US2821254A - Foam-plastic skiving machine - Google Patents
Foam-plastic skiving machine Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- US2821254A US2821254A US460156A US46015654A US2821254A US 2821254 A US2821254 A US 2821254A US 460156 A US460156 A US 460156A US 46015654 A US46015654 A US 46015654A US 2821254 A US2821254 A US 2821254A
- Authority
- US
- United States
- Prior art keywords
- knife
- sheet
- plastic
- foam
- machine
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B26—HAND CUTTING TOOLS; CUTTING; SEVERING
- B26D—CUTTING; DETAILS COMMON TO MACHINES FOR PERFORATING, PUNCHING, CUTTING-OUT, STAMPING-OUT OR SEVERING
- B26D3/00—Cutting work characterised by the nature of the cut made; Apparatus therefor
- B26D3/006—Cutting work characterised by the nature of the cut made; Apparatus therefor specially adapted for cutting blocs of plastic material
- B26D3/008—Cutting work characterised by the nature of the cut made; Apparatus therefor specially adapted for cutting blocs of plastic material by sliding
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B26—HAND CUTTING TOOLS; CUTTING; SEVERING
- B26D—CUTTING; DETAILS COMMON TO MACHINES FOR PERFORATING, PUNCHING, CUTTING-OUT, STAMPING-OUT OR SEVERING
- B26D3/00—Cutting work characterised by the nature of the cut made; Apparatus therefor
- B26D3/28—Splitting layers from work; Mutually separating layers by cutting
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10S—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10S83/00—Cutting
- Y10S83/929—Particular nature of work or product
- Y10S83/952—Moving work
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10T—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER US CLASSIFICATION
- Y10T83/00—Cutting
- Y10T83/02—Other than completely through work thickness
- Y10T83/0267—Splitting
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10T—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER US CLASSIFICATION
- Y10T83/00—Cutting
- Y10T83/04—Processes
- Y10T83/0524—Plural cutting steps
- Y10T83/0572—Plural cutting steps effect progressive cut
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10T—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER US CLASSIFICATION
- Y10T83/00—Cutting
- Y10T83/566—Interrelated tool actuating means and means to actuate work immobilizer
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10T—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER US CLASSIFICATION
- Y10T83/00—Cutting
- Y10T83/869—Means to drive or to guide tool
- Y10T83/887—Parallel draw-cut [e.g., translatory]
Definitions
- the main object of my present invention istoremedy such disadvantage.
- a skiver or knife having a serrated cutting edge is moved through the sheet and subjected to longitudinal oscillations with such frequency that the foamed plastic to be cut cannot resonate.
- the longitudinally oscillatable skiver is a stretched spring-steel band: of
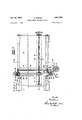
- Fig. 1 shows the machine in elevation
- Fig. 2 is a top plan view thereof
- Fig. 3 is a cross-section on the line III--III of Fig. 2,
- Fig. 4 is a horizontal section on the line IV--IV of Fig. 3, and shows, in an enlarged scale, details of the bearing and driving arrangement of the knife, and
- Figs. 5 to 7 are cross-sections on the lines VV, VI-VI and VII-VII of Fig. 4 respectively.
- the skiving machine comprises a stand which in the main is composed of corner posts 1, a lower frame 2, side sheets 3 and 4, two horizontal and parallel top box-girders 5, and bracing tubes 6 interconnecting the latter.
- a plate 7 e. g. by welding, which serves a table.
- the foamedplastic sheet 8 to be cut into foils, either is secured to said table by adhesive means or simply laid thereon.
- a screw spindle 10 is rotatably but axially immovably mounted in two bearings 9 disposed on transverse members of the stand outside of the side sheets 4. Said spindle coacts with a nut 11 which by means of lateral forked wings 12 is guided on two rails 13 secured to the sheets 4. To nut 11 are secured the ends of two steel cables 14 trained over idling discs 15 mounted on the stand. An electric motor 17 mounted on frame 2 rotates spindle 10 through a belt drive 16 and, thus, moves nut 11 and the two cables 14 in one or the other sense. Outside the girders 5 and parallel thereto are arranged guide rods 18 of which the end faces through gussets 19 are connected to said girders.
- a sleeve 20 On rod 18 is movably mounted a sleeve 20 to which is welded a horizontal plate 21.
- the opposite ends of the cables are fixed to the sleeves 20, as shown in Figs. 2 and 3.
- the sleeves 20 and the parts carried thereby are moved.
- a guide column 23 In a ring 22 welded to the latter is rigidly mounted a guide column 23.
- the two columns 23 are rigidly interconnected ontop througha horizontal transverse member 24 in which two screw spindles 25 are mounted rotatably but axially immovably.
- the spindles 25 through two bevel gears 26 are drivably connected to a shaft 27 which is rotatable in bearings 28 fixed to member 24 and on one end of which is provided a graduated disc 29 and a crank 30.
- Each of the spindles 25 coacts with a threaded bush 31 rigidly inserted in a holder 32.
- the latter is screwed to a lateral lug 33 of a sleeve 34 which is' longitudinally movable on the asso ciated column 23, as shown in- Figs. 3 and 4.
- Lugs 33 and 36 together form arigid carrier for two similar two-arm oscillating levers 37 and 37a of which the bearings are designated by 38.
- Each of' said levers comprises a piece of pipe 39' welded to one of the lugs 33, a sliding bush 40 inserted in pipe 39, a bearingpin 41 welded to said lever, a screw 42 mounted and secured in pin 41', and a disc 43 supported on the upper end face of bush 40 for taking up the small axialforces.
- the front forked ends 44' of the levers 37, 37a are provided with ahoriz-ontal slot 45 in which is inserted one or the other end of. a skiver or knife blade 46-, the latter being mounted on a hardened screw 47.
- the rear ends of the two oscillating levers are interconnected through astretching device comprising a threaded member 48', a threaded wire-receiving sleeve 49, a stretching wire 50 and a member 51.
- Lever 37a has a lug 52 to which ispivoted, on a screw 53, a bar 54 of an eccentric ring- 55.
- arms 68' are pivotally mounted in bosses 67 of the lugs 33.
- pins 69 of a loading roller 70 which is parallel to the cutting; edge of knife blade 46 and slightly in front of'the latter.
- Roller 70 serves to press downthe plastic sheet 8 onto a coating 85 oftable 7", which coating increases the friction.
- Roller 70 in an extreme case may be situated only slightly lower with respect to knife 46 than shown in the drawing, as the arms 68 then rest on member 36.
- Knife 46 is reciprocated at least 800 times per minute by motor 65 through the eccentric drive 55, 57 and lever 37a, and is made of a spring-steel band of which the longitudinal edge forming the cutting edge is serrated and ground sharply towards the underside in a manner similar to that of bread knives.
- the rear longitudinal edge of the knife moves in a guide formed on knife beam 71 of which the underside 72 is parallel to the knife underside, the spacing not exceeding the knife thickness. Such spacing corresponds to the thickness of a sheet 73 which at 75 is riveted to another horizontal sheet 74.
- the rear and top portion of said guide is formed on a solid constructional member 76 of triangular cross-section.
- stepped surfaces at the rear of member 76 are brazed the lower and upper sheets 74 and 77 respectively, of a box-like structure to the somewhat thicker sidewall sheets 78 of which are welded the lugs 36.
- Said structure at the rear is braced by a sheet-iron member 79 of U-shaped cross-section.
- Fig. 6 further shows that the knife-beam upperside 80 rises rearwardly from a front edge 81 which is spaced from knife-beam upperside 80 by one to two knife thicknesses, first only at a slight slope and then somewhat steeper.
- motor 17 is reversed or stopped through limit switches 83 (Fig. 3) secured to the stand and through cams 84 secured to the carriage.
- foils of very good surface property and minimal thickness of approximately of an inch may be cut off from foamplastic sheets up to 3% inches thick, provided that the frequency of the knife oscillations is sufficiently higher than the frequency at which the surface of sheet 8 could resonate. A frequency of 800 per minute is quite sufficient in most cases.
- the machine shown and described is only an example which in many details could be varied without leaving the scope of the invention.
- a method of cutting off foils from a foam-plastic sheet comprising the steps of supporting the sheet in a flat superposed position on a firm supporting surface, advancing a knife having a serrated cutting edge longitudinally of the surface and through said sheet and of simultaneously subjecting said knife to longitudinal oscillations with 'a frequency of such rate that the sheet to be cut cannot resonate;
- a machine for cutting ofi foils from a foam-plastic sheet oomprising a horizontal supporting table on which the sheet is laid flat, a vertically adjustable frame transversely overlying the table, a spring steel cutting knife carried by the frame and positioned transverse of the sheet, said knife having a longitudinal cutting edge facing the sheet, means for longitudinally oscillating the knife,
- the guide is a knife beam which has a slot in which the opposite 1ongitudinal edge of the knife slides, the knife beam having an upper surface which slopes rearwardly from the knife, the front edge of the beam, in which the slot is formed, being a distance of from one to two knife thicknesses above the knife.
- said means for longitudinally oscillating the knife includes a pair of spaced apart, parallel horizontal arms, disposed transversely of the ends of the knife, means connecting the ends of the knife to one of the ends of the arms, axially adjustable stretching means interconnecting the opposite ends of the arms to stretch the knife, means mounting the arms, intermediate their ends, for pivotable movement 7 about vertical axes, and power means connected to one of the arms for oscillating the arms.
Landscapes
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Forests & Forestry (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Nonmetal Cutting Devices (AREA)
Description
H. ,KERNEN FOAM-PLASTIC SKIVING MACHINE Jan. 28, 1958 4 Sheets-Sheet 1 Filed Oct. 4. 1954 &
Jan. 28g 1958' H. KERNEN 2,321,254
FOAM-PLASTIC SKIVING MACHINE Filed Oct. 4, 1954 4 Sheets-Sheet 2 Jan. 28, 1958 H. KERNEN FOAM-PLASTIC SKIVING MACHINE 4 Sheets-Sheet 3 Filed Oct. 4, 1954 H.KERNEN FOAM-PLASTIC SKIVING MACHINE a3am. 28, 1953 4 Sheets-Sheet Filed Oct. 4, 1954 if 3 2 33 a4 2334233132 i Ll United States Patent FOAloi-PLASTIC SKIVING MACHINE I-Ians Kernen, Bern, Switzerland Application October 4, 1954, Serial No. 460,156
Claims priority, application Switzerland October 10, 1953 9 Claims. (Cl. 164-75) In the arts and industry there is a growing demand for foamed-plastic foils. Foamed plastic is rather expensive and is supplied by the manufacturers only in sheets of at least inch thickness and mostly in thicknessesof one inch and more. So far it has been practically impossible to skive or cut up such sheets into foils, and in particular into foils having a smooth surface.
The main object of my present invention istoremedy such disadvantage. According to the method disclosed by my present invention, a skiver or knife having a serrated cutting edge is moved through the sheet and subjected to longitudinal oscillations with such frequency that the foamed plastic to be cut cannot resonate.
In the skiving machine disclosed herein, the longitudinally oscillatable skiver is a stretched spring-steel band: of
which one longitudinal edge forms the cutting edge, being;
ground towards the underside in serrated and pointed manner.
One form of my present invention is shown, by way of example, in the accompanying drawing which also serves to illustrate the method disclosed by the invention. In the drawings:
Fig. 1 shows the machine in elevation,
Fig. 2 is a top plan view thereof,
Fig. 3 is a cross-section on the line III--III of Fig. 2,
Fig. 4 is a horizontal section on the line IV--IV of Fig. 3, and shows, in an enlarged scale, details of the bearing and driving arrangement of the knife, and
Figs. 5 to 7 are cross-sections on the lines VV, VI-VI and VII-VII of Fig. 4 respectively.
As shown in Fig. l, the skiving machine comprises a stand which in the main is composed of corner posts 1, a lower frame 2, side sheets 3 and 4, two horizontal and parallel top box-girders 5, and bracing tubes 6 interconnecting the latter. To the girders 5 is secured a plate 7, e. g. by welding, which serves a table. The foamedplastic sheet 8 to be cut into foils, either is secured to said table by adhesive means or simply laid thereon.
As shown in Fig. 3, a screw spindle 10 is rotatably but axially immovably mounted in two bearings 9 disposed on transverse members of the stand outside of the side sheets 4. Said spindle coacts with a nut 11 which by means of lateral forked wings 12 is guided on two rails 13 secured to the sheets 4. To nut 11 are secured the ends of two steel cables 14 trained over idling discs 15 mounted on the stand. An electric motor 17 mounted on frame 2 rotates spindle 10 through a belt drive 16 and, thus, moves nut 11 and the two cables 14 in one or the other sense. Outside the girders 5 and parallel thereto are arranged guide rods 18 of which the end faces through gussets 19 are connected to said girders. On rod 18 is movably mounted a sleeve 20 to which is welded a horizontal plate 21. The opposite ends of the cables are fixed to the sleeves 20, as shown in Figs. 2 and 3. Thus, when the nut is moved, the sleeves 20 and the parts carried thereby are moved. For example, when the nut 11, as shown in Figs. 1 and 2, is moved to the left, the sleeves 20 and the parts carried thereby are moved to the right. In a ring 22 welded to the latter is rigidly mounted a guide column 23. The two columns 23 are rigidly interconnected ontop througha horizontal transverse member 24 in which two screw spindles 25 are mounted rotatably but axially immovably. The spindles 25 through two bevel gears 26 are drivably connected to a shaft 27 which is rotatable in bearings 28 fixed to member 24 and on one end of which is provided a graduated disc 29 and a crank 30. Each of the spindles 25 coacts with a threaded bush 31 rigidly inserted in a holder 32. The latter is screwed to a lateral lug 33 of a sleeve 34 which is' longitudinally movable on the asso ciated column 23, as shown in- Figs. 3 and 4.
As shown in Figs. 3 and 4, lugs 36 of a. knife beam 71 are inserted between the lugs 33 and. secured thereto by screws 35. Lugs 33 and 36 together form arigid carrier for two similar two-arm oscillating levers 37 and 37a of which the bearings are designated by 38. Each of' said levers comprises a piece of pipe 39' welded to one of the lugs 33, a sliding bush 40 inserted in pipe 39, a bearingpin 41 welded to said lever, a screw 42 mounted and secured in pin 41', and a disc 43 supported on the upper end face of bush 40 for taking up the small axialforces. The front forked ends 44' of the levers 37, 37a are provided with ahoriz-ontal slot 45 in which is inserted one or the other end of. a skiver or knife blade 46-, the latter being mounted on a hardened screw 47. The rear ends of the two oscillating levers are interconnected through astretching device comprising a threaded member 48', a threaded wire-receiving sleeve 49, a stretching wire 50 and a member 51. Lever 37a has a lug 52 to which ispivoted, on a screw 53, a bar 54 of an eccentric ring- 55. The latter by means of balls 56' is mounted on the eccentric pin 57 of a shaft 58 which is rotatable in a bearing 59 whicfr through parts 60, 61 is fixed to the adjacent sleeve 34. Shaft 58 through a belt drive 62 to 64 is connected to an. electric motor 65 which is screwed down on a plate 66 welded to part 61.
As shown in Figs. 4 and 7, arms 68' are pivotally mounted in bosses 67 of the lugs 33. In bores of thelatter are rotatably mounted pins 69 of a loading roller 70 which is parallel to the cutting; edge of knife blade 46 and slightly in front of'the latter. Roller 70 serves to press downthe plastic sheet 8 ontoa coating 85 oftable 7", which coating increases the friction. Roller 70 in an extreme case may be situated only slightly lower with respect to knife 46 than shown in the drawing, as the arms 68 then rest on member 36.
Knife 46 is reciprocated at least 800 times per minute by motor 65 through the eccentric drive 55, 57 and lever 37a, and is made of a spring-steel band of which the longitudinal edge forming the cutting edge is serrated and ground sharply towards the underside in a manner similar to that of bread knives. The rear longitudinal edge of the knife moves in a guide formed on knife beam 71 of which the underside 72 is parallel to the knife underside, the spacing not exceeding the knife thickness. Such spacing corresponds to the thickness of a sheet 73 which at 75 is riveted to another horizontal sheet 74. The rear and top portion of said guide is formed on a solid constructional member 76 of triangular cross-section. To stepped surfaces at the rear of member 76 are brazed the lower and upper sheets 74 and 77 respectively, of a box-like structure to the somewhat thicker sidewall sheets 78 of which are welded the lugs 36. Said structure at the rear is braced by a sheet-iron member 79 of U-shaped cross-section. Fig. 6 further shows that the knife-beam upperside 80 rises rearwardly from a front edge 81 which is spaced from knife-beam upperside 80 by one to two knife thicknesses, first only at a slight slope and then somewhat steeper.
The carriage by the sleeves 20 is guided on the rods 18 which over their entire length are protected from impurities thr'oughcover plates 82 which are secured to the plates 19. For the operation of cutting off foils fiom the sheet 8 stuck to table 7, the carriage is run back until the cutting edge of knife 46 is situated in front of sheet 8 (Figs. G and 7). Byactuating crank 30, the foil thickness :,is set, whereupon a foil may be cut off when motor 65 is operating.
At the end of the forward and rearward runs of the carriage, motor 17 is reversed or stopped through limit switches 83 (Fig. 3) secured to the stand and through cams 84 secured to the carriage.
Tests have shown that with the machine disclosed, foils of very good surface property and minimal thickness of approximately of an inch may be cut off from foamplastic sheets up to 3% inches thick, provided that the frequency of the knife oscillations is sufficiently higher than the frequency at which the surface of sheet 8 could resonate. A frequency of 800 per minute is quite sufficient in most cases. In order to diminish the foil surface roughness, it is advisable to make the tooth back somewhat rounded, i. e. to avoid burrs on the ground face of the knife serrations. The machine shown and described is only an example which in many details could be varied without leaving the scope of the invention.
What I claim as new and desire to secure by Letters Patent is:
1. A method of cutting off foils from a foam-plastic sheet, comprising the steps of supporting the sheet in a flat superposed position on a firm supporting surface, advancing a knife having a serrated cutting edge longitudinally of the surface and through said sheet and of simultaneously subjecting said knife to longitudinal oscillations with 'a frequency of such rate that the sheet to be cut cannot resonate;
2. A method as set out in claim 1, in which the frequency of said longitudinal oscillations is at least 800 per minute.
3. A method as set out in claim 1, in which the sheet portion situated in front of the cutting edge is held down by a slight, non-deforming pressure on the surface.
4. A machine for cutting ofi foils from a foam-plastic sheet oomprising a horizontal supporting table on which the sheet is laid flat, a vertically adjustable frame transversely overlying the table, a spring steel cutting knife carried by the frame and positioned transverse of the sheet, said knife having a longitudinal cutting edge facing the sheet, means for longitudinally oscillating the knife,
4 guide means in which the opposite longitudinal side edge of. the knife is guided as the knife is longitudinally oscillated and means for moving the frame longitudinally of the table to advance the knife through the sheet.
5. A machine as claimed in claim 4, wherein the cutting edge is serrated and sharply ground towards the knife underside.
6. A machine as claimed in claim 4, wherein the guide is carried by the frame and has a slot in which the opposite longitudinal edge of the knife slides, the guide consisting of a knife beam having a flat underside which is spaced from the underside of-the knife by an amount less than the thickness of the knife. I
7. A machine as claimed in claim 4, wherein the guide is a knife beam which has a slot in which the opposite 1ongitudinal edge of the knife slides, the knife beam having an upper surface which slopes rearwardly from the knife, the front edge of the beam, in which the slot is formed, being a distance of from one to two knife thicknesses above the knife. I
8. A machine as claimed in claim 4, wherein said means for longitudinally oscillating the knife includes a pair of spaced apart, parallel horizontal arms, disposed transversely of the ends of the knife, means connecting the ends of the knife to one of the ends of the arms, axially adjustable stretching means interconnecting the opposite ends of the arms to stretch the knife, means mounting the arms, intermediate their ends, for pivotable movement 7 about vertical axes, and power means connected to one of the arms for oscillating the arms.
9. A machine as claimed in claim 8, wherein said last means includes a drive motor, an eccentric driven thereby and a link connection between the eccentric and one of the 'arms.
References Cited in the file of this patent UNITED STATES PATENTS Austria Nov. 10, 1932
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CH2821254X | 1953-10-10 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| US2821254A true US2821254A (en) | 1958-01-28 |
Family
ID=4572031
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US460156A Expired - Lifetime US2821254A (en) | 1953-10-10 | 1954-10-04 | Foam-plastic skiving machine |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US2821254A (en) |
Cited By (17)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3104578A (en) * | 1959-02-16 | 1963-09-24 | Merrill V Peck | Blade-guide system |
| US3204500A (en) * | 1959-06-03 | 1965-09-07 | Continental Can Co | Method and apparatus for slicing honeycomb block |
| US3230803A (en) * | 1965-10-26 | 1966-01-25 | Dow Chemical Co | Method and apparatus for skiving foam sheets |
| US3250161A (en) * | 1964-11-02 | 1966-05-10 | Dow Chemical Co | Apparatus for skiving foam sheets |
| US3298263A (en) * | 1965-04-13 | 1967-01-17 | Snyder Paper Corp | Slitting method and apparatus |
| US3747448A (en) * | 1971-12-29 | 1973-07-24 | Fallacaro E | Reciprocating cutting apparatus |
| US4111085A (en) * | 1977-05-10 | 1978-09-05 | Lockheed Corporation | Compound curvature cutting machine |
| US4197077A (en) * | 1974-10-31 | 1980-04-08 | Internationella Siporex Ab | Apparatus for use in manufacturing of cellular lightweight concrete slabs |
| US4300423A (en) * | 1978-11-08 | 1981-11-17 | Paul Price | Apparatus for severing and separating cup-shaped object supports |
| US4898058A (en) * | 1987-12-24 | 1990-02-06 | Intel Corporation | Apparatus for removing pellicles |
| WO1998001267A1 (en) * | 1996-07-10 | 1998-01-15 | Wolfgang Krumbein | Device for cutting pies and similar types of cakes |
| US20090072457A1 (en) * | 2005-05-02 | 2009-03-19 | Downey Paul C | Vibration damper |
| USRE41945E1 (en) | 2001-08-16 | 2010-11-23 | Ecore International Inc. | Impact sound insulation |
| US8240430B2 (en) | 2002-10-01 | 2012-08-14 | Downey Paul C | Noise and vibration mitigating mat |
| US9914011B2 (en) | 2015-06-25 | 2018-03-13 | Pliteq Inc. | Impact damping mat, equipment accessory and flooring system |
| US10676920B2 (en) | 2015-06-25 | 2020-06-09 | Pliteq Inc | Impact damping mat, equipment accessory and flooring system |
| US11738492B2 (en) | 2016-03-31 | 2023-08-29 | Toray Plastics (America), Inc. | Methods of producing polyolefin foam sheets and articles made thereof |
Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US368758A (en) * | 1887-08-23 | Machine | ||
| US1839383A (en) * | 1930-01-13 | 1932-01-05 | Lawrence P Erpelding | Trimmer for battery separators |
| AT130317B (en) * | 1931-12-10 | 1932-11-10 | Adolf Frogner | Device for cutting off the rubber covering from vehicle tires. |
| US2457301A (en) * | 1946-10-04 | 1948-12-28 | William T Brand | Machine for removing the wax caps from honeycombs |
| US2565400A (en) * | 1946-08-07 | 1951-08-21 | Johns Manville | Method and apparatus for severing sections from compressible materials |
| US2609048A (en) * | 1950-04-05 | 1952-09-02 | Du Pont | Shaping device |
| US2627237A (en) * | 1950-04-29 | 1953-02-03 | Newly Weds Baking Co | Apparatus for manufacturing icecream cake confections and the like |
-
1954
- 1954-10-04 US US460156A patent/US2821254A/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
Patent Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US368758A (en) * | 1887-08-23 | Machine | ||
| US1839383A (en) * | 1930-01-13 | 1932-01-05 | Lawrence P Erpelding | Trimmer for battery separators |
| AT130317B (en) * | 1931-12-10 | 1932-11-10 | Adolf Frogner | Device for cutting off the rubber covering from vehicle tires. |
| US2565400A (en) * | 1946-08-07 | 1951-08-21 | Johns Manville | Method and apparatus for severing sections from compressible materials |
| US2457301A (en) * | 1946-10-04 | 1948-12-28 | William T Brand | Machine for removing the wax caps from honeycombs |
| US2609048A (en) * | 1950-04-05 | 1952-09-02 | Du Pont | Shaping device |
| US2627237A (en) * | 1950-04-29 | 1953-02-03 | Newly Weds Baking Co | Apparatus for manufacturing icecream cake confections and the like |
Cited By (19)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3104578A (en) * | 1959-02-16 | 1963-09-24 | Merrill V Peck | Blade-guide system |
| US3204500A (en) * | 1959-06-03 | 1965-09-07 | Continental Can Co | Method and apparatus for slicing honeycomb block |
| US3250161A (en) * | 1964-11-02 | 1966-05-10 | Dow Chemical Co | Apparatus for skiving foam sheets |
| US3298263A (en) * | 1965-04-13 | 1967-01-17 | Snyder Paper Corp | Slitting method and apparatus |
| US3230803A (en) * | 1965-10-26 | 1966-01-25 | Dow Chemical Co | Method and apparatus for skiving foam sheets |
| US3747448A (en) * | 1971-12-29 | 1973-07-24 | Fallacaro E | Reciprocating cutting apparatus |
| US4197077A (en) * | 1974-10-31 | 1980-04-08 | Internationella Siporex Ab | Apparatus for use in manufacturing of cellular lightweight concrete slabs |
| US4111085A (en) * | 1977-05-10 | 1978-09-05 | Lockheed Corporation | Compound curvature cutting machine |
| US4300423A (en) * | 1978-11-08 | 1981-11-17 | Paul Price | Apparatus for severing and separating cup-shaped object supports |
| US4898058A (en) * | 1987-12-24 | 1990-02-06 | Intel Corporation | Apparatus for removing pellicles |
| WO1998001267A1 (en) * | 1996-07-10 | 1998-01-15 | Wolfgang Krumbein | Device for cutting pies and similar types of cakes |
| USRE41945E1 (en) | 2001-08-16 | 2010-11-23 | Ecore International Inc. | Impact sound insulation |
| US8240430B2 (en) | 2002-10-01 | 2012-08-14 | Downey Paul C | Noise and vibration mitigating mat |
| US8556029B2 (en) | 2002-10-01 | 2013-10-15 | Paul C. Downey | Noise and vibration mitigating mat |
| US20090072457A1 (en) * | 2005-05-02 | 2009-03-19 | Downey Paul C | Vibration damper |
| US8113495B2 (en) | 2005-05-02 | 2012-02-14 | Downey Paul C | Vibration damper |
| US9914011B2 (en) | 2015-06-25 | 2018-03-13 | Pliteq Inc. | Impact damping mat, equipment accessory and flooring system |
| US10676920B2 (en) | 2015-06-25 | 2020-06-09 | Pliteq Inc | Impact damping mat, equipment accessory and flooring system |
| US11738492B2 (en) | 2016-03-31 | 2023-08-29 | Toray Plastics (America), Inc. | Methods of producing polyolefin foam sheets and articles made thereof |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US2821254A (en) | Foam-plastic skiving machine | |
| CN202805268U (en) | Multistation cutting device for phenolic foam board | |
| CN210358654U (en) | Automatic material conveying structure of sheet metal part bending die | |
| US3678792A (en) | Metal plate shears | |
| CN109434984B (en) | Bamboo chipping device | |
| US2436111A (en) | Trimming and grooving machine | |
| CN208697628U (en) | A kind of cross cutting processing waste discharge multilayer stripping off device | |
| CN219484339U (en) | High-temperature material shearing tool | |
| US3154988A (en) | Sheet metal shears | |
| CN115446133B (en) | Wire drawing machine is used in production and processing of tungsten base strip | |
| CN207682468U (en) | A kind of leather tape machine | |
| US3077807A (en) | Roller die apparatus | |
| US4393570A (en) | Method of and apparatus for cutting strips from long plates | |
| US3675525A (en) | Machine for cutting rolls of sheet material | |
| CN214557792U (en) | Steel plate edge cutting machine | |
| CN212266038U (en) | Cutting device to membrane is rolled up on panel surface | |
| CN111438723B (en) | Slicing device for traditional Chinese medicinal materials | |
| CN211194093U (en) | Non-woven fabric cutting device | |
| CN210160527U (en) | Linear cutting mechanism for thin materials | |
| CN212704759U (en) | Diffusion welding forming aluminum plate slicing device for uniform temperature plate radiator | |
| CN105032931B (en) | Aluminum strip billet collating device on rewinding machine | |
| US2227364A (en) | Cutter for vegetables | |
| CN219543722U (en) | Round scissors medium material granulator | |
| CN109262772A (en) | Bamboo cane profiling slicing device | |
| CN214937567U (en) | Cutting device for leather product processing |