JP2005116253A - Manufacturing device of display device, and manufacturing method of display device - Google Patents
Manufacturing device of display device, and manufacturing method of display device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2005116253A JP2005116253A JP2003346956A JP2003346956A JP2005116253A JP 2005116253 A JP2005116253 A JP 2005116253A JP 2003346956 A JP2003346956 A JP 2003346956A JP 2003346956 A JP2003346956 A JP 2003346956A JP 2005116253 A JP2005116253 A JP 2005116253A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- substrate
- buffer layer
- display device
- main surface
- manufacturing apparatus
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 75
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 159
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 50
- 230000004888 barrier function Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 49
- 238000010894 electron beam technology Methods 0.000 claims description 47
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 claims description 43
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 claims description 10
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 claims description 10
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 claims description 10
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 claims description 9
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 claims description 9
- 231100000987 absorbed dose Toxicity 0.000 claims description 7
- 239000007769 metal material Substances 0.000 claims description 6
- 229910010293 ceramic material Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 2
- 230000001678 irradiating effect Effects 0.000 claims description 2
- 229910044991 metal oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 2
- 150000004706 metal oxides Chemical class 0.000 claims description 2
- 230000007774 longterm Effects 0.000 abstract 1
- 230000000717 retained effect Effects 0.000 abstract 1
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 description 129
- 238000005401 electroluminescence Methods 0.000 description 60
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 26
- 239000010408 film Substances 0.000 description 15
- 239000000178 monomer Substances 0.000 description 11
- 238000003860 storage Methods 0.000 description 8
- 238000005192 partition Methods 0.000 description 7
- 239000003990 capacitor Substances 0.000 description 6
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 6
- 238000005566 electron beam evaporation Methods 0.000 description 6
- 239000010409 thin film Substances 0.000 description 6
- 239000000853 adhesive Substances 0.000 description 5
- 230000001070 adhesive effect Effects 0.000 description 5
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 5
- 238000001723 curing Methods 0.000 description 5
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 5
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 5
- 238000007740 vapor deposition Methods 0.000 description 5
- 239000002585 base Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000011575 calcium Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000013021 overheating Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000004544 sputter deposition Methods 0.000 description 4
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium Chemical compound [Al] XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000002274 desiccant Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000001227 electron beam curing Methods 0.000 description 3
- 150000002500 ions Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 239000011159 matrix material Substances 0.000 description 3
- 150000002894 organic compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 239000011368 organic material Substances 0.000 description 3
- OYPRJOBELJOOCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N Calcium Chemical compound [Ca] OYPRJOBELJOOCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910052788 barium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- DSAJWYNOEDNPEQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N barium atom Chemical compound [Ba] DSAJWYNOEDNPEQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910052791 calcium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000000470 constituent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000000151 deposition Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000012535 impurity Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000010030 laminating Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000011777 magnesium Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000002985 plastic film Substances 0.000 description 2
- -1 polyparaphenylene vinylene Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000011734 sodium Substances 0.000 description 2
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000004925 Acrylic resin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920000178 Acrylic resin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Carbon Chemical compound [C] OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Copper Chemical compound [Cu] RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- DGAQECJNVWCQMB-PUAWFVPOSA-M Ilexoside XXIX Chemical compound C[C@@H]1CC[C@@]2(CC[C@@]3(C(=CC[C@H]4[C@]3(CC[C@@H]5[C@@]4(CC[C@@H](C5(C)C)OS(=O)(=O)[O-])C)C)[C@@H]2[C@]1(C)O)C)C(=O)O[C@H]6[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O6)CO)O)O)O.[Na+] DGAQECJNVWCQMB-PUAWFVPOSA-M 0.000 description 1
- WHXSMMKQMYFTQS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Lithium Chemical compound [Li] WHXSMMKQMYFTQS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FYYHWMGAXLPEAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N Magnesium Chemical compound [Mg] FYYHWMGAXLPEAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZLMJMSJWJFRBEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Potassium Chemical compound [K] ZLMJMSJWJFRBEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Titanium Chemical compound [Ti] RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052769 Ytterbium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052783 alkali metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000001340 alkali metals Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229910052784 alkaline earth metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000001342 alkaline earth metals Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- PNEYBMLMFCGWSK-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium oxide Inorganic materials [O-2].[O-2].[O-2].[Al+3].[Al+3] PNEYBMLMFCGWSK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000004982 aromatic amines Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N atomic oxygen Chemical compound [O] QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052799 carbon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010949 copper Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000006866 deterioration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000001704 evaporation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000007789 gas Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 1
- AMGQUBHHOARCQH-UHFFFAOYSA-N indium;oxotin Chemical compound [In].[Sn]=O AMGQUBHHOARCQH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000002347 injection Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000007924 injection Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910010272 inorganic material Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011147 inorganic material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004973 liquid crystal related substance Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052744 lithium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052749 magnesium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052760 oxygen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000001301 oxygen Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000000059 patterning Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229920000767 polyaniline Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229910021420 polycrystalline silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229920002098 polyfluorene Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000642 polymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 230000000379 polymerizing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229920005591 polysilicon Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000123 polythiophene Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229910052700 potassium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011591 potassium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002243 precursor Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052709 silver Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000004332 silver Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002356 single layer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052708 sodium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052719 titanium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010936 titanium Substances 0.000 description 1
- NAWDYIZEMPQZHO-UHFFFAOYSA-N ytterbium Chemical compound [Yb] NAWDYIZEMPQZHO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- YVTHLONGBIQYBO-UHFFFAOYSA-N zinc indium(3+) oxygen(2-) Chemical compound [O--].[Zn++].[In+3] YVTHLONGBIQYBO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Electroluminescent Light Sources (AREA)
- Physical Vapour Deposition (AREA)
Abstract
Description
この発明は、表示装置の製造装置及び表示装置の製造方法に係り、特に、自己発光型表示装置の有効部を封止する封止体の製造装置及びその製造方法に関する。 The present invention relates to a display device manufacturing apparatus and a display device manufacturing method, and more particularly to a sealing body manufacturing apparatus and a manufacturing method thereof for sealing an effective portion of a self-luminous display device.
近年、平面表示装置として、有機エレクトロルミネッセンス(EL)表示装置が注目されている。この有機EL表示装置は、自発光性素子を備えた表示装置であることから、視野角が広く、バックライトを必要とせず薄型化が可能であり、消費電力が抑えられ、且つ応答速度が速いといった特徴を有している。 In recent years, organic electroluminescence (EL) display devices have attracted attention as flat display devices. Since this organic EL display device has a self-luminous element, the organic EL display device has a wide viewing angle, can be thinned without requiring a backlight, can reduce power consumption, and has a high response speed. It has the following features.
これらの特徴から、有機EL表示装置は、液晶表示装置に代わる次世代平面表示装置の有力候補として注目を集めている。このような有機EL表示装置は、陽極と陰極との間に発光機能を有する有機化合物を含む有機活性層を挟持した有機EL素子をマトリックス状に配置して構成されたアレイ基板を備えている。 From these characteristics, the organic EL display device is attracting attention as a promising candidate for a next-generation flat display device that replaces the liquid crystal display device. Such an organic EL display device includes an array substrate in which organic EL elements each having an organic active layer containing an organic compound having a light emitting function sandwiched between an anode and a cathode are arranged in a matrix.
有機EL素子は、外気に含まれる水分や酸素に触れると、その発光特性が急速に劣化する。このため、アレイ基板上の有機EL素子を配置した主面を、外気から遮蔽し封止する技術が各種提案されている。例えば、有機EL素子の表面側に配置された電極上に、有機膜と無機膜とを積層し成膜する膜封止技術が開示されている(例えば、非特許文献1参照)。
有機EL素子を封止するための封止体を形成するに際して、良好な段差被覆性を有し、しかも、ピンホールやクラックなどの欠陥のない膜を成膜することが要求される。しかしながら、完全な無欠陥膜を得ることは現実には困難である。このため、有機EL素子を外気から完全に遮蔽することができず、長期にわたって十分な性能を維持することが困難となる。 When forming a sealing body for sealing an organic EL element, it is required to form a film having good step coverage and having no defects such as pinholes and cracks. However, it is actually difficult to obtain a complete defect-free film. For this reason, the organic EL element cannot be completely shielded from the outside air, and it becomes difficult to maintain sufficient performance over a long period of time.
また、封止体を形成するに際しては、有機膜及び無機膜の成膜時において、基板温度の上昇や、基板への電子やイオンの衝突によって、有機EL素子にダメージを与えてしまうおそれがある。したがって、封止体を構成する各薄膜の成膜時には、有機EL素子への熱及び電子の影響を軽減することが要求される。 Further, when forming the sealing body, there is a possibility that the organic EL element may be damaged due to an increase in the substrate temperature or collision of electrons or ions with the substrate during the formation of the organic film and the inorganic film. . Therefore, it is required to reduce the influence of heat and electrons on the organic EL element when forming each thin film constituting the sealing body.
この発明は、上述した問題点に鑑みなされたものであって、その目的は、長期にわたって良好な表示性能を維持するための封止体の製造に際して、表示素子のダメージを軽減することが可能な表示装置の製造装置及び表示装置の製造方法を提供することにある。 The present invention has been made in view of the above-described problems, and an object of the present invention is to reduce damage to a display element when manufacturing a sealing body for maintaining good display performance over a long period of time. An object of the present invention is to provide a display device manufacturing apparatus and a display device manufacturing method.
この発明の第1の様態による表示装置の製造装置は、
基板主面に形成され、画像を表示するための複数の画素を備えた有効部と、
基板主面の少なくとも前記有効部を覆うように配置され、バッファ層、及び、前記バッファ層より大きなパターンであってしかも各バッファ層を被覆するバリア層を積層した構造を有する封止体と、を備えた表示装置の製造装置であって、
前記バッファ層または前記バリア層を形成するための材料源を収容する収容部と、
前記有効部を備えた前記基板をその主面が前記収容部に対向した状態で保持する基板ホルダと、
前記収容部と前記基板ホルダに保持された前記基板との間に配置された防熱板と、
を備えたことを特徴とする。
The display device manufacturing apparatus according to the first aspect of the present invention comprises:
An effective portion that is formed on the main surface of the substrate and includes a plurality of pixels for displaying an image;
A sealing body that is arranged so as to cover at least the effective portion of the main surface of the substrate and has a structure in which a buffer layer and a barrier layer that covers each buffer layer are stacked in a pattern larger than the buffer layer; A display device manufacturing apparatus comprising:
An accommodating portion for accommodating a material source for forming the buffer layer or the barrier layer;
A substrate holder for holding the substrate having the effective portion in a state in which a main surface thereof faces the accommodating portion;
A heat insulating plate disposed between the housing portion and the substrate held by the substrate holder;
It is provided with.
この発明の第2の様態による表示装置の製造装置は、
基板主面に形成され、画像を表示するための複数の画素を備えた有効部と、
基板主面の少なくとも前記有効部を覆うように配置され、バッファ層、及び、前記バッファ層より大きなパターンであってしかも各バッファ層を被覆するバリア層を積層した構造を有する封止体と、を備えた表示装置の製造装置であって、
前記バリア層を形成するための材料源を収容する収容部と、
前記有効部を備えた前記基板をその主面が前記収容部に対向した状態で保持する基板ホルダと、
前記収容部と前記基板ホルダに保持された前記基板との間に配置され、接地された導電性を有するグリッドと、
を備えたことを特徴とする。
An apparatus for manufacturing a display device according to the second aspect of the present invention provides:
An effective portion that is formed on the main surface of the substrate and includes a plurality of pixels for displaying an image;
A sealing body that is arranged so as to cover at least the effective portion of the main surface of the substrate and has a structure in which a buffer layer and a barrier layer that covers each buffer layer are stacked in a pattern larger than the buffer layer; A display device manufacturing apparatus comprising:
An accommodating portion for accommodating a material source for forming the barrier layer;
A substrate holder for holding the substrate having the effective portion in a state in which a main surface thereof faces the accommodating portion;
A conductive grid disposed between the housing portion and the substrate held by the substrate holder and grounded;
It is provided with.
この発明の第3の様態による表示装置の製造装置は、
基板主面に形成され、画像を表示するための複数の画素を備えた有効部と、
基板主面の少なくとも前記有効部を覆うように配置され、バッファ層、及び、前記バッファ層より大きなパターンであってしかも各バッファ層を被覆するバリア層を積層した構造を有する封止体と、を備えた表示装置の製造装置であって、
電子線を照射する電子線源と、
前記バッファ層を形成するための材料源を成膜した主面が前記電子線源に対向した状態で前記基板を保持する基板ホルダと、
前記電子線源と前記基板ホルダに保持された前記基板との間に配置され、接地された導電性を有するグリッドと、
を備えたことを特徴とする。
An apparatus for manufacturing a display device according to a third aspect of the present invention provides:
An effective portion that is formed on the main surface of the substrate and includes a plurality of pixels for displaying an image;
A sealing body that is arranged so as to cover at least the effective portion of the main surface of the substrate and has a structure in which a buffer layer and a barrier layer that covers each buffer layer are stacked in a pattern larger than the buffer layer; A display device manufacturing apparatus comprising:
An electron beam source for irradiating an electron beam;
A substrate holder for holding the substrate in a state where a main surface on which a material source for forming the buffer layer is formed is opposed to the electron beam source;
A grounded conductive grid disposed between the electron beam source and the substrate held by the substrate holder;
It is provided with.
この発明の第4の様態による表示装置の製造方法は、
基板主面に、画像を表示するための複数の画素を備えた有効部を形成し、
基板主面の少なくとも前記有効部を覆うように封止体を配置する、表示装置の製造方法であって、
前記封止体の製造工程は、
少なくとも2層のバッファ層を形成する工程と、
前記バッファ層より大きなパターンであってしかも各バッファ層を被覆するバリア層を形成する工程と、を含み、
前記バッファ層及び前記バリア層を形成する工程では、前記基板主面に向けて照射される電子線の吸収線量を200J/g以下とすることを特徴とする。
A manufacturing method of a display device according to the fourth aspect of the present invention includes:
On the main surface of the substrate, an effective portion having a plurality of pixels for displaying an image is formed,
A manufacturing method of a display device, wherein a sealing body is disposed so as to cover at least the effective portion of a substrate main surface,
The manufacturing process of the sealing body includes:
Forming at least two buffer layers;
Forming a barrier layer that is a larger pattern than the buffer layer and covers each buffer layer,
In the step of forming the buffer layer and the barrier layer, the absorbed dose of the electron beam irradiated toward the main surface of the substrate is set to 200 J / g or less.
この発明によれば、封止体の製造に際して、表示素子へのダメージを軽減することが可能な表示装置の製造装置及び表示装置の製造方法を提供することができる。 According to the present invention, it is possible to provide a display device manufacturing apparatus and a display device manufacturing method capable of reducing damage to a display element when manufacturing a sealing body.
以下、この発明の一実施の形態に係る表示装置の製造装置及び表示装置の製造方法について図面を参照して説明する。なお、この実施の形態では、表示装置として、自己発光型表示装置、例えば有機EL(エレクトロルミネッセンス)表示装置を例にして説明する。 A display device manufacturing apparatus and a display device manufacturing method according to an embodiment of the present invention will be described below with reference to the drawings. In this embodiment, a self-luminous display device such as an organic EL (electroluminescence) display device will be described as an example of the display device.
図1及び図2に示すように、有機EL表示装置1は、画像を表示する表示エリア102を有するアレイ基板100と、アレイ基板100の少なくとも表示エリア102を密封する封止部材200とを備えて構成される。アレイ基板100の表示エリア102は、マトリクス状に配置された複数の画素PX(R、G、B)によって構成される。
As shown in FIGS. 1 and 2, the organic EL display device 1 includes an
各画素PX(R、G、B)は、オン画素とオフ画素とを電気的に分離しかつオン画素への映像信号を保持する機能を有する画素スイッチ10と、画素スイッチ10を介して供給される映像信号に基づき表示素子へ所望の駆動電流を供給する駆動トランジスタ20と、駆動トランジスタ20のゲート−ソース間電位を所定期間保持する蓄積容量素子30とを備えている。これら画素スイッチ10及び駆動トランジスタ20は、例えば薄膜トランジスタにより構成され、ここではそれらの半導体層にポリシリコンを用いている。
Each pixel PX (R, G, B) is supplied via a
また、各画素PX(R、G、B)は、表示素子としての有機EL素子40(R、G、B)をそれぞれ備えている。すなわち、赤色画素PXRは、赤色に発光する有機EL素子40Rを備え、緑色画素PXGは、緑色に発光する有機EL素子40Gを備え、さらに、青色画素PXBは、青色に発光する有機EL素子40Bを備えている。
Each pixel PX (R, G, B) includes an organic EL element 40 (R, G, B) as a display element. That is, the red pixel PXR includes an
各種有機EL素子40(R、G、B)の構成は、基本的に同一であって、有機EL素子40は、マトリクス状に配置され画素PX毎に独立島状に形成された第1電極60と、第1電極60に対向して配置され全画素PXに共通に形成された第2電極66と、これら第1電極60と第2電極66との間に保持された有機活性層64と、によって構成されている。
The configurations of the various organic EL elements 40 (R, G, B) are basically the same, and the
アレイ基板100は、画素PXの行方向(すなわち図1のY方向)に沿って配置された複数の走査線Ym(m=1、2、…)と、走査線Ymと略直交する方向(すなわち図1のX方向)に沿って配置された複数の信号線Xn(n=1、2、…)と、有機EL素子40の第1電極60側に電源を供給するための電源供給線Pと、を備えている。
The
電源供給線Pは、表示エリア102の周囲に配置された図示しない第1電極電源線に接続されている。有機EL素子40の第2電極66側は、表示エリア102の周囲に配置されコモン電位(ここでは接地電位)を供給する図示しない第2電極電源線に接続されている。
The power supply line P is connected to a first electrode power line (not shown) arranged around the
また、アレイ基板100は、表示エリア102の外周に沿った周辺エリア104に、走査線Ymのそれぞれに走査信号を供給する走査線駆動回路107と、信号線Xnのそれぞれに映像信号を供給する信号線駆動回路108と、を備えている。すべての走査線Ymは、走査線駆動回路107に接続されている。また、すべての信号線Xnは、信号線駆動回路108に接続されている。
Further, the
画素スイッチ10は、ここでは走査線Ymと信号線Xnとの交差部近傍に配置されている。画素スイッチ10のゲート電極は走査線Ymに接続され、ソース電極は信号線Xnに接続され、ドレイン電極は蓄積容量素子30を構成する一方の電極及び駆動トランジスタ20のゲート電極に接続されている。駆動トランジスタ20のソース電極は蓄積容量素子30を構成する他方の電極及び電源供給線Pに接続され、ドレイン電極は有機EL素子40の第1電極60に接続されている。
Here, the
図2に示すように、アレイ基板100は、配線基板120上に配置された有機EL素子40を備えている。なお、配線基板120は、ガラス基板やプラスチックシートなどの絶縁性支持基板上に、画素スイッチ10、駆動トランジスタ20、蓄積容量素子30、走査線駆動回路107、信号線駆動回路108、各種配線(走査線、信号線、電源供給線等)などを備えて構成されたものとする。
As shown in FIG. 2, the
有機EL素子40を構成する第1電極60は、配線基板120表面の絶縁膜上に配置される。この第1電極60は、ここではITO(Indium Tin Oxide:インジウム・ティン・オキサイド)やIZO(インジウム・ジンク・オキサイド)などの光透過性導電部材によって形成され、陽極として機能する。
The
有機活性層64は、少なくとも発光機能を有する有機化合物を含み、各色共通に形成されるホールバッファ層、エレクトロンバッファ層、及び各色毎に形成される有機発光層の3層積層で構成されても良く、機能的に複合された2層または単層で構成されても良い。例えば、ホールバッファ層は、陽極および有機発光層間に配置され、芳香族アミン誘導体やポリチオフェン誘導体、ポリアニリン誘導体などの薄膜によって形成される。有機発光層は、赤、緑、または青に発光する発光機能を有する有機化合物によって形成される。この有機発光層は、例えば高分子系の発光材料を採用する場合には、PPV(ポリパラフェニレンビニレン)やポリフルオレン誘導体またはその前駆体などの薄膜により構成される。
The organic
第2電極66は、有機活性層64上に各有機EL素子40に共通に配置される。この第2電極66は、例えばCa(カルシウム)、Al(アルミニウム)、Ba(バリウム)、Ag(銀)、Yb(イッテルビウム)などの電子注入機能を有する金属膜によって形成され、陰極として機能している。この第2電極66は、陰極として機能する金属膜の表面をカバーメタルで被覆した2層構造であっても良い。カバーメタルは、例えばアルミニウムによって形成される。
The
この第2電極66の表面は、乾燥剤として吸湿性を有する材料で被覆されることが望ましい。すなわち、有機EL素子40は、水分に触れると、その発光特性が急速に劣化する。このため、有機EL素子40を水分から保護する目的で、その表面に相当する第2電極66上に乾燥剤68が配置される。この乾燥剤68は、吸湿性を有する材料であれば良く、例えばリチウム(Li)、ナトリウム(Na)、カリウム(K)などのアルカリ金属単体またはその酸化物、あるいは、マグネシウム(Mg)、カルシウム(Ca)、バリウム(Ba)などのアルカリ土類金属またはその酸化物などで形成される。
The surface of the
また、アレイ基板100は、表示エリア102において、少なくとも隣接する色毎に画素RX(R、G、B)間を分離する隔壁70を備えている。隔壁70は、各画素を分離するよう形成することが望ましく、ここでは、隔壁70は、各第1電極60の周縁に沿って格子状に配置され、第1電極60を露出する隔壁の開口形状が円形または多角形となるよう形成されている。この隔壁70は、樹脂材料によって形成されるが、例えば、親液性を有する有機材料によって形成された第1絶縁層、及び、第1絶縁層上に配置され疎液性を有する有機材料によって形成された第2絶縁層を積層した構造を有している。
In addition, the
このように構成された有機EL素子40では、第1電極60と第2電極66との間に挟持された有機活性層64にホール及び電子を注入し、これらを再結合させることにより励起子を生成し、この励起子の失活時に生じる所定波長の光放出により発光する。ここでは、このEL発光は、アレイ基板100の下面側すなわち第1電極60側から出射され、表示画面を構成する。
In the
ところで、アレイ基板100は、配線基板120の主面に形成された有効部106を備えている。この有効部106は、ここでは少なくとも画像を表示するための複数の画素PX(R、G、B)を備えた表示エリア102を含むものとするが、走査線駆動回路107や信号線駆動回路108などを備えた周辺エリア104を含んでも良い。
Meanwhile, the
アレイ基板100は、配線基板120の主面のうちの少なくとも有効部106を覆うように配置された封止体300を備えている。この封止体300の表面は、ほぼ平坦化されている。封止部材200は、封止体300の表面全体に塗布された接着剤により封止体300に接着されている。この封止部材200は、プラスチックシートなどの光透過性を有する絶縁性フィルムや、ダイアモンドライクカーボン等によって構成される。
The
封止体300は、バッファ層311、312…と、これらのバッファ層より形成面積が大きなパターンであってしかも各バッファ層を外気から遮蔽するよう被覆するバリア層320、321、322…と、を積層した構造を有している。封止体300の最外層及び最内層は、バリア層であることが望ましい。また、各バリア層は、その周囲で下層のバッファ層の側面を被覆することが望ましい。
The sealing
各バッファ層311、312…は、例えばアクリル系樹脂などの有機系材料により、例えば0.1〜5μm程度の膜厚で形成される。特に、ここでは、これらのバッファ層311、312…を形成する材料としては、比較的粘性の低い液体の状態で塗布され、下層の凹凸を吸収した状態で硬化するような材料を選択することが望ましい。このような材料を用いて形成されたバッファ層311、312…は、それらの表面を平坦化する平坦化層としての機能を有する。 Each of the buffer layers 311, 312... Is formed of an organic material such as an acrylic resin with a film thickness of about 0.1 to 5 μm, for example. In particular, as a material for forming these buffer layers 311, 312..., A material that is applied in a relatively low-viscosity liquid state and is cured in a state in which unevenness in the lower layer is absorbed can be selected. desirable. The buffer layers 311, 312... Formed using such a material have a function as a flattening layer for flattening their surfaces.
各バリア層320、321、322…は、例えば、アルミニウムやチタンなどの金属材料、ITOやIZOなどの金属酸化物材料、または、アルミナなどのセラミック系材料などの無機系材料により、例えば0.1μmオーダの膜厚で形成される。EL発光を第1電極60側から取り出す下面発光方式の場合、バリア層320、321、322…の少なくとも1層として適用される材料は、遮光性及び光反射性を有していることが望ましい。また、EL発光を第2電極66側から取り出す上面発光方式の場合、バリア層320、321、322…として適用される材料は光透過性を有していることが望ましい。
Each of the barrier layers 320, 321, 322,... Is, for example, 0.1 μm by an inorganic material such as a metal material such as aluminum or titanium, a metal oxide material such as ITO or IZO, or a ceramic material such as alumina. It is formed with a film thickness of the order. In the case of the bottom emission method in which EL light is extracted from the
次に、有機EL表示装置の製造方法について説明する。
まず、図3の(a)に示すように、基板SUBの主面に、有効部106を形成する。この有効部106は、金属膜及び絶縁膜の成膜やパターニングなどの処理を繰り返すことによって形成された、画素スイッチ10、駆動トランジスタ20、蓄積容量素子30、走査線駆動回路107、信号線駆動回路108の他に、信号線Xn、走査線Ym、電源供給線P等の各種配線、さらには、それぞれ有機EL素子40を備えた複数の画素PXを含むものとする。
Next, a method for manufacturing an organic EL display device will be described.
First, as shown in FIG. 3A, the
続いて、基板SUBの主面の少なくとも有効部106を覆うように封止体300を配置する。まず、図3の(b)に示すように、有効部106を外気から遮蔽するベースバリア層320を形成する。このベースバリア層320は、図4に示したバリア層形成用の第1チャンバ601において、金属材料を蒸着することによって形成される。このとき、ベースバリア層320は、基板主面において、有効部106を含み、且つ、有効部106より大きな範囲にわたって形成される。
Subsequently, the sealing
続いて、図3の(c)に示すように、ベースバリア層320上に、少なくとも有効部106より大きなパターンの第1バッファ層311を形成する。この第1バッファ層311は、まず、図4に示したバッファ層成膜用の第2チャンバ602において、液体のモノマを蒸発させて成膜したのに続いて、バッファ層硬化用の第3チャンバ603において、モノマをポリマ化することによって形成される。このとき、第1バッファ層311は、直下のベースバリア層320より小さな範囲であって、且つ、有効部106より大きな範囲にわたって形成される。
Subsequently, as shown in FIG. 3C, a
なお、モノマとして、感光性樹脂材料(例えば紫外線硬化型樹脂材料)が適用された場合、第3チャンバ603において、所定波長(例えば紫外線波長)の光源を用いてモノマを所定露光量で露光する。これにより、成膜されたモノマがポリマ化されることで硬化し、第1バッファ層311が形成される。
When a photosensitive resin material (for example, an ultraviolet curable resin material) is applied as the monomer, the monomer is exposed at a predetermined exposure amount using a light source having a predetermined wavelength (for example, an ultraviolet wavelength) in the
また、モノマとして、電子線硬化型樹脂材料が適用された場合、第3チャンバ603において、電子線源を用いてモノマに電子ビームを照射する。これにより、成膜されたモノマがポリマ化されることで硬化し、第1バッファ層311が形成される。
When an electron beam curable resin material is applied as the monomer, the electron beam is irradiated to the monomer using the electron beam source in the
ここでは、バッファ層を形成するために、バッファ層成膜用の第2チャンバ602とバッファ層硬化用の第3チャンバ603とを用意したが、第2チャンバ602が所定波長の光源や電子線源を備え、第2チャンバ602にて成膜工程と硬化工程とを同時に行っても良い。また、第2チャンバ602にて気相でポリマ化する樹脂材料を蒸着することで、硬化工程を不要とすることも可能である。
Here, in order to form the buffer layer, the
このような第1バッファ層311を形成した後は、図3の(b)を参照して説明したのと同様に、第1チャンバ601において第1バッファ層311を外気から遮蔽する第1バリア層321を形成する。この第1バリア層321は、直下の第1バッファ層311より大きな範囲にわたって形成される。
After the
そして、図3の(c)を参照して説明したのと同様に、第2チャンバ602及び603において第1バリア層321上に第2バッファ層312を形成する。この第2バッファ層312は、直下の第1バリア層321より小さな範囲であって、且つ、有効部106より大きな範囲にわたって形成される。
Then, as described with reference to FIG. 3C, the second buffer layer 312 is formed on the first barrier layer 321 in the
そして、再び、第1チャンバ601において第2バッファ層312を外気から遮蔽する第2バリア層322を形成する。この第2バリア層322は、直下の第2バッファ層312より大きな範囲にわたって形成される。以上のような工程を経て、図2に示すような構造の封止体300が形成される。
Then, the
続いて、封止体300の表面、すなわち第2バリア層322の表面全体に接着剤を塗布し、封止部材200を接着する。マザー基板上に複数のアレイ部を形成した場合には、この後、マザー基板をアレイ部毎に単個サイズに切り出す。また、必要に応じてEL発光を取り出す側の表面に偏光板を貼り付けても良い。
Subsequently, an adhesive is applied to the entire surface of the sealing
上述したような製造工程によって製造された有機EL表示装置1によれば、下層の影響を受けにくく有効部106に形成された有機EL素子40を確実に被覆することができる。また、これらバッファ層またはバリア層のいずれかにミクロ的な間隙が形成されたとしても、複数層を積層したことにより、有機EL素子40へ到達するまでのルートが長くなり、長寿命化に対して十分な効果がある。したがって、有機EL素子40を外気から遮蔽することができ、長期にわたって十分な性能を維持することができる。また、封止体300上に接着剤によって封止部材200を接着する際、あるいは、封止部材200上に接着剤によって偏向板を接着する際に、接着剤に含まれる不純物の有機EL素子40内への侵入を防止することができ、有機EL素子40の性能の劣化を防止することができる。
According to the organic EL display device 1 manufactured by the manufacturing process as described above, it is possible to reliably cover the
(1)ところで、バリア層を形成する方法としては、スパッタ法や電子ビーム蒸着法などが適用可能である。しかしながら、スパッタ法では、主にイオンが基板に衝突することにより、基板自身が加熱され、基板温度が上昇する。また、電子ビーム蒸着法では、電子(例えば材料源から放出された2次電子や電子線源から放出された電子)が基板に衝突することにより、基板自身が加熱され、基板温度が上昇する。このような基板温度の上昇は、既に有効部に形成された有機EL素子にダメージを与えてしまう。 (1) By the way, as a method for forming the barrier layer, a sputtering method, an electron beam evaporation method, or the like can be applied. However, in the sputtering method, mainly when ions collide with the substrate, the substrate itself is heated and the substrate temperature rises. Further, in the electron beam evaporation method, electrons (for example, secondary electrons emitted from a material source or electrons emitted from an electron beam source) collide with the substrate, whereby the substrate itself is heated and the substrate temperature rises. Such an increase in the substrate temperature damages the organic EL element already formed in the effective portion.
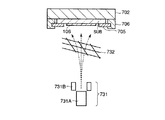
そこで、バリア層形成用の第1チャンバ601は、以下に説明するような製造装置を搭載している。すなわち、この製造装置は、図5に示すように、バリア層を形成するための材料源Sを収容する収容部701と、有効部106を備えた基板SUBをその主面が収容部701に対向した状態で保持する基板ホルダ702と、収容部701と基板ホルダ702に保持された基板SUBとの間に配置された防熱板703と、を備えて構成されている。
Therefore, the
このような防熱板703を備えたことにより、基板温度の上昇を抑制することができ、有機EL素子へのダメージを回避することができる。基板温度の上昇をさらに抑制するためには、防熱板703を積極的に冷却することが望ましく、冷却機構704を設けても良い。例えば、冷却機構704は、防熱板703を循環水で直接冷却する機構であってもよいし、銅などの高熱伝導性の素材で形成された防熱板703と冷却ターミナルとを熱的に接触させた機構であっても良い。
By providing such a
この製造装置では、基板SUBは、有効部106が形成された主面側に対して位置合わせされたマスク705と一体化されている。このマスク705は、マスクホルダ706に保持されている。マスク705は、金属材料によって形成されることが多く、しかも、基板SUBに近接して配置される(基板SUBに密着して配置されることもある)。このため、マスク705の温度上昇を抑えることは、基板温度の上昇を抑えるために有効である。したがって、マスクホルダ706に冷却機構を設けても良い。また、基板ホルダ702も冷却機構を設けて基板SUBの背面を冷却しても良い。
In this manufacturing apparatus, the substrate SUB is integrated with a
また、図5に示したような電子ビーム蒸着法に適用可能な製造装置は、収容部701に収容された材料源Sに対して電子線を照射する電子線源707を備えている。スパッタ法に適用可能な製造装置は、電子線源は不要である。
Further, the manufacturing apparatus applicable to the electron beam evaporation method as shown in FIG. 5 includes an
このように、電子ビーム蒸着法に適用可能な電子線源を備えた製造装置であっても、材料源と基板との間に防熱板を設けたことにより、材料源と電子との衝突によって発生する2次電子や、電子線源から放出された電子による基板の過熱を防止することができる。また、スパッタ法に適用可能な製造装置であっても、イオンによる基板の過熱を防止することができる。したがって、基板上に既に形成された表示素子の熱によるダメージを軽減することが可能となる。 As described above, even in a manufacturing apparatus equipped with an electron beam source applicable to the electron beam evaporation method, a heat insulating plate is provided between the material source and the substrate, thereby generating a collision between the material source and the electron. It is possible to prevent overheating of the substrate due to secondary electrons to be emitted and electrons emitted from the electron beam source. Further, even a manufacturing apparatus applicable to the sputtering method can prevent overheating of the substrate due to ions. Therefore, it is possible to reduce damage caused by heat of the display element already formed on the substrate.
なお、有機EL素子40を構成する有機活性層64として低分子系材料を用いた場合には、基板温度を120度以下とするように冷却することが望ましく、また、有機活性層64として高分子系材料を用いた場合には、基板温度を200度以下とするように冷却することが望ましい。このように、有機活性層を構成する材料に応じて基板温度を所定温度以下となるよう温度制御することにより、素子のダメージを軽減することができる。
In the case where a low molecular weight material is used as the organic
(2)また、バリア層を形成する方法として、上述した電子ビーム蒸着法では、電子の衝突に伴う基板温度の上昇の他に、既に有効部に形成された有機EL素子に直接電子が衝突することによっても有機EL素子にダメージを与えてしまう。また、画素スイッチ及び駆動トランジスタにも、直接電子が衝突することによってダメージを与えてしまう。 (2) As a method for forming the barrier layer, in the above-described electron beam evaporation method, in addition to the increase in the substrate temperature accompanying the collision of electrons, the electrons directly collide with the organic EL element already formed in the effective portion. This also damages the organic EL element. Further, the pixel switch and the driving transistor are also damaged by direct collision of electrons.
そこで、バリア層形成用の第1チャンバ601は、以下に説明するような製造装置を搭載している。なお、図5に示した製造装置と同一の構成については、同一の参照符号を付して詳細な説明を省略する。
Therefore, the
すなわち、この製造装置は、図6に示すように、バリア層を形成するための材料源Sを収容する収容部701と、有効部106を備えた基板SUBをその主面が収容部701に対向した状態で保持する基板ホルダ702と、収容部701と基板ホルダ702に保持された基板SUBとの間に配置され、接地された導電性を有するグリッド711と、を備えて構成されている。
That is, in this manufacturing apparatus, as shown in FIG. 6, the main surface of the substrate SUB provided with the
このような導電性グリッド711を備えたことにより、材料源Sから基板SUBに向かう電子を吸収し、基板温度の上昇を抑制することができるとともに、有機EL素子に直接衝突する電子の数を低減することができる。このため、有機EL素子へのダメージを回避することができる。
By providing such a
この製造装置では、基板SUBは、有効部106が形成された主面側に対して位置合わせされたマスク705と一体化されている。このマスク705は、マスクホルダ706に保持されている。マスク705は、金属材料によって形成されることが多く、しかも、基板SUBに近接して配置される(基板SUBに密着して配置されることもある)。このため、不要な電子を吸収するためには、マスク705も接地することが有効である。
In this manufacturing apparatus, the substrate SUB is integrated with a
また、図6に示したような電子ビーム蒸着法に適用可能な製造装置は、収容部701に収容された材料源Sに対して電子線を照射する電子線源706を備えている。
Further, the manufacturing apparatus applicable to the electron beam vapor deposition method as shown in FIG. 6 includes an
このように、電子ビーム蒸着法に適用可能な電子線源を備えた製造装置であっても、材料源と基板との間に導電性グリッドを設けたことにより、材料源と電子との衝突によって発生する2次電子や、電子線源から放出された電子による基板の過熱及び表示素子への衝突を防止することができる。したがって、基板上に既に形成された表示素子のダメージを軽減することが可能となる。 Thus, even in a manufacturing apparatus equipped with an electron beam source applicable to the electron beam evaporation method, by providing a conductive grid between the material source and the substrate, the collision between the material source and the electrons can be achieved. Overheating of the substrate and collision with the display element due to generated secondary electrons or electrons emitted from the electron beam source can be prevented. Therefore, it is possible to reduce damage to the display element already formed on the substrate.
なお、基板温度の上昇をさらに抑制するためには、図5に示したような防熱板703を設けても良いし、防熱板703、マスクホルダ706、基板ホルダ702に冷却機構を設けて基板を積極的に冷却しても良い。
In order to further suppress the increase in the substrate temperature, a
また、導電性グリッド711は、基板主面に向けて照射される電子線の吸収線量を200J/g以下とすることが望ましい。このように、バリア層を形成する間に照射される電子線の吸収線量を所定値以下となるよう制御することにより、素子のダメージを軽減することができる。
In addition, it is desirable that the
(3)一方で、バッファ層を形成する方法のうち、樹脂材料を成膜する方法としては、加熱蒸着法などが適用可能である。しかしながら、加熱蒸着法では、主に加熱されたユニットからの輻射熱により、基板自身が加熱され、基板温度が上昇する。このような基板温度の上昇は、既に有効部に形成された有機EL素子にダメージを与えてしまう。 (3) On the other hand, among the methods for forming the buffer layer, as a method for forming a resin material, a heating vapor deposition method or the like is applicable. However, in the heating vapor deposition method, the substrate itself is heated mainly by the radiant heat from the heated unit, and the substrate temperature rises. Such an increase in the substrate temperature damages the organic EL element already formed in the effective portion.
そこで、バッファ層成膜用の第2チャンバ602は、以下に説明するような製造装置を搭載している。なお、図5に示した製造装置と同一の構成については、同一の参照符号を付して詳細な説明を省略する。
Therefore, the
すなわち、この製造装置は、図7に示すように、バッファ層を形成するための材料源(樹脂材料のモノマ)Sを収容する収容部721と、有効部106を備えた基板SUBをその主面が収容部721に対向した状態で保持する基板ホルダ702と、収容部721と基板ホルダ702に保持された基板SUBとの間に配置された防熱板722と、を備えて構成されている。
That is, as shown in FIG. 7, this manufacturing apparatus has a main surface of a substrate SUB provided with an
このような加熱蒸着法に適用可能な製造装置は、各種加熱されたユニットを備えている。すなわち、材料源Sの蒸気を生成するために、収容部721に収容された材料源Sは、加熱源723により加熱されている。また、材料源Sの蒸気が付着した際に固まるのを防止するために、収容部721から基板ホルダ702側に向かって延びる側壁部724も加熱されている。
A manufacturing apparatus applicable to such a heating vapor deposition method includes various heated units. That is, in order to generate the vapor of the material source S, the material source S accommodated in the
このような製造装置では、防熱板722を備えたことにより、基板温度の上昇を抑制することができ、有機EL素子へのダメージを回避することができる。特に、基板主面に対向する収容部721からの輻射熱による影響を軽減するためには、防熱板722を収容部721に近接して配置することが望ましい。
In such a manufacturing apparatus, since the
このように、加熱蒸着法に適用可能な各種加熱ユニットを備えた製造装置であっても、材料源と基板との間に防熱板を設けたことにより、加熱ユニットからの輻射熱による基板の過熱を防止することができる。したがって、基板上に既に形成された表示素子の熱によるダメージを軽減することが可能となる。 Thus, even in a manufacturing apparatus equipped with various heating units applicable to the heating vapor deposition method, the substrate is overheated by the radiant heat from the heating unit by providing a heat insulating plate between the material source and the substrate. Can be prevented. Therefore, it is possible to reduce damage caused by heat of the display element already formed on the substrate.
なお、基板温度の上昇をさらに抑制するためには、(1)で説明したように、防熱板722、マスクホルダ706、基板ホルダ702に冷却機構を設けて、基板を積極的に冷却するように構成しても良い。
In order to further suppress the rise in the substrate temperature, as described in (1), a cooling mechanism is provided in the
(4)また、バッファ層を形成する方法のうち、樹脂材料を硬化する方法としては、電子線硬化法などが適用可能である。しかしながら、電子線硬化法では、電子の衝突に伴う基板温度の上昇の他に、既に有効部に形成された有機EL素子に直接電子が衝突することによっても有機EL素子にダメージを与えてしまう。また、画素スイッチ及び駆動トランジスタにも、直接電子が衝突することによってダメージを与えてしまう。 (4) In addition, among the methods for forming the buffer layer, an electron beam curing method or the like is applicable as a method for curing the resin material. However, in the electron beam curing method, in addition to the increase in the substrate temperature accompanying the collision of electrons, the organic EL element is also damaged by the direct collision of electrons with the organic EL element already formed in the effective portion. Further, the pixel switch and the driving transistor are also damaged by direct collision of electrons.
そこで、バッファ層硬化用の第3チャンバ603は、以下に説明するような製造装置を搭載している。なお、図5に示した製造装置と同一の構成については、同一の参照符号を付して詳細な説明を省略する。
Therefore, the
すなわち、この製造装置は、図8に示すように、電子線を照射する電子線源731と、バッファ層を形成するための材料源(樹脂材料のモノマ)を成膜した主面が電子線源731に対向した状態で基板SUBを保持する基板ホルダ702と、電子線源731と基板ホルダ702に保持された基板SUBとの間に配置され、接地された導電性を有するグリッド732と、を備えて構成されている。
That is, as shown in FIG. 8, the manufacturing apparatus has an
電子線源731は、電子ビームを発生する電子ビーム発生部731A、電子ビーム発生部731Aから発生した電子ビームを偏向する偏向部731Bなどを備えて構成されている。
The
このような導電性グリッド732を備えたことにより、電子線源731から基板SUBに向かう電子を吸収し、基板温度の上昇を抑制することができるとともに、有機EL素子に直接衝突する電子の数を低減することができる。このため、有機EL素子へのダメージを回避することができる。
By providing such a
この製造装置では、基板SUBは、有効部106が形成された主面側に対して位置合わせされたマスク705と一体化されている。このマスク705は、マスクホルダ706に保持されている。マスク705は、金属材料によって形成されることが多く、しかも、基板SUBに近接して配置される(基板SUBに密着して配置されることもある)。このため、不要な電子を吸収するためには、マスク705も接地することが有効である。
In this manufacturing apparatus, the substrate SUB is integrated with a
このように、電子線硬化法に適用可能な電子線源を備えた製造装置であっても、電子線源と基板との間に導電性グリッドを設けたことにより、電子線源から放出された電子による基板の過熱及び表示素子への衝突を防止することができる。したがって、基板上に既に形成された表示素子のダメージを軽減することが可能となる。 Thus, even in a manufacturing apparatus equipped with an electron beam source applicable to the electron beam curing method, it was emitted from the electron beam source by providing a conductive grid between the electron beam source and the substrate. Overheating of the substrate due to electrons and collision with the display element can be prevented. Therefore, it is possible to reduce damage to the display element already formed on the substrate.
なお、基板温度の上昇をさらに抑制するためには、図5に示したような防熱板703を設けても良いし、防熱板703、マスクホルダ706、基板ホルダ702に冷却機構を設けて基板を積極的に冷却しても良い。
In order to further suppress the increase in the substrate temperature, a
また、導電性グリッド732は、基板主面に向けて照射される電子線の吸収線量を200J/g以下とすることが望ましい。このように、バッファ層を形成するためにモノマを硬化する間に照射される電子線の吸収線量を所定値以下となるよう制御することにより、素子のダメージを軽減することができる。
In addition, the
以上説明したように、基板主面に形成された有効部は、少なくとも2層のバッファ層及びバッファ層より大きなパターンであって各バッファ層を被覆するバリア層を積層した構造の封止体によって覆われている。このため、有効部に形成された表示素子を確実に被覆することができ、しかも、外部からの不純物や外気に対して高い遮蔽性を確保することができ、長期にわたって良好な表示性能を維持することができる。 As described above, the effective portion formed on the main surface of the substrate is covered with a sealing body having a structure in which at least two buffer layers and a barrier layer that covers each buffer layer are stacked in a pattern larger than the buffer layer. It has been broken. For this reason, it is possible to reliably cover the display element formed in the effective portion, and it is possible to ensure high shielding against external impurities and outside air, and maintain good display performance over a long period of time. be able to.
また、このような構造の封止体を製造するに際して、防熱板を用いて基板温度の過度の上昇を抑制するとともに、導電性グリッドを用いて基板主面に向かう電子を吸収することにより、既に基板主面の有効部に形成された表示素子への熱によるダメージ及び電子の衝突によるダメージを軽減することが可能となる。 Further, when manufacturing a sealing body having such a structure, an excessive rise in the substrate temperature is suppressed using a heat insulating plate, and electrons that are directed toward the main surface of the substrate are absorbed using a conductive grid. It is possible to reduce damage caused by heat and collision of electrons to the display element formed in the effective portion of the substrate main surface.
なお、この発明は、上記実施形態そのままに限定されるものではなく、その実施の段階ではその要旨を逸脱しない範囲で構成要素を変形して具体化できる。また、上記実施形態に開示されている複数の構成要素の適宜な組み合せにより種々の発明を形成できる。例えば、実施形態に示される全構成要素から幾つかの構成要素を削除してもよい。更に、異なる実施形態に亘る構成要素を適宜組み合せてもよい。 Note that the present invention is not limited to the above-described embodiment as it is, and can be embodied by modifying the constituent elements without departing from the spirit of the invention in the stage of implementation. Further, various inventions can be formed by appropriately combining a plurality of constituent elements disclosed in the embodiment. For example, some components may be deleted from all the components shown in the embodiment. Furthermore, you may combine suitably the component covering different embodiment.
上述した各実施例では、封止体を構成するバッファ層が2層でバリア層が3層の場合を例に説明したが、それぞれ2層以上であれば、層数の組み合わせはこの例に限定されるものではない。なお、封止体を10層以上の薄膜を積層して構成するような場合は工程数が多すぎて生産性が低下する。このため、積層する薄膜の層数は、2層以上10層未満であって、望ましくは3乃至5層に設定される。 In each of the embodiments described above, the case where the buffer layer constituting the sealing body is two layers and the barrier layer is three layers has been described as an example. However, the combination of the number of layers is limited to this example as long as each layer is two or more layers. Is not to be done. In the case where the sealing body is formed by laminating ten or more thin films, the number of steps is too large and the productivity is lowered. For this reason, the number of thin film layers to be laminated is 2 or more and less than 10 layers, and preferably 3 to 5 layers.
1…有機EL表示装置、10…画素スイッチ、20…駆動トランジスタ、30…蓄積容量素子、40…有機EL素子、60…第1電極、64…有機活性層、66…第2電極、70…隔壁、100…アレイ基板、106…有効部、120…配線基板、200…封止部材、300…封止体、311,312…バッファ層、320,321,322…バリア層、601…第1チャンバ、602…第2チャンバ、603…第3チャンバ、701…収容部、702…基板ホルダ、703…防熱板、707…電子線源、711…グリッド、722…防熱板、731…電子線源、732…グリッド、PX(R、G、B)…画素、SUB…基板、S…材料源 DESCRIPTION OF SYMBOLS 1 ... Organic EL display apparatus, 10 ... Pixel switch, 20 ... Drive transistor, 30 ... Storage capacitor element, 40 ... Organic EL element, 60 ... 1st electrode, 64 ... Organic active layer, 66 ... 2nd electrode, 70 ... Partition , 100 ... Array substrate, 106 ... Effective portion, 120 ... Wiring substrate, 200 ... Sealing member, 300 ... Sealing body, 311, 312 ... Buffer layer, 320, 321, 322 ... Barrier layer, 601 ... First chamber, 602 ... Second chamber, 603 ... Third chamber, 701 ... Housing unit, 702 ... Substrate holder, 703 ... Heat shield, 707 ... Electron beam source, 711 ... Grid, 722 ... Heat shield, 731 ... Electron beam source, 732 ... Grid, PX (R, G, B) ... Pixel, SUB ... Substrate, S ... Material source
Claims (10)
基板主面の少なくとも前記有効部を覆うように配置され、バッファ層、及び、前記バッファ層より大きなパターンであってしかも各バッファ層を被覆するバリア層を積層した構造を有する封止体と、を備えた表示装置の製造装置であって、
前記バッファ層または前記バリア層を形成するための材料源を収容する収容部と、
前記有効部を備えた前記基板をその主面が前記収容部に対向した状態で保持する基板ホルダと、
前記収容部と前記基板ホルダに保持された前記基板との間に配置された防熱板と、
を備えたことを特徴とする製造装置。 An effective portion that is formed on the main surface of the substrate and includes a plurality of pixels for displaying an image;
A sealing body that is arranged so as to cover at least the effective portion of the main surface of the substrate and has a structure in which a buffer layer and a barrier layer that covers each buffer layer are stacked in a pattern larger than the buffer layer; A display device manufacturing apparatus comprising:
An accommodating portion for accommodating a material source for forming the buffer layer or the barrier layer;
A substrate holder for holding the substrate having the effective portion in a state in which a main surface thereof faces the accommodating portion;
A heat insulating plate disposed between the housing portion and the substrate held by the substrate holder;
A manufacturing apparatus comprising:
基板主面の少なくとも前記有効部を覆うように配置され、バッファ層、及び、前記バッファ層より大きなパターンであってしかも各バッファ層を被覆するバリア層を積層した構造を有する封止体と、を備えた表示装置の製造装置であって、
前記バリア層を形成するための材料源を収容する収容部と、
前記有効部を備えた前記基板をその主面が前記収容部に対向した状態で保持する基板ホルダと、
前記収容部と前記基板ホルダに保持された前記基板との間に配置され、接地された導電性を有するグリッドと、
を備えたことを特徴とする製造装置。 An effective portion that is formed on the main surface of the substrate and includes a plurality of pixels for displaying an image;
A sealing body that is arranged so as to cover at least the effective portion of the main surface of the substrate and has a structure in which a buffer layer and a barrier layer that covers each buffer layer are stacked in a pattern larger than the buffer layer; A display device manufacturing apparatus comprising:
An accommodating portion for accommodating a material source for forming the barrier layer;
A substrate holder for holding the substrate having the effective portion in a state in which a main surface thereof faces the accommodating portion;
A conductive grid disposed between the housing portion and the substrate held by the substrate holder and grounded;
A manufacturing apparatus comprising:
基板主面の少なくとも前記有効部を覆うように配置され、バッファ層、及び、前記バッファ層より大きなパターンであってしかも各バッファ層を被覆するバリア層を積層した構造を有する封止体と、を備えた表示装置の製造装置であって、
電子線を照射する電子線源と、
前記バッファ層を形成するための材料源を成膜した主面が前記電子線源に対向した状態で前記基板を保持する基板ホルダと、
前記電子線源と前記基板ホルダに保持された前記基板との間に配置され、接地された導電性を有するグリッドと、
を備えたことを特徴とする製造装置。 An effective portion that is formed on the main surface of the substrate and includes a plurality of pixels for displaying an image;
A sealing body that is arranged so as to cover at least the effective portion of the main surface of the substrate and has a structure in which a buffer layer and a barrier layer that covers each buffer layer are stacked in a pattern larger than the buffer layer; A display device manufacturing apparatus comprising:
An electron beam source for irradiating an electron beam;
A substrate holder for holding the substrate in a state where a main surface on which a material source for forming the buffer layer is formed is opposed to the electron beam source;
A grounded conductive grid disposed between the electron beam source and the substrate held by the substrate holder;
A manufacturing apparatus comprising:
基板主面の少なくとも前記有効部を覆うように封止体を配置する、表示装置の製造方法であって、
前記封止体の製造工程は、
少なくとも2層のバッファ層を形成する工程と、
前記バッファ層より大きなパターンであってしかも各バッファ層を被覆するバリア層を形成する工程と、を含み、
前記バッファ層及び前記バリア層を形成する工程では、前記基板主面に向けて照射される電子線の吸収線量を200J/g以下とすることを特徴とする表示装置の製造方法。 On the main surface of the substrate, an effective portion having a plurality of pixels for displaying an image is formed,
A manufacturing method of a display device, wherein a sealing body is disposed so as to cover at least the effective portion of a substrate main surface,
The manufacturing process of the sealing body includes:
Forming at least two buffer layers;
Forming a barrier layer that is a larger pattern than the buffer layer and covers each buffer layer,
In the step of forming the buffer layer and the barrier layer, the absorbed dose of the electron beam irradiated toward the main surface of the substrate is set to 200 J / g or less.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003346956A JP2005116253A (en) | 2003-10-06 | 2003-10-06 | Manufacturing device of display device, and manufacturing method of display device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003346956A JP2005116253A (en) | 2003-10-06 | 2003-10-06 | Manufacturing device of display device, and manufacturing method of display device |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2005116253A true JP2005116253A (en) | 2005-04-28 |
Family
ID=34539706
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003346956A Pending JP2005116253A (en) | 2003-10-06 | 2003-10-06 | Manufacturing device of display device, and manufacturing method of display device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2005116253A (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010189756A (en) * | 2009-02-19 | 2010-09-02 | Samsung Mobile Display Co Ltd | Mask tightly-contacting means for vapor deposition apparatus, and vapor deposition apparatus using the same |
| JP2014199789A (en) * | 2012-05-04 | 2014-10-23 | 株式会社半導体エネルギー研究所 | Method of producing light-emitting element, and deposition device |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH05263221A (en) * | 1992-03-16 | 1993-10-12 | Toppan Printing Co Ltd | Vacuum thin film producing device |
| JPH10312883A (en) * | 1997-05-12 | 1998-11-24 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Organic electroluminescent element |
| JP2000306665A (en) * | 1999-04-21 | 2000-11-02 | Tohoku Pioneer Corp | Manufacture of organic el display and its device |
| JP2002329719A (en) * | 2001-01-19 | 2002-11-15 | Tokyo Electron Ltd | Substrate treatment method and substrate treatment apparatus |
| JP2003282241A (en) * | 2002-03-25 | 2003-10-03 | Pioneer Electronic Corp | Organic electroluminescent display panel and its manufacturing method |
-
2003
- 2003-10-06 JP JP2003346956A patent/JP2005116253A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH05263221A (en) * | 1992-03-16 | 1993-10-12 | Toppan Printing Co Ltd | Vacuum thin film producing device |
| JPH10312883A (en) * | 1997-05-12 | 1998-11-24 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Organic electroluminescent element |
| JP2000306665A (en) * | 1999-04-21 | 2000-11-02 | Tohoku Pioneer Corp | Manufacture of organic el display and its device |
| JP2002329719A (en) * | 2001-01-19 | 2002-11-15 | Tokyo Electron Ltd | Substrate treatment method and substrate treatment apparatus |
| JP2003282241A (en) * | 2002-03-25 | 2003-10-03 | Pioneer Electronic Corp | Organic electroluminescent display panel and its manufacturing method |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010189756A (en) * | 2009-02-19 | 2010-09-02 | Samsung Mobile Display Co Ltd | Mask tightly-contacting means for vapor deposition apparatus, and vapor deposition apparatus using the same |
| JP2014199789A (en) * | 2012-05-04 | 2014-10-23 | 株式会社半導体エネルギー研究所 | Method of producing light-emitting element, and deposition device |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US7629740B2 (en) | Display device with stacked layer body | |
| US7019458B2 (en) | Electroluminescent display device | |
| KR102082407B1 (en) | Flexible substrate, flexible display device, and method for manufacturing flexible display device | |
| US20050156513A1 (en) | Display element, optical device, and optical device manufacturing method | |
| JP2010108949A (en) | Organic electroluminescent display device | |
| JP2006269108A (en) | Organic light emitting display device, and restoration method of its defective pixel | |
| JP2004063454A (en) | Vapor deposition device | |
| JP2008021653A (en) | Organic light emitting display device, and method for manufacturing the same | |
| US7692374B2 (en) | Organic light emitting display device with multi-layered electrode and method of using the same | |
| JP2011119223A (en) | Organic light-emitting display device | |
| JP2004095551A (en) | Light emitting device and its manufacturing method | |
| JP2009117181A (en) | Organic el display device, and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP2009117178A (en) | Organic el display device, and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP2006004650A (en) | Display element and optical device | |
| JP2006049057A (en) | Organic el display device | |
| JP4167651B2 (en) | Display device | |
| JP2003233329A (en) | Method for repairing display device | |
| JP2004047458A (en) | Electroluminescence display | |
| JP2005100685A (en) | Display device and manufacturing method of display device | |
| JP4643138B2 (en) | Display device and manufacturing method thereof | |
| US8648335B2 (en) | Organic light emitting diode display | |
| JP2005353398A (en) | Display element, optical device, and manufacturing method of optical device | |
| JP2006190570A (en) | Display device and manufacturing method of the same | |
| JP2005116253A (en) | Manufacturing device of display device, and manufacturing method of display device | |
| JP2009181865A (en) | Display device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20060921 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20091215 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20100112 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20100511 |