WO2013046219A1 - Pharmaceutical composition comprising lecithin and process for preparing thereof - Google Patents
Pharmaceutical composition comprising lecithin and process for preparing thereof Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2013046219A1 WO2013046219A1 PCT/IN2012/000425 IN2012000425W WO2013046219A1 WO 2013046219 A1 WO2013046219 A1 WO 2013046219A1 IN 2012000425 W IN2012000425 W IN 2012000425W WO 2013046219 A1 WO2013046219 A1 WO 2013046219A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- lecithin
- composition
- pharmaceutical composition
- composition according
- present
- Prior art date
Links
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K9/00—Medicinal preparations characterised by special physical form
- A61K9/10—Dispersions; Emulsions
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/66—Phosphorus compounds
- A61K31/683—Diesters of a phosphorus acid with two hydroxy compounds, e.g. phosphatidylinositols
- A61K31/685—Diesters of a phosphorus acid with two hydroxy compounds, e.g. phosphatidylinositols one of the hydroxy compounds having nitrogen atoms, e.g. phosphatidylserine, lecithin
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K9/00—Medicinal preparations characterised by special physical form
- A61K9/10—Dispersions; Emulsions
- A61K9/107—Emulsions ; Emulsion preconcentrates; Micelles
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising lecithin and process for preparing thereof.
- the present invention relates to a liquid pharmaceutical composition, comprising lecithin and process for preparing thereof, wherein the said composition is stable.
- Lecithin is defined chemically as a mixture of the diglycerides of stearic, palmitic, and oleic acids, linked to the choline ester of phosphoric acid (eg, soybean lecithin contains 4% stearic, 1 1.7% palmitic, 9.8% oleic acids, along with others). Lecithins also contain phosphorous and nitrogenous (eg, choline) compounds. Physical properties of lecithin can vary depending upon acid value. It is a waxy mass at acid value 20 and a thick pourable fluid at acid value 30. The color is white when freshly made but turns yellow to brown in air. It is an edible and digestible surfactant and emulsifier.
- lecithin has been a popular treatment for high cholesterol although there is surprisingly little evidence that it works. More recently, lecithin has been proposed as a remedy for various psychological and neurological diseases, such as Tourette's syndrome, Alzheimer's disease, and bipolar disorder.
- Lecithin contains a substance called phosphatidylcholine that is presumed to be responsible for its medicinal effects.
- Phosphatidylcholine is a major part of the membranes surrounding our cells. However, when this substance is consumed, it is broken down into the nutrient choline rather than being carried directly to cell membranes.
- Choline acts like folate, TMG (trimethylglycine), and SAMe (S- adenosylmethionine) to promote methylation. It is also used to make acetylcholine, a nerve chemical essential for proper brain function. It is commonly used to help restoration of the liver functions in a number of disorders, including acute and chronic inflammatory liver disease due to viruses, protozoa and toxin.
- 4252793A relates to a method of preparing an injectable preparation of lecithin including 1 to 10% lecithin comprises the steps of separately preparing a lecithin fraction including lecithin and a non-hydrous liquid, separately preparing an aqueous fraction containing a surfactant, and then combining the two fractions and manually shaking for twenty to thirty seconds.
- Beneficial medicaments are added to either the lecithin fraction or aqueous fraction prior to combining of the two.
- U.S. Patent No. 5288734A relates to a stable parenteral solution of 2-phenyl- 1 ,2- benzisoselenazol-3(2H)-one (Ebselen) comprising additionally one or several phospholipids and, possibly, one or several auxiliary agents, wherein the weight proportion of 2-phenyl- l ,2-benzisoselenazol-3(2H)-one and the phospholipid or phospholipids like soybean lecithin or egg lecithin in the solution being between 1 :2500 to 1 : 15.
- the invention is further related to a process for producing such solutions and their use in the preparation of drug preparations of Ebselen.
- 20090017120A 1 relates to a lecithin organogel composition used to deliver pharmaceutical products transdermally as well as a method for producing the lecithin organogel composition, which may contain up to 40% additive ingredients. Particularly, it relates to include lecithin organogel compositions which provide high penetrating power, which are ready-to-use, which have improved stability, which have a high uptake capacity for active drugs, and which do not grow mold if the gel becomes contaminated.
- the lipid- based, self-emulsifying drug delivery system showed potential in improving oral bioavailability of poorly water soluble drugs. They developed alcohol-free SEDDS formulated with lecithin, linkers, and food-grade additives.
- the linker system is comprised of sorbitan monooleate, a lipophilic linker, decaglyceryi caprylate/caprate and PEG-6-caprylic/capric glycerides which are hydrophilic linkers.
- Ethyl caprate was the carrier oil for lipophilic nutraceuticals beta-sitosterol and beta-carotene.
- Microemulsion preconcentrates were formulated which could be incorporated into pharmaceutical or other applications.
- the diluted preconcentrates form self-emulsified drug delivery systems with drop sizes ranging from 100-250 nm.
- lecithin intends to provide pharmaceutical composition comprising lecithin, wherein lecithin can be used as therapeutic agent, particularly as hepato-protective agent.
- Disorders of hepatic function are commonly seen in medical practice. Hepatitis, especially viral hepatitis, is quite prevalent in various parts of the world, including India. In a study conducted by Mall ML and his colleagues, the overall seroprevalence rate of hepatitis virus A was 65.9%, in five major cities in India. Kumaran and Ananthan, while studying infectious hepatitis in urban India, observed that, children are more susceptible to hepatitis than elders.
- hepatitis disorders like viral hepatitis are quite common in various age groups in India. Treatment of hepatitis remains largely supportive, and is centered on providing adequate rest, maintenance of caloric intake, prevention of complication etc. Under this circumstance, hepatoprotective offers an attractive and logical measure towards restoration of the deranged function of the liver. Essential phospholipids, in the form of lecithin, could be a promising agent in this respect. However, there remains a need to provide an appropriate pharmaceutical dosage form such as liquid comprising hepatoprotective such as lecithin, particularly considering various age groups and the widespread of disease.
- a pharmaceutical composition comprising lecithin can be prepared, wherein the said pharmaceutical composition is liquid dosage form. Additionally, the present pharmaceutical composition is easy to manufacture and physically & chemically stable.
- the present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising lecithin, wherein the said pharmaceutical composition is in the form of liquid dosage form.
- the present invention further relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising lecithin, wherein the lecithin is used as a therapeutic agent.
- the present invention further relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising lecithin, wherein the lecithin is used as a hepato-protective agent.
- the present invention further relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising lecithin, wherein the said pharmaceutical composition is stable.
- the present invention further relates to a stable pharmaceutical composition
- a stable pharmaceutical composition comprising lecithin, wherein the said lecithin comprises essential phospholipid (EPL) from about 10% w/w to about 90% w/w of lecithin.
- EPL essential phospholipid
- the present invention further relates to a process of preparing a pharmaceutical composition comprising lecithin having, wherein the said pharmaceutical composition is stable.
- the present invention also relates to a process of preparing a stable pharmaceutical composition comprising lecithin, wherein the said lecithin comprises EPL from about 10% w/w to about 90% w/w of lecithin.
- stable refers to physical and chemical stability of lecithin with no significant change in pH and assay value, when stored at conditions specified by ICH guidelines for stability testing for not less than 3 months.
- excipients means a component of a pharmaceutical product that is not an active ingredient for example, preservatives, solubilizers, sweeteners, flavours, colours, co-solvents and the like.
- the excipients that are useful in preparing a pharmaceutical composition are preferably safe, non-toxic and neither biologically nor otherwise undesirable, and are acceptable for pharmaceutical use.
- composition in the form of a liquid dosage form of the present ' invention may also contain other pharmaceutically acceptable excipients, such as sweeteners, buffering agents, surfactants, emulsifiers, preservatives, colors or flavours.
- other pharmaceutically acceptable excipients such as sweeteners, buffering agents, surfactants, emulsifiers, preservatives, colors or flavours.
- the surfactants or emulsifiers according to the present invention can be selected from the group consisting of ammonium lauryl sulfate, sodium lauryl sulfate , sodium laureth sulfate, sodium myreth sulfate, dioctyl sodium sulfosuccinate, sodium stearate , sodium lauryl sarcosinate, perfluorononanoate, perfluorooctanoate, cetyl trimethylammonium bromide, hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide, cetyl trimethylammonium chloride, cetylpyridinium chloride, benzalkonium chloride, benzethonium chloride, dimethyl dioctadecyl ammonium chloride, dioctadecyl dimethyl ammonium bromide, sultainescocamidopropyl hydroxysultaine, cocamidopropyl betaine, cetyl
- the surfactants or emulsifiers are present in amount from about 0.5% w/v to about 40% w/v of the composition.
- the buffering agents according to present invention can be selected from the group consisting of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, disodium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate, glycine/sodium hydroxide, sodium carbonate/sodium hydrogen carbonate, sodium tetraborate/sodium hydroxide, sodium bicarbonate/sodium hydroxide and the like.
- the sweeteners according to present invention can be selected from the group consisting of maltitol, sucrose, dextrose, fructose, glucose, glycerin, inulin, isomalt, lactitol, maltose, maltol, mannitoi, sucralose, trehalose, xylitol, propylene glycol, sorbitol, sodium saccharin, thaumatin, sodium cyclamate, sucralose and mixtures thereof and the like.
- sweetener may be present in amount from about 1 % w/v to about 85% w/v of the composition.
- compositions of present invention contain sufficient preservative to prevent microbial growth.
- the preservative according to present invention can be selected from the group consisting of sodium benzoate, sorbates, EDTA, domiphen bromide, butylparaben, propylparaben, ethylparaben, methylparaben, paraben salts and mixtures thereof and the like.
- the preservatives are present in the amount of about 0.001% w/v to about 1.5% w/v of the composition.
- the preferred preservatives are parabens in the amount of about 0.001 % w/v to about 0.5 % w/v are added.
- Optional ingredients include a coloring agent to impart a pleasant color and flavoring to impart a pleasant flavor, thus improving the organoleptic properties of the solution. Color selection can be made consistent with flavor.
- Lecithin is a phospholipid mixture of acetone insoluble phosphatides consisting mainly of phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidyl ethanolamine, phosphatidyl serine, phosphatidyl inositol combined with various other substances including fatty acids and carbohydrates.
- Lecithin is the common name for a series of related compounds called phosphatidylcholines.
- Lecithin is available in different forms such as injcetions, soft gels, tablets etc. Development of liquid lecithin, has a tremendous effect on manufacturing cost and ease of processing.
- hepatoprotective which can be supplied in an adequate dosage form for patient compliance considering the prevalence of a disease in various age groups in India.
- a pharmaceutical composition comprising lecithin can be prepared, wherein the said pharmaceutical composition is in the form of a liquid dosage form wherein lecithin is used as a therapeutic agent as a hepato-protective agent.
- the present inventors found that in order to achieve a stable oral liquid formulation containing lecithin the use of homogenizer is critical. It was also found that the speed and time of homogenization was critical i.e. at not less than 2000 rpm and not less than 10 minutes of homogenization the stable oral liquid formulation with longer shelf life was obtained below this rpm level and homogenization time, the phase separation was observed on storing for longer periods.
- the present pharmaceutical composition is easy to manufacture and physically and chemically stable.
- composition comprising lecithin, wherein the said pharmaceutical composition is in the form of liquid dosage form.
- the present invention provides a pharmaceutical composition comprising lecithin having self emulsifying drug delivery system, wherein the said pharmaceutical composition is stable.
- the present invention provides a stable oral pharmaceutical composition in the form of liquid dosage form comprising lecithin and one or more pharmaceutically acceptable excipients.
- the present invention provides a stable oral pharmaceutical composition in the form of emulsion or dispersion comprising lecithin and one or more pharmaceutically acceptable excipients.
- the present invention relates to a stable oral pharmaceutical composition comprising lecithin and one or more pharmaceutical ly acceptable excipients wherein the said lecithin comprises EPL from about 10% w/w to about 90% w/w of lecithin.
- the present invention provides a process of preparing a stable oral pharmaceutical composition comprising lecithin and one or more pharmaceutically acceptable excipients, wherein the said lecithin comprises EPL from about 10% w/w to about 90% w/w of lecithin.
- the present invention provides a process of preparing a stable oral pharmaceutical composition in the form of emulsion or dispersion comprising lecithin and one or more pharmaceutically acceptable excipients; wherein the process has following steps:
- the present invention provides a process of preparing a stable oral pharmaceutical composition in the form of emulsion or dispersion comprising lecithin and one or more pharmaceutically acceptable excipients; wherein the process has following steps:
- step a) preparing aqueous solution by adding and dissolving additives in purified water; b) adding lecithin to solution of step a) with continuous homogenization
- the present invention provides a stable oral pharmaceutical composition in the form of emulsion or dispersion comprising:
- lecithin from about 5% w/v to about 50% w/v of the composition
- lecithin from about 5% w/v to about 50 % w/v of the composition
- methyl paraben from about 0.001% w/v to about 0.25% w/v of the composition
- propyl paraben from about 0.001% w/v to about 0.25% w/v of the composition
- menthol from about 0.01 % w/v to 0.5% w/v of the composition.
- the liquid pharmaceutical composition in accordance with the present invention contain lecithin in the amount of from about 50 mg/ml to about 400 mg/ml comprising EPL from about 25 mg/ml to about 200 mg/ml i.e. from about 10% w/w to about 90% w/w of lecithin.
- the present invention provides a process to preparing a liquid pharmaceutical composition comprising lecithin, wherein the said pharmaceutical composition is stable.
- the present liquid pharmaceutical compositions can be prepared by heating vehicle water, wherein preservatives, sweeteners, surfactant and/or co-solvents are added step by step till syrup is formed. Followed by cooling and stirring well till all the materials get dissolved.
- Lecithin comprising EPL from about 10% w/w to about 90% w/w of lecithin is mixed with the bulk formed and allowed to emulsify in homogenizer followed by color and flavor addition and to make up the desired volume with water and then finally homogenize / emulsify for few minutes more.
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Dispersion Chemistry (AREA)
- Medicinal Preparation (AREA)
Abstract
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising lecithin and process for preparing thereof. The present invention particularly relates a pharmaceutical composition in the form of a liquid dosage form comprising lecithin and one or more pharmaceutically acceptable excipients wherein the lecithin is used as a hepato-protective agent.
Description
FIELD OF THE INVENTION:
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising lecithin and process for preparing thereof. Particularly, the present invention relates to a liquid pharmaceutical composition, comprising lecithin and process for preparing thereof, wherein the said composition is stable.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION:
Lecithin is defined chemically as a mixture of the diglycerides of stearic, palmitic, and oleic acids, linked to the choline ester of phosphoric acid (eg, soybean lecithin contains 4% stearic, 1 1.7% palmitic, 9.8% oleic acids, along with others). Lecithins also contain phosphorous and nitrogenous (eg, choline) compounds. Physical properties of lecithin can vary depending upon acid value. It is a waxy mass at acid value 20 and a thick pourable fluid at acid value 30. The color is white when freshly made but turns yellow to brown in air. It is an edible and digestible surfactant and emulsifier. For decades, lecithin has been a popular treatment for high cholesterol although there is surprisingly little evidence that it works. More recently, lecithin has been proposed as a remedy for various psychological and neurological diseases, such as Tourette's syndrome, Alzheimer's disease, and bipolar disorder.
Lecithin contains a substance called phosphatidylcholine that is presumed to be responsible for its medicinal effects. Phosphatidylcholine is a major part of the membranes surrounding our cells. However, when this substance is consumed, it is broken down into the nutrient choline rather than being carried directly to cell membranes. Choline acts like folate, TMG (trimethylglycine), and SAMe (S- adenosylmethionine) to promote methylation. It is also used to make acetylcholine, a nerve chemical essential for proper brain function. It is commonly used to help restoration of the liver functions in a number of disorders, including acute and chronic inflammatory liver disease due to viruses, protozoa and toxin. It is also helpful in alcoholic fibrosis, drug induced liver toxicity and hepatitis of unknown etiology. It may also be indicated for the treatment of some manic disorders. There are some evidences
that phosphatidylchloine may be useful in the management of alzheimer's disease and some other cognitive disorders. It is also useful in tardive dyskinesia. A possible future role in cancer therapy is also suggested by recent research. U.S. Patent No. 4252793A relates to a method of preparing an injectable preparation of lecithin including 1 to 10% lecithin comprises the steps of separately preparing a lecithin fraction including lecithin and a non-hydrous liquid, separately preparing an aqueous fraction containing a surfactant, and then combining the two fractions and manually shaking for twenty to thirty seconds. Beneficial medicaments are added to either the lecithin fraction or aqueous fraction prior to combining of the two.
U.S. Patent No. 5288734A relates to a stable parenteral solution of 2-phenyl- 1 ,2- benzisoselenazol-3(2H)-one (Ebselen) comprising additionally one or several phospholipids and, possibly, one or several auxiliary agents, wherein the weight proportion of 2-phenyl- l ,2-benzisoselenazol-3(2H)-one and the phospholipid or phospholipids like soybean lecithin or egg lecithin in the solution being between 1 :2500 to 1 : 15. The invention is further related to a process for producing such solutions and their use in the preparation of drug preparations of Ebselen. U.S. Patent application No. 20090017120A 1 relates to a lecithin organogel composition used to deliver pharmaceutical products transdermally as well as a method for producing the lecithin organogel composition, which may contain up to 40% additive ingredients. Particularly, it relates to include lecithin organogel compositions which provide high penetrating power, which are ready-to-use, which have improved stability, which have a high uptake capacity for active drugs, and which do not grow mold if the gel becomes contaminated.
J. Chu et al. at University of Toronto, Canada studied lecithin based self emulsifying oral delivery systems to improve the oral bioavailability of hydrophobic drugs. The lipid- based, self-emulsifying drug delivery system (SEDDS) showed potential in improving oral bioavailability of poorly water soluble drugs. They developed alcohol-free SEDDS
formulated with lecithin, linkers, and food-grade additives. The linker system is comprised of sorbitan monooleate, a lipophilic linker, decaglyceryi caprylate/caprate and PEG-6-caprylic/capric glycerides which are hydrophilic linkers. Ethyl caprate was the carrier oil for lipophilic nutraceuticals beta-sitosterol and beta-carotene. Microemulsion preconcentrates were formulated which could be incorporated into pharmaceutical or other applications. The diluted preconcentrates form self-emulsified drug delivery systems with drop sizes ranging from 100-250 nm.
None of the above cited prior arts comprising lecithin intends to provide pharmaceutical composition comprising lecithin, wherein lecithin can be used as therapeutic agent, particularly as hepato-protective agent. Disorders of hepatic function are commonly seen in medical practice. Hepatitis, especially viral hepatitis, is quite prevalent in various parts of the world, including India. In a study conducted by Mall ML and his colleagues, the overall seroprevalence rate of hepatitis virus A was 65.9%, in five major cities in India. Kumaran and Ananthan, while studying infectious hepatitis in urban India, observed that, children are more susceptible to hepatitis than elders. Thus, hepatitis disorders like viral hepatitis are quite common in various age groups in India. Treatment of hepatitis remains largely supportive, and is centered on providing adequate rest, maintenance of caloric intake, prevention of complication etc. Under this circumstance, hepatoprotective offers an attractive and logical measure towards restoration of the deranged function of the liver. Essential phospholipids, in the form of lecithin, could be a promising agent in this respect. However, there remains a need to provide an appropriate pharmaceutical dosage form such as liquid comprising hepatoprotective such as lecithin, particularly considering various age groups and the widespread of disease.
Accordingly, the inventors of the present invention have surprisingly found that a pharmaceutical composition comprising lecithin can be prepared, wherein the said pharmaceutical composition is liquid dosage form. Additionally, the present pharmaceutical composition is easy to manufacture and physically & chemically stable.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION:
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising lecithin, wherein the said pharmaceutical composition is in the form of liquid dosage form. The present invention further relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising lecithin, wherein the lecithin is used as a therapeutic agent.
The present invention further relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising lecithin, wherein the lecithin is used as a hepato-protective agent.
The present invention further relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising lecithin, wherein the said pharmaceutical composition is stable.
The present invention further relates to a stable pharmaceutical composition comprising lecithin, wherein the said lecithin comprises essential phospholipid (EPL) from about 10% w/w to about 90% w/w of lecithin.
The present invention further relates to a process of preparing a pharmaceutical composition comprising lecithin having, wherein the said pharmaceutical composition is stable.
The present invention also relates to a process of preparing a stable pharmaceutical composition comprising lecithin, wherein the said lecithin comprises EPL from about 10% w/w to about 90% w/w of lecithin.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION:
Definitions:
The term "stable" as used herein refers to physical and chemical stability of lecithin with no significant change in pH and assay value, when stored at conditions specified by ICH guidelines for stability testing for not less than 3 months.
The term "excipients" as used herein means a component of a pharmaceutical product that is not an active ingredient for example, preservatives, solubilizers, sweeteners, flavours, colours, co-solvents and the like. The excipients that are useful in preparing a pharmaceutical composition are preferably safe, non-toxic and neither biologically nor otherwise undesirable, and are acceptable for pharmaceutical use.
The pharmaceutical composition in the form of a liquid dosage form of the present ' invention may also contain other pharmaceutically acceptable excipients, such as sweeteners, buffering agents, surfactants, emulsifiers, preservatives, colors or flavours.
The surfactants or emulsifiers according to the present invention can be selected from the group consisting of ammonium lauryl sulfate, sodium lauryl sulfate , sodium laureth sulfate, sodium myreth sulfate, dioctyl sodium sulfosuccinate, sodium stearate , sodium lauryl sarcosinate, perfluorononanoate, perfluorooctanoate, cetyl trimethylammonium bromide, hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide, cetyl trimethylammonium chloride, cetylpyridinium chloride, benzalkonium chloride, benzethonium chloride, dimethyl dioctadecyl ammonium chloride, dioctadecyl dimethyl ammonium bromide, sultainescocamidopropyl hydroxysultaine, cocamidopropyl betaine, cetyl alcohol, stearyl alcohol, cetostearyl alcohol, oleyl alcohol, polyoxyethylene glycol alkyl ethers, octaethylene glycol monododecyl ether, pentaethylene glycol monododecyl ether, polyoxypropylene glycol alkyl ethers, glucoside alkyl ethers, decyl glucoside, lauryl glucoside, octyl glucoside, triton x- 100, nonoxynol-9, glyceryl laurate, polysorbate (tweens), spans, cocamide mea, cocamide dea, dodecyldimethylamine oxide, polyethoxylated tallow amine and the like.
The surfactants or emulsifiers are present in amount from about 0.5% w/v to about 40% w/v of the composition. The buffering agents according to present invention can be selected from the group consisting of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, disodium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate,
glycine/sodium hydroxide, sodium carbonate/sodium hydrogen carbonate, sodium tetraborate/sodium hydroxide, sodium bicarbonate/sodium hydroxide and the like.
The sweeteners according to present invention can be selected from the group consisting of maltitol, sucrose, dextrose, fructose, glucose, glycerin, inulin, isomalt, lactitol, maltose, maltol, mannitoi, sucralose, trehalose, xylitol, propylene glycol, sorbitol, sodium saccharin, thaumatin, sodium cyclamate, sucralose and mixtures thereof and the like.
To render the composition pleasant-tasting, sweetener may be present in amount from about 1 % w/v to about 85% w/v of the composition.
The compositions of present invention contain sufficient preservative to prevent microbial growth. The preservative according to present invention can be selected from the group consisting of sodium benzoate, sorbates, EDTA, domiphen bromide, butylparaben, propylparaben, ethylparaben, methylparaben, paraben salts and mixtures thereof and the like.
The preservatives are present in the amount of about 0.001% w/v to about 1.5% w/v of the composition. The preferred preservatives are parabens in the amount of about 0.001 % w/v to about 0.5 % w/v are added.
Optional ingredients include a coloring agent to impart a pleasant color and flavoring to impart a pleasant flavor, thus improving the organoleptic properties of the solution. Color selection can be made consistent with flavor.
Lecithin is a phospholipid mixture of acetone insoluble phosphatides consisting mainly of phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidyl ethanolamine, phosphatidyl serine, phosphatidyl inositol combined with various other substances including fatty acids and carbohydrates. Lecithin is the common name for a series of related compounds called phosphatidylcholines.
Lecithin is available in different forms such as injcetions, soft gels, tablets etc. Development of liquid lecithin, has a tremendous effect on manufacturing cost and ease of processing. Moreover, as discussed above there is a long-felt need for hepatoprotective which can be supplied in an adequate dosage form for patient compliance considering the prevalence of a disease in various age groups in India.
The inventors of the present invention have surprisingly found that a pharmaceutical composition comprising lecithin can be prepared, wherein the said pharmaceutical composition is in the form of a liquid dosage form wherein lecithin is used as a therapeutic agent as a hepato-protective agent. Further the present inventors found that in order to achieve a stable oral liquid formulation containing lecithin the use of homogenizer is critical. It was also found that the speed and time of homogenization was critical i.e. at not less than 2000 rpm and not less than 10 minutes of homogenization the stable oral liquid formulation with longer shelf life was obtained below this rpm level and homogenization time, the phase separation was observed on storing for longer periods.
Additionally, the present pharmaceutical composition is easy to manufacture and physically and chemically stable.
The various embodiments of the present invention can be assembled in several different ways:
In one embodiment of the present invention provides a pharmaceutical composition comprising lecithin, wherein the said pharmaceutical composition is in the form of liquid dosage form.
In yet another embodiment the present invention provides a pharmaceutical composition comprising lecithin having self emulsifying drug delivery system, wherein the said pharmaceutical composition is stable.
In yet another embodiment the present invention provides a stable oral pharmaceutical composition in the form of liquid dosage form comprising lecithin and one or more pharmaceutically acceptable excipients.
In yet another embodiment the present invention provides a stable oral pharmaceutical composition in the form of liquid dosage form comprising lecithin and one or more pharmaceutically acceptable excipients wherein the lecithin is used as a hepato-protective agent
In yet another embodiment the present invention provides a stable oral pharmaceutical composition in the form of emulsion or dispersion comprising lecithin and one or more pharmaceutically acceptable excipients. In yet another embodiment the present invention relates to a stable oral pharmaceutical composition comprising lecithin and one or more pharmaceutical ly acceptable excipients wherein the said lecithin comprises EPL from about 10% w/w to about 90% w/w of lecithin. In yet another embodiment of the present invention provides a process of preparing a stable oral pharmaceutical composition comprising lecithin and one or more pharmaceutically acceptable excipients, wherein the said lecithin comprises EPL from about 10% w/w to about 90% w/w of lecithin. In yet another embodiment the present invention provides a process of preparing a stable oral pharmaceutical composition in the form of emulsion or dispersion comprising lecithin and one or more pharmaceutically acceptable excipients; wherein the process has following steps:
a) preparing aqueous solution by adding and dissolving additives in purified water; b) adding lecithin to solution of step a) with continuous homogenization.
In yet another embodiment the present invention provides a process of preparing a stable oral pharmaceutical composition in the form of emulsion or dispersion comprising lecithin and one or more pharmaceutically acceptable excipients; wherein the process has following steps:
a) preparing aqueous solution by adding and dissolving additives in purified water; b) adding lecithin to solution of step a) with continuous homogenization
wherein the homogenization is carried out at a speed of not less than 2000 rpm and for not less than 10 minutes. In yet another embodiment the present invention provides a stable oral pharmaceutical composition in the form of emulsion or dispersion comprising:
a) lecithin from about 5% w/v to about 50% w/v of the composition;
b) preservative from about 0.001% w/v to about 0.5% w/v of the c'omposition;
c) surfactant from about 0.5% w/v to about 40% w/v of the composition;
d) sweetener from about 1 % w/v to about 80% of the composition
e) optionally, one or more colouring and/or flavouring agents.
In yet another embodiment the present invention provides a stable oral pharmaceutical composition in the form of emulsion or dispersion comprising:
a) lecithin from about 5% w/v to about 50 % w/v of the composition;
b) methyl paraben from about 0.001% w/v to about 0.25% w/v of the composition;
c) propyl paraben from about 0.001% w/v to about 0.25% w/v of the composition;
d) tween 80 from about 0.5% w/v to about 30% w/v of the compositi on;
e) sweetener from about 1% w/v to about 80% of the composition;
f) propylene glycol from about 5% w/v to about 30% of the composition;
g) menthol from about 0.01 % w/v to 0.5% w/v of the composition.
The liquid pharmaceutical composition, in accordance with the present invention contain lecithin in the amount of from about 50 mg/ml to about 400 mg/ml comprising EPL from about 25 mg/ml to about 200 mg/ml i.e. from about 10% w/w to about 90% w/w of lecithin.
In yet another embodiment the present invention provides a process to preparing a liquid pharmaceutical composition comprising lecithin, wherein the said pharmaceutical composition is stable. The present liquid pharmaceutical compositions can be prepared by heating vehicle water, wherein preservatives, sweeteners, surfactant and/or co-solvents are added step by step till syrup is formed. Followed by cooling and stirring well till all the materials get dissolved. Lecithin comprising EPL from about 10% w/w to about 90% w/w of lecithin is mixed with the bulk formed and allowed to emulsify in homogenizer followed by color and flavor addition and to make up the desired volume with water and then finally homogenize / emulsify for few minutes more.
The following examples are provided to enable one skilled in the art to practice the invention and are merely illustrative of the present invention. The examples should not be read as limiting the scope of the present invention.
EXAMPLES:
Example 1 Table No. 1
Procedure:
Purified water (Approx. 300 L) was heated to 70-80°C. Methyl paraben and propyl paraben were added and stirred to dissolve. Sugar was added and stirred until it gets dissolved (sugar syrup). Menthol was dissolved in propylene glycol and added to syrup. Tween 80 was added to sugar syrup with stirring. The syrup was cooled to room temperature with stirring to dissolve all the materials. Homogenizer was started at high speed. Lecithin was added to bulk and ensured complete mixing /bulk movement followed by homogenization / emulsification to form emulsion or dispersion. Color solution and flavor were added to bulk syrup. Final volume was made up with water followed by homogenization / emulsification again for 10 minutes.
Three different batches (A,B,C,) using composition as shown in Table No. I were manufactured and subjected to stability study and results obtained are presented in Table No. 4 Example 2
Table No. 2
Procedure:
Purified water was heated to 70-80°C. Methyl paraben and propyl paraben were added and stirred to dissolve. Sugar was added and stirred until it gets dissolved (sugar syrup). Menthol was dissolved in propylene glycol and added to syrup. Tween 80 was added to sugar syrup with stirring. The syrup was cooled to room temperature with stirring to dissolve all the materials. Homogenizer was started at high speed. Lecithin was added to bulk and ensured complete mixing /bulk movement followed by homogenization / emulsification to form emulsion or dispersion. Color solution and flavor were added to bulk syrup. Final volume was made up with water followed by homogenization / emulsification again for 10 minutes.
Three different batches (D,E,F,) using composition as shown in Table No. 2 were manufactured and subjected to stability study and results obtained are presented in Table No. 4
Example 3
Table No 3
Purified water was heated to 70-80°C. Methyl paraben and propyl paraben were added and stirred to dissolve. Sugar was added and stirred until it gets dissolved (sugar syrup). Menthol was dissolved in propylene glycol and added to syrup. Tween 80 was added to sugar syrup with stirring. The syrup was cooled to room temperature with stirring to dissolve all the materials. Homogenizer was started at high speed. Lecithin was added to bulk and ensured complete mixing /bulk movement followed by homogenization / emulsification to form emulsion or dispersion. Color solution and flavor were added to bulk syrup. Final volume was made up with water followed by homogenization / emulsification again for 10 minutes.
Three different batches (G,H,I) using composition as shown in Table No. 3 were manufactured and subjected to stability study and results obtained are presented in Table No. 4 .
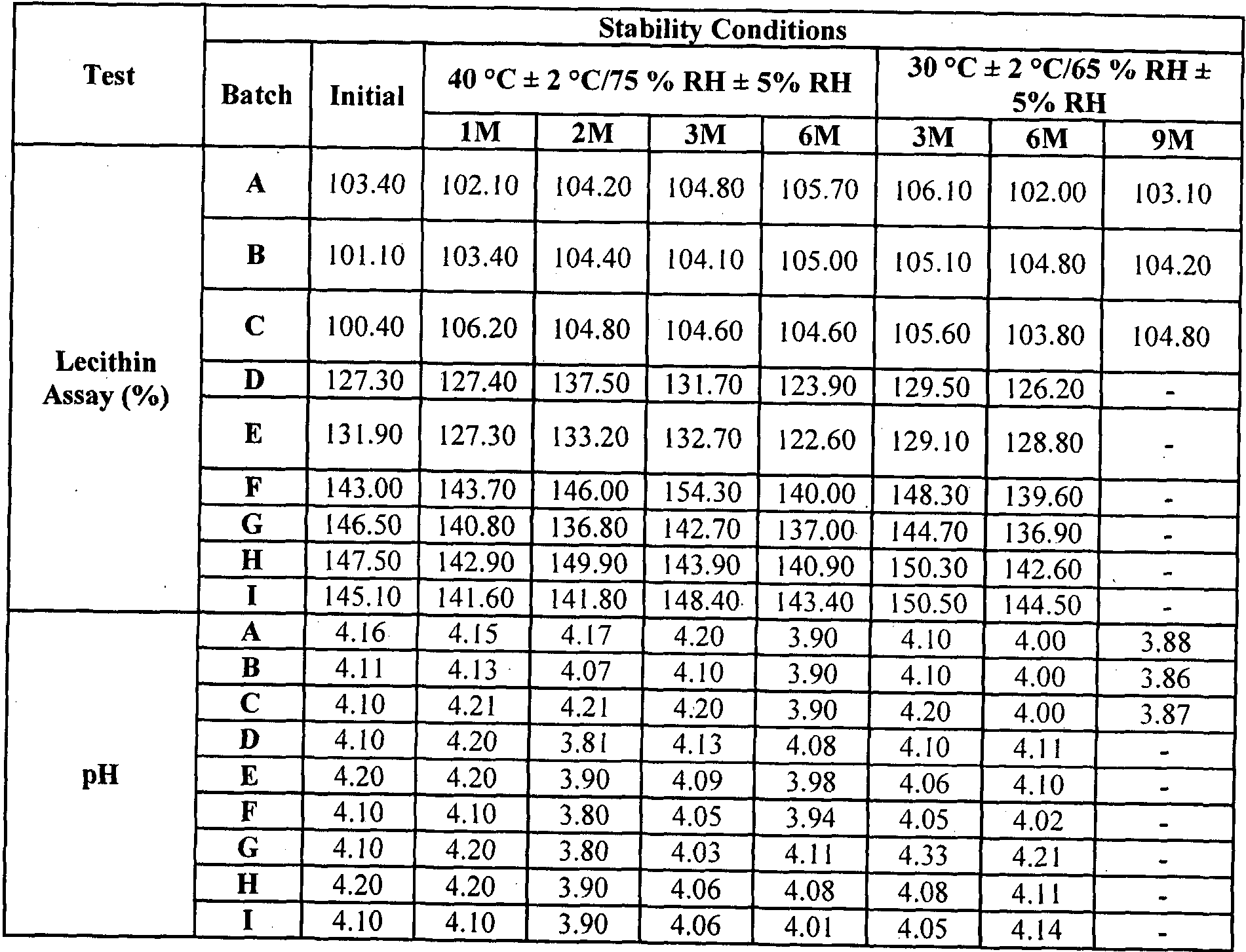
Table No. 4
RH: relative humidity
M: Month(s)
Claims
1. A stable oral pharmaceutical composition in the form of liquid dosage form comprising lecithin and one or more pharmaceutically acceptable excipients.
2. A composition according to claim 1 wherein; the lecithin is present in the amount from about 50 mg/ml to about 400 mg/ml of the composition.
3. A composition according to claim 1 wherein; the said lecithin comprises of EPL from about 10% w/w to about 90% w/w of lecithin.
4. A composition according to claim 1 wherein lecithin is used as hepato- protective agent.
.5. A composition according to claim 1 wherein the composition is prepared using a homogenizer.
6. A stable oral pharmaceutical composition in the form of emulsion or dispersion comprising lecithin and one or more pharmaceutically acceptable excipients.
7. A composition according to claim 6 wherein; the lecithin is present in the amount from about 50 mg/ml to about 400 mg/ml of the composition.
8. A composition according to claim 6 wherein; the said lecithin comprises EPL from about 10% w/w to about 90% w/w of lecithin.
9. A composition according to claim 6 wherein lecithin is used as hepato- protective agent.
10. A composition according to claim 6 wherein the composition is prepared using a homogenizer.
1 1. A stable oral pharmaceutical composition in the form of emulsion or dispersion comprising:
a) lecithin from about 5% w/v to about 50% w/v of the composition;
b) preservative from about 0.001 % w/v to about 0.5% w/v of the composition; c) surfactant from about 0.5% w/v to about 40% w/v of the composition; d) sweetener from about 1% w/v to about 80% of the composition;
e) optionally, one or more colouring and/or flavouring agents.
12. A composition according to claim 1 1 wherein; the said lecithin comprises of EPL from about 10% w/w to about 90% w/w of lecithin.
13. A composition according to claim 1 1 wherein lecithin is used as hepato- protective agent.
14. A composition according to claim 1 1 wherein the composition is prepared using a homogenizer.
15. A stable oral pharmaceutical composition in the form of emulsion or dispersion comprising:
a) lecithin from about 5% w/v to about 50 % w/v of the composition;
b) methyl paraben from about 0.001 % w/v to about 0.25% w/v of the composition;
c) propyl paraben from about 0.00 1 % w/v to about 6.25% w/v of the composition;
d) tween 80 from about 0.5% w/v to about 30% w/v of the composition; e) sweetener from about 1% w/v to about 80% of the composition;
f) propylene glycol from about 5% w/v to about 30% of the composition; g) menthol from about 0.01 % w/v to 0.5% w/v of the composition.
16. A composition according to claim 15 wherein; the said lecithin comprises of EPL from about 10% w/w to about 90% w/w of lecithin.
17. A composition according to claim 1 5 wherein lecithin is used as hepato- protective agent.
18. A composition according to claim 15 wherein the composition is prepared using a homogenizer.
19. A process of preparing a stable oral pharmaceutical composition in the form of liquid dosage form comprising lecithin and one or more pharmaceutically acceptable excipients; wherein the process has following steps:
a) preparing aqueous solution by adding and dissolving additives in purified water;
b) adding lecithin to solution of step a) with continuous homogenization.
20. A process according to claim 19 wherein the homogenization is carried out at a speed of not less than 2000 rpm and for not less than 10 minutes.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| IN1758/MUM/2011 | 2011-06-16 | ||
| IN1758MU2011 | 2011-06-16 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2013046219A1 true WO2013046219A1 (en) | 2013-04-04 |
Family
ID=47994370
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/IN2012/000425 WO2013046219A1 (en) | 2011-06-16 | 2012-06-14 | Pharmaceutical composition comprising lecithin and process for preparing thereof |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| WO (1) | WO2013046219A1 (en) |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4252793A (en) | 1979-06-18 | 1981-02-24 | American Lecithin Company | Injectable lecithin preparation |
| EP0100459A2 (en) * | 1982-07-07 | 1984-02-15 | Eisai Co., Ltd. | An aqueous liquid containing a fat-soluble substance |
| US5223285A (en) * | 1992-03-31 | 1993-06-29 | Abbott Laboratories | Nutritional product for pulmonary patients |
| US5288734A (en) | 1988-10-29 | 1994-02-22 | A. Nattermann & Cie Gmbh | Stable parenteral solution of 2-phenyl-1.2-benzisoselenazol-3(2H)-one and process for producing the same |
| US6180139B1 (en) * | 1998-12-04 | 2001-01-30 | Viva America Marketing, Inc. | Composition and method for treating nonalcoholic steatohepatitis |
| US20090017120A1 (en) | 2007-03-23 | 2009-01-15 | Humco Holding Group, Inc. | Phase stable lecithin organogel composition |
-
2012
- 2012-06-14 WO PCT/IN2012/000425 patent/WO2013046219A1/en unknown
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4252793A (en) | 1979-06-18 | 1981-02-24 | American Lecithin Company | Injectable lecithin preparation |
| EP0100459A2 (en) * | 1982-07-07 | 1984-02-15 | Eisai Co., Ltd. | An aqueous liquid containing a fat-soluble substance |
| US5288734A (en) | 1988-10-29 | 1994-02-22 | A. Nattermann & Cie Gmbh | Stable parenteral solution of 2-phenyl-1.2-benzisoselenazol-3(2H)-one and process for producing the same |
| US5223285A (en) * | 1992-03-31 | 1993-06-29 | Abbott Laboratories | Nutritional product for pulmonary patients |
| US6180139B1 (en) * | 1998-12-04 | 2001-01-30 | Viva America Marketing, Inc. | Composition and method for treating nonalcoholic steatohepatitis |
| US20090017120A1 (en) | 2007-03-23 | 2009-01-15 | Humco Holding Group, Inc. | Phase stable lecithin organogel composition |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| DAVID J. CANTY ET AL: "Lecithin and Choline in Human Health and Disease", NUTRITION REVIEWS, vol. 52, no. 10, 1 October 1994 (1994-10-01), pages 327 - 339, XP055053913, ISSN: 0029-6643, DOI: 10.1111/j.1753-4887.1994.tb01357.x * |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| ES2199338T3 (en) | PHARMACEUTICAL COMPOSITIONS IN EMULSION, CONTAINING (3'-DESOXI-3'-OXO-MEBMT) 1- (VAL) 2-CYCLOSPORIN. | |
| ES2395130T3 (en) | Method and composition for the treatment of rhinitis | |
| ES2609640T3 (en) | Intravenous rolapitant formulations | |
| TW201124425A (en) | Parenteral formulations of gemcitabine derivatives | |
| PT2508170E (en) | Liposome of irinotecan or its hydrochloride and preparation method thereof | |
| US9241922B2 (en) | Pharmaceutical solution of taxanes comprising pH regulator and preparation method thereof | |
| IE48659B1 (en) | Colloidal lipid pharmaceutical composition containing dihexanoyl lecithin | |
| US4328222A (en) | Pharmaceutical compositions for parenteral or local administration | |
| JP3202999B2 (en) | Hepatic liposome preparation | |
| JPWO2006098241A1 (en) | Pharmaceutical composition containing poorly water-soluble drug | |
| ES2274316T3 (en) | INJECTABLE ANESTHETIC COMPOSITION CONTAINING 2,6-DIISOPROPYLPENOL AND PROCEDURES. | |
| RU2571283C2 (en) | Parenteral formulations of elacytarabine derivatives | |
| US20050186230A1 (en) | Elemene compositions containing liquid oil | |
| CN113456591B (en) | Glycosyl polyether compound liposome and preparation method and medicament thereof | |
| JP6230538B2 (en) | Stable oxaliplatin-encapsulated liposome aqueous dispersion and its stabilization method | |
| WO2017097196A1 (en) | Method for preparing liposome | |
| ES2377352T3 (en) | New compositions based on taxoids | |
| WO2011113301A1 (en) | Self-emulsifying formulation of taxanes and preparation method thereof | |
| ES2510416T3 (en) | Injectable injection of a sedative hypnotic agent | |
| EP4037662A1 (en) | Liposomal cannabinoids and uses thereof | |
| WO2013046219A1 (en) | Pharmaceutical composition comprising lecithin and process for preparing thereof | |
| WO1991007973A1 (en) | Fat emulsion | |
| ES2283423T3 (en) | STRUCTURED EMULSION OF Amphotericin B. | |
| AU2019396217A1 (en) | Stable formulations of anesthetics and associated dosage forms | |
| US11331334B2 (en) | Intranasal composition of methylcobalamin |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 12806705 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |