JPWO2018179332A1 - Display device, display device manufacturing method, and display device manufacturing apparatus - Google Patents
Display device, display device manufacturing method, and display device manufacturing apparatus Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JPWO2018179332A1 JPWO2018179332A1 JP2019508105A JP2019508105A JPWO2018179332A1 JP WO2018179332 A1 JPWO2018179332 A1 JP WO2018179332A1 JP 2019508105 A JP2019508105 A JP 2019508105A JP 2019508105 A JP2019508105 A JP 2019508105A JP WO2018179332 A1 JPWO2018179332 A1 JP WO2018179332A1
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- display device
- resin layer
- region
- layer
- carbide
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 title claims description 31
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 82
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 claims abstract description 82
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims description 55
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 claims description 30
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 27
- 230000001678 irradiating effect Effects 0.000 claims description 11
- 239000004642 Polyimide Substances 0.000 claims description 6
- 238000005520 cutting process Methods 0.000 claims description 6
- 229920001721 polyimide Polymers 0.000 claims description 6
- 238000000608 laser ablation Methods 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000011159 matrix material Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 description 148
- 239000010408 film Substances 0.000 description 95
- 239000013256 coordination polymer Substances 0.000 description 25
- 238000005401 electroluminescence Methods 0.000 description 13
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 12
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 10
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 description 9
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 8
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 7
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 6
- 229910052814 silicon oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 6
- 229920000139 polyethylene terephthalate Polymers 0.000 description 5
- 239000005020 polyethylene terephthalate Substances 0.000 description 5
- 229910052581 Si3N4 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 description 4
- 239000011368 organic material Substances 0.000 description 4
- HQVNEWCFYHHQES-UHFFFAOYSA-N silicon nitride Chemical compound N12[Si]34N5[Si]62N3[Si]51N64 HQVNEWCFYHHQES-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- NIXOWILDQLNWCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N acrylic acid group Chemical group C(C=C)(=O)O NIXOWILDQLNWCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000012790 adhesive layer Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000004888 barrier function Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000010936 titanium Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229920002799 BoPET Polymers 0.000 description 2
- OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Carbon Chemical compound [C] OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000004593 Epoxy Substances 0.000 description 2
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical compound [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Titanium Chemical compound [Ti] RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium Chemical compound [Al] XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000003990 capacitor Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052799 carbon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 238000005229 chemical vapour deposition Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000011651 chromium Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000004020 conductor Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000010949 copper Substances 0.000 description 2
- AMGQUBHHOARCQH-UHFFFAOYSA-N indium;oxotin Chemical compound [In].[Sn]=O AMGQUBHHOARCQH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000002347 injection Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000007924 injection Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000036961 partial effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- -1 polyethylene terephthalate Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000002096 quantum dot Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000002829 reductive effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052719 titanium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 230000037303 wrinkles Effects 0.000 description 2
- VYZAMTAEIAYCRO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Chromium Chemical compound [Cr] VYZAMTAEIAYCRO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Copper Chemical compound [Cu] RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZOKXTWBITQBERF-UHFFFAOYSA-N Molybdenum Chemical compound [Mo] ZOKXTWBITQBERF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000004952 Polyamide Substances 0.000 description 1
- HCHKCACWOHOZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Zinc Chemical compound [Zn] HCHKCACWOHOZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000002679 ablation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000853 adhesive Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001070 adhesive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002411 adverse Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910045601 alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000000956 alloy Substances 0.000 description 1
- QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N atomic oxygen Chemical compound [O] QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000005452 bending Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052804 chromium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008030 elimination Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000003379 elimination reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000001704 evaporation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000005283 ground state Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000005525 hole transport Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000012535 impurity Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052738 indium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- APFVFJFRJDLVQX-UHFFFAOYSA-N indium atom Chemical compound [In] APFVFJFRJDLVQX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000011229 interlayer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052750 molybdenum Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011733 molybdenum Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000001579 optical reflectometry Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052760 oxygen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000001301 oxygen Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005192 partition Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000035515 penetration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229920002647 polyamide Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229910021420 polycrystalline silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229920005591 polysilicon Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 230000001681 protective effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005215 recombination Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000006798 recombination Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000002356 single layer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000003068 static effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052715 tantalum Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- GUVRBAGPIYLISA-UHFFFAOYSA-N tantalum atom Chemical compound [Ta] GUVRBAGPIYLISA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000010409 thin film Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000002834 transmittance Methods 0.000 description 1
- WFKWXMTUELFFGS-UHFFFAOYSA-N tungsten Chemical compound [W] WFKWXMTUELFFGS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052721 tungsten Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010937 tungsten Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000009281 ultraviolet germicidal irradiation Methods 0.000 description 1
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10K—ORGANIC ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES
- H10K71/00—Manufacture or treatment specially adapted for the organic devices covered by this subclass
- H10K71/80—Manufacture or treatment specially adapted for the organic devices covered by this subclass using temporary substrates
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10K—ORGANIC ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES
- H10K50/00—Organic light-emitting devices
- H10K50/80—Constructional details
- H10K50/84—Passivation; Containers; Encapsulations
- H10K50/844—Encapsulations
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G09—EDUCATION; CRYPTOGRAPHY; DISPLAY; ADVERTISING; SEALS
- G09F—DISPLAYING; ADVERTISING; SIGNS; LABELS OR NAME-PLATES; SEALS
- G09F9/00—Indicating arrangements for variable information in which the information is built-up on a support by selection or combination of individual elements
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G09—EDUCATION; CRYPTOGRAPHY; DISPLAY; ADVERTISING; SEALS
- G09F—DISPLAYING; ADVERTISING; SIGNS; LABELS OR NAME-PLATES; SEALS
- G09F9/00—Indicating arrangements for variable information in which the information is built-up on a support by selection or combination of individual elements
- G09F9/30—Indicating arrangements for variable information in which the information is built-up on a support by selection or combination of individual elements in which the desired character or characters are formed by combining individual elements
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05B—ELECTRIC HEATING; ELECTRIC LIGHT SOURCES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; CIRCUIT ARRANGEMENTS FOR ELECTRIC LIGHT SOURCES, IN GENERAL
- H05B33/00—Electroluminescent light sources
- H05B33/02—Details
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05B—ELECTRIC HEATING; ELECTRIC LIGHT SOURCES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; CIRCUIT ARRANGEMENTS FOR ELECTRIC LIGHT SOURCES, IN GENERAL
- H05B33/00—Electroluminescent light sources
- H05B33/02—Details
- H05B33/04—Sealing arrangements, e.g. against humidity
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05B—ELECTRIC HEATING; ELECTRIC LIGHT SOURCES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; CIRCUIT ARRANGEMENTS FOR ELECTRIC LIGHT SOURCES, IN GENERAL
- H05B33/00—Electroluminescent light sources
- H05B33/02—Details
- H05B33/06—Electrode terminals
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10K—ORGANIC ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES
- H10K50/00—Organic light-emitting devices
- H10K50/10—OLEDs or polymer light-emitting diodes [PLED]
- H10K50/11—OLEDs or polymer light-emitting diodes [PLED] characterised by the electroluminescent [EL] layers
- H10K50/115—OLEDs or polymer light-emitting diodes [PLED] characterised by the electroluminescent [EL] layers comprising active inorganic nanostructures, e.g. luminescent quantum dots
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10K—ORGANIC ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES
- H10K71/00—Manufacture or treatment specially adapted for the organic devices covered by this subclass
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10K—ORGANIC ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES
- H10K59/00—Integrated devices, or assemblies of multiple devices, comprising at least one organic light-emitting element covered by group H10K50/00
- H10K59/10—OLED displays
- H10K59/12—Active-matrix OLED [AMOLED] displays
- H10K59/131—Interconnections, e.g. wiring lines or terminals
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10K—ORGANIC ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES
- H10K59/00—Integrated devices, or assemblies of multiple devices, comprising at least one organic light-emitting element covered by group H10K50/00
- H10K59/80—Constructional details
- H10K59/87—Passivation; Containers; Encapsulations
- H10K59/873—Encapsulations
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Optics & Photonics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Crystallography & Structural Chemistry (AREA)
- Inorganic Chemistry (AREA)
- Nanotechnology (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Electroluminescent Light Sources (AREA)
- Devices For Indicating Variable Information By Combining Individual Elements (AREA)
Abstract
下面フィルム(10)と、TFT層(4)と、発光素子層(5)とを備える表示デバイス(2)であって、前記下面フィルムよりも上層で前記TFT層よりも下層に樹脂層(12)が設けられ、前記樹脂層の下面に第1領域および第2領域が含まれ、前記第2領域が、前記第1領域よりも単位面積当たりの炭化物の量が大きい炭化物パターン(CP)とされている。A display device (2) comprising a lower film (10), a TFT layer (4), and a light emitting element layer (5), wherein a resin layer (12) is provided above the lower film and below the TFT layer. ) Is provided, a first region and a second region are included on the lower surface of the resin layer, and the second region is a carbide pattern (CP) having a larger amount of carbide per unit area than the first region. ing.
Description
本発明は、表示デバイスに関する。 The present invention relates to a display device.
EL素子を含む表示デバイスを製造する場合、例えば、ガラス基板上に、樹脂層、TFT層、発光素子層等を含む積層体を形成し、ガラス基板の裏面から樹脂層の下面にレーザを照射してガラス基板を剥離し、樹脂層の下面にフィルムを貼り付ける。 In the case of manufacturing a display device including an EL element, for example, a laminate including a resin layer, a TFT layer, a light-emitting element layer, and the like is formed over a glass substrate, and a laser is irradiated from the rear surface of the glass substrate to the lower surface of the resin layer. The glass substrate is peeled off, and a film is attached to the lower surface of the resin layer.
樹脂層の下面にレーザを照射してガラス基板を剥離し、樹脂層の下面にフィルムを貼り付ける工程で積層体が帯電し、発光素子層に悪影響を及ぼすおそれがある。 In the process of irradiating a laser to the lower surface of the resin layer to peel the glass substrate and attaching a film to the lower surface of the resin layer, the laminate may be charged, which may adversely affect the light emitting element layer.
本発明の一態様に係る表示デバイスは、下面フィルムと、TFT層と、発光素子層とを備える表示デバイスであって、前記下面フィルムよりも上層で前記TFT層よりも下層に樹脂層が設けられ、前記樹脂層の下面に第1領域および第2領域が含まれ、前記第2領域が、前記第1領域よりも単位面積当たりの炭化物の量が大きい炭化物パターンとされている。 A display device according to one embodiment of the present invention is a display device including a lower film, a TFT layer, and a light-emitting element layer, wherein a resin layer is provided above the lower film and below the TFT layer. A first region and a second region are included on the lower surface of the resin layer, and the second region has a carbide pattern having a larger amount of carbide per unit area than the first region.
本発明の一態様によれば、樹脂層の下面に形成された炭化物パターンによって表示デバイスの帯電を抑えることができる。 According to one embodiment of the present invention, the charging of the display device can be suppressed by the carbide pattern formed on the lower surface of the resin layer.
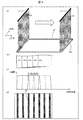
図1は、表示デバイスの製造方法の一例を示すフローチャートである。図2(a)は表示デバイスの形成途中の構成(基板に積層体を形成した状態)を示す断面図であり、図2(b)は表示デバイスの構例を示す断面図である。図3は、表示デバイスの形成途中の構成(基板に積層体を形成した状態)を示す平面図である。 FIG. 1 is a flowchart illustrating an example of a method for manufacturing a display device. FIG. 2A is a cross-sectional view illustrating a configuration in the process of forming a display device (a state in which a laminate is formed on a substrate), and FIG. 2B is a cross-sectional view illustrating a configuration example of the display device. FIG. 3 is a plan view showing a configuration in the process of forming a display device (a state in which a laminate is formed on a substrate).
フレキシブルな表示デバイスを製造する場合、図1、図2(a)および図3に示すように、まず、透光性の基板50(例えば、マザーガラス)上に樹脂層12を形成する(ステップS1)。次いで、無機バリア膜3を形成する(ステップS2)。次いで、TFT層4を形成する(ステップS3)。次いで、発光素子層(例えば、OLED素子層)5を形成する(ステップS4)。次いで、封止層6を形成する(ステップS5)。次いで、封止層6上に接着層8を介して上面フィルム9(例えば、PETフィルム)を貼り付ける(ステップS6)。
When manufacturing a flexible display device, first, as shown in FIGS. 1, 2A and 3, a
次いで、基板50越しに樹脂層12の下面にレーザ光を照射する(ステップS7)。ここでは、基板50の下面に照射され、基板50を透過したレーザ光を樹脂層12が吸収することで、樹脂層12の下面(基板50との界面)がアブレーションによって変質し、樹脂層12およびマザー基板50間の結合力が低下する。次いで、基板50を樹脂層12から剥離する(ステップS8)。次いで、図2(b)に示すように、樹脂層12の下面に、接着層11を介して下面フィルム10(例えばPETフィルム)を貼り付ける(ステップS9)。次いで、下面フィルム10、樹脂層12、バリア層3、TFT層4、発光素子層5、封止層6および上面フィルム9を含む積層体を切り出し線DLで分断し、複数の個片を切り出す(ステップS10)。次いで、個片から上面シート9の一部(端子部44上の部分)を剥離する端子出しを行う(ステップS11)。次いで、個片の封止層6の上側に接着層38を介して機能フィルム39を貼り付ける(ステップS12)。次いで、個片の端子部44に異方性導電材51を介して電子回路基板60を実装する(ステップS13)。これにより、図2(b)に示す表示デバイス2を得る。なお、前記各ステップは表示デバイスの製造装置が行う。
Next, the lower surface of the
樹脂層12の材料としては、例えば、ポリイミド、エポキシ、ポリアミド等が挙げられる。下面フィルム10の材料としては、例えばポリエチレンテレフタレート(PET)が挙げられる。
Examples of the material of the
バリア層3は、表示デバイスの使用時に、水分や不純物が、TFT層4や発光素子層5に到達することを防ぐ層であり、例えば、CVDにより形成される、酸化シリコン膜、窒化シリコン膜、あるいは酸窒化シリコン膜、またはこれらの積層膜で構成することができる。
The
TFT層4は、半導体膜15と、半導体膜15よりも上側に形成される無機絶縁膜16(ゲート絶縁膜)と、ゲート絶縁膜16よりも上側に形成されるゲート電極Gと、ゲート電極Gよりも上側に形成される無機絶縁膜18と、無機絶縁膜18よりも上側に形成される容量配線Cと、容量配線Cよりも上側に形成される無機絶縁膜20と、無機絶縁膜20よりも上側に形成される、ソース電極Sおよびドレイン電極Dと、ソース電極Sおよびドレイン電極Dよりも上側に形成される平坦化膜21とを含む。
The
半導体膜15、無機絶縁膜16(ゲート絶縁膜)、ゲート電極Gを含むように薄膜トランジスタ(TFT)が構成される。ソース電極Sは半導体膜15のソース領域に接続され、ドレイン電極Dは半導体膜15のドレイン領域に接続される。
A thin film transistor (TFT) is configured to include the
半導体膜15は、例えば低温ポリシリコン(LTPS)あるいは酸化物半導体で構成される。ゲート絶縁膜16は、例えば、CVD法によって形成された、酸化シリコン(SiOx)膜あるいは窒化シリコン(SiNx)膜またはこれらの積層膜によって構成することができる。ゲート電極G、ソース配線S、ドレイン配線D、および端子は、例えば、アルミニウム(Al)、タングステン(W)、モリブデン(Mo)、タンタル(Ta)、クロム(Cr)、チタン(Ti)、銅(Cu)の少なくとも1つを含む金属の単層膜あるいは積層膜によって構成される。なお、図2では、半導体膜15をチャネルとするTFTがトップゲート構造で示されているが、ボトムゲート構造でもよい(例えば、TFTのチャネルが酸化物半導体の場合)。
The
無機絶縁膜18・20は、例えば、CVD法によって形成された、酸化シリコン(SiOx)膜あるいは窒化シリコン(SiNx)膜またはこれらの積層膜によって構成することができる。平坦化膜(層間絶縁膜)21は、例えば、ポリイミド、アクリル等の塗布可能な感光性有機材料によって構成することができる。
The inorganic
TFT層4の端部(発光素子層5と重ならない非アクティブ領域NA)には端子部44が設けられる。端子部44は、ICチップ、FPC等の電子回路基板60との接続に用いられる端子TMと、これに接続される端子配線TWとを含む。端子配線TWは、中継配線LWおよび引き出し配線DWを介してTFT層4の各種配線と電気的に接続される。
A
端子TM、端子配線TWおよび引き出し配線DWは、例えばソース電極Sと同一工程で形成されるため、ソース電極Sと同層(無機絶縁膜20上)にかつ同材料(例えば、2枚のチタン膜およびこれらにサンドされたアルミニウム膜)で形成される。中継配線LWは例えば容量電極Cと同一工程で形成される。端子TM、端子配線TWおよび引き出し配線DWの端面(エッジ)は平坦化膜21で覆われている。
The terminal TM, the terminal wiring TW, and the lead wiring DW are formed in the same step as the source electrode S, for example, so that they are formed on the same layer (on the inorganic insulating film 20) and the same material as the source electrode S (for example, two titanium films). And an aluminum film sandwiched between them. The relay wiring LW is formed, for example, in the same step as the capacitor electrode C. The end surfaces (edges) of the terminal TM, the terminal wiring TW, and the lead wiring DW are covered with the flattening
発光素子層5(例えば、有機発光ダイオード層)は、平坦化膜21よりも上側に形成されるアノード電極22と、アクティブ領域DA((発光素子層5と重なる領域)のサブピクセルを規定するバンク23と、アノード電極22よりも上側に形成されるEL(エレクトロルミネッセンス)層24と、EL層24よりも上側に形成されるカソード電極25とを含み、アノード電極22、EL層24、およびカソード電極25によって発光素子(例えば、有機発光ダイオード:OLED)が構成される。
The light emitting element layer 5 (for example, an organic light emitting diode layer) includes an
EL層24は、蒸着法あるいはインクジェット法によって、バンク(隔壁)23によって囲まれた領域(サブピクセル領域)に形成される。発光素子層5が有機発光ダイオード(OLED)層である場合、EL層24は、例えば、下層側から順に、正孔注入層、正孔輸送層、発光層、電子輸送層、電子注入層を積層することで構成される。
The
アノード電極(陽極)22は、例えばITO(Indium Tin Oxide)とAgを含む合金との積層によって構成され、光反射性を有する(後に詳述)。カソード電極25は、ITO(Indium Tin Oxide)、IZO(Indium Zincum Oxide)等の透光性の導電材で構成することができる。
The anode electrode (anode) 22 is made of, for example, a laminate of ITO (Indium Tin Oxide) and an alloy containing Ag, and has light reflectivity (detailed later). The
発光素子層5がOLED層である場合、アノード電極22およびカソード電極25間の駆動電流によって正孔と電子がEL層24内で再結合し、これによって生じたエキシトンが基底状態に落ちることによって、光が放出される。カソード電極25が透光性であり、アノード電極22が光反射性であるため、EL層24から放出された光は上方に向かい、トップエミッションとなる。
When the light emitting
発光素子層5は、OLED素子を構成する場合に限られず、無機発光ダイオードあるいは量子ドット発光ダイオードを構成してもよい。
The light emitting
非アクティブ領域NAには、有機封止膜27のエッジを規定する凸体Taと凸体Tbとが形成される。凸体Taは、有機封止膜27をインクジェット塗付する際の液止めとして機能し、凸体Tbは予備の液止めとして機能する。なお、凸体Tbの下部は平坦化膜21で構成され、引き出し配線DWの端面の保護膜として機能する。バンク23、凸体Taおよび凸体Tbの上部は、ポリイミド、エポキシ、アクリル等の塗布可能な感光性有機材料を用いて、例えば同一工程で形成することができる。
In the inactive region NA, a convex body Ta and a convex body Tb that define the edge of the
封止層6は透光性であり、カソード電極25を覆う第1無機封止膜26と、第1無機封止膜26よりも上側に形成される有機封止膜27と、有機封止膜27を覆う第2無機封止膜28とを含む。
The
第1無機封止膜26および第2無機封止膜28はそれぞれ、例えば、CVDにより形成される、酸化シリコン膜、窒化シリコン膜、あるいは酸窒化シリコン膜、またはこれらの積層膜で構成することができる。有機封止膜27は、第1無機封止膜26および第2無機封止膜28よりも厚い、透光性有機膜であり、ポリイミド、アクリル等の塗布可能な感光性有機材料によって構成することができる。例えば、このような有機材料を含むインクを第1無機封止膜26上にインクジェット塗布した後、UV照射により硬化させる。封止層6は、発光素子層5を覆い、水、酸素等の異物の発光素子層5への浸透を防いでいる。
Each of the first
なお、上面フィルム9は、接着剤8を介して封止層6上に貼り付けられ、基板50の剥離時には支持材としても機能する。上面フィルム9の材料としては、PET(ポリエチレンテレフタレート)等が挙げられる。
In addition, the
下面フィルム10は、PET等で構成され、基板50を剥離した後に樹脂層12の下面に貼り付けられることで、支持材、保護材として機能とする。
The
機能フィルム39は、例えば、光学補償機能、タッチセンサ機能、保護機能等を有する。電子回路基板60は、例えば、複数の端子TM上に実装されるICチップあるいはフレキシブルプリント基板(FPC)である。
The
以上、フレキシブルな表示デバイスを製造する場合について説明したが、非フレキシブルな表示デバイスを製造する場合は、基板剥離等が不要であるため、例えば、図1のステップS6からステップS10に移行する。 The case where a flexible display device is manufactured has been described above. However, in the case of manufacturing a non-flexible display device, for example, the process proceeds from step S6 to step S10 in FIG.
本実施形態では、図2(b)に示すように、図1のステップS7において、樹脂層12の下面に、除電層、または基板50との密着性調整層、あるいは下面フィルム10との接着性調整層として機能する炭化物パターンCPが形成される。
In the present embodiment, as shown in FIG. 2B, in step S7 of FIG. 1, the lower surface of the
〔実施形態1〕
図4は、実施形態1の表示デバイスの形成途中の構成(樹脂層に炭化物パターンを形成した状態)を示す平面図(基板裏面から視た透視平面図)である。図5(a)は、実施形態1における樹脂層へのレーザ照射方法を示す模式図であり、図5(b)は、炭化物パターンを示す平面図である。[Embodiment 1]
FIG. 4 is a plan view (a transparent plan view as viewed from the back surface of the substrate) illustrating a configuration in the middle of forming the display device of Embodiment 1 (a state in which a carbide pattern is formed on a resin layer). FIG. 5A is a schematic diagram illustrating a method for irradiating a resin layer with a laser according to the first embodiment, and FIG. 5B is a plan view illustrating a carbide pattern.
実施形態1では、図4・図5に示すように、基板50(例えば、ガラス基板)上に、樹脂層12、TFT層4、および発光素子層5を含む積層体を形成した後、基板50の裏面から、樹脂層12の下面の第1領域Raおよび第2領域Rbに、照射条件が異なるようにレーザを照射する。具体的には、第2領域Rbでは第1領域Raよりもレーザの照射強度を高めることで、第2領域Rbを、第1領域Raよりも単位面積当たりの炭化物の量(例えば、質量、膜厚)が大きい炭化物パターンCPとする。
In the first embodiment, as shown in FIGS. 4 and 5, after forming a laminate including the
第2領域Rbは、樹脂層12の下面における発光素子層5との重畳部12dに含まれ、図中x方向を横方向としたときの横ストライプ形状としている。このため、図5(b)に示すように、第2領域Rbに形成される炭化物パターンCPも、x方向を横方向としたときの横ストライプ形状となる。
The second region Rb is included in the overlapping
図5(a)のレーザ装置77は、x方向に伸びる長尺状のビーム(第1照射強度)を間欠的にショットしながら第1領域Raのy方向の一端から他端まで(y方向に)走査し、次いで、長尺状のビーム(第2照射強度>第1照射強度)を間欠的にショットしながら第2領域Rbのy方向の一端から他端まで(y方向に)走査する。なお、上記のようにレーザ装置77を移動させてもよいし、レーザ装置77を動かさずに、基板50および樹脂層12を含む積層体を移動させてもよい。なお、第1照射強度については、例えば、第1領域Raと基板50との分離が可能となる最小値とすることができる。第2照射強度については、例えば、除電層あるいは接着調整層としての機能を考慮して設定すればよい。
The
このように、樹脂層12の下面における発光素子層5との重畳部12dに、横ストライプ形状の炭化物パターンCPを形成することで、図1のステップS8〜S9における積層体への帯電を抑えることができる。炭化物パターンCPは、y方向に伸びる縦ストライプでもよい。レーザ装置77の光源には、例えば、固定レーザやエキシマレーザを用いることができる。
As described above, by forming the carbide pattern CP in the form of a horizontal stripe on the lower surface of the
図6は、実施形態1におけるレーザ照射方法の別例を示す模式図である。図6(a)のレーザ装置77は、x方向に伸びる長尺状のビーム(第1照射強度)を間欠的にショットしながら、樹脂層12の下面における発光素子層5との重畳部12dの一端から他端まで(y方向に)走査し、その後、第1領域RaをマスクMpで覆った状態で、x方向に伸びる長尺状のビーム(第1照射強度)を間欠的にショットしながら、樹脂層12の下面における発光素子層5との重畳部12dの一端から他端まで(y方向に)走査する。このように、第2領域Rbの照射回数を第1領域Raの照射回数よりも多くすることで、第2領域Rbを、図5(b)に示す炭化物パターンCPとすることができる。
FIG. 6 is a schematic diagram illustrating another example of the laser irradiation method according to the first embodiment. The
図7(a)(b)は、実施形態1におけるレーザ照射方法のさらなる別例を示す模式図であり、図7(c)は、図7(b)に示す各ショットの強度分布であり、図7(d)は、図7(a)(b)のレーザ照射によって形成される炭化物パターンCPを示す模式図である。図7(a)のレーザ装置77は、x方向に伸びる長尺状のビームを、間欠的にショット(各ショットの照射強度は同一)しながら、樹脂層12の下面における発光素子層5との重畳部12dの一端から他端まで(y方向に)走査する。走査は1回で足りる。ここでは、図7(b)のように、各ショット領域shaのオーバーラップ率を50%未満としている。このように、第2領域Rbの照射回数(2回)が第1領域Raの照射回数(1回)よりも多くなるようにオーバーラップ率を設定することで、第2領域Rbを、図7(d)に示す炭化物パターンCPとすることができる。なお、図7(c)のようなトップハット型の強度分布は、例えばエキシマレーザにより得ることができる。各ショット領域shaのy方向の幅は、例えば20〜40μmである。
FIGS. 7A and 7B are schematic diagrams showing still another example of the laser irradiation method according to the first embodiment, and FIG. 7C is an intensity distribution of each shot shown in FIG. 7B. FIG. 7D is a schematic view showing a carbide pattern CP formed by the laser irradiation in FIGS. 7A and 7B. The
オーバーラップ率を調整するには、例えば、レーザ装置77の繰り返し周波数(単位時間当たりのショット数)あるいは走査速度を変えればよい。例えば、繰り返し周波数を変えずに走査速度を落とすことでオーバーラップ率を高めことができる。図8(a)〜(c)に示すように、各ショット領域shaのオーバーラップ率を50%以上として走査を1回行うことで、図7(d)に示す炭化物パターンCPを得ることができる。
In order to adjust the overlap ratio, for example, the repetition frequency (the number of shots per unit time) or the scanning speed of the
例えば、図5〜図8の構成によって樹脂層12の下面における発光素子層5との重畳部12dの一端から他端まで(y方向に)走査し、次いで、樹脂層12を含む積層体を90度回転させて、樹脂層12の下面における発光素子層5との重畳部12dの一端から他端まで(x方向に)走査することで、第2領域Rbを、図9に示すマトリクス状の炭化物パターンCPとすることができる。
For example, by scanning from the one end to the other end of the overlapping
なお、図10に示すように、表示デバイス製造装置70は、成膜装置76と、レーザ装置77を含む剥離装置80と、これらの装置を制御するコントローラ72とを含んでおり、コントローラ72の制御を受けた剥離装置80が図1のステップS7〜ステップS8を行う。
As shown in FIG. 10, the display device manufacturing apparatus 70 includes a film forming apparatus 76, a peeling apparatus 80 including a
〔実施形態2〕
図11は、実施形態2の表示デバイスの形成途中の構成(樹脂層に炭化物パターンを形成した構成)を示す平面図(基板裏面から視た透視平面図)である。図11に示すように、第2領域Rbを、樹脂層12の下面における発光素子層5との重畳部12dを取り囲む形状とし、第2領域Rbを炭化物パターンCPとしてもよい。こうすれば、除電効果に加えて、基板50との密着性低減効果を奏し、基板50の剥離の際にアクティブ領域DAに皺等が生じ難くなる。[Embodiment 2]
FIG. 11 is a plan view (a transparent plan view as viewed from the back surface of the substrate) illustrating a configuration (a configuration in which a carbide pattern is formed on a resin layer) during the formation of the display device according to the second embodiment. As shown in FIG. 11, the second region Rb may have a shape surrounding the overlapping
〔実施形態3〕
図12は、実施形態3の表示デバイスの形成途中の構成(樹脂層に炭化物パターンを形成した構成)を示す平面図(基板裏面から視た透視平面図)である。図12に示すように、第2領域Rbを、樹脂層12の下面における端子部44との重畳部12tを取り囲む形状とし、第2領域Rbを炭化物パターンCPとしてもよい。こうすれば、除電効果に加えて、基板50との密着性低減効果を奏し、基板50の剥離の際に端子部44に皺等が生じ難くなる。[Embodiment 3]
FIG. 12 is a plan view (a transparent plan view as viewed from the back surface of the substrate) illustrating a configuration (a configuration in which a carbide pattern is formed on a resin layer) during the formation of the display device of the third embodiment. As shown in FIG. 12, the second region Rb may have a shape surrounding the overlapping
〔実施形態4〕
図13は、実施形態4の表示デバイスの形成途中の構成(樹脂層に炭化物パターンを形成した構成)を示す平面図(基板裏面から視た透視平面図)である。図13に示すように、第2領域Rbを、樹脂層12の下面における端子部44との重畳部12tとし、第2領域Rbを炭化物パターンCPとしてもよい。こうすれば、除電効果に加えて、下面フィルム10との接着性低減効果を奏し、例えば、端子部44を裏面側に折り曲げる場合に、下面フィルム10の端子部44と重なる部分を除去し易くなる。また、下面フィルム10を付けたまま端子部44を折り曲げる場合でも、下面フィルム10と樹脂層12の接着性が小さいため、曲げ応力が小さくなるというメリットがある。[Embodiment 4]
FIG. 13 is a plan view (a transparent plan view as viewed from the back surface of the substrate) illustrating a configuration (a configuration in which a carbide pattern is formed on a resin layer) during the formation of the display device according to the fourth embodiment. As shown in FIG. 13, the second region Rb may be a
なお、炭化物パターンCPのエッジを切り出し線DLに合わせなくてもよく、例えば図13(b)のように、炭化物パターンCPを、横方向(端子が並ぶ方向)に並ぶ複数の個片領域を横切るように形成してもよい。 Note that the edge of the carbide pattern CP does not have to be aligned with the cutout line DL. For example, as shown in FIG. 13B, the carbide pattern CP crosses a plurality of individual regions arranged in the horizontal direction (the direction in which the terminals are arranged). It may be formed as follows.
〔実施形態5〕
図14は、実施形態5の表示デバイスの形成途中の構成(樹脂層に炭化物パターンを形成した構成)を示す平面図(基板裏面から視た透視平面図)である。図14に示すように、第2領域Rbを、隣り合う2つの個片の一方に対応する切りだし線DLと、他方に対応する切りだし線DLとの間隙領域とし、第2領域Rbを炭化物パターンCPとしてもよい。こうすれば、除電効果に加えて、基板50との密着性低減効果を奏し、樹脂層から基板50を剥離し易くなるというメリットがある。[Embodiment 5]
FIG. 14 is a plan view (a transparent plan view as viewed from the back surface of the substrate) illustrating a configuration (a configuration in which a carbide pattern is formed on a resin layer) during the formation of the display device of the fifth embodiment. As shown in FIG. 14, the second region Rb is a gap region between a cutting line DL corresponding to one of two adjacent pieces and a cutting line DL corresponding to the other, and the second region Rb is made of carbide. The pattern CP may be used. This has the advantage that, in addition to the charge eliminating effect, an effect of reducing the adhesion to the
〔実施形態6〕
図15は、実施形態6の表示デバイスの形成途中の構成(樹脂層に炭化物パターンを形成した構成)を示す平面図(基板裏面から視た透視平面図)である。図16は、図15の一部の断面図である。[Embodiment 6]
FIG. 15 is a plan view (a transparent plan view as viewed from the back surface of the substrate) illustrating a configuration (a configuration in which a carbide pattern is formed on a resin layer) during the formation of the display device of the sixth embodiment. FIG. 16 is a partial cross-sectional view of FIG.
図15・図16に示すように、発光素子層5を覆うように第2無機封止膜28を形成し、TFT層4には、第2無機封止膜28と重ならない端子部44と、端子部44からアクティブ領域(表示部)DA側へ伸びる端子配線TWとを形成し、平面視における端子部44と第2無機封止膜18のエッジとの間隙に炭化物パターンCPを形成してもよい。この場合、炭化物パターンCPは端子配線TWと交差する。こうすれば、下面フィルム10において、前記間隙および炭化物パターンCPと重なる部分の接着性が低下し、この部分が除去し易くなるため、下面フィルム10のこの部分を(局所的に)除去し、端子部44が下側を向くように折り曲げる構成(狭額縁化構成)に好適となる。
As shown in FIGS. 15 and 16, a second
なお、炭化物パターンCPのエッジを切り出し線DLに合わせなくてもよく、例えば図15(b)のように、炭化物パターンCPを、横方向(端子が並ぶ方向)に並ぶ複数の個片領域(切り出し線DLで囲まれた領域)を横切るように形成してもよい。 Note that the edge of the carbide pattern CP does not have to be aligned with the cutout line DL. For example, as shown in FIG. 15B, the carbide pattern CP is formed by dividing the carbide pattern CP into a plurality of individual regions (cutout lines). (A region surrounded by the line DL).
本実施形態にかかる表示デバイスが備える電気光学素子(電流によって輝度や透過率が制御される電気光学素子)は特に限定されるものではない。本実施形態にかかる表示装置としては、例えば、電気光学素子としてOLED(Organic Light Emitting Diode:有機発光ダイオード)を備えた有機EL(Electro Luminescence:エレクトロルミネッセンス)ディスプレイ、電気光学素子として無機発光ダイオードを備えた無機ELディスプレイ、電気光学素子としてQLED(Quantum dot Light Emitting Diode:量子ドット発光ダイオード)を備えたQLEDディスプレイ等が挙げられる。 An electro-optical element (an electro-optical element whose luminance and transmittance are controlled by current) provided in the display device according to the embodiment is not particularly limited. The display device according to the present embodiment includes, for example, an organic EL (Electro Luminescence) display including an OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) as an electro-optical element, and an inorganic light-emitting diode as an electro-optical element. Inorganic EL displays, QLED displays provided with QLEDs (Quantum dot Light Emitting Diodes) as electro-optical elements, and the like.
〔まとめ〕
態様1:下面フィルムと、TFT層と、発光素子層とを備える表示デバイスであって、前記下面フィルムよりも上層で前記TFT層よりも下層に樹脂層が設けられ、前記樹脂層の下面に第1領域および第2領域が含まれ、前記第2領域が、前記第1領域よりも単位面積当たりの炭化物の量が大きい炭化物パターンとされている表示デバイス。[Summary]
Aspect 1: A display device including a lower film, a TFT layer, and a light emitting element layer, wherein a resin layer is provided above the lower film and below the TFT layer, and a resin layer is formed on a lower surface of the resin layer. A display device including a first region and a second region, wherein the second region has a carbide pattern having a larger amount of carbide per unit area than the first region.
態様2:前記樹脂層の下面には、平面視において前記発光素子層と重なる第1重畳部が含まれ、前記炭化物パターンが前記重畳部に形成されている例えば態様1に記載の表示デバイス。
Aspect 2: The display device according to
態様3:前記炭化物パターンがストライプ状あるいはマトリクス状である例えば態様2に記載の表示デバイス。
Aspect 3: The display device according to
態様4:前記樹脂層の下面には、平面視において前記発光素子層と重なる第1重畳部が含まれ、前記炭化物パターンが、前記重畳部を取り囲むように形成されている例えば態様1に記載の表示デバイス。 Aspect 4: The lower surface of the resin layer includes a first overlapped portion overlapping the light emitting element layer in a plan view, and the carbide pattern is formed so as to surround the overlapped portion. Display device.
態様5:前記TFT層の端部に端子部を備え、前記樹脂層の下面には、平面視において前記端子部と重なる第2重畳部が含まれ、前記炭化物パターンが、前記第2重畳部を取り囲むように形成されている例えば態様1に記載の表示デバイス。
Aspect 5: A terminal portion is provided at an end portion of the TFT layer, and a lower surface of the resin layer includes a second overlapping portion overlapping the terminal portion in a plan view, and the carbide pattern includes the second overlapping portion. The display device according to
態様6:前記樹脂層の下面には、平面視において前記端子部と重なる第2重畳部が含まれ、前記炭化物パターンが、前記第2重畳部に形成されている例えば態様1に記載の表示デバイス。
Aspect 6: The display device according to
態様7:前記発光素子層よりも上層に無機封止膜を備え、前記TFT層は、前記無機封止膜と重ならないように設けられた端子部と、前記端子部からアクティブ領域側へ伸びる端子配線とを備え、平面視においては、前記端子部と前記無機封止膜のエッジとの間隙に形成された前記炭化物パターンが、前記端子配線と交わる例えば態様1〜6のいずれか1項に記載の表示デバイス。
Aspect 7: A terminal portion provided with an inorganic sealing film above the light emitting element layer, wherein the TFT layer is provided so as not to overlap the inorganic sealing film, and a terminal extending from the terminal portion to the active region side. The wiring pattern, wherein in a plan view, the carbide pattern formed in a gap between the terminal portion and an edge of the inorganic sealing film intersects with the terminal wiring, for example, according to any one of
態様8:前記下面フィルムは、前記間隙および前記炭化物パターンと重なる部分が除去されている例えば態様7記載の表示デバイス。 Aspect 8: The display device according to Aspect 7, for example, wherein a portion of the lower surface film overlapping the gap and the carbide pattern is removed.
態様9:前記端子部が下側を向くように折り曲げられている例えば態様8記載の表示デバイス。
Mode 9: The display device according to
態様10:前記炭化物パターンは、有機物のレーザアブレーション痕である例えば態様1〜9のいずれか1項に記載の表示デバイス。
Aspect 10: The display device according to any one of
態様11:前記樹脂層がポリイミドを含む例えば態様1〜10のいずれか1項に記載の表示デバイス。
Aspect 11: The display device according to any one of
態様12:基板上に樹脂層、TFT層、および発光素子層を含む積層体を形成した後、基板裏面から樹脂層の下面にレーザを照射して積層体から基板を剥離する表示デバイスの製造方法であって、前記樹脂層の下面の第1領域および第2領域に、互いに照射条件が異なるようにレーザを照射することで、前記第2領域を、前記第1領域よりも単位面積当たりの炭化物の量が大きい炭化物パターンとする表示デバイスの製造方法。 Aspect 12: A method for manufacturing a display device in which a laminate including a resin layer, a TFT layer, and a light-emitting element layer is formed on a substrate, and then the substrate is separated from the laminate by irradiating a laser from the back surface of the substrate to the lower surface of the resin layer. And irradiating the first region and the second region on the lower surface of the resin layer with laser so that the irradiation conditions are different from each other, so that the second region is made of carbide per unit area more than the first region. Of manufacturing a display device having a carbide pattern having a large amount of carbon.
態様13:前記照射条件は、照射回数である例えば態様12に記載の表示デバイスの製造方法。
Aspect 13: The method for manufacturing a display device according to
態様14:前記照射条件は、照射強度である例えば態様12に記載の表示デバイスの製造方法。
Aspect 14: The method for manufacturing a display device according to
態様15:前記炭化物パターンに合わせて照射のオーバーラップ率を設定する例えば態様12または13に記載の表示デバイスの製造方法。
Aspect 15: The method for manufacturing a display device according to
態様16:前記樹脂層の下面を第1方向にレーザ走査した後に前記積層体を回転させ、前記第1方向と直交する第2方向にレーザ走査する例えば態様12〜15のいずれか1項に記載の表示デバイスの製造方法。
Aspect 16: The method according to any one of
態様17:前記基板を剥離して前記樹脂層の下面に下面フィルムを貼り付けた後、各個片に対応する切り出し線で分断を行い、複数の個片を切り出す例えば態様12〜16のいずれか1項に記載の表示デバイスの製造方法。
Aspect 17: After peeling the substrate and attaching a lower surface film to the lower surface of the resin layer, cutting is performed at a cutting line corresponding to each piece to cut out a plurality of pieces, for example, any one of
態様18:前記第2領域は、隣り合う2つの個片の一方に対応する切りだし線と、他方に対応する切りだし線との間隙に含まれる例えば態様16記載の表示デバイスの製造方法。
Aspect 18: The method of manufacturing a display device according to
態様19:基板上に樹脂層、TFT層、および発光素子層を含む積層体を形成した後、基板裏面から樹脂層の下面にレーザを照射して積層体から基板を剥離する表示デバイスの製造装置であって、前記樹脂層の下面の第1領域および第2領域に、互いに照射条件が異なるようにレーザを照射することで、前記第2領域を、前記第1領域よりも単位面積当たりの炭化物の量が大きい炭化物パターンとする表示デバイスの製造装置。 Aspect 19: Apparatus for manufacturing a display device in which a laminate including a resin layer, a TFT layer, and a light emitting element layer is formed on a substrate, and then the substrate is separated from the laminate by irradiating a laser from the back surface of the substrate to the lower surface of the resin layer And irradiating the first region and the second region on the lower surface of the resin layer with laser so that the irradiation conditions are different from each other, so that the second region is made of carbide per unit area more than the first region. For manufacturing a display device having a carbide pattern having a large amount of carbon.
本発明は上述した実施形態に限定されるものではなく、異なる実施形態にそれぞれ開示された技術的手段を適宜組み合わせて得られる実施形態についても本発明の技術的範囲に含まれる。さらに、各実施形態にそれぞれ開示された技術的手段を組み合わせることにより、新しい技術的特徴を形成することができる。 The present invention is not limited to the above-described embodiments, and embodiments obtained by appropriately combining technical means disclosed in different embodiments are also included in the technical scope of the present invention. Furthermore, new technical features can be formed by combining the technical means disclosed in each embodiment.
2 表示デバイス
4 TFT層
5 発光素子層
6 封止層
10 下面フィルム
12 樹脂層
21 平坦化膜
24 EL層
44 端子部
50 基板
70 表示デバイス製造装置
76 成膜装置
80 剥離装置
TM 端子
NA 非アクティブ領域
DA アクティブ領域
CP 炭化物パターン
DL 切り出し線
Ra 第1領域
Rb 第2領域
Claims (19)
前記下面フィルムよりも上層で前記TFT層よりも下層に樹脂層が設けられ、
前記樹脂層の下面に第1領域および第2領域が含まれ、前記第2領域が、前記第1領域よりも単位面積当たりの炭化物の量が大きい炭化物パターンとされている表示デバイス。A display device including a lower film, a TFT layer, and a light emitting element layer,
A resin layer is provided above the lower film and below the TFT layer,
A display device in which a first region and a second region are included on a lower surface of the resin layer, and the second region has a carbide pattern having a larger amount of carbide per unit area than the first region.
前記炭化物パターンが前記重畳部に形成されている請求項1に記載の表示デバイス。The lower surface of the resin layer includes a first overlapping portion overlapping the light emitting element layer in a plan view,
The display device according to claim 1, wherein the carbide pattern is formed on the overlapping portion.
前記炭化物パターンが、前記重畳部を取り囲むように形成されている請求項1に記載の表示デバイス。The lower surface of the resin layer includes a first overlapping portion overlapping the light emitting element layer in a plan view,
The display device according to claim 1, wherein the carbide pattern is formed so as to surround the overlapping portion.
前記樹脂層の下面には、平面視において前記端子部と重なる第2重畳部が含まれ、
前記炭化物パターンが、前記第2重畳部を取り囲むように形成されている請求項1に記載の表示デバイス。A terminal portion is provided at an end of the TFT layer,
The lower surface of the resin layer includes a second overlapping portion overlapping the terminal portion in a plan view,
The display device according to claim 1, wherein the carbide pattern is formed so as to surround the second overlapping portion.
前記炭化物パターンが、前記第2重畳部に形成されている請求項1に記載の表示デバイス。The lower surface of the resin layer includes a second overlapping portion overlapping the terminal portion in a plan view,
The display device according to claim 1, wherein the carbide pattern is formed on the second overlapping portion.
前記TFT層は、前記無機封止膜と重ならないように設けられた端子部と、前記端子部からアクティブ領域側へ伸びる端子配線とを備え、
平面視においては、前記端子部と前記無機封止膜のエッジとの間隙に形成された前記炭化物パターンが、前記端子配線と交わる請求項1〜6のいずれか1項に記載の表示デバイス。An inorganic sealing film is provided above the light emitting element layer,
The TFT layer includes a terminal portion provided so as not to overlap with the inorganic sealing film, and a terminal wiring extending from the terminal portion to the active region side,
The display device according to claim 1, wherein in a plan view, the carbide pattern formed in a gap between the terminal portion and an edge of the inorganic sealing film intersects with the terminal wiring.
前記樹脂層の下面の第1領域および第2領域に、互いに照射条件が異なるようにレーザを照射することで、前記第2領域を、前記第1領域よりも単位面積当たりの炭化物の量が大きい炭化物パターンとする表示デバイスの製造方法。A method for manufacturing a display device, comprising: forming a laminate including a resin layer, a TFT layer, and a light-emitting element layer on a substrate, and irradiating a laser to a lower surface of the resin layer from a back surface of the substrate to peel the substrate from the laminate. ,
By irradiating a laser to the first region and the second region on the lower surface of the resin layer so that irradiation conditions are different from each other, the amount of carbide per unit area of the second region is larger than that of the first region. A method for manufacturing a display device having a carbide pattern.
前記樹脂層の下面の第1領域および第2領域に、互いに照射条件が異なるようにレーザを照射することで、前記第2領域を、前記第1領域よりも単位面積当たりの炭化物の量が大きい炭化物パターンとする表示デバイスの製造装置。A display device manufacturing apparatus, comprising: forming a laminate including a resin layer, a TFT layer, and a light emitting element layer on a substrate, and irradiating a laser to a lower surface of the resin layer from a back surface of the substrate to peel the substrate from the laminate. ,
By irradiating a laser to the first region and the second region on the lower surface of the resin layer so that irradiation conditions are different from each other, the amount of carbide per unit area of the second region is larger than that of the first region. Manufacturing equipment for display devices with carbide patterns.
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2017/013596 WO2018179332A1 (en) | 2017-03-31 | 2017-03-31 | Display device, display device manufacturing method, and display device manufacturing apparatus |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JPWO2018179332A1 true JPWO2018179332A1 (en) | 2020-02-06 |
| JP6744479B2 JP6744479B2 (en) | 2020-08-19 |
Family
ID=63674688
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2019508105A Active JP6744479B2 (en) | 2017-03-31 | 2017-03-31 | Display device, display device manufacturing method, and display device manufacturing apparatus |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US10553822B2 (en) |
| JP (1) | JP6744479B2 (en) |
| CN (1) | CN110506306B (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2018179332A1 (en) |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2019058485A1 (en) * | 2017-09-21 | 2019-03-28 | シャープ株式会社 | Display device |
| JP2019090879A (en) * | 2017-11-13 | 2019-06-13 | 株式会社Joled | Display device and method for manufacturing display device |
| WO2020129194A1 (en) * | 2018-12-19 | 2020-06-25 | シャープ株式会社 | Display device and production method therefor |
| WO2020183589A1 (en) * | 2019-03-11 | 2020-09-17 | シャープ株式会社 | Display device and method for manufacturing display device |
Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002033464A (en) * | 2000-07-17 | 2002-01-31 | Semiconductor Energy Lab Co Ltd | Method for fabricating semiconductor device |
| JP2003163337A (en) * | 2001-08-10 | 2003-06-06 | Semiconductor Energy Lab Co Ltd | Stripping method and method for producing semiconductor device |
| US20110134018A1 (en) * | 2009-12-03 | 2011-06-09 | Samsung Mobile Display Co., Ltd. | Method of manufacturing flexible display apparatus |
| JP2011248072A (en) * | 2010-05-26 | 2011-12-08 | Hitachi Displays Ltd | Method of manufacturing image display device |
| WO2012049824A1 (en) * | 2010-10-13 | 2012-04-19 | シャープ株式会社 | Thin film transistor substrate and display device using same |
| WO2013035298A1 (en) * | 2011-09-08 | 2013-03-14 | シャープ株式会社 | Display device and method for manufacturing same |
| WO2014073191A1 (en) * | 2012-11-07 | 2014-05-15 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | Electronic device manufacturing method and laminated body used in electronic device manufacturing method |
| JP2017024368A (en) * | 2015-07-27 | 2017-02-02 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | Laminated body and method for manufacturing the same, and electronic device and method for manufacturing the same |
| JP2017041391A (en) * | 2015-08-21 | 2017-02-23 | 旭硝子株式会社 | Peeling device for laminate, peeling method, and manufacturing method of electronic device |
Family Cites Families (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TW554398B (en) * | 2001-08-10 | 2003-09-21 | Semiconductor Energy Lab | Method of peeling off and method of manufacturing semiconductor device |
| JP2004349543A (en) | 2003-05-23 | 2004-12-09 | Seiko Epson Corp | Method of peeling laminate, method of manufacturing thin film device, thin film device, and electronic equipment |
| KR101150994B1 (en) * | 2004-11-11 | 2012-06-01 | 가부시키가이샤 한도오따이 에네루기 켄큐쇼 | Semiconductor Device |
| CN100541803C (en) * | 2004-11-11 | 2009-09-16 | 株式会社半导体能源研究所 | Semiconductor device |
| JP6397654B2 (en) * | 2014-05-13 | 2018-09-26 | 株式会社ジャパンディスプレイ | Organic EL light emitting device |
| JP2017152330A (en) * | 2016-02-26 | 2017-08-31 | 株式会社ジャパンディスプレイ | Display device manufacturing method, display device, and display device manufacturing apparatus |
-
2017
- 2017-03-31 US US16/069,525 patent/US10553822B2/en active Active
- 2017-03-31 JP JP2019508105A patent/JP6744479B2/en active Active
- 2017-03-31 WO PCT/JP2017/013596 patent/WO2018179332A1/en active Application Filing
- 2017-03-31 CN CN201780089213.8A patent/CN110506306B/en active Active
Patent Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002033464A (en) * | 2000-07-17 | 2002-01-31 | Semiconductor Energy Lab Co Ltd | Method for fabricating semiconductor device |
| JP2003163337A (en) * | 2001-08-10 | 2003-06-06 | Semiconductor Energy Lab Co Ltd | Stripping method and method for producing semiconductor device |
| US20110134018A1 (en) * | 2009-12-03 | 2011-06-09 | Samsung Mobile Display Co., Ltd. | Method of manufacturing flexible display apparatus |
| JP2011248072A (en) * | 2010-05-26 | 2011-12-08 | Hitachi Displays Ltd | Method of manufacturing image display device |
| WO2012049824A1 (en) * | 2010-10-13 | 2012-04-19 | シャープ株式会社 | Thin film transistor substrate and display device using same |
| WO2013035298A1 (en) * | 2011-09-08 | 2013-03-14 | シャープ株式会社 | Display device and method for manufacturing same |
| WO2014073191A1 (en) * | 2012-11-07 | 2014-05-15 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | Electronic device manufacturing method and laminated body used in electronic device manufacturing method |
| JP2017024368A (en) * | 2015-07-27 | 2017-02-02 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | Laminated body and method for manufacturing the same, and electronic device and method for manufacturing the same |
| JP2017041391A (en) * | 2015-08-21 | 2017-02-23 | 旭硝子株式会社 | Peeling device for laminate, peeling method, and manufacturing method of electronic device |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP6744479B2 (en) | 2020-08-19 |
| CN110506306B (en) | 2021-07-13 |
| US10553822B2 (en) | 2020-02-04 |
| US20190363291A1 (en) | 2019-11-28 |
| CN110506306A (en) | 2019-11-26 |
| WO2018179332A1 (en) | 2018-10-04 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR101267529B1 (en) | Method of fabricating flexible organic electro luminescent device | |
| US10923553B2 (en) | Display device | |
| US10636996B2 (en) | Display device, production method of display device, production device of display device, and film formation device | |
| US11227553B2 (en) | Display device | |
| JPWO2018179332A1 (en) | Display device, display device manufacturing method, and display device manufacturing apparatus | |
| US20200219423A1 (en) | Flexible display device and method of manufacturing flexible display device | |
| JP2019179696A (en) | Organic el display and method for manufacturing organic el display | |
| US10672854B2 (en) | Display device | |
| US20200152910A1 (en) | Display device | |
| JP2019020509A (en) | Display and method for manufacturing display | |
| JP7178216B2 (en) | DISPLAY DEVICE AND METHOD FOR MANUFACTURING DISPLAY DEVICE | |
| CN112425264B (en) | display device | |
| US11417281B2 (en) | Display device | |
| WO2019155711A1 (en) | Organic el display device | |
| US10621893B2 (en) | Display device, manufacturing method for display device, manufacturing apparatus of display device, mounting device, and controller | |
| US20210288129A1 (en) | Display device | |
| US10862075B2 (en) | Manufacturing method for EL device | |
| US10777633B2 (en) | Display device, display device manufacturing method, and display device manufacturing apparatus | |
| US20190157625A1 (en) | Production method for el device | |
| US11551975B2 (en) | Method for manufacturing electronic device | |
| JP2019174609A (en) | Display and method for manufacturing display | |
| KR102723489B1 (en) | Organic light emitting display device | |
| WO2010125623A1 (en) | Display device | |
| WO2019188116A1 (en) | Organic el display device and method for producing organic el display device | |
| CN115715120A (en) | Electroluminescent display device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20190927 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20190927 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20200707 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20200730 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 6744479 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |