CN103582006A - 用于3gpp-lte系统中的小数据传输的设备和方法 - Google Patents
用于3gpp-lte系统中的小数据传输的设备和方法 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN103582006A CN103582006A CN201310336123.8A CN201310336123A CN103582006A CN 103582006 A CN103582006 A CN 103582006A CN 201310336123 A CN201310336123 A CN 201310336123A CN 103582006 A CN103582006 A CN 103582006A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- small data
- rrc connection
- message
- data payload
- enb
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 24
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 title abstract description 16
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 12
- 241000760358 Enodes Species 0.000 claims description 4
- 238000012790 confirmation Methods 0.000 claims description 4
- 238000007599 discharging Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000007774 longterm Effects 0.000 abstract description 3
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 9
- 230000009471 action Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000005611 electricity Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000011160 research Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000000712 assembly Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000000429 assembly Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002708 enhancing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000036541 health Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000977 initiatory effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010295 mobile communication Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012544 monitoring process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005457 optimization Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000011664 signaling Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04B—TRANSMISSION
- H04B7/00—Radio transmission systems, i.e. using radiation field
- H04B7/24—Radio transmission systems, i.e. using radiation field for communication between two or more posts
- H04B7/26—Radio transmission systems, i.e. using radiation field for communication between two or more posts at least one of which is mobile
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W40/00—Communication routing or communication path finding
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L1/00—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received
- H04L1/12—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received by using return channel
- H04L1/16—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received by using return channel in which the return channel carries supervisory signals, e.g. repetition request signals
- H04L1/18—Automatic repetition systems, e.g. Van Duuren systems
- H04L1/1829—Arrangements specially adapted for the receiver end
- H04L1/1861—Physical mapping arrangements
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F16/00—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor
- G06F16/90—Details of database functions independent of the retrieved data types
- G06F16/95—Retrieval from the web
- G06F16/953—Querying, e.g. by the use of web search engines
- G06F16/9535—Search customisation based on user profiles and personalisation
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F16/00—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor
- G06F16/90—Details of database functions independent of the retrieved data types
- G06F16/95—Retrieval from the web
- G06F16/953—Querying, e.g. by the use of web search engines
- G06F16/9537—Spatial or temporal dependent retrieval, e.g. spatiotemporal queries
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04B—TRANSMISSION
- H04B17/00—Monitoring; Testing
- H04B17/20—Monitoring; Testing of receivers
- H04B17/27—Monitoring; Testing of receivers for locating or positioning the transmitter
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04B—TRANSMISSION
- H04B7/00—Radio transmission systems, i.e. using radiation field
- H04B7/24—Radio transmission systems, i.e. using radiation field for communication between two or more posts
- H04B7/26—Radio transmission systems, i.e. using radiation field for communication between two or more posts at least one of which is mobile
- H04B7/2612—Arrangements for wireless medium access control, e.g. by allocating physical layer transmission capacity
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04J—MULTIPLEX COMMUNICATION
- H04J11/00—Orthogonal multiplex systems, e.g. using WALSH codes
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L1/00—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received
- H04L1/0001—Systems modifying transmission characteristics according to link quality, e.g. power backoff
- H04L1/0009—Systems modifying transmission characteristics according to link quality, e.g. power backoff by adapting the channel coding
- H04L1/0013—Rate matching, e.g. puncturing or repetition of code symbols
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L41/00—Arrangements for maintenance, administration or management of data switching networks, e.g. of packet switching networks
- H04L41/06—Management of faults, events, alarms or notifications
- H04L41/0654—Management of faults, events, alarms or notifications using network fault recovery
- H04L41/0659—Management of faults, events, alarms or notifications using network fault recovery by isolating or reconfiguring faulty entities
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L41/00—Arrangements for maintenance, administration or management of data switching networks, e.g. of packet switching networks
- H04L41/08—Configuration management of networks or network elements
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L41/00—Arrangements for maintenance, administration or management of data switching networks, e.g. of packet switching networks
- H04L41/08—Configuration management of networks or network elements
- H04L41/0803—Configuration setting
- H04L41/0813—Configuration setting characterised by the conditions triggering a change of settings
- H04L41/082—Configuration setting characterised by the conditions triggering a change of settings the condition being updates or upgrades of network functionality
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L41/00—Arrangements for maintenance, administration or management of data switching networks, e.g. of packet switching networks
- H04L41/08—Configuration management of networks or network elements
- H04L41/0803—Configuration setting
- H04L41/0823—Configuration setting characterised by the purposes of a change of settings, e.g. optimising configuration for enhancing reliability
- H04L41/0836—Configuration setting characterised by the purposes of a change of settings, e.g. optimising configuration for enhancing reliability to enhance reliability, e.g. reduce downtime
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L43/00—Arrangements for monitoring or testing data switching networks
- H04L43/08—Monitoring or testing based on specific metrics, e.g. QoS, energy consumption or environmental parameters
- H04L43/0805—Monitoring or testing based on specific metrics, e.g. QoS, energy consumption or environmental parameters by checking availability
- H04L43/0811—Monitoring or testing based on specific metrics, e.g. QoS, energy consumption or environmental parameters by checking availability by checking connectivity
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L45/00—Routing or path finding of packets in data switching networks
- H04L45/28—Routing or path finding of packets in data switching networks using route fault recovery
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L45/00—Routing or path finding of packets in data switching networks
- H04L45/302—Route determination based on requested QoS
- H04L45/306—Route determination based on the nature of the carried application
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L45/00—Routing or path finding of packets in data switching networks
- H04L45/302—Route determination based on requested QoS
- H04L45/308—Route determination based on user's profile, e.g. premium users
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L45/00—Routing or path finding of packets in data switching networks
- H04L45/38—Flow based routing
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L47/00—Traffic control in data switching networks
- H04L47/10—Flow control; Congestion control
- H04L47/27—Evaluation or update of window size, e.g. using information derived from acknowledged [ACK] packets
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L5/00—Arrangements affording multiple use of the transmission path
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L5/00—Arrangements affording multiple use of the transmission path
- H04L5/003—Arrangements for allocating sub-channels of the transmission path
- H04L5/0032—Distributed allocation, i.e. involving a plurality of allocating devices, each making partial allocation
- H04L5/0035—Resource allocation in a cooperative multipoint environment
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L5/00—Arrangements affording multiple use of the transmission path
- H04L5/003—Arrangements for allocating sub-channels of the transmission path
- H04L5/0053—Allocation of signaling, i.e. of overhead other than pilot signals
- H04L5/0057—Physical resource allocation for CQI
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L65/00—Network arrangements, protocols or services for supporting real-time applications in data packet communication
- H04L65/1066—Session management
- H04L65/1101—Session protocols
- H04L65/1104—Session initiation protocol [SIP]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L65/00—Network arrangements, protocols or services for supporting real-time applications in data packet communication
- H04L65/40—Support for services or applications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L65/00—Network arrangements, protocols or services for supporting real-time applications in data packet communication
- H04L65/60—Network streaming of media packets
- H04L65/61—Network streaming of media packets for supporting one-way streaming services, e.g. Internet radio
- H04L65/613—Network streaming of media packets for supporting one-way streaming services, e.g. Internet radio for the control of the source by the destination
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L65/00—Network arrangements, protocols or services for supporting real-time applications in data packet communication
- H04L65/80—Responding to QoS
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L67/00—Network arrangements or protocols for supporting network services or applications
- H04L67/01—Protocols
- H04L67/02—Protocols based on web technology, e.g. hypertext transfer protocol [HTTP]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L67/00—Network arrangements or protocols for supporting network services or applications
- H04L67/2866—Architectures; Arrangements
- H04L67/30—Profiles
- H04L67/303—Terminal profiles
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L67/00—Network arrangements or protocols for supporting network services or applications
- H04L67/2866—Architectures; Arrangements
- H04L67/30—Profiles
- H04L67/306—User profiles
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L67/00—Network arrangements or protocols for supporting network services or applications
- H04L67/50—Network services
- H04L67/51—Discovery or management thereof, e.g. service location protocol [SLP] or web services
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L67/00—Network arrangements or protocols for supporting network services or applications
- H04L67/50—Network services
- H04L67/52—Network services specially adapted for the location of the user terminal
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L67/00—Network arrangements or protocols for supporting network services or applications
- H04L67/50—Network services
- H04L67/75—Indicating network or usage conditions on the user display
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N21/00—Selective content distribution, e.g. interactive television or video on demand [VOD]
- H04N21/20—Servers specifically adapted for the distribution of content, e.g. VOD servers; Operations thereof
- H04N21/23—Processing of content or additional data; Elementary server operations; Server middleware
- H04N21/234—Processing of video elementary streams, e.g. splicing of video streams or manipulating encoded video stream scene graphs
- H04N21/2343—Processing of video elementary streams, e.g. splicing of video streams or manipulating encoded video stream scene graphs involving reformatting operations of video signals for distribution or compliance with end-user requests or end-user device requirements
- H04N21/23439—Processing of video elementary streams, e.g. splicing of video streams or manipulating encoded video stream scene graphs involving reformatting operations of video signals for distribution or compliance with end-user requests or end-user device requirements for generating different versions
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N21/00—Selective content distribution, e.g. interactive television or video on demand [VOD]
- H04N21/20—Servers specifically adapted for the distribution of content, e.g. VOD servers; Operations thereof
- H04N21/25—Management operations performed by the server for facilitating the content distribution or administrating data related to end-users or client devices, e.g. end-user or client device authentication, learning user preferences for recommending movies
- H04N21/258—Client or end-user data management, e.g. managing client capabilities, user preferences or demographics, processing of multiple end-users preferences to derive collaborative data
- H04N21/25808—Management of client data
- H04N21/25825—Management of client data involving client display capabilities, e.g. screen resolution of a mobile phone
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W12/00—Security arrangements; Authentication; Protecting privacy or anonymity
- H04W12/06—Authentication
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W16/00—Network planning, e.g. coverage or traffic planning tools; Network deployment, e.g. resource partitioning or cells structures
- H04W16/18—Network planning tools
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W24/00—Supervisory, monitoring or testing arrangements
- H04W24/02—Arrangements for optimising operational condition
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W24/00—Supervisory, monitoring or testing arrangements
- H04W24/04—Arrangements for maintaining operational condition
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W24/00—Supervisory, monitoring or testing arrangements
- H04W24/10—Scheduling measurement reports ; Arrangements for measurement reports
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W28/00—Network traffic management; Network resource management
- H04W28/02—Traffic management, e.g. flow control or congestion control
- H04W28/0205—Traffic management, e.g. flow control or congestion control at the air interface
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W28/00—Network traffic management; Network resource management
- H04W28/02—Traffic management, e.g. flow control or congestion control
- H04W28/0247—Traffic management, e.g. flow control or congestion control based on conditions of the access network or the infrastructure network
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W28/00—Network traffic management; Network resource management
- H04W28/02—Traffic management, e.g. flow control or congestion control
- H04W28/08—Load balancing or load distribution
- H04W28/086—Load balancing or load distribution among access entities
- H04W28/0861—Load balancing or load distribution among access entities between base stations
- H04W28/0865—Load balancing or load distribution among access entities between base stations of different Radio Access Technologies [RATs], e.g. LTE or WiFi
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W4/00—Services specially adapted for wireless communication networks; Facilities therefor
- H04W4/02—Services making use of location information
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W4/00—Services specially adapted for wireless communication networks; Facilities therefor
- H04W4/02—Services making use of location information
- H04W4/023—Services making use of location information using mutual or relative location information between multiple location based services [LBS] targets or of distance thresholds
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W4/00—Services specially adapted for wireless communication networks; Facilities therefor
- H04W4/70—Services for machine-to-machine communication [M2M] or machine type communication [MTC]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W40/00—Communication routing or communication path finding
- H04W40/02—Communication route or path selection, e.g. power-based or shortest path routing
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W40/00—Communication routing or communication path finding
- H04W40/02—Communication route or path selection, e.g. power-based or shortest path routing
- H04W40/20—Communication route or path selection, e.g. power-based or shortest path routing based on geographic position or location
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W40/00—Communication routing or communication path finding
- H04W40/24—Connectivity information management, e.g. connectivity discovery or connectivity update
- H04W40/246—Connectivity information discovery
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W40/00—Communication routing or communication path finding
- H04W40/34—Modification of an existing route
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W48/00—Access restriction; Network selection; Access point selection
- H04W48/02—Access restriction performed under specific conditions
- H04W48/06—Access restriction performed under specific conditions based on traffic conditions
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W48/00—Access restriction; Network selection; Access point selection
- H04W48/08—Access restriction or access information delivery, e.g. discovery data delivery
- H04W48/14—Access restriction or access information delivery, e.g. discovery data delivery using user query or user detection
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W48/00—Access restriction; Network selection; Access point selection
- H04W48/18—Selecting a network or a communication service
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W52/00—Power management, e.g. TPC [Transmission Power Control], power saving or power classes
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W52/00—Power management, e.g. TPC [Transmission Power Control], power saving or power classes
- H04W52/02—Power saving arrangements
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W52/00—Power management, e.g. TPC [Transmission Power Control], power saving or power classes
- H04W52/02—Power saving arrangements
- H04W52/0209—Power saving arrangements in terminal devices
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W52/00—Power management, e.g. TPC [Transmission Power Control], power saving or power classes
- H04W52/02—Power saving arrangements
- H04W52/0209—Power saving arrangements in terminal devices
- H04W52/0212—Power saving arrangements in terminal devices managed by the network, e.g. network or access point is master and terminal is slave
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W52/00—Power management, e.g. TPC [Transmission Power Control], power saving or power classes
- H04W52/02—Power saving arrangements
- H04W52/0209—Power saving arrangements in terminal devices
- H04W52/0212—Power saving arrangements in terminal devices managed by the network, e.g. network or access point is master and terminal is slave
- H04W52/0216—Power saving arrangements in terminal devices managed by the network, e.g. network or access point is master and terminal is slave using a pre-established activity schedule, e.g. traffic indication frame
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W52/00—Power management, e.g. TPC [Transmission Power Control], power saving or power classes
- H04W52/02—Power saving arrangements
- H04W52/0209—Power saving arrangements in terminal devices
- H04W52/0225—Power saving arrangements in terminal devices using monitoring of external events, e.g. the presence of a signal
- H04W52/0229—Power saving arrangements in terminal devices using monitoring of external events, e.g. the presence of a signal where the received signal is a wanted signal
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W52/00—Power management, e.g. TPC [Transmission Power Control], power saving or power classes
- H04W52/02—Power saving arrangements
- H04W52/0209—Power saving arrangements in terminal devices
- H04W52/0225—Power saving arrangements in terminal devices using monitoring of external events, e.g. the presence of a signal
- H04W52/0235—Power saving arrangements in terminal devices using monitoring of external events, e.g. the presence of a signal where the received signal is a power saving command
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W52/00—Power management, e.g. TPC [Transmission Power Control], power saving or power classes
- H04W52/02—Power saving arrangements
- H04W52/0209—Power saving arrangements in terminal devices
- H04W52/0261—Power saving arrangements in terminal devices managing power supply demand, e.g. depending on battery level
- H04W52/0274—Power saving arrangements in terminal devices managing power supply demand, e.g. depending on battery level by switching on or off the equipment or parts thereof
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W72/00—Local resource management
- H04W72/04—Wireless resource allocation
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W72/00—Local resource management
- H04W72/20—Control channels or signalling for resource management
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W74/00—Wireless channel access
- H04W74/02—Hybrid access
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W74/00—Wireless channel access
- H04W74/08—Non-scheduled access, e.g. ALOHA
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W74/00—Wireless channel access
- H04W74/08—Non-scheduled access, e.g. ALOHA
- H04W74/0808—Non-scheduled access, e.g. ALOHA using carrier sensing, e.g. carrier sense multiple access [CSMA]
- H04W74/0816—Non-scheduled access, e.g. ALOHA using carrier sensing, e.g. carrier sense multiple access [CSMA] with collision avoidance
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W74/00—Wireless channel access
- H04W74/08—Non-scheduled access, e.g. ALOHA
- H04W74/0833—Random access procedures, e.g. with 4-step access
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W76/00—Connection management
- H04W76/10—Connection setup
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W76/00—Connection management
- H04W76/10—Connection setup
- H04W76/11—Allocation or use of connection identifiers
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W76/00—Connection management
- H04W76/10—Connection setup
- H04W76/14—Direct-mode setup
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W76/00—Connection management
- H04W76/10—Connection setup
- H04W76/15—Setup of multiple wireless link connections
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W76/00—Connection management
- H04W76/10—Connection setup
- H04W76/15—Setup of multiple wireless link connections
- H04W76/16—Involving different core network technologies, e.g. a packet-switched [PS] bearer in combination with a circuit-switched [CS] bearer
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W76/00—Connection management
- H04W76/20—Manipulation of established connections
- H04W76/28—Discontinuous transmission [DTX]; Discontinuous reception [DRX]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W8/00—Network data management
- H04W8/005—Discovery of network devices, e.g. terminals
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W8/00—Network data management
- H04W8/22—Processing or transfer of terminal data, e.g. status or physical capabilities
- H04W8/24—Transfer of terminal data
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W80/00—Wireless network protocols or protocol adaptations to wireless operation
- H04W80/02—Data link layer protocols
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W80/00—Wireless network protocols or protocol adaptations to wireless operation
- H04W80/08—Upper layer protocols
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W88/00—Devices specially adapted for wireless communication networks, e.g. terminals, base stations or access point devices
- H04W88/02—Terminal devices
- H04W88/06—Terminal devices adapted for operation in multiple networks or having at least two operational modes, e.g. multi-mode terminals
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L65/00—Network arrangements, protocols or services for supporting real-time applications in data packet communication
- H04L65/10—Architectures or entities
- H04L65/1016—IP multimedia subsystem [IMS]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L65/00—Network arrangements, protocols or services for supporting real-time applications in data packet communication
- H04L65/60—Network streaming of media packets
- H04L65/75—Media network packet handling
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L67/00—Network arrangements or protocols for supporting network services or applications
- H04L67/01—Protocols
- H04L67/12—Protocols specially adapted for proprietary or special-purpose networking environments, e.g. medical networks, sensor networks, networks in vehicles or remote metering networks
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W16/00—Network planning, e.g. coverage or traffic planning tools; Network deployment, e.g. resource partitioning or cells structures
- H04W16/24—Cell structures
- H04W16/28—Cell structures using beam steering
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W28/00—Network traffic management; Network resource management
- H04W28/02—Traffic management, e.g. flow control or congestion control
- H04W28/08—Load balancing or load distribution
- H04W28/0827—Triggering entity
- H04W28/0831—Core entity
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W28/00—Network traffic management; Network resource management
- H04W28/02—Traffic management, e.g. flow control or congestion control
- H04W28/08—Load balancing or load distribution
- H04W28/09—Management thereof
- H04W28/0925—Management thereof using policies
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W52/00—Power management, e.g. TPC [Transmission Power Control], power saving or power classes
- H04W52/02—Power saving arrangements
- H04W52/0209—Power saving arrangements in terminal devices
- H04W52/0251—Power saving arrangements in terminal devices using monitoring of local events, e.g. events related to user activity
- H04W52/0258—Power saving arrangements in terminal devices using monitoring of local events, e.g. events related to user activity controlling an operation mode according to history or models of usage information, e.g. activity schedule or time of day
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02D—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES IN INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES [ICT], I.E. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES AIMING AT THE REDUCTION OF THEIR OWN ENERGY USE
- Y02D30/00—Reducing energy consumption in communication networks
- Y02D30/70—Reducing energy consumption in communication networks in wireless communication networks
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Multimedia (AREA)
- Databases & Information Systems (AREA)
- Computer Security & Cryptography (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Environmental & Geological Engineering (AREA)
- Computer Graphics (AREA)
- Electromagnetism (AREA)
- Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- General Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- Data Mining & Analysis (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Quality & Reliability (AREA)
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
Abstract
本公开涉及用于3GPP-LTE系统中的小数据传输的设备和方法。在与3GPP长期演进(LTE)网络的机器类型通信(MTC)中,常常需要传送和接收小数据有效载荷。新信息元素(IE)定义成便于小数据有效载荷的传输和接收。方法和系统能够使用新IE来更有效地传送和接收数据。新IE包括小数据ACKIE和小数据容器IE。其它新消息包括RRC释放指示符和RRC连接释放。
Description
技术领域
实施例涉及无线通信。一些实施例涉及长期演进(LTE)网络中使用的无线通信。
背景技术
机器常常需要以极少或者没有人为干预来与其它机器进行通信。在过去,这类通信经由有线进行。随时间推移,无线通信开始被使用。随着移动宽带的增加可用性,经由移动宽带的机器类型通信(MTC)变得越来越普遍。MTC实现远程机器之间的通信,以用于交换信息和操作命令,而无需人为干预。机器类型通信的示范使用包括远程传感器、电子健康、遥控公用事业仪表、监控照相装置、收费、生产链自动化等。例如,装置能够监测另一个装置的操作状态,并且向中央服务器报告状态;装置能够读取公用事业仪表,并且将数据提供给计费部门供准备每月公用事业帐单;或者汽车中的装置能够感测汽车经过了收费站,并且将信息传送给收费机构供计费目的。
在MTC应用中发送的数据量通常在大小方面比人为发起通信中存在的数据要小。该少量数据流量是跨许多MTC应用的公共特征。MTC配置中使用的用户设备(UE)可将其时间的大部分花费在空闲状态,并且主要需要唤醒以发送或接收少量数据。
附图说明
图1是示出本公开的一个实施例的操作的流程图。
图2示出本公开的一个实施例的帧结构。
图3示出本公开的一个实施例的帧结构。
图4示出本公开的一个实施例的概述。
具体实施方式
以下描述和附图充分示出具体实施例,以便使本领域的技术人员能够实施这些实施例。其它实施例可结合结构、逻辑、电、过程和其它变更。示例只代表可能的变化。除非另作要求,否则单独组件和功能是可选的,并且操作的顺序可改变。一些实施例的部分和特征可包含在其它实施例中,或者替代其它实施例的部分或特征。权利要求中提出的实施例包含那些权利要求的所有可用等同。
在以下详细描述中,提出大量特定细节,以便提供对本公开的透彻了解。但是,本领域的技术人员将会理解,即使没有这些具体细节,也可实施本公开。在其它情况下,没有详细描述众所周知的方法、过程、组件、和电路,以免影响对本公开的理解。
虽然本公开的实施例并不限于这个方面,但是本文所使用的术语“多个”可包括例如“多”或者“两个或更多”。术语“多个”可在本说明书中通篇用于描述两个或更多组件、装置、元件、单元、参数等。例如,“多个站”可包括两个或更多站。
第三代合作伙伴项目(3GPP)是在1998年12月所建立的聚集多个电信标准团体、称作“组织伙伴”的合作协议,这些团体当前包括无线电工业和商业协会(ARIB)、中国通信标准协会(CCSA)、欧洲电信标准学会(ETSI)、电信工业解决方案联盟(ATIS)、电信技术协会(TTA)和电信技术委员会(TTC)。3GPP的建立在1998年12月通过签署“第三代合作伙伴项目协议”来正式化。
3GPP提供全球适用标准作为用于基于演进GSM核心网络和它们支持的无线电接入技术(例如,频分双工(FDD)和时分双工(TDD)模式的通用地面无线电接入(UTRA))的第三代移动系统的技术规范和技术报告。3GPP还提供用于维护和开发全球移动通信系统的标准作为技术规范和技术报告,包括演进无线电接入技术(例如通用分组无线电业务(GPRS)和的增强数据速率GSM演进(EDGE))。与移动电话相关的当前标准的技术规范一般从3GPP组织可用于公众。
3GPP当前正研究3G移动系统的演进,并且考虑针对UTRA网络(UTRAN)的演进的贡献(视图和建议)。由3GPP研究组识别一组高级要求,包括:每比特的降低成本;增加的服务提供(即,以更低成本的具有更好质量的更多服务);现有和新频带的使用的灵活性;具有开放接口的简化架构;以及降低/适当终端功率消耗。关于UTRA和UTRAN长期演进(UTRAN-LTE,又称作3GPP-LTE和演进UTRAN(E-UTRA))的研究开始于2004年12月,目的是开发3GPP无线电接入技术朝高数据速率、低等待时间和分组优化无线电接入技术的演进的框架。研究考虑对无线电接口物理层(下行链路(DL)和上行链路(UL))的修改,例如支持高达20 MHz的灵活传输带宽的部件、新传输方案的引入和高级多天线技术。
3GPP-LTE基于结合了正交频分复用(OFDM)技术的无线电接口。OFDM是数字多载波调制格式,它使用大量紧密间隔正交副载波来携带相应用户数据信道。每个副载波采用与射频(RF)传输速率相比(较)低符号速率采用常规调制方案、例如正交幅度调制(QAM)来调制。实际上,OFDM信号使用快速傅立叶变换(FFT)算法来生成。
如上所述,机器类型通信(MTC)用于在无需人工输入的情况下与用户设备(UE)的通信。一些MTC UE可能花费其时间的大部分在RRC空闲状态或者超低功率消耗状态(例如深层空闲或优化空闲状态),并且主要将唤醒以发送或接收少量数据。操作UE的更有效方法是期望的。
以下示例假定UE处于不活动状态但是向网络注册。例如,UE可处于无线电资源控制(RRC)空闲状态。当网络想要触发UE或者具有少量数据要传送给UE(下行链路数据)时,网络可通过使用寻呼消息来通知UE或者甚至直接在寻呼消息中发送小数据有效载荷。另外,另一个新定义消息可在上行链路传输中用于通知RRC连接释放请求指示或者从UE发送小数据ACK。小数据有效载荷的长度通常为1至128字节。但是,应当理解,小数据有效载荷在一些情况下可以更大。
图1是示出使用寻呼消息来向UE传送小数据有效载荷的流程图。在图1的顶部是三个实体:用户设备(UE)150、演进节点B(eNB)160和移动管理实体(MME)170。所示的各个线条示出哪一个实体正执行任务。
MME 170向UE 150发送寻呼消息。寻呼消息可包含小数据有效载荷(102)。在接收这个通知之后,UE 150向eNB 160发送RRC连接请求(RRC Connection Request)消息,从而请求连接的建立(104)。在接收RRC连接请求并且假定网络没有拒绝连接之后,eNB 160采用RRC连接建立完成消息(RRC Connection Setup Complete)来应答UE 150(106)。
在向eNB发送RRC连接建立完成消息的同时,UE可包括“小数据ACK(Small Data ACK)”和“RRC释放指示(RRC Release Indication)”两个所定义信息元素(IE)之一。这两个IE可执行下列动作:
1) 小数据ACK – UE 150确认小数据接收(下行链路数据)。
2) RRC释放指示 – 如果UE 150没有任何上行链路数据要传送,则UE 150指示其释放其连接的意向,因为网络已经指示只有小数据将在下行链路连接中发送。因此,没有预计其它动作会来自网络。
此后,eNB 160向MME 170转发小数据ACK(110)。MME 170向eNB 160发送释放命令(112)。然后,eNB 160向UE 150发送RRC连接释放(RRC Connection Release)消息,以便终止连接(114)。
继续参照图1,在另一个实施例中能够以少许变化来沿用图1的元件。在(102),MME 170向UE 150发送具有小数据有效载荷的寻呼消息。寻呼消息可指示向UE 150传送小数据的需要。在接收这个通知之后,UE 150向eNB 160发送RRC连接请求消息,以便执行连接建立(104)。在接收RRC连接请求并且假定网络没有拒绝连接之后,eNB 160应答UE 150,从而在寻呼仅指示将来传输时添加小数据有效载荷(106)。
在向eNB 160发送RRC连接建立完成消息的同时,UE 150可包括两个所定义信息元素(IE)之一(108):“小数据ACK”和“RRC释放指示符”,从而执行下列动作:
1) UE确认小数据接收(下行链路数据)。
2) 如果UE没有任何上行链路数据要传送,则它指示其释放其连接的意向,因为网络已经指示只有小数据将在下行链路中发送。因此,没有预计其它动作会来自网络。
此后,eNB 160向MME 170转发小数据ACK(Small Data ACK)消息(110)。MME 170向eNB 160发送释放命令(112)。然后,eNB 160向UE 150发送RRC连接释放消息,以便终止连接(114)。
在另一个实施例中,如果网络供应商偏好具有对UE的连接释放的进一步控制,则在小数据有效载荷的传输或接收(108)之后,“RRC连接释放”消息可能由eNB 160发送给UE 150,作为对RRC连接建立完成消息中发送的RRC释放指示的肯定响应。因此,图1的其余步骤无需执行,因为eNB 160与UE 150之间的连接已经释放。
在另一个实施例中,UE 150可在(108)向eNB 160发送新RRC消息。这个消息指示释放连接的意向,并且同时确认小数据的接收,而不是以RRC连接建立完成消息来确认接收。消息可称作“RRC连接释放请求(RRC Connection Release Request)”。这个消息可由eNB使用现有“RRC连接释放”消息来应答。
在另一个实施例中,RRC连接建立完成消息(在106所述)能够用于在上行链路连接中发送小数据有效载荷。继续参照图1,在102,UE 150向eNB 160发送具有小数据指示符的RRC连接请求。eNB 160通过向UE 150发送RRC连接建立消息进行应答(104)。小数据指示符由UE 150使用以用于通知eNB 160关于小数据有效载荷将附加到RRC连接建立完成消息中(106)。在UE 150发送具有小数据有效载荷的RRC连接建立完成消息之后,如果eNB 160没有任何附加信息要发送给UE 150,则eNB 160将通过发送RRC连接释放消息来释放UE 150(108)。这个RRC连接释放消息还可携带关于接收到小数据有效载荷的确认。
在另一个实施例中,RRC连接释放消息(114)可用于发送任何下行链路(DL)小数据以及eNB 160必须转发到UE 150的上行链路(UL)小数据的确认(ACK)。小数据指示符可经由寻呼消息来发送。在该备选方案中,eNB 160可存储小数据指示符,并且将它作为RRC连接建立完成消息的一部分发送给UE 150。
当eNB 160从无线电接口接收到第一UL网络接入层(NAS)消息时,eNB 160调用NAS传输过程。它向MME 170发送INITIAL UE MESSAGE消息,其中包括作为NAS协议数据单元(NAS-PDU)信息元素(IE)的NAS消息。
初始UE消息格式在3GPP规范的第36.413小节中定义。这个消息由eNB来发送,以便通过S1接口向MME传递初始第3层消息。
以下图2中的格式定义其中包含小数据的初始UE消息。已经定义的新的小数据容器(SDC)信息元素(IE)将携带从eNB到MME的小数据有效载荷。修改的初始UE消息如下所示:
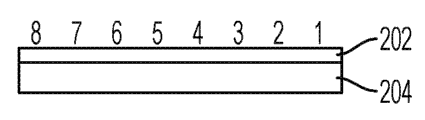
图2中示出小数据ACK IE的帧结构。小数据ACK IEI字段(202)是小数据ACK IE的标识符。大小为一个八位组。结果字段(204)指示传输的成功或失败。大小为一个八位组。
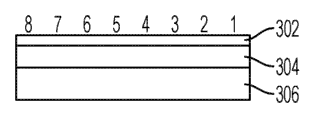
图3中示出小数据容器IE的帧结构。小数据容器(SDC)IE定义成在NAS信令消息上发送小数据。将SDC IE作为可选IE包含在“初始UE消息”消息内容中。小数据容器IEI字段(302)是这个小数据容器IE的标识符。大小为一个八位组(8比特)。小数据容器长度字段(304)是包含在这个IE中的小数据的大小。这个字段的大小为两个八位组(16比特)。数据有效载荷字段(306) – 携带需要向/从网络传送的小数据有效载荷。这个字段的大小从1到128个八位组(8比特到1024比特)改变,这取决于待发送数据量。
SDC IE是类型6信息元素。关于不同类型的信息元素的详细说明在3GPP技术规范的第24.007小节中描述。
图4示出能够执行本公开的实施例的示范UE的框图。UE 400包括处理器402。处理器402设置成执行可包含在存储器450中的指令。UE还可包括收发器430和天线组装件440。处理器402可设置成对信号执行计算和其它操作,然后将那些信号发送给收发器430,收发器430准备信号以供经由天线组装件440向UE外部传输。来自UE外部的信号可由天线组装件440来接收。这些信号则通过收发器430进行到处理器402供处理。应当理解,UE 400可包含图4中未示出的其它元件,例如用户接口输入(例如触摸屏和/或按钮)和输出(例如显示器、扬声器等)。
各种消息中可存在新信息元素。应当理解,为了便于使用,称作“RRC连接释放”的消息可不带空格书写:“RRCConnectionRelease”。这没有改变消息的功能性。
RRC连接建立完成消息可包含新信息元素。在一个实施例中,RRC连接建立完成消息可包含若干新消息,其中包括smallDataAck、rrcRelease-Indication和nonCriticalExtension。SmallDataRelease消息可包括smallDataPayload和nonCriticalExtension信息元素。
RRCConnectionRelease消息还可包含新信息元素。类似地,可带有和不带空格来表示其它消息。在一个实施例中,RRCConnectionRelease包括smallDataRelease、smallDataAck和nonCriticalExtension。smallDataRelease信息元素可包含smallDataPayload和nonCriticalExtension信息元素。
RRCConnectionReleaseRequest消息还可包含新信息元素。在一个实施例中,RRCConnectionReleaseRequest消息包括RRC-TransactionIdentifier、SmallDataRelease和SmallDataPayload信息元素。
另一个新信息元素可以是AccessCause信息元素,它可连同RRCConnectionRequest消息一起使用。
以下示例涉及其它实施例。
在一个实施例中,用户设备(UE)可包括设置成执行下列步骤的处理器:接收向UE发送小数据有效载荷的请求;向演进节点B(eNB)发送无线电资源控制(RRC)连接请求消息;从eNB接收RRC连接建立消息;向eNB发送RRC连接建立完成消息;以及从eNB接收RRC连接释放消息。RRC连接建立消息包括小数据有效载荷;以及RRC连接建立完成消息包括设置成指示小数据有效载荷的接收的小数据ACK消息。
UE可设置成执行机器类型通信(MTC)。
在一个实施例中,向UE发送小数据有效载荷的请求包括小数据有效载荷。
在一个实施例中,向UE发送小数据有效载荷的请求包括设置成通知UE关于接收小数据有效载荷的需要的小数据指示符。
在一个实施例中,小数据有效载荷包括长度小于或等于128个八位组的数据。
在一个实施例中,UE还设置成接收RRC连接释放消息。在一个实施例中,从eNB接收RRC连接释放消息。
在一个实施例中,RRC连接释放请求消息包括设置成指示小数据有效载荷的接收的小数据ACK消息。
在一个实施例中,RRC连接请求消息包括设置成指示UE具有第二小数据有效载荷要发送给eNB的小数据指示符;以及RRC连接建立完成消息包括第二小数据有效载荷。
在一个实施例中,RRC连接建立消息包括设置成指示小数据有效载荷的存在的指示符;以及 RRC连接释放消息包括小数据有效载荷。
在另一个实施例中,一种用于向用户设备(UE)发送小数据有效载荷的方法包括:向UE发送寻呼消息;接收无线电资源控制(RRC)连接请求消息;向UE发送RRC连接建立消息;接收RRC连接建立完成消息;以及发送RRC连接释放消息;其中,寻呼消息包括小数据有效载荷;以及RRC连接建立完成消息包括设置成指示小数据有效载荷的接收的小数据ACK消息。
在一个实施例中,寻呼消息包括小数据指示符;以及RRC连接建立消息包括小数据有效载荷。
在一个实施例中,RRC连接请求消息可包括关于UE想要发送上行链路小数据有效载荷的指示;RRC连接建立完成消息包括上行链路小数据有效载荷;以及RRC连接释放消息包括上行链路小数据有效载荷的接收的确认。
在一个实施例中,小数据有效载荷可包括小于或等于128个八位组的数据。
在一个实施例中,小数据有效载荷可包括小数据容器信息元素(IE),其中包括:小数据容器信息元素标识符字段;设置成指示小数据容器的长度的字段;以及设置成包含小数据有效载荷的有效载荷字段。
在一个实施例中,小数据容器信息元素标识符字段具有1个八位组的长度;设置成指示小数据容器的长度的字段具有2个八位组的长度;以及有效载荷字段具有在1个八位组与128个八位组之间的长度。
在一个实施例中,小数据ACK消息包括小数据ACK信息元素,其中包括: 长度为1个八位组的小数据ACK标识符字段;以及长度为1个八位组的结果字段。
在另一个实施例中,一种用于向UE发送小数据有效载荷的方法可包括:向UE发送寻呼消息;接收RRC连接请求消息;向UE发送RRC连接建立消息;接收RRC连接建立完成消息;以及发送RRC连接释放消息;其中,RRC连接释放请求消息包括设置成指示小数据有效载荷的接收的小数据ACK消息。
在另一个实施例中,一种使UE接收小数据有效载荷的方法可包括:从MME接收寻呼消息;向eNB发送RRC连接请求消息;以及在从eNB接收RRC连接建立消息之后,向eNB发送RRC连接建立完成消息。RRC连接建立完成消息可包括小数据有效载荷。
在一个实施例中,RRC连接建立完成消息还可包括关于UE已经接收到小数据有效载荷的指示。
在一个实施例中,RRC连接建立完成消息还可包括释放UE与eNB之间的连接的请求。
在一个实施例中,UE还可在发送RRC连接建立完成消息之后向eNB发送RRC连接释放请求消息。
在一个实施例中,UE还可在从eNB接收RRC连接释放消息之后释放UE与eNB之间的连接。
在一个实施例中,RRC连接释放消息可包括小数据有效载荷。
虽然本文中示出和描述了本公开的某些特征,但是本领域的技术人员可想到许多修改、替换、变更以及等同。因此要理解,所附权利要求书意在涵盖落入本公开的范围之内的所有这类修改和变更。
Claims (25)
1.一种用户设备UE,包括:
处理器;以及
收发器;其中所述处理器设置成:
从所述收发器接收向所述UE发送小数据有效载荷的请求;
指示所述收发器向演进节点B eNB发送无线电资源控制RRC连接请求消息;
从所述收发器接收来自所述eNB的RRC连接建立消息;
指示所述收发器向所述eNB发送RRC连接建立完成消息;以及
从所述收发器接收来自所述eNB的RRC连接释放消息;其中:
所述RRC连接建立消息包括所述小数据有效载荷;以及
所述RRC连接建立完成消息包括设置成指示所述小数据有效载荷的接收的小数据确认(ACK)消息。
2. 如权利要求1所述的UE,其中,所述UE设置成执行机器类型通信(MTC)。
3. 如权利要求1所述的UE,其中,向所述UE发送小数据有效载荷的所述请求包括所述小数据有效载荷。
4.如权利要求1所述的UE,其中,向所述UE发送小数据有效载荷的所述请求包括设置成通知所述UE关于接收小数据有效载荷的需要的小数据指示符。
5. 如权利要求1所述的UE,其中,所述小数据有效载荷包括长度小于或等于128个八位组的数据。
6. 如权利要求1所述的UE,其中,所述UE还设置成接收RRC连接释放消息。
7. 如权利要求6所述的UE,其中,从eNB接收所述RRC连接释放消息。
8. 如权利要求1所述的UE,其中,所述RRC连接释放请求消息包括设置成指示所述小数据有效载荷的接收的小数据确认(ACK)消息。
9. 如权利要求1所述的UE,其中:
所述RRC连接请求消息包括设置成指示所述UE具有第二小数据有效载荷要发送给所述eNB的小数据指示符;以及
所述RRC连接建立完成消息包括所述第二小数据有效载荷。
10. 如权利要求1所述的UE,其中:
所述RRC连接建立消息包括设置成指示小数据有效载荷的存在的指示符;以及
所述RRC连接释放消息包括所述小数据有效载荷。
11. 如权利要求1所述的UE,还包括耦合到所述收发器的天线组装件,其中所述收发器配置成使用所述天线组装件来传送和接收信号。
12. 一种用于向用户设备UE发送小数据有效载荷的方法,包括:
向所述UE发送寻呼消息;
从所述UE接收无线电资源控制RRC连接请求消息;
向所述UE发送RRC连接建立消息;
从所述UE接收RRC连接建立完成消息;以及
向所述UE发送RRC连接释放消息;其中:
所述寻呼消息包括小数据有效载荷;以及
所述RRC连接建立完成消息包括设置成指示所述小数据有效载荷的接收的小数据确认ACK消息。
13.如权利要求12所述的方法,其中:
所述寻呼消息包括小数据指示符;以及
所述RRC连接建立消息包括小数据有效载荷。
14.如权利要求12所述的方法,其中:
所述RRC连接请求消息包括关于所述UE想要发送上行链路小数据有效载荷的指示;
所述RRC连接建立完成消息包括所述上行链路小数据有效载荷;以及
所述RRC连接释放消息包括所述上行链路小数据有效载荷的接收的确认。
15. 如权利要求12所述的方法,其中,所述小数据有效载荷包括长度小于或等于128个字节的数据。
16. 如权利要求12所述的方法,其中,所述小数据有效载荷包括小数据容器信息元素(IE),其中包括:
小数据容器信息元素标识符字段;
设置成指示所述小数据容器的长度的字段;以及
设置成包含所述小数据有效载荷的有效载荷字段。
17. 如权利要求16所述的方法,其中:
所述小数据容器信息元素标识符字段具有1个八位组的长度;
设置成指示所述小数据容器的长度的字段具有2个八位组的长度;
所述有效载荷字段具有在1个八位组与128个八位组之间的长度。
18. 如权利要求12所述的方法,其中,所述小数据ACK消息包括小数据ACK信息元素,其中包括:
长度为1个八位组的小数据ACK标识符字段;以及
长度为1个八位组的结果字段。
19. 一种使用户设备UE接收小数据有效载荷的方法,包括:
从移动管理实体(MME)接收寻呼消息;
向演进节点B eNB发送RRC连接请求消息;以及
在从所述eNB接收RRC连接建立消息之后,向所述eNB发送RRC连接建立完成消息;
其中所述RRC连接建立完成消息包括小数据有效载荷。
20. 如权利要求19所述的方法,其中,所述RRC连接建立完成消息还包括关于所述UE已经接收到所述小数据有效载荷的指示。
21.如权利要求19所述的方法,其中,所述RRC连接建立完成消息还包括释放所述UE与所述eNB之间的连接的请求。
22. 如权利要求19所述的方法,还包括:
在发送所述RRC连接建立完成消息之后向所述eNB发送RRC连接释放请求消息。
23. 如权利要求19所述的方法,还包括:
在从所述eNB接收RRC连接释放消息之后释放所述UE与所述eNB之间的连接。
24. 如权利要求23所述的方法,其中,所述RRC连接释放消息包括小数据有效载荷。
25.一种用于向用户设备UE发送小数据有效载荷的设备,包括:
用于向所述UE发送寻呼消息的部件;
用于从所述UE接收无线电资源控制RRC连接请求消息的部件;
用于向所述UE发送RRC连接建立消息的部件;
用于从所述UE接收RRC连接建立完成消息的部件;以及
用于向所述UE发送RRC连接释放消息的部件;其中:
所述寻呼消息包括小数据有效载荷;以及
所述RRC连接建立完成消息包括设置成指示所述小数据有效载荷的接收的小数据确认(ACK)消息。
Applications Claiming Priority (6)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US201261679627P | 2012-08-03 | 2012-08-03 | |
| US61/679627 | 2012-08-03 | ||
| US13/790630 | 2013-03-08 | ||
| US13/790,630 US9100160B2 (en) | 2012-08-03 | 2013-03-08 | Apparatus and method for small data transmission in 3GPP-LTE systems |
| PCT/US2013/044445 WO2014021987A1 (en) | 2012-08-03 | 2013-06-06 | Apparatus and method for small data transmission in 3gpp-lte systems |
| USPCT/US2013/044445 | 2013-06-06 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN103582006A true CN103582006A (zh) | 2014-02-12 |
| CN103582006B CN103582006B (zh) | 2017-04-12 |
Family
ID=74555375
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201310336123.8A Active CN103582006B (zh) | 2012-08-03 | 2013-08-05 | 用于3gpp‑lte系统中的小数据传输的设备和方法 |
Country Status (13)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (2) | US9100160B2 (zh) |
| EP (1) | EP2880784B1 (zh) |
| KR (2) | KR20150016612A (zh) |
| CN (1) | CN103582006B (zh) |
| BE (1) | BE1021410B1 (zh) |
| ES (1) | ES2481265B2 (zh) |
| FI (1) | FI20135807L (zh) |
| FR (1) | FR2994357A1 (zh) |
| IT (1) | ITMI20131289A1 (zh) |
| NL (1) | NL2011257C2 (zh) |
| SE (1) | SE540741C2 (zh) |
| TW (1) | TWI503032B (zh) |
| WO (1) | WO2014021987A1 (zh) |
Cited By (15)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US9100160B2 (en) | 2012-08-03 | 2015-08-04 | Intel Corporation | Apparatus and method for small data transmission in 3GPP-LTE systems |
| US9363702B2 (en) | 2012-08-03 | 2016-06-07 | Intel Corporation | Method and system for enabling device-to-device communication |
| US9374783B2 (en) | 2012-08-03 | 2016-06-21 | Intel Corporation | Enhanced node B, user equipment and methods for discontinuous reception in inter-eNB carrier aggregation |
| US9554296B2 (en) | 2012-08-03 | 2017-01-24 | Intel Corporation | Device trigger recall/replace feature for 3GPP/M2M systems |
| US9681354B2 (en) | 2013-08-08 | 2017-06-13 | Intel IP Corporation | Signaling radio bearer optimizations and other techniques for supporting small data transmissions |
| US9860732B2 (en) | 2013-08-08 | 2018-01-02 | Intel IP Corporation | User equipment and method for packet based device-to-device (D2D) discovery in an LTE network |
| CN107646197A (zh) * | 2015-04-22 | 2018-01-30 | 康维达无线有限责任公司 | 3gpp网络中的小数据使用使能够 |
| US9900786B2 (en) | 2013-08-08 | 2018-02-20 | Intel IP Corporation | Coverage extension level for coverage limited device |
| WO2018098702A1 (zh) * | 2016-11-30 | 2018-06-07 | 华为技术有限公司 | 一种下行数据发送的方法及装置 |
| CN108370606A (zh) * | 2016-02-05 | 2018-08-03 | 捷开通讯(深圳)有限公司 | 早期连接释放 |
| US10111118B2 (en) | 2012-08-03 | 2018-10-23 | Intel Corporation | Network assistance for device-to-device discovery |
| CN108810795A (zh) * | 2017-04-26 | 2018-11-13 | 财团法人资讯工业策进会 | 用于大量小数据传输的机器类型通讯系统 |
| WO2020087484A1 (zh) * | 2018-11-02 | 2020-05-07 | 华为技术有限公司 | 一种数据传输方法及装置 |
| US10992722B2 (en) | 2012-08-03 | 2021-04-27 | Apple Inc. | High efficiency distributed device-to-device (D2D) channel access |
| CN113966631A (zh) * | 2020-05-20 | 2022-01-21 | 北京小米移动软件有限公司 | 数据传输方法、装置、通信设备及存储介质 |
Families Citing this family (26)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5514949B2 (ja) * | 2010-03-23 | 2014-06-04 | インターデイジタル パテント ホールディングス インコーポレイテッド | マシンタイプ通信のための効率的なシグナリング |
| US9420511B2 (en) | 2012-11-01 | 2016-08-16 | Intel Corporation | Signaling QoS requirements and UE power preference in LTE-A networks |
| EP3537844A1 (en) * | 2013-01-08 | 2019-09-11 | IOT Holdings, Inc. | Method and apparatus for triggering devices and delivering small data |
| JP2014143616A (ja) * | 2013-01-24 | 2014-08-07 | Ntt Docomo Inc | ユーザ装置、ゲートウェイ装置、無線基地局、移動通信システム及び移動通信方法 |
| EP2983384B1 (en) * | 2013-04-23 | 2019-04-10 | Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. | Data packet transmission method and device |
| GB2514357A (en) * | 2013-05-20 | 2014-11-26 | Nec Corp | Communications system |
| US9848334B2 (en) * | 2013-10-31 | 2017-12-19 | Nec Corporation | Apparatus, system and method for MTC |
| EP3099091B1 (en) * | 2014-02-26 | 2024-04-10 | Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. | Uplink resource allocation method, access terminal, and access point |
| US9924406B2 (en) * | 2015-03-02 | 2018-03-20 | Verizon Patent And Licensing Inc. | Blended data transmission network for machine type communications |
| EP3310063A4 (en) * | 2015-06-12 | 2018-12-05 | Nec Corporation | Relay device, terminal device, communication system, pdu relay method, pdu reception method, and program |
| US10299244B2 (en) * | 2015-06-19 | 2019-05-21 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Small data transmission in a wireless communications system |
| WO2016210329A1 (en) * | 2015-06-25 | 2016-12-29 | Agility Fuel Systems, Inc. | Tailgate fuel system mounting system |
| WO2017017931A1 (ja) * | 2015-07-24 | 2017-02-02 | 日本電気株式会社 | 移動通信システム、mme、端末、及び通信方法 |
| US10728842B2 (en) | 2015-12-28 | 2020-07-28 | Telecom Italia S.P.A. | Methods and systems for opportunistically connecting devices to a communication network |
| WO2017126942A1 (ko) * | 2016-01-21 | 2017-07-27 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | 데이터 수신 방법 및 사용자기기와, 데이터 전송 방법 및 기지국 |
| EP3410776A4 (en) | 2016-05-11 | 2019-05-22 | Guangdong OPPO Mobile Telecommunications Corp., Ltd. | COMMUNICATION METHOD, DEVICE DEVICE AND NETWORK DEVICE |
| US10356837B2 (en) * | 2016-09-29 | 2019-07-16 | Acer Incorporated | State transitioning method and electronic device using the same |
| CN108184214A (zh) * | 2016-12-08 | 2018-06-19 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | 一种确定数据发送方式的方法及装置 |
| EP3563540B1 (en) | 2016-12-27 | 2024-02-28 | Telecom Italia S.p.A. | Method and system for providing variable quality streaming video services in mobile communication networks |
| KR102421645B1 (ko) * | 2016-12-30 | 2022-07-18 | 한국전자통신연구원 | NB-IoT 시스템에서 다운링크 데이터와 업링크 데이터를 전송하는 방법 및 장치 |
| US10721763B2 (en) | 2017-01-20 | 2020-07-21 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Small packet optimizations for internet-of-things applications |
| CN107949072A (zh) * | 2017-12-27 | 2018-04-20 | 北京松果电子有限公司 | 释放连接的方法、装置和存储介质 |
| US11751279B2 (en) * | 2020-01-07 | 2023-09-05 | Mediatek Inc. | Apparatuses and methods for multi-radio access technology (RAT) coordination |
| US11963248B2 (en) * | 2020-10-21 | 2024-04-16 | Intel Corporation | Small data transmission (SDT) procedures and failure recovery during an inactive state |
| CN112953687B (zh) * | 2021-02-20 | 2022-07-22 | 杭州卯方科技有限公司 | 基于统计预测的丢包重传方法 |
| CN113259062B (zh) * | 2021-05-31 | 2021-10-29 | 恒生电子股份有限公司 | 丢包重传的方法、装置、可读介质以及设备 |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2011119680A2 (en) * | 2010-03-23 | 2011-09-29 | Interdigital Patent Holdings, Inc. | Efficient signaling for machine type communication |
| US20110250892A1 (en) * | 2010-04-09 | 2011-10-13 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Methods and apparatus for facilitating robust forward handover in long term evolution (lte) communication systems |
| CN102333293A (zh) * | 2011-09-21 | 2012-01-25 | 电信科学技术研究院 | 一种小数据的传输方法和设备 |
Family Cites Families (24)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH08321882A (ja) * | 1995-05-24 | 1996-12-03 | Fujitsu Ltd | 複数呼同時転送システム |
| US6795407B2 (en) | 2000-04-22 | 2004-09-21 | Atheros Communications, Inc. | Methods for controlling shared access to wireless transmission systems and increasing throughput of the same |
| US7474686B2 (en) | 2003-02-28 | 2009-01-06 | Texas Instruments Incorporated | Wireless personal area networks with rotation of frequency hopping sequences |
| KR101466897B1 (ko) | 2007-07-09 | 2014-12-02 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 이동통신 시스템에서 피어투피어 통신의 연속성을 제공하기위한 방법 및 장치 |
| US8204505B2 (en) | 2008-06-17 | 2012-06-19 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Managing network-initiated quality of service setup in mobile device and network |
| US8577363B2 (en) | 2008-07-14 | 2013-11-05 | Nokia Corporation | Setup of device-to-device connection |
| US8761099B2 (en) | 2009-01-16 | 2014-06-24 | Nokia Corporation | Apparatus and method of scheduling resources for device-to-device communications |
| JP5510032B2 (ja) | 2009-05-14 | 2014-06-04 | 日産自動車株式会社 | 非接触給電装置 |
| KR20110049622A (ko) * | 2009-11-04 | 2011-05-12 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 무선 통신 네트워크 시스템에서 데이터 전송 방법 및 장치 |
| KR101674222B1 (ko) | 2010-02-09 | 2016-11-09 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | 무선 통신 시스템에서 로그된 측정 보고 방법 및 장치 |
| KR101824987B1 (ko) | 2010-02-11 | 2018-02-02 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | 이동통신 시스템에서의 다운링크 mtc 데이터 전송 방법 |
| WO2011112051A2 (ko) | 2010-03-11 | 2011-09-15 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | 무선 통신 시스템에서 mtc를 위한 방법 및 장치 |
| US8867458B2 (en) | 2010-04-30 | 2014-10-21 | Nokia Corporation | Network controlled device to device / machine to machine cluster operation |
| US8416741B2 (en) | 2010-09-07 | 2013-04-09 | Verizon Patent And Licensing Inc. | Machine-to-machine communications over fixed wireless networks |
| KR101684999B1 (ko) | 2010-09-27 | 2016-12-09 | 삼성전자 주식회사 | 휴대 단말기의 네트워크 연결 방법 및 장치 |
| GB2484921B (en) | 2010-10-25 | 2014-10-08 | Sca Ipla Holdings Inc | Communications device and method |
| WO2012068731A1 (en) | 2010-11-25 | 2012-05-31 | Nokia Corporation | Network assisted sensing on a shared band for local communications |
| KR101561474B1 (ko) * | 2010-12-23 | 2015-10-20 | 한국전자통신연구원 | 소량의 상향 링크 데이터 전송 방법 및 소량의 상향 링크 데이터 수신 방법 |
| EP2509345A1 (en) | 2011-04-05 | 2012-10-10 | Panasonic Corporation | Improved small data transmissions for machine-type-communication (MTC) devices |
| US8965415B2 (en) | 2011-07-15 | 2015-02-24 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Short packet data service |
| CN102300331B (zh) * | 2011-08-19 | 2013-11-27 | 电信科学技术研究院 | 数据传输方法和设备 |
| EP2880782B8 (en) | 2012-08-03 | 2021-01-13 | Apple Inc. | Device trigger recall/replace feature for 3gpp/m2m systems |
| EP2880955B1 (en) | 2012-08-03 | 2021-03-31 | Apple Inc. | Method for enabling device-to-device communication |
| US9100160B2 (en) | 2012-08-03 | 2015-08-04 | Intel Corporation | Apparatus and method for small data transmission in 3GPP-LTE systems |
-
2013
- 2013-03-08 US US13/790,630 patent/US9100160B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2013-06-06 KR KR1020147036954A patent/KR20150016612A/ko active Search and Examination
- 2013-06-06 WO PCT/US2013/044445 patent/WO2014021987A1/en active Application Filing
- 2013-06-06 KR KR1020167005515A patent/KR101721031B1/ko active IP Right Grant
- 2013-06-06 EP EP13825895.9A patent/EP2880784B1/en active Active
- 2013-07-31 IT IT001289A patent/ITMI20131289A1/it unknown
- 2013-08-01 FR FR1357687A patent/FR2994357A1/fr not_active Withdrawn
- 2013-08-01 TW TW102127609A patent/TWI503032B/zh not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2013-08-02 FI FI20135807A patent/FI20135807L/fi not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2013-08-02 NL NL2011257A patent/NL2011257C2/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2013-08-02 BE BE2013/0521A patent/BE1021410B1/fr not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2013-08-02 ES ES201331208A patent/ES2481265B2/es not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2013-08-02 SE SE1350931A patent/SE540741C2/sv unknown
- 2013-08-05 CN CN201310336123.8A patent/CN103582006B/zh active Active
-
2015
- 2015-08-03 US US14/816,282 patent/US20160192408A1/en not_active Abandoned
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2011119680A2 (en) * | 2010-03-23 | 2011-09-29 | Interdigital Patent Holdings, Inc. | Efficient signaling for machine type communication |
| US20110250892A1 (en) * | 2010-04-09 | 2011-10-13 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Methods and apparatus for facilitating robust forward handover in long term evolution (lte) communication systems |
| CN102333293A (zh) * | 2011-09-21 | 2012-01-25 | 电信科学技术研究院 | 一种小数据的传输方法和设备 |
Cited By (23)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US10425846B2 (en) | 2012-08-03 | 2019-09-24 | Intel Corporation | Network assistance for device-to-device discovery |
| US9374783B2 (en) | 2012-08-03 | 2016-06-21 | Intel Corporation | Enhanced node B, user equipment and methods for discontinuous reception in inter-eNB carrier aggregation |
| US11122647B2 (en) | 2012-08-03 | 2021-09-14 | Apple Inc. | Enhanced node B, user equipment and methods for discontinuous reception in inter-eNB carrier aggregation |
| US9554296B2 (en) | 2012-08-03 | 2017-01-24 | Intel Corporation | Device trigger recall/replace feature for 3GPP/M2M systems |
| US10992722B2 (en) | 2012-08-03 | 2021-04-27 | Apple Inc. | High efficiency distributed device-to-device (D2D) channel access |
| US9686817B2 (en) | 2012-08-03 | 2017-06-20 | Intel Corporation | Apparatus of user equipment (UE) configurable for connectivity with multiple cell groups |
| US9363702B2 (en) | 2012-08-03 | 2016-06-07 | Intel Corporation | Method and system for enabling device-to-device communication |
| US9100160B2 (en) | 2012-08-03 | 2015-08-04 | Intel Corporation | Apparatus and method for small data transmission in 3GPP-LTE systems |
| US10405371B2 (en) | 2012-08-03 | 2019-09-03 | Intel Corporation | Enhanced node B, user equipment and methods for discontinuous reception in inter-eNB carrier aggregation |
| US10111118B2 (en) | 2012-08-03 | 2018-10-23 | Intel Corporation | Network assistance for device-to-device discovery |
| US10321294B2 (en) | 2013-08-08 | 2019-06-11 | Intel IP Corporation | Signaling for proximity services and D2D discovery in an LTE network |
| US9900786B2 (en) | 2013-08-08 | 2018-02-20 | Intel IP Corporation | Coverage extension level for coverage limited device |
| US9860732B2 (en) | 2013-08-08 | 2018-01-02 | Intel IP Corporation | User equipment and method for packet based device-to-device (D2D) discovery in an LTE network |
| US9681354B2 (en) | 2013-08-08 | 2017-06-13 | Intel IP Corporation | Signaling radio bearer optimizations and other techniques for supporting small data transmissions |
| CN107646197A (zh) * | 2015-04-22 | 2018-01-30 | 康维达无线有限责任公司 | 3gpp网络中的小数据使用使能够 |
| CN107646197B (zh) * | 2015-04-22 | 2020-07-28 | 康维达无线有限责任公司 | 用于3gpp网络中的小数据使用使能的设备和方法 |
| CN108370606B (zh) * | 2016-02-05 | 2022-05-06 | 捷开通讯(深圳)有限公司 | 早期连接释放 |
| CN108370606A (zh) * | 2016-02-05 | 2018-08-03 | 捷开通讯(深圳)有限公司 | 早期连接释放 |
| WO2018098702A1 (zh) * | 2016-11-30 | 2018-06-07 | 华为技术有限公司 | 一种下行数据发送的方法及装置 |
| CN108810795A (zh) * | 2017-04-26 | 2018-11-13 | 财团法人资讯工业策进会 | 用于大量小数据传输的机器类型通讯系统 |
| WO2020087484A1 (zh) * | 2018-11-02 | 2020-05-07 | 华为技术有限公司 | 一种数据传输方法及装置 |
| CN113966631A (zh) * | 2020-05-20 | 2022-01-21 | 北京小米移动软件有限公司 | 数据传输方法、装置、通信设备及存储介质 |
| CN113966631B (zh) * | 2020-05-20 | 2023-10-03 | 北京小米移动软件有限公司 | 数据传输方法、装置、通信设备及存储介质 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP2880784B1 (en) | 2022-08-24 |
| ES2481265A2 (es) | 2014-07-29 |
| KR20160031043A (ko) | 2016-03-21 |
| TWI503032B (zh) | 2015-10-01 |
| ES2481265R1 (es) | 2014-10-06 |
| BE1021410B1 (fr) | 2015-11-18 |
| US9100160B2 (en) | 2015-08-04 |
| SE1350931A1 (sv) | 2014-02-04 |
| FR2994357A1 (fr) | 2014-02-07 |
| ES2481265B2 (es) | 2015-05-26 |
| EP2880784A1 (en) | 2015-06-10 |
| FI20135807L (fi) | 2014-02-04 |
| NL2011257C2 (en) | 2014-08-05 |
| US20140036795A1 (en) | 2014-02-06 |
| CN103582006B (zh) | 2017-04-12 |
| KR101721031B1 (ko) | 2017-03-29 |
| NL2011257A (en) | 2014-02-04 |
| EP2880784A4 (en) | 2016-03-09 |
| ITMI20131289A1 (it) | 2014-02-04 |
| SE540741C2 (sv) | 2018-10-30 |
| KR20150016612A (ko) | 2015-02-12 |
| TW201410054A (zh) | 2014-03-01 |
| WO2014021987A1 (en) | 2014-02-06 |
| US20160192408A1 (en) | 2016-06-30 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN103582006A (zh) | 用于3gpp-lte系统中的小数据传输的设备和方法 | |
| EP3491567B1 (en) | On-demand system information for wireless telecommunications | |
| CN102045862B (zh) | 一种载波聚合实现方法、装置与系统 | |
| EP3605932A1 (en) | Beam management method, terminal device, and network device | |
| CN107734553B (zh) | 用于功耗优化的ue数据传输方法、用户设备及其存储器 | |
| CN102056300B (zh) | 分量载波配置方法、用户设备及基站 | |
| US11902185B2 (en) | Sidelink information transmission method, communications device, and network device | |
| CN104378825A (zh) | 一种上报缓存状态报告的方法、装置及系统 | |
| CN107926072A (zh) | 连接建立的方法和装置 | |
| WO2017049615A1 (zh) | 测量结果上报方法、定时器计数的方法、装置及用户设备 | |
| EP2798861A1 (en) | Bearer configuration for background traffic | |
| CN104284320A (zh) | 用户设备直连通信的资源分配方法和设备 | |
| CN104221463B (zh) | 用于自发执行隐式分离操作的设备和方法 | |
| WO2013029553A1 (zh) | 组呼的方法及设备 | |
| CN102104933B (zh) | 承载物理下行控制信道信息的载波传输方法、设备和系统 | |
| CN108810991A (zh) | 子载波间隔类型的确定方法、装置 | |
| CN104113913B (zh) | 数据传输方法及装置 | |
| CN105900468B (zh) | 数据发送方法、通用业务实体及底层网络实体 | |
| CN103118437B (zh) | 上行链路变更的方法、装置及系统 | |
| CN108183782B (zh) | 在非对称载波聚合中信号传输方法、基站和用户设备 | |
| Hwang et al. | A study on management of access in industry IoT based 5G new radio standalone system | |
| CN114145069B (zh) | 无线通信的方法、装置、通信设备及存储介质 | |
| CN105682127A (zh) | 一种d2d发现资源冲突的解决方法 | |
| EP2629580B1 (en) | Method of handling transmission configuration of a communication device and communication system | |
| EP2919522A1 (en) | Method, base station, user equipment and communication apparatus for transmitting data |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| TR01 | Transfer of patent right |
Effective date of registration: 20200414 Address after: California, USA Patentee after: Apple Inc. Address before: California, USA Patentee before: INTEL Corp. |
|
| TR01 | Transfer of patent right |