ఉనునెన్నియం
| Ununennium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˌuːn.uːnˈɛniəm/ ( | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative names | element 119, eka-francium | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ununennium in the periodic table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Group | మూస:Infobox element/symbol-to-group/format | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Period | period 8 (theoretical, extended table) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Block | s-block | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electron configuration | [Og] 8s1 (predicted)[1] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phase at STP | unknown phase | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of fusion | 2.01–2.05 kJ/mol (extrapolated)[2] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Oxidation states | (+1), (+3), (+5) (predicted)[1][3] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
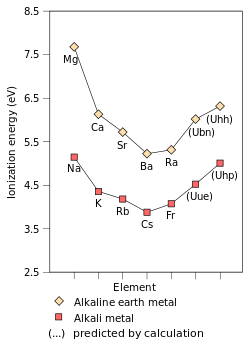
| Ionization energies |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic radius | empirical: 240 pm (predicted)[1] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Covalent radius | 263–281 pm (extrapolated)[2] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Number | 54846-86-5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Naming | IUPAC systematic element name | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Isotopes of ununennium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Template:infobox ununennium isotopes does not exist | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

ఉనునెన్నియం, ఎకా-ఫ్రాంషియం అని కూడా పిలుస్తారు లేదా కేవలం మూలకం 119, పరమాణు సంఖ్య 119, చిహ్నం Uue తో రసాయన అంశం కలిగిన మూలకం. ఉనునెన్నియం, Uue తాత్కాలిక క్రమ IUPAC పేరు, చిహ్నమైన ఈ మూలకం శాశ్వత పేరు తదుపరి నిర్ణయించ బడుతుంది. అంతవరకు తాత్కాలిక క్రమ IUPAC పేరు, చిహ్నం మీదనే పిలుస్తారు.
ఆవర్తన పట్టికలో మూలకం స్థానం
[మార్చు]అంశాల ఆవర్తన పట్టికలో, ఇది ఒక s-బ్లాక్ మూలకం, క్షార మెటల్,, ఎనిమిదవ కాలంలో మొదటి మూలకం అయి ఉండాలి అని భావిస్తున్నారు,
తయారీ
[మార్చు]ఉనునెన్నియం ఇంకా కృత్రిమంగా తయారు చేయలేదు అత్యల్ప పరమాణు సంఖ్యతో మూలకం ఉంది. నేటికి, ఈ మూలకం సమీకరణకు అన్ని ప్రయత్నాలు విజయవంతం కాలేదు.
ఏడవ క్షారము లోహంగా దీని స్థానం. క్షారము లోహాలు, లిథియం, సోడియం, పొటాషియం, రుబీడియం, సీసియం,, ఫ్రాంషియం పోలిన లక్షణాలు కలిగి ఉంటుంది అని సూచిస్తుంది; అయితే, సాపేక్ష ప్రభావాలు ఆవర్తన ధోరణులు నేరుగా అప్లికేషన్ నుండి అంచనాకు భిన్నంగా దాని లక్షణాలు కొన్ని కారణం కావచ్చు. ఉదాహరణకు, ఉనునెన్నియం మూలకం సీసియం, ఫ్రాంషియం కంటే తక్కువ రియాక్టివ్ కలిగి ఉంటుందని భావిస్తున్నారు. ఇది పొటాషియం లేదా రుబీడియం ప్రవర్తనకు దగ్గరగా ఉంటుంది., ఇది క్షారము లోహాల యొక్క లక్షణం +1 ఆక్సీకరణ స్థితి చూపించాలి అయితే, అది కూడా ఏ ఇతర క్షారము మెటల్ తెలియని +3 ఆక్సీకరణ స్థితి చూపించినట్లు అంచనా.
చిత్రాలు
[మార్చు] |
 |
 |
మూలాలు
[మార్చు]- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 Hoffman, Darleane C.; Lee, Diana M.; Pershina, Valeria (2006). "Transactinides and the future elements". In Morss; Edelstein, Norman M.; Fuger, Jean (eds.). The Chemistry of the Actinide and Transactinide Elements (3rd ed.). Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Springer Science+Business Media. ISBN 978-1-4020-3555-5. ఉల్లేఖన లోపం: చెల్లని
<ref>ట్యాగు; "Haire" అనే పేరును విభిన్న కంటెంటుతో అనేక సార్లు నిర్వచించారు - ↑ 2.0 2.1 Bonchev, Danail; Kamenska, Verginia (1981). "Predicting the Properties of the 113–120 Transactinide Elements". Journal of Physical Chemistry. 85 (9). American Chemical Society: 1177–1186. doi:10.1021/j150609a021.
- ↑ Cao, Chang-Su; Hu, Han-Shi; Schwarz, W. H. Eugen; Li, Jun (2022). "Periodic Law of Chemistry Overturns for Superheavy Elements". ChemRxiv (preprint). doi:10.26434/chemrxiv-2022-l798p. Retrieved 16 November 2022.
- ↑ Fricke, Burkhard (1975). "Superheavy elements: a prediction of their chemical and physical properties". Recent Impact of Physics on Inorganic Chemistry. 21: 89–144. doi:10.1007/BFb0116498. Retrieved 4 October 2013.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Hofmann, Sigurd (2013). Overview and Perspectives of SHE Research at GSI SHIP. p. 23–32. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-00047-3.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Pyykkö, Pekka (2011). "A suggested periodic table up to Z ≤ 172, based on Dirac–Fock calculations on atoms and ions". Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. 13 (1): 161–8. Bibcode:2011PCCP...13..161P. doi:10.1039/c0cp01575j. PMID 20967377.
