JP7516797B2 - Fixing device and image forming apparatus - Google Patents
Fixing device and image forming apparatus Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP7516797B2 JP7516797B2 JP2020054119A JP2020054119A JP7516797B2 JP 7516797 B2 JP7516797 B2 JP 7516797B2 JP 2020054119 A JP2020054119 A JP 2020054119A JP 2020054119 A JP2020054119 A JP 2020054119A JP 7516797 B2 JP7516797 B2 JP 7516797B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- nip
- roller
- fixing device
- pressure
- fixing
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 claims description 44
- 238000011144 upstream manufacturing Methods 0.000 claims description 39
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 claims description 24
- 238000012546 transfer Methods 0.000 description 46
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 33
- 230000000052 comparative effect Effects 0.000 description 30
- 239000000314 lubricant Substances 0.000 description 21
- 238000002844 melting Methods 0.000 description 14
- 230000008018 melting Effects 0.000 description 14
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 13
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 13
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 11
- 238000002474 experimental method Methods 0.000 description 9
- 238000012795 verification Methods 0.000 description 9
- 230000037303 wrinkles Effects 0.000 description 9
- 108091008695 photoreceptors Proteins 0.000 description 8
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 7
- YCKRFDGAMUMZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-N Fluorine atom Chemical compound [F] YCKRFDGAMUMZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 229910052731 fluorine Inorganic materials 0.000 description 6
- 239000011737 fluorine Substances 0.000 description 6
- XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N Iron Chemical compound [Fe] XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Nickel Chemical compound [Ni] PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 238000004140 cleaning Methods 0.000 description 4
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 4
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 229920001973 fluoroelastomer Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 239000004519 grease Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229910052736 halogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 150000002367 halogens Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 238000009434 installation Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 3
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000007747 plating Methods 0.000 description 3
- 229920002379 silicone rubber Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 239000004945 silicone rubber Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000004642 Polyimide Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium Chemical compound [Al] XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000011248 coating agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000004744 fabric Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229920006015 heat resistant resin Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 229910052742 iron Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 229910052759 nickel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 229920001721 polyimide Polymers 0.000 description 2
- -1 polytetrafluoroethylene Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 229920001343 polytetrafluoroethylene Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000004810 polytetrafluoroethylene Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000007704 transition Effects 0.000 description 2
- VYZAMTAEIAYCRO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Chromium Chemical compound [Cr] VYZAMTAEIAYCRO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920000106 Liquid crystal polymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004977 Liquid-crystal polymers (LCPs) Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004734 Polyphenylene sulfide Substances 0.000 description 1
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical group [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000004760 aramid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920006231 aramid fiber Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000000919 ceramic Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000007547 defect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000000151 deposition Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000835 fiber Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002657 fibrous material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000005484 gravity Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000003779 heat-resistant material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001788 irregular Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000007769 metal material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000003921 oil Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000003973 paint Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920000069 polyphenylene sulfide Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920001296 polysiloxane Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000011148 porous material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910001220 stainless steel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010935 stainless steel Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000003860 storage Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000003746 surface roughness Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Fixing For Electrophotography (AREA)
Description
本発明は、定着装置およびこれを備えた画像形成装置に関する。 The present invention relates to a fixing device and an image forming apparatus equipped with the same.
従来、トナー像を用紙上に形成し、熱と圧力により画像を用紙に定着させる定着装置において、省エネ性を向上させるために、ニップを構成するローラと熱源を備えた加熱ローラをエンドレスベルト内部に配置し、エンドレスベルトを張架するベルト定着方式が提案されている。 Conventionally, in fixing devices that form a toner image on paper and fix the image to the paper using heat and pressure, a belt fixing method has been proposed in order to improve energy efficiency, in which a roller that forms a nip and a heating roller equipped with a heat source are placed inside an endless belt and the endless belt is tensioned.
更なる省エネ性向上のため、特開2019-40144号公報(特許文献1)、特開2019-40013号公報(特許文献2)、特開2013-218225号公報(特許文献3)に開示されているように、ニップを構成するローラを固定のパッド部材(定着部材)に変更した定着方式が提案されている。 To further improve energy efficiency, a fixing method has been proposed in which the roller that constitutes the nip is replaced with a fixed pad member (fixing member), as disclosed in JP 2019-40144 A (Patent Document 1), JP 2019-40013 A (Patent Document 2), and JP 2013-218225 A (Patent Document 3).
しかしながら、特許文献1に開示の定着装置においては、記録媒体の搬送方向において、パッド部材の上流側が平坦に形成され、パッド部材の下流側が曲面に形成されている。このため、パッド部材と加圧ローラーとによって形成されるニップ部の後半側(具体的にはニップ部の出口部近傍)において、パッドが加圧ローラーに対して凸となる部分が発生する。パッドにおいて加圧ローラーに対して凸となる部分では、摺動抵抗によるせん断力が働くことでトナーの微小な移動が発生することが懸念される。この場合には、下地の紙が露出することで白みがかった画像になることが起こり得る。すなわち、画像濃度が低下してしまう。
However, in the fixing device disclosed in
特許文献2に開示の定着装置においては、パッド部材において、加圧ローラーとニップ部を形成するニップ形成領域は、円弧状の湾曲面で構成されており、ニップ形成領域から下流側の領域は、搬送方向の下流側に向かうにつれて加圧ローラー側に傾斜する傾斜面で構成されている。当該傾斜面は、加圧ローラーには非接触の状態となっている。このような場合においては、ニップ部の後半側にピーク圧を設けることが困難となり、トナーの溶融性が悪くなることが起こり得る。 In the fixing device disclosed in Patent Document 2, the nip formation region of the pad member that forms a nip with the pressure roller is configured with an arc-shaped curved surface, and the region downstream from the nip formation region is configured with an inclined surface that slopes toward the pressure roller as it moves downstream in the conveying direction. The inclined surface is not in contact with the pressure roller. In such a case, it becomes difficult to provide a peak pressure in the latter half of the nip portion, which may result in poor toner melting properties.
特許文献3に記載の定着装置においては、パッド部材の上流側および下流側のそれぞれを加圧ローラーに対して凹となる曲面で構成し、上流側におけるパッド部材の曲面の曲率が、下流側におけるパッド部材の曲面の曲率よりも大きくなっている。このような場合においては、ニップ部の前半側にピーク圧が存在し、トナーの溶融性が悪くなることが起こり得る。 In the fixing device described in Patent Document 3, the upstream and downstream sides of the pad member are each configured with a curved surface that is concave with respect to the pressure roller, and the curvature of the curved surface of the pad member on the upstream side is greater than the curvature of the curved surface of the pad member on the downstream side. In such a case, a peak pressure exists in the front half of the nip portion, which can cause the toner to melt poorly.
本発明は、上記のような問題に鑑みてなされたものであり、本発明の目的は、画像濃度の低下を抑制しつつ、トナーの溶融効率を向上させることができる定着装置、および画像形成装置を提供することにある。 The present invention has been made in consideration of the above problems, and the object of the present invention is to provide a fixing device and an image forming apparatus that can improve the toner melting efficiency while suppressing a decrease in image density.
本発明に基づく定着装置は、無端ベルトと、上記無端ベルトの内側に配置された定着部材と、上記無端ベルトの外側において上記定着部材に対向して配置され、上記定着部材とともにニップ部を形成するローラーと、上記無端ベルトを加熱する加熱部材と、を備える。上記定着部材は、上記ニップ部を形成するニップ部形成領域において、上記無端ベルトの回転方向における上流側に設けられた曲面部と、上記回転方向の下流側に設けられ、上記曲面部に接続された平面部とを有する。上記曲面部は、上記ローラーに対して凹となるように円弧状に湾曲している。上記平面部は、上記曲面部に接続される接続位置に接する上記曲面部の接線上に位置するか、上記接線よりも上記ローラー側に傾斜するように設けられている。上記ニップ部形成領域に印加される圧力の分布において、ピーク位置が上記平面部に存在する。 The fixing device according to the present invention includes an endless belt, a fixing member disposed inside the endless belt, a roller disposed outside the endless belt facing the fixing member and forming a nip portion together with the fixing member, and a heating member for heating the endless belt. The fixing member has a curved surface portion disposed upstream in the direction of rotation of the endless belt in a nip portion forming region forming the nip portion, and a flat surface portion disposed downstream in the direction of rotation and connected to the curved surface portion. The curved surface portion is curved in an arc shape so as to be concave with respect to the roller. The flat surface portion is located on a tangent to the curved surface portion that is in contact with a connecting position connected to the curved surface portion, or is provided so as to be inclined toward the roller from the tangent. In the distribution of pressure applied to the nip portion forming region, a peak position exists on the flat surface portion.
上記本発明に基づく定着装置にあっては、上記平面部は、上記接線上に位置するように設けられていることが好ましい。 In the fixing device according to the present invention, it is preferable that the flat portion is located on the tangent line.
上記本発明に基づく定着装置にあっては、上記曲面部の曲率半径は、上記ローラーの曲率半径よりも大きいことが好ましい。 In the fixing device according to the present invention, it is preferable that the radius of curvature of the curved surface portion is greater than the radius of curvature of the roller.
上記本発明に基づく定着装置にあっては、上記ニップ部形成領域に印加される圧力の分布において、上記ピーク位置が上記接続位置に存在することが好ましい。 In the fixing device according to the present invention, it is preferable that the peak position in the distribution of pressure applied to the nip forming region is located at the connection position.
上記本発明に基づく定着装置にあっては、上記接続位置は、上記ローラーを上記定着部材に圧接させる圧接方向に上記ローラーの中心から伸ばした仮想線よりも、上記無端ベルトの回転方向において下流側に位置することが好ましい。 In the fixing device according to the present invention, it is preferable that the connection position is located downstream in the rotation direction of the endless belt from an imaginary line extending from the center of the roller in the pressure contact direction in which the roller is pressed against the fixing member.
本発明に基づく画像形成装置は、上記定着装置を備える。 The image forming apparatus according to the present invention is equipped with the fixing device described above.
本発明によれば、画像濃度の低下を抑制しつつ、トナーの溶融効率を向上させることができる定着装置、および画像形成装置を提供することができる。 The present invention provides a fixing device and an image forming device that can improve the toner melting efficiency while suppressing a decrease in image density.
以下、本発明の実施の形態について、図を参照して詳細に説明する。なお、以下に示す実施の形態においては、同一のまたは共通する部分について図中同一の符号を付し、その説明は繰り返さない。 The following describes in detail the embodiments of the present invention with reference to the drawings. In the embodiments described below, the same or common parts are given the same reference numerals in the drawings, and their description will not be repeated.
(実施の形態1)
図1は、実施の形態1に係る画像形成装置を示す概略図である。図1を参照して、実施の形態1に係る画像形成装置100について説明する。
(Embodiment 1)
Fig. 1 is a schematic diagram showing an image forming apparatus according to
図1には、カラープリンタとしての画像形成装置100が示されている。以下では、カラープリンタとしての画像形成装置100について説明するが、画像形成装置100は、カラープリンタに限定されない。たとえば、画像形成装置100は、モノクロプリンタであってもよいし、ファックスであってもよいし、モノクロプリンタ、カラープリンタおよびファックスの複合機(MFP:Multi-Functional Peripheral)であってもよい。
In FIG. 1, an
画像形成装置100は、画像形成ユニット1Y,1M,1C,1Kと、中間転写ベルト30と、一次転写ローラー31と、二次転写ローラー33と、カセット37と、従動ローラー38と、駆動ローラー39と、タイミングローラー40と、定着装置50と、筐体80と、制御装置101とを備える。
The
筐体80は、画像形成装置100の外殻を規定する。筐体80は、内部に、画像形成ユニット1Y,1M,1C,1Kと、中間転写ベルト30と、一次転写ローラー31と、二次転写ローラー33と、カセット37と、従動ローラー38と、駆動ローラー39と、タイミングローラー40と、定着装置50と、制御装置101とを収容する。
The
画像形成ユニット1Y,1M,1C,1Kと、中間転写ベルト30と、一次転写ローラー31と、二次転写ローラー33と、カセット37と、従動ローラー38と、駆動ローラー39と、タイミングローラー40とによって画像形成部が構成される。この画像形成部は、後述する搬送経路41に沿って搬送される記録媒体としての用紙S上にトナー画像を形成する。
The image forming unit is made up of
画像形成ユニット1Y,1M,1C,1Kは、中間転写ベルト30に沿って順に並べられている。画像形成ユニット1Yは、トナーボトル15Yからトナーの供給を受けてイエロー(Y)のトナー像を形成する。画像形成ユニット1Mは、トナーボトル15Mからトナーの供給を受けてマゼンタ(M)のトナー像を形成する。画像形成ユニット1Cは、トナーボトル15Cからトナーの供給を受けてシアン(C)のトナー像を形成する。画像形成ユニット1Kは、トナーボトル15Kからトナーの供給を受けてブラック(BK)のトナー像を形成する。
画像形成ユニット1Y,1M,1C,1Kは、それぞれ、中間転写ベルト30に沿って中間転写ベルト30の回転方向の順に配置されている。画像形成ユニット1Y,1M,1C,1Kは、それぞれ、感光体10と、帯電装置11と、露光装置12と、現像装置13と、クリーニング装置17とを備える。
帯電装置11は、感光体10の表面を一様に帯電する。露光装置12は、制御装置101からの制御信号に応じて感光体10にレーザー光を照射し、入力された画像パターンに従って感光体10の表面を露光する。これにより、入力画像に応じた静電潜像が感光体10上に形成される。
The charging
現像装置13は、現像ローラー14を回転させながら、現像ローラー14に現像バイアスを印加し、現像ローラー14の表面にトナーを付着させる。これにより、トナーが現像ローラー14から感光体10に転写され、静電潜像に応じたトナー像が感光体10の表面に現像される。
The developing
感光体10と中間転写ベルト30とは、一次転写ローラー31を設けている部分で互いに接触している。一次転写ローラー31は、ローラー形状を有し、回転可能に構成される。トナー像と反対極性の転写電圧が一次転写ローラー31に印加されることによって、トナー像が感光体10から中間転写ベルト30に転写される。イエロー(Y)のトナー像、マゼンタ(M)のトナー像、シアン(C)のトナー像、およびブラック(BK)のトナー像が順に重ねられて感光体10から中間転写ベルト30に転写される。これにより、カラーのトナー像が中間転写ベルト30上に形成される。
The
中間転写ベルト30は、従動ローラー38および駆動ローラー39に張架されている。駆動ローラー39は、たとえばモーター(図示しない)によって回転駆動される。中間転写ベルト30および従動ローラー38は、駆動ローラー39に連動して回転する。これにより、中間転写ベルト30上のトナー像が二次転写ローラー33に搬送される。
The
クリーニング装置17は、感光体10に圧接されている。クリーニング装置17は、トナー像の転写後に感光体10の表面に残留するトナーを回収する。
The
カセット37には、用紙Sがセットされる。用紙Sは、カセット37から1枚ずつタイミングローラー40によって搬送経路41に沿って二次転写ローラー33に送られる。二次転写ローラー33は、ローラー形状を有し、回転可能に構成される。二次転写ローラー33は、トナー像と反対極性の転写電圧を搬送中の用紙Sに印加する。これにより、トナー像は、中間転写ベルト30から二次転写ローラー33に引き付けられ、中間転写ベルト30上のトナー像が用紙Sに転写される。このように一次転写ローラー31、中間転写ベルト30,および二次転写ローラー33は、トナー像を感光体10から用紙Sに転写する転写部に相当する。
Paper S is set in
二次転写ローラー33への用紙Sの搬送タイミングは、中間転写ベルト30上のトナー像の位置に合わせてタイミングローラー40によって調整される。タイミングローラー40により、中間転写ベルト30上のトナー像は、用紙Sの適切な位置に転写される。
The timing of conveying the paper S to the
定着装置50は、自身を通過する用紙Sを加圧および加熱する。これにより、トナー像は用紙Sに定着する。このように、定着装置50は、搬送経路41に沿って搬送される用紙S上のトナー画像を定着させる。トナー像が定着された用紙Sは、トレイ48に排紙される。
The fixing
なお、上述では、印刷方式としてタンデム方式を採用している画像形成装置100について説明したが、画像形成装置100の印刷方式は、タンデム方式に限定されない。画像形成装置100内における各構成の配置は、採用される印刷方式に従って適宜変更され得る。画像形成装置100の印刷方式として、ロータリー方式や直接転写方式が採用されてもよい。ロータリー方式の場合、画像形成装置100は、1つの感光体10と、同軸上で回転可能に構成される複数の現像装置13で構成される。画像形成装置100は、印刷時には、各現像装置13を感光体10に順に導き、各色のトナー像を現像する。直接転写方式の場合、画像形成装置100は、感光体10上に形成されたトナー像が用紙Sに直接転写される。
In the above, the
図2は、実施の形態に係る定着装置の概略断面図である。図2を参照して、定着装置50について説明する。
Figure 2 is a schematic cross-sectional view of a fixing device according to an embodiment. The fixing
定着装置50は、加圧ローラー51と、定着部材としてのパッド部材52と、加熱部材としての加熱ローラー53と、定着ベルト54と、固定部材55と、潤滑剤塗布部56と、保持部材57と、摺動部材58とを含む。
The fixing
加圧ローラー51は、定着ベルト54の外側に配置されている。加圧ローラー51は、パッド部材52に対向する。加圧ローラー51は、パッド部材52との間に定着ベルト54を挟み込んでパッド部材52を加圧する。これにより、加圧ローラー51は、パッド部材52とともに、記録媒体が搬送されるニップ部Nを形成する。
The
加圧ローラー51は、駆動源からのトルクによって回転する。加圧ローラー51の回転に伴って定着ベルト54が回転する。加圧ローラー51が回転することにより、定着ベルト54は、加圧ローラー51の回転方向と反対方向に回転する。
The
加圧ローラー51は、たとえば、芯金、弾性層、および離型層で構成されている。加圧ローラー51の外形は、任意であるが、20mm以上100mm以下であることが好ましい。
The
芯金は、アルミまたは鉄等の金属によって構成されている。芯金は、パイプ形状を有していてもよく、この場合には、厚さが0.1mm以上10mm以下であることが好ましい。なお、芯金は、中実のもの、または断面形状が三ツ矢形状等の異型のものであってもよい。弾性層は、たとえばシリコーンゴム、フッ素ゴム等の耐熱性の高い樹脂によって構成されている。弾性層の厚さは、1mm以上20mm以下であることが好ましい。離型層は、弾性層を覆うように設けられている。離型層は、フッ素チューブまたはフッ素系コーティング等の離型性を付与した構成が好ましい。離型層の厚さは、5μm以上100μm以下であることが好ましい。 The core is made of a metal such as aluminum or iron. The core may have a pipe shape, in which case it is preferable that the thickness is 0.1 mm or more and 10 mm or less. The core may be solid or have an irregular cross-sectional shape such as a three-arrow shape. The elastic layer is made of a highly heat-resistant resin such as silicone rubber or fluororubber. It is preferable that the thickness of the elastic layer is 1 mm or more and 20 mm or less. The release layer is provided so as to cover the elastic layer. It is preferable that the release layer is made of a fluorine tube or a fluorine-based coating that provides release properties. It is preferable that the thickness of the release layer is 5 μm or more and 100 μm or less.
パッド部材52は、定着ベルト54の内側に配置されている。パッド部材52は、定着ベルト54を間に挟んで加圧ローラー51に対向するように配置されている。パッド部材52は、たとえば、ポリフェニレンサルファイド、ポリイミド、または液晶ポリマーなどの耐熱性の樹脂、鉄等の金属材料、またはセラミック等によって構成されている。パッド部材52は、シリコーンゴムまたはフッ素ゴム等から成る固定部材と、上記の材料による2部品によって構成されていてもよい。
The
摺動部材58は、定着ベルト54とパッド部材52とに挟み込まれている。摺動部材58によって定着ベルト54とパッド部材52との摺動抵抗が減少する。これにより、定着ベルト54が安定して回転する。
The sliding
摺動部材58としては、ガラスクロスを基材とし、摺動面をフッ素系樹脂で被覆したものが用いられる。具体的には、摺動部材58として、フッ素繊維の織物、フッ素樹脂シート、またはガラスコートなどが用いられる。
The sliding
なお、定着ベルト54と摺動部材58は摺動を続けることで摩耗が生じてしまう。このような場合は、摺動抵抗が増加し、定着ベルト54の回転不良が発生することが懸念される。このため、定着ベルト54と摺動部材58との間には、潤滑剤が供給される。これにより、定着ベルト54と摺動部材58の摩耗を抑制でき、耐久性を向上させることができる。潤滑剤は、耐熱性の高いシリコン系またはフッ素系の潤滑剤が好ましく、より特定的にはフッ素グリスが好ましい。粘度が高く、固形成分を含むグリスを用いることでニップ部Nに潤滑剤が残りやすくなる。このため、グリスを用いる場合には、オイルを用いる場合と比較して、より長期間、定着ベルト54と摺動部材58の摩耗を抑制できる。さらに、潤滑剤をニップ部Nに保持するために摺動部材58の表面は凹凸を有することが好ましい。凹凸の大きさは任意である。潤滑剤を維持する機能と凹凸に起因した画像ムラを抑制する観点から、摺動部材58の表面粗さRaは、1μm以上50μm以下であることが好ましい。
Note that the fixing
加熱ローラー53は、定着ベルト54の内側に配置されている。加熱ローラー53は、内部に加熱源53aを有する。加熱源53aは、定着ベルト54を加熱する。加熱源53aは、たとえば、ハロゲンランプである。加熱源53aは、ハロゲンランプの他に、定着ベルト54を誘導加熱(IH)するもの、定着ベルト54を抵抗発熱体とし発熱させるものを利用してもよい。
The
加熱ローラー53は、円筒形状を有し、アルミおよびステンレス鋼(SUS)等の金属から成る。加熱ローラー53の外形は任意であるが、10mm以上100mm以下が好ましい。また、加熱ローラー53の厚みは、0.1mm以上5.0mm以下であることが好ましい。
The
加熱源53aにハロゲンランプを用いる場合、加熱ローラー53の内周面を黒色にすることが好ましい。異物等による外表面への傷を防止するため、加熱ローラー53の外周面にポリテトラフルオロエチレン(PTFE)等をコーティングしてもよい。
When a halogen lamp is used as the
定着ベルト54は、無端状に設けられている。定着ベルト54は、パッド部材52および加熱ローラー53に回転可能に張架されている。定着ベルト54は、基層と、弾性層と、離形層とを含む。
The fixing
定着ベルトの外径は任意であるが、10mm以上100mm以下が好ましい。基層は、ポリイミド、SUS、およびニッケル電鋳等によって構成されることが好ましい。基層の厚さは、5μm以上100μm以下が好ましい。弾性層は、シリコーンゴム、およびフッ素ゴム等の耐熱性の高い材料が好ましい。弾性層の厚みは、10μm以上300μm以下が好ましい。離型層は、フッ素樹脂およびフッ素系コーティング等の離型性を付与した構成が好ましい。離型層の厚みは、5μm以上100μm以下が好ましい。 The outer diameter of the fixing belt is arbitrary, but is preferably 10 mm or more and 100 mm or less. The base layer is preferably made of polyimide, SUS, nickel electrocasting, etc. The thickness of the base layer is preferably 5 μm or more and 100 μm or less. The elastic layer is preferably made of a highly heat-resistant material such as silicone rubber or fluororubber. The thickness of the elastic layer is preferably 10 μm or more and 300 μm or less. The release layer is preferably made of a material that has releasability, such as fluororesin or fluorine-based coating. The thickness of the release layer is preferably 5 μm or more and 100 μm or less.
固定部材55には、パッド部材52および保持部材57が固定される。固定部材55は、定着ベルト54の幅方向(紙面垂直方向)に沿って見た場合に、角張ったU字形状を有する。固定部材55は、U字形状の先端側が加熱ローラー53に向くように配置されている。固定部材55におけるU字形状の底部55a(固定部材55のうち加圧ローラー51に対向する部分)に、パッド部材52が固定されている。固定部材55において用紙Sの搬送方向(図2中矢印B方向)の下流側の部分55bに、保持部材57が固定されている。
The
潤滑剤塗布部56は、定着ベルト54の内周面に接触するように配置される。潤滑剤塗布部56は、定着ベルトの回転方向(図2中矢印C方向)においてパッド部材52の下流側かつ加熱ローラー53の上流側に配置されている。
The
定着ベルト54に供給された潤滑剤は、ニップ部Nの圧力によって長手方向の端部から押し出されて、量が減少する場合がある。潤滑剤塗布部56は、押し出された潤滑剤を捕集するとともに、潤滑剤を再塗布する。潤滑剤としては、上記と同様のものを採用することができる。
The lubricant supplied to the fixing
潤滑剤塗布部56としては、アラミド繊維およびフッ素繊維など耐熱性の高い繊維状の物、シリコンスポンジ等の耐熱性の高い多孔質状の物、ならびにフェルト部材等を採用することができる。
The
なお、潤滑剤塗布部56は、上記のような部材に限定されず、硬質クロムメッキ層または、ニッケルメッキ液にフッ素樹脂を分散させ、同時に析出したメッキ層でもよい。
The
保持部材57には、ニップ部Nを通過し、加熱ローラー53に向かう定着ベルト54が巻き掛けられている。保持部材57は、定着ベルト54の回転を案内するとともに、潤滑剤塗布部56を保持する。保持部材57は、潤滑剤塗布部56を収容する収容凹部57aを有する。当該収容凹部57aは、定着ベルト54の回転方向において保持部材57の略中央に設けられている。収容凹部57a内で潤滑剤塗布部56を保持することにより、潤滑剤塗布部56を安定して定着ベルト54に接触させることができる。
The fixing
図3は、実施の形態1に係る定着装置において加圧ローラーがパッド部材を加圧している状態を示す図である。なお、図3においては、便宜上摺動部材58を省略している。図3を参照して、パッド部材52の具体的な形状について説明する。
Figure 3 is a diagram showing the state in which the pressure roller presses the pad member in the fixing device according to the first embodiment. For convenience, the sliding
図3に示すように、パッド部材52は、ニップ部Nを形成するニップ部形成領域Rにおいて、無端ベルトの回転方向の上流側に設けられた曲面部R1と、当該回転方向における下流側に設けられた平面部R2とを有する。ニップ部形成領域Rは、曲面部R1と平面部R2とによって構成されている。
As shown in FIG. 3, the
曲面部R1は、加圧ローラー51の軸方向から見た場合に、加圧ローラー51に対して凹となる円弧状に湾曲する。曲面部R1における曲率半径は、パッド部材52を加圧していない状態における加圧ローラー51の外周面の曲率半径よりも大きくなっている。
When viewed from the axial direction of the
一般的に、曲面部R1の曲率半径が、上述の加圧ローラー51の外周面の曲率半径よりも小さい場合には、ニップ幅を大きくすることができるが、加圧ローラー51への定着ベルト54の巻き掛け角度が大きくなる。このような場合には、ニップ部Nを通過する際に、ニップ部の入口部で記録媒体が大きく湾曲することになる。本実施の形態のように、曲面部R1における曲率半径を加圧ローラー51の外周面の曲率半径よりも大きくした場合には、記録媒体が大きく湾曲することを抑制することができる。
Generally, if the radius of curvature of the curved surface R1 is smaller than the radius of curvature of the outer peripheral surface of the
平面部R2は、接続位置P1において曲面部R1に接続されている。すなわち、平面部R2は、上記回転方向における上流側において曲面部R1に接続される上流端部を有する。平面部R2は、加圧ローラー51の軸方向から見た場合に、上記接続位置P1に接する曲面部R1の接線TL1上に位置するように設けられている。
The flat portion R2 is connected to the curved portion R1 at the connection position P1. That is, the flat portion R2 has an upstream end portion that is connected to the curved portion R1 on the upstream side in the rotation direction. When viewed from the axial direction of the
接続位置P1は、加圧ローラー51の軸方向から見た場合に、加圧ローラー51がパッド部材52に圧接する圧接方向(図中DR1方向)に、加圧ローラー51の中心O1から伸ばした仮想線VL1に対して、上記定着ベルト54の回転方向の上流側に位置する。
When viewed from the axial direction of the
加圧ローラー51の軸方向から見た場合に、接続位置P1から平面部R2に対して垂直となる法線VL2は、上記仮想線VL1に対して平行であり、上記仮想線VL1に対してニップ部Nの入口側に位置する。
When viewed from the axial direction of the
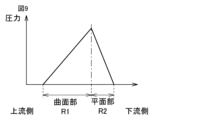
図4は、実施の形態1に係る定着装置において、ニップ部形成領域に印加される圧力の分布を示す図である。図4を参照して、加圧ローラー51がパッド部材52に圧接する圧接状態において、ニップ部形成領域Rに印加される圧力の分布について説明する。
Figure 4 is a diagram showing the distribution of pressure applied to the nip formation region R in the fixing device according to
なお、当該圧力分布は、たとえばパッド部材52と加圧ローラー51との間にセンサシート(ニッタ株式会社制)を搬送し、面圧分布測定システム(ニッタ株式会社制)を用いることで、測定することができる。
The pressure distribution can be measured, for example, by conveying a sensor sheet (manufactured by Nitta Corporation) between the
図4に示すように、ニップ形成領域Rの圧力分布は、ニップ部の上流側(入口部)から下流側(出口部)に向かうにつれて、一旦圧力が増加していき、圧力がピークに達した後、圧力が低下していく。このような圧力分布において、圧力のピーク位置は、平面部R2に存在する。また、曲面部R1での圧力の増加率は、平面部R2の圧力の増加率よりも小さくなっている。 As shown in FIG. 4, the pressure distribution in the nip formation region R increases from the upstream side (entrance portion) of the nip portion toward the downstream side (exit portion), reaches a peak, and then decreases. In this pressure distribution, the pressure peak is located in the flat portion R2. Furthermore, the rate of increase in pressure in the curved portion R1 is smaller than the rate of increase in pressure in the flat portion R2.
上記のように、実施の形態1に係る定着装置においては、加圧ローラー51に対して凹となる曲面部R1と平面部R2とによってニップ部形成領域Rを構成することにより、ニップ部Nの入口側において、圧力が急激に増加することを抑制することができる。これにより、ニップ部Nの入口側において、記録媒体にしわが発生することを抑制することができる。
As described above, in the fixing device according to the first embodiment, the nip forming region R is formed by the curved portion R1 and the flat portion R2 that are concave with respect to the
図5から図7は、比較の形態に係る定着装置において、トナー像がニップ部を移動する第1状態から第3状態を示す図である。図5から図7を参照して、ニップ部形成領域Rにおいて、加圧ローラー51に対して凸となる部分が形成されている場合のトナー像の定着について説明する。
Figures 5 to 7 are diagrams showing the first to third states in which a toner image moves through the nip portion in a fixing device according to a comparative embodiment. With reference to Figures 5 to 7, the fixing of a toner image when a convex portion is formed in the nip portion forming region R relative to the
図5から図7に示すように、比較の形態に係る定着装置においては、トナーの溶融性を向上させることを目的として、ニップ部形成領域Rの下流側において、加圧ローラー51に対して凸となる凸部52aが形成されている。これにより、ニップ部の下流側でニップ圧が最大にすることができる。
As shown in Figures 5 to 7, in the fixing device according to the comparative embodiment, a
図5は、トナー像Tがニップ部Nを通過する第1状態、具体的には、トナー像Tが凸部52aを通過する直前の状態を示している。なお、トナー像Tが形成されている用紙Sは、凹凸紙である。用紙Sは、凹部Saを有する。
Figure 5 shows the first state in which the toner image T passes through the nip portion N, specifically, the state immediately before the toner image T passes through the
ここで、凸部52aは、凹凸紙の凹部Saよりも相当程度大きいものである。このため、凹凸紙の凹凸形状に追従することが困難である。このため、図6に示す第2状態すなわち、凹部Saが凸部52aに対向する状態においては、凹部Saと凸部52aとの間に存在するトナー像Tの一部が、溶融不足となる。また、定着ベルト54は回転しているため、定着ベルト54とパッド部材52との摺動抵抗によってせん断力が、溶融不足のトナー像Tに作用する。当該せん断力は、凸部52aにおいて大きく作用する。
Here, the
図7に示すように、第3状態、すなわち用紙Sの凹部Saが凸部52aを通過する状態においては、上記せん断力によって、溶融不足のトナー像が、搬送方向の上流側に微小に移動する。この結果、下地の記録媒体が局所的に露出することで画像濃度が低下してしまう。
As shown in FIG. 7, in the third state, i.e., when the concave portion Sa of the paper S passes over the
再び図3を参照して、実施の形態1に係る定着装置50においては、上記のように、加圧ローラー51に対して凹となる曲面部R1と平面部R2とによってニップ部形成領域Rを構成することにより、ニップ部形成領域Rにおいて、加圧ローラー51に対して凸となる部分が形成されなくなる。このため、トナー像Tがニップ部Nを通過する際に、定着ベルト54とパッド部材52との摺動抵抗によって当該トナー像Tに作用するせん断力を抑制できる。この結果、トナー像Tが搬送方向の上流側に移動することを抑制でき、画像濃度の低下を抑制することができる。
Referring again to FIG. 3, in the fixing
さらに、図4に示すように、ニップ形成領域Rでの圧力分布において、平面部R2側、すなわちニップ部Nの下流側においてピーク圧が存在することにより、トナーの溶融性を向上させることができる。 Furthermore, as shown in FIG. 4, in the pressure distribution in the nip formation region R, the presence of a peak pressure on the flat surface portion R2 side, i.e., downstream of the nip portion N, can improve the melting property of the toner.
以上のように、実施の形態1に係る定着装置50およびこれを備えた画像形成装置100においては、画像濃度の低下を抑制しつつ、トナーの溶融効率を向上させることができる。
As described above, the fixing
(実施の形態2)
図8は、実施の形態2に係る定着装置において、加圧ローラーがパッド部材を加圧している状態を示す図である。図8を参照して、実施の形態2に係る定着装置50Aについて説明する。
(Embodiment 2)
8 is a diagram showing a state in which the pressure roller presses the pad member in the fixing device according to the second embodiment. A fixing
図8に示すように、実施の形態2に係る定着装置50Aは、実施の形態1に係る定着装置50と比較した場合に、平面部R2が曲面部R1に接続される接続位置P1が相違する。その他の構成については、ほぼ同様である。
As shown in FIG. 8, the fixing
実施の形態2においては、接続位置P1は、加圧ローラー51の軸方向から見た場合に、加圧ローラー51がパッド部材52に圧接する圧接方向(図中DR1方向)に加圧ローラー51の中心O1から伸ばした仮想線VL1上に位置する。また、加圧ローラー51の軸方向から見た場合に、接続位置P1から平面部R2に対して垂直となる法線VL2は、上記仮想線VL1に重なる。
In the second embodiment, when viewed from the axial direction of the
図9は、実施の形態2に係る定着装置において、ニップ部形成領域に印加される圧力の分布を示す図である。図9を参照して、上記圧接状態において、ニップ部形成領域R2に印加される圧力の分布について説明する。 Figure 9 is a diagram showing the distribution of pressure applied to the nip portion forming region in the fixing device according to embodiment 2. With reference to Figure 9, the distribution of pressure applied to the nip portion forming region R2 in the above-mentioned pressure contact state will be described.
図9に示すように、ニップ部形成領域に印加される圧力分布は、ニップ部の上流側(入口部)から下流側(出口部)に向かうにつれて、一旦圧力が増加していき、圧力がピークに達した後、圧力が低下していく。このような圧力分布において、圧力のピーク位置は、平面部R2における上流端部、すなわち、接続位置P1に存在している。 As shown in FIG. 9, the pressure distribution applied to the nip formation region increases from the upstream side (entrance) to the downstream side (exit) of the nip, reaches a peak, and then decreases. In this pressure distribution, the pressure peak is located at the upstream end of the flat portion R2, i.e., at the connection position P1.
このように構成される場合においても、ニップ部形成領域Rの上流側が、加圧ローラー51に対して凹となる円弧状の曲面部R1で構成され、ニップ部形成領域Rの下流側が平面部R2で構成されている。さらに、平面部R2は、接続位置P1に接する曲面部R1の接線TL1上に位置し、ニップ部形成領域Rに印加される圧力の分布において、ピーク位置が平面部R2に存在する。このため、実施の形態2に係る定着装置50Aにあっては、実施の形態1とほぼ同様の効果が得られる。
Even when configured in this manner, the upstream side of the nip forming region R is configured with an arc-shaped curved surface portion R1 that is concave with respect to the
図10は、参考例1に係る定着装置において、ニップ部形成領域に印加される圧力の分布を示す図である。図10を参照して、参考例1に係る定着装置について説明する。 Figure 10 is a diagram showing the distribution of pressure applied to the nip portion forming region in the fixing device of Reference Example 1. The fixing device of Reference Example 1 will be described with reference to Figure 10.
参考例1に係る定着装置は、実施の形態1に係る定着装置50と比較して、接続位置P1の位置が異なる点で相違する。その他の構成については、ほぼ同様である。参考例1に係る定着装置においては、接続位置P1が実施の形態1に係る定着装置50と比較して、接続位置P1が、ニップ部Nの上流側にずれている。
The fixing device of Reference Example 1 differs from the fixing
図10に示すように、接続位置P1がニップ部の上流側にずれることにより、曲面部R1から平面部R2に圧力が変化する遷移点の位置もニップ部の上流側にずれる。 As shown in FIG. 10, by shifting the connection position P1 upstream of the nip portion, the position of the transition point where the pressure changes from the curved portion R1 to the flat portion R2 also shifts upstream of the nip portion.
図11は、参考例2に係る定着装置において、ニップ部形成領域に印加される圧力の分布を示す図である。図11を参照して、参考例2に係る定着装置について説明する。 Figure 11 is a diagram showing the distribution of pressure applied to the nip portion forming region in the fixing device of Reference Example 2. The fixing device of Reference Example 2 will be described with reference to Figure 11.
参考例2に係る定着装置は、実施の形態1に係る定着装置50と比較して、接続位置P1の位置が異なる点で相違する。その他の構成については、ほぼ同様である。参考例2に係る定着装置においては、接続位置P1が実施の形態1に係る定着装置50と比較して、接続位置P1が、ニップ部Nの下流側にずれている。
The fixing device of Reference Example 2 differs from the fixing
図11に示すように、接続位置P1がニップ部の下流側にずれることにより、曲面部R1から平面部R2に圧力が変化する遷移点の位置もニップ部の下流側にずれる。 As shown in FIG. 11, by shifting the connection position P1 downstream of the nip, the position of the transition point where the pressure changes from the curved portion R1 to the flat portion R2 also shifts downstream of the nip.
このため、実施の形態1に係る定着装置50においては、参考例1および参考例2のように、設置誤差により接続位置P1の位置ずれが起こった場合に、ニップ部形成領域Rに印加される圧力分布が大きく変動し得る。
For this reason, in the fixing
一方で、実施の形態2に係るニップ部の圧力分布においては、上述のように、圧力ピークに至るまで、略一定に圧力が増加する。このため、実施の形態2に係る定着装置50Aにあっては、ニップ部の圧力分布において圧力の変動を抑制することができる。また、接続位置P1の設置誤差の変動によるニップ幅の変動も抑制することができる。
On the other hand, in the pressure distribution of the nip portion according to the second embodiment, as described above, the pressure increases substantially constantly until the pressure peaks. Therefore, in the
(実施の形態3)
図12は、実施の形態3に係る定着装置において、加圧ローラーがパッド部材を加圧している状態を示す図である。図12を参照して、実施の形態3に係る定着装置50Bについて説明する。
(Embodiment 3)
12 is a diagram showing a state in which the pressure roller presses the pad member in the fixing device according to the third embodiment. A fixing
図12に示すように、実施の形態3に係る定着装置50Bは、実施の形態1に係る定着装置50と比較した場合に、平面部R2が曲面部R1に接続される接続位置P1が相違する。その他の構成については、ほぼ同様である。
As shown in FIG. 12, the fixing
実施の形態3においては、接続位置P1は、加圧ローラー51の軸方向から見た場合に、加圧ローラー51がパッド部材52に圧接する圧接方向(図中DR1方向)に加圧ローラー51の中心O1から伸ばした仮想線VL1よりも、定着ベルト54の回転方向において下流側(ニップ部Nの下流側)に位置する。また、加圧ローラー51の軸方向から見た場合に、接続位置P1から平面部R2に対して垂直となる法線VL2は、加圧ローラー51の中心O1を通過する。
In the third embodiment, when viewed from the axial direction of the
図13は、実施の形態3に係る定着装置において、ニップ部形成領域に印加される圧力の分布を示す図である。図13を参照して、上記圧接状態において、ニップ部形成領域Rに印加される圧力の分布について説明する。 Figure 13 is a diagram showing the distribution of pressure applied to the nip portion forming region R in the fixing device according to embodiment 3. With reference to Figure 13, the distribution of pressure applied to the nip portion forming region R in the above-mentioned pressure contact state will be described.
図13に示すように、ニップ部形成領域Rの圧力分布は、ニップ部の上流側(入口部)から下流側(出口部)に向かうにつれて、一旦圧力が増加していき、圧力がピークに達した後、圧力が低下していく。このような圧力分布において、圧力のピーク位置は、平面部R2における上流端部、すなわち、接続位置P1に存在している。 As shown in FIG. 13, the pressure distribution in the nip forming region R increases from the upstream side (entrance portion) of the nip toward the downstream side (exit portion), reaches a peak, and then decreases. In this pressure distribution, the pressure peak is located at the upstream end of the flat portion R2, i.e., the connection position P1.
このように構成される場合においても、ニップ部形成領域Rの上流側が、加圧ローラー51に対して凹となる円弧状の曲面部R1で構成され、ニップ部形成領域Rの下流側が平面部R2で構成されている。さらに、平面部R2は、接続位置P1に接する曲面部R1の接線TL1上に位置し、ニップ部形成領域Rに印加される圧力の分布において、ピーク位置が平面部R2に存在する。このため、実施の形態3に係る定着装置50Bにあっては、実施の形態1とほぼ同様の効果が得られる。
Even when configured in this manner, the upstream side of the nip forming region R is configured with an arc-shaped curved surface portion R1 that is concave with respect to the
さらに、実施の形態3に係る上記圧力分布においては、圧力ピークに至るまで、略一定に圧力が増加する。このため、実施の形態3に係る定着装置50Bにあっては、ニップ部の圧力分布において圧力の変動を抑制することができる。また、接続位置P1の設置誤差の変動によるニップ幅の変動も抑制することができる。
Furthermore, in the above pressure distribution according to embodiment 3, the pressure increases at a substantially constant rate until the pressure peaks. Therefore, in the
また、上述のように、接続位置P1が、加圧ローラー51の軸方向から見た場合に、上記仮想線VL1よりも、定着ベルト54の回転方向において下流側(ニップ部Nの下流側)に位置する。すなわち、実施の形態3においては、上記仮想線VL1が、パッド部材52の重心付近を通過する。このため、接続位置P1が、仮想線VL1よりも上流側、あるいは仮想線VL1上に位置する場合と比較して、パッド部材52を回転させるように作用する力を抑制することができる。これにより、組立性を考慮して、部品間に緩みを設けた場合であっても、パッド部材52が回転することを抑制できる。この結果、上記のような圧力分布を得られやすくなる。
As described above, when viewed from the axial direction of the
(検証実験)
図14は、実施の形態の効果を検証するために行なった第1検証実験の条件および結果を示す図である。図15は、実施の形態の効果を検証するために行なった第2検証実験の条件および結果を示す図である。図16から図19は、比較例1から比較例4に係る各定着装置において、加圧ローラーがパッド部材を加圧している状態を示す図である。図14から図19を参照して、検証実験について説明する。
(Verification experiment)
Fig. 14 is a diagram showing the conditions and results of a first verification experiment conducted to verify the effects of the embodiment. Fig. 15 is a diagram showing the conditions and results of a second verification experiment conducted to verify the effects of the embodiment. Figs. 16 to 19 are diagrams showing the state in which the pressure roller presses the pad member in each fixing device according to Comparative Example 1 to Comparative Example 4. The verification experiments will be described with reference to Figs. 14 to 19.
図14に示すように、第1検証実験においては、比較例1、比較例2、および実施例1に係る定着装置を用いて、紙しわの評価、ニップ幅の測定、および圧力ピークの位置の確認を行なった。 As shown in FIG. 14, in the first verification experiment, the fixing devices of Comparative Example 1, Comparative Example 2, and Example 1 were used to evaluate paper wrinkles, measure the nip width, and confirm the position of the pressure peak.
紙しわの評価は、記録媒体である用紙をニップ部に通過させて、用紙に対して品質不良となる紙しわが発生するか否かを確認した。ニップ幅の測定は、ニップ部を測定用フィルム(たとえばOHP(Over Head Projector))が通過するタイミングで、当該フィルムの搬送を停止し、フィルムの一部を熱変形させた。続いて、当該フィルムをニップ部を通過させ、変形した部分の長さを測定した。圧力ピークの位置を確認するにあたり、パッド部材52と加圧ローラー51との間にセンサシート(ニッタ株式会社制)を搬送し、面圧分布測定システム(ニッタ株式会社制)を用いて、圧力分布を測定した。当該圧力分布において、圧力がピークとなる位置を確認した。なお、ニップ幅が大きく、圧力ピークがニップ部Nの下流側に位置する方が、トナーの溶融効率は向上する。
To evaluate paper wrinkles, a recording medium, paper, was passed through the nip to check whether paper wrinkles that would cause quality defects occurred on the paper. To measure the nip width, the transport of a measurement film (e.g., an overhead projector (OHP)) was stopped when the film passed through the nip, and a part of the film was thermally deformed. The film was then passed through the nip, and the length of the deformed part was measured. To check the position of the pressure peak, a sensor sheet (manufactured by Nitta Corporation) was transported between the
実施例1に係る定着装置は、実施の形態1に係る定着装置50と同じ構成を有するものである。比較例1および比較例2に係る定着装置50X1、50X2は、実施の形態1に係る定着装置50と比較した場合に、パッド部材52におけるニップ部形成領域Rの形状が相違する。
The fixing device according to Example 1 has the same configuration as the fixing
図14および図16に示すように、比較例1に係るパッド部材52においては、ニップ部形成領域Rの上流側が、加圧ローラー51に対して凸となる凸部で構成されており、ニップ部形成領域Rの下流側が、平面部で構成されている。
As shown in Figures 14 and 16, in the
図14および17に示すように、比較例2に係るパッド部材52においては、ニップ部形成領域Rの上流側が、平面部で構成されており、ニップ部形成領域Rの下流側も、平面部で構成されている。
As shown in Figures 14 and 17, in the
再び図14に示すように、比較例1においては、ニップ部形成領域Rの上流側が、凸部で構成されることにより、ニップ部の上流側において凸部近傍で圧力が急激に高くなる。このため、ニップ部に用紙がスムーズに進入することが困難となり、品質不良となる紙しわが発生した。これにより、紙しわの評価は、不可とした。また、ニップ幅は、9.8mmとなり、上記圧力分布におけるピーク位置は、ニップ部形成領域Rの上流側に存在した。このため、比較例1では、ニップ部Nでのトナーの溶融効率は悪かった。 As shown in FIG. 14 again, in Comparative Example 1, the upstream side of the nip formation region R is configured with a convex portion, so that the pressure increases suddenly near the convex portion upstream of the nip. This makes it difficult for the paper to smoothly enter the nip portion, and paper wrinkles that result in poor quality are generated. As a result, the paper wrinkles cannot be evaluated. In addition, the nip width is 9.8 mm, and the peak position in the above pressure distribution is located upstream of the nip formation region R. Therefore, in Comparative Example 1, the toner melting efficiency in the nip portion N was poor.
比較例2においては、ニップ部形成領域Rの上流側は、平面部で構成されているものの、ニップ部の上流側において圧力が依然として高い。このため、ニップ部に用紙がスムーズに進入することが困難となり、品質不良となる紙しわが発生した。これにより、紙しわの評価は、不可とした。また、ニップ幅は、11.1mmとなり、上記圧力分布におけるピーク位置は、ニップ部形成領域Rの中央側に存在した。このため、ニップ部Nでのトナー溶融効率は不十分であった。 In Comparative Example 2, although the upstream side of the nip formation region R is composed of a flat portion, the pressure on the upstream side of the nip is still high. This makes it difficult for the paper to smoothly enter the nip, and paper wrinkles that result in poor quality are generated. As a result, the paper wrinkles cannot be evaluated. In addition, the nip width is 11.1 mm, and the peak position in the above pressure distribution is located on the central side of the nip formation region R. For this reason, the toner melting efficiency in the nip N is insufficient.
実施例1においては、ニップ部形成領域Rの上流側は、加圧ローラー51に対して凹となる曲面部で構成されることにより、ニップ部Nの上流側で圧力の増加を抑制することができる。このため、ニップ部Nに用紙がスムーズに進入することができ、品質不良となる紙しわは発生しなかった。さらに、ニップ幅は、16.7mmとなり、上記圧力分布におけるピーク位置は、ニップ部形成領域の下流側に存在した。このため、ニップ部Nでのトナー溶融効率が向上した。
In Example 1, the upstream side of the nip formation region R is formed with a curved surface that is concave with respect to the
図15に示すように、第2検証実験においては、比較例3、実施例1、および比較例4に係る定着装置を用いて、画像濃度の評価、および圧力ピークの位置の確認を行なった。 As shown in FIG. 15, in the second verification experiment, the fixing devices of Comparative Example 3, Example 1, and Comparative Example 4 were used to evaluate the image density and confirm the position of the pressure peak.
画像濃度の評価としては、画像定着後の記録媒体を観察し、下地の記録媒体が局所的に露出している部分が存在するか否かを確認した。このように記録媒体が露出する部分が存在する場合には、画像濃度が低下する。なお、記録媒体の露出は、定着装置によるトナー像の定着中に、溶融不足によるトナー像が搬送方向の上流側に微小に移動することで発生する。 To evaluate image density, the recording medium after the image was fixed was observed to confirm whether there were any areas where the underlying recording medium was locally exposed. When there are any areas where the recording medium is exposed in this way, the image density decreases. Note that exposure of the recording medium occurs when the toner image moves slightly upstream in the transport direction due to insufficient melting while the toner image is being fixed by the fixing device.
実施例1に係る定着装置は、実施の形態1に係る定着装置50と同じ構成を有するものである。比較例3および比較例4に係る定着装置50X3、50X4は、実施の形態1に係る定着装置50と比較した場合に、パッド部材52におけるニップ部形成領域Rの形状が相違する。
The fixing device according to Example 1 has the same configuration as the fixing
図15および図18に示すように、比較例3に係るパッド部材52においては、ニップ部形成領域Rの上流側が、加圧ローラー51に対して凹となる凹部で構成されており、ニップ部形成領域Rの下流側が、加圧ローラー51に対して凸となる凸部で構成されている。
As shown in Figures 15 and 18, in the
図15および図19に示すように、比較例4に係るパッド部材52においては、ニップ部形成領域Rの上流側が、加圧ローラー51に対して凹となる凹部で構成されており、ニップ部形成領域Rの下流側が、加圧ローラー51に対して凸となる凸部で構成されている。
As shown in Figures 15 and 19, in the
再び図15に示すように、比較例3においては、ニップ部形成領域Rの上流側が、凹部で構成され、下流側が凸部で構成されることにより、上記圧力分布におけるピーク位置は、ニップ部形成領域Rの下流側に存在した。一方で、ニップ部形成領域Rの下流側が凸部で構成されることにより、記録媒体の露出部が確認され、画像濃度が低下していた。このため、画像濃度は、不良と評価された。 As shown again in FIG. 15, in Comparative Example 3, the upstream side of the nip forming region R was composed of concave portions and the downstream side was composed of convex portions, so that the peak position in the above pressure distribution was located downstream of the nip forming region R. On the other hand, because the downstream side of the nip forming region R was composed of convex portions, exposed areas of the recording medium were confirmed and the image density was reduced. For this reason, the image density was evaluated as poor.
比較例3においては、ニップ部形成領域Rの下流側に形成された凸部が、記録媒体の凹凸に追従しにくため、トナー像が部分的に溶融不足となる。また、定着ベルト54とパッド部材52との摺動抵抗によって発生するせん断力が、凸部で大きく作用する。このため、溶融不足となったトナー像の一部が、せん断力によって移動することで、上記記録媒体の露出部が確認された。
In Comparative Example 3, the convex portion formed downstream of the nip portion forming region R has difficulty following the unevenness of the recording medium, so the toner image is partially insufficiently melted. In addition, the shear force generated by the sliding resistance between the fixing
比較例4においては、ニップ部形成領域Rの上流側および下流側の双方が凹部で構成されており、ニップ部形成領域Rにおいて凸部が形成されていない。このため、比較例4においては、比較例3のような記録媒体の露出部は確認されず、画像濃度の低下は発生しなかった。この結果、画像濃度は、良と評価された。 In Comparative Example 4, both the upstream and downstream sides of the nip forming region R are configured with recesses, and no protrusions are formed in the nip forming region R. Therefore, in Comparative Example 4, no exposed areas of the recording medium were observed as in Comparative Example 3, and no reduction in image density occurred. As a result, the image density was evaluated as good.
一方で、ニップ部形成領域Rの上流側および下流側の双方が凹部で構成されるため、上記圧力分布におけるピーク位置は、ニップ部形成領域Rの略中央に確認された。このため、ニップ部形成領域Rの下流側にピーク圧が存在する実施例1と比較して、トナーの溶融効率は低下していた。 However, because both the upstream and downstream sides of the nip forming region R are made up of recesses, the peak position in the pressure distribution was confirmed to be approximately in the center of the nip forming region R. For this reason, the toner melting efficiency was reduced compared to Example 1, in which the peak pressure was present downstream of the nip forming region R.
実施例1では、ニップ部形成領域Rの上流側が凹部で構成されており、ニップ部形成領域Rの下流側は平面部で形成されており、ニップ部形成領域Rにおいて凸部が形成されていない。このため、実施例1においても、比較例3のような記録媒体の露出部は確認されず、画像濃度の低下は発生しなかった。この結果、画像濃度は、良と評価された。 In Example 1, the upstream side of the nip forming region R is configured with a recess, and the downstream side of the nip forming region R is formed with a flat portion, and no protrusions are formed in the nip forming region R. Therefore, even in Example 1, no exposed portion of the recording medium was observed as in Comparative Example 3, and no decrease in image density occurred. As a result, the image density was evaluated as good.
さらに、上記圧力分布におけるピーク位置は、ニップ部形成領域Rの下流側で確認され、上述の第1検証実験で説明したように、ニップ部Nでのトナー溶融効率が向上した。 Furthermore, the peak position in the above pressure distribution was confirmed downstream of the nip forming region R, and as explained in the first verification experiment above, the toner melting efficiency in the nip N was improved.
以上、実施の形態に係る定着装置にあっては、画像濃度の低下を抑制しつつ、トナーの溶融効率を向上させることができることが実験的に確認された。 As described above, it has been experimentally confirmed that the fixing device according to the embodiment can improve the toner melting efficiency while suppressing the decrease in image density.
(変形例1)
図20は、変形例1に係る定着装置において、加圧ローラーがパッド部材を加圧している状態を示す図である。上述した実施の形態1から3においては、ニップ部形成領域Rの下流側に形成された平面部R2が、接続位置P1に接する曲面部R1の接線TL1上に位置する場合を例示して説明したが、これに限定されない。変形例1に係る定着装置50Cのように、平面部R2は、上記接線TL1よりも加圧ローラー51側に傾斜していてもよい。
(Variation 1)
20 is a diagram showing a state in which the pressure roller presses the pad member in the fixing device according to
この場合においても、ニップ部形成領域に印加される圧力の分布において、ピーク位置が平面部に存在することとなり、実施の形態1に係る定着装置50とほぼ同様の効果が得られる。
Even in this case, the peak position in the distribution of pressure applied to the nip forming region is present on the flat surface, and the same effect as that of the fixing
以上、今回発明された実施の形態はすべての点で例示であって制限的なものではない。本発明の範囲は特許請求の範囲によって示され、特許請求の範囲と均等の意味および範囲内でのすべての変更が含まれる。 The above-mentioned embodiments of the present invention are illustrative in all respects and are not restrictive. The scope of the present invention is defined by the claims, and includes all modifications within the meaning and scope of the claims.
1C,1K,1M,1Y 画像形成ユニット、10 感光体、11 帯電装置、12 露光装置、13 現像装置、14 現像ローラー、15C,15K,15M,15Y トナーボトル、17 クリーニング装置、30 中間転写ベルト、31 一次転写ローラー、33 二次転写ローラー、37 カセット、38 従動ローラー、39 駆動ローラー、40 タイミングローラー、41 搬送経路、48 トレイ、50,50A,50B,50C,50X1,50X2,50X3,50X4 定着装置、51 加圧ローラー、52 パッド部材、52a 凸部、53 加熱ローラー、53a 加熱源、54 定着ベルト、55 固定部材、55a 底部、56 潤滑剤塗布部、57 保持部材、57a 収容凹部、58 摺動部材、80 筐体、100 画像形成装置、101 制御装置。 1C, 1K, 1M, 1Y Image forming unit, 10 Photoconductor, 11 Charging device, 12 Exposure device, 13 Developing device, 14 Developing roller, 15C, 15K, 15M, 15Y Toner bottle, 17 Cleaning device, 30 Intermediate transfer belt, 31 Primary transfer roller, 33 Secondary transfer roller, 37 Cassette, 38 Driven roller, 39 Drive roller, 40 Timing roller, 41 Transport path, 48 Tray, 50, 50A, 50B, 50C, 50X1, 50X2, 50X3, 50X4 Fixing device, 51 Pressure roller, 52 Pad member, 52a Convex portion, 53 Heating roller, 53a Heat source, 54 Fixing belt, 55 Fixed member, 55a Bottom, 56 Lubricant application portion, 57 Holding member, 57a Storage recess, 58 Sliding member, 80 housing, 100 image forming device, 101 control device.
Claims (6)
前記無端ベルトの内側に配置された定着部材と、
前記無端ベルトの外側において前記定着部材に対向して配置され、前記定着部材とともにニップ部を形成するローラーと、
前記無端ベルトを加熱する加熱部材と、を備え、
前記定着部材は、前記ニップ部を形成するニップ部形成領域において、前記無端ベルトの回転方向における上流側に設けられた曲面部と、前記回転方向の下流側に設けられ、前記曲面部に接続された平面部とを有し、
前記曲面部は、前記ローラーに対して凹となるように円弧状に湾曲しており、
前記平面部は、前記曲面部に接続される接続位置に接する前記曲面部の接線上に位置するか、前記接線よりも前記ローラー側に傾斜するように設けられ、
前記ニップ部形成領域に印加される圧力の分布において、ピーク位置が前記平面部に存在し、
前記曲面部および前記平面部は、連続して設けられている、定着装置。 An endless belt,
a fixing member disposed inside the endless belt;
a roller disposed outside the endless belt and facing the fixing member, the roller forming a nip portion together with the fixing member;
a heating member for heating the endless belt,
the fixing member has a curved surface portion provided on an upstream side in a rotation direction of the endless belt in a nip portion forming region that forms the nip portion, and a flat surface portion provided on a downstream side in the rotation direction and connected to the curved surface portion,
The curved surface portion is curved in an arc shape so as to be concave with respect to the roller,
the flat portion is located on a tangent line of the curved portion that contacts a connection position where the flat portion is connected to the curved portion, or is inclined toward the roller from the tangent line,
In the distribution of pressure applied to the nip portion forming region, a peak position exists on the flat portion ,
The curved surface portion and the flat surface portion are provided continuously .
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020054119A JP7516797B2 (en) | 2020-03-25 | 2020-03-25 | Fixing device and image forming apparatus |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020054119A JP7516797B2 (en) | 2020-03-25 | 2020-03-25 | Fixing device and image forming apparatus |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2021156927A JP2021156927A (en) | 2021-10-07 |
| JP7516797B2 true JP7516797B2 (en) | 2024-07-17 |
Family
ID=77917719
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020054119A Active JP7516797B2 (en) | 2020-03-25 | 2020-03-25 | Fixing device and image forming apparatus |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP7516797B2 (en) |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010262137A (en) | 2009-05-07 | 2010-11-18 | Fuji Xerox Co Ltd | Fixing device and image forming apparatus |
| JP2011008062A (en) | 2009-06-26 | 2011-01-13 | Konica Minolta Business Technologies Inc | Fixing device and image forming apparatus |
| JP2016057528A (en) | 2014-09-11 | 2016-04-21 | 富士ゼロックス株式会社 | Fixing device and image forming apparatus |
| JP2019040013A (en) | 2017-08-24 | 2019-03-14 | 京セラドキュメントソリューションズ株式会社 | Fixing device and image forming apparatus |
| JP2019184759A (en) | 2018-04-06 | 2019-10-24 | コニカミノルタ株式会社 | Fixing device and image forming apparatus |
| JP2019211628A (en) | 2018-06-05 | 2019-12-12 | コニカミノルタ株式会社 | Fixing device and image forming apparatus |
-
2020
- 2020-03-25 JP JP2020054119A patent/JP7516797B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010262137A (en) | 2009-05-07 | 2010-11-18 | Fuji Xerox Co Ltd | Fixing device and image forming apparatus |
| JP2011008062A (en) | 2009-06-26 | 2011-01-13 | Konica Minolta Business Technologies Inc | Fixing device and image forming apparatus |
| JP2016057528A (en) | 2014-09-11 | 2016-04-21 | 富士ゼロックス株式会社 | Fixing device and image forming apparatus |
| JP2019040013A (en) | 2017-08-24 | 2019-03-14 | 京セラドキュメントソリューションズ株式会社 | Fixing device and image forming apparatus |
| JP2019184759A (en) | 2018-04-06 | 2019-10-24 | コニカミノルタ株式会社 | Fixing device and image forming apparatus |
| JP2019211628A (en) | 2018-06-05 | 2019-12-12 | コニカミノルタ株式会社 | Fixing device and image forming apparatus |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2021156927A (en) | 2021-10-07 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US8472855B2 (en) | Fixing device and image forming apparatus incorporating same | |
| JP6857324B2 (en) | Fixing device and image forming device | |
| US7392005B2 (en) | Image heating apparatus | |
| JP5332927B2 (en) | Fixing apparatus and image forming apparatus | |
| JP6701569B2 (en) | Fixing device and image forming apparatus | |
| JP4595447B2 (en) | Fixing device and image forming apparatus | |
| US20130202334A1 (en) | Image heating apparatus | |
| JP5428402B2 (en) | Fixing apparatus, image forming apparatus, and endless belt for fixing | |
| JP2005173441A (en) | Fixing device and image forming apparatus | |
| JP5550271B2 (en) | Image heating device | |
| JP6684462B2 (en) | Fixing device and image forming device | |
| JP6864257B2 (en) | Fixing device and image forming device | |
| JP2009047959A (en) | Fixing device and image forming device | |
| JP7087602B2 (en) | Fixing device and image forming device | |
| JP4770944B2 (en) | Fixing apparatus and image forming apparatus | |
| JP4548548B2 (en) | Fixing apparatus and image forming apparatus | |
| JP7516797B2 (en) | Fixing device and image forming apparatus | |
| JP2009251311A (en) | Fixing device and image forming apparatus having the same | |
| JP4872853B2 (en) | Fixing apparatus and image forming apparatus | |
| JP6686445B2 (en) | Fixing device and image forming device | |
| JP7247518B2 (en) | Fixing device, image forming device | |
| JP2020056888A (en) | Endless belt and fixing device | |
| JP2019191332A (en) | Fixing device and image forming apparatus | |
| JP2005266716A (en) | Fixing device and image forming apparatus | |
| JP7552402B2 (en) | Fixing device and image forming apparatus |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20230216 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20231204 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20231205 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20240416 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20240521 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20240604 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20240617 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 7516797 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |