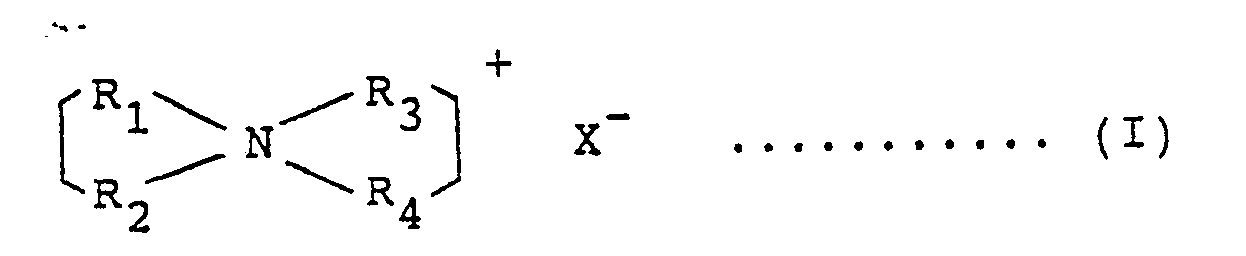EP0335404A2 - Liquid softener composition - Google Patents
Liquid softener composition Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0335404A2 EP0335404A2 EP89105663A EP89105663A EP0335404A2 EP 0335404 A2 EP0335404 A2 EP 0335404A2 EP 89105663 A EP89105663 A EP 89105663A EP 89105663 A EP89105663 A EP 89105663A EP 0335404 A2 EP0335404 A2 EP 0335404A2
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- component
- softener composition
- liquid softener
- carbon atoms
- group
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Withdrawn
Links
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C11—ANIMAL OR VEGETABLE OILS, FATS, FATTY SUBSTANCES OR WAXES; FATTY ACIDS THEREFROM; DETERGENTS; CANDLES
- C11D—DETERGENT COMPOSITIONS; USE OF SINGLE SUBSTANCES AS DETERGENTS; SOAP OR SOAP-MAKING; RESIN SOAPS; RECOVERY OF GLYCEROL
- C11D3/00—Other compounding ingredients of detergent compositions covered in group C11D1/00
- C11D3/16—Organic compounds
- C11D3/37—Polymers
- C11D3/3746—Macromolecular compounds obtained by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds
- C11D3/3757—(Co)polymerised carboxylic acids, -anhydrides, -esters in solid and liquid compositions
- C11D3/3765—(Co)polymerised carboxylic acids, -anhydrides, -esters in solid and liquid compositions in liquid compositions
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C11—ANIMAL OR VEGETABLE OILS, FATS, FATTY SUBSTANCES OR WAXES; FATTY ACIDS THEREFROM; DETERGENTS; CANDLES
- C11D—DETERGENT COMPOSITIONS; USE OF SINGLE SUBSTANCES AS DETERGENTS; SOAP OR SOAP-MAKING; RESIN SOAPS; RECOVERY OF GLYCEROL
- C11D1/00—Detergent compositions based essentially on surface-active compounds; Use of these compounds as a detergent
- C11D1/66—Non-ionic compounds
- C11D1/835—Mixtures of non-ionic with cationic compounds
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C11—ANIMAL OR VEGETABLE OILS, FATS, FATTY SUBSTANCES OR WAXES; FATTY ACIDS THEREFROM; DETERGENTS; CANDLES
- C11D—DETERGENT COMPOSITIONS; USE OF SINGLE SUBSTANCES AS DETERGENTS; SOAP OR SOAP-MAKING; RESIN SOAPS; RECOVERY OF GLYCEROL
- C11D3/00—Other compounding ingredients of detergent compositions covered in group C11D1/00
- C11D3/0005—Other compounding ingredients characterised by their effect
- C11D3/001—Softening compositions
- C11D3/0015—Softening compositions liquid
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C11—ANIMAL OR VEGETABLE OILS, FATS, FATTY SUBSTANCES OR WAXES; FATTY ACIDS THEREFROM; DETERGENTS; CANDLES
- C11D—DETERGENT COMPOSITIONS; USE OF SINGLE SUBSTANCES AS DETERGENTS; SOAP OR SOAP-MAKING; RESIN SOAPS; RECOVERY OF GLYCEROL
- C11D1/00—Detergent compositions based essentially on surface-active compounds; Use of these compounds as a detergent
- C11D1/38—Cationic compounds
- C11D1/62—Quaternary ammonium compounds
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C11—ANIMAL OR VEGETABLE OILS, FATS, FATTY SUBSTANCES OR WAXES; FATTY ACIDS THEREFROM; DETERGENTS; CANDLES
- C11D—DETERGENT COMPOSITIONS; USE OF SINGLE SUBSTANCES AS DETERGENTS; SOAP OR SOAP-MAKING; RESIN SOAPS; RECOVERY OF GLYCEROL
- C11D1/00—Detergent compositions based essentially on surface-active compounds; Use of these compounds as a detergent
- C11D1/66—Non-ionic compounds
- C11D1/72—Ethers of polyoxyalkylene glycols
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a softener composition which can impart, for example, an excellent softness and antistatic property to fiber, clothing, and hair. More specifically, it relates to an aqueous liquid softener composition which can impart an excellent softness and antistatic property to chemical textile products such as of acryl, nylon, polyester, and also has an excellent dispersion stability.
- a softener containing a quaternary ammonium salt having two long chain alkyl groups or alkenyl groups in the molecule as the main component has been employed.
- Representative examples of the quaternary ammonium salts include di-hardened tallow alkyldimethylammonium chloride, and methyl-1-tallow amidoethyl-2-alkylimidazolinium methylsulfate, but these single products, although they are capable of imparting excellent softness to cotton products, have no sufficient effect from the view point of imparting softness and an antistatic property to chemical fiber products.
- an object of the present invention is to obviate the above-mentioned problems in the prior art and to provide an aqueous liquid softener composition which can impart the same softness to cotton as that of the prior art products, but a much greater softness and antistatic property to chemical fibers, compared with the prior art products in softening treatment practiced in the washing and rinsing steps at home, and further, has an excellent dispersion stability.
- liquid softener composition comprising:
- the slightly water-soluble quaternary ammonium salt of the component (A) usable in the present invention may be exemplified by those represented by the formula (I) or (II) shown below. These compounds can be used alone or as a mixture of two or more compounds, and these are cationic surfactants having 2 or 3 straight or branched alkyl or alkenyl groups with 14 to 24 carbon atoms in the molecule which may be respectively optionally substituted or intermingled with functional groups such as -OH, -O-, - -NH-, - -O-.
- R1 - R4 represent straight or branched alkyl or alkenyl groups which may be unsubstituted or optionally substituted by -OH-, -O-, - -NH-, - -O-, etc., the remainder of the groups of R1 - R4 represent an alkyl group with 1 to 3 carbon atoms, a hydroxyalkyl group or a group represented by the formula -(C2H4) l H (where l is an integer of 1 to 5, and X represents a halogen or a monoalkylsulfate group represented by R5SO4 where R5 represents an alkyl group with 1 to 3 carbon atoms).
- R6 represents an alkyl group with 1 to 4, preferably 1 to 2 carbon atoms
- R7 and R8 each represent an alkyl or alkenyl group with 14 to 24 carbon atoms
- R9 represents hydrogen or an alkyl group with 1 to 4 carbon atoms
- X has the same meaning as in the formula (I).
- At least two groups of R1 - R4 in the above formula (I) have 14 to 24, preferably 16 to 22 carbon atoms, R7 and R8 in the above formula (II) have 14 to 24, preferably 15 to 21 carbon atoms, each group may have a distribution within these ranges, and the respective groups may be either the same or different from each other.
- the carbon number is lower than this range, for example, when a mixture of quaternary ammonium salts of (I) or (II) synthesized from coconut fatty acids is used, the softness will be poor.
- component (A) include one or a mixture of two or more of di-hardened tallow alkyldimethylammonium chloride, di-tallow alkyldimethylammonium bromide, dioleyldimethylammonium chloride, dipalmitylhydroxyethylammonium methylsulfate, distearylmethylpolyoxyethylene (average degree of polymerization is 3)ammonium chloride, diisostearyldimethylammonium methylsulfate, dieicosyldimethylammonium chloride, dibehenylmethylpolyoxyethylene (average degree of polymerization is 5)ammonium chloride, dierucyldimethylammonium chloride, di[2-dodecanoylamino)ethyl]-dimethylammonium chloride, di[2-stearoylamino)propyl]dimethylammonium ethylsulfate, di(2-ethylpalmitoy
- carboxylic acid type anionic polymer of the component (B) homopolymers of ethylenically unsaturated carboxylic acids or anhydrides thereof or copolymers of said monomers can be used.
- the salts of these homopolymers and copolymers may be used.
- these polymers may be used either as such or in the form of water soluble neutral salts such as alkali metal salts or alkaline earth metal salts.
- the component (B) has an average molecular weight generally of 500 to 50,000, preferably 500 to 20,000, and more preferably 500 to 10,000.
- the above-mentioned anionic polymrs to be used as the component (B) should be the so-called "oligomers" which have a relatively low molecular weight.
- the molecular weight thereof is higher, the desired sufficient dispersion stability obtained from the addition of the component (C) as mentioned hereinbelow is prevented. Contrarily, when the molecular weight is lower, the effect obtained from addition of the component (B) as mentioned hereinbelow becomes insufficient.
- component (B) may include one or a mixture of two or more of polyacrylic acid, polymethacrylic acid, polycrotonic acid, polyacotinic acid, poly- ⁇ -hydroxyacrylic acid, polymaleic acid, polysorbic acid, polyitaconic acid, poly(maleic anhydride), poly(itaconic anhydride) their copolymers, or salts of these homopolymers or copolymers.
- the reason why excellent effect can be obtained by using the component (A) and the component (B) in combination is not clear, but it may be considered to be as follows. That is, although the ion bonding between the both may not be so strong, by forming a cation-anion complex with a part of the dispersed particles of the component (A), the component (A) can be made further hydrophobic to promote adsorption of the component (A) onto chemical fibers such as acrylic or polyester fibers which are hydrophobic fibers, whereby softness and antistatic property of the chemical fibers can be consequently further improved as compared with the case of the component (A) alone.
- chemical fibers such as acrylic or polyester fibers which are hydrophobic fibers
- the component (B) which is a water soluble polymer will not be incorporated into the dispersed particles of the component (A) and will not destroy the adsorption structure of the component (A), as different from a some kinds of anionic surfactant, and consequently will not give any adverse effect on the softness of cotton fibers.
- these compounds are formulated, in terms of the ratio of positive charge mols (a) of the component (A) to the negative charge mols (b) of the component (B), at a ratio (a)/(b) of 1/0.2 to 1/2.0, preferably 1/0.5 to 1/1.0. If the ratio of the component (B) to the component (A) is outside this range, the above effect of combined use is difficult to obtain.
- the third essential component for accomplishing the object of the present invention is the component (C). That is, a sufficient dispersion stability is an essential condition for use as a softener for domestic use, but only with the components (A), (B), (D), the required dispersibility cannot be obtained, and accordingly the emulsifying stabilizing action of the component (C) is necessary.
- the component (C) usable in the present invention may be exemplified by polyoxyethylene alkylphenyl ether, polyoxyethylene alkyl (or alkenyl) ether, polyoxyethylene fatty acid amide, polyoxyethylene alkyl (or alkenyl) amine, and polyoxyethylene sorbitane fatty acid ester.
- Preferable average additional moles of ethylene oxide are at least 20, more preferably 20 to 100.
- each POE represents polyoxyethylene
- p denotes the average adducted mols of ethylene oxide
- C the carbon number of the alkyl or alkenyl group (hereinafter the same).
- the component (C) improves the emulsifying dispersion of the dispersed particles of the component (A) alone and the anion-cation complex of the dispersed particles of the component (A) with the component (B), which may be considered to form a random coil structure dissolved in the aqueous phase in the composition, and thus the amount of the component (C) formulated is preferably 100/1 to 3/1 as a weight ratio of (A)/(C), more preferably 50/1 to 5/10. If the ratio of the component (C) to the component (A) is outside of this range, the above effect cannot be exhibited, and conversely, the above effect of combined use of the component (A) and the component (B) is frequently inhibited.
- the component (D) is used as the carrier for the essential components and the optional components of the present invention, and the amount thereof in the composition is the balance which makes up the total amount to 100%, in addition to the essential components and the optional components formulated.
- the softener composition of the present invention can include optional components in addition to the above essential components, including viscosity controllers such as inorganic electrolytes like sodium chloride, potassium chloride, magnesium chloride, aluminum chloride, sodium sulfate, ammonium sulfate, sodium nitrate, or magnesium nitrate; and polyethylene glycol or other water soluble organic polymers; hydrotropes such as lower alcohols like ethanol, or isopropanol, ethylene glycol, glycerine, and urea; and pH controllers, sterilizers, pigment dyes, perfumes, antioxidants, UV-ray absorbers, and fluorescent brighteners.
- viscosity controllers such as inorganic electrolytes like sodium chloride, potassium chloride, magnesium chloride, aluminum chloride, sodium sulfate, ammonium sulfate, sodium nitrate, or magnesium nitrate
- polyethylene glycol or other water soluble organic polymers such as lower alcohols like ethanol, or isopropanol
- the softener composition of the present invention can be prepared according to known methods. More specifically, it is desirable that the component (A) should be finely and uniformly dispersed, and for this purpose, it is preferable to use the method in which the components (B), (C) and optical components are previously dissolved in an aqueous vehicle, and to this solution is successively added, under heating to 40°C to 80°C if desired, the component (A) in a molten state to be mixed under stirring. On the other hand, when optional components susceptible to denaturation at high temperature are used, it is desirable to cool the above dispersion to about room temperature, followed by addition while stirring.
- a pH controller can be added to the softener composition of the present invention, but the pH of the composition is not limited. Usually, the pH is that when the respective components are formulated, but it is desirable to control pH to 4 to 8. For this purpose, an organic or inorganic acid or a basic compound can be formulated, as desired.
- the softener composition of the present invention which can impart an excellent softness to not only cotton fibers but also chemical fibers, and further gives an excellent antistatic property to chemical fibers is valuable.
- the present composition is excellent in practical application.
- the above component (A) is available as a mixture with isopropanol, and therefore, the compositions were contaminated with about 1.7 (%) thereof.
- the softener compositions of the present invention have excellent performance and dispersion stability. More specifically, although considerable softness is exhibited in the case of di-hardened tallow alkyldimethylammonium chloride alone, the softness and antistatic property of the acrylic cloth are clearly improved by addition of the component (B). Particularly, No. 1 and No. 5 can be appreciated to exhibit a very excellent antistatic property.
- a rise in viscosity under the above storage conditions may be permissible up to about 1500 centipoise in commercial product value, and it can be seen that the products of the present invention satisfy this condition without causing phase separation due to the addition effect of the component (C) and the presence of ethylene glycol in the component (D).
- the above component (A), is provided as a mixture with isopropanol, and therefore, the compositions were contaminated with about 3 (%) thereof.
- the carboxylic acid type anionic polymers used in the present invention have performance improvement effects on all of the slightly water soluble quaternary ammonium salts having different structures from each other. More specifically, in Table 4, it can be seen that by an addition of sodium polyacrylate in equivalent amount to the component (A), in all cases, the performances, particularly softness and antistatic property of the acrylic cloths are greatly improved. Also, all of the above compositions of the present invention have good dispersion stability.
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Oil, Petroleum & Natural Gas (AREA)
- Wood Science & Technology (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Treatments For Attaching Organic Compounds To Fibrous Goods (AREA)
- Cosmetics (AREA)
Abstract
- (A) a slightly water-soluble quaternary ammonium salt type cationic surfactant having 2 or 3 alkyl or alkenyl groups with 14 to 24 carbon atoms in the molecule;
- (B) a carboxylic acid type anionic polymer;
- (C) a polyoxyethylene adducted nonionic surfactant; and
- (D) an aqueous vehicle,
Description
- The present invention relates to a softener composition which can impart, for example, an excellent softness and antistatic property to fiber, clothing, and hair. More specifically, it relates to an aqueous liquid softener composition which can impart an excellent softness and antistatic property to chemical textile products such as of acryl, nylon, polyester, and also has an excellent dispersion stability.
- Heretofore, to prevent deterioration of the touch and antistatic properties of textile products after repeated wear and washing, a softener containing a quaternary ammonium salt having two long chain alkyl groups or alkenyl groups in the molecule as the main component has been employed. Representative examples of the quaternary ammonium salts include di-hardened tallow alkyldimethylammonium chloride, and methyl-1-tallow amidoethyl-2-alkylimidazolinium methylsulfate, but these single products, although they are capable of imparting excellent softness to cotton products, have no sufficient effect from the view point of imparting softness and an antistatic property to chemical fiber products. Accordingly, proposals have been made to modify the quaternary ammonium salt itself (Japanese Unexamined Patent Publication (Kokai) No. 55-51876); use of the quaternary ammonium salt in combination with another specific di-long chain alkyl quaternary salt (Japanese Unexamined Patent Publication (Kokai) Nos. 55-51874, 55-62268, 55-103364, 55-103365); use of the quaternary ammonium salt in combination with a tri-long chain alkyl quaternary salt (Japanese Unexamined Patent Publication (Kokai) Nos. 55-112375, 55-1112377, 56-79768); use of the quaternary ammonium salt in combination with a specific mono-long chain alkyl quaternary salt (Japanese Unexamined Patent Publication (Kokai) No. 57-205581); or, use of the quaternary ammonium salt in combination with an anionic surfactant (Japanese Unexamined Patent Publication (Kokai) Nos. 53-19497, 53-38794, 53-52799, 58-13775). Nevertheless, although some improvement can be observed when these compositions are used, the effects are still unsatisfactory, or on the contrary, the softness of cotton may be worsened in some cases. Thus, up to data, a softener for domestic use which can impart a sufficient softness to both textile products of cotton and chemical fibers, and provide an excellent antistatic effect for chemical fibers, is not available.
- On the other hand, the present Applicant has found that an excellent effect can be obtained by use of a carboxylic acid type anionic polymer in combination with a quaternary ammonium salt and has filed a patent application therefor (Japanese Patent Application No. 62-127722). Nevertheless, when only these two components are used, it has been found that a phase separation after a lapse of days for storage or abrupt rise in viscosity elevation occurs, whereby no sufficient dispersion stability which is essential to the commercial product cannot be satisfactorily obtained. Separately from these, proposals have been made for granular additives to a detergent by using a dilong chain alkyl quaternary ammonium salt in combination with a specific anionic polymer (Japanese Unexamined Patent Publication (Kokai) Nos. 59-6298, 61-7398), but such granular products can not be sufficiently dispersed or dissolved in water, and therefore, the object of the present invention cannot be accomplished even by using such a granular additive for the conventional washing and rinsing steps.
- Accordingly, an object of the present invention is to obviate the above-mentioned problems in the prior art and to provide an aqueous liquid softener composition which can impart the same softness to cotton as that of the prior art products, but a much greater softness and antistatic property to chemical fibers, compared with the prior art products in softening treatment practiced in the washing and rinsing steps at home, and further, has an excellent dispersion stability.
- Other objects and advantages of the present invention will be apparent from the description set forth hereinbelow.
- In accordance with the present invention, there is provided a liquid softener composition, comprising:
- (A) a slightly water-soluble quaternary ammonium salt type cationic surfactant having 2 or 3 alkyl or alkenyl groups with 14 to 24 carbon atoms in the molecule;
- (B) a carboxylic acid type anionic polymer;
- (C) a polyoxyethylene adducted nonionic surfactant; and
- (D) an aqueous vehicle, with the weight ratio of (A)/(C) being within range of from 100/1 to 3/1.
- It has been found that the above-mentioned object of the present invention can be accomplished by using a specific slightly water-soluble quaternary ammonium salt type cationic surfactant in combination with a carboxylic acid type anionic polymer and a polyoxyethylene adducted nonionic surfactant.
- The slightly water-soluble quaternary ammonium salt of the component (A) usable in the present invention may be exemplified by those represented by the formula (I) or (II) shown below. These compounds can be used alone or as a mixture of two or more compounds, and these are cationic surfactants having 2 or 3 straight or branched alkyl or alkenyl groups with 14 to 24 carbon atoms in the molecule which may be respectively optionally substituted or intermingled with functional groups such as
-OH, -O-, --NH-, --O-.
-OH-, -O-, --NH-, --O-, etc.,
the remainder of the groups of R₁ - R₄ represent an alkyl group with 1 to 3 carbon atoms, a hydroxyalkyl group or a group represented by the formula -(C₂H₄)ℓH (where ℓ is an integer of 1 to 5, and X represents a halogen or a monoalkylsulfate group represented by R₅SO₄ where R₅ represents an alkyl group with 1 to 3 carbon atoms). - At least two groups of R₁ - R₄ in the above formula (I) have 14 to 24, preferably 16 to 22 carbon atoms, R₇ and R₈ in the above formula (II) have 14 to 24, preferably 15 to 21 carbon atoms, each group may have a distribution within these ranges, and the respective groups may be either the same or different from each other. When the carbon number is lower than this range, for example, when a mixture of quaternary ammonium salts of (I) or (II) synthesized from coconut fatty acids is used, the softness will be poor.
- Specific examples of the component (A) include one or a mixture of two or more of di-hardened tallow alkyldimethylammonium chloride, di-tallow alkyldimethylammonium bromide, dioleyldimethylammonium chloride, dipalmitylhydroxyethylammonium methylsulfate, distearylmethylpolyoxyethylene (average degree of polymerization is 3)ammonium chloride, diisostearyldimethylammonium methylsulfate, dieicosyldimethylammonium chloride, dibehenylmethylpolyoxyethylene (average degree of polymerization is 5)ammonium chloride, dierucyldimethylammonium chloride, di[2-dodecanoylamino)ethyl]-dimethylammonium chloride, di[2-stearoylamino)propyl]dimethylammonium ethylsulfate, di(2-ethylpalmitoyl)hydroxyethylmethylammonium methylsulfate, trioleylmethylammonium chloride, dioleylmonostearylmethylammonium chloride, dioleylmonobehenylmethylammonium chloride, monooleyldierucylmethylammonium chloride, tristearylmethylammonium methylsulfate, methyl-1-tallow amidoethyl-2-tallow alkylimidazolinium methylsulfate, methyl-1-hexadecanolylamidoethyl-2-pentadecylimidazolinium chloride, ethyl-1-octadecenoylamidoethyl-2-heptadecenylimidazolinium ethylsulfate, and the like. The content of the component (A) in the softener composition may be as desired but is preferably 3 to 50% by weight (hereinafter abbreviated merely as %), more preferably 4 to 20%.
- As the carboxylic acid type anionic polymer of the component (B), homopolymers of ethylenically unsaturated carboxylic acids or anhydrides thereof or copolymers of said monomers can be used. The salts of these homopolymers and copolymers may be used. Also, these polymers may be used either as such or in the form of water soluble neutral salts such as alkali metal salts or alkaline earth metal salts. The component (B) has an average molecular weight generally of 500 to 50,000, preferably 500 to 20,000, and more preferably 500 to 10,000.
- The above-mentioned anionic polymrs to be used as the component (B) should be the so-called "oligomers" which have a relatively low molecular weight. When the molecular weight thereof is higher, the desired sufficient dispersion stability obtained from the addition of the component (C) as mentioned hereinbelow is prevented. Contrarily, when the molecular weight is lower, the effect obtained from addition of the component (B) as mentioned hereinbelow becomes insufficient.
- Specific examples of the component (B) may include one or a mixture of two or more of polyacrylic acid, polymethacrylic acid, polycrotonic acid, polyacotinic acid, poly-α-hydroxyacrylic acid, polymaleic acid, polysorbic acid, polyitaconic acid, poly(maleic anhydride), poly(itaconic anhydride) their copolymers, or salts of these homopolymers or copolymers.
- In the liquid softener composition, the reason why excellent effect can be obtained by using the component (A) and the component (B) in combination is not clear, but it may be considered to be as follows. That is, although the ion bonding between the both may not be so strong, by forming a cation-anion complex with a part of the dispersed particles of the component (A), the component (A) can be made further hydrophobic to promote adsorption of the component (A) onto chemical fibers such as acrylic or polyester fibers which are hydrophobic fibers, whereby softness and antistatic property of the chemical fibers can be consequently further improved as compared with the case of the component (A) alone. On the other hand, the component (B) which is a water soluble polymer will not be incorporated into the dispersed particles of the component (A) and will not destroy the adsorption structure of the component (A), as different from a some kinds of anionic surfactant, and consequently will not give any adverse effect on the softness of cotton fibers.
- In view of the above mechanism, it is important to control the amount of the component (B) formulated as the relative value to the component (A). Specifically, these compounds are formulated, in terms of the ratio of positive charge mols (a) of the component (A) to the negative charge mols (b) of the component (B), at a ratio (a)/(b) of 1/0.2 to 1/2.0, preferably 1/0.5 to 1/1.0. If the ratio of the component (B) to the component (A) is outside this range, the above effect of combined use is difficult to obtain.
- The third essential component for accomplishing the object of the present invention is the component (C). That is, a sufficient dispersion stability is an essential condition for use as a softener for domestic use, but only with the components (A), (B), (D), the required dispersibility cannot be obtained, and accordingly the emulsifying stabilizing action of the component (C) is necessary.
- The component (C) usable in the present invention may be exemplified by polyoxyethylene alkylphenyl ether, polyoxyethylene alkyl (or alkenyl) ether, polyoxyethylene fatty acid amide, polyoxyethylene alkyl (or alkenyl) amine, and polyoxyethylene sorbitane fatty acid ester. Preferable average additional moles of ethylene oxide are at least 20, more preferably 20 to 100. Examples of such a component (C) are POE (
p =20 - 100) alkyl(C₈₋₁₂)phenyl ether, POE(p =20 - 100) alkyl or alkenyl(C₁₀₋₂₂) ether, POE(p =20 - 100) alkyl or alkenyl (C₁₀₋₂₀) amine, or mixtures thereof. In the above compounds, each POE represents polyoxyethylene,p denotes the average adducted mols of ethylene oxide, and C the carbon number of the alkyl or alkenyl group (hereinafter the same). - The component (C) improves the emulsifying dispersion of the dispersed particles of the component (A) alone and the anion-cation complex of the dispersed particles of the component (A) with the component (B), which may be considered to form a random coil structure dissolved in the aqueous phase in the composition, and thus the amount of the component (C) formulated is preferably 100/1 to 3/1 as a weight ratio of (A)/(C), more preferably 50/1 to 5/10. If the ratio of the component (C) to the component (A) is outside of this range, the above effect cannot be exhibited, and conversely, the above effect of combined use of the component (A) and the component (B) is frequently inhibited.
- The component (D) is used as the carrier for the essential components and the optional components of the present invention, and the amount thereof in the composition is the balance which makes up the total amount to 100%, in addition to the essential components and the optional components formulated.
- The softener composition of the present invention can include optional components in addition to the above essential components, including viscosity controllers such as inorganic electrolytes like sodium chloride, potassium chloride, magnesium chloride, aluminum chloride, sodium sulfate, ammonium sulfate, sodium nitrate, or magnesium nitrate; and polyethylene glycol or other water soluble organic polymers; hydrotropes such as lower alcohols like ethanol, or isopropanol, ethylene glycol, glycerine, and urea; and pH controllers, sterilizers, pigment dyes, perfumes, antioxidants, UV-ray absorbers, and fluorescent brighteners.
- The softener composition of the present invention can be prepared according to known methods. More specifically, it is desirable that the component (A) should be finely and uniformly dispersed, and for this purpose, it is preferable to use the method in which the components (B), (C) and optical components are previously dissolved in an aqueous vehicle, and to this solution is successively added, under heating to 40°C to 80°C if desired, the component (A) in a molten state to be mixed under stirring. On the other hand, when optional components susceptible to denaturation at high temperature are used, it is desirable to cool the above dispersion to about room temperature, followed by addition while stirring. A pH controller can be added to the softener composition of the present invention, but the pH of the composition is not limited. Usually, the pH is that when the respective components are formulated, but it is desirable to control pH to 4 to 8. For this purpose, an organic or inorganic acid or a basic compound can be formulated, as desired.
- The softener composition of the present invention which can impart an excellent softness to not only cotton fibers but also chemical fibers, and further gives an excellent antistatic property to chemical fibers is valuable.
- Also it has excellent freeze-tham stability, whereas it shows neither remarkable viscosity rise nor abnormal phase separation even when stored for a long term. Thus, the present composition is excellent in practical application.
- The present invention now will be further illustrated by, but is by no means limited to, the following examples.
- The preparation, performance evaluation and dispersion stability evaluation of the softener compositions in Examples were conducted according to the following methods.
- Other components except for the component (A) were dissolved in water, the resultant solution was heated to 45°C and to this was added dropwise under stirring the molten product of the component (A) to be dispersed uniformly, followed by cooling to 25°C.
- Commercially available cotton towel, acrylic cloth were washed repeatedly twice with a commercially available detergent for clothing by means of an electric washing machine at 50°C, and then thoroughly rinsed with tap water at normal temperature to provide test cloths.
- Next, into 30 liters of tap water of 25°C was added the softener composition to an amount of the component (A) added of 1 g to form a uniform solution. Each test cloth was dipped in this solution at a bath ratio of 30-fold to carry out the treatment for 3 minutes, and then dehydrated for 2 minutes. The cloth thus treated was dried on air, and then the cotton towel for evaluation of softening effect was left to stand under the conditions of 25°C, 65% RH for 24 hours, while the acrylic cloth for evaluation of antistatic effect under the conditions of 20°C, 50% RH for 72 hours, before use for the respective evaluation tests.
-
- (a) Softness: Touch feelings of cotton towel before and after treatment were compared and evaluated according to the following standards:
+ 5 ..... very soft
+ 4 ..... considerably soft
+ 3 ..... soft
+ 2 ..... some softness
+ 1 ..... slightly soft
0 ..... unchanged, as before treatment; - (b) antistatic property: By means of a static honestometer (manufactured by Shishido Shokai), the polyester cloth was charged at an application voltage of 7 KV at a target distance of 20 mm, and the half life (sec.) of the residual voltage after the removal of the applied voltage was measured.
-
- (a) viscosity change: The viscosities for each softener composition prepared, one composition immediately after preparation, one freezed at -15°C for 40 hours and then thawed at 25°C and one stored at 45°C for one month were measured by means of a B type viscometer (manufactured by Tokyo Keiki) (measurement was conducted at 25°C);
- (b) judgement of phase separation: each softener composition prepared was charged into a transparent cylinder bottle of 45 mm in inner diameter to 70 mm from the bottom of the bottle, stationarily stored at 5°C for one month, and then the separated length was measured. Evaluation:
o: not separated
Δ: separated length less than 3 mm
x: separated length of 3 mm or longer -
-
- From Table 1, it can be understood that the softener compositions of the present invention have excellent performance and dispersion stability. More specifically, although considerable softness is exhibited in the case of di-hardened tallow alkyldimethylammonium chloride alone, the softness and antistatic property of the acrylic cloth are clearly improved by addition of the component (B). Particularly, No. 1 and No. 5 can be appreciated to exhibit a very excellent antistatic property. Also, according to the experience of the present inventors, a rise in viscosity under the above storage conditions may be permissible up to about 1500 centipoise in commercial product value, and it can be seen that the products of the present invention satisfy this condition without causing phase separation due to the addition effect of the component (C) and the presence of ethylene glycol in the component (D).
-
- From Table 2, it can be understood that all of the products of the present invention have good performances and also excellent dispersion stability. In contrast, as shown in Comparative examples, if the ratio of the component (C) relative to the component (A) is too low, i.e., outside the range defined in the present invention (No. 14), viscosity elevation after a lapse of days for storage is marked, while if it is too much (No. 15), phase separation is liable to occur, and there is also an undesirable tendency that the performance to be improved by addition of the component (B) is contrariwise inhibited.
-
- The above component (A), is provided as a mixture with isopropanol, and therefore, the compositions were contaminated with about 3 (%) thereof.
Table 3 - No. Amount of the component (B) (%) Component (A)/Component (B) charge molar ratio (a)/(b) Performance evaluation results Softness Antistatic property Cotton towel Acrylic cloth Acrylic cloth Comparative example 16 (no addition) 1/0 +3 +3 100 (sec) Present products 17 0.11 1/0.1 +3 +3 80 18 0.23 1/0.2 +3 +3 50 19 0.57 1/0.5 +3 +3 - +4 15 20 0.91 1/0.8 +3 - +4 +3 - +4 3 21 1.14 1/1.0 +3 - +4 +3 - +4 2 22 1.71 1/1.5 +3 +3 - +4 30 23 2.29 1/2.0 +3 +3 70 24 2.86 1/2.5 +3 +3 90 - From Table 3, it can be understood that softness and/or antistatic property of the acrylic cloth can be improved by an addition of the component (B). Furthermore, it is also clear that the softness of the cotton towel is improved in some cases. Thus, these effects are more marked when the charge molar ratio (a)/(b) is within the range from 1/0.2 to 1/2.0, more preferably from 1/0.5 to 1/1.0. Also all of the above compositions of the present invention have a good dispersion stability, which may be attributed to the addition effects of the component (C) and glycerine in the component (D).
- Using various slightly water soluble di/tri-long chain alkyl/alkenyl quaternary ammonium salts as the component (A) and sodium polyacrylate as the component (A) at equivalent charge molar ratio (a)/(b), softener compositions with the compositions shown below were prepared and their performances were evaluated and compared with the case when sodium polyacrylate was not added. The results are shown in Table 4.
- From Table 4, it can be understood that the carboxylic acid type anionic polymers used in the present invention have performance improvement effects on all of the slightly water soluble quaternary ammonium salts having different structures from each other. More specifically, in Table 4, it can be seen that by an addition of sodium polyacrylate in equivalent amount to the component (A), in all cases, the performances, particularly softness and antistatic property of the acrylic cloths are greatly improved. Also, all of the above compositions of the present invention have good dispersion stability.
Claims (8)
-OH-, -O-, --NH-, or --O-,
the remainder of the groups of R₁ - R₄ represent an alkyl group with 1 to 3 carbon atoms, a hydroxyalkyl group or a group represented by the formula -(C₂H₄)ℓH where ℓ is an integer of 1 to 5, and X represents a halogen or a monoalkylsulfate group represented by R₅SO₄ where R₅ represents an alkyl group with 1 to 3 carbon atoms.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP79228/88 | 1988-03-31 | ||
| JP7922888A JPH01250473A (en) | 1988-03-31 | 1988-03-31 | Liquid softening agent composition |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0335404A2 true EP0335404A2 (en) | 1989-10-04 |
| EP0335404A3 EP0335404A3 (en) | 1990-12-27 |
Family
ID=13684042
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP19890105663 Withdrawn EP0335404A3 (en) | 1988-03-31 | 1989-03-30 | Liquid softener composition |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0335404A3 (en) |
| JP (1) | JPH01250473A (en) |
Cited By (22)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0425853A2 (en) * | 1989-10-30 | 1991-05-08 | Lang & Co., chemisch-technische Produkte Kommanditgesellschaft | Aqueous cleaning agent for compressors, particularly gas turbines |
| WO1992015664A1 (en) * | 1991-03-04 | 1992-09-17 | Ciba-Geigy Ag | Aqueous textile auxiliary composition |
| WO1992019714A1 (en) * | 1991-04-30 | 1992-11-12 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Fabric softener containing substituted imidazoline and highly ethoxylated compounds |
| US5242607A (en) * | 1990-10-05 | 1993-09-07 | Kao Corporation | Concentrated softener |
| US5356443A (en) * | 1992-09-08 | 1994-10-18 | Ciba-Geigy Corporation | Stabilization of dyeings of polyamide fibres |
| EP0590604A3 (en) * | 1992-09-29 | 1996-03-27 | Amerchol Corp | Hairsprays and acrylic polymer compositions for use therein |
| WO1998040452A1 (en) * | 1997-03-11 | 1998-09-17 | Unilever Plc | Hard-surface cleaning compositions |
| GB2323391A (en) * | 1997-03-20 | 1998-09-23 | Akzo Nobel Nv | Dryer-activated fabric conditioning and antistatic compositions |
| US6017860A (en) * | 1996-04-15 | 2000-01-25 | Stepan Company | Cleaning, conditioning and styling hair care compositions |
| WO2001025387A1 (en) * | 1999-10-01 | 2001-04-12 | Unilever Plc | Fabric care composition |
| US6254859B1 (en) | 1995-09-18 | 2001-07-03 | Stepan Company | Hair and skin conditioning compositions |
| WO2004024856A2 (en) * | 2002-09-13 | 2004-03-25 | Nippon Shokubai Co., Ltd. | Liquid detergent builder and liquid detergent containing the same |
| WO2006124338A1 (en) * | 2005-05-12 | 2006-11-23 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Fabric softening compositions stable under freeze-thaw conditions |
| US8728530B1 (en) | 2012-10-30 | 2014-05-20 | The Clorox Company | Anionic micelles with cationic polymeric counterions compositions thereof |
| US8728454B1 (en) | 2012-10-30 | 2014-05-20 | The Clorox Company | Cationic micelles with anionic polymeric counterions compositions thereof |
| US8765114B2 (en) | 2012-10-30 | 2014-07-01 | The Clorox Company | Anionic micelles with cationic polymeric counterions methods thereof |
| KR101424551B1 (en) * | 2006-01-18 | 2014-08-01 | 인비스타 테크놀러지스 에스.에이 알.엘. | Non-textile polymer compositions and methods |
| US8883705B2 (en) | 2012-10-30 | 2014-11-11 | The Clorox Company | Cationic micelles with anionic polymeric counterions systems thereof |
| US8883706B2 (en) | 2012-10-30 | 2014-11-11 | The Clorox Company | Anionic micelles with cationic polymeric counterions systems thereof |
| CN104762812A (en) * | 2015-03-11 | 2015-07-08 | 刘晓 | Clothes softening agent |
| WO2018044639A1 (en) * | 2016-08-31 | 2018-03-08 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Fabric enhancer composition |
| WO2022042277A1 (en) * | 2020-08-28 | 2022-03-03 | Ecolab Usa Inc. | Method and extraction agent for methanol to olefins wash water system antifouling |
Families Citing this family (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB9011785D0 (en) * | 1990-05-25 | 1990-07-18 | Unilever Plc | Fabric treatment compositions |
| KR100389684B1 (en) * | 2000-05-10 | 2003-07-04 | 김진원 | Novel viscose rayon coated with anti-electrostatic agent and process of preparation thereof |
| JP4956821B2 (en) * | 2007-12-27 | 2012-06-20 | ライオン株式会社 | Liquid softener composition |
| CN104508199B (en) * | 2012-06-15 | 2017-11-07 | 罗地亚经营管理公司 | Recover or increase the method for polyester textile water imbibition |
| JP6053507B2 (en) * | 2012-12-26 | 2016-12-27 | 花王株式会社 | Softener composition |
| CN105803775A (en) * | 2014-12-30 | 2016-07-27 | 上海氟聚化学产品有限公司 | Softening agent for polyester sewing thread |
| JP6913862B2 (en) * | 2017-01-30 | 2021-08-04 | 白元アース株式会社 | Antistatic composition and spray antistatic agent |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3537993A (en) * | 1966-06-21 | 1970-11-03 | Procter & Gamble | Detergent compositions |
| DE2459125A1 (en) * | 1973-12-15 | 1975-06-26 | Ciba Geigy Ag | PREPARATION AND ITS USE FOR THE CARE OF TEXTILE MATERIALS |
| FR2407261A1 (en) * | 1977-10-26 | 1979-05-25 | Unilever Nv | SOIL RELEASE COMPOSITIONS, THEIR PREPARATION METHOD AND THEIR USE FOR TREATMENT OF STOOLS |
| GB2151252A (en) * | 1983-12-10 | 1985-07-17 | Sandoz Ltd | Detergent composition |
-
1988
- 1988-03-31 JP JP7922888A patent/JPH01250473A/en active Granted
-
1989
- 1989-03-30 EP EP19890105663 patent/EP0335404A3/en not_active Withdrawn
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3537993A (en) * | 1966-06-21 | 1970-11-03 | Procter & Gamble | Detergent compositions |
| DE2459125A1 (en) * | 1973-12-15 | 1975-06-26 | Ciba Geigy Ag | PREPARATION AND ITS USE FOR THE CARE OF TEXTILE MATERIALS |
| FR2407261A1 (en) * | 1977-10-26 | 1979-05-25 | Unilever Nv | SOIL RELEASE COMPOSITIONS, THEIR PREPARATION METHOD AND THEIR USE FOR TREATMENT OF STOOLS |
| GB2151252A (en) * | 1983-12-10 | 1985-07-17 | Sandoz Ltd | Detergent composition |
Cited By (32)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0425853A3 (en) * | 1989-10-30 | 1991-12-11 | Lang & Co., Chemisch-Technische Produkte Kommanditgesellschaft | Aqueous cleaning agent for compressors, particularly gas turbines |
| EP0425853A2 (en) * | 1989-10-30 | 1991-05-08 | Lang & Co., chemisch-technische Produkte Kommanditgesellschaft | Aqueous cleaning agent for compressors, particularly gas turbines |
| US5242607A (en) * | 1990-10-05 | 1993-09-07 | Kao Corporation | Concentrated softener |
| WO1992015664A1 (en) * | 1991-03-04 | 1992-09-17 | Ciba-Geigy Ag | Aqueous textile auxiliary composition |
| WO1992019714A1 (en) * | 1991-04-30 | 1992-11-12 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Fabric softener containing substituted imidazoline and highly ethoxylated compounds |
| US5356443A (en) * | 1992-09-08 | 1994-10-18 | Ciba-Geigy Corporation | Stabilization of dyeings of polyamide fibres |
| EP0590604A3 (en) * | 1992-09-29 | 1996-03-27 | Amerchol Corp | Hairsprays and acrylic polymer compositions for use therein |
| US5589157A (en) * | 1992-09-29 | 1996-12-31 | Amerchol Corporation | Hairsprays and acrylic polymer compositions for use therein |
| US6254859B1 (en) | 1995-09-18 | 2001-07-03 | Stepan Company | Hair and skin conditioning compositions |
| US6218346B1 (en) | 1996-04-15 | 2001-04-17 | Stepan Company | Methods for cleaning, conditioning and styling hair |
| US6017860A (en) * | 1996-04-15 | 2000-01-25 | Stepan Company | Cleaning, conditioning and styling hair care compositions |
| EP0904052B1 (en) * | 1996-04-15 | 2002-12-11 | Stepan Company | Cleaning, conditioning and styling hair care compositions |
| AU734919B2 (en) * | 1997-03-11 | 2001-06-28 | Unilever Plc | Hard-surface cleaning compositions |
| WO1998040452A1 (en) * | 1997-03-11 | 1998-09-17 | Unilever Plc | Hard-surface cleaning compositions |
| GB2323391A (en) * | 1997-03-20 | 1998-09-23 | Akzo Nobel Nv | Dryer-activated fabric conditioning and antistatic compositions |
| WO2001025387A1 (en) * | 1999-10-01 | 2001-04-12 | Unilever Plc | Fabric care composition |
| US6793684B1 (en) | 1999-10-01 | 2004-09-21 | Unilever Home & Personal Care Usa, Division Of Conopco, Inc. | Fabric care composition |
| WO2004024856A2 (en) * | 2002-09-13 | 2004-03-25 | Nippon Shokubai Co., Ltd. | Liquid detergent builder and liquid detergent containing the same |
| US7390776B2 (en) | 2002-09-13 | 2008-06-24 | Nippon Shokubai Co., Ltd. | Liquid detergent builder and liquid detergent containing the same |
| WO2004024856A3 (en) * | 2002-09-13 | 2004-06-10 | Nippon Catalytic Chem Ind | Liquid detergent builder and liquid detergent containing the same |
| WO2006124338A1 (en) * | 2005-05-12 | 2006-11-23 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Fabric softening compositions stable under freeze-thaw conditions |
| KR101424551B1 (en) * | 2006-01-18 | 2014-08-01 | 인비스타 테크놀러지스 에스.에이 알.엘. | Non-textile polymer compositions and methods |
| US8728530B1 (en) | 2012-10-30 | 2014-05-20 | The Clorox Company | Anionic micelles with cationic polymeric counterions compositions thereof |
| US8765114B2 (en) | 2012-10-30 | 2014-07-01 | The Clorox Company | Anionic micelles with cationic polymeric counterions methods thereof |
| US8728454B1 (en) | 2012-10-30 | 2014-05-20 | The Clorox Company | Cationic micelles with anionic polymeric counterions compositions thereof |
| US8883705B2 (en) | 2012-10-30 | 2014-11-11 | The Clorox Company | Cationic micelles with anionic polymeric counterions systems thereof |
| US8883706B2 (en) | 2012-10-30 | 2014-11-11 | The Clorox Company | Anionic micelles with cationic polymeric counterions systems thereof |
| US8933010B2 (en) | 2012-10-30 | 2015-01-13 | The Clorox Company | Cationic micelles with anionic polymeric counterions compositions thereof |
| CN104762812A (en) * | 2015-03-11 | 2015-07-08 | 刘晓 | Clothes softening agent |
| WO2018044639A1 (en) * | 2016-08-31 | 2018-03-08 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Fabric enhancer composition |
| US10487292B2 (en) | 2016-08-31 | 2019-11-26 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Fabric enhancer composition |
| WO2022042277A1 (en) * | 2020-08-28 | 2022-03-03 | Ecolab Usa Inc. | Method and extraction agent for methanol to olefins wash water system antifouling |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP0335404A3 (en) | 1990-12-27 |
| JPH01250473A (en) | 1989-10-05 |
| JPH024709B2 (en) | 1990-01-30 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0335404A2 (en) | Liquid softener composition | |
| CA1179806A (en) | Fabric softener concentrate | |
| US3928213A (en) | Fabric softener and soil-release composition and method | |
| USRE34062E (en) | Fabric softening composition contains water-insoluble surfactant and aliphatic mono-carboxylic acid | |
| EP0056695B2 (en) | Textile treatment compositions | |
| EP0060003B1 (en) | Textile treatment compositions and preparation thereof | |
| CA1110015A (en) | Fabric softener composition and method | |
| US4157307A (en) | Liquid fabric softener | |
| EP0385749B1 (en) | Fabric softening composition | |
| EP0086105B1 (en) | Fabric softening composition | |
| EP0787793B1 (en) | Fabric softening composition | |
| EP0086106B1 (en) | Fabric softening composition | |
| EP0381487A1 (en) | Detergent formulations | |
| EP0188349B1 (en) | Fabric conditioning composition | |
| EP0188350B1 (en) | Fabric conditioning method | |
| US5254268A (en) | Anti-static rinse added fabric softener | |
| US4891143A (en) | Water insoluble antistatic compositions | |
| JP2757892B2 (en) | Composition for softening liquid textile products | |
| CA1232709A (en) | Aqueous concentrated fabric softening composition | |
| JPH01229877A (en) | Liquid softener composition | |
| JPS61160482A (en) | Softener composition | |
| JPH04333666A (en) | Liquid softening agent composition | |
| CA1226407A (en) | Aqueous fabric softening composition | |
| JPH062983B2 (en) | Method of manufacturing softening agent | |
| JPS636099A (en) | Softener composition |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19890427 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE ES FR GB IT LI NL SE |
|
| RAP1 | Party data changed (applicant data changed or rights of an application transferred) |
Owner name: LION CORPORATION |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE ES FR GB IT LI NL SE |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 19940203 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE APPLICATION IS DEEMED TO BE WITHDRAWN |
|
| 18D | Application deemed to be withdrawn |
Effective date: 19940614 |