JP2009012779A - Cylindrical shrink label, container having cylindrical shrink label, and method for manufacturing them - Google Patents
Cylindrical shrink label, container having cylindrical shrink label, and method for manufacturing them Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2009012779A JP2009012779A JP2007173315A JP2007173315A JP2009012779A JP 2009012779 A JP2009012779 A JP 2009012779A JP 2007173315 A JP2007173315 A JP 2007173315A JP 2007173315 A JP2007173315 A JP 2007173315A JP 2009012779 A JP2009012779 A JP 2009012779A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- label
- film
- shrink label
- cylindrical shrink
- container
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C65/00—Joining or sealing of preformed parts, e.g. welding of plastics materials; Apparatus therefor
- B29C65/02—Joining or sealing of preformed parts, e.g. welding of plastics materials; Apparatus therefor by heating, with or without pressure
- B29C65/08—Joining or sealing of preformed parts, e.g. welding of plastics materials; Apparatus therefor by heating, with or without pressure using ultrasonic vibrations
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C53/00—Shaping by bending, folding, twisting, straightening or flattening; Apparatus therefor
- B29C53/36—Bending and joining, e.g. for making hollow articles
- B29C53/38—Bending and joining, e.g. for making hollow articles by bending sheets or strips at right angles to the longitudinal axis of the article being formed and joining the edges
- B29C53/40—Bending and joining, e.g. for making hollow articles by bending sheets or strips at right angles to the longitudinal axis of the article being formed and joining the edges for articles of definite length, i.e. discrete articles
- B29C53/42—Bending and joining, e.g. for making hollow articles by bending sheets or strips at right angles to the longitudinal axis of the article being formed and joining the edges for articles of definite length, i.e. discrete articles using internal forming surfaces, e.g. mandrels
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C63/00—Lining or sheathing, i.e. applying preformed layers or sheathings of plastics; Apparatus therefor
- B29C63/38—Lining or sheathing, i.e. applying preformed layers or sheathings of plastics; Apparatus therefor by liberation of internal stresses
- B29C63/42—Lining or sheathing, i.e. applying preformed layers or sheathings of plastics; Apparatus therefor by liberation of internal stresses using tubular layers or sheathings
- B29C63/423—Lining or sheathing, i.e. applying preformed layers or sheathings of plastics; Apparatus therefor by liberation of internal stresses using tubular layers or sheathings specially applied to the mass-production of externally coated articles, e.g. bottles
- B29C63/426—Lining or sheathing, i.e. applying preformed layers or sheathings of plastics; Apparatus therefor by liberation of internal stresses using tubular layers or sheathings specially applied to the mass-production of externally coated articles, e.g. bottles in combination with the in situ shaping of the external tubular layer
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C65/00—Joining or sealing of preformed parts, e.g. welding of plastics materials; Apparatus therefor
- B29C65/78—Means for handling the parts to be joined, e.g. for making containers or hollow articles, e.g. means for handling sheets, plates, web-like materials, tubular articles, hollow articles or elements to be joined therewith; Means for discharging the joined articles from the joining apparatus
- B29C65/7841—Holding or clamping means for handling purposes
- B29C65/7847—Holding or clamping means for handling purposes using vacuum to hold at least one of the parts to be joined
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C65/00—Joining or sealing of preformed parts, e.g. welding of plastics materials; Apparatus therefor
- B29C65/78—Means for handling the parts to be joined, e.g. for making containers or hollow articles, e.g. means for handling sheets, plates, web-like materials, tubular articles, hollow articles or elements to be joined therewith; Means for discharging the joined articles from the joining apparatus
- B29C65/7897—Means for discharging the joined articles from the joining apparatus
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C66/00—General aspects of processes or apparatus for joining preformed parts
- B29C66/01—General aspects dealing with the joint area or with the area to be joined
- B29C66/05—Particular design of joint configurations
- B29C66/10—Particular design of joint configurations particular design of the joint cross-sections
- B29C66/11—Joint cross-sections comprising a single joint-segment, i.e. one of the parts to be joined comprising a single joint-segment in the joint cross-section
- B29C66/112—Single lapped joints
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C66/00—General aspects of processes or apparatus for joining preformed parts
- B29C66/01—General aspects dealing with the joint area or with the area to be joined
- B29C66/05—Particular design of joint configurations
- B29C66/10—Particular design of joint configurations particular design of the joint cross-sections
- B29C66/11—Joint cross-sections comprising a single joint-segment, i.e. one of the parts to be joined comprising a single joint-segment in the joint cross-section
- B29C66/112—Single lapped joints
- B29C66/1122—Single lap to lap joints, i.e. overlap joints
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C66/00—General aspects of processes or apparatus for joining preformed parts
- B29C66/01—General aspects dealing with the joint area or with the area to be joined
- B29C66/05—Particular design of joint configurations
- B29C66/10—Particular design of joint configurations particular design of the joint cross-sections
- B29C66/13—Single flanged joints; Fin-type joints; Single hem joints; Edge joints; Interpenetrating fingered joints; Other specific particular designs of joint cross-sections not provided for in groups B29C66/11 - B29C66/12
- B29C66/135—Single hemmed joints, i.e. one of the parts to be joined being hemmed in the joint area
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C66/00—General aspects of processes or apparatus for joining preformed parts
- B29C66/40—General aspects of joining substantially flat articles, e.g. plates, sheets or web-like materials; Making flat seams in tubular or hollow articles; Joining single elements to substantially flat surfaces
- B29C66/41—Joining substantially flat articles ; Making flat seams in tubular or hollow articles
- B29C66/43—Joining a relatively small portion of the surface of said articles
- B29C66/432—Joining a relatively small portion of the surface of said articles for making tubular articles or closed loops, e.g. by joining several sheets ; for making hollow articles or hollow preforms
- B29C66/4322—Joining a relatively small portion of the surface of said articles for making tubular articles or closed loops, e.g. by joining several sheets ; for making hollow articles or hollow preforms by joining a single sheet to itself
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C66/00—General aspects of processes or apparatus for joining preformed parts
- B29C66/40—General aspects of joining substantially flat articles, e.g. plates, sheets or web-like materials; Making flat seams in tubular or hollow articles; Joining single elements to substantially flat surfaces
- B29C66/49—Internally supporting the, e.g. tubular, article during joining
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C66/00—General aspects of processes or apparatus for joining preformed parts
- B29C66/70—General aspects of processes or apparatus for joining preformed parts characterised by the composition, physical properties or the structure of the material of the parts to be joined; Joining with non-plastics material
- B29C66/72—General aspects of processes or apparatus for joining preformed parts characterised by the composition, physical properties or the structure of the material of the parts to be joined; Joining with non-plastics material characterised by the structure of the material of the parts to be joined
- B29C66/723—General aspects of processes or apparatus for joining preformed parts characterised by the composition, physical properties or the structure of the material of the parts to be joined; Joining with non-plastics material characterised by the structure of the material of the parts to be joined being multi-layered
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C66/00—General aspects of processes or apparatus for joining preformed parts
- B29C66/70—General aspects of processes or apparatus for joining preformed parts characterised by the composition, physical properties or the structure of the material of the parts to be joined; Joining with non-plastics material
- B29C66/73—General aspects of processes or apparatus for joining preformed parts characterised by the composition, physical properties or the structure of the material of the parts to be joined; Joining with non-plastics material characterised by the intensive physical properties of the material of the parts to be joined, by the optical properties of the material of the parts to be joined, by the extensive physical properties of the parts to be joined, by the state of the material of the parts to be joined or by the material of the parts to be joined being a thermoplastic or a thermoset
- B29C66/737—General aspects of processes or apparatus for joining preformed parts characterised by the composition, physical properties or the structure of the material of the parts to be joined; Joining with non-plastics material characterised by the intensive physical properties of the material of the parts to be joined, by the optical properties of the material of the parts to be joined, by the extensive physical properties of the parts to be joined, by the state of the material of the parts to be joined or by the material of the parts to be joined being a thermoplastic or a thermoset characterised by the state of the material of the parts to be joined
- B29C66/7371—General aspects of processes or apparatus for joining preformed parts characterised by the composition, physical properties or the structure of the material of the parts to be joined; Joining with non-plastics material characterised by the intensive physical properties of the material of the parts to be joined, by the optical properties of the material of the parts to be joined, by the extensive physical properties of the parts to be joined, by the state of the material of the parts to be joined or by the material of the parts to be joined being a thermoplastic or a thermoset characterised by the state of the material of the parts to be joined oriented or heat-shrinkable
- B29C66/73711—General aspects of processes or apparatus for joining preformed parts characterised by the composition, physical properties or the structure of the material of the parts to be joined; Joining with non-plastics material characterised by the intensive physical properties of the material of the parts to be joined, by the optical properties of the material of the parts to be joined, by the extensive physical properties of the parts to be joined, by the state of the material of the parts to be joined or by the material of the parts to be joined being a thermoplastic or a thermoset characterised by the state of the material of the parts to be joined oriented or heat-shrinkable oriented
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C66/00—General aspects of processes or apparatus for joining preformed parts
- B29C66/70—General aspects of processes or apparatus for joining preformed parts characterised by the composition, physical properties or the structure of the material of the parts to be joined; Joining with non-plastics material
- B29C66/73—General aspects of processes or apparatus for joining preformed parts characterised by the composition, physical properties or the structure of the material of the parts to be joined; Joining with non-plastics material characterised by the intensive physical properties of the material of the parts to be joined, by the optical properties of the material of the parts to be joined, by the extensive physical properties of the parts to be joined, by the state of the material of the parts to be joined or by the material of the parts to be joined being a thermoplastic or a thermoset
- B29C66/737—General aspects of processes or apparatus for joining preformed parts characterised by the composition, physical properties or the structure of the material of the parts to be joined; Joining with non-plastics material characterised by the intensive physical properties of the material of the parts to be joined, by the optical properties of the material of the parts to be joined, by the extensive physical properties of the parts to be joined, by the state of the material of the parts to be joined or by the material of the parts to be joined being a thermoplastic or a thermoset characterised by the state of the material of the parts to be joined
- B29C66/7371—General aspects of processes or apparatus for joining preformed parts characterised by the composition, physical properties or the structure of the material of the parts to be joined; Joining with non-plastics material characterised by the intensive physical properties of the material of the parts to be joined, by the optical properties of the material of the parts to be joined, by the extensive physical properties of the parts to be joined, by the state of the material of the parts to be joined or by the material of the parts to be joined being a thermoplastic or a thermoset characterised by the state of the material of the parts to be joined oriented or heat-shrinkable
- B29C66/73711—General aspects of processes or apparatus for joining preformed parts characterised by the composition, physical properties or the structure of the material of the parts to be joined; Joining with non-plastics material characterised by the intensive physical properties of the material of the parts to be joined, by the optical properties of the material of the parts to be joined, by the extensive physical properties of the parts to be joined, by the state of the material of the parts to be joined or by the material of the parts to be joined being a thermoplastic or a thermoset characterised by the state of the material of the parts to be joined oriented or heat-shrinkable oriented
- B29C66/73712—General aspects of processes or apparatus for joining preformed parts characterised by the composition, physical properties or the structure of the material of the parts to be joined; Joining with non-plastics material characterised by the intensive physical properties of the material of the parts to be joined, by the optical properties of the material of the parts to be joined, by the extensive physical properties of the parts to be joined, by the state of the material of the parts to be joined or by the material of the parts to be joined being a thermoplastic or a thermoset characterised by the state of the material of the parts to be joined oriented or heat-shrinkable oriented mono-axially
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C66/00—General aspects of processes or apparatus for joining preformed parts
- B29C66/70—General aspects of processes or apparatus for joining preformed parts characterised by the composition, physical properties or the structure of the material of the parts to be joined; Joining with non-plastics material
- B29C66/73—General aspects of processes or apparatus for joining preformed parts characterised by the composition, physical properties or the structure of the material of the parts to be joined; Joining with non-plastics material characterised by the intensive physical properties of the material of the parts to be joined, by the optical properties of the material of the parts to be joined, by the extensive physical properties of the parts to be joined, by the state of the material of the parts to be joined or by the material of the parts to be joined being a thermoplastic or a thermoset
- B29C66/737—General aspects of processes or apparatus for joining preformed parts characterised by the composition, physical properties or the structure of the material of the parts to be joined; Joining with non-plastics material characterised by the intensive physical properties of the material of the parts to be joined, by the optical properties of the material of the parts to be joined, by the extensive physical properties of the parts to be joined, by the state of the material of the parts to be joined or by the material of the parts to be joined being a thermoplastic or a thermoset characterised by the state of the material of the parts to be joined
- B29C66/7371—General aspects of processes or apparatus for joining preformed parts characterised by the composition, physical properties or the structure of the material of the parts to be joined; Joining with non-plastics material characterised by the intensive physical properties of the material of the parts to be joined, by the optical properties of the material of the parts to be joined, by the extensive physical properties of the parts to be joined, by the state of the material of the parts to be joined or by the material of the parts to be joined being a thermoplastic or a thermoset characterised by the state of the material of the parts to be joined oriented or heat-shrinkable
- B29C66/73715—General aspects of processes or apparatus for joining preformed parts characterised by the composition, physical properties or the structure of the material of the parts to be joined; Joining with non-plastics material characterised by the intensive physical properties of the material of the parts to be joined, by the optical properties of the material of the parts to be joined, by the extensive physical properties of the parts to be joined, by the state of the material of the parts to be joined or by the material of the parts to be joined being a thermoplastic or a thermoset characterised by the state of the material of the parts to be joined oriented or heat-shrinkable heat-shrinkable
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C66/00—General aspects of processes or apparatus for joining preformed parts
- B29C66/80—General aspects of machine operations or constructions and parts thereof
- B29C66/81—General aspects of the pressing elements, i.e. the elements applying pressure on the parts to be joined in the area to be joined, e.g. the welding jaws or clamps
- B29C66/814—General aspects of the pressing elements, i.e. the elements applying pressure on the parts to be joined in the area to be joined, e.g. the welding jaws or clamps characterised by the design of the pressing elements, e.g. of the welding jaws or clamps
- B29C66/8141—General aspects of the pressing elements, i.e. the elements applying pressure on the parts to be joined in the area to be joined, e.g. the welding jaws or clamps characterised by the design of the pressing elements, e.g. of the welding jaws or clamps characterised by the surface geometry of the part of the pressing elements, e.g. welding jaws or clamps, coming into contact with the parts to be joined
- B29C66/81433—General aspects of the pressing elements, i.e. the elements applying pressure on the parts to be joined in the area to be joined, e.g. the welding jaws or clamps characterised by the design of the pressing elements, e.g. of the welding jaws or clamps characterised by the surface geometry of the part of the pressing elements, e.g. welding jaws or clamps, coming into contact with the parts to be joined being toothed, i.e. comprising several teeth or pins, or being patterned
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C66/00—General aspects of processes or apparatus for joining preformed parts
- B29C66/70—General aspects of processes or apparatus for joining preformed parts characterised by the composition, physical properties or the structure of the material of the parts to be joined; Joining with non-plastics material
- B29C66/71—General aspects of processes or apparatus for joining preformed parts characterised by the composition, physical properties or the structure of the material of the parts to be joined; Joining with non-plastics material characterised by the composition of the plastics material of the parts to be joined
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C66/00—General aspects of processes or apparatus for joining preformed parts
- B29C66/90—Measuring or controlling the joining process
- B29C66/92—Measuring or controlling the joining process by measuring or controlling the pressure, the force, the mechanical power or the displacement of the joining tools
- B29C66/929—Measuring or controlling the joining process by measuring or controlling the pressure, the force, the mechanical power or the displacement of the joining tools characterized by specific pressure, force, mechanical power or displacement values or ranges
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C66/00—General aspects of processes or apparatus for joining preformed parts
- B29C66/90—Measuring or controlling the joining process
- B29C66/94—Measuring or controlling the joining process by measuring or controlling the time
- B29C66/949—Measuring or controlling the joining process by measuring or controlling the time characterised by specific time values or ranges
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29L—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBCLASS B29C, RELATING TO PARTICULAR ARTICLES
- B29L2031/00—Other particular articles
- B29L2031/744—Labels, badges, e.g. marker sleeves
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Details Of Rigid Or Semi-Rigid Containers (AREA)
- Wrappers (AREA)
- Lining Or Joining Of Plastics Or The Like (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、延伸方向で切断したラベルの両端を筒状に重ねた後に超音波で溶着してなる筒状シュリンクラベル、該筒状シュリンクラベルを装着した容器およびこれらの製造方法に関する。 The present invention relates to a cylindrical shrink label formed by laminating both ends of a label cut in the stretching direction in a cylindrical shape and then welding with ultrasonic waves, a container equipped with the cylindrical shrink label, and a method for manufacturing the same.
従来から、飲料などの容器に全周にわたる筒状シュリンクラベルが使用され、このようなシュリンクラベルを装着した容器として、予め筒状のシュリンクラベルを調製し、これを容器外周に外嵌し、ついで熱処理してシュリンク形成するものがある(特許文献1)。該特許文献1では、筒状シュリンクラベルを製造する際に、シュリンクラベルの両端部にホットメルト型接着剤を貼付し、このホットメルト型接着剤を介してラベル両端を筒状に張り合わせている。 Conventionally, a cylindrical shrink label is used for a container such as a beverage, and a cylindrical shrink label is prepared in advance as a container equipped with such a shrink label. There exists what heat-processes and shrink-forms (patent document 1). In this patent document 1, when manufacturing a cylindrical shrink label, a hot-melt-type adhesive is affixed to the both ends of a shrink label, and both ends of a label are stuck together cylindrically via this hot-melt-type adhesive.
また、筒状にシュリンクラベルを接着する際に、レーザー光によって溶着し、得られた筒状シュリンクラベルを容器に外嵌装着する方法もある(特許文献2)。前記特許文献2で使用するラベルは、印刷が施された合成樹脂製フィルムの両端部を重ね合わせてレーザー光の照射によって溶着して筒状に形成したラベルであって、基材と、該基材の両面側に積層された表面層とを備え、該表面層は、前記基材よりも融点の低い材料からなり、前記両端部の溶着面は、印刷が施されていない無印刷部に形成されている、というものである。 In addition, there is a method in which when a shrink label is bonded in a cylindrical shape, it is welded by laser light, and the obtained cylindrical shrink label is externally attached to a container (Patent Document 2). The label used in Patent Document 2 is a label formed in a cylindrical shape by superimposing both ends of a printed synthetic resin film and welding them by laser light irradiation. A surface layer laminated on both sides of the material, and the surface layer is made of a material having a melting point lower than that of the base material, and the weld surfaces of the both end portions are formed in a non-printed portion where printing is not performed. It has been said.
また、石油樹脂を含有するポリプロピレン系樹脂からなる表面層および中間層とを含む多層構造の熱収縮フィルムを、その熱収縮方向の両端部同士を相互に重ね合わせて筒状に形成し、その重ね合わせ部分の内周面側に、前記熱収縮フィルムの熱収縮方向に延びる多数の突条を備えたローレットを圧接し、前記重ね合わせ部分の外周面側から超音波シールしてなる筒状シュリンクラベルもある(特許文献3)。多層の熱収縮フィルムの端面が開放された状態であると、熱収縮処理やその後のレトルト殺菌処理によって各層が個別に収縮するため開放端部分で層間のズレが生じ外観を損ねる場合がある。しかしながら、前記多数の突条を備えたローレットを使用すると、その突条に対応して加振子に接触している外側の熱収縮フィルムが溶融され、その溶融部分が突条と加振子とによって圧接されて潰されるため、外側の熱収縮フィルムの表面層のみならず中間層が内側の熱収縮フィルムの表面層に溶着されるので、この筒状シュリンクラベルをガラス瓶に装着した状態でレトルト殺菌処理した場合でも、レトルト殺菌に伴う加熱によって表面層が熱収縮を起こすことがなく、表面層がずれて外観を損ねるといった問題が生じない、という。 Further, a heat shrink film having a multilayer structure including a surface layer and an intermediate layer made of a polypropylene resin containing petroleum resin is formed into a cylindrical shape by overlapping both ends in the heat shrink direction with each other. A cylindrical shrink label formed by pressing a knurl provided with a plurality of protrusions extending in the heat shrink direction of the heat shrinkable film on the inner peripheral surface side of the mating portion and ultrasonically sealing from the outer peripheral surface side of the overlapping portion There is also (patent document 3). When the end face of the multilayer heat-shrinkable film is in an open state, each layer is shrunk individually by heat shrinkage treatment or subsequent retort sterilization treatment, so that the gap between the layers may occur at the open end portion and the appearance may be impaired. However, when a knurl having a large number of protrusions is used, the outer heat-shrink film in contact with the shaker corresponding to the protrusions is melted, and the melted portion is pressed by the protrusions and the shaker. Since the intermediate layer as well as the outer heat shrink film surface layer is welded to the inner heat shrink film surface layer, the tubular shrink label is attached to the glass bottle and retort sterilized. Even in such a case, the surface layer does not cause heat shrinkage due to heating accompanying retort sterilization, and the problem that the surface layer is displaced and the appearance is not deteriorated is not caused.
また、筒状シュリンクラベルの製造方法として、検出マークが印刷されたシュリンクラベル用ロールを切断マーク位置で切断した後に筒状に成形してなる筒状シュリンクラベルもある(特許文献4)。長尺の熱収縮性のフィルム基材には、所定間隔ごとに検出マークが印刷され、該検出マークをセンサで検出することによりラベルの位置合わせなどを行うが、前記検出マークを熱収縮時の熱で消去可能なインキで印刷することで、別途特別な加熱工程を経ることなく検出マークを目立たなくすることができ、各ラベル及びフィルムに施したデザイン等の所定の表示の邪魔になるのを防止できる、という。特許文献4では、熱収縮フィルムの熱収縮方向の両端部を接着して筒状に成形するため、熱収縮フィルムを切断した後に切断ラベルを90度回転させ、ラベル両端を筒状に接着している。
しかしながら、上記特許文献1記載の筒状シュリンクラベルは、ホットメルト型接着剤によって容器と筒状シュリンクラベルとを接着する方法であるため、接着後に容器が高温条件下にある場合には、ホットメルト型接着剤が溶融し外観を損なう場合がある。特に、該容器の内容物が加温製品の場合には、内容物の保管温度によって移送中や販売期間内にホットメルト型接着剤が溶融する恐れがあり、シュリンクラベルの場合には熱収縮処理を行う際にホットメルト型接着剤が溶け出す場合がある。加えて、反応性ホットメルト型接着剤を使用すると、硬化後に熱に対する耐性を有するが、反応時間が長いために生産性が低下する。 However, since the cylindrical shrink label described in Patent Document 1 is a method of bonding a container and the cylindrical shrink label with a hot melt adhesive, if the container is in a high temperature condition after bonding, The mold adhesive may melt and impair the appearance. In particular, when the contents of the container are heated products, the hot melt adhesive may melt during transfer or within the sales period depending on the storage temperature of the contents. In some cases, the hot-melt adhesive may melt out. In addition, when a reactive hot melt adhesive is used, it has heat resistance after curing, but the productivity is lowered due to the long reaction time.
また、特許文献2記載のラベルは、レーザー光によって筒状ラベルとしたものであるが、レーザーでの接着性を確保するため、使用するラベルの層構成が複雑となる場合がある。同様に、特許文献3記載のラベルも、本来石油樹脂の含有量の異なるポリプロピレン系樹脂を積層したラベルを使用するものであり、従来のラベルを筒状シュリンクラベルとして使用できる、というものではない。また、超音波シールには、特殊なロートレットが必要であり、装置が複雑である。 Moreover, although the label of patent document 2 is used as the cylindrical label with the laser beam, in order to ensure the adhesiveness with a laser, the layer structure of the label to be used may become complicated. Similarly, the label described in Patent Document 3 uses a label in which polypropylene resins having different petroleum resin contents are originally stacked, and does not mean that a conventional label can be used as a cylindrical shrink label. Moreover, a special rotlet is required for ultrasonic sealing, and the apparatus is complicated.
シュリンクラベルは延伸方向に熱収縮するため、延伸方向と胴巻き方向とを一致させて容器に装着する。従来は、横一軸延伸フィルムを使用し、例えば特許文献4の図3に示すように、所定ラベル長さに切断した後に切断ラベルを90度回転させた後に筒状に成形し、直立する容器の上部から筒状ラベルを鉛直方向に装着していた。すなわち、シュリンクラベル用ロールの切断面を接着部として使用できないため、筒状に接着する際にラベルを90度回転させる工程が必要となっている。しかしながら、このような工程をなくすことができれば、筒状シュリンクラベルの製造がより簡単な工程で製造できる。
Since the shrink label is thermally shrunk in the stretching direction, the shrink label is attached to the container so that the stretching direction matches the body winding direction. Conventionally, a laterally uniaxially stretched film is used. For example, as shown in FIG. 3 of
更に、シュリンクラベルには、美粧性を確保したり製品内容を表示する目的で印刷層が形成され、またラベル装着位置を特定するために検出マークなどが印刷されるが、レーザー光は印刷層を透過できないため、レーザー溶着を行うことができず、接着部の近傍には印刷層を形成することができない場合がある。しかしながら、印刷層であっても接着方法があれば、より消費者のニーズに適する筒状シュリンクラベルを提供することができる。 Furthermore, a printed layer is formed on the shrink label for the purpose of ensuring cosmetics and displaying the product content, and a detection mark is printed to identify the label mounting position. Since it cannot transmit, laser welding cannot be performed, and a printed layer may not be formed in the vicinity of the adhesion part. However, even if it is a printed layer, if there is an adhesion method, a cylindrical shrink label more suitable for consumer needs can be provided.
上記現状に鑑み、本発明は、接着剤を使用することなく製造される筒状シュリンクラベルを提供するものである。 In view of the above-mentioned present situation, the present invention provides a cylindrical shrink label manufactured without using an adhesive.
また本発明は、凹凸が際立つ容器にも装着することができ、容器形状の多様化、消費者の購買意欲を満たしうる、熱収縮率に優れる筒状シュリンクラベルを提供するものである。 In addition, the present invention provides a cylindrical shrink label that can be attached to a container with concavities and convexities, can satisfy the diversification of the container shape, and satisfy the consumer's desire to purchase, and has an excellent heat shrinkage rate.
また本発明は、このような筒状シュリンクラベルを装着した容器を提供するものである。 The present invention also provides a container equipped with such a cylindrical shrink label.
更に本発明は、簡便な工程で迅速に、生産効率に優れる筒状シュリンクラベルの製造方法を提供するものである。 Furthermore, this invention provides the manufacturing method of the cylindrical shrink label which is excellent in production efficiency rapidly by a simple process.
本発明者は、筒状シュリンクラベルについて詳細に検討した結果、熱収縮率に優れる縦一軸延伸フィルムを使用して筒状シュリンクラベルを製造すれば、延伸方向と移送方向とを同方向にできるため、フィルムを所定のラベル長に切断した後に切断面を溶着部として筒状に形成でき、ラベルを90度回転する工程を省略できること、ラベル重ね部を超音波で溶着すれば接着剤の使用を行うことなく、かつ短時間で効率的に溶着することができること、および超音波によれば、印刷層を有する部分でも溶着でき、従来から溶着が困難であった発泡白色フィルムもシュリンクラベルとして使用できることを見出し、本発明を完成させた。
As a result of examining the cylindrical shrink label in detail, the inventor can produce a cylindrical shrink label using a longitudinally uniaxially stretched film having an excellent heat shrinkage rate, so that the stretching direction and the transport direction can be made the same direction. After cutting the film into a predetermined label length, the cut surface can be formed into a cylindrical shape as a welded portion, the step of rotating the
すなわち本発明は、熱収縮性基材フィルムの延伸方向にあるラベル両端を溶着してなる筒状シュリンクラベルであって、縦一軸延伸した熱収縮性基材フィルムを延伸方向の所定サイズに切断してラベルを切り出し、前記ラベルを筒状に成形して前記切断した両端を重ね、前記重ね部を超音波で溶着することを特徴とする、筒状シュリンクラベルを提供するものである。 That is, the present invention is a cylindrical shrink label formed by welding both ends of the label in the stretching direction of the heat-shrinkable base film, and the heat-shrinkable base film stretched in the longitudinal direction is cut into a predetermined size in the stretching direction. The label is cut out, the label is formed into a cylindrical shape, the cut ends are overlapped, and the overlapped portion is welded with ultrasonic waves.
また、前記筒状シュリンクラベルを装着し、熱収縮処理してなる筒状シュリンクラベル付き容器を提供するものである。 The present invention also provides a container with a cylindrical shrink label, which is provided with the cylindrical shrink label and subjected to a heat shrink process.
また、縦一軸延伸してなる熱収縮性基材フィルムを延伸方向に搬送し、前記フィルムを延伸方向の所定ラベル長に切断し、前記ラベルを筒状に成形して前記切断した両端を重ね、前記重ね部を超音波で溶着することを特徴とする、筒状シュリンクラベルの製造方法を提供するものである。 In addition, a heat-shrinkable base film formed by longitudinal uniaxial stretching is conveyed in the stretching direction, the film is cut into a predetermined label length in the stretching direction, the label is formed into a cylindrical shape, and the cut ends are overlapped, A method for producing a cylindrical shrink label, characterized in that the overlapping portion is welded by ultrasonic waves.
さらに、縦一軸延伸してなる熱収縮性基材フィルムを延伸方向に搬送し、前記フィルムを延伸方向の所定ラベル長に切断し、前記ラベルを鉛直に配置されたシリンダにまき付けて前記切断端を重ね、前記重ね部を超音波で溶着して筒状シュリンクラベルを成形し、前記筒状シュリンクラベルの下部側または上部側から前記シリンダを抜き出し、かつラベルの上部側または下部側から容器を挿入して前記容器に筒状シュリンクラベルを装着し、ついで熱収縮処理することを特徴とする、筒状シュリンクラベル付き容器の製造方法を提供するものである。 Furthermore, the heat-shrinkable base film formed by longitudinally uniaxially stretching is conveyed in the stretching direction, the film is cut into a predetermined label length in the stretching direction, and the label is attached to a vertically arranged cylinder to cut the cut end. And stacking the overlapped portion with ultrasonic waves to form a cylindrical shrink label, withdrawing the cylinder from the lower side or upper side of the cylindrical shrink label, and inserting a container from the upper side or lower side of the label Then, a cylindrical shrink label is attached to the container, and then heat shrink treatment is performed, and a method for producing a container with a cylindrical shrink label is provided.
本発明の筒状シュリンクラベルは接着剤を使用しないため、生産工程を簡略化することができ、コストも低下させることができる。また、ホットメルト型接着剤を使用する場合と比較して、広い温度幅の環境で保管、流通させることができる。 Since the cylindrical shrink label of the present invention does not use an adhesive, the production process can be simplified and the cost can be reduced. In addition, it can be stored and distributed in an environment with a wide temperature range as compared with the case of using a hot melt adhesive.
本発明の筒状シュリンクレベルは超音波によって溶着するため、発泡白色シュリンクフィルムをシュリンクラベルとして使用することができ、また、発泡ポリオレフィン系フィルムなど厚みのあるフィルムに適し、シュリンクラベルの範囲を拡げることができる。 Since the tubular shrink level of the present invention is welded by ultrasonic waves, a foam white shrink film can be used as a shrink label, and it is suitable for a thick film such as a foamed polyolefin film and expands the range of the shrink label. Can do.
本発明の筒状シュリンクレベルは、超音波で筒状に溶着するため、外観に優れるシュリンクラベル付き容器を提供することができると共に、短時間で溶着しうるため生産効率に優れる。 Since the cylindrical shrink level of the present invention is welded in a cylindrical shape with ultrasonic waves, it is possible to provide a container with a shrink label that is excellent in appearance, and because it can be welded in a short time, it is excellent in production efficiency.
本発明の第一は、熱収縮性基材フィルムの延伸方向にあるラベル両端を溶着してなる筒状シュリンクラベルであって、縦一軸延伸した熱収縮性基材フィルムを延伸方向の所定サイズに切断してラベルを切り出し、前記ラベルの切断した両端を筒状に重ね、重ね部を超音波で溶着したことを特徴とする、筒状シュリンクラベルである。 The first of the present invention is a cylindrical shrink label formed by welding both ends of the label in the stretching direction of the heat-shrinkable base film, and the heat-shrinkable base film stretched uniaxially to a predetermined size in the stretching direction. It is a cylindrical shrink label characterized by cutting out a label by cutting, overlapping the cut ends of the label into a cylindrical shape, and welding the overlapped portion with ultrasonic waves.
縦一軸延伸基材フィルムを使用することで、延伸方向にフィルムを移送して切断し、切断面を筒状に重ねて溶着することで筒状シュリンクラベルを製造することができ、このため溶着の際にラベル方向を90度回転させる必要がなく、従来よりもラベラーの構造を簡略化することができる。また、超音波で溶着するため不透明の発泡基材フィルムや印刷でも溶着することができる。以下、本発明の筒状シュリンクラベル、筒状シュリンクラベル付き容器、筒状シュリンクラベルの製造方法について説明する。 By using a longitudinally uniaxially stretched substrate film, it is possible to produce a cylindrical shrink label by transferring and cutting the film in the stretching direction, and stacking the cut surfaces in a cylindrical shape and welding them. At this time, it is not necessary to rotate the label direction by 90 degrees, and the structure of the labeler can be simplified as compared with the conventional case. Moreover, since it welds with an ultrasonic wave, it can be welded also by an opaque foam base film and printing. Hereinafter, the manufacturing method of the cylindrical shrink label of this invention, the container with a cylindrical shrink label, and a cylindrical shrink label is demonstrated.
(1)筒状シュリンクラベルの構成
本発明の筒状シュリンクラベルは、縦一軸延伸した熱収縮性基材フィルムを延伸方向の所定サイズに切断し、前記ラベルの切断した両端を筒状に重ね、重ね部を超音波で溶着して調製される。従って、図1に示すように、得られた筒状シュリンクラベル(100)は、ラベル(30)の両端の重ね部(37)に超音波シール部(35)が形成されたものであり、円周方向と二重矢印で示すラベル延伸方向とが同方向となっている。
(1) Configuration of cylindrical shrink label The cylindrical shrink label of the present invention is a longitudinally uniaxially stretched heat-shrinkable base film cut into a predetermined size in the stretching direction, and the cut ends of the label are stacked in a tubular shape. It is prepared by welding the overlapping portion with ultrasonic waves. Therefore, as shown in FIG. 1, the obtained cylindrical shrink label (100) is formed by forming ultrasonic seal portions (35) on the overlapping portions (37) at both ends of the label (30). The circumferential direction and the label extending direction indicated by a double arrow are the same direction.
筒状シュリンクラベルの長さや太さは、装着する容器の形状や装着の態様に応じて適宜選択することができる。一方、超音波シール(35)の幅は、0.5〜15mmであることが好ましく、より好ましくは3〜13mm、特に好ましくは5〜10mmである。この範囲で、十分な溶着強度を確保することができる。 The length and thickness of the cylindrical shrink label can be appropriately selected according to the shape of the container to be attached and the manner of attachment. On the other hand, the width of the ultrasonic seal (35) is preferably 0.5 to 15 mm, more preferably 3 to 13 mm, and particularly preferably 5 to 10 mm. In this range, sufficient welding strength can be ensured.
また、超音波シールのための筒状シュリンクラベルの溶着部の重ね部(37)の幅は、5〜25mmであることが好ましく、より好ましくは5〜20mmである。この範囲であれば、上記超音波シール幅を十分に確保することができ、かつラベルの美粧性を確保することができる。 Moreover, it is preferable that the width | variety of the overlap part (37) of the welding part of the cylindrical shrink label for ultrasonic sealing is 5-25 mm, More preferably, it is 5-20 mm. If it is this range, the said ultrasonic seal width | variety can fully be ensured and the cosmetics of a label can be ensured.
本発明の筒状シュリンクラベル(100)は、熱収縮性基材フィルムのラベル最内層または最外層にデザイン印刷層を有するものであってもよい。レーザー光による溶着の場合には、印刷層がレーザー光の吸収を阻害するため、溶着部に印刷層を形成することができなかった。しかしながら、本発明では超音波振動によって溶着するものであり、溶着部分は印刷層の有無を問わず溶着することができる。 The cylindrical shrink label (100) of this invention may have a design printing layer in the label innermost layer or outermost layer of a heat-shrinkable base film. In the case of welding with a laser beam, the printed layer hinders the absorption of the laser beam, so that the printed layer could not be formed at the welded portion. However, in the present invention, welding is performed by ultrasonic vibration, and the welded portion can be welded with or without the printed layer.
なお、前記重ね部の溶着部と平行に、1以上のミシン目列が形成されていてもよい。使用後の容器からラベルを離脱することが容易だからである。 One or more perforation rows may be formed in parallel with the welded portion of the overlapped portion. This is because it is easy to remove the label from the container after use.
(i)熱収縮性基材フィルム
本発明の筒状シュリンクラベルは、縦一軸延伸した熱収縮性基材フィルムを使用する。
(I) Heat-shrinkable base film The cylindrical shrink label of the present invention uses a heat-shrinkable base film that has been longitudinally uniaxially stretched.
熱収縮性基材フィルムとしては、ポリオレフィン系フィルム、ポリエステル系フィルム、ポリスチレン系フィルム、ポリ乳酸系フィルム、発泡ポリオレフィン系フィルム、発泡ポリエステル系フィルム、発泡ポリスチレン系フィルム、およびこれらのフィルムの2種以上の積層フィルムであって、縦一軸延伸したものを好適に使用することができる。より好ましくは、前記ポリオレフィン系フィルムが縦一軸延伸ポリプロピレン系フィルムであり、前記ポリエステル系フィルムが縦一軸延伸ポリエチレンテレフタレート系フィルムであり、前記発泡ポリオレフィン系フィルムが発泡縦一軸延伸ポリプロピレン系フィルムであり、発泡ポリエステル系フィルムが、発泡縦一軸延伸ポリエチレンテレフタレート系フィルム、ポリエステル−ポリスチレン共押出しフィルムの縦一軸延伸フィルムなどである。従来から、縦一軸延伸フィルムは存在したが、縦一軸延伸フィルムをシュリンクラベルとして使用することはなかった。しかしながら、本発明では縦一軸延伸フィルムを使用することで製造工程を簡略化できることを見出し、特に縦一軸延伸フィルムに限定して使用することにした。 Examples of the heat-shrinkable base film include polyolefin film, polyester film, polystyrene film, polylactic acid film, foamed polyolefin film, foamed polyester film, foamed polystyrene film, and two or more of these films A laminated film that has been longitudinally uniaxially stretched can be suitably used. More preferably, the polyolefin film is a vertically uniaxially stretched polypropylene film, the polyester film is a vertically uniaxially stretched polyethylene terephthalate film, the foamed polyolefin film is a foamed vertically uniaxially stretched polypropylene film, and foamed. Examples of the polyester film include a foam longitudinally uniaxially stretched polyethylene terephthalate film and a longitudinally uniaxially stretched film of a polyester-polystyrene coextruded film. Conventionally, although a longitudinally uniaxially stretched film exists, the longitudinally uniaxially stretched film has not been used as a shrink label. However, in this invention, it discovered that a manufacturing process could be simplified by using a longitudinally uniaxially stretched film, and decided to use it limiting especially to a longitudinally uniaxially stretched film.
一般には、ポリオレフィン系樹脂、ポリエステル系樹脂、ポリスチレン系樹脂、ポリ乳酸系樹脂の1種または2種以上を使用し、押し出し法、キャスト成形法、Tダイ法、切削法、インフレーション法、その他等の製膜化法を用いて単層で製膜化したもの、または2種以上の樹脂を使用して共押し出しなどで多層製膜したもの、または2種以上の樹脂を混合使用して製膜したものを使用することができ、テンター方式やチューブラー方式等で縦一軸延伸してなる各種の延伸フィルムを使用することができる。 Generally, one or more of polyolefin resin, polyester resin, polystyrene resin, polylactic acid resin is used, and extrusion method, cast molding method, T-die method, cutting method, inflation method, etc. Films formed in a single layer using the film-forming method, films formed by coextrusion using two or more resins, or films formed using a mixture of two or more resins What is used can be used, and various stretched films formed by longitudinal uniaxial stretching by a tenter method, a tubular method, or the like can be used.
本発明において、熱収縮性基材フィルムの厚みは特に限定されないが、耐熱性、剛性、機械適性、外観等を損なわない範囲で適宜選択され、非発泡性縦一軸延伸フィルムの場合には15〜50μmである。また、発泡縦一軸延伸フィルムの場合には、50〜200μmである。上記範囲であれば、容器に装着して使用する際に、十分な機械的強度を確保しうると共に、超音波による溶着強度に優れるからである。特に、本発明では超音波によりラベル端部を溶着するため、従来よりも厚みのあるラベルでも、実用的な強度に溶着することができる。なお、前記ラベル厚は、熱収縮前の層厚である。 In the present invention, the thickness of the heat-shrinkable substrate film is not particularly limited, but is appropriately selected within a range that does not impair heat resistance, rigidity, mechanical suitability, appearance, etc. In the case of a non-foaming vertically uniaxially stretched film, 15 to 50 μm. Moreover, in the case of a foam longitudinally uniaxially stretched film, it is 50-200 micrometers. This is because, within the above range, sufficient mechanical strength can be ensured and the welding strength by ultrasonic waves is excellent when mounted on a container and used. In particular, in the present invention, since the label edge is welded by ultrasonic waves, even a label having a thickness greater than that of the conventional one can be welded to a practical strength. The label thickness is a layer thickness before heat shrinkage.
上記の熱収縮性基材フィルムには、必要に応じて、滑剤、充填剤、熱安定剤、酸化防止剤、紫外線吸収剤、帯電防止剤、難燃剤、着色剤等の各種添加剤が添加されたものであってもよい。また、熱収縮性基材フィルムの表面には、印刷性を向上させるためにコロナ放電処理、プラズマ処理、火炎処理、酸処理などの慣用の表面処理を施してもよい。 Various additives such as a lubricant, a filler, a heat stabilizer, an antioxidant, an ultraviolet absorber, an antistatic agent, a flame retardant, and a colorant are added to the heat-shrinkable base film as necessary. It may be. In addition, the surface of the heat-shrinkable base film may be subjected to conventional surface treatment such as corona discharge treatment, plasma treatment, flame treatment, and acid treatment in order to improve printability.
本発明では、上記熱収縮性基材フィルムとして、縦方向の熱収縮率が温度95℃で5〜85%、より好ましくは15〜50%のものを好適に使用することができる。熱収縮率に優れるため凹部を有する容器にも好適に使用することができる。なお、本発明における熱収縮率とは、100℃の温水による熱収縮率であって、延伸方向の熱収縮率が下記式に従うものとする。従って、縦一軸延伸フィルムの場合には、収縮方向は、フィルム流れ方向であるため、流れ方向に対する熱収縮率が5〜85%である。 In the present invention, as the heat-shrinkable base film, a film having a heat shrinkage in the vertical direction of 5 to 85%, more preferably 15 to 50% at a temperature of 95 ° C. can be suitably used. Since it has an excellent heat shrinkage rate, it can be suitably used for a container having a recess. In addition, the heat shrinkage rate in this invention is a heat shrinkage rate by 100 degreeC hot water, Comprising: The heat shrinkage rate of an extending | stretching direction shall follow a following formula. Therefore, in the case of a longitudinally uniaxially stretched film, the shrinkage direction is the film flow direction, and thus the thermal shrinkage rate with respect to the flow direction is 5 to 85%.
本発明では、熱収縮性基材フィルムとして市販のフィルムを使用してもよい。このようなフィルムとしてPET縦一軸延伸フィルム(熱収縮率;100℃、10秒、50%、)、ポリプロピレン縦一軸延伸フィルム(熱収縮率;80℃、10秒;10%、100℃、10秒、25%)、ポリサックプラスチックインダストリーリミテッド(Polysack Plastic Industries Ltd.)の商品名「ポリファンFIT ST(Polyphane FIT ST)」などの100℃での縦方向最大収縮率19%、130℃で70%の縦一軸延伸ポリスチレンフィルム、エクロンモービル社製、商品名「Label−Lyte−Roll−On−Shink−on LR210」、縦方向最大収縮率18%などの縦一軸延伸ポリプロピレンフィルム、日生工業社製の縦一軸延伸白色ポリプロピレンフィルム、発泡ポリプロピレン縦一軸延伸フィルム(熱収縮率;120℃、10秒、40%)、商品名「サニパール」などの縦一軸延伸白色発泡ポリプロピレンフィルム、縦一軸延伸PLA系フィルムなどを好適に使用することができる。 In the present invention, a commercially available film may be used as the heat-shrinkable substrate film. As such a film, a PET longitudinally uniaxially stretched film (heat shrinkage rate: 100 ° C., 10 seconds, 50%), a polypropylene longitudinally uniaxially stretched film (heat shrinkage rate: 80 ° C., 10 seconds; 10%, 100 ° C., 10 seconds) 25%), Polysack Plastic Industries Ltd. trade name "Polyphane FIT ST (Polyphane FIT ST)", etc., maximum shrinkage in longitudinal direction at 100 ° C 19%, 70% at 130 ° C Uniaxially stretched polystyrene film, manufactured by Eclone Mobil, trade name “Label-Lyte-Roll-On-Sink-on LR210”, longitudinally uniaxially stretched polypropylene film such as 18% maximum shrinkage in the longitudinal direction, manufactured by Nissei Kogyo Co., Ltd. Longitudinal uniaxially stretched white polypropylene film, expanded polypropylene longitudinally uniaxially stretched film (heat shrinkage rate: 120 ° C., 0 sec, 40%), it is possible to longitudinal uniaxial stretching white foam polypropylene film, etc. suitably longitudinal uniaxial stretching PLA-based film used in such trade name "Saniparu".
なお、本発明において「シュリンクラベル」とは、熱処理によって収縮しうるラベルであるが熱収縮の有無は問わない。従って、熱収縮前後のいずれにおいても、シュリンクラベルである。 In the present invention, the “shrink label” is a label that can be shrunk by heat treatment. Therefore, it is a shrink label both before and after heat shrinkage.
(ii)デザイン印刷層
本発明の筒状シュリンクラベルは、熱収縮性基材フィルムの内側や外側に印刷層が積層されていてもよい。この際、熱収縮性基材フィルムのラベル内側とは、熱収縮性基材フィルムに接して形成される場合に限定されない。また、本発明では、筒状シュリンクラベルの溶着部にデザイン印刷層を設けなくてもよいが、全長に亘って印刷層を形成してもよい。レーザー溶着と相違して、超音波振動によって溶着する場合にはフィルムに印刷層が設けられていても溶着できるからである。
(Ii) Design Print Layer The cylindrical shrink label of the present invention may have a print layer laminated on the inside or outside of the heat-shrinkable base film. In this case, the inside of the label of the heat-shrinkable base film is not limited to the case where it is formed in contact with the heat-shrinkable base film. Moreover, in this invention, although a design printing layer does not need to be provided in the welding part of a cylindrical shrink label, you may form a printing layer over the full length. This is because, unlike laser welding, when welding is performed by ultrasonic vibration, welding can be performed even if a printing layer is provided on the film.
印刷方法に限定はなく、例えばグラビア印刷で印刷層を形成することができる。印刷層としては、樹脂と溶媒から通常のインキビヒクルの1種ないし2種以上を調製し、これに、必要ならば、可塑剤、安定剤、酸化防止剤、光安定剤、紫外線吸収剤、硬化剤、架橋剤、滑剤、帯電防止剤、充填剤、その他等の助剤の1種ないし2種以上を任意に添加し、更に、染料・顔料等の着色剤を添加し、溶媒、希釈剤等で充分に混練してインキ組成物を調整して得たインキ組成物を使用することができる。 There is no limitation in the printing method, for example, a printing layer can be formed by gravure printing. As the printing layer, one or more ordinary ink vehicles are prepared from a resin and a solvent, and if necessary, a plasticizer, a stabilizer, an antioxidant, a light stabilizer, an ultraviolet absorber, and a curing agent. 1 to 2 or more kinds of auxiliaries such as additives, crosslinking agents, lubricants, antistatic agents, fillers, etc. are optionally added, and further colorants such as dyes and pigments are added, and solvents, diluents, etc. The ink composition obtained by sufficiently kneading and adjusting the ink composition can be used.
このようなインキビヒクルとしては、公知のもの、例えば、あまに油、きり油、大豆油、炭化水素油、ロジン、ロジンエステル、ロジン変性樹脂、シェラック、アルキッド樹脂、フェノール系樹脂、マレイン酸樹脂、天然樹脂、炭化水素樹脂、ポリ塩化ビニル系樹脂、ポリ酢酸系樹脂、ポリスチレン系樹脂、ポリビニルブチラール樹脂、アクリルまたはメタクリル系樹脂、ポリアミド系樹脂、ポリエステル系樹脂、ポリウレタン系樹脂、エポキシ系樹脂、尿素樹脂、メラミン樹脂、アミノアルキッド系樹脂、ニトロセルロース、エチルセルロース、塩化ゴム、環化ゴム、その他などの1種または2種以上を併用することができる。インクビヒクルは、版から被印刷物に着色剤を運び、被膜として固着させる働きをする。 As such an ink vehicle, known ones such as sesame oil, drill oil, soybean oil, hydrocarbon oil, rosin, rosin ester, rosin modified resin, shellac, alkyd resin, phenolic resin, maleic resin, Natural resin, hydrocarbon resin, polyvinyl chloride resin, polyacetic acid resin, polystyrene resin, polyvinyl butyral resin, acrylic or methacrylic resin, polyamide resin, polyester resin, polyurethane resin, epoxy resin, urea resin , Melamine resin, amino alkyd resin, nitrocellulose, ethyl cellulose, chlorinated rubber, cyclized rubber, etc. can be used alone or in combination. The ink vehicle serves to carry the colorant from the plate to the substrate and fix it as a coating.
また、溶剤によってインキの乾燥性が異なる。印刷インキに使用される主な溶剤は、トルエン、MEK、酢酸エチル、IPAであり、速く乾燥させるために沸点の低い溶剤を用いるが、乾燥が速すぎると印刷物がかすれたり、うまく印刷できない場合があり、沸点の高い溶剤を適宜混合することができる。これによって、細かい文字もきれいに印刷できるようになる。着色剤には、溶剤に溶ける染料と、溶剤には溶けない顔料とがあり、グラビアインキでは顔料を使用する。顔料は無機顔料と有機顔料に分けられ、無機顔料としては酸化チタン(白色)、カーボンブラック(黒色)、アルミ粉末(金銀色)などがあり、有機顔料としてはアゾ系のものを好適に使用することができる。 Further, the drying property of the ink varies depending on the solvent. The main solvents used in printing inks are toluene, MEK, ethyl acetate, and IPA. Solvents with a low boiling point are used for quick drying. However, if the drying is too fast, the printed matter may be faded or printing may not be successful. Yes, a solvent having a high boiling point can be appropriately mixed. This makes it possible to print fine characters neatly. Colorants include dyes that are soluble in solvents and pigments that are insoluble in solvents, and gravure inks use pigments. Pigments are classified into inorganic pigments and organic pigments. Examples of inorganic pigments include titanium oxide (white), carbon black (black), and aluminum powder (gold and silver), and organic pigments are preferably azo. be able to.
上記は、グラビア印刷で説明したが、凸版印刷、スクリーン印刷、転写印刷、フレキソ印刷、その他等の印刷方式であってもよい。また、印刷は、裏印刷でも、表印刷でもよい。 Although the above was demonstrated by gravure printing, printing systems, such as letterpress printing, screen printing, transfer printing, flexographic printing, etc., may be sufficient. The printing may be back printing or front printing.
(iii)外層
本発明の筒状シュリンクラベルは、前記熱収縮性基材フィルムの表面側に更に外層を設けてもよい。このような外層としては、筒状シュリンクラベルの用途や意匠性などによって適宜選択することができ、ラベル表面の滑り性を付与する場合にはOPニスを、ラベルを触ったときの触感を付与する場合にはスエードインキによる印刷層を、マット感を付与する場合にはマットOPなどを使用することが好ましい。なお、外層は、2層以上の積層とすることができ、外層にデザイン印刷層を形成してもよい。
(iii) Outer layer The cylindrical shrink label of this invention may provide an outer layer further on the surface side of the said heat-shrinkable base film. As such an outer layer, it can be appropriately selected depending on the use and design properties of the cylindrical shrink label, and OP varnish is given when the label surface is touched to give the label surface slipperiness. In some cases, it is preferable to use a printed layer of suede ink, and in the case of giving a matte feeling, a mat OP or the like. The outer layer can be a laminate of two or more layers, and a design print layer may be formed on the outer layer.
(2)容器
本発明の筒状シュリンクラベルを添付しうる容器としては、ガラス容器;PETなどの合成樹脂性容器;セラミックボトルなどの無機物容器;アルミや鉄、SUSなどの金属製容器;ガラス、合成樹脂、セラミック、金属、紙などを含む複合材からなる容器に好適に装着することができる。
(2) Container As a container to which the cylindrical shrink label of the present invention can be attached, a glass container; a synthetic resin container such as PET; an inorganic container such as a ceramic bottle; a metal container such as aluminum, iron, or SUS; It can be suitably mounted on a container made of a composite material including synthetic resin, ceramic, metal, paper and the like.
一方、前記容器が合成樹脂製容器である場合には、該容器を構成する熱可塑性樹脂層としては、PETなどのポリエステル樹脂、PPなどのポリオレフィン系樹脂を使用することが、軽量で、機械的強度、耐熱性、ガス遮断性、耐薬品性、保香性、衛生性等に優れるため好ましい。容器は、ポリエステル樹脂やポリオレフィン系樹脂を射出成形、真空成形、圧空成形等することにより製造することができる。 On the other hand, when the container is a synthetic resin container, it is lightweight and mechanical to use a polyester resin such as PET and a polyolefin resin such as PP as the thermoplastic resin layer constituting the container. It is preferable because it is excellent in strength, heat resistance, gas barrier properties, chemical resistance, aroma retention, hygiene and the like. The container can be manufactured by injection molding, vacuum forming, pressure forming, or the like of polyester resin or polyolefin resin.
容器の形状としては、筒状シュリンクラベルが装着される容器の横断面が丸型に限定されず、四角、八角などの多角型であってもよい。また、筒状シュリンクラベルが装着される容器胴部は、胴部の全長に亘って同一径である場合に限定されず、容器の胴部縦断面が四角である以外に、たとえばひょうたん型などであってもよい。むしろ、本発明では、熱収縮率に優れる縦一軸延伸フィルムを使用するため、容器が凹凸のある形状であっても好適に装着することができる。従って、図2に示すように、容器の筒状シュリンクラベル装着部の最大周径に対する最小周径(最小周径×100/最大周径(%))が50〜100%、より好ましくは70〜90%、特に好ましくは75〜85%のものを好適に使用することができる。 As the shape of the container, the cross section of the container to which the cylindrical shrink label is attached is not limited to a round shape, and may be a polygonal shape such as a square or an octagon. Further, the container body to which the cylindrical shrink label is attached is not limited to the same diameter over the entire length of the body, and other than the case where the container body has a rectangular vertical section, for example, a gourd type There may be. Rather, in the present invention, since a longitudinally uniaxially stretched film having an excellent heat shrinkage rate is used, even if the container has an uneven shape, it can be suitably mounted. Therefore, as shown in FIG. 2, the minimum circumference (minimum circumference x 100 / maximum circumference (%)) with respect to the maximum circumference of the cylindrical shrink label mounting portion of the container is 50 to 100%, more preferably 70 to 90%, particularly preferably 75 to 85%, can be suitably used.
本発明の筒状シュリンクラベルを図2の容器に装着し、熱収縮処理した後の筒状シュリンクラベル付き容器を図3に示す。 FIG. 3 shows a container with a cylindrical shrink label after the cylindrical shrink label of the present invention is attached to the container of FIG.
(3)筒状シュリンクラベルの製造方法
本発明の筒状シュリンクラベルは、上記構成となるのであれば従来公知の方法で製造することができる。一方、縦一軸延伸してなる熱収縮性基材フィルムを延伸方向に搬送し、前記フィルムを延伸方向の所定ラベル長に切断し、前記ラベルを筒状に成形して前記切断した両端を重ね、この重ね部を超音波で溶着することで筒状シュリンクラベルを製造することができる。この方法によれば、フィルム搬送方向と延伸方向とが同方向であるから、切断したラベルを筒状に成形して切断端を重ねると延伸方向の両端部を溶着することができる。すなわち、フィルムを水平方向に移動させるだけでフィルム切断、ラベル筒状溶着を行うことができるために、横一軸延伸フィルムを使用する場合のように、ラベルを90度回転させる工程が不要となる。また、超音波で溶着するため、接着剤を使用することなく接着でき、短時間で効率的な溶着が行え、溶着部に印刷層を有する場合でも確実に溶着することができる。更に、超音波シールによれば、重ね合わせ部分を少なくすることができ、デザイン印刷部分を隠蔽する部分を少なくすることができる。また、容器リサイクル時にラベルを剥がした際、接着剤で接着する場合と相違して、溶着部分が汚れることがなくリサイクル性に優れる。
(3) Manufacturing method of cylindrical shrink label If the cylindrical shrink label of this invention becomes the said structure, it can manufacture by a conventionally well-known method. On the other hand, a heat-shrinkable base film formed by longitudinal uniaxial stretching is conveyed in the stretching direction, the film is cut into a predetermined label length in the stretching direction, the label is formed into a cylindrical shape, and the cut ends are overlapped, A cylindrical shrink label can be manufactured by welding the overlapping portion with ultrasonic waves. According to this method, since the film conveying direction and the stretching direction are the same direction, both ends in the stretching direction can be welded by forming the cut label into a cylindrical shape and overlapping the cut ends. That is, since the film cutting and label cylindrical welding can be performed only by moving the film in the horizontal direction, the step of rotating the label by 90 degrees as in the case of using a laterally uniaxially stretched film becomes unnecessary. Moreover, since it welds by an ultrasonic wave, it can adhere | attach without using an adhesive agent, can perform efficient welding in a short time, and can weld reliably, even when it has a printing layer in a welding part. Furthermore, according to the ultrasonic seal, the overlapping portion can be reduced, and the portion concealing the design printing portion can be reduced. In addition, when the label is peeled off when recycling the container, the welded portion is not contaminated unlike the case of bonding with an adhesive, and the recyclability is excellent.
本発明の筒状シュリンクラベルは、図4に示すように、鉛直に配置されたシリンダ(20)にまきつけるように前記熱収縮性基材フィルム(10)を繰り出し、所定のラベル長に切断し、シリンダ(20)にまきつけたラベル(30)の前記切断端を重ね、前記重ね部(35)を超音波で溶着し、超音波シール(37)部を幅0.5〜15mmで形成し、筒状シュリンクラベル(100)を製造してもよい。使用するシリンダ(20)は、その表面に空気を吸引しまたは排出する空気孔(25)が多数設けられたものであれば、切断されたラベル(30)を前記シリンダ表面で吸引しながら安定してまき付けることができる。その際、シリンダ(20)を鉛直方向を軸として回転させればラベル(30)のまき付けが容易となる。切断端を5〜25mmで重ね、重ね部(37)を超音波で熱溶着する。超音波シールは、溶着の際にシール部(35)の加圧が必要であるため、前記重ね部(37)をシリンダ(20)と超音波振動発生装置(40)とではさみ、所定の溶着圧で接触させると、簡便かつ確実に超音波シールを行うことができる。 As shown in FIG. 4, the cylindrical shrink label of the present invention pays out the heat-shrinkable base film (10) so as to be attached to a vertically arranged cylinder (20), cut into a predetermined label length, The cut end of the label (30) attached to the cylinder (20) is overlapped, the overlap portion (35) is welded with ultrasonic waves, and the ultrasonic seal (37) portion is formed with a width of 0.5 to 15 mm. A shaped shrink label (100) may be manufactured. If the cylinder (20) to be used has many air holes (25) for sucking or discharging air on its surface, the cylinder (20) is stable while sucking the cut label (30) on the cylinder surface. Can be attached. At that time, if the cylinder (20) is rotated about the vertical direction, the label (30) can be easily attached. The cut ends are overlapped at 5 to 25 mm, and the overlap portion (37) is thermally welded with ultrasonic waves. Since the ultrasonic seal requires pressurization of the seal portion (35) at the time of welding, the overlap portion (37) is sandwiched between the cylinder (20) and the ultrasonic vibration generator (40), and predetermined welding is performed. When contacting with pressure, ultrasonic sealing can be performed easily and reliably.
超音波振動発生装置(40)としては、例えば、電圧を加えると伸びたり縮んだりするピエゾ素子と呼ばれるセラミックの一種を、金属でできたホーンAとホーンBで挟み込み固定し、ピエゾ素子とホーンとの間に駆動端子とアース端子を設け、この端子に交流電圧を加えてホーンAの先端部分を高速振動させたものを使用することができる。ホーンAの先端部分をラベル接着部として超音波振動を発生させれば、超音波シーラとして使用することができる。ピエゾ素子の形態にも種々あるが、20kHz以上の超音波振動を発生し、シュリンクラベルを熱溶着できるものであれば、特に限定はない。なお、超音波振動発生装置は上記に限定されるものでない。 As the ultrasonic vibration generator (40), for example, a kind of ceramic called a piezo element that expands or contracts when a voltage is applied is sandwiched and fixed between a horn A and a horn B made of metal, and the piezo element and the horn A drive terminal and a ground terminal are provided between the two terminals, and an AC voltage is applied to this terminal to vibrate the tip of the horn A at high speed. If ultrasonic vibration is generated by using the tip portion of the horn A as a label adhesion portion, it can be used as an ultrasonic sealer. There are various types of piezoelectric elements, but there is no particular limitation as long as ultrasonic vibrations of 20 kHz or higher can be generated and the shrink label can be thermally welded. The ultrasonic vibration generator is not limited to the above.
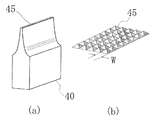
前記したように、超音波シールの際には、前記ホーンのラベル接触面をシール部に接触し、及び加圧し、前記ラベル接触面から超音波振動を発生させて溶着部を溶融し、加圧によって上下のシュリンクラベルを接着させる。超音波振動発生装置(40)の形状としては特に限定はないが、例えば、図5(a)に示すように少なくとも超音波振動を発生および伝播するラベル接触面(45)を有し、ラベルを加圧できる形状であればよく、より好ましくは、前記ラベル接触面(45)が超音波シール幅と同幅であり、かつ図5(b)に示すように、所定のピッチ幅(W)のダイヤカット状の溶着目を有するものを好適に使用することができる。ピッチ幅(W)は、好ましくは0.5〜4mmであり、超音波の周波数やラベル接触面への圧力、ラベル基材の厚さや種類などに応じて適宜選択することができる。 As described above, at the time of ultrasonic sealing, the label contact surface of the horn is brought into contact with and pressurized, and ultrasonic vibration is generated from the label contact surface to melt the welded portion and pressurize. Adhere the upper and lower shrink labels. The shape of the ultrasonic vibration generator (40) is not particularly limited. For example, the ultrasonic vibration generator (40) has at least a label contact surface (45) that generates and propagates ultrasonic vibration as shown in FIG. The label contact surface (45) has the same width as the ultrasonic seal width and has a predetermined pitch width (W) as shown in FIG. 5 (b). What has a diamond-cut-like melt attention can be used suitably. The pitch width (W) is preferably 0.5 to 4 mm, and can be appropriately selected according to the frequency of ultrasonic waves, the pressure applied to the label contact surface, the thickness and type of the label base material, and the like.
超音波処理は、使用するラベルの熱収縮性基材フィルムの種類、ラベル厚さ、筒状シュリンクラベルのサイズ、超音波振動の周波数などによって適宜選択することができるが、例えば、加工幅(超音波振動発生装置のラベル接触面幅)10mm、ラベル接触面(45)が、前記ピッチ幅(W)が1.0mm、高さ0.5mmのピラミッド型を有する超音波振動発生装置(40)を使用した場合には、発振時間0.1〜2.0秒、接触圧200〜500Nで十分である。 The ultrasonic treatment can be appropriately selected depending on the type of heat-shrinkable substrate film of the label to be used, the label thickness, the size of the cylindrical shrink label, the frequency of ultrasonic vibration, and the like. An ultrasonic vibration generator (40) having a pyramid shape with a label contact surface width (10 mm) and a label contact surface (45) having a pitch width (W) of 1.0 mm and a height of 0.5 mm. When used, an oscillation time of 0.1 to 2.0 seconds and a contact pressure of 200 to 500 N are sufficient.
前記したように、超音波シール幅は好ましくは0.5〜15mmであり、また、超音波シールのための筒状シュリンクラベルの溶着部の重ね合わせ幅は5〜25mmである。上記超音波シールによれば、上記範囲の超音波シール幅で実際の使用に十分な溶着強度を確保することができる。 As described above, the ultrasonic seal width is preferably 0.5 to 15 mm, and the overlapping width of the welded portion of the cylindrical shrink label for ultrasonic seal is 5 to 25 mm. According to the ultrasonic seal, a welding strength sufficient for actual use can be secured with an ultrasonic seal width in the above range.
重ね部に超音波シール部を形成すれば、筒状シュリンクラベルが製造される。 If an ultrasonic seal part is formed in the overlapped part, a cylindrical shrink label is manufactured.
(4)筒状シュリンクラベル付き容器の製造方法
本発明の筒状シュリンクラベル付き容器は、上記で製造した筒状シュリンクラベルに、ラベルの上部から容器を挿入して容器に筒状シュリンクラベルを装着し、ついで熱収縮処理することで製造することができる。
(4) Manufacturing method of container with cylindrical shrink label The container with cylindrical shrink label of this invention inserts a container from the upper part of a label to the cylindrical shrink label manufactured above, and attaches a cylindrical shrink label to a container Then, it can be manufactured by heat shrink treatment.
例えば、図6、図7に示すように、(a)ラベル(30)をシリンダ(20)にまき付け、(b)ラベル切断端の重ね部(37)を形成し、(c)重ね部(37)に超音波シール部(35)を形成して筒状に溶着する。次いで、(d)シリンダ(20)を下方から引き抜く。具体的には、シリンダ(20)には多数の空気孔(25)が設けられており、超音波溶着後にシリンダ(20)の前記空気孔(25)から空気を排出させると、シリンダ(20)とラベル(30)との間に空気を送り込むことができる。この状態で、シリンダ(20)をラベルの下端から下方に移動させると、容易に筒状シュリンクラベルからシリンダ(20)を引き抜くことができる。(e)これにより筒状シュリンクラベル(100)を鉛直した状態で製造することができる。 For example, as shown in FIG. 6 and FIG. 7, (a) the label (30) is attached to the cylinder (20), (b) the overlapping portion (37) of the label cutting end is formed, and (c) the overlapping portion ( An ultrasonic seal portion (35) is formed on 37) and welded in a cylindrical shape. Next, (d) the cylinder (20) is pulled out from below. Specifically, the cylinder (20) is provided with a large number of air holes (25). When air is discharged from the air holes (25) of the cylinder (20) after ultrasonic welding, the cylinder (20) And label (30). When the cylinder (20) is moved downward from the lower end of the label in this state, the cylinder (20) can be easily pulled out from the cylindrical shrink label. (E) Thereby, the cylindrical shrink label (100) can be manufactured in a vertical state.
次いで、(f)筒状シュリンクラベルの上部から容器(90)を降下させ、(g)筒状シュリンクラベル(100)を容器(90)に装着し、次いで(h)熱収縮処理を順次行う。熱収縮処理は、ラベルの熱収縮性基材フィルムの種類や厚さ、延伸率などによって適宜選択することができ、例えば、60〜230℃の熱風や、水蒸気及び水蒸気が結露した湯気により加熱するスチームや、赤外線等の輻射熱を作用させてシュリンクラベルを周方向に高収縮させ、容器の胴部をシュリンクラベルで被覆することができる。なお、上記は、シリンダ(20)を、筒状シュリンクラベルの下部側から引き抜き、上部側から容器を挿入する態様を示したが、筒状シュリンクラベルの上部側から引き抜き、下部側から容器を挿入する態様であってもよい。 Next, (f) the container (90) is lowered from the upper part of the cylindrical shrink label, (g) the cylindrical shrink label (100) is attached to the container (90), and then (h) heat shrinkage treatment is sequentially performed. The heat shrink treatment can be appropriately selected depending on the type and thickness of the heat shrinkable base film of the label, the stretching ratio, and the like. For example, the heat shrink treatment is performed with hot air at 60 to 230 ° C. or steam with condensation of water vapor and water vapor. The shrink label can be highly shrunk in the circumferential direction by applying radiant heat such as steam or infrared rays, and the body of the container can be covered with the shrink label. In addition, although the above showed the aspect which pulls out a cylinder (20) from the lower side of a cylindrical shrink label and inserts a container from an upper side, it pulls out from the upper side of a cylindrical shrink label and inserts a container from the lower side It is also possible to use this mode.
本発明では、前記したように、フィルムを水平方向に移動するだけでフィルムの切断、ラベルの筒状溶着を行うことができるため、鉛直に配置されたシリンダにまきつければラベルの筒状化を円滑かつ容易に行うことができ、シリンダに超音波振動発生装置を接触させることで、簡便かつ確実に超音波シールを行うことができる。 In the present invention, as described above, the film can be cut and the label can be welded by simply moving the film in the horizontal direction. It can be carried out smoothly and easily, and ultrasonic sealing can be performed simply and reliably by bringing the ultrasonic vibration generator into contact with the cylinder.
なお、重ね部(37)に超音波振動発生装置のラベル接触面を接触させて超音波シールする際には、ラベル端部を図8(c)に示すように、二枚のラベル重ね部(37)に超音波振動発生装置のラベル接触面を押しあて、これを加工幅として超音波シールすることができる。一方、重ね部(37)に超音波振動発生装置のラベル接触面を接触させて超音波シールする際に、ラベル端部を図8(a)に示すように、上前を内側に折り曲げてから超音波振動発生装置のラベル接触面を押しあて、この加工幅に超音波シールを行ってもよい。ラベルの硬度が高い場合や熱収縮後に硬度が増す場合に、切断端によって手を切る恐れを回避することができる。また、重ね部と超音波振動発生装置のラベル接触面との位置を、例えば、図8(b)に示すように上前の切断端が前記加工幅(ラベル接触面の幅)に収まるようにして超音波シールしても、切断端が溶着されるため切断端によって手を切る恐れや、熱収縮後に切断端が立ち上がるのを回避し、筒状シュリンクラベルの外観を向上させることができる。 When the ultrasonic wave sealing is performed by bringing the label contact surface of the ultrasonic vibration generator into contact with the overlapping portion (37), the label end portion is formed of two label overlapping portions (see FIG. 8C). 37), the label contact surface of the ultrasonic vibration generator can be pressed, and this can be used as a processing width for ultrasonic sealing. On the other hand, when the ultrasonic contact is made by bringing the label contact surface of the ultrasonic vibration generator into contact with the overlapping portion (37), the label end is folded inward as shown in FIG. 8 (a). The label contact surface of the ultrasonic vibration generator may be pressed to perform ultrasonic sealing on this processing width. When the label has a high hardness or when the hardness increases after heat shrinkage, it is possible to avoid the risk of cutting the hand by the cut end. Further, the positions of the overlapping portion and the label contact surface of the ultrasonic vibration generator are set such that the upper and lower cut ends are within the processing width (the width of the label contact surface) as shown in FIG. 8B, for example. Even if ultrasonic sealing is performed, since the cut end is welded, it is possible to avoid the possibility of cutting the hand by the cut end and to prevent the cut end from rising after heat shrinkage, and to improve the appearance of the cylindrical shrink label.
(5)筒状シュリンクラベル付き容器
本発明の筒状シュリンクラベル付き容器は、上記筒状シュリンクラベル(100)が容器(90)の全長に亘って被覆するように装着されたものでもよく、容器(90)の上部のみ、下部のみ、蓋部のみ、など容器の一部のみに装着してもよい。更に、容器底部を包み込むように熱収縮させたり、容器蓋部から底部の全体に筒状シュリンクラベルを装着し、熱収縮させて、全面被覆することもできる。
(5) Container with cylindrical shrink label The container with cylindrical shrink label of the present invention may be one in which the cylindrical shrink label (100) is mounted so as to cover the entire length of the container (90). (90) Only the upper part, only the lower part, only the lid part, etc. may be attached to only a part of the container. Furthermore, it is possible to heat-shrink so as to wrap the container bottom, or to attach a cylindrical shrink label to the entire bottom from the container lid and heat-shrink to cover the entire surface.
次に実施例を挙げて本発明を具体的に説明するが、これらの実施例は何ら本発明を制限するものではない。 EXAMPLES Next, although an Example is given and this invention is demonstrated concretely, these Examples do not restrict | limit this invention at all.
(実施例1)
760mm巾、フィルム厚さが190μmの発泡白色ポリプロピレン縦一軸延伸フィルム(熱収縮率;120℃、10秒、40%)を使用し、ラベルの両端を除いてラベルデザイン印刷を表刷りした後、72mm巾で10列のラベルをスリットして延伸方向に巻き取った。
Example 1
Using a foamed white polypropylene longitudinally uniaxially stretched film (heat shrinkage rate: 120 ° C., 10 seconds, 40%) having a width of 760 mm and a film thickness of 190 μm, the label design print was printed on the surface except for both ends of the label, and then 72 mm The 10 rows of labels were slit and wound in the stretching direction.
ラベラーに上記幅72mmの印刷ロールラベルをセット、延伸方向に繰り出してロータリーカッター部分で238mmの長さにカットして枚葉ラベルとした。 The above-mentioned printing roll label having a width of 72 mm was set on a labeler, fed out in the stretching direction, and cut into a length of 238 mm at a rotary cutter portion to obtain a sheet label.
前記枚葉ラベルの切断した両端が溶着部となるように前記シリンダにエアーで吸引しながら巻きつけ、ラベル両端部に重なりを設けた。重ね部は、外側からシリンダに向けて、発泡PP/発泡PPとなる。 The both ends of the single-wafer label were wound around the cylinder while being sucked with air so that both ends were welded portions, and overlapping was provided at both ends of the label. The overlapping portion becomes foamed PP / foamed PP from the outside toward the cylinder.
次いで、前記両端部を超音波シールした。超音波発生装置としてブランソン2000Xを使用し、振幅20kHzで、10×76mmのラベル接触面で、図5(b)に示すように、1mmのピッチ幅で、先端が高さ0.5mmのピラミッド状にカットされたものを実行圧210Nで0.2秒発振して溶着した後、0.2秒冷却し、筒状シュリンクラベルを調製した。 Next, the both ends were ultrasonically sealed. A Branson 2000X is used as an ultrasonic generator, and a 10 × 76 mm label contact surface with an amplitude of 20 kHz, as shown in FIG. 5 (b), a 1 mm pitch width and a pyramid shape with a 0.5 mm tip. After being cut and welded by oscillating at an execution pressure of 210 N for 0.2 seconds, it was cooled for 0.2 seconds to prepare a cylindrical shrink label.
次いで、前記筒状シュリンクラベルを500mLの変形PETボトルの上部から装着し、熱風式シュリンクトンネルで120℃×10秒加熱してラベルを収縮させた。 Next, the cylindrical shrink label was attached from the top of a 500 mL modified PET bottle, and the label was contracted by heating at 120 ° C. for 10 seconds in a hot air type shrink tunnel.
得られた筒状シュリンクラベルは、熱収縮時にも溶着部分が剥がれることなかった。また、得られたシュリンクラベル装着容器は、50cmの高さから落下してもラベルの脱落がなく、十分な溶着強度を有していた。結果を表1に示す。 The obtained cylindrical shrink label did not peel off the welded part even during heat shrinkage. Further, the obtained shrink label mounting container did not drop off the label even when dropped from a height of 50 cm, and had sufficient welding strength. The results are shown in Table 1.
(実施例2)
超音波溶着を、実行圧470Nで行った以外は、実施例1と同様に操作した。
(Example 2)
The same operation as in Example 1 was performed except that ultrasonic welding was performed at an execution pressure of 470N.
得られた筒状シュリンクラベルは、熱収縮時にも溶着部分が剥がれることなかった。また、得られたシュリンクラベル装着容器は、50cmの高さから落下してもラベルの脱落がなく、十分な溶着強度を有していた。結果を表1に示す。 The obtained cylindrical shrink label did not peel off the welded part even during heat shrinkage. Further, the obtained shrink label mounting container did not drop off the label even when dropped from a height of 50 cm, and had sufficient welding strength. The results are shown in Table 1.
115mm巾、フィルム厚さが25μmのPET縦一軸延伸フィルム(熱収縮率;100℃、10秒、50%)を使用し、ラベルの両端部をのぞいた内面に藍格子のラベルデザイン印刷を行い、延伸方向に巻き取った。
Using a PET longitudinally uniaxially stretched film (heat shrinkage rate: 100 ° C., 10 seconds, 50%) with a width of 115 mm and a film thickness of 25 μm, the label design printing of the indigo lattice is performed on the inner surface except for both ends of the label. It wound up in the extending | stretching direction.
ラベラーに上記印刷ロールラベルをセット、延伸方向に繰り出してロータリーカッター部分で238mmの長さにカットして枚葉ラベルとした。 The above-mentioned printing roll label was set on a labeler, fed out in the stretching direction, and cut into a length of 238 mm at a rotary cutter portion to obtain a single wafer label.
前記枚葉ラベルの切断した両端が溶着部となるように前記シリンダにエアーで吸引しながら巻きつけ、ラベル両端部に重なりを設けた。重ね部は、外側からシリンダに向けて、PET/PETとなる。 The both ends of the single-wafer label were wound around the cylinder while being sucked with air so that both ends were welded portions, and overlapping was provided at both ends of the label. The overlapping portion becomes PET / PET from the outside toward the cylinder.
次いで、前記両端部を超音波シールした。超音波発生装置としてブランソン2000Xを使用し、振幅20kHzで、10×76mmのラベル接触面で、図5(b)に示すように、1mmのピッチ幅で、先端が高さ0.5mmのピラミッド状にカットされたものを実行圧460Nで0.2秒発振して溶着した後、0.2秒冷却し、筒状シュリンクラベルを調製した。 Next, the both ends were ultrasonically sealed. A Branson 2000X is used as an ultrasonic generator, and a 10 × 76 mm label contact surface with an amplitude of 20 kHz, as shown in FIG. 5 (b), a 1 mm pitch width and a pyramid shape with a 0.5 mm tip. After being cut and welded by oscillating at an execution pressure of 460 N for 0.2 seconds, it was cooled for 0.2 seconds to prepare a cylindrical shrink label.
次いで、前記筒状シュリンクラベルを500mLの変形PETボトルの上部から装着し、熱風式シュリンクトンネルで95℃×10秒加熱してラベルを収縮させた。 Next, the cylindrical shrink label was attached from the top of a 500 mL modified PET bottle, and the label was shrunk by heating at 95 ° C. for 10 seconds in a hot air type shrink tunnel.
得られた筒状シュリンクラベルは、熱収縮時にも溶着部分が剥がれることなかった。また、得られたシュリンクラベル装着容器は、50cmの高さから落下してもラベルの脱落がなく、十分な溶着強度を有していた。結果を表2に示す。 The obtained cylindrical shrink label did not peel off the welded part even during heat shrinkage. Further, the obtained shrink label mounting container did not drop off the label even when dropped from a height of 50 cm, and had sufficient welding strength. The results are shown in Table 2.
(実施例4)
実施例3の藍格子の印刷層に代えて、ラベルの後端部を除いて白ベタ印刷を行い、筒状シュリンクラベルの外側から内側に向けて、PET/PET/白ベタ印刷と重ね、PET側から超音波溶着処理を行った。
Example 4
Instead of the printed layer of the indigo lattice of Example 3, white solid printing is performed except for the rear end portion of the label, and PET / PET / white solid printing is overlapped from the outside to the inside of the cylindrical shrink label. The ultrasonic welding process was performed from the side.
得られた筒状シュリンクラベルは、熱収縮時にも溶着部分が剥がれることなかった。また、得られたシュリンクラベル装着容器は、50cmの高さから落下してもラベルの脱落がなく、十分な溶着強度を有していた。結果を表2に示す。 The obtained cylindrical shrink label did not peel off the welded part even during heat shrinkage. Further, the obtained shrink label mounting container did not drop off the label even when dropped from a height of 50 cm, and had sufficient welding strength. The results are shown in Table 2.
(実施例5)
実施例3の藍格子の印刷層に代えて、ラベルの前端部を除いて白ベタ印刷を行い、筒状シュリンクラベルの外側から内側に向けて、PET/白ベタ印刷/PETと重ね、PET側から超音波溶着処理を行った。
(Example 5)
Instead of the printed layer of the indigo lattice of Example 3, white solid printing is performed except for the front end portion of the label, and PET / white solid printing / PET is overlapped from the outside to the inside of the cylindrical shrink label, and the PET side Then, ultrasonic welding treatment was performed.
得られた筒状シュリンクラベルは、熱収縮時にも溶着部分が剥がれることなかった。また、得られたシュリンクラベル装着容器は、50cmの高さから落下してもラベルの脱落がなく、十分な溶着強度を有していた。結果を表2に示す。 The obtained cylindrical shrink label did not peel off the welded part even during heat shrinkage. Further, the obtained shrink label mounting container did not drop off the label even when dropped from a height of 50 cm, and had sufficient welding strength. The results are shown in Table 2.
115mm巾、フィルム厚さが50μmのポリプロピレン系縦一軸延伸フィルム(熱収縮率;80℃、10秒;10%、100℃、10秒、25%)を使用し、ラベルの両端をのぞいた内面にラベルデザイン印刷を行い、延伸方向に巻き取った。
Use a polypropylene-based longitudinally uniaxially stretched film (heat shrinkage rate: 80 ° C., 10 seconds; 10%, 100 ° C., 10 seconds, 25%) having a width of 115 mm and a film thickness of 50 μm on the inner surface except for both ends of the label. Label design printing was performed and wound up in the stretching direction.
ラベラーに上記印刷ロールラベルをセット、延伸方向に繰り出してロータリーカッター部分で238mmの長さにカットして枚葉ラベルとした。 The above-mentioned printing roll label was set on a labeler, fed out in the stretching direction, and cut into a length of 238 mm at a rotary cutter portion to obtain a single wafer label.
前記枚葉ラベルの切断した両端が溶着部となるように前記シリンダにエアーで吸引しながら巻きつけ、ラベル両端部に重なりを設けた。重ね部はPP/PPとなり、PP側から超音波溶着処理を行った。 The both ends of the single-wafer label were wound around the cylinder while being sucked with air so that both ends were welded portions, and overlapping was provided at both ends of the label. The overlapped portion was PP / PP, and ultrasonic welding treatment was performed from the PP side.
次いで、前記両端部を超音波シールした。超音波発生装置としてブランソン2000Xを使用し、振幅20kHzで、10×76mmのラベル接触面で、図5(b)に示すように、1mmのピッチ幅で、先端が高さ0.5mmのピラミッド状にカットされたものを実行圧210Nで0.2秒発振して溶着した後、0.2秒冷却し、筒状シュリンクラベルを調製した。 Next, the both ends were ultrasonically sealed. A Branson 2000X is used as an ultrasonic generator, and a 10 × 76 mm label contact surface with an amplitude of 20 kHz, as shown in FIG. 5 (b), a 1 mm pitch width and a pyramid shape with a 0.5 mm tip. After being cut and welded by oscillating at an execution pressure of 210 N for 0.2 seconds, it was cooled for 0.2 seconds to prepare a cylindrical shrink label.
次いで、前記筒状シュリンクラベルを500mLの変形PETボトルの上部から装着し、熱風式シュリンクトンネルで120℃×10秒加熱してラベルを収縮させた。 Next, the cylindrical shrink label was attached from the top of a 500 mL modified PET bottle, and the label was contracted by heating at 120 ° C. for 10 seconds in a hot air type shrink tunnel.
得られた筒状シュリンクラベルは、熱収縮時にも溶着部分が剥がれることなかった。また、得られたシュリンクラベル装着容器は、50cmの高さから落下してもラベルの脱落がなく、十分な溶着強度を有していた。結果を表3に示す。 The obtained cylindrical shrink label did not peel off the welded part even during heat shrinkage. Further, the obtained shrink label mounting container did not drop off the label even when dropped from a height of 50 cm, and had sufficient welding strength. The results are shown in Table 3.
(実施例7)
フィルム厚さが50μmのポリプロピレン系縦一軸延伸フィルムに代えた以外は実施例6と同様に操作して、筒状シュリンクラベルおよびラベル付容器を製造した。
(Example 7)
A cylindrical shrink label and a labeled container were manufactured in the same manner as in Example 6 except that the film thickness was changed to a polypropylene-based longitudinally uniaxially stretched film having a thickness of 50 μm.
得られた筒状シュリンクラベルは、熱収縮時にも溶着部分が剥がれることなかった。また、得られたシュリンクラベル装着容器は、50cmの高さから落下してもラベルの脱落がなく、十分な溶着強度を有していた。結果を表3に示す。 The obtained cylindrical shrink label did not peel off the welded part even during heat shrinkage. Further, the obtained shrink label mounting container did not drop off the label even when dropped from a height of 50 cm, and had sufficient welding strength. The results are shown in Table 3.
(実施例8)
フィルム厚さを25μmに代えた以外は実施例6と同様に操作して、筒状シュリンクラベルおよびラベル付容器を製造した。
(Example 8)
A cylindrical shrink label and a labeled container were manufactured in the same manner as in Example 6 except that the film thickness was changed to 25 μm.
得られた筒状シュリンクラベルは、熱収縮時にも溶着部分が剥がれることなかった。また、得られたシュリンクラベル装着容器は、50cmの高さから落下してもラベルの脱落がなく、十分な溶着強度を有していた。結果を表3に示す。 The obtained cylindrical shrink label did not peel off the welded part even during heat shrinkage. Further, the obtained shrink label mounting container did not drop off the label even when dropped from a height of 50 cm, and had sufficient welding strength. The results are shown in Table 3.
フィルム厚さを50μmとし、印刷層なしのフィルムを使用した以外は実施例3と同様に操作して、筒状シュリンクラベルおよびラベル付容器を製造した。
A cylindrical shrink label and a labeled container were manufactured in the same manner as in Example 3 except that the film thickness was 50 μm and a film without a printing layer was used.
得られた筒状シュリンクラベルは、熱収縮時にも溶着部分が剥がれることなかった。また、得られたシュリンクラベル装着容器は、50cmの高さから落下してもラベルの脱落がなく、十分な溶着強度を有していた。結果を表4に示す。 The obtained cylindrical shrink label did not peel off the welded part even during heat shrinkage. Further, the obtained shrink label mounting container did not drop off the label even when dropped from a height of 50 cm, and had sufficient welding strength. The results are shown in Table 4.
(実施例10)
ラベル接触面が、1mmのピッチ幅で、先端が高さ0.5mmのピラミッド状にカットされたものに代えて、斜線1mm巾シール、空隙0.7mmのものを使用した以外は実施例3と同様に操作して、筒状シュリンクラベルおよびラベル付容器を製造した。
Example 10
Example 3 with the exception that a label contact surface with a 1 mm pitch width and a tip cut into a pyramid with a height of 0.5 mm was used instead of an oblique 1 mm wide seal and a gap of 0.7 mm. The same operation was performed to produce a cylindrical shrink label and a labeled container.
得られた筒状シュリンクラベルは、熱収縮時にも溶着部分が剥がれることなかった。また、得られたシュリンクラベル装着容器は、50cmの高さから落下してもラベルの脱落がなく、十分な溶着強度を有していた。結果を表4に示す。 The obtained cylindrical shrink label did not peel off the welded part even during heat shrinkage. Further, the obtained shrink label mounting container did not drop off the label even when dropped from a height of 50 cm, and had sufficient welding strength. The results are shown in Table 4.
超音波発生装置としてブランソン2000aedを使用し、振幅20kHzで、ラベル接触面が直径0.5mmの丸点形状からなるホーンを使用し、振幅70(%)、加工速度300mm/秒、ホーンと受けのクリアラス30μm、加工幅2.5mmで加工した以外は、実施例3と同様に操作した。
A Branson 2000aed is used as an ultrasonic generator, a horn having a round dot shape with an amplitude of 20 kHz and a label contact surface of 0.5 mm in diameter, an amplitude of 70 (%), a processing speed of 300 mm / sec, The same operation as in Example 3 was performed except that processing was performed with a clear lath of 30 μm and a processing width of 2.5 mm.
得られた筒状シュリンクラベルは、熱収縮時にも溶着部分が剥がれることなかった。また、得られたシュリンクラベル装着容器は、50cmの高さから落下してもラベルの脱落がなく、十分な溶着強度を有していた。結果を表5に示す。 The obtained cylindrical shrink label did not peel off the welded part even during heat shrinkage. Further, the obtained shrink label mounting container did not drop off the label even when dropped from a height of 50 cm, and had sufficient welding strength. The results are shown in Table 5.
(実施例12)
超音波発生装置としてブランソン2000dを使用し、振幅40kHzで、振幅100(%)、加工速度500mm/秒、ホーンと受けのクリアラス30μm、加工幅2.5mmで加工した以外は、実施例3と同様に操作した。
(Example 12)
Example 3 except that Branson 2000d was used as an ultrasonic generator, the amplitude was 40 kHz, the amplitude was 100 (%), the processing speed was 500 mm / second, the horn and the receiving clearus were 30 μm, and the processing width was 2.5 mm. Operated.
得られた筒状シュリンクラベルは、熱収縮時にも溶着部分が剥がれることなかった。また、得られたシュリンクラベル装着容器は、50cmの高さから落下してもラベルの脱落がなく、十分な溶着強度を有していた。結果を表5に示す。 The obtained cylindrical shrink label did not peel off the welded part even during heat shrinkage. Further, the obtained shrink label mounting container did not drop off the label even when dropped from a height of 50 cm, and had sufficient welding strength. The results are shown in Table 5.
(実施例13)
シリンダに枚葉ラベルを巻きつける際に、図8(a)に示すようにラベル後端の1mmをラベル内側に折込んだ後に、ラベル前端部の上に重ねて、PET三枚重ねの重ね部を形成し、加工幅を3mmとした以外は実施例11と同様に操作した。
(Example 13)
When winding a single wafer label around the cylinder, as shown in FIG. 8 (a), after folding 1mm of the rear end of the label inside the label, it is stacked on the front end of the label, and the overlapping part of the three PET stacks And the same operation as in Example 11 was performed except that the processing width was 3 mm.
得られた筒状シュリンクラベルは、熱収縮時にも溶着部分が剥がれることなかった。また、得られたシュリンクラベル装着容器は、50cmの高さから落下してもラベルの脱落がなく、十分な溶着強度を有していた。結果を表5に示す。 The obtained cylindrical shrink label did not peel off the welded part even during heat shrinkage. Further, the obtained shrink label mounting container did not drop off the label even when dropped from a height of 50 cm, and had sufficient welding strength. The results are shown in Table 5.
(実施例14)
シリンダに枚葉ラベルを巻きつける際に、図8(a)に示すようにラベル後端の1mmをラベル内側に折込んだ後に、ラベル前端部の上に重ねて、PET三枚重ねの重ね部を形成し、加工幅を3mmとした以外は実施例12と同様に操作した。
(Example 14)
When winding a single wafer label around the cylinder, as shown in FIG. 8 (a), after folding 1mm of the rear end of the label inside the label, it is stacked on the front end of the label, and the overlapping part of the three PET stacks And the same operation as in Example 12 was performed except that the processing width was 3 mm.
得られた筒状シュリンクラベルは、熱収縮時にも溶着部分が剥がれることなかった。また、得られたシュリンクラベル装着容器は、50cmの高さから落下してもラベルの脱落がなく、十分な溶着強度を有していた。結果を表5に示す。 The obtained cylindrical shrink label did not peel off the welded part even during heat shrinkage. Further, the obtained shrink label mounting container did not drop off the label even when dropped from a height of 50 cm, and had sufficient welding strength. The results are shown in Table 5.
本発明に係る筒状シュリンクラベルは、超音波振動によりラベルを筒状に成形するものであり、従来困難であった厚手のラベルや接着部に印刷層を有するラベルでも溶着することができ、有用である。 The cylindrical shrink label according to the present invention is formed into a cylindrical shape by ultrasonic vibration, and can be welded even with a thick label or a label having a printed layer on the adhesive portion, which has been difficult in the past, and is useful. It is.
10・・・熱収縮性基材フィルム、
20・・・シリンダ、
25・・・空気孔、
30・・・ラベル、
35・・・超音波シール部、
37・・・ラベル重ね部、
40・・・超音波振動発生装置、
45・・・超音波振動発生装置のラベル接触面、
90・・・容器、
100・・・筒状シュリンクラベル、
W・・・超音波振動発生装置のラベル接触面のピッチ幅。
10 ... heat-shrinkable substrate film,
20 ... Cylinder,
25 ... Air holes,
30 ... label,
35 ... Ultrasonic seal part,
37: Label overlapping part,
40 ... ultrasonic vibration generator,
45 ... Label contact surface of ultrasonic vibration generator,
90 ... container,
100 ... cylindrical shrink label,
W: Pitch width of the label contact surface of the ultrasonic vibration generator.
Claims (9)
縦一軸延伸した熱収縮性基材フィルムを延伸方向の所定サイズに切断してラベルを切り出し、
前記ラベルを筒状に成形して前記切断した両端を重ね、
前記重ね部を超音波で溶着することを特徴とする、筒状シュリンクラベル。 A cylindrical shrink label formed by welding both ends of the label in the stretching direction of the heat-shrinkable base film,
Cut the heat-shrinkable base film stretched uniaxially to a predetermined size in the stretching direction, cut out the label,
Forming the label into a cylindrical shape and overlapping the cut ends,
A cylindrical shrink label, wherein the overlapped portion is welded with ultrasonic waves.
前記フィルムを延伸方向の所定ラベル長に切断し、
前記ラベルを筒状に成形して前記切断した両端を重ね、
前記重ね部を超音波で溶着することを特徴とする、筒状シュリンクラベルの製造方法。 A heat-shrinkable base film formed by uniaxial stretching is conveyed in the stretching direction,
Cutting the film into a predetermined label length in the stretching direction,
Forming the label into a cylindrical shape and overlapping the cut ends,
A method of manufacturing a cylindrical shrink label, wherein the overlapping portion is welded by ultrasonic waves.
前記フィルムを延伸方向の所定ラベル長に切断し、
前記ラベルを鉛直に配置されたシリンダにまき付けて前記切断端を重ね、
前記重ね部を超音波で溶着して筒状シュリンクラベルを成形し、
前記筒状シュリンクラベルの下部側または上部側から前記シリンダを抜き出し、かつラベルの上部側または下部側から容器を挿入して前記容器に筒状シュリンクラベルを装着し、
ついで熱収縮処理することを特徴とする、筒状シュリンクラベル付き容器の製造方法。 A heat-shrinkable base film formed by uniaxial stretching is conveyed in the stretching direction,
Cutting the film into a predetermined label length in the stretching direction,
The label is attached to a vertically arranged cylinder and the cut end is overlapped,
The overlapping portion is welded with ultrasonic waves to form a cylindrical shrink label,
The cylinder is extracted from the lower side or the upper side of the cylindrical shrink label, and a container is inserted from the upper side or the lower side of the label, and the cylindrical shrink label is attached to the container,
Next, a method for producing a container with a cylindrical shrink label, which is subjected to heat shrinkage treatment.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007173315A JP2009012779A (en) | 2007-06-29 | 2007-06-29 | Cylindrical shrink label, container having cylindrical shrink label, and method for manufacturing them |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007173315A JP2009012779A (en) | 2007-06-29 | 2007-06-29 | Cylindrical shrink label, container having cylindrical shrink label, and method for manufacturing them |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2009012779A true JP2009012779A (en) | 2009-01-22 |
Family
ID=40354167
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007173315A Pending JP2009012779A (en) | 2007-06-29 | 2007-06-29 | Cylindrical shrink label, container having cylindrical shrink label, and method for manufacturing them |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2009012779A (en) |
Cited By (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ITTO20120337A1 (en) * | 2012-04-17 | 2013-10-18 | Sidel Spa Con Socio Unico | METHOD AND UNIT FOR FORMING TUBULAR SHEETS OF MATERIAL IN THE FORM OF TAPE, IN PARTICULAR IN A LABELING MACHINE |
| EP2730393A1 (en) * | 2012-11-07 | 2014-05-14 | Borealis AG | Sealing oriented films |
| WO2014148891A1 (en) * | 2013-02-12 | 2014-09-25 | Carlier Group | Method and device for sealing a wristband |
| EP2944466A1 (en) | 2014-05-12 | 2015-11-18 | Borealis AG | Sealing oriented films |
| EP2944465A1 (en) | 2014-05-12 | 2015-11-18 | Borealis AG | Sealing films |
| KR101775215B1 (en) * | 2015-05-06 | 2017-09-06 | 김수열 | Manufacturing method of a signal panel for circular object mounting |
| CN107850802A (en) * | 2015-07-23 | 2018-03-27 | 富士胶片株式会社 | The manufacture method of liquid crystal cells, three-dimensional structure liquid crystal cells precursor and three-dimensional structure liquid crystal cells |
Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS59169913U (en) * | 1983-04-26 | 1984-11-14 | 株式会社フジヤマ技研 | Envelope-shaped seal structure of thermoplastic film |
| JPS61249739A (en) * | 1985-04-30 | 1986-11-06 | Toyo Glass Kk | Manufacture of plastic sleeve and its device |
| JPS6286388A (en) * | 1985-10-11 | 1987-04-20 | 東レ株式会社 | Heat shrinking label |
| JPH01213125A (en) * | 1988-02-22 | 1989-08-25 | Mitsui Toatsu Chem Inc | Method and apparatus for attaching label to container |
| JPH06238752A (en) * | 1993-02-19 | 1994-08-30 | Sekisui Chem Co Ltd | Production of heat-shrinkable film |
| JPH0977037A (en) * | 1995-09-13 | 1997-03-25 | Saraya Kk | Container |
| JPH09226738A (en) * | 1996-02-23 | 1997-09-02 | Toyobo Co Ltd | Metal can and synthetic resin film for metal can |
| US20070056679A1 (en) * | 2005-09-12 | 2007-03-15 | Sacmi Labelling S.P.A. | Apparatus and method for obtaining labels |
| JP2007084696A (en) * | 2005-09-22 | 2007-04-05 | Nissei Kagaku Kk | Foamed film for shrinkable label |
-
2007
- 2007-06-29 JP JP2007173315A patent/JP2009012779A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS59169913U (en) * | 1983-04-26 | 1984-11-14 | 株式会社フジヤマ技研 | Envelope-shaped seal structure of thermoplastic film |
| JPS61249739A (en) * | 1985-04-30 | 1986-11-06 | Toyo Glass Kk | Manufacture of plastic sleeve and its device |
| JPS6286388A (en) * | 1985-10-11 | 1987-04-20 | 東レ株式会社 | Heat shrinking label |
| JPH01213125A (en) * | 1988-02-22 | 1989-08-25 | Mitsui Toatsu Chem Inc | Method and apparatus for attaching label to container |
| JPH06238752A (en) * | 1993-02-19 | 1994-08-30 | Sekisui Chem Co Ltd | Production of heat-shrinkable film |
| JPH0977037A (en) * | 1995-09-13 | 1997-03-25 | Saraya Kk | Container |
| JPH09226738A (en) * | 1996-02-23 | 1997-09-02 | Toyobo Co Ltd | Metal can and synthetic resin film for metal can |
| US20070056679A1 (en) * | 2005-09-12 | 2007-03-15 | Sacmi Labelling S.P.A. | Apparatus and method for obtaining labels |
| JP2007084696A (en) * | 2005-09-22 | 2007-04-05 | Nissei Kagaku Kk | Foamed film for shrinkable label |
Cited By (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ITTO20120337A1 (en) * | 2012-04-17 | 2013-10-18 | Sidel Spa Con Socio Unico | METHOD AND UNIT FOR FORMING TUBULAR SHEETS OF MATERIAL IN THE FORM OF TAPE, IN PARTICULAR IN A LABELING MACHINE |
| EP2730393A1 (en) * | 2012-11-07 | 2014-05-14 | Borealis AG | Sealing oriented films |
| WO2014072403A1 (en) * | 2012-11-07 | 2014-05-15 | Borealis Ag | Sealing oriented films |
| CN104768733A (en) * | 2012-11-07 | 2015-07-08 | 博里利斯股份公司 | Sealing oriented films |
| US10501223B2 (en) | 2012-11-07 | 2019-12-10 | Borealis Ag | Sealing oriented films |
| WO2014148891A1 (en) * | 2013-02-12 | 2014-09-25 | Carlier Group | Method and device for sealing a wristband |
| EP2944466A1 (en) | 2014-05-12 | 2015-11-18 | Borealis AG | Sealing oriented films |
| EP2944465A1 (en) | 2014-05-12 | 2015-11-18 | Borealis AG | Sealing films |
| KR101775215B1 (en) * | 2015-05-06 | 2017-09-06 | 김수열 | Manufacturing method of a signal panel for circular object mounting |
| CN107850802A (en) * | 2015-07-23 | 2018-03-27 | 富士胶片株式会社 | The manufacture method of liquid crystal cells, three-dimensional structure liquid crystal cells precursor and three-dimensional structure liquid crystal cells |
| JPWO2017014305A1 (en) * | 2015-07-23 | 2018-05-31 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | Liquid crystal cell, three-dimensional structure liquid crystal cell precursor, and method for producing three-dimensional structure liquid crystal cell |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5088019B2 (en) | Cylindrical shrink label, container with cylindrical shrink label, and manufacturing method thereof | |
| US10906218B2 (en) | In-mould labelling process | |
| JP2009012779A (en) | Cylindrical shrink label, container having cylindrical shrink label, and method for manufacturing them | |
| JP6210991B2 (en) | Cylindrical shrink label and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP2009096527A (en) | Shrink label, container with tubular shrink label and manufacturing process therefor | |
| JP5157145B2 (en) | Wound label, container with roll label, and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP5866898B2 (en) | Label manufacturing method | |
| JP5381085B2 (en) | Wrapped shrink label, container with rolled shrink label, and method for producing them | |
| JP5476814B2 (en) | LASER PRINTED LAMINATE, LASER PRINTING METHOD, AND PACKAGE BODY USING THE LASER PRINTING LAMINATE | |
| CN103282284A (en) | Film for wrapping, methods of making and using | |
| JP5266673B2 (en) | Cylindrical shrink label, container with cylindrical shrink label | |
| JP5169100B2 (en) | Laser-markable packaging materials and packaging bags | |
| JP2009048147A (en) | Thermal-shrinkable label and method of sticking same | |
| JP2012032657A (en) | Roll shrink label, container with roll shrink label, and method of manufacturing those | |
| JP2006027675A (en) | Heat-shrinkable label and labelled container | |
| JP2022082378A (en) | Laminated sheet for tube container and tube container | |
| JP5948006B2 (en) | Roll shrink label, container with roll shrink label, and manufacturing method thereof. | |
| EP4028335B1 (en) | Flexible packaging with internal release | |
| JP2000089679A (en) | Label for plastic bottle and plastic bottle using the same | |
| JP2012032658A (en) | Roll shrink label, and container with roll shrink label | |
| JP5699312B2 (en) | Roll shrink label and method for producing container with roll shrink label | |
| JP2006096012A (en) | Synthetic resin cup-shaped container with label and method for bonding of label | |
| JP6398424B2 (en) | LAMINATE, COVER, DISTRIBUTION PACKAGE CONTAINER, AND DISTRIBUTION PACKAGE | |
| JPH11174962A (en) | Heat shrinkable bellyband label and container attached with the label | |
| JP2015146049A (en) | Roll shrinkable label, container with roll shrinkable label and manufacturing method thereof |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20100126 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20111104 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20111122 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20120123 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20120508 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20120918 |