Corrective Action & Preventive Action
- 1. This presentation is compiled by “ Drug Regulations” a non profit organization which provides free online resource to the Pharmaceutical Professional. Visit https://www.drugregulations.org for latest information from the world of Pharmaceuticals. 1/2/2014 1
- 2. This presentation is compiled from freely available resources like the websites of FDA, EMA, WHO. “Drug Regulations” is a non profit organization which provides free online resource to the Pharmaceutical Professional. Visit https://www.drugregulations.org for latest information from the world of Pharmaceuticals. Drug Regulations : Online Resource for Latest Information 1/2/2014 2
- 3. ◦ Collect and Analyse Information based on appropriate Statistical Methodology as necessary to detect recurring quality problems ◦ Identify and Investigate Existing and Potential Product and Quality Problems ◦ Take Appropriate, Effective, and Comprehensive Corrective and/or Preventive Actions Drug Regulations : Online Resource for Latest Information 1/2/2014 3
- 4. ◦ A structured approach to the investigation process should be used with the objective of determining the root cause. ◦ The level of effort, formality, and documentation of the investigation should be commensurate with the level of risk, in line with ICH Q9. Drug Regulations : Online Resource for Latest Information 1/2/2014 4
- 5. ◦ CAPA methodology should result in product and process improvements and enhanced product and process understanding. Drug Regulations : Online Resource for Latest Information 1/2/2014 5
- 6. Corrective action is aiming to correct an existing non-conformity and to avoid reoccurrence of the same non-conformity.• Corrective action may arise e.g. from manufacturing deviations, OOS investigations, complaints, audit findings, recalls.• A systematic investigation should be performed to determine the reason(s) for the non-conformities and to agree upon appropriate corrective action.• Agreed corrective actions should be closely followed-up and monitored until their completion. In the frame of the management review, management should be notified about the costs and impact of failure including the respective corrective actions. Drug Regulations : Online Resource for Latest Information 1/2/2014 6
- 7. ◦ Corrective Action: Action to eliminate the cause of a detected nonconformity or other undesirable is taken to situation. ◦ NOTE: Corrective action prevent recurrence whereas preventive action is taken to prevent occurrence. (ISO 9000:2005) Drug Regulations : Online Resource for Latest Information 1/2/2014 7
- 8. Preventive action is aiming to avoid the initial occurrence of a non-conformity by proactively implementing improvements. Preventive action may result i.e. from trending of in process data, of analytical data, of audit findings, trending of root causes for non-conformities or complaints, from product quality reviews (annual product reviews), quality risk analyses, etc. Similar to corrective actions, agreed preventive actions should be closely followed-up and monitored until their completion. Effectiveness of preventive actions should be reviewed regularly, i.e. as part of the product quality review (annual product review).• Information regarding preventive actions including costs and cost savings should be regularly subject to management review in support of maintaining and improving the effectiveness of the Quality Management System. Drug Regulations : Online Resource for Latest Information 1/2/2014 8
- 9. ◦ Preventive Action: Action to eliminate the cause of a potential nonconformity or other undesirable is taken to potential situation. ◦ NOTE: Preventive action prevent occurrence whereas corrective action is taken to prevent recurrence. (ISO 9000:2005) Drug Regulations : Online Resource for Latest Information 1/2/2014 9
- 10. Responsibilities of a quality control unit...to assure that no errors have occurred or, if errors have occurred, that they have been fully investigated. Drug Regulations : Online Resource for Latest Information 10
- 11. Written production and process control procedures shall be followed …. Any deviation from the written procedures shall be recorded and justified. Drug Regulations : Online Resource for Latest Information 11
- 12. ◦ Any unexplained discrepancy…or the failure of a batch or any of its components to meet any of its specifications shall be thoroughly investigated… ◦ The investigation shall extend to other batches of the same drug product and other drug products that may have been associated with the specific failure or discrepancy. ◦ A written record of the investigation shall be made and shall include the conclusions and follow-up. Drug Regulations : Online Resource for Latest Information 12
- 13. Article 10 Production 1. The different production operations shall be carried out in accordance with pre established instructions and procedures and in accordance with good manufacturing practice. Adequate and sufficient resources shall be made available for the in process controls. All process deviations and product defects shall be documented and thoroughly investigated. Drug Regulations : Online Resource for Latest Information 13
- 14. Article 13 - Complaints ◦ Any complaint concerning a defect shall be recorded and investigated by the manufacturer… Article 14 - Inspections ◦ The manufacturer shall conduct repeated self-inspections as part of the quality assurance system in order to monitor the implementation and respect of good manufacturing practice and to propose any necessary corrective measures. Records shall be maintained of such self-inspections and any corrective action subsequently taken. Drug Regulations : Online Resource for Latest Information 14
- 15. 1.4 A Pharmaceutical Quality System appropriate for the manufacture of medicinal products should ensure that: ◦ (xiv) An appropriate level of root cause analysis should be applied during the investigation of deviations, suspected product defects and other problems. ◦ This can be determined using Quality Risk Management principles. In cases where the true root cause(s) of the issue cannot be determined, consideration should be given to identifying the most likely root cause(s) and to addressing those. Drug Regulations : Online Resource for Latest Information 15
- 16. 1.4 A Pharmaceutical Quality System appropriate for the manufacture of medicinal products should ensure that: ◦ (xiv). Where human error is suspected or identified as the cause, this should be justified having taken care to ensure that process, procedural or system based errors or problems have not been overlooked, if present. ◦ Appropriate (CAPAs) corrective should be actions identified and/or and preventative taken in actions response to investigations. ◦ The effectiveness of such actions should be monitored and assessed, in line with Quality Risk Management principles. Drug Regulations : Online Resource for Latest Information 16
- 17. Identification Define the Problem Impact / Risk Assessment Initial assessment of the impact and the magnitude of the problem. Immediate Action Protect the customer from the problem. 17
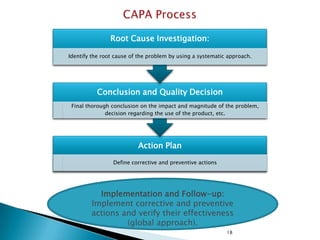
- 18. Root Cause Investigation: Identify the root cause of the problem by using a systematic approach. Conclusion and Quality Decision Final thorough conclusion on the impact and magnitude of the problem, decision regarding the use of the product, etc. Action Plan Define corrective and preventive actions Implementation and Follow-up: Implement corrective and preventive actions and verify their effectiveness (global approach). 18
- 19. To enable an efficient root cause investigation, the problem has to be clearly defined.• Collect all available information, ask questions: Who, when, what, why, how Summarize the problem in a detailed and concise description. Drug Regulations : Online Resource for Latest Information 19
- 20. Deviations Nonconformance Out of Specifications Out of Trend Equipment Data Yield Data Rework Data Returned Products Self Inspections Incoming Inspections Process Control Data Drug Regulations : Online Resource for Latest Information 20 Supplier Audits
- 21. Complaints Customer Audits Warning Letter Adverse Events Regulatory Audit Recalls Drug Regulations : Online Resource for Latest Information 21 483 Observations
- 22. What is the process for events that “trigger” a CAPA ◦ – Not every complaint is a CAPA ◦ – Not every non-conformance is a CAPA Employ appropriate statistical methodology where necessary to detect recurring quality problems. Drug Regulations : Online Resource for Latest Information 22
- 23. Common Statistical Techniques Drug Regulations : Online Resource for Latest Information 23
- 24. Other Analysis Techniques ◦ Management reviews ◦ Quality review ◦ Material review ◦ Other internal reviews Drug Regulations : Online Resource for Latest Information 24
- 25. The problem must be evaluated to determine the need for immediate, corrective and preventive actions and the level of action required, based on the impact and risk of the problem. The evaluation should include: ◦ Potential Impact of the problem. ◦ Risk to its customers and/or the company (i.e. risk to the patient related to the quality, efficacy or safety of the product; risk for the reputation of the company; risk of adverse regulatory actions; financial risk) ◦ Immediate action that may be required Drug Regulations : Online Resource for Latest Information 25
- 26. FDA expects that the degree of corrective and preventive action taken to eliminate or minimize actual or potential nonconformities must be appropriate to the magnitude of the problem and commensurate with the risks encountered… FDA does expect the manufacturer to develop procedures for assessing the risk, the actions that need to be taken for different levels of risk, and how to correct or prevent the problem from recurring, depending on that risk assessment.” Drug Regulations : Online Resource for Latest Information 26
- 27. Risk analysis allows a manufacturer to: ◦ Determine priorities ◦ Assign resources ◦ Determine the severity of impact Determine the depth of investigation ◦ • Common tools Hazard analysis ◦ Used early for potential problems Failure Mode Effects Analysis (FMEA) ◦ Bottom up Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) ◦ Top down Drug Regulations : Online Resource for Latest Information 27
- 28. Immediate action is necessary, when the quality, efficacy or safety may be compromised by the problem. Examples for immediate action:• ◦ Product recall ◦ Blockage of the stock of a product ◦ Rejection of a batch ◦ Interruption of the production (i.e. until problem is assessed and fixed) Drug Regulations : Online Resource for Latest Information 28
- 29. A systematic approach should be applied to ensure that no potential root cause is lost through focusing only on a few assumed root causes. Tools can be applied to facilitate the investigation, i.e. ◦ Start with a brainstorming, i.e. using an Ishikawa diagram (fishbone or cause and effect diagram): Drug Regulations : Online Resource for Latest Information 29
- 30. List all potential root causes and evaluate their likelihood (also using available supportive data and information): ◦ Likely– ◦ Possible (but less likely)– ◦ Remote, unlikely If more than one root cause is likely, a simulation of the potential root cause can help to prove the root cause. Finding the primary root cause is essential for determining appropriate corrective and/or preventive actions. These “root causes” suggest that the failure investigation did not go far enough– ◦ Training, operator error or similar „obvious“ root causes Drug Regulations : Online Resource for Latest Information 30
- 31. Summarize the identified root cause(s).• Summarize the impact and the risk for the customer and/or company. Document the quality decision, i.e.– ◦ No impact of the deviation on the product quality, efficacy or safety – product can be released.– ◦ Product is rejected due to major impact of the failure on product quality.– ◦ Product is recalled. Drug Regulations : Online Resource for Latest Information 31
- 32. Based on the result of the root cause analysis, all tasks required to correct the problem and prevent a reoccurrence are identified and included in an action plan. The plan assigns responsibilities and due dates for implementation. Enough detail must be included regarding the required action and the expected outcome.• Pay attention on correct order of activities. Drug Regulations : Online Resource for Latest Information 32
- 33. The Action Plan is executed and all tasks are completed.• The actions that were taken are documented.• The appropriateness and effectiveness of the actions taken is evaluated:– ◦ Have all recommended changes been completed and verified?– ◦ Have all objectives been met?– ◦ Has training been performed to ensure that all affected employees understand the changes that have been made?– ◦ Was an assessment made that the actions taken have not had an adverse effect on other properties or aspects of a product or process. Closure of CAPA after successful implementation. Drug Regulations : Online Resource for Latest Information 33
- 34. Inspections 2001 to 2006 Non-conformances Expand scope; Emphasize investigation quality; little risk management 1995 to 2001 Quality Incidents Expand scope to include more types of discrepancies Management Review & Quality Plan Risk Based Approach Implemented Inspections Prior to 1995 Deviation Reports Report only major departures from procedure Overwhelmed the System with Numbers Life Cycle Approach Today Non-conformances Risk based, Strong Governance with action oriented management review 1/2/2014 34
- 35. Pharmaceutical Development Product or Technology Transfer Commercial Manufacturing Product Discontinuation process CAPA can be used as CAPA should be used CAPA should variability is explored. an effective system and the effectiveness continue after the CAPA methodology is for useful feedback, feed of the actions should product where forward and continual be evaluated. is discontinued. The corrective actions and improvement. impact on product preventive actions are remaining incorporated into the market iterative design and considered as well development process. as should other which on the be products might be impacted. 1/2/2014 35
- 36. Warning Letter to a Canadian Company ◦ In addition, our investigator found that you do not determine and implement corrective and preventive actions (CAPAs) in a timely manner to prevent recurrence of manufacturing deviations. ◦ For example, the inspection noted that some CAPAs remained open for approximately 500-700 days (one was open for 761 days) without implementation of corrections. ◦ Your firm’s response stated that you have now completed these CAPAs. ◦ However, you failed to address why you had not completed these CAPAs in a timely manner to prevent repetition of manufacturing problems. ◦ We are concerned that your response corrects the FDA 483 observation, but does not provide for a systematic and sustainable correction to ensure timely and effective CAPAs. Drug Regulations : Online Resource for Latest Information 36
- 37. Observation from form 483 from an International Sterile Manufacturer. ◦ d. A 1/20/2010 CAPA, TRK# 93875, was implemented to address execution of varied manual interventions (b)(4) specifically defined interventions) performed during aseptic filling operations. ◦ However, not all of the personnel that are currently engaged in the manufacture of finished products have completed the CAPA’s requisite training. ◦ The number of employees and manual interventions range, for example, from (b)(4) employees performing “stopper bowl change out” and “use trayer plastic to tray vials, respectively (Note: aforementioned examples are not intended to be an all inclusive lists of the number of employees and manual interventions to be accomplished); Drug Regulations : Online Resource for Latest Information 37
- 38. Warning letter to a large Indian Company ◦ The inspection found that the laboratory manager had documented “NIL,” (i.e. no growth for this plate), while the same laboratory manager confirmed microbial growth in the presence of the investigators. ◦ Later during the inspection, the FDA investigator asked to see the original plate and was told that it had been destroyed. ◦ On December 21, 2010, your firm prepared a corrective and preventive action (CAPA) stating that the laboratory manager misread the plate count, and that this deficiency was the result of a human error. ◦ We are concerned that your firm lacks documentation to support this conclusion and moreover, that the original plate was destroyed during the FDA inspection, as reported. ◦ Drug Regulations : Online Resource for Latest Information 38
- 39. Expect FDA to review the actions taken Be prepared to discuss the ◦ appropriateness of the action taken ◦ Why was corrective action taken? ◦ Does the corrective action extend to include any additional actions (component suppliers, training, acceptance activities, field actions) if necessary? Drug Regulations : Online Resource for Latest Information 39
- 40. Verifying or validating the corrective and preventive action to ensure that such action is effective. Effectiveness: ◦ Did the solution work? ◦ Did it create other potential non-conformances? Drug Regulations : Online Resource for Latest Information 40
- 41. Verify that verification/validation protocols were established Review data associated with verification or validation activities Review the effectiveness of the corrective and preventive actions by reviewing data to determine if similar quality problems exist after implementation. Drug Regulations : Online Resource for Latest Information 41
- 42. Implement and record changes in methods and procedures needed to correct and prevent identified quality problems. Drug Regulations : Online Resource for Latest Information 42
- 43. Tie CAPA implementation to: ◦ Document control for products and processes ◦ Change control ◦ Ensure that controlled documents are reviewed and approved if changes are made. Drug Regulations : Online Resource for Latest Information 43
- 44. Expect FDA to verify implementation of changes by viewing actual processes and equipment Implemented changes may directly link to design or production and process controls Drug Regulations : Online Resource for Latest Information 44
- 45. Ensure that information related to quality problems or nonconforming product is disseminated to those directly responsible for assuring the quality of such product or the prevention of such problems. Drug Regulations : Online Resource for Latest Information 45
- 46. Submit relevant information on identified quality problems, as well as corrective and preventive actions, for management review. The significance of the problem impacts the level of management review. Need management awareness and buy-in so that resources are allocated, Drug Regulations : Online Resource for Latest Information 46
- 47. Document all activities and their results. Drug Regulations : Online Resource for Latest Information 47
- 48. CAPA is a “pulse check” for FDA on how well a firm’s Quality System is operating – ◦ Strong CAPA systems are usually indicative of strong Quality Systems Feedback Loop between CAPA, Complaints, and Nonconforming Product is essential CAPA Subsystem is all about identifying and resolving problems that can or have resulted in nonconforming product. Drug Regulations : Online Resource for Latest Information 48
- 49. CAPA is much more than just “corrective actions” and “preventive actions”. Any opportunity to improve quality in your organization is a CAPA! 49
- 50. This presentation was compiled from freely available resources like the websites of FDA, EMA, WHO. “Drug Regulations” is a non profit organization which provides free online resource to the Pharmaceutical Professional. Visit https://www.drugregulations.org for latest information from the world of Pharmaceuticals. Drug Regulations : Online Resource for Latest Information 1/2/2014 50