JP5741567B2 - 半導体装置 - Google Patents
半導体装置 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5741567B2 JP5741567B2 JP2012501498A JP2012501498A JP5741567B2 JP 5741567 B2 JP5741567 B2 JP 5741567B2 JP 2012501498 A JP2012501498 A JP 2012501498A JP 2012501498 A JP2012501498 A JP 2012501498A JP 5741567 B2 JP5741567 B2 JP 5741567B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- conductivity type
- region
- type region
- semiconductor device
- layer
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 title claims description 227
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 claims description 336
- 239000012535 impurity Substances 0.000 claims description 124
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 claims description 88
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 claims description 21
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000002344 surface layer Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 230000015556 catabolic process Effects 0.000 description 116
- 150000002500 ions Chemical class 0.000 description 60
- 108091006146 Channels Proteins 0.000 description 44
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 28
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 description 24
- 230000005684 electric field Effects 0.000 description 22
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 17
- 102000004129 N-Type Calcium Channels Human genes 0.000 description 13
- 108090000699 N-Type Calcium Channels Proteins 0.000 description 13
- 238000009792 diffusion process Methods 0.000 description 11
- 238000004088 simulation Methods 0.000 description 11
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 description 8
- 230000003252 repetitive effect Effects 0.000 description 7
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 6
- 238000005468 ion implantation Methods 0.000 description 4
- 210000004027 cell Anatomy 0.000 description 3
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000007935 neutral effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000003247 decreasing effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000000737 periodic effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000002441 reversible effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000000969 carrier Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000001704 evaporation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000005669 field effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000011229 interlayer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005304 joining Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/68—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor controllable by only the electric current supplied, or only the electric potential applied, to an electrode which does not carry the current to be rectified, amplified or switched
- H01L29/76—Unipolar devices, e.g. field effect transistors
- H01L29/772—Field effect transistors
- H01L29/78—Field effect transistors with field effect produced by an insulated gate
- H01L29/7801—DMOS transistors, i.e. MISFETs with a channel accommodating body or base region adjoining a drain drift region
- H01L29/7802—Vertical DMOS transistors, i.e. VDMOS transistors
- H01L29/7811—Vertical DMOS transistors, i.e. VDMOS transistors with an edge termination structure
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/06—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions
- H01L29/0603—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions
- H01L29/0607—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions for preventing surface leakage or controlling electric field concentration
- H01L29/0611—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions for preventing surface leakage or controlling electric field concentration for increasing or controlling the breakdown voltage of reverse biased devices
- H01L29/0615—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions for preventing surface leakage or controlling electric field concentration for increasing or controlling the breakdown voltage of reverse biased devices by the doping profile or the shape or the arrangement of the PN junction, or with supplementary regions, e.g. junction termination extension [JTE]
- H01L29/063—Reduced surface field [RESURF] pn-junction structures
- H01L29/0634—Multiple reduced surface field (multi-RESURF) structures, e.g. double RESURF, charge compensation, cool, superjunction (SJ), 3D-RESURF, composite buffer (CB) structures
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/06—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions
- H01L29/08—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions with semiconductor regions connected to an electrode carrying current to be rectified, amplified or switched and such electrode being part of a semiconductor device which comprises three or more electrodes
- H01L29/0843—Source or drain regions of field-effect devices
- H01L29/0847—Source or drain regions of field-effect devices of field-effect transistors with insulated gate
- H01L29/0852—Source or drain regions of field-effect devices of field-effect transistors with insulated gate of DMOS transistors
- H01L29/0873—Drain regions
- H01L29/0878—Impurity concentration or distribution
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/06—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions
- H01L29/0603—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions
- H01L29/0607—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions for preventing surface leakage or controlling electric field concentration
- H01L29/0611—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions for preventing surface leakage or controlling electric field concentration for increasing or controlling the breakdown voltage of reverse biased devices
- H01L29/0615—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions for preventing surface leakage or controlling electric field concentration for increasing or controlling the breakdown voltage of reverse biased devices by the doping profile or the shape or the arrangement of the PN junction, or with supplementary regions, e.g. junction termination extension [JTE]
- H01L29/0619—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions for preventing surface leakage or controlling electric field concentration for increasing or controlling the breakdown voltage of reverse biased devices by the doping profile or the shape or the arrangement of the PN junction, or with supplementary regions, e.g. junction termination extension [JTE] with a supplementary region doped oppositely to or in rectifying contact with the semiconductor containing or contacting region, e.g. guard rings with PN or Schottky junction
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/06—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions
- H01L29/0603—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions
- H01L29/0607—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions for preventing surface leakage or controlling electric field concentration
- H01L29/0638—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions for preventing surface leakage or controlling electric field concentration for preventing surface leakage due to surface inversion layer, e.g. with channel stopper
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/06—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions
- H01L29/0684—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by the shape, relative sizes or dispositions of the semiconductor regions or junctions between the regions
- H01L29/0692—Surface layout
- H01L29/0696—Surface layout of cellular field-effect devices, e.g. multicellular DMOS transistors or IGBTs
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/40—Electrodes ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/402—Field plates
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/40—Electrodes ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/402—Field plates
- H01L29/404—Multiple field plate structures
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/40—Electrodes ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/41—Electrodes ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape, relative sizes or dispositions
- H01L29/417—Electrodes ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape, relative sizes or dispositions carrying the current to be rectified, amplified or switched
- H01L29/41725—Source or drain electrodes for field effect devices
- H01L29/41741—Source or drain electrodes for field effect devices for vertical or pseudo-vertical devices
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Ceramic Engineering (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Composite Materials (AREA)
- Insulated Gate Type Field-Effect Transistor (AREA)
- Electrodes Of Semiconductors (AREA)
- Thin Film Transistor (AREA)
Description
図1は、実施の形態1にかかる半導体装置の平面図である。図2は、実施の形態1にかかる半導体装置の横断面図である。図3は、実施の形態1にかかる半導体装置の図1A−A’における縦断面図である。図4は、実施の形態1にかかる半導体装置の図1B−B’における縦断面図である。なお、図1および図2には、半導体装置の1/4の部分が示されている(図5、図6、図13、図14、図27、図34、図37、図38、図43〜図53においても同じ)。図1には、並列pn層、n型チャネルストッパー領域、素子活性部の最も外側のpベース領域およびp型ガードリング領域のそれぞれの第1主面における形状が示されている(図5、図13においても同じ)。図2には、素子活性部および素子周縁部のいずれにおいても並列pn層を横切る断面、例えば素子活性部の並列pn層の1/2の深さでの断面における形状が示されている(図6、図14、図46〜図53においても同じ)。
図5は、実施の形態2にかかる半導体装置の平面図である。図6は、実施の形態2にかかる半導体装置の横断面図である。図7は、実施の形態2にかかる半導体装置の図5A−A’における縦断面図である。図8は、実施の形態2にかかる半導体装置の図5B−B’における縦断面図である。図5〜図8に示すように、実施の形態2が実施の形態1と異なるのは、次の2点である。第1の点は、並列pn層のピッチの変わり目、すなわち第1の並列pn層12と第2の並列pn層15との境界がn-表面領域18の下にあることである。第2の点は、各p型ガードリング領域19,20,21がそれぞれ別々のフィールドプレート電極23,27,28に電気的に接続していることである。各フィールドプレート電極23,27,28は、それぞれが電気的に接続するp型ガードリング領域19,20,21とn-表面領域18とに跨って設けられている。すなわち、各フィールドプレート電極23,27,28は、それぞれが電気的に接続するp型ガードリング領域19,20,21とn-表面領域18との第1主面における接合部よりも内周方向または外周方向へ張り出している。なお、p型ガードリング領域の数は、2本または3本以上であってもよい。また、最も外側に位置するp型ガードリング領域を除いて、フィールドプレート電極に電気的に接続していないp型ガードリング領域があってもよい。その他の構成は、実施の形態1と同様である。
図13は、実施の形態3にかかる半導体装置の平面図である。図14は、実施の形態3にかかる半導体装置の横断面図である。図15は、実施の形態3にかかる半導体装置の図13A−A’における縦断面図である。図16は、実施の形態3にかかる半導体装置の図13B−B’における縦断面図である。図13〜図16に示すように、実施の形態3が実施の形態2と異なるのは、第2の並列pn層15のストライプの向きが第1の並列pn層12のストライプの向きと異なることである。例えば、第2の並列pn層15のストライプの向きは、第1の並列pn層12のストライプの向きと直交していてもよい。その他の構成は、実施の形態2と同様である。
図17および図18は、実施の形態4にかかる半導体装置の縦断面図である。実施の形態4にかかる半導体装置の平面図は、図1と同様であり、第1の並列pn層12、第1のn型領域13および第1のp型領域14がそれぞれ並列pn層31、n型領域32およびp型領域33となる。図17は、図1A−A’における縦断面図に相当する。図18は、図1B−B’における縦断面図に相当する。図17および図18に示すように、実施の形態4が実施の形態1と異なるのは、第1主面とn+ドレイン領域2との間に、n型領域(第4の第1導電型領域)32およびp型領域(第4の第2導電型領域)33が交互に配置された並列pn層31が設けられていることである。すなわち、並列pn層31のピッチは、素子活性部1と素子周縁部3とで同じである。n-表面領域18の不純物濃度は、並列pn層31のn型領域32の不純物濃度よりも低い。n-表面領域18の厚さは、素子活性部1の下における並列pn層31の厚さの1/2以下である。n-表面領域18と素子活性部1の下における並列pn層31との接合部はチャージインバランスとなり、耐圧の低下を招くおそれがある。従って、n-表面領域18と素子活性部1の下における並列pn層31との接合部の厚さTは、素子活性部1の下における並列pn層31の厚さの1/2以下であるのが望ましい。その他の構成は、実施の形態1と同様である。
図23および図24は、実施の形態5にかかる半導体装置の縦断面図である。実施の形態5にかかる半導体装置の平面図は、図1と同様であり、第1の並列pn層12、第1のn型領域13および第1のp型領域14がそれぞれ並列pn層31、n型領域32およびp型領域33となる。図23は、図1A−A’における縦断面図に相当する。図24は、図1B−B’における縦断面図に相当する。図23および図24に示すように、実施の形態5が実施の形態4と異なるのは、最も内側に位置するp型ガードリング領域21以外のp型ガードリング領域19,20がフィールドプレート電極23,27に電気的に接続していることである。最も内側に位置するp型ガードリング領域21は、フィールドプレート電極に電気的に接続していない。各フィールドプレート電極23,27は、互いに独立している。なお、p型ガードリング領域の数は、2本または4本以上であってもよい。その他の構成は、実施の形態4と同様である。
図25および図26は、実施の形態6にかかる半導体装置の縦断面図である。実施の形態6にかかる半導体装置の平面図は、図1と同様であり、第1の並列pn層12、第1のn型領域13および第1のp型領域14がそれぞれ並列pn層31、n型領域32およびp型領域33となる。図25は、図1A−A’における縦断面図に相当する。図26は、図1B−B’における縦断面図に相当する。図25および図26に示すように、実施の形態6が実施の形態4と異なるのは、全てのp型ガードリング領域19,20,21がフィールドプレート電極23,27,28に電気的に接続していることである。各フィールドプレート電極23,27,28は、互いに独立している。その他の構成は、実施の形態4と同様である。
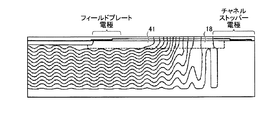
図27は、実施の形態7にかかる半導体装置の平面図である。図28は、実施の形態7にかかる半導体装置の図27A−A’における縦断面図である。図29は、実施の形態7にかかる半導体装置の図27B−B’における縦断面図である。図27には、並列pn層、n型チャネルストッパー領域、素子活性部の最も外側のpベース領域、n-表面領域およびp-表面領域のそれぞれの第1主面における形状が示されている(図34においても同じ)。図27〜図29に示すように、実施の形態7が実施の形態4と異なるのは、素子周縁部3において、並列pn層31と第1主面との間にn-表面領域18およびp-表面領域(第5の第2導電型領域)41が設けられていることと、n-表面領域18にp型ガードリング領域が設けられていないことである。
図34は、実施の形態8にかかる半導体装置の平面図である。図35は、実施の形態8にかかる半導体装置の図34A−A’における縦断面図である。図36は、実施の形態8にかかる半導体装置の図34B−B’における縦断面図である。図34〜図36に示すように、実施の形態8が実施の形態7と異なるのは、p-表面領域41に不純物濃度の異なる複数の領域42,43が含まれていることである。p-表面領域41に含まれる複数の領域42,43の不純物濃度が、素子活性部1から素子周縁部3の終端へ向かうに連れて低くなっていてもよい。つまり、p-表面領域41が、素子活性部1から素子周縁部3の終端へ向かうに連れて低くなるような不純物濃度の勾配を有していてもよい。例えば、p-表面領域41に含まれる複数の領域42,43のうち、素子活性部1に近いp-表面領域42の不純物濃度が2.0×1015cm-3であり、素子周縁部3の終端に近いp-表面領域43の不純物濃度が1.0×1015cm-3であってもよい。なお、p-表面領域41が3以上の不純物濃度の異なる領域を含んでいてもよい。また、p-表面領域41の不純物濃度が、素子活性部1側の端部から素子周縁部3の終端側の端部に至るまで連続的に低くなっていてもよい。その他の構成は、実施の形態4と同様である。
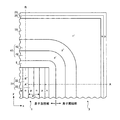
図37は、実施の形態9にかかる半導体装置の平面図である。図38は、実施の形態9にかかる半導体装置の並列pn層の平面図である。図39は、実施の形態9にかかる半導体装置の図38A−A’における縦断面図である。図37には、フィールドプレート電極、チャネルストッパー電極、素子周縁部におけるNリッチ領域(実質的にn型となる領域)および素子周縁部におけるPリッチ領域(実質的にp型となる領域)が示されている(図43〜図45においても同じ)。図38には、並列pn層およびn型チャネルストッパー領域のそれぞれの第1主面における形状が示されている。図37〜図39に示すように、実施の形態9は、実施の形態7において、n-表面領域およびp-表面領域の代わりにそれぞれNリッチ領域51およびPリッチ領域52を設けたものである。素子活性部1および素子活性部1からフィールドプレート電極23の最上段(最も素子周縁部3の終端領域に近い段)の途中まで、繰り返しピッチP1の第1の並列pn層12が配置されている。フィールドプレート電極23の最上段の途中から素子周縁部3の終端領域にかけて、繰り返しピッチP2の第2の並列pn層15が設けられている。P2<P1である。
実施の形態9において、Nリッチ領域51における第2のn型領域16の幅や、Pリッチ領域52における第2のp型領域17の幅が、ストライプごとに変化していたり、各第2のn型領域16や各第2のp型領域17の伸びる方向(図38のy方向)で徐々にもしくは段階的に変化していてもよい。実施の形態10は、実施の形態9において、Nリッチ領域51における第2のn型領域16の幅や、Pリッチ領域52における第2のp型領域17の幅を、ストライプごとに変化させたり、各第2のn型領域16や各第2のp型領域17が伸びる方向(図38のy方向)で徐々にもしくは段階的に変化させたものである。この場合、Nリッチ領域51では、第2のn型領域16の幅がチャネルストッパー電極24から遠ざかるに連れて狭くなるようにして、チャージバランスに近づけるのがよい。また、Pリッチ領域52では、第2のp型領域17の幅がフィールドプレート電極23から遠ざかるに連れて狭くなるようにして、チャージバランスに近づけるのがよい。このようにすると、空乏層がより一層広がりやすくなるので、高耐圧を保持することができるからである。
実施の形態9において、Nリッチ領域51とPリッチ領域52とがより近づいて、Nリッチ領域51とPリッチ領域52との間のチャージバランス領域54ができるだけないようになっていてもよい。ただし、Nリッチ領域51とPリッチ領域52との間には、少なくとも第2の並列pn層15の1/2ピッチ分に相当する幅のチャージバランス領域54が入る。また、Nリッチ領域51とPリッチ領域52との間のチャージバランス領域54の幅がより広くなっていてもよい。チャージバランス領域54の幅が広いほど、空乏層が広がりやすくなるので、耐圧が向上する。ただし、チャージバランス領域54の幅がフィールドプレート電極23とチャネルストッパー電極24との間の距離の1/3程度以下であれば、素子周縁部3の長さが長くなり過ぎないので、好ましい。Nリッチ領域51とPリッチ領域52との間のチャージバランス領域54の幅をより広くした半導体装置の平面図を図43に示す。実施の形態11によれば、実施の形態9と同様の効果が得られる。
図44は、実施の形態12にかかる半導体装置の平面図である。図44に示すように、実施の形態12が実施の形態9と異なるのは、Nリッチ領域51の外側にチャージバランス領域が設けられていないことである。図44に示す例では、実施の形態9においてチャージバランス領域55となっている領域もNリッチ領域51となっている。実施の形態12によれば、実施の形態9と同様の効果が得られる。
図45は、実施の形態13にかかる半導体装置の平面図である。図45に示すように、実施の形態13が実施の形態9と異なるのは、第1の並列pn層12と第2の並列pn層15との境界が、素子活性部1と素子周縁部3との境界に一致していることである。この場合、第1の並列pn層12と第2の並列pn層15との境界付近で並列pn層のピッチが徐々に変わるようにするとよい。第1の並列pn層12と第2の並列pn層15との境界で並列pn層のピッチが急激に変わると、例えば製造プロセスにおいて不純物をイオン注入する際に用いられるマスクの開口幅のばらつきや、イオン注入量のばらつきや、注入された不純物の再蒸発によるばらつきなどの影響によって、耐圧が変動しやすくなってしまう。また、チャージバランスからずれた位置の耐圧が低くなってしまう。第1の並列pn層12と第2の並列pn層15との境界付近で並列pn層のピッチが徐々に変わるようにすれば、耐圧の変動や低下を抑制することができる。実施の形態13によれば、実施の形態9と同様の効果が得られる。
図46および図47は、実施の形態14にかかる半導体装置の平面図である。図46に示すように、実施の形態1〜13において、n型領域72に平面形状が円形状のp型領域73が配置された構成の並列pn層71であってもよい。このような構成の並列pn層71は、素子活性部1および素子周縁部3に配置されていてもよいし(図46のパターン)、素子活性部1のみに配置されていてもよいし(図47のパターン)、素子周縁部3のみに配置されていてもよい(図示省略)。図47に示すパターンでは、素子周縁部3に、第2のn型領域(第2の第1導電型領域)76と第2のp型領域(第2の第2導電型領域)77とがストライプ状に交互に繰り返し接合されてできた微細ピッチの第2の並列pn層75が設けられている。第2のn型領域76と第2のp型領域77の繰り返しピッチが素子活性部1の並列pn層71の繰り返しピッチと同じであってもよい。なお、p型領域73に平面形状が円形状のn型領域72が配置された構成でもよい。実施の形態14によれば、実施の形態1〜13と同様の効果が得られる。
図48および図49は、実施の形態15にかかる半導体装置の平面図である。図48に示すように、実施の形態1〜13において、n型領域72に平面形状が正方形状のp型領域73が配置された構成の並列pn層71であってもよい。このような構成の並列pn層71は、素子活性部1および素子周縁部3に配置されていてもよいし(図48のパターン)、素子活性部1のみに配置されていてもよいし(図49のパターン)、素子周縁部3のみに配置されていてもよい(図示省略)。なお、p型領域73に平面形状が正方形状のn型領域72が配置された構成でもよい。実施の形態15によれば、実施の形態1〜13と同様の効果が得られる。
図50および図51は、実施の形態16にかかる半導体装置の平面図である。図50に示すように、実施の形態1〜13において、n型領域72に平面形状が多角形状(例えば、八角形状)のp型領域73が配置された構成の並列pn層71であってもよい。このような構成の並列pn層71は、素子活性部1および素子周縁部3に配置されていてもよいし(図50のパターン)、素子活性部1のみに配置されていてもよいし(図51のパターン)、素子周縁部3のみに配置されていてもよい(図示省略)。なお、p型領域73に平面形状が多角形状(例えば、八角形状)のn型領域72が配置された構成でもよい。実施の形態16によれば、実施の形態1〜13と同様の効果が得られる。
図52および図53は、実施の形態17にかかる半導体装置の平面図である。図52に示すように、実施の形態1〜13において、n型領域72に平面形状が多角形状(例えば、六角形状)のp型領域73が配置された構成の並列pn層71であってもよい。このような構成の並列pn層71は、素子活性部1および素子周縁部3に配置されていてもよいし(図52のパターン)、素子活性部1のみに配置されていてもよいし(図53のパターン)、素子周縁部3のみに配置されていてもよい(図示省略)。なお、p型領域73に平面形状が多角形状(例えば、六角形状)のn型領域72が配置された構成でもよい。実施の形態17によれば、実施の形態1〜13と同様の効果が得られる。
2 低抵抗層
3 素子周縁部
12 第1の並列pn層
13 第1の第1導電型領域
14 第1の第2導電型領域
15 第2の並列pn層
16 第2の第1導電型領域
17 第2の第2導電型領域
18 第3の第1導電型領域
19,20,21 第3の第2導電型領域
22 絶縁膜
23,27,28 第1の導電層
24 第2の導電層
31 並列pn層
32 第4の第1導電型領域
33 第4の第2導電型領域
41,42,43 第5の第2導電型領域
Claims (28)
- 第1主面側に設けられた素子活性部と、
第2主面側に設けられた低抵抗層と、
前記素子活性部と前記低抵抗層との間に設けられた、第1の第1導電型領域および第1の第2導電型領域が交互に配置された第1の並列pn層と、
前記素子活性部を囲む素子周縁部に設けられた、前記第1の第1導電型領域および前記第1の第2導電型領域の繰り返しピッチよりも狭いピッチで第2の第1導電型領域および第2の第2導電型領域が交互に配置された第2の並列pn層と、
前記第2の並列pn層と前記第1主面との間に設けられ、前記素子活性部の前記素子周縁部に隣接する部分まで伸びている第3の第1導電型領域と、
前記第3の第1導電型領域の前記第1主面側に互いに離れて設けられた複数の第3の第2導電型領域と、
前記素子周縁部の前記素子活性部側に対して反対側において、前記第1主面と前記低抵抗層との間に設けられ、前記低抵抗層に接する第1導電型の終端領域と、
前記複数の第3の第2導電型領域のうちの最も外側に位置する第3の第2導電型領域に電気的に接続する第1の導電層と、
前記終端領域に電気的に接続する第2の導電層と、
を備え、
前記第1の並列pn層と前記第2の並列pn層との境界が前記第3の第1導電型領域の下にあることを特徴とする半導体装置。 - 前記第3の第1導電型領域の不純物濃度が前記第1の第1導電型領域の不純物濃度よりも低いことを特徴とする請求項1に記載の半導体装置。
- 前記第3の第2導電型領域の不純物濃度が前記第3の第1導電型領域の不純物濃度よりも高いことを特徴とする請求項1または2に記載の半導体装置。
- 前記複数の第3の第2導電型領域のうちの一部または全部がそれぞれ前記第1の導電層を含む別々の導電層に電気的に接続することを特徴とする請求項1〜3のいずれか一つに記載の半導体装置。
- 前記複数の第3の第2導電型領域にそれぞれ電気的に接続する前記別々の導電層は、それぞれ、該導電層が電気的に接続する第3の第2導電型領域から、前記第3の第1導電型領域を覆う絶縁層上に延在し、該絶縁層を介して前記第3の第1導電型領域の一部を覆うことを特徴とする請求項4に記載の半導体装置。
- 隣り合う前記第3の第2導電型領域の間隔が前記素子周縁部の終端へ向かうに連れて広くなることを特徴とする請求項1〜5のいずれか一つに記載の半導体装置。
- 前記第1の第1導電型領域および前記第1の第2導電型領域の平面形状がストライプ状であるか、前記第1の第1導電型領域および前記第1の第2導電型領域のいずれか一方の平面形状が正方形状または多角形状であり、前記第2の第1導電型領域および前記第2の第2導電型領域の平面形状がストライプ状であるか、前記第2の第1導電型領域および前記第2の第2導電型領域のいずれか一方の平面形状が正方形状または多角形状であることを特徴とする請求項1〜6のいずれか一つに記載の半導体装置。
- 前記終端領域の前記第1主面側の表面層に選択的に設けられた第2導電型の最外周領域をさらに備え、
前記第2の導電層は、前記最外周領域に接続されていることを特徴とする請求項1〜7のいずれか一つに記載の半導体装置。 - 第1主面側に設けられた素子活性部と、
第2主面側に設けられた低抵抗層と、
前記素子活性部を囲む素子周縁部と、
前記第1主面と前記低抵抗層との間に設けられた、第4の第1導電型領域および第4の第2導電型領域が交互に配置された並列pn層と、
前記素子周縁部の前記素子活性部側に対して反対側において、前記第1主面と前記低抵抗層との間に設けられ、前記低抵抗層に接する第1導電型の終端領域と、
前記素子周縁部の前記並列pn層と前記第1主面との間に設けられた、前記終端領域よりも不純物濃度の低い第3の第1導電型領域と、
前記素子周縁部の前記並列pn層と前記第1主面との間に設けられた、前記第3の第1導電型領域の前記素子活性部側に隣接し、前記素子活性部の前記素子周縁部に隣接する部分まで伸びている第5の第2導電型領域と、
絶縁層を介して前記第5の第2導電型領域の一部を覆う第1の導電層と、
前記終端領域に電気的に接続するとともに絶縁層を介して前記第3の第1導電型領域の一部を覆う第2の導電層と、
を備えることを特徴とする半導体装置。 - 前記第3の第1導電型領域と前記第5の第2導電型領域との接合部が前記第1の導電層と前記第2の導電層との間にあることを特徴とする請求項9に記載の半導体装置。
- 前記第3の第1導電型領域の不純物濃度が前記第4の第1導電型領域の不純物濃度よりも低いことを特徴とする請求項9または10に記載の半導体装置。
- 前記第5の第2導電型領域の不純物濃度が前記第4の第2導電型領域の不純物濃度よりも低いことを特徴とする請求項9〜11のいずれか一つに記載の半導体装置。
- 前記第5の第2導電型領域に不純物濃度が異なる複数の領域があることを特徴とする請求項9〜12のいずれか一つに記載の半導体装置。
- 前記第5の第2導電型領域の、不純物濃度が異なる複数の領域の不純物濃度が前記素子活性部から前記素子周縁部の終端へ向かうに連れて低くなることを特徴とする請求項13に記載の半導体装置。
- 前記第4の第1導電型領域および前記第4の第2導電型領域の平面形状がストライプ状であるか、前記第4の第1導電型領域および前記第4の第2導電型領域のいずれか一方の平面形状が正方形状または多角形状であることを特徴とする請求項9〜14のいずれか一つに記載の半導体装置。
- 第1主面側に設けられた素子活性部と、
第2主面側に設けられた低抵抗層と、
前記第1主面と前記低抵抗層との間に設けられた、一定の繰り返しピッチで第1導電型領域および第2導電型領域が交互に配置された並列pn層と、
前記素子活性部を囲む素子周縁部における前記並列pn層を覆う絶縁層と、
前記素子周縁部の前記素子活性部側に対して反対側において、前記第1主面と前記低抵抗層との間に設けられ、前記低抵抗層に接する第1導電型の終端領域と、
前記絶縁層を介して前記素子周縁部における前記並列pn層の前記素子活性部側の一部を覆う第1の導電層と、
前記終端領域に電気的に接続するとともに前記絶縁層を介して前記素子周縁部における前記並列pn層の前記終端領域側の一部を覆う第2の導電層と、
を備え、
前記素子周縁部における前記並列pn層の前記第1主面側の前記素子活性部寄りの領域が実質的に第2導電型となり、
前記素子周縁部における前記並列pn層の前記第1主面側の前記終端領域寄りの領域が実質的に第1導電型となり、
前記実質的に第2導電型となる領域は、前記第1の導電層よりも前記終端領域に近い位置から前記第1の導電層の下まで伸びており、
前記実質的に第1導電型となる領域は、前記第2の導電層よりも前記素子活性部に近い位置から前記第2の導電層の下まで伸びており、
前記第1導電型領域および前記第2導電型領域の繰り返しピッチを一定に保ったまま、
前記実質的に第2導電型となる領域は、前記第2導電型領域の幅を広くする分、前記第1導電型領域の幅を狭くすることによって、前記第1導電型領域よりも前記第2導電型領域の不純物量が多くなっており、
前記実質的に第1導電型となる領域は、前記第1導電型領域の幅を広くする分、前記第2導電型領域の幅を狭くすることによって、前記第2導電型領域よりも前記第1導電型領域の不純物量が多くなっていることを特徴とする半導体装置。 - 前記実質的に第2導電型となる領域では、前記第2導電型領域の前記第1導電型領域に対する比率が一定であることを特徴とする請求項16に記載の半導体装置。
- 前記実質的に第1導電型となる領域では、前記第2導電型領域の前記第1導電型領域に対する比率が一定であることを特徴とする請求項16に記載の半導体装置。
- 前記実質的に第2導電型となる領域では、前記第2導電型領域の前記第1導電型領域に対する比率が前記終端領域に近づくに連れて小さくなって1に近づくことを特徴とする請求項16に記載の半導体装置。
- 前記実質的に第1導電型となる領域では、前記第2導電型領域の前記第1導電型領域に対する比率が前記素子活性部に近づくに連れて大きくなって1に近づくことを特徴とする請求項16に記載の半導体装置。
- 前記実質的に第2導電型となる領域と前記実質的に第1導電型となる領域との間に実質的にチャージバランスとなる領域が存在し、
前記第1導電型領域および前記第2導電型領域の繰り返しピッチを一定に保ったまま、
前記実質的にチャージバランスとなる領域は、前記第1導電型領域の幅と前記第2導電型領域の幅とを同じにすることによって、前記第1導電型領域の不純物量と前記第2導電型領域の不純物量とがほぼ同じになっていることを特徴とする請求項16に記載の半導体装置。 - 前記実質的にチャージバランスとなる領域の幅が前記第1の導電層と前記第2の導電層との間の距離の1/3以下であることを特徴とする請求項21に記載の半導体装置。
- 前記第1の導電層または前記第2の導電層が1段の階段状になっていることを特徴とする請求項16〜22のいずれか一つに記載の半導体装置。
- 前記第1の導電層または前記第2の導電層が2段の階段状になっていることを特徴とする請求項16〜22のいずれか一つに記載の半導体装置。
- 前記第1の導電層または前記第2の導電層が3段以上の階段状になっていることを特徴とする請求項16〜22のいずれか一つに記載の半導体装置。
- 前記第1導電型領域および前記第2導電型領域の平面形状がストライプ状であることを特徴とする請求項16〜25のいずれか一つに記載の半導体装置。
- 前記実質的に第2導電型となる領域と前記実質的に第1導電型となる領域との間に実質的にチャージバランスとなる領域が存在し、
前記第1導電型領域および前記第2導電型領域の繰り返しピッチを一定に保ったまま、
前記実質的にチャージバランスとなる領域は、当該実質的にチャージバランスとなる領域に対する前記第1導電型領域の占有面積と前記第2導電型領域の占有面積とを同じにすることによって、前記第1導電型領域の不純物量と前記第2導電型領域の不純物量とがほぼ同じになっていることを特徴とする請求項16に記載の半導体装置。 - 前記第1導電型領域および前記第2導電型領域のいずれか一方の平面形状が正方形状または多角形状であることを特徴とする請求項16〜20,27のいずれか一つに記載の半導体装置。
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012501498A JP5741567B2 (ja) | 2009-07-31 | 2010-07-29 | 半導体装置 |
Applications Claiming Priority (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009180131 | 2009-07-31 | ||
| JP2009180131 | 2009-07-31 | ||
| PCT/JP2010/004825 WO2011013379A1 (en) | 2009-07-31 | 2010-07-29 | Semiconductor apparatus |
| JP2012501498A JP5741567B2 (ja) | 2009-07-31 | 2010-07-29 | 半導体装置 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2012533167A JP2012533167A (ja) | 2012-12-20 |
| JP5741567B2 true JP5741567B2 (ja) | 2015-07-01 |
Family
ID=43529049
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012501498A Active JP5741567B2 (ja) | 2009-07-31 | 2010-07-29 | 半導体装置 |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US9577087B2 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP5741567B2 (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN102473721B (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2011013379A1 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (30)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012074441A (ja) * | 2010-09-28 | 2012-04-12 | Toshiba Corp | 電力用半導体装置 |
| CN102420240B (zh) * | 2011-07-05 | 2013-09-11 | 上海华虹Nec电子有限公司 | 超级结器件的终端保护结构及制造方法 |
| JP2013038329A (ja) * | 2011-08-10 | 2013-02-21 | Toshiba Corp | 半導体装置 |
| DE112012004043B4 (de) * | 2011-09-28 | 2018-03-22 | Mitsubishi Electric Corporation | Halbleitereinrichtung |
| JP5915076B2 (ja) * | 2011-10-21 | 2016-05-11 | 富士電機株式会社 | 超接合半導体装置 |
| JP2013149761A (ja) * | 2012-01-18 | 2013-08-01 | Fuji Electric Co Ltd | 半導体装置 |
| JP2013179251A (ja) * | 2012-02-09 | 2013-09-09 | Renesas Electronics Corp | 半導体装置 |
| JP6107156B2 (ja) * | 2012-05-21 | 2017-04-05 | 富士電機株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| KR20140022518A (ko) * | 2012-08-13 | 2014-02-25 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 반도체 장치 및 그 제조 방법 |
| US9117899B2 (en) | 2012-11-26 | 2015-08-25 | D3 Semiconductor LLC | Device architecture and method for improved packing of vertical field effect devices |
| WO2014148400A1 (ja) * | 2013-03-21 | 2014-09-25 | 富士電機株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| JP6277623B2 (ja) * | 2013-08-01 | 2018-02-14 | 住友電気工業株式会社 | ワイドバンドギャップ半導体装置 |
| JP6576926B2 (ja) * | 2013-12-16 | 2019-09-18 | アーベーベー・シュヴァイツ・アクチエンゲゼルシャフト | 半導体装置のエッジ終端および対応する製造方法 |
| US9293528B2 (en) | 2013-12-31 | 2016-03-22 | Infineon Technologies Austria Ag | Field-effect semiconductor device and manufacturing therefor |
| JP6146486B2 (ja) * | 2014-01-16 | 2017-06-14 | 富士電機株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| JP6369173B2 (ja) * | 2014-04-17 | 2018-08-08 | 富士電機株式会社 | 縦型半導体装置およびその製造方法 |
| US10468479B2 (en) | 2014-05-14 | 2019-11-05 | Infineon Technologies Austria Ag | VDMOS having a drift zone with a compensation structure |
| CN105900245B (zh) * | 2014-07-04 | 2019-08-06 | 富士电机株式会社 | 半导体装置 |
| JP6477174B2 (ja) * | 2015-04-02 | 2019-03-06 | 富士電機株式会社 | 半導体装置および半導体装置の製造方法 |
| JP6758592B2 (ja) * | 2015-09-18 | 2020-09-23 | サンケン電気株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| DE112017002113B4 (de) * | 2016-04-21 | 2023-05-17 | Mitsubishi Electric Corporation | Halbleitereinheit |
| JP6730078B2 (ja) | 2016-04-27 | 2020-07-29 | ローム株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| DE102016108125B4 (de) * | 2016-05-02 | 2023-11-23 | Infineon Technologies Ag | Halbleitervorrichtung und Herstellung davon |
| CN108475704B (zh) * | 2016-07-15 | 2021-10-22 | 富士电机株式会社 | 碳化硅半导体装置 |
| CN106571394B (zh) * | 2016-11-01 | 2018-05-11 | 杭州士兰微电子股份有限公司 | 功率器件及其制造方法 |
| JP6336165B2 (ja) * | 2017-03-14 | 2018-06-06 | 三菱電機株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| DE102017105548A1 (de) | 2017-03-15 | 2018-09-20 | Infineon Technologies Dresden Gmbh | Halbleitervorrichtung, die eine gatekontaktstruktur enthält |
| EP3490006A1 (en) | 2017-11-24 | 2019-05-29 | Nexperia B.V. | Semiconductor device with edge termination structure and method of manufacture |
| CN111092123A (zh) * | 2019-12-10 | 2020-05-01 | 杰华特微电子(杭州)有限公司 | 横向双扩散晶体管及其制造方法 |
| JP2024044679A (ja) * | 2022-09-21 | 2024-04-02 | 株式会社東芝 | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 |
Family Cites Families (35)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2585331B2 (ja) * | 1986-12-26 | 1997-02-26 | 株式会社東芝 | 高耐圧プレーナ素子 |
| CN1019720B (zh) | 1991-03-19 | 1992-12-30 | 电子科技大学 | 半导体功率器件 |
| DE4309764C2 (de) | 1993-03-25 | 1997-01-30 | Siemens Ag | Leistungs-MOSFET |
| JP3424635B2 (ja) * | 1994-09-20 | 2003-07-07 | 株式会社日立製作所 | 半導体装置及びそれを使った電力変換装置 |
| US5629552A (en) * | 1995-01-17 | 1997-05-13 | Ixys Corporation | Stable high voltage semiconductor device structure |
| JPH09266311A (ja) | 1996-01-22 | 1997-10-07 | Fuji Electric Co Ltd | 半導体装置及びその製造方法 |
| JP4774580B2 (ja) | 1999-08-23 | 2011-09-14 | 富士電機株式会社 | 超接合半導体素子 |
| JP4765012B2 (ja) * | 2000-02-09 | 2011-09-07 | 富士電機株式会社 | 半導体装置及びその製造方法 |
| JP4483001B2 (ja) | 2000-02-17 | 2010-06-16 | 富士電機システムズ株式会社 | 半導体素子 |
| JP3546955B2 (ja) * | 2000-12-15 | 2004-07-28 | 関西日本電気株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| JP3731520B2 (ja) * | 2001-10-03 | 2006-01-05 | 富士電機デバイステクノロジー株式会社 | 半導体装置及びその製造方法 |
| JP4126910B2 (ja) * | 2002-01-08 | 2008-07-30 | 富士電機デバイステクノロジー株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| JP4126915B2 (ja) | 2002-01-30 | 2008-07-30 | 富士電機デバイステクノロジー株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| JP3908572B2 (ja) * | 2002-03-18 | 2007-04-25 | 株式会社東芝 | 半導体素子 |
| JP3634830B2 (ja) | 2002-09-25 | 2005-03-30 | 株式会社東芝 | 電力用半導体素子 |
| US7169634B2 (en) * | 2003-01-15 | 2007-01-30 | Advanced Power Technology, Inc. | Design and fabrication of rugged FRED |
| JP4253558B2 (ja) | 2003-10-10 | 2009-04-15 | 株式会社豊田中央研究所 | 半導体装置 |
| JP4867131B2 (ja) * | 2004-01-15 | 2012-02-01 | 富士電機株式会社 | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 |
| JP4904673B2 (ja) | 2004-02-09 | 2012-03-28 | 富士電機株式会社 | 半導体装置および半導体装置の製造方法 |
| JP2006005275A (ja) * | 2004-06-21 | 2006-01-05 | Toshiba Corp | 電力用半導体素子 |
| CN100530679C (zh) * | 2004-08-04 | 2009-08-19 | 富士电机电子技术株式会社 | 半导体元件 |
| JP4967236B2 (ja) * | 2004-08-04 | 2012-07-04 | 富士電機株式会社 | 半導体素子 |
| JP4940546B2 (ja) | 2004-12-13 | 2012-05-30 | 株式会社デンソー | 半導体装置 |
| JP4930894B2 (ja) * | 2005-05-13 | 2012-05-16 | サンケン電気株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| JP2006332217A (ja) * | 2005-05-25 | 2006-12-07 | Hitachi Ltd | 高耐圧p型MOSFET及びそれを用いた電力変換装置 |
| JP4865260B2 (ja) | 2005-06-23 | 2012-02-01 | 株式会社豊田中央研究所 | 半導体装置 |
| JP2007157799A (ja) * | 2005-11-30 | 2007-06-21 | Toyota Central Res & Dev Lab Inc | 半導体装置 |
| JP5188037B2 (ja) | 2006-06-20 | 2013-04-24 | 株式会社東芝 | 半導体装置 |
| JP5124999B2 (ja) | 2006-06-15 | 2013-01-23 | 富士電機株式会社 | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 |
| JP2008078282A (ja) * | 2006-09-20 | 2008-04-03 | Toshiba Corp | 半導体装置及びその製造方法 |
| JP5196766B2 (ja) | 2006-11-20 | 2013-05-15 | 株式会社東芝 | 半導体装置 |
| JP2008187125A (ja) | 2007-01-31 | 2008-08-14 | Toshiba Corp | 半導体装置 |
| JP2008227236A (ja) * | 2007-03-14 | 2008-09-25 | Toyota Central R&D Labs Inc | 半導体装置 |
| JP2008294028A (ja) | 2007-05-22 | 2008-12-04 | Toshiba Corp | 半導体装置 |
| JP4621708B2 (ja) | 2007-05-24 | 2011-01-26 | 株式会社東芝 | 半導体装置及びその製造方法 |
-
2010
- 2010-07-29 JP JP2012501498A patent/JP5741567B2/ja active Active
- 2010-07-29 WO PCT/JP2010/004825 patent/WO2011013379A1/en active Application Filing
- 2010-07-29 CN CN201080026398.6A patent/CN102473721B/zh active Active
-
2011
- 2011-12-07 US US13/313,583 patent/US9577087B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| WO2011013379A1 (en) | 2011-02-03 |
| US20120126315A1 (en) | 2012-05-24 |
| CN102473721B (zh) | 2015-05-06 |
| CN102473721A (zh) | 2012-05-23 |
| US9577087B2 (en) | 2017-02-21 |
| JP2012533167A (ja) | 2012-12-20 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5741567B2 (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| US8957502B2 (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| JP7471267B2 (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| US6825565B2 (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| US7372111B2 (en) | Semiconductor device with improved breakdown voltage and high current capacity | |
| EP3433880B1 (en) | Superjunction power semiconductor devices with fast switching capability | |
| JP4621708B2 (ja) | 半導体装置及びその製造方法 | |
| US8450800B2 (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| JP6009731B2 (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| US8188521B2 (en) | Power semiconductor device | |
| JP4289123B2 (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| JP7001104B2 (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| US6768170B2 (en) | Superjunction device with improved avalanche capability and breakdown voltage | |
| JP2018026450A (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| JP7505217B2 (ja) | 超接合半導体装置および超接合半導体装置の製造方法 | |
| JP2012109599A (ja) | 半導体素子 | |
| US20110169080A1 (en) | Charge balance power device and manufacturing method thereof | |
| KR20220143249A (ko) | 슈퍼정션 반도체 소자 및 제조방법 | |
| JP2012204379A (ja) | 電力用半導体装置 | |
| KR101127501B1 (ko) | 트렌치 게이트 구조를 가지는 전력 반도체 소자 | |
| US11430862B2 (en) | Superjunction semiconductor device including parallel PN structures and method of manufacturing thereof | |
| KR101574319B1 (ko) | 주입 효과를 이용한 전력 반도체 소자 | |
| JP7524527B2 (ja) | 超接合半導体装置および超接合半導体装置の製造方法 | |
| US11757031B2 (en) | Power transistor with integrated Schottky diode | |
| WO2018003064A1 (ja) | 半導体装置 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20131119 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20140120 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20140311 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20140512 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20150106 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20150309 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20150331 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20150413 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5741567 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |