JP2022034835A - Manufacturing method of torque measuring device and torque load member - Google Patents
Manufacturing method of torque measuring device and torque load member Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2022034835A JP2022034835A JP2020138720A JP2020138720A JP2022034835A JP 2022034835 A JP2022034835 A JP 2022034835A JP 2020138720 A JP2020138720 A JP 2020138720A JP 2020138720 A JP2020138720 A JP 2020138720A JP 2022034835 A JP2022034835 A JP 2022034835A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- torque
- shot peening
- detected
- circumferential direction
- load member
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Force Measurement Appropriate To Specific Purposes (AREA)
- Power Steering Mechanism (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、トルクを測定するために用いられるトルク測定装置と、トルクを負荷されるトルク負荷部材の製造方法に関する。 The present invention relates to a torque measuring device used for measuring torque and a method for manufacturing a torque load member to which torque is applied.
近年、自動車の分野では、パワートレイン(動力伝達機構)を構成する回転軸により伝達しているトルクを測定し、その測定結果を利用して、動力源であるエンジンや電動モータの出力制御や、変速機の変速制御を実行するシステムの開発が進んでいる。 In recent years, in the field of automobiles, the torque transmitted by the rotating shaft that constitutes the power train (power transmission mechanism) is measured, and the measurement results are used to control the output of the engine or electric motor that is the power source. Development of a system for executing shift control of a transmission is in progress.
また、従来、回転軸などのトルク負荷部材により伝達しているトルクを測定する装置として、磁歪式のトルク測定装置が知られている(たとえば、特開2017-96825号公報(特許文献1)、特開2017-96826号公報(特許文献2)、特公平7-10011号公報(特許文献3)、特開2018-112451号公報(特許文献4)参照)。磁歪式のトルク測定装置では、トルク負荷部材の透磁率が、負荷されるトルクに応じて変化する現象(逆磁歪効果)を利用して、該トルクを測定する。具体的には、トルク負荷部材の被検出面に対向させたコイルを交流励磁し、該コイルの周囲に発生した磁束を、被検出面の表層部に通過させる。そして、トルク負荷部材に負荷されたトルクを、被検出面の表層部の透磁率の変化、すなわち、コイルの自己インダクタンスの変化として測定する。なお、このようなコイルを備えたトルクセンサを、磁歪式のトルクセンサという。 Further, conventionally, as a device for measuring torque transmitted by a torque load member such as a rotating shaft, a magnetic strain type torque measuring device is known (for example, Japanese Patent Application Laid-Open No. 2017-96825 (Patent Document 1). See Japanese Patent Application Laid-Open No. 2017-96826 (Patent Document 2), Japanese Patent Application Laid-Open No. 7-10011 (Patent Document 3), and Japanese Patent Application Laid-Open No. 2018-112451 (Patent Document 4). In the magnetostriction type torque measuring device, the torque is measured by utilizing a phenomenon (reverse magnetostriction effect) in which the magnetic permeability of the torque load member changes according to the applied torque. Specifically, a coil facing the detected surface of the torque load member is AC-excited, and the magnetic flux generated around the coil is passed through the surface layer portion of the detected surface. Then, the torque applied to the torque load member is measured as a change in the magnetic permeability of the surface layer portion of the detected surface, that is, a change in the self-inductance of the coil. A torque sensor provided with such a coil is called a magnetostrictive torque sensor.
ところで、自動車の分野では、パワートレインを構成する回転軸などの回転速度を測定し、その測定結果を車両制御に活用することが一般的に行われている。このため、上述したような磁歪式のトルク測定装置によって、トルクだけでなく回転速度も測定できれば、車両に搭載する測定装置の数を減らすことが可能になる。しかしながら、従来の磁歪式のトルク測定装置では、回転軸などのトルク負荷部材の回転速度が変化するだけではコイルの自己インダクタンスが変化しないため、トルク負荷部材の回転速度を測定することができない。 By the way, in the field of automobiles, it is generally practiced to measure the rotation speed of a rotating shaft or the like constituting a power train and utilize the measurement result for vehicle control. Therefore, if not only the torque but also the rotation speed can be measured by the magnetostriction type torque measuring device as described above, the number of measuring devices mounted on the vehicle can be reduced. However, in the conventional magnetic strain type torque measuring device, the self-inductance of the coil does not change only by changing the rotation speed of the torque load member such as the rotating shaft, so that the rotation speed of the torque load member cannot be measured.
本発明は、上述のような事情に鑑み、トルク負荷部材に負荷されたトルクだけでなく、トルク負荷部材の回転速度も測定することができる構造を実現することを目的とする。 In view of the above circumstances, it is an object of the present invention to realize a structure capable of measuring not only the torque applied to the torque load member but also the rotation speed of the torque load member.
本発明のトルク測定装置は、回転中心軸と、前記回転中心軸を中心とする円環状(例えば円筒面状又は円輪面状)の被検出面とを有するトルク負荷部材と、前記被検出面に対向させたコイルを有する磁歪式のトルクセンサとを備える。
前記被検出面は、円周方向に関する1乃至複数箇所にのみショットピーニング処理部を有する。なお、ショットピーニング処理部とは、ショットピーニング処理が施された部分である。
前記コイルは、前記回転中心軸を中心とする一部の円周方向範囲にのみ配置されている。
The torque measuring device of the present invention has a torque load member having a rotation center axis and an annular (for example, cylindrical surface or annular surface) detected surface centered on the rotation center axis, and the detected surface. It is provided with a magnetic distortion type torque sensor having a coil facing the center.
The surface to be detected has shot peening processing units only at one or a plurality of locations in the circumferential direction. The shot peening processing unit is a portion to which shot peening processing has been performed.
The coil is arranged only in a part of the circumferential direction centered on the rotation center axis.
本発明のトルク測定装置の一態様では、前記ショットピーニング処理部は、円周方向に関して等間隔となる複数箇所に配置されている。 In one aspect of the torque measuring device of the present invention, the shot peening processing units are arranged at a plurality of locations at equal intervals in the circumferential direction.
本発明のトルク測定装置の一態様では、前記被検出面において、全周に対する30%以上(より好ましくは50%以上、さらに好ましくは70%以上)の円周方向範囲に、前記ショットピーニング処理部が存在する。 In one aspect of the torque measuring device of the present invention, the shot peening processing unit covers the area to be detected in a circumferential direction of 30% or more (more preferably 50% or more, still more preferably 70% or more) with respect to the entire circumference. Exists.
本発明のトルク測定装置の一態様では、前記トルク負荷部材を回転可能に支持する転がり軸受をさらに備え、前記トルクセンサが前記転がり軸受に支持されている。
この場合に、前記トルクセンサは、例えば、前記転がり軸受が備える使用時にも回転しない静止輪に対し、直接又はセンサホルダなどの他の部材を介して間接的に支持することができる。
In one aspect of the torque measuring device of the present invention, a rolling bearing that rotatably supports the torque load member is further provided, and the torque sensor is supported by the rolling bearing.
In this case, the torque sensor can be directly or indirectly supported by another member such as a sensor holder with respect to the stationary wheel provided in the rolling bearing which does not rotate even when used.
本発明の製造対象となるトルク負荷部材は、回転中心軸と、前記回転中心軸を中心とする円環状の被検出面とを備え、前記被検出面は、円周方向に関する1乃至複数箇所にのみショットピーニング処理部を有する。 The torque load member to be manufactured according to the present invention includes a rotation center axis and an annular detected surface centered on the rotation center axis, and the detected surface is located at one or a plurality of locations in the circumferential direction. Only has a shot peening processing unit.
本発明のトルク負荷部材の製造方法の第1の態様は、前記トルク負荷部材の中間素材のうち前記被検出面を形成すべき部分において、円周方向に関する1乃至複数箇所のみを露出させ、かつ、残りの箇所をマスキングした状態で、ショットピーニング処理を行うことにより、該1乃至複数箇所にのみ前記ショットピーニング処理部を形成する工程を備える。 The first aspect of the method for manufacturing a torque load member of the present invention is to expose only one or a plurality of points in the circumferential direction in a portion of the intermediate material of the torque load member on which the surface to be detected is to be formed. A step of forming the shot peening processing unit only at the one or a plurality of locations by performing the shot peening processing with the remaining portions masked is provided.
本発明のトルク負荷部材の製造方法の第2の態様は、前記トルク負荷部材の中間素材のうち前記被検出面を形成すべき部分において、全体にショットピーニング処理を施した後、円周方向に関する1乃至複数箇所から外れた箇所の表層部を除去することにより、該1乃至複数箇所のみを前記ショットピーニング処理部とする工程を備える。 A second aspect of the method for manufacturing a torque load member of the present invention relates to the circumferential direction after shot peening treatment is applied to the portion of the intermediate material of the torque load member to which the surface to be detected is to be formed. The present invention comprises a step of removing only the surface layer portion of a portion deviated from the one or a plurality of locations to use only the one or a plurality of locations as the shot peening processing portion.
本発明のトルク測定装置によれば、トルク負荷部材に負荷されたトルクだけでなく、トルク負荷部材の回転速度も測定することができる。 According to the torque measuring device of the present invention, not only the torque applied to the torque load member but also the rotation speed of the torque load member can be measured.
[実施の形態の第1例]
実施の形態の第1例について、図1~図7を用いて説明する。
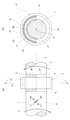
図1は、トルク測定装置を示している。このトルク測定装置は、トルク負荷部材に相当する回転軸1と、転がり軸受2と、磁歪式のトルクセンサ3とを備える。
[First example of the embodiment]
The first example of the embodiment will be described with reference to FIGS. 1 to 7.
FIG. 1 shows a torque measuring device. This torque measuring device includes a
なお、本例に関する以下の説明中、トルク測定装置に関して、軸方向一方側は、図1における右側であり、軸方向他方側は、図1における左側である。 In the following description of this example, regarding the torque measuring device, one side in the axial direction is the right side in FIG. 1, and the other side in the axial direction is the left side in FIG.
回転軸1は、自動車のパワートレインを構成する、変速機の回転軸、デファレンシャルギヤの回転軸、プロペラシャフト、ドライブシャフトなどのトルク伝達軸であり、回転中心軸Xを有する。回転軸1は、回転中心軸Xを中心とする円柱状に構成されている。なお、回転軸は、例えば、回転中心軸Xを中心とする円筒状に構成することもできる。回転軸1は、磁歪特性を有する材料製であり、本例では、SCr420(クロム鋼)、SCM420(クロムモリブデン鋼)、SNCM420(ニッケルクロムモリブデン鋼)などの鋼(鉄合金)製である。
The
回転軸1は、軸方向一部外周面に、回転中心軸Xを中心とする円筒面状の内輪軌道4を有する。回転軸1は、外周面のうちで内輪軌道4の軸方向一方側に隣接する部分(図1及び図2(a)において、2本の鎖線α同士の間に挟まれた部分)に、回転中心軸Xを中心とする円筒面状の被検出面5を有する。
The
被検出面5は、円周方向1箇所にのみ、ショットピーニング処理が施された部分であるショットピーニング処理部26(図1、図2(a)、図2(b)において斜格子を付した部分)を有し、残りの円周方向箇所に、ショットピーニング処理が施されていない部分であるショットピーニング非処理部27を有する。本例では、被検出面5において、ショットピーニング処理部26は、全周に対する50%の円周方向範囲(中心角が180度の円周方向範囲)に存在しており、ショットピーニング非処理部27は、全周に対する残りの50%の円周方向範囲に存在している。ただし、本発明を実施する場合、ショットピーニング処理部26は、本例の場合よりも小さい又は大きい円周方向範囲に存在させることもできる。ただし、後述する出力Vのレベルを大きく確保する観点から、ショットピーニング処理部は、被検出面において、全周に対する30%以上(より好ましくは50%以上、さらに好ましくは70%以上)の円周方向範囲に存在するようにするのが良い。
The surface to be detected 5 is provided with a diagonal grid in the shot peening processing unit 26 (FIGS. 1, FIG. 2 (a), and FIG. 2 (b)), which is a portion to which the shot peening process is applied only at one position in the circumferential direction. A portion), and a shot peening
回転軸1は、転がり軸受2により、自動車のパワートレインを構成するハウジングなどの使用時に回転しない静止部材に対して、回転中心軸Xを中心とする回転可能に支持されている。
The
転がり軸受2は、ニードル軸受であり、使用時にも回転しない静止輪である外輪6と、複数個のニードル7と、保持器8とを備える。
The rolling
外輪6は、軸受鋼などの鋼製で、円筒状に構成されている。外輪6は、軸方向両側の端部に径方向内側に折れ曲がった内向鍔部9を有する。外輪6は、1対の内向鍔部9に挟まれた軸方向中間部内周面に、円筒面状の外輪軌道10を有する。このような外輪6は、自動車のパワートレインを構成するハウジングなどの静止部材に内嵌された状態で、使用時にも回転しない。複数個のニードル7は、それぞれが軸受鋼などの鋼製で、円柱状に構成されている。これらのニードル7は、外輪軌道10と内輪軌道4との間に転動自在に配置されている。保持器8は、鋼製又は合成樹脂製で、円筒状に構成されている。保持器8は、円周方向複数箇所にポケットを有し、かつ、これらのポケット内にニードル7を1つずつ転動自在に保持している。
The
トルクセンサ3は、センサホルダ11を介して、外輪6に支持されている。センサホルダ11は、金属、合成樹脂などにより円筒状に構成されており、外輪6の軸方向一方側に隣接配置された状態で、外輪6に取り付けられている。このために、具体的には、センサホルダ11の軸方向他方側端部に備えられた嵌合筒部12を、外輪6の軸方向一方側の内向鍔部9に内嵌固定している。なお、センサホルダは、外輪6と一体に形成することもできる。
The
トルクセンサ3は、磁性材製で円筒状のバックヨーク13と、バックヨーク13の径方向内側に接着などの適宜の固定手段によって保持固定された検出部14とを備える。このようなトルクセンサ3は、回転軸1の被検出面5の周囲に、被検出面5と同軸に配置された状態、すなわち、被検出面5に検出部14を径方向に対向させた状態で、センサホルダ11に内嵌保持されている。
The
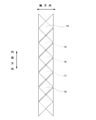
検出部14は、多数のコイル(第一~第四検出コイル19~22)を含んで構成され、回転軸1の回転中心軸Xを中心とする一部の円周方向範囲にのみ配置されている。すなわち、検出部14は、部分円筒状に構成されている。特に、本例では、検出部14は、半円筒状に構成されており、回転軸1の回転中心軸Xを中心とする中心角が180度の円周方向範囲に配置されている。ただし、本発明を実施する場合、検出部14は、本例の場合よりも小さい又は大きい円周方向範囲に配置することもできる。また、本例では、バックヨーク13は、円筒状に構成されているが、本発明を実施する場合には、バックヨークを、検出部14と同じ円周方向範囲にのみ存在する部分円筒状に構成することもできる。
The
検出部14は、図2(b)に示すように、それぞれが円筒状に構成された4つのコイル層である、第一~第四コイル層15~18を備える。第一~第四コイル層15~18は、径方向内側から、第一コイル層15、第二コイル層16、第三コイル層17、第四コイル層18の順に並べた状態で、径方向に積層配置されている。第一コイル層15と第二コイル層16とは、図示しない帯状のフレキシブル基板の片側面と他側面とに分けて成形され、かつ、該フレキシブル基板を半円筒状に湾曲させることにより、半円筒状に構成されている。第三コイル層17と第四コイル層18とは、図示しない別の帯状のフレキシブル基板の片側面と他側面とに分けて成形され、かつ、該フレキシブル基板を半円筒状に湾曲させることにより、半円筒状に構成されている。第二コイル層16と第三コイル層17との間には、絶縁層が設けられている。
As shown in FIG. 2B, the
図3は、検出部14を径方向外側から見た展開図を示している。図4(a)~図4(d)は、検出部14を構成する第一~第四コイル層15~18をそれぞれ個別に径方向外側から見た展開図を示している。
FIG. 3 shows a developed view of the
第一コイル層15は、図4(a)に示すように、複数個の第一検出コイル19を備える。これらの第一検出コイル19は、円周方向に関して等ピッチに並べて配置されている。これらの第一検出コイル19は、円周方向に隣り合うもの同士が直列に接続されている。
As shown in FIG. 4A, the
第二コイル層16は、図4(b)に示すように、複数個の第二検出コイル20を備える。これらの第二検出コイル20は、円周方向に関して等ピッチに並べて配置されている。これらの第二検出コイル20は、円周方向に隣り合うもの同士が直列に接続されている。
As shown in FIG. 4B, the
第三コイル層17は、図4(c)に示すように、複数個の第三検出コイル21を備える。これらの第三検出コイル21は、円周方向に関して等ピッチに並べて配置されている。これらの第三検出コイル21は、円周方向に隣り合うもの同士が直列に接続されている。
As shown in FIG. 4C, the
第四コイル層18は、図4(d)に示すように、複数個の第四検出コイル22を備える。これらの第四検出コイル22は、円周方向に関して等ピッチに並べて配置されている。これらの第四検出コイル22は、円周方向に隣り合うもの同士が直列に接続されている。
As shown in FIG. 4D, the
第一検出コイル19及び第四検出コイル22のそれぞれは、円周方向両側部に、回転軸1の軸方向に対して+45゜傾斜した配線を含んで構成されている。これに対し、第二検出コイル20及び第三検出コイル21のそれぞれは、円周方向両側部に、回転軸1の軸方向に対して-45゜傾斜した配線を含んで構成されている。
Each of the
なお、本例では、第一~第四コイル層15~18のそれぞれを、フレキシブル基板の側面に成形しているが、第一~第四コイル層のそれぞれを、ボビンなどの支持部材に導線を巻き付けることによって構成することもできる。 In this example, each of the first to fourth coil layers 15 to 18 is formed on the side surface of the flexible substrate, but each of the first to fourth coil layers has a conducting wire connected to a support member such as a bobbin. It can also be configured by wrapping.
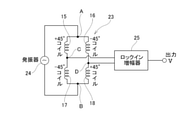
第一~第四コイル層15~18は、図5に示すような、ブリッジ回路23を構成している。ブリッジ回路23は、第一~第四コイル層15~18の他、A点とB点との間に交流電圧を印加するための発振器24と、C点とD点との間の電位差(中点電圧、差動電圧)を検出及び増幅するためのロックイン増幅器25とを含んで構成されている。
The first to fourth coil layers 15 to 18 constitute a
上述のような本例のトルク測定装置を構成する回転軸1の製造方法では、次のようにして被検出面5を形成する。すなわち、回転軸1を製造する際に得られる中間素材の外周面のうち、被検出面5を形成すべき部分、及び、該部分の周辺部分において、被検出面5を形成すべき部分の一部の円周方向箇所のみを露出させ、かつ、残りの箇所をマスキングした状態で、ショットピーニング処理を行う。これにより、被検出面5を形成すべき部分のうち、前記一部の円周方向箇所にのみ、ショットピーニング処理部26を形成し、残りの円周方向箇所をショットピーニング非処理部27とすることで、被検出面5を形成する。
In the method of manufacturing the
なお、本発明を実施する場合には、次のようにして被検出面5を形成することもできる。すなわち、回転軸1を製造する際に得られる中間素材の外周面のうち、被検出面5を形成すべき部分の全体にショットピーニング処理を施す。その後、被検出面5を形成すべき部分の一部の円周方向箇所から外れた円周方向箇所の表層部(例えば表面から100~200μmまでの部分)を切削などにより除去することで、該一部の円周方向箇所のみをショットピーニング処理部26とし、表層部を除去した箇所をショットピーニング非処理部27とすることで、被検出面5を形成する。
In addition, when carrying out this invention, the detected
本例のトルク測定装置の使用時には、発振器24により、ブリッジ回路23のA点とB点との間に交流電圧を印加し、第一~第四コイル層15~18に交流電流を流す。すると、第一~第四コイル層15~18には、図4(a)~図4(d)に矢印イ、ロ、ハ、ニで示すように、円周方向に隣り合う検出コイル19~22同士で互いに逆向きの電流が流れる。言い換えれば、このような向きの電流が流れるように各検出コイル19~22が巻かれている。この結果、第一~第四コイル層15~18の周囲に交流磁界が発生し、この交流磁界の磁束が、回転軸1の被検出面5の表層部を通過する。
When using the torque measuring device of this example, an AC voltage is applied between points A and B of the
この状態で、回転軸1に、図2(a)に示す方向のトルクTが加わると、回転軸1には、軸方向に対して+45゜方向の引っ張り応力(+σ)と、軸方向に対して-45゜方向の圧縮応力(-σ)とが作用する。そして、逆磁歪効果により、引っ張り応力(+σ)が作用する方向である+45゜方向では、回転軸1の透磁率が増加し、圧縮応力(-σ)が作用する方向である-45゜方向では、回転軸1の透磁率が減少する。
In this state, when the torque T in the direction shown in FIG. 2A is applied to the
一方、第一コイル層15及び第四コイル層18は、回転軸1の軸方向に対して+45゜傾斜した配線を含んで構成されており、該配線の周囲に発生する交流磁界の磁束の一部は、回転軸1の被検出面5の表層部を、透磁率が減少した方向である-45゜方向に通過する。このため、第一コイル層15及び第四コイル層18の自己インダクタンスは、それぞれ減少する。第二コイル層16及び第三コイル層17は、回転軸1の軸方向に対して-45゜傾斜した配線を含んで構成されており、該配線の周囲に発生する交流磁界の磁束の一部は、回転軸1の被検出面5の表層部を、透磁率が増加した方向である+45゜方向に通過する。このため、第二コイル層16及び第三コイル層17の自己インダクタンスは、それぞれ増大する。
On the other hand, the
これに対し、回転軸1に、図2(a)に示す方向とは逆方向のトルクTが加わると、上述した場合とは逆の作用により、第一コイル層15及び第四コイル層18の自己インダクタンスが増大し、第二コイル層16及び第三コイル層17の自己インダクタンスが減少する。
On the other hand, when the torque T in the direction opposite to the direction shown in FIG. 2A is applied to the
いずれにしても、ブリッジ回路23では、C点とD点との間の電位差(中点電圧、差動電圧)をロックイン増幅器25により検出及び増幅することによって、回転軸1に負荷されているトルクTの方向及び大きさに応じた出力Vが得られるようになっている。
In any case, in the
また、本例の構造では、回転軸1が回転している場合には、回転軸1に負荷されているトルクTが一定であっても、ブリッジ回路23の出力V(センサ出力)は、例えば図7(a)に示すように周期的に変化する。次に、この理由について説明する。
Further, in the structure of this example, when the
本例の構造では、回転軸1の被検出面5は、円周方向1箇所にのみショットピーニング処理部26を有し、残りの円周方向箇所にショットピーニング非処理部27を有する。また、トルクセンサ3の検出部14は、回転軸1の回転中心軸Xを中心とする一部の円周方向範囲にのみ配置されている。このため、本例の構造では、回転軸1が回転することに伴って、検出部14と対向する部分を、ショットピーニング処理部26とショットピーニング非処理部27とが交互に通過する。
In the structure of this example, the detected
一方、被検出面5において、ショットピーニング処理部26は、ショットピーニング非処理部27に比べて、磁歪特性が改善されており、検出部14がショットピーニング処理部26に対向している場合は、検出部14がショットピーニング非処理部27に対向している場合に比べて、ブリッジ回路23の出力Vが大きくなり、トルクの検出感度が向上する。なお、このような効果が得られる理由は、例えば、特公平7-10011号公報、特開2018-112451号公報などに記載されているように、種々存在するが、当該理由自体は本発明の特徴ではないため、説明を省略する。
On the other hand, on the surface to be detected 5, the shot
いずれにしても、本例の構造では、トルクセンサ3の検出部14がショットピーニング処理部26に対向している場合には、トルクセンサ3の検出部14がショットピーニング非処理部27に対向している場合に比べて、ブリッジ回路23の出力Vが大きくなる。このため、回転軸1が回転することに伴って、検出部14と対向する部分を、ショットピーニング処理部26とショットピーニング非処理部27とが交互に通過すると、ブリッジ回路23の出力Vは、例えば図7(a)に示すように周期的に変化する。
In any case, in the structure of this example, when the
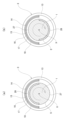
なお、図7(a)に示した出力Vにおいて、最大値(ピーク値)Vmaxは、図6(a)に示すように、被検出面5のうち検出部14が対向している部分における、ショットピーニング処理部26の割合が最大(本例では100%)になった状態での値である。これに対して、最小値Vminは、図6(b)に示すように、被検出面5のうち検出部14が対向している部分における、ショットピーニング処理部26の割合が最小(本例では0%)になった状態での値である。
In the output V shown in FIG. 7A, the maximum value (peak value) V max is, as shown in FIG. 6A, in the portion of the surface to be detected 5 where the
本例の構造では、出力Vのレベル(例えば、最大値Vmax、平均値など)は、回転軸1に負荷されているトルクTが大きくなるほど大きくなる。このため、出力Vのレベルに基づいて、トルクTの大きさを測定することができる。また、出力Vの極性(±)は、トルクTの方向によって変化する。このため、出力Vの極性(±)に基づいて、トルクTの方向を把握することができる。
In the structure of this example, the level of the output V (for example, the maximum value V max , the average value, etc.) increases as the torque T loaded on the
また、本例の構造では、出力Vの周波数(周期)は、回転軸1の回転速度によって変化する。このため、出力Vの周波数(周期)に基づいて、回転速度を測定することができる。
Further, in the structure of this example, the frequency (period) of the output V changes depending on the rotation speed of the
なお、被検出面の全周をショットピーニング処理部(又はショットピーニング非処理部)とした比較例の構造では、トルクTが一定の場合には、回転軸が回転しても、トルクセンサの出力Vは、図7(b)に示すように、一定値になる。このため、出力Vに基づいて、回転軸の回転速度を測定することはできない。 In the structure of the comparative example in which the entire circumference of the detected surface is a shot peening processing unit (or a shot peening non-processing unit), when the torque T is constant, the output of the torque sensor is output even if the rotation shaft rotates. V becomes a constant value as shown in FIG. 7 (b). Therefore, it is not possible to measure the rotation speed of the rotating shaft based on the output V.
以上のような本例のトルク測定装置を車両に搭載すれば、測定したトルクT及び回転速度を車両制御に活用することができる。また、本例のトルク測定装置によれば、トルクTだけでなく、回転速度も測定できるため、車両に搭載する測定装置の数を減らすことができる。 If the torque measuring device of this example as described above is mounted on the vehicle, the measured torque T and the rotational speed can be utilized for vehicle control. Further, according to the torque measuring device of this example, not only the torque T but also the rotation speed can be measured, so that the number of measuring devices mounted on the vehicle can be reduced.
[実施の形態の第2例]
実施の形態の第2例について、図8及び図9を用いて説明する。
[Second example of the embodiment]
A second example of the embodiment will be described with reference to FIGS. 8 and 9.
本例の構造では、回転軸1の被検出面5aは、円周方向等間隔となる複数箇所(図示の例では8箇所)にショットピーニング処理部26を備える。換言すれば、被検出面5aは、ショットピーニング処理部26とショットピーニング非処理部27とを複数(図示の例では8つ)ずつ備えており、ショットピーニング処理部26とショットピーニング非処理部27とが円周方向に関して交互にかつ等ピッチに配置されている。また、本例の構造でも、トルクセンサ3の検出部14aは、一部の円周方向範囲(図示の例では、中心角が約205度の円周方向範囲)にのみ配置されている。なお、本発明を実施する場合には、被検出面5aが備えるショットピーニング処理部26(ショットピーニング非処理部27)の数は、本例の場合よりも少なく又は多くすることもできる。また、本発明を実施する場合には、検出部14aは、本例の場合よりも小さい又は大きい円周方向範囲に配置することもできる。
In the structure of this example, the detected
以上のような本例の構造でも、回転軸1の回転に伴って、被検出面5aのうち検出部14aが対向している部分における、ショットピーニング処理部26の割合が、周期的に変化する。具体的には、回転軸1の回転に伴って、図9(a)に示すように、5箇所のショットピーニング処理部26が検出部14aに対向する状態と、図9(b)に示すように、4箇所のショットピーニング処理部26が検出部14aに対向する状態とが、交互に繰り返される。そして、これに伴い、ブリッジ回路23の出力Vが周期的に変化する。このため、この出力Vの周波数(周期)に基づいて、回転軸1の回転速度を測定することができる。
Even in the structure of this example as described above, the ratio of the shot
特に、本例の構造では、被検出面5aのショットピーニング処理部26が円周方向複数箇所に存在するため、実施の形態の第1例の構造(例えば図2参照)のように、被検出面5のショットピーニング処理部26が円周方向1箇所にしか存在しない場合に比べて、回転軸1が回転する際の出力Vの周波数を高く(周期を短く)することができる。したがって、本例の構造では、実施の形態の第1例の構造よりも短い時間間隔で、回転軸1の回転速度の変化を検出することができる。
その他の構成及び作用効果は、実施の形態の第1例と同じである。
In particular, in the structure of this example, since the shot
Other configurations and effects are the same as in the first embodiment.
なお、本発明を実施する場合、磁歪式のトルクセンサを構成するコイルは、円周方向複数箇所(例えば、直径方向反対側となる2箇所)に配置することもできる。 When the present invention is carried out, the coils constituting the magnetostrictive torque sensor may be arranged at a plurality of locations in the circumferential direction (for example, two locations on opposite sides in the radial direction).
本発明の対象となるトルク負荷部材は、回転軸に限らず、たとえば、回転軸に外嵌固定され、かつ、該回転軸と共にトルクを負荷されるスリーブとすることもできる。 The torque load member that is the subject of the present invention is not limited to the rotation shaft, and may be, for example, a sleeve that is externally fitted and fixed to the rotation shaft and to which torque is applied together with the rotation shaft.
トルク負荷部材は、周面に被検出面を有する部材に限らず、たとえば特開2017-96825号公報や特開2017-96826号公報に記載されているような、軸方向側面に被検出面を有する部材とすることもできる。 The torque load member is not limited to a member having a detected surface on the peripheral surface, and the detected surface is provided on an axial side surface as described in, for example, JP-A-2017-96825 and JP-A-2017-96828. It can also be a member to have.
本発明の対象となるトルク負荷部材を自動車のパワートレインに組み込んで使用する場合、対象となる装置は、特に問わない。たとえば、マニュアルトランスミッション(MT)、オートマチックトランスミッション(AT)、ベルト式無段変速機、トロイダル型無段変速機、オートマチックマニュアルトランスミッション(AMT)、デュアルクラッチトランスミッション(DCT)などの車側の制御で変速を行うトランスミッション、又はトランスファーを対象とすることができる。対象となる車両の駆動方式(FF、FR、MR、RR、4WDなど)も、特に問わない。 When the torque load member of the present invention is incorporated into a power train of an automobile and used, the target device is not particularly limited. For example, manual transmission (MT), automatic transmission (AT), belt type continuously variable transmission, toroidal type continuously variable transmission, automatic manual transmission (AMT), dual clutch transmission (DCT), etc. It can be targeted for transmissions or transfers to be performed. The drive system (FF, FR, MR, RR, 4WD, etc.) of the target vehicle is also not particularly limited.
本発明の対象となるトルク負荷部材は、自動車のパワートレインを構成する回転軸に限らず、たとえば、風車の回転軸(主軸、増速器の回転軸)、圧延機のロールネック、鉄道車両の回転軸(車軸、減速機の回転軸)、工作機械の回転軸(主軸、送り系の回転軸)、建設機械・農業機械・家庭用電気器具・モータの回転軸等、各種機械装置の回転軸などを採用することができる。 The torque load member that is the object of the present invention is not limited to the rotary shaft constituting the power train of the automobile, for example, the rotary shaft of the wind turbine (main shaft, the rotary shaft of the speed increaser), the roll neck of the rolling mill, and the railway vehicle. Rotating shafts of various mechanical devices such as rotating shafts (axles, rotating shafts of speed reducers), rotating shafts of machine tools (main shafts, rotating shafts of feed systems), rotating shafts of construction machinery, agricultural machinery, household electric appliances, motors, etc. Etc. can be adopted.
本発明のトルク測定装置を実施する場合、トルクセンサは、転がり軸受に限らず、ハウジングなどの他の部材に支持されていても良い。 When implementing the torque measuring device of the present invention, the torque sensor may be supported not only by a rolling bearing but also by another member such as a housing.
本発明のトルク測定装置を実施する場合で、トルクセンサが転がり軸受に支持されている構成を採用する場合には、該転がり軸受は、ニードル軸受に限らず、玉軸受、ころ軸受、円すいころ軸受などの他の形式の転がり軸受であっても良い。 In the case of implementing the torque measuring device of the present invention, when the configuration in which the torque sensor is supported by the rolling bearing is adopted, the rolling bearing is not limited to the needle bearing, but also a ball bearing, a roller bearing, and a tapered roller bearing. Other types of rolling bearings such as may be used.
1 回転軸
2 転がり軸受
3 トルクセンサ
4 内輪軌道
5 被検出面
6 外輪
7 ニードル
8 保持器
9 内向鍔部
10 外輪軌道
11 センサホルダ
12 嵌合筒部
13 バックヨーク
14 検出部
15 第一コイル層
16 第二コイル層
17 第三コイル層
18 第四コイル層
19 第一検出コイル
20 第二検出コイル
21 第三検出コイル
22 第四検出コイル
23 ブリッジ回路
24 発振器
25 ロックイン増幅器
26 ショットピーニング処理部
27 ショットピーニング非処理部
1 Rotating
Claims (6)
前記被検出面に対向させたコイルを有する磁歪式のトルクセンサと、を備え、
前記被検出面は、円周方向に関する1乃至複数箇所にのみショットピーニング処理部を有しており、
前記コイルは、前記回転中心軸を中心とする一部の円周方向範囲にのみ配置されている、
トルク測定装置。 A torque load member having a rotation center axis and an annular detected surface centered on the rotation center axis,
A magnetostrictive torque sensor having a coil facing the surface to be detected is provided.
The surface to be detected has shot peening processing units only at one or a plurality of locations in the circumferential direction.
The coil is arranged only in a partial circumferential range centered on the rotation center axis.
Torque measuring device.
請求項1に記載のトルク測定装置。 The shot peening processing units are arranged at a plurality of locations at equal intervals in the circumferential direction.
The torque measuring device according to claim 1.
請求項1又は2に記載のトルク測定装置。 On the surface to be detected, the shot peening processing unit exists in a circumferential direction range of 30% or more with respect to the entire circumference.
The torque measuring device according to claim 1 or 2.
前記トルクセンサが前記転がり軸受に支持されている、
請求項1~3のうちのいずれかに記載のトルク測定装置。 Further provided with a rolling bearing that rotatably supports the torque load member,
The torque sensor is supported by the rolling bearing,
The torque measuring device according to any one of claims 1 to 3.
前記トルク負荷部材の中間素材のうち前記被検出面を形成すべき部分において、円周方向に関する1乃至複数箇所のみを露出させ、かつ、残りの箇所をマスキングした状態で、ショットピーニング処理を行うことにより、該1乃至複数箇所にのみ前記ショットピーニング処理部を形成する工程を備える、
トルク負荷部材の製造方法。 Manufacture of a torque load member having a rotation center axis and an annular detected surface centered on the rotation center axis, and the detected surface has shot peening processing portions only at one or a plurality of locations in the circumferential direction. It ’s a method,
In the intermediate material of the torque load member, in the portion where the surface to be detected is to be formed, the shot peening process is performed with only one or a plurality of locations in the circumferential direction exposed and the remaining portions masked. A step of forming the shot peening processing unit only at the one or a plurality of locations is provided.
Manufacturing method of torque load member.
前記トルク負荷部材の中間素材のうち前記被検出面を形成すべき部分において、全体にショットピーニング処理を施した後、円周方向に関する1乃至複数箇所から外れた箇所の表層部を除去することにより、該1乃至複数箇所のみを前記ショットピーニング処理部とする工程を備える、
トルク負荷部材の製造方法。 Manufacture of a torque load member having a rotation center axis and an annular detected surface centered on the rotation center axis, and the detected surface has shot peening processing portions only at one or a plurality of locations in the circumferential direction. It ’s a method,
In the intermediate material of the torque load member, the portion where the surface to be detected is to be formed is subjected to shot peening treatment as a whole, and then the surface layer portion is removed from one or a plurality of locations in the circumferential direction. A step of using only the one or a plurality of locations as the shot peening processing unit is provided.
Manufacturing method of torque load member.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020138720A JP2022034835A (en) | 2020-08-19 | 2020-08-19 | Manufacturing method of torque measuring device and torque load member |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020138720A JP2022034835A (en) | 2020-08-19 | 2020-08-19 | Manufacturing method of torque measuring device and torque load member |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2022034835A true JP2022034835A (en) | 2022-03-04 |
Family
ID=80443842
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020138720A Pending JP2022034835A (en) | 2020-08-19 | 2020-08-19 | Manufacturing method of torque measuring device and torque load member |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2022034835A (en) |
-
2020
- 2020-08-19 JP JP2020138720A patent/JP2022034835A/en active Pending
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US20080170817A1 (en) | Bearing Assemly With Integrated Sensor System | |
| US20010030533A1 (en) | Magnetic encoder, wheel bearing and method of manfacturing magnetic encoder | |
| JP6361316B2 (en) | Rotation transmission device with torque measuring device | |
| JP6375767B2 (en) | Rotation transmission device with torque measuring device | |
| JP6500649B2 (en) | Rotational transmission device with torque measuring device | |
| JP2022034835A (en) | Manufacturing method of torque measuring device and torque load member | |
| WO2022070581A1 (en) | Torque load member and method for producing same, and torque measurement device | |
| JP7067297B2 (en) | Torque measuring device | |
| JP2018194433A (en) | Rotating body supporting device, and diagnosis system and diagnosis method thereof | |
| US8727626B2 (en) | Method and device for adjusting the bearing play in a ceramic hybrid bearing | |
| US20140219593A1 (en) | Torque sensor bearing arrangement and method | |
| JP6956575B2 (en) | Torque load member and torque transmission device | |
| JP6655960B2 (en) | Sensor for torque measurement and bearing with sensor | |
| JP6682931B2 (en) | Rotation transmission device with torque measuring device | |
| JP6654025B2 (en) | Sensor for torque measurement and bearing with sensor | |
| JP2006162557A (en) | Torque sensor | |
| JP2023127313A (en) | torque measuring device | |
| JP2008026009A (en) | Method for measuring state of rotation of bearing | |
| JP2023127315A (en) | Torque measurement device, and manufacturing method of the same | |
| US11629756B2 (en) | Method for manufacturing a sensor bearing unit | |
| JPH08122346A (en) | Number of spins measuring apparatus for rolling element for roller bearing | |
| JPH08278318A (en) | Rotary sensor for wheel support bearing | |
| JP6922485B2 (en) | Wheel drive | |
| JP2019078671A (en) | Torque transmission device | |
| JP2008082403A (en) | Rolling bearing, pulley device having this rolling bearing and method of manufacturing its rolling bearing |