优选为单螺环烷基和双螺环烷基。 更优选为 4元 /4元、 4 元 /5元、 4元 /6元、 5元 /5元或 5元 /6元单螺环烷基。 螺环烷基的非限制性实施例 包含
"稠杂环基"指 5至 20元, 系统中的每个环与体系中的其他环共享毗邻的一对 原子的多环杂环基团, 一个或多个环可以含有一个或多个双键, 但没有一个环具 有完全共轭的 π电子系统, 其中一个或多个环原子选自氮、 氧或 S(0)m (其中 m是 整数 0至 2)的杂原子, 其余环原子为碳。 优选为 6至 14元, 更优选为 7至 10元。 根据组成环的数目可以分为双环、 三环、 四环或多环稠杂环基, 优选为双环或三 环, 更优选为 5元 /5元或 5元 /6元双环稠杂环基。 稠杂环基的非限制性实施例包 含
"桥杂环基"指 5至 14元, 任意两个环共用两个不直接连接的原子的多环杂环 基团, 这些可以含有一个或多个双键, 但没有一个环具有完全共轭的 π电子系统, 其中一个或多个环原子选自氮、 氧或 S(0)m (其中 m是整数 0至 2)的杂原子, 其余 环原子为碳。 优选为 6至 14元, 更优选为 7至 10元。 7至 10元。 根据组成环的 数目可以分为双环、 三环、 四环或多环桥环烷基, 优选为双环、 三环或四环, 更 有选为双环或三环。 桥环烷基的非限制性实施例包含:
等。 杂环基可以是任选取代的或未取代的, 当被取代时, 取代基优选为一个或多 个以下基团, 独立地选自烷基、 烯基、 块基、 烷氧基、 烷硫基、 烷基氨基、 卤素、 巯基、 羟基、 硝基、 氰基、 环烷基、 杂环基、 芳基、 杂芳基、 环烷氧基、 杂环浣 氧基、 环烷硫基、 杂环烷硫基、 -NR7R8、 -C(0) NR7R8、 -S(0)mR9、 -OR9、 -C(0)R9、 -OC(0)R9或 -C(0)OR9。
"芳基 "指 6至 14元具有共轭的 π电子体系的全碳单环或稠合多环 (也就是共 享毗邻碳原子对的环)基团, 优选为 6至 10元, 例如苯基和萘基。所述芳基环可以
稠合于杂芳基、 杂环基或环烷基环上, 其中与母体结构连接在一起的环为芳基环, 非限制性实施例包含:
芳基可以是取代的或未取代的, 当被取代时, 取代基优选为一个或多个以下 基团, 独立地选自烷基、 烯基、 块基、 烷氧基、 烷硫基、 烷基氨基、 ^素、 巯基、 羟基、 硝基、 氰基、 环烷基、 杂环基、 芳基、 杂芳基、 环烷氧基、 杂环烷氧基、 环烷硫基、杂环烷硫基、 -NR7R8、 -C(O) NR7R8、 -S(0)mR9、 -OR9、 -C(0)R9、 -OC(0)R9 或 -C(0)OR9。
"杂芳基"指包含 1至 4个杂原子, 5至 14个环原子的杂芳族体系, 其中杂原 子包括氧、硫和氮。优选为 5至 10元。杂芳基优选为是 5元或 6元, 例如呋喃基、 噻吩基、 吡啶基、 吡唑基、 吡咯基、 N-烷基吡咯基、 嘧啶基、 吡嗪基、 咪唑基、 四唑基等。 所述杂芳基环可以稠合于芳基、 杂环基或环烷基环上, 其中与母体结 一起的环为杂芳基环, 非限制性实施例包含:
杂芳基可以是任选取代的或未取代的, 当被取代时, 取代基优选为一个或多 个以下基团, 独立地选自烷基、 烯基、 块基、 烷氧基、 烷硫基、 烷基氨基、 卤素、 巯基、 羟基、 硝基、 氰基、 环烷基、 杂环基、 芳基、 杂芳基、 环烷氧基、 杂环烷 氧基、 环烷硫基、 杂环烷硫基、 -NR7R8、 -C(0) NR7R8、 -S(0)mR9、 -OR9、 -C(0)R9、 -OC(0)R9或 -C(0)OR9。
"烷氧基" 指 -o- (浣基)和 -o- (未取代的环烷基), 其中烷基、 环烷基的定义如上 所述。 非限制性实施例包含甲氧基、 乙氧基、 丙氧基、 丁氧基、 环丙氧基、 环丁 氧基、 环戊氧基、 环己氧基等。 烷氧基可以是任选取代的或未取代的, 当被取代 时, 取代基优选为一个或多个以下基团, 独立地选自为烷基、 烯基、 块基、 烷氧 基、 烷硫基、 烷基氨基、 卤素、 巯基、 羟基、 硝基、 氰基、 环烷基、 杂环基、 芳 基、杂芳基、环烷氧基、杂环烷氧基、环烷硫基、杂环烷硫基、 -NR7R8、 -C(O) NR7R8、
-S(0)mR9、 -OR9、 -C(0)R9、 -OC(0)R9或 -C(0)OR9。
"羟基 "指 -OH基团。
"羟烷基" 指 HO-(烷基)和 HO-(未取代的环烷基), 其中烷基、 环烷基的定义 如上所述。
"卤素"指氟、 氯、 溴或碘。
"氰基 "指 -CN。
"硝基 "指 -N02。
"节基 "指 -CH2-苯基。
"氨基 "指 -NH2。
"任选 "或"任选地 "意味着随后所描述地事件或环境可以但不必发生, 该说明 包括该事件或环境发生或不发生地场合。例如, "任选被烷基取代的杂环基团"意味 着烷基可以但不必须存在, 该说明包括杂环基团被烷基取代的情形和杂环基团不 被烷基取代的情形。
"取代的"指基团中的一个或多个氢原子, 优选为最多 5个, 更优选为 1〜3个 氢原子彼此独立地被相应数目的取代基取代。 不言而喻, 取代基仅处在它们的可 能的化学位置, 本领域技术人员能够在不付出过多努力的情况下确定 (通过实验或 理论)可能或不可能的取代。例如,具有游离氢的氨基或羟基与具有不饱和 (如烯属) 键的碳原子结合时可能是不稳定的。
"药物组合物 "表示含有一种或多种本文所述化合物或其生理学 /可药用的盐 或前体药物与其他化学组分的混合物, 以及其他组分例如生理学 /可药用的载体和 赋形剂。 药物组合物的目的是促进对生物体的给药, 利于活性成分的吸收进而发 挥生物活性。
m和 R7〜R9的定义如通式( I )化合物中所述。 本发明化合物的合成方法
为了完成本发明的目的, 本发明采用如下技术方案:
(1-1) (I-2) (I-3)
(l-B) (
将硝基取代的环 A丙酸酯 (1-1)化合物在溶液中, 催化剂下还原为氨基取代的 环 A 丙酸酯 (1-2)化合物, 通式 (1-2)化合物在溶剂中, 氢化钠下成环得到通式 (1-3) 化合物;通式 (1-3)化合物在溶剂中与卤素取代的嘧啶,加热下得到通式 (I-A)化合物, 通式 (I-A)化合物和通式 (I-B)化合物在溶剂中, 酸性条件下微波加热进行反应, 得 到通式 (I)化合物;
其中: X为离去基团, 优选为卤素或磺酰氧基, 更优选为卤素; 其中 E、 Z、 环 、 B、 Ri〜R4的定义如通式 (I) 中所定义。
(Π)所述的化合物或其可药用的盐的制备方法, 包括以下步骤:
(II-A) (I-B) (II) 将硝基取代的芳基丙酸酯 (Π-1)化合物在溶液中, 催化剂下还原为氨基取代的 芳基丙酸酯 (Π-2)化合物, 通式 (Π-2)化合物在溶剂中, 氢化钠下成环得到通式 (Π-3) 化合物; 通式 (Π-3)化合物在溶剂中与卤素取代的嘧啶, 加热下得到通式 (Π-Α)化合 物,通式 (Π-Α)化合物和通式 (I-B)化合物在溶剂中,酸性条件下微波加热进行反应, 得到通式 (Π)化合物;
其中: X为离去基团, 优选为卤素或磺酰氧基, 更优选为卤素; 其中 E、 Z、
Y, 环 B, Ri〜R4的定义如通式 (Π) 中所定义。
:
(Ι-Β)
将硝基取代的苯基丙酸酯 (ΠΙ-1)化合物在溶液中, 催化剂下还原为氨基取代的 苯基丙酸酯 (ΙΠ-2)化合物,通式 (ΠΙ-2)化合物在溶剂中,氢化钠下成环得到通式 (ΠΙ-3) 化合物; 通式 (ΠΙ-3)化合物在溶剂中与卤素取代的嘧啶, 加热下得到通式 (ΙΠ-Α)化
合物,通式 (ΠΙ)化合物和通式 (I-B)化合物在溶剂中,酸性条件下微波加热进行反应, 得到通式 (ΠΙ)化合物;
其中: X为离去基团, 优选为卤素或磺酰氧基, 更优选为卤素; 其中 E、 Z、 环^ Ri〜R4的定义如通式 (III) 中所定义。
本发明通式 (IV)所述的化合物或其可药用的盐的制备方法, 包括以下步骤:
(IV-A) (l-B) (IV) 将硝基取代的吡啶丙酸酯 (IV-1)化合物在溶液中, 催化剂下还原为氨基取代的 吡啶丙酸酯 (IV-2)化合物,通式 (IV-2)化合物在溶剂中,氢化钠下成环得到通式 (IV-3) 化合物; 通式 (IV-3)化合物在溶剂中与卤素取代的嘧啶, 加热下得到通式 (IV-A)化 合物, 通式 (IV-A)化合物和通式 (I-B)化合物在溶剂中, 酸性条件下微波加热进行反 应, 得到通式 (IV)化合物;
其中: X为离去基团, 优选为卤素或磺酰氧基, 更优选为卤素; 其中 E、 Z、 环8、 Ri〜R4的定义如通式 (IV) 中所定义。
上述的反应提供酸性条件包括有机酸和无机酸类, 所述的无机酸类包括但不 限于盐酸, 硫酸, 硝酸类强酸, 优选为浓盐酸;
催化剂包括但不限于四-三苯基膦钯、三苯基膦、二氯化钯、醋酸钯、 1,1 '-双 (二 苄基磷)二氯二戊铁钯、 三 (二亚苄基丙酮)二钯、 钯 /碳或兰尼镍。
所用溶剂包括但不限于: 醋酸、 甲醇、 乙醇、 乙腈、 四氢呋喃、 二氯甲烷、 二甲基亚砜、 1,4-二氧六环、 水、 N, N-二甲基乙酰胺或 N,N-二甲基甲酰胺, 优选 极性溶剂, 更优选为乙醇;
所述微波加热的温度为 140-180°C, 优选反应条件为 160°C。 具体实施方式
以下结合实施例用于进一步描述本发明,但这些实施例并非限制着本发明的范 围。
本发明实施例中未注明具体条件的实验方法, 通常按照常规条件, 或按照原 料或商品制造厂商所建议的条件。 未注明具体来源的试剂, 为市场购买的常规试 剂。
实施例
化合物的结构是通过核磁共振 (NMR)或 /和质谱 (MS)来确定的。 NMR位移 (δ) 以 10—6 (ppm)的单位给出。 NMR的测定是用 Bruker AVANCE-400核磁仪, 测定溶 剂为氘代二甲基亚砜 氘代氯仿 (CDC13), 氘代甲醇 (CD3OD),内标为四 甲基硅烷 CTMS)。
MS的测定用 FINMGAN LCQAd (ESI)质谱仪 (生产商: Thermo, 型号: Finnigan
LCQ advantage MAX)。
HPLC的测定使用安捷伦 1200DAD高压液相色谱仪 (Sunfire C18 150x4.6mm色 谱柱)和 Waters 2695-2996高压液相色谱仪 (Gimini C18 150x4.6mm色谱柱)。
激酶平均抑制率及 IC5Q值的测定用 NovoStar酶标仪 (德国 BMG公司)。
薄层层析硅胶板使用烟台黄海 HSGF254或青岛 GF254硅胶板, 薄层色谱法
(TLC)使用的硅胶板采用的规格是 0.15 mm〜0.2 mm, 薄层层析分离纯化产品采用 的规格是 0.4 mm〜0.5 mm。
柱层析一般使用烟台黄海硅胶 200〜300目硅胶为载体。
本发明的已知的起始原料可以采用或按照本领域已知的方法来合成,或可购买 自 ABCR GmbH & Co. KG, Acros Organics, Aldrich Chemical Company, 韶远化学 科技 (Accela ChemBio Inc) 、 达瑞化学品等公司。
实施例中无特殊说明, 反应能够均在氩气氛或氮气氛下进行。
氩气氛或氮气氛是指反应瓶连接一个约 1L容积的氩气或氮气气球。
氢气氛是指反应瓶连接一个约 1L容积的氢气气球。
加压氢化反应使用 Parr 3916EKX 型氢化仪和清蓝 QL-500 型氢气发生器或
HC2-SS型氢化仪。
氢化反应通常抽真空, 充入氢气, 反复操作 3次。
微波反应使用 CEM Discover-S 908860型微波反应器。
实施例中无特殊说明, 溶液是指水溶液。
实施例中无特殊说明, 反应的温度为室温, 为 20°C〜30°C。
实施例中的反应进程的监测采用薄层色谱法 (TLC), 反应所使用的展开剂的体 系有: A: 二氯甲烷和甲醇体系, B: 正己烷和乙酸乙酯体系, C: 正己烷, 乙酸 乙酯和二氯甲烷, D:丙酮体系,溶剂的体积比根据化合物的极性不同而进行调节。
纯化化合物采用的柱层析的洗脱剂的体系和薄层色谱法的展开剂体系包括: A: 二氯甲烷和甲醇体系, B: 正己烷和乙酸乙酯体系, C: 正己烷, 乙酸乙酯和 二氯甲烷, D: 丙酮体系, 溶剂的体积比根据化合物的极性不同而进行调节, 也可 以加入少量的三乙胺和醋酸等碱性或酸性试剂进行调节。 实施例 1
7-(5-氟 -2-(3,4,5-三甲氧基苯基氨基)嘧啶 -4-基氨基 )-3,3-二甲基 -2,3-二氢吡啶并
[3,2-b][l,4]氧氮杂环庚 -4(5H 酮
第一步
3-羟基 -2,6-二硝基吡啶
将硝酸 (2.4 mL, 57.10 mmol)溶解于 5.6 mL醋酸酐中, 冷却至 0°C, 加入 3- 羟基 -2-硝基吡啶 la(2 g, 14.27 mmol), 升温至 20°C, 搅拌反应 2小时。 将反应液 倒入冰水中, 用乙酸乙酯萃取 (20 mLx3), 合并有机相, 用饱和氯化钠溶液洗涤 (30 mL), 无水硫酸镁干燥, 过滤, 减压浓縮滤液, 用硅胶柱色谱法以洗脱剂体系 A 纯化所得残余物, 得到标题产物 3-羟基 -2,6-二硝基吡啶 lb(1.20 g, 黄色固体), 产 率: 46.0 %
MS m/z (ESI): 184.0 [M-l]
第二步
3-羟基 -2,2-二甲基丙酸甲酯
将 3-羟基 -2,2-二甲基丙酸 lc(10 g, 84.60 mmol)溶解于 50 mL甲醇中,加入 5 mL 浓硫酸, 回流搅拌反应 5小时。 减压浓縮反应液, 加入 100 mL乙酸乙酯, 依次用 水 (20 mL)和饱和碳酸氢钠溶液 (20 mL)洗涤, 再用水 (20 mL)洗涤, 减压浓縮滤液, 得到粗品标题产物 3-羟基 -2,2-二甲基丙酸甲酯 ld(5.50 g, 无色油状物), 产物不经 纯化直接进行下一步反应。
第三步
3-(2,6-二硝基吡啶 -3-基氧代 )-2,2-二甲基丙酸甲酯 将 3-羟基 -2,6-二硝基吡啶 lb(300 mg, 1.62 mmol), 粗品 3-羟基 -2,2-二甲基丙 酸甲酯 ld(222 mg, 1.80 mmol)和三苯基膦 (510 mg, 1.95 mmol)溶解于 10 mL二氧 六环中, 滴加入偶氮二甲酸二异丙酯 (0.4 mL, 1.95 mmol), 升温至 75 °C, 搅拌反 应 12小时。 减压浓縮反应液, 用硅胶柱色谱法以洗脱剂体系 B纯化所得残余物, 得到标题产物 3-(2,6-二硝基吡啶 -3-基氧代 )-2,2-二甲基丙酸甲酯 le(480 mg, 黄色 固体), 产率: 100 %。
MS m/z (ESI): 317.1 [M+18]
第四步
3-(2,6-二氨基吡啶 -3-基氧代 )-2,2-二甲基丙酸甲酯 将 3-(2,6-二硝基吡啶 -3-基氧代 )-2,2-二甲基丙酸甲酯 le(480 mg, 1.60 mmol) 溶于 10 mL甲醇中, 加入钯 /碳 (200 mg, 10 %), 搅拌反应 4小时。 过滤, 减压浓 縮滤液, 得到粗品标题产物 3-(2,6-二氨基吡啶 -3-基氧代 )-2,2-二甲基丙酸甲酯 lf(300 mg, 褐色油状物), 产物不经纯化直接进行下一步反应。
MS m/z (ESI): 240.1 [M+l]
第五步
7-氨基 -3,3-二甲基 -2,3-二氢吡啶并 [3,2-b][l,4]氧氮杂环庚 -4(5H 酮 将粗品 3-(2,6-二氨基吡啶 -3-基氧代 )-2,2-二甲基丙酸甲酯 lf(300 mg, 1.25 mmol)溶于 5 mL二甲亚砜中, 加入氢化钠 (60 mg, 1.50 mmol), 升温至 30°C, 搅 拌反应 12小时。 加入 20 mL冰水, 用乙酸乙酯萃取 (20 mLx3), 合并有机相, 用 水洗涤 (10 mL), 无水硫酸镁干燥, 过滤, 减压浓縮滤液, 得到粗品标题产物 7-氨 基 -3,3-二甲基 -2,3-二氢吡啶并 [3,2-b][l,4]氧氮杂环庚 -4(5H 酮 lg(240 mg, 黄色固 体), 产物不经纯化直接进行下一步反应。
MS m/z (ESI): 208.2 [M+l]
第六步
7-(2-氯 -5-氟 -嘧啶 -4-基氨基 )-3,3-二甲基 -2,3-二氢吡啶并 [3,2-b][l,4]氧氮杂环庚
-4(5H 酮
将粗品 7-氨基 -3,3-二甲基 -2,3-二氢吡啶并 [3,2-b][l,4]氧氮杂环庚 -4(5H 酮 lg(240 mg, 1.16 mmol)和 2,6-二氯 -5-氟 -嘧啶 (212 mg, 1.27 mmol)溶解于 7 mL甲 醇和水 (V/V = 1 : 1)混合溶剂中, 升温至 70°C, 搅拌反应 24小时。 冷却至室温, 过 滤, 用正己烷洗涤 (20 mLx3), 烘干, 得到粗品标题产物 7-(2-氯 -5-氟 -嘧啶 -4-基氨 基) -3,3-二甲基 -2,3-二氢吡啶并 [3,2-b][l,4]氧氮杂环庚 -4C5H)-酮 lhClOO mg, 白色固 体), 产物不经纯化直接进行下一步反应。
MS m/z (ESI): 338.1 [M+l]
第七步
7-(5-氟 -2-(3,4,5-三甲氧基苯基氨基)嘧啶 -4-基氨基 )-3,3-二甲基 -2,3-二氢吡啶并
[3,2-b][l,4]氧氮杂环庚 -4(5H 酮
将粗品 7-P-氯 -5-氟 -嘧啶 -4-基氨基 )-3,3-二甲基 -2,3-二氢吡啶并 [3,2-b][l,4]氧 氮杂环庚 -4(5H 酮 lh(100 mg, 0.30 mmol)和 3,4,5-三甲氧基苯胺 (110 mg, 0.60 mmol) 溶解于 1 mL乙醇中, 加入 1滴浓盐酸, 160°C微波反应 1小时。 加入 3 mL乙酸, 减压浓縮反应液, 加入 10 mL乙酸乙酯, 过滤, 减压浓縮滤液, 用薄层色谱法以 展开剂体系 A纯化所得残余物,得到标题产物 7-(5-氟 -2-(3,4,5-三甲氧基苯基氨基) 嘧啶 -4-基氨基 )-3,3-二甲基 -2,3-二氢吡啶并 [3,2-b][l,4]氧氮杂环庚 -4C5H)-酮 1(70
mg, 灰色固体), 产率: 48.2 %。
MS m/z (ESI): 485.3 [M+l]
1H NMR (400 MHz, CDC13) δ 8.94 (s, 1H), 8.06 (s, 1H), 8.01 (s, 1H), 7.84 (d, 1H), 7.41 (s, 1H), 7.31 (d, 1H), 6.82 (s, 2H), 3.98 (s, 2H), 3.84-3.82 (m, 9H), 1.43 (s, 6H)。 实施例 2
7 5-氟 -2- 3-氟 -4-吗啉 -苯基氨基)嘧啶 -4-基氨基 )-3,3-二甲基 -2,3-二氢吡啶并
3,2-b][l,4]氧氮杂环庚 -4(5H 酮
将 7-0氯 -5-氟 -嘧啶 -4-基氨基 )-3,3-二甲基 -2,3-二氢吡啶并 [3,2-b][l,4]氧氮杂 环庚 -4(5H 酮 lh(50 mg, 0.15 mmol)和 3-氟 -4-吗啉苯胺 2a(44 mg, 0.22 mmol)溶解 于 1 mL乙醇中,加入 1滴浓盐酸, 160°C微波反应 1小时。加入 3 mL乙醇, 过滤, 用乙醇洗涤 (10 mLx2), 减压浓縮滤液, 得到标题产物 7-(5-氟 -2-(3-氟 -4-吗啉 -苯基 氨基)嘧啶 -4-基氨基 )-3,3-二甲基 -2,3-二氢吡啶并 [3,2-b][l,4]氧氮杂环庚 -4(5H 酮 2(30 mg, 白色固体), 产率: 40 %。
MS m/z (ESI): 498.3 [M+l]
1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO) δ 9.42 (s, 1H), 9.33 (s, 1H), 9.22 (s, 1H), 8.15 (1H, d), 7.65 (dd, 1H), 7.54-7.52 (d, 1H), 7.30 (d, 1H), 7.28 (dd, 1H), 6.91 (t, 1H), 4.05 (s, 2H), 3.73-3.70 (m, 4H), 2.92 (m, 4H), 1.20(s, 6H)。 实施例 3
7-(5-氟 -2-(3,4,5-三甲氧基苯基氨基)嘧啶 -4-基氨基 )-2'H-螺环 [环丙基 -1,3'-吡啶并
-b][l,4]氧氮杂环庚] -4'(5'H 酮
1- (羟甲基)环丙基甲酸甲酯
将 1- (;甲氧基羰基)环丙基甲酸 3a(500 mg, 3.47 mmol, 采用公知的方法"专利 EP1577301"制备而得)溶解于 10 mL四氢呋喃中,加入三乙胺 (0.6 mL, 4.16 mmol), 冷却至 0°C, 加入氯甲酸异丙酯 (521 mg, 3.82 mmol), 搅拌反应 1小时。 加入硼氢 化钠 (393 mg, 10.40 mmol)和 5 mL甲醇, 搅拌反应 1小时。 加入 15 mL水, 滴加 1 M盐酸至反应液 pH为 5, 用乙酸乙酯萃取 (20 mIX3), 合并有机相, 用饱和氯化 钠溶液洗涤 (30 mL), 无水硫酸镁干燥, 过滤, 减压浓縮滤液, 用硅胶柱色谱法以 洗脱剂体系 B纯化所得残余物, 得到标题产物 1- (羟甲基)环丙基甲酸甲酯 3b(200 mg, 无色油状物), 产率: 44.3 %。
第二步
1 -((2,6-二硝基吡啶 -3-基氧代)甲基)环丙基甲酸甲酯 将 3-羟基 -2,6-二硝基吡啶 lbC300 mg, 1.62 mmol), 1- (;羟甲基)环丙基甲酸甲酯 3b(220 mg, 1.69 mmol)和三苯基膦 (503 mg, 1.92 mmol)溶解于 20 mL二氧六环中, 滴加入偶氮二甲酸二异丙酯 388 mg, 1.92 mmol),升温至 75 °C,搅拌反应 12小时。 减压浓縮反应液, 用硅胶柱色谱法以洗脱剂体系 B纯化所得残余物, 得到标题产 物 1-((2,6-二硝基吡啶 -3-基氧代)甲基)环丙基甲酸甲酯 3c(200 mg, 黄色油状物), 产率: 42.1 %。
第三步
1 -((2,6-二氨基吡啶 -3-基氧代)甲基)环丙基甲酸甲酯 将 1-((2,6-二硝基吡啶 -3-基氧代)甲基)环丙基甲酸甲酯 3c(200 mg, 0.67 mmol) 溶于 10 mL甲醇中, 加入钯 /碳 (lOO mg, 10 %), 搅拌反应 3小时。 过滤, 减压浓 縮滤液, 得到粗品标题产物 1-((2,6-二氨基吡啶 -3-基氧代)甲基)环丙基甲酸甲酯 3d(140 mg, 黄色油状物), 产物不经纯化直接进行下一步反应。
MS m/z (ESI): 238.1 [M+l]
第四步
7'-氨基 -2'H-螺环 [环丙基 -1,3'-吡啶并 [3,2-b][l,4]氧氮杂环庚] -4'(5'H 酮 将粗品 1-((2,6-二氨基吡啶 -3-基氧代)甲基)环丙基甲酸甲酯 3d(140 mg, 0.59 mmol)溶于 2 mL二甲亚砜中, 加入氢化钠 (28 mg, 0.71 mmol), 升温至 75 °C, 搅 拌反应 3小时。 加入 20 mL冰水, 用乙酸乙酯萃取 (20 mIX3), 合并有机相, 用水
洗涤 (10 mL), 无水硫酸镁干燥, 过滤, 减压浓縮滤液, 得到粗品标题产物 7'-氨基 -2'H-螺环 [环丙基 -1,3'-吡啶并 [3,2-b][l,4]氧氮杂环庚] -4'(5'H 酮 3e(110 mg, 黄色固 体), 产物不经纯化直接进行下一步反应。
MS m/z (ESI): 206.1 [M+l]
第五步
7 2-氯 -5-氟嘧啶 -4-基氨基 )-2'H-螺环 [环丙基 -1,3'-吡啶并 [3,2-b][l,4]氧氮杂环 庚] -4'(5Ή 酮
将粗品 7-氨基 -2'H-螺环 [环丙基 -1,3'-吡啶并 [3,2-b][l,4]氧氮杂环庚] -4'(5'H 酮 3e(110 mg, 0.54 mmol)和 2,6-二氯 -5-氟 -嘧啶 (98 mg, 0.59 mmol)溶解于 4 mL甲醇 和水 (V/V = 1 : 1)混合溶剂中, 升温至 75 °C, 搅拌反应 12小时。冷却至室温, 过滤, 用正己烷洗涤 (20 mLx3),烘干,得到粗品标题产物 7-(2-氯 -5-氟嘧啶 -4-基氨基 )-2'H- 螺环 [环丙基 -1,3'-吡啶并 [3,2-b][l,4]氧氮杂环庚] -4'C5'H 酮 3 50 mg, 白色固体), 产物不经纯化直接进行下一步反应。
MS m/z (ESI): 336.0 [M+l]
第六步
7-(5-氟 -2-(3,4,5-三甲氧基苯基氨基)嘧啶 -4-基氨基 )-2'H-螺环 [环丙基 -1,3'-吡啶并
[3,2-b][l,4]氧氮杂环庚] -4'(5Ή 酮
将粗品 氯 -5-氟嘧啶 -4-基氨基 )-2'H-螺环 [环丙基 -1,3'-吡啶并 [3,2-b][l,4]氧 氮杂环庚] -4'(5'H 酮 3f(50 mg, 0.15 mmol)和 3,4,5-三甲氧基苯胺 (32 mg, 0.18 mmol) 溶解于 1 mL乙醇中, 加入 1滴浓盐酸, 160°C微波反应 1小时。 减压浓縮反应液, 用薄层色谱法以展开剂体系 A纯化所得残余物, 得到标题产物 7-(5-氟 -2-(3,4,5-三 甲氧基苯基氨基)嘧啶 -4-基氨基 2'H-螺环 [环丙基 -1,3'-吡啶并 [3,2-b][l,4]氧氮杂环 庚] -4'(5'H 酮 3(30 mg, 灰色固体), 产率: 42.3 %。
MS m/z (ESI): 481.2 [M-l]
1H NMR (400 MHz, CDC13) δ 8.21 (s, 1H), 7.97 (s, 1H), 7.90 (d, 1H), 7.75 (s, 1H),
7.29 (s, 2H), 4.02 (s, 2H), 3.85 (s, 3H), 3.83 (s, 6H), 1.59-1.56 (m, 2H), 1.05-1.00 (m,
2H)。 实施例 4
5-(4-(3,3-二甲基 -4-羰基 -2,3,4,5-四氢吡啶并 [3,2-b][l,4]氧氮杂环庚 -7-基氨基 )-5-氟 嘧啶 -2-基氨基 )-2-甲基苯基磺酰胺
将 7-0氯 -5-氟 -嘧啶 -4-基氨基 )-3,3-二甲基 -2,3-二氢吡啶并 [3,2-b][l,4]氧氮杂 环庚 -4(5H 酮 lh(50 mg, 0.15 mmol)和 5-氨基 -2-甲基苯基磺酰胺 4a(41 mg, 0.22 mmol)溶解于 1 mL乙醇中, 加入 1滴浓盐酸, 160°C微波反应 1小时。 加入 3 mL 乙醇, 过滤, 用乙醇洗涤 (10 mLx2), 减压浓縮滤液, 得到标题产物 5-(4- 3,3-二甲 基 -4-羰基 -2,3,4,5-四氢吡啶并 [3,2-b][l,4]氧氮杂环庚 -7-基氨基 )-5-氟嘧啶 -2-基氨 基) -2-甲基苯基磺酰胺 4(35 mg, 淡黄色固体), 产率: 47.9 %。
MS m/z (ESI): 488.2 [M+l]
1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO) δ 9.51 (s, 1H), 9.40 (s, 1H), 9.09 (s, 1H), 8.13 (dd, 1H), 7.90 (dd, 1H), 7.70(d, 1H), 7.43 (d, 1H), 7.43 (s, 1H), 7.26 (s, 2H), 7.20 (d, 1H), 4.04 (s, 2H), 2.50 (s, 3H), 1.20 (s, 6H)。 实施例 5
7-(5-氟 -2-(3,4,5-三甲氧基苯基氨基)嘧啶 -4-基氨基 )-3,3-二甲基 -2,3-二氢苯并 [b][l,4]
2_羟基 -5-硝基苯氨基甲酸叔丁酯
将 2-氨基 -4-硝基苯酚 5a(2 g, 13 mmol)和二碳酸二叔丁酯 (3.40 g, 15.60 mmol) 溶解于 30 mL乙醇中, 加入胍盐酸盐 (186 mg, 1.98 mmol), 加热至 37°C, 搅拌反 应 12小时。 减压浓縮反应液, 用硅胶柱色谱法以洗脱剂体系 A纯化所得残余物,
得到标题产物 2-羟基 -5-硝基苯氨基甲酸叔丁酯 5b(2.70 g, 黄色固体), 产率: 81.8
%。
MS m/z (ESI): 253.1 [M-l]
第二步
3-(2- (叔丁氧基羰基氨基 )-4-硝基苯氧基) -2,2-二甲基丙酸甲酯 将 2-羟基 -5-硝基苯氨基甲酸叔丁酯 5bC500 mg, 2 mmol), 3-羟基 -2,2-二甲基 丙酸甲酯 ld(271 mg, 2.20 mmol)和三苯基膦 (630 mg, 2.40 mmol)溶解于 20 mL二 氧六环中, 滴加入偶氮二甲酸二异丙酯 (0.5 mL, 2.40 mmol), 升温至 70°C, 搅拌 反应 12小时。减压浓縮反应液,用硅胶柱色谱法以洗脱剂体系 B纯化所得残余物, 得到标题产物 3-(2- (叔丁氧基羰基氨基 )-4-硝基苯氧基) -2,2-二甲基丙酸甲酯 5c(580 mg, 黄色固体), 产率: 78.7 %。
MS m/z (ESI): 367.1 [M-l]
第三步
3-(2-氨基 -4-硝基苯氧基) -2,2-二甲基丙酸甲酯 将 3-(2- (叔丁氧基羰基氨基 )-4-硝基苯氧基) -2,2-二甲基丙酸甲酯 5c(580 mg,
1.57 mmol)溶解于 20 mL二氯甲烷中, 加入三氟乙酸 (1.2 mL, 15.70 mmol), 升温 至 25 °C, 搅拌反应 3小时。 减压浓縮反应液, 加入 20 mL乙酸乙酯, 用饱和碳酸 氢钠溶液 (20 mLx2), 无水硫酸钠干燥, 过滤, 减压浓縮滤液, 得到粗品标题产物 3-(2-氨基 -4-硝基苯氧基) -2,2-二甲基丙酸甲酯 5d(421 mg, 黄色固体), 产物不经纯 化直接进行下一步反应。
MS m/z (ESI): 269.1 [M+l]
第四步
3,3-二甲基 -7-硝基 -2,3-二氢苯并 [b][l,4]氧氮杂环庚 -4(5H 酮 将粗品 3-(2-氨基 -4-硝基苯氧基) -2,2-二甲基丙酸甲酯 5d(420 mg, 1.57 mmol) 溶于 10 mL二甲亚砜中, 加入氢化钠 (75 mg, 1.88 mmol), 升温至 25 °C, 搅拌反应 12小时。 加入 20 mL冰水, 过滤, 用水洗涤 (20 mLx2), 烘干, 得到粗品标题产物 3,3-二甲基 -7-硝基 -2,3-二氢苯并 [b][l,4]氧氮杂环庚 -4C5H)-酮 5eC370 mg, 类白色固 体), 产物不经纯化直接进行下一步反应。
MS m/z (ESI): 237.1 [M+l]
第五步
7-氨基 -3,3-二甲基 -2,3-二氢苯并 [b][l,4]氧氮杂环庚 -4(5H 酮 将粗品 3,3-二甲基 -7-硝基 -2,3-二氢苯并 [b][l,4]氧氮杂环庚 -4(5H 酮 5φ70 mg, 1.57 mmol)溶于 30 mL甲醇和乙酸乙酯 (V/V = 1 : 1)混合溶剂中,加入钯 /碳 (180 mg, 10 %),搅拌反应 3小时。过滤,减压浓縮滤液,得到粗品标题产物 7-氨基 -3,3- 二甲基 -2,3-二氢苯并 [b][l,4]氧氮杂环庚 -4C5H)-酮 5fC370 mg,类白色固体),产物不 经纯化直接进行下一步反应。
MS m/z (ESI): 207.2 [M+l]
第六步
氯 -5-氟嘧啶 -4-基氨基 )-3,3-二甲基 -2,3-二氢苯并 [b][l,4]氧氮杂环庚 -4(5H 酮 将粗品 7-氨基 -3,3-二甲基 -2,3-二氢苯并 [b][l,4]氧氮杂环庚 -4(5H 酮 5f(320 mg, 1.55 mmol)禾卩 2,6-二氯 -5-氟 -嘧啶 (285 mg, 17 mmol)溶解于 10 mL甲醇和水 (V/V = 1 : 1)混合溶剂中, 升温至 75 V, 搅拌反应 12小时。 冷却至室温, 过滤, 用正己 烷洗涤 (20 mLx3), 烘干滤饼, 得到粗品标题产物 7-(2-氯 -5-氟嘧啶 -4-基氨基 )-3,3- 二甲基 -2,3-二氢苯并 [b][l,4]氧氮杂环庚 -4C5H)-酮 5gC320 mg, 灰色固体), 产物不 经纯化直接进行下一步反应。
MS m/z (ESI): 337.1 [M+l]
第七步
7-(5-氟 -2-(3,4,5-三甲氧基苯基氨基)嘧啶 -4-基氨基 )-3,3-二甲基 -2,3-二氢苯并 [b][l,4] 氧氮杂环庚 -4(5H 酮
将粗品 7-P-氯 -5-氟嘧啶 -4-基氨基 )-3,3-二甲基 -2,3-二氢苯并 [b][l,4]氧氮杂环 庚 -4(5H 酮 5g(50 mg, 0.15 mmol)和 3,4,5-三甲氧基苯胺 (41 mg, 0.23 mmol)溶解 于 1 mL乙醇中, 加入 1滴浓盐酸, 160°C微波反应 1小时。 减压浓縮反应液, 用 薄层色谱法以展开剂体系 A纯化所得残余物, 得到标题产物 7-(5-氟 -2-(3,4,5-三甲 氧基苯基氨基)嘧啶 -4-基氨基 )-3,3-二甲基 -2,3-二氢苯并 [b][l,4]氧氮杂环庚 -4(5H 酮 5(30 mg, 白色固体), 产率: 41.4 %。
MS m/z (ESI): 484.3 [M+l]
1H NMR (400 MHz, CDC13) δ 8.20 (s, 1H), 7.99 (s, 1H), 7.77 (s, 1H), 7.20 (s, 1H), 7.05 (d, 1H), 6.94 (d, 1H), 6.90 (s, 2H), 6.73 (s, 1H), 3.96 (s, 2H), 3.82 (s, 3H), 3.79(s, 6H),
实施例 6
N-(3-(4-(3,3-二甲基 -4-羰基 -2,3,4,5-四氢吡啶并 [3,2-b][l,4]氧氮杂环庚 -7-基氨基) - 氟嘧啶 -2-基氨基 )-5-甲基苯基)环丙基甲酰胺
第一步
ΛΚ3-氨基 -5-甲基苯基)环丙基甲酰胺
将 5-甲苯 -i,3-二氨基 6a(244 mg, 2 mmol,采用公知的方法"专利 CN1272308C" 制备而得)溶解于 10 mL二氯甲烷中, 加入三乙胺 (0.3 mL, 2 mmol)降温至 0°C, 加 入 10 mL环丙基甲酰氯 (210 mg, 2 mmol)的二氯甲烷溶液, 缓慢升至室温, 搅拌反 应 12小时。 加入 10 mL水, 分液, 有机相用水洗涤 (10 mLx l), 无水硫酸镁干燥, 减压浓縮滤液, 用硅胶柱色谱法以洗脱剂体系 B纯化所得残余物, 得到标题产物 ΛΚ3-氨基 -5-甲基苯基)环丙基甲酰胺 6b(160 mg, 黄色固体), 产率: 42.0 %。
MS m/z (ESI): 191.2 [M+l]
第二步
N-(3-(4-(3,3-二甲基 -4-羰基 -2,3,4,5-四氢吡啶并 [3,2-b][l,4]氧氮杂环庚 -7-基氨基 )-5- 氟嘧啶 -2-基氨基 )-5-甲基苯基)环丙基甲酰胺 将 7-0氯 -5-氟 -嘧啶 -4-基氨基 )-3,3-二甲基 -2,3-二氢吡啶并 [3,2-b][l,4]氧氮杂 环庚 -4(5H 酮 lh(50 mg, 0.15 mmol)和 N-(3-氨基 -5-甲基苯基)环丙基甲酰胺 6b(42 mg, 0.22 mmol)溶解于 2 mL异丙醇中, 加入 1滴三氟乙酸, 150°C微波反应 1小 时。 减压浓縮反应液, 用薄层色谱法以展开剂体系 A纯化所得残余物, 得到标题 产物 N-(3-(4-(3,3-二甲基 -4-羰基 -2,3,4,5-四氢吡啶并 [3,2-b][l,4]氧氮杂环庚 -7-基氨 基) -5-氟嘧啶 -2-基氨基 )-5-甲基苯基)环丙基甲酰胺 6(50 mg, 淡黄色固体), 产率: 68.5 %。
MS m/z (ESI): 492.3 [M+l]
1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO) δ 10.00 (s, 1H), 9.40 (s, 1H), 9.23 (s, 1H), 8.95 (d, 1H), 8.12 (dd, 1H), 7.78 (d, 1H), 7.59 (s, 1H), 7.37 (t, 1H), 7.19 (s, 1H), 7.03 (s, 1H), 4.01 (d, 2H), 2.19 (s, 3H), 1.86-1.69 (m, 1H), 1.32-1.08 (m, 6H), 0.85-0.62 (m, 4H)。 实施例 7
N-(3-(4-(3,3-二甲基 -4-羰基 -2,3,4,5-四氢吡啶并 [3,2-b][l,4]氧氮杂环庚 -7-基氨基 )-5- 氟嘧啶 -2-基氨基 )-5-甲基苯基)乙酰胺
将 7-0氯 -5-氟 -嘧啶 -4-基氨基 )-3,3-二甲基 -2,3-二氢吡啶并 [3,2-b][l,4]氧氮杂 环庚 -4(5H)-酮 lh(50 mg,0.15 mmol)和 N-(3-氨基 -5-甲基苯基)乙酰胺 7a(42 mg, 0.22 mmol,采用公知的方法"文献 Tetrahedron Letters, 49(10), 1660-1664; 2008"制备而得)
溶解于 1 mL异丙醇中, 加入 1滴三氟乙酸, 150°C微波反应 1小时。 减压浓縮反 应液, 用薄层色谱法以展开剂体系 A纯化所得残余物, 得到标题产物 N-(3-(4-(3,3- 二甲基 -4-羰基 -2,3,4,5-四氢吡啶并 [3,2-b][l,4]氧氮杂环庚 -7-基氨基 )-5-氟嘧啶 -2-基 氨基) -5-甲基苯基)乙酰胺 7(40 mg, 淡黄色固体), 产率: 57.1 %。
MS m/z (ESI): 466.3 [M+l]
1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO) δ 9.73 (s, 1H), 9.41 (s, 1H), 9.30-9.14 (m, 1H), 9.03 (s, 1H), 8.14 (d, 1H), 7.78 (d, 1H), 7.57 (s, 1H), 7.36 (d, 1H), 7.22 (s, 1H), 7.01 (s, 1H), 4.03 (s, 2H), 2.20 (s, 3H), 2.05-1.91 (m, 3H), 1.21 (d, 6H)。 实施例 8
7-(5-氯 -2-(3,4,5-三甲氧基苯基氨基)嘧啶 -4-基氨基 )-3,3-二甲基 -2,3-二氢吡啶并
-b][l,4]氧氮杂环庚 -4(5H 酮
第一步
7-(2,5-二氯 -嘧啶 -4-基氨基 )-3,3-二甲基 -2,3-二氢吡啶并 [3,2-b][l,4]氧氮杂环庚
-4(5H 酮
将粗品 7-氨基 -3,3-二甲基 -2,3-二氢吡啶并 [3,2-b][l,4]氧氮杂环庚 -4(5H 酮 lg(100 mg, 0.48 mmol)和 2,5,6-三氯 -嘧啶 8a(106 mg, 0.58 mmol)溶解于 4 mL甲醇 和水 (V/V = 1 : 1)混合溶剂中, 升温至 70°C, 搅拌反应 12小时。冷却至室温, 过滤, 用正己烷洗涤 (20 mLx3) , 再用正己烷和乙酸乙酯 (V/V = 2: 1)混合溶剂洗涤 (10 mLx3), 烘干滤饼, 得到粗品标题产物 7-(2,5-二氯 -嘧啶 -4-基氨基 )-3,3-二甲基 -2,3- 二氢吡啶并 [3,2-b][l,4]氧氮杂环庚 -4(5H 酮 8b(90 mg, 白色固体), 产物不经纯化 直接进行下一步反应。
MS m/z (ESI): 354.1 [M+l]
第二步
7-(5-氯 -2-(3,4,5-三甲氧基苯基氨基)嘧啶 -4-基氨基 )-3,3-二甲基 -2,3-二氢吡啶并
[3,2-b][l,4]氧氮杂环庚 -4(5H 酮
将粗品 7-(2,5-二氯 -嘧啶 -4-基氨基 )-3,3-二甲基 -2,3-二氢吡啶并 [3,2-b][l,4]氧氮 杂环庚 -4(5H 酮 8b(90 mg, 0.25 mmol)和 3,4,5-三甲氧基苯胺 (70 mg, 0.38 mmol)
溶解于 2 mL异丙醇中, 加入 1滴三氟乙酸, 150°C微波反应 1小时。 减压浓縮反 应液, 加入 5 mL乙酸乙酯, 过滤, 用乙酸乙酯洗涤 (10 mLx3), 减压浓縮滤液, 得到标题产物 7-(5-氯 -2-C3,4,5-三甲氧基苯基氨基)嘧啶 -4-基氨基 )-3,3-二甲基 -2,3- 二氢吡啶并 [3,2-b][l,4]氧氮杂环庚 -4(5H 酮 8(80 mg, 白色固体 产率: 62.9 %。 MS m/z (ESI): 501.3 [M+l]
1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO) δ 9.75 (s, 1H), 9.34 (s, 1H), 8.22 (s, 1H), 8.13 (s, 1H), 7.83 (s, 1H), 7.37 (d, 1H), 7.02 (s, 2H), 4.04 (s, 2H), 3.70 (t, 9H), 1.23-1.12 (m, 6H)。 实施例 9
2-(3-(4-(3,3-二甲基 -4-羰基 -2,3,4,5-四氢吡啶并 [3,2-b][l,4]氧氮杂环庚 -7-基氨 基 -5-氟嘧啶 -2-基氨基 )-5-甲基苯氧基) 甲基乙酰胺
第三步
3-羟基 -5-甲基苯基氨基甲酸叔丁酯
将 3-羟基 -5-甲基苯胺 9a(1.23 g, 10 mmol)和二碳酸二叔丁酯 (2.38 g, 11 mmol) 溶解于 10 mL四氢呋喃中, 升温至 60°C, 搅拌反应 3小时, 降温至 25 °C, 搅拌反 应 12小时。 减压浓縮反应液, 加入 30 mL乙酸乙酯, 依次用硫酸氢钾 (5 mLx2), 水 (5 mLx l), 饱和食盐水洗涤 (5 mLx l), 无水硫酸镁干燥, 过滤, 减压浓縮滤液, 得到粗品标题产物 3-羟基 -5-甲基苯基氨基甲酸叔丁酯 9b(2.60 g, 紫色粘稠物), 产 物不经纯化直接进行下一步反应。
MS m/z (ESI): 222.1 [M-l]
第二步
3-甲 ¾-5-(2-(甲氨基) -2-羰基乙氧基)苯基氨基甲酸叔丁酯
将粗品 3-羟基 -5-甲基苯基氨基甲酸叔丁酯 9b(1.30 g, 5 mmol), 2-溴 甲基 乙酰胺 C830 mg, 5.50 mmol), 碳酸钾 (1.38 g, 10 mmol)溶解于 20 mL丙酮中, 回流 搅拌反应 2小时, 降温至 50°C, 搅拌反应 12小时。 过滤, 减压浓縮滤液, 用硅胶
柱色谱法以洗脱剂体系 B纯化所得残余物, 得到标题产物 3-甲基 -5-(2- (甲氨基) -2- 羰基乙氧基)苯基氨基甲酸叔丁酯 9c(1.10 g, 红色固体), 产率: 74.8 %。
MS m/z (ESI): 223.2 [M+l]
第三步
2-(3-氨基 -5-甲基苯氧基) -N-甲基乙酰胺
将 3-甲基 -5-(2- (甲氨基) -2-羰基乙氧基)苯基氨基甲酸叔丁酯 9c(600 mg, 2 mmol)溶解于 5 mL二氯甲烷中, 加入三氟乙酸 (2 mL, 3 mmol), 搅拌反应 2小时。 减压浓縮反应液, 加入 30 mL乙酸乙酯, 饱和碳酸氢钠溶液洗涤 (10 mLx2), 无水 硫酸镁干燥,过滤,减压浓縮滤液,得到粗品标题产物 2-(3-氨基 -5-甲基苯氧基) 甲基乙酰胺 9d(400 mg, 红色固体), 产物不经纯化直接进行下一步反应。
MS m/z (ESI): 195.1 [M+l]
第四步
2-(3-(4-(3,3-二甲基 -4-羰基 -2,3,4,5-四氢吡啶并 [3,2-b][l,4]氧氮杂环庚 -7-基氨 基) -5-氟嘧啶 -2-基氨基 )-5-甲基苯氧基) 甲基乙酰胺 将 7-0氯 -5-氟 -嘧啶 -4-基氨基 )-3,3-二甲基 -2,3-二氢吡啶并 [3,2-b][l,4]氧氮杂 环庚 -4(5H)-酮 lh(34 mg, 0.10 mmol)和粗品 2-(3-氨基 -5-甲基苯氧基) 甲基乙酰 胺 9d(20 mg, 0.10 mmol)溶解于 1 mL异丙醇中, 加入 1滴三氟乙酸, 150°C微波 反应 1小时。 减压浓縮反应液, 用薄层色谱法以展开剂体系 A纯化所得残余物, 得到标题产物 2-(3-(4-(3,3-二甲基-4-羰基-2,3,4,5-四氢吡啶并[3,2- [1,4]氧氮杂环 庚 -7-基氨基 )-5-氟嘧啶 -2-基氨基 )-5-甲基苯氧基) 甲基乙酰胺 9(20 mg, 淡黄色固 体), 产率: 40.0 %。
MS m/z (ESI): 496.3 [M+l]
1H NMR (400 MHz, CDC13) δ 9.45(s, 1H), 9.36(s, 1H), 9.27(s, 1H), 8.18(d, 1H), 7.96(d 1H), 7.69(d, 1H), 7.42(d, 1H), 7.11(s, 2H), 6.37(s, 1H), 4.35(s, 2H), 4.03(s, 2H), 2.65(d, 3H), 2.20(s, 3H), 1.19(s, 6H)。 实施例 10
dN- H4-(3,3-二甲基 -4-羰基 -2,3,4,5-四氢吡啶并 [3,2-b][l,4]氧氮杂环庚 -7- 基氨基 )-5- -2-基氨基 )-5-甲基苯基) -2-羟基丙酰胺
第一步
3-氨基 -5-甲基苯基氨基甲酸叔丁酯
将 5-甲苯 -1,3-二氨基 6a(500 mg, 4.10 mmol)和三乙胺 (0.6 mL, 4.10 mmol)溶 解于 15 mL甲醇中, 降温至 0°C,加入 10 mL二碳酸二叔丁酯 (900 mg, 4.10 mmol) 的甲醇溶液, 搅拌反应 2小时。减压浓縮反应液, 用硅胶柱色谱法以洗脱剂体系 B 纯化所得残余物, 得到标题产物 3-氨基 -5-甲基苯基氨基甲酸叔丁酯 10a(560 mg, 黄色固体), 产率: 61.5 %。
MS m/z (ESI): 223.2 [M+l]
第二步
2-羟基丙酸 ( -1-(3- (叔丁氧基羰基氨基 )-5-甲基苯基氨基 )-1-羰基丙烷 -2-基酯 将 3-氨基 -5-甲基苯基氨基甲酸叔丁酯 10a(100 mg, 0.45 mmol), ( -2-羟基- 丙酸 (49 mg, 0.54 mmol), 双 (2-氧代 -3-恶唑烷基)次磷酰氯 (138 mg, 0.54 mmol)和 三乙胺 (0.1 mL, 0.68 mmol)溶解于 5 mL二氯甲烷中, 升温至 30°C, 搅拌反应 12 小时。 加入 15 mL二氯甲烷, 用水洗涤 C10 mIX3), 无水硫酸镁干燥, 过滤, 减压 浓縮滤液,得到粗品标题产物 2-羟基丙酸 ( -1-(3- (叔丁氧基羰基氨基 )-5-甲基苯基 氨基) -1-羰基丙烷 -2-基酯 10b(132 mg, 白色固体), 产物不经纯化直接进行下一步 反应。
MS m/z (ESI): 365.1 [M-l]
第三步
( -3-(2-羟基丙酰胺基 )-5-甲基苯基氨基甲酸叔丁酯
将粗品 2-羟基丙酸 ( -1-(3- (叔丁氧基羰基氨基 )-5-甲基苯基氨基 )-1-羰基丙浣 -2-基酯 10bC165 mg, 0.45 mmol)溶解于 5 mL甲醇中, 加入 0.5 M氢氧化钠溶液, 搅拌反应 2小时。 减压浓縮反应液, 加入 10 mL水, 用乙酸乙酯萃取 (20 mLx3), 合并有机相, 无水硫酸镁干燥, 过滤, 减压浓縮滤液, 用硅胶柱色谱法以洗脱剂 体系 B纯化所得残余物, 得到标题产物 ( -3-(2-羟基丙酰胺基 )-5-甲基苯基氨基甲 酸叔丁酯 10cC90 mg, 白色固体), 产率: 68.2 %。
MS m/z (ESI): 293.2 [M-l]
第四步
)-ΛΚ3-氨基 -5-甲基苯基) -2-羟基丙酰胺
将 羟基丙酰胺基 )-5-甲基苯基氨基甲酸叔丁酯 10c(90 mg, 0.30 mmol)
溶解于 4 mL二氯甲烷中, 加入三氟乙酸 (0.2 mL, 0.30 mmol), 搅拌反应 4小时。 加入 10 mL二氯甲烷, 再加入 10 mL饱和碳酸钠溶液, 分液, 水相用乙酸乙酯萃 取 (20 mLx3), 合并有机相, 无水硫酸镁干燥, 过滤, 减压浓縮滤液, 得到粗品标 题产物 ( - N-(3-氨基 -5-甲基苯基) -2-羟基丙酰胺 10d(50 mg, 棕色油状物), 产率: 5 86.2 %。
MS m/z (ESI): 195.2 [M+l]
第五步
( -4-羰基 -2,3,4,5-四氢吡啶并 [3,2-b][l,4]氧氮杂环庚 -7-基 氨基) -5-氟嘧啶 -2-基氨基 )-5-甲基苯基) -2-羟基丙酰胺
10 将 7-(2-氯 -5-氟 -嘧啶 -4-基氨基 )-3,3-二甲基 -2,3-二氢吡啶并 [3,2-b][l,4]氧氮杂 环庚 -4(5H)-酮 lh(50 mg, 0.15 mmol)和 ( -N-(3-氨基 -5-甲基苯基) -2-羟基丙酰胺 10d(44 mg, 0.23 mmol)溶解于 2 mL异丙醇中, 加入 1滴三氟乙酸, 180°C微波反 应 1小时。 减压浓縮反应液, 用薄层色谱法以展开剂体系 A纯化所得残余物, 得 到标题产物 dN- H4-(3,3-二甲基 -4-羰基 -2,3,4,5-四氢吡啶并 [3,2-b][l,4]氧氮杂环
15 庚 -7-基氨基 )-5-氟嘧啶 -2-基氨基 )-5-甲基苯基) -2-羟基丙酰胺 10(40 mg, 淡黄色固 体), 产率: 53.8 %。
MS m/z (ESI): 496.3 [M+l]
1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO) δ 9.47 (s, 1H), 9.34 (s, 1H), 9.24 (s, 1H), 9.10 (s, 1H), 8.15 (d, 1H), 7.80 (d, 1H), 7.67 (s, 1H), 7.37 (d, 1H), 7.25 (s, 1H), 7.09 (s, 1H), 5.69 (d, 20 1H), 4.03 (s, 2H), 2.22 (s, 3H), 2.11 (s, 1H), 1.37-1.28 (m, 3H), 1.20 (s, 6H)。 实施例 11
N- H4-(3,3-二甲基 -4-羰基 -2,3,4,5-四氢吡啶并 [3,2-b][l,4]氧氮杂环庚 -7-基氨 基) -5- -2-基氨基 5-甲基苯基 2-羟基乙酰胺
厶 J
第一步
3-(2-羟基乙酰胺基 )-5-甲基苯基氨基甲酸叔丁酉
将 3-氨基 -5-甲基苯基氨基甲酸叔丁酯 10a(100 mg, 0.45 mmol), 2-羟基 -乙酸 (34 mg, 0.45 mmol), 1-乙基 -3-(3-二甲胺丙基)碳二亚胺盐酸盐 (86 mg, 0.45 mmol) 禾口 1-羟基苯并三唑 (61 mg, 0.45 mmol)溶解于 5 mL四氢呋喃中, 加入 Ν,Ν-二异丙 基乙胺 (0.2 mL, 0.90 mmol), 升温至 30°C, 搅拌反应 12小时。 加入 15 mL水, 水 相用乙酸乙酯萃取 (20 mLx3), 合并有机相, 无水硫酸镁干燥, 过滤, 减压浓縮滤 液, 用硅胶柱色谱法以洗脱剂体系 B纯化所得残余物, 得到标题产物 3-(2-羟基乙 酰胺基 )-5-甲基苯基氨基甲酸叔丁酯 lla(45 mg, 白色固体), 产率: 35.7 %。
MS m/z (ESI): 279.1 [M-l]
第二步
N-(3-氨基 -5-甲基苯基) -2-羟基乙酰胺
将 3-(2-羟基乙酰胺基 )-5-甲基苯基氨基甲酸叔丁酯 lla(45 mg, 0.16 mmol)溶 解于 2 mL二氯甲烷中, 加入三氟乙酸 (0.1 mL, 1.6 mmol), 搅拌反应 4小时。 加 入 10 mL二氯甲烷, 再加入 10 mL饱和碳酸钠溶液, 分液, 水相用乙酸乙酯萃取 (20 mLx3), 合并有机相, 无水硫酸镁干燥, 过滤, 减压浓縮滤液, 得到粗品标题 产物 ΛΚ3-氨基 -5-甲基苯基) -2-羟基乙酰胺 llb(29 mg, 棕色油状物), 产率: 86.2 %。
MS m/z (ESI): 181.1 [M+l]
第三步
N- H4-(3,3-二甲基 -4-羰基 -2,3,4,5-四氢吡啶并 [3,2-b][l,4]氧氮杂环庚 -7-基氨 基) -5-氟嘧啶 -2-基氨基 5-甲基苯基 2-羟基乙酰胺 将 7-0氯 -5-氟 -嘧啶 -4-基氨基 )-3,3-二甲基 -2,3-二氢吡啶并 [3,2-b][l,4]氧氮杂 环庚 -4(5H)-酮 lh(50 mg,0.15 mmol)和 N-(3-氨基 -5-甲基苯基) -2-羟基乙酰胺 llb(27 mg, 0.15 mmol)溶解于 2 mL异丙醇中, 加入 1滴三氟乙酸, 180°C微波反应 1小 时。 减压浓縮反应液, 用薄层色谱法以展开剂体系 A纯化所得残余物, 得到标题 产物 N-(3-(4-(3,3-二甲基 -4-羰基 -2,3,4,5-四氢吡啶并 [3,2-b][l,4]氧氮杂环庚 -7-基氨 基) -5-氟嘧啶 -2-基氨基 )-5-甲基苯基) -2-羟基乙酰胺 11(30 mg, 白色固体), 产率: 41.7 %。
MS m/z (ESI): 482.3 [M+l]
1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO) δ 9.44 (s, 1H), 9.37 (s, 1H), 9.25 (s, 1H), 9.08 (s, 1H), 8.15 (d, 1H), 7.79 (d, 1H), 7.66 (s, 1H), 7.38 (d, 1H), 7.27 (s, 1H), 7.07 (s, 1H), 4.04 (s, 2H), 3.97 (d, 2H), 2.22 (s, 3H), 1.20 (s, 6H)。 实施例 12
N-(3-(4-(3,3-二甲基 -4-羰基 -2,3,4,5-四氢吡啶并 [3,2-b][l,4]氧氮杂环庚 -7-基氨基) - 氟嘧啶 -2-基氨基 )-5-甲基苯基)丙酰胺
第一步
N-(3-氨基 -5-甲基苯基)丙酰胺
将 5-甲苯 -1,3-二氨基 6a(122 mg, 1 mmol)和三乙胺 (202 mg, 2 mmol)溶解于
10 mL二氯甲烷中, 降温至 0°C, 加入 1 mL丙酰氯 (88 mg, 0.95 mmol)的二氯甲浣 溶液, 缓慢升至室温, 搅拌反应 2小时。 加入 20 mL水, 分液, 有机相用水洗漆 (lO mLx l), 无水硫酸镁干燥, 减压浓縮滤液, 用薄层色谱法以展开剂体系 A纯化 所得残余物,得到标题产物 N-(3-氨基 -5-甲基苯基)丙酰胺 12a(80 mg,棕色油状物), 产率: 44.9 %。
MS m/z (ESI): 179.1 [M+l]
第二步
N-(3-(4-(3,3-二甲基 -4-羰基 -2,3,4,5-四氢吡啶并 [3,2-b][l,4]氧氮杂环庚 -7-基氨基 )-5- 氟嘧啶 -2-基氨基 )-5-甲基苯基)丙酰胺
将 7-(2-氯 -5-氟 -嘧啶 -4-基氨基 )-3,3-二甲基 -2,3-二氢吡啶并 [3,2-b][l,4]氧氮杂 环庚 -4(5H)-酮 lh(50 mg, 0.15 mmol)和 N-(3-氨基 -5-甲基苯基)丙酰胺 12a(27 mg, 0.15 mmol)溶解于 1 mL异丙醇中, 加入 1滴三氟乙酸, 180°C微波反应 1.5小时。 减压浓縮反应液, 用薄层色谱法以展开剂体系 A纯化所得残余物, 得到标题产物 N-(3-(4-(3,3-二甲基 -4-羰基 -2,3,4,5-四氢吡啶并 [3,2-b][l,4]氧氮杂环庚 -7-基氨基 )-5- 氟嘧啶 -2-基氨基 )-5-甲基苯基)丙酰胺 12(20 mg, 白色固体), 产率: 27.8 %。
MS m/z (ESI): 480.3 [M+l]
1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO) δ 9.66 (s, 1H), 9.44 (s, 1H), 9.22 (s, 1H), 9.07 (s, 1H), 8.14 (d, 1H), 7.80 (d, 1H), 7.60 (s, 1H), 7.35 (d, 1H), 7.20 (s, 1H), 7.04 (s, 1H), 4.03 (s, 2H), 2.37-2.24 (m, 2H), 2.21 (s, 3H), 1.19 (d, 6H), 1.07 (t, 3H)。 实施例 13
将 7-(2,5-二氯 -嘧啶 -4-基氨基 )-3,3-二甲基 -2,3-二氢吡啶并 [3,2-b][l,4]氧氮杂环 庚 -4(5H 酮 8b(106 mg, 0.30 mmol)禾 B N-(3-氨基 -5-甲基苯基)乙酰胺 7a(58 mg, 0.33 mmol)溶解于 2 mL异丙醇中, 加入 1滴三氟乙酸, 150°C微波反应 1小时。减压浓 縮反应液, 用薄层色谱法以展开剂体系 A 纯化所得残余物, 得到标题产物 N-(3-(4-(3,3-二甲基 -4-羰基 -2,3,4,5-四氢吡啶并 [3,2-b][l,4]氧氮杂环庚 -7-基氨基 )-5- 氯嘧啶 -2-基氨基 )-5-甲基苯基)乙酰胺 13(60 mg, 白色固体), 产率: 41.7%。
MS m/z (ESI): 482.3 [M+l]
1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO- ) δ 9.76 (s, 2H), 9.44 (s, 1H), 8.21 (s, 1H), 8.08 (s, 1H), 7.83-7.85 (d, 1H), 7.56 (s, 1H), 7.34-7.36(d, 1H), 7.20 (s, 1H),7.03 (s, 1H), 4.02(s, 2H), 2.20 (s, 3H), 2.01 (s, 3H), 1.13 (s, 6H)。 测试例:
生物学评价
以下结合测试例进一步描述解释本发明, 但这些测试例并非意味着限制本发 明的范围。 测试例 1、 本发明化合物对 Syk激酶的活性抑制的测定
以下所述的体外激酶实验可测定受试化合物对 Syk激酶 (Invitrogen, PV3857) 的抑制活性。 用 Invitrogen公司试剂盒 Z'-LYTE® Kinase Assay Kit- Tyrosine 2 Peptide (Invitrogen, PV3191 ) 对 Syk抑制剂进行体外活性检测。 按试剂盒使用说 明,配置相应浓度的酶缓冲液(50 mM HEPES PH7.5, 0.01% BRIJ-35, 10mM MgCl2, 4 mM MnCl2, 1 mM EGTA, 2 mMDTT), 酶 /底物肽段溶液, ATP溶液和完全磷酸 化底物肽段,轻轻混合均匀;用蒸馏水配制 4 X浓度的待测化合物溶液,混合均匀。
将配置好的酶 /底物肽段溶液和完全磷酸化底物肽段 5 μ 加入 384孔板, 然 后在实验组中加入 2.5 ATP溶液及 2.5uL化合物溶液, 在完全抑制对照组中加 入 2.5uL酶缓冲液及 2.5 μL相应浓度 DMSO溶液, 在无抑制对照组中加入 2.5 μL ATP溶液及 2.5 μL相应浓度 DMSO溶液, 在完全磷酸化底物对照组中加入 2.5 μL 酶缓冲液及 2.5 μ 相应浓度 DMSO溶液; 贴好封板贴在振荡器上振荡 30秒使各 溶液混合均匀, 室温孵育 1小时。
按使用说明将显影液按相应比例配制显影试剂, 混合均匀后加入反应孔各 5 μL, 贴好封板贴在振荡器上振荡 30秒使各溶液混合均匀, 室温孵育 1小时。 每孔 加入 5 终止液, 混合均匀后, 用 400 nm激发在 445 nm和 520 nm处读荧光。
本发明化合物的生物化学活性通过以上的试验进行测定, 测得的 IC5。值见下 表 1。
表 1 本发明化合物对 Syk激酶的活性抑制的 IC5o
以下所述的体外细胞实验可测定受试化合物对 SU-DHL-6 免疫性细胞增殖的 抑制活性。
1、 材料
(1) RPMI-1640: RPMI-1640培养基 (Hyclone , Cat# SH30809.01B , Lot#
NWC0381) ;
(2) FBS: 小牛血清 (GIBCO, Lot# 8172881) ;
(3) P/S(Pen Strep): 链霉素 (GIBCO15140, Lot# 451034) ;
(5) PBS(Phosphate-buffered saline): 磷酸盐缓冲液, PH7.2, 常规配制。
2、 方法
SU-DHL-6细胞 (ATCC, 货号 CRL-2959™) 培养在 RPMI-1640培养基中 (添 加 10% FBS, 100 units/ml P/S), 用 PBS洗三遍重新悬浮于 RPMI-1640(添力口 2% FBS, 100 units/ml P/S)培养基中, 密度为 2.5 X 105细胞 /ml。 于 96孔板中每孔加入 90 μ1。 将药物配置成 20 mM的储存液, 用 100% DMSO (二甲基亚砜)梯度稀释成 200 X浓 度梯度, 再用 RPMI-1640(添力口 2% FBS, 100 units/ml P/S)培养基稀释 20倍 (以此保 证各培养体系中 DMSO浓度均为 0.5%)。 每孔加入 10 μΐ药物, 轻轻振荡混匀, 对照
组和空白组只含 100 μΐ RPMI-1640(添力口 2% FBS, 100 units/ml P/S),放置 37°C、 5% C02培养箱中培养, 72小时后由 ATPlite™试剂盒 (PerkinElmer, Cat# 6016947) 检测。
本发明化合物的生物化学活性通过以上的试验进行测定, 测得的 IC5Q值见下 表 2。
表 2 本发明化合物对 SU-DHL-6细胞的增殖活性抑制的 IC:
1、 摘要
以大鼠为受试动物, 应用 LC/MS/MS法测定了大鼠灌胃给予实施例 1化合物、 实施例 5化合物、 实施例 6化合物、 实施例 7化合物、 实施例 8化合物和实施例 12化 合物后不同时刻血浆中的药物浓度。 研究本发明的化合物在大鼠体内的药代动力 学行为, 评价其药动学特征。
2、 试验方案
2.1 试验药品
实施例 1化合物、 实施例 5化合物、 实施例 6化合物、 实施例 7化合物、 实施例 8 化合物和实施例 12化合物。
2.2 试验动物
健康成年 SD大鼠 24只, 雌雄各半, 平均分成 6组, 每组 4只, 购自上海西普尔- 必凯实验动物有限公司, 动物生产许可证号: SCXK (沪 )2008-0016。
2.3 药物配制
称取适量样品, 加入 0.5% CMC-Na, 超声制成 0.5 mg/ml混悬液。
2.4 给药
SD大鼠 24只,雌雄各半,平均分成 6组,禁食一夜后分别灌胃给药,剂量为 10.0 mg/kg, 给药体积 10 ml/kg。
3、 操作
大鼠灌胃给药实施例 1化合物、 实施例 5化合物、 实施例 6化合物、 实施例 7 化合物、 实施例 8化合物和实施例 12化合物, 于给药前及给药后 0.5, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0, 6.0, 8.0, 11.0, 24.0 小时采血 0.1 ml, 置于肝素化试管中, 3500 rpm离心 5 min 分离血浆, 于 20°C保存。 给药后 2 小时进食。
用 LC/MS/MS法测定不同浓度的化合物灌胃给药后大鼠血浆中的待测化合物 含量。 方法的线性范围均为 1.00〜2000 ng/ml; 血浆样品经甲醇沉淀蛋白处理后进 行分析。
4、 药代动力学参数结果
本发明化合物的药代动力学参数如下:
结论: 本发明化合物的药代吸收良好, 具有明显的药代动力学优势。
Claims
1、 一种通式( I )所示的化合物或其互变异构体、 内消旋体、 外消旋体、 对映 异构体、 非对映异构 、 及其混合物形式、 及其可药用的盐:
( I )
其巾:
E选自 S、 0或 C;
Z为 C(R5R6);
环 A, 环 B为芳基或杂芳基;
R1选自氢原子、 卤素、 羟基、 氰基、 硝基、 烷基、 烷氧基、 烯基、 块基、 环 烷基、 -C(0)NR7R8、 -OR9、 -C(0)OR9、 芳基或杂芳基;
R2、 R3 或 R4各自独立地选自氢原子、 卤素、 氰基、 硝基、 羟基、 烷基、 烷氧 基、环烷基、杂环基、芳基、杂芳基、 -NR7R8、 -C(0)NR7R8、 -NHS(0)mR9、 -OS(0)mR9、 -S(0)m NR7R8、 -NHC(0)R9、 -OR9、 -C(0)R9、 -OC(0)R9或 -C(0)OR9, 其中所述的 烷基、 烷氧基、 环烷基、 杂环基、 芳基或杂芳基各自独立地任选进一步被一个或 多个选自羟基、卤素、烷基、环烷基、杂环基、芳基、杂芳基、 -NR7R8、 -C(O) NR7R8、 -S(0)mR9、 -C(0)R9、 -OC(0)R9或 -C(0)OR9的取代基所取代;
或者, R2和 R3形成环烷基或杂环基, 其中所述的杂环基内含有一个或多个选 g N、 0或 S(0)m的杂原子, 并且所述杂环基任选进一步被一个或多个选自烷基、 卤素、氰基、环烷基、杂环基、芳基、杂芳基、 -NR7R8、 -C(0)NR7R8、 -NHS(0)mR9、 -S(0)mR9、 -NHC(0)R9、 -OR9、 -C(0)R9、 -OC(0)R9或 -C(0)OR9的取代基所取代;
R5或 R6各自独立地选自氢原子、 卤素、 烷基、 环烷基、 羟基、 烷氧基、 芳基 或杂芳基, 其中所述的烷基、 环烷基、 芳基或杂芳基各自独立地任选进一步被一 个或多个选自羟基、 卤素、 烷基、 环烷基、 杂环基、 芳基、 杂芳基、 -NR7R8、 -C(0)NR7R8、 -NHS(0)mR9、 -S(0)mR9、 -NHC(0)R9、 -OR9、 -C(0)R9、 -OC(0)R9 或 -C(0)OR9的取代基所取代;
或者, R5和 R6与其相连接的 C原子一起形成一个环烷基或杂环基, 所述的环 烷基或杂环基各自独立地任选进一步被一个或多个选自羟基、 卤素、 烷基、 烷氧 基、 环烷基或杂环基的取代基所取代;
R7或 R8各自独立地选自氢原子、 烷基、 环烷基、 杂环基、 芳基或杂芳基, 所 述的烷基、 环烷基、 杂环基、 芳基或杂芳基各自独立地任选进一步被一个或多个 选自羟基、 ^素、 烷基、 烷氧基、 环烷基或杂环基的取代基所取代;
或者, R7和 R8与其相连接的 N原子一起形成一个 3〜8元杂环基, 其中所述 3〜8元杂环基内含有一个或多个 N、 0或 3(0)„1杂原子, 并且所述 3〜8元杂环基 任选进一步被一个或多个选自烷基、 卤素、 羟基、 氨基、 氰基、 烷氧基、 环烷基、 杂环基、 芳基或杂芳基的取代基所取代;
R9选自氢原子、 烷基、 氨基、 环烷基、 杂环基、 芳基或杂芳基, 所述的烷基、 环烷基、 杂环基、 芳基或杂芳基各自独立地任选进一步被一个或多个选自烷基、 卤素、 羟基、 氨基、 氰基、 烷氧基、 环烷基、 杂环基、 芳基或杂芳基的取代基所 取代; 和
m为 0、 1或 2。
2、 根据权利要求 1所述的通式(I )所示的化合物或其互变异构体、 内消旋体、 外消旋体、 对映异构体、 非对映异构体、 及其混合物形式、 及其可药用的盐, 其 中 E为氧原子。
3、 根据权利要求 1所述的通式( I )所示的化合物或其互变异构体、 内消旋体、 外消旋体、 对映异构体、 非对映异构体、 及其混合物形式、 及其可药用的盐, 其 中环 B为芳基。
4、 根据权利要求 1所述的通式(I )所示的化合物或其互变异构体、 内消旋体、 外消旋体、 对映异构体、 非对映异构体、 及其混合物形式、 及其可药用的盐, 其 中 R5或 R6各自独立地选自卤素或烷基。
5、 根据权利要求 1所述的通式(I )所示的化合物或其互变异构体、 内消旋体、 外消旋体、 对映异构体、 非对映异构体、 及其混合物形式、 及其可药用的盐, 其 中 R5和 R6—起形成环烷基。
6、 根据权利要求 1所述的通式(I )所示的化合物或其互变异构体、 内消旋体、 外消旋体、 对映异构体、 非对映异构体、 及其混合物形式、 及其可药用的盐, 其 中 R1为卤素。
7、 根据权利要求 1所述的通式(I )所示的化合物或其互变异构体、 内消旋体、 外消旋体、 对映异构体、 非对映异构体、 及其混合物形式、 及其可药用的盐, 其 中 R2、R3 或 R4各自独立地选自氢原子、卤素、烷基、烷氧基、杂环基、 -S(0)mNR7R8、 -NHC(0)R9或 -OR9, 其中所述的烷基、 烷氧基或杂环基各自独立地任选进一步被 一个或多个选自羟基、 卤素、 烷基、 环烷基、 杂环基或 -C(O) NR7R8的取代基所取 代;
R7或 R8各自独立地选自氢原子或烷基;
R9选自氢原子、 烷基、 氨基、 环烷基或杂环基, 所述的烷基、 环烷基或杂环 基各自独立地任选进一步被一个或多个选自烷基、 卤素、 羟基或氨基的取代基所 取代; 和
m为 0、 1或 2。
8、根据权利要求 1〜7任意一项所述的通式( I )所示的化合物或其互变异构体、 内消旋体、 外消旋体、 对映异构体、 非对映异构体、 及其混合物形式、 及其可药 用的盐, 其为通式 (II) 所示 内消旋体和外消旋体、对映 异构体、 非对映异构 及其混合物形式、 及其可药用的盐:
(I I)
其中: Y为氮或碳原子; E、 Z、 环^ Ι^〜Ι 4的定义如权利要求 1中所述。
9、根据权利要求 1〜8任意一项所述的通式( I )所示的化合物或其互变异构体、 内消旋体、 外消旋体、 对映异构体、 非对映异构体、 及其混合物形式、 及其可药 用的盐, 其为通式 (III) 所示的化合物或其互变异构体、 内消旋体和外消旋体、 对 映异构体、 非对映异 盐:
其中: E、 Z、 环8、 Ri〜R4的定义如权利要求 1中所述。
10、 根据权利要求 1〜8任意一项所述的通式( I )所示的化合物或其互变异构 体、 内消旋体、 外消旋体、 对映异构体、 非对映异构体、 及其混合物形式、 及其 可药用的盐, 其为通式 (IV) 所示的化合物或其互变异构体、 内消旋体和外消旋体、 对映异构体、 非对映 的盐:
(IV)
其中: E、 Z、 环8、 Ri〜R4的定义如权利要求 1中所述。
11、 根据权利要求 i~io任意一项所述的通式( I )所示的化合物或其互变异构 体、 内消旋体、 外消旋体、 对映异构体、 非对映异构体、 及其混合物形式、 及其 可药
12、 一种通式 (I-A)所示
(l-A )
E选自 S、 O或 C;
Z为 C(R5R6):
环 A为芳基或杂芳基;
R1选自氢原子、 卤素、 羟基、 氰基、 硝基、 烷基、 烷氧基、 烯基、 块基、 环 浣基、 -C(0)NR7R8、 -OR9、 -C(0)OR9、 芳基或杂芳基;
R5或 R6各自独立地选自氢原子、 卤素、 烷基、 环烷基、 羟基、 烷氧基、 芳基 或杂芳基, 其中所述的烷基、 环烷基、 芳基或杂芳基各自独立地任选进一步被一 个或多个选自羟基、 卤素、 烷基、 环烷基、 杂环基、 芳基、 杂芳基、 -NR7R8、 -C(0)NR7R8、 -N -S(0)mR9、 -NHC(0)R9、 -OR9、 -C(0)R9、 -OC(0)R9 或 -C(0)OR9的取代基所取代;
或者, R5和 R6与其相连接的 C原子一起形成一个环烷基或杂环基, 所述的环 浣基或杂环基各自独立地任选进一步被一个或多个选自羟基、 卤素、 烷基、 烷氧 基、 环烷基或杂环基的取代基所取代; 和
X为离去基团, 优选为卤素。
13、 根据权利要求 12所述的通式( I-A )所示的化合物及其可药用的盐, 其为 通式 (ΠΙ-Α)及 (IV-A) 所示的化合物及其可药用的盐:
(I N-A) (IV-A)
其中: E、 Z、 X、 R1的定义如权利要求 12中所述。
14、 一种制备根据权利要求 1所述的通式( I )所示的化合物或其互变异构体、 内消旋体、 外消旋体、 对映异构体、 非对映异构体、 及其混合物形式、 及其可药 用的
通式 (I-A)化合物和通式 (I-B)化合物在溶剂中, 酸性条件下加热进行反应, 得 到通式(I )化合物;
其中: X为离去基团, 优选为卤素; 其中 E、 Z、 环 、 环8、 1^〜1 4的定义 如权利要求 1中所述。
15、一种药物组合物, 所述药物组合物含有治疗有效量的根据权利要求 1〜11 任意一项所述的通式(I )所示的化合物或其互变异构体、 内消旋体、 外消旋体、 对 映异构体、 非对映异构体、 及其混合物形式、 及其可药用的盐及药学上可接受的 载体。
16、 根据权利要求 1〜11任意一项所述的通式( I )所示的化合物或其互变异构 体、 内消旋体、 外消旋体、 对映异构体、 非对映异构体、 及其混合物形式、 及其 可药用的盐, 或根据权利要求 15所述的药物组合物在制备蛋白激酶抑制剂, 优选 为 Syk蛋白激酶抑制剂中的用途。
17、 根据权利要求 1〜11任意一项所述的通式( I )所示的化合物或其互变异构 体、 内消旋体、 外消旋体、 对映异构体、 非对映异构体、 及其混合物形式、 及其 可药用的盐, 或根据权利要求 15所述的药物组合物在制备治疗与蛋白激酶有关的 疾病, 优选为与 Syk蛋白激酶有关的疾病的药物中的用途。
18、 根据权利要求 17所述的用途, 其中所述的与 Syk蛋白激酶有关的疾病选 自恶性淋巴瘤、 自身免疫性疾病、 结疤、 过敏性疾病、 与组织破坏有关的疾病和 与组织发炎有关的疾病;
所述的自身免疫性疾病优选为全身红斑狼疮、 风湿性关节炎、 舍格伦综合症、 赖特尔综合症、 多肌炎-皮肌炎、 身体组织硬化、 多动脉炎、 多样三角化、 大类天 疤疮和银屑病;
所述的过敏性疾病优选为结膜炎、 鼻炎、 哮喘、 特应性皮肤炎和食物过敏。
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201380004071.2A CN103958526B (zh) | 2012-06-20 | 2013-06-06 | 嘧啶二胺类衍生物、其制备方法及其在医药上的应用 |
Applications Claiming Priority (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201210205641.1 | 2012-06-20 | ||
| CN201210205641 | 2012-06-20 | ||
| CN201310208038.3 | 2013-05-30 | ||
| CN201310208038 | 2013-05-30 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2013189241A1 true WO2013189241A1 (zh) | 2013-12-27 |
Family
ID=49768098
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/CN2013/076837 WO2013189241A1 (zh) | 2012-06-20 | 2013-06-06 | 嘧啶二胺类衍生物、其制备方法及其在医药上的应用 |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN103958526B (zh) |
| TW (1) | TW201400490A (zh) |
| WO (1) | WO2013189241A1 (zh) |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN107108586A (zh) * | 2014-09-29 | 2017-08-29 | 山东轩竹医药科技有限公司 | 多环类间变性淋巴瘤激酶抑制剂 |
| US9815850B2 (en) | 2016-02-05 | 2017-11-14 | Denali Therapeutics Inc. | Compounds, compositions and methods |
| US11072618B2 (en) | 2016-12-09 | 2021-07-27 | Denali Therapeutics Inc. | Compounds, compositions and methods |
| US11999750B2 (en) | 2022-01-12 | 2024-06-04 | Denali Therapeutics Inc. | Crystalline forms of (S)-5-benzyl-N-(5-methyl-4-oxo-2,3,4,5-tetrahydropyrido [3,2-B][1,4]oxazepin-3-yl)-4H-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxamide |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2007120980A2 (en) * | 2006-02-17 | 2007-10-25 | Rigel Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | 2,4-pyrimidinediamine compounds for treating or preventing autoimmune diseases |
| WO2007124221A1 (en) * | 2006-04-18 | 2007-11-01 | Rigel Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Methods of treating cell proliferative disorders by using pyrimidinediamine compounds |
| WO2008088303A1 (en) * | 2005-12-06 | 2008-07-24 | Rigel, Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Pyrimidine-2,4-diamines and their uses |
| WO2011009075A2 (en) * | 2009-07-17 | 2011-01-20 | Rigel Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Deuterated 2, 4-pyrimidinediamine compounds and prodrugs thereof and their uses |
| WO2011063241A1 (en) * | 2009-11-20 | 2011-05-26 | Rigel Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | 2,4-pyrimidinediamine compounds and prodrugs thereof and their uses |
| WO2011130390A1 (en) * | 2010-04-13 | 2011-10-20 | Rigel Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | 2, 4-pyrimidinediamine compounds and prodrugs thereof and their uses |
-
2013
- 2013-06-06 CN CN201380004071.2A patent/CN103958526B/zh not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2013-06-06 WO PCT/CN2013/076837 patent/WO2013189241A1/zh active Application Filing
- 2013-06-19 TW TW102121692A patent/TW201400490A/zh unknown
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2008088303A1 (en) * | 2005-12-06 | 2008-07-24 | Rigel, Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Pyrimidine-2,4-diamines and their uses |
| WO2007120980A2 (en) * | 2006-02-17 | 2007-10-25 | Rigel Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | 2,4-pyrimidinediamine compounds for treating or preventing autoimmune diseases |
| WO2007124221A1 (en) * | 2006-04-18 | 2007-11-01 | Rigel Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Methods of treating cell proliferative disorders by using pyrimidinediamine compounds |
| WO2011009075A2 (en) * | 2009-07-17 | 2011-01-20 | Rigel Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Deuterated 2, 4-pyrimidinediamine compounds and prodrugs thereof and their uses |
| WO2011063241A1 (en) * | 2009-11-20 | 2011-05-26 | Rigel Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | 2,4-pyrimidinediamine compounds and prodrugs thereof and their uses |
| WO2011130390A1 (en) * | 2010-04-13 | 2011-10-20 | Rigel Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | 2, 4-pyrimidinediamine compounds and prodrugs thereof and their uses |
Cited By (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN107108586A (zh) * | 2014-09-29 | 2017-08-29 | 山东轩竹医药科技有限公司 | 多环类间变性淋巴瘤激酶抑制剂 |
| US9815850B2 (en) | 2016-02-05 | 2017-11-14 | Denali Therapeutics Inc. | Compounds, compositions and methods |
| US9896458B2 (en) | 2016-02-05 | 2018-02-20 | Denali Therapeutics Inc. | Compounds, compositions and methods |
| US10131676B2 (en) | 2016-02-05 | 2018-11-20 | Denali Therapeutics Inc. | Compounds, compositions and methods |
| US10604535B2 (en) | 2016-02-05 | 2020-03-31 | Denali Therapeutics Inc. | Compounds, compositions and methods |
| US11072618B2 (en) | 2016-12-09 | 2021-07-27 | Denali Therapeutics Inc. | Compounds, compositions and methods |
| US11999750B2 (en) | 2022-01-12 | 2024-06-04 | Denali Therapeutics Inc. | Crystalline forms of (S)-5-benzyl-N-(5-methyl-4-oxo-2,3,4,5-tetrahydropyrido [3,2-B][1,4]oxazepin-3-yl)-4H-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxamide |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN103958526B (zh) | 2015-09-09 |
| TW201400490A (zh) | 2014-01-01 |
| CN103958526A (zh) | 2014-07-30 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6828229B2 (ja) | ベンゾフラン誘導体、その製造方法および医薬におけるその使用 | |
| JP7299837B2 (ja) | 化合物、組成物、および使用方法 | |
| TWI662026B (zh) | 吡啶酮類衍生物、其製備方法及其在醫藥上的應用 | |
| CN112351778B (zh) | 稠合三环杂环类化合物及其治疗用途 | |
| JP6801159B2 (ja) | イミダゾイソインドール誘導体、その製造方法及びその医薬用途 | |
| WO2020108590A1 (zh) | 嘧啶并五元氮杂环类衍生物、其制备方法及其在医药上的应用 | |
| WO2020259679A1 (zh) | 嘧啶并五元氮杂环类衍生物、其制备方法及其在医药上的应用 | |
| BR122023006150B1 (pt) | Compostos inibidores de hpk1, seu uso, e composição farmacêutica que os compreende | |
| JP2022542669A (ja) | Irak4キナーゼ阻害剤及びその調製方法 | |
| TW201910328A (zh) | 雜環化合物 | |
| WO2016155545A1 (zh) | 含氨磺酰基的1,2,5-噁二唑类衍生物、其制备方法及其在医药上的应用 | |
| JP2016535772A (ja) | 自己免疫疾患治療のためのピラゾール | |
| WO2020158762A1 (ja) | 複素環化合物 | |
| CN106187915A (zh) | 具有alk与egfr双重活性的抑制剂及其制备方法和应用 | |
| JP7148709B2 (ja) | バニン阻害剤としてのヘテロ芳香族化合物 | |
| JP6805172B2 (ja) | ヒストンデアセチラーゼ阻害薬及び組成物並びにそれらの使用の方法 | |
| JP2023520595A (ja) | ピラゾロピリダジノン化合物、その医薬組成物及びその用途 | |
| WO2019062328A1 (zh) | 苯胺取代的1,2-二氢吡咯并[3,4-c]吡啶/嘧啶-3-酮衍生物及用途 | |
| WO2013189241A1 (zh) | 嘧啶二胺类衍生物、其制备方法及其在医药上的应用 | |
| WO2022117090A1 (zh) | 一种多环化合物及其制备方法和用途 | |
| CN112574212B (zh) | 一种嘧啶并五元氮杂环类衍生物、其制备方法及其在医药上的应用 | |
| JP2020519647A (ja) | グループii代謝型グルタミン酸受容体のアロステリックモジュレーターとしての置換複素環式化合物 | |
| WO2022237890A1 (zh) | 氮杂卓类稠环化合物及其医药用途 | |
| CN113912608B (zh) | 嘧啶并嘧啶酮类衍生物、其制备方法及其在医药上的应用 | |
| WO2023109540A1 (zh) | 具有akt激酶抑制活性的杂环化合物及其制备方法和医药用途 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 13807411 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 13807411 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |