JP6019330B2 - THIN FILM TRANSISTOR, METHOD FOR PRODUCING THIN FILM TRANSISTOR, DISPLAY DEVICE, AND ELECTRONIC DEVICE - Google Patents
THIN FILM TRANSISTOR, METHOD FOR PRODUCING THIN FILM TRANSISTOR, DISPLAY DEVICE, AND ELECTRONIC DEVICE Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6019330B2 JP6019330B2 JP2012026250A JP2012026250A JP6019330B2 JP 6019330 B2 JP6019330 B2 JP 6019330B2 JP 2012026250 A JP2012026250 A JP 2012026250A JP 2012026250 A JP2012026250 A JP 2012026250A JP 6019330 B2 JP6019330 B2 JP 6019330B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- oxide
- layer
- electrode
- semiconductor layer
- drain electrode
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 239000010409 thin film Substances 0.000 title claims description 103
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 title claims description 42
- 239000010408 film Substances 0.000 claims description 159
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 claims description 143
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 46
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 claims description 27
- 230000001681 protective effect Effects 0.000 claims description 25
- QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N atomic oxygen Chemical compound [O] QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 20
- 239000001301 oxygen Substances 0.000 claims description 20
- 229910052760 oxygen Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 20
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 claims description 14
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims description 13
- 238000000059 patterning Methods 0.000 claims description 13
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 claims description 9
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 8
- 229910052814 silicon oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 8
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 claims description 7
- TWNQGVIAIRXVLR-UHFFFAOYSA-N oxo(oxoalumanyloxy)alumane Chemical compound O=[Al]O[Al]=O TWNQGVIAIRXVLR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 7
- LIVNPJMFVYWSIS-UHFFFAOYSA-N silicon monoxide Chemical compound [Si-]#[O+] LIVNPJMFVYWSIS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- 230000000149 penetrating effect Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 description 243
- 238000004544 sputter deposition Methods 0.000 description 19
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 description 19
- 238000005401 electroluminescence Methods 0.000 description 15
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 14
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 14
- 230000007547 defect Effects 0.000 description 11
- 238000005530 etching Methods 0.000 description 9
- 239000007789 gas Substances 0.000 description 9
- 101100153525 Homo sapiens TNFRSF25 gene Proteins 0.000 description 7
- 102100022203 Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 25 Human genes 0.000 description 7
- 230000006866 deterioration Effects 0.000 description 7
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 7
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 7
- GQPLMRYTRLFLPF-UHFFFAOYSA-N Nitrous Oxide Chemical compound [O-][N+]#N GQPLMRYTRLFLPF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- XLOMVQKBTHCTTD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Zinc monoxide Chemical compound [Zn]=O XLOMVQKBTHCTTD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 6
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium Chemical compound [Al] XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 239000003990 capacitor Substances 0.000 description 6
- 238000005229 chemical vapour deposition Methods 0.000 description 6
- 230000000052 comparative effect Effects 0.000 description 6
- 238000000206 photolithography Methods 0.000 description 6
- 238000000151 deposition Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000005070 sampling Methods 0.000 description 5
- XKRFYHLGVUSROY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Argon Chemical compound [Ar] XKRFYHLGVUSROY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- KRHYYFGTRYWZRS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Fluorane Chemical compound F KRHYYFGTRYWZRS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- GYHNNYVSQQEPJS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Gallium Chemical compound [Ga] GYHNNYVSQQEPJS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrochloric acid Chemical compound Cl VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 230000008021 deposition Effects 0.000 description 4
- 229910052733 gallium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 230000006872 improvement Effects 0.000 description 4
- 229910052738 indium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- APFVFJFRJDLVQX-UHFFFAOYSA-N indium atom Chemical compound [In] APFVFJFRJDLVQX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000009832 plasma treatment Methods 0.000 description 4
- UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrogen Chemical compound [H][H] UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- ZOKXTWBITQBERF-UHFFFAOYSA-N Molybdenum Chemical compound [Mo] ZOKXTWBITQBERF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 229910052581 Si3N4 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- BLRPTPMANUNPDV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silane Chemical compound [SiH4] BLRPTPMANUNPDV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 229910045601 alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 239000000956 alloy Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000001312 dry etching Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000001257 hydrogen Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229910052739 hydrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 239000004973 liquid crystal related substance Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229910052750 molybdenum Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 239000011733 molybdenum Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229960001730 nitrous oxide Drugs 0.000 description 3
- 235000013842 nitrous oxide Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- 230000003647 oxidation Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000007254 oxidation reaction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000001590 oxidative effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 229910000077 silane Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- HQVNEWCFYHHQES-UHFFFAOYSA-N silicon nitride Chemical compound N12[Si]34N5[Si]62N3[Si]51N64 HQVNEWCFYHHQES-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 238000003860 storage Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000010936 titanium Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000011787 zinc oxide Substances 0.000 description 3
- QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ammonia Chemical compound N QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N Atomic nitrogen Chemical compound N#N IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical compound [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- ATJFFYVFTNAWJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tin Chemical compound [Sn] ATJFFYVFTNAWJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Titanium Chemical compound [Ti] RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910052786 argon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000000470 constituent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000010949 copper Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000012535 impurity Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000011159 matrix material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000009751 slip forming Methods 0.000 description 2
- OFIYHXOOOISSDN-UHFFFAOYSA-N tellanylidenegallium Chemical compound [Te]=[Ga] OFIYHXOOOISSDN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- JBQYATWDVHIOAR-UHFFFAOYSA-N tellanylidenegermanium Chemical compound [Te]=[Ge] JBQYATWDVHIOAR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910052719 titanium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 238000001039 wet etching Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910000838 Al alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Copper Chemical compound [Cu] RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MYMOFIZGZYHOMD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dioxygen Chemical compound O=O MYMOFIZGZYHOMD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052779 Neodymium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- BQCADISMDOOEFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silver Chemical compound [Ag] BQCADISMDOOEFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LXFUCSMCVAEMCD-UHFFFAOYSA-N acetic acid;nitric acid;phosphoric acid Chemical compound CC(O)=O.O[N+]([O-])=O.OP(O)(O)=O LXFUCSMCVAEMCD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000009471 action Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910021529 ammonia Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910021417 amorphous silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000919 ceramic Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004020 conductor Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000002425 crystallisation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008025 crystallization Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910001882 dioxygen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 101150013423 dsl-1 gene Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 239000007772 electrode material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000002349 favourable effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- AMGQUBHHOARCQH-UHFFFAOYSA-N indium;oxotin Chemical compound [In].[Sn]=O AMGQUBHHOARCQH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000011229 interlayer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000002739 metals Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- QEFYFXOXNSNQGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N neodymium atom Chemical compound [Nd] QEFYFXOXNSNQGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052757 nitrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000001552 radio frequency sputter deposition Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005546 reactive sputtering Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052709 silver Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000004332 silver Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002356 single layer Substances 0.000 description 1
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Chemical compound O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Electroluminescent Light Sources (AREA)
- Internal Circuitry In Semiconductor Integrated Circuit Devices (AREA)
- Physical Deposition Of Substances That Are Components Of Semiconductor Devices (AREA)
- Thin Film Transistor (AREA)
Description
本開示は、酸化物半導体を用いた薄膜トランジスタ(TFT:Thin Film Transistor)、薄膜トランジスタの製造方法、表示装置および電子機器に関する。 The present disclosure relates to a thin film transistor (TFT) using an oxide semiconductor, a method for manufacturing the thin film transistor, a display device, and an electronic apparatus.
亜鉛(Zn)、インジウム(In)、ガリウム(Ga)、スズ(Sn)あるいはそれらの混合物の酸化物(酸化物半導体)は、優れた半導体特性を示すことが知られている。例えば、酸化物半導体を用いた薄膜トランジスタは、アモルファスシリコンを用いたものと比べて10倍以上の電子移動度を示し、かつ良好なオフ特性を示す。従って、この酸化物半導体を用いた薄膜トランジスタは、大画面、高精細および高フレームレートの液晶表示装置や、有機EL(Electro Luminescence)表示装置向けの駆動素子として応用が期待されている。 It is known that oxides (oxide semiconductors) of zinc (Zn), indium (In), gallium (Ga), tin (Sn), or a mixture thereof exhibit excellent semiconductor characteristics. For example, a thin film transistor using an oxide semiconductor exhibits an electron mobility that is 10 times or more that of using amorphous silicon, and favorable off characteristics. Therefore, the thin film transistor using the oxide semiconductor is expected to be applied as a driving element for a large-screen, high-definition and high-frame-rate liquid crystal display device or an organic EL (Electro Luminescence) display device.
ところが、酸化物半導体は耐熱性が十分ではなく、薄膜トランジスタの製造プロセスでの熱処理やプラズマ処理により酸素が脱離し、格子欠陥を形成する。この格子欠陥は、電気的には浅い不純物準位を形成し、酸化物半導体の低抵抗化を引き起こす。そのため、酸化物半導体を活性層に用いた場合、欠陥準位の増大によって閾値電圧が小さくなり、リーク電流が増大する。これにより、ゲート電流を印加しなくてもドレイン電流が流れる、いわゆるデプレッション型の動作を引き起こす。更には、欠陥準位が増大し続けると、トランジスタ動作から導電体動作へと移行してしまう。これは、特に多元系の酸化物半導体の場合、熱的に不安定な元素の含有比率によって安定性が変化することによると考えられる。また、上記したような格子欠陥の他にも、浅い不純物準位を形成する元素として、水素が報告されている(非特許文献1)。 However, an oxide semiconductor does not have sufficient heat resistance, and oxygen is desorbed by heat treatment or plasma treatment in a thin film transistor manufacturing process to form lattice defects. This lattice defect forms a shallow impurity level electrically and causes a reduction in resistance of the oxide semiconductor. Therefore, in the case where an oxide semiconductor is used for the active layer, the threshold voltage is reduced due to an increase in the defect level, and the leakage current is increased. This causes a so-called depletion type operation in which a drain current flows without applying a gate current. Furthermore, if the defect level continues to increase, the transistor operation shifts to the conductor operation. This is considered to be due to the fact that the stability changes depending on the content ratio of a thermally unstable element, particularly in the case of a multi-element oxide semiconductor. In addition to the lattice defects as described above, hydrogen has been reported as an element that forms a shallow impurity level (Non-Patent Document 1).
上記のように、酸化物半導体を用いた薄膜トランジスタでは、その製造プロセスにおいて酸化物半導体の特性が劣化し、電気的特性に影響を与え易い。このため、酸化物半導体の特性劣化の抑制し、電気的特性を向上することが望まれる。 As described above, in a thin film transistor using an oxide semiconductor, characteristics of the oxide semiconductor are deteriorated in a manufacturing process thereof, which easily affects electrical characteristics. For this reason, it is desired to suppress deterioration of characteristics of the oxide semiconductor and improve electrical characteristics.
本開示はかかる問題点に鑑みてなされたもので、その目的は、電気的特性の向上を実現することが可能な薄膜トランジスタ、薄膜トランジスタの製造方法、表示装置および電子機器を提供することにある。 The present disclosure has been made in view of such problems, and an object of the present disclosure is to provide a thin film transistor, a manufacturing method of the thin film transistor, a display device, and an electronic device that can realize improvement in electrical characteristics.
本開示の薄膜トランジスタは、ゲート電極、ソース電極およびドレイン電極と、ゲート電極の一方の側に絶縁膜を介して設けられると共に、ソース電極およびドレイン電極に非対向な領域に設けられ、かつソース電極およびドレイン電極に電気的に接続された酸化物半導体層と、酸化物半導体層に隣接すると共に、ソース電極およびドレイン電極の各々に対向する領域に設けられ、かつ酸化物半導体層よりも電気抵抗率の低い低抵抗酸化物層と、ゲート電極と同層に設けられた配線層と、配線層に対向して設けられると共に絶縁膜を貫通する貫通孔とを備える。低抵抗酸化物層は、貫通孔の内部まで延在すると共に配線層を覆って形成され、ソース電極またはドレイン電極は、貫通孔上に低抵抗酸化物層を介して設けられ、配線層に電気的に接続されているものである。 The thin film transistor of the present disclosure is provided with a gate electrode, a source electrode, a drain electrode, and an insulating film on one side of the gate electrode, and is provided in a region not facing the source electrode and the drain electrode. An oxide semiconductor layer electrically connected to the drain electrode; adjacent to the oxide semiconductor layer; provided in a region facing each of the source electrode and the drain electrode; and having an electrical resistivity higher than that of the oxide semiconductor layer A low-resistance oxide layer , a wiring layer provided in the same layer as the gate electrode, and a through-hole provided so as to face the wiring layer and penetrating the insulating film are provided. The low resistance oxide layer extends to the inside of the through hole and covers the wiring layer. The source electrode or the drain electrode is provided on the through hole via the low resistance oxide layer, and the wiring layer is electrically Connected .
本開示の薄膜トランジスタでは、ソース電極およびドレイン電極に非対向な領域に酸化物半導体層が設けられ、ソース電極およびドレイン電極の各々に対向し、かつ酸化物半導体層に隣接する領域に、低抵抗酸化物層が設けられている。これにより、製造プロセスにおいて、酸化物半導体層(チャネル層)の形成をソース電極およびドレイン電極の形成後に行うことができる。酸化物半導体では、電極の成膜時やパターニング時に受けるダメージによって酸素が離脱し、これによって格子欠陥を生じるが、上記のように電極形成後に酸化物半導体層が形成されることで、そのような格子欠陥の発生が抑制され、酸化物半導体層の劣化が抑制される。また、この酸化物半導体層に隣接して低抵抗酸化物層が設けられることにより、酸化物半導体層とソース電極およびドレイン電極との良好な電気的接続が確保される。 In the thin film transistor of the present disclosure, an oxide semiconductor layer is provided in a region not facing the source electrode and the drain electrode, and low resistance oxidation is performed in a region facing each of the source electrode and the drain electrode and adjacent to the oxide semiconductor layer. A material layer is provided. Thus, in the manufacturing process, the oxide semiconductor layer (channel layer) can be formed after the source electrode and the drain electrode are formed. In an oxide semiconductor, oxygen is released due to damage received during electrode deposition or patterning, which causes lattice defects. However, by forming an oxide semiconductor layer after electrode formation as described above, Generation of lattice defects is suppressed, and deterioration of the oxide semiconductor layer is suppressed. In addition, by providing the low resistance oxide layer adjacent to the oxide semiconductor layer, good electrical connection between the oxide semiconductor layer and the source and drain electrodes is ensured.
本開示の薄膜トランジスタの製造方法は、ゲート電極、ソース電極およびドレイン電極を各々形成する工程と、ゲート電極の一方の側に絶縁膜を介して設けられると共に、ソース電極およびドレイン電極に非対向な領域に設けられ、かつソース電極およびドレイン電極に電気的に接続される酸化物半導体層を形成する工程と、ゲート電極と同層に配線層を形成する工程と、配線層に対向して絶縁膜を貫通する貫通孔を形成する工程とを含むものである。酸化物半導体層を形成する工程では、酸化物半導体層に隣接すると共に、ソース電極およびドレイン電極の各々に対向する領域に、酸化物半導体層よりも電気抵抗率の低い低抵抗酸化物層を形成する。低抵抗酸化物層は、貫通孔の内部まで延在すると共に配線層を覆って形成され、ソース電極またはドレイン電極は、貫通孔上に低抵抗酸化物層を介して設けられ、配線層に電気的に接続されている。 A method of manufacturing a thin film transistor according to the present disclosure includes a step of forming a gate electrode, a source electrode, and a drain electrode, and a region that is provided on one side of the gate electrode via an insulating film and that is not opposed to the source electrode and the drain electrode. Forming an oxide semiconductor layer electrically connected to the source electrode and the drain electrode, forming a wiring layer in the same layer as the gate electrode, and forming an insulating film facing the wiring layer Forming a through hole that penetrates . In the step of forming the oxide semiconductor layer, a low-resistance oxide layer having a lower electrical resistivity than the oxide semiconductor layer is formed in a region adjacent to the oxide semiconductor layer and facing each of the source electrode and the drain electrode. To do. The low resistance oxide layer extends to the inside of the through hole and covers the wiring layer. The source electrode or the drain electrode is provided on the through hole via the low resistance oxide layer, and the wiring layer is electrically Connected.
本開示の薄膜トランジスタの製造方法では、酸化物半導体層を形成する工程において、ソース電極およびドレイン電極に非対向な領域に酸化物半導体層を形成し、ソース電極およびドレイン電極の各々に対向し、かつ酸化物半導体層に隣接する領域に、低抵抗酸化物層を形成する。これにより、酸化物半導体層(チャネル層)の形成をソース電極およびドレイン電極形成後に行うことができる。酸化物半導体では、電極の成膜時やパターニング時に受けるダメージによって酸素が離脱し、これによって格子欠陥を生じるが、上記のように電極形成後に酸化物半導体層が形成されることで、そのような格子欠陥の発生が抑制され、酸化物半導体層の劣化が抑制される。また、酸化物半導体層に隣接して低抵抗酸化物層が形成されることにより、酸化物半導体層とソース電極およびドレイン電極との良好な電気的接続が確保される。 In the method of manufacturing a thin film transistor according to the present disclosure, in the step of forming the oxide semiconductor layer, the oxide semiconductor layer is formed in a region not facing the source electrode and the drain electrode, facing each of the source electrode and the drain electrode, and A low-resistance oxide layer is formed in a region adjacent to the oxide semiconductor layer. Accordingly, the oxide semiconductor layer (channel layer) can be formed after the source electrode and the drain electrode are formed. In an oxide semiconductor, oxygen is released due to damage received during electrode deposition or patterning, which causes lattice defects. However, by forming an oxide semiconductor layer after electrode formation as described above, Generation of lattice defects is suppressed, and deterioration of the oxide semiconductor layer is suppressed. In addition, since the low-resistance oxide layer is formed adjacent to the oxide semiconductor layer, good electrical connection between the oxide semiconductor layer and the source and drain electrodes is ensured.
本開示の表示装置は、上記本開示の薄膜トランジスタを備えたものである。 A display device according to the present disclosure includes the thin film transistor according to the present disclosure.
本開示の電子機器は、上記本開示の薄膜トランジスタを備えた表示装置を有するものである。 An electronic device according to the present disclosure includes a display device including the thin film transistor according to the present disclosure.
本開示の薄膜トランジスタによれば、ソース電極およびドレイン電極に非対向な領域に酸化物半導体層を設け、ソース電極およびドレイン電極の各々に対向し、かつ酸化物半導体層に隣接する領域に、低抵抗酸化物層を設けたので、製造プロセスにおける酸化物半導体層の劣化を抑制できる。また、低抵抗酸化物層により、酸化物半導体層とソース電極およびドレイン電極との良好な電気的接続を確保することができる。よって、電気的特性の向上を実現可能となる。 According to the thin film transistor of the present disclosure, an oxide semiconductor layer is provided in a region not facing the source electrode and the drain electrode, and a low resistance is provided in a region facing each of the source electrode and the drain electrode and adjacent to the oxide semiconductor layer. Since the oxide layer is provided, deterioration of the oxide semiconductor layer in the manufacturing process can be suppressed. In addition, the low-resistance oxide layer can ensure good electrical connection between the oxide semiconductor layer and the source and drain electrodes. Therefore, improvement in electrical characteristics can be realized.
本開示の薄膜トランジスタの製造方法によれば、ソース電極およびドレイン電極に非対向な領域に酸化物半導体層を形成し、ソース電極およびドレイン電極の各々に対向し、かつ酸化物半導体層に隣接する領域に、低抵抗酸化物層を形成するようにしたので、酸化物半導体層の劣化を抑制できる。また、低抵抗酸化物層により、酸化物半導体層とソース電極およびドレイン電極との良好な電気的接続が確保される。よって、電気的特性の向上を実現可能となる。 According to the method for manufacturing a thin film transistor of the present disclosure, an oxide semiconductor layer is formed in a region not facing the source electrode and the drain electrode, the region facing each of the source electrode and the drain electrode and adjacent to the oxide semiconductor layer In addition, since the low-resistance oxide layer is formed, deterioration of the oxide semiconductor layer can be suppressed. In addition, the low-resistance oxide layer ensures good electrical connection between the oxide semiconductor layer and the source and drain electrodes. Therefore, improvement in electrical characteristics can be realized.
本開示の表示装置によれば、上記本開示の薄膜トランジスタを備えるようにしたので、薄膜トランジスタにおける電気的特性の向上を実現可能となる。 According to the display device of the present disclosure, since the thin film transistor of the present disclosure is provided, the electrical characteristics of the thin film transistor can be improved.
本開示の電子機器によれば、上記本開示の薄膜トランジスタを備えた表示装置を有するので、薄膜トランジスタにおける電気的特性の向上を実現可能となる。 According to the electronic device of the present disclosure, since the display device including the thin film transistor of the present disclosure is included, the electrical characteristics of the thin film transistor can be improved.
以下、本開示の実施の形態について図面を参照して詳細に説明する。尚、説明は以下の順序で行う。
1.第1の実施の形態(ソース・ドレイン電極形成後に、低抵抗な酸化物膜の一部を高抵抗化することで、チャネルとしての酸化物半導体層を形成する薄膜トランジスタの例)
2.変形例1(高抵抗化処理を保護膜形成時に行う場合の例)
3.第2の実施の形態(酸化物膜の一部を結晶化させることにより酸化物半導体層を形成する薄膜トランジスタの例)
4.適用例(表示装置,電子機器の例)
Hereinafter, embodiments of the present disclosure will be described in detail with reference to the drawings. The description will be given in the following order.
1. First Embodiment (Example of thin film transistor in which an oxide semiconductor layer as a channel is formed by increasing the resistance of a part of a low-resistance oxide film after forming source / drain electrodes)
2. Modification 1 (example in which high resistance treatment is performed when forming a protective film)
3. Second Embodiment (Example of thin film transistor in which an oxide semiconductor layer is formed by crystallizing part of an oxide film)
4). Application examples (examples of display devices and electronic devices)
<第1の実施の形態>
[構成]
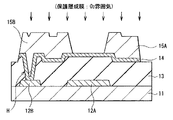
図1は、本開示の第1の実施の形態に係る薄膜トランジスタ(薄膜トランジスタ10A)の断面構造を表すものである。薄膜トランジスタ10Aは、例えばアクティブマトリクス型の有機EL表示装置(後述)や液晶表示装置の駆動素子として用いられるものである。この薄膜トランジスタ10Aでは、ゲート電極12Aの一面側に、ゲート絶縁膜13を介して酸化物半導体層14Cが配置され、この酸化物半導体層14Cに電気的に接続されるように一対のソース・ドレイン電極15A,15Bが設けられている。
<First Embodiment>
[Constitution]
FIG. 1 illustrates a cross-sectional structure of a thin film transistor (
ここでは、薄膜トランジスタ10Aは、いわゆるボトムゲート構造(逆スタガー構造)を有しており、例えばガラス等よりなる基板11上の選択的な領域にゲート電極12Aを備えている。ゲート電極12Aを覆うように基板11の全面に渡ってゲート絶縁膜13が形成され、ゲート絶縁膜13上の選択的な領域(ゲート電極12Aに対向する領域)には、酸化物半導体層14Cが形成されている。酸化物半導体層14Cよりも上層には、ソース・ドレイン電極15A,15Bが配設されており、これらの酸化物半導体層14Cおよびソース・ドレイン電極15A,15Bを覆うように、保護膜16が設けられている。
Here, the
本実施の形態の薄膜トランジスタ10Aでは、酸化物半導体層14Cが、ソース・ドレイン電極15A,15Bに非対向の領域(ソース・ドレイン電極15A,15Bから露出した領域)に形成されている。ゲート絶縁膜13上には、この酸化物半導体層14Cに隣接すると共に、ソース・ドレイン電極15A,15Bの各々と対向する領域に、低抵抗酸化物層14A,14Bが設けられている。即ち、本実施の形態では、酸化物半導体層14Cとソース・ドレイン電極15A,15Bの各々とは、低抵抗酸化物層14A,14Bを介して電気的に接続されている。
In the
薄膜トランジスタ10Aには、また、基板11上の任意の領域に、ゲート電極12Aと同層に設けられた電極または配線(ゲート層)と、ソース・ドレイン電極15A,15Bと同層に設けられた電極または配線(ソース・ドレイン層)との層間接続のためのコンタクト部(配線コンタクト部20)が設けられている。配線コンタクト部20において、ゲート絶縁膜13は、ゲート電極12Aと同層に設けられた配線層12B上にコンタクトホールHを有している。このコンタクトホールHの内部を覆って、低抵抗酸化物層14Bが形成されており、更に、このコンタクトホールH上に、低抵抗酸化物層14Bを介してソース・ドレイン電極15Bが設けられている。以下、各構成要素について説明する。
The
ゲート電極12Aは、薄膜トランジスタ10Aに印加されるゲート電圧(Vg)によって酸化物半導体層14C中のキャリア密度を制御するものである。このゲート電極12Aは、例えばモリブデン(Mo),アルミニウム,銀(Ag)および銅(Cu)のうちの1種からなる単体もしくは合金、もしくはこれらのうちの2種以上からなる積層膜である。アルミニウム合金としては、例えばアルミニウムとネオジウム(Nd)との合金(AlNd合金)が挙げられる。ゲート電極12Aは、あるいはITO(酸化インジウム錫)、AZO(アルミニウムドープ酸化亜鉛)およびGZO(ガリウムドープ酸化亜鉛)等の透明導電膜から構成されていてもよい。
The
配線層12Bは、例えばゲート電極12Aと同層に設けられ、かつゲート電極12Aと同一材料により構成されている。これらの配線層12Bおよびゲート電極12Aは、互いに同一の工程において、一括してパターン形成される。この配線層12Bは、例えば後述の表示装置における駆動回路に設けられた、いずれかの配線に相当するものである。ここで、駆動回路内には、後述するように、複数のトランジスタ、キャパシタ、およびそれらを接続する配線が設けられるが、これらのうちの電極および配線はいずれも、ゲート層またはソース・ドレイン層に配設される。つまり、ゲート層およびソース・ドレイン層の各層では、複雑な配線のレイアウトを実現するために、トランジスタのゲート、ソースおよびドレインとして機能する電極だけでなく、他の様々な配線を引き回したり、配線同士を層間接続させたりする必要がある。例えば、より厚膜(即ち低抵抗)な金属を使用可能なソース・ドレイン層において、配線を引き回すのが理想であるが、このソース・ドレイン層には、多くの信号線が張り巡らされている。そのため、ソース・ドレイン層からゲート層に配線の形成領域をシフトさせることで、様々な配線を交差させて設けることができ、複雑な配線のレイアウトを実現可能となる。配線層12Bおよび配線コンタクト部20は、そのようなソース・ドレイン層とゲート層とのコンタクト部分(ブリッジ)に相当する。
The
ゲート絶縁膜13は、例えば酸化シリコン(SiOX)、窒化シリコン(SiN)および酸化窒化シリコン(SiON)等のうちの1種よりなる単層膜、または2種以上よりなる積層膜である。
The
酸化物半導体層14Cは、活性層(チャネル)として機能する(ゲート電圧の印加によりチャネルを形成する)ものであり、例えばインジウム(In),ガリウム(Ga)、スズ(Sn)および亜鉛(Zn)等のうちの1種または2種以上の混合物の酸化物よりなる。このような酸化物としては、例えば、酸化インジウムガリウム亜鉛(IGZO,InGaZnO)が挙げられる。この酸化物半導体層14Cの厚みは、例えば20nm〜100nmである。この酸化物半導体層14Cは、詳細は後述するが、低抵抗酸化物層14A,14Bを構成する酸化物膜(低抵抗酸化物膜14)の一部が高抵抗化されることにより形成されたものである(高抵抗化された部分に相当する)。
The
低抵抗酸化物層14A,14Bは、酸化物半導体層14Cと互いに同一の酸化物により構成され、酸化物半導体層14Cと同等の厚みを有する。この低抵抗酸化物層14A,14Bは、詳細は後述するが、後述の酸化物膜(低抵抗酸化物膜14)の一部が高抵抗化された後(酸化物半導体層14Cの形成後)、高抵抗化されることなく残存した他の領域に相当するものである。このため、低抵抗酸化物層14A,14Bでは、酸化物半導体層14Cよりも電気抵抗率が低くなっており、具体的には、20μΩ・m〜40Ω・m程度である。このような低抵抗酸化物層14A,14B上に、ソース・ドレイン電極15A,15Bが積層されており、これらの基板面に沿った面形状は略等しくなっている。これにより、低抵抗酸化物層14A,14Bは、酸化物半導体層14Cとソース・ドレイン電極15A,15Bとの電気的なコンタクト層として機能する。
The low
これらの酸化物半導体層14Cおよび低抵抗酸化物層14A,14Bを構成する上記酸化物は、ソース・ドレイン電極15A,15Bのパターニング時に使用する薬液に対して耐性を有している。例えば、薬液として、PAN系(リン酸−酢酸−硝酸系)、フッ酸系または塩酸系のものが用いられる場合には、それぞれ使用される薬液に対してエッチング耐性を有していればよい。あるいは、酸化物半導体層14Cおよびソース・ドレイン電極15A,15Bの各構成材料が、ウェットエッチング選択性が得られない組み合わせである場合には、ドライエッチングのガスを適当に選択することにより、選択的な加工が可能である。また、本実施の形態では、このような酸化物が、結晶性(結晶化可能な性質)を有しておらず、酸化物半導体層14Cおよび低抵抗酸化物層14A,14Bのいずれも非晶質となっている。
The oxides constituting the
ソース・ドレイン電極15A,15Bは、ソース電極またはドレイン電極として機能するものであり、ここでは、一方がソース電極、他方がドレイン電極となっている。このソース・ドレイン電極15A,15Bの構成材料としては、上記ゲート電極12Aにおいて列挙したものと同等の金属または透明導電膜が挙げられるが、例えば厚み50nmのチタン(Ti)、厚み200nm〜1μmのアルミニウム(Al)および厚み50nmのモリブデン(Mo)を積層した3層膜から構成されている。
The source /
保護膜16は、例えば酸化アルミニウム(AlOX)または酸化シリコン(SiOX)よりなり、薄膜トランジスタ10A内部を保護すると共に、酸化物半導体層14Cへの外気(例えば水素)の混入を抑制するものである。
The
[製造方法]
図2〜図6は、薄膜トランジスタ10Aの製造方法を説明するための断面図である。薄膜トランジスタ10Aは、例えば次のようにして製造することができる。
[Production method]
2 to 6 are cross-sectional views for explaining a method of manufacturing the
まず、図2(A)に示したように、ゲート電極12A,配線層12Bを形成した後、ゲート絶縁膜13を成膜する。具体的には、まず、基板11上の全面に、上述した材料よりなる金属膜を、例えばスパッタリング法(以下、単に「スパッタ法」という)あるいはCVD(Chemical Vapor Deposition ;化学気相成長)法により堆積させた後、例えばフォトリソグラフィ法を用いたエッチングによりパターニングする。これにより、基板11上の選択的な領域にゲート電極12Aおよび配線層12Bを形成する。続いて、基板11上の全面に渡って、例えばCVD法により、ゲート絶縁膜13を成膜する。この際、原料ガスとしては、ゲート絶縁膜13としてシリコン窒化膜を形成する場合には、例えばシラン(SiH4)、アンモニア(NH3)、窒素を含む混合ガスを用いる。あるいは、ゲート絶縁膜13としてシリコン酸化膜を形成する場合には、例えばシランおよび一酸化二窒素(N2O)を含む混合ガスを用いる。
First, as shown in FIG. 2A, after forming the
次いで、図2(B)に示したように、成膜したゲート絶縁膜13の配線層12B上の領域(配線層12Bに対向する領域)に、例えばフォトリソグラフィ法を用いたエッチングによりコンタクトホールHを形成する。尚、このコンタクトホールHは、ゲート層に設けられた配線層12Bと、ソース・ドレイン層に設けられた配線(ここでは、ソース・ドレイン電極15A,15B)との間において、良好な電気的接続が得られるように加工されることが望ましい。
Next, as shown in FIG. 2B, a contact hole H is formed in a region on the
次に、図3(A)に示したように、酸化物膜14(後工程において最終的に酸化物半導体層14Cおよび低抵抗酸化物層14A,14Bとなる膜)を、例えばスパッタ法により、基板11の全面にわたって成膜する。この際、酸化物膜14は、コンタクトホールHの内部までも覆って形成する。尚、スパッタ法を用いて成膜することにより、大型基板への成膜やプロセスの低温化が可能となり、シリコン系の薄膜トランジスタの製造ラインで使用されている既存の設備を利用できる、といった利点がある。
Next, as shown in FIG. 3A, the oxide film 14 (film that finally becomes the
具体的には、酸化物としてIGZOを用いる場合には、IGZOのセラミックをターゲットとした反応性スパッタ(DCスパッタ,RFスパッタあるいはACスパッタ)を行う。例えば、スパッタ装置において、チャンバー内を所定の真空度(例えば、1×10-4Pa以下)となるまで排気した後、ターゲットおよび基板11を配置し、例えばアルゴン(Ar)と酸素(O2)の混合ガスを導入してプラズマ放電させる。これにより、ゲート絶縁膜13上に、IGZOよりなる酸化物膜14が堆積する。
Specifically, when IGZO is used as the oxide, reactive sputtering (DC sputtering, RF sputtering, or AC sputtering) is performed using IGZO ceramic as a target. For example, in a sputtering apparatus, after evacuating the chamber to a predetermined degree of vacuum (for example, 1 × 10 −4 Pa or less), the target and the
但し、この際、成膜される酸化物膜14が低い電気抵抗率を示すように、上記スパッタの各条件を調整する。具体的には、スパッタ出力(パワー)、酸素濃度、水蒸気濃度およびスパッタ背圧のうちの少なくとも1つを調整することにより、成膜材料中の金属元素の組成比や結晶性を変化させ、電気抵抗率(キャリア密度)を制御することができる。特に、上記各条件のうち、酸素濃度を低く設定することにより、低抵抗を実現し易い。この酸化物膜14の一部が、最終的に低抵抗酸化物層14A,14Bとなるため、酸化物膜14の成膜直後の電気抵抗率が、上述した低抵抗酸化物層14A,14Bの電気抵抗率となる(酸化物膜14および低抵抗酸化物層14A,14Bの電気抵抗率は同等である)。
However, at this time, the sputtering conditions are adjusted so that the
次いで、図3(B)に示したように、金属層15(ソース・ドレイン電極15A,15B)を成膜する。具体的には、酸化物膜14上に、上述した電極材料(例えばチタン,アルミニウム,モリブデン)をこの順に、例えばスパッタ法により堆積させることにより、金属層15(ソース・ドレイン電極15A,15B)を成膜する。
Next, as shown in FIG. 3B, a metal layer 15 (source /
この金属層15の成膜工程は、上記酸化物膜14の成膜工程に連続して行い、即ち、酸化物膜14をパターニングする前に、ソース・ドレイン電極15A,15Bとなる金属層15を成膜する。
The
続いて、図4に示したように、金属層15を、例えばフォトリソグラフィ法を用いたウェットエッチングまたはドライエッチングによりパターニングし、ソース・ドレイン電極15A,15Bを形成する。この際、下層の酸化物膜14とエッチング選択比をとることが可能な条件において、エッチングを行う。例えば、PAN系、フッ酸系または塩酸系等の、酸化物膜14が耐性を有する薬液を用いて、エッチングを行う。このようにして、酸化物膜14上において、ソース・ドレイン電極15A,15Bのみを選択的にパターニングする。尚、この際、ソース・ドレイン電極15Bの一部をコンタクトホールH上の領域に残存させることにより、ソース・ドレイン電極15Bが、酸化物膜14(低抵抗酸化物層14B)を介して配線層12Bに電気的に接続される。
Subsequently, as shown in FIG. 4, the
次いで、図5に示したように、酸化物膜14を、例えばフォトリソグラフィ法を用いたエッチングにより、例えば島形状にパターニングする。これにより、酸化物膜14を、ソース・ドレイン電極15A,15Bと、これらのソース・ドレイン電極15A,15B間の領域にのみ残存させ、他の領域との導通を防ぐことができる。但し、後の高抵抗化処理が施された状態において特に支障が生じない場合には、酸化物膜14はパターニングしなくともよく、基板11上の全面に形成されていてもよい。あるいは、後の保護膜16の形成工程において、保護膜16と共に酸化物膜14をパターニングしてもよい。
Next, as shown in FIG. 5, the
この後、図6に示したように、酸化物膜14の選択的な領域、具体的には、ソース・ドレイン電極15A,15B間のソース・ドレイン電極15A,15Bから露出した領域に対し、高抵抗化処理を施す。例えば、酸化雰囲気において、加熱処理あるいはプラズマ処理を施すことにより、高抵抗化が可能である。この際、先に形成したソース・ドレイン電極15A,15Bがマスクとなり、上記選択的な領域が酸化されて高抵抗化され、この高抵抗化された部分が酸化物半導体層14Cとなる。一方、酸化物膜14のうちのソース・ドレイン電極15A,15Bに対向する領域では、酸素雰囲気に曝されないために、高抵抗化されず、酸化物膜14の電気抵抗率が維持される。また、コンタクトホールH内に延在形成された部分についても、ソース・ドレイン電極15A,15Bによってマスクされるため、低抵抗が保持される。これらの高抵抗化されなかった部分(低抵抗が保持された部分)が、低抵抗酸化物層14A,14Bとなる。このようにして、ソース・ドレイン電極15A,15Bの形成後に、酸化物膜14の選択的な領域を高抵抗化させることにより、酸化物半導体層14Cを形成することができる。また、同時に、酸化物半導体層14Cとソース・ドレイン電極15A,15Bとのコンタクト層となる低抵抗酸化物層14A,14Bを形成することができる。
Thereafter, as shown in FIG. 6, the selective region of the
最後に、保護膜16を形成する。具体的には、上述した材料よりなる酸化膜を、例えばスパッタ法またはCVD法により、基板11の全面にわたって成膜する。例えば、酸化アルミニウムを用いる場合には、スパッタ法を用い、例えばアルミニウムもしくは酸化アルミニウムをターゲットとして使用して、アルゴンと酸素の混合ガスによるプラズマ放電を行って形成する。あるいは、酸化シリコンを用いる場合には、CVD法により、例えばシランおよび一酸化二窒素を含むガス雰囲気において成膜を行う。この後、保護膜16を、例えばフォトリソグラフィ法を用いたエッチングにより、所望の形状にパターニングする。以上により、図1に示した薄膜トランジスタ10Aを完成する。
Finally, the
[作用、効果]
本実施の形態では、薄膜トランジスタ10Aの製造プロセスにおいて、ソース・ドレイン電極15A,15Bに非対向な領域に酸化物半導体層14Cを形成する一方、ソース・ドレイン電極15A,15Bの各々に対向し、かつ酸化物半導体層14Cに隣接する領域に、低抵抗酸化物層14A,14Bを形成する。これにより、酸化物半導体層14Cの形成をソース・ドレイン電極15A,15Bの形成後に行うことができる。ここで、酸化物半導体では、一般に、電極の成膜時やパターニング時に受けるダメージにより酸素が離脱し、これによって格子欠陥を生じるが、本実施の形態のように電極形成後に酸化物半導体層14Cが形成されることで、そのような格子欠陥の発生が抑制され、酸化物半導体層の劣化が抑制される。また、酸化物半導体層14Cに隣接して低抵抗酸化物層14A,14Bが形成されることにより、酸化物半導体層14Cとソース・ドレイン電極15A,15Bとの良好な電気的接続が確保される。
[Action, effect]
In the present embodiment, in the manufacturing process of the
図7に、薄膜トランジスタ10Aの電気特性の一例を示す。図中実線は、高抵抗化処理を行った(酸化物半導体層14Cを有する)薄膜トランジスタのIV特性(ドレイン電流Idsとゲート電圧Vgsとの関係)を示し、図中破線は、高抵抗化処理をせずに作製した(酸化物膜14をそのままチャネルに用いた)薄膜トランジスタのIV特性を示している。また、酸化物半導体層14Cとしては、スパッタ成膜時の酸素分圧を0%として、膜厚40nmのIGZOを成膜し、パターニング後に、酸素雰囲気において加熱処理(300℃,2時間)を行った。このように、高抵抗化処理を施すことにより、特に、オフ動作時のドレイン電流が抑制され、トランジスタ動作を示すことがわかる。
FIG. 7 shows an example of electrical characteristics of the
また、本実施の形態では、酸化物半導体層14Cおよび低抵抗酸化物層14A,14Bとなる酸化物膜14と、ソース・ドレイン電極15A,15Bとなる金属層15とを連続成膜した後、金属層15をパターニングしてソース・ドレイン電極15A,15Bを形成する。この後、ソース・ドレイン電極15A,15Bをマスクとした高抵抗化処理を行うことで、上記のような酸化物半導体層14Cおよび低抵抗酸化物層14A,14Bを形成することができる。
In the present embodiment, after the
ここで、本実施の形態の比較例に係る薄膜トランジスタ(薄膜トランジスタ100)について説明する。図8は、薄膜トランジスタ100の断面構造を表したものであり、図9は、その製造方法を説明するためのものである。薄膜トランジスタ100においても、本実施の形態と同様、基板11上において、ゲート電極102Aおよび配線層102Bを覆うように、ゲート絶縁膜103が形成され、このゲート絶縁膜103には、配線層102Bに対向してコンタクトホールHが設けられている。但し、比較例では、ゲート絶縁膜103上の選択的な領域(ゲート電極102Aに対向する領域)にのみ、酸化物半導体層104がパターン形成されており、この酸化物半導体層104の一部に重畳して、ソース・ドレイン電極105A,105Bが設けられている。コンタクトホールHには、ソース・ドレイン電極105Bのみが埋め込まれており、これにより配線層102Bと、ソース・ドレイン電極105Bとの電気的接続が確保されている。
Here, a thin film transistor (thin film transistor 100) according to a comparative example of the present embodiment will be described. FIG. 8 illustrates a cross-sectional structure of the
このような比較例の薄膜トランジスタ100の製造プロセスでは、ゲート絶縁膜103の形成後、図8(A)に示したように、酸化物半導体層104を形成する。この際、まず、基板10の全面にわたって酸化物半導体膜を成膜した後、フォトリソグラフィ法を用いたエッチングによりパターニングする工程を経る。この後、図8(B)に示したように、ソース・ドレイン電極105A,105Bを形成するが、この際も、成膜工程およびパターニング工程を順に行う。従って、比較例のような製造プロセスでは、酸化物半導体層104とソース・ドレイン電極105A,105Bとのスパッタリングによる成膜プロセスがそれぞれ必要となり、コスト高となり易い。
In the manufacturing process of the
本実施の形態では、上述のように、低抵抗な状態で酸化物膜14を予め成膜しておき、ソース・ドレイン電極15A,15Bの形成後において、これらのソース・ドレイン電極15A,15Bをマスクとして酸化処理(高抵抗化処理)を行う。これにより、酸化物膜14のうち、必要な部分のみを選択的に高抵抗化し、チャネルとして機能する酸化物半導体層14Cを形成することができる。また、酸化物膜14のうち、酸化物半導体層14Cに隣接すると共に、ソース・ドレイン電極15A,15Bに対向する領域では、低抵抗状態が維持され、良好なコンタクト層となる。一般的な製造プロセスに比べ、スパッタリングによる成膜プロセスが削減され、低コスト化を図ることもできる。
In the present embodiment, as described above, the
また、上記比較例では、酸化物半導体層104がコンタクトホールH内を覆ってしまうと、配線層102Bとソース・ドレイン電極105Bとの電気的接続を確保しにくくなることから、パターニング時にコンタクトホールH内に成膜された半導体材料を除去する必要がある。これに対し、本実施の形態では、酸化物膜14を予め低抵抗な状態で成膜しておくことから、コンタクトホールH内から除去する必要がなく、パターニングも不要である。
In the above comparative example, if the
以上説明したように、本実施の形態では、ソース・ドレイン電極15A,15Bに非対向な領域に酸化物半導体層14Cを設け、ソース・ドレイン電極15A,15Bの各々に対向し、かつ酸化物半導体層14Cに隣接する領域に、低抵抗酸化物層14A,14Bを設けたので、製造プロセスにおける酸化物半導体層14Cの劣化を抑制できる。また、低抵抗酸化物層14A,14Bにより、酸化物半導体層14Cとソース・ドレイン電極15A,15Bとの良好な電気的接続を確保することができる。よって、電気的特性の向上を実現可能となる。
As described above, in the present embodiment, the
以下、上記第1の実施の形態の変形例および他の実施の形態について説明する。尚、上記第1の実施の形態と同様の構成要素については同一の符号を付し、適宜説明を省略する。 Hereinafter, modifications of the first embodiment and other embodiments will be described. In addition, the same code | symbol is attached | subjected about the component similar to the said 1st Embodiment, and description is abbreviate | omitted suitably.
<変形例1>
上記第1の実施の形態では、製造プロセスにおいて、酸化物膜14の高抵抗化を、酸化雰囲気における加熱処理あるいはプラズマ処理によって、保護膜16の形成前に行ったが、本変形例のように、高抵抗化処理を、保護膜16の形成過程において行ってもよい。即ち、上述のように、保護膜16は、例えば酸素ガスを用いたスパッタ法、あるいは一酸化二窒素を含むガスを用いたCVD法により、成膜する。このため、図10に示したように、保護膜16の成膜雰囲気(酸素雰囲気)に、酸化物膜14を曝すことにより、酸化物膜14を選択的に酸化することができる。即ち、保護膜16の形成工程が、上記第1の実施の形態における酸化工程(高抵抗化工程)を兼ねることができる。これにより、図11に示したように、保護膜16の形成と同時に、酸化物半導体層14Cおよび低抵抗酸化物層14A,14Bをそれぞれ形成可能となる。
<
In the first embodiment, in the manufacturing process, the resistance of the
<第2の実施の形態>
図12は、本開示の第2の実施の形態に係る薄膜トランジスタ(薄膜トランジスタ10B)の断面構造を表すものである。薄膜トランジスタ10Bは、上記第1の実施の形態の薄膜トランジスタ10Aと同様、ボトムゲート構造を有し、ゲート絶縁膜13上において、ソース・ドレイン電極15A,15Bに非対向な領域に酸化物半導体層17Cが形成されたものである。また、この酸化物半導体層17Cに隣接し、かつソース・ドレイン電極15A,15Bに対向する領域には、低抵抗酸化物層17A,17Bが形成されている。
<Second Embodiment>
FIG. 12 illustrates a cross-sectional structure of a thin film transistor (thin film transistor 10B) according to the second embodiment of the present disclosure. The thin film transistor 10B, like the
酸化物半導体層17Cおよび低抵抗酸化物層17A,17Bは、上記第1の実施の形態の酸化物半導体層14Cと同様の元素(インジウム等)を含む酸化物から構成されている。また、低抵抗酸化物層17A,17Bは、酸化物半導体層17Cよりも低い電気抵抗率を示し、低抵抗酸化物層17Bは、コンタクトホールH内を覆って形成されている。
The
但し、本実施の形態では、酸化物半導体層17Cおよび低抵抗酸化物層17A,17Bを構成する酸化物として、結晶性(結晶化可能な性質)を有するものが用いられる。製造プロセスにおいて、非晶質状態で成膜された後、ソース・ドレイン電極15A,15Bの形成後に、選択的な領域において結晶化されるようになっている。これにより、酸化物半導体層17Cでは、結晶化された状態を有し、低抵抗酸化物層17A,17Bでは、非晶質状態を有している。以下、本実施の形態の製造プロセスについて説明する。
However, in this embodiment, as the oxide included in the
具体的には、まず、上記第1の実施の形態と同様にして、基板11上に、ゲート電極12Aおよび配線層12Bを形成した後、コンタクトホールHを有するゲート絶縁膜13を成膜する。この後、図13に示したように、ゲート絶縁膜13上に、酸化物膜17および金属層15を、例えば上述したようなスパッタ法により連続成膜する。この際、酸化物膜17は、低い電気抵抗率を示し、かつ非晶質状態で成膜されるように、スパッタ条件を調整する。
Specifically, first, similarly to the first embodiment, after forming the
続いて、図14に示したように、上記第1の実施の形態と同様にして、金属層15のパターニングを行って、ソース・ドレイン電極15A,15Bを形成した後、酸化物膜17をパターニングする。
Subsequently, as shown in FIG. 14, the
この後、図15に示したように、酸化物膜17の選択的な領域、具体的には、ソース・ドレイン電極15A,15B間のソース・ドレイン電極15A,15Bから露出した領域に対し、高抵抗化処理を施す。例えば、酸化雰囲気において、加熱処理あるいはプラズマ処理を施すことにより、非晶質状態にあった酸化物膜17の上記選択的な領域を酸素雰囲気に曝しつつ、結晶化させ、これにより高抵抗化させることが可能である。この際、上記第1の実施の形態と同様、先に形成したソース・ドレイン電極15A,15Bがマスクとなり、上記選択的な領域が高抵抗化され、この高抵抗化された部分が酸化物半導体層17Cとなる。一方、酸化物膜17のうちのソース・ドレイン電極15A,15Bに対向する領域では、その一部が結晶化される可能性もあるが、仮に結晶化されたとしても、酸素雰囲気には曝されないために、十分な低抵抗率を保持することができる。この高抵抗化に寄与しなかった部分が、低抵抗酸化物層17A,17Bとなる。このようにして、本実施の形態においても、ソース・ドレイン電極15A,15Bの形成後に、酸化物膜17の選択的な領域を高抵抗化させることにより、酸化物半導体層17Cを形成すると共に、コンタクト層としての低抵抗酸化物層14A,14Bを形成することができる。
Thereafter, as shown in FIG. 15, the selective region of the
最後に、上記第1の実施の形態と同様にして、保護膜16を形成することにより、図12に示した薄膜トランジスタ10Bを完成する。
Finally, the
上記のように、結晶性を有する酸化物を用いて酸化物膜17を成膜し、この酸化膜17を選択的に結晶化させることにより、高抵抗化させることもできる。このような場合であっても、低抵抗酸化物層17A,17Bでは、酸化物膜17とほぼ同等の電気抵抗率を保持できるため、上記第1の実施の形態と同等の効果を得ることができる。
As described above, the resistance can be increased by forming the
<適用例>
[表示装置]
次に、上記各実施の形態および変形例に係る薄膜トランジスタ(薄膜トランジスタ10A,10B)は、例えば以下に説明するような表示装置および電子機器に適用可能である。図16は、有機ELディスプレイとして用いられる表示装置の周辺回路を含む全体構成を表すものである。このように、例えば基板11上には、有機EL素子を含む複数の画素PXLCがマトリクス状に配置されてなる表示領域30が形成され、この表示領域30の周辺に、信号線駆動回路としての水平セレクタ(HSEL)31と、走査線駆動回路としてのライトスキャナ(WSCN)32と、電源線駆動回路としての電源スキャナ(DSCN)33とが設けられている。
<Application example>
[Display device]
Next, the thin film transistors (
表示領域30において、列方向には複数(整数n個)の信号線DTL1〜DTLnが配置され、行方向には、複数(整数m個)の走査線WSL1〜WSLmおよび電源線DSL1〜DSLmがそれぞれ配置されている。また、各信号線DTLと各走査線WSLとの交差点に、各画素PXLC(R、G、Bに対応する画素のいずれか1つ)が設けられている。各信号線DTLは水平セレクタ31に接続され、この水平セレクタ31から各信号線DTLへ映像信号が供給されるようになっている。各走査線WSLはライトスキャナ32に接続され、このライトスキャナ32から各走査線WSLへ走査信号(選択パルス)が供給されるようになっている。各電源線DSLは電源スキャナ33に接続され、この電源スキャナ33から各電源線DSLへ電源信号(制御パルス)が供給されるようになっている。
In the
図17は、画素PXLCにおける具体的な回路構成例を表したものである。各画素PXLCは、有機EL素子3Dを含む画素回路40を有している。この画素回路40は、サンプリング用トランジスタ3Aおよび駆動用トランジスタ3Bと、保持容量素子3Cと、有機EL素子3Dとを有するアクティブ型の駆動回路である。これらのうち、トランジスタ3A(またはトランジスタ3B)が、上記実施の形態等の薄膜トランジスタ10A,10Bに相当する。
FIG. 17 illustrates a specific circuit configuration example in the pixel PXLC. Each pixel PXLC has a
サンプリング用トランジスタ3Aは、そのゲートが対応する走査線WSLに接続され、そのソースおよびドレインのうちの一方が対応する信号線DTLに接続され、他方が駆動用トランジスタ3Bのゲートに接続されている。駆動用トランジスタ3Bは、そのドレインが対応する電源線DSLに接続され、ソースが有機EL素子3Dのアノードに接続されている。また、この有機EL素子3Dのカソードは、接地配線5Hに接続されている。なお、この接地配線5Hは、全ての画素PXLCに対して共通に配線されている。保持容量素子3Cは、駆動用トランジスタ3Bのソースとゲートとの間に配置されている。
サンプリング用トランジスタ3Aは、走査線WSLから供給される走査信号(選択パルス)に応じて導通することにより、信号線DTLから供給される映像信号の信号電位をサンプリングし、保持容量素子3Cに保持するものである。駆動用トランジスタ3Bは、所定の第1電位(図示せず)に設定された電源線DSLから電流の供給を受け、保持容量素子3Cに保持された信号電位に応じて、駆動電流を有機EL素子3Dへ供給するものである。有機EL素子3Dは、この駆動用トランジスタ3Bから供給された駆動電流により、映像信号の信号電位に応じた輝度で発光するようになっている。
The
このような回路構成では、走査線WSLから供給される走査信号(選択パルス)に応じてサンプリング用トランジスタ3Aが導通することにより、信号線DTLから供給された映像信号の信号電位がサンプリングされ、保持容量素子3Cに保持される。また、上記第1電位に設定された電源線DSLから駆動用トランジスタ3Bへ電流が供給され、保持容量素子3Cに保持された信号電位に応じて、駆動電流が有機EL素子3D(赤色、緑色および青色の各有機EL素子)へ供給される。そして、各有機EL素子3Dは、供給された駆動電流により、映像信号の信号電位に応じた輝度で発光する。これにより、表示装置において、映像信号に基づく映像表示がなされる。
In such a circuit configuration, the
上記のような薄膜トランジスタ10A,10Bを用いた表示装置は、例えば次のような電子機器に適用可能である。電子機器としては、例えばテレビジョン装置,デジタルカメラ,ノート型パーソナルコンピュータ、携帯電話等の携帯端末装置あるいはビデオカメラ等が挙げられる。言い換えると、上記表示装置は、外部から入力された映像信号あるいは内部で生成した映像信号を、画像あるいは映像として表示するあらゆる分野の電子機器に適用することが可能である。
The display device using the
(モジュール)
上記表示装置は、例えば図18に示したようなモジュールとして、後述の適用例1〜6などの種々の電子機器に組み込まれる。このモジュールは、例えば、基板11の一辺に、封止用基板60から露出した領域210を設け、この露出した領域210に、水平セレクタ31、ライトスキャナ32および電源スキャナ33の配線を延長して外部接続端子(図示せず)を形成したものである。この外部接続端子には、信号の入出力のためのフレキシブルプリント配線基板(FPC;Flexible Printed Circuit)220が設けられていてもよい。
(module)
The display device is incorporated into various electronic devices such as application examples 1 to 6 described later, for example, as a module shown in FIG. In this module, for example, an
(適用例1)
図19は、テレビジョン装置の外観を表したものである。このテレビジョン装置は、例えば、フロントパネル310およびフィルターガラス320を含む映像表示画面部300を有しており、この映像表示画面部300が上記表示装置に相当する。
(Application example 1)
FIG. 19 illustrates the appearance of a television device. This television apparatus has, for example, a video display screen unit 300 including a front panel 310 and a filter glass 320, and the video display screen unit 300 corresponds to the display device.
(適用例2)
図20は、デジタルカメラの外観を表したものである。このデジタルカメラは、例えば、フラッシュ用の発光部410、表示部420、メニュースイッチ430およびシャッターボタン440を有しており、この表示部420が上記表示装置に相当する。
(Application example 2)
FIG. 20 shows the appearance of a digital camera. The digital camera includes, for example, a flash light emitting unit 410, a display unit 420, a menu switch 430, and a
(適用例3)
図21は、ノート型パーソナルコンピュータの外観を表したものである。このノート型パーソナルコンピュータは、例えば、本体510,文字等の入力操作のためのキーボード520および画像を表示する表示部530を有しており、この表示部530が上記表示装置に相当する。
(Application example 3)
FIG. 21 shows the appearance of a notebook personal computer. The notebook personal computer has, for example, a main body 510, a keyboard 520 for inputting characters and the like, and a display unit 530 for displaying an image. The display unit 530 corresponds to the display device.
(適用例4)
図22は、ビデオカメラの外観を表したものである。このビデオカメラは、例えば、本体部610,この本体部610の前方側面に設けられた被写体撮影用のレンズ620,撮影時のスタート/ストップスイッチ630および表示部640を有している。この表示部640が上記表示装置に相当する。
(Application example 4)
FIG. 22 shows the appearance of the video camera. This video camera includes, for example, a main body 610, a subject photographing lens 620 provided on the front side surface of the main body 610, a start /
(適用例5)
図23は、携帯電話機の外観を表したものである。この携帯電話機は、例えば上側筐体710と下側筐体720とを連結部(ヒンジ部)730で連結したものであり、ディスプレイ740,サブディスプレイ750,ピクチャーライト760およびカメラ770を有している。そして、これらのうちのディスプレイ740またはサブディスプレイ750が、上記表示装置に相当する。
(Application example 5)
FIG. 23 shows the appearance of a mobile phone. This mobile phone is obtained by connecting, for example, an
(適用例6)
図24は、スマートフォンの外観を表している。このスマートフォンは、例えば、表示部810および非表示部(筐体)820と、操作部830とを備えている。操作部830は、(A)に示したように非表示部820の前面に設けられていてもよいし、(B)に示したように上面に設けられていてもよい。
(Application example 6)
FIG. 24 shows the appearance of the smartphone. The smartphone includes a
以上、実施の形態および変形例を挙げて本開示を説明したが、本開示はこれらの実施の形態等に限定されず、種々の変形が可能である。例えば、上記実施の形態等では、ボトムゲート構造の薄膜トランジスタを例に挙げて説明したが、本開示の薄膜トランジスタは、トップゲート構造の薄膜トランジスタであってもよい。 As described above, the present disclosure has been described with reference to the embodiment and the modification. However, the present disclosure is not limited to the embodiment and the like, and various modifications can be made. For example, in the above-described embodiments and the like, a bottom gate thin film transistor has been described as an example. However, the thin film transistor of the present disclosure may be a top gate thin film transistor.
また、上記実施の形態等では、ソース・ドレイン電極とゲート配線層との配線コンタクト部を有する場合を例示したが、この配線コンタクト部は設けられていなくともよい。例えば、有機EL表示装置では、配線コンタクト部が形成されるが、液晶表示装置では、形成されないことが多い。 In the above-described embodiment and the like, the case where the wiring contact portion between the source / drain electrodes and the gate wiring layer is illustrated, but this wiring contact portion may not be provided. For example, a wiring contact portion is formed in an organic EL display device, but is often not formed in a liquid crystal display device.
更に、本開示の薄膜トランジスタは、上記実施の形態で説明した積層構造に限定されず、各層の材料や厚み、製造プロセス等も、上述したものに限定されない。 Furthermore, the thin film transistor of the present disclosure is not limited to the stacked structure described in the above embodiment, and the material, thickness, manufacturing process, and the like of each layer are not limited to those described above.
尚、本開示内容は、以下のような構成であってもよい。
(1)
ゲート電極、ソース電極およびドレイン電極と、
前記ゲート電極の一方の側に絶縁膜を介して設けられると共に、前記ソース電極および前記ドレイン電極に非対向な領域に設けられ、かつ前記ソース電極および前記ドレイン電極に電気的に接続された酸化物半導体層と、
前記酸化物半導体層に隣接すると共に、前記ソース電極および前記ドレイン電極の各々に対向する領域に設けられ、かつ前記酸化物半導体層よりも電気抵抗率の低い低抵抗酸化物層と
を備えた薄膜トランジスタ。
(2)
前記ゲート電極上に、前記絶縁膜を介して、前記酸化物半導体層および前記低抵抗酸化物層が設けられ、
前記ソース電極および前記ドレイン電極は、前記低抵抗酸化物層上に設けられている
上記(1)に記載の薄膜トランジスタ。
(3)
前記酸化物半導体層および前記低抵抗酸化物層は、互いに同一の酸化物材料からなる
上記(1)または(2)に記載の薄膜トランジスタ。
(4)
前記低抵抗酸化物層は非晶質状態を有し、前記酸化物半導体層は、結晶化された状態を有する
上記(1)〜(3)のいずれかに記載の薄膜トランジスタ。
(5)
前記酸化物材料は、前記ソース電極および前記ドレイン電極をパターニングする際に用いる薬液に対して耐性を有する
上記(1)〜(4)のいずれかに記載の薄膜トランジスタ。
(6)
前記絶縁膜は、前記ゲート電極と同層に設けられた配線層上に貫通孔を有し、
前記低抵抗酸化物層の一部は、前記貫通孔の内部を覆って形成されている
上記(1)〜(5)のいずれかに記載の薄膜トランジスタ。
(7)
前記ソース電極または前記ドレイン電極は、前記貫通孔上に、前記低抵抗酸化物層を介して設けられ、前記配線層と電気的に接続されている
上記(6)に記載の薄膜トランジスタ。
(8)
前記酸化物半導体層、前記ソース電極および前記ドレイン電極を覆って、保護膜が設けられている
上記(1)〜(7)のいずれかに薄膜トランジスタ。
(9)
前記保護膜は酸化シリコン(SiOx)または酸化アルミニウム(AlOX)からなる
上記(8)に記載の薄膜トランジスタ。
(10)
ゲート電極、ソース電極およびドレイン電極を各々形成する工程と、
前記ゲート電極の一方の側に絶縁膜を介して設けられると共に、前記ソース電極および前記ドレイン電極に非対向な領域に設けられ、かつ前記ソース電極および前記ドレイン電極に電気的に接続される酸化物半導体層を形成する工程とを含み、
前記酸化物半導体層を形成する工程では、
前記酸化物半導体層に隣接すると共に、前記ソース電極および前記ドレイン電極の各々に対向する領域に、前記酸化物半導体層よりも電気抵抗率の低い低抵抗酸化物層を形成する
薄膜トランジスタの製造方法。
(11)
前記ゲート電極を形成した後、
前記ゲート電極上に、前記絶縁膜を介して、一部が前記低抵抗酸化物層に対応する酸化物膜を成膜し、
成膜した酸化物膜上に、前記ソース電極および前記ドレイン電極を形成し、
前記ソース電極および前記ドレイン電極を形成した後、前記酸化物膜のうちの前記ソース電極および前記ドレイン電極から露出した選択的な領域に高抵抗化処理を施すことにより、前記酸化物半導体層を形成する
上記(10)に記載の薄膜トランジスタの製造方法。
(12)
前記高抵抗化処理として、酸素雰囲気における加熱処理を行う
上記(11)に記載の薄膜トランジスタの製造方法。
(13)
前記ソース電極および前記ドレイン電極を形成した後、酸素雰囲気において保護膜を形成する工程を含み、
前記保護膜の形成過程において、前記酸化物膜の前記選択的な領域を酸素雰囲気に曝すことにより、前記高抵抗化処理を行う
上記(11)または(12)に記載の薄膜トランジスタの製造方法。
(14)
前記保護膜として、酸化シリコン(SiOx)または酸化アルミニウム(AlOX)を形成する
上記(13)に記載の薄膜トランジスタの製造方法。
(15)
前記酸化物膜を非晶質状態となるように成膜し、
前記高抵抗化処理として、前記酸化物膜の前記選択的な領域を結晶化させる処理を行う
上記(11)に記載の薄膜トランジスタの製造方法。
(16)
前記酸化物膜は、前記ソース電極および前記ドレイン電極をパターニングする際に用いる薬液に対して耐性を有する
上記(11)〜(15)のいずれかに記載の薄膜トランジスタ。
(17)
前記絶縁膜のうちの前記ゲート電極と同層に設けられた配線層上に貫通孔を形成し、
前記酸化物膜を、前記貫通孔の内部を覆って形成する
上記(11)〜(16)のいずれかに記載の薄膜トランジスタの製造方法。
(18)
前記ソース電極または前記ドレイン電極を、前記貫通孔内または前記貫通孔上に、前記酸化物膜を介して形成することにより、前記ソース電極または前記ドレイン電極を前記配線層と電気的に接続させる
上記(17)に記載の薄膜トランジスタの製造方法。
(19)
ゲート電極、ソース電極およびドレイン電極と、
前記ゲート電極の一方の側に絶縁膜を介して設けられると共に、前記ソース電極および前記ドレイン電極と非対向な領域に設けられ、かつ前記ソース電極および前記ドレイン電極に電気的に接続された酸化物半導体層と、
前記酸化物半導体層に隣接すると共に、前記ソース電極および前記ドレイン電極の各々に対向する領域に設けられ、かつ前記酸化物半導体層よりも電気抵抗率の低い低抵抗酸化物層と
を備えた薄膜トランジスタを有する表示装置。
(20)
薄膜トランジスタを有する表示装置を備え、
前記薄膜トランジスタは、
ゲート電極、ソース電極およびドレイン電極と、
前記ゲート電極の一方の側に絶縁膜を介して設けられると共に、前記ソース電極および前記ドレイン電極と非対向な領域に設けられ、かつ前記ソース電極および前記ドレイン電極に電気的に接続された酸化物半導体層と、
前記酸化物半導体層に隣接すると共に、前記ソース電極および前記ドレイン電極の各々に対向する領域に設けられ、かつ前記酸化物半導体層よりも電気抵抗率の低い低抵抗酸化物層と
を備えた電子機器。
Note that the present disclosure may have the following configuration.
(1)
A gate electrode, a source electrode and a drain electrode;
An oxide provided on one side of the gate electrode via an insulating film, provided in a region not facing the source electrode and the drain electrode, and electrically connected to the source electrode and the drain electrode A semiconductor layer;
A thin film transistor comprising: a low-resistance oxide layer adjacent to the oxide semiconductor layer and provided in a region facing each of the source electrode and the drain electrode and having a lower electrical resistivity than the oxide semiconductor layer .
(2)
The oxide semiconductor layer and the low-resistance oxide layer are provided on the gate electrode via the insulating film,
The thin film transistor according to (1), wherein the source electrode and the drain electrode are provided on the low-resistance oxide layer.
(3)
The thin film transistor according to (1) or (2), wherein the oxide semiconductor layer and the low-resistance oxide layer are made of the same oxide material.
(4)
The thin film transistor according to any one of (1) to (3), wherein the low-resistance oxide layer has an amorphous state, and the oxide semiconductor layer has a crystallized state.
(5)
The thin film transistor according to any one of (1) to (4), wherein the oxide material has resistance to a chemical solution used when patterning the source electrode and the drain electrode.
(6)
The insulating film has a through hole on a wiring layer provided in the same layer as the gate electrode,
The thin film transistor according to any one of (1) to (5), wherein a part of the low resistance oxide layer is formed so as to cover an inside of the through hole.
(7)
The thin film transistor according to (6), wherein the source electrode or the drain electrode is provided on the through hole via the low-resistance oxide layer and is electrically connected to the wiring layer.
(8)
A protective film is provided so as to cover the oxide semiconductor layer, the source electrode, and the drain electrode. The thin film transistor according to any one of (1) to (7).
(9)
The thin film transistor according to (8), wherein the protective film is made of silicon oxide (SiO x ) or aluminum oxide (AlO x ).
(10)
Forming each of a gate electrode, a source electrode and a drain electrode;
An oxide provided on one side of the gate electrode through an insulating film, provided in a region not facing the source electrode and the drain electrode, and electrically connected to the source electrode and the drain electrode Forming a semiconductor layer,
In the step of forming the oxide semiconductor layer,
A method for manufacturing a thin film transistor, wherein a low-resistance oxide layer having an electrical resistivity lower than that of the oxide semiconductor layer is formed in a region adjacent to the oxide semiconductor layer and facing each of the source electrode and the drain electrode.
(11)
After forming the gate electrode,
An oxide film partially corresponding to the low-resistance oxide layer is formed on the gate electrode via the insulating film,
Forming the source electrode and the drain electrode on the formed oxide film;
After forming the source electrode and the drain electrode, the oxide semiconductor layer is formed by subjecting a selective region of the oxide film exposed from the source electrode and the drain electrode to high resistance. The manufacturing method of the thin-film transistor as described in said (10).
(12)
The method for manufacturing a thin film transistor according to (11), wherein a heat treatment in an oxygen atmosphere is performed as the high resistance treatment.
(13)
Forming a protective film in an oxygen atmosphere after forming the source electrode and the drain electrode,
In the process of forming the protective film, the high resistance treatment is performed by exposing the selective region of the oxide film to an oxygen atmosphere. The method for manufacturing a thin film transistor according to the above (11) or (12).
(14)
Silicon oxide (SiO x ) or aluminum oxide (AlO x ) is formed as the protective film. The method for manufacturing a thin film transistor according to (13) above.
(15)
Forming the oxide film in an amorphous state;
The method for manufacturing a thin film transistor according to (11), wherein a treatment for crystallizing the selective region of the oxide film is performed as the high resistance treatment.
(16)
The oxide film is a thin film transistor according to any one of (11) to (15), wherein the oxide film has resistance to a chemical solution used when patterning the source electrode and the drain electrode.
(17)
A through hole is formed on a wiring layer provided in the same layer as the gate electrode in the insulating film,
The method for manufacturing a thin film transistor according to any one of (11) to (16), wherein the oxide film is formed so as to cover an inside of the through hole.
(18)
The source electrode or the drain electrode is electrically connected to the wiring layer by forming the source electrode or the drain electrode in the through hole or on the through hole via the oxide film. (17) The manufacturing method of the thin-film transistor as described in (17).
(19)
A gate electrode, a source electrode and a drain electrode;
An oxide provided on one side of the gate electrode via an insulating film, provided in a region not facing the source electrode and the drain electrode, and electrically connected to the source electrode and the drain electrode A semiconductor layer;
A thin film transistor comprising: a low-resistance oxide layer adjacent to the oxide semiconductor layer and provided in a region facing each of the source electrode and the drain electrode and having a lower electrical resistivity than the oxide semiconductor layer A display device.
(20)
A display device having a thin film transistor;
The thin film transistor
A gate electrode, a source electrode and a drain electrode;
An oxide provided on one side of the gate electrode via an insulating film, provided in a region not facing the source electrode and the drain electrode, and electrically connected to the source electrode and the drain electrode A semiconductor layer;
An electron comprising: a low resistance oxide layer adjacent to the oxide semiconductor layer and provided in a region facing each of the source electrode and the drain electrode and having a lower electrical resistivity than the oxide semiconductor layer. machine.
10A,10B…薄膜トランジスタ、11…基板、12A…ゲート電極、13…ゲート絶縁膜、14C,17C…酸化物半導体層、14A,14B,17A,17B…低抵抗酸化物層、15A,15B…ソース・ドレイン電極、16…保護膜、14…酸化物膜、15…金属層、20…配線コンタクト部、12B…配線層、H…コンタクトホール。 10A, 10B ... thin film transistor, 11 ... substrate, 12A ... gate electrode, 13 ... gate insulating film, 14C, 17C ... oxide semiconductor layer, 14A, 14B, 17A, 17B ... low resistance oxide layer, 15A, 15B ... source Drain electrode, 16 ... protective film, 14 ... oxide film, 15 ... metal layer, 20 ... wiring contact portion, 12B ... wiring layer, H ... contact hole.
Claims (16)
前記ゲート電極の一方の側に絶縁膜を介して設けられると共に、前記ソース電極および前記ドレイン電極に非対向な領域に設けられ、かつ前記ソース電極および前記ドレイン電極に電気的に接続された酸化物半導体層と、
前記酸化物半導体層に隣接すると共に、前記ソース電極および前記ドレイン電極の各々に対向する領域に設けられ、かつ前記酸化物半導体層よりも電気抵抗率の低い低抵抗酸化物層と、
前記ゲート電極と同層に設けられた配線層と、
前記配線層に対向して設けられると共に前記絶縁膜を貫通する貫通孔と
を備え、
前記低抵抗酸化物層は、前記貫通孔の内部まで延在すると共に前記配線層を覆って形成され、
前記ソース電極または前記ドレイン電極は、前記貫通孔上に前記低抵抗酸化物層を介して設けられ、前記配線層に電気的に接続されている
薄膜トランジスタ。 A gate electrode, a source electrode and a drain electrode;
An oxide provided on one side of the gate electrode via an insulating film, provided in a region not facing the source electrode and the drain electrode, and electrically connected to the source electrode and the drain electrode A semiconductor layer;
A low resistance oxide layer adjacent to the oxide semiconductor layer and provided in a region facing each of the source electrode and the drain electrode, and having a lower electrical resistivity than the oxide semiconductor layer ;
A wiring layer provided in the same layer as the gate electrode;
A through hole provided opposite to the wiring layer and penetrating the insulating film;
With
The low-resistance oxide layer extends to the inside of the through hole and covers the wiring layer,
The source electrode or the drain electrode is a thin film transistor provided on the through hole via the low-resistance oxide layer and electrically connected to the wiring layer .
前記ソース電極および前記ドレイン電極は、前記低抵抗酸化物層上に設けられている
請求項1に記載の薄膜トランジスタ。 The oxide semiconductor layer and the low-resistance oxide layer are provided on the gate electrode via the insulating film,
The thin film transistor according to claim 1, wherein the source electrode and the drain electrode are provided on the low-resistance oxide layer.
請求項1に記載の薄膜トランジスタ。 The thin film transistor according to claim 1, wherein the oxide semiconductor layer and the low-resistance oxide layer are made of the same oxide material.
請求項3に記載の薄膜トランジスタ。 The thin film transistor according to claim 3, wherein the low-resistance oxide layer has an amorphous state, and the oxide semiconductor layer has a crystallized state.
請求項3に記載の薄膜トランジスタ。 The thin film transistor according to claim 3, wherein the oxide material is resistant to a chemical solution used when patterning the source electrode and the drain electrode.
請求項2に記載の薄膜トランジスタ。 The thin film transistor according to claim 2, wherein a protective film is provided to cover the oxide semiconductor layer, the source electrode, and the drain electrode.
請求項6に記載の薄膜トランジスタ。 The thin film transistor according to claim 6, wherein the protective film is made of silicon oxide (SiO x ) or aluminum oxide (AlO x ).
前記ゲート電極の一方の側に絶縁膜を介して設けられると共に、前記ソース電極および前記ドレイン電極に非対向な領域に設けられ、かつ前記ソース電極および前記ドレイン電極に電気的に接続される酸化物半導体層を形成する工程と、
前記ゲート電極と同層に配線層を形成する工程と、
前記配線層に対向して前記絶縁膜を貫通する貫通孔を形成する工程と
を有し、
前記酸化物半導体層を形成する工程では、前記酸化物半導体層に隣接すると共に、前記ソース電極および前記ドレイン電極の各々に対向する領域に、前記酸化物半導体層よりも電気抵抗率の低い低抵抗酸化物層を形成し、
前記低抵抗酸化物層は、前記貫通孔の内部まで延在すると共に前記配線層を覆って形成され、
前記ソース電極または前記ドレイン電極は、前記貫通孔上に前記低抵抗酸化物層を介して設けられ、前記配線層に電気的に接続されている
薄膜トランジスタの製造方法。 Forming each of a gate electrode, a source electrode and a drain electrode;
An oxide provided on one side of the gate electrode through an insulating film, provided in a region not facing the source electrode and the drain electrode, and electrically connected to the source electrode and the drain electrode Forming a semiconductor layer ;
Forming a wiring layer in the same layer as the gate electrode;
Forming a through-hole penetrating the insulating film facing the wiring layer;
Have
In the step of forming the oxide semiconductor layer, a low resistance having an electrical resistivity lower than that of the oxide semiconductor layer in a region adjacent to the oxide semiconductor layer and facing each of the source electrode and the drain electrode. Forming an oxide layer ,
The low-resistance oxide layer extends to the inside of the through hole and covers the wiring layer,
The method of manufacturing a thin film transistor, wherein the source electrode or the drain electrode is provided on the through hole via the low-resistance oxide layer and is electrically connected to the wiring layer .
前記ゲート電極上に、前記絶縁膜を介して、一部が前記低抵抗酸化物層に対応する酸化物膜を成膜し、
成膜した酸化物膜上に、前記ソース電極および前記ドレイン電極を形成し、
前記ソース電極および前記ドレイン電極を形成した後、前記酸化物膜のうちの前記ソース電極および前記ドレイン電極から露出した選択的な領域に高抵抗化処理を施すことにより、前記酸化物半導体層を形成する
請求項8に記載の薄膜トランジスタの製造方法。 After forming the gate electrode,
An oxide film partially corresponding to the low-resistance oxide layer is formed on the gate electrode via the insulating film,
Forming the source electrode and the drain electrode on the formed oxide film;
After forming the source electrode and the drain electrode, the oxide semiconductor layer is formed by subjecting a selective region of the oxide film exposed from the source electrode and the drain electrode to high resistance. The manufacturing method of the thin-film transistor of Claim 8.
請求項9に記載の薄膜トランジスタの製造方法。 The method for manufacturing a thin film transistor according to claim 9, wherein heat treatment in an oxygen atmosphere is performed as the high resistance treatment.
前記保護膜の形成過程において、前記酸化物膜の前記選択的な領域を酸素雰囲気に曝すことにより、前記高抵抗化処理を行う
請求項9に記載の薄膜トランジスタの製造方法。 Forming a protective film in an oxygen atmosphere after forming the source electrode and the drain electrode,
10. The method of manufacturing a thin film transistor according to claim 9, wherein in the formation process of the protective film, the high resistance treatment is performed by exposing the selective region of the oxide film to an oxygen atmosphere.
請求項11に記載の薄膜トランジスタの製造方法。 The method for manufacturing a thin film transistor according to claim 11, wherein silicon oxide (SiO x ) or aluminum oxide (AlO x ) is formed as the protective film.
前記高抵抗化処理として、前記酸化物膜の前記選択的な領域を結晶化させる処理を行う
請求項9に記載の薄膜トランジスタの製造方法。 Forming the oxide film in an amorphous state;
The method for manufacturing a thin film transistor according to claim 9, wherein a treatment for crystallizing the selective region of the oxide film is performed as the high resistance treatment.
請求項9に記載の薄膜トランジスタの製造方法。 The method for manufacturing a thin film transistor according to claim 9, wherein the oxide film is resistant to a chemical solution used when patterning the source electrode and the drain electrode.
前記ゲート電極の一方の側に絶縁膜を介して設けられると共に、前記ソース電極および前記ドレイン電極と非対向な領域に設けられ、かつ前記ソース電極および前記ドレイン電極に電気的に接続された酸化物半導体層と、
前記酸化物半導体層に隣接すると共に、前記ソース電極および前記ドレイン電極の各々に対向する領域に設けられ、かつ前記酸化物半導体層よりも電気抵抗率の低い低抵抗酸化物層と、
前記ゲート電極と同層に設けられた配線層と、
前記配線層に対向して設けられると共に前記絶縁膜を貫通する貫通孔と
を備え、
前記低抵抗酸化物層は、前記貫通孔の内部まで延在すると共に前記配線層を覆って形成され、
前記ソース電極または前記ドレイン電極は、前記貫通孔上に前記低抵抗酸化物層を介して設けられ、前記配線層に電気的に接続されている
薄膜トランジスタを有する表示装置。 A gate electrode, a source electrode and a drain electrode;
An oxide provided on one side of the gate electrode via an insulating film, provided in a region not facing the source electrode and the drain electrode, and electrically connected to the source electrode and the drain electrode A semiconductor layer;
A low resistance oxide layer adjacent to the oxide semiconductor layer and provided in a region facing each of the source electrode and the drain electrode, and having a lower electrical resistivity than the oxide semiconductor layer ;
A wiring layer provided in the same layer as the gate electrode;
A through hole provided opposite to the wiring layer and penetrating the insulating film;
With
The low-resistance oxide layer extends to the inside of the through hole and covers the wiring layer,
The display device having a thin film transistor in which the source electrode or the drain electrode is provided on the through hole via the low-resistance oxide layer and is electrically connected to the wiring layer .
前記薄膜トランジスタは、
ゲート電極、ソース電極およびドレイン電極と、
前記ゲート電極の一方の側に絶縁膜を介して設けられると共に、前記ソース電極および前記ドレイン電極と非対向な領域に設けられ、かつ前記ソース電極および前記ドレイン電極に電気的に接続された酸化物半導体層と、
前記酸化物半導体層に隣接すると共に、前記ソース電極および前記ドレイン電極の各々に対向する領域に設けられ、かつ前記酸化物半導体層よりも電気抵抗率の低い低抵抗酸化物層と、
前記ゲート電極と同層に設けられた配線層と、
前記配線層に対向して設けられると共に前記絶縁膜を貫通する貫通孔と
を備え、
前記低抵抗酸化物層は、前記貫通孔の内部まで延在すると共に前記配線層を覆って形成され、
前記ソース電極または前記ドレイン電極は、前記貫通孔上に前記低抵抗酸化物層を介して設けられ、前記配線層に電気的に接続されている
電子機器。 A display device having a thin film transistor;
The thin film transistor
A gate electrode, a source electrode and a drain electrode;
An oxide provided on one side of the gate electrode via an insulating film, provided in a region not facing the source electrode and the drain electrode, and electrically connected to the source electrode and the drain electrode A semiconductor layer;
A low resistance oxide layer adjacent to the oxide semiconductor layer and provided in a region facing each of the source electrode and the drain electrode, and having a lower electrical resistivity than the oxide semiconductor layer ;
A wiring layer provided in the same layer as the gate electrode;
A through hole provided opposite to the wiring layer and penetrating the insulating film;
With
The low-resistance oxide layer extends to the inside of the through hole and covers the wiring layer,
The electronic device in which the source electrode or the drain electrode is provided on the through hole via the low-resistance oxide layer and is electrically connected to the wiring layer .
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012026250A JP6019330B2 (en) | 2012-02-09 | 2012-02-09 | THIN FILM TRANSISTOR, METHOD FOR PRODUCING THIN FILM TRANSISTOR, DISPLAY DEVICE, AND ELECTRONIC DEVICE |
| US13/732,948 US8981368B2 (en) | 2012-01-11 | 2013-01-02 | Thin film transistor, method of manufacturing thin film transistor, display, and electronic apparatus |
| CN201310002100.3A CN103208527B (en) | 2012-01-11 | 2013-01-04 | Thin film transistor, method of manufacturing thin film transistor, display, and electronic apparatus |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012026250A JP6019330B2 (en) | 2012-02-09 | 2012-02-09 | THIN FILM TRANSISTOR, METHOD FOR PRODUCING THIN FILM TRANSISTOR, DISPLAY DEVICE, AND ELECTRONIC DEVICE |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2013165108A JP2013165108A (en) | 2013-08-22 |
| JP6019330B2 true JP6019330B2 (en) | 2016-11-02 |
Family
ID=49176306
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012026250A Active JP6019330B2 (en) | 2012-01-11 | 2012-02-09 | THIN FILM TRANSISTOR, METHOD FOR PRODUCING THIN FILM TRANSISTOR, DISPLAY DEVICE, AND ELECTRONIC DEVICE |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6019330B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US10670933B2 (en) * | 2016-05-10 | 2020-06-02 | Sharp Kabushiki Kaisha | Active matrix substrate, method for producing same, and display device |
| WO2019171505A1 (en) * | 2018-03-07 | 2019-09-12 | シャープ株式会社 | Thin film transistor, method for producing same and display device |
Family Cites Families (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2674516B2 (en) * | 1994-07-21 | 1997-11-12 | 日本電気株式会社 | Active matrix substrate and manufacturing method thereof |
| JP2005268724A (en) * | 2004-03-22 | 2005-09-29 | Sony Corp | Electronic element and method for manufacturing same |
| TWI478347B (en) * | 2007-02-09 | 2015-03-21 | Idemitsu Kosan Co | A thin film transistor, a thin film transistor substrate, and an image display device, and an image display device, and a semiconductor device |
| TWI467761B (en) * | 2008-01-17 | 2015-01-01 | Idemitsu Kosan Co | Field effect transistor, semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof |
| JP5325446B2 (en) * | 2008-04-16 | 2013-10-23 | 株式会社日立製作所 | Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof |
| JP5319961B2 (en) * | 2008-05-30 | 2013-10-16 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | Manufacturing method of semiconductor device |
| KR101671210B1 (en) * | 2009-03-06 | 2016-11-01 | 가부시키가이샤 한도오따이 에네루기 켄큐쇼 | Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same |
| KR101810699B1 (en) * | 2009-06-30 | 2018-01-25 | 가부시키가이샤 한도오따이 에네루기 켄큐쇼 | Method for manufacturing semiconductor device |
| JP5683179B2 (en) * | 2009-09-24 | 2015-03-11 | 株式会社半導体エネルギー研究所 | Method for manufacturing display device |
| KR101779349B1 (en) * | 2009-10-14 | 2017-09-18 | 가부시키가이샤 한도오따이 에네루기 켄큐쇼 | Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof |
| JP2011091110A (en) * | 2009-10-20 | 2011-05-06 | Canon Inc | Circuit using oxide semiconductor element and method of manufacturing the same, and display device |
-
2012
- 2012-02-09 JP JP2012026250A patent/JP6019330B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2013165108A (en) | 2013-08-22 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5668917B2 (en) | Thin film transistor and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP4752925B2 (en) | Thin film transistor and display device | |
| JP5515281B2 (en) | THIN FILM TRANSISTOR, DISPLAY DEVICE, ELECTRONIC DEVICE, AND METHOD FOR PRODUCING THIN FILM TRANSISTOR | |
| JP5679143B2 (en) | Thin film transistor, display device and electronic device | |
| JP5743064B2 (en) | THIN FILM TRANSISTOR, MANUFACTURING METHOD THEREOF, AND DISPLAY DEVICE | |
| TWI479662B (en) | Thin film transistor and display device | |
| JP4844617B2 (en) | Thin film transistor substrate and display device | |
| JP5552753B2 (en) | Thin film transistor and display device | |
| JP6019329B2 (en) | Display device and electronic device | |
| JP2011187506A (en) | Thin-film transistor, method of manufacturing the thin-film transistor, and display device | |
| JP2010182819A (en) | Thin-film transistor, and display device | |
| US8581245B2 (en) | Thin film transistor, method of manufacturing thin film transistor, display unit, and electronic device | |
| JP2010205987A (en) | Thin film transistor, method for manufacturing the same, and display | |
| JP6111458B2 (en) | Semiconductor device, display device and electronic apparatus | |
| JP2011159908A (en) | Thin film transistor and method of manufacturing the same, and display device | |
| JP2011222767A (en) | Thin film transistor, display device, and electronic device | |
| JP2012004371A (en) | Thin film transistor and display device | |
| TW201240100A (en) | Thin-film transistor, display apparatus and electronic apparatus | |
| JP2014229814A (en) | Thin-film transistor, display device, and electronic apparatus | |
| JP2015149467A (en) | Manufacturing method of thin film transistor substrate | |
| JP2012191008A (en) | Display device and electronic apparatus | |
| JP2013211410A (en) | Thin film transistor, manufacturing method of the same, display device and electronic apparatus | |
| US8981368B2 (en) | Thin film transistor, method of manufacturing thin film transistor, display, and electronic apparatus | |
| JP6019331B2 (en) | Transistor, semiconductor device, display device, electronic device, and method for manufacturing semiconductor device | |
| JP6019330B2 (en) | THIN FILM TRANSISTOR, METHOD FOR PRODUCING THIN FILM TRANSISTOR, DISPLAY DEVICE, AND ELECTRONIC DEVICE |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20150113 |
|
| A711 | Notification of change in applicant |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A712 Effective date: 20150327 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20160114 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20160216 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20160412 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20160809 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20160826 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 6019330 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| S303 | Written request for registration of pledge or change of pledge |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R316303 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |
|
| S803 | Written request for registration of cancellation of provisional registration |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R316803 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| S111 | Request for change of ownership or part of ownership |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313113 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |