KR20130013810A - Quantum-dot light emitting diode - Google Patents
Quantum-dot light emitting diode Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR20130013810A KR20130013810A KR1020110075637A KR20110075637A KR20130013810A KR 20130013810 A KR20130013810 A KR 20130013810A KR 1020110075637 A KR1020110075637 A KR 1020110075637A KR 20110075637 A KR20110075637 A KR 20110075637A KR 20130013810 A KR20130013810 A KR 20130013810A
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- light emitting
- quantum
- layer
- electrode
- quantum light
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10K—ORGANIC ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES
- H10K50/00—Organic light-emitting devices
- H10K50/10—OLEDs or polymer light-emitting diodes [PLED]
- H10K50/11—OLEDs or polymer light-emitting diodes [PLED] characterised by the electroluminescent [EL] layers
- H10K50/115—OLEDs or polymer light-emitting diodes [PLED] characterised by the electroluminescent [EL] layers comprising active inorganic nanostructures, e.g. luminescent quantum dots
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10K—ORGANIC ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES
- H10K50/00—Organic light-emitting devices
- H10K50/10—OLEDs or polymer light-emitting diodes [PLED]
- H10K50/11—OLEDs or polymer light-emitting diodes [PLED] characterised by the electroluminescent [EL] layers
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B82—NANOTECHNOLOGY
- B82Y—SPECIFIC USES OR APPLICATIONS OF NANOSTRUCTURES; MEASUREMENT OR ANALYSIS OF NANOSTRUCTURES; MANUFACTURE OR TREATMENT OF NANOSTRUCTURES
- B82Y20/00—Nanooptics, e.g. quantum optics or photonic crystals
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10K—ORGANIC ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES
- H10K2101/00—Properties of the organic materials covered by group H10K85/00
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10K—ORGANIC ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES
- H10K2101/00—Properties of the organic materials covered by group H10K85/00
- H10K2101/30—Highest occupied molecular orbital [HOMO], lowest unoccupied molecular orbital [LUMO] or Fermi energy values
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Optics & Photonics (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Crystallography & Structural Chemistry (AREA)
- Inorganic Chemistry (AREA)
- Nanotechnology (AREA)
- Electroluminescent Light Sources (AREA)
Abstract
Description
본 발명은 양자 발광 소자에 관한 것으로, 양자점으로 주입되는 정공의 에너지 장벽을 낮추어 발광 효율을 향상시킬 수 있는 양자 발광 소자에 관한 것이다.The present invention relates to a quantum light emitting device, and relates to a quantum light emitting device capable of improving luminous efficiency by lowering an energy barrier of holes injected into quantum dots.
정보화 사회에서 디스플레이(Display)는 시각정보 전달매체로서 그 중요성이 한층 강조되고 있으며, 향후 주요한 위치를 점하기 위해서는 저소비전력화, 박형화, 경량화, 고화질화 등의 요건을 충족시켜야 한다. 이러한 디스플레이 중 발광 재료를 이용하여 표시가 가능하며, 슬림화가 가능하며, 색순도가 높고 또한, 장시간 구동이 가능한 양자 발광 소자가 근래 연구되고 있다.In the information society, display is emphasized as a visual information transmission medium, and in order to occupy a major position in the future, it is necessary to satisfy requirements such as low power consumption, thinness, light weight, and high definition. Among such displays, a quantum light emitting device capable of displaying, slimming, high color purity, and long driving time has been recently studied.
양자점(Quantum Dot; QD)은 반도체 나노 입자이다. 직경이 나노미터 크기의 양자점은 불안정한 상태의 전자가 전도대에서 가전자대로 내려오면서 발광하는데, 양자점의 입자가 작을수록 짧은 파장의 빛이 발생하고, 입자가 클수록 긴 파장의 빛이 발생한다. 이는 기존의 반도체 물질과 다른 독특한 전기적이며 광학적인 특성이다. 따라서 양자점의 크기를 조절하면 원하는 파장의 가시광선을 표현하고, 여러 크기의 양자점과 양자점 성분을 달리하여 다양한 색을 동시에 구현할 수 있다.Quantum dots (QDs) are semiconductor nanoparticles. Quantum dots with a diameter of nanometers emit light when electrons in an unstable state descend from the conduction band to the valence band. Smaller particles of the quantum dots generate shorter wavelengths of light, and larger particles generate long wavelengths of light. This is a unique electrical and optical characteristic that differs from conventional semiconductor materials. Therefore, by adjusting the size of the quantum dot to represent the visible light of the desired wavelength, it is possible to implement a variety of colors at the same time by different quantum dot and quantum dot components of different sizes.
일반적인 유기 발광 표시 소자는 발광층의 재료로 유기 발광 재료를 사용하며, 유기 발광 재료를 사용하는 유기 발광 다이오드(Organic Light Emitting Diode; OLED)는 소자의 종류에 따라 백색, 적색, 청색 등 단일색을 구현하는데, 많은 빛을 화려하게 표현하기에는 한계가 있다. 이에 반해, 양자 발광 소자는 발광층의 재료로 양자점을 사용하는 표시 소자로, 양자점의 크기를 제어하여 원하는 천연색을 구현할 수 있으며, 색재현율이 좋고 휘도 또한 발광 다이오드에 뒤쳐지지 않아 차세대 광원으로 주목받는 발광 다이오드(Light Emitting Diode; LED)의 단점을 보완할 수 있는 소재로 각광받고 있다.In general, an organic light emitting display device uses an organic light emitting material as a material of an emission layer, and an organic light emitting diode (OLED) using an organic light emitting material realizes a single color such as white, red, and blue according to the type of device. However, there is a limit to expressing a lot of light colorfully. On the other hand, the quantum light emitting device is a display device using quantum dots as a material of the light emitting layer, and can control the size of the quantum dots to achieve a desired natural color. It has been spotlighted as a material that can compensate for the shortcomings of light emitting diodes (LEDs).
이하, 일반적인 양자 발광 소자의 구조를 구체적으로 설명한다.Hereinafter, the structure of a general quantum light emitting device will be described in detail.
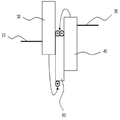
도 1a는 일반적인 양자 발광 소자의 단면도이며, 도 1b는 일반적인 양자 발광 소자의 밴드갭 에너지 다이어그램도이다.1A is a cross-sectional view of a general quantum light emitting device, and FIG. 1B is a bandgap energy diagram of a general quantum light emitting device.
도 1a를 참조하면, 일반적인 양자 발광 소자는 기판(100), 기판(100) 상에 형성되며 서로 대향된 제 1 전극(10) 및 제 2 전극(50), 제 1 전극(10)과 제 2 전극(50) 사이에 형성된 양자 발광층(30), 제 1 전극(10)과 양자 발광층(30) 사이에 형성된 정공 수송층(20), 그리고, 양자 발광층(30)과 제 2 전극(50) 사이에 형성된 전자 수송층(40)을 포함하여 이루어진다.Referring to FIG. 1A, a general quantum light emitting device is formed on a
양자 발광층(30)은 직경이 나노미터 크기인 복수개의 양자점(60)으로 구성되며, 용매에 복수개의 양자점(60)을 분산시켜 용액 공정(Solution Process)으로 복수개의 양자점(60)이 분산된 용매를 정공 수송층(20) 상에 도포하고 용매를 휘발시켜 형성된다.The quantum
양자점(60)은 코어(Core)(60a), 쉘(Shell)(60b) 및 리간드(Ligand)(60c)로 이루어진다. 빛을 내는 역할을 하는 코어(60a)를 감싸며 코어(60a)의 표면에 형성되는 쉘(60b)은 코어(60a)를 보호하는 역할을 한다. 그리고, 쉘(60b)을 감싸도록 쉘(60b)의 표면에는 리간드(60c)가 형성되며, 리간드(60c)는 양자 발광층(30) 형성시 양자점(60)이 용매에 잘 분산될 수 있도록 도와주는 역할을 한다.The
그런데, 도 1b와 같이, 일반적인 양자 발광 소자는 양자점(60)과 정공 수송층(20)의 에너지 장벽이 커 정공의 주입이 수월하지 않아 소자의 구동 전압이 높고 신뢰성이 저하된다. 또한, 양자점(60)과 전자 수송층(40) 사이의 에너지 장벽보다 양자점(60)과 정공 수송층(20) 사이의 에너지 장벽이 더 높으므로 정공보다 전자가 양자점(60)으로 더 많이 주입된다.However, as shown in FIG. 1B, a general quantum light emitting device has a high energy barrier between the
따라서, 양자점(60)으로 주입된 전자 중 발광에 참여하지 못한 전자들이 양자점(60)에 쌓이게 되고, 전자와 정공이 만나 방출하는 에너지가 발광에 쓰이지 않고 쌓여있는 전자들에게 전이되는 비발광 에너지 전이(Auger Recombination)가 발생하여 양자 발광 소자의 효율이 떨어지는 문제점이 발생한다.Therefore, electrons that do not participate in light emission among electrons injected into the
본 발명은 상기와 같은 문제점을 해결하기 위해 안출한 것으로, HOMO(Highest Occupied Molecular Orbital) 준위가 낮은 인광 호스트 물질층을 통해 양자점으로 정공이 원활하게 주입될 수 있는 양자 발광 소자를 제공하는데, 그 목적이 있다.The present invention has been made to solve the above problems, and provides a quantum light emitting device that can be injected into the quantum dots smoothly through a phosphorescent host material layer having a low HOOC (Highest Occupied Molecular Orbital) level, the object There is this.
상기와 같은 목적을 달성하기 위한 본 발명의 양자 발광 소자는, 기판 상에 형성된 제 1 전극; 상기 제 1 전극 상에 형성된 인광 호스트 물질층; 상기 인광 호스트 물질층 상에 형성되며, 양자점을 포함하는 양자 발광층; 상기 양자 발광층 상에 형성된 전자 수송층; 및 상기 전자 수송층 상에 형성된 제 2 전극을 포함한다.A quantum light emitting device of the present invention for achieving the above object, the first electrode formed on the substrate; A phosphorescent host material layer formed on the first electrode; A quantum light emitting layer formed on the phosphorescent host material layer and including a quantum dot; An electron transport layer formed on the quantum light emitting layer; And a second electrode formed on the electron transport layer.
상기 인광 호스트 물질층은 상기 양자점에 정공을 전달한다.The phosphorescent host material layer delivers holes to the quantum dots.
상기 인광 호스트 물질층은 CBP 또는 mCP로 형성된다.The phosphorescent host material layer is formed of CBP or mCP.
또한, 동일 목적을 달성하기 위한 본 발명의 양자 발광 소자는, 기판 상에 형성된 제 1 전극; 상기 제 1 전극 상에 형성되며, 인광 호스트 물질과 양자점이 혼합되어 형성된 양자 발광층; 상기 양자 발광층 상에 형성된 전자 수송층; 및 상기 전자 수송층 상에 형성된 제 2 전극을 포함한다.In addition, a quantum light emitting device of the present invention for achieving the same object, the first electrode formed on the substrate; A quantum light emitting layer formed on the first electrode and formed by mixing a phosphorescent host material and a quantum dot; An electron transport layer formed on the quantum light emitting layer; And a second electrode formed on the electron transport layer.
상기 양자 발광층은 상기 인광 호스트 물질과 상기 양자점을 용매에 분산시켜 형성된다.The quantum light emitting layer is formed by dispersing the phosphorescent host material and the quantum dots in a solvent.
상기 인광 호스트 물질은 상기 양자점에 정공을 전달한다.The phosphorescent host material delivers holes to the quantum dots.
상기 인광 호스트 물질은 CBP 또는 mCP이다.The phosphorescent host material is CBP or mCP.
상기와 같은 본 발명의 양자 발광 소자는 다음과 같은 효과가 있다.The quantum light emitting device of the present invention as described above has the following effects.
첫째, HOMO(Highest Occupied Molecular Orbital) 준위가 낮은 인광 호스트 물질층을 통해 정공이 양자점으로 주입되므로, 정공의 에너지 장벽을 낮추어 정공이 원활하게 양자점으로 주입된다. 따라서, 양자 발광 소자의 효율을 향상시킬 수 있다.First, since holes are injected into the quantum dots through a phosphorescent host material layer having a low HOOC (Highest Occupied Molecular Orbital) level, holes are smoothly injected into the quantum dots by lowering the energy barrier of the holes. Therefore, the efficiency of a quantum light emitting element can be improved.
둘째, 인광 호스트 물질과 양자점을 혼합하여 양자 발광층을 형성하는 경우, 소자의 구조 및 공정을 단순화할 수 있으며 양자 발광층을 두껍게 형성할 수 있으므로 발광 영역이 증가한다. 또한, 용액 공정(Soluble Process)으로 양자 발광층을 형성할 수 있으므로, 제조 비용을 절감할 수 있다.Second, when the phosphorescent host material and the quantum dot are mixed to form the quantum light emitting layer, the structure and the process of the device can be simplified and the quantum light emitting layer can be formed thick, thereby increasing the light emitting area. In addition, since the quantum light emitting layer may be formed by a solution process, manufacturing costs may be reduced.
도 1a는 일반적인 양자 발광 소자의 단면도.
도 1b는 일반적인 양자 발광 소자의 밴드갭 에너지 다이어그램도.
도 2a는 본 발명의 제 1 실시 예의 양자 발광 소자의 단면도.
도 2b는 본 발명의 제 1 실시 예의 양자 발광 소자의 밴드갭 에너지 다이어그램도.
도 3a는 본 발명의 제 2 실시 예의 양자 발광 소자의 단면도.
도 3b는 본 발명의 제 2 실시 예의 양자 발광 소자의 밴드갭 에너지 다이어그램도.1A is a cross-sectional view of a typical quantum light emitting device.
1B is a bandgap energy diagram of a typical quantum light emitting device.
2A is a cross-sectional view of a quantum light emitting device according to a first embodiment of the present invention.
2B is a bandgap energy diagram of the quantum light emitting device of the first embodiment of the present invention.
3A is a cross-sectional view of a quantum light emitting device according to a second embodiment of the present invention.
3B is a bandgap energy diagram of a quantum light emitting device according to a second embodiment of the present invention.
이하, 첨부된 도면을 참조하여, 본 발명의 제 1 실시 예의 양자 발광 소자를 상세히 설명하면 다음과 같다.Hereinafter, the quantum light emitting device according to the first embodiment of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings.
*제 1 실시 예** First Embodiment *
도 2a는 본 발명의 제 1 실시 예의 양자 발광 소자의 단면도이며, 도 2b는 본 발명의 제 1 실시 예의 양자 발광 소자의 밴드갭 에너지 다이어그램도이다.2A is a cross-sectional view of a quantum light emitting device according to a first embodiment of the present invention, and FIG. 2B is a bandgap energy diagram of the quantum light emitting device according to a first embodiment of the present invention.
도 2a와 같이, 본 발명의 제 1 실시 예의 양자 발광 소자는 기판(200), 기판(200) 상에 형성된 제 1 전극(110), 제 1 전극(110) 상에 형성된 인광 호스트 물질층(120b), 인광 호스트 물질층(120b)상에 형성되며 양자점(160)을 포함하는 양자 발광층(130), 양자 발광층(130) 상에 형성된 전자 수송층(140) 및 전자 수송층(140) 상에 형성된 제 2 전극(150)을 포함한다.As shown in FIG. 2A, the quantum light emitting device according to the first exemplary embodiment of the present invention includes a
기판(200)의 종류는 특별히 한정되지 않고 다양하게 가능하며, 유리 기판, 플라스틱 기판 또는 실리콘 기판 등이 가능하다. 도시하지는 않았으나, 기판(200) 상에는 액티브층, 게이트 전극, 소스 전극 및 드레인 전극을 포함하는 박막 트랜지스터가 형성된다. 그리고, 박막 트랜지스터는 양극인 제 1 전극(110)과 전기적으로 접속된다.The type of the
한편, 본 발명의 양자 발광 표시 소자는 양자 발광층(130)에서 발생된 광이 기판(200)을 통해 하부로 방출되는 하부 발광 방식 또는 양자 발광층(130)에서 발생된 광이 기판(200)의 반대쪽으로 방출되는 상부 발광 방식일 수 있다. 따라서, 양자 발광 소자가 하부 발광 방식일 경우, 제 1 전극(110)은 틴 옥사이드(Tin Oxide; TO), 인듐 틴 옥사이드(Indium Tin Oxide; ITO), 인듐 징크 옥사이드(Indium Zinc Oxide; IZO), 인듐 틴 징크 옥사이드(Indium Tin Zinc Oxide; ITZO) 등과 같은 투명 도전성 물질로 형성된다.Meanwhile, in the quantum light emitting display device of the present invention, the light emitted from the quantum
반대로, 양자 발광 소자가 상부 발광 방식인 경우, 제 1 전극(110)은 일함수가 낮은 마그네슘(Mg), 은(Ag), 알루미늄(Al), 칼슘(Ca) 등과 같이 반사율이 높은 불투명 도전성 물질로 형성되는 것이 바람직하다. 그리고, 제 1 전극(110) 상에는 제 1 전극(110)으로부터 주입된 정공을 양자점(160)으로 주입하기 위한 정공 주입층(120a)을 형성한다.On the contrary, when the quantum light emitting device is a top emission type, the
그런데, 상술한 바와 같이 일반적인 양자 발광 소자는 양자점과 정공 수송층의 에너지 장벽이 커 정공이 양자점으로 수월하게 주입되기 어렵다. 따라서, 일반적인 양자 발광 소자는 구동 전압이 높고 신뢰성이 낮다.However, as described above, the general quantum light emitting device has a large energy barrier between the quantum dot and the hole transport layer, and thus it is difficult to easily inject holes into the quantum dots. Therefore, the general quantum light emitting device has a high driving voltage and low reliability.
예를 들어, TPD(N,N'-dipheny-N,N'-bis(3-methylphenyl)-(1,1' biphenyl)-4,4' diamine), NTP(N,N'-diphenyl-N,N'-bis(1-naphthylphenyl)-1,1'-biphenyl-4,4'-diamine)와 같은 정공 수송층의 HOMO(Highest Occupied Molecular Orbital)준위는 각각 5.4eV, 5.5eV이며, 양자점의 HOMO준위는 약 6.7eV 이다. 또한, 양자점과 전자 수송층 사이의 에너지 장벽보다 양자점과 정공 수송층 사이의 에너지 장벽이 더 높으므로 정공보다 전자가 양자점으로 더 많이 주입된다.For example, TPD (N, N'-dipheny-N, N'-bis (3-methylphenyl)-(1,1 'biphenyl) -4,4'diamine), NTP (N, N'-diphenyl-N The highest Occupied Molecular Orbital (HOMO) levels of the hole transport layer, such as N'-bis (1-naphthylphenyl) -1,1'-biphenyl-4,4'-diamine, are 5.4 eV and 5.5 eV, respectively. The level is about 6.7 eV. In addition, since the energy barrier between the quantum dots and the hole transport layer is higher than the energy barrier between the quantum dots and the electron transport layer, more electrons are injected into the quantum dots than holes.
따라서, 본 발명의 제 1 실시 예의 양자 발광 소자는, 정공이 양자점(160)으로 주입되기 위한 에너지 장벽을 낮추기 위해 HOMO 준위가 낮은 인광 호스트 물질층(120b)을 통해 양자점으로 정공이 주입되어 발광 효율을 향상시킬 수 있다. 즉, 본 발명의 양자 발광 소자는 인광 호스트 물질층(120b)이 정공 수송층의 기능을 수행한다.Accordingly, in the quantum light emitting device of the first embodiment of the present invention, in order to lower the energy barrier for injecting holes into the
예를 들어, 인광 호스트 물질은 HOMO 준위가 약 6.3eV인 CBP(carbazole biphenyl), HOMO 준위가 약 5.9eV인 mCP(1,3-bis(carbazol-9-yl) 등과 같은 물질이다. 이 때, 인광 호스트 물질층(120b)은 CBP, mCP 등과 같은 인광 호스트 물질을 용매에 분산시켜 잉크 젯(Ink Jet), 노즐 코팅(Nozzle Coating), 스프레이 코팅(Spray Coating), 롤 프린팅(Roll Printing) 등과 같은 용액 공정(Soluble Process)을 통해 형성되거나, 진공 증착 방법으로 형성된다.For example, the phosphorescent host material is a substance such as carbazole biphenyl (CBP) having a HOMO level of about 6.3 eV, mCP (1,3-bis (carbazol-9-yl), etc. having a HOMO level of about 5.9 eV, etc. The phosphorescent
즉, 도 2b와 같이, 본 발명의 양자 발광 소자는 인광 호스트 물질층(120b)의 HOMO 준위와 양자점(160)의 HOMO 준위의 차이가 줄어, 정공이 양자점(160)으로 주입될 때 에너지 장벽이 낮아져 정공이 쉽게 양자점(160)으로 주입될 수 있다. 따라서, 양자 발광 소자의 구동 전압이 낮아지며 신뢰성이 향상된다.That is, as shown in FIG. 2B, in the quantum light emitting device of the present invention, the difference between the HOMO level of the phosphorescent
인광 호스트 물질층(120b)상에 형성된 양자 발광층(130)은 1nm~100nm의 직경을 갖는 나노 크기의 양자점(160)들로 이루어진다. 양자 발광층(130)은 상기와 같은 용액 공정으로 형성되며, 용매에 복수개의 양자점(160)을 분산시켜 복수개의 양자점(160)이 분산된 용매를 인광 호스트 물질층(120b)상에 도포하고 용매를 휘발시켜 형성된다.The quantum
양자점(160)은 2-6족 또는 3-5족의 나노 반도체 화합물을 포함한다. 예를 들어, 양자점(160)을 이루는 나노 반도체 화합물은 카드뮴셀레나이드(CdSe), 카드뮴설파이드(CdS), 카드뮴텔레라이드(CdTe), 징크셀레나이드(ZnSe), 징크텔레라이드(ZnTe), 징크설파이드(ZnS), 머큐리텔레라이드(HgTe), 인듐 아세나이드(InAs), Cd1-xZnxSe1-ySy', CdSe/ZnS, 인듐 포스포러스(InP) 및 갈륨 아세나이드(GaAs) 중 어느 하나로 이루어질 수 있다. 그리고, 용매는 헥세인(Hezane), 톨루엔(Toluene), 클로로포름(Chloroform) 등과 같은 다양한 유기용매에서 선택된다.The
양자점(160)은 빛을 내는 역할을 하는 코어(Core), 코어를 감싸며 코어의 표면에 형성되어 코어를 보호하는 쉘(Shell) 및 쉘을 감싸며 쉘의 표면에 형성된 리간드(Ligand)로 이루어진다. 리간드는 양자 발광층(130)을 형성할 때, 양자점(160)이 용매에 잘 분산될 수 있도록 도와주는 역할을 한다.The
양자 발광층(130) 상에는 제 2 전극(150)으로부터 주입된 전자를 양자 발광층(130)에 전달하기 위한 전자 수송층(140)과 전자 주입층이 차례로 형성되며, 도면에서는 전자 수송층(140)만을 도시하였다. 전자 수송층(140)은 알루미늄 퀴놀레이트(Quoleate)과 같이 전자 수송 능력이 뛰어난 물질로 형성되며, 전자 주입층은 리튬 플로라이드(LiF)와 같은 금속화합물을 사용할 수 있다.The
전자 수송층(140)과 전자 주입층은 선택적으로 하나의 층으로 형성될 수도 있다. 이 경우에는 하나의 층이 전자 수송층(140)과 전자 주입층의 기능을 수행하여 재료비를 절감하고, 생산성과 수율을 향상시킬 수 있다. 또한, 전하가 이동하는 계면(Interface)을 감소시켜 구동 전압을 낮출 수 있어 양자 발광 소자의 소비 전력을 감소시킬 수 있다.The
전자 수송층(140) 상에 형성된 제 2 전극(150)은 양자점(160)에 전자를 공급하는 음극으로 진공 증착 방법으로 형성된다. 제 2 전극(150)은 양자 발광 표시 소자가 하부 발광 방식일 때는, 일함수가 낮은 마그네슘(Mg), 은(Ag), 알루미늄(Al), 칼슘(Ca) 등과 같이 반사율이 높은 불투명 도전성 물질로 형성된다. 그리고, 상부 발광 방식일 때는, 틴 옥사이드(Tin Oxide; TO), 인듐 틴 옥사이드(Indium Tin Oxide; ITO), 인듐 징크 옥사이드(Indium Zinc Oxide; IZO), 인듐 틴 징크 옥사이드(Indium Tin Zinc Oxide; ITZO) 등과 같은 투명 도전성 물질로 형성된다.The
상기와 같은 양자 발광 소자는 제 1 전극(110)과 제 2 전극(150) 사이에 전압을 인가하면 제 1 전극(110)으로부터 정공이, 제 2 전극(150)으로부터 전자가 주입되어 양자 발광층(130)에서 재결합하여 엑시톤(Exciton)이 생성된다. 그리고, 엑시톤이 기저상태로 떨어지면서 발광한다.In the quantum light emitting device as described above, when a voltage is applied between the
*제 2 실시 예** Second Embodiment *
이하, 첨부된 도면을 참조하여, 본 발명의 제 2 실시 예의 양자 발광 소자를 상세히 설명하면 다음과 같다.Hereinafter, a quantum light emitting device according to a second embodiment of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings.
도 3a는 본 발명의 제 2 실시 예의 양자 발광 소자의 단면도이며, 도 3b는 본 발명의 제 2 실시 예의 양자 발광 소자의 밴드갭 에너지 다이어그램도이다.3A is a cross-sectional view of a quantum light emitting device according to a second embodiment of the present invention, and FIG. 3B is a bandgap energy diagram of the quantum light emitting device according to a second embodiment of the present invention.
도 3a와 같이, 본 발명의 제 2 실시 예의 양자 발광 소자는 기판(300), 기판(300) 상에 형성된 제 1 전극(210), 제 1 전극(210) 상에 형성되며, 인광 호스트 물질(220b)과 양자점(260)이 혼합된 양자 발광층(230), 양자 발광층(230) 상에 형성된 전자 수송층(240) 및 전자 수송층(240) 상에 형성된 제 2 전극(250)을 포함한다.As shown in FIG. 3A, the quantum light emitting device according to the second embodiment of the present invention is formed on a
즉, 본 발명의 제 2 실시 예의 양자 발광 소자는 구조 및 공정을 단순화하기 위해 인광 호스트 물질(220b)과 양자점(260)을 혼합하여 양자 발광층(230)을 형성한다. 이 때, 인광 호스트 물질(220b)은 양자점(260)으로 정공을 전달한다. That is, the quantum light emitting device according to the second embodiment of the present invention forms the quantum
구체적으로, 인광 호스트 물질(220b)과 양자점(260)을 용매에 분산시킨 후, 분산된 혼합물을 용액 공정으로 제 1 전극(210) 상에 코팅하고 용매를 휘발시켜 형성한다. 그리고, 제 1 전극(210)과 양자 발광층(230) 사이에 정공 주입층(220a)이 더 형성될 수도 있다.Specifically, after the
일반적으로 양자 발광 소자는 양자 발광층으로 주입된 정공 및 전자가 양자점의 리간드로 인해 다른 양자점으로 쉽게 이동하지 못하므로, 양자 발광층을 두껍게 형성하여도 양자 발광층과 정공 수송층 또는 양자 발광층과 전자 수송층 사이의 계면에서 가장 많은 발광이 일어난다. 따라서, 정공, 전자 수송층 계면의 부하가 발생하므로, 양자 발광층의 두께를 30㎚ 미만으로 얇게 형성하여 발광 영역이 좁아져 신뢰성을 확보하기 어렵다.In general, the quantum light emitting device does not easily move holes and electrons injected into the quantum light emitting layer to other quantum dots due to the ligand of the quantum dot, so even when the quantum light emitting layer is formed thick, the interface between the quantum light emitting layer and the hole transport layer or the quantum light emitting layer and the electron transport layer The most luminescence occurs at. Therefore, since the load of the hole and the electron transporting layer interface is generated, the thickness of the quantum light emitting layer is made thinner than 30 nm, so that the light emitting area is narrowed and reliability is difficult to be secured.
그러나, 본 발명의 양자 발광 소자는 양자점(260)과 혼합된 인광 호스트 물질(220b)을 통해 정공 및 전자가 다른 양자점(260)으로 쉽게 이동할 수 있다. 따라서, 양자 발광층(260)과 정공 주입층(220a) 또는 양자 발광층(260)과 전자 수송층(240) 사이의 계면뿐만 아니라 양자 발광층(230) 내부의 양자점(260)에서 정공과 전자가 만나 발광할 수 있으므로 발광 효율을 향상시킬 수 있다.However, the quantum light emitting device of the present invention may easily move holes and electrons to other
이에 따라, 본 발명의 양자 발광 소자는 양자 발광층(230)의 두께를 30㎚ 이상으로 형성하여 발광 영역이 넓어진다. 따라서, 소자의 신뢰성을 확보할 수 있을 뿐만 아니라 정공 수송층을 형성하는 공정이 제거되어 공정을 단순화할 수 있으며 제조 비용을 절감할 수 있다.Accordingly, the quantum light emitting device of the present invention forms the thickness of the quantum
한편, 이상에서 설명한 본 발명은 상술한 실시 예 및 첨부된 도면에 한정되는 것이 아니고, 본 발명의 기술적 사상을 벗어나지 않는 범위 내에서 여러 가지 치환, 변형 및 변경이 가능하다는 것이 본 발명이 속하는 기술분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자에게 있어 명백할 것이다.While the present invention has been described in connection with what is presently considered to be the most practical and preferred embodiment, it is to be understood that the invention is not limited to the disclosed embodiments, but, on the contrary, is intended to cover various modifications and equivalent arrangements included within the spirit and scope of the appended claims. Will be apparent to those of ordinary skill in the art.
200, 300: 기판 110, 210: 제 1 전극
120a, 220a: 정공 주입층 120b: 인광 호스트 물질층
130, 230: 양자 발광층 140, 240: 전자 수송층
150, 250: 제 2 전극 160, 260: 양자점
220b: 인광 호스트 물질200, 300:
120a and 220a:
130, 230: quantum
150, 250:
220b: phosphorescent host material
Claims (7)
상기 제 1 전극 상에 형성된 인광 호스트 물질층;
상기 인광 호스트 물질층 상에 형성되며, 양자점을 포함하는 양자 발광층;
상기 양자 발광층 상에 형성되어 상기 양자 발광층에 전자를 전달하는 전자 수송층; 및
상기 전자 수송층 상에 형성된 제 2 전극을 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 양자 발광 소자.A first electrode formed on the substrate;
A phosphorescent host material layer formed on the first electrode;
A quantum light emitting layer formed on the phosphorescent host material layer and including a quantum dot;
An electron transport layer formed on the quantum light emitting layer to transfer electrons to the quantum light emitting layer; And
And a second electrode formed on the electron transport layer.
상기 인광 호스트 물질층은 상기 양자점에 정공을 전달하는 것을 특징으로 하는 양자 발광 소자.The method of claim 1,
The phosphorescent host material layer transfers holes to the quantum dots.
상기 인광 호스트 물질층은 CBP 또는 mCP로 형성된 것을 특징으로 하는 양자 발광 소자.The method of claim 1,
The phosphorescent host material layer is formed of CBP or mCP.
상기 제 1 전극 상에 형성되며, 인광 호스트 물질과 양자점이 혼합되어 형성된 양자 발광층;
상기 양자 발광층 상에 형성된 전자 수송층; 및
상기 전자 수송층 상에 형성된 제 2 전극을 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 양자 발광 소자.A first electrode formed on the substrate;
A quantum light emitting layer formed on the first electrode and formed by mixing a phosphorescent host material and a quantum dot;
An electron transport layer formed on the quantum light emitting layer; And
And a second electrode formed on the electron transport layer.
상기 양자 발광층은 상기 인광 호스트 물질과 상기 양자점을 용매에 분산시켜 형성된 것을 특징으로 하는 양자 발광 소자.The method of claim 4, wherein
The quantum light emitting layer is formed by dispersing the phosphorescent host material and the quantum dots in a solvent.
상기 인광 호스트 물질은 상기 양자점에 정공을 전달하는 것을 특징으로 하는 양자 발광 소자.The method of claim 4, wherein
The phosphorescent host material transfers holes to the quantum dots.
상기 인광 호스트 물질은 CBP 또는 mCP인 것을 특징으로 하는 양자 발광 소자.The method of claim 4, wherein
The phosphorescent host material is CBP or mCP, characterized in that the quantum light emitting device.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020110075637A KR102081101B1 (en) | 2011-07-29 | 2011-07-29 | Quantum-dot light emitting diode |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020110075637A KR102081101B1 (en) | 2011-07-29 | 2011-07-29 | Quantum-dot light emitting diode |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20130013810A true KR20130013810A (en) | 2013-02-06 |
| KR102081101B1 KR102081101B1 (en) | 2020-02-26 |
Family
ID=47894213
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020110075637A KR102081101B1 (en) | 2011-07-29 | 2011-07-29 | Quantum-dot light emitting diode |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR102081101B1 (en) |
Cited By (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN105514294A (en) * | 2016-01-27 | 2016-04-20 | 京东方科技集团股份有限公司 | Quantum dot electroluminescent device, hole transport method thereof and display device |
| CN106159099A (en) * | 2015-04-03 | 2016-11-23 | 南京瀚宇彩欣科技有限责任公司 | Quanta point electroluminescent unit and quanta point electroluminescent device |
| CN110890471A (en) * | 2018-09-07 | 2020-03-17 | 三星电子株式会社 | Electroluminescent device and display apparatus including the same |
| CN111384263A (en) * | 2018-12-29 | 2020-07-07 | Tcl集团股份有限公司 | Quantum dot light-emitting diode and preparation method thereof |
| US11005060B2 (en) | 2018-03-19 | 2021-05-11 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Electroluminescent device, and display device comprising thereof |
| US11737301B2 (en) | 2018-03-19 | 2023-08-22 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Electroluminescent device, and display device comprising thereof |
| US11859116B2 (en) | 2020-09-28 | 2024-01-02 | Samsung Display Co., Ltd. | Quantum dot composition and method of manufacturing light-emitting device using the quantum dot composition |
| US12016190B2 (en) | 2018-09-07 | 2024-06-18 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Electroluminescent device, and display device comprising thereof |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20070092079A (en) * | 2006-03-08 | 2007-09-12 | 한국전자통신연구원 | High efficiency organic light emitting diodes and manufacturing method |
| KR20080062907A (en) | 2006-12-29 | 2008-07-03 | 엘지디스플레이 주식회사 | Fabricating methode of electroluminescent device |
| JP2008300270A (en) * | 2007-06-01 | 2008-12-11 | Canon Inc | Light emitting element |
| JP2009199738A (en) * | 2008-02-19 | 2009-09-03 | Idemitsu Kosan Co Ltd | Organic/inorganic hybrid type electroluminescent element |
| KR20100017024A (en) * | 2008-08-05 | 2010-02-16 | 한국과학기술연구원 | Ac-driven light emitting device having single active layer of consolidated core-shell structure |
| KR20100043994A (en) * | 2008-10-21 | 2010-04-29 | 경희대학교 산학협력단 | Organic light emitting diode and method for fabricating the same |
-
2011
- 2011-07-29 KR KR1020110075637A patent/KR102081101B1/en active IP Right Grant
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20070092079A (en) * | 2006-03-08 | 2007-09-12 | 한국전자통신연구원 | High efficiency organic light emitting diodes and manufacturing method |
| KR20080062907A (en) | 2006-12-29 | 2008-07-03 | 엘지디스플레이 주식회사 | Fabricating methode of electroluminescent device |
| JP2008300270A (en) * | 2007-06-01 | 2008-12-11 | Canon Inc | Light emitting element |
| JP2009199738A (en) * | 2008-02-19 | 2009-09-03 | Idemitsu Kosan Co Ltd | Organic/inorganic hybrid type electroluminescent element |
| KR20100017024A (en) * | 2008-08-05 | 2010-02-16 | 한국과학기술연구원 | Ac-driven light emitting device having single active layer of consolidated core-shell structure |
| KR20100043994A (en) * | 2008-10-21 | 2010-04-29 | 경희대학교 산학협력단 | Organic light emitting diode and method for fabricating the same |
Cited By (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN106159099A (en) * | 2015-04-03 | 2016-11-23 | 南京瀚宇彩欣科技有限责任公司 | Quanta point electroluminescent unit and quanta point electroluminescent device |
| CN105514294A (en) * | 2016-01-27 | 2016-04-20 | 京东方科技集团股份有限公司 | Quantum dot electroluminescent device, hole transport method thereof and display device |
| US10236462B2 (en) | 2016-01-27 | 2019-03-19 | Boe Technology Group Co., Ltd. | Quantum dot electroluminescent device and display apparatus |
| US11005060B2 (en) | 2018-03-19 | 2021-05-11 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Electroluminescent device, and display device comprising thereof |
| US11737301B2 (en) | 2018-03-19 | 2023-08-22 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Electroluminescent device, and display device comprising thereof |
| CN110890471A (en) * | 2018-09-07 | 2020-03-17 | 三星电子株式会社 | Electroluminescent device and display apparatus including the same |
| US11957046B2 (en) | 2018-09-07 | 2024-04-09 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Electroluminescent device, and display device comprising thereof |
| US12016190B2 (en) | 2018-09-07 | 2024-06-18 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Electroluminescent device, and display device comprising thereof |
| CN111384263A (en) * | 2018-12-29 | 2020-07-07 | Tcl集团股份有限公司 | Quantum dot light-emitting diode and preparation method thereof |
| CN111384263B (en) * | 2018-12-29 | 2021-11-19 | Tcl科技集团股份有限公司 | Quantum dot light-emitting diode and preparation method thereof |
| US12101953B2 (en) | 2018-12-29 | 2024-09-24 | Tcl Technology Group Corporation | Quantum dot light-emitting diode and method for fabricating the same |
| US11859116B2 (en) | 2020-09-28 | 2024-01-02 | Samsung Display Co., Ltd. | Quantum dot composition and method of manufacturing light-emitting device using the quantum dot composition |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR102081101B1 (en) | 2020-02-26 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR101686104B1 (en) | Quantum-dot light emitting diode | |
| KR102081101B1 (en) | Quantum-dot light emitting diode | |
| US10403690B2 (en) | Light emitting device including tandem structure with quantum dots and nanoparticles | |
| KR101777136B1 (en) | Quantum-dot light emitting diode and method for fabricating the same | |
| US10700236B2 (en) | Quantum dot spacing for high efficiency quantum dot LED displays | |
| KR101686107B1 (en) | Quantum-dot light emitting diode and method for fabrication the same | |
| KR101274068B1 (en) | Quantum Dot Light Emitting Diode Device and Display Using the Same | |
| US9768404B1 (en) | Quantum dot spacing for high efficiency quantum dot LED displays | |
| KR101794645B1 (en) | Quantum-dot light emitting diode | |
| Kim et al. | Performance of light-emitting-diode based on quantum dots | |
| KR101357045B1 (en) | Tunable Light Emitting Diode using Graphene conjugated Metal oxide semiconductor-Graphene core-shell Quantum dots and its fabrication process thereof | |
| KR102156760B1 (en) | Quantum dot light emitting display device and method for fabricating the same | |
| US20160155970A1 (en) | Vertical organic light-emitting transistor and organic led illumination apparatus having the same | |
| US20140374696A1 (en) | Light-emitting element, display panel and manufacturing method thereof | |
| KR20110127897A (en) | Quantum-dot light emitting diode and method for fabrication the same | |
| JP7465074B2 (en) | Display device | |
| KR101726630B1 (en) | Quantum-dot light emitting diode | |
| WO2018161552A1 (en) | Light-emitting diode, array substrate, light-emitting unit and display device | |
| KR20120050146A (en) | Quantum-dot light emitting diode | |
| KR20200078515A (en) | Display device | |
| KR20220092736A (en) | Organic light-emitting diode and display apparatus including the same | |
| TW201923433A (en) | Display device | |
| KR20120016342A (en) | Quantum-dot light emitting diode | |
| KR20130015671A (en) | Organic light emitting device and method for fabricating the same | |
| US20220359845A1 (en) | Light-emitting element, light-emitting device, and method for manufacturing light-emitting element |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A201 | Request for examination | ||
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| AMND | Amendment | ||
| E90F | Notification of reason for final refusal | ||
| AMND | Amendment | ||
| E601 | Decision to refuse application | ||
| AMND | Amendment | ||
| J201 | Request for trial against refusal decision | ||
| J301 | Trial decision |
Free format text: TRIAL NUMBER: 2018101001395; TRIAL DECISION FOR APPEAL AGAINST DECISION TO DECLINE REFUSAL REQUESTED 20180329 Effective date: 20190801 |
|
| S901 | Examination by remand of revocation | ||
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| GRNO | Decision to grant (after opposition) | ||
| GRNT | Written decision to grant |