KR100889978B1 - Method of selectively etching semiconductor region, separation method of semiconductor layer and separation method of semiconductor device from substrate - Google Patents
Method of selectively etching semiconductor region, separation method of semiconductor layer and separation method of semiconductor device from substrate Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR100889978B1 KR100889978B1 KR1020070103186A KR20070103186A KR100889978B1 KR 100889978 B1 KR100889978 B1 KR 100889978B1 KR 1020070103186 A KR1020070103186 A KR 1020070103186A KR 20070103186 A KR20070103186 A KR 20070103186A KR 100889978 B1 KR100889978 B1 KR 100889978B1
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- substrate
- semiconductor
- semiconductor layer
- etching
- gan
- Prior art date
Links
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 125
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 68
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 36
- 238000005530 etching Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 30
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 title abstract description 6
- MUBZPKHOEPUJKR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Oxalic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C(O)=O MUBZPKHOEPUJKR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 24
- 238000000866 electrolytic etching Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 15
- 239000003792 electrolyte Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 10
- 235000006408 oxalic acid Nutrition 0.000 claims abstract description 8
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 claims description 6
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 6
- 230000001681 protective effect Effects 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000008151 electrolyte solution Substances 0.000 description 8
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 6
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 6
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 3
- 229910052594 sapphire Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 239000010980 sapphire Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000002474 experimental method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910052733 gallium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 125000000896 monocarboxylic acid group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- 238000002161 passivation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000002411 adverse Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004299 exfoliation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000017525 heat dissipation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052738 indium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000002360 preparation method Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/04—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer
- H01L21/18—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer the devices having semiconductor bodies comprising elements of Group IV of the Periodic Table or AIIIBV compounds with or without impurities, e.g. doping materials
- H01L21/30—Treatment of semiconductor bodies using processes or apparatus not provided for in groups H01L21/20 - H01L21/26
- H01L21/302—Treatment of semiconductor bodies using processes or apparatus not provided for in groups H01L21/20 - H01L21/26 to change their surface-physical characteristics or shape, e.g. etching, polishing, cutting
- H01L21/306—Chemical or electrical treatment, e.g. electrolytic etching
- H01L21/3063—Electrolytic etching
- H01L21/30635—Electrolytic etching of AIIIBV compounds
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Weting (AREA)
- Led Devices (AREA)
Abstract
Description
본 발명은 반도체 영역의 선택적 식각방법에 관한 것으로, 전해에칭 방식을 적용할 때 반도체층의 도전 유형에 따라서 식각속도가 달라지는 현상을 이용하는 반도체 영역의 선택적 식각방법, 반도체층의 분리방법 및 반도체소자를 기판으로부터 분리하는 방법에 관한 것이다.The present invention relates to a selective etching method of the semiconductor region, the selective etching method of the semiconductor region, the method of separating the semiconductor layer and the semiconductor device using the phenomenon that the etching speed is changed according to the conductivity type of the semiconductor layer when applying the electrolytic etching method A method of separating from a substrate.
발광다이오드의 고효율, 고출력 동작이 요구됨에 따라 LED 칩에서 발생한 열을 신속하게 외부로 방출해야 하는 필요성이 커지고 있다. 현재 가장 높은 열방출 효율을 보이는 구조는 사파이어 기판 위에 성장된 LED 에피를 박리(lift-off) 공정으로 떼어내서 금속 기판에 접착하는 방법을 사용하고 있다. 이로서 낮은 열전도도를 갖는 사파이어 기판을 통하지 않고 높은 열전도도의 금속기판을 통해 열을 방출 할 수 있게 되어 고출력의 LED제작에 응용할 수 있다. 또한, 한국등록공보 495215호는 이러한 방식의 한 예를 설명하고 있다.As high efficiency and high power operation of the light emitting diodes is required, the necessity of quickly dissipating heat generated from the LED chip to the outside is increasing. Currently, the structure showing the highest heat dissipation efficiency uses a method of peeling off the LED epi grown on the sapphire substrate by a lift-off process and bonding it to the metal substrate. As a result, it is possible to release heat through a high thermal conductive metal substrate without passing through a sapphire substrate having a low thermal conductivity, and thus it can be applied to manufacturing high-power LEDs. In addition, Korean Patent Publication No. 495215 describes an example of such a method.
그러나, 레이저 광을 이용하는 방식은 공정비용이 많이 소요되고 레이저 노광 영역이 작아서 공정 시간도 많이 걸리는 문제점이 있는 것은 물론이고 레이저 노광에 의해 발생되는 응력 또한 소자의 신뢰성에 나쁜 영향을 미치는 문제점이 있었다.However, the method using the laser light has a problem that the process cost is high and the laser exposure area is small, so that the process time is too long, and the stress generated by the laser exposure also adversely affects the reliability of the device.
본 발명은 이러한 문제점을 해결하기 위한 것으로서 본 발명의 목적은 고효율은 물론, 제조가 용이하고, 제조 단가를 절감할 수 있는 반도체층의 분리방법 및 반도체소자를 기판으로부터 분리하는 방법을 제공 하는데 있다.SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION The present invention has been made to solve such a problem, and an object of the present invention is to provide a method of separating a semiconductor layer and a method of separating a semiconductor device from a substrate, which is easy to manufacture, and can reduce manufacturing cost as well as high efficiency.
상술한 문제점을 해결하기 위한 기술적 수단으로서, 본 발명의 제1측면은 N형 GaN 계열의 제1 반도체영역과 상기 제1 반도체영역과 다른 도핑 유형을 갖는 GaN계열의 제2반도체 영역을 기판 상에 준비하는 단계와 제1 반도체영역과 제2 반도체 영역을 양극으로 하고 전해액을 음극으로 하여 전해 에칭을 수행하는 단계와, 제1 반도체영역의 에칭 속도가 상기 제2 반도체 영역의 에칭 속도에 비해 큰 반도체 영역의 선택적 식각방법을 제공한다.As a technical means for solving the above-described problems, the first aspect of the present invention is a first semiconductor region of the N-type GaN series and the second semiconductor region of the GaN series having a doping type different from the first semiconductor region on the substrate Preparing and performing electrolytic etching with the first semiconductor region and the second semiconductor region as the anode and the electrolyte as the cathode, and the etching rate of the first semiconductor region being greater than that of the second semiconductor region. Provides selective etching of regions.
"GaN 계열"이라 함은 Ga, N 만으로 이루어진 물질 일수도 있고, Ga, N 이외의 In, Al 등 III족 또는 P, As, Sb 등 V족이 함유된 물질도 포함하는 것으로 해석되어야 한다."GaN-based" may be a material consisting of only Ga and N, and should also be interpreted to include materials containing Group III, such as In, Al, or Group V, other than Ga, N, or the like.
바람직하게는, 전해액은 옥살산 또는 KOH를 함유한다.Preferably, the electrolyte contains oxalic acid or KOH.
한편, 제1 반도체영역과 다른 도핑 유형을 갖는 GaN계열은 도핑되지 않거나 P형 도핑되는 것을 의미한다.Meanwhile, a GaN series having a doping type different from that of the first semiconductor region may be undoped or P-doped.
본 발명의 제2 측면은 제1 기판 상에 N형 GaN계열의 반도체층을 포함하는 반도체 구조물을 준비하는 단계와, 반도체 구조물을 제2 기판에 부착하는 단계와, 반도체 구조물을 양극으로 하고 전해액을 음극으로 하여 전해 에칭을 수행하는 단계와, 반도체층의 식각에 의해 제1 기판과 제2 기판이 서로 분리되는 반도체 구조물의 분리방법을 제공한다.According to a second aspect of the present invention, there is provided a semiconductor structure including an N-type GaN-based semiconductor layer on a first substrate, attaching the semiconductor structure to a second substrate, and using the semiconductor structure as an anode and A method of separating a semiconductor structure in which the first substrate and the second substrate are separated from each other by performing an electrolytic etching with a cathode and etching the semiconductor layer is provided.
본 발명의 제3 측면은 제1 기판 상에 N형 GaN계열의 제1 반도체층과 상기 제1 반도체영역과 다른 도핑 유형을 갖는 GaN계열의 제2 반도체층 및 반도체 구조물을 순차적으로 준비하는 단계와, 반도체 구조물을 제2 기판에 부착하는 단계와, 제1 기판과 상기 제2 기판을 양극으로 하고 전해액을 음극으로 하여 전해 에칭을 수행하는 단계와, 제1 반도체층의 에칭 속도가 상기 제2 반도체층의 에칭 속도에 비해 큼을 이용하여 상기 제1 반도체층이 상기 제2 반도체 보다 빨리 제거되어 상기 제1 기판과 상기 제2 기판은 상기 제1 반도체층의 식각에 의해 분리되는 것으로 특징으로 하는 반도체 구조물을 기판으로부터 분리하는 방법을 제공한다.According to a third aspect of the present invention, there is provided a method of sequentially preparing an N-type GaN-based first semiconductor layer and a GaN-based second semiconductor layer having a different doping type from the first semiconductor region and a semiconductor structure on a first substrate; Attaching the semiconductor structure to the second substrate, performing electrolytic etching with the first substrate and the second substrate as the anode and the electrolyte as the cathode, and the etching rate of the first semiconductor layer being the second semiconductor. The semiconductor structure is characterized in that the first semiconductor layer is removed faster than the second semiconductor using a larger than the etching rate of the layer so that the first substrate and the second substrate are separated by etching of the first semiconductor layer. It provides a method for separating the from the substrate.
한편, 제2 반도체층은 응용하고자 하는 소자에 따라 반도체 LED 및 LD 구조를 포함할 수도 있다. 즉, 제2 반도체층은 상기 반도체 소자부의 일부를 구성하거나 더미 형태로 반도체 소자의 일부를 형성하지는 않고 반도체소자를 기판으로부터 분리하기 위한 필요에서 삽입될 수도 있다. Meanwhile, the second semiconductor layer may include a semiconductor LED and an LD structure according to the device to be applied. That is, the second semiconductor layer may be inserted in the need for separating the semiconductor element from the substrate without forming part of the semiconductor element portion or forming part of the semiconductor element in a dummy form.
제1 기판은 반도체 기판이고, 제2 기판은 금속 기판으로 하면 금속 기판에서는 열을 효과적으로 방출할 수 있는 구조를 가질 수 있다.When the first substrate is a semiconductor substrate and the second substrate is a metal substrate, the metal substrate may have a structure capable of effectively dissipating heat.
본 발명에 의하면, 전해액을 이용한 전해에칭 방식을 통해 기판에 성장된 반도체 구조물을 손쉽게 분리할 수 있어 이 반도체 구조물을 다른 기판에 전이할 수 있게 된다.According to the present invention, a semiconductor structure grown on a substrate can be easily separated through an electrolytic etching method using an electrolyte solution, so that the semiconductor structure can be transferred to another substrate.
본 발명을 LED 제조에 응용하면, 낮은 열전도도를 갖는 사파이어 기판에 성장이 용이한 GaN 계열의 물질을 포함하는 광소자를 성장시키고 이를 높은 열전도도의 금속기판으로 전이함으로써 금속기판을 통해 열을 용이하게 방출할 수 있게 되어 고출력의 LED를 제작할 수 있게 되는 효과가 있다.When the present invention is applied to LED manufacturing, an optical device including a GaN-based material that is easy to grow is grown on a sapphire substrate having a low thermal conductivity, and the heat is easily transferred to the metal substrate having a high thermal conductivity by transferring it. Being able to emit light has the effect of being able to produce a high-power LED.
이하, 본 발명이 속하는 기술 분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자가 본 발명의 기술적 사상을 용이하게 실시할 수 있을 정도로 상세히 설명하기 위하여, 본 발명의 가장 바람직한 실시 예를 첨부된 도면을 참조하여 설명하기로 한다. 본 발명은 이하에서 개시되는 실시 예에 한정되는 것이 아니라 서로 다른 다양한 형태로 구현될 수 있으며, 단지 본 실시의 예는 본 발명의 개시가 완전하도록 하며 통상의 지식을 가진 자에게 발명의 범주를 완전하게 알려주기 위해 제공되는 것이다.DETAILED DESCRIPTION Hereinafter, exemplary embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings so that those skilled in the art may easily implement the technical idea of the present invention. do. The present invention is not limited to the embodiments disclosed below, but can be implemented in various different forms, only the embodiments of the present invention to make the disclosure of the present invention complete and complete the scope of the invention to those skilled in the art. It is provided to inform you.
도 1은 본 발명의 실시예에 따라서 반도체 영역의 선택적 식각방법을 설명하기 위한 단면도이다.1 is a cross-sectional view illustrating a selective etching method of a semiconductor region in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention.
도 1을 참조하면, 기판(110) 상에 n-GaN계열의 제1 반도체층(130)과 undoped-GaN계열의 제2 반도체층(120,140)을 적층한 구조가 도시되어 있다. 제1 반도체층(130)과 p-GaN계열의 제2반도체층(120,140)을 양극으로 하고 전해액을 음극으로 하여 전해 에칭을 수행한다. 전해액은 옥살산 또는 KOH를 함유하는 것이 바람직하다.Referring to FIG. 1, an n-GaN-based
상기 전해액을 이용하여 전해 에칭을 수행하면 n-GaN계열의 제1 반도체층(130)은 undoped-GaN계열의 제2 반도체층(120,140)에 비해 에칭속도가 월등하게 크다. When the electrolytic etching is performed using the electrolyte solution, the etching rate of the
본 발명자들은 상술한 옥살산 또는 KOH 전해 용액을 이용하여 에칭을 수행하면 n-GaN계열의 제1 반도체층이 이와는 다른 전도타입인 undoped GaN계열, p-GaN계열의 반도체층에 비해 에칭 속도가 훨씬 빠른 사실을 확인하였다. 이러한 점을 GaN 계열의 반도체 소자를 제조에 이용하면, 다양한 제조 공정의 응용이 가능하게 된다. When the etching is performed using the above-described oxalic acid or KOH electrolytic solution, the inventors of the present invention have a much faster etching rate than that of the undoped GaN and p-GaN semiconductor layers. I confirmed the fact. Using this point in manufacturing GaN-based semiconductor devices, it is possible to apply a variety of manufacturing processes.
도 2a 및 도 2b는 본 발명의 실험예에 따라서 반도체층이 분리되고 있는 상황을 도시한 사진들이다.2A and 2B are photographs showing a situation in which a semiconductor layer is separated according to an experimental example of the present invention.
본 실험에서는 전해액 옥살산 (COOH)2, 농도 0.3 M, 전압 40 V, 온도 10oC에서 실험을 수행한 결과를 도시하고 있다. This experiment shows the results of the experiment at the electrolyte oxalic acid (COOH) 2 concentration 0.3 M, voltage 40 V, temperature 10 ° C.
도 2c는 본 발명의 실시예에 따라서 전압에 따른 에칭비율을 도시한 그래프 이다.Figure 2c is a graph showing the etching rate according to the voltage in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention.
전해액 옥살산 (COOH)2, 농도 0.3 M, 온도 10oC 에서 전압을 변화시키면서 에칭되는 비율을 그래프로 나타내었다. 그 결과에 의하면, 20V에서 60V 까지의 영역에서 특히 높은 에칭비율을 나타내었다.The ratio etched while varying the voltage at the electrolyte solution oxalic acid (COOH) 2 , concentration 0.3 M, temperature 10 ° C is shown graphically. As a result, the etching rate was particularly high in the range from 20V to 60V.
(반도체 구조물을 기판으로부터 분리하는 방법)(Method of separating semiconductor structure from substrate)
다음으로, 도 3a 및 도 3b는 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 반도체 구조물을 기판으로부터 분리하는 방법을 설명하기 위한 도면들이다.3A and 3B are diagrams for describing a method of separating a semiconductor structure from a substrate according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 3a를 참조하면, 제1 기판(210) 상에 n-GaN계열의 제1 반도체층(230)과 상기 제1 반도체층(230)과 다른 도전유형을 갖는 GaN계열의 제2 반도체층(220,240) 및 반도체 구조물(300)이 순차적으로 준비된 기판이 마련된다. Referring to FIG. 3A, an n-GaN-based
다음으로, 반도체 구조물(300)을 제2 기판(500)에 부착한다. 부착하는 방식은 부착하기 위한 점착층을 이용하는 방법 등 공지의 방식을 이용한다.Next, the
반도체 구조물(300)은 반도체 소자의 일부 또는 전부가 적층되는 것이 가능함은 물론이고, 본 실시예에 있어서는 성장이 용이하지만 열전달이 불리한 제1 기판(210) 상에 반도체층들을 성장시킨 다음, 열전달이 우수한 제2 기판에 이들 반도체층들을 옮겨 부착시킴으로써 목적을 달성할 수 있다.Of course, the
도 3a에서는 반도체 구조물(300)의 각 층은 전해 에칭시 노출이 되지 않도록 하고(그 일예는 도 4b에 상세히 설명함), n-GaN 계열의 반도체층(230)이 전해액에 노출되도록 함으로써 n-GaN 계열의 반도체층(230)이 식각되어 양 기판이 분리될 수 있도록 한다. 결과적으로, 반도체구조물(300)은 제1 기판(210)으로부터 전이되어 제2 기판(500)에 부착될 수 있게 된다.In FIG. 3A, each layer of the
본 실시예에서 n-GaN 계열의 반도체층(230)이 식각에 의해 희생층으로서의 기능을 수행하여 제1 기판(210)과 제2 기판(500)을 분리할 수 있으면 본 발명의 기술적 사상의 범위에 포함되는 것으로 해석해야한다. 즉, n-GaN 계열의 반도체층(230)과 전해 에칭에 의할 때 식각 선택비가 우수한 다른 물질들을 도입하면 본 발명은 제1 반도체층(230)과 다른 도전유형을 갖는 GaN계열을 반드시 채택하지 않을 수 있다.In this embodiment, if the n-GaN-based
(반도체 소자를 기판으로부터 분리하는 방법)(Method for Separating Semiconductor Device from Substrate)
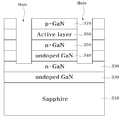
도 4a 및 도 4b는 앞의 도 3의 박리공정을 위한 반도체 구조물의 준비를 설명하기 위한 도면들이다. 전해에칭이 일어나기 위해서는 아래쪽 n-GaN층(330)에 전해액이 접촉해야 하고, 반면 위쪽 n-GaN층(350)은 LED 구조의 일부로 제거하지 않는 것이 바람직하다.4A and 4B are views for explaining preparation of a semiconductor structure for the exfoliation process of FIG. 3. In order for the electroetching to occur, the electrolyte solution should contact the lower n-
도 4a를 참조하면, 제1 기판(310) 상에 undoped GaN층(320), n-GaN계열의 반도체층(330)과 undoped GaN층(340)을 순차적으로 형성하고 그 상부에 n-GaN층(350), 활성층(360), 및 p-GaN층을 형성한다. Referring to FIG. 4A, an undoped GaN
다음으로, n-GaN계열의 반도체층(330)을 기준으로 전해 에칭을 통하여 분리작업을 진행하되, 다른 n-GaN 계열의 층에는 전해액이 접근하지 못하고 n-GaN계열 의 반도체층(330)에만 전해액이 접근할 수 있도록 홀(Hole)을 형성한다. Next, the separation operation is performed by electrolytic etching based on the n-GaN-based
도 4b를 참조하면, 이러한 홀에 의해서 전해액은 n-GaN계열의 반도체층(330)에만 닿도록 하기 위해서 홀(Hole)의 측부에 보호막(410)을 형성한다. 보호막(410)은 전해 에칭에 의해 n-GaN계열의 반도체층에 비해 식각 속도가 낮은 물질을 채택하여 형성한다.Referring to FIG. 4B, a
이러한 보호막(410)에 의하면 반도체 소자부에 n-GaN 계열의 물질이 적층되어 있더라도 n-GaN계열의 반도체층(330)이 기판 분리 역할을 하는데 지장이 없게 된다.According to the
이 경우는 반도체 소자부를 제2 기판에 부착하기 전에, n-GaN계열의 반도체층(330)의 적어도 일부를 노출시켜 홀을 형성하기 위해 선택적으로 식각한다.In this case, before attaching the semiconductor element portion to the second substrate, at least a portion of the n-GaN
도 1은 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 반도체층의 분리방법을 설명하기 위한 평면도이다.1 is a plan view illustrating a method of separating a semiconductor layer in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention.
도 2a 및 도 2b는 본 발명의 실험예에 따라서 반도체층이 분리되고 있는 상황을 도시한 사진들이다.2A and 2B are photographs showing a situation in which a semiconductor layer is separated according to an experimental example of the present invention.
도 2c는 본 발명의 실시예에 따라서 전압에 따른 에칭비율을 도시한 그래프이다.Figure 2c is a graph showing the etching rate according to the voltage in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention.
도 3a 및 도 3b는 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 반도체 구조물을 기판으로부터 분리하는 방법을 설명하기 위한 도면들이다.3A and 3B are diagrams for describing a method of separating a semiconductor structure from a substrate according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 4a 및 도 4b는 본 발명의 다른 실시예에 따른 반도체소자를 기판으로부터 분리하는 방법을 설명하기 위한 도면들이다.4A and 4B are diagrams for describing a method of separating a semiconductor device from a substrate according to another embodiment of the present invention.
Claims (13)
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020070103186A KR100889978B1 (en) | 2007-10-12 | 2007-10-12 | Method of selectively etching semiconductor region, separation method of semiconductor layer and separation method of semiconductor device from substrate |
| PCT/KR2008/005913 WO2009048265A1 (en) | 2007-10-12 | 2008-10-09 | Method of selectively etching semiconductor region, separation method of semiconductor layer and separation method of semiconductor device from substrate |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020070103186A KR100889978B1 (en) | 2007-10-12 | 2007-10-12 | Method of selectively etching semiconductor region, separation method of semiconductor layer and separation method of semiconductor device from substrate |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR100889978B1 true KR100889978B1 (en) | 2009-03-25 |
Family
ID=40698577
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020070103186A KR100889978B1 (en) | 2007-10-12 | 2007-10-12 | Method of selectively etching semiconductor region, separation method of semiconductor layer and separation method of semiconductor device from substrate |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR100889978B1 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20180100386A (en) * | 2016-04-12 | 2018-09-10 | 우한 차이나 스타 옵토일렉트로닉스 테크놀로지 컴퍼니 리미티드 | Stripping method of flexible substrate |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH07302889A (en) * | 1994-03-10 | 1995-11-14 | Canon Inc | Manufacture of semiconductor substrate |
| KR19990063376A (en) * | 1997-12-26 | 1999-07-26 | 이데이 노부유끼 | Semiconductor Substrates, Thin Film Semiconductor Devices, Methods of Manufacturing Them and Polarization Devices |
| KR20030059281A (en) * | 2000-11-27 | 2003-07-07 | 에스. 오. 이. 떼끄 씰리꽁 오 냉쉴라또흐 떼끄놀로지 | Method for making a substrate in particular for optics, electronics or optoelectronics and resulting substrate |
| KR20030077423A (en) * | 2002-03-26 | 2003-10-01 | 닛뽄덴끼 가부시끼가이샤 | Group ⅲ nitride based semiconductor substrate and process for manufacture thereof |
-
2007
- 2007-10-12 KR KR1020070103186A patent/KR100889978B1/en active IP Right Grant
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH07302889A (en) * | 1994-03-10 | 1995-11-14 | Canon Inc | Manufacture of semiconductor substrate |
| KR19990063376A (en) * | 1997-12-26 | 1999-07-26 | 이데이 노부유끼 | Semiconductor Substrates, Thin Film Semiconductor Devices, Methods of Manufacturing Them and Polarization Devices |
| KR20030059281A (en) * | 2000-11-27 | 2003-07-07 | 에스. 오. 이. 떼끄 씰리꽁 오 냉쉴라또흐 떼끄놀로지 | Method for making a substrate in particular for optics, electronics or optoelectronics and resulting substrate |
| KR20030077423A (en) * | 2002-03-26 | 2003-10-01 | 닛뽄덴끼 가부시끼가이샤 | Group ⅲ nitride based semiconductor substrate and process for manufacture thereof |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20180100386A (en) * | 2016-04-12 | 2018-09-10 | 우한 차이나 스타 옵토일렉트로닉스 테크놀로지 컴퍼니 리미티드 | Stripping method of flexible substrate |
| KR102081014B1 (en) * | 2016-04-12 | 2020-02-24 | 우한 차이나 스타 옵토일렉트로닉스 테크놀로지 컴퍼니 리미티드 | Stripping method of flexible substrate |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US8344412B2 (en) | Chip level package of light-emitting diode | |
| US8470621B2 (en) | Method for fabricating a flip-chip semiconductor optoelectronic device | |
| US20110215292A1 (en) | Semiconductor light emitting device and method for manufacturing the same | |
| CN101969089B (en) | Method for manufacturing gallium nitride-based light-emitting diode with current barrier layer | |
| US20070221927A1 (en) | Light-emitting diode and method for manufacturing the same | |
| JP2007088480A (en) | Manufacturing method of light emitting diode having vertical structure | |
| JP7043551B2 (en) | Method of forming a p-shaped layer of a light emitting device | |
| US8178891B2 (en) | Semiconductor light emitting device and method for manufacturing the same | |
| JP5363973B2 (en) | Light emitting device including Zener diode and method for manufacturing the same | |
| KR20100035846A (en) | Light emitting device and method for fabricating the same | |
| TW201037859A (en) | Light emitting diode chip and manufacturing method thereof | |
| US8574935B2 (en) | Manufacturing method of solid state light emitting element | |
| JP2009049371A (en) | Nitride-based compound semiconductor light emitting element, and method of manufacturing the same | |
| US8178886B2 (en) | Multi-layered LED epitaxial structure with light emitting unit | |
| JP5616960B2 (en) | Extending contact pad to die edge using electrical isolation | |
| KR101001782B1 (en) | Separation Method of Semiconductor Device From Substrate | |
| JP2007207869A (en) | Nitride semiconductor light-emitting device | |
| KR100889978B1 (en) | Method of selectively etching semiconductor region, separation method of semiconductor layer and separation method of semiconductor device from substrate | |
| KR101001773B1 (en) | Method of Selectively Etching Semiconductor region | |
| US8253160B2 (en) | Light-emitting diode chip structure and fabrication method thereof | |
| KR100730756B1 (en) | Light emitting device having zenor diode therein and method of fabricating the same | |
| JP5758518B2 (en) | Manufacturing method of semiconductor light emitting device | |
| KR101189474B1 (en) | Light emitting diode with current spreading electrodes and manufacturing method thereof | |
| KR101319218B1 (en) | Method of lifting-off substrate | |
| KR20120032779A (en) | High efficiency light emitting diode and method of fabricating the same |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A201 | Request for examination | ||
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right | ||
| GRNT | Written decision to grant | ||
| FPAY | Annual fee payment |
Payment date: 20130207 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| FPAY | Annual fee payment |
Payment date: 20131211 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| FPAY | Annual fee payment |
Payment date: 20150112 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| FPAY | Annual fee payment |
Payment date: 20160104 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| FPAY | Annual fee payment |
Payment date: 20161212 Year of fee payment: 9 |
|
| FPAY | Annual fee payment |
Payment date: 20171211 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| FPAY | Annual fee payment |
Payment date: 20200103 Year of fee payment: 12 |