JP3979586B2 - Fire detectors and fire alarm equipment - Google Patents
Fire detectors and fire alarm equipment Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP3979586B2 JP3979586B2 JP2002195884A JP2002195884A JP3979586B2 JP 3979586 B2 JP3979586 B2 JP 3979586B2 JP 2002195884 A JP2002195884 A JP 2002195884A JP 2002195884 A JP2002195884 A JP 2002195884A JP 3979586 B2 JP3979586 B2 JP 3979586B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- fire
- circuit
- signal
- transmission
- switching operation
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Alarm Systems (AREA)
- Fire Alarms (AREA)
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は、火災感知器および火災報知設備に関する。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
従来のいわゆるP型火災報知設備は、火災受信機が複数の感知器回線に接続され、これら複数の感知器回線のうちのそれぞれの感知器回線に、火災感知器が複数、接続され、上記火災感知器が、スイッチング動作によって火災信号を出力する。
【0003】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
上記従来のP型火災報知設備において、所定の火災感知器が火災信号を出力すると、この火災信号を出力した上記所定の火災感知器が接続されている感知器回線を、複数の感知器回線の中から、火災受信機が特定することができる。したがって、火災監視区域毎に、感知器回線を異ならせて敷設してあれば、火災信号を送出した感知器回線を特定することによって、火災が発生した火災監視区域を特定することができる。
【0004】
しかし、上記従来例においては、火災信号が送出された感知器回路は、どの火災感知器がスイッチング動作したかにかかわらず、略短絡状態である低インピーダンス状態を継続し、火災受信機では、同一の感知器回線に接続されている複数の火災感知器のうちで、どの火災感知器が火災信号を出力したかを知ることができず、したがって、より具体的な火災発生場所を特定することができない。
【0005】
本発明は、P型の火災報知設備を用いる場合に、火災信号を出力している火災感知器を、火災受信機が特定することができ、これに基づいて、火災発生場所の特定等に利用することができる火災感知器および火災報知設備を提供することを目的とするものである。
【0006】
【課題を解決するための手段】
本発明は、いわゆるP型の火災受信機を用いた火災報知設備において、スイッチング動作によって火災信号を送出する火災感知器が、スイッチングのパルス動作によって、火災感知器のアドレス情報を同時に送出するものである。
【0007】
【発明の実施の形態および実施例】
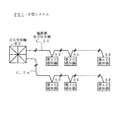
図1は、本発明の一実施例であるP型システムPS1を示す図である。
【0008】
P型システムPS1では、P型火災報知設備として、1台の火災受信機REに、複数の火災感知器SEが接続されている。
【0009】
各火災感知器SEは、火災受信機REから電源が供給され、煙濃度や周辺温度等の物理量を計測し、これによって、火災監視を行っている。
【0010】
ここでは、いわゆるATF(自己点検機能)感知器を用い、P型受信機が自己点検情報を収集可能である場合、火災信号を送出するときに、火災信号を送出する火災感知器のアドレスを、火災受信機が収集できるようにしたものである。したがって、火災受信機REは、火災が発生した区域に加え、火災感知器SEのアドレスに基づく詳細な位置を判別することができる。そのため、火災受信機REには、各回線の各火災感知器SEのアドレス毎に、設置位置情報が設定されている。
【0011】
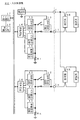
図2は、火災受信機REの構成を示すブロック図である。
【0012】
火災受信機REは、図1に示す火災受信機REとして用いられるものである。また、火災受信機REは、電源部11と、信号送信回路12と、信号受信回路13と、火災検出回路14と、断線検出回路15と、制御回路16と、メイン制御部17と、表示操作部18とを有し、電源兼信号線が接続されるコモン端子Cと複数のライン端子L1〜Lnとを有し、複数の火災感知器SEが接続されている。これらの端子CとL1〜Lnとの間で、各感知器回線が接続され、それぞれの端末部分に終端器が配置されている。そして、火災受信機RE内のブロック構成のうち、感知器回線毎に、信号送信回路12と、信号受信回路13と、火災検出回路14と、断線検出回路15と、制御回路16とが配置され、端子L1、……、Ln毎に配置されている。また、コモン端子Cは、各感知器回線に共通に接続されている。
【0013】
図3は、火災感知器SE1の具体的な構成を示すブロック図である。
【0014】
火災感知器SE1は、図1、図2に示す火災感知器SEとして用いられるものであり、発光回路31a1と、受光回路31a2と、増幅回路31bと、伝送送信回路41と、伝送受信回路42と、定電圧回路51と、電源回路52と、充電回路53と、計時回路61と、制御回路としてのマイコン71と、クロック発振回路81と、アドレス等が格納されるEEPROM91と、ダイオードブリッジDBとを有する。
【0015】
火災感知器SE1は、火災発生時に、火災信号を送信する直前に、火災感知器SE1のアドレス情報を送信する。つまり、通常のP型システムでは、受信機に対してスイッチング動作による火災信号を送信するが、火災感知器SE1は、火災信号を送信する直前に、パルスコードによって、火災感知器SE1のアドレス情報を送信し、発報した火災感知器を、火災受信機REが特定することができる。
【0016】
次に、上記実施例において、火災信号を出力する動作について説明する。
【0017】
図4は、上記実施例における端子C−L間の信号波形(火災感知器SE1が出力する信号波形)を示す図である。図4において、火災レベルは、伝送送信回路41をスイッチング動作させた場合のレベルであり、マイコン71による伝送送信回路41のオンオフ制御によって、図4に示すような波形を形成することができる。
【0018】
火災感知器SE1では、火災信号を送出するときに、自己のアドレス情報を送出する。この場合、パルスコードを制御することによって、上記自己のアドレス情報を送出する。
【0019】
火災感知器SE1が送出したアドレス情報を、火災受信機REが、受信し、これを解析することによって、アドレス情報を送出した火災感知器SE1を特定し、これによって、その火災感知器SE1が設置されている場所(つまり火災発生場所)を特定することができる。なお、各火災感知器SEが送出すべきアドレス情報としてのパルスコードと、各火災感知器SEとの対応が、テーブルとして、火災受信機REが保持している。
【0020】
次に、上記実施例において、アドレス情報を出力する動作について説明する。
【0021】
火災感知器SE1において、火災を検出するときに、マイコン71は、伝送送信回路41をスイッチング動作させ、このスイッチング動作によって、感知器回線が略短絡状態である低インピーダンスとし(火災感知器SEが動作可能な残り電圧は備える)、火災信号を出力する。この場合、伝送送信回路41のスイッチング動作を継続して火災信号とし、また、その当初に、伝送送信回路41をパルス動作させてアドレス情報を出力させる。
【0022】
火災感知器SE1において、伝送送信回路41の動作によって、信号線C、Ln間のレベルが、通常監視レベルから火災レベルに変位する。この火災レベルを、火災受信機REの信号受信回路13と火災検出回路14とが検出する。アドレス情報を送信している途中では、信号受信回路13がパルスコードを検出し、アドレス情報を検出し、このアドレス情報の送信が終了し、火災レベルが所定時間、継続したことを検出すると、火災信号を検出したことを、火災検出回路14が判断する。
【0023】
この実施例において、信号線C、L1〜Ln間のレベル変化は、火災信号送出においても、アドレス情報送出においても、通常監視レベルから火災レベルへの変化であるので、火災感知器SE1は、伝送送信回路41をオンオフすれば、火災信号を送出することができ、また、アドレス情報を送出することができ、それらと異なるレベルを形成する必要がない。
【0024】
この信号線C、L1〜Ln間のレベルは、火災受信機REにおいて、同じレベルを信号受信回路13と火災検出回路14とが検出し、火災信号の判別には、継続時間の要素があるので、火災信号として火災レベルの継続時間を、火災検出回路14が判別する。
【0025】
信号受信回路13の出力信号に基づいて、上記火災レベルの継続時間を、制御回路16がソフト的に処理するようにしてもよい。この場合、火災検出回路14を省略することができる。なお、火災発生時に、火災信号送出前にアドレス情報を出力すると、火災レベルの継続時間が遅れるが、アドレス情報を出力する時間は実質的に短く、警報動作として問題とはならない。
【0026】
また、上記実施例において、火災信号の送出開始点から、所定時間が経過したときにパルス復旧させ(火災信号の送出を停止し)、その後に、アドレス情報を送出するように、伝送送信回路41を構成するようにしてもよく、また、パルス復旧のタイミングを契機として、火災信号の送出開始点からパルス復旧のタイミングまでの時間幅でアドレスを表し、アドレス情報を判別するようにしてもよい。
【0027】
図5は、本発明における第2の実施例である火災感知器SE2を示すブロック図である。
【0028】
火災感知器SE2は、図5に示すように、火災感知器SE1において、伝送送信回路41の代わりに、第1の送信回路411と、第2の送信回路412とを設けた火災感知器である。
【0029】
第1の送信回路411は、火災信号を表すスイッチング動作を行う回路であり、第2の送信回路412は、火災感知器の自己のアドレス情報を送出する回路である。
【0030】
次に、火災感知器SE2の動作について説明する。
【0031】
図6は、上記第2の実施例における端子C−L間の信号波形(火災感知器SE2が出力する信号波形)を示す図である。
【0032】
第2の実施例である火災感知器SE2において、第1の送信回路411が、火災信号を表すスイッチング動作を行い、第2の送信回路412が、アドレス情報を送信する。
【0033】
つまり、火災感知器SE2が火災を検出したときに、第1の送信回路411をスイッチング動作させることによって火災信号を送出し、また、第2の送信回路412をパルス動作させることによって、自己のアドレス情報を送信する。
【0034】
火災感知器SE2では、第1の送信回路411の動作によって、信号線CとLnとの間のレベルが、通常監視レベルから火災レベルに変位するとともに、さらに、第2の送信回路412が動作することによって、火災レベルからさらに下方に、レベルが変位することによって、パルスコードを形成する。したがって、火災受信機REの信号受信回路13と火災検出回路14とが検出するレベルを、上記レベルに予め合わせておけばよい。
【0035】
つまり、火災検出回路14は、第1の送信回路411の動作による火災レベルを検出し、アドレス情報の有無に係わらず火災信号を検出することができ、信号受信回路13は、第2の送信回路412の動作によるパルスを表すレベルを検出し、これによって、アドレス情報を検出することができる。
【0036】
図7は、上記第2の実施例における端子C−L間の別の信号波形(火災感知器SE2が出力する別の信号波形)を示す図である。
【0037】
火災感知器SE2において、第2の送信回路412が出力する別のアドレス情報は、パルスコードで表現するものではなく、図7に示すように、パルス幅を変えることによってアドレス情報を示すものである。
【0038】
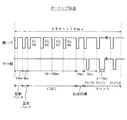
図8は、上記各実施例において、上記自己点検結果を送出する伝送の説明図である。
【0039】
図8において、「親」は、図1における火災受信機REであり、「子」は、火災感知器SEである。
【0040】
上記各実施例においてポーリング伝送する場合、火災受信機REが、回線毎に、複数設けられる火災感知器SEに個別のアドレスが付与され、そのアドレスに基づいて火災感知器SEをグループ化し、15アドレス単位で、火災感知器SEのデータを収集し、起動パルス、基準パルス、制御コマンドCM1を信号送信回路12から送出する。
【0041】
図9は、上記各実施例において、パルスコードを生成する場合に、そのパルスコードの要素となる波形を示す図である。
【0042】
起動パルスは、火災感知器SEのマイコン71を起動させるための起動パルスであり、火災受信機REは、パルス幅2msのLoパルスを送出する。火災感知器SEは、伝送受信回路42を介して、起動パルスを受け、マイコン71をスリープモードから復帰させ、基準パルス受信に備える。なお、マイコン71は、火災検出動作等の必要な動作後は、スリープモードに入るものであり、この状態からスタートして安定する時間が必要になる。
【0043】
基準パルスは、伝送上のパルス間隔の基本長となる基準パルスであり、立ち下がりエッヂ間隔(H→L〜H→L)で4msとする。
【0044】
制御コマンドCM1は、火災感知器SEへの制御コマンドであり、8ビットのコードを4つのパルス間隔で示し、各パルス間隔のそれぞれについて、図8に示すように、各パルス間隔を判断してコードに置き換える。また、各パルス間隔は、図9に示すように、立ち下がりエッヂ間隔(tb)で、2ビットのコードを示す。
【0045】
図10は、上記各実施例におけるコマンドとその内容とを示す図である。
【0046】
たとえば、図10に示す制御コマンドCM1は、10110101b=B5hになる。そして、制御コマンドCM1のコード内容は、図10に示すようにする。つまり、b7〜b3の5ビットによって、ここでは10110bによって、回線を指定し、b2,b1の2ビットによって、ここでは10によって、火災感知器SEの制御コマンドとセレクティングを指示し、b0の奇数パリティを付加する。火災感知器SEは、パリティエラーを検出した場合、無応答とする。
【0047】
なお、コマンドの形式として、回線指定または1F(1回線対応)中継器を、b7〜b3で指定できるようになっているが、上記P型システムPS1では、回線毎に送受信回路を構成するので、1F中継器からのコマンドと同様とすることができる。すなわち、回線指定のコマンドの利用は、火災受信機REにおける送受信回路を共通化するときに用いることができる。また、P−ATF受信機は、このP型システムPS1に用いられるような火災受信機REである。
【0048】
そして、伝送待機時に、火災感知器SEは、制御コマンドCM1の解析等を行う。
【0049】
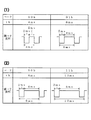
図11は、上記実施例におけるコマンドとアドレスとスロットとの関係を示す図である。
【0050】
スロット0〜14は、図8に示す伝送フレームにおいて火災感知器SEから火災受信機REへ送信するタイミングであり、ポーリング1or2を区別して自己のアドレスに基づくスロット位置が、図11(1)に示すように規定されている。
【0051】
火災感知器SEは、規定されたスロットに、図11(2)に示すパルスを送信する。
【0052】
この火災感知器SEからのパルスは、マイコン71が、図3における伝送送信回路41を介して送出し、この火災感知器SEからのコードは、パルス幅によって表され、図11(2)では、各火災感知器SEの自己点検結果を返送するときの結果について表している。すなわち、自己点検結果として感知器が正常であれば、パルス幅2msで、異常であれば、パルス幅4msで1つのパルスが返送される。
【0053】
なお、感知器が正常であるか異常であるかを示す結果については、制御コマンドを受信した後における短期の動作による自己点検結果でよいが、常時出力レベルを監視するような定常状態の監視動作による良否判別の結果であってもよい。
【0054】
図12は、上記実施例における図8とは異なる伝送に関するパルスの説明図である。
【0055】
セレクティング伝送は、1アドレス単位で、火災感知器SEのデータを収集し、図12に示すように、起動パルス、基準パルス、制御コマンドCM1および伝送待機に、制御コマンドCM2を加算し、受信機REが火災感知器SEに送出する。
【0056】
この起動パルス、基準パルスおよび制御コマンドCM1は、上記の通りであり、制御コマンドCM2は、制御コマンドCM1と同様の8ビットの制御コードであり、コードの送・受信方法は、制御コマンドCM1と同様である。
【0057】
そして、これらCM1とCM2との内容によって、制御内容を表す。具体的には、セレクティング伝送であることを、制御コマンドCM1で示し、制御コマンドCM2によってアドレスを指定し、これによって、特定の火災感知器SEのみが自己点検結果を返送することができる(図12における感知器返送の部分)。
【0058】
このような信号伝送を用い、火災受信機REは、制御コマンドCM1内にポーリング1またはポーリング2の制御内容を含め、送信することによって、電源兼伝送線C、L1〜Ln間に接続された火災感知器SEの情報を収集することができ、ここでは火災受信機REは、各火災感知器SEから自己点検結果を収集している。なお、この実施例では、図2に示すように、電源兼信号線C、L1〜Lnの回線毎に信号送信回路12と信号受信回路13とが設けられているので、回線毎の火災感知器SEとの間で信号のやり取りを行い、このために、上記制御コマンドCM1中の回線指定の部分を無視してよい。そして、1つの回線に接続される自己点検機能付のアドレス指定される火災感知器SEは、30個までということになる。なお、グループ数、グループ内の個数は、それぞれ任意に設定でき、30個に限らず、30個以上に対応することも可能である。
【0059】
上記のようにして、P型システムPS1において、各火災感知器SEからの火災信号は、回線毎に火災検出回路14によって、火災受信機REが検出し、また、必要な火災感知器SEから、信号送信回路12と信号受信回路13とによって、自己点検結果を収集することができ、異常となっている火災感知器SEがあることを、火災受信機REが認識できる。
【0060】
なお、各端子C、L1〜Ln間の信号伝送に基づいて、各制御回路16が試験結果を収集するタイミングを、メイン制御部17が制御する。つまり、複数の火災感知器から同時に火災信号が発生しないようにすれば、各感知器回線が、電源兼信号線として、電圧の安定性が阻害されない。
【0061】
各実施例における火災感知器は、火災監視の過程で、火災を検出した場合に、いわゆるスイッチング動作によって、火災信号を出力し、また、自己点検結果を判別し、火災受信機からの問いかけに応じて、自己点検結果を送出する。
【0062】
上記実施例によれば、火災信号とともに火災感知器のアドレス情報を、火災受信機REに認識させることができるので、火災受信機REが、火災警報動作を実行することができるとともに、アドレス情報によって特定された火災発生場所の表示等、適切な処置を実行することができる。
【0063】
また、上記実施例によれば、アドレス情報の送出について、スイッチング動作を行う場合、パルス的なコード信号を用いるので、高度な伝送送信回路を備えなくても、アドレス情報を出力することができる。
【0064】
さらに、上記実施例によれば、火災信号をスイッチング動作で示しながら、電気的状態を変化させるので、アドレス情報を送出することによって、感知器回線を監視する火災受信機は、アドレス情報の有無に係わらずスイッチング動作を確実に検出することができる。
【0065】
つまり、上記各実施例は、感知器回線に接続される火災受信機と、上記感知器回線に接続されスイッチング動作によって火災信号を上記感知器回線に出力する火災感知器とを具備する火災報知設備において、上記火災受信機は、上記感知器回線毎に、上記スイッチング動作を検出する信号検出回路と、上記感知器回線毎に、パルス的なスイッチング動作を検出し、アドレス情報を取得する伝送送信回路とを有し、上記火災感知器は、アドレス情報を保持する制御回路と、上記制御回路の制御に応じて、パルス的なスイッチング動作を行うスイッチング回路とを有し、上記制御回路は、火災検出時に上記スイッチング回路に、スイッチング動作を維持させながら、上記パルス的にスイッチング動作を行い、上記アドレス情報を送出する動作を行わせる回路である。
【0066】
この場合、上記火災受信機は、感知器回線C、L1に着目すると、上記火災感知器が火災検出時に行うスイッチング動作を検出する受信抵抗と、上記火災感知器のアドレス情報を示すパルス的に行うスイッチング動作を検出する受信抵抗とを、抵抗R1で共用している。また、他の感知器回線においても、上記と同様に、受信抵抗を共用し、感知器回線C、Lnに着目すると、受信抵抗Rnで共用している。
【0067】
また、火災受信機が、火災感知器回線のライン線とコモン線とに接続され、各感知器回線のライン線は、信号検出回路と送受信回路とに接続され、コモン線は、相互に接続され、共通化されていることによって、コモン線を配線することが容易であり、しかも、従来のP型の火災報知設備の配線と同様であるので、リニューアルに対応し易い。
【0068】
また、上記実施例において、上記火災感知器は、火災信号の直前に、上記火災感知器のアドレス情報を送信する感知器の例である。
【0069】
さらに、上記制御回路は、火災検出時に、パルス的なスイッチング動作を行うことによってアドレス情報を送出した後に、火災信号を出力する上記スイッチング動作を維持するように、上記スイッチング回路を制御する回路の例である。
【0070】
【発明の効果】
本発明によれば、P型の火災報知設備を用いる場合に、アドレス情報を利用するので、火災信号を出力している火災感知器を、火災受信機が特定することができ、これに基づいて、火災発生場所の特定等に利用することができるという効果を奏する。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】本発明の一実施例であるP型システムPS1を示す図である。
【図2】火災受信機REの構成を示すブロック図である。
【図3】火災感知器SE1の具体的な構成を示すブロック図である。
【図4】上記実施例における端子C−L間の信号波形(火災感知器SE1が出力する信号波形)を示す図である。
【図5】本発明における第2の実施例である火災感知器SE2のブロック図である。
【図6】上記第2の実施例における端子C−L間の信号波形(火災感知器SE2が出力する信号波形)を示す図である。
【図7】上記第2の実施例における端子C−L間の別の信号波形(火災感知器SE2が出力する別の信号波形)を示す図である。
【図8】上記実施例において、上記自己点検結果を送出する伝送の説明図である。
【図9】上記実施例において、パルスコードを生成する場合に、そのパルスコードの要素となる波形を示す図である。
【図10】上記第2の実施例におけるコマンドとその内容とを示す図である。
【図11】上記実施例におけるコマンドとアドレスとスロットとの関係を示す図である。
【図12】上記実施例における図8とは異なる伝送に関するパルスの説明図である。
【符号の説明】
PS1…P型システム、
RE…火災受信機、
SE1、SE2…火災感知器、
13…信号受信回路、
14…火災検出回路、
42…伝送受信回路、
411…第1の送信回路、
412…第2の送信回路、
71…制御回路、
R1〜Rn…受信抵抗。[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a fire detector and a fire alarm facility.
[0002]
[Prior art]
In a conventional so-called P-type fire alarm system, a fire receiver is connected to a plurality of sensor lines, and a plurality of fire detectors are connected to each of the sensor lines. The sensor outputs a fire signal by switching operation.
[0003]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
In the conventional P-type fire alarm system, when a predetermined fire detector outputs a fire signal, a sensor line connected to the predetermined fire sensor that outputs the fire signal is connected to a plurality of sensor lines. From inside, the fire receiver can be identified. Therefore, if the sensor lines are laid differently for each fire monitoring area, the fire monitoring area where the fire has occurred can be specified by specifying the sensor line that sent the fire signal.
[0004]
However, in the above conventional example, the detector circuit to which the fire signal is sent continues in the low impedance state, which is a substantially short-circuited state, regardless of which fire detector performs the switching operation. Of the multiple fire detectors connected to the sensor line, it is impossible to know which fire detector output the fire signal, so it is possible to identify a more specific fire location Can not.
[0005]
In the present invention, when a P-type fire alarm system is used, a fire receiver can identify a fire detector that outputs a fire signal, and based on this, it can be used for identifying a fire occurrence location. An object of the present invention is to provide a fire detector and a fire alarm facility that can be used.
[0006]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
The present invention relates to a fire alarm system using a so-called P-type fire receiver, in which a fire detector that transmits a fire signal by switching operation simultaneously transmits address information of the fire detector by switching pulse operation. is there.
[0007]
BEST MODE FOR CARRYING OUT THE INVENTION
FIG. 1 is a diagram showing a P-type system PS1 which is an embodiment of the present invention.
[0008]
In the P-type system PS1, a plurality of fire detectors SE are connected to one fire receiver RE as P-type fire alarm equipment.
[0009]
Each fire detector SE is supplied with power from the fire receiver RE, measures physical quantities such as smoke concentration and ambient temperature, and performs fire monitoring.
[0010]
Here, when using a so-called ATF (self-inspection function) sensor and the P-type receiver can collect self-inspection information, when sending a fire signal, the address of the fire sensor that sends out the fire signal, The fire receiver can collect. Therefore, the fire receiver RE can determine the detailed position based on the address of the fire detector SE in addition to the area where the fire has occurred. Therefore, installation position information is set in the fire receiver RE for each address of each fire detector SE of each line.
[0011]
FIG. 2 is a block diagram showing a configuration of the fire receiver RE.
[0012]
The fire receiver RE is used as the fire receiver RE shown in FIG. The fire receiver RE includes a power supply unit 11, a signal transmission circuit 12, a
[0013]
FIG. 3 is a block diagram showing a specific configuration of the fire detector SE1.
[0014]
The fire detector SE1 is used as the fire detector SE shown in FIGS. 1 and 2, and includes a light emitting circuit 31a1, a light receiving circuit 31a2, an
[0015]
The fire detector SE1 transmits address information of the fire detector SE1 immediately before transmitting a fire signal when a fire occurs. That is, in a normal P-type system, a fire signal due to switching operation is transmitted to the receiver, but the fire detector SE1 uses the pulse code to obtain the address information of the fire detector SE1 immediately before transmitting the fire signal. The fire receiver RE can identify the fire detector that has transmitted and reported.
[0016]
Next, an operation for outputting a fire signal in the above embodiment will be described.
[0017]
FIG. 4 is a diagram illustrating a signal waveform between the terminals CL in the above embodiment (a signal waveform output from the fire detector SE1). In FIG. 4, the fire level is a level when the transmission /
[0018]
The fire detector SE1 sends its own address information when sending a fire signal. In this case, the self address information is transmitted by controlling the pulse code.
[0019]
The fire receiver RE receives the address information sent from the fire detector SE1 and analyzes it to identify the fire detector SE1 that sent the address information, thereby installing the fire detector SE1. It is possible to identify the location where the fire has occurred (that is, the location of the fire). Note that the correspondence between the pulse code as address information to be transmitted by each fire detector SE and each fire detector SE is held in the fire receiver RE as a table.
[0020]
Next, an operation for outputting address information in the above embodiment will be described.
[0021]
When the fire detector SE1 detects a fire, the microcomputer 71 performs a switching operation of the transmission /
[0022]
In the fire detector SE1, the level between the signal lines C and Ln is shifted from the normal monitoring level to the fire level by the operation of the
[0023]
In this embodiment, since the level change between the signal lines C and L1 to Ln is a change from the normal monitoring level to the fire level in both the fire signal transmission and the address information transmission, the fire detector SE1 transmits. If the
[0024]
The level between the signal lines C and L1 to Ln is detected by the
[0025]
Based on the output signal of the
[0026]
In the above-described embodiment, the transmission /
[0027]
FIG. 5 is a block diagram showing a fire detector SE2 according to the second embodiment of the present invention.
[0028]
As shown in FIG. 5, the fire sensor SE2 is a fire sensor in which a first transmission circuit 411 and a second transmission circuit 412 are provided in place of the
[0029]
The first transmission circuit 411 is a circuit that performs a switching operation representing a fire signal, and the second transmission circuit 412 is a circuit that sends out address information of the fire detector itself.
[0030]
Next, the operation of the fire detector SE2 will be described.
[0031]
FIG. 6 is a diagram illustrating a signal waveform between the terminals CL in the second embodiment (signal waveform output from the fire detector SE2).
[0032]
In the fire detector SE2 of the second embodiment, the first transmission circuit 411 performs a switching operation representing a fire signal, and the second transmission circuit 412 transmits address information.
[0033]
That is, when the fire detector SE2 detects a fire, a fire signal is transmitted by switching the first transmission circuit 411, and a self-address is generated by pulsing the second transmission circuit 412. Send information.
[0034]
In the fire detector SE2, the level between the signal lines C and Ln is shifted from the normal monitoring level to the fire level by the operation of the first transmission circuit 411, and further, the second transmission circuit 412 operates. As a result, the level is displaced further down from the fire level to form a pulse code. Therefore, the level detected by the
[0035]
That is, the
[0036]
FIG. 7 is a diagram illustrating another signal waveform (another signal waveform output from the fire detector SE2) between the terminals CL in the second embodiment.
[0037]
In the fire detector SE2, the other address information output from the second transmission circuit 412 is not expressed by a pulse code, but indicates address information by changing the pulse width as shown in FIG. .
[0038]
FIG. 8 is an explanatory diagram of transmission for sending the self-check result in each of the above embodiments.
[0039]
In FIG. 8, “parent” is the fire receiver RE in FIG. 1, and “child” is the fire detector SE.
[0040]
In the case of polling transmission in each of the above-described embodiments, the fire receiver RE is assigned an individual address to a plurality of fire detectors SE provided for each line, and the fire detectors SE are grouped based on the addresses to obtain 15 addresses. Data of the fire detector SE is collected in units, and a start pulse, a reference pulse, and a control command CM1 are transmitted from the signal transmission circuit 12.
[0041]
FIG. 9 is a diagram illustrating waveforms that are elements of a pulse code when the pulse code is generated in each of the above embodiments.
[0042]
The activation pulse is an activation pulse for activating the microcomputer 71 of the fire detector SE, and the fire receiver RE transmits a Lo pulse having a pulse width of 2 ms. The fire detector SE receives the activation pulse via the
[0043]
The reference pulse is a reference pulse that is a basic length of a transmission pulse interval, and is 4 ms at a falling edge interval (H → L to H → L).
[0044]
The control command CM1 is a control command to the fire detector SE, and indicates an 8-bit code with four pulse intervals. For each pulse interval, as shown in FIG. Replace with Further, as shown in FIG. 9, each pulse interval is a falling edge interval (tb) and represents a 2-bit code.
[0045]
FIG. 10 is a diagram showing commands and their contents in the above embodiments.
[0046]
For example, the control command CM1 shown in FIG. 10 is 10110101b = B5h. The code contents of the control command CM1 are as shown in FIG. That is, the line is specified by 5 bits b7 to b3, here by 10110b, the control command and selecting of the fire detector SE are instructed by 2 bits b2 and b1, here by 10, and the odd number of b0 Add parity. The fire detector SE makes no response when it detects a parity error.
[0047]
As a command format, a line designation or 1F (one line correspondence) repeater can be designated by b7 to b3. However, in the P-type system PS1, a transmission / reception circuit is configured for each line. It can be the same as the command from the 1F repeater. That is, the use of the line designation command can be used when the transmission / reception circuit in the fire receiver RE is shared. The P-ATF receiver is a fire receiver RE used in the P-type system PS1.
[0048]
Then, when waiting for transmission, the fire detector SE analyzes the control command CM1.
[0049]
FIG. 11 is a diagram showing the relationship among commands, addresses and slots in the above embodiment.
[0050]
[0051]
The fire sensor SE transmits the pulse shown in FIG. 11 (2) to the specified slot.
[0052]
The pulse from the fire detector SE is sent out by the microcomputer 71 via the transmission /
[0053]
The result indicating whether the sensor is normal or abnormal may be a self-check result by a short-term operation after receiving the control command, but a steady-state monitoring operation that constantly monitors the output level It may be a result of pass / fail judgment by.
[0054]
FIG. 12 is an explanatory diagram of pulses related to transmission different from that in FIG. 8 in the above embodiment.
[0055]
In the selective transmission, the data of the fire detector SE is collected in units of one address, and as shown in FIG. 12, the control command CM2 is added to the start pulse, the reference pulse, the control command CM1, and the transmission standby, and the receiver The RE sends out to the fire detector SE.
[0056]
The start pulse, the reference pulse, and the control command CM1 are as described above. The control command CM2 is an 8-bit control code similar to the control command CM1, and the code transmission / reception method is the same as that of the control command CM1. It is.
[0057]
The contents of control are represented by the contents of CM1 and CM2. Specifically, it is indicated that the transmission is a selection transmission by a control command CM1, and an address is designated by the control command CM2, whereby only a specific fire detector SE can return a self-inspection result (see FIG. 12 sensor return part).
[0058]
Using such signal transmission, the fire receiver RE includes the control content of
[0059]
As described above, in the P-type system PS1, the fire signal from each fire detector SE is detected by the fire detector RE for each line by the
[0060]
The main control unit 17 controls the timing at which each
[0061]
The fire detector in each embodiment outputs a fire signal by so-called switching operation when a fire is detected during the process of fire monitoring, determines the self-inspection result, and responds to inquiries from the fire receiver. Send the self-check result.
[0062]
According to the above embodiment, since the fire receiver RE can recognize the fire detector address information together with the fire signal, the fire receiver RE can execute the fire alarm operation, and the address information Appropriate measures such as displaying the location of the identified fire can be executed.
[0063]
Further, according to the above-described embodiment, when a switching operation is performed for sending address information, a pulse code signal is used. Therefore, address information can be output without an advanced transmission / transmission circuit.
[0064]
Furthermore, according to the above embodiment, since the electrical state is changed while the fire signal is indicated by the switching operation, the fire receiver that monitors the sensor line by sending the address information can detect whether or not the address information is present. Regardless, the switching operation can be reliably detected.
[0065]
In other words, each of the above embodiments is a fire alarm system comprising a fire receiver connected to a sensor line, and a fire detector connected to the sensor line and outputting a fire signal to the sensor line by a switching operation. The fire receiver includes a signal detection circuit that detects the switching operation for each of the sensor lines, and a transmission transmission circuit that detects a pulse-like switching operation and acquires address information for each of the sensor lines. The fire detector has a control circuit for holding address information and a switching circuit for performing a pulse-like switching operation according to the control of the control circuit, and the control circuit detects a fire. Occasionally, the switching circuit performs the switching operation in pulses and sends the address information while maintaining the switching circuit in the switching circuit. It is a circuit that.
[0066]
In this case, when the fire receiver pays attention to the sensor lines C and L1, the fire receiver performs a pulse-like operation indicating a receiving resistor for detecting a switching operation performed by the fire detector when a fire is detected and address information of the fire detector. The receiving resistor for detecting the switching operation is shared by the resistor R1. Also, in the other sensor lines, similarly to the above, the receiving resistance is shared, and when attention is paid to the sensor lines C and Ln, the receiving resistance Rn is shared.
[0067]
The fire receiver is connected to the line and common line of the fire detector line, the line line of each detector line is connected to the signal detection circuit and the transmission / reception circuit, and the common line is connected to each other. Since it is common, it is easy to wire the common line, and since it is the same as the wiring of the conventional P-type fire alarm facility, it is easy to cope with the renewal.
[0068]
In the embodiment, the fire sensor is an example of a sensor that transmits address information of the fire sensor immediately before the fire signal.
[0069]
Further, the control circuit is an example of a circuit that controls the switching circuit so as to maintain the switching operation of outputting a fire signal after sending address information by performing a pulse-like switching operation when a fire is detected. It is.
[0070]
【The invention's effect】
According to the present invention, since the address information is used when using the P-type fire alarm equipment, the fire receiver can specify the fire detector outputting the fire signal, based on this. There is an effect that it can be used for specifying the location of the fire.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a diagram showing a P-type system PS1 which is an embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 2 is a block diagram showing a configuration of a fire receiver RE.
FIG. 3 is a block diagram showing a specific configuration of a fire detector SE1.
FIG. 4 is a diagram showing a signal waveform (a signal waveform output from a fire detector SE1) between terminals CL in the embodiment.
FIG. 5 is a block diagram of a fire detector SE2 according to a second embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 6 is a diagram illustrating a signal waveform (a signal waveform output from a fire detector SE2) between terminals CL in the second embodiment.
FIG. 7 is a diagram illustrating another signal waveform between terminals CL in the second embodiment (another signal waveform output from the fire detector SE2).
FIG. 8 is an explanatory diagram of transmission for sending out the self-inspection result in the embodiment.
FIG. 9 is a diagram illustrating waveforms that are elements of a pulse code when the pulse code is generated in the embodiment.
FIG. 10 is a diagram showing commands and their contents in the second embodiment.
FIG. 11 is a diagram showing the relationship among commands, addresses, and slots in the embodiment.
12 is an explanatory diagram of pulses related to transmission different from that in FIG. 8 in the embodiment. FIG.
[Explanation of symbols]
PS1 ... P type system,
RE ... Fire receiver,
SE1, SE2 ... Fire detectors,
13: Signal receiving circuit,
14 ... Fire detection circuit,
42. Transmission and reception circuit,
411 ... first transmission circuit,
412 ... second transmission circuit,
71 ... Control circuit,
R1 to Rn: reception resistors.
Claims (4)
上記火災受信機は、
上記感知器回線毎に、上記スイッチング動作に基づいて火災を検出する火災検出回路と;
上記感知器回線毎に、パルス的なスイッチング動作を検出し、アドレス情報を取得する信号受信回路と;
を有し、
上記各火災感知器は、
アドレス情報を保持する制御回路と;
上記制御回路の制御に応じて、スイッチング動作を行う伝送送信回路と;
を有し、上記制御回路は、火災を検出すると、その当初に、上記伝送送信回路のオンオフ制御により、通常監視レベルと火災レベルとの間で、信号レベルを切り替えることによって、パルス的にスイッチング動作を行って、上記アドレス情報を送出する動作を行わせた後に、火災レベルの信号を出力するスイッチング動作を維持するように制御する回路であることを特徴とする火災報知設備。In a fire alarm facility comprising a fire receiver connected to a sensor line and a plurality of fire detectors connected to the sensor line and outputting a fire signal to the sensor line by a switching operation,
The above fire receiver
A fire detection circuit for detecting a fire based on the switching operation for each of the sensor lines;
A signal receiving circuit for detecting a pulse-like switching operation and acquiring address information for each of the sensor lines;
Have
Each of the above fire detectors
A control circuit for holding address information;
A transmission / transmission circuit that performs a switching operation according to the control of the control circuit ;
When the fire is detected , the control circuit initially performs a switching operation in a pulse manner by switching the signal level between the normal monitoring level and the fire level by the on / off control of the transmission / transmission circuit. The fire alarm equipment is a circuit that performs control to maintain a switching operation for outputting a fire level signal after performing the operation of transmitting the address information .
上記火災受信機は、上記火災感知器が火災検出時に行うスイッチング動作を検出する受信抵抗と、上記火災感知器のアドレス情報を示すパルス的に行うスイッチング動作を検出する受信抵抗とを、共用していることを特徴とする火災報知設備。In claim 1,
The fire receiver shares a receiving resistor for detecting a switching operation performed by the fire detector when a fire is detected and a receiving resistor for detecting a switching operation performed in a pulse manner indicating address information of the fire detector. Fire alarm equipment characterized by
アドレス情報を保持する制御回路と;
上記制御回路の制御に応じて、スイッチング動作を行う伝送送信回路と;
を有し、上記制御回路は、火災を検出すると、その当初に、上記伝送送信回路のオンオフ制御により、通常監視レベルと火災レベルとの間で、信号レベルを切り替えることによって、パルス的にスイッチング動作を行って、上記アドレス情報を送出する動作を行わせた後に、火災レベルの信号を出力するスイッチング動作を維持するように制御する回路であることを特徴とする火災感知器。In a fire detector that outputs a fire signal to the sensor line by a switching operation connected to the sensor line,
A control circuit for holding address information;
A transmission / transmission circuit that performs a switching operation according to the control of the control circuit ;
When the fire is detected , the control circuit initially performs a switching operation in a pulse manner by switching the signal level between the normal monitoring level and the fire level by the on / off control of the transmission / transmission circuit. The fire detector is a circuit that performs control to maintain a switching operation for outputting a fire level signal after performing the operation for transmitting the address information .
上記スイッチング動作による火災信号の直前に送出される上記火災感知器のアドレス情報であって、上記パルス的にスイッチング動作することによって発生するアドレス情報を送信することを特徴とする火災感知器。In claim 3,
A fire sensor for transmitting address information of the fire sensor sent immediately before a fire signal by the switching operation, the address information generated by the pulse-like switching operation.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002195884A JP3979586B2 (en) | 2002-07-04 | 2002-07-04 | Fire detectors and fire alarm equipment |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002195884A JP3979586B2 (en) | 2002-07-04 | 2002-07-04 | Fire detectors and fire alarm equipment |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007157103A Division JP4058100B2 (en) | 2007-06-14 | 2007-06-14 | Fire detectors and fire alarm equipment |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2004038647A JP2004038647A (en) | 2004-02-05 |
| JP3979586B2 true JP3979586B2 (en) | 2007-09-19 |
Family
ID=31704140
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002195884A Expired - Fee Related JP3979586B2 (en) | 2002-07-04 | 2002-07-04 | Fire detectors and fire alarm equipment |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP3979586B2 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007226844A (en) * | 2007-06-14 | 2007-09-06 | Nohmi Bosai Ltd | Fire sensor and fire alarm facility |
Families Citing this family (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4344269B2 (en) | 2004-03-30 | 2009-10-14 | 能美防災株式会社 | Fire detector and its status information acquisition system |
| JP4699707B2 (en) * | 2004-04-01 | 2011-06-15 | ホーチキ株式会社 | Fire alarm system |
| JP2005352919A (en) * | 2004-06-11 | 2005-12-22 | Hochiki Corp | Fire alarm system |
| JP4615902B2 (en) * | 2004-06-11 | 2011-01-19 | ホーチキ株式会社 | Fire alarm system |
| JP5067900B2 (en) * | 2010-03-08 | 2012-11-07 | ホーチキ株式会社 | Fire alarm system |
| JP5037647B2 (en) * | 2010-04-19 | 2012-10-03 | ホーチキ株式会社 | Fire alarm system |
| CN103530997B (en) * | 2013-11-01 | 2016-05-11 | 浙江爱德电子有限公司 | Fire alarm control system and control method thereof |
| JP6481933B2 (en) * | 2015-02-05 | 2019-03-13 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | Automatic fire alarm system slave unit and automatic fire alarm system using the same |
Family Cites Families (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH0719315B2 (en) * | 1985-04-09 | 1995-03-06 | ホーチキ株式会社 | Fire alarm |
| JP2862552B2 (en) * | 1989-02-15 | 1999-03-03 | 能美防災株式会社 | Fire alarm system |
| JP3140530B2 (en) * | 1992-02-04 | 2001-03-05 | 能美防災株式会社 | Fire alarm system |
| JP3196091B2 (en) * | 1992-12-24 | 2001-08-06 | 能美防災株式会社 | Disaster prevention equipment |
| JPH08180272A (en) * | 1994-12-22 | 1996-07-12 | Matsushita Electric Works Ltd | Fire sensor |
| JP3931999B2 (en) * | 1997-05-28 | 2007-06-20 | 能美防災株式会社 | fire alarm |
-
2002
- 2002-07-04 JP JP2002195884A patent/JP3979586B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007226844A (en) * | 2007-06-14 | 2007-09-06 | Nohmi Bosai Ltd | Fire sensor and fire alarm facility |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2004038647A (en) | 2004-02-05 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP3695635B2 (en) | Fire alarm system | |
| JP3979586B2 (en) | Fire detectors and fire alarm equipment | |
| JP3788711B2 (en) | Fire alarm system | |
| JP4058100B2 (en) | Fire detectors and fire alarm equipment | |
| JP3563254B2 (en) | Fire alarm and detector | |
| JP4683474B2 (en) | Fire alarm system | |
| JP3963442B2 (en) | Fire detectors and fire alarm equipment | |
| JP6655808B2 (en) | Handset of automatic fire alarm system and automatic fire alarm system using the same | |
| JP2004133770A (en) | Fire alarm facility and fire sensor | |
| JP4702871B2 (en) | Fire alarm system | |
| JP2000187784A (en) | Fire sensor, fire warning receiver, fire warning reception system using them | |
| JPH10334358A (en) | Fire alarm | |
| JP2005293234A (en) | P-type fire alarm facility, and its fire detector | |
| JPH11185189A (en) | Fire alarming system | |
| JP3602284B2 (en) | fire alarm | |
| JP3711466B2 (en) | Fire detector | |
| JP2829772B2 (en) | Fire alarm repeater | |
| JPH0444799B2 (en) | ||
| JP4789235B2 (en) | Fire detector | |
| JP3267885B2 (en) | Fire alarm and fire detector | |
| JPH0827874B2 (en) | Fire alarm | |
| JP3155902B2 (en) | Disaster prevention monitoring device | |
| JP4090037B2 (en) | Fire alarm system | |
| JP4095631B2 (en) | Fire alarm system | |
| JP3094202B2 (en) | Remote sensor inspection system |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20050701 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20060804 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20060908 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20061222 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20070221 |
|
| A911 | Transfer of reconsideration by examiner before appeal (zenchi) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A911 Effective date: 20070326 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20070525 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20070531 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20070622 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20070622 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 3979586 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20100706 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20110706 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120706 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120706 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130706 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |