CN102623454A - 具有电磁干扰滤波器的垂直瞬态电压抑制器 - Google Patents
具有电磁干扰滤波器的垂直瞬态电压抑制器 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN102623454A CN102623454A CN2012100736336A CN201210073633A CN102623454A CN 102623454 A CN102623454 A CN 102623454A CN 2012100736336 A CN2012100736336 A CN 2012100736336A CN 201210073633 A CN201210073633 A CN 201210073633A CN 102623454 A CN102623454 A CN 102623454A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- transient voltage
- multichannel
- voltage suppressor
- vertical
- vertical transient
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- 230000001052 transient effect Effects 0.000 title claims description 58
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 58
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 36
- 238000002955 isolation Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 10
- 210000000746 body region Anatomy 0.000 claims description 31
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 11
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 claims description 11
- 239000004020 conductor Substances 0.000 claims description 5
- 230000005611 electricity Effects 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000004888 barrier function Effects 0.000 claims 6
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 28
- 229910021420 polycrystalline silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 19
- 229920005591 polysilicon Polymers 0.000 description 19
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 18
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 14
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 14
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 12
- 230000000087 stabilizing effect Effects 0.000 description 12
- 238000002347 injection Methods 0.000 description 10
- 239000007924 injection Substances 0.000 description 10
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 9
- 230000015556 catabolic process Effects 0.000 description 7
- 230000010354 integration Effects 0.000 description 7
- 206010003497 Asphyxia Diseases 0.000 description 6
- 238000005457 optimization Methods 0.000 description 6
- 230000003071 parasitic effect Effects 0.000 description 6
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 description 5
- 230000000903 blocking effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000000151 deposition Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000008021 deposition Effects 0.000 description 4
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical compound [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000011248 coating agent Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 description 3
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000001960 triggered effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 229910052785 arsenic Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- RQNWIZPPADIBDY-UHFFFAOYSA-N arsenic atom Chemical compound [As] RQNWIZPPADIBDY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 2
- -1 boron ion Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 230000000295 complement effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000006378 damage Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000013461 design Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000009792 diffusion process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000005530 etching Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000000059 patterning Methods 0.000 description 2
- UGFAIRIUMAVXCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N Carbon monoxide Chemical compound [O+]#[C-] UGFAIRIUMAVXCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phosphorus Chemical compound [P] OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910045601 alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000000956 alloy Substances 0.000 description 1
- HAYXDMNJJFVXCI-UHFFFAOYSA-N arsenic(5+) Chemical compound [As+5] HAYXDMNJJFVXCI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052796 boron Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000003990 capacitor Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002019 doping agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000000407 epitaxy Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000002513 implantation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000003780 insertion Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000037431 insertion Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000011810 insulating material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052698 phosphorus Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011574 phosphorus Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000000452 restraining effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000013517 stratification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001629 suppression Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012546 transfer Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000007 visual effect Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L27/00—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate
- H01L27/02—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components specially adapted for rectifying, oscillating, amplifying or switching and having potential barriers; including integrated passive circuit elements having potential barriers
- H01L27/04—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components specially adapted for rectifying, oscillating, amplifying or switching and having potential barriers; including integrated passive circuit elements having potential barriers the substrate being a semiconductor body
- H01L27/06—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components specially adapted for rectifying, oscillating, amplifying or switching and having potential barriers; including integrated passive circuit elements having potential barriers the substrate being a semiconductor body including a plurality of individual components in a non-repetitive configuration
- H01L27/07—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components specially adapted for rectifying, oscillating, amplifying or switching and having potential barriers; including integrated passive circuit elements having potential barriers the substrate being a semiconductor body including a plurality of individual components in a non-repetitive configuration the components having an active region in common
- H01L27/0705—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components specially adapted for rectifying, oscillating, amplifying or switching and having potential barriers; including integrated passive circuit elements having potential barriers the substrate being a semiconductor body including a plurality of individual components in a non-repetitive configuration the components having an active region in common comprising components of the field effect type
- H01L27/0727—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components specially adapted for rectifying, oscillating, amplifying or switching and having potential barriers; including integrated passive circuit elements having potential barriers the substrate being a semiconductor body including a plurality of individual components in a non-repetitive configuration the components having an active region in common comprising components of the field effect type in combination with diodes, or capacitors or resistors
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L27/00—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate
- H01L27/02—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components specially adapted for rectifying, oscillating, amplifying or switching and having potential barriers; including integrated passive circuit elements having potential barriers
- H01L27/04—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components specially adapted for rectifying, oscillating, amplifying or switching and having potential barriers; including integrated passive circuit elements having potential barriers the substrate being a semiconductor body
- H01L27/06—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components specially adapted for rectifying, oscillating, amplifying or switching and having potential barriers; including integrated passive circuit elements having potential barriers the substrate being a semiconductor body including a plurality of individual components in a non-repetitive configuration
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/04—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer
- H01L21/18—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer the devices having semiconductor bodies comprising elements of Group IV of the Periodic Table or AIIIBV compounds with or without impurities, e.g. doping materials
- H01L21/22—Diffusion of impurity materials, e.g. doping materials, electrode materials, into or out of a semiconductor body, or between semiconductor regions; Interactions between two or more impurities; Redistribution of impurities
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/06—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/06—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions
- H01L29/10—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions with semiconductor regions connected to an electrode not carrying current to be rectified, amplified or switched and such electrode being part of a semiconductor device which comprises three or more electrodes
- H01L29/1004—Base region of bipolar transistors
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/40—Electrodes ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/402—Field plates
- H01L29/407—Recessed field plates, e.g. trench field plates, buried field plates
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66007—Multistep manufacturing processes
- H01L29/66075—Multistep manufacturing processes of devices having semiconductor bodies comprising group 14 or group 13/15 materials
- H01L29/66227—Multistep manufacturing processes of devices having semiconductor bodies comprising group 14 or group 13/15 materials the devices being controllable only by the electric current supplied or the electric potential applied, to an electrode which does not carry the current to be rectified, amplified or switched, e.g. three-terminal devices
- H01L29/66234—Bipolar junction transistors [BJT]
- H01L29/66272—Silicon vertical transistors
- H01L29/66295—Silicon vertical transistors with main current going through the whole silicon substrate, e.g. power bipolar transistor
- H01L29/66303—Silicon vertical transistors with main current going through the whole silicon substrate, e.g. power bipolar transistor with multi-emitter, e.g. interdigitated, multi-cellular or distributed emitter
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/68—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor controllable by only the electric current supplied, or only the electric potential applied, to an electrode which does not carry the current to be rectified, amplified or switched
- H01L29/70—Bipolar devices
- H01L29/72—Transistor-type devices, i.e. able to continuously respond to applied control signals
- H01L29/73—Bipolar junction transistors
- H01L29/7302—Bipolar junction transistors structurally associated with other devices
- H01L29/7304—Bipolar junction transistors structurally associated with other devices the device being a resistive element, e.g. ballasting resistor
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/68—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor controllable by only the electric current supplied, or only the electric potential applied, to an electrode which does not carry the current to be rectified, amplified or switched
- H01L29/70—Bipolar devices
- H01L29/72—Transistor-type devices, i.e. able to continuously respond to applied control signals
- H01L29/73—Bipolar junction transistors
- H01L29/732—Vertical transistors
- H01L29/7322—Vertical transistors having emitter-base and base-collector junctions leaving at the same surface of the body, e.g. planar transistor
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/86—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor controllable only by variation of the electric current supplied, or only the electric potential applied, to one or more of the electrodes carrying the current to be rectified, amplified, oscillated or switched
- H01L29/861—Diodes
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/86—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor controllable only by variation of the electric current supplied, or only the electric potential applied, to one or more of the electrodes carrying the current to be rectified, amplified, oscillated or switched
- H01L29/861—Diodes
- H01L29/8618—Diodes with bulk potential barrier, e.g. Camel diodes, Planar Doped Barrier diodes, Graded bandgap diodes
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/86—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor controllable only by variation of the electric current supplied, or only the electric potential applied, to one or more of the electrodes carrying the current to be rectified, amplified, oscillated or switched
- H01L29/861—Diodes
- H01L29/866—Zener diodes
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/86—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor controllable only by variation of the electric current supplied, or only the electric potential applied, to one or more of the electrodes carrying the current to be rectified, amplified, oscillated or switched
- H01L29/92—Capacitors having potential barriers
- H01L29/94—Metal-insulator-semiconductors, e.g. MOS
- H01L29/945—Trench capacitors
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/06—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions
- H01L29/0603—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions
- H01L29/0607—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions for preventing surface leakage or controlling electric field concentration
- H01L29/0611—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions for preventing surface leakage or controlling electric field concentration for increasing or controlling the breakdown voltage of reverse biased devices
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/0001—Technical content checked by a classifier
- H01L2924/0002—Not covered by any one of groups H01L24/00, H01L24/00 and H01L2224/00
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Ceramic Engineering (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Metal-Oxide And Bipolar Metal-Oxide Semiconductor Integrated Circuits (AREA)
- Semiconductor Integrated Circuits (AREA)
- Element Separation (AREA)
- Bipolar Integrated Circuits (AREA)
- Junction Field-Effect Transistors (AREA)
Abstract
一种具有电磁干扰滤波器的垂直瞬态电压抑制器。一垂直TVS电路包括一半导体衬底以支撑垂直TVS器件,在半导体衬底上有一延伸到衬底底部的重掺杂层。深沟槽提供了多通道垂直TVS间的隔离。沟槽栅极也用于增加整合有EMI滤波器的垂直TVS的电容。
Description
本案是分案申请
原案发明名称:具有电磁干扰滤波器的垂直瞬态电压抑制器(TVS)的电路结构及制造方法
原案国际申请号:PCT/US2007/024149
原案国际申请日:2007年11月16日
原案国家申请号:200780040577.3
原案进入中国日:2009年4月30日
技术领域
本发明一般涉及一种瞬态电压抑制器(TVS)的电路结构及其制造方法,更特别的是,本发明涉及一种具有电磁干扰滤波器的垂直瞬态电压抑制器(VTVS)的电路结构及制造方法。
背景技术
瞬态电压抑制器(TVS)一般用来保护集成电路不被意外产生的过量电压所损坏。集成电路被设计为可以在超出电压的一个正常范围内运行。然而,在诸如静电放电(ESD)、电快速瞬变及闪电等情况下、非预期且无法控制的高电压等皆可能瞬间施加到电路上。TVS器件即被要求用于提供电路保护的功能,以在这样的过电压情况发生时,使集成电路避免受到类似的损害。随着集成电路上易受过电压破坏的器件数量的增加,对于TVS的保护需求也随之增加。TVS的具体应用范例可见于USB电源供应器及数据线防护、数字视频接口、高速以太网、笔记本电脑、显示器及平板显示器。
图1A-1所示为典型商用多通道TVS阵列10。具有两组控向二极管,即二极管15-H、15-L和20-H、20-L分别作为两输入/输出(I/O)端I/O-1及I/O-2。另外,具有稳压二极管,即二极管30,其具有较大尺寸功能,用以作为从高电压端,即Vcc端,到接地端,即Gnd端之间的雪崩二极管。当正电压施加到I/O衬垫时,高电压侧二极管15-H和20-H提供一正向偏压,并被较大的Vcc-Gnd二极管,即稳压二极管30压制。控向二极管15-H、15-L、20-H和20-L被设计为小尺寸,用以减少I/O电容,并由此减少如以太网应用这样的高速线路中的插入损耗。图1A-2所示为反向电流IR相对于图1A-1中的TVS10上的电压源Vcc与接地电压之间的稳压二极管的反向阻断电压BV特征的示意图。在图1A-2中所示的反向电流IR表示通过稳压二极管,即在Vcc及Gnd之间,传导的一反向电流。假设每个控向二极管的反向BV都高于稳压二极管的反向BV。但需要注意到高电流时,当Vcc至Gnd的衬垫电压等于或大于控向二极管的反向阻断电压的总和时,电流会通过所有两列路径上的控向二极管。由于稳压二极管与双极结晶体管BJT或硅控整流器SCR加上双极结晶体管相较之下,稳压二极管每一单位区域具有较高的阻抗,在高电流情况下这确实是一个缺点,因为控向二极管也需要在反向传导时坚固耐用。在SCR+BJT的例子中,稳压二极管压制电压在高电流时较低,因此控向二极管的路径不会被导通。Vcc-Gnd二极管30以及控向二极管15和20的击穿电压应大于其运行电压(Vrwm),使这些二极管只在电压瞬变期间导通。Vcc-Gnd压制二极管的问题在于,在反向阻断模式下,这些二极管的阻抗通常较大,且需要大面积以减少阻抗。如图1A-2所示,高阻抗使阻断电压BV在高电流时增加。所不期望的高BV不但造成上述的控向二极管的击穿,还会损坏TVS器件所要保护的电路。在这样的TVS电路的实现中,对大尺寸二极管的需求限制了器件的进一步最小化。
为了缩小瞬态电压抑制器(TVS)电路的尺寸及所占的表面积,垂直TVS二极管可以以图1B-1的形式实现。TVS以标准P型衬底连接至N+型稳压雪崩二极管来实现,TVS在P-衬底掺杂的顶部表面上形成一阴极端,并在阴极下方具有一N+区域。一金属层形成于衬底底部作为阳极。P型衬底通常具有10-20欧姆-厘米的电阻率,由此造成二极管具有高电阻值。图1B-2所示为一双通道垂直TVS二极管的等效电路。如图1C-1及图1C-2所示,TVS二极管也可以与一EMI滤波器整合。垂直整合结构类似于在两个垂直TVS二极管间额外内连接一电阻的垂直TVS二极管。如图1B-1至图1C-2中所示的这样的垂直二极管及EMI滤波器结构需要承受巨大的结电容和低箝制效果这样的缺点,这是由于高电阻率的衬底导致的高二极管串联电阻所形成的。
因此,在本领域中仍然对电路设计和器件的制造存在一种需求,即提供一种新的优化的电路结构和制作方法以解决上述的问题。特别是存在提供一种新的优化的TVS电路的需求以能够提供一种用于便携式电子器件的低成本高密度的TVS和EMI滤波器。
发明内容
因此,本发明的一个方面是提供一种应用DMOS技术的优化的具有EMI滤波器的垂直TVS电路,以实现利用主流DMOS工艺生产低成本的具有EMI滤波器的TVS电路,其具有小的硅芯片足迹面积以此来克服上述的限制及困难。
此外,本发明的另一个方面提供了一种具有EMI滤波器的垂直TVS电路的优化的器件结构及制造方法,其使用主流垂直沟槽DMOS技术,其中沟槽栅极做为TVS结构的一部分,作用是隔离通道和滤波器电容。
本发明的另一个方面提供了一种应用DMOS技术的优化的具有EMI滤波器的垂直TVS电路结构,以实现利用主流沟槽DMOS工艺,其中具有EMI滤波器的TVS的垂直结构能够形成小的硅芯片足迹面积并增加集成电路单元密度,从而进一步减少制作成本。
本发明的一个优选实施例大致公开了一种整合有EMI滤波器的瞬态电压抑制器(TVS)的电路结构,用以抑制瞬态电压,其包括第一及第二VTVS,其中每个VTVS包括一设置于井中,即本体区域中的具有第一导电类型的阴极连接掺杂区域,该井具有第二导电类型,其被第一导电类型的外延层所包围的,该外延层设置于具有第一导电类型的半导体衬底上,并连接设置在半导体衬底底部表面的阳极,并具有设置于半导体器件顶部表面的阴极且与阴极连接掺杂区相连接,从而形成第一和第二垂直TVS。整合有EMI滤波器的VTVS还包括一独立导电区,其与第一和第二VTVS的阴极电连接,从而与第一和第二VTVS共同作用,以作为EMI滤波器。在另一实施例中,导电区域是设置在半导体衬底顶部的多晶硅层,用以与第一和第二VTVS的阴极电连接。在另一实施例中,半导体衬底为一N型衬底,而第一及第二VTVS的井为P型井。在另一实施例中,半导体衬底为一P型衬底,而第一及第二VTVS的井为N型井。在另一实施例中,第一及第二VTVS还各自包括一第二导电类型的掺杂区域,其设置在阴极掺杂区域下,用以调节二极管的击穿电压。
在另一优选实施例中,本发明还公开了一种形成为集成电路(IC)的电子器件,其中该电子器件还包括一瞬态电压抑制(TVS)器件。TVS器件包括一半导体衬底用以支撑该VTVS器件,该半导体衬底的前侧做为VTVS的阳极而后侧则做为VTVS的阴极。该VTVS还包括一固有二极管及一寄生晶体管,其结构为一沟槽DMOS,其中源极区域及本体区域即做为固有二极管,而源极区域、本体区域及外延层则作为具有一沟槽栅极的寄生晶体管,该沟槽栅极作为一隔离沟槽。DMOS还具有一沟槽栅极引道,其与设置在后侧作为阴极的漏极短接。在另一优选实施例中,半导体衬底还包括一N型衬底,其支撑N型外延层,该外延层具有形成于N-源极与P-本体区域之间的固有二极管以及形成于N-源极、P-本体区域和N-外延层之间的NPN晶体管。在另一实施例中,沟槽栅极引道设置于半导体衬底的边缘,其宽度大于隔离沟槽,以将沟槽栅极引道通过外延层短接到阴极。在另一实施例中,本体区域的掺杂浓度使MOSFET栅极阈值电压约为6伏,并且沟槽栅极的栅极氧化层提供所能承受的击穿电压约为15伏,由此,当加载在VTVS上的电压超过6伏时,VTVS导通,并且提供寄生晶体管用以传送瞬时电流,从而将电压维持在箝制电压之下。
本发明进一步公开了一种具有整合了瞬态电压抑制器(TVS)电路的电子器件的制造方法。该方法包括应用标准DMOS制程制造一垂直DMOS器件的步骤,该器件具有一固有PN结二极管及一寄生NPN型或PNP型晶体管,以作为一垂直TVS。
本领域的普通技术人员在结合多幅附图阅读了后续的对于优选实施例的详细叙述后,上述及其它本发明的内容及优点将变得显而易见。
附图说明
图1A-1所示为现有TVS器件的电路图;图1A-2为I-V图,即电流电压对比图,用以描述TVS器件的反向特征。
图1B-1为垂直TVS二极管的剖视图;图1B-2为现有的垂直TVS二极管的等效电路图。
图1C-1为整合了EMI滤波器的垂直TVS二极管的剖视图,图1C-2为现有的整合了EMI滤波器的垂直TVS二极管的等效电路图。
图2A和图2B分别是以垂直沟槽DMOS技术制成的垂直沟槽DMOS结构的垂直TVS的剖视图和等效电路图。
图3A至图3D分别是以垂直沟槽DMOS技术制成的垂直TVS的两个实施例的剖视图和等效电路图。
图4为利用DMOS技术制成的垂直二极管结构的TVS电路的剖视图。
图5A至5E为利用DMOS技术制成的双极晶体管结构的垂直TVS的实施例的剖视图。
图6为利用DMOS技术制成的整合了EMI滤波器的垂直TVS的剖视图,其结构为以一电阻元件连接的二极管。
图7A至7B为利用DMOS技术制成的整合了EMI滤波器的垂直TVS的剖视图,其结构为以一电阻元件连接的双极晶体管。
图8为利用DMOS技术制成的整合了EMI滤波器的垂直TVS的剖视图,其结构为通过沟槽隔离的二极管并与电阻元件连接。
图9A至9D为利用DMOS技术制成的整合了EMI滤波器的垂直TVS的剖视图,其结构为通过沟槽隔离的双极晶体管以并与电阻元件连接。
图10A至10B为利用DMOS技术制成的垂直TVS的剖视图,其结构为控向二极管并且TVS具有位于二极管间的沟槽隔离。
图11、12A及12B为利用DMOS技术制成的整合有EMI滤波器的垂直TVS的剖视图,其结构为在输入输出通道之间设置沟槽间隔,其中多晶硅填充沟槽进一步作为多晶硅电容。
图13A及13B分别为利用DMOS技术制成的整合了EMI滤波器的垂直TVS的侧面剖视图和俯视图,其结构为通过隔离沟槽间隔的垂直二极管,并且通过沟槽电感内部连接。
图14A至14G为本发明中使用主流沟槽DMOS制程来制造的整合了EMI滤波器的多通道VTVS的一系列制程步骤的侧面剖视图。
具体实施方式
参考图2A和图2B所示的以标准DMOS工艺制成的垂直瞬态电压抑制器(VTVS)100的侧面剖示图和电路图。设置于一重掺杂半导体衬底105上的VTVS 100包含一作为阳极端110的前侧以及作为阴极端120的背侧,以形成包含一固有二极管与一NPN型晶体管的垂直TVS。由于产品是通过应用标准沟槽DMOS制程制造的,故剖视图图2A所示为一沟槽NMOS结构,其包含形成于本体区域130上的源极区125,本体区域130位于作为漏极的N+衬底105上的N外延层115的顶部。隔离沟槽栅极135与栅极引道135-GR内部连接于边缘区域,并在三维空间穿过其它沟槽栅极。如图2A所示,本VTVS器件与其它一般沟槽DMOS的不同之处在于栅极引道135-GR通过与N外延层115相连接的、位于栅极沟槽接触(或栅极衬垫)区域中的栅极金属140短接到漏极105。这是通过在DMOS接触开口制程时不使用额外的掩模,并蚀刻宽度大于栅极引道沟槽135-GR的栅极接触开口140来实现的。因此,图2B所示的等效电路图中,栅极短接至漏极。在制作一使用于5V器件的VTVS时,P-本体区域130的掺杂浓度可能会通过多次注入来增加,以符合MOSFET的栅极阈值电压约为6V的等级,并且栅极氧化层145的厚度会增加以能够承受15V的击穿电压。因此,当接入一般为5V的运行电压时,VTVS不会导通。然而,在本例中会产生超过5V的瞬态电压,该电压加载于栅极并导通MOS。寄生NPN也会被导通,因此大量的电流将会流过该不具有太多阻抗的器件,以此提供对二极管的优化的箝制。图2A也显示出DMOS本体区域130与一般DMOS器件一样被短接至源极125。
图3A为另一与图2所示相似的器件结构的可选实施例的剖视图,区别是本体区域130′是浮动的。如等效电路图图3B所示,栅极135与漏极105连接结合,器件作为MOS+NPN。栅极135也可以与源极125连接结合,在这个情形下MOS晶体管不会被导通,且此器件作为NPN。栅极135的深度可以延伸穿过N-外延层115并进入到N+衬底105中的一定深度,以此来改善通道间以及输出与输入端间的间隔。更进一步,沟槽栅极135可以由氧化物145′或其它绝缘材料填充,以代替图3C中所示的导体材料。N+区域125、P本体区域130和N-外延层115构成一如图3D所示的开放基极NPN。可以通过改变P本体区域130的掺杂浓度来调整本体区域130到N+区域125或N-外延结115之间具有6V的击穿电压,从而当更高的瞬时电压冲击结合处,会发生电压击穿,该击穿会触发NPN导通,从而来保护其它电路。除了在图2和图3所显示的器件结构外,一个P-沟道DMOS和VTVS的PNP可以使用类似通过改变半导体极性的方式来制成。
参考图4为一个应用于VTVS的优化二极管。该二极管200基于重掺杂P+衬底205以减低阻抗。相较于现有技术中使用标准IC制程所制造的二极管中所使用的P衬底所具有的10-20欧姆厘米的电阻率,使用于DMOS里的P+重掺杂衬底在仅提供只有几微欧姆厘米的电阻率。此外,也可以使用一个具有重掺杂底层的轻掺杂衬底来降低电阻率。通过向P-外延层210注入砷或磷离子来形成一N-本体区域215,借此,通过控制掺杂浓度,以调整N-本体区域215和P-外延层210间的击穿电压至6V或是任何需要的电压值。P-外延层210的厚度只有几微米以将电阻降到最小。更进一步的,N+区域220被形成于N-本体区域215的顶部,以改善阴极225与形成于衬底205底部的阳极电极230的欧姆连接。
图5A至图5C为应用于VTVS的双极晶体管。如图5A中所示的NPN,一N+区域220′被注入到N+衬底205′上的N-外延层210′顶部的P-井中,用来形成一连接到阴极电极225′的阴极区域。也可以在N+阴极区220′下设置一可选择的P区域235,用以通过改变P掺杂浓度来调整击穿电压。P-井215′通过连接金属240和N-外延层210′短接到阳极230。当一超过预设器件工作电压的瞬间高电压加载在位于N+阴极区220′与其下方的P区域235之间的结点时,会发生电压击穿,导致电子流经短接金属240到N-外延层210以及到达阳极230。当电流增加,在区域220′、235、215′和210′间形成的NPN会被导通,以更低的电阻值来传导更高的电流,从而改善箝制性能。在图5B中,击穿调整P区域235′被设置于N+型阴极区域220′的侧面。此举提供一项优势,即使得在发生电压击穿的金属电极240、225′和N+/P区域结点间的空间间隔可以弹性地调整来避免过热。
图5C是另一基于PNP双极晶体管的改良VTVS。相较于图4中的二极管200,图5C中的器件更进一步包含了一个在连接到阴极的N-本体区域215内的P+注入区域220″。P+区域220″、N-井215和P-外延层210或P+衬底205的结构为一PNP晶体管,由N-本体区域215与P-外延层210之间的结点击穿来提供触发。VTVS器件的箝制也由此得到改善。
图5D为另一具有类似工作原理的可替代实施例的剖视图,其结构为一对称TVS。当半导体衬底的底部为浮动时,P-井215′被短接到N+220′,且直接连接到分别被设计为输入、接地(GND)和输出的电极端226、227和228。输入、接地和输出通道进一步被多个栅极沟槽135′所隔离。在高电压瞬变时,P-井215′与N-外延层210′之间的结会产生电压击穿,并触发导通由N+220′、P-井215′和N-外延层210′构成的NPN。一正的高电压瞬间加载于输出或输入端时,将会触发TVS的接地通道,同样的一个负的高电压瞬间加载于输出或输入端时,将会触发TVS的输出或输入通道。由于所有的通道都是同时制作的,所以触发TVS沟道的正负瞬间电压本质上是大小相等的,因此该TVS装置是对称的。图5E为一个与图5D所示器件结构相似的可替代实施例的剖视图,不同点在于去除了N+220′,使得箝制功能是由P-井215′和N-外延层210′间的结面二极管所提供的,但仍保持对称运作。
图6为一多通道TVS和一EMI滤波器的剖视图,其器件结构是基于图4所示的TVS器件结构实现的。第一和第二垂直TVS(VTVS)被形成作为基于P+衬底205的第一二极管和第二二极管,以降低阻抗。每一个第一二极管和第二二极管都包含一由在P-外延层210中注入砷或磷离子形成的N-本体区域215。通过控制P-外延层210的掺杂浓度,这些二极管的N-本体区域215和P-外延层210间的击穿电压被调整到6V左右或任何需要的电压,P-外延层210只有几微米的厚度,以此来降低阻抗。对于每一个二极管,在N-本体区域215的顶部形成N+区域220,以此来优化第一和第二阴极电极225-1和225-2与形成于衬底205底部的阳极端230之间的欧姆连接。此器件更进一步作为一个EMI滤波器,其中,阴极电极225-1作为输入端,第二阴极电极225-2作为输出端,并有一形成于隔离层255之上的多晶硅层250,其电连接第一电极225-1和第二电极225-2。多晶硅层250作用为一电阻内连接分别作为输入和输出端的第一和第二阴极电极225-1和225-2。
图7A为一整合有EMI滤波器的多通道TVS的器件结构剖视图,其包含基于如图5A所示的器件结构的第一和第二垂直TVS。第一和第二VTVS的阴极电极225′-1以及225′-2通过多晶硅层250′内部连接,该多晶硅层250′周围填补有隔离层255′。该多晶硅层250′作为一个介于EMI滤波器输入和输出端之间的电阻,这些端点分别为第一和第二阴极电极225′-1以及225′-2。图7B是图7A中所示的整合有EMI滤波器的多通道TVS的器件结构的PNP互补结构,其包含基于图5C所示的器件结构的第一和第二垂直TVS。一可选的P注入区域214可以被形成于N-本体区域215之下,目的是调整击穿电压。
图8所示为一整合有EMI滤波器的多通道TVS,该器件结构类似于图6所示的多通道TVS和EMI滤波器的器件结构,不同点在于数个隔离沟槽270形成于多晶硅层250的下方,该多晶硅层250的周围填补有隔离层255。图9A所示为另一个整合有EMI滤波器的多通道TVS,该器件结构类似于图7A所示的多通道TVS和EMI滤波器的器件结构,不同点在于数个隔离沟槽270形成于多晶硅层250′下方,该多晶硅层250′的周围填补有一隔离层255′。图9B所示为另一个整合有EMI滤波器的多通道TVS,该器件结构类似于图7B所示的TVS和EMI滤波器的器件结构,不同点在于数个隔离沟槽270形成于多晶硅层250′下方,该多晶硅层250′的周围填补有一隔离层255′。如图9C所示,可以使用更多个沟槽来改善输出和输入之间的隔离。更进一步来说,图9D所示为一整合有EMI滤波器的多通道对称TVS,其建构于图5D中的对称TVS的器件结构之上,且通过一电阻或电感连接输入端226和输出端228。也可以通过切换掺杂极性来制造PNP互补结构。
图10A和10B所示为多通道TVS的剖视图,其具有类似于图1A-1所示的电路,但通过一新的器件结构来实现。图10A中的TVS 300形成于支撑P-型外延层310的P+衬底305上。多个N-本体区域320形成于隔离沟槽315之间。在N-本体区域320中形成一个P+欧姆连接掺杂区域330,用来连接输入输出(I/O)端325。一可选的N+埋入层322可以借由高能量N+注入形成于P+结点之下,以此降低PNP增益。一P-本体区域335设置于N-本体区域320和一可选的N+埋入层322之下,作为稳压二极管。P+欧姆连接掺杂区域330和N-本体区域320提供功能为连接IO端325和Vcc 340的上层二极管。形成于外延层310和N-本体区域320间的二极管被连接于IO端325和接地电位的阳极端350间。同时,稳压二极管连接于Vcc 340和阳极350的接地电压之间,且并联上层和下层二极管,其连接位于上层和下层二极管中点的IO端325。每个二极管都被隔离沟槽315隔离。图10B为进一步改良的结构,其使用PNP来代替稳压二极管。在可选的注入N+区域322期间,使用一掩模来阻挡P+区域334所在的N-井320。由P+区域334、N-井320和P本体区域335组成的PNP晶体管可以被N-井320和P本体区域335间的结点击穿电压所触发。
图11为一多通道TVS的剖视图,其整合有图8所示的内部连接于输出和输入端点225′-1和225′-2之间的EMI滤波器,且具有额外的沟槽275来增加形成于沟槽栅极275和外延层210′之间的寄生电容的电容值。这些电容如图11所示那样并联。EMI滤波器的截止频率可以通过改变电容值来调整。可以注入P-扩散区域276以封闭沟槽电容,并通过制造良好的与衬底间的低阻抗连接来降低电容的等效串连电阻(ESR)。图12A与其具有类似的器件结构,并具有分离沟槽栅极275′以进一步增加电容值。图12B是另一个沿着B-B′方向的器件剖视图,用以显示分离沟槽电容间的并联关系。
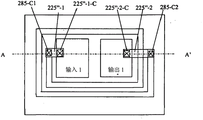
图13A和13B所示分别为在器件内使用沟槽电感布局设计的侧面剖视图和俯视图,其包含如图4所示的形成为第一和第二二极管的一多通道TVS,其具有作为输入端的第一阴极电极225″-1和作为输出端的第二阴极电极225″-2。第一和第二二极管通过隔离沟槽280隔离,并由一沟槽电感285连接。输入和输出端的连接开口分别为所示的225″-1-C和225″-2-C。连接开口到沟槽电感的连接分别为所示的285-C1和285-C2,其分别连接到到输入和输出电极。
参考图14A至图14G,为根据本发明通过使用主流沟槽DMOS制程制造整合有EMI滤波器的多通道VTVS的制造过程。在图14A中,通过蚀刻贯穿一氧化物硬掩模(图中未表示)在一个N+衬底405顶部上的N外延层410之中形成多个沟槽470。衬底405是一个典型用于垂直DMOS器件的重掺杂衬底,所具有的掺杂浓度高于1E18/cm3,相当于电阻率小于N型的20微-欧姆-厘米或P型40微-欧姆-厘米,相较于典型的集成电路制程衬底,其拥有小于1E16的掺杂浓度和数欧姆-厘米的电阻率。也可选择,使用一具有重掺杂底层的轻掺杂衬底来降低电阻率。沟槽最好蚀刻贯穿外延层410到达衬底405,以提供最好的隔离。也可以实施一些可选的流程以移除氧化物硬掩模,如在沟槽DMOS制程中生长牺牲氧化物和圆滑化沟槽底部。在图14B中,一栅极氧化物层455被热生长,接着沉积多晶硅以填充沟槽,然后使用毯式回蚀制程来去除沟槽上超出的多晶硅。氧化物层455的厚度可以透过热增长或沉积来增加到希望的厚度。在图14C中,实施精密控制厚度和掺杂物密度的第二多晶硅沉积,之后使用掩模来图案化以形成第二多晶硅450从而形成EMI滤波器电阻。氧化物层455也被清除以进行后续的注入步骤。在图14D中,P本体区域415和初始击穿电压调整区域435被P型掺杂物注入并扩散。为了获得一深的P本体区域415可以实施高能量注入。在一个实施例中,实施硼离子注入的能量等级介于700KeV到1000KeV之间,且剂量范围从5E13到1E14,以形成一2-3um深度的P本体。在图14E中,实施N型注入以形成N+区域420和423。在图14F中,氧化物层460被形成于顶部表面,接下来进行可选的沉积并回流硼磷硅玻璃以使表面平面化。在连接开口被蚀刻贯穿氧化层460后,实施一P+连接注入以形成P-本体连接区域424。不需要反掺杂N+区域423,由此提供外延层欧姆连接用以将P-本体区域短接到外延层和衬底。在一实施例中,连接注入使用B/BF2离子,剂量为2E15/cm2,能量60KeV,同时N+区域由双注入形成,先进行剂量为4E15、注入能量为80KeV的砷离子注入,随后进行剂量为4E15、能量为80KeV的磷注入。N+区域420反掺杂至击穿电压控制P区域435的中央部分,该P区域435已经被进行了低浓度注入,其剂量为1E13到4E13,并具有较低的能量50KeV,剩下的未受影响的435区域的边缘用以形成一具有N+区域420的侧边二极管以提供初始崩溃电压。在图14G中,金属层被沉积并图案化来形成输入电极425-1和输出电极425-2,并且P-本体外延层也短接到电极440。金属层430也被沉积在底部表面以形成阳极。
上述制程提供一个整合有EMI滤波器的垂直TVS,其结构为被沟槽隔离并通过一电阻元件连接的NPN晶体管,其通过使用类似于图9所示的实施例中的DMOS技术制造而成,其具有设置于侧面的一初始击穿电压二极管。其它实施例可以开始于适当的衬底并通过增加或跳过某些步骤的类似程序制造。特别是没有隔离沟槽的实施例,它可能跳过形成沟槽的制程;不整合有EMI滤波器的TVS的实施例可以跳过第二多晶硅沉积制程。此外,如图13A和13B所示的,为了增加电容而具有分隔栅极的实施例可能还包含多个多晶硅沉积和回蚀制程的步骤。
尽管本发明已经通过现有的优选实施例进行了叙述,但应当认识到这样的公开不应被视为对本发明的限制。在阅读了上述公开内容后,对本领域的技术人员而言,多种变化和修改都会变得显而易见。相应的,附后的权利要求应当被视为覆盖了所有落入本发明真正精神和范围内的变化和修改。
Claims (25)
1.一种多通道垂直瞬态电压抑制器,其特征在于,包括:
一衬底,其包含延伸至所述衬底的底部表面的一重掺杂层,和一设置于所述重掺杂层顶部的外延层;其中所述的重掺杂层和所述的外延层具有第一导电类型;
多个开设于所述外延层的隔离沟槽,该隔离沟槽填充有绝缘层用于形成所述多通道垂直瞬态电压抑制器每个通道间的隔离;
其中,每个所述的隔离沟槽与连接所述的多通道垂直瞬态电压抑制器的外部电极完全绝缘。
2.如权利要求1所述的多通道垂直瞬态电压抑制器,其特征在于,所述的每一通道包括一设置于所述外延层顶部区域的具有与所述第一导电类型相反的第二导电类型的本体区域,该本体区域与所述的外延层形成一PN结。
3.如权利要求2所述的多通道垂直瞬态电压抑制器,其特征在于,所述的每一通道还包括:一具有第一导电类型的顶部半导体区域,其掺杂浓度大于所述的本体区域的掺杂浓度,该顶部半导体区域位于所述的本体区域的顶部;
所述的顶部半导体区域、所述的本体区域、所述的外延层和衬底形成一垂直双极晶体管。
4.如权利要求3所述的多通道垂直瞬态电压抑制器,其特征在于,其中:所述的第一导电类型是N型,所述的第二导电类型是P型,而所述的瞬态电压抑制器还包含一金属电极,用于电性连接所述的本体区域和外延层。
5.如权利要求3所述的多通道垂直瞬态电压抑制器,其特征在于,其中:所述的第一导电类型是P型,所述的第二导电类型是N型,而所述的瞬态电压抑制器还包含一金属电极,用于电性连接所述的本体区域通和顶部半导体区域。
6.如权利要求1所述的多通道垂直瞬态电压抑制器,其特征在于,其中:所述的沟槽开设贯穿所述的外延层并进入所述的重掺杂层衬底。
7.如权利要求3所述的多通道垂直瞬态电压抑制器,其特征在于,其中:所述的沟槽还开设贯穿所述的顶部半导体区域及该本体区域。
8.如权利要求1所述的多通道垂直瞬态电压抑制器,其特征在于,其中:所述的沟槽还填充有导电材料。
9.如权利要求1所述的多通道垂直瞬态电压抑制器,其特征在于,还包括一连接至第一通道的所述顶部半导体区域的输入电极;一连接至第二通道的所述顶部半导体区域的接地电极;一连接至第三通道的所述顶部半导体区域的输出电极;一连接至所述衬底底部的浮动电压,由此所述的多通道垂直瞬态电压抑制器作为一对称垂直瞬态电压抑制器。
10.如权利要求1所述的多通道垂直瞬态电压抑制器,其特征在于,还包括:若干设置在所述的半导体衬底顶部的电极,每个电极对应连接至所述的每个通道,该若干电极是被隔离沟槽分隔开的。
11.如权利要求3所述的多通道垂直瞬态电压抑制器,其特征在于,还包括:若干设置在半导体衬底顶部的电极,每个电极对应与被隔离沟槽分隔开的每个垂直双极晶体管的顶部半导体区域连接;以及一连接至所述衬底底部的浮动电压,由此所述的多通道垂直瞬态电压抑制器作为一对称垂直瞬态电压抑制器。
12.如权利要求3所述的多通道垂直瞬态电压抑制器,其特征在于,还包括:若干设置在半导体衬底顶部的电极,每个电极对应与被隔离沟槽分隔开的每个通道的顶部半导体区域连接;其中,第一电极连接至一输入电压,第二电极连接至一输出电压,第三电极连接至一Vcc电压。
13.一种集成有电磁干扰滤波器的多通道垂直瞬态电压抑制器,其特征在于,包括:
一衬底,其包含延伸至所述衬底的底部表面的重掺杂层,和一设置于所述重掺杂层顶部的外延层;其中,所述的重掺杂层和所述的外延层具有第一导电类型,所述外延层具有一顶部表面,而所述重掺杂层具有一底部表面;
多个开设于所述外延层的隔离沟槽,该隔离沟槽填充有绝缘层用于形成所述多通道垂直瞬态电压抑制器每个通道间的隔离;
其中,每个所述的隔离沟槽与连接所述的多通道垂直瞬态电压抑制器的外部电极完全绝缘;
一连接至第一通道的半导体区域顶部的输入电极;一连接至第二通道的半导体区域顶部的输出电极;以及一作为电阻而电串联于所述输入电极与所述输出电极之间的隔离导电区域;
其中每一通道还包括:一设置于所述外延层顶部区域的具有与第一导电类型相反的第二导电类型本体区域,该本体区域与所述的外延层形成一PN结。
14.如权利要求13所述的集成有电磁干扰滤波器的多通道垂直瞬态电压抑制器,其特征在于,所述的每一通道还包括:具有第一导电类型的一顶部半导体区域,其掺杂浓度大于所述本体区域的掺杂浓度,该顶部半导体区域设置于所述本体区域的顶部,并具有与所述外延层的顶部表面处于同一平面的顶部表面;
所述的顶部半导体区域、所述的本体区域、所述的外延层和衬底形成一垂直双极晶体管。
15.如权利要求14所述的集成有电磁干扰滤波器的多通道垂直瞬态电压抑制器,其特征在于,其中:所述的第一导电类型是N型,所述的第二导电类型是P型,而所述的本体区域通过一金属电极短接到所述的外延层。
16.如权利要求14所述的集成有电磁干扰滤波器的多通道垂直瞬态电压抑制器,其特征在于,其中:所述的第一导电类型是P型,所述的第二导电类型是N型,而所述的本体区域通过一金属电极短接到所述的顶部半导体区域。
17.如权利要求14所述的集成有电磁干扰滤波器的多通道垂直瞬态电压抑制器,其特征在于,其中:所述的沟槽开设贯穿所述的外延层,并进入所述的重掺杂衬底。
18.如权利要求17所述的集成有电磁干扰滤波器的多通道垂直瞬态电压抑制器,其特征在于,其中:所述沟槽进一步开设贯穿所述的顶部半导体区域及所述的本体区域。
19.如权利要求16所述的集成有电磁干扰滤波器的多通道垂直瞬态电压抑制器,其特征在于,其中:所述的沟槽还填充有导电材料。
20.如权利要求16所述的集成有电磁干扰滤波器的多通道垂直瞬态电压抑制器,其特征在于,还包括:一连接至第三通道的所述顶部半导体区域的接地电极;一连接至所述衬底底部的浮动电压,由此所述的多通道垂直瞬态电压抑制器作为一集成有电磁干扰滤波器的对称垂直瞬态电压抑制器。
21.如权利要求13所述的集成有电磁干扰滤波器的多通道垂直瞬态电压抑制器,其特征在于,还包括:所述沟槽具有利用第一绝缘层确定的一侧壁及一底部,所述的第一导电类型是P型。
22.如权利要求13所述的集成有电磁干扰滤波器的多通道垂直瞬态电压抑制器,其特征在于,还包括:所述沟槽具有利用第一绝缘层确定的一侧壁及一底部;一连接至第三通道的所述顶部半导体区域的接地电极;
一连接至所述衬底底部的浮动电压,由此所述的多通道垂直瞬态电压抑制器作为一集成有电磁干扰滤波器的对称垂直瞬态电压抑制器。
23.如权利要求13所述的集成有电磁干扰滤波器的多通道垂直瞬态电压抑制器,其特征在于,还包括:所述沟槽具有利用第一绝缘层确定的一侧壁及一底部,该第一绝缘层隔离所述沟槽中填充的导电材料。
24.如权利要求23所述的集成有电磁干扰滤波器的多通道垂直瞬态电压抑制器,其特征在于,其中:所述的填充有导电材料的沟槽被分成互相绝缘的多个导电层;每个所述沟槽中的导电层分别电连接至所述顶部半导体区域或所述衬底的底部。
25.如权利要求13所述的集成有电磁干扰滤波器的多通道垂直瞬态电压抑制器,其特征在于,其中:所述的隔离导电区域作为一具有螺旋结构的电阻,进一步可作为一电感。
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US11/600,696 US7781826B2 (en) | 2006-11-16 | 2006-11-16 | Circuit configuration and manufacturing processes for vertical transient voltage suppressor (TVS) and EMI filter |
| US11/600,696 | 2006-11-16 | ||
| CN2007800405773A CN101536189B (zh) | 2006-11-16 | 2007-11-16 | 具有电磁干扰滤波器的垂直瞬态电压抑制器(tvs) |
Related Parent Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2007800405773A Division CN101536189B (zh) | 2006-11-16 | 2007-11-16 | 具有电磁干扰滤波器的垂直瞬态电压抑制器(tvs) |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN102623454A true CN102623454A (zh) | 2012-08-01 |
| CN102623454B CN102623454B (zh) | 2015-09-23 |
Family
ID=39430352
Family Applications (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2007800405773A Active CN101536189B (zh) | 2006-11-16 | 2007-11-16 | 具有电磁干扰滤波器的垂直瞬态电压抑制器(tvs) |
| CN201210073633.6A Active CN102623454B (zh) | 2006-11-16 | 2007-11-16 | 具有电磁干扰滤波器的垂直瞬态电压抑制器 |
Family Applications Before (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2007800405773A Active CN101536189B (zh) | 2006-11-16 | 2007-11-16 | 具有电磁干扰滤波器的垂直瞬态电压抑制器(tvs) |
Country Status (7)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (2) | US7781826B2 (zh) |
| EP (1) | EP2087520A4 (zh) |
| JP (1) | JP5273394B2 (zh) |
| KR (1) | KR101164082B1 (zh) |
| CN (2) | CN101536189B (zh) |
| TW (1) | TWI380429B (zh) |
| WO (1) | WO2008063592A2 (zh) |
Families Citing this family (90)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US7544545B2 (en) | 2005-12-28 | 2009-06-09 | Vishay-Siliconix | Trench polysilicon diode |
| TWI435430B (zh) * | 2006-01-18 | 2014-04-21 | Vishay Siliconix | 具高靜電放電性能之低電壓輸出驅動器 |
| US7859814B2 (en) | 2006-10-19 | 2010-12-28 | Littelfuse, Inc. | Linear low capacitance overvoltage protection circuit using a blocking diode |
| US9793256B2 (en) * | 2006-11-30 | 2017-10-17 | Alpha And Omega Semiconductor Incorporated | Optimized configurations to integrate steering diodes in low capacitance transient voltage suppressor (TVS) |
| US7579632B2 (en) * | 2007-09-21 | 2009-08-25 | Semiconductor Components Industries, L.L.C. | Multi-channel ESD device and method therefor |
| US8633521B2 (en) | 2007-09-26 | 2014-01-21 | Stmicroelectronics N.V. | Self-bootstrapping field effect diode structures and methods |
| WO2009042807A2 (en) * | 2007-09-26 | 2009-04-02 | Lakota Technologies, Inc. | Adjustable field effect rectifier |
| US8148748B2 (en) | 2007-09-26 | 2012-04-03 | Stmicroelectronics N.V. | Adjustable field effect rectifier |
| US8643055B2 (en) | 2007-09-26 | 2014-02-04 | Stmicroelectronics N.V. | Series current limiter device |
| ITTO20080046A1 (it) * | 2008-01-18 | 2009-07-19 | St Microelectronics Srl | Schiera di fotodiodi operanti in modalita' geiger reciprocamente isolati e relativo procedimento di fabbricazione |
| ITTO20080045A1 (it) | 2008-01-18 | 2009-07-19 | St Microelectronics Srl | Schiera di fotodiodi operanti in modalita' geiger reciprocamente isolati e relativo procedimento di fabbricazione |
| US20090212354A1 (en) * | 2008-02-23 | 2009-08-27 | Force Mos Technology Co. Ltd | Trench moseft with trench gates underneath contact areas of esd diode for prevention of gate and source shortate |
| US8093133B2 (en) * | 2008-04-04 | 2012-01-10 | Semiconductor Components Industries, Llc | Transient voltage suppressor and methods |
| US7842969B2 (en) * | 2008-07-10 | 2010-11-30 | Semiconductor Components Industries, Llc | Low clamp voltage ESD device and method therefor |
| US7955941B2 (en) * | 2008-09-11 | 2011-06-07 | Semiconductor Components Industries, Llc | Method of forming an integrated semiconductor device and structure therefor |
| US8089095B2 (en) * | 2008-10-15 | 2012-01-03 | Semiconductor Components Industries, Llc | Two terminal multi-channel ESD device and method therefor |
| IT1392366B1 (it) * | 2008-12-17 | 2012-02-28 | St Microelectronics Rousset | Fotodiodo operante in modalita' geiger con resistore di soppressione integrato e controllabile, schiera di fotodiodi e relativo procedimento di fabbricazione |
| JP5525736B2 (ja) * | 2009-02-18 | 2014-06-18 | セミコンダクター・コンポーネンツ・インダストリーズ・リミテッド・ライアビリティ・カンパニー | 半導体装置及びその製造方法 |
| KR101016183B1 (ko) * | 2009-03-13 | 2011-02-24 | 주식회사 시지트로닉스 | Tvs급 제너 다이오드 및 그 제조 방법 |
| TWI447895B (zh) * | 2009-04-09 | 2014-08-01 | Raydium Semiconductor Corp | 半導體電路 |
| IT1393781B1 (it) * | 2009-04-23 | 2012-05-08 | St Microelectronics Rousset | Fotodiodo operante in modalita' geiger con resistore di soppressione integrato e controllabile ad effetto jfet, schiera di fotodiodi e relativo procedimento di fabbricazione |
| US10205017B2 (en) * | 2009-06-17 | 2019-02-12 | Alpha And Omega Semiconductor Incorporated | Bottom source NMOS triggered Zener clamp for configuring an ultra-low voltage transient voltage suppressor (TVS) |
| US7989887B2 (en) * | 2009-11-20 | 2011-08-02 | Force Mos Technology Co., Ltd. | Trench MOSFET with trenched floating gates as termination |
| FR2953062B1 (fr) * | 2009-11-24 | 2011-12-16 | St Microelectronics Tours Sas | Diode de protection bidirectionnelle basse tension |
| IT1399690B1 (it) | 2010-03-30 | 2013-04-26 | St Microelectronics Srl | Fotodiodo a valanga operante in modalita' geiger ad elevato rapporto segnale rumore e relativo procedimento di fabbricazione |
| JP2012004350A (ja) * | 2010-06-17 | 2012-01-05 | On Semiconductor Trading Ltd | 半導体装置及びその製造方法 |
| US8169000B2 (en) * | 2010-07-15 | 2012-05-01 | Amazing Microelectronic Corp. | Lateral transient voltage suppressor with ultra low capacitance |
| EP2663806B1 (en) | 2011-01-14 | 2018-01-03 | Philips Lighting Holding B.V. | Lighting device |
| KR101041752B1 (ko) * | 2011-02-01 | 2011-06-17 | 주식회사 시지트로닉스 | 다단형 구조의 반도체 필터 및 그 제조방법 |
| US8698196B2 (en) | 2011-06-28 | 2014-04-15 | Alpha And Omega Semiconductor Incorporated | Low capacitance transient voltage suppressor (TVS) with reduced clamping voltage |
| US8710627B2 (en) * | 2011-06-28 | 2014-04-29 | Alpha And Omega Semiconductor Incorporated | Uni-directional transient voltage suppressor (TVS) |
| EP2555241A1 (en) * | 2011-08-02 | 2013-02-06 | Nxp B.V. | IC die, semiconductor package, printed circuit board and IC die manufacturing method |
| US8648386B2 (en) * | 2011-08-31 | 2014-02-11 | Macronix International Co., Ltd. | Semiconductor structure and manufacturing method for the same and ESD circuit |
| US8569780B2 (en) * | 2011-09-27 | 2013-10-29 | Force Mos Technology Co., Ltd. | Semiconductor power device with embedded diodes and resistors using reduced mask processes |
| US9184255B2 (en) | 2011-09-30 | 2015-11-10 | Infineon Technologies Austria Ag | Diode with controllable breakdown voltage |
| WO2013085869A1 (en) | 2011-12-05 | 2013-06-13 | Smith International Inc. | Rotating cutting elements for pdc bits |
| JP2013201164A (ja) * | 2012-03-23 | 2013-10-03 | Toshiba Corp | 半導体装置 |
| EP2725615B1 (en) * | 2012-10-29 | 2019-01-23 | IMEC vzw | Semiconductor device comprising a diode and a bipolar transistor and method for producing such a device |
| US9337178B2 (en) | 2012-12-09 | 2016-05-10 | Semiconductor Components Industries, Llc | Method of forming an ESD device and structure therefor |
| US9048106B2 (en) * | 2012-12-13 | 2015-06-02 | Diodes Incorporated | Semiconductor diode assembly |
| GB2525774A (en) | 2013-02-28 | 2015-11-04 | Murata Manufacturing Co | Semiconductor device |
| JP5796692B2 (ja) | 2013-02-28 | 2015-10-21 | 株式会社村田製作所 | Esd保護デバイス |
| CN205508776U (zh) * | 2013-02-28 | 2016-08-24 | 株式会社村田制作所 | 半导体装置 |
| WO2014162795A1 (ja) | 2013-04-05 | 2014-10-09 | 株式会社村田製作所 | Esd保護デバイス |
| KR101495736B1 (ko) * | 2013-05-15 | 2015-02-25 | 전북대학교산학협력단 | Esd-emi 공통모드 반도체 필터 소자 및 그 제조방법 |
| US8841174B1 (en) | 2013-07-01 | 2014-09-23 | International Business Machines Corporation | Silicon controlled rectifier with integral deep trench capacitor |
| US20150014825A1 (en) * | 2013-07-15 | 2015-01-15 | United Microelectronics Corp. | Esd protection device |
| CN103413807B (zh) * | 2013-07-15 | 2015-11-25 | 常州子睦半导体有限公司 | 低电容单向瞬态电压抑制器 |
| US9070790B2 (en) * | 2013-08-29 | 2015-06-30 | Infineon Technologies Ag | Vertical semiconductor device and method of manufacturing thereof |
| US9202935B2 (en) | 2013-10-01 | 2015-12-01 | Vishay General Semiconductor Llc | Zener diode haviing a polysilicon layer for improved reverse surge capability and decreased leakage current |
| US9257420B2 (en) * | 2014-02-04 | 2016-02-09 | Stmicroelectronics (Tours) Sas | Overvoltage protection device |
| US10103540B2 (en) * | 2014-04-24 | 2018-10-16 | General Electric Company | Method and system for transient voltage suppression devices with active control |
| US9806157B2 (en) | 2014-10-03 | 2017-10-31 | General Electric Company | Structure and method for transient voltage suppression devices with a two-region base |
| CN106298511A (zh) * | 2015-06-05 | 2017-01-04 | 北大方正集团有限公司 | 瞬态抑制二极管的制造方法和瞬态抑制二极管 |
| US10217733B2 (en) | 2015-09-15 | 2019-02-26 | Semiconductor Components Industries, Llc | Fast SCR structure for ESD protection |
| CN105489657B (zh) * | 2016-02-24 | 2016-11-23 | 江苏捷捷微电子股份有限公司 | 一种单向低压tvs器件及其制造方法 |
| CN105789332B (zh) * | 2016-04-25 | 2019-02-26 | 矽力杰半导体技术(杭州)有限公司 | 整流器件、整流器件的制造方法及esd保护器件 |
| US10388781B2 (en) | 2016-05-20 | 2019-08-20 | Alpha And Omega Semiconductor Incorporated | Device structure having inter-digitated back to back MOSFETs |
| US9941265B2 (en) * | 2016-07-01 | 2018-04-10 | Nexperia B.V. | Circuitry with voltage limiting and capactive enhancement |
| US10510741B2 (en) * | 2016-10-06 | 2019-12-17 | Semtech Corporation | Transient voltage suppression diodes with reduced harmonics, and methods of making and using |
| CN106252226A (zh) * | 2016-10-17 | 2016-12-21 | 上海先进半导体制造股份有限公司 | Tvs管的制作方法 |
| CN106684040A (zh) * | 2017-01-13 | 2017-05-17 | 上海长园维安微电子有限公司 | 一种低容低残压瞬态电压抑制二极管器件及其制造方法 |
| KR20180094248A (ko) | 2017-02-15 | 2018-08-23 | 주식회사 파인수처스 | 피부 결손 및 꺼짐 부위 충진재 및 그 용기 |
| US10062682B1 (en) | 2017-05-25 | 2018-08-28 | Alpha And Omega Semiconductor (Cayman) Ltd. | Low capacitance bidirectional transient voltage suppressor |
| US10157904B2 (en) | 2017-03-31 | 2018-12-18 | Alpha And Omega Semiconductor (Cayman) Ltd. | High surge bi-directional transient voltage suppressor |
| US10211199B2 (en) | 2017-03-31 | 2019-02-19 | Alpha And Omega Semiconductor (Cayman) Ltd. | High surge transient voltage suppressor |
| CN107256883B (zh) * | 2017-05-08 | 2019-12-03 | 苏州矽航半导体有限公司 | 一种两路双向tvs二极管及其制作方法 |
| CN107316863B (zh) * | 2017-07-12 | 2019-05-07 | 新昌县佳良制冷配件厂 | 瞬态电压抑制器及其制作方法 |
| CN107301998B (zh) * | 2017-07-21 | 2023-11-10 | 北京燕东微电子有限公司 | 瞬态电压抑制器及其制造方法 |
| US10141300B1 (en) | 2017-10-19 | 2018-11-27 | Alpha And Omega Semiconductor (Cayman) Ltd. | Low capacitance transient voltage suppressor |
| US10475787B2 (en) * | 2017-11-17 | 2019-11-12 | Littelfuse, Inc. | Asymmetric transient voltage suppressor device and methods for formation |
| US10574212B2 (en) * | 2017-11-21 | 2020-02-25 | Mediatek Inc. | Method and circuit for low-noise reference signal generation |
| KR102037157B1 (ko) * | 2017-12-27 | 2019-10-29 | 광전자 주식회사 | 정전기 보호용 고내압 제너 다이오드 및 그 제조방법 |
| TWI643335B (zh) * | 2017-12-29 | 2018-12-01 | 新唐科技股份有限公司 | 半導體裝置及其製造方法 |
| CN109360822B (zh) * | 2018-09-19 | 2021-04-20 | 张辉 | 一种瞬态电压抑制器及其制作方法 |
| CN109244069B (zh) * | 2018-09-19 | 2020-12-15 | 浙江昌新生物纤维股份有限公司 | 瞬态电压抑制器及其制备方法 |
| KR102171862B1 (ko) * | 2019-05-23 | 2020-10-29 | 주식회사 케이이씨 | 단방향 과도 전압 억제 소자 및 그 제조 방법 |
| CN111223919A (zh) * | 2020-03-27 | 2020-06-02 | 上海维安半导体有限公司 | 一种利用深槽刻蚀并填充高浓度多晶硅的tvs及其制造方法 |
| CN111413818B (zh) * | 2020-03-31 | 2021-02-02 | 精电(河源)显示技术有限公司 | 一种抵抗电性干扰的液晶显示模组 |
| CN111564438A (zh) * | 2020-04-27 | 2020-08-21 | 上海韦尔半导体股份有限公司 | 一种瞬态电压抑制保护器件、制作工艺及电子产品 |
| KR20210155431A (ko) * | 2020-06-15 | 2021-12-23 | 삼성디스플레이 주식회사 | 시스템 인 패키지 및 이를 포함하는 전자 모듈 |
| US11508853B2 (en) | 2020-07-28 | 2022-11-22 | Amazing Microelectronic Corp. | Vertical bipolar transistor device |
| US11271099B2 (en) | 2020-07-28 | 2022-03-08 | Amazing Microelectronic Corp. | Vertical bipolar transistor device |
| CN114512489A (zh) * | 2020-11-16 | 2022-05-17 | 力旺电子股份有限公司 | 非挥发性存储器的存储单元 |
| US20220399717A1 (en) * | 2021-06-11 | 2022-12-15 | Semiconductor Components Industries, Llc | Interference filter and electrostatic discharge / electrical surge protection circuit and device |
| US12087759B2 (en) | 2021-06-30 | 2024-09-10 | Alpha And Omega Semiconductor International Lp | Low capacitance two channel and multi-channel TVS with effective inter-connection |
| US20230168298A1 (en) * | 2021-11-29 | 2023-06-01 | Amazing Microelectronic Corp. | Diode test module for monitoring leakage current and its method thereof |
| TWM628743U (zh) * | 2022-02-24 | 2022-06-21 | 杰力科技股份有限公司 | 溝渠式功率半導體裝置 |
| CN114664817A (zh) * | 2022-03-07 | 2022-06-24 | 杭州士兰集昕微电子有限公司 | 瞬间电压抑制器件及其制造方法 |
| US11978809B2 (en) * | 2022-06-27 | 2024-05-07 | Amazing Microelectronic Corp. | Transient voltage suppression device |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5326711A (en) * | 1993-01-04 | 1994-07-05 | Texas Instruments Incorporated | High performance high voltage vertical transistor and method of fabrication |
| US5818084A (en) * | 1996-05-15 | 1998-10-06 | Siliconix Incorporated | Pseudo-Schottky diode |
| CN1450638A (zh) * | 2002-04-05 | 2003-10-22 | 华邦电子股份有限公司 | 双向过电压与静电放电防护装置 |
| US7030447B2 (en) * | 2001-05-04 | 2006-04-18 | Semiconductor Components Industries, L.L.C. | Low voltage transient voltage suppressor |
| US7064691B2 (en) * | 1997-09-02 | 2006-06-20 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Noise suppression circuit, ASIC, navigation apparatus, communication circuit, and communication apparatus having the same |
Family Cites Families (14)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS6066473A (ja) * | 1983-09-22 | 1985-04-16 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Mos型半導体装置の入力保護回路 |
| JP3216743B2 (ja) * | 1993-04-22 | 2001-10-09 | 富士電機株式会社 | トランジスタ用保護ダイオード |
| JP2988871B2 (ja) * | 1995-06-02 | 1999-12-13 | シリコニックス・インコーポレイテッド | トレンチゲートパワーmosfet |
| US5998833A (en) * | 1998-10-26 | 1999-12-07 | North Carolina State University | Power semiconductor devices having improved high frequency switching and breakdown characteristics |
| JP2000223705A (ja) * | 1999-01-29 | 2000-08-11 | Nissan Motor Co Ltd | 半導体装置 |
| JP3264262B2 (ja) * | 1999-02-19 | 2002-03-11 | 日本電気株式会社 | 半導体装置及びその製造方法 |
| US6198127B1 (en) * | 1999-05-19 | 2001-03-06 | Intersil Corporation | MOS-gated power device having extended trench and doping zone and process for forming same |
| US6812526B2 (en) * | 2000-03-01 | 2004-11-02 | General Semiconductor, Inc. | Trench DMOS transistor structure having a low resistance path to a drain contact located on an upper surface |
| JP4528460B2 (ja) * | 2000-06-30 | 2010-08-18 | 株式会社東芝 | 半導体素子 |
| US6633063B2 (en) * | 2001-05-04 | 2003-10-14 | Semiconductor Components Industries Llc | Low voltage transient voltage suppressor and method of making |
| JP4004843B2 (ja) * | 2002-04-24 | 2007-11-07 | Necエレクトロニクス株式会社 | 縦型mosfetの製造方法 |
| US7045857B2 (en) * | 2004-03-26 | 2006-05-16 | Siliconix Incorporated | Termination for trench MIS device having implanted drain-drift region |
| US7880223B2 (en) * | 2005-02-11 | 2011-02-01 | Alpha & Omega Semiconductor, Ltd. | Latch-up free vertical TVS diode array structure using trench isolation |
| JP5070693B2 (ja) * | 2005-11-11 | 2012-11-14 | サンケン電気株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
-
2006
- 2006-11-16 US US11/600,696 patent/US7781826B2/en active Active
-
2007
- 2007-10-26 TW TW096140388A patent/TWI380429B/zh active
- 2007-11-16 JP JP2009537234A patent/JP5273394B2/ja active Active
- 2007-11-16 KR KR1020097011394A patent/KR101164082B1/ko active IP Right Grant
- 2007-11-16 WO PCT/US2007/024149 patent/WO2008063592A2/en active Application Filing
- 2007-11-16 CN CN2007800405773A patent/CN101536189B/zh active Active
- 2007-11-16 EP EP07867521A patent/EP2087520A4/en not_active Withdrawn
- 2007-11-16 CN CN201210073633.6A patent/CN102623454B/zh active Active
-
2010
- 2010-08-18 US US12/806,659 patent/US8338915B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5326711A (en) * | 1993-01-04 | 1994-07-05 | Texas Instruments Incorporated | High performance high voltage vertical transistor and method of fabrication |
| US5818084A (en) * | 1996-05-15 | 1998-10-06 | Siliconix Incorporated | Pseudo-Schottky diode |
| US7064691B2 (en) * | 1997-09-02 | 2006-06-20 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Noise suppression circuit, ASIC, navigation apparatus, communication circuit, and communication apparatus having the same |
| US7030447B2 (en) * | 2001-05-04 | 2006-04-18 | Semiconductor Components Industries, L.L.C. | Low voltage transient voltage suppressor |
| CN1450638A (zh) * | 2002-04-05 | 2003-10-22 | 华邦电子股份有限公司 | 双向过电压与静电放电防护装置 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN101536189A (zh) | 2009-09-16 |
| KR20090086569A (ko) | 2009-08-13 |
| US7781826B2 (en) | 2010-08-24 |
| WO2008063592A3 (en) | 2008-08-07 |
| JP2010510662A (ja) | 2010-04-02 |
| KR101164082B1 (ko) | 2012-07-12 |
| WO2008063592A2 (en) | 2008-05-29 |
| TW200826276A (en) | 2008-06-16 |
| US8338915B2 (en) | 2012-12-25 |
| CN101536189B (zh) | 2012-06-06 |
| US20100314716A1 (en) | 2010-12-16 |
| JP5273394B2 (ja) | 2013-08-28 |
| EP2087520A4 (en) | 2011-05-25 |
| US20080121988A1 (en) | 2008-05-29 |
| CN102623454B (zh) | 2015-09-23 |
| TWI380429B (en) | 2012-12-21 |
| EP2087520A2 (en) | 2009-08-12 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN101536189B (zh) | 具有电磁干扰滤波器的垂直瞬态电压抑制器(tvs) | |
| US10038062B2 (en) | Circuit configuration and manufacturing processes for vertical transient voltage suppressor (TVS) and EMI filter | |
| US8896093B2 (en) | Circuit configuration and manufacturing processes for vertical transient voltage suppressor (TVS) and EMI filter | |
| US10818516B2 (en) | Semiconductor device having biasing structure for self-isolating buried layer and method therefor | |
| US8835977B2 (en) | TVS with low capacitance and forward voltage drop with depleted SCR as steering diode | |
| US8338854B2 (en) | TVS with low capacitance and forward voltage drop with depleted SCR as steering diode | |
| CN104851919B (zh) | 双向穿通半导体器件及其制造方法 | |
| US7968936B2 (en) | Quasi-vertical gated NPN-PNP ESD protection device | |
| US9911728B2 (en) | Transient voltage suppressor (TVS) with reduced breakdown voltage | |
| US9793256B2 (en) | Optimized configurations to integrate steering diodes in low capacitance transient voltage suppressor (TVS) | |
| CN101847663A (zh) | 一种瞬间电压抑制器及形成瞬间电压抑制器的方法 | |
| CN103489913A (zh) | 半导体装置及其制造方法 | |
| KR20090031221A (ko) | 고용량 다이오드를 형성하는 방법 및 그 구조 | |
| CN212750894U (zh) | 超低压触发器件 | |
| CN209016064U (zh) | 电子器件 | |
| DE102006028721B3 (de) | Halbleiterschutzstruktur für eine elektrostatische Entladung | |
| CN100423256C (zh) | 半导体集成电路中的静电放电保护电路 | |
| CN102299102B (zh) | 具备漏极电压保护的功率半导体组件及其制作方法 | |
| CN109585530B (zh) | 高浪涌瞬变电压抑制器 | |
| US20240347527A1 (en) | Low Capacitance High Holding Voltage Transient Voltage Suppressing Device | |
| CN118016702A (zh) | 一种震荡抑制功率器件及其制作方法 | |
| CN117878115A (zh) | Dcscr器件的结构、制造方法及电子设备 | |
| CN115472604A (zh) | 具有高维持电压、低触发电压的电阻电容耦合硅控整流器结构 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C14 | Grant of patent or utility model | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| TR01 | Transfer of patent right | ||
| TR01 | Transfer of patent right |
Effective date of registration: 20200423 Address after: Ontario, Canada Patentee after: World semiconductor International Limited Partnership Address before: 475 oakmead Park Road, Sunnyvale, California, USA Patentee before: Alpha and Omega Semiconductor Inc. |