JP2009253642A - Class-d amplifier, and switching driving method for class-d amplifier - Google Patents
Class-d amplifier, and switching driving method for class-d amplifier Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2009253642A JP2009253642A JP2008098696A JP2008098696A JP2009253642A JP 2009253642 A JP2009253642 A JP 2009253642A JP 2008098696 A JP2008098696 A JP 2008098696A JP 2008098696 A JP2008098696 A JP 2008098696A JP 2009253642 A JP2009253642 A JP 2009253642A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- pair
- switching elements
- circuit
- class amplifier
- switching
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Amplifiers (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明はDクラスアンプ、Dクラスアンプのスイッチング駆動方法に係り、とくに片電源を用いたDクラスアンプ、Dクラスアンプのスイッチング駆動方法に関する。 The present invention relates to a D class amplifier and a switching drive method for the D class amplifier, and more particularly to a D class amplifier using a single power supply and a switching drive method for the D class amplifier.
オーディオパワーアンプでは電力効率の高いDクラスアンプが用いられるようになってきている。Dクラスアンプにはハイサイドとローサイドの一対のスイッチング素子を1組有するハーフブリッジ接続と、ハイサイドとローサイドの一対のスイッチング素子を2組用いたフルブリッジ接続がある。また、電源形式には片電源(+B)と両電源(±B)があり、車載用パワーアンプでは、バッテリ電圧をDC/DCコンバータで昇圧して+Bまたは±Bを作成している。特開2006−60278号の図2には両電源とハーフブリッジ接続を組み合わせた構成例が開示されている。図1に概略の構成を示す。直列接続されて交互にオン・オフを繰り返すスイッチング素子1、2の各々に個別にフライホイールダイオードD1、D2が並列接続されており、2つのスイッチング素子1、2の接続点P(電圧をV0とする)とグランドとの間にLC回路10と負荷RLが接続されている。スイッチング素子1、2の両端には電源部20から±Bが供給されている。スイッチング素子1、2は入力信号により高周波の三角波をPWM変調して作成した駆動パルスDP1、DP2(DP2はDP1の反転)に基づき交互にオン・オフされる。スイッチング素子1がオン、2がオフの場合、V0は+Bとなり、スイッチング素子1がオフ、2がオンの場合、V0は−Bとなる。今、V0の平均電圧が+となっており、スイッチング素子1のオン期間がオフ期間より長く、LC回路10のコイルLFにPから負荷RLの方向へ電流が流れていたとして(図1(1)参照)、スイッチング素子1がオン、2がオフの状態から1がオフ、2がオンの状態に切り替わったとき、コイルLFに流れる電流が連続性を保とうとするため引き続き、Pから負荷RLの方向へ流れる(図1(2)参照)。このときの電流方向は電源部11から見て本来流れる方向とは逆な回生電流となるため電源部11の−B側の大容量コンデンサが充電されて−BがΔVだけ大きくなってしまう電源パンピング現象が起きる。また、入力信号が零で駆動パルスDP1、DP2のデューティ比が50%の場合、V0には+B/2の直流バイアスが生じる。
In audio power amplifiers, D-class amplifiers with high power efficiency have been used. The D-class amplifier includes a half-bridge connection having a pair of high-side and low-side switching elements and a full-bridge connection using two pairs of high-side and low-side switching elements. In addition, there are a single power source (+ B) and a dual power source (± B) in the power source format, and in-vehicle power amplifiers create + B or ± B by boosting the battery voltage with a DC / DC converter. FIG. 2 of Japanese Patent Application Laid-Open No. 2006-60278 discloses a configuration example in which both power supplies and half-bridge connection are combined. FIG. 1 shows a schematic configuration. Flywheel diodes D1 and D2 are individually connected in parallel to each of
特表2000−513159号の図5には片電源とフルブリッジ接続を組み合わせた構成例が開示されている。図2に概略の構成を示す。直列接続されて交互にオン・オフを繰り返すスイッチング素子1、2の各々に個別にフライホイールダイオードD1、D2が並列接続されており、2つのスイッチング素子1、2の接続点P1(電圧をV1とする)がLC回路10を介して負荷RLの一端と接続されている。また直列接続されて交互にオン・オフを繰り返すスイッチング素子3、4の各々に個別にフライホイールダイオードD3、D4が並列接続されており、2つのスイッチング素子3、4の接続点P2(電圧をV2とする)がLC回路11を介して負荷RLの他端と接続されている。LC回路10と11のコンデンサCFの一端はグランドに接続されている。スイッチング素子1、2の両端と3、4の両端には片電源の電源部21から+Bが供給されている。スイッチング素子1、2は入力信号により高周波の三角波をPWM変調して作成した駆動パルスDP1、DP2(DP2はDP1の反転)に基づき交互にオン・オフされる。スイッチング素子3、4は駆動パルスDP2、DP1に基づき交互にオン・オフされる。スイッチング素子1、4がオン、2、3がオフの場合、V1−V2は+Bとなり、スイッチング素子1、4がオフ、2、3がオンの場合、V1−V2は−Bとなる。よって、負荷RLには+Bの2倍の電圧が掛かるので、両電源並の出力電力を得ることができる。また、片電源なので両電源の場合よりもパンピング現象は小さくなるが、電源部21に回生電流が流れるのでパンピング現象自体を無くすことはできない。
FIG. 5 of JP-T-2000-513159 discloses a configuration example in which a single power source and a full bridge connection are combined. FIG. 2 shows a schematic configuration. Flywheel diodes D1 and D2 are individually connected in parallel to each of
ところで、図2の駆動パルスDP1、DP2のデューティ比が50%の場合、原理的にはV1、V2ともに約+B/2となり、グランドから見た場合に直流バイアスが生じる。 Incidentally, when the duty ratio of the drive pulses DP1 and DP2 in FIG. 2 is 50%, in principle, both V1 and V2 are about + B / 2, and a DC bias is generated when viewed from the ground.
本発明は上記した従来技術の問題に鑑み、片電源により出力電力が大きく取れ、回生電流によるパンピング現象が発生しにくいDクラスアンプを提供することを、その目的とする。 An object of the present invention is to provide a D-class amplifier in which a large output power can be obtained by a single power source and a pumping phenomenon due to a regenerative current is unlikely to occur.
本発明のDクラスアンプの1つは、ハイサイドとローサイドの第1の一対のスイッチング素子と、第1の一対のスイッチング素子の各々に並列接続した第1の一対のダイオードと、ハイサイドとローサイドの第2の一対のスイッチング素子と、第2の一対のスイッチング素子の各々に並列接続した第2の一対のダイオードと、入力信号の振幅の正負に応じて第1の一対のスイッチング素子を交互にオン・オフ駆動する第1の駆動手段と、入力信号をPWM変調したパルスに基づき第2の一対のスイッチング素子を交互にオン・オフ駆動する第2の駆動手段と、第1、第2の一対のスイッチング素子の両端に接続された片電源と、第1の一対のスイッチング素子の間の第1の接続点と、第2の一対のスイッチング素子の間の第2の接続点との間に接続されたLC回路とを備え、LC回路のコンデンサの一端をグランドと接続し、LC回路のコンデンサと並列に負荷を接続するようにしたこと、を特徴としている。
本発明のDクラスアンプの他の1つは、第1のDクラスアンプ回路と第2のDクラスアンプ回路を有し、第1のDクラスアンプ回路は、ハイサイドとローサイドの第1の一対のスイッチング素子と、第1の一対のスイッチング素子の各々に並列接続した第1の一対のダイオードと、ハイサイドとローサイドの第2の一対のスイッチング素子と、第2の一対のスイッチング素子の各々に並列接続した第2の一対のダイオードと、入力信号の振幅の正負に応じて第1の一対のスイッチング素子を交互にオン・オフ駆動する第1の駆動手段と、入力信号をPWM変調したパルスに基づき第2の一対のスイッチング素子を交互にオン・オフ駆動する第2の駆動手段と、第1、第2の一対のスイッチング素子の両端に接続された第1の片電源と、第1の一対のスイッチング素子の間の第1の接続点と、第2の一対のスイッチング素子の間の第2の接続点との間に接続された第1のLC回路とを備え、第2のDクラスアンプ回路は、ハイサイドとローサイドの第1の一対のスイッチング素子と、第1の一対のスイッチング素子の各々に並列接続した第1の一対のダイオードと、ハイサイドとローサイドの第2の一対のスイッチング素子と、第2の一対のスイッチング素子の各々に並列接続した第2の一対のダイオードと、入力信号の振幅の正負に応じて第1の一対のスイッチング素子を交互にオン・オフ駆動する第1の駆動手段と、入力信号をPWM変調したパルスに基づき第2の一対のスイッチング素子を交互にオン・オフ駆動する第2の駆動手段と、第1、第2の一対のスイッチング素子の両端に接続された第2の片電源と、第1の一対のスイッチング素子の間の第1の接続点と、第2の一対のスイッチング素子の間の第2の接続点との間に接続された第2のLC回路とを備え、第1のLC回路のコンデンサの一端と第2のLC回路のコンデンサの一端をグランドと接続し、第1のLC回路と第2のLC回路の間に負荷を接続するようにし、第1のDクラスアンプ回路の第1の駆動手段が第1の一対のスイッチング素子のハイサイドをオン(オフ)するとき、第2のDクラスアンプ回路の第1の駆動手段は第1の一対のスイッチング素子のローサイドをオン(オフ)し、第1のDクラスアンプ回路の第2の駆動手段が第2の一対のスイッチング素子のハイサイドをオン(オフ)するとき、第2のDクラスアンプ回路の第2の駆動手段は第2の一対のスイッチング素子のローサイドをオン(オフ)するようにしたこと、を特徴としている。
本発明のDクラスアンプのスイッチング駆動方法の1つは、ハイサイドとローサイドの第1の一対のスイッチング素子の各々に第1の一対のダイオードを並列接続し、ハイサイドとローサイドの第2の一対のスイッチング素子の各々に第2の一対のダイオードを並列接続し、第1、第2の一対のスイッチング素子の両端に片電源を接続し、第1の一対のスイッチング素子の間の第1の接続点と、第2の一対のスイッチング素子の間の第2の接続点との間にLC回路を接続し、LC回路のコンデンサの一端をグランドと接続するとともにLC回路のコンデンサと並列に負荷を接続し、入力信号の正負に応じて第1の一対のスイッチング素子を交互にオン・オフ駆動し、入力信号をPWM変調したパルスに基づき第2の一対のスイッチング素子を交互にオン・オフ駆動するようにしたこと、を特徴としている。
本発明のDクラスアンプのスイッチング駆動方法の他の1つは、第1のDクラスアンプ回路のハイサイドとローサイドの第1の一対のスイッチング素子の各々に第1の一対のダイオードを並列接続し、ハイサイドとローサイドの第2の一対のスイッチング素子の各々に第2の一対のダイオードを並列接続し、第1、第2の一対のスイッチング素子の両端に第1の片電源を接続し、第1の一対のスイッチング素子の間の第1の接続点と、第2の一対のスイッチング素子の間の第2の接続点との間に第1のLC回路を接続し、第2のDクラスアンプ回路のハイサイドとローサイドの第1の一対のスイッチング素子の各々に第1の一対のダイオードを並列接続し、ハイサイドとローサイドの第2の一対のスイッチング素子の各々に第2の一対のダイオードを並列接続し、第1、第2の一対のスイッチング素子の両端に第2の片電源を接続し、第1の一対のスイッチング素子の間の第1の接続点と、第2の一対のスイッチング素子の間の第2の接続点との間に第2のLC回路を接続し、第1のLC回路のコンデンサの一端と第2のLC回路のコンデンサの一端をグランドと接続するとともに、第1のLC回路と第2のLC回路の間に負荷を接続し、入力信号の正負に応じて第1、第2のDクラスアンプ回路の第1の一対のスイッチング素子を交互にオン・オフ駆動するとともに、入力信号をPWM変調したパルスに基づき第1、第2のDクラスアンプ回路の第2の一対のスイッチング素子を交互にオン・オフ駆動するようにし、この際、第1のDクラスアンプ回路の第1の一対のスイッチング素子のハイサイドをオン(オフ)するとき、第2のDクラスアンプ回路の第1の一対のスイッチング素子のローサイドをオン(オフ)し、第1のDクラスアンプ回路の第2の一対のスイッチング素子のハイサイドをオン(オフ)するとき、第2のDクラスアンプ回路の第2の一対のスイッチング素子のローサイドをオン(オフ)するようにしたこと、を特徴としている。
One of the D-class amplifiers of the present invention includes a first pair of high-side and low-side switching elements, a first pair of diodes connected in parallel to each of the first pair of switching elements, a high-side and a low-side The second pair of switching elements, the second pair of diodes connected in parallel to each of the second pair of switching elements, and the first pair of switching elements alternately according to the positive / negative of the amplitude of the input signal First driving means for on / off driving, second driving means for alternately turning on / off the second pair of switching elements based on a pulse obtained by PWM modulating an input signal, and first and second pairs A single power source connected to both ends of the switching element, a first connection point between the first pair of switching elements, and a second connection point between the second pair of switching elements. And a connected LC circuit, connected to ground one end of the capacitor of the LC circuit, it has to connect the load in parallel with the capacitor of the LC circuit is characterized.
Another one of the D class amplifiers of the present invention includes a first D class amplifier circuit and a second D class amplifier circuit, and the first D class amplifier circuit includes a first pair of a high side and a low side. A first pair of diodes connected in parallel to each of the first pair of switching elements, a second pair of switching elements on the high side and the low side, and each of the second pair of switching elements A second pair of diodes connected in parallel, a first driving means for alternately turning on and off the first pair of switching elements according to the positive / negative of the amplitude of the input signal, and a pulse obtained by PWM modulating the input signal Based on a second driving means for alternately turning on and off the second pair of switching elements, a first single power source connected to both ends of the first and second pair of switching elements, A first LC circuit connected between a first connection point between the pair of switching elements and a second connection point between the second pair of switching elements, and a second D class The amplifier circuit includes a first pair of switching elements on the high side and the low side, a first pair of diodes connected in parallel to each of the first pair of switching elements, and a second pair of switching on the high side and the low side. A first pair of diodes that are connected in parallel to each of the second pair of switching elements, and a first pair of switching elements that are alternately turned on / off according to the positive / negative of the amplitude of the input signal. Driving means, a second driving means for alternately turning on and off the second pair of switching elements based on a pulse obtained by PWM modulating the input signal, and a first pair of switching elements Connected between a second single power source connected to the end, a first connection point between the first pair of switching elements, and a second connection point between the second pair of switching elements. A second LC circuit, one end of the capacitor of the first LC circuit and one end of the capacitor of the second LC circuit are connected to the ground, and a load is provided between the first LC circuit and the second LC circuit. When the first driving means of the first D class amplifier circuit turns on (turns off) the high side of the first pair of switching elements, the first driving of the second D class amplifier circuit Means turns on (off) the low side of the first pair of switching elements, and when the second driving means of the first D class amplifier circuit turns on (off) the high side of the second pair of switching elements, Second driving means of second D class amplifier circuit Is characterized in that the low side of the second pair of switching elements is turned on (off).
One of the switching driving methods of the D-class amplifier according to the present invention includes a first pair of diodes connected in parallel to each of the first pair of switching elements on the high side and the low side, and a second pair of high side and the low side. A second pair of diodes are connected in parallel to each of the switching elements, a single power source is connected to both ends of the first and second pair of switching elements, and a first connection between the first pair of switching elements The LC circuit is connected between the point and the second connection point between the second pair of switching elements, one end of the capacitor of the LC circuit is connected to the ground, and a load is connected in parallel with the capacitor of the LC circuit. Then, the first pair of switching elements are alternately turned on / off according to whether the input signal is positive or negative, and the second pair of switching elements is turned on based on a pulse obtained by PWM-modulating the input signal. It was adapted to each other on and off the drive, is characterized in.
Another one of the switching driving methods of the D class amplifier of the present invention is to connect a first pair of diodes in parallel to each of the first pair of switching elements on the high side and the low side of the first D class amplifier circuit. A second pair of diodes are connected in parallel to each of the second pair of switching elements on the high side and the low side, a first single power source is connected to both ends of the first and second pair of switching elements, A first LC circuit connected between a first connection point between one pair of switching elements and a second connection point between a second pair of switching elements; A first pair of diodes are connected in parallel to each of the first pair of switching elements on the high side and the low side of the circuit, and a second pair of dies are connected to each of the second pair of switching elements on the high side and the low side. Are connected in parallel, a second single power source is connected to both ends of the first and second pair of switching elements, a first connection point between the first pair of switching elements and a second pair of switching elements. A second LC circuit is connected to the second connection point between the switching elements, and one end of the capacitor of the first LC circuit and one end of the capacitor of the second LC circuit are connected to the ground, A load is connected between the first LC circuit and the second LC circuit, and the first pair of switching elements of the first and second D class amplifier circuits are alternately turned on and off according to the positive and negative of the input signal. And the second pair of switching elements of the first and second D class amplifier circuits are alternately turned on / off based on a pulse obtained by PWM modulating the input signal. At this time, the first D class A first pair of switches in an amplifier circuit When the high side of the element is turned on (off), the low side of the first pair of switching elements of the second D class amplifier circuit is turned on (off), and the second pair of switching of the first D class amplifier circuit It is characterized in that when the high side of the element is turned on (off), the low side of the second pair of switching elements of the second D class amplifier circuit is turned on (off).
請求項1、3の発明によれば、スイッチンク素子をフルブリッジ接続したので、片電源により両電源並の大きな出力電力を取ることができる。また、回生電流が電源を流れないので、パンピング現象が発生しにくく、出力電圧がグランドを中心に変化するので直流バイアスが発生しない。
請求項2、4の発明によれば、シングルエンドの第1、第2のDクラスアンプ回路をブリッジ接続したことで、片電源の4倍の出力電圧を得ることができ、より大きな出力電力を取ることができる。また、回生電流が電源を流れないので、パンピング現象が発生しにくく、出力電圧がグランドを中心に変化するので直流バイアスが発生しない。
According to the first and third aspects of the present invention, since the switching elements are connected by a full bridge, it is possible to obtain a large output power equivalent to that of both power sources by a single power source. In addition, since the regenerative current does not flow through the power source, the pumping phenomenon is unlikely to occur, and the output voltage changes centered on the ground, so that no DC bias is generated.
According to the second and fourth aspects of the present invention, by connecting the single-ended first and second D class amplifier circuits by bridge connection, it is possible to obtain an output voltage that is four times that of a single power supply, and a larger output power. Can be taken. In addition, since the regenerative current does not flow through the power source, the pumping phenomenon is unlikely to occur, and the output voltage changes centered on the ground, so that no DC bias is generated.
以下、本発明の最良の形態を実施例に基づき説明する。 Hereinafter, the best mode of the present invention will be described based on examples.
次に図3を参照して本発明の第1実施例を説明する。図3は本発明に係るオーディオ用Dクラスアンプの構成を示す回路図である。
図3において、1と2は直列接続されたハイサイドとローサイドの第1の一対のスイッチング素子、3と4は直列接続されたハイサイドとローサイドの第2の一対のスイッチング素子、D1とD2は各々スイッチング素子1と2に並列接続されたフライホイールダイオード、D3とD4は各々スイッチング素子3と4に並列接続されたフライホイールダイオード、21は+Bの片電源であり、フローティング状態で第1、第2の一対のスイッチング素子1と2、3と4の両端に接続されている。10はコイルLFとコンデンサCFから成る低域通過用のLC回路であり、コンデンサCFの一端がグランドと接続されてシングルエンドを構成している。RLはLC回路10の出力側でコンデンサCFと並列接続された負荷(スピーカ)である。
Next, a first embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIG. FIG. 3 is a circuit diagram showing a configuration of an audio D-class amplifier according to the present invention.
In FIG. 3, 1 and 2 are a first pair of high-side and low-side switching elements connected in series, 3 and 4 are a second pair of high-side and low-side switching elements connected in series, and D1 and D2 are Flywheel diodes connected in parallel to switching
30は入力信号の瞬時値の正負に応じて第1の一対のスイッチング素子1、2を交互にオン・オフ駆動する第1の駆動回路であり、図4に具体的な回路構成を示す。図4において、第1の駆動回路30の内、31は入力信号をグランド電位と比較するコンパレータであり、入力信号の瞬時値が正の期間ローレベル、負の期間ハイレベルとなる第1パルスを出力する。第1パルスは遅延回路32とAND回路33の一方の入力端子に入力され、遅延回路32の出力がAND回路33の他方の入力端子に入力されている。AND回路33からはデッドタイム付の第1スイッチングパルスSP1がドライバ34を介してスイッチング素子1に出力される。第1スイッチングパルスSP1は入力信号の瞬時値が負の間ハイとなり(但し、ハイ期間はデッドタイム分だけ短い)、スイッチング素子1をオンし、正の間ローとなり、スイッチング素子1をオフする。
35はコンパレータ31の出力を反転する反転回路であり、入力信号の瞬時値が正の期間ハイレベル、負の期間ローレベルとなる第2パルスを出力する。第2パルスは遅延回路36とAND回路37の一方の入力端子に入力され、遅延回路36の出力がAND回路37の他方の入力端子に入力されている。AND回路37からはデッドタイム付の第2スイッチングパルスSP2がドライバ38を介してスイッチング素子2に出力される。第2スイッチングパルスSP2は入力信号の瞬時値が正の期間ハイとなり(但し、ハイ期間はデッドタイム分だけ短い)、スイッチング素子2をオンし、期間の間ローとなり、スイッチング素子2をオンする(図6参照)。
Reference numeral 35 denotes an inverting circuit that inverts the output of the comparator 31 and outputs a second pulse in which the instantaneous value of the input signal is high during a positive period and low during a negative period. The second pulse is input to one input terminal of the
40は入力信号をPWM変調したパルスに基づき第2の一対のスイッチング素子3、4を交互にオン・オフする第2の駆動回路であり、図5に具体的な回路構成を示す。図5において、第2の駆動回路40の内、41は高周波の三角波を発生する三角波発生器、42は入力信号と三角波を比較し、入力信号の瞬時値が三角波の瞬時値より大きい期間ハイレベル、入力信号の瞬時値が三角波の瞬時値より小さい期間ローレベルとなる第3パルスを出力するコンパレータ、43は入力信号の極性を反転する反転回路、44は極性反転された入力信号と三角波を比較し、反転後の入力信号の瞬時値が三角波の瞬時値より大きい期間ハイレベル、入力信号の瞬時値が三角波の瞬時値より小さい期間ローレベルとなる第4パルスを出力するコンパレータ、45は第3パルスと第4パルスの排他的論理和をとるXOR回路、46は第3パルスと第4パルスの排他的否定和をとるXNOR回路、47は第1の駆動回路30のコンパレータ31の出力に基づき入力信号の瞬時値が正の間、XOR回路45の出力を選択出力し、負の間、XNOR回路46の出力を選択出力するスイッチ回路であり、スイッチ回路47から第5パルスが出力される。第5パルスは遅延回路48とAND回路49の一方の入力端子に入力され、遅延回路48の出力がAND回路49の他方の入力端子に入力されている。AND回路49からはデッドタイム付の第3スイッチングパルスSP3がドライバ50を介してスイッチング素子3に出力される。第3スイッチングパルスSP3は入力信号の瞬時値が三角波の瞬時値より大きい期間と、極性反転した入力信号の瞬時値が三角波の瞬時値より大きい期間にハイとなり(但し、ハイ期間はデッドタイム分だけ短い)、スイッチング素子3をオンし、他の期間ローとなり、スイッチング素子3をオフする。
51はスイッチ回路47の出力を反転する反転回路であり、第6パルスを出力する。第6パルスは遅延回路52とAND回路53の一方の入力端子に入力され、遅延回路52の出力がAND回路53の他方の入力端子に入力されている。AND回路53からはデッドタイム付の第4スイッチングパルスSP4がドライバ54を介してスイッチング素子4に出力される。第4スイッチングパルスSP4は入力信号の瞬時値が三角波の瞬時値より小さい期間と、極性反転した入力信号の瞬時値が三角波の瞬時値より小さい期間にハイとなり(但し、ハイ期間はデッドタイム分だけ短い)、スイッチング素子4をオンし、他の期間ローとなり、スイッチング素子4をオフする(図7参照)。
Reference numeral 51 denotes an inverting circuit that inverts the output of the
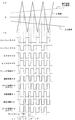
図6は第1の駆動回路30の動作を示す線図、図7は入力信号が正の期間の第2の駆動回路40の動作を示す線図、図8、図9は入力信号が正の期間の回生電流の経路を示す説明図、図10は入力信号が負の期間の第2の駆動回路40の動作を示す線図、図11、図12は入力信号が負の期間の回生電流の経路を示す説明図であり、以下、これらの図を参照して上記した実施例の動作を説明する。
(1)入力信号の瞬時値が正の期間(図3、図6〜図9参照)
入力信号の瞬時値が正の期間は第1スイッチングパルスSP1がロー、第2スイッチングパルスSP2がハイとなっている(但し、第2スイッチングパルスSP2のロー期間はデッドタイム分だけ短い)。このため、第1の一対のスイッチング素子の内、スイッチング素子1がオフを維持し、2がオンを維持する。一方、第3スイッチングパルスSP3は入力信号の瞬時値に比例するPWM変調をされてハイとローを繰り返し(但し、ハイ期間はデッドタイム分だけ短い)、ハイの間、第2の一対のスイッチング素子の内、スイッチング素子3をオンし、ローの間オフする。第4スイッチングパルスSP4は第3スイッチングパルスSP3がハイの間ローとなり、ローの間ハイとなり(但し、ハイ期間はデッドタイム分だけ短い)、ハイの間、第2の一対のスイッチング素子の内、スイッチング素子4をオンし、ローの間オフする。これにより、第2の一対のスイッチング素子3、4は交互にオンオフを繰り返す(図3のスイッチング素子1、2の実線の状態、図8、図9参照)。
6 is a diagram showing the operation of the
(1) Period in which the instantaneous value of the input signal is positive (see FIGS. 3 and 6 to 9)
During the period when the instantaneous value of the input signal is positive, the first switching pulse SP1 is low and the second switching pulse SP2 is high (however, the low period of the second switching pulse SP2 is shorter by the dead time). For this reason, of the first pair of switching elements, the switching
時系列的に見ると、例えば図6の時点t1でスイッチング素子3がオン、スイッチング素子4がオフとなり(図3のスイッチング素子3、4の実線の状態参照)、時点t2でスイッチング素子3、4ともにオフとなり(デッドタイム。図8参照)、時点t3でスイッチング素子3がオフ、4がオンとなり(図9参照)、時点t4でスイッチング素子3、4がともにオフとなり(デッドタイム。図8参照)、時点t5で再びスイッチング素子3がオン、4がオフとなり(図3のスイッチング素子3、4の実線の状態参照)、以下、同様の動作を繰り返す。
t1−t2の期間は、第1の一対のスイッチング素子1、2の接続点P1の電位V0がグランドとなり、第2の一対のスイッチング素子3、4の接続点P2の電位V1が+Bとなり、この+Bがスイッチング素子3、LC回路10を介して負荷RLのグランド側とは反端側に印加される。t2−t5の期間は、スイッチング素子3がオフしているので、片電源21はフローティング状態となる。一方、t1−t2の期間にコイルLFを電流が接続点P2からコンデンサCFの方向に流れていたとすると(図3の符号I参照)、t2でスイッチング素子3がオフしたあともコイルLFには同じ方向に電流が流れ続けようとするが、この回生電流はt2−t3の期間とt4−T5の期間では負荷RL、スイッチング素子2、フライホイールダイオードD4、コイルLFの経路で流れ(図8参照)、t3−t4の期間では負荷RL、スイッチング素子2、スイッチング素子4とフライホイールダイオードD4、コイルLFの経路で流れる(図9参照)。従って、回生電流は片電源21に流れ込むことはない。
When viewed in time series, for example, the switching
During the period from t1 to t2, the potential V0 of the connection point P1 of the first pair of switching
(1)入力信号の瞬時値が負の期間(図3、図6、図10、図11、図12参照)
入力信号の瞬時値が負の期間は第1スイッチングパルスSP1がハイ、第2スイッチングパルスSP2がローとなっている(但し、第1スイッチングパルスSP1のロー期間はデッドタイム分だけ短い)。このため、第1の一対のスイッチング素子の内、スイッチング素子1がオンを維持し、2がオフを維持する。一方、第3スイッチングパルスSP3は入力信号の瞬時値に比例するPWM変調をされてハイとローを繰り返し(但し、ハイ期間はデッドタイム分だけ短い)、ハイの間、第2の一対のスイッチング素子の内、スイッチング素子3をオンし、ローの間オフする。第4スイッチングパルスSP4は第3スイッチングパルスSP3がハイの間ローとなり、ローの間ハイとなり(但し、ハイ期間はデッドタイム分だけ短い)、ハイの間、第2の一対のスイッチング素子の内、スイッチング素子4をオンし、ローの間オフする。これにより、第2の一対のスイッチング素子3、4は交互にオンオフを繰り返す(図3のスイッチング素子1、2の破線の状態、図11、図12参照)。
(1) Period in which the instantaneous value of the input signal is negative (see FIGS. 3, 6, 10, 11, and 12)
During a period when the instantaneous value of the input signal is negative, the first switching pulse SP1 is high and the second switching pulse SP2 is low (however, the low period of the first switching pulse SP1 is shorter by the dead time). For this reason, among the first pair of switching elements, the switching
時系列的に見ると、例えば図10の時点t1’でスイッチング素子3がオフ、スイッチング素子4がオンとなり(図3のスイッチング素子3、4の破線の状態)、時点t2’でスイッチング素子3、4ともにオフとなり(デッドタイム。図11参照)、時点t3’でスイッチング素子3がオン、4がオフとなり(図12参照)、時点t4’でスイッチング素子3、4がともにオフとなり(デッドタイム。図11参照)、時点t5’で再びスイッチング素子3がオフ、4がオンとなり(図3のスイッチング素子3、4の破線の状態)、以下、同様の動作を繰り返す。
t1’−t2’の期間は、第1の一対のスイッチング素子1、2の接続点P1の電位V0がグランドとなり、第2の一対のスイッチング素子3、4の接続点P2の電位V1が−Bとなり、この−Bがスイッチング素子3、LC回路10を介して負荷RLのグランド側とは反端側に印加される。t2’−t5’の期間は、スイッチング素子4がオフしているので、片電源21はフローティング状態となる。一方、t1’−t2’の期間にコイルLFを電流がコンデンサCFの側から接続点P2の方向に流れていたとすると(図3の符号I’参照)、t2’でスイッチング素子4がオフしたあともコイルLFには同じ方向に電流が流れ続けようとするが、この回生電流はt2’−t3’の期間とt4’−t5’の期間ではP2、フライホイールダイオードD3、スイッチング素子1、負荷RLの経路で流れ(図11参照)、t3’−t4’の期間ではスイッチング素子3とフライホイールダイオードD3、スイッチング素子1、負荷RLの経路で流れる(図12参照)。従って、入力信号が負の期間も回生電流が片電源21に流れ込むことはない。
Looking at time series, for example, the switching
During the period t1′-t2 ′, the potential V0 at the connection point P1 of the first pair of switching
この実施例によれば、負荷RLのグランドとは反対側にグランドを中心としてほぼ±Bに変化する電圧が印加されるので、出力電力が両電源並に大きくなるとともに、直流バイアスが生じない。また、回生電流が片電源21に流れ込まないので、パンピング現象が起きない。
According to this embodiment, a voltage that changes to approximately ± B with respect to the ground is applied to the opposite side of the ground of the load RL, so that the output power becomes as large as both power supplies and no DC bias is generated. Further, since the regenerative current does not flow into the
次に図13を参照して本発明の第2実施例を説明する。図13は本発明に係るオーディオ用Dクラスアンプの構成を示す回路図である。
図13では、図3のDクラスアンプと全く同様に構成された2組の第1、第2のDクラスアンプ回路70、80を備え、第1のDクラスアンプ回路70の第1のLC回路10AのコンデンサCFの一端と第2のDクラスアンプ回路80の第2のLC回路10BのコンデンサCFの一端をグランドと接続し、第1のDクラスアンプ回路70の第1のLC回路10Aと第2のDクラスアンプ回路80の第2のLC回路10Bの間に負荷RLを接続してある。
また、第1のDクラスアンプ回路70の第1の駆動回路30が第1の一対のスイッチング素子のハイサイドをオン(オフ)するとき、第2のDクラスアンプ回路80の第1の駆動回路30は第1の一対のスイッチング素子のローサイドをオン(オフ)し、第1のDクラスアンプ回路70の第2の駆動回路40が第2の一対のスイッチング素子のハイサイドをオン(オフ)するとき、第2のDクラスアンプ回路80の第2の駆動回路40は第2の一対のスイッチング素子のローサイドをオン(オフ)するようにしてある。即ち、第1のDクラスアンプ回路70では第1の駆動回路30のスイッチングパルスSP1とSP2はスイッチング素子1と2に印加されているが、第2のDクラスアンプ回路80では第1の駆動回路30のスイッチングパルスSP1とSP2はスイッチング素子2と1に印加されている。第1のDクラスアンプ回路70では第2の駆動回路40のスイッチングパルスSP3とSP4はスイッチング素子3と4に印加されているが、第2のDクラスアンプ回路80では第2の駆動回路40のスイッチングパルスSP3とSP4はスイッチング素子4と3に印加されている。
Next, a second embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIG. FIG. 13 is a circuit diagram showing a configuration of an audio D-class amplifier according to the present invention.
13 includes two sets of first and second D class amplifier circuits 70 and 80 configured in exactly the same manner as the D class amplifier of FIG. 3, and includes a first LC circuit of the first D class amplifier circuit 70. One end of the capacitor CF of 10A and one end of the capacitor CF of the
Further, when the
図13のDクラスアンプにおいて、入力信号が正の期間は、第1のDクラスアンプ回路70のスイッチング素子1がオフ、2がオンを継続し、第2のDクラスアンプ回路80のスイッチング素子1がオン、2がオフを継続する。そして、入力信号の瞬時値に応じてPWM変調されたスイッチングパルスSP3、SP4により、第1のDクラスアンプ回路70の第2の一対のスイッチング素子3と4が交互にオン・オフし、これに同期して、第2のDクラスアンプ回路80の第2の一対のスイッチング素子3、4が交互にオン・オフする(但し、第1のDクラスアンプ回路70と第2のDクラスアンプ回路80とではオン・オフするサイドが逆)。或る時点で、第1のDクラスアンプ回路70のスイッチング素子3がオン、4がオフ、第2のDクラスアンプ回路80のスイッチング素子3がオフ、4がオンとなっているとき(図13参照)、第1のDクラスアンプ回路70の接続点P2の電位V2が+B、第2のDクラスアンプ回路80の接続点P2の電位V2が−Bとなるので、負荷RLには第2のDクラスアンプ回路80の側から見て第1のDクラスアンプ回路70の側にほぼ+2Bが印加される。
In the D class amplifier of FIG. 13, during a period when the input signal is positive, the switching
このとき、第1のDクラスアンプ回路70の第1のLC回路10AのコイルLFに第1のDクラスアンプ回路70から負荷RLの方向へ電流が流れており、第2のDクラスアンプ回路80の第2のLC回路10BのコイルLFに負荷RLから第2のDクラスアンプ回路80の方向へ電流が流れていたとすると(図13のI参照。電流経路は第1のDクラスアンプ回路70の第1の片電源21A、スイッチング素子3、接続点P2、第1のLC回路10A、負荷RL、第2のDクラスアンプ回路80の第2のLC回路10B、接続点P2、スイッチング素子4、第2の片電源21B、スイッチング素子1、接続点P1、グランド、第1のDクラスアンプ回路70の接続点P1、スイッチング素子2、第1の片電源21A)、その後、デッドタイムに入り第1のDクラスアンプ回路70と第2のDクラスアンプ回路80の第2のスイッチング素子3、4がともにオフとなったとき、回生電流は図14の如く、第2のDクラスアンプ回路80のD3、スイッチング素子1、接続点P1、グランド、第1のDクラスアンプ回路70の接続点P1、スイッチング素子2、D4の経路で流れ、第1、第2の片電源21A、21Bには流れない。
次に、デッドタイムが終わり第1のDクラスアンプ回路70のスイッチング素子3がオフ、4がオン、第2のDクラスアンプ回路80のスイッチング素子3がオン、4がオフとなったとき、回生電流は図15の如く、第2のDクラスアンプ回路80のスイッチング素子3とD3、スイッチング素子1、接続点P1、グランド、第1のDクラスアンプ回路70の接続点P1、スイッチング素子2、スイッチング素子4とD4、接続点P2の経路で流れ、やはり第1、第2の片電源21A、21Bには流れない。
At this time, a current flows from the first D class amplifier circuit 70 toward the load RL in the coil LF of the
Next, when the dead time is over and the
これと異なり図13のDクラスアンプにおいて、入力信号が負の期間は、第1のDクラスアンプ回路70のスイッチング素子1がオン、2がオフを継続し、第2のDクラスアンプ回路80のスイッチング素子1がオフ、2がオンを継続する。そして、入力信号の瞬時値に応じてPWM変調されたスイッチングパルスSP3、SP4により、第1のDクラスアンプ回路70の第2の一対のスイッチング素子3と4が交互にオン・オフし、これに同期して、第2のDクラスアンプ回路80の第2の一対のスイッチング素子3、4が交互にオン・オフする(但し、第1のDクラスアンプ回路70と第2のDクラスアンプ回路80とではオン・オフするサイドが逆)。或る時点で、第1のDクラスアンプ回路70のスイッチング素子3がオフ、4がオン、第2のDクラスアンプ回路80のスイッチング素子3がオン、4がオフとなっているとき、第1のDクラスアンプ回路70の接続点P2の電位V2が−B、第2のDクラスアンプ回路80の接続点P2の電位V2が+Bとなるので、負荷RLには第2のDクラスアンプ回路80の側から見て第1のDクラスアンプ回路70の側にほぼ−2Bが印加される。
In contrast, in the D class amplifier of FIG. 13, during the period when the input signal is negative, the switching
このとき、第1のDクラスアンプ回路70の第1のLC回路10AのコイルLFに負荷RLから第1のDクラスアンプ回路70の方向へ電流が流れており、第2のDクラスアンプ回路80の第2のLC回路10BのコイルLFに第2のDクラスアンプ回路80から負荷RLの方向へ電流が流れていたとすると(図16のI’参照)、電流経路は第2のDクラスアンプ回路80の第2の片電源21B、スイッチング素子3、接続点P2、第2のLC回路10B、負荷RL、第1のDクラスアンプ回路70の第1のLC回路10A、接続点P2、スイッチング素子4、第1の片電源21A、スイッチング素子1、接続点P1、グランド、第2のDクラスアンプ回路80の接続点P1、スイッチング素子2、第2の片電源21B)、その後、デッドタイムに入り第1のDクラスアンプ回路70と第2のDクラスアンプ回路80の第2のスイッチング素子3、4がともにオフとなったとき、回生電流は図17の如く、第1のDクラスアンプ回路70のD3、スイッチング素子1、接続点P1、グランド、第2のDクラスアンプ回路80の接続点P1、スイッチング素子2、D4の経路で流れ、第1、第2の片電源21A、21Bには流れない。
次に、デッドタイムが終わり第1のDクラスアンプ回路70のスイッチング素子3がオン、4がオフ、第2のDクラスアンプ回路80のスイッチング素子3がオフ、4がオンとなったとき、回生電流は図18の如く、第1のDクラスアンプ回路70のスイッチング素子3とD3、スイッチング素子1、接続点P1、グランド、第2のDクラスアンプ回路80の接続点P1、スイッチング素子2、スイッチング素子4とD4、接続点P2の経路で流れ、やはり第1、第2の片電源21A、21Bには流れない。
At this time, a current flows from the load RL toward the first D class amplifier circuit 70 through the coil LF of the
Next, when the dead time is over and the
図13の実施例によれば、負荷RLの一端側をから見て他端側には±2Bに変化する電圧が印加されるので、出力電力を非常に大きくすることができる。また、回生電流が第1、第2の片電源21A、21Bに流れ込まないので、パンピング現象が起きない。
According to the embodiment of FIG. 13, since the voltage changing to ± 2B is applied to the other end side when viewed from one end side of the load RL, the output power can be greatly increased. Further, since the regenerative current does not flow into the first and second
本発明は、オーディオ用、その他の用途の片電源を用いたDクラスアンプに適用できる。 The present invention can be applied to a D class amplifier using a single power source for audio and other purposes.
1、2、3、4 スイッチング素子
10 LC回路
10A 第1のLC回路
10B 第2のLC回路
21 片電源
21A 第1の片電源
21B 第2の片電源
30 第1の駆動回路
40 第2の駆動回路
70 第1のDクラスアンプ回路
80 第2のDクラスアンプ回路
RL 負荷
LF コイル
1, 2, 3, 4
Claims (4)
第1の一対のスイッチング素子の各々に並列接続した第1の一対のダイオードと、
ハイサイドとローサイドの第2の一対のスイッチング素子と、
第2の一対のスイッチング素子の各々に並列接続した第2の一対のダイオードと、
入力信号の正負に応じて第1の一対のスイッチング素子を交互にオン・オフ駆動する第1の駆動手段と、
入力信号をPWM変調したパルスに基づき第2の一対のスイッチング素子を交互にオン・オフ駆動する第2の駆動手段と、
第1、第2の一対のスイッチング素子の両端に接続された片電源と、
第1の一対のスイッチング素子の間の第1の接続点と、第2の一対のスイッチング素子の間の第2の接続点との間に接続されたLC回路とを備え、
LC回路のコンデンサの一端をグランドと接続し、
LC回路のコンデンサと並列に負荷を接続するようにしたこと、
を特徴とするDクラスアンプ。 A first pair of switching elements on the high side and the low side;
A first pair of diodes connected in parallel to each of the first pair of switching elements;
A second pair of switching elements, a high side and a low side;
A second pair of diodes connected in parallel to each of the second pair of switching elements;
First driving means for alternately turning on and off the first pair of switching elements according to the positive and negative of the input signal;
Second driving means for alternately turning on and off the second pair of switching elements based on a PWM modulated pulse of the input signal;
A single power source connected to both ends of the first and second pair of switching elements;
An LC circuit connected between a first connection point between the first pair of switching elements and a second connection point between the second pair of switching elements;
Connect one end of the LC circuit capacitor to the ground,
The load was connected in parallel with the capacitor of the LC circuit,
D-class amplifier characterized by
第1のDクラスアンプ回路は、ハイサイドとローサイドの第1の一対のスイッチング素子と、
第1の一対のスイッチング素子の各々に並列接続した第1の一対のダイオードと、
ハイサイドとローサイドの第2の一対のスイッチング素子と、
第2の一対のスイッチング素子の各々に並列接続した第2の一対のダイオードと、
入力信号の振幅の正負に応じて第1の一対のスイッチング素子を交互にオン・オフ駆動する第1の駆動手段と、
入力信号をPWM変調したパルスに基づき第2の一対のスイッチング素子を交互にオン・オフ駆動する第2の駆動手段と、
第1、第2の一対のスイッチング素子の両端に接続された第1の片電源と、
第1の一対のスイッチング素子の間の第1の接続点と、第2の一対のスイッチング素子の間の第2の接続点との間に接続された第1のLC回路とを備え、
第2のDクラスアンプ回路は、ハイサイドとローサイドの第1の一対のスイッチング素子と、
第1の一対のスイッチング素子の各々に並列接続した第1の一対のダイオードと、
ハイサイドとローサイドの第2の一対のスイッチング素子と、
第2の一対のスイッチング素子の各々に並列接続した第2の一対のダイオードと、
入力信号の振幅の正負に応じて第1の一対のスイッチング素子を交互にオン・オフ駆動する第1の駆動手段と、
入力信号をPWM変調したパルスに基づき第2の一対のスイッチング素子を交互にオン・オフ駆動する第2の駆動手段と、
第1、第2の一対のスイッチング素子の両端に接続された第2の片電源と、
第1の一対のスイッチング素子の間の第1の接続点と、第2の一対のスイッチング素子の間の第2の接続点との間に接続された第2のLC回路とを備え、
第1のLC回路のコンデンサの一端と第2のLC回路のコンデンサの一端をグランドと接続し、
第1のLC回路と第2のLC回路の間に負荷を接続するようにし、
第1のDクラスアンプ回路の第1の駆動手段が第1の一対のスイッチング素子のハイサイドをオン(オフ)するとき、第2のDクラスアンプ回路の第1の駆動手段は第1の一対のスイッチング素子のローサイドをオン(オフ)し、第1のDクラスアンプ回路の第2の駆動手段が第2の一対のスイッチング素子のハイサイドをオン(オフ)するとき、第2のDクラスアンプ回路の第2の駆動手段は第2の一対のスイッチング素子のローサイドをオン(オフ)するようにしたこと、
を特徴とするDクラスアンプ。 A first D-class amplifier circuit and a second D-class amplifier circuit;
The first D-class amplifier circuit includes a first pair of high-side and low-side switching elements,
A first pair of diodes connected in parallel to each of the first pair of switching elements;
A second pair of switching elements, a high side and a low side;
A second pair of diodes connected in parallel to each of the second pair of switching elements;
First driving means for alternately turning on and off the first pair of switching elements according to the positive and negative of the amplitude of the input signal;
Second driving means for alternately turning on and off the second pair of switching elements based on a PWM modulated pulse of the input signal;
A first single power source connected to both ends of the first and second pair of switching elements;
A first LC circuit connected between a first connection point between the first pair of switching elements and a second connection point between the second pair of switching elements;
The second D-class amplifier circuit includes a first pair of switching elements on the high side and the low side,
A first pair of diodes connected in parallel to each of the first pair of switching elements;
A second pair of switching elements, a high side and a low side;
A second pair of diodes connected in parallel to each of the second pair of switching elements;
First driving means for alternately turning on and off the first pair of switching elements according to the positive and negative of the amplitude of the input signal;
Second driving means for alternately turning on and off the second pair of switching elements based on a PWM modulated pulse of the input signal;
A second single power source connected to both ends of the first and second pair of switching elements;
A second LC circuit connected between a first connection point between the first pair of switching elements and a second connection point between the second pair of switching elements;
One end of the capacitor of the first LC circuit and one end of the capacitor of the second LC circuit are connected to the ground,
A load is connected between the first LC circuit and the second LC circuit;
When the first driving means of the first D class amplifier circuit turns on (off) the high side of the first pair of switching elements, the first driving means of the second D class amplifier circuit is the first pair of switching elements. When the low side of the switching element is turned on (off) and the second driving means of the first D class amplifier circuit turns on (off) the high side of the second pair of switching elements, the second D class amplifier The second driving means of the circuit is configured to turn on (off) the low side of the second pair of switching elements;
D-class amplifier characterized by
ハイサイドとローサイドの第2の一対のスイッチング素子の各々に第2の一対のダイオードを並列接続し、
第1、第2の一対のスイッチング素子の両端に片電源を接続し、
第1の一対のスイッチング素子の間の第1の接続点と、第2の一対のスイッチング素子の間の第2の接続点との間にLC回路を接続し、
LC回路のコンデンサの一端をグランドと接続するとともにLC回路のコンデンサと並列に負荷を接続し、
入力信号の正負に応じて第1の一対のスイッチング素子を交互にオン・オフ駆動し、
入力信号をPWM変調したパルスに基づき第2の一対のスイッチング素子を交互にオン・オフ駆動するようにしたこと、
を特徴とするDクラスアンプのスイッチング駆動方法。 A first pair of diodes are connected in parallel to each of the first pair of switching elements on the high side and the low side,
A second pair of diodes are connected in parallel to each of the second pair of switching elements on the high side and the low side,
A single power source is connected to both ends of the first and second pair of switching elements,
Connecting an LC circuit between a first connection point between the first pair of switching elements and a second connection point between the second pair of switching elements;
Connect one end of the capacitor of the LC circuit to the ground and connect a load in parallel with the capacitor of the LC circuit.
The first pair of switching elements are alternately turned on and off according to the positive and negative of the input signal,
The second pair of switching elements are alternately turned on / off based on a pulse obtained by PWM-modulating the input signal,
A switching drive method for a D-class amplifier characterized by the above.
ハイサイドとローサイドの第2の一対のスイッチング素子の各々に第2の一対のダイオードを並列接続し、
第1、第2の一対のスイッチング素子の両端に第1の片電源を接続し、
第1の一対のスイッチング素子の間の第1の接続点と、第2の一対のスイッチング素子の間の第2の接続点との間に第1のLC回路を接続し、
第2のDクラスアンプ回路のハイサイドとローサイドの第1の一対のスイッチング素子の各々に第1の一対のダイオードを並列接続し、
ハイサイドとローサイドの第2の一対のスイッチング素子の各々に第2の一対のダイオードを並列接続し、
第1、第2の一対のスイッチング素子の両端に第2の片電源を接続し、
第1の一対のスイッチング素子の間の第1の接続点と、第2の一対のスイッチング素子の間の第2の接続点との間に第2のLC回路を接続し、
第1のLC回路のコンデンサの一端と第2のLC回路のコンデンサの一端をグランドと接続するとともに、第1のLC回路と第2のLC回路の間に負荷を接続し、
入力信号の正負に応じて第1、第2のDクラスアンプ回路の第1の一対のスイッチング素子を交互にオン・オフ駆動するとともに、
入力信号をPWM変調したパルスに基づき第1、第2のDクラスアンプ回路の第2の一対のスイッチング素子を交互にオン・オフ駆動するようにし、
この際、第1のDクラスアンプ回路の第1の一対のスイッチング素子のハイサイドをオン(オフ)するとき、第2のDクラスアンプ回路の第1の一対のスイッチング素子のローサイドをオン(オフ)し、第1のDクラスアンプ回路の第2の一対のスイッチング素子のハイサイドをオン(オフ)するとき、第2のDクラスアンプ回路の第2の一対のスイッチング素子のローサイドをオン(オフ)するようにしたこと、
を特徴とするDクラスアンプのスイッチング駆動方法。 A first pair of diodes connected in parallel to each of the first pair of switching elements on the high side and the low side of the first D-class amplifier circuit;
A second pair of diodes are connected in parallel to each of the second pair of switching elements on the high side and the low side,
A first single power source is connected to both ends of the first and second pair of switching elements,
Connecting the first LC circuit between a first connection point between the first pair of switching elements and a second connection point between the second pair of switching elements;
A first pair of diodes connected in parallel to each of the first pair of switching elements on the high side and the low side of the second D-class amplifier circuit;
A second pair of diodes are connected in parallel to each of the second pair of switching elements on the high side and the low side,
A second single power source is connected to both ends of the first and second pair of switching elements;
A second LC circuit is connected between a first connection point between the first pair of switching elements and a second connection point between the second pair of switching elements;
One end of the capacitor of the first LC circuit and one end of the capacitor of the second LC circuit are connected to the ground, and a load is connected between the first LC circuit and the second LC circuit,
The first pair of switching elements of the first and second D class amplifier circuits are alternately turned on and off according to the positive and negative of the input signal, and
Based on a pulse obtained by PWM-modulating the input signal, the second pair of switching elements of the first and second D class amplifier circuits are alternately turned on and off,
At this time, when the high side of the first pair of switching elements of the first D class amplifier circuit is turned on (off), the low side of the first pair of switching elements of the second D class amplifier circuit is turned on (off). When the high side of the second pair of switching elements of the first D class amplifier circuit is turned on (off), the low side of the second pair of switching elements of the second D class amplifier circuit is turned on (off). )
A switching drive method for a D-class amplifier characterized by the above.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008098696A JP5131002B2 (en) | 2008-04-04 | 2008-04-04 | D class amplifier, switching driving method of D class amplifier |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008098696A JP5131002B2 (en) | 2008-04-04 | 2008-04-04 | D class amplifier, switching driving method of D class amplifier |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2009253642A true JP2009253642A (en) | 2009-10-29 |
| JP5131002B2 JP5131002B2 (en) | 2013-01-30 |
Family
ID=41313888
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008098696A Active JP5131002B2 (en) | 2008-04-04 | 2008-04-04 | D class amplifier, switching driving method of D class amplifier |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5131002B2 (en) |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS6359213A (en) * | 1986-08-29 | 1988-03-15 | Toshiba Corp | Pulse width modulation circuit |
| JPS63111710A (en) * | 1986-10-29 | 1988-05-17 | Toshiba Corp | Drive circuit for pulse amplifier |
| JP3412417B2 (en) * | 1996-10-04 | 2003-06-03 | 日新電機株式会社 | Power amplifier |
| JP3499236B1 (en) * | 2002-08-28 | 2004-02-23 | 株式会社フライングモール | Digital power amplifier |
| JP2006060273A (en) * | 2004-08-17 | 2006-03-02 | Nec Engineering Ltd | Class d amplifier with lc filter |
| JP2006093764A (en) * | 2004-09-21 | 2006-04-06 | Renesas Technology Corp | Digital power amplifier |
-
2008
- 2008-04-04 JP JP2008098696A patent/JP5131002B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS6359213A (en) * | 1986-08-29 | 1988-03-15 | Toshiba Corp | Pulse width modulation circuit |
| JPS63111710A (en) * | 1986-10-29 | 1988-05-17 | Toshiba Corp | Drive circuit for pulse amplifier |
| JP3412417B2 (en) * | 1996-10-04 | 2003-06-03 | 日新電機株式会社 | Power amplifier |
| JP3499236B1 (en) * | 2002-08-28 | 2004-02-23 | 株式会社フライングモール | Digital power amplifier |
| JP2006060273A (en) * | 2004-08-17 | 2006-03-02 | Nec Engineering Ltd | Class d amplifier with lc filter |
| JP2006093764A (en) * | 2004-09-21 | 2006-04-06 | Renesas Technology Corp | Digital power amplifier |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP5131002B2 (en) | 2013-01-30 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US7965141B2 (en) | Class D audio amplifier | |
| CN103414354B (en) | Device for power switching pulse transformer isolated drive circuit | |
| US7579910B2 (en) | Low distortion switching amplifier circuits and methods | |
| KR100760024B1 (en) | Gate control circuit with soft start/stop function | |
| JP4735826B2 (en) | Power converter | |
| US10985717B2 (en) | Multi-level class D audio power amplifiers | |
| US9577582B2 (en) | Method of reducing power dissipation in a switching amplifier and circuit implementing such method | |
| WO2016166941A1 (en) | Signal transmission circuit and driving for device switching element | |
| US9048794B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for efficient and distortion compensated digital class-D amplifier ternary modulation scheme | |
| US20130106493A1 (en) | Switching system and method for control thereof | |
| US20140125411A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for filter-less analog input class d audio amplifier clipping | |
| US10256779B2 (en) | Multi-level class D amplifier | |
| US20070024361A1 (en) | Systems for pseudo-BD modulation | |
| JP4146418B2 (en) | Gate driver that does not require power supply with level shift between static wells | |
| IT201800002255A1 (en) | SWITCHING CIRCUIT, CORRESPONDING DEVICE AND PROCEDURE | |
| US9270180B2 (en) | DC-DC converter with adaptive minimum on-time | |
| JP5131002B2 (en) | D class amplifier, switching driving method of D class amplifier | |
| CN101022268A (en) | D type amplifier and modulating method thereof | |
| US6967527B2 (en) | Pulse width modulation amplifier | |
| JP2008301192A (en) | Pwm drive circuit and driving method | |
| US11309853B1 (en) | Common mode output voltage biasing in class-D audio amplifiers having selectable differential or dual single-ended operation | |
| JP7201045B2 (en) | power converter | |
| JP6478848B2 (en) | Modulation method and circuit using the modulation method | |
| Saponara et al. | Switching-based topologies for high-efficiency audio amplifiers | |
| CN115133889A (en) | BD type pulse width modulation circuit for D type amplifier and modulation method thereof |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20100922 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20110825 |
|
| A711 | Notification of change in applicant |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A712 Effective date: 20111012 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20120215 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20120223 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20120417 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20121009 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20121022 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20151116 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Ref document number: 5131002 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |