JP2007525470A - Novel compounds and compositions comprising sterols and / or stanols and cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitors and their use in the treatment or prevention of various diseases and conditions - Google Patents
Novel compounds and compositions comprising sterols and / or stanols and cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitors and their use in the treatment or prevention of various diseases and conditions Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2007525470A JP2007525470A JP2006517922A JP2006517922A JP2007525470A JP 2007525470 A JP2007525470 A JP 2007525470A JP 2006517922 A JP2006517922 A JP 2006517922A JP 2006517922 A JP2006517922 A JP 2006517922A JP 2007525470 A JP2007525470 A JP 2007525470A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- reducing
- preventing
- cholesterol
- treating
- cholesterol biosynthesis
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Withdrawn
Links
- HVYWMOMLDIMFJA-DPAQBDIFSA-N cholesterol Chemical compound C1C=C2C[C@@H](O)CC[C@]2(C)[C@@H]2[C@@H]1[C@@H]1CC[C@H]([C@H](C)CCCC(C)C)[C@@]1(C)CC2 HVYWMOMLDIMFJA-DPAQBDIFSA-N 0.000 title claims abstract description 272
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 title claims abstract description 128
- 235000012000 cholesterol Nutrition 0.000 title claims abstract description 126
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 title claims abstract description 108
- 239000003112 inhibitor Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 78
- 229930182558 Sterol Natural products 0.000 title claims abstract description 72
- 150000003432 sterols Chemical class 0.000 title claims abstract description 72
- 235000003702 sterols Nutrition 0.000 title claims abstract description 72
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 68
- 208000037265 diseases, disorders, signs and symptoms Diseases 0.000 title claims abstract description 27
- 201000010099 disease Diseases 0.000 title claims abstract description 12
- 230000002265 prevention Effects 0.000 title abstract description 8
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 61
- 150000003839 salts Chemical class 0.000 claims abstract description 35
- 239000012453 solvate Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 22
- 239000000651 prodrug Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 11
- 229940002612 prodrug Drugs 0.000 claims abstract description 11
- 229940121710 HMGCoA reductase inhibitor Drugs 0.000 claims description 54
- CIWBSHSKHKDKBQ-JLAZNSOCSA-N Ascorbic acid Chemical compound OC[C@H](O)[C@H]1OC(=O)C(O)=C1O CIWBSHSKHKDKBQ-JLAZNSOCSA-N 0.000 claims description 48
- -1 kodisosterol Chemical compound 0.000 claims description 48
- 239000002471 hydroxymethylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitor Substances 0.000 claims description 35
- 210000002966 serum Anatomy 0.000 claims description 33
- 239000011668 ascorbic acid Substances 0.000 claims description 28
- LGJMUZUPVCAVPU-UHFFFAOYSA-N beta-Sitostanol Natural products C1CC2CC(O)CCC2(C)C2C1C1CCC(C(C)CCC(CC)C(C)C)C1(C)CC2 LGJMUZUPVCAVPU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 28
- 201000001320 Atherosclerosis Diseases 0.000 claims description 26
- 229960005070 ascorbic acid Drugs 0.000 claims description 26
- 208000024172 Cardiovascular disease Diseases 0.000 claims description 24
- 239000005557 antagonist Substances 0.000 claims description 24
- 235000010323 ascorbic acid Nutrition 0.000 claims description 24
- 150000002632 lipids Chemical class 0.000 claims description 23
- 208000024891 symptom Diseases 0.000 claims description 23
- 230000003647 oxidation Effects 0.000 claims description 22
- 238000007254 oxidation reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 22
- 229960005370 atorvastatin Drugs 0.000 claims description 20
- 230000001965 increasing effect Effects 0.000 claims description 20
- 102000004895 Lipoproteins Human genes 0.000 claims description 19
- 108090001030 Lipoproteins Proteins 0.000 claims description 19
- 229960002855 simvastatin Drugs 0.000 claims description 18
- RYMZZMVNJRMUDD-HGQWONQESA-N simvastatin Chemical compound C([C@H]1[C@@H](C)C=CC2=C[C@H](C)C[C@@H]([C@H]12)OC(=O)C(C)(C)CC)C[C@@H]1C[C@@H](O)CC(=O)O1 RYMZZMVNJRMUDD-HGQWONQESA-N 0.000 claims description 18
- RYMZZMVNJRMUDD-UHFFFAOYSA-N SJ000286063 Natural products C12C(OC(=O)C(C)(C)CC)CC(C)C=C2C=CC(C)C1CCC1CC(O)CC(=O)O1 RYMZZMVNJRMUDD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 17
- 208000029078 coronary artery disease Diseases 0.000 claims description 17
- LGJMUZUPVCAVPU-HRJGVYIJSA-N stigmastanol Chemical compound C([C@@H]1CC2)[C@@H](O)CC[C@]1(C)[C@@H]1[C@@H]2[C@@H]2CC[C@H]([C@H](C)CC[C@@H](CC)C(C)C)[C@@]2(C)CC1 LGJMUZUPVCAVPU-HRJGVYIJSA-N 0.000 claims description 17
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 claims description 17
- XUKUURHRXDUEBC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Atorvastatin Natural products C=1C=CC=CC=1C1=C(C=2C=CC(F)=CC=2)N(CCC(O)CC(O)CC(O)=O)C(C(C)C)=C1C(=O)NC1=CC=CC=C1 XUKUURHRXDUEBC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 16
- 206010061218 Inflammation Diseases 0.000 claims description 16
- 230000004054 inflammatory process Effects 0.000 claims description 16
- 239000008194 pharmaceutical composition Substances 0.000 claims description 16
- 238000003786 synthesis reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 16
- 229940122502 Cholesterol absorption inhibitor Drugs 0.000 claims description 15
- OILXMJHPFNGGTO-UHFFFAOYSA-N (22E)-(24xi)-24-methylcholesta-5,22-dien-3beta-ol Natural products C1C=C2CC(O)CCC2(C)C2C1C1CCC(C(C)C=CC(C)C(C)C)C1(C)CC2 OILXMJHPFNGGTO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 14
- 208000035475 disorder Diseases 0.000 claims description 14
- 150000003626 triacylglycerols Chemical class 0.000 claims description 14
- 208000035150 Hypercholesterolemia Diseases 0.000 claims description 13
- 125000002887 hydroxy group Chemical group [H]O* 0.000 claims description 13
- BFDNMXAIBMJLBB-UHFFFAOYSA-N stigmasterol Natural products CCC(C=CC(C)C1CCCC2C3CC=C4CC(O)CCC4(C)C3CCC12C)C(C)C BFDNMXAIBMJLBB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 13
- ARYTXMNEANMLMU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 24alpha-methylcholestanol Natural products C1CC2CC(O)CCC2(C)C2C1C1CCC(C(C)CCC(C)C(C)C)C1(C)CC2 ARYTXMNEANMLMU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 12
- XUKUURHRXDUEBC-KAYWLYCHSA-N Atorvastatin Chemical group C=1C=CC=CC=1C1=C(C=2C=CC(F)=CC=2)N(CC[C@@H](O)C[C@@H](O)CC(O)=O)C(C(C)C)=C1C(=O)NC1=CC=CC=C1 XUKUURHRXDUEBC-KAYWLYCHSA-N 0.000 claims description 12
- 238000008214 LDL Cholesterol Methods 0.000 claims description 12
- PCZOHLXUXFIOCF-UHFFFAOYSA-N Monacolin X Natural products C12C(OC(=O)C(C)CC)CC(C)C=C2C=CC(C)C1CCC1CC(O)CC(=O)O1 PCZOHLXUXFIOCF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 12
- ARYTXMNEANMLMU-ATEDBJNTSA-N campestanol Chemical compound C([C@@H]1CC2)[C@@H](O)CC[C@]1(C)[C@@H]1[C@@H]2[C@@H]2CC[C@H]([C@H](C)CC[C@@H](C)C(C)C)[C@@]2(C)CC1 ARYTXMNEANMLMU-ATEDBJNTSA-N 0.000 claims description 12
- 239000003937 drug carrier Substances 0.000 claims description 12
- PCZOHLXUXFIOCF-BXMDZJJMSA-N lovastatin Chemical compound C([C@H]1[C@@H](C)C=CC2=C[C@H](C)C[C@@H]([C@H]12)OC(=O)[C@@H](C)CC)C[C@@H]1C[C@@H](O)CC(=O)O1 PCZOHLXUXFIOCF-BXMDZJJMSA-N 0.000 claims description 12
- OQMZNAMGEHIHNN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 7-Dehydrostigmasterol Natural products C1C(O)CCC2(C)C(CCC3(C(C(C)C=CC(CC)C(C)C)CCC33)C)C3=CC=C21 OQMZNAMGEHIHNN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 11
- 108010022535 Farnesyl-Diphosphate Farnesyltransferase Proteins 0.000 claims description 11
- 108090000895 Hydroxymethylglutaryl CoA Reductases Proteins 0.000 claims description 11
- 241001465754 Metazoa Species 0.000 claims description 11
- LGJMUZUPVCAVPU-JFBKYFIKSA-N Sitostanol Natural products O[C@@H]1C[C@H]2[C@@](C)([C@@H]3[C@@H]([C@H]4[C@@](C)([C@@H]([C@@H](CC[C@H](C(C)C)CC)C)CC4)CC3)CC2)CC1 LGJMUZUPVCAVPU-JFBKYFIKSA-N 0.000 claims description 11
- 229960004844 lovastatin Drugs 0.000 claims description 11
- QLJODMDSTUBWDW-UHFFFAOYSA-N lovastatin hydroxy acid Natural products C1=CC(C)C(CCC(O)CC(O)CC(O)=O)C2C(OC(=O)C(C)CC)CC(C)C=C21 QLJODMDSTUBWDW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 11
- TUZYXOIXSAXUGO-PZAWKZKUSA-N pravastatin Chemical group C1=C[C@H](C)[C@H](CC[C@@H](O)C[C@@H](O)CC(O)=O)[C@H]2[C@@H](OC(=O)[C@@H](C)CC)C[C@H](O)C=C21 TUZYXOIXSAXUGO-PZAWKZKUSA-N 0.000 claims description 11
- 230000001225 therapeutic effect Effects 0.000 claims description 11
- VGSSUFQMXBFFTM-UHFFFAOYSA-N (24R)-24-ethyl-5alpha-cholestane-3beta,5,6beta-triol Natural products C1C(O)C2(O)CC(O)CCC2(C)C2C1C1CCC(C(C)CCC(CC)C(C)C)C1(C)CC2 VGSSUFQMXBFFTM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 10
- 102100037997 Squalene synthase Human genes 0.000 claims description 10
- 230000002708 enhancing effect Effects 0.000 claims description 10
- 230000001747 exhibiting effect Effects 0.000 claims description 10
- 108010000775 Hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA synthase Proteins 0.000 claims description 9
- TUZYXOIXSAXUGO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Pravastatin Chemical group C1=CC(C)C(CCC(O)CC(O)CC(O)=O)C2C(OC(=O)C(C)CC)CC(O)C=C21 TUZYXOIXSAXUGO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 9
- 102000005782 Squalene Monooxygenase Human genes 0.000 claims description 9
- 108020003891 Squalene monooxygenase Proteins 0.000 claims description 9
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 9
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 claims description 9
- 229960002965 pravastatin Drugs 0.000 claims description 9
- SGNBVLSWZMBQTH-FGAXOLDCSA-N Campesterol Natural products O[C@@H]1CC=2[C@@](C)([C@@H]3[C@H]([C@H]4[C@@](C)([C@H]([C@H](CC[C@H](C(C)C)C)C)CC4)CC3)CC=2)CC1 SGNBVLSWZMBQTH-FGAXOLDCSA-N 0.000 claims description 8
- BTEISVKTSQLKST-UHFFFAOYSA-N Haliclonasterol Natural products CC(C=CC(C)C(C)(C)C)C1CCC2C3=CC=C4CC(O)CCC4(C)C3CCC12C BTEISVKTSQLKST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 8
- 206010020772 Hypertension Diseases 0.000 claims description 8
- 208000007536 Thrombosis Diseases 0.000 claims description 8
- QYIXCDOBOSTCEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N alpha-cholestanol Natural products C1CC2CC(O)CCC2(C)C2C1C1CCC(C(C)CCCC(C)C)C1(C)CC2 QYIXCDOBOSTCEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 8
- NJKOMDUNNDKEAI-UHFFFAOYSA-N beta-sitosterol Natural products CCC(CCC(C)C1CCC2(C)C3CC=C4CC(O)CCC4C3CCC12C)C(C)C NJKOMDUNNDKEAI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 8
- SGNBVLSWZMBQTH-PODYLUTMSA-N campesterol Chemical compound C1C=C2C[C@@H](O)CC[C@]2(C)[C@@H]2[C@@H]1[C@@H]1CC[C@H]([C@H](C)CC[C@@H](C)C(C)C)[C@@]1(C)CC2 SGNBVLSWZMBQTH-PODYLUTMSA-N 0.000 claims description 8
- 235000000431 campesterol Nutrition 0.000 claims description 8
- QYIXCDOBOSTCEI-NWKZBHTNSA-N coprostanol Chemical compound C([C@H]1CC2)[C@@H](O)CC[C@]1(C)[C@@H]1[C@@H]2[C@@H]2CC[C@H]([C@H](C)CCCC(C)C)[C@@]2(C)CC1 QYIXCDOBOSTCEI-NWKZBHTNSA-N 0.000 claims description 8
- 238000011161 development Methods 0.000 claims description 8
- KZJWDPNRJALLNS-VJSFXXLFSA-N sitosterol Chemical compound C1C=C2C[C@@H](O)CC[C@]2(C)[C@@H]2[C@@H]1[C@@H]1CC[C@H]([C@H](C)CC[C@@H](CC)C(C)C)[C@@]1(C)CC2 KZJWDPNRJALLNS-VJSFXXLFSA-N 0.000 claims description 8
- 229950005143 sitosterol Drugs 0.000 claims description 8
- NLQLSVXGSXCXFE-UHFFFAOYSA-N sitosterol Natural products CC=C(/CCC(C)C1CC2C3=CCC4C(C)C(O)CCC4(C)C3CCC2(C)C1)C(C)C NLQLSVXGSXCXFE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 8
- 206010003210 Arteriosclerosis Diseases 0.000 claims description 7
- AJLFOPYRIVGYMJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N SJ000287055 Natural products C12C(OC(=O)C(C)CC)CCC=C2C=CC(C)C1CCC1CC(O)CC(=O)O1 AJLFOPYRIVGYMJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 7
- 208000011775 arteriosclerosis disease Diseases 0.000 claims description 7
- 210000004204 blood vessel Anatomy 0.000 claims description 7
- 125000003178 carboxy group Chemical group [H]OC(*)=O 0.000 claims description 7
- 230000001413 cellular effect Effects 0.000 claims description 7
- 230000006378 damage Effects 0.000 claims description 7
- 230000002401 inhibitory effect Effects 0.000 claims description 7
- 230000037356 lipid metabolism Effects 0.000 claims description 7
- AJLFOPYRIVGYMJ-INTXDZFKSA-N mevastatin Chemical compound C([C@H]1[C@@H](C)C=CC2=CCC[C@@H]([C@H]12)OC(=O)[C@@H](C)CC)C[C@@H]1C[C@@H](O)CC(=O)O1 AJLFOPYRIVGYMJ-INTXDZFKSA-N 0.000 claims description 7
- BOZILQFLQYBIIY-UHFFFAOYSA-N mevastatin hydroxy acid Natural products C1=CC(C)C(CCC(O)CC(O)CC(O)=O)C2C(OC(=O)C(C)CC)CCC=C21 BOZILQFLQYBIIY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 7
- 230000003000 nontoxic effect Effects 0.000 claims description 7
- 229960002797 pitavastatin Drugs 0.000 claims description 7
- VGYFMXBACGZSIL-MCBHFWOFSA-N pitavastatin Chemical compound OC(=O)C[C@H](O)C[C@H](O)\C=C\C1=C(C2CC2)N=C2C=CC=CC2=C1C1=CC=C(F)C=C1 VGYFMXBACGZSIL-MCBHFWOFSA-N 0.000 claims description 7
- RQOCXCFLRBRBCS-UHFFFAOYSA-N (22E)-cholesta-5,7,22-trien-3beta-ol Natural products C1C(O)CCC2(C)C(CCC3(C(C(C)C=CCC(C)C)CCC33)C)C3=CC=C21 RQOCXCFLRBRBCS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- 208000024827 Alzheimer disease Diseases 0.000 claims description 6
- 206010012289 Dementia Diseases 0.000 claims description 6
- DNVPQKQSNYMLRS-NXVQYWJNSA-N Ergosterol Natural products CC(C)[C@@H](C)C=C[C@H](C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2C3=CC=C4C[C@@H](O)CC[C@]4(C)[C@@H]3CC[C@]12C DNVPQKQSNYMLRS-NXVQYWJNSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- 208000017170 Lipid metabolism disease Diseases 0.000 claims description 6
- 208000001132 Osteoporosis Diseases 0.000 claims description 6
- 229910052783 alkali metal Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 6
- 229910052784 alkaline earth metal Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 6
- 150000001342 alkaline earth metals Chemical class 0.000 claims description 6
- 229960005110 cerivastatin Drugs 0.000 claims description 6
- SEERZIQQUAZTOL-ANMDKAQQSA-N cerivastatin Chemical compound COCC1=C(C(C)C)N=C(C(C)C)C(\C=C\[C@@H](O)C[C@@H](O)CC(O)=O)=C1C1=CC=C(F)C=C1 SEERZIQQUAZTOL-ANMDKAQQSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- 230000002526 effect on cardiovascular system Effects 0.000 claims description 6
- DNVPQKQSNYMLRS-SOWFXMKYSA-N ergosterol Chemical compound C1[C@@H](O)CC[C@]2(C)[C@H](CC[C@]3([C@H]([C@H](C)/C=C/[C@@H](C)C(C)C)CC[C@H]33)C)C3=CC=C21 DNVPQKQSNYMLRS-SOWFXMKYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- 230000003902 lesion Effects 0.000 claims description 6
- 150000002739 metals Chemical class 0.000 claims description 6
- 231100000252 nontoxic Toxicity 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000002904 solvent Substances 0.000 claims description 6
- 150000003505 terpenes Chemical class 0.000 claims description 6
- UFTFJSFQGQCHQW-UHFFFAOYSA-N triformin Chemical compound O=COCC(OC=O)COC=O UFTFJSFQGQCHQW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- KZJWDPNRJALLNS-VPUBHVLGSA-N (-)-beta-Sitosterol Natural products O[C@@H]1CC=2[C@@](C)([C@@H]3[C@H]([C@H]4[C@@](C)([C@H]([C@H](CC[C@@H](C(C)C)CC)C)CC4)CC3)CC=2)CC1 KZJWDPNRJALLNS-VPUBHVLGSA-N 0.000 claims description 5
- CSVWWLUMXNHWSU-UHFFFAOYSA-N (22E)-(24xi)-24-ethyl-5alpha-cholest-22-en-3beta-ol Natural products C1CC2CC(O)CCC2(C)C2C1C1CCC(C(C)C=CC(CC)C(C)C)C1(C)CC2 CSVWWLUMXNHWSU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 5
- KLEXDBGYSOIREE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 24xi-n-propylcholesterol Natural products C1C=C2CC(O)CCC2(C)C2C1C1CCC(C(C)CCC(CCC)C(C)C)C1(C)CC2 KLEXDBGYSOIREE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 5
- 206010002383 Angina Pectoris Diseases 0.000 claims description 5
- LPZCCMIISIBREI-MTFRKTCUSA-N Citrostadienol Natural products CC=C(CC[C@@H](C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2C3=CC[C@H]4[C@H](C)[C@@H](O)CC[C@]4(C)[C@H]3CC[C@]12C)C(C)C LPZCCMIISIBREI-MTFRKTCUSA-N 0.000 claims description 5
- 206010010904 Convulsion Diseases 0.000 claims description 5
- ARVGMISWLZPBCH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dehydro-beta-sitosterol Natural products C1C(O)CCC2(C)C(CCC3(C(C(C)CCC(CC)C(C)C)CCC33)C)C3=CC=C21 ARVGMISWLZPBCH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 5
- 208000034189 Sclerosis Diseases 0.000 claims description 5
- HZYXFRGVBOPPNZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N UNPD88870 Natural products C1C=C2CC(O)CCC2(C)C2C1C1CCC(C(C)=CCC(CC)C(C)C)C1(C)CC2 HZYXFRGVBOPPNZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 5
- 230000002159 abnormal effect Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- 230000002429 anti-coagulating effect Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- 230000001028 anti-proliverative effect Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- 210000002565 arteriole Anatomy 0.000 claims description 5
- 230000003143 atherosclerotic effect Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- MJVXAPPOFPTTCA-UHFFFAOYSA-N beta-Sistosterol Natural products CCC(CCC(C)C1CCC2C3CC=C4C(C)C(O)CCC4(C)C3CCC12C)C(C)C MJVXAPPOFPTTCA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 5
- 210000000988 bone and bone Anatomy 0.000 claims description 5
- 230000004097 bone metabolism Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- 230000002860 competitive effect Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- 125000004435 hydrogen atom Chemical group [H]* 0.000 claims description 5
- 230000002519 immonomodulatory effect Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- 230000036542 oxidative stress Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- 230000004983 pleiotropic effect Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- 229960001495 pravastatin sodium Drugs 0.000 claims description 5
- 235000015500 sitosterol Nutrition 0.000 claims description 5
- 230000000087 stabilizing effect Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- HCXVJBMSMIARIN-PHZDYDNGSA-N stigmasterol Chemical compound C1C=C2C[C@@H](O)CC[C@]2(C)[C@@H]2[C@@H]1[C@@H]1CC[C@H]([C@H](C)/C=C/[C@@H](CC)C(C)C)[C@@]1(C)CC2 HCXVJBMSMIARIN-PHZDYDNGSA-N 0.000 claims description 5
- 229940032091 stigmasterol Drugs 0.000 claims description 5
- 235000016831 stigmasterol Nutrition 0.000 claims description 5
- 230000004614 tumor growth Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- OSELKOCHBMDKEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N (10R)-3c-Hydroxy-10r.13c-dimethyl-17c-((R)-1-methyl-4-isopropyl-hexen-(4c)-yl)-(8cH.9tH.14tH)-Delta5-tetradecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren Natural products C1C=C2CC(O)CCC2(C)C2C1C1CCC(C(C)CCC(=CC)C(C)C)C1(C)CC2 OSELKOCHBMDKEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- CQSRUKJFZKVYCY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5alpha-isofucostan-3beta-ol Natural products C1CC2CC(O)CCC2(C)C2C1C1CCC(C(C)CCC(=CC)C(C)C)C1(C)CC2 CQSRUKJFZKVYCY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- VGMFHMLQOYWYHN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Compactin Natural products OCC1OC(OC2C(O)C(O)C(CO)OC2Oc3cc(O)c4C(=O)C(=COc4c3)c5ccc(O)c(O)c5)C(O)C(O)C1O VGMFHMLQOYWYHN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- BDCFUHIWJODVNG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Desmosterol Natural products C1C=C2CC(O)C=CC2(C)C2C1C1CCC(C(C)CCC(CC)C(C)C)C1(C)CC2 BDCFUHIWJODVNG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- ODCZJZWSXPVLAW-KXCGKLMDSA-N Hymeglusin Chemical compound OC(=O)/C=C(\C)/C=C(C)/C[C@H](C)CCCC[C@H]1OC(=O)[C@@H]1CO ODCZJZWSXPVLAW-KXCGKLMDSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- OSELKOCHBMDKEJ-VRUYXKNBSA-N Isofucosterol Natural products CC=C(CC[C@@H](C)[C@H]1CC[C@@H]2[C@H]3CC=C4C[C@@H](O)CC[C@]4(C)[C@@H]3CC[C@]12C)C(C)C OSELKOCHBMDKEJ-VRUYXKNBSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- 150000001340 alkali metals Chemical class 0.000 claims description 4
- FQCKMBLVYCEXJB-MNSAWQCASA-L atorvastatin calcium Chemical compound [Ca+2].C=1C=CC=CC=1C1=C(C=2C=CC(F)=CC=2)N(CC[C@@H](O)C[C@@H](O)CC([O-])=O)C(C(C)C)=C1C(=O)NC1=CC=CC=C1.C=1C=CC=CC=1C1=C(C=2C=CC(F)=CC=2)N(CC[C@@H](O)C[C@@H](O)CC([O-])=O)C(C(C)C)=C1C(=O)NC1=CC=CC=C1 FQCKMBLVYCEXJB-MNSAWQCASA-L 0.000 claims description 4
- AVSXSVCZWQODGV-DPAQBDIFSA-N desmosterol Chemical compound C1C=C2C[C@@H](O)CC[C@]2(C)[C@@H]2[C@@H]1[C@@H]1CC[C@H]([C@@H](CCC=C(C)C)C)[C@@]1(C)CC2 AVSXSVCZWQODGV-DPAQBDIFSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- 229960003765 fluvastatin Drugs 0.000 claims description 4
- OSELKOCHBMDKEJ-WGMIZEQOSA-N isofucosterol Chemical compound C1C=C2C[C@@H](O)CC[C@]2(C)[C@@H]2[C@@H]1[C@@H]1CC[C@H]([C@H](C)CC/C(=C/C)C(C)C)[C@@]1(C)CC2 OSELKOCHBMDKEJ-WGMIZEQOSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000004615 ingredient Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- FJLGEFLZQAZZCD-JUFISIKESA-N (3S,5R)-fluvastatin Chemical compound C12=CC=CC=C2N(C(C)C)C(\C=C\[C@H](O)C[C@H](O)CC(O)=O)=C1C1=CC=C(F)C=C1 FJLGEFLZQAZZCD-JUFISIKESA-N 0.000 claims 6
- 102000004286 Hydroxymethylglutaryl CoA Reductases Human genes 0.000 claims 6
- 102100028888 Hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA synthase, cytoplasmic Human genes 0.000 claims 6
- VDSBXXDKCUBMQC-HNGSOEQISA-N (4r,6s)-6-[(e)-2-[2-(4-fluoro-3-methylphenyl)-4,4,6,6-tetramethylcyclohexen-1-yl]ethenyl]-4-hydroxyoxan-2-one Chemical compound C1=C(F)C(C)=CC(C=2CC(C)(C)CC(C)(C)C=2\C=C\[C@H]2OC(=O)C[C@H](O)C2)=C1 VDSBXXDKCUBMQC-HNGSOEQISA-N 0.000 claims 3
- OILXMJHPFNGGTO-NRHJOKMGSA-N Brassicasterol Natural products O[C@@H]1CC=2[C@@](C)([C@@H]3[C@H]([C@H]4[C@](C)([C@H]([C@@H](/C=C/[C@H](C(C)C)C)C)CC4)CC3)CC=2)CC1 OILXMJHPFNGGTO-NRHJOKMGSA-N 0.000 claims 3
- OILXMJHPFNGGTO-ZRUUVFCLSA-N UNPD197407 Natural products C1C=C2C[C@@H](O)CC[C@]2(C)[C@@H]2[C@@H]1[C@@H]1CC[C@H]([C@H](C)C=C[C@H](C)C(C)C)[C@@]1(C)CC2 OILXMJHPFNGGTO-ZRUUVFCLSA-N 0.000 claims 3
- VXDSGTRNDFHIJB-QQPOVDNESA-N [(1s,4ar)-8-[2-[(2r,4r)-4-hydroxy-6-oxooxan-2-yl]ethyl]-7-methyl-1,2,3,4,4a,7,8,8a-octahydronaphthalen-1-yl] (2s)-2-methylbutanoate Chemical compound C([C@H]1CCC[C@@H](C21)OC(=O)[C@@H](C)CC)=CC(C)C2CC[C@@H]1C[C@@H](O)CC(=O)O1 VXDSGTRNDFHIJB-QQPOVDNESA-N 0.000 claims 3
- XKXHCNPAFAXVRZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzylazanium;chloride Chemical compound [Cl-].[NH3+]CC1=CC=CC=C1 XKXHCNPAFAXVRZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims 3
- OILXMJHPFNGGTO-ZAUYPBDWSA-N brassicasterol Chemical compound C1C=C2C[C@@H](O)CC[C@]2(C)[C@@H]2[C@@H]1[C@@H]1CC[C@H]([C@H](C)/C=C/[C@H](C)C(C)C)[C@@]1(C)CC2 OILXMJHPFNGGTO-ZAUYPBDWSA-N 0.000 claims 3
- 235000004420 brassicasterol Nutrition 0.000 claims 3
- 229950003040 dalvastatin Drugs 0.000 claims 3
- VXDSGTRNDFHIJB-UHFFFAOYSA-N dihydrocompactin Natural products C12C(OC(=O)C(C)CC)CCCC2C=CC(C)C1CCC1CC(O)CC(=O)O1 VXDSGTRNDFHIJB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims 3
- 125000000956 methoxy group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])O* 0.000 claims 3
- 229950009116 mevastatin Drugs 0.000 claims 3
- 150000002197 fecosterols Chemical class 0.000 claims 2
- 231100000956 nontoxicity Toxicity 0.000 claims 1
- 150000002148 esters Chemical class 0.000 abstract description 11
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 30
- 108010010234 HDL Lipoproteins Proteins 0.000 description 29
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 24
- RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Diethyl ether Chemical compound CCOCC RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 20
- 108010007622 LDL Lipoproteins Proteins 0.000 description 18
- 102000007330 LDL Lipoproteins Human genes 0.000 description 18
- 239000003814 drug Substances 0.000 description 18
- 125000003289 ascorbyl group Chemical group [H]O[C@@]([H])(C([H])([H])O*)[C@@]1([H])OC(=O)C(O*)=C1O* 0.000 description 16
- YXFVVABEGXRONW-UHFFFAOYSA-N Toluene Chemical compound CC1=CC=CC=C1 YXFVVABEGXRONW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 15
- 229940079593 drug Drugs 0.000 description 14
- 229910019142 PO4 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 13
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 13
- 235000021317 phosphate Nutrition 0.000 description 13
- UHOVQNZJYSORNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N Benzene Chemical compound C1=CC=CC=C1 UHOVQNZJYSORNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 12
- WYURNTSHIVDZCO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tetrahydrofuran Chemical compound C1CCOC1 WYURNTSHIVDZCO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 12
- 210000004185 liver Anatomy 0.000 description 12
- 239000010452 phosphate Substances 0.000 description 12
- LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethanol Chemical compound CCO LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 11
- 108010062497 VLDL Lipoproteins Proteins 0.000 description 11
- 239000002253 acid Substances 0.000 description 11
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 11
- NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-K phosphate Chemical compound [O-]P([O-])([O-])=O NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 description 11
- QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sulfuric acid Chemical compound OS(O)(=O)=O QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 10
- XHXFXVLFKHQFAL-UHFFFAOYSA-N phosphoryl trichloride Chemical compound ClP(Cl)(Cl)=O XHXFXVLFKHQFAL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 10
- 239000000243 solution Substances 0.000 description 10
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 9
- 239000002775 capsule Substances 0.000 description 8
- 230000001906 cholesterol absorption Effects 0.000 description 8
- 235000017471 coenzyme Q10 Nutrition 0.000 description 8
- 235000019441 ethanol Nutrition 0.000 description 8
- 229940068065 phytosterols Drugs 0.000 description 8
- 108010046315 IDL Lipoproteins Proteins 0.000 description 7
- 239000004480 active ingredient Substances 0.000 description 7
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 7
- ACTIUHUUMQJHFO-UPTCCGCDSA-N coenzyme Q10 Chemical compound COC1=C(OC)C(=O)C(C\C=C(/C)CC\C=C(/C)CC\C=C(/C)CC\C=C(/C)CC\C=C(/C)CC\C=C(/C)CC\C=C(/C)CC\C=C(/C)CC\C=C(/C)CCC=C(C)C)=C(C)C1=O ACTIUHUUMQJHFO-UPTCCGCDSA-N 0.000 description 7
- BNIILDVGGAEEIG-UHFFFAOYSA-L disodium hydrogen phosphate Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].OP([O-])([O-])=O BNIILDVGGAEEIG-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 7
- 238000005886 esterification reaction Methods 0.000 description 7
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 7
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 description 7
- 239000000047 product Substances 0.000 description 7
- 159000000000 sodium salts Chemical class 0.000 description 7
- 239000000725 suspension Substances 0.000 description 7
- 239000003826 tablet Substances 0.000 description 7
- 102100029077 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase Human genes 0.000 description 6
- 102000004190 Enzymes Human genes 0.000 description 6
- 108090000790 Enzymes Proteins 0.000 description 6
- 208000031226 Hyperlipidaemia Diseases 0.000 description 6
- OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methanol Chemical compound OC OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 102100031538 Phosphatidylcholine-sterol acyltransferase Human genes 0.000 description 6
- JUJWROOIHBZHMG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Pyridine Chemical compound C1=CC=NC=C1 JUJWROOIHBZHMG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- WQDUMFSSJAZKTM-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sodium methoxide Chemical compound [Na+].[O-]C WQDUMFSSJAZKTM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 210000004027 cell Anatomy 0.000 description 6
- 0 C*CC(C)C1CC=CCC1 Chemical compound C*CC(C)C1CC=CCC1 0.000 description 5
- PEDCQBHIVMGVHV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Glycerine Chemical compound OCC(O)CO PEDCQBHIVMGVHV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- JVTAAEKCZFNVCJ-UHFFFAOYSA-M Lactate Chemical compound CC(O)C([O-])=O JVTAAEKCZFNVCJ-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 5
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 5
- 239000008298 dragée Substances 0.000 description 5
- 238000009472 formulation Methods 0.000 description 5
- 230000000670 limiting effect Effects 0.000 description 5
- 239000003960 organic solvent Substances 0.000 description 5
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 5
- 239000001488 sodium phosphate Substances 0.000 description 5
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 108010071619 Apolipoproteins Proteins 0.000 description 4
- 102000007592 Apolipoproteins Human genes 0.000 description 4
- FBPFZTCFMRRESA-FSIIMWSLSA-N D-Glucitol Natural products OC[C@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)CO FBPFZTCFMRRESA-FSIIMWSLSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 241000196324 Embryophyta Species 0.000 description 4
- 108010010803 Gelatin Proteins 0.000 description 4
- VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrochloric acid Chemical compound Cl VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 241000124008 Mammalia Species 0.000 description 4
- 108010011964 Phosphatidylcholine-sterol O-acyltransferase Proteins 0.000 description 4
- NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phosphoric acid Chemical compound OP(O)(O)=O NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 108010080283 Pre-beta High-Density Lipoproteins Proteins 0.000 description 4
- LCTONWCANYUPML-UHFFFAOYSA-M Pyruvate Chemical compound CC(=O)C([O-])=O LCTONWCANYUPML-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 4
- 239000003849 aromatic solvent Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000007796 conventional method Methods 0.000 description 4
- 235000014113 dietary fatty acids Nutrition 0.000 description 4
- 239000002552 dosage form Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000000194 fatty acid Substances 0.000 description 4
- 229930195729 fatty acid Natural products 0.000 description 4
- 239000008273 gelatin Substances 0.000 description 4
- 229920000159 gelatin Polymers 0.000 description 4
- 229940014259 gelatin Drugs 0.000 description 4
- 235000019322 gelatine Nutrition 0.000 description 4
- 235000011852 gelatine desserts Nutrition 0.000 description 4
- 210000000936 intestine Anatomy 0.000 description 4
- 239000000546 pharmaceutical excipient Substances 0.000 description 4
- 235000002378 plant sterols Nutrition 0.000 description 4
- 235000013855 polyvinylpyrrolidone Nutrition 0.000 description 4
- 239000001267 polyvinylpyrrolidone Substances 0.000 description 4
- 229920000036 polyvinylpyrrolidone Polymers 0.000 description 4
- VWBQYTRBTXKKOG-IYNICTALSA-M pravastatin sodium Chemical compound [Na+].C1=C[C@H](C)[C@H](CC[C@@H](O)C[C@@H](O)CC([O-])=O)[C@H]2[C@@H](OC(=O)[C@@H](C)CC)C[C@H](O)C=C21 VWBQYTRBTXKKOG-IYNICTALSA-M 0.000 description 4
- 239000000376 reactant Substances 0.000 description 4
- 230000009257 reactivity Effects 0.000 description 4
- 239000000600 sorbitol Substances 0.000 description 4
- 235000010356 sorbitol Nutrition 0.000 description 4
- 239000004059 squalene synthase inhibitor Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000006188 syrup Substances 0.000 description 4
- 235000020357 syrup Nutrition 0.000 description 4
- 239000003784 tall oil Substances 0.000 description 4
- YLQBMQCUIZJEEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N tetrahydrofuran Natural products C=1C=COC=1 YLQBMQCUIZJEEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- JOXIMZWYDAKGHI-UHFFFAOYSA-N toluene-4-sulfonic acid Chemical compound CC1=CC=C(S(O)(=O)=O)C=C1 JOXIMZWYDAKGHI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 230000032258 transport Effects 0.000 description 4
- 235000015112 vegetable and seed oil Nutrition 0.000 description 4
- 239000008158 vegetable oil Substances 0.000 description 4
- QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetic acid Chemical compound CC(O)=O QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- CSCPPACGZOOCGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetone Chemical compound CC(C)=O CSCPPACGZOOCGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 102000005666 Apolipoprotein A-I Human genes 0.000 description 3
- 108010059886 Apolipoprotein A-I Proteins 0.000 description 3
- FBPFZTCFMRRESA-JGWLITMVSA-N D-glucitol Chemical compound OC[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H](O)CO FBPFZTCFMRRESA-JGWLITMVSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 102000002284 Hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA Synthase Human genes 0.000 description 3
- PVNIIMVLHYAWGP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Niacin Chemical compound OC(=O)C1=CC=CN=C1 PVNIIMVLHYAWGP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- DNIAPMSPPWPWGF-UHFFFAOYSA-N Propylene glycol Chemical compound CC(O)CO DNIAPMSPPWPWGF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 229920002472 Starch Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 230000005856 abnormality Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000000654 additive Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000002411 adverse Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000007864 aqueous solution Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000002585 base Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229940076810 beta sitosterol Drugs 0.000 description 3
- 239000003613 bile acid Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000015556 catabolic process Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000003054 catalyst Substances 0.000 description 3
- ITVPBBDAZKBMRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N chloro-dioxido-oxo-$l^{5}-phosphane;hydron Chemical group OP(O)(Cl)=O ITVPBBDAZKBMRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 230000004087 circulation Effects 0.000 description 3
- 229910000397 disodium phosphate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 235000019800 disodium phosphate Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- 239000003995 emulsifying agent Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000032050 esterification Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000000499 gel Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229930182470 glycoside Natural products 0.000 description 3
- 230000002440 hepatic effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 229910052500 inorganic mineral Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000010534 mechanism of action Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000004060 metabolic process Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000002207 metabolite Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000000693 micelle Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000011707 mineral Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000002245 particle Substances 0.000 description 3
- UMJSCPRVCHMLSP-UHFFFAOYSA-N pyridine Natural products COC1=CC=CN=C1 UMJSCPRVCHMLSP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 102000005962 receptors Human genes 0.000 description 3
- 108020003175 receptors Proteins 0.000 description 3
- 230000004141 reverse cholesterol transport Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000003381 stabilizer Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000007858 starting material Substances 0.000 description 3
- 210000001519 tissue Anatomy 0.000 description 3
- 239000003981 vehicle Substances 0.000 description 3
- HSINOMROUCMIEA-FGVHQWLLSA-N (2s,4r)-4-[(3r,5s,6r,7r,8s,9s,10s,13r,14s,17r)-6-ethyl-3,7-dihydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-1h-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]-2-methylpentanoic acid Chemical compound C([C@@]12C)C[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1[C@@H](CC)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1[C@@H]2CC[C@]2(C)[C@@H]([C@H](C)C[C@H](C)C(O)=O)CC[C@H]21 HSINOMROUCMIEA-FGVHQWLLSA-N 0.000 description 2
- ZGGHKIMDNBDHJB-NRFPMOEYSA-M (3R,5S)-fluvastatin sodium Chemical compound [Na+].C12=CC=CC=C2N(C(C)C)C(\C=C\[C@@H](O)C[C@@H](O)CC([O-])=O)=C1C1=CC=C(F)C=C1 ZGGHKIMDNBDHJB-NRFPMOEYSA-M 0.000 description 2
- YYGNTYWPHWGJRM-UHFFFAOYSA-N (6E,10E,14E,18E)-2,6,10,15,19,23-hexamethyltetracosa-2,6,10,14,18,22-hexaene Chemical compound CC(C)=CCCC(C)=CCCC(C)=CCCC=C(C)CCC=C(C)CCC=C(C)C YYGNTYWPHWGJRM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- KJTLQQUUPVSXIM-ZCFIWIBFSA-M (R)-mevalonate Chemical compound OCC[C@](O)(C)CC([O-])=O KJTLQQUUPVSXIM-ZCFIWIBFSA-M 0.000 description 2
- IIZPXYDJLKNOIY-JXPKJXOSSA-N 1-palmitoyl-2-arachidonoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)OC[C@H](COP([O-])(=O)OCC[N+](C)(C)C)OC(=O)CCC\C=C/C\C=C/C\C=C/C\C=C/CCCCC IIZPXYDJLKNOIY-JXPKJXOSSA-N 0.000 description 2
- VWFJDQUYCIWHTN-YFVJMOTDSA-N 2-trans,6-trans-farnesyl diphosphate Chemical compound CC(C)=CCC\C(C)=C\CC\C(C)=C\CO[P@](O)(=O)OP(O)(O)=O VWFJDQUYCIWHTN-YFVJMOTDSA-N 0.000 description 2
- QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-M Acetate Chemical compound CC([O-])=O QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 2
- 102000009081 Apolipoprotein A-II Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 108010087614 Apolipoprotein A-II Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 108010024976 Asparaginase Proteins 0.000 description 2
- IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N Atomic nitrogen Chemical compound N#N IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- FERIUCNNQQJTOY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Butyric acid Chemical compound CCCC(O)=O FERIUCNNQQJTOY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 108010061846 Cholesterol Ester Transfer Proteins Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 102000012336 Cholesterol Ester Transfer Proteins Human genes 0.000 description 2
- ACTIUHUUMQJHFO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Coenzym Q10 Natural products COC1=C(OC)C(=O)C(CC=C(C)CCC=C(C)CCC=C(C)CCC=C(C)CCC=C(C)CCC=C(C)CCC=C(C)CCC=C(C)CCC=C(C)CCC=C(C)C)=C(C)C1=O ACTIUHUUMQJHFO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- KJTLQQUUPVSXIM-UHFFFAOYSA-N DL-mevalonic acid Natural products OCCC(O)(C)CC(O)=O KJTLQQUUPVSXIM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- LCGLNKUTAGEVQW-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dimethyl ether Chemical compound COC LCGLNKUTAGEVQW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 241000233866 Fungi Species 0.000 description 2
- 235000010469 Glycine max Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 241000282412 Homo Species 0.000 description 2
- 150000000996 L-ascorbic acids Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 102000000853 LDL receptors Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 108010001831 LDL receptors Proteins 0.000 description 2
- GUBGYTABKSRVRQ-QKKXKWKRSA-N Lactose Natural products OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](O[C@H]2[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)C(O)O[C@@H]2CO)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O GUBGYTABKSRVRQ-QKKXKWKRSA-N 0.000 description 2
- FYYHWMGAXLPEAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N Magnesium Chemical compound [Mg] FYYHWMGAXLPEAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 201000002481 Myositis Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 208000023137 Myotoxicity Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 240000007594 Oryza sativa Species 0.000 description 2
- 235000007164 Oryza sativa Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- KAESVJOAVNADME-UHFFFAOYSA-N Pyrrole Chemical compound C=1C=CNC=1 KAESVJOAVNADME-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- BHEOSNUKNHRBNM-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tetramethylsqualene Natural products CC(=C)C(C)CCC(=C)C(C)CCC(C)=CCCC=C(C)CCC(C)C(=C)CCC(C)C(C)=C BHEOSNUKNHRBNM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- GWEVSGVZZGPLCZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Titan oxide Chemical compound O=[Ti]=O GWEVSGVZZGPLCZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- DPXJVFZANSGRMM-UHFFFAOYSA-N acetic acid;2,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxyhexanal;sodium Chemical compound [Na].CC(O)=O.OCC(O)C(O)C(O)C(O)C=O DPXJVFZANSGRMM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000003377 acid catalyst Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000002378 acidificating effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000009471 action Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000002671 adjuvant Substances 0.000 description 2
- 235000010443 alginic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 229920000615 alginic acid Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 150000004703 alkoxides Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 229910000147 aluminium phosphate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000003529 anticholesteremic agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229940127226 anticholesterol agent Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 239000003963 antioxidant agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 235000006708 antioxidants Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 159000000032 aromatic acids Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 229940072107 ascorbate Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 210000000941 bile Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 239000011230 binding agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000004071 biological effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 210000004369 blood Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 239000008280 blood Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000036770 blood supply Effects 0.000 description 2
- 125000004432 carbon atom Chemical group C* 0.000 description 2
- 239000001768 carboxy methyl cellulose Substances 0.000 description 2
- 210000000170 cell membrane Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000003098 cholesteric effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000003086 colorant Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000009833 condensation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000005494 condensation Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000006482 condensation reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 125000004122 cyclic group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- 230000034994 death Effects 0.000 description 2
- 231100000517 death Toxicity 0.000 description 2
- KXGVEGMKQFWNSR-LLQZFEROSA-N deoxycholic acid Chemical compound C([C@H]1CC2)[C@H](O)CC[C@]1(C)[C@@H]1[C@@H]2[C@@H]2CC[C@H]([C@@H](CCC(O)=O)C)[C@@]2(C)[C@@H](O)C1 KXGVEGMKQFWNSR-LLQZFEROSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 235000013367 dietary fats Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 235000011180 diphosphates Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- PRAKJMSDJKAYCZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N dodecahydrosqualene Natural products CC(C)CCCC(C)CCCC(C)CCCCC(C)CCCC(C)CCCC(C)C PRAKJMSDJKAYCZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 231100000673 dose–response relationship Toxicity 0.000 description 2
- 238000002651 drug therapy Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000005538 encapsulation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000011156 evaluation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 150000004665 fatty acids Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 239000010685 fatty oil Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000945 filler Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000012467 final product Substances 0.000 description 2
- 235000013305 food Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 235000011187 glycerol Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 150000002338 glycosides Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 210000003494 hepatocyte Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 238000001727 in vivo Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000002347 injection Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000007924 injection Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000003993 interaction Effects 0.000 description 2
- 150000002500 ions Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 230000000302 ischemic effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000008101 lactose Substances 0.000 description 2
- 235000010445 lecithin Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 239000000787 lecithin Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229940067606 lecithin Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 230000008604 lipoprotein metabolism Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000012669 liquid formulation Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000314 lubricant Substances 0.000 description 2
- 210000002540 macrophage Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 229910052749 magnesium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000011777 magnesium Substances 0.000 description 2
- HQKMJHAJHXVSDF-UHFFFAOYSA-L magnesium stearate Chemical compound [Mg+2].CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC([O-])=O.CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC([O-])=O HQKMJHAJHXVSDF-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 2
- 238000007726 management method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000012528 membrane Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229920000609 methyl cellulose Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 125000002496 methyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 2
- 239000001923 methylcellulose Substances 0.000 description 2
- 235000010981 methylcellulose Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 238000002156 mixing Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 2
- 210000005087 mononuclear cell Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 210000000663 muscle cell Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 235000001968 nicotinic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 239000011664 nicotinic acid Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000003921 oil Substances 0.000 description 2
- 235000019198 oils Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 210000000056 organ Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- CTSLXHKWHWQRSH-UHFFFAOYSA-N oxalyl chloride Chemical compound ClC(=O)C(Cl)=O CTSLXHKWHWQRSH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 150000003904 phospholipids Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 229940096701 plain lipid modifying drug hmg coa reductase inhibitors Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 229920001223 polyethylene glycol Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000002243 precursor Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000003755 preservative agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000002829 reductive effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000011160 research Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 description 2
- 235000009566 rice Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 230000028327 secretion Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000008159 sesame oil Substances 0.000 description 2
- 235000011803 sesame oil Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 229910000162 sodium phosphate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 235000011008 sodium phosphates Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 229940031439 squalene Drugs 0.000 description 2
- TUHBEKDERLKLEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N squalene Natural products CC(=CCCC(=CCCC(=CCCC=C(/C)CCC=C(/C)CC=C(C)C)C)C)C TUHBEKDERLKLEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000008107 starch Substances 0.000 description 2
- 235000019698 starch Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000009897 systematic effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000000454 talc Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052623 talc Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 230000002792 vascular Effects 0.000 description 2
- LSPHULWDVZXLIL-UHFFFAOYSA-N (+/-)-Camphoric acid Chemical compound CC1(C)C(C(O)=O)CCC1(C)C(O)=O LSPHULWDVZXLIL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LNAZSHAWQACDHT-XIYTZBAFSA-N (2r,3r,4s,5r,6s)-4,5-dimethoxy-2-(methoxymethyl)-3-[(2s,3r,4s,5r,6r)-3,4,5-trimethoxy-6-(methoxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy-6-[(2r,3r,4s,5r,6r)-4,5,6-trimethoxy-2-(methoxymethyl)oxan-3-yl]oxyoxane Chemical compound CO[C@@H]1[C@@H](OC)[C@H](OC)[C@@H](COC)O[C@H]1O[C@H]1[C@H](OC)[C@@H](OC)[C@H](O[C@H]2[C@@H]([C@@H](OC)[C@H](OC)O[C@@H]2COC)OC)O[C@@H]1COC LNAZSHAWQACDHT-XIYTZBAFSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LPZCCMIISIBREI-JXMPMKKESA-N (Z)-24-ethylidenelophenol Chemical compound C[C@@H]1[C@@H](O)CC[C@]2(C)[C@@H](CC[C@@]3([C@@H]([C@H](C)CC/C(=C/C)C(C)C)CC[C@H]33)C)C3=CC[C@H]21 LPZCCMIISIBREI-JXMPMKKESA-N 0.000 description 1
- WDXQLZXORYGXJN-WVLIHFOGSA-N (e)-n-ethyl-6,6-dimethyl-n-[[3-[(4-thiophen-3-ylthiophen-2-yl)methoxy]phenyl]methyl]hept-2-en-4-yn-1-amine;hydrochloride Chemical compound Cl.CC(C)(C)C#C/C=C/CN(CC)CC1=CC=CC(OCC=2SC=C(C=2)C2=CSC=C2)=C1 WDXQLZXORYGXJN-WVLIHFOGSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZORQXIQZAOLNGE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,1-difluorocyclohexane Chemical compound FC1(F)CCCCC1 ZORQXIQZAOLNGE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LDMOEFOXLIZJOW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-dodecanesulfonic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCS(O)(=O)=O LDMOEFOXLIZJOW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- IXPNQXFRVYWDDI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-methyl-2,4-dioxo-1,3-diazinane-5-carboximidamide Chemical compound CN1CC(C(N)=N)C(=O)NC1=O IXPNQXFRVYWDDI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NGNBDVOYPDDBFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-[2,4-di(pentan-2-yl)phenoxy]acetyl chloride Chemical compound CCCC(C)C1=CC=C(OCC(Cl)=O)C(C(C)CCC)=C1 NGNBDVOYPDDBFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- HZLCGUXUOFWCCN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-hydroxynonadecane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(C(O)=O)C(O)(C(O)=O)CC(O)=O HZLCGUXUOFWCCN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LBLYYCQCTBFVLH-UHFFFAOYSA-M 2-methylbenzenesulfonate Chemical compound CC1=CC=CC=C1S([O-])(=O)=O LBLYYCQCTBFVLH-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 229940080296 2-naphthalenesulfonate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- BALNAVKTUKBYSD-KVNPXXKRSA-N 24-isopropenyl-22E-dehydrocholesterol Chemical compound C1C=C2C[C@@H](O)CC[C@]2(C)[C@@H]2[C@@H]1[C@@H]1CC[C@H]([C@H](C)/C=C/C(C(C)C)C(C)=C)[C@@]1(C)CC2 BALNAVKTUKBYSD-KVNPXXKRSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZRPLANDPDWYOMZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-cyclopentylpropionic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)CCC1CCCC1 ZRPLANDPDWYOMZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 101710158485 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase Proteins 0.000 description 1
- FHVDTGUDJYJELY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 6-{[2-carboxy-4,5-dihydroxy-6-(phosphanyloxy)oxan-3-yl]oxy}-4,5-dihydroxy-3-phosphanyloxane-2-carboxylic acid Chemical compound O1C(C(O)=O)C(P)C(O)C(O)C1OC1C(C(O)=O)OC(OP)C(O)C1O FHVDTGUDJYJELY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OTYCUXCZGNDFQD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 7-naphthalen-1-ylheptanoic acid Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C(CCCCCCC(=O)O)=CC=CC2=C1 OTYCUXCZGNDFQD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000035502 ADME Effects 0.000 description 1
- 208000004998 Abdominal Pain Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 244000215068 Acacia senegal Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000251468 Actinopterygii Species 0.000 description 1
- 229920001817 Agar Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 235000019489 Almond oil Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- GUBGYTABKSRVRQ-XLOQQCSPSA-N Alpha-Lactose Chemical compound O[C@@H]1[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@H]1O[C@@H]1[C@@H](CO)O[C@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O GUBGYTABKSRVRQ-XLOQQCSPSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 101710095342 Apolipoprotein B Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102100040202 Apolipoprotein B-100 Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 241000228212 Aspergillus Species 0.000 description 1
- 208000037260 Atherosclerotic Plaque Diseases 0.000 description 1
- BTBUEUYNUDRHOZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Borate Chemical compound [O-]B([O-])[O-] BTBUEUYNUDRHOZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OYPRJOBELJOOCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N Calcium Chemical compound [Ca] OYPRJOBELJOOCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920002134 Carboxymethyl cellulose Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 206010007556 Cardiac failure acute Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 206010048610 Cardiotoxicity Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 108010078791 Carrier Proteins Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102000003780 Clusterin Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108090000197 Clusterin Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 208000002330 Congenital Heart Defects Diseases 0.000 description 1
- RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Copper Chemical compound [Cu] RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920002261 Corn starch Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 102000002004 Cytochrome P-450 Enzyme System Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108010015742 Cytochrome P-450 Enzyme System Proteins 0.000 description 1
- FBPFZTCFMRRESA-KVTDHHQDSA-N D-Mannitol Chemical compound OC[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H](O)CO FBPFZTCFMRRESA-KVTDHHQDSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920002307 Dextran Polymers 0.000 description 1
- FEWJPZIEWOKRBE-JCYAYHJZSA-N Dextrotartaric acid Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)C(O)=O FEWJPZIEWOKRBE-JCYAYHJZSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QXNVGIXVLWOKEQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Disodium Chemical class [Na][Na] QXNVGIXVLWOKEQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 208000032928 Dyslipidaemia Diseases 0.000 description 1
- LVGKNOAMLMIIKO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Elaidinsaeure-aethylester Natural products CCCCCCCCC=CCCCCCCCC(=O)OCC LVGKNOAMLMIIKO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VWFJDQUYCIWHTN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Farnesyl pyrophosphate Natural products CC(C)=CCCC(C)=CCCC(C)=CCOP(O)(=O)OP(O)(O)=O VWFJDQUYCIWHTN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000007309 Fischer-Speier esterification reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- HEMJJKBWTPKOJG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Gemfibrozil Chemical compound CC1=CC=C(C)C(OCCCC(C)(C)C(O)=O)=C1 HEMJJKBWTPKOJG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920000084 Gum arabic Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004354 Hydroxyethyl cellulose Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920000663 Hydroxyethyl cellulose Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 206010021143 Hypoxia Diseases 0.000 description 1
- CQSRUKJFZKVYCY-WZJYZIMXSA-N Isofucostanol Chemical compound C/C=C(/CCC(C)[C@H]1CC[C@@H]2[C@@]1(CC[C@H]3[C@H]2CCC4[C@@]3(CCC(C4)O)C)C)\C(C)C CQSRUKJFZKVYCY-WZJYZIMXSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MIJPAVRNWPDMOR-ZAFYKAAXSA-N L-ascorbic acid 2-phosphate Chemical compound OC[C@H](O)[C@H]1OC(=O)C(OP(O)(O)=O)=C1O MIJPAVRNWPDMOR-ZAFYKAAXSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CKLJMWTZIZZHCS-REOHCLBHSA-N L-aspartic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CC(O)=O CKLJMWTZIZZHCS-REOHCLBHSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FBOZXECLQNJBKD-ZDUSSCGKSA-N L-methotrexate Chemical compound C=1N=C2N=C(N)N=C(N)C2=NC=1CN(C)C1=CC=C(C(=O)N[C@@H](CCC(O)=O)C(O)=O)C=C1 FBOZXECLQNJBKD-ZDUSSCGKSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000010643 Leucaena leucocephala Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 240000007472 Leucaena leucocephala Species 0.000 description 1
- 102000004882 Lipase Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108090001060 Lipase Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 229930195725 Mannitol Natural products 0.000 description 1
- 108010052285 Membrane Proteins Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 208000001145 Metabolic Syndrome Diseases 0.000 description 1
- AFVFQIVMOAPDHO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methanesulfonic acid Chemical compound CS(O)(=O)=O AFVFQIVMOAPDHO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 108010085220 Multiprotein Complexes Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102000007474 Multiprotein Complexes Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 208000029549 Muscle injury Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000021642 Muscular disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 201000009623 Myopathy Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 229910002651 NO3 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 206010028980 Neoplasm Diseases 0.000 description 1
- NHNBFGGVMKEFGY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Nitrate Chemical compound [O-][N+]([O-])=O NHNBFGGVMKEFGY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 102000016979 Other receptors Human genes 0.000 description 1
- MUBZPKHOEPUJKR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Oxalic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C(O)=O MUBZPKHOEPUJKR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910019213 POCl3 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 241000228153 Penicillium citrinum Species 0.000 description 1
- 108090000216 Phospholipid Transfer Proteins Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102000003867 Phospholipid Transfer Proteins Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 239000002202 Polyethylene glycol Substances 0.000 description 1
- XBDQKXXYIPTUBI-UHFFFAOYSA-M Propionate Chemical compound CCC([O-])=O XBDQKXXYIPTUBI-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 235000019484 Rapeseed oil Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 206010039020 Rhabdomyolysis Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 241000219061 Rheum Species 0.000 description 1
- 240000004808 Saccharomyces cerevisiae Species 0.000 description 1
- KEAYESYHFKHZAL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sodium Chemical class [Na] KEAYESYHFKHZAL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920002125 Sokalan® Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 101710184796 Squalene synthase 2 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 241000862969 Stella Species 0.000 description 1
- 229930006000 Sucrose Natural products 0.000 description 1
- CZMRCDWAGMRECN-UGDNZRGBSA-N Sucrose Chemical compound O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@@]1(CO)O[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O1 CZMRCDWAGMRECN-UGDNZRGBSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-L Sulfate Chemical compound [O-]S([O-])(=O)=O QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- 235000019486 Sunflower oil Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- ZMZDMBWJUHKJPS-UHFFFAOYSA-M Thiocyanate anion Chemical compound [S-]C#N ZMZDMBWJUHKJPS-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 229920001615 Tragacanth Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 102000003929 Transaminases Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108090000340 Transaminases Proteins 0.000 description 1
- DTQVDTLACAAQTR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Trifluoroacetic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C(F)(F)F DTQVDTLACAAQTR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000021068 Western diet Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- HCHKCACWOHOZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Zinc Chemical compound [Zn] HCHKCACWOHOZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ATZKAUGGNMSCCY-VVFNRDJMSA-N [(1r,2r,3r)-2-[(3e)-4,8-dimethylnona-3,7-dienyl]-2-methyl-3-[(1e,5e)-2,6,10-trimethylundeca-1,5,9-trienyl]cyclopropyl]methyl phosphono hydrogen phosphate Chemical class CC(C)=CCC\C(C)=C\CC\C(C)=C\[C@@H]1[C@@H](COP(O)(=O)OP(O)(O)=O)[C@]1(C)CC\C=C(/C)CCC=C(C)C ATZKAUGGNMSCCY-VVFNRDJMSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 201000000690 abdominal obesity-metabolic syndrome Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 238000010521 absorption reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 235000010489 acacia gum Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000000205 acacia gum Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000009825 accumulation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000008043 acidic salts Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 230000004913 activation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002730 additional effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- WNLRTRBMVRJNCN-UHFFFAOYSA-L adipate(2-) Chemical compound [O-]C(=O)CCCCC([O-])=O WNLRTRBMVRJNCN-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- 230000001919 adrenal effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000008272 agar Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000010419 agar Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229940040563 agaric acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229940072056 alginate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000000783 alginic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229960001126 alginic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 150000004781 alginic acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 125000001931 aliphatic group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 150000001447 alkali salts Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000008168 almond oil Substances 0.000 description 1
- CEGOLXSVJUTHNZ-UHFFFAOYSA-K aluminium tristearate Chemical compound [Al+3].CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC([O-])=O.CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC([O-])=O.CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC([O-])=O CEGOLXSVJUTHNZ-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 description 1
- 229940063655 aluminum stearate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 230000000879 anti-atherosclerotic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003110 anti-inflammatory effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229940121375 antifungal agent Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 230000003078 antioxidant effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 150000004982 aromatic amines Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 206010003246 arthritis Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 229940009098 aspartate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000000305 astragalus gummifer gum Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000009286 beneficial effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- SRSXLGNVWSONIS-UHFFFAOYSA-M benzenesulfonate Chemical compound [O-]S(=O)(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 SRSXLGNVWSONIS-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 229940077388 benzenesulfonate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229940050390 benzoate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- WPYMKLBDIGXBTP-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzoic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 WPYMKLBDIGXBTP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000033228 biological regulation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000006696 biosynthetic metabolic pathway Effects 0.000 description 1
- QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-M bisulphate group Chemical group S([O-])(O)(=O)=O QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 230000000903 blocking effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000037396 body weight Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000004556 brain Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 239000000872 buffer Substances 0.000 description 1
- MPIWSMKTTRZOKT-UHFFFAOYSA-N butanoic acid;2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCC(O)=O.OC(=O)CC(O)(C(O)=O)CC(O)=O MPIWSMKTTRZOKT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000006227 byproduct Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052791 calcium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011575 calcium Substances 0.000 description 1
- MIOPJNTWMNEORI-UHFFFAOYSA-N camphorsulfonic acid Chemical compound C1CC2(CS(O)(=O)=O)C(=O)CC1C2(C)C MIOPJNTWMNEORI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 201000011510 cancer Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 235000010948 carboxy methyl cellulose Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229920003123 carboxymethyl cellulose sodium Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000008112 carboxymethyl-cellulose Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940105329 carboxymethylcellulose Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229940063834 carboxymethylcellulose sodium Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 231100000259 cardiotoxicity Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- 239000000969 carrier Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000003197 catalytic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003915 cell function Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 1
- 150000001805 chlorine compounds Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 150000001851 cinnamic acid derivatives Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000011260 co-administration Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000003240 coconut oil Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000019864 coconut oil Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000002648 combination therapy Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229940125904 compound 1 Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229940125782 compound 2 Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229940126214 compound 3 Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229940125898 compound 5 Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000012141 concentrate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000470 constituent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010949 copper Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002285 corn oil Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000005687 corn oil Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000008120 corn starch Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000002425 crystallisation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008025 crystallization Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003247 decreasing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003412 degenerative effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000006731 degradation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 206010012601 diabetes mellitus Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 238000003745 diagnosis Methods 0.000 description 1
- WVPKAWVFTPWPDB-UHFFFAOYSA-M dichlorophosphinate Chemical compound [O-]P(Cl)(Cl)=O WVPKAWVFTPWPDB-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 235000005911 diet Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 230000037213 diet Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000009792 diffusion process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000029087 digestion Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000001177 diphosphate Substances 0.000 description 1
- XPPKVPWEQAFLFU-UHFFFAOYSA-J diphosphate(4-) Chemical compound [O-]P([O-])(=O)OP([O-])([O-])=O XPPKVPWEQAFLFU-UHFFFAOYSA-J 0.000 description 1
- 239000007884 disintegrant Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000004090 dissolution Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000003828 downregulation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008406 drug-drug interaction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000001035 drying Methods 0.000 description 1
- 201000006549 dyspepsia Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 239000008157 edible vegetable oil Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920001971 elastomer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 238000004945 emulsification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000839 emulsion Substances 0.000 description 1
- 210000002889 endothelial cell Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000003511 endothelial effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007613 environmental effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002255 enzymatic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000006911 enzymatic reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 210000003617 erythrocyte membrane Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- BEFDCLMNVWHSGT-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethenylcyclopentane Chemical compound C=CC1CCCC1 BEFDCLMNVWHSGT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000001495 ethyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- LVGKNOAMLMIIKO-QXMHVHEDSA-N ethyl oleate Chemical compound CCCCCCCC\C=C/CCCCCCCC(=O)OCC LVGKNOAMLMIIKO-QXMHVHEDSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229940093471 ethyl oleate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 210000003414 extremity Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 239000003925 fat Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000019197 fats Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000011049 filling Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000001914 filtration Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000796 flavoring agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000019634 flavors Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229960000868 fluvastatin sodium Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 210000000497 foam cell Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 238000001640 fractional crystallisation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002538 fungal effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- PUGBZUWUTZUUCP-ZRKHGVCBSA-N fungisterol Chemical compound C1[C@@H](O)CC[C@]2(C)[C@@H](CC[C@@]3([C@@H]([C@H](C)CC[C@H](C)C(C)C)CC[C@H]33)C)C3=CC[C@H]21 PUGBZUWUTZUUCP-ZRKHGVCBSA-N 0.000 description 1
- UHQOYWRQNBWEAM-NBPRQAIYSA-N fungisterol Natural products CC(C)[C@@H](C)C=C[C@H](C)[C@@H]1CC[C@@H]2C3=C(CC[C@]12C)[C@@]4(C)CC[C@@H](O)C[C@H]4C=C3 UHQOYWRQNBWEAM-NBPRQAIYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000007789 gas Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229960003627 gemfibrozil Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 230000002068 genetic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005469 granulation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000003179 granulation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000008202 granule composition Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940093915 gynecological organic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 125000005843 halogen group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 230000005831 heart abnormality Effects 0.000 description 1
- MNWFXJYAOYHMED-UHFFFAOYSA-N heptanoic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCC(O)=O MNWFXJYAOYHMED-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000008241 heterogeneous mixture Substances 0.000 description 1
- FUZZWVXGSFPDMH-UHFFFAOYSA-N hexanoic acid Chemical compound CCCCCC(O)=O FUZZWVXGSFPDMH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 102000054823 high-density lipoprotein particle receptor activity proteins Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 230000003284 homeostatic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 235000006486 human diet Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- XMBWDFGMSWQBCA-UHFFFAOYSA-N hydrogen iodide Chemical compound I XMBWDFGMSWQBCA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZMZDMBWJUHKJPS-UHFFFAOYSA-N hydrogen thiocyanate Natural products SC#N ZMZDMBWJUHKJPS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000007062 hydrolysis Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000006460 hydrolysis reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000003301 hydrolyzing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002209 hydrophobic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 235000019447 hydroxyethyl cellulose Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229940071826 hydroxyethyl cellulose Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 235000010979 hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000001866 hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920003088 hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose Polymers 0.000 description 1
- UFVKGYZPFZQRLF-UHFFFAOYSA-N hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose Chemical compound OC1C(O)C(OC)OC(CO)C1OC1C(O)C(O)C(OC2C(C(O)C(OC3C(C(O)C(O)C(CO)O3)O)C(CO)O2)O)C(CO)O1 UFVKGYZPFZQRLF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000001146 hypoxic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000006872 improvement Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000000338 in vitro Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000005764 inhibitory process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 150000007529 inorganic bases Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 230000031891 intestinal absorption Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000033227 intestinal cholesterol absorption Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000968 intestinal effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000004020 intracellular membrane Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 238000010253 intravenous injection Methods 0.000 description 1
- FZWBNHMXJMCXLU-BLAUPYHCSA-N isomaltotriose Chemical compound O[C@@H]1[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@@H]1OC[C@@H]1[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H](OC[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)C=O)O1 FZWBNHMXJMCXLU-BLAUPYHCSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000004922 lacquer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000003446 ligand Substances 0.000 description 1
- 108010022197 lipoprotein cholesterol Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 239000002502 liposome Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940057995 liquid paraffin Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 238000012792 lyophilization process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000003120 macrolide antibiotic agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940041033 macrolides Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 150000002681 magnesium compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 235000019359 magnesium stearate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229940049920 malate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- BJEPYKJPYRNKOW-UHFFFAOYSA-N malic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C(O)CC(O)=O BJEPYKJPYRNKOW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WPBNNNQJVZRUHP-UHFFFAOYSA-L manganese(2+);methyl n-[[2-(methoxycarbonylcarbamothioylamino)phenyl]carbamothioyl]carbamate;n-[2-(sulfidocarbothioylamino)ethyl]carbamodithioate Chemical compound [Mn+2].[S-]C(=S)NCCNC([S-])=S.COC(=O)NC(=S)NC1=CC=CC=C1NC(=S)NC(=O)OC WPBNNNQJVZRUHP-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- 239000000594 mannitol Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000010355 mannitol Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229960000485 methotrexate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000004292 methyl p-hydroxybenzoate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000010270 methyl p-hydroxybenzoate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229960002900 methylcellulose Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229940099246 mevacor Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 230000005012 migration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000013508 migration Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000003801 milling Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000007522 mineralic acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 230000000116 mitigating effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000005787 mitochondrial ATP synthesis coupled electron transport Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000004065 mitochondrial dysfunction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002438 mitochondrial effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000004898 mitochondrial function Effects 0.000 description 1
- 150000004712 monophosphates Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000012452 mother liquor Substances 0.000 description 1
- 210000003205 muscle Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000002107 myocardial effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 208000010125 myocardial infarction Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000031225 myocardial ischemia Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 210000004165 myocardium Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- KVBGVZZKJNLNJU-UHFFFAOYSA-M naphthalene-2-sulfonate Chemical compound C1=CC=CC2=CC(S(=O)(=O)[O-])=CC=C21 KVBGVZZKJNLNJU-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- BALNAVKTUKBYSD-UHFFFAOYSA-N nervisterol Natural products C1C=C2CC(O)CCC2(C)C2C1C1CCC(C(C)C=CC(C(C)C)C(C)=C)C1(C)CC2 BALNAVKTUKBYSD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960003512 nicotinic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229910052757 nitrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000012457 nonaqueous media Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000035764 nutrition Effects 0.000 description 1
- 235000016709 nutrition Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 235000014593 oils and fats Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000006186 oral dosage form Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000008183 oral pharmaceutical preparation Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000007524 organic acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 235000005985 organic acids Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 150000007530 organic bases Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000003791 organic solvent mixture Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000004792 oxidative damage Effects 0.000 description 1
- 108010071584 oxidized low density lipoprotein Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 230000020477 pH reduction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007911 parenteral administration Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000825 pharmaceutical preparation Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000003013 phosphoric acid derivatives Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000003014 phosphoric acid esters Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000003017 phosphorus Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 230000026731 phosphorylation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000006366 phosphorylation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001766 physiological effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000035790 physiological processes and functions Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000049 pigment Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229950010765 pivalate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- IUGYQRQAERSCNH-UHFFFAOYSA-N pivalic acid Chemical compound CC(C)(C)C(O)=O IUGYQRQAERSCNH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000036470 plasma concentration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000004014 plasticizer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 210000004258 portal system Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 231100000683 possible toxicity Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- 229920001592 potato starch Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 230000003334 potential effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000843 powder Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940089484 pravachol Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 238000001556 precipitation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000002360 preparation method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000009862 primary prevention Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000035755 proliferation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 235000010232 propyl p-hydroxybenzoate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000004405 propyl p-hydroxybenzoate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000013772 propylene glycol Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- QELSKZZBTMNZEB-UHFFFAOYSA-N propylparaben Chemical compound CCCOC(=O)C1=CC=C(O)C=C1 QELSKZZBTMNZEB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000006318 protein oxidation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 102000004169 proteins and genes Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108090000623 proteins and genes Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 239000003586 protic polar solvent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002994 raw material Substances 0.000 description 1
- NPCOQXAVBJJZBQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N reduced coenzyme Q9 Natural products COC1=C(O)C(C)=C(CC=C(C)CCC=C(C)CCC=C(C)CCC=C(C)CCC=C(C)CCC=C(C)CCC=C(C)CCC=C(C)CCC=C(C)C)C(O)=C1OC NPCOQXAVBJJZBQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000002040 relaxant effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229940100486 rice starch Drugs 0.000 description 1
- YGSDEFSMJLZEOE-UHFFFAOYSA-M salicylate Chemical compound OC1=CC=CC=C1C([O-])=O YGSDEFSMJLZEOE-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 229960001860 salicylate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229920006395 saturated elastomer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 102000014452 scavenger receptors Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108010078070 scavenger receptors Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 230000009863 secondary prevention Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000010802 sludge Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002002 slurry Substances 0.000 description 1
- 210000000329 smooth muscle myocyte Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 239000000344 soap Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000010413 sodium alginate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000000661 sodium alginate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940005550 sodium alginate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 235000019812 sodium carboxymethyl cellulose Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229920001027 sodium carboxymethylcellulose Polymers 0.000 description 1
- RLWRROYWKHUVKF-OKDJMAGBSA-M sodium;(3r,5r)-7-[(1s,2s,6r,8s,8ar)-8-(2,2-dimethylbutanoyloxy)-2,6-dimethyl-1,2,6,7,8,8a-hexahydronaphthalen-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoate Chemical compound [Na+].C1=C[C@H](C)[C@H](CC[C@@H](O)C[C@@H](O)CC([O-])=O)[C@H]2[C@@H](OC(=O)C(C)(C)CC)C[C@@H](C)C=C21 RLWRROYWKHUVKF-OKDJMAGBSA-M 0.000 description 1
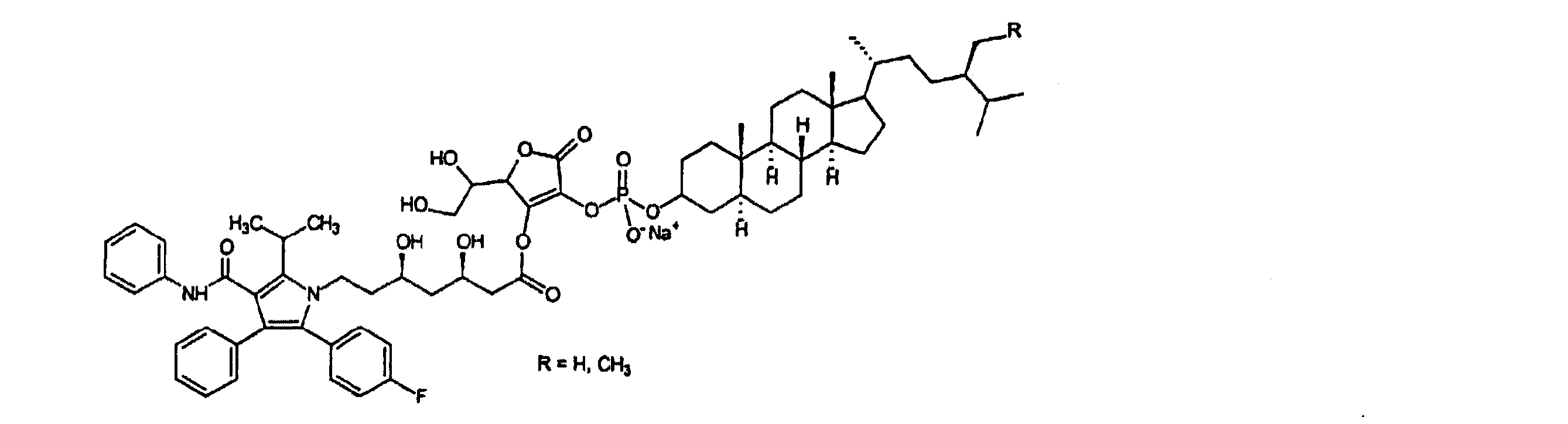
- VVRPOCPLIUDBSA-CNZCJKERSA-M sodium;(3r,5r)-7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-5-propan-2-ylpyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoate Chemical compound [Na+].C=1C=CC=CC=1C1=C(C=2C=CC(F)=CC=2)N(CC[C@@H](O)C[C@@H](O)CC([O-])=O)C(C(C)C)=C1C(=O)NC1=CC=CC=C1 VVRPOCPLIUDBSA-CNZCJKERSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 239000007901 soft capsule Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000012439 solid excipient Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000010199 sorbic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000004334 sorbic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940075582 sorbic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 235000011069 sorbitan monooleate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000001593 sorbitan monooleate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940035049 sorbitan monooleate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 235000020712 soy bean extract Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000012798 spherical particle Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000011272 standard treatment Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000003860 storage Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000006467 substitution reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- KDYFGRWQOYBRFD-UHFFFAOYSA-L succinate(2-) Chemical compound [O-]C(=O)CCC([O-])=O KDYFGRWQOYBRFD-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- 239000005720 sucrose Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000007940 sugar coated tablet Substances 0.000 description 1
- BDHFUVZGWQCTTF-UHFFFAOYSA-M sulfonate Chemical compound [O-]S(=O)=O BDHFUVZGWQCTTF-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 239000002600 sunflower oil Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000375 suspending agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000013268 sustained release Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012730 sustained-release form Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000002195 synergetic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001839 systemic circulation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 235000012222 talc Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229940095064 tartrate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 150000003512 tertiary amines Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229940124597 therapeutic agent Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 238000002560 therapeutic procedure Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000002562 thickening agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004408 titanium dioxide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 231100000331 toxic Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- 230000002588 toxic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- RYFMWSXOAZQYPI-UHFFFAOYSA-K trisodium phosphate Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[Na+].[O-]P([O-])([O-])=O RYFMWSXOAZQYPI-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 description 1
- 229940035936 ubiquinone Drugs 0.000 description 1
- ZDPHROOEEOARMN-UHFFFAOYSA-N undecanoic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCC(O)=O ZDPHROOEEOARMN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 208000019553 vascular disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 235000013311 vegetables Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000005406 washing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000010497 wheat germ oil Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940100445 wheat starch Drugs 0.000 description 1
- HBOMLICNUCNMMY-XLPZGREQSA-N zidovudine Chemical compound O=C1NC(=O)C(C)=CN1[C@@H]1O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](N=[N+]=[N-])C1 HBOMLICNUCNMMY-XLPZGREQSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960002555 zidovudine Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000011701 zinc Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052725 zinc Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229940072168 zocor Drugs 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07J—STEROIDS
- C07J9/00—Normal steroids containing carbon, hydrogen, halogen or oxygen substituted in position 17 beta by a chain of more than two carbon atoms, e.g. cholane, cholestane, coprostane
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/70—Carbohydrates; Sugars; Derivatives thereof
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P19/00—Drugs for skeletal disorders
- A61P19/08—Drugs for skeletal disorders for bone diseases, e.g. rachitism, Paget's disease
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P25/00—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system
- A61P25/04—Centrally acting analgesics, e.g. opioids
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P25/00—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system
- A61P25/28—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system for treating neurodegenerative disorders of the central nervous system, e.g. nootropic agents, cognition enhancers, drugs for treating Alzheimer's disease or other forms of dementia
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P3/00—Drugs for disorders of the metabolism
- A61P3/06—Antihyperlipidemics
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P3/00—Drugs for disorders of the metabolism
- A61P3/08—Drugs for disorders of the metabolism for glucose homeostasis
- A61P3/10—Drugs for disorders of the metabolism for glucose homeostasis for hyperglycaemia, e.g. antidiabetics
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P35/00—Antineoplastic agents
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P39/00—General protective or antinoxious agents
- A61P39/06—Free radical scavengers or antioxidants
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P43/00—Drugs for specific purposes, not provided for in groups A61P1/00-A61P41/00
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P7/00—Drugs for disorders of the blood or the extracellular fluid
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P7/00—Drugs for disorders of the blood or the extracellular fluid
- A61P7/02—Antithrombotic agents; Anticoagulants; Platelet aggregation inhibitors
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P9/00—Drugs for disorders of the cardiovascular system
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P9/00—Drugs for disorders of the cardiovascular system
- A61P9/10—Drugs for disorders of the cardiovascular system for treating ischaemic or atherosclerotic diseases, e.g. antianginal drugs, coronary vasodilators, drugs for myocardial infarction, retinopathy, cerebrovascula insufficiency, renal arteriosclerosis
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P9/00—Drugs for disorders of the cardiovascular system
- A61P9/12—Antihypertensives
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Diabetes (AREA)
- Hematology (AREA)
- Neurosurgery (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Neurology (AREA)
- Cardiology (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Physical Education & Sports Medicine (AREA)
- Obesity (AREA)
- Vascular Medicine (AREA)
- Endocrinology (AREA)
- Emergency Medicine (AREA)
- Hospice & Palliative Care (AREA)
- Urology & Nephrology (AREA)
- Toxicology (AREA)
- Psychiatry (AREA)
- Pain & Pain Management (AREA)
- Orthopedic Medicine & Surgery (AREA)
- Biochemistry (AREA)
- Rheumatology (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Pharmaceuticals Containing Other Organic And Inorganic Compounds (AREA)
- Steroid Compounds (AREA)
- Medicines That Contain Protein Lipid Enzymes And Other Medicines (AREA)
Abstract
【課題】ステロール及び/又はスタノール及びコレステロール生合成阻害剤を含む新規化合物及び組成物、並びに様々な病気及び症状の治療又は防止へのそれらの使用
【解決手段】本発明は、一つの局面において、ステロール及び/又はスタノール及びコレステロール生合成阻害剤を含む新規化合物(それら化合物の塩、及びそれら化合物及び/又は塩の溶媒和物及びプロドラッグを含む。)を提供する。別の局面において、本発明は、少なくとも一つのステロール及び/又はスタノールエステル、並びに、少なくとも一つのコレステロール生合成阻害剤を含む組成物を提供する。また、本明細書に示された化合物又は組成物を投与することによって、様々な疾患、症状及び障害を治療及び予防する方法をも提供する。
【選択図】 なし
Novel compounds and compositions containing sterols and / or stanols and cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitors, and their use in the treatment or prevention of various diseases and conditions. Novel compounds comprising sterols and / or stanols and cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitors (including salts of these compounds, and solvates and prodrugs of these compounds and / or salts) are provided. In another aspect, the present invention provides a composition comprising at least one sterol and / or stanol ester and at least one cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitor. Also provided are methods for treating and preventing various diseases, conditions and disorders by administering the compounds or compositions provided herein.
[Selection figure] None
Description
本発明はステロール、スタノール及びそれらの新規誘導体分野に関し、並びに、心血管疾患及びその他の疾患の治療及び予防におけるそれらの使用に関する。 The present invention relates to the field of sterols, stanols and their novel derivatives and to their use in the treatment and prevention of cardiovascular and other diseases.
科学技術における近年の進歩はヒトの生活の質を改善し寿命を延ばすことに役立っているが、アテローム性動脈硬化症、すなわち心血管疾患(CVD)の根本原因の予防は十分に対処されていない。実際、心血管疾患は、あらゆる形態のガンを全て含めたその他の疾患よりも、年間に多くの死者を計上する(非特許文献1)。米国に限っても、毎年100万件以上の心臓発作が起こっており、そしてそれが原因で50万人以上が亡くなっている。この甚大な犠牲者は、CVDの原因とそれを予防及び治療する手段を決定するための継続的な研究を必要としている。 Recent advances in science and technology have helped to improve human life quality and prolong life, but the prevention of atherosclerosis, the root cause of cardiovascular disease (CVD), has not been adequately addressed . In fact, cardiovascular disease accounts for more deaths per year than other diseases including all forms of cancer (Non-Patent Document 1). Even in the United States, more than 1 million heart attacks occur every year, and more than 500,000 people die from it. This enormous victim needs ongoing research to determine the cause of CVD and the means to prevent and treat it.
CVDの根本原因はアテローム性動脈硬化症、すなわち、血管路の狭窄及び最終的には脈管系の硬化をもたらす動脈血管壁へのコレステロールなどの脂質の沈殿を特徴とする疾患である。アテローム性動脈硬化症は遺伝(遺伝子)因子及び食生活や生活習慣などの環境因子の相互作用に起因する変性プロセスである。今日までの研究は、コレステロールが、血管に動脈硬化性プラークを形成し、動脈系図のプラークの位置に応じて心筋又は脳又は四肢への血液供給を最終的には絶つことによって、アテローム性動脈硬化症の一因となり得ることを示唆している(非特許文献1、2)。225−250mg/dlを上回る総コレステロール量は、血管障害などのCVDの有意に高いリスクと関連する。概観は、ヒトの総血清コレステロールにおける1%の減少が、冠動脈イベントのリスクにおける2%の減少をもたらすことを示している(非特許文献3)。統計的には、平均血清コレステロールにおける10%の減少(たとえば6.0mmol/Lから5.3mmol/L)が米国内において年間100,000人の死亡を防ぐ結果になり得る(非特許文献4)。 The root cause of CVD is atherosclerosis, a disease characterized by the precipitation of lipids, such as cholesterol, into the arterial vessel wall that results in vascular narrowing and ultimately vascular stiffness. Atherosclerosis is a degenerative process resulting from the interaction of genetic factors and environmental factors such as diet and lifestyle. Studies to date have shown that cholesterol forms atherosclerotic plaques in blood vessels and ultimately cuts off blood supply to the myocardium or brain or extremities depending on the location of plaques in the arterial tree. This suggests that it may contribute to the disease (Non-Patent Documents 1 and 2). Total cholesterol levels above 225-250 mg / dl are associated with a significantly higher risk of CVD such as vascular disorders. An overview shows that a 1% reduction in human total serum cholesterol results in a 2% reduction in the risk of coronary events (3). Statistically, a 10% reduction in average serum cholesterol (eg, 6.0 mmol / L to 5.3 mmol / L) can result in the prevention of 100,000 deaths annually in the United States (4). .
コレステリルエステルはアテローム性病変の主要成因であり、動脈壁細胞のコレステロールの主要な貯蔵形態である。コレステリルエステル形成はまた、恒常性のコントロールメカニズムを介して、食事性コレステロールの腸内吸収における一段階である。これらコントロールメカニズムは、食事性コレステロール、コレステロール生合成及びコレステロール含有血漿リポタンパク質の異化反応の相互関連する規制を含んでいる。コレステロール生合成及び異化反応は最初に肝臓で起こり、それゆえ、血漿コレステロール値の主要な決定要因である。 Cholesteryl esters are a major cause of atheromatous lesions and the major storage form of cholesterol in arterial wall cells. Cholesteryl ester formation is also a step in the intestinal absorption of dietary cholesterol through a homeostatic control mechanism. These control mechanisms include interrelated regulation of dietary cholesterol, cholesterol biosynthesis and catabolism of cholesterol-containing plasma lipoproteins. Cholesterol biosynthesis and catabolism first occur in the liver and are therefore a major determinant of plasma cholesterol levels.
リポタンパク質は非共有結合で結合された脂質とタンパク質の複合体である。各種のリポタンパク質類は、特有の質量、化学組成、密度及び生理学的役割を有する。密度又は粒子サイズに関係なく、循環脂質はコレステリルエステルとトリグリセリドの核、及びリン脂質、遊離コレステロール及びアポリポタンパク質の膜で構成される。アポリポタンパク質はリポタンパク質の集合及び分泌に関与し、構造的完全性を与え、リポタンパク質変性酵素を活性化し、そして多くの種類のレセプターや膜タンパク質に対するリガンドである。血漿中に見られるリポタンパク質類はHDL、LDL、中間密度リポタンパク質(IDL)及び極低密度リポタンパク質(VLDL)を含む。 Lipoproteins are non-covalently bound lipid and protein complexes. Various lipoproteins have a unique mass, chemical composition, density and physiological role. Regardless of density or particle size, circulating lipids are composed of a core of cholesteryl esters and triglycerides, and a membrane of phospholipids, free cholesterol and apolipoprotein. Apolipoproteins are involved in lipoprotein assembly and secretion, impart structural integrity, activate lipoprotein denaturing enzymes, and are ligands for many types of receptors and membrane proteins. Lipoproteins found in plasma include HDL, LDL, intermediate density lipoprotein (IDL) and very low density lipoprotein (VLDL).
各種のリポタンパク質は、特有のアポリポタンパク質組成又は比率を有する。HDL中で最も有名なアポリポタンパク質はアポリポタンパク質−AI(アポ−AI)であり、それはタンパク質質量の約70%を占め、もう20%をアポ−AIIが占める。アポA−Iの
アポA−IIに対する比率は、HDL機能特性及び抗動脈硬化特性を決定し得る。循環しているHDL粒子は、質量200乃至400キロダルトン、直径7乃至10nmの円板状並びに球状粒子の異質混合物からなる。
Each type of lipoprotein has a unique apolipoprotein composition or ratio. The most famous apolipoprotein in HDL is apolipoprotein-AI (apo-AI), which accounts for about 70% of the protein mass and another 20% is apo-AII. The ratio of ApoA-I to ApoA-II can determine HDL functional properties and anti-arteriosclerotic properties. The circulating HDL particles are composed of a heterogeneous mixture of disk-like and spherical particles having a mass of 200 to 400 kilodaltons and a diameter of 7 to 10 nm.
HDLは血漿中で脂質の輸送において機能するリポタンパク質の主要な種類の一つであり、また、コレステロール逆輸送、胆汁酸合成のためのコレステロール分子基質の供給、クラステリン輸送、パラオキサネーゼ輸送、リポタンパク質酸化防止、及び、副腎細胞によるコレステロールの選択的摂取などの、体内における多様な機能を有する。HDLに関連する主要な脂質はコレステロール、コレステリルエステル、トリグリセリド、リン脂質及び脂肪酸が挙げられる。 HDL is one of the major types of lipoproteins that function in the transport of lipids in plasma, and also reverse cholesterol transport, supply of cholesterol molecular substrates for bile acid synthesis, clusterin transport, paraoxanase transport, It has various functions in the body such as protein oxidation prevention and selective intake of cholesterol by adrenal cells. Major lipids associated with HDL include cholesterol, cholesteryl esters, triglycerides, phospholipids and fatty acids.
HDLがどのように抗動脈硬化性であるかを十分に理解するために、動脈硬化プロセスの簡単な説明が必要である。動脈硬化プロセスは、LDLが血管壁内部に捕捉されることから始まる。このLDLの酸化は、単核細胞の血管壁の内側を覆う内皮細胞への結合を生じさせる。これら単核細胞は活性化され、そして内皮空間へ入り込み、そこでマクロファージへと変形され、LDLのさらなる酸化を導く。酸化されたLDLは、スカベンジャーレセプターによってマクロファージに取りこまれ、泡沫細胞の形成を導く。線維性被膜が、動脈平滑筋細胞の増殖と移動によって発生し、これにより動脈硬化性プラークが形成される。 In order to fully understand how HDL is anti-atherosclerotic, a brief description of the arteriosclerosis process is necessary. The arteriosclerosis process begins with LDL being trapped inside the vessel wall. This oxidation of LDL causes binding to endothelial cells that line the blood vessel walls of mononuclear cells. These mononuclear cells are activated and enter the endothelial space where they are transformed into macrophages leading to further oxidation of LDL. Oxidized LDL is taken up by macrophages by the scavenger receptor, leading to foam cell formation. Fibrous capsules are generated by the proliferation and migration of arterial smooth muscle cells, thereby forming arteriosclerotic plaques.
HDLは、肝臓外の組織から肝臓へコレステロールを輸送するのに必須なものであり、肝臓において遊離コレステロールとして又はコレステロールから形成される胆汁酸として胆汁中に排出される。該プロセスは幾つかの段階を必要とする。第一プロセスは肝臓及び腸内における新生又はプレ−βHDL粒子の形成である。過剰コレステロールがABC A1トランポーターの働きによって細胞膜を通って新生HDL中に移動する。レシチンコレステロールアシルトランスフェラーゼ(LCAT)がコレステロールをコレステリルエステルに変換し、続いて新生HDLを成熟HDLへの変換する。エステル化されたコレステロールは続いて、コレステリルエステル転送タンパク質(CETP)によってHDLからアポリポタンパク質−Bを含むリポタンパク質へ転送され、該リポタンパク質は多数の受容体によって肝臓内に取りこまれる(非特許文献1)。新生HDLは肝臓トリグリセリドリパーゼ及びリン脂質転送タンパク質によって再生され、このサイクルが繰り返される。抹消細胞から除去されたコレステロールに加え、HDLはLDL及び赤血球膜からコレステロールを受け取る。逆コレステロール輸送の別のメカニズムは、コレステロールに乏しい膜とHDL又は他の受容体分子の間のコレステロールの受動的拡散を含み得る。 HDL is essential for transporting cholesterol from tissues outside the liver to the liver and is excreted in the bile as free cholesterol or as a bile acid formed from cholesterol in the liver. The process requires several steps. The first process is the formation of newborn or pre-β HDL particles in the liver and intestine. Excess cholesterol moves through the cell membrane and into nascent HDL by the action of the ABC A1 transporter. Lecithin cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT) converts cholesterol to cholesteryl ester, followed by conversion of nascent HDL to mature HDL. Esterified cholesterol is subsequently transferred from HDL to lipoproteins, including apolipoprotein-B, by cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP), which is taken up into the liver by a number of receptors (non-patent literature). 1). The nascent HDL is regenerated by liver triglyceride lipase and phospholipid transfer protein, and this cycle is repeated. In addition to cholesterol removed from peripheral cells, HDL receives cholesterol from LDL and erythrocyte membranes. Another mechanism for reverse cholesterol transport may involve passive diffusion of cholesterol between cholesterol-poor membranes and HDL or other receptor molecules.
HDLは逆コレステロール輸送におけるその役割を通して、あるいは恐らくLDL酸化を妨げることの双方によってアテローム性動脈硬化症の発生を防ぐ。幾つかのHDL関連酵素が該プロセスに関与している。パーオキソナーゼ(PON1)、LCAT、及び血小板活性化因子アセチルヒドロラーゼ(PAFAH)の全てが、LDL酸化の間に生成したリン脂質ヒドロペルオキシドを加水分解することによって関与し、そしてLDL中の酸化脂質の蓄積を協力して防止する働きをする。これら酵素はHDLの抗酸化及び抗炎症特性に関与する。研究論文は、HDLコレステロールの低血漿濃度がアテローム性動脈硬化症の発生の重要なリスク因子であり(非特許文献5)、そしてその高レベル値が防止することを示している。 HDL prevents the development of atherosclerosis both through its role in reverse cholesterol transport or possibly by preventing LDL oxidation. Several HDL related enzymes are involved in the process. Peroxonase (PON1), LCAT, and platelet activating factor acetylhydrolase (PAFAH) are all involved by hydrolyzing the phospholipid hydroperoxide produced during LDL oxidation, and of the oxidized lipids in LDL Work to prevent accumulation in cooperation. These enzymes are involved in the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of HDL. Research papers show that low plasma concentrations of HDL cholesterol are an important risk factor for the development of atherosclerosis (Non-Patent Document 5), and its high level values prevent.
肝臓はVLDL類の合成及び分泌に関する主要な臓器であり、VLDL類は上述の通り循環中に代謝されてLDLとなる。LDL類は血漿中でコレステロールを輸送する主要なリポタンパク質であり、それゆえ、その濃度上昇がアテローム性動脈硬化症に直接的に関連する。簡潔に言えば、腸内のコレステロール吸収が減少すると、どうしても、より少ないコレステロールが肝臓へ配送されることになる。結果として、VLDL産生が減少し、同
時に大部分はLDL形態にある血漿コレステロールの肝クリアランスが増加する。
The liver is a major organ involved in the synthesis and secretion of VLDLs, and VLDLs are metabolized in the circulation to LDL as described above. LDLs are the major lipoproteins that transport cholesterol in plasma, and therefore their elevated levels are directly related to atherosclerosis. Simply put, less cholesterol absorption in the intestine will inevitably result in less cholesterol being delivered to the liver. As a result, VLDL production is reduced and at the same time hepatic clearance of plasma cholesterol, mostly in LDL form, is increased.
その結果、コレステロールはそれ自体の合成を調整するために3つの異なる段階で作用する。第一に、HMG CoAレダクターゼ酵素を抑制することによって、内因性コレステロール合成を抑える。第二に、LCATを活性化する。第三に、LDL−レセプターの合成を調整して、十分量のコレステロールを既に有する細胞がさらなるコレステロールを取りこまないことを確実にする。 As a result, cholesterol acts in three different stages to regulate its own synthesis. First, it suppresses endogenous cholesterol synthesis by inhibiting the HMG CoA reductase enzyme. Second, activate LCAT. Third, the synthesis of the LDL-receptor is adjusted to ensure that cells that already have a sufficient amount of cholesterol do not take up additional cholesterol.
ステロールは多くの重要な細胞機能を果たす、天然由来の化合物である。植物中のカンペステロール、スチグマステロール及びβ−シトステロール、菌類中のエルゴステロール、並びに動物中のコレステロールなどのステロール類はそれぞれ、各々の細胞タイプにおいて細胞膜及び細胞内膜の各主要成分である。ヒトの食事由来のフィトステロールは野菜や植物油などの植物性物質に由来する。標準的な西洋食中の一日あたりの推定フィトステロール含有量は、一日あたり約500ミリグラムを供給する菜食料理とは対照的に、約60−80ミリグラムである。 Sterols are naturally derived compounds that perform many important cellular functions. Sterols such as campesterol, stigmasterol and β-sitosterol in plants, ergosterol in fungi, and cholesterol in animals are the major components of the cell membrane and intracellular membrane, respectively, in each cell type. Human diet-derived phytosterols are derived from plant substances such as vegetables and vegetable oils. The estimated daily phytosterol content in a typical Western diet is about 60-80 milligrams, as opposed to a vegetarian dish that provides about 500 milligrams per day.
フィトステロールは、ヒトなどの多くの哺乳類に供給した場合に血清コレステロール値を下げる能力によって、多くの注目を集めている。正確な作用メカニズムの多くは解明されていないものの、コレステロールとフィトステロールとの関係は、1つにはそれぞれの化学構造間の類似性(分子の側鎖に起因する相違)によるらしい。コレステロール吸収プロセスにおいて、フィトステロールはミセル相のコレステロールと置き換わり、それにより、その吸収を減少させるか、受容体及び/又は担体サイトと競合することが推測される。 Phytosterol has received much attention due to its ability to lower serum cholesterol levels when supplied to many mammals such as humans. Although many of the exact mechanisms of action have not been elucidated, the relationship between cholesterol and phytosterols appears to be due in part to the similarity between their chemical structures (differences due to the side chains of the molecule). In the cholesterol absorption process, it is speculated that phytosterols replace micelle phase cholesterol, thereby reducing its absorption or competing with receptor and / or carrier sites.
40年以上前、イーライリリー社は、ある論文によると約9%まで血清コレステロールを下げることが見出された、シテリン(登録商標:Cytellin)と呼ばれるトール油由来(後に大豆油由来)のステロール製剤を市販した(非特許文献6)。その後の様々な研究者らが、血漿脂質及びリポタンパク質濃度へのコレステロール製剤の効果(非特許文献7)、並びに、血清コレステロールへの大豆油及びトール油源由来のシトステロール及びカンペステロールの効果の調査(非特許文献8)を行ってきた。血清コレステロールを下げることに非常に有効であることが発見されているフィトステロールの組成物は、米国特許第5,770,749号明細書においてカトニーらに開示され、それは70質量%以下のβ−シトステロール、少なくとも10質量%のカンペステロール及びスチグマスタノール(β−シトスタノール)を含有する。構成要素のフィトステロールの間に何らかの相互作用が存在し、以前に得られたものよりさらに優れたコレステロール低下結果を与えることが、この特許において注目されている。 Over 40 years ago, Eli Lilly found a sterol formulation derived from tall oil (later derived from soy oil) called Cytelin that was found to lower serum cholesterol by about 9% according to a paper. Was commercially available (Non-Patent Document 6). Various subsequent researchers have investigated the effects of cholesterol preparations on plasma lipid and lipoprotein concentrations (7) and the effects of sitosterol and campesterol from soy and tall oil sources on serum cholesterol. (Non-Patent Document 8). A composition of phytosterols that has been found to be very effective in lowering serum cholesterol is disclosed in US Pat. No. 5,770,749 to Katney et al., Which contains up to 70% by weight of β-sitosterol. , Containing at least 10% by weight campesterol and stigmasteranol (β-sitostanol). It is noted in this patent that some interaction exists between the constituent phytosterols, giving a cholesterol lowering result even better than previously obtained.
多くの他の化合物及び組成物が、血清LDLコレステロールの低下、血清HDLコレステロールの増加、及び、CVDの他の重大なリスク因子の防止の目的で、過去10年間に開発されている。
本発明の目的は、CVD及び、脂質障害などのその根底となる障害の治療に用いられていた以前の既知化合物における不利点を未然に防ぐか又は軽減し得る新規化合物を提供することである。 The object of the present invention is to provide novel compounds that can obviate or reduce the disadvantages of previously known compounds that have been used to treat CVD and its underlying disorders such as lipid disorders.
本発明の目的は、CVD及び、脂質障害などのその根底となる障害の治療に用いられた以前の既知組成物における不利点を未然に防ぐか又は軽減し得る新規組成物を提供することである。 The object of the present invention is to provide a novel composition that can obviate or reduce the disadvantages of previously known compositions used to treat CVD and its underlying disorders such as lipid disorders. .
本発明は、一つの局面において、下記化学式、
反応性カルボキシル基を有するコレステロール生合成阻害剤を表し;R3は少なくとも一
つの遊離性及び反応性水酸基を有するコレステロール生合成阻害剤を表し;R4はアスコ
ルビン酸に由来し、Xは水素原子であるか、又は、金属、アルカリ土類金属及びアルカリ金属からなる群から選択され、並びに、nは1−5を表す。)の一つ以上を有する新規化合物(生物学的に許容される塩又は溶媒和物、又は少なくとも一つの前記化合物の又はそれらの塩の又はそれらの溶媒和物のプロドラッグを含む。)を提供する。
In one aspect, the present invention provides the following chemical formula:
本発明は、別の局面において、
a)
びにnは1−5を表す。)の一般式を有する化合物(あらゆる生物学的に許容される塩又は溶媒和物、又は少なくとも一つの前記化合物の又はそれらの塩の又はそれらの溶媒和物のプロドラッグを含む。)から選択される少なくとも一つのコレステロール吸収阻害剤
b)少なくとも一つのコレステロール生合成阻害剤
を含む組成物を提供する。
In another aspect, the present invention provides:
a)
本発明は、別の局面において、以下の治療目的;
a)一般にCVDに関連し、動脈硬化、アテローム性動脈硬化、細動脈硬化、狭心症および血栓症などの一つ以上の症状を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
b)CVDに関連するリスク因子の一つ以上を減らし及び/又は排除すること、
c)アテローム性動脈硬化症を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
d)高コレステロール血症を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
e)高脂質症状を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
f)脂質代謝異常を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
g)高血圧症を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
h)冠動脈疾患を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
i)冠動脈プラーク発生を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
j)冠動脈プラーク炎症を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
k)血清LDLコレステロールを低下すること、
l)血清HDLコレステロールを増加すること、
m)血清トリグリセリド値を減少すること、
n)コレステロール生合成を減少すること、
o)脂質代謝異常状態又は障害を予防し、減らし、排除し、又は改善すること、
p)高コレステロール血症又は低アルファリポタンパク質血症を予防し、減らし、排除し、又は改善すること、
q)アテローム性病変またはプラークの発生を予防し、減らし、排除し、安定化させ、又は改善すること、
r)心血管疾患及び冠動脈疾患の発生に関連する炎症の発生を予防し、減らし、排除し、又は改善すること、
s)血清HDLの不足、若しくはLDL、VLDL、Lp(a)、ベータ−BLDL、I
DL又は残留リポタンパク質の過剰をその基礎として有するか、又は、それらにより悪化する、あらゆる症状、疾患又は障害を予防し、減らし、排除し、又は改善すること、
t)発作のリスクを減少すること、
u)イソプレノイド合成を抑制すること、
v)アルツハイマー病を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
w)認知症を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
x)骨粗鬆症を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
y)酸化ストレスによる損傷を予防し、減らし、排除し、又は改善すること、
z)酸化からHDLの安定性を増強し及び/又は維持すること、
aa)酸化からLDL、VLDL、又はIDLの安定性を増強し及び/又は維持すること、
bb)酸化からトリグリセリド(TG)の安定性を増強し及び/又は維持すること、
cc)抗凝固特性を示すこと、
dd)抗増殖特性を示すこと、
ee)免疫調節特性を示すこと、
ff)血管由来特性を示すこと、
gg)腫瘍の成長を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
hh)骨質量及び/又は骨代謝を増加すること、及び、
ii)特に細胞又は分子レベルにおいて、スタチンの投与によって得られる非脂質関連の多面発現効果の何れかを増強すること、
の一つ以上を達成する方法を提供し、それらは本明細書に説明され主張される化合物又は組成物の無毒性かつ治療有効量を動物に投与することを含む。
In another aspect, the present invention provides the following therapeutic purposes;
a) preventing, treating or alleviating one or more symptoms generally related to CVD, such as arteriosclerosis, atherosclerosis, arteriole sclerosis, angina and thrombosis,
b) reducing and / or eliminating one or more of the risk factors associated with CVD;
c) preventing, treating or reducing atherosclerosis,
d) preventing, treating or reducing hypercholesterolemia,
e) prevent, treat or alleviate high lipid symptoms;
f) preventing, treating or reducing lipid metabolism disorders;
g) preventing, treating or reducing hypertension,
h) preventing, treating or reducing coronary artery disease;
i) preventing, treating or reducing the occurrence of coronary plaque,
j) preventing, treating or reducing coronary plaque inflammation;
k) lowering serum LDL cholesterol,
l) increasing serum HDL cholesterol,
m) reducing serum triglyceride levels,
n) reducing cholesterol biosynthesis,
o) preventing, reducing, eliminating or ameliorating abnormal lipid metabolism conditions or disorders;
p) preventing, reducing, eliminating or ameliorating hypercholesterolemia or low alpha lipoproteinemia,
q) preventing, reducing, eliminating, stabilizing or ameliorating the development of atherosclerotic lesions or plaques;
r) preventing, reducing, eliminating or ameliorating the occurrence of inflammation associated with the occurrence of cardiovascular and coronary artery disease;
s) Lack of serum HDL or LDL, VLDL, Lp (a), beta-BLDL, I
Preventing, reducing, eliminating or ameliorating any symptoms, diseases or disorders that have or are exacerbated by excess DL or residual lipoproteins,
t) reducing the risk of seizures,
u) inhibiting isoprenoid synthesis;
v) preventing, treating or reducing Alzheimer's disease;
w) prevent, treat or alleviate dementia;
x) preventing, treating or reducing osteoporosis,
y) prevent, reduce, eliminate or ameliorate oxidative stress damage;
z) enhance and / or maintain the stability of HDL from oxidation,
aa) enhancing and / or maintaining the stability of LDL, VLDL, or IDL from oxidation,
bb) enhancing and / or maintaining the stability of triglycerides (TG) from oxidation;
cc) exhibit anticoagulant properties;
dd) exhibit anti-proliferative properties;
ee) exhibiting immunomodulatory properties;
ff) exhibiting blood vessel-derived properties;
gg) preventing, treating or reducing tumor growth;
hh) increasing bone mass and / or bone metabolism; and
ii) enhance any of the non-lipid related pleiotropic effects obtained by administration of statins, especially at the cellular or molecular level;
A method is provided for accomplishing one or more of the following, comprising administering to an animal a non-toxic and therapeutically effective amount of a compound or composition described and claimed herein.
本発明は、さらなる別の局面において、心血管疾患及びその根底となる症状(アテローム性動脈硬化症、高コレステロール血症、高脂質血症、脂質代謝異常、高血圧症、血栓症、冠動脈疾患などを含むがこれに限定されない)を治療し又は予防する方法、又は、冠動脈プラーク炎症などの炎症を治療し又は減らす方法を提供し、前記方法は上記に示された一つ以上の化合物の無毒性かつ治療有効量を動物へ投与することを含む。 In yet another aspect, the present invention relates to cardiovascular diseases and underlying symptoms (atherosclerosis, hypercholesterolemia, hyperlipidemia, lipid metabolism abnormality, hypertension, thrombosis, coronary artery disease, etc.) Including, but not limited to, a method of treating or preventing, or a method of treating or reducing inflammation, such as coronary plaque inflammation, said method comprising the non-toxic and non-toxic properties of one or more of the compounds set forth above Administration of a therapeutically effective amount to the animal.
本発明は、さらなる別の局面において、心血管疾患及びその根底となる症状(アテローム性動脈硬化症、高コレステロール血症、高脂質血症、脂質代謝異常、高血圧症、血栓症、冠動脈疾患などを含むがこれに限定されない)を治療し又は予防する方法、又は、冠動脈プラーク炎症などの炎症を治療し又は減らす方法を提供し、前期方法は上記に示された一つ以上の組成物の無毒性かつ治療有効量を動物へ投与することを含む。 In yet another aspect, the present invention relates to cardiovascular diseases and underlying symptoms (atherosclerosis, hypercholesterolemia, hyperlipidemia, lipid metabolism abnormality, hypertension, thrombosis, coronary artery disease, etc.) Including, but not limited to, methods of treating or preventing, or methods of treating or reducing inflammation, such as coronary plaque inflammation, wherein the prior methods are non-toxic of one or more of the compositions set forth above And administering a therapeutically effective amount to the animal.
更なる別の局面において、本発明は、一つ以上の本明細書に示された新規化合物の有効量又は治療量、並びに、薬剤的に許容される担体を含む医薬組成物に関する。さらなる局面において、本発明は、少なくとも一つのコレステロール生合成阻害剤の有効量又は治療量とともに、式i)−iv)の一つを有する少なくとも一つのコレステロール吸収阻害剤の有効量又は治療量、並びに、薬剤的に許容される担体を含む医薬組成物に関する。 In yet another aspect, the present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising an effective or therapeutic amount of one or more of the novel compounds presented herein, and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. In a further aspect, the present invention provides an effective amount or therapeutic amount of at least one cholesterol absorption inhibitor having one of formulas i) -iv) together with an effective amount or therapeutic amount of at least one cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitor, and And a pharmaceutical composition comprising a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier.
最終局面において、本発明は、1つの容器中に式i)−iv)の一つを有する少なくとも一つのコレステロール吸収阻害剤の有効量及び薬剤的に許容される担体、そして、別の容器中に少なくとも一つのコレステロール生合成阻害剤の有効量及び薬剤的に許容される担体、を含むキットを提供する。 In a final aspect, the present invention provides an effective amount of at least one cholesterol absorption inhibitor having one of formulas i) -iv) in one container and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, and in another container A kit comprising an effective amount of at least one cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitor and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier is provided.
本発明の最も重要な点は、ステロール及び/又はスタノールと、例えば好ましくはスタチンなどのコレステロール生合成阻害剤との供給及び同時投与である。これは二つの方法にて遂行し得る。
1)ステロール及び/又はスタノールが選択されたコレステロール生合成阻害剤と一体構
造で化学的に結合している新規化合物の形成による;並びに、
2)選択されたコレステロール吸収阻害剤(ステロール及び/又はスタノールエステル又は誘導体の形態にて)が選択されたコレステロール生合成阻害剤と混合している新規組成物の形成による。
The most important aspect of the present invention is the supply and co-administration of a sterol and / or stanol with a cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitor such as preferably a statin. This can be accomplished in two ways.
1) by formation of a novel compound in which sterols and / or stanols are chemically linked in a unitary structure with the selected cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitor; and
2) By formation of a novel composition in which the selected cholesterol absorption inhibitor (in the form of a sterol and / or stanol ester or derivative) is mixed with the selected cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitor.
コレステロール生合成阻害剤が、本明細書に説明される通り、ステロール/スタノール成分で誘導体化されるか、あるいは組成物中でステロール/スタノールと単に同時投与される場合、低投与量の選択されたコレステロール生合成阻害剤が望ましい効果を得るために要求され得ると考えられる。これは、たとえばある種のスタチンなどのある種のコレステロール生合成阻害剤における立証された不都合な副作用のために重要である。潜在的な副作用の減少はまた、患者のコンプライアンスの観点からも重要であるとみなされている。 If the cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitor is derivatized with a sterol / stanol component, as described herein, or simply co-administered with sterol / stanol in the composition, a low dosage is selected. It is believed that cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitors may be required to obtain the desired effect. This is important because of proven adverse side effects in certain cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitors such as certain statins. The reduction of potential side effects is also considered important from a patient compliance perspective.
本発明の幾つかの化合物(上記式(e)及び(f)並びにi)乃至iv)に表現されるもの)はアスコルビル部分を含む。これら特定の化合物は多くの有利点を有する。特に、水などの水溶液への溶解度はアスコルビル部分によって改善されており、そのためそれ自体の経口投与を可能にする。同様に、他の投与形態も容易にする。したがって、本発明のこれら選択された化合物はそのままそれ自体で製造され用いられるか、又は、組み込む医薬製剤が水性であるか否かに関わらずその医薬製剤へ容易に組み込むことができる。この増強された溶解度は、一般に、目的とする治療効果を得るために、低投与量の化合物を要すと解釈される。 Some compounds of the present invention (expressed in the above formulas (e) and (f) and i) to iv) contain an ascorbyl moiety. These particular compounds have many advantages. In particular, the solubility in aqueous solutions such as water is improved by the ascorbyl moiety, thus allowing its own oral administration. Similarly, other dosage forms are facilitated. Accordingly, these selected compounds of the present invention can be prepared and used as such or can be readily incorporated into the pharmaceutical formulation whether or not the pharmaceutical formulation to be incorporated is aqueous. This enhanced solubility is generally interpreted as requiring low doses of the compound to achieve the desired therapeutic effect.
これらの効果及び他の重要な有利点が以降に明らかになる。 These effects and other important advantages will become apparent hereinafter.
本発明は、以下の限定されない図により説明され、
図1はアスコルビル シトスタニル又はカンペスタニル アトルバスタチンリン酸エステル及びそのナトリウム塩の調製方法を示す概略図であり;
図2はアスコルビル シトスタニル又はカンペスタニル シンバスタチンリン酸エステル及びそのナトリウム塩の調製方法を示す概略図であり;
図3はシトスタニル又はカンペスタニル シンバスタチンリン酸エステルの調製方法を示す概略図であり;
図4はシトスタニル又はカンペスタニル アトルバスタチンカルボン酸エステルの調製方法を示す概略図である。
The invention is illustrated by the following non-limiting figures,
FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram showing a method for preparing ascorbyl sitostanyl or campestanyl atorvastatin phosphate and its sodium salt;
FIG. 2 is a schematic diagram illustrating a method for preparing ascorbyl sitostanyl or campestanil simvastatin phosphate and its sodium salt;
FIG. 3 is a schematic diagram showing a method for preparing cytostanyl or campestanyl simvastatin phosphate;
FIG. 4 is a schematic diagram showing a method for preparing cytostanyl or campestanyl atorvastatin carboxylic acid ester.
下記の詳細な説明は、本発明を実施するにあたり当業者を助けるために提供されている。しかしながら、この詳細な説明は、本発明の範囲を不当に限定するものと解釈されるべきではない。本明細書中で論じられている実施態様の改良及び変形は、本発明の精神及び範囲を離れることなく当業者により行われ得る。 The following detailed description is provided to assist those skilled in the art in practicing the present invention. However, this detailed description should not be construed to unduly limit the scope of the present invention. Modifications and variations of the embodiments discussed herein can be made by those skilled in the art without departing from the spirit and scope of the invention.
本明細書において、「動物」とは、全ての哺乳類を含み、最も好ましくはヒトである、動物界のどんな一員をも意味する。 As used herein, “animal” means any member of the animal kingdom, including all mammals, most preferably humans.
本明細書において、「プロドラッグ」という用語は薬剤前駆物質である化合物であって、患者への投与後、何らかの化学的又は生理学的なプロセス(例えば、生理学的なpHががもたらされるか、又は酵素反応によって、プロドラッグが目的とする薬剤形態へ変換される。)を介して体内で薬剤が放出される化合物を指す。 As used herein, the term “prodrug” is a compound that is a drug precursor that, after administration to a patient, results in some chemical or physiological process (eg, a physiological pH, or It refers to a compound in which the drug is released in the body via enzymatic reaction, which converts the prodrug into the desired drug form.
本明細書において、「溶媒和物」という用語は、溶媒の分子又はイオンと溶質(例えば、式a)乃至f)の化合物又は化合物a)乃至f)のプロドラッグ。)の分子又はイオンとからなる分子複合体又はイオン複合体を指す。限定されない有用な溶媒としては、水及び
/又はアルコール(例えばメタノール)などの極性、プロトン性溶媒がある。
As used herein, the term “solvate” refers to a solvent molecule or ion and a solute (eg, a compound of formula a) to f) or a prodrug of compounds a) to f). ) Molecule or ion complex. Non-limiting useful solvents include polar, protic solvents such as water and / or alcohol (eg methanol).
本明細書において、「化合物」という用語は「誘導体」「構造」及び「類似体」という用語と置き換え可能である。 In the present specification, the term “compound” can be replaced with the terms “derivative”, “structure” and “analog”.
本明細書において、「有効」又は「治療有効」という用語は、化合物(類)又は組成物を投与する人が求める細胞組織、システム、動物又は哺乳類における生物学的又は医学的反応を発現させるために、動物、特にヒトへ投与される前記化合物(類)又は組成物の量であって、一つ以上の以下の目的を達成する量を限定することを目的としている。
a)一般にCVDに関連し、動脈硬化、アテローム性動脈硬化、細動脈硬化、狭心症および血栓症などの一つ以上の症状を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
b)CVDに関連するリスク因子の一つ以上を減らし及び/又は排除すること、
c)アテローム性動脈硬化症を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
d)高コレステロール血症を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
e)高脂質症状を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
f)脂質代謝異常を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
g)高血圧症を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
h)冠動脈疾患を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
i)冠動脈プラーク発生を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
j)冠動脈プラーク炎症を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
k)血清LDLコレステロールを低下すること、
l)血清HDLコレステロールを増加すること、
m)血清トリグリセリド値を減少すること、
n)コレステロール生合成を減少すること、
o)脂質代謝異常状態又は障害を予防し、減らし、排除し、又は改善すること、
p)高コレステロール血症又は低アルファリポタンパク質血症を予防し、減らし、排除し、又は改善すること、
q)アテローム性病変またはプラークの発生を予防し、減らし、排除し、安定化させ、又は改善すること、
r)心血管疾患及び冠動脈疾患の発生に関連する炎症の発生を予防し、減らし、排除し、又は改善すること、
s)血清HDLの不足、若しくはLDL、VLDL、Lp(a)、ベータ−BLDL、IDL又は残留リポタンパク質の過剰をその基礎として有するか、又は、それらにより悪化する、あらゆる症状、疾患又は障害を予防し、減らし、排除し、又は改善すること、
t)発作のリスクを減少すること、
u)イソプレノイド合成を抑制すること、
v)アルツハイマー病を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
w)認知症を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
x)骨粗鬆症を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
y)酸化ストレスによる損傷を予防し、減らし、排除し、又は改善すること、
z)酸化からHDLの安定性を増強し及び/又は維持すること、
aa)酸化からLDL、VLDL、又はIDLの安定性を増強し及び/又は維持すること、
bb)酸化からトリグリセリド(TG)の安定性を増強し及び/又は維持すること、
cc)抗凝固特性を示すこと、
dd)抗増殖特性を示すこと、
ee)免疫調節特性を示すこと、
ff)血管由来特性を示すこと、
gg)腫瘍の成長を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
hh)骨質量及び/又は骨代謝を増加すること、及び、
ii)特に細胞又は分子レベルにおいて、スタチンの投与によって得られる非脂質関連の多面発現効果の何れかを増強すること。
As used herein, the term “effective” or “therapeutically effective” is used to develop a biological or medical response in a cellular tissue, system, animal or mammal sought by a person administering the compound (s) or composition. In addition, it is intended to limit the amount of the compound (s) or composition administered to an animal, particularly a human, that achieves one or more of the following objectives.
a) preventing, treating or alleviating one or more symptoms generally related to CVD, such as arteriosclerosis, atherosclerosis, arteriole sclerosis, angina and thrombosis,
b) reducing and / or eliminating one or more of the risk factors associated with CVD;
c) preventing, treating or reducing atherosclerosis,
d) preventing, treating or reducing hypercholesterolemia,
e) prevent, treat or alleviate high lipid symptoms;
f) preventing, treating or reducing lipid metabolism disorders;
g) preventing, treating or reducing hypertension,
h) preventing, treating or reducing coronary artery disease;
i) preventing, treating or reducing the occurrence of coronary plaque,
j) preventing, treating or reducing coronary plaque inflammation;
k) lowering serum LDL cholesterol,
l) increasing serum HDL cholesterol,
m) reducing serum triglyceride levels,
n) reducing cholesterol biosynthesis,
o) preventing, reducing, eliminating or ameliorating abnormal lipid metabolism conditions or disorders;
p) preventing, reducing, eliminating or ameliorating hypercholesterolemia or low alpha lipoproteinemia,
q) preventing, reducing, eliminating, stabilizing or ameliorating the development of atherosclerotic lesions or plaques;
r) preventing, reducing, eliminating or ameliorating the occurrence of inflammation associated with the occurrence of cardiovascular and coronary artery disease;
s) Prevent any symptoms, diseases or disorders that have or are exacerbated by a lack of serum HDL or LDL, VLDL, Lp (a), beta-BLDL, IDL or excess of residual lipoproteins Reduce, eliminate or improve,
t) reducing the risk of seizures,
u) inhibiting isoprenoid synthesis;
v) preventing, treating or reducing Alzheimer's disease;
w) prevent, treat or alleviate dementia;
x) preventing, treating or reducing osteoporosis,
y) prevent, reduce, eliminate or ameliorate oxidative stress damage;
z) enhance and / or maintain the stability of HDL from oxidation,
aa) enhancing and / or maintaining the stability of LDL, VLDL, or IDL from oxidation,
bb) enhancing and / or maintaining the stability of triglycerides (TG) from oxidation;
cc) exhibit anticoagulant properties;
dd) exhibit anti-proliferative properties;
ee) exhibiting immunomodulatory properties;
ff) exhibiting blood vessel-derived properties;
gg) preventing, treating or reducing tumor growth;
hh) increasing bone mass and / or bone metabolism; and
ii) enhance any of the non-lipid related pleiotropic effects obtained by administration of statins, especially at the cellular or molecular level.
本明細書において、「スタチン」という用語はHMG CoAレダクターゼ上の基質結合部位を得るために3−ヒドロキシ−3−メチルグルタン酸と競うことによって3−ヒドロキシ−3−メチルグルタリル コエンザイムA レダクターゼを抑制する、いずれの天然又は合成化合物も含む。 As used herein, the term “statin” inhibits 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase by competing with 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutanic acid to obtain a substrate binding site on HMG CoA reductase. , Including any natural or synthetic compound.
本明細書において、「ステロール」という用語は、限定無く全てのステロールが含まれ、例えば、(任意の供給源から及び任意の形態(α、β及びγ)で)シトステロール、カンペステロール、スチグマステロール、ブラシカステロール(ジヒドロブラシカステロールを含む)、デスモステロール、カリノステロール、ポリフェラステロール、クリオナステロール、エルゴステロール、コプロステロール、コジステロール、イソフコステロール、フコステロール、クレロステロール、ネルビステロール、ラトステロール、ステラステロール、スピナステロール、コンドリラステロール、ペポステロール、アベナステロール、イソアベナステロール、フェコステロール、ポリナスタステロール、コレステロール及びそれらの全ての天然又は合成形態及び誘導体(異性体を含む)である。 As used herein, the term “sterol” includes, without limitation, all sterols, eg, sitosterol, campesterol, stigmasterol (from any source and in any form (α, β and γ)). , Brush castrol (including dihydrobrass castrol), desmosterol, carinosterol, polyferasterol, cryoasterol, ergosterol, coprosterol, kodisosterol, isofucosterol, fucostosterol, clerolosterol, nervisterol, latosterol, stella Sterols, spinasterols, chondrasterols, pepostols, abenasterols, isoavenasterols, fecostosterols, polynassterols, cholesterol and all natural or synthetic forms thereof And a derivative (including isomers).
「スタノール」という用語は、例えば:(任意の供給源から及び任意の形態(α、β及びγ)で)全ての天然又は合成形態及びそれらの誘導体及び異性体を含む飽和又は水素化ステロール類、例えばシトスタノール、カンペスタノール、スチグマスタノール、ブラシカスタノール(ジヒドロブラシカスタノールを含む)、デスモスタノール、カリノスタノール、ポリフェラスタノール、クリオナスタノール、エルゴスタノール、コプロスタノール、コジスタノール、イソフコスタノール、フコスタノール、クリロスタノール、ネルビスタノール、ラトスタノール、ステラスタノール、スピナスタノール、コンドリラスタノール、ペポスタノール、アベナスタノール、イソアベナスタノール、フェコスタノール及びポリナスタノールを指す。 The term “stanol” means, for example: saturated or hydrogenated sterols, including all natural or synthetic forms and derivatives and isomers thereof (from any source and in any form (α, β and γ)) For example, sitostanol, campestanol, stigmasteranol, brush castanol (including dihydrobrush castanol), desmostanol, carinostanol, polyferrastanol, cliostananol, ergostanol, coprostanol, codistanol, isofucostanol, fucostanol, crilo Refers to stanol, nervistanol, latostanol, stellastanol, spinastanol, chondrastanol, pepostanol, abenastanol, isoavenastanol, fecostanol and polynastanol.
ステロール及びスタノールの変更、すなわち、側鎖を含むこともまた本発明の範囲に含まれることが理解される。明細書全体に渡って判別がつかず、そして特に規定がなければ、「ステロール」という用語はステロール及びスタノールの双方を包含する。「フィトステロール」及び「フィトスタノール」という用語もまた使用され得、それぞれ植物由来のステロール又はスタノールを指す。 It is understood that modifications of sterols and stanols, ie including side chains, are also within the scope of the present invention. Unless otherwise specified throughout the specification and unless otherwise specified, the term “sterol” encompasses both sterols and stanols. The terms “phytosterol” and “phytostanol” may also be used, referring to plant-derived sterols or stanols, respectively.
本発明による誘導体の形成に使用するステロール及びスタノールは、様々な天然源から入手され得、あるいは、それらは人工的に合成され得る。例えば、それらは、コーン油及び他の植物油、小麦胚種油、大豆抽出、米抽出、米ぬか、菜種油、ひまわり油、ごま油などの植物油(水生植物を含む)並びに魚(及び他の海洋原料)油の加工から得られ得る。それらはまた、酵母やエルゴステロールなどの菌類に由来し得る。したがって、本発明は、特定のステロール源に限定されない。米国特許第4,420,427号明細書は、メタノールなどの溶媒を用いた植物油汚泥からのステロール製造法を教える。また、フィトステロール及びフィトスタノールは、参照することにより本明細書に組み込まれる、米国特許第5,770,749号明細書に記載されたように林業業務の副生産物であるトール油ピッチ又は石鹸から得られ得る。トール油ピッチからステロール及びスタノールを抽出するさらなる方法は、1998年2月20日に出願されたカナダ国特許出願第2,230,373号明細書(1999年2月19日に出願された国際出願第CA99/00140号に対応)、及び、2002年1月28日に出願された米国特許出願第10/060,022号明細書に記載され、それらの内容の全てが参照することにより本明細書に組み込まれる。 The sterols and stanols used to form the derivatives according to the invention can be obtained from a variety of natural sources or they can be artificially synthesized. For example, they include corn oil and other vegetable oils, wheat germ oil, soybean extract, rice extract, rice bran, rapeseed oil, sunflower oil, sesame oil and other vegetable oils (including aquatic plants) and fish (and other marine raw materials) oils Can be obtained from the following processing. They can also be derived from fungi such as yeast and ergosterol. Thus, the present invention is not limited to a particular sterol source. U.S. Pat. No. 4,420,427 teaches a method for producing sterols from vegetable oil sludge using a solvent such as methanol. Also, phytosterols and phytostanols are derived from tall oil pitch or soap, which is a by-product of forestry operations, as described in US Pat. No. 5,770,749, incorporated herein by reference. Can be obtained. A further method for extracting sterols and stanols from tall oil pitch is described in Canadian Patent Application No. 2,230,373 filed Feb. 20, 1998 (international application filed Feb. 19, 1999). No. 10 / 060,022 filed on Jan. 28, 2002, the entire contents of which are hereby incorporated herein by reference. Incorporated into.
したがって、遊離ステロール及びスタノール、脂肪酸又は芳香族酸とのエステル化ステロール及びスタノール(その結果、それぞれ脂肪酸エステル又は芳香族酸エステルを形成する)、フェノール酸エステル、ケイ皮酸エステル、フェルラートエステル、フィトステロール及びフィトスタノールグリコシド及びアシル化グリコシド又はアシルグリコシドを含むがこれに限定されない、最大限に可能な定義が、本明細書において「ステロール」及び「スタノール」という用語に与えられることが理解される。それゆえ、「ステロール」及び「スタノール」という用語は、あらゆる類似体を包含し、それらは、多くの天然ステロールのように環状ユニット中の5番目の位置に二重結合をさらに有し得、又は環の他の位置(例えば6,7,8(9),8(14),14 5/7など)に一つ以上の二重結合を有し得、又はスタノールのように環状ユニット中に二重結合を有さなくても良い。さらに、たとえばα1−シトステロールのように更なるメチル基が存在し得る。 Thus, free sterols and stanols, esterified sterols and stanols with fatty acids or aromatic acids (resulting in the formation of fatty acid esters or aromatic acid esters, respectively), phenolic acid esters, cinnamic acid esters, ferrate esters, phytosterols and It is understood that the maximum possible definitions, including but not limited to phytostanol glycosides and acylated glycosides or acyl glycosides, are given herein for the terms “sterol” and “stanol”. Thus, the terms “sterol” and “stanol” encompass all analogs, which may further have a double bond at the fifth position in the cyclic unit, like many natural sterols, or It may have one or more double bonds at other positions in the ring (eg 6, 7, 8 (9), 8 (14), 14 5/7, etc.), or two in a cyclic unit like stanol It is not necessary to have a double bond. In addition, further methyl groups can be present, for example α 1 -sitosterol.
コレステロール生合成阻害剤
本発明の範囲内、並びに本明細書において、「コレステロール生合成阻害剤」という用語は、どんなメカニズムを用いてでもあれ体内コレステロール生成への悪影響を有するいずれの化合物をも示す。前記化合物の限定されない例としては、1)3−ヒドロキシ−3−メチルグルタリルコエンザイムA還元酵素「HMG CoAレダクターゼ」、2)3−ヒドロキシ−3−メチルグルタリルコエンザイムA合成酵素「HMG CoAシンターゼ」、3)スクアレンシンターゼ、及び4)スクアレンエポキシダーゼの拮抗阻害剤などがある。
Cholesterol Biosynthesis Inhibitor Within the scope of the present invention, and herein, the term “cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitor” refers to any compound that has an adverse effect on body cholesterol production, whatever the mechanism. Non-limiting examples of such compounds include 1) 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase “HMG CoA reductase”, 2) 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A synthase “HMG CoA synthase” 3) squalene synthase, and 4) competitive inhibitors of squalene epoxidase.
HMG CoAレダクターゼ阻害剤はより一般的には「スタチン」として知られている。これら薬剤は冠動脈疾患の第一次及び第二次予防のために使用されてきた。HMG CoAレダクターゼは、コレステロール生合成経路における鍵酵素である。スタチンは肝臓コレステロール生合成を減少させ(循環コレステロールの約50%が主にLDLコレステロールとして内因的に合成されている)、代わってLDLレセプターの生成を増加させることにより、血漿総コレステロール及びLDLコレステロールを減少させる。薬剤及び用量に応じて、スタチンは血清トリグリセリド値をもまた減少させ得、血清HDLを増加させ得る。スタチンはLDLコレステロール低下の標準的な治療法になっている。 HMG CoA reductase inhibitors are more commonly known as “statins”. These drugs have been used for primary and secondary prevention of coronary artery disease. HMG CoA reductase is a key enzyme in the cholesterol biosynthesis pathway. Statins reduce plasma total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol by reducing hepatic cholesterol biosynthesis (about 50% of circulating cholesterol is synthesized primarily endogenously as LDL cholesterol) and instead increasing production of LDL receptors. Decrease. Depending on the drug and dose, statins can also decrease serum triglyceride levels and increase serum HDL. Statins have become the standard treatment for lowering LDL cholesterol.
消化不良、腹痛及び腸内ガス充満は、スタチン投与の最も一般的な副作用である。スタチンの最も重篤な副作用は血清トランスアミナーゼ値の上昇と筋炎の発生である。 Indigestion, abdominal pain and intestinal gas filling are the most common side effects of statin administration. The most serious side effects of statins are elevated serum transaminase levels and the development of myositis.
筋毒性は高用量におけるあらゆるスタチンの共通作用である。そのメカニズムはミトコンドリアの酸化的損傷であるようにみられる。スタチンは乳酸塩/ピルビン酸塩値の降下を引き起こす。乳酸塩/ピルビン酸塩比率はミトコンドリア機能異常と酸化状態の高感度の指標である。スタチンは、エネルギー生産に必要な必須補因子、すなわちコエンザイムQを激減させることが臨床研究で示されてきた。コエンザイムQの減少は用量依存性である。
コエンザイムQは、酸化過程に由来するエネルギーを供給するミトコンドリア電子輸送プロセスの不可欠な部分である。スタチンはHMG CoAレダクターゼ触媒過程にてコレステロール合成を阻止して機能する。
Coenzyme Q is an integral part of the mitochondrial electron transport process that supplies energy from the oxidation process. Statins function by blocking cholesterol synthesis in the catalytic process of HMG CoA reductase.
メバロネートは、一連の酵素段階を経て、コレステロールを合成するために使用される。メバロネートはまたコエンザイムQの前駆体である。それゆえ、コレステロール合成の抑
制はコエンザイムQ合成を抑制する。高いエネルギー必要量を有する筋細胞がスタチンによる損傷に対して最も影響を受けやすいのと同時に、肝細胞もまた損傷が生じやすい。後者はおそらく、主要な血液供給が肝門脈系からである、小葉中心性肝細胞の相対的な低酸素状態の結果である。筋肉損傷の最も重篤な病態は、筋細胞含有物が体循環に放出される時に起こる(横紋筋融解)。重大な合併症としては急性心不全及び心異常がある。心毒性は心筋コエンザイムQ値におけるスタチンの直接の作用であり得る。
Mevalonate is used to synthesize cholesterol through a series of enzymatic steps. Mevalonate is also a precursor of coenzyme Q. Therefore, inhibition of cholesterol synthesis suppresses coenzyme Q synthesis. At the same time muscle cells with high energy requirements are most susceptible to damage by statins, hepatocytes are also susceptible to damage. The latter is probably the result of the relative hypoxic state of centrilobular hepatocytes, where the main blood supply is from the hepatic portal system. The most serious condition of muscle damage occurs when muscle cell contents are released into the systemic circulation (rhabdomyolysis). Serious complications include acute heart failure and heart abnormalities. Cardiotoxicity can be a direct effect of statins on myocardial coenzyme Q values.
これら悪影響は、スタチンと、アゾール系抗真菌剤、シメチジン(cimetadine)及びメトトレキセートなどの、シトクロームP450システムを抑制する他の薬剤とを併用するときに起こることが多い。スタチン関連性筋炎のリスクは、ゲムフィブロジル、ニコチン酸又はマクロライドを服用している患者において増加する。 These adverse effects often occur in combination with statins and other drugs that suppress the cytochrome P450 system, such as azole antifungals, cimetadine and methotrexate. The risk of statin-related myositis is increased in patients taking gemfibrozil, nicotinic acid or macrolides.
スタチン適応症が報告された文献は広く知られている。 The literature reporting statin indications is widely known.
薬物間相互作用の可能性がたとえないとしても、筋肉におけるスタチンの主要な副作用は、患者に対して前記薬物治療を続けることの重要な阻害要因となる。筋毒性は用量依存性であるため、少ないスタチン用量の使用を可能にし、なおもターゲットLDLコレステロール値を達成できるいずれの補助的療法も非常に望ましい。よって、同時に副作用のリスクを増加させることなしに、LDLコレステロールのさらなる低下をもたらすためにスタチンと共に付加的に働き得る、本発明の範囲内の化合物及び組成物に対する独自市場がある。 Even if there is no possibility of drug-drug interactions, the major side effects of statins in muscle are important inhibitors of continuing the drug treatment for patients. Since myotoxicity is dose dependent, any adjunct therapy that allows the use of small statin doses and still achieves target LDL cholesterol levels is highly desirable. Thus, there is a unique market for compounds and compositions within the scope of the present invention that can additionally work with statins to provide further reductions in LDL cholesterol without simultaneously increasing the risk of side effects.
以下のリストは、本発明による好ましいスタチン類及びそれらの参照特許を含み、本明細書に示したように、該参照文献は参照することにより本明細書に完全に組み込まれる。
以下のリストは幾つかの好ましいスタチンの化学式を説明する。
ロバスタチン: [1S[1a(R)3アルファ、7ベータ、8ベータ(2S、4S)、8aベータ]]1,2,3,7,8,8a−ヘキサヒドロ−3,7−ジメチル−8−[2−(テトラヒドロ−4−ヒドロキシ−6−オキソ−2H−ピラン−2−イル)エチル]−1−ナフタレニル−2−メチルブタノエート。
プラバスタチンナトリウム:1−ナフタレン−ヘプタン酸,1,2,6,7,8a−ヘキサヒドロ−ベータ,δ,6−トリヒドロキシ−2−メチル−8−(2−エチル−1−オキシブトキシ)−1−モノナトリウム塩[1S−[1アルファ(ベータs,δ,S),2アルファ,6アルファ,8ベータ(R),8aアルファ。
シンバスタチン:ブタン酸,2,2ジメチル−1,2,3,7,8,8a−ヘキサヒドロ−3,7−ジメチル−8−[2−(テトラヒドロ−4−ヒドロキシ−6−オキソ−2H−ピラン−2−イル)エチル]−1−ナフタレニルエステル[1S−[1アルファ,3アルファ,7ベータ,8ベータ,(2S,4S),−8aベータ。
フルバスタチンナトリウム:[R,S(E)]−(+/−)−7−[3(4−フルオロフェニル)−1−(1メチルエチル)−1H−インドール−2−イル]−3,5−ジヒドロキシ−6−ヘプテン酸,モノナトリウム塩。
The following list illustrates some preferred statin formulas.
Lovastatin: [1S [1a (R) 3alpha, 7beta, 8beta (2S, 4S), 8abeta]] 1,2,3,7,8,8a-hexahydro-3,7-dimethyl-8- [ 2- (Tetrahydro-4-hydroxy-6-oxo-2H-pyran-2-yl) ethyl] -1-naphthalenyl-2-methylbutanoate.
Pravastatin sodium: 1-naphthalene-heptanoic acid, 1,2,6,7,8a-hexahydro-beta, δ, 6-trihydroxy-2-methyl-8- (2-ethyl-1-oxybutoxy) -1- Monosodium salt [1S- [1alpha (betas, δ, S), 2alpha, 6alpha, 8beta (R), 8aalpha.
Simvastatin: butanoic acid, 2,2dimethyl-1,2,3,7,8,8a-hexahydro-3,7-dimethyl-8- [2- (tetrahydro-4-hydroxy-6-oxo-2H-pyran- 2-yl) ethyl] -1-naphthalenyl ester [1S- [1alpha, 3alpha, 7beta, 8beta, (2S, 4S),-8abeta.
Fluvastatin sodium: [R, S (E)]-(+/−)-7- [3 (4-fluorophenyl) -1- (1 methylethyl) -1H-indol-2-yl] -3,5 -Dihydroxy-6-heptenoic acid, monosodium salt.
本発明は前述のスタチンのみに限られるとみなされるべきではない。天然由来のスタチンはピシウム・ウルティマム、モナクス・ラバー、ペニシリウム・シトリヌム、ペニシルム・ブレビコンパクタム及びアスペルギルス・テレウスから単離された菌類代謝産物(ML
−236B/コンパクチン/モノカリン K)の誘導体であるが、先に示されたように、これらは合成的にもまた製造され得る。スタチン誘導体は文献中で周知であり、米国特許第4,397,786号明細書に開示された方法で製造され得る。現在、別の方法が当技術分野で周知である。
The present invention should not be regarded as limited to the aforementioned statins alone. Naturally derived statins are fungal metabolites (ML) isolated from Psium Ultimum, Monax rubber, Penicillium citrinum, Penicillum brevicompactum and Aspergillus tereus
-236B / compactin / monocalin K), but as indicated above, they can also be produced synthetically. Statin derivatives are well known in the literature and can be prepared by the methods disclosed in US Pat. No. 4,397,786. Currently, other methods are well known in the art.
本発明に使用する最も好ましいスタチンの構造は以下のとおりである。
スクアレンシンターゼ阻害剤はスクアレンシンターゼの活性を減少させ、それゆえ、ファルネシルピロリン酸塩のスクアレンへの変換を抑制する。スクアレンシンターゼ阻害剤は、
1)スクアレンシンターゼの活性化に関与する一種以上の酵素又は補因子の活性を減少させること
2)スクアレンシンターゼのダウンレギュレーションに関与する一種以上の酵素又は補因子の活性を増加させること
によって、スクアレンシンターゼに直接的に又は間接的に作用し得る。
Squalene synthase inhibitors decrease the activity of squalene synthase and thus inhibit the conversion of farnesyl pyrophosphate to squalene. Squalene synthase inhibitors
1) reducing the activity of one or more enzymes or cofactors involved in the activation of squalene synthase 2) increasing the activity of one or more enzymes or cofactors involved in the down-regulation of squalene synthase, thereby increasing the activity of squalene synthase Can act directly or indirectly.
好適なスクアレンシンターゼ阻害剤としては、イソプレノイド(ホスフィニル−メチル)ホスホン酸塩などの米国特許第5,712,396号明細書に開示されたα−フォスフォノ−スルホネート及び、例えば米国特許4,871,721号明細書に開示されたテルペノイドピロリン酸塩、ファルネシルジリン酸塩類似体A及びプレスクアレンピロリン酸塩類似体などの他の既知のスクアレンシンターゼ阻害剤もまた含まれるが、これらに限らない。 Suitable squalene synthase inhibitors include α-phosphono-sulfonates disclosed in US Pat. No. 5,712,396, such as isoprenoid (phosphinyl-methyl) phosphonates, and, for example, US Pat. No. 4,871,721. Other known squalene synthase inhibitors such as, but not limited to, terpenoid pyrophosphates, farnesyl diphosphate analog A and presqualene pyrophosphate analogs disclosed in US Pat.
好ましくは、本発明の使用のために、コレステロール生合成阻害剤は、ロバスタチン(例えばメルク社から入手可能なメバコール(登録商標:MEVACOR))、プラバスタチン(例えばブリストル・マイヤーズ・スクイブ社から入手可能なプラバコール(登録商標:PRAVACHOL))、フルバスタチン、シンバスタチン(例えばメルク社から入手可能なゾコール(登録商標:ZOCOL))、アトルバスタチン、セリバスタチン、CI−981及びピタバスタチン(ネグマ・コーワ・オブ・ジャパン社のNK−104など)からなる群から選択されるHMG CoAレダクターゼ阻害剤;HMG CoAシンターゼ阻害剤、例えばL−659,699((E,E)−11−[3R’−(ヒドロキシル−メチル)−4’−オキソ−2’R−オキセタニル]−3,5,7R−トリメチル−2,4−ウンデカジエン酸)など;スクアレン合成阻害剤、例えばスクアレスタチン1など;及びスクアレンエポキシダーゼ阻害剤、例えばNB−598((E)−N−エチル−N−(6,6−ジメチル−2−ヘプテン−4−イニル)−3−[(3,3’−ビチオフェン5−イル)メトキシ]ベンゼン−メタンアミン ヒドロクロリド)など;からなる群から選択される。 Preferably, for use in the present invention, the cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitor is lovastatin (eg, Mevacor® available from Merck), pravastatin (eg, Pravacol available from Bristol-Myers Squibb) (Registered trademark: PRAVACHOL)), fluvastatin, simvastatin (for example, zocor (registered trademark: ZOCOL) available from Merck), atorvastatin, cerivastatin, CI-981 and pitavastatin (Negma Kowa of Japan NK- HMG CoA reductase inhibitor selected from the group consisting of: HMG CoA synthase inhibitors such as L-659,699 ((E, E) -11- [3R ′-(hydroxyl-methyl) -4′- Oxo-2 ' R-oxetanyl] -3,5,7R-trimethyl-2,4-undecadienoic acid) and the like; squalene synthesis inhibitors such as squalesatin 1; and squalene epoxidase inhibitors such as NB-598 ((E)- N-ethyl-N- (6,6-dimethyl-2-hepten-4-ynyl) -3-[(3,3′-bithiophen5-yl) methoxy] benzene-methanamine hydrochloride) and the like Selected.
化合物
本発明の化合物はステロール又はスタノール部分、及び、以下の式の一つ以上で表されるコレステロール生合成阻害剤部分を含む。
反応性カルボキシル基を有するコレステロール生合成阻害剤を表し;R3は少なくとも一
つの遊離性及び反応性水酸基を有するコレステロール生合成阻害剤を表し;R4はアスコ
ルビン酸に由来し、Xは水素原子であるか、又は、金属、アルカリ土類金属及びアルカリ金属からなる群から選択され、並びに、nは1−5を表す。)本発明の範囲にある化合物は、全ての生物学的に許容される塩又は溶媒和物、又は少なくとも一つの前記化合物の又はそれらの塩の又はそれらの溶媒和物のプロドラッグを含む。
Compounds The compounds of the present invention comprise a sterol or stanol moiety and a cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitor moiety represented by one or more of the following formulae.
前記化合物の好ましい形態において、コレステロール生合成阻害剤、R2及びR3は、HMG CoAレダクターゼ拮抗阻害剤、HMG CoAシンターゼ拮抗阻害剤、スクアレンシンターゼ拮抗阻害剤及びスクアレンエポキシダーゼ拮抗阻害剤からなる群から選択される。本発明のさらに好ましい実施態様において、R2はアトルバスタチン又はプラバスタ
チンナトリウムのいずれか一方である。さらに好ましい実施態様において、R3はシンバ
スタチン又はロバスタチンのいずれか一方である。
In a preferred form of the compound, the cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitor, R 2 and R 3 are selected from the group consisting of HMG CoA reductase antagonist, HMG CoA synthase antagonist, squalene synthase antagonist and squalene epoxidase antagonist. Selected. In a further preferred embodiment of the invention, R 2 is either atorvastatin or pravastatin sodium. In a further preferred embodiment, R 3 is either simvastatin or lovastatin.
注意しておくことは、化合物a)、b)、c)及びe)の形成は、少なくとも一つの遊離性及び反応性カルボキシル基を有するコレステロール生合成阻害剤を選択することによってのみ達成できるということである。同様に化合物d)及びf)の形成は、少なくとも一つの遊離性及び反応性水酸基を有するコレステロール生合成阻害剤を選択することによってのみ達成できる。これに基づき、適切なコレステロール生合成阻害剤が選択される必要があるが、そうすることは化学の学生であってさえ完全にその活動範囲内にある。 It should be noted that the formation of compounds a), b), c) and e) can only be achieved by selecting cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitors having at least one free and reactive carboxyl group. It is. Similarly, the formation of compounds d) and f) can only be achieved by selecting cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitors having at least one free and reactive hydroxyl group. Based on this, appropriate cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitors need to be selected, but doing so is completely within the scope of its activity, even for chemistry students.
本発明の最も好ましい局面において、ステロール及び/又はスタノール部分、及び選択されたコレステロール生合成阻害剤の間に形成された化合物は下記からなる群から選択される。 In the most preferred aspect of the invention, the compound formed between the sterol and / or stanol moiety and the selected cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitor is selected from the group consisting of:
化合物1:アスコルビルフィトスタニルアトルバスタチンリン酸エステルナトリウム
化合物2:アスコルビルフィトスタニルプラバスタチンリン酸エステル二ナトリウム
化合物3:アスコルビルフィトスタニルシンバスタチンリン酸エステルナトリウム
化合物4:アスコルビルフィトスタニルロバスタチンリン酸エステル二ナトリウム
化合物5:シトスタノール−シンバスタチンリン酸エステル
化合物6:シトスタノール(又はカンペスタノール)ロバスタチンリン酸エステルナトリウム塩
化合物7:シトスタノールアトルバスタチンエステル
化合物8:シトスタノールプラバスタチンエステル
所望により、本発明の化合物は天然由来又は人工的に合成されたベータ−シトステロール、カンペスタノール、シトスタノール及びカンペステロールで形成され、そのように形成されたこれら化合物の各々は、デリバリーに先立ち、様々な割合で医薬組成物中に混合される。最も好ましい形態において、本発明の化合物は、二つの主要成分:アスコルビルカンペスタニルリン酸二ナトリウム(「DACP」)とアスコルビルシトスタニルリン酸二ナトリウム(「DASP」)を含む、一つ以上のアスコルビルフィトスタニルリン酸二ナトリウム(「FM−VP4」として本明細書に示される)の間に化学結合を含む。 If desired, the compounds of the present invention are formed with naturally-occurring or artificially synthesized beta-sitosterol, campestanol, sitostanol and campesterol, and each of these so-formed compounds may be modified prior to delivery. Mixed in the pharmaceutical composition in a small proportion. In the most preferred form, the compound of the present invention comprises one or more ascorbyl phytoides comprising two major components: ascorbylcampestanyl disodium phosphate (“DACP”) and ascorbyl sitostanil disodium phosphate (“DASP”). A chemical bond is included between stannyl phosphate disodium (denoted herein as “FM-VP4”).
塩類
本明細書において、「生物学的に許容される塩」という用語は、本明細書に説明された化合物の望ましい生物学的及び/又は生理学的活性を保有し、わずかな好ましくない毒性効
果しか示さない、いずれの塩をも指す。したがって、式a)からf)の化合物への参照は、無機及び/又は有機酸及び塩基と共に形成されたそれらの酸性及び/又は塩基性塩への参照を含む。
Salts As used herein, the term “biologically acceptable salt” refers to the desirable biological and / or physiological activity of the compounds described herein, with only minor undesirable toxic effects. Refers to any salt not shown. Thus, references to compounds of formula a) to f) include references to their acidic and / or basic salts formed with inorganic and / or organic acids and bases.
典型的な酸付加塩としてはアセテート(例えば酢酸又はトリフルオロ(trifluro)酢酸などのトリハロ酢酸と形成されたもの)、アジペート、アルギネート、アスコルベート、アスパルテート、ベンゾエート、ベンゼンスルホネート、ビスルフェート、ボレート、ブチレート、シトレート、カンホレート、カンファースルホネート、シクロペンタンプロピオネート、ジグルコネート、ドデシルスルホネート、ヘプタノエート、ヘキサノエート、ヒドロクロリドシロブロミド、ヒドロアイオダイド、2−ヒドロエタンスルホネート、ラクテート、マレート、メタンスルホネート、2−ナフタレンスルホネート、ニコチネート、ニトレート、オキサレート、ペクチネート、パースルホネート、3−フェニルプロピロネート、ホスフェート、ピクレート、ピバレート、プロピオネート、サリチレート、スクシネート、スルフェート、スルフォネート、タートレート、チオシアネート、トルエンスルホネート、ウンデカノエートなどがある。 Typical acid addition salts include acetate (eg, formed with acetic acid or trihaloacetic acid such as trifluroacetic acid), adipate, alginate, ascorbate, aspartate, benzoate, benzenesulfonate, bisulphate, borate, butyrate Citrate, camphorate, camphorsulfonate, cyclopentanepropionate, digluconate, dodecylsulfonate, heptanoate, hexanoate, hydrochloride silobromide, hydroiodide, 2-hydroethanesulfonate, lactate, malate, methanesulfonate, 2-naphthalenesulfonate, Nicotinate, Nitrate, Oxalate, Pectinate, Persulfonate, 3-Phenylpropyronate, Phosphate, Piclay There pivalate, propionate, salicylate, succinate, sulfate, sulfonate, tartrate, thiocyanate, toluenesulfonate, and the like undecanoate.
酸部分を含むこれら化合物は、様々な有機塩基及び無機塩基と塩を形成し得る。 These compounds containing an acid moiety can form salts with various organic and inorganic bases.
したがって、本発明は、ステロール及び/又はスタノール並びにコレステロール生合成阻害剤を含む親化合物を包含するだけでなく、可能であれば(すなわち、親化合物が遊離水酸基を含めば)、本発明は開示された化合物の生物学的に許容される金属、アルカリ土類金属又はアルカリ金属塩をも包含する。 Thus, the present invention not only encompasses the parent compound comprising a sterol and / or stanol and a cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitor, but if possible (ie, the parent compound includes a free hydroxyl group), the present invention is disclosed. Also included are biologically acceptable metals, alkaline earth metals or alkali metal salts of such compounds.
本明細書に説明される塩類は、対応する親化合物よりはるかに水溶性であり、それゆえ、生体外及び生体内の双方におけるそれらの有効性及び評価が増強され得る。 The salts described herein are much more water soluble than the corresponding parent compound, and therefore their effectiveness and evaluation both in vitro and in vivo can be enhanced.
本発明の化合物の塩形成は、例えば、一連の塩基(例えばナトリウムメトキシド又は他の金属アルコキシドなど)で遊離OH基を含むいずれかの親化合物を処置することによって容易に実行可能であり、対応するアルカリ金属塩が生成する。カルシウム、マグネシウム、マンガン、銅、亜鉛などの他の金属塩は、親化合物を適切な金属アルコキシドと反応させることによって生成され得る。 Salt formation of the compounds of the present invention can be readily performed, for example, by treating any parent compound containing a free OH group with a series of bases such as sodium methoxide or other metal alkoxides. An alkali metal salt is formed. Other metal salts such as calcium, magnesium, manganese, copper, zinc, etc. can be generated by reacting the parent compound with a suitable metal alkoxide.
化合物の形成
ステロール及び/又はスタノール並びに選択されたコレステロール生合成阻害剤からなる新規化合物が形成され得る多くのプロセスがある。あるプロセスにおいて、そこではコレステロール生合成阻害剤は少なくとも一つの遊離性及び反応性カルボキシル基を有すが、選択されたステロール又はスタノール(又はそれらのハロホスフェート、ハロカーボネート、又はハロ−オキサレート誘導体)並びにコレステロール生合成阻害剤が、「酸」部分と「アルコール」(フィトステロール)との縮合を可能にする反応条件下で一緒に混合される。これらの条件は、酸成分から形成された酸クロリドとアルコール成分が直接又は、鉱酸、硫酸、リン酸、p−トルエンスルホン酸などの適切な酸触媒の存在で反応することができるような、他の一般的なエステル化反応にて使用されるものと同様である。前記エステル化反応に一般的に用いられる有機溶媒は、ジエチルエーテル、テトラヒドロフランなどのエーテル、又はベンゼン、トルエン又は類似の芳香族系溶媒であり、反応を起こす反応物質の反応性によって温度は室温から高温まで様々であり得る。
Compound Formation There are many processes by which new compounds consisting of sterols and / or stanols and selected cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitors can be formed. In some processes, where cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitors have at least one free and reactive carboxyl group, but are selected sterols or stanols (or their halophosphates, halocarbonates, or halo-oxalate derivatives) and Cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitors are mixed together under reaction conditions that allow condensation of the “acid” moiety with the “alcohol” (phytosterol). These conditions are such that the acid chloride formed from the acid component and the alcohol component can react directly or in the presence of a suitable acid catalyst such as mineral acid, sulfuric acid, phosphoric acid, p-toluenesulfonic acid, etc. This is the same as that used in other general esterification reactions. The organic solvent generally used in the esterification reaction is an ether such as diethyl ether or tetrahydrofuran, or benzene, toluene or a similar aromatic solvent, and the temperature is increased from room temperature to a high temperature depending on the reactivity of the reactant that causes the reaction. Can vary.
別の好ましい実施態様において、エステル誘導体を形成するプロセスは、エステル(例えば酢酸エステルなど)又はエーテル(例えばメチエルエーテル)としてコレステロール生合成阻害剤の水酸基を「保護すること」、そしてそれから保護されたコレステロール生合成阻害剤を、適切な反応条件下で、反応性ステロール/スタノール(又はそれらのハロホ
スフェート、ハロカーボネート又はハロ−オキサレート)と縮合させることを含む。一般に、前記縮合反応はジエチルエーテル、テトラヒドロフラン、又はベンゼン、トルエン又は類似の芳香族系溶媒などの有機溶媒中で行われる。反応物質の種類及び反応性に応じて、反応温度は低温(−15度)から高温まで様々であり得る。
In another preferred embodiment, the process of forming the ester derivative comprises “protecting” the hydroxyl group of the cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitor as an ester (eg, acetate ester) or an ether (eg, methyl ether), and then protected cholesterol Condensing the biosynthesis inhibitor with a reactive sterol / stanol (or their halophosphate, halocarbonate or halo-oxalate) under appropriate reaction conditions. In general, the condensation reaction is carried out in an organic solvent such as diethyl ether, tetrahydrofuran, or benzene, toluene or similar aromatic solvents. Depending on the type and reactivity of the reactants, the reaction temperature can vary from low temperature (-15 degrees) to high temperature.
限定されない例として、図1はアルコルビルシトスタニル又はカンペスタニルアトバスタチンリン酸エステル及びそれらのナトリウム塩の形成を示す図である。以前に開発された方法によって製造された出発原料は、古典的なエステル化プロセスにおいて、触媒として硫酸の存在下でアトルバスタチンと縮合され、連結された生成物が形成される。後者はそれからナトリウムメトキシドで処理され、最終生成物としてナトリウム塩を得る。 As a non-limiting example, FIG. 1 shows the formation of alkorvir cytostanyl or campestanyl atovastatin phosphates and their sodium salts. Starting materials produced by previously developed methods are condensed with atorvastatin in the presence of sulfuric acid as a catalyst in a classic esterification process to form a linked product. The latter is then treated with sodium methoxide to give the sodium salt as the final product.
図2の図中に例示された、他の限定されない代替手法で、アスコルビルシトスタニル又はカンペスタニルシンバスタチンリン酸エステル及びそれらのナトリウム塩の製造プロセスが説明される。出発物質は、オキシ塩化リンで図1に既に示した出発物質を処理することによって得られ、示されたジクロロホスフェートを得る。後者はそれからシンバスタチンで処理され、それにより前記スタチンの遊離水酸基がより反応性のクロロホスフェート基のハロゲン原子と置き換わり、連結された生成物を得る。鉱酸による酸性化に続き、ナトリウムメトキシドとの処理によって、二ナトリウム塩として最終生成物が生じる。 In another non-limiting alternative approach, illustrated in the diagram of FIG. 2, the process for producing ascorbyl sitostanyl or campestanyl simvastatin phosphate and their sodium salts is described. The starting material is obtained by treating the starting material already shown in FIG. 1 with phosphorus oxychloride to give the indicated dichlorophosphate. The latter is then treated with simvastatin, whereby the free hydroxyl group of the statin is replaced with a halogen atom of the more reactive chlorophosphate group to give a linked product. Following acidification with mineral acid, treatment with sodium methoxide yields the final product as the disodium salt.
図3の図中に例示された、他の限定されない代替手法で、シトスタニル又はカンペスタニルシンバスタチンリン酸エステルの製造プロセスが説明される。シトスタノール又はカンペスタノールは、オキシ塩化リンで処理され、対応するクロロホスフェートエステルを得る。この中間体をそれから、シンバスタチンの水酸基によって塩化物の置換に影響を与えるために、ピリジン/THF混合物中で前記スタチンと反応させる。得られた連結された生成物は水で処理され、最終リン酸エステルの合成が完結する。 In another non-limiting alternative approach illustrated in the diagram of FIG. 3, the process for producing sitostanyl or campestanyl simvastatin phosphate is described. Sitostanol or campestanol is treated with phosphorus oxychloride to give the corresponding chlorophosphate ester. This intermediate is then reacted with the statin in a pyridine / THF mixture in order to affect the chloride substitution by the hydroxyl group of simvastatin. The resulting linked product is treated with water to complete the synthesis of the final phosphate ester.
図4の図中に例示された、他の限定されない代替手法で、シトスタニル又はカンペスタニルアトルバスタチンカルボン酸エステルの製造プロセスが説明される。シトスタノール又はカンペスタノールは、触媒としての硫酸の存在下でアトルバスタチンで処理され、古典的なエステル化プロセスを通じてエステルを得る。 In another non-limiting alternative approach, illustrated in the diagram of FIG. 4, the process for producing sitostanyl or campestanyl atorvastatin carboxylate is described. Sitostanol or campestanol is treated with atorvastatin in the presence of sulfuric acid as a catalyst to give the ester through a classic esterification process.
これら誘導体の形成に関して、選択された合成プロセスが説明されてはいるが、開示及び特許請求された各種誘導体が製造でき得る他の多くの他の手法が存在することが理解される。ひとたび特定の誘導体が選択されれば、当技術分野で一般に利用可能な技術を用いて合成を行うことは、十分に当化学分野における当業者の活動範囲内にある。このため、特許請求されたありとあらゆる誘導体の合成一式は説明されない。 Although selected synthetic processes have been described for the formation of these derivatives, it is understood that there are many other ways in which the various disclosed and claimed derivatives can be made. Once a particular derivative is selected, it is well within the scope of the skilled artisan to perform the synthesis using techniques generally available in the art. For this reason, the synthetic suite of all the claimed derivatives is not described.
本明細書に説明される化合物及びそれらの塩がそれらの互変異性型で存在し得る場合、全ての前記互変異性型が本明細書中の本発明の一部として考えられる。 If the compounds described herein and their salts can exist in their tautomeric form, all such tautomeric forms are considered as part of the invention herein.
鏡像異性形態(非対称の炭素原子の不在下でも存在し得る)及びジアステレオマー形態を含む、様々な構成要素における非対称の炭素原子によって存在し得る立体異性体等の、本発明の化合物の全ての立体異性体が、本発明の範囲内に考えられる。本発明の化合物の個々の立体異性体は、例えば、ラセミ化合物として混合され得、又は他の全ての若しくは他の選択された立体異性体と混合され得る。化合物のキラル中心は、IUPAC1974勧告によって定義されたS配置又はR配置を有する。ジアステレオマー型又は鏡像異性型生成物が製造される場合、クロマトグラフィー結晶化又は分別結晶化などの、従来の手法によって分離され得る。 All of the compounds of the present invention, such as stereoisomers that may exist with asymmetric carbon atoms in various components, including enantiomeric forms (which may exist in the absence of asymmetric carbon atoms) and diastereomeric forms Stereoisomers are contemplated within the scope of the present invention. Individual stereoisomers of the compounds of the present invention can be mixed, for example, as a racemate, or can be mixed with all other or other selected stereoisomers. The chiral center of the compound has the S or R configuration as defined by the IUPAC 1974 recommendation. When diastereomeric or enantiomeric products are produced, they can be separated by conventional techniques such as chromatographic crystallization or fractional crystallization.
組成物
本発明の別の局面によれば、本明細書に説明されるように、少なくとも一つのコレステロール生合成阻害剤と混合された、少なくとも一つのステロール/スタノールベースのコレステロール吸収阻害剤を含む新規組成物が提供され、該組成物はCVD並びに、アテローム性動脈硬化症、高コレステロール血症、高脂血症、脂質代謝異常、高血圧、血栓症、冠動脈疾患及び冠動脈プラーク炎症などの炎症などを含むがこれに限定されないその根底となる症状の治療又は予防への使用に好適である。
Compositions According to another aspect of the present invention, a novel comprising at least one sterol / stanol-based cholesterol absorption inhibitor mixed with at least one cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitor, as described herein. Compositions are provided, which include CVD and inflammation such as atherosclerosis, hypercholesterolemia, hyperlipidemia, dyslipidemia, hypertension, thrombosis, coronary artery disease and coronary plaque inflammation, etc. Is suitable for use in the treatment or prevention of the underlying symptoms, but not limited thereto.
さらに具体的には、該組成物は
a)一般式
びにnは1−5を表す。)を有する化合物(あらゆる生物学的に許容される塩又は溶媒和物、又は少なくとも一つの前記化合物の又はそれらの塩の又はそれらの溶媒和物のプロドラッグを含む。)から選択される少なくとも一つのコレステロール吸収阻害剤、及び
b)少なくとも一つのコレステロール生合成阻害剤
を含む。
More specifically, the composition comprises a) a general formula
式i)乃至iv)の化合物は、例えば、以下の方法及び国際出願PCT/CA00/00730号(2000年6月20日出願、米国特許出願第09/339,903号(1999年6月23日出願)による優先権を主張)に記載されているような既知の方法にて製造され得、その全ての内容が参照によって本明細書に組み込まれる。 The compounds of formulas i) to iv) can be prepared, for example, by the following method and international application PCT / CA00 / 00730 (filed June 20, 2000, U.S. patent application 09 / 339,903 (June 23, 1999)). Can be produced in a known manner as described in (claiming priority) from the application), the entire contents of which are hereby incorporated by reference.
一般に、式i)乃至iv)の化合物は以下のようにに製造され得る。選択されたステロール又はスタノール(又はそれらのハロホスフェート、ハロカーボネート又はハロ−オキサネート誘導体)及びアスコルビン酸を、「酸」部分と「アルコール」(ステロール)との縮合ができる反応条件下で一緒に混合する。こうした条件は、酸成分及びアルコール成分が直接、又は、鉱酸、硫酸、リン酸、p−トルエンスルホン酸などの適切な酸触媒の存在下で反応することができる、フィッシャーエステル化プロセスなどの他の一般的なエステル化反応で用いられるものと同様である。前記エステル化反応に一般に用いられる有機溶媒は、ジエチルエーテル、テトラヒドロフランなどのエーテル、又はベンゼン、トルエン又は類似の芳香族系溶媒であり、反応を起こす反応物質の反応性によって温度は室温から高温まで様々であり得る。 In general, the compounds of formulas i) to iv) can be prepared as follows. The selected sterol or stanol (or their halophosphate, halocarbonate or halo-oxanate derivative) and ascorbic acid are mixed together under reaction conditions that allow condensation of the “acid” moiety with the “alcohol” (sterol). . These conditions include other conditions such as the Fischer esterification process where the acid and alcohol components can react directly or in the presence of a suitable acid catalyst such as mineral acid, sulfuric acid, phosphoric acid, p-toluenesulfonic acid. These are the same as those used in the general esterification reaction. The organic solvent generally used for the esterification reaction is an ether such as diethyl ether or tetrahydrofuran, or benzene, toluene or a similar aromatic solvent, and the temperature varies from room temperature to a high temperature depending on the reactivity of the reactant causing the reaction. It can be.
好ましい実施態様において、エステルを形成するプロセスは、エステル(例えば酢酸エステルなど)又はエーテル(例えばメチエルエーテル)としてアスコルビン酸又はそれらの誘導体の水酸基を「保護すること」、そしてそれから保護されたアスコルビン酸を、適切な反応条件下で、ステロール/スタノール ハロホスフェート、ハロカーボネート又はハロ−オキサレートと縮合させることを含む。一般に、前記縮合反応はジエチルエーテル、テトラヒドロフラン、又はベンゼン、トルエン又は類似の芳香族系溶媒などの有機溶媒中で行われる。反応物質の種類及び反応性に応じて、反応温度は低温(−15度)から高温まで様々であり得る。 In a preferred embodiment, the process of forming the ester comprises “protecting” the hydroxyl group of ascorbic acid or a derivative thereof as an ester (eg acetate ester) or ether (eg methyl ether) and then protecting the protected ascorbic acid. Condensing with sterol / stanol halophosphate, halocarbonate or halo-oxalate under appropriate reaction conditions. In general, the condensation reaction is carried out in an organic solvent such as diethyl ether, tetrahydrofuran, or benzene, toluene or similar aromatic solvents. Depending on the type and reactivity of the reactants, the reaction temperature can vary from low temperature (-15 degrees) to high temperature.
より詳細には、下記事項が式i)乃至iv)、とりわけ式i)の化合物を製造する一つの好ましい方法である:最初に、5,6−イソプロピリデン−アスコルビン酸の形成によってアスコルビン酸を分解から保護する。これは、アセトンをアスコルビン酸並びに硫酸又は塩酸などの酸性触媒と適切な反応条件下で混合することによって達成され得る。フィトスタノールクロロホスフェートは、トルエン及びピリジン(とはいえ例えば脂肪族又は芳香族アミンなどの他の窒素塩基を代わりに使用し得る)中でフィトスタノール溶液を形成すること、そしてこの溶液をオキシ塩化リンなどのリン誘導体で処理することによって、製造される。母液の濾過及び濃縮後に形成された残留物がフィトスタノールクロロホスフェートである。後者は次に5,6−イソプロピリデン−アスコルビン酸と混合され、エタノールなどの適切なアルコールとHClを加えた後、濃縮される。あるいは、ピリジン/THFが加えられ得、生成物を濃縮する。最終洗浄及び乾燥の後、得られた新規生成物がスタノール−ホスフェート−アルコルベートである。 More particularly, the following is one preferred method for preparing compounds of formulas i) to iv), in particular of formula i): First, ascorbic acid is degraded by formation of 5,6-isopropylidene-ascorbic acid. Protect from. This can be achieved by mixing acetone with ascorbic acid and an acidic catalyst such as sulfuric acid or hydrochloric acid under suitable reaction conditions. Phytostanol chlorophosphate forms a phytostanol solution in toluene and pyridine (although other nitrogen bases such as, for example, aliphatic or aromatic amines can be used instead) and this solution is converted to phosphorus oxychloride. It is manufactured by processing with phosphorus derivatives such as. The residue formed after filtration and concentration of the mother liquor is phytostanol chlorophosphate. The latter is then mixed with 5,6-isopropylidene-ascorbic acid and concentrated after adding an appropriate alcohol such as ethanol and HCl. Alternatively, pyridine / THF can be added to concentrate the product. After final washing and drying, the new product obtained is stanol-phosphate-alcolbate .
式i)乃至iv)の化合物を製造するプロセスの他の好ましい形態は、アスコルビン酸が、5,6−イソプロピリデン−アスコルビン酸としてではなく、エステル(例えばアセテート、ホスフェートなどの)として水酸基位置において保護される。後者は、次に上述の通り誘導体化されたステロール又はスタノールと既知のエステル化手法を用いて縮合され得、最終的に前記化合物が生成する。アスコルビン酸のモノホスフェート及びジホスフェートの形成は文献に完全に記載されている。例えば、参照として本明細書に組み込まれる、米国特許第4,939,128号明細書(カトウら)、はアスコルビン酸のリン酸エステルの形成を教える。同様に、参照として本明細書に組み込まれる、米国特許第4,999,437号明細書(ドブラーら)、はアスコルビン酸 2−ホスフェートの製造法を記載する。ドブラーらにおいて、第三アミンの存在下におけるアスコルビン酸又はアスコルビン酸誘導体のPOCl3でのリン酸化のコア反応(独国特許出願公開第2,719,303号明細書に開示)は、反応溶液にマグネシウム化合物、好ましくはマグネシウム化合物水溶液を加えることによって改善される。いずれの既知のアスコルビン酸誘導体が使用され得る。 Another preferred form of the process for producing the compounds of formulas i) to iv) is that ascorbic acid is protected at the hydroxyl position as an ester (eg acetate, phosphate etc.) rather than as 5,6-isopropylidene-ascorbic acid. Is done. The latter can then be condensed with sterols or stanols derivatized as described above using known esterification techniques to ultimately produce the compound. The formation of monophosphate and diphosphate of ascorbic acid is fully described in the literature. For example, US Pat. No. 4,939,128 (Kato et al.), Incorporated herein by reference, teaches the formation of phosphate esters of ascorbic acid. Similarly, US Pat. No. 4,999,437 (Dobler et al.), Incorporated herein by reference, describes a process for producing ascorbic acid 2-phosphate. In Dobler et al., The core reaction of phosphorylation of ascorbic acid or an ascorbic acid derivative with POCl3 in the presence of a tertiary amine (disclosed in German Offenlegungsschrift 2,719,303) is carried out with magnesium in the reaction solution. Improvement is achieved by adding a compound, preferably an aqueous magnesium compound solution. Any known ascorbic acid derivative can be used.
より詳細には、下記事項が、式i)乃至iv)、とりわけ式ii)の化合物を製造する別の好ましい方法である:「保護された」アスコルビン酸を準備し、上記に詳細に説明されたものと同様のプロセスが続く;しかしながら、オキシ塩化リンが塩化オキサリルに置き換わることによって、スタノール−オキサレート−アスコルベートが生じる。 More specifically, the following is another preferred method for preparing compounds of formulas i) to iv), especially formula ii): “Protected” ascorbic acid is provided and described in detail above. A process similar to that follows; however, the replacement of phosphorus oxychloride with oxalyl chloride yields stanol-oxalate-ascorbate.
好ましい形態において、本発明の組成物は、少なくとも一つのスタチンと一緒になって、二つの主要成分:アスコルビルカンペスタニルリン酸二ナトリウム(「DACP」)とアスコルビルシトスタニルリン酸二ナトリウム(「DASP」)を含む、一つ以上のアスコルビルフィトスタニルリン酸二ナトリウム塩(「FM−VP4」と呼ばれる)を含む。 In a preferred form, the composition of the present invention, together with at least one statin, has two major components: ascorbylcampestanyl disodium phosphate ("DACP") and ascorbyl sitostanyl phosphate disodium ("DASP"). ) Including one or more ascorbyl phytostanil phosphate disodium salts (referred to as “FM-VP4”).
別の好ましい実施態様において、ステロール及び/又はスタノール部分は、選択されたコレステロール生合成阻害剤との結合前又は結合後にミセル内へ組み込まれ得る。このミセ
ルは、レシチン又はいずれの他の好適な乳化剤を用い、そして、既知のそして当技術分野で広く適用される方法を用いて、生成され得る。
In another preferred embodiment, sterol and / or stanol moieties can be incorporated into micelles before or after coupling with selected cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitors. The micelles can be produced using lecithin or any other suitable emulsifier and using methods known and widely applied in the art.
本発明の組成物は、コレステロール吸収阻害剤及びコレステロール生合成阻害剤が、たとえば固定比率の有効成分を有する単一錠剤又はカプセルなどにて、実質的に同時の方法で併用投与されるか、又は、治療薬毎に複数分離投与される、「併用療法」を可能にする。この分離投与は連続投与形態を含む。 The composition of the present invention is such that the cholesterol absorption inhibitor and the cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitor are co-administered in a substantially simultaneous manner, such as in a single tablet or capsule having a fixed ratio of active ingredient, or This allows for "combination therapy" in which multiple therapeutic agents are administered separately. This separate administration includes continuous dosage forms.
使用法
本発明は以下の治療目的
a)一般にCVDに関連し、動脈硬化、アテローム性動脈硬化、細動脈硬化、狭心症および血栓症などの一つ以上の症状を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
b)CVDに関連するリスク因子の一つ以上を減らし及び/又は排除すること、
c)アテローム性動脈硬化症を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
d)高コレステロール血症を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
e)高脂質症状を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
f)脂質代謝異常を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
g)高血圧症を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
h)冠動脈疾患を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
i)冠動脈プラーク発生を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
j)冠動脈プラーク炎症を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
k)血清LDLコレステロールを低下すること、
l)血清HDLコレステロールを増加すること、
m)血清トリグリセリド値を減少すること、
n)コレステロール生合成を減少すること、
o)脂質代謝異常状態又は障害を予防し、減らし、排除し、又は改善すること、
p)高コレステロール血症又は低アルファリポタンパク質血症を予防し、減らし、排除し、又は改善すること、
q)アテローム性病変またはプラークの発生を予防し、減らし、排除し、安定化させ、又は改善すること、
r)心血管疾患及び冠動脈疾患の発生に関連する炎症の発生を予防し、減らし、排除し、又は改善すること、
s)血清HDLの不足、若しくはLDL、VLDL、Lp(a)、ベータ−BLDL、IDL又は残留リポタンパク質の過剰をその基礎として有するか、又は、それらにより悪化する、あらゆる症状、疾患又は障害を予防し、減らし、排除し、又は改善すること、
t)発作のリスクを減少すること、
u)イソプレノイド合成を抑制すること、
v)アルツハイマー病を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
w)認知症を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
x)骨粗鬆症を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
y)酸化ストレスによる損傷を予防し、減らし、排除し、又は改善すること、
z)酸化からHDLの安定性を増強し及び/又は維持すること、
aa)酸化からLDL、VLDL、又はIDLの安定性を増強し及び/又は維持すること、
bb)酸化からトリグリセリド(TG)の安定性を増強し及び/又は維持すること、
cc)抗凝固特性を示すこと、
dd)抗増殖特性を示すこと、
ee)免疫調節特性を示すこと、
ff)血管由来特性を示すこと、
gg)腫瘍の成長を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
hh)骨質量及び/又は骨代謝を増加すること、及び、
ii)特に細胞又は分子レベルにおいて、スタチンの投与によって得られる非脂質関連の多面発現効果の何れかを増強すること、
の一つ以上を達成する方法を提供し、本明細書に説明され特許請求された化合物又は組成物の無毒性かつ治療有効量を動物に投与することを含む。
本発明はさらに、本明細書に説明される症状に対して、さらに具体的には、上記に定義された治療目的の一つ以上の達成に使用するための、開示された化合物及び組成物のいずれかの使用を含む。
USES OF THE INVENTION The following therapeutic objectives a) are generally related to CVD and prevent or treat one or more symptoms such as arteriosclerosis, atherosclerosis, arteriole sclerosis, angina and thrombosis, or Mitigating,
b) reducing and / or eliminating one or more of the risk factors associated with CVD;
c) preventing, treating or reducing atherosclerosis,
d) preventing, treating or reducing hypercholesterolemia,
e) prevent, treat or alleviate high lipid symptoms;
f) preventing, treating or reducing lipid metabolism disorders;
g) preventing, treating or reducing hypertension,
h) preventing, treating or reducing coronary artery disease;
i) preventing, treating or reducing the occurrence of coronary plaque,
j) preventing, treating or reducing coronary plaque inflammation;
k) lowering serum LDL cholesterol,
l) increasing serum HDL cholesterol,
m) reducing serum triglyceride levels,
n) reducing cholesterol biosynthesis,
o) preventing, reducing, eliminating or ameliorating abnormal lipid metabolism conditions or disorders;
p) preventing, reducing, eliminating or ameliorating hypercholesterolemia or low alpha lipoproteinemia,
q) preventing, reducing, eliminating, stabilizing or ameliorating the development of atherosclerotic lesions or plaques;
r) preventing, reducing, eliminating or ameliorating the occurrence of inflammation associated with the occurrence of cardiovascular and coronary artery disease;
s) Prevent any symptoms, diseases or disorders that have or are exacerbated by a lack of serum HDL or LDL, VLDL, Lp (a), beta-BLDL, IDL or excess of residual lipoproteins Reduce, eliminate or improve,
t) reducing the risk of seizures,
u) inhibiting isoprenoid synthesis;
v) preventing, treating or reducing Alzheimer's disease;
w) prevent, treat or alleviate dementia;
x) preventing, treating or reducing osteoporosis,
y) prevent, reduce, eliminate or ameliorate oxidative stress damage;
z) enhance and / or maintain the stability of HDL from oxidation,
aa) enhancing and / or maintaining the stability of LDL, VLDL, or IDL from oxidation,
bb) enhancing and / or maintaining the stability of triglycerides (TG) from oxidation;
cc) exhibit anticoagulant properties;
dd) exhibit anti-proliferative properties;
ee) exhibiting immunomodulatory properties;
ff) exhibiting blood vessel-derived properties;
gg) preventing, treating or reducing tumor growth;
hh) increasing bone mass and / or bone metabolism; and
ii) enhance any of the non-lipid related pleiotropic effects obtained by administration of statins, especially at the cellular or molecular level;
A method is provided for accomplishing one or more of the above, comprising administering to an animal a non-toxic and therapeutically effective amount of a compound or composition described and claimed herein.
The present invention further relates to the disclosed compounds and compositions for use in achieving one or more of the therapeutic purposes defined above for the symptoms described herein. Including any use.
とりわけ、本発明の化合物及び組成物は心血管疾患の多重要因の症状に寄与する少なくとも二つの重要因子:腸コレステロール吸収及び体内コレステロール生合成:への対処にとりわけ有用であることが示されている。血清コレステロール値は主として二つの臓器:肝臓(コレステロール及び胆汁酸(消化に使用)を生成する)及び腸(食物及び胆汁(肝臓にて生成)の双方からコレステロールを吸収する):によってコントロールされる。ステロールは、腸内でコレステロール吸収を抑制することによる独自の作用機序によってLDL血清コレステロール値を下げる。この作用機序はステロールにスタチンなどの肝臓で働くコレステロール生合成阻害剤を補完させる。そのため、スタチンとともにステロールを摂取する患者は、LDL及び総コレステロールのさらなる低下を達成できる。 In particular, the compounds and compositions of the present invention have been shown to be particularly useful in addressing at least two important factors that contribute to the multifactorial symptoms of cardiovascular disease: intestinal cholesterol absorption and internal cholesterol biosynthesis. . Serum cholesterol levels are controlled primarily by two organs: the liver (which produces cholesterol and bile acids (used for digestion)) and the intestine (which absorbs cholesterol from both food and bile (produced in the liver)). Sterols lower LDL serum cholesterol levels by a unique mechanism of action by inhibiting cholesterol absorption in the intestine. This mechanism of action complements sterols with cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitors that work in the liver, such as statins. Thus, patients taking sterols with statins can achieve further reductions in LDL and total cholesterol.
したがって、コレステロール吸収を同時に低下させる(例えばステロール/スタノール)一部分と、コレステロール生合成を減少させる(例えばスタチン)別の部分を投与することは、非常に有利である。これは、式a)乃至式f)の化合物の少なくとも一つの投与によってか、或いは、コレステロール吸収阻害剤(式i)乃至iv)の一つを有する)及びコレステロール生合成阻害剤を含む組成物の投与によって、達成される。 Therefore, it is highly advantageous to administer a portion that simultaneously reduces cholesterol absorption (eg, sterol / stanol) and another portion that reduces cholesterol biosynthesis (eg, statin). This is due to the administration of at least one compound of the formulas a) to f) or of one of the cholesterol absorption inhibitors (formulas i) to iv)) and a cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitor This is achieved by administration.
最終的に、本明細書に説明される化合物及び組成物の使用によって生じる最も重要な利点は、血清HDLコレステロールの増加及び血清トリグリセリドの減少によって得られたさらなる有益な効果とともに、血清LDLコレステロールの減少及び総血清コレステロールの減少である。これら利点はスタチン投与に付随する副作用なしに達成される。 Ultimately, the most important benefits arising from the use of the compounds and compositions described herein are a reduction in serum LDL cholesterol, along with the additional beneficial effects obtained by increasing serum HDL cholesterol and decreasing serum triglycerides. And a reduction in total serum cholesterol. These benefits are achieved without the side effects associated with statin administration.
加えて、本発明の化合物について、本明細書に説明されたステロールベースのコレステロール吸収阻害剤で共有結合的に修飾することによって、コレステロール生合成阻害剤(例えばスタチンなど)の全般的な疎水性を変化させることの重大な生物学的影響(及び利点)が存在する。具体的に、本発明の化合物は天然スタチンよりも全般的に高い疎水性を有する。このことは少なくとも二つの面において重要である。第一に、スタチンの多面発現(pleotropic)効果の増加となり得る。第二に、化合物がそのままに吸収される場合、スタチンのADME特性が異なり得るので、数ある利点の中でも特に潜在的な毒性を減少させ得る。 In addition, the overall hydrophobicity of cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitors (such as statins) can be reduced by covalently modifying the compounds of the present invention with the sterol-based cholesterol absorption inhibitors described herein. There are significant biological effects (and benefits) of changing. Specifically, the compounds of the present invention are generally more hydrophobic than natural statins. This is important in at least two aspects. First, it can increase the pleotrophic effect of statins. Second, if the compound is absorbed as is, the ADME properties of statins can be different, which can reduce potential toxicity, among other advantages.
作用機序についていずれの一つの理論に縛られることを意図しないが、遊離スタチンと比べ化合物の構造変化は、血清リポタンパク質プールへの高い比例配分をもたらすため、特にHDLによって薬剤が運搬される場合、末梢組織へより大きな割合で活性成分が輸送される。これは、数多く報告されてきた「スタチン」の症状、例えばアルツハイマー病や骨粗鬆症に対する本発明の化合物の潜在的効果を大いに増加させ得る。 While not intending to be bound by any one theory about the mechanism of action, the structural change of the compound, compared to the free statin, results in a high proportional distribution to the serum lipoprotein pool, so that the drug is transported specifically by HDL A greater proportion of the active ingredient is transported to peripheral tissues. This can greatly increase the potential effects of the compounds of the invention on the many reported “statin” symptoms, such as Alzheimer's disease and osteoporosis.
さらに、本発明の化合物(式(e)乃至(f)及びi)乃至iv)で表されるもの)のいくつかは、アスコルビル部分を含む。これら特定の化合物は数々のさらなる有利点を有する。何よりもまず、化合物の溶解度が水溶液及び油や脂肪などの非水溶性媒体のいずれにおいても非常に増加する。この優れた溶解度のため、効果的な食物量及び薬用量、及び付随的にはコストをも、低減できる。第二に、一つの構造で結ばれていると、心血管疾患だ
けでなくアテローム性動脈硬化症や高脂血症などのその根底となる症状の治療又は予防において、フィトステロール部分とアスコルビン酸の間に相乗的又は付加的な効果でさえも存在し得る。第三に、これら化合物の形成は、分解を排除すると共に、アスコルビン酸の最大の可能性が実現されることを可能にする。第四に、これら誘導体は、幾つかの加工機序に必須である耐熱性(酸化及び加水分解に安定)である。
Furthermore, some of the compounds of the present invention (represented by formulas (e) to (f) and i) to iv) contain an ascorbyl moiety. These particular compounds have a number of additional advantages. First and foremost, the solubility of the compound is greatly increased in both aqueous solutions and non-aqueous media such as oils and fats. This excellent solubility can also reduce effective food and dosage, and concomitant costs. Secondly, when combined in a single structure, not only cardiovascular disease but also the underlying symptoms such as atherosclerosis and hyperlipidemia can be treated with phytosterols and ascorbic acid. There can even be synergistic or even additional effects. Third, the formation of these compounds eliminates degradation and allows the full potential of ascorbic acid to be realized. Fourth, these derivatives are heat resistant (stable to oxidation and hydrolysis) essential for some processing mechanisms.
本明細書に説明される望ましい効果は、様々な異なる方法で達成し得る。本発明の化合物及び組成物は、医薬品と一緒の使用に利用可能ないずれかの従来手法を用いて投与され得る。したがって、本発明は、一局面において、式a)乃至f)の化合物の一つ以上及び薬剤的に許容される担体を含む医薬組成物に関する。本発明は、別の局面において、式i)−iv)の一つを有する少なくとも一つのコレステロール吸収阻害剤の有効量又は治療量を、有効量及び治療量の少なくとも一つのコレステロール生合成阻害剤及び薬剤的に許容される担体とともに含む、医薬組成物に関する。これら化合物及び/又は組成物は、いずれかの一般的な調剤形にて、好ましくは錠剤、カプセル、粉剤、カシェット、懸濁液又は溶液などの経口調剤形にて、投与され得る。医薬組成物は「活性」成分(コレステロール吸収阻害剤及びコレステロール生合成阻害剤)約1%乃至99%、好ましくは活性成分を約5%乃至95%含み得る。 The desired effects described herein can be achieved in a variety of different ways. The compounds and compositions of the invention can be administered using any conventional technique available for use with pharmaceuticals. Accordingly, the present invention in one aspect relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising one or more compounds of formulas a) to f) and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. In another aspect, the present invention provides an effective amount or therapeutic amount of at least one cholesterol absorption inhibitor having one of formulas i) -iv), an effective amount and a therapeutic amount of at least one cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitor and It relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. These compounds and / or compositions can be administered in any common dosage form, preferably in oral dosage forms such as tablets, capsules, powders, cachets, suspensions or solutions. The pharmaceutical composition may comprise from about 1% to 99% “active” ingredients (cholesterol absorption inhibitors and cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitors), preferably from about 5% to 95% active ingredients.
製剤及び医薬組成物は、従来の、薬剤的に許容される賦形剤及び添加剤を用いて、従来の手法によって製造され得る。前記薬剤的に許容される賦形剤及び添加剤としては、無毒性の相溶性充填剤、結合剤、崩壊剤、バッファー、防腐剤、抗酸化剤、滑剤、香味料、増粘剤、着色剤、及び乳化剤などが挙げられる。 Formulations and pharmaceutical compositions can be prepared by conventional techniques using conventional, pharmaceutically acceptable excipients and additives. The pharmaceutically acceptable excipients and additives include non-toxic compatible fillers, binders, disintegrants, buffers, preservatives, antioxidants, lubricants, flavorings, thickeners, colorants. And emulsifiers.
望ましい効果の達成に必要とされる化合物及び組成物の正確な量又は用量は、もちろん、特定の化合物又は組成物の選択、投与された化合物又は組成物の効能、投与法、及び年齢、体重、症状、及び患者の反応などの、多くの要因に依存する。とりわけ、これら要因の全てが、担当医によって各個人又は患者毎に対して考慮される。 The exact amount or dose of compound and composition required to achieve the desired effect will, of course, be determined by selection of the particular compound or composition, efficacy of the administered compound or composition, method of administration, and age, weight, Depends on many factors such as symptoms and patient response. In particular, all of these factors are considered for each individual or patient by the attending physician.
式i)−iv)の一つを有する少なくとも一つのコレステロール吸収阻害剤を少なくとも一つのコレステロール生合成阻害剤及び薬剤的に許容される担体とともに含む医薬組成物について、通常一日1回又は2回の単一投与又は複数投与で投与される、コレステロール生合成阻害剤の典型的な一日用量は、一日あたり哺乳類の体重に対して約0.1mg乃至160mg/kgにおよび得、好ましくは、2mg乃至80mgにおよび得る。例えば、HMG CoAレダクターゼ阻害剤について、投与当たり約0.25mg乃至40mgが一日当たり1回乃至2回与えられ、一日当たり総一日用量約0.5mg乃至80mgが与えられる。他のコレステロール生合成阻害剤については、投与当たり約1mg乃至約1000mgが一日あたり1回ないし2回与えられ、一日当たり総一日用量約1mg乃至約2000mが与えられる。 For pharmaceutical compositions comprising at least one cholesterol absorption inhibitor having one of the formulas i) -iv) together with at least one cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitor and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, usually once or twice a day A typical daily dose of a cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitor administered in a single dose or multiple doses of can range from about 0.1 mg to 160 mg / kg of mammal body weight per day, preferably It can range from 2 mg to 80 mg. For example, for an HMG CoA reductase inhibitor, about 0.25 mg to 40 mg per dose is given once or twice per day, giving a total daily dose of about 0.5 mg to 80 mg per day. For other cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitors, about 1 mg to about 1000 mg per dose is given once or twice per day, giving a total daily dose of about 1 mg to about 2000 m per day.
一般に、式i)−iv)の一つを有し、ステロール及び/又はスタノールを含むコレステロール吸収阻害剤の総一日用量は、単一投与又は複数投与で一日当たり10mg乃至約20g、より好ましくは10mg乃至1.5gの一日用量範囲にて投与され得る。 In general, the total daily dose of a cholesterol absorption inhibitor having one of formulas i) -iv) and comprising sterols and / or stanols is 10 mg to about 20 g per day in a single dose or multiple doses, more preferably A daily dose range of 10 mg to 1.5 g may be administered.
本化合物の成分が別々に投与される場合、投与回数及び一日当たり与えられる各成分の前記用量の総量は、同じである必要ない。例えば、コレステロール吸収阻害剤が、コレステロール生合成阻害剤よりも一日当たり多数の投与を必要とし得、及び/又はより大量の用量を必要とし得る。 When the components of the compound are administered separately, the number of administrations and the total amount of each dose given per day need not be the same. For example, cholesterol absorption inhibitors may require a larger number of doses per day and / or require larger doses than cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitors.
これら化合物及び組成物の一日用量は、必要とするならば、単一投与又は複数投与にて個人に投与される。持続放出用量が使用され得る。 Daily doses of these compounds and compositions are administered to an individual as a single dose or multiple doses, as needed. Sustained release doses can be used.
体内投与に好適な用量における本発明の実践のために、本明細書に開示された化合物及び組成物を処方するための薬剤的に許容される担体の使用は、本発明の範囲内である。適切な担体の選択と好適な製造の実践によって、本発明の化合物及び組成物は、とりわけ、溶液として処方されたものは、静脈注射などによって非経口の投与をなされ得る。本化合物及び組成物は当業者に既知の薬剤的に許容される担体を用いて、経口投与に好適な製剤に容易に処方できる。前記担体は、本発明の化合物及び組成物が、治療される患者による経口摂取のために、タブレット、錠剤、カプセル、液体、ゲル、シロップ、スラリー、懸濁液などとして処方されることを可能にする。 The use of pharmaceutically acceptable carriers to formulate the compounds and compositions disclosed herein for the practice of the invention in dosages suitable for in vivo administration is within the scope of the invention. By selection of appropriate carriers and suitable manufacturing practices, the compounds and compositions of the present invention, especially those formulated as solutions, can be administered parenterally, such as by intravenous injection. The compounds and compositions can be readily formulated into formulations suitable for oral administration using pharmaceutically acceptable carriers known to those skilled in the art. The carrier allows the compounds and compositions of the invention to be formulated as tablets, tablets, capsules, liquids, gels, syrups, slurries, suspensions, etc., for oral consumption by the patient being treated. To do.
本発明の化合物の一つ以上を含む医薬組成物は、活性成分がそれらの本来意図した目的を達成するに効果的な量で含まれている組成物を含む。有効量の決定は、特に本明細書に提供された詳細な開示を踏まえて、当業者の能力の十分範囲内にある。 Pharmaceutical compositions containing one or more of the compounds of the present invention include those wherein the active ingredients are contained in an amount effective to achieve their originally intended purpose. Determination of an effective amount is well within the capability of those skilled in the art, especially in light of the detailed disclosure provided herein.
活性成分に加え、これら医薬組成物は、薬剤的に使用でき、製剤中において活性化合物の処理を促進する賦形剤及び補助剤を含む、薬剤的に許容される好適な担体を含み得る。経口投与用に処方された製剤は、タブレット、糖衣錠、カプセル又は溶液の形態にあり得る。 In addition to the active ingredient, these pharmaceutical compositions can contain suitable pharmaceutically acceptable carriers that can be used pharmaceutically and include excipients and adjuvants that facilitate the processing of the active compound in the formulation. Formulations formulated for oral administration can be in the form of tablets, dragees, capsules or solutions.
本発明の医薬組成物は、それ自体既知の方法で、例えば、従来からある混合、溶解、造粒、糖衣錠形成、水簸、乳化、カプセル化、封入又は凍結乾燥プロセスなどによる方法で製造され得る。 The pharmaceutical composition of the present invention can be manufactured by a method known per se, for example, by a conventional method such as mixing, dissolution, granulation, sugar-coated tablet formation, starch syrup, emulsification, encapsulation, encapsulation or lyophilization process. .
非経口投与用の医薬品製剤としては、水溶性形態の活性化合物の水溶液が挙げられる。加えて、活性化合物の懸濁液は適当な油性の注射用懸濁液として製造され得る。好適な親油性溶媒又はビヒクルとしては、ごま油などの脂肪油、又はエチルオレート又はトリグリセリドなどの合成脂肪酸エステル、又はリポソームがある。水性の注射用懸濁液は、懸濁液の粘度を増加させるカルボキシルメチルセルロースナトリウム、ソルビトール又はデキストランなどの物質を含み得る。所望により、懸濁液はまた、化合物の溶解度を増加させて高濃度溶液の製造を可能にする適当な安定剤又は薬剤を含み得る。 Pharmaceutical formulations for parenteral administration include aqueous solutions of the active compounds in water-soluble form. In addition, suspensions of the active compounds can be prepared as appropriate oily injection suspensions. Suitable lipophilic solvents or vehicles include fatty oils such as sesame oil, or synthetic fatty acid esters such as ethyl oleate or triglycerides, or liposomes. Aqueous injection suspensions may contain substances such as sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, sorbitol or dextran that increase the viscosity of the suspension. If desired, the suspension may also contain suitable stabilizers or agents that increase the solubility of the compounds to allow for the production of highly concentrated solutions.
経口用の医薬品製剤は活性化合物を固形賦形剤と組み合わせることによって、所望により、得られた混合物を粉砕し、適当な補助剤を加えた後、顆粒の混合物の加工を行うことによって得られ得、必要ならばタブレット又は糖衣錠コアを得る。好適な賦形剤としては、ラクトース、スクロース、マンニトール、ソルビトール、とうもろこしでんぷん、小麦でんぷん、米でんぷん、じゃがいもでんぷん、ゼラチン、トラガカントゴム、メチルセルロース、ヒドロキシプロピルメチル−セルロース、カルボキシメチルセルロースナトリウム、及びポリビニルピロリドン(PVP)がある。必要に応じて、例えば架橋ポリビニルピロリドン、寒天又はアルギン酸又はアルギン酸ナトリウムなどのそれらの塩などの崩壊剤を加えられ得る。 Oral pharmaceutical preparations can be obtained by combining the active compound with solid excipients, optionally milling the resulting mixture, adding appropriate adjuvants, and then processing the granule mixture. If necessary, obtain a tablet or dragee core. Suitable excipients include lactose, sucrose, mannitol, sorbitol, corn starch, wheat starch, rice starch, potato starch, gelatin, tragacanth gum, methylcellulose, hydroxypropylmethyl-cellulose, carboxymethylcellulose sodium, and polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) There is. If desired, disintegrating agents may be added, such as the cross-linked polyvinyl pyrrolidone, agar, or alginic acid or a salt thereof such as sodium alginate.
糖衣錠コアは適当なコーティングを施される。この目的のために、濃縮砂糖溶液が使用され得、それらは所望によりアラビアガム、タルク、ポリビニルピロリドン、カルボポールゲル、ポリエチレングリコール、及び/又は二酸化チタン、ラッカー溶液、及び適当な有機溶剤又は溶剤混合物を含み得る。識別のため、又は活性化合物用量の異なる組み合わせを特徴付けるために、染料又は顔料がタブレット又は糖衣錠のコーティングに加えられ得る。 Dragee cores are provided with suitable coatings. For this purpose, concentrated sugar solutions may be used, which are optionally gum arabic, talc, polyvinylpyrrolidone, carbopol gel, polyethylene glycol and / or titanium dioxide, lacquer solutions, and suitable organic solvents or solvent mixtures. Can be included. Dyestuffs or pigments may be added to the tablets or dragee coatings for identification or to characterize different combinations of active compound doses.
経口使用可能な医薬品製剤としては、ゼラチンでできた押し込み型カプセル、並びに、ゼラチン及びグリセロール又はソルビトールなどの可塑剤でできた密封ソフトカプセルが挙
げられる。押し込み型カプセルは、ラクトースなどの充填剤、でんぷんなどの結合剤、及び/又は、タルク又はステアリン酸マグネシウムなどの滑剤、所望により安定剤と混合して活性成分を含み得る。ソフトカプセルにおいて、活性化合物は脂肪油、液体パラフィン又は液体ポリエチレングリコールなどの好適な液体中に溶解又は懸濁され得る。
加えて、安定剤もまた加えられ得る。
Pharmaceutical preparations that can be used orally include push-fit capsules made of gelatin, as well as soft, sealed capsules made of gelatin and a plasticizer, such as glycerol or sorbitol. Push-in capsules may contain the active ingredient in admixture with a filler such as lactose, a binder such as starch, and / or a lubricant such as talc or magnesium stearate, and optionally a stabilizer. In soft capsules, the active compounds can be dissolved or suspended in suitable liquids, such as fatty oils, liquid paraffin, or liquid polyethylene glycols.
In addition, stabilizers can also be added.
経口液体製剤は、エマルジョン、シロップ又はエリキシル剤などの形態であり得、又は
使用前に水又は他の適当な媒体とともに再構成される乾燥製品として提示される。前記液体製剤は、懸濁化剤、たとえばソルビトール、シロップ、メチルセルロース、ゼラチン、ヒドロキシエチルセルロース、カルボキシメチルセルロース、ステアリン酸アルミニウムゲル、水素化食用脂など;乳化剤、例えばレシチン、ソルビタンモノオレート又はアカシアなど;非水性ビヒクル(食用油を含み得る)、例えばアーモンド油、分画ヤシ油、グリセリン、プロピレングリコール又はエチルアルコールのエステルなどの油性エステルなど;防腐剤、たとえばメチル又はプロピルp−ヒドロキシベンゾエート、又はソルビン酸など;及び必要であれば従来の香味料又は着色剤、などの従来の添加剤を含み得る。
Oral liquid formulations may be in the form of an emulsion, syrup or elixir, or presented as a dry product that is reconstituted with water or other suitable vehicle prior to use. The liquid formulation may be a suspending agent such as sorbitol, syrup, methylcellulose, gelatin, hydroxyethylcellulose, carboxymethylcellulose, aluminum stearate gel, hydrogenated edible fat, etc .; emulsifier such as lecithin, sorbitan monooleate or acacia; Vehicles (which may include edible oils), such as almond oil, fractionated coconut oil, oily esters such as esters of glycerin, propylene glycol or ethyl alcohol; preservatives such as methyl or propyl p-hydroxybenzoate, or sorbic acid; And, if necessary, conventional additives such as conventional flavors or colorants may be included.
本発明は、同時投与又は分離投与され得る活性成分の組み合わせを有する組成物に関するので、本明細書において、前記目的のためのキットもまた提供する。キットは二つの別のユニット:本明細書に説明される少なくとも一つのコレステロール生合成阻害剤を含む医薬組成物、及び、本明細書に説明される少なくとも一つのコレステロール吸収阻害剤を含む別の医薬組成物:を組み合わせることが意図される。キットは好ましくは別々の成分の投与のための説明書を含む。このキット型の配置は、別々の成分が異なる用量形態(例えば経口及び非経口)で投与されねばならないとき、あるいは、異なる投与間隔で投与されるときに、特に有用である。 Since the present invention relates to a composition having a combination of active ingredients that can be co-administered or separately administered, a kit for said purpose is also provided herein. The kit comprises two separate units: a pharmaceutical composition comprising at least one cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitor described herein, and another medicament comprising at least one cholesterol absorption inhibitor described herein. Composition: is intended to be combined. The kit preferably includes instructions for administration of the separate components. This kit type arrangement is particularly useful when the separate components must be administered in different dosage forms (eg, oral and parenteral) or are administered at different dosage intervals.
さらなる詳細な説明はなしに、前述の記載が本発明を十分に説明しているため、他者は、現在又は将来の知識を応用して、本明細書に説明され特許請求される様々な状況下での使用のために、本発明を適合させ得る。 Without further elaboration, the foregoing description fully describes the present invention, so that others can apply their current or future knowledge under the various circumstances described and claimed herein. The present invention can be adapted for use in.
参照文献
1.Levi RI Declining Mortality in Coronary Heart Diseases Atherosclerosis 1981;1:312−325
2.ロー M.R.、ワルド N.J.、ウー.、ハックソー ZA.、ベイリー A.;Systemic Understimation of association between serum cholesterol concentration and ischemic heart disease in observational studies:Data from BUPA Study;Br.Med.J.1994;308:363−366
3.ロー M.R.、ワルド N.J.、トンプソン S.G.;By how much and how quickly does reduction in serum cholesterol concentration lower risk of ischemic heart disease? Br.Med.J.1994;308:367−373
4.ラ ローサ J.C.、ハニングヘイク D.、ブッシュ D.ら;The cholesterol facts:A summary of the evidence
relating to dietary fats,serum cholesterol and coronary heart disease:A joint statement by the American Heart Association and the National Heart,Lung and Blood
Institute.Circulation 1990;81:1721−17335.ハベル R.J.、ラパポート E.;Drug Therapy:Management of Primary Hyperlipidemia.New England Journal of Medicine,1995;332:1491−14986.バーカー及びライ;Atherosclerosis 1996;121:1−12
7.クコドゥカーら;Effects of plant sterols on cholesterol metabolism.Atherosclerosis,1976;23:239−248
8.リーズ R.S.、リーズ A.M.;Effects of sitosterol therapy on plasma lipid and lipoprotein concentrations. in:Greten H(Ed) Lipoprotein Metabolism.Springer−Verlag,Berlin,Heidelberg,New York,1976:119−124
9.リーズ A.M.、モク H.Y.I.、リーズ R.S.、マックラスキー M.A.、グルンディ S.M.;Plant sterols as cholesterol−lowering agents:clinical trials in patients with hypercholesterolemia and studies of sterol balance.Atherosclerosis 1977;28:325−338
10.
11.フォン クーツ E、シュルター G;Preclinical safety evaluation of cerivastatin,a novel HMG−CoA reductase inhibitor.Am J Cardiol 1998
Aug 27;82(4B):11J−17J
12.デ ピニュクス G、シャリオト P、アミ−セイド M、ロウアーン F、レジョンク JL、アスティエール A、ジャコトト B、ジェラルディ R;Lipid−lowering drugs and mitochondrial function:effect of HMG−CoA reductase inhibitors
on serum ubiquinone and blood lactase/pyruvate ratio.Br J Clin Pharmacol 1996 Sep;42(3):333−7
13.シャリオト P、モンネット I、モウシェト M、ロアー M、レファウシェウアー JP、ドゥブレウイル−レマイル ML、チョウステマン M、ジャラルディ R;Determination of the blood lactate:pyruvate ratio as a noninvasive test for the
diagnosis of zidovudine myopathy.Arthritis Rheum 1994 Apr;37(4):583−6
14.ミヤケ Y、ショウズ A、ニシカワ M、ヨネモト T、シミズ H、オモト S、ハヤカワ T、イナダ M;Effect of treatment with 3−hydroxy−3−methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitors on serum coenzyme Q10
in diabetic patients.Arzneimittelforschung 1999 Apr;49(4):324−9
15.モーテンセン SA、レス A、アグナー E、ローデ M;Dose−related decrease of serum coenzyme Q10 during treatment with HMG−CoA reductase inhibitors.Mol Aspects Med 1997;18 Suppl:S137−44
16.ファンガーン CJ;Prevention of stroke and dementia with statins:Effects beyond lipid
lowering.Cardiology Division,Department
of Medicine,Weill Medical College of Cornell University,New York,New York 10021,USA.cjv2001@med.cornell.edu Am J Cardiol.2003 Feb 20;91(4A):23B−29B
17.ブリントン EA;Lipid abnormalities in the metabolic syndrome.Carl T.Hayden VA Medical Center,Section of Metabolism,Endocrinology,& Nutrition, Department of Internal medicine,111 E,650 East Indian School Road,Phoenix,AZ 85012,USA,Curr Diab Rep.2003 Feb;3(1):65−72
18.シーゲル−アクセル DI;Cerivastatin:a cellular and molecular drug for the future? Department of Medicine III(Cardiology),University of Tubingen,Otfried−Muller St.10,D−72076 Tubingen,Germany.daaxel@med.uni−tuebingen.de Cell Mol Life Sci.2003 Jan;60(1):144−64
Reference 1. Levi RI Declining Mortality in Coronary Heart Diseases Aerosclerosis 1981; 1: 312-325
2. Law R. Waldo N. J. et al. Wu. Hacksaw ZA. Bailey A. Systematic of of Between serum cholesteric concentration and ischemic heart dissertation in observative studies: Data from BUP Med. J. et al. 1994; 308: 363-366
3. Law R. Waldo N. J. et al. Thompson G. By how much and how quick does reduction in serum cholesterol concentration lower risk of ischemic heart disease? Br. Med. J. et al. 1994; 308: 367-373
4). La Rosa J.H. C. Hanning Hake D. Bush D. The cholesterol facts: A summary of the evidence
relaxing to dietary fats, serum cholesterol and coronary heart disease: A joint statement by the American Heart Association and the National Heart, Lund
Institute. Circulation 1990; 81: 1721- 17335. Havel R. J. et al. Lapaport E. Drug Therapy: Management of Primary Hyperlipidemia. New England Journal of Medicine, 1995; 332: 1491-14986. Barker and Rye; Atherosclerosis 1996; 121: 1-12
7). Effects of plant sterols on cholesterol metabolism. Atherosclerosis, 1976; 23: 239-248
8). Leeds R. S. Leeds A. M.M. Effects of situterotherapy on plasma lipid and lipoprotein contents. in: Greten H (Ed) Lipoprotein Metabolism. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, 1976: 119-124.
9. Leeds A. M.M. Moku H. Y. I. Leeds S. McClassy M. A. Grundi S. M.M. Plant sterols as cholesterol-lowering agents: clinical trials in patents with hypercholesteria and studies of sterol balance. Atherosclerosis 1977; 28: 325-338.
10.
11. Von Couts E, Schulter G; Preclinical safety evaluation of cerivastatin, a novel HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor. Am J Cardiol 1998
Aug 27; 82 (4B): 11J-17J
12 Depinux G, Chariot P, Ami-Said M, Rowan F, Legionk JL, Astierre A, Jakototo B, Geraldi R; Lipid-lowering drugs and mitochondrial function: effect of HMG-CoAt
on serum ubiquinone and blood lactate / pyruvate ratio. Br J Clin Pharmacol 1996 Sep; 42 (3): 333-7
13. Chariot P, Monnet I, Moouchet M, Rohr M, Lefaucher JP, Dubreuil-Lemile ML, Chou Steman M, Jalaldi R; Determination of the blood lactate: pyruvate ratio asa nonvestef
diagnosis of zidovudine myopathy. Arthritis Rheum 1994 Apr; 37 (4): 583-6
14 Miyake Y, Shozu A, Nishikawa M, Yonemoto T, Shimizu H, Omoto S, Hayakawa T, Inada M; Effect of treatment with 3-hydroxy-methyl-recognition
in diabetic patents. Arzneimtelforschung 1999 Apr; 49 (4): 324-9
15. Mortensen SA, Les A, Agner E, Rohde M; Dose-relevant decrease of serum coenyme Q10 during treatment with HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. Mol Aspects Med 1997; 18 Suppl: S137-44.
16. Fangarn CJ: Prevention of stroke and dementia with statins: Effects behind lipid
lowering. Cardiology Division, Department
of Medicine, Weill Medical College of Cornell University, New York, New York 10021, USA. cjv2001 @ med. cornell. edu Am J Cardiol. 2003 Feb 20; 91 (4A): 23B-29B
17. Blinton EA; Lipid Abnormalities in the metabolic syndrome. Carl T. Hayden VA Medical Center, Section of Metabolism, Endocrinology, & Nutrition, Department of Internal medicine, 111 E, 650 East Ind. 2003 Feb; 3 (1): 65-72
18. Siegel-Axel DI; Cerivastatin: a cellular and molecular drug for the future? Department of Medicine III (Cardiology), University of Tubingen, Otfried-Muller St. 10, D-72076 Tubingen, Germany. daaxel @ med. uni-tubingen. de Cell Mol Life Sci. 2003 Jan; 60 (1): 144-64
Claims (43)
反応性カルボキシル基を有するコレステロール生合成阻害剤を表し;R3は少なくとも一
つの遊離性及び反応性水酸基を有するコレステロール生合成阻害剤を表し;R4はアスコ
ルビン酸に由来し、Xは水素原子であるか、又は、生物学的に許容される金属又はアルカリ土類金属からなる群から選択され、並びに、nは1−5を表す。)の一つ以上を有することを特徴とする化合物(生物学的に許容される塩又は溶媒和物、又は少なくとも一つの前記化合物の又はそれらの塩の又はそれらの溶媒和物のプロドラッグを含む。)。 Including sterols or stanols (including biologically acceptable salts thereof)
合物。 Wherein R 3 is equal to or representing the simvastatin or lovastatin, a compound according to claim 1.
びにnは1−5を表す。)を有する化合物(あらゆる生物学的に許容される塩又は溶媒和物、又は少なくとも一つの前記化合物の又はそれらの塩の又はそれらの溶媒和物のプロドラッグを含む。)から選択される少なくとも一つのコレステロール吸収阻害剤;及び
b)少なくとも一つのコレステロール生合成阻害剤
を含む組成物。 a) General formula
反応性カルボキシル基を有するコレステロール生合成阻害剤を表し;R3は少なくとも一
つの遊離性及び反応性水酸基を有するコレステロール生合成阻害剤を表し;R4はアスコ
ルビン酸に由来し、Xは水素原子であるか、又は、金属、アルカリ土類金属及びアルカリ金属からなる群から選択され、並びに、nは1−5を表す。)の一つ以上を有する少なくとも一つの化合物(生物学的に許容される塩又は溶媒和物、又は少なくとも一つの前記化合物の又はそれらの塩の又はそれらの溶媒和物のプロドラッグを含む。)、並びにそれらのための薬剤的に許容される担体を含むことを特徴とする医薬組成物。 The following chemical formula
組成物。 Wherein R 3 is equal to or representing the simvastatin or lovastatin, 25. A composition according.
びにnは1−5を表す。)を有する化合物(あらゆる生物学的に許容される塩又は溶媒和物、又は少なくとも一つの前記化合物の又はそれらの塩の又はそれらの溶媒和物のプロドラッグを含む。)から選択される少なくとも一つのコレステロール吸収阻害剤;
b)少なくとも一つのコレステロール生合成阻害剤;及び
c)それらのための薬剤的に許容される担体
を含む医薬組成物。 a) General formula
A pharmaceutical composition comprising b) at least one cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitor; and c) a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier therefor.
テロール、ラトステロール、ステラステロール、スピナステロール、コンドリラステロール、ペポステロール、アベナステロール、イソアベナステロール、フェコステロール及びポリナスタステロールからなる群から選択されることを特徴とする、請求項25又は請求項29に記載の組成物。 The sterols are sitosterol, campesterol, stigmasterol, brassicasterol (including dihydrobrass castrol), desmosterol, carinosterol, polyferasterol, cryonasterol, ergosterol, coprosterol, kodisosterol, isofucosterol, fuco It is selected from the group consisting of sterols, clerolosterols, nerbisterols, latosterols, stellaterols, spinasterols, chondirasterols, pepostolols, abenasterols, isoabenasterols, fecosterols and polynassterols 30. A composition according to claim 25 or claim 29.
a)一般にCVDに関連し、動脈硬化、アテローム性動脈硬化、細動脈硬化、狭心症および血栓症などの一つ以上の症状を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
b)CVDに関連するリスク因子の一つ以上を減らし及び/又は排除すること、
c)アテローム性動脈硬化症を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
d)高コレステロール血症を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
e)高脂質症状を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
f)脂質代謝異常を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
g)高血圧症を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
h)冠動脈疾患を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
i)冠動脈プラーク発生を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
j)冠動脈プラーク炎症を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
k)血清LDLコレステロールを低下すること、
l)血清HDLコレステロールを増加すること、
m)血清トリグリセリド値を減少すること、
n)コレステロール生合成を減少すること、
o)脂質代謝異常状態又は障害を予防し、減らし、排除し、又は改善すること、
p)高コレステロール血症又は低アルファリポタンパク質血症を予防し、減らし、排除し、又は改善すること、
q)アテローム性病変またはプラークの発生を予防し、減らし、排除し、安定化させ、又は改善すること、
r)心血管疾患及び冠動脈疾患の発生に関連する炎症の発生を予防し、減らし、排除し、又は改善すること、
s)血清HDLの不足、若しくはLDL、VLDL、Lp(a)、ベータ−BLDL、IDL又は残留リポタンパク質の過剰をその基礎として有するか、又は、それらにより悪化する、あらゆる症状、疾患又は障害を予防し、減らし、排除し、又は改善すること、
t)発作のリスクを減少すること、
u)イソプレノイド合成を抑制すること、
v)アルツハイマー病を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
w)認知症を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
x)骨粗鬆症を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
y)酸化ストレスによる損傷を予防し、減らし、排除し、又は改善すること、
z)酸化からHDLの安定性を増強し及び/又は維持すること、
aa)酸化からLDL、VLDL、又はIDLの安定性を増強し及び/又は維持すること、
bb)酸化からトリグリセリド(TG)の安定性を増強し及び/又は維持すること、
cc)抗凝固特性を示すこと、
dd)抗増殖特性を示すこと、
ee)免疫調節特性を示すこと、
ff)血管由来特性を示すこと、
gg)腫瘍の成長を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
hh)骨質量及び/又は骨代謝を増加すること、及び、
ii)特に細胞又は分子レベルにおいて、スタチンの投与によって得られる非脂質関連の多面発現効果の何れかを増強すること、
の一つ以上を達成する方法であって、以下の化学式
反応性カルボキシル基を有するコレステロール生合成阻害剤を表し;R3は少なくとも一
つの遊離性及び反応性水酸基を有するコレステロール生合成阻害剤を表し;R4はアスコ
ルビン酸に由来し、Xは水素原子であるか、又は、金属、アルカリ土類金属及びアルカリ金属からなる群から選択され、並びに、nは1−5を表す。)を有する一つ以上の化合物(生物学的に許容される塩又は溶媒和物、又は少なくとも一つの前記化合物の又はそれらの塩の又はそれらの溶媒和物のプロドラッグを含む。)の無毒性かつ治療有効量を動物に投与することを含む方法。 The following therapeutic purposes:
a) preventing, treating or alleviating one or more symptoms generally related to CVD, such as arteriosclerosis, atherosclerosis, arteriole sclerosis, angina and thrombosis,
b) reducing and / or eliminating one or more of the risk factors associated with CVD;
c) preventing, treating or reducing atherosclerosis,
d) preventing, treating or reducing hypercholesterolemia,
e) prevent, treat or alleviate high lipid symptoms;
f) preventing, treating or reducing lipid metabolism disorders;
g) preventing, treating or reducing hypertension,
h) preventing, treating or reducing coronary artery disease;
i) preventing, treating or reducing the occurrence of coronary plaque,
j) preventing, treating or reducing coronary plaque inflammation;
k) lowering serum LDL cholesterol,
l) increasing serum HDL cholesterol,
m) reducing serum triglyceride levels,
n) reducing cholesterol biosynthesis,
o) preventing, reducing, eliminating or ameliorating abnormal lipid metabolism conditions or disorders;
p) preventing, reducing, eliminating or ameliorating hypercholesterolemia or low alpha lipoproteinemia,
q) preventing, reducing, eliminating, stabilizing or ameliorating the development of atherosclerotic lesions or plaques;
r) preventing, reducing, eliminating or ameliorating the occurrence of inflammation associated with the occurrence of cardiovascular and coronary artery disease;
s) Prevent any symptoms, diseases or disorders that have or are exacerbated by a lack of serum HDL or LDL, VLDL, Lp (a), beta-BLDL, IDL or excess of residual lipoproteins Reduce, eliminate or improve,
t) reducing the risk of seizures,
u) inhibiting isoprenoid synthesis;
v) preventing, treating or reducing Alzheimer's disease;
w) prevent, treat or alleviate dementia;
x) preventing, treating or reducing osteoporosis,
y) prevent, reduce, eliminate or ameliorate oxidative stress damage;
z) enhance and / or maintain the stability of HDL from oxidation,
aa) enhancing and / or maintaining the stability of LDL, VLDL, or IDL from oxidation,
bb) enhancing and / or maintaining the stability of triglycerides (TG) from oxidation;
cc) exhibit anticoagulant properties;
dd) exhibit anti-proliferative properties;
ee) exhibiting immunomodulatory properties;
ff) exhibiting blood vessel-derived properties;
gg) preventing, treating or reducing tumor growth;
hh) increasing bone mass and / or bone metabolism; and
ii) enhance any of the non-lipid related pleiotropic effects obtained by administration of statins, especially at the cellular or molecular level;
A method for achieving one or more of the following chemical formulas:
方法。 Wherein R 3 is equal to or representing the simvastatin or lovastatin method of claim 35, wherein.
a)一般にCVDに関連し、動脈硬化、アテローム性動脈硬化、細動脈硬化、狭心症および血栓症などの一つ以上の症状を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
b)CVDに関連するリスク因子の一つ以上を減らし及び/又は排除すること、
c)アテローム性動脈硬化症を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
d)高コレステロール血症を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
e)高脂質症状を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
f)脂質代謝異常を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
g)高血圧症を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
h)冠動脈疾患を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
i)冠動脈プラーク発生を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
j)冠動脈プラーク炎症を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
k)血清LDLコレステロールを低下すること、
l)血清HDLコレステロールを増加すること、
m)血清トリグリセリド値を減少すること、
n)コレステロール生合成を減少すること、
o)脂質代謝異常状態又は障害を予防し、減らし、排除し、又は改善すること、
p)高コレステロール血症又は低アルファリポタンパク質血症を予防し、減らし、排除し、又は改善すること、
q)アテローム性病変またはプラークの発生を予防し、減らし、排除し、安定化させ、又は改善すること、
r)心血管疾患及び冠動脈疾患の発生に関連する炎症の発生を予防し、減らし、排除し、又は改善すること、
s)血清HDLの不足、若しくはLDL、VLDL、Lp(a)、ベータ−BLDL、IDL又は残留リポタンパク質の過剰をその基礎として有するか、又は、それらにより悪化する、あらゆる症状、疾患又は障害を予防し、減らし、排除し、又は改善すること、
t)発作のリスクを減少すること、
u)イソプレノイド合成を抑制すること、
v)アルツハイマー病を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
w)認知症を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
x)骨粗鬆症を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
y)酸化ストレスによる損傷を予防し、減らし、排除し、又は改善すること、
z)酸化からHDLの安定性を増強し及び/又は維持すること、
aa)酸化からLDL、VLDL、又はIDLの安定性を増強し及び/又は維持すること、
bb)酸化からトリグリセリド(TG)の安定性を増強し及び/又は維持すること、
cc)抗凝固特性を示すこと、
dd)抗増殖特性を示すこと、
ee)免疫調節特性を示すこと、
ff)血管由来特性を示すこと、
gg)腫瘍の成長を予防し、治療し、又は軽減すること、
hh)骨質量及び/又は骨代謝を増加すること、及び、
ii)特に細胞又は分子レベルにおいて、スタチンの投与によって得られる非脂質関連の
多面発現効果の何れかを増強すること、
の一つ以上を達成する方法であって、
a)一般式
びにnは1−5を表す。)を有する化合物(あらゆる生物学的に許容される塩又は溶媒和物、又は少なくとも一つの前記化合物の又はそれらの塩又はそれらの溶媒和物のプロドラッグを含む。)から選択される少なくとも一つのコレステロール吸収阻害剤;及び
b)少なくとも一つのコレステロール生合成阻害剤
の無毒性かつ治療有効量を動物に投与することを含む方法。 The following therapeutic purposes:
a) preventing, treating or alleviating one or more symptoms generally related to CVD, such as arteriosclerosis, atherosclerosis, arteriole sclerosis, angina and thrombosis,
b) reducing and / or eliminating one or more of the risk factors associated with CVD;
c) preventing, treating or reducing atherosclerosis,
d) preventing, treating or reducing hypercholesterolemia,
e) prevent, treat or alleviate high lipid symptoms;
f) preventing, treating or reducing lipid metabolism disorders;
g) preventing, treating or reducing hypertension,
h) preventing, treating or reducing coronary artery disease;
i) preventing, treating or reducing the occurrence of coronary plaque,
j) preventing, treating or reducing coronary plaque inflammation;
k) lowering serum LDL cholesterol,
l) increasing serum HDL cholesterol,
m) reducing serum triglyceride levels;
n) reducing cholesterol biosynthesis,
o) preventing, reducing, eliminating or ameliorating abnormal lipid metabolism conditions or disorders;
p) preventing, reducing, eliminating or ameliorating hypercholesterolemia or low alpha lipoproteinemia,
q) preventing, reducing, eliminating, stabilizing or ameliorating the development of atherosclerotic lesions or plaques;
r) preventing, reducing, eliminating or ameliorating the occurrence of inflammation associated with the occurrence of cardiovascular and coronary artery disease;
s) Prevent any symptoms, diseases or disorders that have or are exacerbated by a lack of serum HDL or LDL, VLDL, Lp (a), beta-BLDL, IDL or excess of residual lipoproteins Reduce, eliminate or improve,
t) reducing the risk of seizures,
u) inhibiting isoprenoid synthesis;
v) preventing, treating or reducing Alzheimer's disease;
w) prevent, treat or alleviate dementia;
x) preventing, treating or reducing osteoporosis,
y) prevent, reduce, eliminate or ameliorate oxidative stress damage;
z) enhance and / or maintain the stability of HDL from oxidation,
aa) enhancing and / or maintaining the stability of LDL, VLDL, or IDL from oxidation,
bb) enhancing and / or maintaining the stability of triglycerides (TG) from oxidation;
cc) exhibit anticoagulant properties;
dd) exhibit anti-proliferative properties;
ee) exhibiting immunomodulatory properties;
ff) exhibiting blood vessel-derived properties;
gg) preventing, treating or reducing tumor growth;
hh) increasing bone mass and / or bone metabolism; and
ii) enhance any of the non-lipid related pleiotropic effects obtained by administration of statins, especially at the cellular or molecular level;
A method of achieving one or more of the following:
a) General formula
a)一般式
びにnは1−5を表す。)を有する化合物(あらゆる生物学的に許容される塩又は溶媒和物、又は少なくとも一つの前記化合物の又はそれらの塩の又はそれらの溶媒和物のプロドラッグを含む。)から選択される少なくとも一つのコレステロール吸収阻害剤を含む組成物;及び
b)少なくとも一つのコレステロール生合成阻害剤を含む組成物、
を各組成物の投与を説明する説明書を伴って含むキット。
At least two other ingredients:
a) General formula
In combination with instructions describing the administration of each composition.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US61545603A | 2003-07-09 | 2003-07-09 | |
| PCT/CA2004/000999 WO2005005453A2 (en) | 2003-07-09 | 2004-07-09 | Novel compounds and compositions comprising sterols and/or stanols and cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitors and use thereof in treating or preventing a variety of diseases and conditions. |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2007525470A true JP2007525470A (en) | 2007-09-06 |
Family
ID=34062381
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006517922A Withdrawn JP2007525470A (en) | 2003-07-09 | 2004-07-09 | Novel compounds and compositions comprising sterols and / or stanols and cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitors and their use in the treatment or prevention of various diseases and conditions |
Country Status (13)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP1644399A2 (en) |
| JP (1) | JP2007525470A (en) |
| KR (1) | KR20060052792A (en) |
| CN (1) | CN1832957A (en) |
| AU (1) | AU2004255285A1 (en) |
| BR (1) | BRPI0412439A (en) |
| CA (1) | CA2531836A1 (en) |
| MX (1) | MXPA06000326A (en) |
| NO (1) | NO20060632L (en) |
| NZ (1) | NZ545087A (en) |
| PL (1) | PL379516A1 (en) |
| RU (1) | RU2006103797A (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2005005453A2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (35)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BRPI0715160A2 (en) | 2006-08-08 | 2013-06-11 | Sanofi Aventis | arylamimoaryl-alkyl-substituted imidazolidine-2,4-diones, process for preparing them, drugs comprising these compounds, and their use |
| KR100886466B1 (en) * | 2006-09-12 | 2009-03-04 | (주)한국씨엔에스팜 | New stigmasterol derivatives or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, process for the preparation thereof and composition comprising the same for inhibiting obesity or for preventing and treating hyperlipidemia |
| DE102007005045B4 (en) | 2007-01-26 | 2008-12-18 | Sanofi-Aventis | Phenothiazine derivatives, process for their preparation and their use as medicines |
| EP2025674A1 (en) | 2007-08-15 | 2009-02-18 | sanofi-aventis | Substituted tetra hydro naphthalines, method for their manufacture and their use as drugs |
| DE102007054497B3 (en) | 2007-11-13 | 2009-07-23 | Sanofi-Aventis Deutschland Gmbh | New crystalline hydrate form of dodecanedioic acid 4-((2S,3R)-3-((S)-3-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-3-hydroxy-propyl)-2-(4-methoxy-phenyl)-4-oxo-azetidin-1-yl)-benzylamide ((2S,3R,4R,5R)-pentahydroxy-hexyl)-amide useful e.g. to treat hyperlipidemia |
| EP2310372B1 (en) | 2008-07-09 | 2012-05-23 | Sanofi | Heterocyclic compounds, processes for their preparation, medicaments comprising these compounds, and the use thereof |
| WO2010068601A1 (en) | 2008-12-08 | 2010-06-17 | Sanofi-Aventis | A crystalline heteroaromatic fluoroglycoside hydrate, processes for making, methods of use and pharmaceutical compositions thereof |
| SG178880A1 (en) | 2009-08-26 | 2012-04-27 | Sanofi Sa | Novel crystalline heteroaromatic fluoroglycoside hydrates, pharmaceuticals comprising these compounds and their use |
| EP2582709B1 (en) | 2010-06-18 | 2018-01-24 | Sanofi | Azolopyridin-3-one derivatives as inhibitors of lipases and phospholipases |
| WO2012120053A1 (en) | 2011-03-08 | 2012-09-13 | Sanofi | Branched oxathiazine derivatives, method for the production thereof, use thereof as medicine and drug containing said derivatives and use thereof |
| US8828994B2 (en) | 2011-03-08 | 2014-09-09 | Sanofi | Di- and tri-substituted oxathiazine derivatives, method for the production thereof, use thereof as medicine and drug containing said derivatives and use thereof |
| EP2683700B1 (en) | 2011-03-08 | 2015-02-18 | Sanofi | Tetra-substituted oxathiazine derivatives, method for their preparation, their usage as medicament and medicament containing same and its use |
| WO2012120051A1 (en) | 2011-03-08 | 2012-09-13 | Sanofi | Benzyl-oxathiazine derivates substituted with adamantane or noradamantane, medicaments containing said compounds and use thereof |
| WO2012120055A1 (en) | 2011-03-08 | 2012-09-13 | Sanofi | Di- and tri-substituted oxathiazine derivates, method for the production thereof, use thereof as medicine and drug containing said derivatives and use thereof |
| EP2683702B1 (en) | 2011-03-08 | 2014-12-24 | Sanofi | New substituted phenyl oxathiazine derivatives, method for their manufacture, medicines containing these compounds and their application |
| EP2766349B1 (en) | 2011-03-08 | 2016-06-01 | Sanofi | Oxathiazine derivatives substituted with carbocycles or heterocycles, method for producing same, drugs containing said compounds, and use thereof |
| WO2012120057A1 (en) | 2011-03-08 | 2012-09-13 | Sanofi | Novel substituted phenyl-oxathiazine derivatives, method for producing them, drugs containing said compounds and the use thereof |
| EP2683701B1 (en) | 2011-03-08 | 2014-12-24 | Sanofi | Oxathiazine derivatives substituted with benzyl or heteromethylene groups, method for their preparation, their usage as medicament, medicament containing same and its use |
| EP2567959B1 (en) | 2011-09-12 | 2014-04-16 | Sanofi | 6-(4-hydroxy-phenyl)-3-styryl-1h-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridine-4-carboxylic acid amide derivatives as kinase inhibitors |
| JP6262723B2 (en) | 2012-05-07 | 2018-01-17 | ザ リージェンツ オブ ザ ユニバーシティ オブ カリフォルニアThe Regents Of The University Of California | Oxysterol analog OXY133 induces bone development and hedgehog signaling and inhibits adipogenesis |
| KR20140081339A (en) * | 2012-12-21 | 2014-07-01 | 부경대학교 산학협력단 | Pharmaceutical composition for prevention or treatment of neurodegenerative disease comprising fucosterol |
| CA2911205A1 (en) | 2013-05-02 | 2014-11-06 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Bone-selective osteogenic oxysterol-bone targeting agents |
| CN107427526B (en) | 2014-12-09 | 2021-08-03 | 华沙整形外科股份有限公司 | Compounds and methods relating to sterols |
| CN104434927A (en) * | 2014-12-16 | 2015-03-25 | 吉林农业大学 | Application of bicyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene malonate B in preparing hypotensive drugs |
| US9987289B2 (en) | 2015-07-10 | 2018-06-05 | Warsaw Orthopedic, Inc. | Slow release oxysterols and methods of use |
| US10632230B2 (en) | 2015-07-10 | 2020-04-28 | Warsaw Orthopedic, Inc. | Implants having a high drug load of an oxysterol and methods of use |
| US9877836B2 (en) | 2015-07-10 | 2018-01-30 | Warsaw Orthopedic, Inc. | Compression resistant implants including an oxysterol and methods of use |
| CN105087609B (en) * | 2015-08-19 | 2018-10-23 | 四川大学 | A kind of recombinant slow virus and its purposes in the drug for preparing treatment cocaine habituation |
| CN105055404B (en) * | 2015-08-19 | 2017-07-18 | 四川大学 | Purposes of the HMGCS2 inhibitor in the medicine for preparing treatment cocaine habituation |
| US10688222B2 (en) | 2016-11-21 | 2020-06-23 | Warsaw Orthopedic, Inc. | Lyophilized moldable implants containing an oxysterol |
| US11384114B2 (en) | 2016-12-09 | 2022-07-12 | Warsaw Orthopedic, Inc. | Polymorphic forms of an oxysterol and methods of making them |
| US10434106B2 (en) * | 2017-05-19 | 2019-10-08 | Warsaw Orthopedic, Inc. | Oxysterol-statin compounds for bone growth |
| US11464888B2 (en) | 2017-06-12 | 2022-10-11 | Warsaw Orthopedic, Inc. | Moldable formulations containing an oxysterol in an acellular tissue matrix |
| KR102139994B1 (en) * | 2017-10-25 | 2020-07-31 | 대구대학교 산학협력단 | Pharmaceutical composition for use in preventing or treating osteoporosis containing stigmasterol as an active ingredient |
| CN113143935B (en) * | 2021-02-01 | 2022-10-11 | 广东药科大学 | Application of stigmasterol in preparation of medicine for improving myocardial hypertrophy |
Family Cites Families (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5216015A (en) * | 1991-02-05 | 1993-06-01 | Rhone-Poulenc Rorer Pharmaceuticals Inc. | Compounds having hypocholesterolemic properties |
| KR100711861B1 (en) * | 1999-06-23 | 2007-04-25 | 포비스 메디-테크 인코포레이티드 | Conjugates of phytosterol or phytostanol with ascorbic acid and use thereof in treating or preventing cardiovascular disease |
-
2004
- 2004-07-09 CA CA002531836A patent/CA2531836A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2004-07-09 MX MXPA06000326A patent/MXPA06000326A/en unknown
- 2004-07-09 PL PL379516A patent/PL379516A1/en unknown
- 2004-07-09 WO PCT/CA2004/000999 patent/WO2005005453A2/en active Search and Examination
- 2004-07-09 AU AU2004255285A patent/AU2004255285A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2004-07-09 KR KR1020067000470A patent/KR20060052792A/en not_active Application Discontinuation
- 2004-07-09 BR BRPI0412439-1A patent/BRPI0412439A/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2004-07-09 NZ NZ545087A patent/NZ545087A/en unknown
- 2004-07-09 CN CNA2004800228667A patent/CN1832957A/en active Pending
- 2004-07-09 RU RU2006103797/04A patent/RU2006103797A/en not_active Application Discontinuation
- 2004-07-09 JP JP2006517922A patent/JP2007525470A/en not_active Withdrawn
- 2004-07-09 EP EP04737936A patent/EP1644399A2/en not_active Withdrawn
-
2006
- 2006-02-09 NO NO20060632A patent/NO20060632L/en not_active Application Discontinuation
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR20060052792A (en) | 2006-05-19 |
| WO2005005453A3 (en) | 2005-06-09 |
| CA2531836A1 (en) | 2005-01-20 |
| CN1832957A (en) | 2006-09-13 |
| MXPA06000326A (en) | 2006-03-30 |
| BRPI0412439A (en) | 2006-09-05 |
| NO20060632L (en) | 2006-04-06 |
| AU2004255285A1 (en) | 2005-01-20 |
| RU2006103797A (en) | 2006-07-27 |
| EP1644399A2 (en) | 2006-04-12 |
| NZ545087A (en) | 2009-10-30 |
| PL379516A1 (en) | 2006-10-02 |
| WO2005005453A2 (en) | 2005-01-20 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP2007525470A (en) | Novel compounds and compositions comprising sterols and / or stanols and cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitors and their use in the treatment or prevention of various diseases and conditions | |
| US7645748B2 (en) | Sterol/stanol phosphorylnitroderivatives and use thereof | |
| US20080299187A1 (en) | Substances for Reducing Occurence of Major Cardiac Events in Humans | |
| US8895079B2 (en) | Combinations of botanical extracts for promoting cardiovascular health | |
| US7645749B2 (en) | Sterol/stanol nitroderivatives and use thereof | |
| EP1189924B1 (en) | Conjugates of phytosterol or phytostanol with ascorbic acid and use thereof in treating or preventing cardiovascular disease | |
| JP2005533810A (en) | Novel anticholesterol composition and method of use thereof | |
| Van Heek et al. | Pharmacology of ezetimibe | |
| US20050234025A1 (en) | Compositions comprising one or more policosanols and/or policosanoic acids combined with sterol and/or steroid based ascorbic acid derivatives, and uses thereof | |
| EA010373B1 (en) | Pharmaceutical compositions comprising higher primary alcohols and ezetimibe and process of preparation thereof | |
| WO2001066560A2 (en) | Novel derivatives comprising phytosterols and/or phytostanols and alpha-lipoic and use thereof in treating or preventing cardiovascular disease, its underlying conditions and other disorders | |
| Endo | Discovery and development of statins | |
| ITRM970390A1 (en) | PHARMACEUTICAL COMPOSITION FOR THE TREATMENT OF PATHOLOGIES CAUSED BY ALTERED LIPID METABOLISM | |
| US20210106541A1 (en) | Natural combination products and methods for regulation of total blood cholesterol | |
| JP2003503342A (en) | Combinations of MTP inhibitors and HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors and their use in medicine | |
| JP2005535611A (en) | Novel androstane and androstene derivatives with ascorbic acid and their use in the treatment or prevention of various diseases, disorders and disorders | |
| WO2011149766A2 (en) | Lipid-tailored pharmaceutical agents | |
| WO2001085155A1 (en) | Method and compositions for inhibiting arteriosclerosis | |
| CN113271931A (en) | New application of carbamate beta phenylethanolamine analogue in enhancing clearance of intracellular LDL cholesterol and combination with statins | |
| US20080070938A1 (en) | Medicinal composition for mitigating blood lipid or lowering blood homocysteine | |
| JP4868648B2 (en) | Hypertriglyceridemia treatment | |
| AU2005205165B2 (en) | Pharmaceutical compositions comprising higher primary aliphatic alcohols and HMG CoA reductase inhibitor and process of preparation thereof | |
| KR20020025066A (en) | Antilipemic combinations comprising HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors and carnitines | |
| CA2676583C (en) | Composition comprising red yeast rice and an omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid | |
| EP1432425A1 (en) | A method of reducing the "in vivo" cholesterol ester transfer protein mediated transfer of cholesteryl esters between high density lipoproteins (hdl) and low density lipoproteins (ldl) |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20070706 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20070706 |
|
| A761 | Written withdrawal of application |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A761 Effective date: 20110106 |