JP4653764B2 - Semiconductor device design method, design support system, and program - Google Patents
Semiconductor device design method, design support system, and program Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4653764B2 JP4653764B2 JP2007045122A JP2007045122A JP4653764B2 JP 4653764 B2 JP4653764 B2 JP 4653764B2 JP 2007045122 A JP2007045122 A JP 2007045122A JP 2007045122 A JP2007045122 A JP 2007045122A JP 4653764 B2 JP4653764 B2 JP 4653764B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- model
- impedance
- power supply
- circuit
- pad
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/30—Technical effects
- H01L2924/301—Electrical effects
- H01L2924/3011—Impedance
Landscapes
- Design And Manufacture Of Integrated Circuits (AREA)
Description
本発明は、半導体パッケージにおける半導体チップのパワーインテグリティを目的とした設計方法、当該設計方法に従った設計を支援する設計支援システム及びプログラムに関する。 The present invention relates to a design method for the purpose of power integrity of a semiconductor chip in a semiconductor package, a design support system and a program for supporting a design according to the design method.
半導体パッケージの設計や半導体パッケージを含むシステムの設計を行う場合、半導体チップの電源パッド及び/又はグランドパッドにおける電圧変動を許容値以下としなければならず、その適否を判断するため電圧変動の解析が行われている。 When designing a semiconductor package or a system including a semiconductor package, voltage fluctuations in the power supply pad and / or ground pad of the semiconductor chip must be less than an allowable value, and analysis of voltage fluctuations is necessary to determine the suitability. Has been done.
従来、かかる電圧変動の解析として、一般的には、SPICEモデルを用いた過渡解析が行われていた。かかる過渡解析の場合、電圧変動が許容値を超えていたときには、例えばレイアウト修正などを行い、再度過渡解析を実行して電圧変動が許容値以下になったか否かを判断するといったことが繰り返し行われる(例えば、特許文献1)。 Conventionally, a transient analysis using a SPICE model has been generally performed as an analysis of the voltage fluctuation. In the case of such transient analysis, when the voltage fluctuation exceeds the allowable value, for example, the layout is corrected, and the transient analysis is performed again to determine whether or not the voltage fluctuation is below the allowable value. (For example, Patent Document 1).
これに対して、最近では、時間領域ではなく周波数領域における解析を導入しようという試みも提案されている(例えば、特許文献2)。 On the other hand, recently, an attempt to introduce analysis in the frequency domain instead of the time domain has been proposed (for example, Patent Document 2).
しかしながら、特許文献1に代表されるような時間領域における解析では、レイアウト修正のたびに過渡解析を行うため、計算量が多く、設計期間の長期化を避けることができない。
However, in the analysis in the time domain as typified by
一方、特許文献2に提案された技術は、半導体パッケージに含まれる半導体チップ上のレイアウトを主たる対象としているものであり、既に設計されてしまった半導体チップを用いての半導体パッケージの設計に適用するのは困難である。
On the other hand, the technique proposed in
そこで、本発明は、既に設計されてしまった半導体チップを用いて半導体パッケージを設計する際であっても設計期間を短縮することのできる新たな設計方法を提案すると共に、当該設計方法に従った設計を支援する設計支援システム及びプログラムを提供することを目的とする。 Accordingly, the present invention proposes a new design method capable of shortening the design period even when designing a semiconductor package using a semiconductor chip that has already been designed, and has followed the design method. An object of the present invention is to provide a design support system and program for supporting design.
既に設計されてしまった半導体チップを用いた半導体パッケージの設計において、電圧変動解析の結果を反映させるように設計変更できるのは半導体チップ以外の部分、具体的にはパッケージ配線等である。 In designing a semiconductor package using a semiconductor chip that has already been designed, it is possible to change the design so as to reflect the result of the voltage variation analysis, specifically, the part other than the semiconductor chip, specifically the package wiring.
一方、DRAMチップなどに代表される半導体チップにおいて電源パッド及び/又はグランドパッドに電圧変動が発生するのは、例えば、出力段のドライバがスイッチングして半導体チップの出力が遷移する際に電源パッド及びグランドパッドに過渡電流が流れるためである。 On the other hand, in a semiconductor chip typified by a DRAM chip or the like, voltage fluctuations occur in the power pad and / or the ground pad, for example, when the driver of the output stage switches and the output of the semiconductor chip transitions. This is because a transient current flows through the ground pad.
そこで、本発明では、半導体チップの出力が“L”から“H”に遷移する場合(L→H:「第1遷移ケース」という。)と“H”から“L”に遷移する場合(H→L:「第2遷移ケース」という。)の2つの場合のそれぞれについて半導体チップをモデル化すると共に、モデル化した半導体チップ(「チップモデル」という。)を用いて周波数領域における解析を行うことにより、少ない計算量で正確な解析結果を取得し、パッケージ配線等の調整対象系に対する設計指針又は設計変更指針を提供することとした。 Therefore, in the present invention, the output of the semiconductor chip transitions from “L” to “H” (L → H: referred to as “first transition case”) and the transition from “H” to “L” (H → L: A semiconductor chip is modeled for each of the two cases of “second transition case”), and analysis in the frequency domain is performed using the modeled semiconductor chip (referred to as “chip model”). As a result, an accurate analysis result is obtained with a small amount of calculation, and a design guideline or a design change guideline for an adjustment target system such as package wiring is provided.
具体的には、本発明は、半導体チップを含む半導体パッケージの設計方法であって、
互いに異なる第1チップモデル及び第2チップモデルと調整対象系インピーダンスモデルに基づいて第1調整対象値及び第2調整対象値を算出する調整対象値算出ステップであって、前記第1チップモデル及び前記第2チップモデルは、前記半導体チップの出力値がローレベルからハイレベルに遷移する第1遷移ケースとハイレベルからローレベルに遷移する第2遷移ケースとの2つの遷移ケースのそれぞれに対応させて前記半導体チップを周波数領域にて表現するようにして作成されたモデルであり、前記調整対象系インピーダンスモデルは、前記半導体パッケージにおける前記半導体チップ以外の構成要素のうちの調整対象構成要素からなる調整対象系を周波数領域にて表現するようにして作成されたモデルであり、前記第1調整対象値及び前記第2調整対象値は、前記第1遷移ケースと前記第2遷移ケースとのそれぞれにおける調整対象値である、調整対象値算出ステップと、
前記第1調整対象値と前記第2調整対象値を比較し、調整必要性のより高い一方を選択する調整対象値選択ステップと、
周波数領域において予め定められた制約値と前記第1調整対象値及び前記第2調整対象値のうちの選択された調整対象値とを比較して、当該比較結果に基づき前記調整対象系に対する設計指針を決定する設計指針決定ステップと
を備える設計方法を提供する。
Specifically, the present invention is a method for designing a semiconductor package including a semiconductor chip,
An adjustment target value calculation step of calculating a first adjustment target value and a second adjustment target value based on a first chip model, a second chip model, and an adjustment target system impedance model that are different from each other, wherein the first chip model, The second chip model corresponds to each of two transition cases, a first transition case in which the output value of the semiconductor chip transitions from a low level to a high level and a second transition case in which the output value transitions from a high level to a low level. It is a model created so as to represent the semiconductor chip in a frequency domain, and the adjustment target system impedance model is an adjustment target composed of adjustment target components of components other than the semiconductor chip in the semiconductor package A model created by expressing the system in the frequency domain, and the first adjustment target value Fine said second adjustment target value, said an adjustment target value in each of the first transition case and the second transition case, the adjustment target value calculation step,
An adjustment target value selection step of comparing the first adjustment target value and the second adjustment target value and selecting one of the higher adjustment needs;
A design guideline for the adjustment target system based on the comparison result by comparing a predetermined constraint value in the frequency domain with the adjustment target value selected from the first adjustment target value and the second adjustment target value. A design method comprising a design guideline determining step for determining
また、本発明は、当該設計方法に従った設計を支援する設計支援システムとして、
互いに異なる第1チップモデル及び第2チップモデルを提供するチップモデル提供部であって、前記第1チップモデル及び前記第2チップモデルは、前記半導体チップの出力値がローレベルからハイレベルに遷移する第1遷移ケースとハイレベルからローレベルに遷移する第2遷移ケースとの2つの遷移ケースのそれぞれに対応させて前記半導体チップを周波数領域にて表現するようにして作成されたモデルである、チップモデル提供部と、
前記半導体パッケージにおける前記半導体チップ以外の構成要素のうちの調整対象構成要素からなる調整対象系を周波数領域にて表現してなる調整対象系インピーダンスモデルを提供するインピーダンスモデル提供部と、
前記第1チップモデル及び前記第2チップモデルのそれぞれを前記調整対象系インピーダンスモデルと接続して前記第1遷移ケースと前記第2遷移ケースとのそれぞれにおける調整対象値である第1調整対象値及び第2調整対象値を算出する調整対象値算出部と、
前記第1調整対象値と前記第2調整対象値を比較し、調整必要性のより高い一方を選択する調整対象値選択部と、
周波数領域において予め定められた制約値を提供する制約値提供部と、
該制約値と前記第1調整対象値及び前記第2調整対象値のうちの選択された調整対象値とを比較して、当該比較結果に基づき前記調整対象系に対する設計支援情報を決定する設計支援情報決定部と、
前記設計支援情報を表示する表示部と
を備える設計支援システムを提供する。
Further, the present invention provides a design support system that supports design according to the design method.
A chip model providing unit that provides a first chip model and a second chip model that are different from each other, wherein the output value of the semiconductor chip transitions from a low level to a high level in the first chip model and the second chip model. A chip that is a model created by expressing the semiconductor chip in the frequency domain in correspondence with each of two transition cases, a first transition case and a second transition case that transitions from a high level to a low level. A model provider,
An impedance model providing unit that provides an adjustment target system impedance model that expresses an adjustment target system including an adjustment target component of components other than the semiconductor chip in the semiconductor package in a frequency domain;
A first adjustment target value that is an adjustment target value in each of the first transition case and the second transition case by connecting each of the first chip model and the second chip model to the adjustment target system impedance model; An adjustment target value calculation unit for calculating a second adjustment target value;
An adjustment target value selection unit that compares the first adjustment target value and the second adjustment target value and selects one of the higher adjustment needs;
A constraint value providing unit that provides a predetermined constraint value in the frequency domain;
A design support that compares the constraint value with a selected adjustment target value among the first adjustment target value and the second adjustment target value and determines design support information for the adjustment target system based on the comparison result. An information determination unit;
A design support system comprising a display unit for displaying the design support information is provided.
更に、本発明は、演算部、記憶部及び表示部を備えたコンピュータシステムにおいて前記演算部に対して所定の処理を実行させ前記コンピュータシステムを、前記設計方法に従った設計を支援する設計支援システムとして機能させるためのプログラムであって、
前記所定の処理は、
互いに異なる第1チップモデル及び第2チップモデルと調整対象系インピーダンスモデルに基づいて第1調整対象値及び第2調整対象値を算出する調整対象値算出ステップであって、前記第1チップモデル及び前記第2チップモデルは、前記半導体チップの出力値がローレベルからハイレベルに遷移する第1遷移ケースとハイレベルからローレベルに遷移する第2遷移ケースとの2つの遷移ケースのそれぞれに対応させて前記半導体チップを周波数領域にて表現するようにして作成されたモデルであり、前記調整対象系インピーダンスモデルは、前記半導体パッケージにおける前記半導体チップ以外の構成要素のうちの調整対象構成要素からなる調整対象系を周波数領域にて表現するようにして作成されたモデルであり、前記第1調整対象値及び前記第2調整対象値は、前記第1遷移ケースと前記第2遷移ケースとのそれぞれにおける調整対象値である、調整対象値算出ステップと、
前記第1調整対象値と前記第2調整対象値を比較し、調整必要性のより高い一方を選択する調整対象値選択ステップと、
周波数領域において予め定められた制約値と前記第1調整対象値及び前記第2調整対象値のうちの選択された調整対象値とを比較して、当該比較結果に基づき前記調整対象系に対する設計支援情報を決定する設計支援情報決定ステップと、
前記設計支援情報を前記表示部に表示する表示ステップと
を備えるプログラムを提供する。
Furthermore, the present invention provides a design support system for supporting a design according to the design method by causing the calculation unit to execute predetermined processing in a computer system including a calculation unit, a storage unit, and a display unit. Is a program for functioning as
The predetermined process is:
An adjustment target value calculation step of calculating a first adjustment target value and a second adjustment target value based on a first chip model, a second chip model, and an adjustment target system impedance model that are different from each other, wherein the first chip model, The second chip model corresponds to each of two transition cases, a first transition case in which the output value of the semiconductor chip transitions from a low level to a high level and a second transition case in which the output value transitions from a high level to a low level. It is a model created so as to represent the semiconductor chip in a frequency domain, and the adjustment target system impedance model is an adjustment target composed of adjustment target components of components other than the semiconductor chip in the semiconductor package A model created by expressing the system in the frequency domain, and the first adjustment target value Fine said second adjustment target value, said an adjustment target value in each of the first transition case and the second transition case, the adjustment target value calculation step,
An adjustment target value selection step of comparing the first adjustment target value and the second adjustment target value and selecting one of the higher adjustment needs;
A design support for the adjustment target system based on the comparison result by comparing a predetermined restriction value in the frequency domain with the adjustment target value selected from the first adjustment target value and the second adjustment target value. A design support information determination step for determining information;
A display step of displaying the design support information on the display unit is provided.
本発明によれば、電源/GND電圧の変動するケースとして第1遷移ケース(L→H)と第2遷移ケース(H→L)の2つのケースのそれぞれに対応する第1チップモデル及び第2チップモデルを用いて解析を行うことから、正確な解析結果を得ることができる。また、第1チップモデル及び第2チップモデル及び調整対象系インピーダンスモデルに基づく第1調整対象値及び第2調整対象値の算出や、その一方と制約値との比較など、周波数領域における処理を用いることから、過渡解析と比較して、計算量を少なくすることができる。 According to the present invention, the first chip model and the second chip corresponding to the two cases of the first transition case (L → H) and the second transition case (H → L) as the cases where the power supply / GND voltage fluctuates. Since the analysis is performed using the chip model, an accurate analysis result can be obtained. In addition, processing in the frequency domain, such as calculation of the first adjustment target value and the second adjustment target value based on the first chip model, the second chip model, and the adjustment target system impedance model, and comparison between one value and the constraint value is used. Therefore, the amount of calculation can be reduced as compared with the transient analysis.
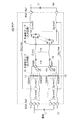
以下、本発明の実施の形態による設計方法として、図1に示されるような半導体チップ10及び半導体チップ20を備えるマルチチップパッケージ(MCP)100の設計に適用した場合について説明する。図示された半導体チップ10はDRAMチップであり、図示された半導体チップ20はプロセッサなどが搭載されたロジックチップである。
Hereinafter, a case where the present invention is applied to the design of a multichip package (MCP) 100 including the
半導体チップ10には、電源パッド11及びグランドパッド12が設けられている。実際のチップにおいては、図1に模式的に示されるように、複数の電源パッド11及び複数のグランドパッド12が設けられているが、以下に説明する設計方法においては、それぞれまとめることで1つの電源パッド11及び1つのグランドパッド12として取り扱う。
The
また、半導体チップ10の電源パッド11とグランドパッド12の間には複数の出力ドライバが設けられている。各出力ドライバは、図1には示されていないが、pMOS回路とnMOS回路とを直列に接続してなるものであり、pMOS回路とnMOS回路の接続部からはそれぞれ出力パッド13が引き出されている。実際のチップにおいては、少なくともデータ線(DQ線)の数に相当する出力ドライバ及び出力パッド13が設けられているが、以下に説明する設計方法においては、複数の出力パッド及び複数の出力ドライバをそれぞれ一まとめにして、電源パッド11及びグランドパッド12における電源/GND電圧変動の解析を行うこととする。
A plurality of output drivers are provided between the
本実施の形態においては、図1に示されるようなMCP100を図2に示されるように半導体チップ10をモデル化したものとパッケージ配線等のインピーダンスモデルに分けて表現し、それらを接続した上で、電源パッド11及びグランドパッド12における電圧変動を算出して、周波数領域において予め定められた制約値との対比を行うことにより、電源/GND電圧の変動が許容値内におさまっているか否かを判断する。なお、以下においては、パッケージ配線やプリント配線基板上の配線など、調整対象となる回路網を調整対象系といい、そのインピーダンスモデルを調整対象系インピーダンスモデルという。
In the present embodiment, the
ここで、図2に示される内部インピーダンスZchp_int(f)14は、半導体チップ10に含まれる構成のうち出力ドライバ(pMOS回路及びnMOS回路)を除いた部分を出力側から見た場合に電源パッド11及びグランドパッド12の間に見えるインピーダンスである。また、Zp_x及びZn_yは、出力ドライバを構成するpMOS回路及びnMOS回路をそれぞれの状態にかかわらず総括的に示すものであり、出力ドライバを構成するpMOS回路及びnMOS回路の具体的な状態をも考慮して作成された図においては、Zp_on(オン状態のpMOS回路のインピーダンス)又はZp_off(オフ状態のpMOS回路のインピーダンス)及びZn_on(オン状態のnMOS回路のインピーダンス)又はZn_off(オフ状態のnMOS回路のインピーダンス)として表現されるものである。
Here, the internal impedance Z chp_int (f) 14 shown in FIG. 2 is a power pad when a portion excluding the output driver (pMOS circuit and nMOS circuit) in the configuration included in the
より詳しくは、本実施の形態による設計方法においては、半導体チップ10のチップモデルとして、図3乃至図6の4通りの場合を考慮したチップモデルを用意して、それぞれを調整対象系インピーダンスモデルと接続することとする。
More specifically, in the design method according to the present embodiment, as a chip model of the
このうち、図3及び図4に示されるチップモデルは、半導体チップ10の出力値がローレベルからハイレベルに遷移する第1遷移ケースを想定して半導体チップ10をモデル化してなる第1チップモデルである。第1チップモデルは、pMOS回路及びnMOS回路をそれぞれインピーダンス表現してなるpMOS回路インピーダンス及びnMOS回路インピーダンスを直列に接続したものを電源パッド11及びグランドパッド12間に接続すると共に、それと並列に内部インピーダンス14を接続し、更に、第1遷移ケースにおける変動電流値を考慮した電流源である第1電流源をpMOS回路インピーダンスに並列に接続するようにして作成される。
Among these, the chip model shown in FIGS. 3 and 4 is a first chip model obtained by modeling the
詳しくは、図3に示される第1チップモデルは電源パッド11における電圧変動値算出用のチップモデルであり、pMOS回路インピーダンスとしてはpMOS回路のオン状態におけるインピーダンスを用い、nMOS回路インピーダンスとしてはnMOS回路のオフ状態におけるインピーダンスを用いた上で、電源電圧変動値算出用の第1電流源Is_L2H_vdqをpMOS回路インピーダンスに並列接続するようにして作成されている。
Specifically, the first chip model shown in FIG. 3 is a chip model for calculating the voltage fluctuation value in the
また、図4に示される第1チップモデルはグランドパッド12における電圧変動値算出用のチップモデルであり、pMOS回路インピーダンス及びnMOS回路インピーダンスのいずれに関しても対応するpMOS回路及びnMOS回路のオン状態におけるインピーダンスを用いた上で、グランド電圧変動値算出用の第1電流源Is_L2H_vsqをpMOS回路インピーダンスに並列接続するようにして作成されている。
Further, the first chip model shown in FIG. 4 is a chip model for calculating a voltage fluctuation value in the
一方、図5及び図6に示されるチップモデルは、半導体チップ10の出力値がハイレベルからローレベルに遷移する第2遷移ケースを想定して半導体チップ10をモデル化してなる第2チップモデルである。第2チップモデルは、pMOS回路インピーダンス及びnMOS回路インピーダンスを直列に接続したものを電源パッド11及びグランドパッド12間に接続すると共に、それと並列に内部インピーダンス14を接続し、更に、第2遷移ケースにおける変動電流値を考慮した電流源である第2電流源をnMOS回路インピーダンスに並列に接続するようにして作成される。
On the other hand, the chip model shown in FIGS. 5 and 6 is a second chip model obtained by modeling the
詳しくは、図5に示される第2チップモデルは電源パッド11における電圧変動値算出用のチップモデルであり、pMOS回路インピーダンス及びnMOS回路インピーダンスのいずれに関しても対応するpMOS回路及びnOS回路のオン状態におけるインピーダンスを用いた上で、電源電圧変動値算出用の第2電流源ls_H2L_vdqをnMOS回路インピーダンスに並列接続するようにして作成されている。
Specifically, the second chip model shown in FIG. 5 is a chip model for calculating the voltage fluctuation value in the
また、図6に示される第2チップモデルはグランドパッド12における電圧変動値算出用のチップモデルであり、pMOS回路インピーダンスとしてはpMOS回路のオフ状態におけるインピーダンスを用い、nMOS回路インピーダンスとしてはnMOS回路のオン状態におけるインピーダンスを用いた上で、グランド電圧変動値算出用の第2電流源ls_H2L_vsqをnMOS回路インピーダンスに並列接続するようにして作成されている。
Further, the second chip model shown in FIG. 6 is a chip model for calculating a voltage fluctuation value in the
なお、図3乃至図6に示されるpMOS回路及びnMOS回路の等価回路モデルは、物理描像を考慮して、キャパシタ及び抵抗を直列接続してなるものを出力パッド13に対して互いに対称となるように配置してなるものである。より具体的には、出力パッド13から電源パッド11及びGNDパッド12側を見た場合に、まずはキャパシタが見えるようにキャパシタ及び抵抗を配置してなるものである。しかしながら、キャパシタ及び抵抗を直列接続してなるものを出力パッド13に対して互いに非対称となるように配置してpMOS回路及びnMOS回路の等価回路モデルを構成することとしても良い。即ち、例えば、出力パッド13から電源パッド11及びGNDパッド12側を見た場合に、pMOS回路については抵抗、キャパシタの順に並べる一方で、nMOS回路についてはキャパシタ、抵抗の順に並べることとしても良い。
Note that the equivalent circuit models of the pMOS circuit and the nMOS circuit shown in FIGS. 3 to 6 are symmetrical with respect to the
図7乃至図10には、図3乃至図6に示されたpMOS回路インピーダンス及びnMOS回路インピーダンスの等価回路モデルとは異なる等価回路モデルを用いた例が示されている。なお、図7乃至図10は、それぞれ、図3乃至図6に対応するものである。 FIGS. 7 to 10 show examples using an equivalent circuit model different from the equivalent circuit models of the pMOS circuit impedance and the nMOS circuit impedance shown in FIGS. 7 to 10 correspond to FIGS. 3 to 6, respectively.
図3乃至図6においては、pMOS回路及びnMOS回路のそれぞれについてオン/オフの状態にかかわらず同じ等価回路モデルを用いていたが、図7乃至図10を参照すると、pMOS回路及びnMOS回路のそれぞれに関し、オン状態とオフ状態とで異なる等価回路モデルが用いられている。これは、pMOS回路及びnMOS回路においては、それぞれ、オン状態においては抵抗成分が支配的になるのに対して、オフ状態においてはキャパシタ成分が支配的になることを考慮したためである。 3 to 6, the same equivalent circuit model is used for each of the pMOS circuit and the nMOS circuit regardless of the on / off state. However, referring to FIGS. 7 to 10, each of the pMOS circuit and the nMOS circuit is used. For the above, different equivalent circuit models are used in the on state and the off state. This is because, in the pMOS circuit and the nMOS circuit, the resistance component is dominant in the on state, whereas the capacitor component is dominant in the off state.
より具体的には、オン状態のpMOS回路インピーダンスは、電源パッド11と出力パッド13との間にキャパシタ及び抵抗が並列に接続されてなる等価回路モデルにて表現され、オフ状態のpMOS回路インピーダンスは、電源パッド11と出力パッド13との間にキャパシタ及び抵抗が直列に接続されてなる等価回路モデルにて表現されている。同様に、オン状態のnMOS回路インピーダンスは、出力パッド13とGNDパッド12との間にキャパシタ及び抵抗が並列に接続されてなる等価回路モデルにて表現され、オフ状態のnMOS回路インピーダンスは、出力パッド13とGNDパッド12との間にキャパシタ及び抵抗が直列に接続されてなる等価回路モデルにて表現されている。かかる等価回路モデルを用いてオン/オフ状態のpMOS回路インピーダンス/nMOS回路インピーダンスを算出することとすれば、図3乃至図6に示される例と比較して、より精度の高い解析結果を得ることができる。
More specifically, the pMOS circuit impedance in the on state is expressed by an equivalent circuit model in which a capacitor and a resistor are connected in parallel between the
以下、図11乃至図22をも参照して、上述した4種類のチップモデルの作成方法も含め、本実施の形態による設計方法について具体的に説明する。 Hereinafter, the design method according to the present embodiment will be specifically described with reference to FIGS. 11 to 22 as well as the above-described four types of chip model creation methods.
まず、半導体チップ10についての設計データなどの情報から、図3及び図4(又は図7及び図8)に示されるような第1チップモデル(電源電圧変動用/GND電圧変動用)並びに図5及び図6(又は図9及び図10)に示されるような第2チップモデル(電源電圧変動用/GND電圧変動用)を作成する(図11:ステップS101)。
First, from information such as design data about the
具体的には、図12に示されるように半導体チップ10についてSPICEモデルをAC解析してZパラメータを算出する。本実施の形態においては、Zパラメータを直接算出することとするが、これに代えて、まずはSパラメータを算出し、その後、そのSパラメータをZパラメータに変換することとしても良い。
Specifically, as shown in FIG. 12, the Z parameter is calculated by AC analysis of the SPICE model for the
一方、本実施の形態におけるチップモデルのうちインピーダンスに関する部分のみを抽出すると図13に示されるようなものとなる。図2に関連して説明したように、Zp_x及びZn_yは出力ドライバの状態にかかわらず、pMOS回路及びnMOS回路を表現するために導入した表記である。即ち、具体的には、半導体チップ10の出力値がハイレベルの場合、Zp_xはオン状態にあるpMOS回路のインピーダンスZp_onを示し、Zn_yはオフ状態にあるnMOS回路のインピーダンスZn_offを示す。同様に、半導体チップ10の出力値がローレベルの場合、Zp_xはオフ状態にあるpMOS回路のインピーダンスZp_offを示し、Zn_yはオン状態にあるnMOS回路のインピーダンスZn_onを示す。
On the other hand, when only the portion related to the impedance is extracted from the chip model in the present embodiment, it is as shown in FIG. As described in connection with FIG. 2, Z p_x and Z N_y regardless of the state of the output driver, a notation is introduced to represent the pMOS circuit, and nMOS circuit. That is, specifically, when the output value of the
上記の図13に示されるインピーダンスモデルを2ポート回路網としてより分かりやすい形に変形したものが図14に示される回路である。この図14に示される回路網におけるZパラメータは、下記式(1)に示される。 A circuit shown in FIG. 14 is obtained by modifying the impedance model shown in FIG. 13 into a more easily understandable form as a two-port network. The Z parameter in the circuit network shown in FIG. 14 is expressed by the following equation (1).
この式(1)に含まれる行列の各要素の関係を整理して、Zp_x、Zn_y及びZchp_intのそれぞれについて解くと、以下に掲げる式(2)〜(4)が得られる。 By arranging the relationship of each element of the matrix included in the equation (1) and solving for each of Z p — x , Z n — y and Z chp — int , equations (2) to (4) listed below are obtained.
式(2)及び式(3)から理解されるように、出力ドライバの出力値がハイレベルの場合におけるZ11,Z12及びZ22を用いればZp_on及びZn_offを算出することができ、出力ドライバの出力値がローレベルの場合におけるZ11,Z12及びZ22を用いればZp_off及びZn_onを算出することができる。なお、本実施の形態においては、SPICE解析により算出したZ11,Z12,Z21及びZ22に基づいて各部のインピーダンスを求めているが、Z11,Z12,Z21及びZ22を実測し、その結果を利用することとしても良い。即ち、出力ドライバの出力値がハイレベルの場合及びローレベルの場合のそれぞれについてZ11,Z12,Z21及びZ22を実測し(又は、図13におけるI1,I2,V1,V2を計測してZ11,Z12,Z21及びZ22を算出し)、そのようにして得られたZ11,Z12,Z21及びZ22を上記式(2)及び式(3)に代入することにより、pMOS回路24及びnMOS回路25の各状態におけるインピーダンスを算出することとしても良い。 As understood from the equations (2) and (3), Z p_on and Z n_off can be calculated by using Z 11 , Z 12 and Z 22 when the output value of the output driver is high level, Z p_off and Z n_on can be calculated by using Z 11 , Z 12 and Z 22 when the output value of the output driver is at a low level. In the present embodiment, the impedance of each part is obtained based on Z 11 , Z 12 , Z 21 and Z 22 calculated by SPICE analysis, but Z 11 , Z 12 , Z 21 and Z 22 are measured. However, the result may be used. That is, Z 11 , Z 12 , Z 21 and Z 22 are measured for each of the cases where the output value of the output driver is high level and low level (or I1, I2, V1, V2 in FIG. 13 are measured). the Te calculates Z 11, Z 12, Z 21 and Z 22), and substitutes the so Z 11, Z 12, Z 21 and Z 22 obtained in the equation (2) and (3) Thus, the impedance in each state of the pMOS circuit 24 and the nMOS circuit 25 may be calculated.
上記のようにして各インピーダンスの値を求めた後、図15乃至図18に示されるようにして、第1電流源(電源用/GND用)及び第2電流源(電源用/GND用)を導出する。ここで、図15は、電源電圧変動値算出用の第1電流源導出に関する図であり、図16は、グランド電圧変動値算出用の第1電流源導出に関する図である。また、図17は、電源電圧変動値算出用の第2電流源導出に関する図であり、図18は、グランド電圧変動値算出用の第2電流源導出に関する図である。なお、図15乃至図18においては、オン状態のpMOS回路及びオン状態のnMOS回路の等価回路モデルとしてそれぞれCR並列回路を用いているが、pMOS回路及びnMOS回路のいずれについてもオン状態においては抵抗が支配的であることからそれぞれの等価回路を抵抗のみで表現しても良い。また、解析結果に対して要求されている精度によっては、図3乃至図6に示されたように、オン状態のpMOS回路又はnMOS回路の等価回路モデルとしてCR直列回路を用いても良い。 After obtaining the impedance values as described above, the first current source (for power supply / GND) and the second current source (for power supply / GND) are connected as shown in FIGS. To derive. Here, FIG. 15 is a diagram relating to derivation of the first current source for calculating the power supply voltage fluctuation value, and FIG. 16 is a diagram relating to derivation of the first current source for calculating the ground voltage fluctuation value. FIG. 17 is a diagram relating to derivation of the second current source for calculating the power supply voltage fluctuation value, and FIG. 18 is a diagram relating to derivation of the second current source for calculating the ground voltage fluctuation value. 15 to 18, CR parallel circuits are used as equivalent circuit models of the on-state pMOS circuit and the on-state nMOS circuit, respectively. However, both the pMOS circuit and the nMOS circuit have resistance in the on-state. Therefore, each equivalent circuit may be expressed only by resistance. Depending on the accuracy required for the analysis result, a CR series circuit may be used as an equivalent circuit model of an on-state pMOS circuit or nMOS circuit, as shown in FIGS.
電源電圧変動値算出用の第1電流源Is_L2H_vdqを導出する際には、まず、図15に示されるように、出力パッド13とグランドパッド12の間に所定の外部負荷モデルZload(無負荷でも良い)を接続する。ここで、所定の外部負荷モデルのインピーダンスZloadがオフ状態のnMOS回路インピーダンスZn_offよりも遥かに小さいと仮定すると、第1遷移ケース(L→H)において電源パッド11を流れる電流Iv_L2Hのほとんどが、オン状態のpMOS回路インピーダンスZp_onと所定の外部負荷モデルZloadに流れることとなる。その場合、第1遷移ケース(L→H)において電源パッド11を流れる電流Iv_L2Hが分かれば、下記式(5)により、第1電流源の電流値Is_L2H_vdqを導出することができる。
When deriving the first current source Is_L2H_vdq for calculating the power supply voltage fluctuation value, first, as shown in FIG. 15, a predetermined external load model Z load (no load) is provided between the
同様に、グランド電圧変動値算出用の第1電流源Is_L2H_vsqを導出する際には、まず、図16に示されるように、出力パッド13とグランドパッド12の間に所定の外部負荷モデルZload(無負荷でも良い)を接続する。ここで、オン状態のnMOS回路インピーダンスZn_onが所定の外部負荷モデルのインピーダンスZloadよりも遥かに小さいと仮定すると、第1遷移ケース(L→H)においてグランドパッド12を流れる電流Ig_L2Hのほとんどが、オン状態のpMOS回路インピーダンスZp_on及びオン状態のnMOS回路インピーダンスZn_onに流れることとなる。その場合、第1遷移ケース(L→H)においてグランドパッド12を流れる電流Ig_L2Hが分かれば、下記式(6)により、第1電流源の電流値Is_L2H_vsqを導出することができる。
Similarly, when deriving the first current source Is_L2H_vsq for calculating the ground voltage fluctuation value, first, as shown in FIG. 16, a predetermined external load model Z load is provided between the
電源電圧変動値算出用の第2電流源Is_H2L_vdqを導出する際には、まず、図17に示されるように、出力パッド13とグランドパッド12の間に所定の外部負荷モデルZload(無負荷でも良い)を接続する。ここで、所定の外部負荷モデルのインピーダンスZloadがオン状態のnMOS回路インピーダンスZn_onよりも遥かに大きいと仮定すると、第2遷移ケース(H→L)において電源パッド11を流れる電流Iv_H2Lのほとんどが、オン状態のpMOS回路インピーダンスZp_onとオン状態のnMOS回路インピーダンスZn_onに流れることとなる。この場合、第2遷移ケース(H→L)において電源パッド11を流れる電流Iv_H2Lが分かれば、下記式(7)により、第2電流源の電流値Is_H2L_vdqを導出することができる。
When deriving the second current source Is_H2L_vdq for calculating the power supply voltage fluctuation value, first, as shown in FIG. 17, a predetermined external load model Z load (no load) is provided between the
同様に、グランド電圧変動値算出用の第2電流源Is_H2L_vsqを導出する際には、まず、図18に示されるように、出力パッド13とグランドパッド12の間に所定の外部負荷モデルZload(無負荷でも良い)を接続する。ここで、所定の外部負荷モデルのインピーダンスZloadがオフ状態のpMOS回路インピーダンスZp_onがよりも遥かに小さいと仮定すると、第2遷移ケース(H→L)においてグランドパッド12を流れる電流Ig_H2Lのほとんどが、オン状態のnMOS回路インピーダンスZn_on及び所定の外部負荷モデルのインピーダンスZloadに流れることとなる。その場合、第2遷移ケース(H→L)においてグランドパッド12を流れる電流Ig_H2Lが分かれば、下記式(8)により、第2電流源の電流値Is_H2L_vsqを導出することができる。
Similarly, when deriving the second current source Is_H2L_vsq for calculating the ground voltage fluctuation value, first, as shown in FIG. 18, a predetermined external load model Z load between the
なお、本実施の形態においては、第1遷移ケース(L→H)及び第2遷移ケース(H→L)において電源パッド11及びグランドパッド12を流れる電流をSPICEのトランジェント解析にて算出し、更に、フーリエ変換処理を行って、周波数領域表現による電流Iv_L2H及び電流Ig_L2H並びにIv_H2L及び電流Ig_H2Lを得ることとしたが、これに代えて、スペクトラムアナライザやオシロスコープなどを用いて対象になる半導体チップのパッドの状態を直接計測することとしてもよい。
In the present embodiment, the current flowing through the
このようにして、本実施の形態においては、半導体チップ情報に基づいて、第1遷移ケース用及び第2遷移ケース用の第1チップモデル及び第2チップモデルを、それぞれ電源電圧変動値算出用とGND電圧変動値算出用の2種類(従って、チップモデルは計4種類)作成する(図11:ステップS101)。上述したように、これらのチップモデルを作成するにあたってはSPICEモデルをトランジェント解析する場面も考えられるが、一旦、チップモデルを作成してしまった後は、半導体チップ10の構成が変わらぬ限り、作成されたチップモデルを用いることができる。
Thus, in the present embodiment, the first chip model and the second chip model for the first transition case and the second transition case are respectively used for calculating the power supply voltage fluctuation value based on the semiconductor chip information. Two types of GND voltage fluctuation value calculation (thus, a total of four types of chip models) are created (FIG. 11: Step S101). As described above, when creating these chip models, transient analysis of the SPICE model is also conceivable, but once the chip model is created, it will be created as long as the configuration of the
一方、パッケージ配線長などの調整対象系の情報に基づいて、図2に示されるような調整対象系インピーダンスモデルを作成し(図11:ステップS102)、ステップS101で作成した電源変動値算出用/GND変動値算出用の第1チップモデル及び第2チップモデルのそれぞれと、ステップS102で作成した調整対象系インピーダンスモデルとを、図19乃至図22に示されるようにして接続し、閉路回路方程式を解くことにより、トランジェント解析をすることなく、電源/GND電圧変動スペクトラムを算出する。ここで、図19は、第1遷移ケースにおける電源電圧変動スペクトラム算出に関する図であり、図20は、第1遷移ケースにおけるグランド電圧変動スペクトラム算出に関する図である。また、図21は、第2遷移ケースにおける電源電圧変動スペクトラム算出に関する図であり、図22は、第2遷移ケースにおけるグランド電圧変動スペクトラム算出に関する図である。ここで、図19〜図22を作成するにあたっては、Zvc_mcpを開放にし、Zgc_mcp、Zv_mcp3、Zg_mcp3をそれぞれゼロとした。 On the other hand, an adjustment target system impedance model as shown in FIG. 2 is created based on the information of the adjustment target system such as the package wiring length (FIG. 11: step S102). Each of the first chip model and the second chip model for calculating the GND fluctuation value is connected to the adjustment target system impedance model created in step S102 as shown in FIG. 19 to FIG. By solving, the power supply / GND voltage fluctuation spectrum is calculated without performing transient analysis. Here, FIG. 19 is a diagram related to power supply voltage fluctuation spectrum calculation in the first transition case, and FIG. 20 is a diagram related to ground voltage fluctuation spectrum calculation in the first transition case. FIG. 21 is a diagram related to power supply voltage fluctuation spectrum calculation in the second transition case, and FIG. 22 is a diagram related to ground voltage fluctuation spectrum calculation in the second transition case. Here, in creating FIGS. 19 to 22, Z vc_mcp was opened, and Z gc_mcp , Z v_mcp 3 , and Z g_mcp 3 were set to zero.
第1遷移ケースにおける調整対象値として電源電圧変動スペクトラムΔVDDQ_L2Hを算出する場合、図19に示される3つの閉路について回路方程式をたて(下記式(9))、それを解くことにより、下記式(10)に示される電源電圧変動スペクトラムΔVDDQ_L2Hが得られる。 When calculating the power supply voltage fluctuation spectrum ΔV DDQ_L2H as the adjustment target value in the first transition case, a circuit equation is established for the three closed loops shown in FIG. 19 (the following equation (9)), and the following equation is obtained by solving it. The power supply voltage fluctuation spectrum ΔV DDQ_L2H shown in (10) is obtained.
ここで、│A│、E及びZは、それぞれ、下記式(11)〜(13)で示される。 Here, | A |, E, and Z are represented by the following formulas (11) to (13), respectively.
同様に、第1遷移ケースにおける調整対象値としてグランド電圧変動スペクトラムΔVSSQ_L2Hを算出する場合、図20に示される3つの閉路について回路方程式をたて(下記式(14))、それを解くことにより、下記式(15)に示される電源電圧変動スペクトラムΔVSSQ_L2Hが得られる。 Similarly, when the ground voltage fluctuation spectrum ΔV SSQ_L2H is calculated as the adjustment target value in the first transition case, a circuit equation is established for the three closed loops shown in FIG. 20 (formula (14) below) and is solved. A power supply voltage fluctuation spectrum ΔV SSQ_L2H represented by the following formula (15) is obtained.
ここで、│A│、E及びZは、それぞれ、下記式(16)〜(18)で示される。 Here, | A |, E, and Z are represented by the following formulas (16) to (18), respectively.
一方、第2遷移ケースにおける調整対象値として電源電圧変動スペクトラムΔVDDQ_H2Lを算出する場合、図21に示される3つの閉路について回路方程式をたて(下記式(19))、それを解くことにより、下記式(20)に示される電源電圧変動スペクトラムΔVDDQ_H2Lが得られる。 On the other hand, when calculating the power supply voltage fluctuation spectrum ΔV DDQ_H2L as the adjustment target value in the second transition case, a circuit equation is established for the three closed circuits shown in FIG. 21 (the following equation (19)), and by solving it, A power supply voltage fluctuation spectrum ΔV DDQ_H2L represented by the following equation (20) is obtained.
ここで、│A│、E及びZは、それぞれ、下記式(21)〜(23)で示される。 Here, | A |, E, and Z are represented by the following formulas (21) to (23), respectively.
同様に、第2遷移ケースにおける調整対象値としてグランド電圧変動スペクトラムΔVSSQ_H2Lを算出する場合、図22に示される3つの閉路について回路方程式をたて(下記式(24))、それを解くことにより、下記式(25)に示される電源電圧変動スペクトラムΔVSSQ_H2Lが得られる。 Similarly, when the ground voltage fluctuation spectrum ΔV SSQ_H2L is calculated as the adjustment target value in the second transition case, a circuit equation is established for the three closed circuits shown in FIG. 22 (the following equation (24)), and is solved. Thus, a power supply voltage fluctuation spectrum ΔV SSQ_H2L represented by the following equation (25) is obtained.
ここで、│A│、E及びZは、それぞれ、下記式(26)〜(28)で示される。 Here, | A |, E, and Z are represented by the following formulas (26) to (28), respectively.
なお、本実施の形態においては、上述したように、Zvc_mcpを開放にし、Zgc_mcp、Zv_mcp3、Zg_mcp3をそれぞれゼロとして回路方程式を立てたが、これらを短絡したりインピーダンスゼロにしたりせず、4種のチップモデルのそれぞれと調整対象計インピーダンスモデルの組み合わせのそれぞれについて、4つの閉路を考慮して回路方程式を立てることとしても良い。
In the present embodiment, as described above, Z vc_mcp is opened, and Z gc_mcp , Z v_mcp3 , and
このようにして、第1遷移ケース及び第2遷移ケースの双方について調整対象値の算出(図11:ステップS103)を行った後、第1遷移ケースにおける電源/GND電圧変動スペクトラムと第2遷移ケースにおける電源/GND電圧変動スペクトラムとを比較して、調整必要性のより高い一方を選択する(ステップS104)。 In this way, after calculating the adjustment target value for both the first transition case and the second transition case (FIG. 11: step S103), the power supply / GND voltage fluctuation spectrum and the second transition case in the first transition case. Is compared with the power supply / GND voltage fluctuation spectrum in step S104, and one of the higher adjustment needs is selected (step S104).
ここで、本実施の形態においては、制約値に関しても、第1遷移ケースを想定して設定された制約値である第1制約値と第2遷移ケースを想定して設定された制約値である第2制約値の2種類用意してあり、ステップS104においていずれの遷移ケースに関する電源/GND電圧変動スペクトラムが選択されたのかを示す調整対象値選択情報に従って、第1制約値と第2制約値のいずれか一方を選択する(ステップS105)。 Here, in the present embodiment, the constraint values are also the constraint values set assuming the first and second transition cases, which are the constraint values set assuming the first transition case. Two types of second constraint values are prepared, and the first constraint value and the second constraint value are determined according to the adjustment target value selection information indicating which transition case the power supply / GND voltage fluctuation spectrum is selected in step S104. Either one is selected (step S105).
次いで、ステップS104で選択された第1遷移ケース又は第2遷移ケースにおける電源/GND電圧変動スペクトラムと、ステップS105において選択された第1制約値又は第2制約値とを比較し(ステップS106)、その比較結果に基づいて、設計指針を決定する(ステップS107)。 Next, the power supply / GND voltage fluctuation spectrum in the first transition case or the second transition case selected in step S104 is compared with the first constraint value or the second constraint value selected in step S105 (step S106). A design guideline is determined based on the comparison result (step S107).
ここで、決定される設計指針の例としては、例えば、1)電源/グランドパッド11,12における電圧変動値及びMCP内電源/グランド配線の良否判定結果、2)MCP電源/グランド配線のインピーダンスの最適値、3)MCP内電源/グランド配線の幅、長さ、厚さの最適値、4)電源/グランドパッド11,12から電源/グランド用端子までの距離の最適値、5)パッケージ基板層数の最適値、6)MCP内電源/グランド配線の配線長に対する最適配線幅、並びに、7)MCP内電源/グランド配線の配線幅に対する最適配線長などが挙げられる。また、これに代えて、電圧変動スペクトラムから、調整対象系において問題となりそうな箇所を特定し、その箇所を調整対象箇所として指摘するだけとしてもよい。
Here, as examples of design guidelines to be determined, for example, 1) the voltage fluctuation value in the power /
以上説明したように、本実施の形態によれば、一旦、チップモデルを作成してししまった後は、調整対象系に関する調整対象値は関連する閉路について回路方程式を解くだけで算出することができることから、例えば、パッケージ配線長を調整する等して設計変更した場合など、再チェックを簡易且つ短時間で行うことができる。 As described above, according to the present embodiment, once the chip model has been created, the adjustment target value related to the adjustment target system can be calculated simply by solving the circuit equation for the associated cycle. Therefore, the recheck can be performed easily and in a short time, for example, when the design is changed by adjusting the package wiring length.
なお、上述した実施の形態におけるステップS105(図11)では、一対の第1制約値及び第2制約値のうちから、いずれか一方を選択することとしていたが、例えば、図23に示されるように、既に動作確認された半導体パッケージに基づいて絶対基準ペア(使用条件にかかわらず選択されうるペア)や複数の制約値ペア1〜3といった複数の制約値ペアを用意しておき、パッケージの使用条件(動作周波数や負荷など)を示す選択基礎情報に基づいて制約値ペアを選択し(図23:ステップS105a)、その後、ステップS104における選択結果に関連した調整対象値選択情報に従って、ステップS105aにて選択された制約値ペアを構成する第1制約値と第2制約値のいずれか一方を選択する(ステップS105b)こととしても良い。 In step S105 (FIG. 11) in the above-described embodiment, one of the pair of first constraint values and second constraint values is selected. For example, as shown in FIG. In addition, a plurality of constraint value pairs such as an absolute reference pair (a pair that can be selected regardless of use conditions) and a plurality of constraint value pairs 1 to 3 are prepared based on a semiconductor package whose operation has already been confirmed. A constraint value pair is selected based on selection basic information indicating conditions (such as operating frequency and load) (FIG. 23: step S105a), and then, in step S105a, according to the adjustment target value selection information related to the selection result in step S104. And selecting one of the first constraint value and the second constraint value constituting the constraint value pair selected in step S105b. It may be.
また、図23に示されるように、設計指針を決定した後(ステップS107)、設計指針に従って調整対象系情報に変更を加え(ステップS108)、その後、再度、調整対象系インピーダンスモデルを算出して(ステップS102)、当該調整対象系インピーダンスモデルと先の処理において作成された第1チップモデル及び第2チップモデルとの組み合わせに基づいて、ステップS103以降の処理を自動的に再度行うこととしても良い。 As shown in FIG. 23, after the design guideline is determined (step S107), the adjustment target system information is changed according to the design guideline (step S108), and then the adjustment target system impedance model is calculated again. (Step S102) Based on the combination of the adjustment target system impedance model and the first chip model and the second chip model created in the previous processing, the processing after Step S103 may be automatically performed again. .
以上、マルチチップパッケージの場合を例にとり説明してきたが、本発明の概念は、マルチチップパッケージのみならず、シングルチップのパッケージにも適用可能であること明らかである。 As described above, the case of a multi-chip package has been described as an example. However, it is apparent that the concept of the present invention can be applied not only to a multi-chip package but also to a single-chip package.
また、本発明の概念は、パッケージ設計のみならず、例えば、図24に示されるようなパッケージを搭載したシステムの設計にも適用することができる。 The concept of the present invention can be applied not only to package design but also to the design of a system equipped with a package as shown in FIG.
図24を参照すると、当該システムは、電源(PS)部及びグランド(GND)部を有する電源装置110、プリント配線基板(PCB)120及びマルチチップパッケージ(MCP)100を備えている。プリント配線基板120上には、電気的構成要素として、大容量コンデンサ122、PCB上電源配線(又はPCB上電源プレーン)124、PCB上バイパスコンデンサ126、PCBの裏面上に設けられたバイパスコンデンサ128などが設けられている。マルチチップパッケージ100は、電源パッド11及びグランドパッド12を有する半導体チップ10及び半導体チップ20をパッケージ基板101上に積層してなるものである。半導体チップ10の電源パッド11には、電源用端子(ボール)102、スルーホール103及びMCP内電源配線104等を介して、電源が供給される。一方、半導体チップ10のグランドパッド12は、グランド用端子(ボール)105、スルーホール106及びMCP内グランド配線107等を介して、グランドに接続される。
Referring to FIG. 24, the system includes a
かかるシステムの電気的構成要素は、図25上段に示されるように、すべてRLCからなる受動回路ブロックとして表現することができる。この受動回路ブロックからなる調整対象系インピーダンスモデルを、図2に示されるように、図3〜図6に示される各チップモデルと接続し、図19〜図22を用いて説明したように回路方程式を解くことにより、多少計算量は増えるものの、トランジェント解析よりは少ない計算量で、変圧変動値を算出することができる。 The electrical components of such a system can be expressed as a passive circuit block consisting entirely of RLC, as shown in the upper part of FIG. As shown in FIG. 2, the adjustment target system impedance model composed of the passive circuit block is connected to each chip model shown in FIGS. 3 to 6, and the circuit equation as described with reference to FIGS. By solving the equation, although the calculation amount is somewhat increased, the transformation variation value can be calculated with a smaller calculation amount than the transient analysis.
そして、例えば、図11のステップS106に示されるようにして、調整対象値と制約値の比較をすることにより、調整対象値が制約値を超えてしまうような周波数部分に対応する調整対象系の部位を特定し、その部位を調整対象箇所として設計指針を決定することとしても良い(図25下段の例においては、MCP−PKG電源配線部分)。 Then, for example, as shown in step S106 of FIG. 11, by comparing the adjustment target value with the constraint value, the adjustment target system corresponding to the frequency portion where the adjustment target value exceeds the constraint value. A part may be specified, and the design guideline may be determined with the part as an adjustment target part (in the lower part of FIG. 25, the MCP-PKG power supply wiring part).
以上説明してきた設計方法は、その少なくとも一部をプログラム化することにより、設計支援用プログラム及び設計支援システムとして具現化することができる。 The design method described above can be embodied as a design support program and a design support system by programming at least a part thereof.
以下、設計支援システムの実現例について説明する。実現例による設計支援システムは、図26に示されるように、演算部210、主記憶220、補助記憶230、入力部240及び表示部250を備えている。
Hereinafter, an implementation example of the design support system will be described. As shown in FIG. 26, the design support system according to the implementation includes a
主記憶220は、例えば、DRAM装置で構成され、補助記憶230は、例えば、HDDやCD−ROMなどで構成される。また、入力部240は、例えば、キーボード及びマウスなどで構成され、表示部250は、例えば、CRTや、液晶ディスプレイなどで構成される。
The
より具体的には、上述した各実施の形態における設計方法の少なくとも一部を実装してなるプログラムは補助記憶230に格納されている。このプログラムは、主記憶220上に展開され、演算部210によって実行される。演算部210が当該プログラムを実行することにより、図26に示されるシステムは、前述した設計方法の少なくとも一部を具現化し、設計支援システムとして機能する。また、主記憶220上には、演算部210が当該プログラムに従って動作している間に生成したデータ及び演算部210により利用されるデータが一時的に記憶される。なお、一般にはコンピュータシステム上で本発明を実現する場合、上記したように主記憶220と補助記憶230とを分ける構成が主として採用されるが、概念的には両者をまとめて記憶部として捉えることも可能である。
More specifically, a program in which at least a part of the design method in each embodiment described above is implemented is stored in the
上述した各実施の形態による設計方法をプログラム上に実装して設計支援システムを構築する場合、調整対象値と制約値との周波数領域における比較結果に基づいて決定された設計指針を表示部250に表示させるステップを更に備えることとしても良い。
When a design support system is constructed by implementing the design method according to each of the above-described embodiments on a program, a design guideline determined based on a comparison result in the frequency domain between the adjustment target value and the constraint value is displayed on the
10 半導体チップ
11 電源パッド
12 グランドパッド
13 出力パッド
14 内部インピーダンス
20 半導体チップ
100 マルチチップパッケージ
101 パッケージ基板
102 電源用端子(ボール)
103 スルーホール
104 MCP内電源配線
105 グランド用端子(ボール)
106 スルーホール
107 MCP内グランド配線
110 電源
120 プリント配線基板(PCB)
122 大容量コンデンサ
124 PCB電源配線/プレーン
126 バイパスコンデンサ
128 バイパスコンデンサ
210 演算部
220 主記憶
230 補助記憶
240 入力部
250 表示部
DESCRIPTION OF
103 Through
106 Through-
122
Claims (40)
前記演算部が、互いに異なる第1チップモデル及び第2チップモデルと調整対象系インピーダンスモデルに基づいて第1電源/GND電圧変動スペクトラム及び第2電源/GND電圧変動スペクトラムを算出する算出ステップであって、前記第1チップモデル及び前記第2チップモデルは、前記半導体チップの出力値がローレベルからハイレベルに遷移する第1遷移ケースとハイレベルからローレベルに遷移する第2遷移ケースとの2つの遷移ケースのそれぞれに対応させて前記半導体チップを周波数領域にて表現するようにして作成されたモデルであり、前記調整対象系インピーダンスモデルは、前記半導体パッケージにおける前記半導体チップ以外の構成要素のうちの調整対象構成要素からなる調整対象系を周波数領域にて表現するようにして作成されたモデルであり、前記第1電源/GND電圧変動スペクトラム及び前記第2電源/GND電圧変動スペクトラムは、前記第1遷移ケースと前記第2遷移ケースとのそれぞれにおける電源/GND電圧変動スペクトラムである、算出ステップと、
前記演算部が、前記第1電源/GND電圧変動スペクトラムと前記第2電源/GND電圧変動スペクトラムのいずれか一方を選択する選択ステップと、
前記演算部が、周波数領域において予め定められた制約値と前記第1電源/GND電圧変動スペクトラム及び前記第2電源/GND電圧変動スペクトラムのうちの選択された電源/GND電圧変動スペクトラムとを比較して、当該比較結果に基づき前記調整対象系に対する設計指針を決定する設計指針決定ステップと
を備える設計方法。 A design method for a semiconductor package including a semiconductor chip, which causes a computer unit to function as a design support system by causing the calculation unit to execute a program stored in the storage unit in a computer system including a calculation unit and a storage unit. And
The arithmetic unit, in calculation output step calculate a first voltage fluctuation of power supply / GND spectrum and the second voltage fluctuation of power supply / GND spectrum based on the mutually different first chip model and a second chip model and adjusted based impedance model The first chip model and the second chip model include a first transition case in which an output value of the semiconductor chip transits from a low level to a high level and a second transition case in which the output value transits from a high level to a low level. It is a model created by expressing the semiconductor chip in the frequency domain corresponding to each of the two transition cases, and the adjustment target system impedance model is a component of the semiconductor package other than the semiconductor chip. To express the adjustment target system consisting of the adjustment target components in the frequency domain And a model created by the first voltage fluctuation of power supply / GND spectrum and said second voltage fluctuation of power supply / GND Spectrum voltage fluctuation of power supply / GND in each of the first transition case and the second transition case it is a spectrum, and the step de San,
The calculation unit, said first power supply / GND voltage selection step you select one of fluctuation spectrum and the second voltage fluctuation of power supply / GND spectrum,
The arithmetic unit compares the selected voltage fluctuation of power supply / GND spectrum of predetermined constraint value and the first voltage fluctuation of power supply / GND spectrum and said second voltage fluctuation of power supply / GND spectrum in the frequency domain And a design guideline determining step for determining a design guideline for the adjustment target system based on the comparison result.
請求項1記載の設計方法。 Of the first constraint value, which is a constraint value set assuming the first transition case, and the second constraint value, which is a constraint value set assuming the second transition case, constraints of transitions case corresponding to the selected voltage fluctuation of power supply / GND spectrum by hexene-option step, said selecting as a predetermined constraint value used for the comparison in the design guidelines determining step, the constraint value selection step In addition,
The design method according to claim 1.
前記算出ステップにおいて、前記演算部は、前記第1チップモデルを前記調整対象系インピーダンスモデルに接続して前記第1電源/GND電圧変動スペクトラムを算出すると共に前記第2チップモデルを前記調整対象系インピーダンスモデルに接続して前記第2電源/GND電圧変動スペクトラムを算出する、
請求項1乃至請求項2のいずれかに記載の設計方法。 The computing unit creates the first chip model and the second chip model based on semiconductor chip information about the semiconductor chip, and based on adjustment target system information about the adjustment target system, creating adjustment object system impedance model, and further comprising an impedance model building step,
Prior hexane out step, the arithmetic unit, the adjustment target the second chip model with and connecting the first chip model to the adjustment target system impedance model to calculate a first voltage fluctuation of power supply / GND Spectrum Connecting to a system impedance model to calculate the second power supply / GND voltage fluctuation spectrum ;
Design method according to any one of claims 1 to 2.
前記チップモデル作成ステップにおいて前記演算部が実行する処理は、
前記pMOS回路及び前記nMOS回路をそれぞれインピーダンス表現してなるpMOS回路インピーダンス及びnMOS回路インピーダンスを直列に接続してなる出力部インピーダンスと前記内部インピーダンスとを前記電源パッド及び前記グランドパッド間において並列に接続し、且つ、前記第1遷移ケースにおける変動電流値を考慮した電流源である第1電流源を当該第1遷移ケースに対応した前記pMOS回路インピーダンスに並列に接続することにより、前記第1チップモデルを作成する第1チップモデル作成ステップと、
前記pMOS回路及び前記nMOS回路をそれぞれインピーダンス表現してなるpMOS回路インピーダンス及びnMOS回路インピーダンスを直列に接続してなる出力部インピーダンスと前記内部インピーダンスとを前記電源パッド及び前記グランドパッド間において並列に接続し、且つ、前記第2遷移ケースにおける変動電流値を考慮した電流源である第2電流源を当該第2遷移ケースに対応した前記nMOS回路インピーダンスに並列に接続することにより、前記第2チップモデルを作成する第2チップモデル作成ステップと
を備えている、請求項3記載の設計方法。 The semiconductor chip includes a power supply pad and a ground pad, an output part composed of a pMOS circuit and an nMOS circuit connected between the power supply pad and the ground pad, an output pad drawn from a connection part with the pMOS circuit and the nMOS circuit, And an internal component represented by an internal impedance inserted in parallel with the output unit between the power supply pad and the ground pad,
The processing executed by the calculation unit in the chip model creation step is as follows:
An output impedance obtained by connecting a pMOS circuit impedance and an nMOS circuit impedance representing impedance of the pMOS circuit and the nMOS circuit in series and an internal impedance are connected in parallel between the power supply pad and the ground pad. In addition, the first chip model is obtained by connecting a first current source, which is a current source in consideration of a fluctuation current value in the first transition case, in parallel to the pMOS circuit impedance corresponding to the first transition case. A first chip model creation step to be created;
An output impedance obtained by connecting a pMOS circuit impedance and an nMOS circuit impedance representing impedance of the pMOS circuit and the nMOS circuit in series and an internal impedance are connected in parallel between the power supply pad and the ground pad. In addition, the second chip model is obtained by connecting a second current source, which is a current source considering the fluctuation current value in the second transition case, in parallel to the nMOS circuit impedance corresponding to the second transition case. The design method according to claim 3 , further comprising: a second chip model creation step of creating.
前記第1チップモデル作成ステップにおいて、前記演算部は、オン状態の前記pMOS回路に対応する前記pMOS回路インピーダンスを用いると共にオフ状態の前記nMOS回路に対応する前記nMOS回路インピーダンスを用いて、前記第1チップモデルを作成し、
前記第2チップモデル作成ステップにおいて、前記演算部は、いずれもオン状態の前記pMOS回路及び前記nMOS回路に対応する前記pMOS回路インピーダンス及び前記nMOS回路インピーダンスを用いて、前記第2チップモデルを作成する、
請求項4記載の設計方法。 When creating a model for power supply voltage fluctuation,
In the first chip model creating step , the arithmetic unit uses the pMOS circuit impedance corresponding to the pMOS circuit in the on state and uses the nMOS circuit impedance corresponding to the nMOS circuit in the off state. Create a chip model,
In the second chip model creation step , the calculation unit creates the second chip model using the pMOS circuit impedance and the nMOS circuit impedance corresponding to the pMOS circuit and the nMOS circuit , both of which are on. ,
The design method according to claim 4 .
前記オフ状態のnMOS回路インピーダンスは、前記出力パッドと前記グランドパッドとの間にキャパシタ及び抵抗が直列に接続されてなる等価回路モデルを用いて算出されるものであり、
前記オン状態のnMOS回路インピーダンスは、前記出力パッドと前記グランドパッドとの間にキャパシタ及び抵抗が並列に接続されてなる等価回路モデルを用いて算出されるものである
請求項5記載の設計方法。 The on-state pMOS circuit impedance is calculated using an equivalent circuit model in which a capacitor and a resistor are connected in parallel between the power supply pad and the output pad,
The off-state nMOS circuit impedance is calculated using an equivalent circuit model in which a capacitor and a resistor are connected in series between the output pad and the ground pad.
The design method according to claim 5, wherein the on-state nMOS circuit impedance is calculated using an equivalent circuit model in which a capacitor and a resistor are connected in parallel between the output pad and the ground pad.
前記第2チップモデル作成ステップは、前記演算部が、前記出力パッドと前記グランドパッドとの間に前記所定の外部負荷モデルを接続した上で、該所定の外部負荷モデルのインピーダンスがオン状態の前記nMOS回路に対応する前記nMOS回路インピーダンスよりも遥かに大きいと仮定して、前記第2遷移ケースにおいて前記電源パッドを流れる電流のほとんどが、オン状態の前記pMOS回路に対応する前記pMOS回路インピーダンスとオン状態の前記nMOS回路に対応する前記nMOS回路インピーダンスに流れるものとし、前記第2電流源を算出するものである、
請求項5又は請求項6記載の設計方法。 In the first chip model creation step, the calculation unit connects the predetermined external load model between the output pad and the ground pad, and then the impedance of the predetermined external load model is in an off state. Assuming that it is much smaller than the nMOS circuit impedance corresponding to the circuit, most of the current flowing through the power supply pad in the first transition case is the pMOS circuit impedance corresponding to the pMOS circuit in the on state and the predetermined The first current source is calculated by flowing into the external load model of
In the second chip model creation step, the computing unit connects the predetermined external load model between the output pad and the ground pad, and the impedance of the predetermined external load model is in an ON state. Assuming that it is much larger than the nMOS circuit impedance corresponding to the nMOS circuit, most of the current flowing through the power supply pad in the second transition case is substantially equal to the pMOS circuit impedance corresponding to the on-state pMOS circuit. Flow into the nMOS circuit impedance corresponding to the nMOS circuit in the state, and calculate the second current source;
The design method according to claim 5 or 6 .
前記第1チップモデル作成ステップにおいて、前記演算部は、いずれもオン状態の前記pMOS回路及び前記nMOS回路に対応する前記pMOS回路インピーダンス及び前記nMOS回路インピーダンスを用いて、前記第1チップモデルを作成し、
前記第2チップモデル作成ステップにおいて、前記演算部は、オフ状態の前記pMOS回路に対応する前記pMOS回路インピーダンスを用いると共にオン状態の前記nMOS回路に対応する前記nMOS回路インピーダンスを用いて、前記第2チップモデルを作成する、
請求項4乃至請求項7のいずれかに記載の設計方法。 When creating a model for GND voltage fluctuation,
In the first chip model creation step , the calculation unit creates the first chip model using the pMOS circuit impedance and the nMOS circuit impedance corresponding to the pMOS circuit and the nMOS circuit , both of which are in the on state. ,
In the second chip model creating step , the arithmetic unit uses the pMOS circuit impedance corresponding to the pMOS circuit in the off state and uses the nMOS circuit impedance corresponding to the nMOS circuit in the on state. Create a chip model,
Design method according to any one of claims 4 to 7.
前記オフ状態のpMOS回路インピーダンスは、前記電源パッドと前記出力パッドとの間にキャパシタ及び抵抗が直列に接続されてなる等価回路モデルを用いて算出されるものであり、
前記オン状態のnMOS回路インピーダンスは、前記出力パッドと前記グランドパッドとの間にキャパシタ及び抵抗が並列に接続されてなる等価回路モデルを用いて算出されるものである
請求項8記載の設計方法。 The on-state pMOS circuit impedance is calculated using an equivalent circuit model in which a capacitor and a resistor are connected in parallel between the power supply pad and the output pad,
The off-state pMOS circuit impedance is calculated using an equivalent circuit model in which a capacitor and a resistor are connected in series between the power supply pad and the output pad,
The design method according to claim 8, wherein the on-state nMOS circuit impedance is calculated using an equivalent circuit model in which a capacitor and a resistor are connected in parallel between the output pad and the ground pad.
前記第2チップモデル作成ステップは、前記演算部が、前記出力パッドと前記グランドパッドとの間に前記所定の外部負荷モデルを接続した上で、該所定の外部負荷モデルのインピーダンスがオフ状態の前記pMOS回路に対応する前記pMOS回路インピーダンスよりも遥かに小さいと仮定して、前記第2遷移ケースにおいて前記グランドパッドを流れる電流のほとんどが、オン状態の前記nMOS回路に対応する前記nMOS回路インピーダンスと前記所定の外部負荷モデルを流れるものとし、前記第2電流源を算出するものである、
請求項8又は請求項9記載の設計方法。 In the first chip model creation step, the computing unit connects a predetermined external load model between the output pad and the ground pad, and the impedance of the predetermined external load model is on. Assuming that it is much larger than the nMOS circuit impedance corresponding to the circuit, most of the current flowing through the ground pad in the first transition case is the pMOS circuit impedance corresponding to the pMOS circuit in the on state and the on state. A current flowing through the nMOS circuit impedance corresponding to the nMOS circuit, and calculating the first current source,
In the second chip model creation step, the computing unit connects the predetermined external load model between the output pad and the ground pad, and the impedance of the predetermined external load model is in an off state. Assuming that it is much smaller than the pMOS circuit impedance corresponding to the pMOS circuit, most of the current flowing through the ground pad in the second transition case is the nMOS circuit impedance corresponding to the nMOS circuit in the on state and the The second current source is calculated by flowing through a predetermined external load model.
The design method according to claim 8 or 9 .
請求項1乃至請求項10のいずれかに記載の設計方法。 Prior hexane out step, the arithmetic unit is connected to the first chip model and the adjustment target system impedance model, by solving the closed circuit equation, while calculating the first voltage fluctuation of power supply / GND Spectrum The second power supply / GND voltage fluctuation spectrum is calculated by connecting the adjustment target system impedance model and the second chip model and solving a closed circuit equation.
Design method according to any one of claims 1 to 10.
前記調整対象系インピーダンスモデルは、当該調整対象系を前提として作成されたものである、
請求項1乃至請求項11のいずれかに記載の設計方法。 The adjustment target system includes an electrical component on a printed wiring board on which the semiconductor package is mounted,
The adjustment target system impedance model is created on the assumption of the adjustment target system.
Design method according to any one of claims 1 to 11.
請求項1乃至請求項12のいずれかに記載の設計方法。 In the design guideline determination step , the calculation unit sets the design target part as a part to be adjusted corresponding to a frequency part where the selected power supply / GND voltage fluctuation spectrum exceeds the constraint value. Determine the guidelines,
Design method according to any one of claims 1 to 12.
互いに異なる第1チップモデル及び第2チップモデルを提供するチップモデル提供部であって、前記第1チップモデル及び前記第2チップモデルは、前記半導体チップの出力値がローレベルからハイレベルに遷移する第1遷移ケースとハイレベルからローレベルに遷移する第2遷移ケースとの2つの遷移ケースのそれぞれに対応させて前記半導体チップを周波数領域にて表現するようにして作成されたモデルである、チップモデル提供部と、
前記半導体パッケージにおける前記半導体チップ以外の構成要素のうちの調整対象構成要素からなる調整対象系を周波数領域にて表現してなる調整対象系インピーダンスモデルを提供するインピーダンスモデル提供部と、
前記第1チップモデル及び前記第2チップモデルのそれぞれを前記調整対象系インピーダンスモデルと接続して前記第1遷移ケースと前記第2遷移ケースとのそれぞれにおける電源/GND電圧変動スペクトラムである第1電源/GND電圧変動スペクトラム及び第2電源/GND電圧変動スペクトラムを算出する算出部と、
前記第1電源/GND電圧変動スペクトラムと前記第2電源/GND電圧変動スペクトラムのいずれか一方を選択する選択部と、
周波数領域において予め定められた制約値を提供する制約値提供部と、
該制約値と前記第1電源/GND電圧変動スペクトラム及び前記第2電源/GND電圧変動スペクトラムのうちの選択された電源/GND電圧変動スペクトラムとを比較して、当該比較結果に基づき前記調整対象系に対する設計支援情報を決定する設計支援情報決定部と、
前記設計支援情報を表示する表示部と
を備える設計支援システム。 A design support system for a semiconductor package including a semiconductor chip,
A chip model providing unit that provides a first chip model and a second chip model that are different from each other, wherein the output value of the semiconductor chip transitions from a low level to a high level in the first chip model and the second chip model. A chip that is a model created by expressing the semiconductor chip in the frequency domain in correspondence with each of two transition cases, a first transition case and a second transition case that transitions from a high level to a low level. A model provider,
An impedance model providing unit that provides an adjustment target system impedance model that expresses an adjustment target system including an adjustment target component of components other than the semiconductor chip in the semiconductor package in a frequency domain;
A first power supply that is a power supply / GND voltage fluctuation spectrum in each of the first transition case and the second transition case by connecting each of the first chip model and the second chip model to the adjustment target system impedance model. a calculation output section you calculate a / GND voltage fluctuation spectrum and the second voltage fluctuation of power supply / GND spectrum,
And that selection selecting section to select one of the first voltage fluctuation of power supply / GND spectrum and the second voltage fluctuation of power supply / GND spectrum,
A constraint value providing unit that provides a predetermined constraint value in the frequency domain;
The restriction value is compared with the selected power supply / GND voltage fluctuation spectrum of the first power supply / GND voltage fluctuation spectrum and the second power supply / GND voltage fluctuation spectrum, and the adjustment target system is based on the comparison result. A design support information determination unit for determining design support information for
A design support system comprising: a display unit that displays the design support information.
前記制約値提供部は、
前記第1遷移ケースを想定して設定された制約値である第1制約値と前記第2遷移ケースを想定して設定された制約値である第2制約値を少なくとも保持する制約値保持部と、
前記電源/GND電圧変動スペクトラム選択情報に従って、前記選択された電源/GND電圧変動スペクトラムに対応する遷移ケースに関する前記第1制約値又は前記第2制約値のいずれか一方を、前記設計指針決定部において前記比較に用いられる前記予め定められた制約値として選択する制約値選択部とを
備える、請求項14記載の設計支援システム。 Before cyclohexene selecting section, the first voltage fluctuation of power supply / GND spectrum and the second power supply / GND power supply information indicating the selected one of the voltage fluctuation spectrum with respect to the constraint value providing unit / GND voltage fluctuation spectrum Output as selection information,
The constraint value providing unit includes:
A constraint value holding unit that holds at least a first constraint value that is a constraint value set assuming the first transition case and a second constraint value that is a constraint value set assuming the second transition case; ,
In accordance with the power supply / GND voltage fluctuation spectrum selection information, either the first constraint value or the second constraint value related to the transition case corresponding to the selected power supply / GND voltage fluctuation spectrum is determined in the design guideline determination unit. The design support system of Claim 14 provided with the constraint value selection part selected as the said predetermined constraint value used for the said comparison.
前記チップモデル提供部は、
前記pMOS回路及び前記nMOS回路をそれぞれインピーダンス表現してなるpMOS回路インピーダンス及びnMOS回路インピーダンスを直列に接続してなる出力部インピーダンスと前記内部インピーダンスとを前記電源パッド及び前記グランドパッド間において並列に接続し、且つ、前記第1遷移ケースにおける変動電流値を考慮した電流源である第1電流源を当該第1遷移ケースに対応した前記pMOS回路インピーダンスに並列に接続することにより、前記第1チップモデルを作成する第1チップモデル作成部と、
前記pMOS回路及び前記nMOS回路をそれぞれインピーダンス表現してなるpMOS回路インピーダンス及びnMOS回路インピーダンスを直列に接続してなる出力部インピーダンスと前記内部インピーダンスとを前記電源パッド及び前記グランドパッド間において並列に接続し、且つ、前記第2遷移ケースにおける変動電流値を考慮した電流源である第2電流源を当該第2遷移ケースに対応した前記nMOS回路インピーダンスに並列に接続することにより、前記第2チップモデルを作成する第2チップモデル作成部と
を備えている、請求項14乃至請求項15のいずれかに記載の設計支援システム。 The semiconductor chip includes a power supply pad and a ground pad, an output part composed of a pMOS circuit and an nMOS circuit connected between the power supply pad and the ground pad, an output pad drawn from a connection part with the pMOS circuit and the nMOS circuit, And an internal component represented by an internal impedance inserted in parallel with the output unit between the power supply pad and the ground pad,
The chip model providing unit includes:
An output impedance obtained by connecting a pMOS circuit impedance and an nMOS circuit impedance representing impedance of the pMOS circuit and the nMOS circuit in series and an internal impedance are connected in parallel between the power supply pad and the ground pad. In addition, the first chip model is obtained by connecting a first current source, which is a current source in consideration of a fluctuation current value in the first transition case, in parallel to the pMOS circuit impedance corresponding to the first transition case. A first chip model creation unit to be created;
An output impedance obtained by connecting a pMOS circuit impedance and an nMOS circuit impedance representing impedance of the pMOS circuit and the nMOS circuit in series and an internal impedance are connected in parallel between the power supply pad and the ground pad. In addition, the second chip model is obtained by connecting a second current source, which is a current source considering the fluctuation current value in the second transition case, in parallel to the nMOS circuit impedance corresponding to the second transition case. The design support system according to any one of claims 14 to 15, further comprising: a second chip model creation unit to create.
前記第2チップモデル作成部は、電源電圧変動用のモデルを作成する場合において、いずれもオン状態の前記pMOS回路及び前記nMOS回路に対応する前記pMOS回路インピーダンス及び前記nMOS回路インピーダンスを用いて、前記第2チップモデルを作成する、
請求項16記載の設計支援システム。 The first chip model creation unit uses the pMOS circuit impedance corresponding to the pMOS circuit in the on state and the nMOS circuit impedance corresponding to the nMOS circuit in the off state when creating a model for power supply voltage fluctuation The first chip model is created using
The second chip model creation unit uses the pMOS circuit impedance and the nMOS circuit impedance corresponding to the pMOS circuit and the nMOS circuit, both of which are turned on, when creating a model for power supply voltage fluctuation, Create a second chip model,
The design support system according to claim 16 .
前記オフ状態のnMOS回路インピーダンスは、前記出力パッドと前記グランドパッドとの間にキャパシタ及び抵抗が直列に接続されてなる等価回路モデルを用いて算出されるものであり、
前記オン状態のnMOS回路インピーダンスは、前記出力パッドと前記グランドパッドとの間にキャパシタ及び抵抗が並列に接続されてなる等価回路モデルを用いて算出されるものである
請求項17記載の設計支援システム。 The on-state pMOS circuit impedance is calculated using an equivalent circuit model in which a capacitor and a resistor are connected in parallel between the power supply pad and the output pad,
The off-state nMOS circuit impedance is calculated using an equivalent circuit model in which a capacitor and a resistor are connected in series between the output pad and the ground pad.
18. The design support system according to claim 17, wherein the on-state nMOS circuit impedance is calculated using an equivalent circuit model in which a capacitor and a resistor are connected in parallel between the output pad and the ground pad. .
前記第2チップモデル作成部は、電源電圧変動用のモデルを作成する場合において、前記出力パッドと前記グランドパッドとの間に前記所定の外部負荷モデルを接続した上で、該所定の外部負荷モデルのインピーダンスがオン状態の前記nMOS回路に対応する前記nMOS回路インピーダンスよりも遥かに大きいと仮定して、前記第2遷移ケースにおいて前記電源パッドを流れる電流のほとんどが、オン状態の前記pMOS回路に対応する前記pMOS回路インピーダンスとオン状態の前記nMOS回路に対応する前記nMOS回路インピーダンスに流れるものとし、前記第2電流源を算出するものである、
請求項17又は請求項18記載の設計支援システム。 The first chip model creating unit connects a predetermined external load model between the output pad and the ground pad when creating a model for power supply voltage fluctuation, and then determines the predetermined external load model. Assuming that the impedance is much smaller than the nMOS circuit impedance corresponding to the nMOS circuit in the off state, most of the current flowing through the power supply pad in the first transition case corresponds to the pMOS circuit in the on state. The pMOS circuit impedance and the predetermined external load model are assumed to flow, and the first current source is calculated.
The second chip model creation unit connects the predetermined external load model between the output pad and the ground pad when generating a model for power supply voltage fluctuation, and then the predetermined external load model Assuming that the impedance of the nMOS circuit is much larger than the nMOS circuit impedance corresponding to the nMOS circuit in the on state, most of the current flowing through the power supply pad corresponds to the pMOS circuit in the on state in the second transition case. The second current source is calculated by flowing into the pMOS circuit impedance and the nMOS circuit impedance corresponding to the on-state nMOS circuit.
The design support system according to claim 17 or claim 18 .
前記第2チップモデル作成部は、GND電圧変動用のモデルを作成する場合において、オフ状態の前記pMOS回路に対応する前記pMOS回路インピーダンスを用いると共にオン状態の前記nMOS回路に対応する前記nMOS回路インピーダンスを用いて、前記第2チップモデルを作成する、
請求項16乃至請求項19のいずれかに記載の設計支援システム。 The first chip model creation unit uses the pMOS circuit impedance and the nMOS circuit impedance corresponding to the pMOS circuit and the nMOS circuit, both of which are turned on, when creating a model for GND voltage fluctuation, Create the first chip model,
The second chip model creating unit uses the pMOS circuit impedance corresponding to the pMOS circuit in the off state and the nMOS circuit impedance corresponding to the nMOS circuit in the on state when creating a model for GND voltage fluctuation. The second chip model is created using
The design support system according to any one of claims 16 to 19 .
前記オフ状態のpMOS回路インピーダンスは、前記電源パッドと前記出力パッドとの間にキャパシタ及び抵抗が直列に接続されてなる等価回路モデルを用いて算出されるものであり、
前記オン状態のnMOS回路インピーダンスは、前記出力パッドと前記グランドパッドとの間にキャパシタ及び抵抗が並列に接続されてなる等価回路モデルを用いて算出されるものである
請求項20記載の設計支援システム。 The on-state pMOS circuit impedance is calculated using an equivalent circuit model in which a capacitor and a resistor are connected in parallel between the power supply pad and the output pad,
The off-state pMOS circuit impedance is calculated using an equivalent circuit model in which a capacitor and a resistor are connected in series between the power supply pad and the output pad,
The design support system according to claim 20, wherein the on-state nMOS circuit impedance is calculated using an equivalent circuit model in which a capacitor and a resistor are connected in parallel between the output pad and the ground pad. .
前記第2チップモデル作成部は、GND電圧変動用のモデルを作成する場合において、前記出力パッドと前記グランドパッドとの間に前記所定の外部負荷モデルを接続した上で、該所定の外部負荷モデルのインピーダンスがオフ状態の前記pMOS回路に対応する前記pMOS回路インピーダンスよりも遥かに小さいと仮定して、前記第2遷移ケースにおいて前記グランドパッドを流れる電流のほとんどが、オン状態の前記nMOS回路に対応する前記nMOS回路インピーダンスと前記所定の外部負荷モデルを流れるものとし、前記第2電流源を算出するものである、
請求項20又は請求項21記載の設計支援システム。 The first chip model creation unit connects a predetermined external load model between the output pad and the ground pad when creating a GND voltage variation model, and then determines the predetermined external load model. Assuming that the impedance is much larger than the nMOS circuit impedance corresponding to the nMOS circuit in the on state, most of the current flowing through the ground pad in the first transition case corresponds to the pMOS circuit in the on state. The first current source is calculated by flowing into the nMOS circuit impedance corresponding to the pMOS circuit impedance and the nMOS circuit in the on state.
The second chip model creation unit connects the predetermined external load model between the output pad and the ground pad when creating a GND voltage variation model, and then the predetermined external load model. Assuming that the impedance of the pMOS circuit is much smaller than the pMOS circuit impedance corresponding to the pMOS circuit in the off state, most of the current flowing through the ground pad in the second transition case corresponds to the nMOS circuit in the on state. The nMOS circuit impedance and the predetermined external load model are assumed to flow, and the second current source is calculated.
The design support system according to claim 20 or claim 21 .
請求項14乃至請求項22のいずれかに記載の設計支援システム。 Before hexane detecting section, and connect the first chip model and the adjustment target system impedance model, by solving the closed circuit equation, while calculating the first voltage fluctuation of power supply / GND spectrum, the adjustment object system Calculating the second power supply / GND voltage fluctuation spectrum by connecting an impedance model and the second chip model and solving a closed circuit equation;
The design support system according to any one of claims 14 to 22 .
前記調整対象系インピーダンスモデルは、当該調整対象系を前提として作成されたものである、
請求項14乃至請求項23のいずれかに記載の設計支援システム。 The adjustment target system includes an electrical component on a printed wiring board on which the semiconductor package is mounted,
The adjustment target system impedance model is created on the assumption of the adjustment target system.
The design support system according to any one of claims 14 to 23 .
請求項14乃至請求項24のいずれかに記載の設計支援システム。 The design support information determination unit determines the design support information by using a part of the adjustment target system corresponding to a frequency portion where the selected power supply / GND voltage fluctuation spectrum exceeds the constraint value as an adjustment target part. To
The design support system according to any one of claims 14 to 24 .
前記所定の処理は、
互いに異なる第1チップモデル及び第2チップモデルと調整対象系インピーダンスモデルに基づいて第1電源/GND電圧変動スペクトラム及び第2電源/GND電圧変動スペクトラムを算出する算出ステップであって、前記第1チップモデル及び前記第2チップモデルは、前記半導体チップの出力値がローレベルからハイレベルに遷移する第1遷移ケースとハイレベルからローレベルに遷移する第2遷移ケースとの2つの遷移ケースのそれぞれに対応させて前記半導体チップを周波数領域にて表現するようにして作成されたモデルであり、前記調整対象系インピーダンスモデルは、前記半導体パッケージにおける前記半導体チップ以外の構成要素のうちの調整対象構成要素からなる調整対象系を周波数領域にて表現するようにして作成されたモデルであり、前記第1電源/GND電圧変動スペクトラム及び前記第2電源/GND電圧変動スペクトラムは、前記第1遷移ケースと前記第2遷移ケースとのそれぞれにおける電源/GND電圧変動スペクトラムである、算出ステップと、
前記第1電源/GND電圧変動スペクトラムと前記第2電源/GND電圧変動スペクトラムのいずれか一方を選択する選択ステップと、
周波数領域において予め定められた制約値と前記第1電源/GND電圧変動スペクトラム及び前記第2電源/GND電圧変動スペクトラムのうちの選択された電源/GND電圧変動スペクトラムとを比較して、当該比較結果に基づき前記調整対象系に対する設計支援情報を決定する設計支援情報決定ステップと、
前記設計支援情報を前記表示部に表示する表示ステップと
を備えるプログラム。 A program for causing a computer unit to perform predetermined processing in a computer system including a calculation unit, a storage unit, and a display unit, and causing the computer system to function as a design support system for a semiconductor package including a semiconductor chip. ,
The predetermined process is:
A calculated output step you calculate a first voltage fluctuation of power supply / GND spectrum and the second voltage fluctuation of power supply / GND spectrum based on the mutually different first chip model and a second chip model and adjusted based impedance model, the first The one-chip model and the second chip model include two transition cases, a first transition case in which the output value of the semiconductor chip transitions from a low level to a high level and a second transition case in which the output value transitions from a high level to a low level. It is a model created so as to represent the semiconductor chip in the frequency domain in correspondence with each, and the adjustment target system impedance model is an adjustment target configuration among components other than the semiconductor chip in the semiconductor package Created to express the adjustment target system consisting of elements in the frequency domain. A model, the first voltage fluctuation of power supply / GND spectrum and said second voltage fluctuation of power supply / GND spectrum is voltage fluctuation of power supply / GND spectrum at each of the said first transition case the second transition case, calculation Step out,
A selection step you select one of the first voltage fluctuation of power supply / GND spectrum and the second voltage fluctuation of power supply / GND spectrum,
By comparing the selected voltage fluctuation of power supply / GND spectrum of predetermined constraint value and the first voltage fluctuation of power supply / GND spectrum and said second voltage fluctuation of power supply / GND spectrum in the frequency domain, the comparison result Design support information determination step for determining design support information for the adjustment target system based on
A display step of displaying the design support information on the display unit.
前記所定の処理は、前記選択ステップにより選択された電源/GND電圧変動スペクトラムに対応する遷移ケースに関する前記第1制約値又は前記第2制約値のいずれか一方を、前記設計指針決定ステップにおいて前記比較に用いる前記予め定められた制約値として選択する制約値選択ステップを更に備える、
請求項26記載のプログラム。 The storage unit holds at least a first constraint value that is a constraint value set assuming the first transition case and a second constraint value that is a constraint value set assuming the second transition case. Has been
The predetermined process is either before the first constraint of transitions case corresponding to the selected voltage fluctuation of power supply / GND spectrum by hexene-option step or the second constraint value, in the design guideline decision step Further comprising a constraint value selection step of selecting the predetermined constraint value used for the comparison.
The program according to claim 26 .
前記算出ステップは、前記第1チップモデルを前記調整対象系インピーダンスモデルに接続して前記第1電源/GND電圧変動スペクトラムを算出すると共に前記第2チップモデルを前記調整対象系インピーダンスモデルに接続して前記第2電源/GND電圧変動スペクトラムを算出する、
請求項26乃至請求項27のいずれかに記載のプログラム。 The predetermined processing is based on the chip model creation step of creating the first chip model and the second chip model based on the semiconductor chip information on the semiconductor chip, and on the adjustment target system information on the adjustment target system, An impedance model creating step of creating the adjustment target system impedance model,
Before hexane output step, connecting said first chip model to the adjustment target system impedance model the second chip model to calculate the first voltage fluctuation of power supply / GND spectrum connected to the adjustment target system impedance model And calculating the second power supply / GND voltage fluctuation spectrum .
The program according to any one of claims 26 to 27 .
前記チップモデル作成ステップは、
前記pMOS回路及び前記nMOS回路をそれぞれインピーダンス表現してなるpMOS回路インピーダンス及びnMOS回路インピーダンスを直列に接続してなる出力部インピーダンスと前記内部インピーダンスとを前記電源パッド及び前記グランドパッド間において並列に接続し、且つ、前記第1遷移ケースにおける変動電流値を考慮した電流源である第1電流源を当該第1遷移ケースに対応した前記pMOS回路インピーダンスに並列に接続することにより、前記第1チップモデルを作成する第1チップモデル作成ステップと、
前記pMOS回路及び前記nMOS回路をそれぞれインピーダンス表現してなるpMOS回路インピーダンス及びnMOS回路インピーダンスを直列に接続してなる出力部インピーダンスと前記内部インピーダンスとを前記電源パッド及び前記グランドパッド間において並列に接続し、且つ、前記第2遷移ケースにおける変動電流値を考慮した電流源である第2電流源を当該第2遷移ケースに対応した前記nMOS回路インピーダンスに並列に接続することにより、前記第2チップモデルを作成する第2チップモデル作成ステップと
を備えている、請求項28記載のプログラム。 The semiconductor chip includes a power supply pad and a ground pad, an output part composed of a pMOS circuit and an nMOS circuit connected between the power supply pad and the ground pad, an output pad drawn from a connection part with the pMOS circuit and the nMOS circuit, And an internal component represented by an internal impedance inserted in parallel with the output unit between the power supply pad and the ground pad,
The chip model creation step includes
An output impedance obtained by connecting a pMOS circuit impedance and an nMOS circuit impedance representing impedance of the pMOS circuit and the nMOS circuit in series and an internal impedance are connected in parallel between the power supply pad and the ground pad. In addition, the first chip model is obtained by connecting a first current source, which is a current source in consideration of a fluctuation current value in the first transition case, in parallel to the pMOS circuit impedance corresponding to the first transition case. A first chip model creation step to be created;
An output impedance obtained by connecting a pMOS circuit impedance and an nMOS circuit impedance representing impedance of the pMOS circuit and the nMOS circuit in series and an internal impedance are connected in parallel between the power supply pad and the ground pad. In addition, the second chip model is obtained by connecting a second current source, which is a current source considering the fluctuation current value in the second transition case, in parallel to the nMOS circuit impedance corresponding to the second transition case. The program according to claim 28 , further comprising: a second chip model creating step for creating.
前記第2チップモデル作成ステップは、電源電圧変動用のモデルを作成する場合において、いずれもオン状態の前記pMOS回路及び前記nMOS回路に対応する前記pMOS回路インピーダンス及び前記nMOS回路インピーダンスを用いて、前記第2チップモデルを作成する、
請求項29記載のプログラム。 The first chip model creating step uses the pMOS circuit impedance corresponding to the pMOS circuit in the on state and the nMOS circuit impedance corresponding to the nMOS circuit in the off state when creating a model for power supply voltage fluctuation. The first chip model is created using
The second chip model creating step uses the pMOS circuit impedance and the nMOS circuit impedance corresponding to the pMOS circuit and the nMOS circuit, both of which are turned on, when creating a model for power supply voltage fluctuation, Create a second chip model,
30. The program according to claim 29 .
前記オフ状態のnMOS回路インピーダンスは、前記出力パッドと前記グランドパッドとの間にキャパシタ及び抵抗が直列に接続されてなる等価回路モデルを用いて算出されるものであり、
前記オン状態のnMOS回路インピーダンスは、前記出力パッドと前記グランドパッドとの間にキャパシタ及び抵抗が並列に接続されてなる等価回路モデルを用いて算出されるものである
請求項30記載のプログラム。 The on-state pMOS circuit impedance is calculated using an equivalent circuit model in which a capacitor and a resistor are connected in parallel between the power supply pad and the output pad,
The off-state nMOS circuit impedance is calculated using an equivalent circuit model in which a capacitor and a resistor are connected in series between the output pad and the ground pad.
The program according to claim 30, wherein the on-state nMOS circuit impedance is calculated using an equivalent circuit model in which a capacitor and a resistor are connected in parallel between the output pad and the ground pad.
前記第2チップモデル作成ステップは、電源電圧変動用のモデルを作成する場合において、前記出力パッドと前記グランドパッドとの間に前記所定の外部負荷モデルを接続した上で、該所定の外部負荷モデルのインピーダンスがオン状態の前記nMOS回路に対応する前記nMOS回路インピーダンスよりも遥かに大きいと仮定して、前記第2遷移ケースにおいて前記電源パッドを流れる電流のほとんどが、オン状態の前記pMOS回路に対応する前記pMOS回路インピーダンスとオン状態の前記nMOS回路に対応する前記nMOS回路インピーダンスに流れるものとし、前記第2電流源を算出するものである、
請求項30又は請求項31記載のプログラム。 In the first chip model creation step, when creating a model for power supply voltage fluctuation, a predetermined external load model is connected between the output pad and the ground pad, and then the predetermined external load model Assuming that the impedance is much smaller than the nMOS circuit impedance corresponding to the nMOS circuit in the off state, most of the current flowing through the power supply pad in the first transition case corresponds to the pMOS circuit in the on state. The pMOS circuit impedance and the predetermined external load model are assumed to flow, and the first current source is calculated.
The second chip model creation step includes the step of connecting the predetermined external load model between the output pad and the ground pad when generating a model for power supply voltage fluctuation, and then the predetermined external load model. Assuming that the impedance of the nMOS circuit is much larger than the nMOS circuit impedance corresponding to the nMOS circuit in the on state, most of the current flowing through the power supply pad corresponds to the pMOS circuit in the on state in the second transition case. The second current source is calculated by flowing into the pMOS circuit impedance and the nMOS circuit impedance corresponding to the on-state nMOS circuit.
The program according to claim 30 or 31 .
前記第2チップモデル作成ステップは、電源電圧変動用のモデルを作成する場合において、前記半導体チップに関するSPICEモデルを前記第2遷移ケースに関してトランジェント解析することにより得られる電流波形をフーリエ変換して、前記第2遷移ケースにおいて前記電源パッドを流れる電流のスペクトラムを算出する
請求項32記載のプログラム。 The first chip model creating step, when creating a model for power supply voltage fluctuation, Fourier transforms a current waveform obtained by performing a transient analysis on the SPICE model related to the semiconductor chip with respect to the first transition case, Calculating a spectrum of current flowing through the power pad in the first transition case;
The second chip model creating step, when creating a model for power supply voltage fluctuation, Fourier transforms the current waveform obtained by performing a transient analysis on the SPICE model related to the semiconductor chip with respect to the second transition case, The program according to claim 32 , wherein a spectrum of a current flowing through the power supply pad is calculated in a second transition case.
前記第2チップモデル作成ステップは、GND電圧変動用のモデルを作成する場合において、オフ状態の前記pMOS回路に対応する前記pMOS回路インピーダンスを用いると共にオン状態の前記nMOS回路に対応する前記nMOS回路インピーダンスを用いて、前記第2チップモデルを作成する、
請求項29乃至請求項33のいずれかに記載のプログラム。 The first chip model creation step uses the pMOS circuit impedance and the nMOS circuit impedance corresponding to the pMOS circuit and the nMOS circuit, both of which are in an on state when creating a model for GND voltage fluctuation, Create the first chip model,
The second chip model creating step uses the pMOS circuit impedance corresponding to the pMOS circuit in the off state and the nMOS circuit impedance corresponding to the nMOS circuit in the on state when creating a model for GND voltage fluctuation. The second chip model is created using
The program according to any one of claims 29 to 33 .
前記オフ状態のpMOS回路インピーダンスは、前記電源パッドと前記出力パッドとの間にキャパシタ及び抵抗が直列に接続されてなる等価回路モデルを用いて算出されるものであり、
前記オン状態のnMOS回路インピーダンスは、前記出力パッドと前記グランドパッドとの間にキャパシタ及び抵抗が並列に接続されてなる等価回路モデルを用いて算出されるものである
請求項34記載のプログラム。 The on-state pMOS circuit impedance is calculated using an equivalent circuit model in which a capacitor and a resistor are connected in parallel between the power supply pad and the output pad,
The off-state pMOS circuit impedance is calculated using an equivalent circuit model in which a capacitor and a resistor are connected in series between the power supply pad and the output pad,
The program according to claim 34, wherein the on-state nMOS circuit impedance is calculated using an equivalent circuit model in which a capacitor and a resistor are connected in parallel between the output pad and the ground pad.
前記第2チップモデル作成ステップは、GND電圧変動用のモデルを作成する場合において、前記出力パッドと前記グランドパッドとの間に前記所定の外部負荷モデルを接続した上で、該所定の外部負荷モデルのインピーダンスがオフ状態の前記pMOS回路に対応する前記pMOS回路インピーダンスよりも遥かに小さいと仮定して、前記第2遷移ケースにおいて前記グランドパッドを流れる電流のほとんどが、オン状態の前記nMOS回路に対応する前記nMOS回路インピーダンスと前記所定の外部負荷モデルを流れるものとし、前記第2電流源を算出するものである、
請求項34又は請求項35記載のプログラム。 In the first chip model creation step, when creating a model for GND voltage variation, a predetermined external load model is connected between the output pad and the ground pad, and then the predetermined external load model Assuming that the impedance is much larger than the nMOS circuit impedance corresponding to the nMOS circuit in the on state, most of the current flowing through the ground pad in the first transition case corresponds to the pMOS circuit in the on state. The first current source is calculated by flowing into the nMOS circuit impedance corresponding to the pMOS circuit impedance and the nMOS circuit in the on state.
In the second chip model creation step, when creating a model for GND voltage fluctuation, the predetermined external load model is connected between the output pad and the ground pad, and then the predetermined external load model is connected. Assuming that the impedance of the pMOS circuit is much smaller than the pMOS circuit impedance corresponding to the pMOS circuit in the off state, most of the current flowing through the ground pad in the second transition case corresponds to the nMOS circuit in the on state. The nMOS circuit impedance and the predetermined external load model are assumed to flow, and the second current source is calculated.
36. The program according to claim 34 or claim 35 .
前記第2チップモデル作成ステップは、GND電圧変動用のモデルを作成する場合において、前記半導体チップに関するSPICEモデルを前記第2遷移ケースに関してトランジェント解析することにより得られる電流波形をフーリエ変換して、前記第2遷移ケースにおいて前記グランドパッドを流れる電流のスペクトラムを算出する
請求項36記載のプログラム。 In the first chip model creation step, when a model for GND voltage fluctuation is created, the current waveform obtained by performing a transient analysis on the SPICE model related to the semiconductor chip with respect to the first transition case is Fourier-transformed, Calculating the spectrum of the current flowing through the ground pad in the first transition case;
In the second chip model creation step, when a model for GND voltage fluctuation is created, the current waveform obtained by performing a transient analysis on the SPICE model related to the semiconductor chip with respect to the second transition case is Fourier-transformed, The program according to claim 36 , wherein a spectrum of a current flowing through the ground pad is calculated in a second transition case.
請求項26乃至請求項37のいずれかに記載のプログラム。 Before hexane output step is to connect the first chip model and the adjustment target system impedance model, by solving the closed circuit equation, while calculating the first voltage fluctuation of power supply / GND spectrum, the adjustment object system Calculating the second power supply / GND voltage fluctuation spectrum by connecting an impedance model and the second chip model and solving a closed circuit equation;
The program according to any one of claims 26 to 37 .
前記調整対象系インピーダンスモデルは、当該調整対象系を前提として作成されたものである、
請求項26乃至請求項38のいずれかに記載のプログラム。 The adjustment target system includes an electrical component on a printed wiring board on which the semiconductor package is mounted,
The adjustment target system impedance model is created on the assumption of the adjustment target system.
The program according to any one of claims 26 to 38 .
請求項26乃至請求項39のいずれかに記載のプログラム。 In the design support information determining step, the design support information is determined by using a part of the adjustment target system corresponding to a frequency portion where the selected power supply / GND voltage fluctuation spectrum exceeds the constraint value as an adjustment target part. To
40. The program according to any one of claims 26 to 39 .
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007045122A JP4653764B2 (en) | 2006-02-28 | 2007-02-26 | Semiconductor device design method, design support system, and program |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006052360 | 2006-02-28 | ||
| JP2007045122A JP4653764B2 (en) | 2006-02-28 | 2007-02-26 | Semiconductor device design method, design support system, and program |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2007265398A JP2007265398A (en) | 2007-10-11 |
| JP4653764B2 true JP4653764B2 (en) | 2011-03-16 |
Family
ID=38638268
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007045122A Expired - Fee Related JP4653764B2 (en) | 2006-02-28 | 2007-02-26 | Semiconductor device design method, design support system, and program |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4653764B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008071204A (en) | 2006-09-14 | 2008-03-27 | Elpida Memory Inc | Method for designing device containing semiconductor chip, design support system and program |
Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005196406A (en) * | 2004-01-06 | 2005-07-21 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Method for designing semiconductor integrated circuit with reduced power source noise |
-
2007
- 2007-02-26 JP JP2007045122A patent/JP4653764B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005196406A (en) * | 2004-01-06 | 2005-07-21 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Method for designing semiconductor integrated circuit with reduced power source noise |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2007265398A (en) | 2007-10-11 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4389224B2 (en) | Semiconductor device design method, design support system and program, and semiconductor package | |
| US8543952B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for thermal analysis of through-silicon via (TSV) | |
| US7016794B2 (en) | Floor plan development electromigration and voltage drop analysis tool | |
| US6675139B1 (en) | Floor plan-based power bus analysis and design tool for integrated circuits | |
| US8104007B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for thermal analysis | |
| Menezes et al. | A sequential quadratic programming approach to concurrent gate and wire sizing | |
| JP2010218252A (en) | Cell library preparation device for analyzing statistical timing, statistical timing analyzer, method of preparing cell library for analyzing statistical timing, and statistical timing analyzing method | |
| CN103810316B (en) | The method for reducing parasitic mismatch | |
| KR100398850B1 (en) | Power model for emi simulation to semiconductor integrated circuit, method of designing the power model, emi simulator, and storage medium storing the same as well as power model design support system | |
| US20040025136A1 (en) | Method for designing a custom ASIC library | |
| JP2001175702A (en) | Method for designing circuit | |
| JP5262176B2 (en) | Power supply circuit design support apparatus and design support method | |
| JP4653764B2 (en) | Semiconductor device design method, design support system, and program | |
| JP2008071204A (en) | Method for designing device containing semiconductor chip, design support system and program | |
| US20100199239A1 (en) | Simulation method and simulation program | |
| JP5304460B2 (en) | Printed wiring board power circuit design apparatus, printed wiring board power circuit design method and program | |
| US7694245B2 (en) | Method for designing semiconductor package, system for aiding to design semiconductor package, and computer program product therefor | |
| JPWO2006109750A1 (en) | Integrated circuit device evaluation device, evaluation method, and evaluation program | |
| US7594212B1 (en) | Automatic pin placement for integrated circuits to aid circuit board design | |
| JP6252494B2 (en) | Design support apparatus, design support method, and program | |
| JP5332972B2 (en) | Decoupling capacity determination method, decoupling capacity determination device and program | |
| JP2007299268A (en) | Board layout check system and method | |
| JP4056613B2 (en) | Integrated circuit design method and integrated circuit design support apparatus | |
| JP2024141855A (en) | Parameter set generation method, parameter set generation device, and program | |
| JP2008276612A (en) | Circuit design device, method and program |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| RD01 | Notification of change of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7421 Effective date: 20080410 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20080612 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20100720 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20100917 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20101124 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20101217 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20131224 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| S111 | Request for change of ownership or part of ownership |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313117 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20131224 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |
|
| S111 | Request for change of ownership or part of ownership |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313113 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |