IC 1101 Galaxy Facts (UGC 9752)
Key Facts
Name:
IC 1101Type:
Elliptical GalaxyAlternative Names:
IC 1101, UGC 9752Constellation:
VirgoNearest Major Star:
3 SerpentisRight Ascension (R.A.) :
15h 10m 56.1sDeclination:
+05:44:41Distance from Earth (Lt.Yr):
1,040,000,000Calculated Diameter (Lt.Yr):
265,313.32Apparent Dimension
: 1.2x0.6Visual / Apparent Magnitude:
13.22Naked Eye Visible:
Requires a 8 - 10 Inch TelescopeYear of Discovery:
1790Discoverer:
William HerschelMorphological Type:
E/S0 DAngular Size (arcmin):
0.877 0.491 30 (NIR) CRadial Velocity (km/s):
22419Information
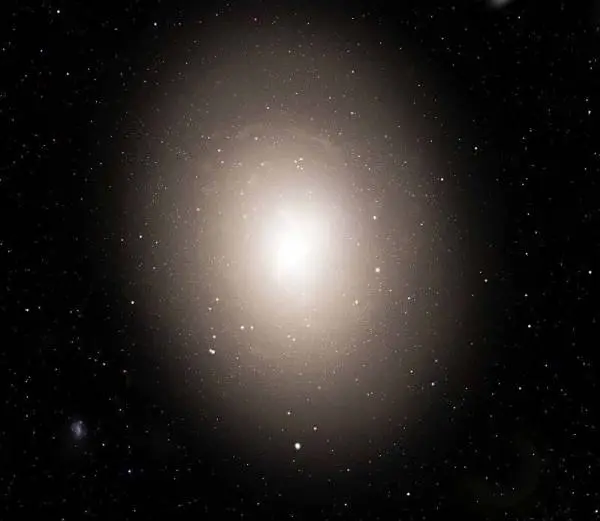
IC 1101 was, for a long time, known as the largest galaxy in the Universe. The new challenger to the title is Alcyoneus, located in the constellation of Lynx. IC 1101's location is disputed because it's on the borders of the Virgo constellation and Serpens constellation. Some will refer to it as being in Virgo, others Serpens.


Interesting Fun Facts
- IC 1101 is the largest galaxy within the Abell 2029 galaxy cluster. The cluster is located predominantly within the Virgo constellation.
- IC 1101 was discovered by William Herschel, of Uranus fame, on 19th June 1790. Source
- IC 1101 is classed as a Lenticular Galaxy due to intermediate-scale component plus the outer stellar halo and the outwardly rising ellipticity profile. OUP. Lenticular galaxies are between Elliptical and Spiral. They are flat like spirals but have a central bulge like a lens.
- IC 1101 is too far away and too dim to be seen by the naked eye. It has an apparent magnitude of 13.22 Caltech
- IC 1101 is a dying galaxy, having used up most of its dust.
- IC 1101 has grown large by merging with other galaxies
- IC 1101 has an estimated 100 trillion stars
- IC 1101 distance from Earth is 1.045 billion light-years / 320.4 MegaParsecs, Planets Education
- IC 1101's Radial Velocity is 0.07780 km/s. Simbad
- IC 1101 name comes from the fact it is the 1101st Item in the Index Catalogue of nebulas and Star Clusters
- Our galaxy is estimated to have about 200-400 billion stars (400,000,000,000), which might seem a lot, but IC 1101 has an estimated 100 trillion stars (100,000,000,000,000).
- Nothing indicates that IC 1101 can't contain alien life forms or planets orbiting any of the many stars the galaxy has.
- IC 1101 is a separate, distinct galaxy.
- When you look at the IC 1101, you are not looking at its present form but how it looked millions or billions of years ago.
- Based on its Morphological Type (E/S0 D), IC 1101 is classified as a Lenticular Elliptical Galaxy.
- IC 1101 is not a Messier Object and doesn't have a Messier Number.
Largest Galaxy in the Universe
IC 1101 is the largest known Elliptical Galaxy type, for that matter, that we have so far discovered in the Universe. In addition to it being the largest galaxy, it also has the largest supermassive black hole in any galaxy so far spotted. Supermassive Black Holes are at the centres of most galaxies that are many trillions of times the size and power of stars that orbit them. Largest
Alcyoneus
Since February 2022, IC 1101 is no longer referred to as the largest known galaxy of any type in the Universe, although it may still be the largest elliptical galaxy. The new current largest, belonging to the galaxy, is called Alcyoneus, located in the constellation of Lynx. Alcyoneus is 5 MegaParsecs, or to make it easier to compare, it is 16 million light-years across. ARXIV
Alcyoneus is over 3.5 Billion Light Years away. To put that in context, Earth, our planet, is roughly 4.5 billion years old. We are seeing what Alcyoneus was like billions of years ago when we look at it because of the vast distance of space and the relative slowness of light.
Therefore, which is larger, Alcyoneus or IC 1101? The answer is that Alcyoneus is larger than IC 1101.
Dying Galaxy
It is classed as a dying galaxy as it doesn't have many new stars being born, unlike our galaxy, the Milky Way. Some stars are being born but at a prolonged rate. Our galaxy continues to produce new stars, not at the same rate as it once did, but it continues to do so, unlike IC 1101. The only way this galaxy will survive is to consume other galaxies as it has done in its past. Just because the galaxy is a dead galaxy, it doesn't mean that there aren't alien life forms in that part of the Universe, it's just referring to the birth rate of new stars.
The galaxy grows by cannibalising smaller galaxies that get too close to it. It is so far away you cannot see it without an observational aid. It will be a long time until our galaxy and that galaxy cross paths, if ever. Before the collision of our galaxies occurs, we'll have merged with other galaxies such as Andromeda's, which won't be for another five billion years. The Hubble Site has a brief video about galaxies and how they've grown with scale
We know it's a dying galaxy by the colour that the galaxy gives off. A blue-coloured galaxy is full of the activity of young stars, but a yellowy galaxy such as IC 1101 is docile and dying. IC1101 is an elliptical galaxy in which older galaxies tend to be, whereas our galaxy is believed to be a spiral galaxy. It's believed so because it's been calculated as a spiral galaxy. No one has ever and will probably ever see it. Cosmosup
Although it is too far away to spot any, it is inconceivable that the galaxy doesn't contain any planets. We know that planets exist in other galaxies. We've spotted them in the Andromeda Galaxy, which is the nearest large galaxy to us.
When is IC 1101 Visible
With such a dim visual apparent magnitude (13.22), you will need a telescope of about 8-10 inches. Get professional advice before rushing out and buying the first 8 to 10-inch telescope. Caltech
Northern Hemisphere
For the northern hemisphere, the details are based on viewing from London at about 9 p.m. Depending on where in the northern hemisphere you are, you will need to adjust to seeing it. It should be visible from about mid-April on the eastern horizon, but May will be better. The last chance to see the constellation is at the beginning of October when it will be on the horizon. The constellation will have gone, but the galaxy should just be visible.
Southern Hemisphere
For the southern hemisphere, I assume you are viewing from Sydney, Australia, at about 9 p.m. You won't be able to see IC1101 until May at 9 p.m. However, the galaxy is visible on the horizon at about 10 p.m. the month before. The galaxy is at the very southern edge of the constellation, so although you might be able to see the constellation, the galaxy won't be visible.
The last good chance to see the constellation before disappearing below the horizon is at the end of August. The constellation will have virtually disappeared, but the galaxy is now at the top end of the constellation and should be viewable.
IC 1101 Size / Radius
The diameter of the galaxy is disputed, in a lot of places on the internet, it will say that the galaxy is around 6 million light-years across. If you look in Caltech's Extragalactic Database, the diameter is 125.62 kiloparsec which works out at 410,000 light-years across, not as big as you probably had been led to believe. It is still roughly about 4 times the size of our galaxy and double the size of the Andromeda Galaxy. There doesn't really seem to be any primary papers out there that does state the galaxy's size.
The actual diameter which includes what we can't see and therefore call dark could make the galaxy 10 times more than what we see so the actual diameter could actually be 2 million light-years or more. NRAO.
IC 1101 Location
IC 1101's location is 15h 10m 56.1s (R.A.) and +05:44:41 (Dec.). They are celestial equivalents of Longitude and Latitude. The right ascension (longitude) is the angular distance of an object along the celestial equator from the March Equinox. As a rough guide, the March Equinox is located in the constellation of Pisces. If the number is negative, it is "west" of the March Equinox.
The declination (latitude) is the elliptical galaxy's angle from the celestial equator. A negative value indicates it is in the southern hemisphere.
Based on the location of Virgo, IC 1101 can be located in the equatorial region of the celestial sky. The celestial hemisphere is equivalent to the hemispheres on Earth.
As IC 1101 is in the equatorial region, it can be seen in both terrestrial hemispheres, but there is a caveat depending on how far south and north you are.
IC 1101 is on the Ecliptic. The Ecliptic is the path the Earth takes as it orbits the Sun. As the Earth is titled, we have Celestial and Ecliptic hemispheres.
A naked-eye star is a star that can be seen in the night sky without using binoculars or a telescope. As a guide, the nearest naked-eye star to IC 1101 is 3 Serpentis. Although visible eye stars can reach 6.5 in magnitude, the dimmest star for this will be 6.0.
Map of IC 1101 Location in Virgo
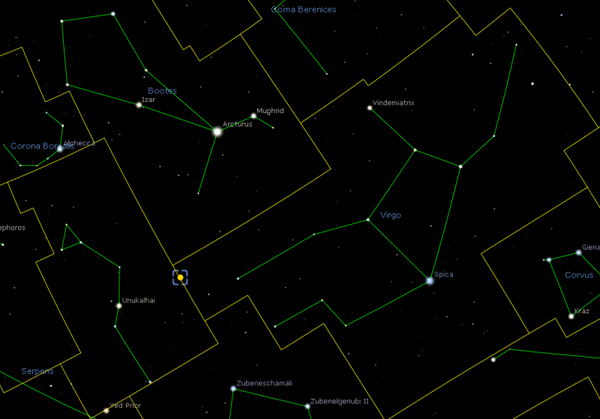
The image above showing the location of the object was generated using Stellarium. The circle identify the location is not relative to the size.
Attributes of IC 1101
Radial Velocity
Radial velocity is the speed at which an object moves away/towards the Sun. For IC 1101, the radial velocity is 22,419.00 km/s. When the value is negative, the deep space object and the Sun are getting closer. Likewise, a positive number means that the two things are moving away.
Visual Brightness
IC 1101's Visual (Apparent) Brightness is 13.22 Magnitude. Anything with a magnitude of less than 6.5 can be seen with visual aids. The lower the number, the brighter the object is to see. Looking without a visual aid, the elliptical galaxy can not be seen from Earth.
IC 1101 Angular Size
The Angular Size is the size given as arc minutes, which can be roughly turned into light years if you know the distance to the elliptical galaxy. Parsecs, Light Years, and Megaparsecs can be used to measure the distance. The formula is Distance * Tan ((MA/60)/(180/Pi)) MA is the Major Axis value. It probably won't give you a peer-reviewed size, but it'll give you an idea of how big it is.
- 0.877 is the major axis of the object, the length.
- 0.491 is the minor axis of the object, the width.
- 30 is the angle of orientation of IC 1101.
- C indicates quality, with A being the best quality and E being the worst.
IC 1101 Distance from Earth
IC 1101's distance to Earth is an approximation as we don't know the exact distance. It is based on calculations and observations. The currently recognised distance at the time of writing is roughly
1,040,000,000.00 light-years.
The list below is how long it will take at various speeds to get to IC 1101.
The New Horizons space probe is the fastest probe we've sent into space at the time of writing. Its primary mission was to visit Pluto, which, at the time of launch (2006), Pluto was still a planet.
Light from IC 1101 started its journey to Earth before the dinosaurs were wiped out by a meteor strike 65 Million Years Ago.
- Walking - 174,360,323,540,000,000
- Car - 9,963,447,059,428,571.429
- Airbus A380 - 947,610,454,021,739.13
- Mach 1 - 908,991,884,410,812.896
- Mach 2 - 515,096,967,621,861.152
- New Horizons - 19,160,475,114,285.714
- Speed of Light - 1,040,000,000