WO2023184415A1 - Transimpedance amplifier having filtering function - Google Patents
Transimpedance amplifier having filtering function Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2023184415A1 WO2023184415A1 PCT/CN2022/084603 CN2022084603W WO2023184415A1 WO 2023184415 A1 WO2023184415 A1 WO 2023184415A1 CN 2022084603 W CN2022084603 W CN 2022084603W WO 2023184415 A1 WO2023184415 A1 WO 2023184415A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- terminal
- switching device
- coupled
- load
- amplifier
- Prior art date
Links
- 238000001914 filtration Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 61
- 230000003321 amplification Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 44
- 238000003199 nucleic acid amplification method Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 44
- 239000003990 capacitor Substances 0.000 claims description 63
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 claims description 10
- 230000000087 stabilizing effect Effects 0.000 claims description 8
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 43
- 238000013461 design Methods 0.000 description 15
- 101710170231 Antimicrobial peptide 2 Proteins 0.000 description 14
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 12
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 11
- 101710170230 Antimicrobial peptide 1 Proteins 0.000 description 9
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 description 8
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 description 8
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 description 8
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 8
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 7
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 description 6
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 5
- 230000003068 static effect Effects 0.000 description 5
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000009286 beneficial effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000011160 research Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000009471 action Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002238 attenuated effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000011161 development Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000005684 electric field Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000006872 improvement Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000010354 integration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000010355 oscillation Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H03—ELECTRONIC CIRCUITRY
- H03F—AMPLIFIERS
- H03F1/00—Details of amplifiers with only discharge tubes, only semiconductor devices or only unspecified devices as amplifying elements
- H03F1/32—Modifications of amplifiers to reduce non-linear distortion
Definitions
- the present application relates to the field of chip technology, and in particular to a transimpedance amplifier with filtering function.
- the traditional RF receiving chain includes circuits such as Low Noise Amplifier (LNA), Mixer, Low Pass Filter (LPF) and Variable Gain Amplifier (VGA).
- LNA Low Noise Amplifier
- LPF Low Pass Filter
- VGA Variable Gain Amplifier
- the number of amplifiers can be reduced by reducing the order of filters in the radio frequency receiving chain, thereby saving power consumption.
- a Transimpedance Amplifier (TIA) and LPF can be combined to save the number of amplifiers.
- LPF can use a 2-stage TIA, but it requires two amplifiers, and the radio frequency receiving link is usually a total of two in-phase (in-phase, I) links and a quadrature (quadrature, Q) link, referred to as I path and Q path, so there are a total of 4 amplifiers in the RF receiving chain.
- the amplifier consumes a large amount of static power, which is not conducive to reducing the power consumption of the entire link.
- the signal bandwidth of each filter in the LPF is determined by resistors and capacitors. For radio frequency receiving links with lower bandwidth, resistors and capacitors will occupy a considerable area, which is not conducive to cost reduction.
- Embodiments of the present application provide a transimpedance amplifier with a filtering function, which can be implemented with low area, low complexity, and low power consumption.
- a transimpedance amplifier with a filtering function has an open-loop structure and includes a differential input terminal and a differential output terminal.
- the differential input terminal includes a positive input terminal and a negative input terminal.
- the differential output terminal includes a positive output terminal. terminal and negative output terminal.
- the first signal path where the positive input terminal and the negative output terminal are located is coupled with a first amplification circuit and a first load; the second signal path where the negative input terminal and the positive output terminal are located is coupled with a second amplification circuit and a second load.
- a first amplifier is coupled between an amplifier circuit and a second amplifier circuit; the first amplifier circuit is used to control the current flowing through the first load; the second amplifier circuit is used to control the current flowing through the second load; the first amplifier , used to improve the filtering characteristics of the first signal path, and to improve the filtering characteristics of the second signal path.
- the first amplification circuit and the second amplification circuit can stabilize the currents at the positive input terminal and the negative input terminal of the transimpedance amplifier, so that the gain of the transimpedance amplifier is equal to the current multiplied by the current.
- the filtering characteristics of the transimpedance amplifier can be improved, for example, to exhibit second-order filtering characteristics, thereby realizing a transimpedance amplifier with filtering effect.
- the transimpedance amplifier with filtering function provided by this application occupies a smaller area, has lower complexity, and lower power consumption.
- a first amplification circuit and a first load connected in series are coupled to the first signal path where the positive input terminal and the negative output terminal are located;
- the first amplification circuit includes a first amplifier circuit connected across the first switching device. capacitor, a second capacitor, and a first current source coupled to the positive input terminal;
- a second amplification circuit and a second load in series are coupled to the second signal path where the negative input terminal and the positive output terminal are located;
- the second amplification circuit includes a transverse The third capacitor and the fourth capacitor are connected to the second switching device, and the second current source is coupled to the negative input terminal.
- the radio frequency receiving link When the open-group amplifier is used in a radio frequency receiving link, the radio frequency receiving link includes two parallel links, I and Q, with the phase difference between I and I being 90 degrees.
- the circuit structures of the I path and the Q path are the same, that is, the circuit structures of the second signal path and the first signal path are symmetrical.
- the first amplification circuit, the second amplification circuit and the first amplifier occupy a smaller area, the number of amplifiers is also reduced compared with the existing technology, and the power consumption is reduced.
- the first terminal of the first switching device is coupled to the first terminal of the first load
- the second terminal of the first switching device is coupled to the positive input terminal
- the first terminal of the first switching device is coupled to the first terminal of the first load.
- a first capacitor is connected across the second end of a switching device
- a second capacitor is connected across the second end of the first switching device and the third end of the first switching device
- the first output end of the first amplifier is coupled to the second between the first terminal of the capacitor and the third terminal of the first switching device
- the first input terminal of the first amplifier is coupled between the positive input terminal and the first terminal of the first current source
- the first terminal of the second switching device is coupled to the first terminal of the second load, the second terminal of the second switching device is coupled to the negative input terminal, and the first terminal of the second switching device and the second terminal of the second switching device span A third capacitor is connected, a fourth capacitor is connected across the second terminal of the second switching device and the third terminal of the second switching device, and the second output terminal of the first amplifier is coupled between the first terminal and the second terminal of the fourth capacitor.
- between the third terminal of the switching device, and the second input terminal of the first amplifier is coupled between the negative input terminal and the first terminal of the second current source; the second terminal of the first load and the second terminal of the second load are coupled;
- the second terminal of the first current source is coupled to the second terminal of the second current source.
- the first amplification circuit in this application includes a first switching device, a first capacitor and a second capacitor, which are used to stabilize the current flowing through the first signal path.
- the area occupied by capacitors and resistors is greatly reduced.
- the circuit structure of the present application has low complexity.
- the first current source is used to generate a first quiescent current, and the first quiescent current flows through the first load, so that the gain of the negative output terminal changes with the change of the resistance of the first load;
- the second current The source is used to generate a second quiescent current, and the second quiescent current flows through the second load, so that the gain of the positive output terminal changes as the resistance of the second load changes.
- the gain of the transimpedance amplifier can be equal to the quiescent current multiplied by the load resistance while the quiescent current at the input end of the transimpedance amplifier is stabilized. This allows the gain of the transimpedance amplifier to be adjusted by changing the value of the load resistor.
- the first amplifier circuit and the first current source can also control the stability of the signal current on the first signal path, so that the gain of the negative output terminal on the first signal path changes with the change of the resistance of the first load. Just change. The gain changes on the second signal path are the same.
- the second capacitor and the first switching device generate a first pole
- the first load and the first capacitor generate a second pole
- the fourth capacitor and the second switching device generate a third pole
- the second load and the third capacitor produces the fourth pole
- the first amplifier when the first capacitor is connected across the first terminal of the first switching device and the second terminal of the first switching device, a first zero point of the feedforward is generated; the first amplifier is used to control the first zero point of the feedforward. The position of the zero point is at a high frequency, so that the first signal path has a second-order filter characteristic; when the third capacitor is connected across the first end of the second switching device and the second end of the second switching device, a feedforward is generated the second zero point; the first amplifier is used to control the position of the second zero point at high frequency, so that the first signal path has second-order filter characteristics.
- this application uses the control of the first amplifier to push the position of the zero away, and the offset effect of the zero will not occur, and at high frequency, causing the transimpedance amplifier to exhibit second-order filtering characteristics.
- the transimpedance amplifier also includes a voltage stabilizing circuit, which is used to form negative feedback and control the voltage at the positive output terminal and the voltage at the negative output terminal to be consistent with the reference voltage.
- This design takes into account that once the gain required for the circuit is determined, the purpose is to keep the voltages at the positive and negative output terminals constant.
- the voltage at the negative output terminal can be kept constant by adjusting the current on the first signal path.
- the second-order TIA transimpedance amplifier with filter function
- the second-order TIA receives a large signal, such as a large current signal at the positive input terminal, the The signal will be compressed or not processed properly.
- the transconductance of the first switching device will also change with the current. Therefore, this application can add a voltage stabilizing circuit on the basis of the transimpedance amplifier with filtering function provided in the first aspect to form negative feedback and control the voltage of the positive output terminal and the voltage of the negative output terminal to be consistent with the reference voltage.
- the voltage stabilizing circuit includes a third switching device and a fourth switching device coupled in series, and also includes a second amplifier; a signal path where the third switching device and the fourth switching device are located, and a first load and a third switching device.
- the signal path where the two loads are located is coupled in parallel between the positive output terminal and the negative output terminal;
- the output terminal of the second amplifier is coupled between the gate of the third switching device and the gate of the fourth switching device;
- the first terminal of the second amplifier The input terminal is coupled between the first load and the second load coupled in series, and the second input terminal of the second amplifier is used to input the reference voltage.
- a second aspect provides a radio frequency receiving device, which includes a transimpedance amplifier with a filtering function as described in the first aspect or any possible design of the first aspect.
- a third aspect provides a chip, which includes the radio frequency receiving device as described in the second aspect.
- a fourth aspect provides a communication device, which includes the chip described in the third aspect.
- any of the radio frequency receiving devices, chips, communication equipment, etc. provided above can be applied to the transimpedance amplifier with filtering function provided above. Therefore, the beneficial effects it can achieve can be referred to the corresponding The beneficial effects of the method will not be repeated here.
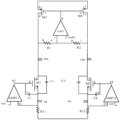
- Figure 1 is a schematic structural diagram of a traditional radio frequency receiving link provided by an embodiment of the present application
- Figure 2 is a schematic circuit diagram of a 2-stage TIA with LPF provided by an embodiment of the present application
- Figure 3 is a schematic circuit diagram of a TIA provided by an embodiment of the present application.
- Figure 4 is a schematic circuit diagram of a transimpedance amplifier TIA with filtering function provided by an embodiment of the present application
- Figure 5 is a schematic circuit diagram of a transimpedance amplifier TIA with filtering function provided by an embodiment of the present application
- Figure 6 is a schematic diagram of a TIA frequency response curve with filtering function provided by an embodiment of the present application.
- Figure 7 is a schematic diagram of a 2-stage TIA circuit provided by an embodiment of the present application.
- Figure 8 is a schematic diagram of a 2-stage TIA circuit provided by an embodiment of the present application.
- Figure 9 is a schematic diagram of a 2-stage TIA circuit provided by an embodiment of the present application.
- Figure 10 is a schematic diagram of a 2-stage TIA circuit provided by an embodiment of the present application.
- FIG. 11 is a schematic structural diagram of a system chip provided by an embodiment of the present application.
- LPF Remove unnecessary high-frequency components from the input signal and remove high-frequency interference.
- TIA It is a type of amplifier.
- VGA It is a key module in the radio frequency reception (ReceiveX, RX) link.
- the automatic gain control circuit composed of a feedback loop provides constant signal power to the analog-to-digital converter (Analog to Digital Converter, ADC).
- ADC Analog to Digital Converter
- VGA plays a vital role in the analog front-end of the wireless communication receiver/transmitter.
- the VGA at the fundamental frequency compensates for the gain attenuation of the RF module and IF module. And the VGA amplifies the output signal to the amplitude required by the ADC.
- the LNA When a weak signal is amplified, the noise of the amplifier itself may seriously interfere with the signal, so it is hoped to reduce this noise.
- the LNA is an amplifier with a very low noise figure. It is generally used as a high-frequency or medium-frequency preamplifier for various types of radio receivers (such as WiFi modules in mobile phones, computers, or iPads), as well as amplification circuits for high-sensitivity electronic detection equipment.
- Amplifier especially an instrument that uses transistors or tubes to amplify electronic signals.
- first and second are used for descriptive purposes only and cannot be understood as indicating or implying relative importance or implicitly indicating the quantity of indicated technical features. Therefore, features defined as “first” and “second” may explicitly or implicitly include one or more of these features. In the description of this embodiment, unless otherwise specified, “plurality” means two or more.
- the traditional RF receiving chain includes circuits such as LNA, Mixer, LPF, VGA, local oscillator (LO) and ADC.
- the LNA can superimpose the RF signal obtained by low-noise amplification of the signal received from the antenna and the mixed signal output by the LO and output it to the Mixer; the Mixer down-converts the received superimposed signal to an intermediate frequency and outputs it to the LPF.
- LPF filters the received intermediate frequency signal, removes high-frequency interference, and outputs the high-frequency-removed signal to VGA
- VGA amplifies the received signal and provides constant signal power to the ADC
- ADC Perform analog-to-digital conversion on the signal, and output the resulting digital signal to other modules of the radio frequency receiving link for processing, such as output to the processing module for processing.
- the number of amplifiers in the link can be reduced by reducing the order of the filter.
- the number of amplifiers here refers to the number of amplifiers in the LPF.
- the 2-stage TIA shown in Figure 2 is a design of LPF. It is understandable that two amplifiers are needed in this 2-stage TIA.
- the radio frequency receiving chain usually includes two channels, I and Q, if Figure 1 shows one of the I or Q, the two channels There are four amplifiers in the LPF, and the amplifiers consume a lot of static power, which is not conducive to reducing the power consumption of the entire radio frequency receiving link.
- this solution adopts a closed-loop structure and has good linearity, a certain gain control can be achieved by changing the resistance in the second-order TIA, but the implementation is more complicated.
- the signal bandwidth of each amplifier in the LPF is determined by the resistors and capacitors in the LPF. For a low-bandwidth radio frequency receiving link, the resistors and capacitors will occupy a considerable area, which is not conducive to cost reduction.
- Figure 3 shows the structure of another TIA, which adopts an open-loop structure, and the power consumption is reduced compared to the TIA with a closed-loop structure.
- inp and inn are two current input terminals
- outn and outp are two voltage output terminals
- Vref is a reference voltage input terminal.
- the TIA shown in Figure 3 can achieve common mode control and increase the output impedance.
- the power consumption of the TIA has nothing to do with the signal bandwidth, and lower power consumption can be designed.
- the input impedance is the reciprocal of the transconductance of the NMOS transistor 31 and NMOS transistor 32 at the input end.
- the input impedance is designed to be too low, the input current of the TIA needs to be increased, and the power consumption will increase. Therefore, the input impedance cannot be designed too low.
- the TIA shown in Figure 3 has no filtering function but only a signal amplification function. If there is no filtering function, when using the TIA shown in Figure 3, it is necessary to design a second-order or higher filter in the subsequent stage of the TIA. The overall power consumption of the radio frequency receiving link system is not reduced. In addition, this solution requires a common-mode stable amplifier 33, which also adds additional power consumption.
- this application proposes an LPF circuit design to address the problems of large power consumption, high cost, and high complexity in the design of LPF in the radio frequency receiving link.
- This application designs a circuit for LPF that can simultaneously realize the TIA function of a second-order filter, in order to reduce the power consumption, cost and area of the LPF.
- the transimpedance amplifier with filtering function provided by this application can be applied to the LPF of the radio frequency receiving link.
- the radio frequency receiving link includes two parallel links, I and Q.
- the phase difference between I and I is 90 degrees.
- the circuit structures of the I path and the Q path are the same, and the embodiment of this application introduces the circuit structure of one of them.
- radio frequency receiving link can be used in radio frequency receiving systems, which is suitable for both high-bandwidth systems, such as WiFi, and low-bandwidth and low-power consumption systems, such as Bluetooth (BlueTooth, BLE) systems.
- high-bandwidth systems such as WiFi
- low-bandwidth and low-power consumption systems such as Bluetooth (BlueTooth, BLE) systems.
- the radio frequency receiving link can be used in a radio frequency transceiver chip.
- the radio frequency transceiver chip can be used in terminal equipment and network equipment, for example, and can also be used in other equipment that can transmit and receive signals. This application does not limit it.
- the transimpedance amplifier by coupling a first amplification circuit between the positive input terminal and the negative output terminal, and coupling a second amplification circuit between the negative input terminal and the positive output terminal, the transimpedance amplifier can be The currents at the positive and negative inputs are stable, so that the gain of the transimpedance amplifier can be adjusted by changing the resistance of the load in the case where the gain of the transimpedance amplifier is equal to the current times the resistance of the load.
- the filtering characteristics of the transimpedance amplifier can be improved, for example, it can exhibit second-order filtering characteristics, thereby realizing a transimpedance amplifier with filtering effect.
- the transimpedance amplifier with filtering function provided by this application occupies a smaller area, has lower complexity and lower power consumption.
- the transimpedance amplifier with filtering function provided by this application is introduced below.
- this application provides a transimpedance amplifier TIA with a filtering function.
- the TIA has a switching structure and includes a differential input terminal and a differential output terminal.
- the differential input terminal includes a positive input terminal inp and a negative input terminal inn.
- the output terminal includes a positive output terminal outp and a negative output terminal outn.
- a first amplification circuit and a first load are coupled to the first signal path where the positive input terminal inp and the negative output terminal outn are located, and a second amplification circuit is coupled to the second signal path where the negative input terminal inn and the positive output terminal outp are located.
- circuit and a second load a first amplifier AMP1 is coupled between the first amplification circuit and the second amplification circuit;
- the first amplifier circuit is used to control the current flowing through the first load
- the second amplifier circuit is used to control the current flowing through the second load
- the first amplifier AMP1 is used to improve the filtering characteristics of the first signal path and to improve the filtering characteristics of the second signal path.
- the first load and the second load are resistors.
- the first amplification circuit and the second amplification circuit can stabilize the currents at the positive input terminal and the negative input terminal of the transimpedance amplifier, thereby increasing the gain of the transimpedance amplifier.
- the gain of the transimpedance amplifier on the first signal path is adjusted by changing the resistance of the first load
- the gain of the transimpedance amplifier on the first signal path is adjusted by changing the resistance of the second load.
- the gain of the transimpedance amplifier on the second signal path is adjusted through the first amplifier, the filtering characteristics of the transimpedance amplifier can be improved, for example, to exhibit second-order filtering characteristics, thereby realizing a transimpedance amplifier with filtering effect.
- the signal bandwidth of the filter is determined by resistors and capacitors in the prior art. For systems with low bandwidth, capacitors and resistors occupy a considerable area.
- This application Through the coupling of the first amplification circuit, the second amplification circuit and the first amplifier, a transimpedance amplifier with filtering function can be realized, which occupies a smaller area, has lower complexity and lower power consumption.
- the number of amplifiers required in a single I or Q path is smaller than in the existing technology. For example, in the filter circuit of Figure 2, a single I or Q path requires two amplifiers. In the filter provided by this application, a single I Channel or Q channel only requires one amplifier, and the power consumption is low.
- the first amplification circuit and the first load in series are coupled to the first signal path where the positive input terminal inp and the negative output terminal outn are located, and the first load is connected in series with a resistor.
- R1 shows;
- the first amplification circuit includes a first capacitor C1 and a second capacitor C2 connected across the first switching device M1, and a first current source S1 coupled with the positive input terminal inp;
- the second amplifier circuit and the second load in series are coupled to the second signal path where the negative input terminal inn and the positive output terminal outp are located.
- the second load is represented by a resistor R2; the second The amplifying circuit includes a third capacitor C3 and a fourth capacitor C4 connected across the second switching device, and a second current source S2 coupled to the negative input terminal inn.
- the first load is the first resistor R1 and the second load is the second resistor R2.
- the first terminal a of the first switching device M1 is coupled to the first terminal b of the first resistor R1
- the second terminal c of the first switching device M1 is coupled to the positive input terminal inp
- the first terminal c of the first switching device M1 is coupled to the positive input terminal inp.
- the first terminal a of a switching device and the second terminal c of the first switching device M1 are connected across the first capacitor C1, and the second terminal c of the first switching device M1 and the third terminal d of the first switching device M1 are connected across There is a second capacitor C2, the first output terminal e of the first amplifier AMP1 is coupled between the first terminal f of the second capacitor C2 and the third terminal d of the first switching device M1, and the first input terminal of the first amplifier M1 g is coupled between the positive input terminal inp and the first terminal A of the first current source S1.
- the first terminal h of the second switching device M2 and the first terminal i of the second resistor R2 are coupled, and the second switch
- the second terminal j of the device M2 is coupled to the negative input terminal inn.
- the first terminal h of the second switching device M2 and the second terminal j of the second switching device M2 are connected across a third capacitor C3.
- the second terminal j and the third terminal k of the second switching device M2 are connected across a fourth capacitor C4, and the second output terminal l of the first amplifier AMP1 is coupled between the first terminal m of the fourth capacitor C4 and the second switching device M2.
- between the third terminal k, and the second input terminal n of the first amplifier AMP2 is coupled between the negative input terminal inn and the first terminal B of the second current source S2;
- the second terminal o of the first resistor R1 is coupled to the second terminal p of the second resistor R2;
- the second terminal C of the first current source S1 and the second terminal D of the second current source S2 are coupled.
- the positive input terminal inp and the negative input terminal inn are coupled with the two output terminals of the mixer Mixer, and are used to receive the current output by the two output terminals of the Mixer.
- the negative output terminal outn and the positive output terminal outp are used to couple with the two input terminals of the VGA or ADC of the subsequent stage.
- the switching devices in this application may be MOS transistors, specifically PMOS or NMOS, etc.
- both the first current source S1 and the second current source S2 can provide a stable current, and the stable current can be understood as the quiescent current required by the TIA with a filtering function. In this way, the input end of the TIA can be made to have low impedance.
- the gain output by the terminal outn is the stable current generated by the first current source S1 multiplied by the first resistor R1
- the gain output by the positive output terminal outp is the stable current generated by the second current source S2 multiplied by the second resistor R2.
- the first current source S1 is used to generate a stable first quiescent current, and the first quiescent current flows through the first resistor R1, so that the gain of the negative output terminal outn changes with the change of the resistance of the first resistor R1.
- the second current source S2 is used to generate a stable second quiescent current.
- the second quiescent current flows through the second resistor R2, so that the gain of the positive output terminal outp changes with the change of the resistance of the second resistor R2.
- the second capacitor C2 and the first switching device M1 on the first signal path, the second capacitor C2 and the first switching device M1 will generate the first pole, and the first resistor R1 and the first capacitor C1 will A second pole is generated, forming a second-order filter. Since the first capacitor C1 is connected across the first signal path, a feedforward zero point will be formed. However, due to the feedback effect of the first amplifier AMP1, the current flowing through the first signal path and the second signal path can remain unchanged, so that there is always a gain with TIA, and the zero point is always at a high frequency. The zero points do not cancel the poles, and the TIA still exhibits second-order filtering characteristics. Therefore, a TIA with a filtering function can maintain the second-order filtering characteristics well while changing the gain.
- the zero point can be understood as, when the signal input amplitude of the TIA is not zero and the input frequency causes the TIA output to be zero, the input frequency value is the zero point.
- the pole can be understood as, when the input amplitude of TIA is not zero and the input frequency makes the output of TIA infinite (TIA stability is destroyed and oscillation occurs), this frequency value is the pole. Poles can be used to suppress noise, and zeros can be used to worsen noise. The poles and zeros are in pairs, and a zero cancels a pole.
- This application uses the control of the first amplifier AMP1 to push the position of the zero point away, and the offset effect of the zero point will not occur, and at high frequencies, the TIA still exhibits second-order filter characteristics.
- FIG. 6 shows the configuration of the present application.
- the TIA frequency response curve of the filter function includes curve 1, curve 2 and curve 3.
- the horizontal axis represents the frequency of the signal received by the TIA with filtering function from the mixer, in Hz
- the vertical axis represents the gain on the first signal path in the TIA with filtering function, that is, the current value on the first signal path and
- the voltage value obtained by multiplying the resistance of the first resistor R1 is in V or dB, and dB is the gain in decibels.
- the gain of TIA when receiving signals is about 74V
- the gain is approximately 86V.
- the gain of the TIA at the negative output terminal outn can be adjusted.
- the gain adjustment for the second signal path is similar to that for the first signal path.
- the position of the first pole is determined by the capacitance C2 of the second capacitor C2 and the transconductance gm of the first switching device M1.
- the position of the first pole remains unchanged.
- the position of the second pole is determined by the resistance of the first resistor R1 and the capacitance of the first capacitor C1.
- the second pole The position of the pole remains unchanged.
- the bandwidth of the TIA remains unchanged.
- the frequency of the current signal received by the positive input terminal inp remains unchanged, for example, when the frequency is 10 3 Hz
- the resistance of the first resistor R1 is increased
- the negative The gain of the output terminal outn increases from 74V to 84V. In this way, the TIA's gain can be changed while keeping the TIA's bandwidth constant.
- curve 1 When the frequency of the current signal is less than or equal to 10 6 Hz, curve 1, curve 2 and curve 3 are flat curves, that is, in the frequency range where the frequency of the current signal is less than or equal to 10 6 Hz, the gain of the TIA can be changed. At the same time, the bandwidth of the TIA remains unchanged, and the signals in the frequency range less than or equal to 10 6 Hz are amplified through the gain and output to the subsequent module, such as VGA.
- the gain of the TIA decreases sharply.
- the current signal with a frequency greater than 10 6 Hz is attenuated.
- the signal with a frequency greater than 10 6 Hz cannot be output to the TIA's subsequent module while achieving gain amplification. .
- the TIA with filtering function provided by this application maintains the second-order filtering characteristics while changing the TIA gain.
- the stable current provided by the first current source S1 and the stable current provided by the second current source S2 can control the current input terminals (inn and inp) of the TIA through the reference voltage vref. voltage, and at the same time generate the quiescent current required by the TIA through the reference voltage vref, that is, the first quiescent current and the second quiescent current mentioned above.
- the first amplifier AMP1 is used to form negative feedback, the current input end of the TIA can be made to exhibit low resistance.
- the gain of the TIA is equal to the small signal current multiplied by the load resistor (R1 and R2), the gain of the TIA can be adjusted by changing the value of the load resistor.
- the 2-stage TIA provided in Figure 7 is another implementation of the 2-stage TIA circuit provided in Figure 5 of the present application.
- Figure 7 shows two amplifiers AMP11 and AMP12, as well as resistors R11 and R12.
- One input terminal of the amplifier AMP11 is used to input the reference voltage vref, and an input terminal 61 and an output terminal 62 are connected across the first switching device M1
- An input terminal of the amplifier AMP12 is used to input the reference voltage vref between one terminal d and the positive input terminal inp.
- An input terminal 63 and an output terminal 64 are connected across one terminal k of the second switching device M2 and the negative input terminal inn.
- resistor R11 One end of the resistor R11 is coupled to the positive input terminal inp, the other end is coupled to the resistor R12, and the other end of the resistor R12 is coupled to the negative input terminal inn.
- the amplifiers AMP11 and AMP12 in Figure 7 and the resistors R11 and R12 can be replaced by AMP1, the first current source S1 and the second current source S2 in Figure 5.
- the present application can input the reference voltage vref to an input terminal of the amplifier AMP11.
- the ratio of the reference voltage vref to the resistance of the resistor R11 is the first quiescent current on the first signal path.
- the first quiescent current remains unchanged.
- the common mode voltage of the positive input terminal inp can be designed to be lower, and the switch size of the mixer Mixer coupled to the positive input terminal inp can be designed to be lower, thereby reducing the area occupied by the device.
- the positive input terminal inp When the 2-stage TIA receives a signal from the mixer Mixer, the positive input terminal inp will receive the signal current, and the positive input terminal inp will generate a voltage.
- the amplifier AMP11 When the voltage of the positive input terminal inp rises, the amplifier AMP11 will compare the reference voltage vref and The voltage difference at the positive input terminal inp is amplified.
- the amplified voltage difference is input to the input terminal of the first switching device M1, the first switching device M1 will generate a voltage to suppress the voltage rise at the positive input terminal inp, so that the reference The voltage difference between the voltage vref and the positive input terminal inp decreases, which will eventually make the reference voltage vref and the voltage of the positive input terminal inp the same, making the signal current of the positive input terminal inp fixed.
- the first switching device M1 will form negative feedback, causing the positive input terminal inp to exhibit low resistance.
- the first signal The path is a low resistance path.
- the voltage value of the reference voltage vref of the amplifier AMP11 the voltage value of the positive input terminal inp can be controlled, so that the voltage value of the positive input terminal inp is stabilized, so that the voltage value flowing through the first signal path to the third signal path is stabilized.
- a small signal current in resistor R1 is stable.
- the gain of the second-order TIA can be adjusted by changing the resistance of the first resistor R1 on the first signal path.
- the voltage of the negative input terminal inn can also be controlled to stabilize the small signal current of the second resistor R2 on the second signal path, thereby achieving adjustment.
- the resistance of the second resistor R2 is used to adjust the gain of the second-order TIA.
- the 2-order TIA shown in Figure 7 also has 2-order filter characteristics.
- the second-order TIA When the second-order TIA receives a large signal, for example, when the positive input terminal outp receives a large current signal, the signal will are compressed or cannot be processed normally. However, while adjusting the first quiescent current, the transconductance gm of the first switching device M1 will also change with the first quiescent current.
- this application also provides a circuit architecture of a 2-stage TIA, as shown in Figure 8. This application improves on the circuit of Figure 4.
- the transimpedance amplifier also includes a voltage stabilizing circuit, which is used to form negative feedback and control the voltage of the positive output terminal outp and the voltage of the negative output terminal outn to be consistent with the reference The voltage vcom remains consistent.
- the voltage stabilizing circuit includes a third switching device M3 and a fourth switching device M4 coupled in series, and also includes a second amplifier AMP2;
- the signal path where the third switching device M3 and the fourth switching device M4 are located and the signal path where the first load R1 and the second load R2 are located are coupled in parallel between the positive output terminal outp and the Between the negative output terminal outn;
- the output terminal q of the second amplifier AMP2 is coupled between the gate of the third switching device M3 and the gate of the fourth switching device M4; the first input terminal t of the second amplifier AMP2 is coupled between Between the first load R1 and the second load R2 coupled in series, the second input terminal of the second amplifier AMP2 is used to input the reference voltage vcom.
- the output terminal q of the second amplifier AMP2 is coupled between the first terminal r of the third switching device M3 and the first terminal s of the fourth switching device M4, and the first input terminal of the second amplifier AMP2
- the coupling t is between the second terminal o of the first resistor R1 and the second terminal p of the second resistor R2, and the second input terminal of the second amplifier AMP2 inputs the reference voltage vcom;
- the second terminal u of the third switching device M3 is coupled to the second terminal v of the fourth switching device M4; the third terminal w of the third switching device M3 is coupled to the first terminal b of the first resistor R1.
- the fourth switching device M4 The third terminal x is coupled to the first terminal i of the second resistor R2.
- the first resistor R1 and the second resistor R2 are connected in parallel to the circuit, and negative feedback can be formed through the second amplifier AMP2 and the third switching device M3 and the fourth switching device M4, so that the output common mode voltage of the TIA is always maintained.
- vcom or in other words, the voltages of the negative output terminal outn and the positive output terminal outp of the TIA are always maintained at vcom. In this way, even if the first resistor R1 or the second resistor R2 is switched, or the resistance value of the first resistor R1 or the second resistor R2 is changed, the output common mode voltage of the TIA remains unchanged.
- the second amplifier AMP2 can amplify the voltage error.
- the output terminal of the second amplifier AMP2 outputs current to the third switching tube M3 and the fourth switching tube M4. After the switch M3 is turned on, the current flows through the first resistor R1. After the fourth switch M4 is turned on, the current flows through the second resistor R2.
- the voltage at the second terminal o of the first resistor R1 is compared with the reference voltage vcom. , the voltage at the second terminal p of the second resistor R2 will also be compared with the reference voltage.
- the second amplifier AMP2 will continue to amplify the voltage error and output it.
- the voltage of the second terminal o of the first resistor R1 and the voltage of the second terminal p of the second resistor R2 will be consistent with the reference voltage vcom.
- the voltages of the negative output terminal outn and the positive output terminal outp are consistent with the reference voltage vcom.
- the first quiescent current does not flow into both ends of the first resistor R1
- the second quiescent current does not flow into both ends of the second resistor R2. current, there is no voltage drop across the first resistor R1 and the second resistor R2, and no voltage drop will offset the voltage margin.
- both the first resistor R1 and the second resistor R2 have static current flowing through them, and there will be a voltage drop, which reduces the working range of the second-order TIA circuit.
- Figure 10 can be understood as a 2-stage TIA circuit obtained by combining Figures 7 and 9.
- the second-order TIA provided by this application compared with the number of amplifiers required by the second-order TIA provided in Figure 2, the number of amplifiers required by the second-order TIA provided by this application is reduced, and the power consumption on the link is reduced. And the bandwidth control has changed from pure resistance and capacitance control to transconductance gm (such as M1) and capacitance (such as capacitance C1 and C2). Compared with the area occupied by resistors and capacitors, switching devices such as MOS tubes and capacitors occupy a smaller area. Small. Moreover, compared with the TIA provided in Figure 3, the second-order TIA provided by this application also has a filtering function and is less complex.
- the embodiment of the present application also provides a system chip.
- the system chip 110 includes: a processor and a transceiver.
- the transceiver may include, for example, an input/output interface, pins or circuits.
- the circuit may It includes the radio frequency receiving link in this application, and the radio frequency receiving link includes the transimpedance amplifier with filtering function in this application.
- the processor executes computer instructions.
- the transimpedance amplifier in any of the radio frequency receiving links provided in the above embodiments of the present application may be included in the transceiver.
- system chip may also include memory.
- the memory is a storage unit within the chip, such as a register, cache, etc.
- the memory may also be a storage unit located outside the chip in a communication device (such as a terminal device or network device), such as a read-only memory (read only memory (ROM) or other types of static storage devices that can store static information and instructions, random access memory (random access memory, RAM), etc.
- a communication device such as a terminal device or network device
- ROM read-only memory
- RAM random access memory
- the processor mentioned in any of the above places can be a CPU, microprocessor, ASIC, etc.
- the processor and the memory can be decoupled, respectively arranged on different physical devices, and connected through wired or wireless means to realize the respective functions of the processing unit and the memory, so as to support the system chip to implement the above embodiments.
- Various functions are possible.
- the processor and memory may be coupled on the same device.
- the processor in the embodiment of the present application can be a central processing unit (CPU for short), and the processor can also be other general-purpose processors, digital signal processing (Digital Signal Processing, DSP for short), dedicated Integrated circuits (Application Specific Integrated Circuit, ASIC), field-programmable gate array (Field-Programmable Gate Array, FPGA) or other programmable logic devices, discrete gate or transistor logic devices, discrete hardware components, etc.
- a general-purpose processor may be a microprocessor or the processor may be any conventional processor, etc.
- system chip provided by this application can be applied to a variety of terminal equipment and network equipment.
- the disclosed devices and methods can be implemented in other ways.
- the device embodiments described above are only illustrative.
- the division of modules or units is only a logical function division.
- there may be other division methods for example, multiple units or components may be The combination can either be integrated into another device, or some features can be omitted, or not implemented.
- the coupling or direct coupling or communication connection between each other shown or discussed may be through some interfaces, and the indirect coupling or communication connection of the devices or units may be in electrical, mechanical or other forms.
- the units described as separate components may or may not be physically separated.
- the components shown as units may be one physical unit or multiple physical units, that is, they may be located in one place, or they may be distributed to multiple different places. . Some or all of the units can be selected according to actual needs to achieve the purpose of the solution of this embodiment.
- each functional unit in each embodiment of the present application can be integrated into one processing unit, each unit can exist physically alone, or two or more units can be integrated into one unit.
- the above integrated units can be implemented in the form of hardware or software functional units.
- the integrated unit is implemented in the form of a software functional unit and sold or used as an independent product, it may be stored in a readable storage medium.
- the technical solutions of the embodiments of the present application are essentially or contribute to the existing technology, or all or part of the technical solution can be embodied in the form of a software product, and the software product is stored in a storage medium , including several instructions to cause a device (which can be a microcontroller, a chip, etc.) or a processor to execute all or part of the steps of the methods described in various embodiments of this application.
- the aforementioned storage media include: U disk, mobile hard disk, ROM, RAM, magnetic disk or optical disk and other media that can store program codes.
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Nonlinear Science (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Amplifiers (AREA)
Abstract
The present application relates to the technical field of chips and discloses a transimpedance amplifier having a filtering function, for use in enabling the transimpedance amplifier having the filtering function to be small in occupied area, low in complexity, and low in power consumption. The transimpedance amplifier is of an open-loop structure and comprises a differential input end and a differential output end, the differential input end comprising a positive input end and a negative input end, and the differential output end comprising a positive output end and a negative output end. A first amplification circuit and a first load are coupled to a first signal path where the positive input end and the negative output end are located, a second amplification circuit and a second load are coupled to a second signal path where the negative input end and the positive output end are located, and a first amplifier is coupled between the first amplification circuit and the second amplification circuit; the first amplification circuit is used for controlling current flowing through the first load; the second amplification circuit is used for controlling current flowing through the second load; and the first amplifier is used for improving the filtering characteristic of the first signal path and improving the filtering characteristic of the second signal path.
Description
本申请涉及芯片技术领域,尤其涉及一种具有滤波功能的跨阻放大器。The present application relates to the field of chip technology, and in particular to a transimpedance amplifier with filtering function.
传统的射频接收链路包括低噪声放大器(Low Noise Amplifier,LNA)、混频器(Mixer)、低通滤波器(Low Pass Filter,LPF)和可变增益放大器(Variable Gain Amplifier,VGA)等电路。随着工艺的发展,以及功能增加、集成度的提高,追求低功耗射频接收链路一直是研究的方向。The traditional RF receiving chain includes circuits such as Low Noise Amplifier (LNA), Mixer, Low Pass Filter (LPF) and Variable Gain Amplifier (VGA). . With the development of technology, the increase of functions and the improvement of integration, the pursuit of low-power radio frequency receiving links has always been the direction of research.
常用的方法中,可通过降低射频接收链路中滤波器的阶数,达到降低放大器数量,从而节省功耗的目的。或者还可将跨阻放大器(Transimpedance Amplifier,TIA)和LPF结合,达到节省放大器数量的目的。例如,LPF可采用2阶TIA,但是需要两个放大器,而射频接收链路通常为同相的(in-phase,I)链路和正交的(quadrature,Q)链路共两路,简称I路和Q路,因此射频接收链路中共4个放大器。放大器会消耗较大的静态功耗,不利于降低整个链路功耗。而且该方法中,LPF中的每个滤波器的信号带宽由电阻和电容决定,对于带宽较低的射频接收链路,电阻和电容会占据相当大的面积,不利于降低成本。Among the commonly used methods, the number of amplifiers can be reduced by reducing the order of filters in the radio frequency receiving chain, thereby saving power consumption. Alternatively, a Transimpedance Amplifier (TIA) and LPF can be combined to save the number of amplifiers. For example, LPF can use a 2-stage TIA, but it requires two amplifiers, and the radio frequency receiving link is usually a total of two in-phase (in-phase, I) links and a quadrature (quadrature, Q) link, referred to as I path and Q path, so there are a total of 4 amplifiers in the RF receiving chain. The amplifier consumes a large amount of static power, which is not conducive to reducing the power consumption of the entire link. Moreover, in this method, the signal bandwidth of each filter in the LPF is determined by resistors and capacitors. For radio frequency receiving links with lower bandwidth, resistors and capacitors will occupy a considerable area, which is not conducive to cost reduction.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本申请实施例提供一种具有滤波功能的跨阻放大器,能够使得具有滤波功能的跨阻放大器以低面积、低复杂度和低功耗实现。Embodiments of the present application provide a transimpedance amplifier with a filtering function, which can be implemented with low area, low complexity, and low power consumption.
为达到上述目的,本申请实施例采用如下技术方案。In order to achieve the above objectives, the embodiments of this application adopt the following technical solutions.
第一方面,提供一种具有滤波功能的跨阻放大器,跨阻放大器为开环结构,包括差分输入端和差分输出端,差分输入端包括正输入端和负输入端,差分输出端包括正输出端和负输出端。正输入端和负输出端所在的第一信号通路上耦合有第一放大电路和第一负载;负输入端和正输出端所在的第二信号通路上耦合有第二放大电路和第二负载,第一放大电路和第二放大电路间耦合有第一放大器;第一放大电路,用于控制流经第一负载的电流;第二放大电路,用于控制流经第二负载的电流;第一放大器,用于提升第一信号通路的滤波特性,以及提升第二信号通路的滤波特性。In the first aspect, a transimpedance amplifier with a filtering function is provided. The transimpedance amplifier has an open-loop structure and includes a differential input terminal and a differential output terminal. The differential input terminal includes a positive input terminal and a negative input terminal. The differential output terminal includes a positive output terminal. terminal and negative output terminal. The first signal path where the positive input terminal and the negative output terminal are located is coupled with a first amplification circuit and a first load; the second signal path where the negative input terminal and the positive output terminal are located is coupled with a second amplification circuit and a second load. A first amplifier is coupled between an amplifier circuit and a second amplifier circuit; the first amplifier circuit is used to control the current flowing through the first load; the second amplifier circuit is used to control the current flowing through the second load; the first amplifier , used to improve the filtering characteristics of the first signal path, and to improve the filtering characteristics of the second signal path.
本申请提供的具有滤波功能的跨阻放大器中,通过第一放大电路和第二放大电路,可使得跨阻放大器的正输入端和负输入端的电流稳定,从而在跨阻放大器的增益等于电流乘以第一负载(或第二负载)的电阻的基础上,通过改变第一负载的阻值调整跨阻放大器在第一信号通路上的增益,以及通过改变第二负载的阻值调整跨阻放大器在第二信号通路上的增益。而且,通过第一放大器,可提升跨阻放大器的滤波特性,例如呈现2阶滤波特性,从而实现具有滤波作用的跨阻放大器。此外,本申请提供的具有滤波作用的跨阻放大器,占用面积较小,复杂度较低,功耗也较低。In the transimpedance amplifier with filtering function provided by the present application, the first amplification circuit and the second amplification circuit can stabilize the currents at the positive input terminal and the negative input terminal of the transimpedance amplifier, so that the gain of the transimpedance amplifier is equal to the current multiplied by the current. Based on the resistance of the first load (or the second load), adjusting the gain of the transimpedance amplifier on the first signal path by changing the resistance of the first load, and adjusting the transimpedance amplifier by changing the resistance of the second load Gain on the second signal path. Moreover, through the first amplifier, the filtering characteristics of the transimpedance amplifier can be improved, for example, to exhibit second-order filtering characteristics, thereby realizing a transimpedance amplifier with filtering effect. In addition, the transimpedance amplifier with filtering function provided by this application occupies a smaller area, has lower complexity, and lower power consumption.
在一种可能的设计中,正输入端和负输出端所在的第一信号通路上耦合有串联的第一放大电路和第一负载;第一放大电路包括跨接在第一开关器件的第一电容和第二 电容,以及与正输入端耦合的第一电流源;负输入端和正输出端所在的第二信号通路上耦合有串联的第二放大电路和第二负载;第二放大电路包括跨接在第二开关器件的第三电容和第四电容,以及与负输入端耦合的第二电流源。In one possible design, a first amplification circuit and a first load connected in series are coupled to the first signal path where the positive input terminal and the negative output terminal are located; the first amplification circuit includes a first amplifier circuit connected across the first switching device. capacitor, a second capacitor, and a first current source coupled to the positive input terminal; a second amplification circuit and a second load in series are coupled to the second signal path where the negative input terminal and the positive output terminal are located; the second amplification circuit includes a transverse The third capacitor and the fourth capacitor are connected to the second switching device, and the second current source is coupled to the negative input terminal.
该开组放大器用于射频接收链路时,射频接收链路包括I路和Q路并行的两个链路,I路和I路的相位差90度。I路和Q路的电路结构相同,即第二信号通路和第一信号通路的电路结构是对称的。而且,本申请中第一放大电路和第二放大电路以及第一放大器占用的面积较小,放大器数量也相较现有技术有所降低,功耗减小。When the open-group amplifier is used in a radio frequency receiving link, the radio frequency receiving link includes two parallel links, I and Q, with the phase difference between I and I being 90 degrees. The circuit structures of the I path and the Q path are the same, that is, the circuit structures of the second signal path and the first signal path are symmetrical. Moreover, in this application, the first amplification circuit, the second amplification circuit and the first amplifier occupy a smaller area, the number of amplifiers is also reduced compared with the existing technology, and the power consumption is reduced.
在一种可能的设计中,第一开关器件的第一端和第一负载的第一端耦合,第一开关器件的第二端与正输入端耦合,第一开关器件的第一端和第一开关器件的第二端跨接有第一电容,第一开关器件的第二端和第一开关器件的第三端跨接有第二电容,第一放大器的第一输出端耦合在第二电容的第一端和第一开关器件的第三端间,且第一放大器的第一输入端耦合在正输入端和第一电流源的第一端间;In a possible design, the first terminal of the first switching device is coupled to the first terminal of the first load, the second terminal of the first switching device is coupled to the positive input terminal, and the first terminal of the first switching device is coupled to the first terminal of the first load. A first capacitor is connected across the second end of a switching device, a second capacitor is connected across the second end of the first switching device and the third end of the first switching device, and the first output end of the first amplifier is coupled to the second between the first terminal of the capacitor and the third terminal of the first switching device, and the first input terminal of the first amplifier is coupled between the positive input terminal and the first terminal of the first current source;
第二开关器件的第一端和第二负载的第一端耦合,第二开关器件的第二端与负输入端耦合,第二开关器件的第一端和第二开关器件的第二端跨接有第三电容,第二开关器件的第二端和第二开关器件的第三端跨接有第四电容,第一放大器的第二输出端耦合在第四电容的第一端和第二开关器件的第三端间,且第一放大器的第二输入端耦合在负输入端和第二电流源的第一端间;第一负载的第二端和第二负载的第二端耦合;第一电流源的第二端和第二电流源的第二端耦合。The first terminal of the second switching device is coupled to the first terminal of the second load, the second terminal of the second switching device is coupled to the negative input terminal, and the first terminal of the second switching device and the second terminal of the second switching device span A third capacitor is connected, a fourth capacitor is connected across the second terminal of the second switching device and the third terminal of the second switching device, and the second output terminal of the first amplifier is coupled between the first terminal and the second terminal of the fourth capacitor. between the third terminal of the switching device, and the second input terminal of the first amplifier is coupled between the negative input terminal and the first terminal of the second current source; the second terminal of the first load and the second terminal of the second load are coupled; The second terminal of the first current source is coupled to the second terminal of the second current source.
也就是说,本申请中的第一放大电路包括第一开关器件、第一电容和第二电容,用于实现电流的流经第一信号通路的电流的稳定。相较现有技术中由电阻和电容控制电流的稳定,极大地减少了电容电阻占用面积。而且相较现有的具有滤波功能的跨阻放大器,本申请的电路结构复杂度低。That is to say, the first amplification circuit in this application includes a first switching device, a first capacitor and a second capacitor, which are used to stabilize the current flowing through the first signal path. Compared with the current stability controlled by resistors and capacitors in the prior art, the area occupied by capacitors and resistors is greatly reduced. Moreover, compared with existing transimpedance amplifiers with filtering functions, the circuit structure of the present application has low complexity.
在一种可能的设计中,第一电流源用于产生第一静态电流,第一静态电流流经第一负载,使负输出端的增益随第一负载的阻值的变化而变化;第二电流源用于产生第二静态电流,第二静态电流流经第二负载,使正输出端的增益随第二负载的阻值的变化而变化。In a possible design, the first current source is used to generate a first quiescent current, and the first quiescent current flows through the first load, so that the gain of the negative output terminal changes with the change of the resistance of the first load; the second current The source is used to generate a second quiescent current, and the second quiescent current flows through the second load, so that the gain of the positive output terminal changes as the resistance of the second load changes.
这样一来,当跨阻放大器中没有信号输入,即未产生信号电流时,在使得跨阻放大器的输入端的静态电流稳定的情况下,可使得跨阻放大器的增益等于静态电流乘以负载电阻,这样可通过改变负载电阻的阻值调整跨阻放大器的增益。当有信号输入时,第一放大电路和第一电流源也可控制第一信号通路上的信号电流的稳定,使得第一信号通路上的负输出端的增益随第一负载的阻值的变化而变化即可。第二信号通路上的增益变化同理。In this way, when there is no signal input into the transimpedance amplifier, that is, no signal current is generated, the gain of the transimpedance amplifier can be equal to the quiescent current multiplied by the load resistance while the quiescent current at the input end of the transimpedance amplifier is stabilized. This allows the gain of the transimpedance amplifier to be adjusted by changing the value of the load resistor. When there is a signal input, the first amplifier circuit and the first current source can also control the stability of the signal current on the first signal path, so that the gain of the negative output terminal on the first signal path changes with the change of the resistance of the first load. Just change. The gain changes on the second signal path are the same.
在一种可能的设计中,第二电容和第一开关器件产生第一极点,第一负载和第一电容产生第二极点;第四电容和第二开关器件产生第三极点,第二负载和第三电容产生第四极点。In a possible design, the second capacitor and the first switching device generate a first pole, the first load and the first capacitor generate a second pole; the fourth capacitor and the second switching device generate a third pole, and the second load and the third capacitor produces the fourth pole.
在一种可能的设计中,第一电容跨接在第一开关器件的第一端和第一开关器件的第二端间时,产生前馈的第一零点;第一放大器用于控制第一零点的位置在高频处,使第一信号通路为2阶滤波特性;第三电容跨接在第二开关器件的第一端和第二开关器件的第二端间时,产生前馈的第二零点;第一放大器用于控制第二零点的位置在高 频处,使第一信号通路为2阶滤波特性。In a possible design, when the first capacitor is connected across the first terminal of the first switching device and the second terminal of the first switching device, a first zero point of the feedforward is generated; the first amplifier is used to control the first zero point of the feedforward. The position of the zero point is at a high frequency, so that the first signal path has a second-order filter characteristic; when the third capacitor is connected across the first end of the second switching device and the second end of the second switching device, a feedforward is generated the second zero point; the first amplifier is used to control the position of the second zero point at high frequency, so that the first signal path has second-order filter characteristics.
由此,在极点和零点时成对的,一个零点可抵消一个极点的情况下,本申请利用第一放大器的控制,可将零点的位置推离,零点的抵消作用不会产生,且在高频处,使得跨阻放大器呈现2阶滤波特性。Therefore, when poles and zeros are paired and one zero can offset one pole, this application uses the control of the first amplifier to push the position of the zero away, and the offset effect of the zero will not occur, and at high frequency, causing the transimpedance amplifier to exhibit second-order filtering characteristics.
在一种可能的设计中,跨阻放大器还包括稳压电路,稳压电路用于形成负反馈,控制正输出端的电压和负输出端的电压与基准电压保持一致。In one possible design, the transimpedance amplifier also includes a voltage stabilizing circuit, which is used to form negative feedback and control the voltage at the positive output terminal and the voltage at the negative output terminal to be consistent with the reference voltage.
这种设计是考虑到,一旦确定电路需要的增益时,目的是要保持正输出端和负输出端的电压不变的。以第一信号通路为例,此时,可通过调整第一信号通路上的电流使得负输出端的电压保持不变。但是一旦负输出端的电压变化,会影响到2阶TIA(具有滤波功能的跨阻放大器)电路的工作范围,当2阶TIA接收到大信号,例如正输入端接收到大电流的信号时,该信号会被压缩或不能被正常处理。但是,调整第一信号通路上的电流的同时,第一开关器件的跨导也会随该电流而变化。因此,本申请可在第一方面提供的具有滤波功能的跨阻放大器的基础上,增加稳压电路,用于形成负反馈,控制正输出端的电压和负输出端的电压与基准电压保持一致。This design takes into account that once the gain required for the circuit is determined, the purpose is to keep the voltages at the positive and negative output terminals constant. Taking the first signal path as an example, at this time, the voltage at the negative output terminal can be kept constant by adjusting the current on the first signal path. However, once the voltage at the negative output terminal changes, it will affect the working range of the second-order TIA (transimpedance amplifier with filter function) circuit. When the second-order TIA receives a large signal, such as a large current signal at the positive input terminal, the The signal will be compressed or not processed properly. However, while adjusting the current on the first signal path, the transconductance of the first switching device will also change with the current. Therefore, this application can add a voltage stabilizing circuit on the basis of the transimpedance amplifier with filtering function provided in the first aspect to form negative feedback and control the voltage of the positive output terminal and the voltage of the negative output terminal to be consistent with the reference voltage.
此外,由于第一负载和第二负载是并联在2阶TIA电路中的,第一负载的两端并未流入静态电流,第二负载的两端也并未流入静态电流,第一负载和第二负载上没有压降,没有压降就不会抵消电压裕度。In addition, since the first load and the second load are connected in parallel in the second-order TIA circuit, quiescent current does not flow into both ends of the first load, and quiescent current does not flow into both ends of the second load. There is no voltage drop across the second load, and without voltage drop it will not offset the voltage margin.
在一种可能的设计中,稳压电路包括串联耦合的第三开关器件和第四开关器件,还包括第二放大器;第三开关器件和第四开关器件所在的信号通路以及第一负载和第二负载所在的信号通路,并联耦合在正输出端和负输出端间;第二放大器的输出端耦合在第三开关器件的栅极和第四开关器件的栅极间;第二放大器的第一输入端耦合在串联耦合的第一负载和第二负载间,第二放大器的第二输入端用于输入基准电压。In a possible design, the voltage stabilizing circuit includes a third switching device and a fourth switching device coupled in series, and also includes a second amplifier; a signal path where the third switching device and the fourth switching device are located, and a first load and a third switching device. The signal path where the two loads are located is coupled in parallel between the positive output terminal and the negative output terminal; the output terminal of the second amplifier is coupled between the gate of the third switching device and the gate of the fourth switching device; the first terminal of the second amplifier The input terminal is coupled between the first load and the second load coupled in series, and the second input terminal of the second amplifier is used to input the reference voltage.
第二方面,提供一种射频接收装置,该射频接收装置包括如第一方面或第一方面的任一种可能的设计所述的具有滤波功能的跨阻放大器。A second aspect provides a radio frequency receiving device, which includes a transimpedance amplifier with a filtering function as described in the first aspect or any possible design of the first aspect.
第三方面,提供一种芯片,所述芯片包括如第二方面所述的射频接收装置。A third aspect provides a chip, which includes the radio frequency receiving device as described in the second aspect.
第四方面,提供一种通信设备,该通信设备包括如第三方面所述的芯片。A fourth aspect provides a communication device, which includes the chip described in the third aspect.
可以理解的是,上述提供的任一种射频接收装置、芯片、通信设备等均可以应用于上文所提供的具有滤波功能的跨阻放大器,因此,其所能达到的有益效果可参考对应的方法中的有益效果,此处不再赘述。It can be understood that any of the radio frequency receiving devices, chips, communication equipment, etc. provided above can be applied to the transimpedance amplifier with filtering function provided above. Therefore, the beneficial effects it can achieve can be referred to the corresponding The beneficial effects of the method will not be repeated here.
本申请的这些方面或其他方面在以下的描述中会更加简明易懂。These and other aspects of the present application will be more clearly understood in the following description.
图1为本申请实施例提供的一种传统的射频接收链路的结构示意图;Figure 1 is a schematic structural diagram of a traditional radio frequency receiving link provided by an embodiment of the present application;
图2为本申请实施例提供的一种LPF为2阶TIA的电路示意图;Figure 2 is a schematic circuit diagram of a 2-stage TIA with LPF provided by an embodiment of the present application;
图3为本申请实施例提供的一种TIA的电路示意图;Figure 3 is a schematic circuit diagram of a TIA provided by an embodiment of the present application;
图4为本申请实施例提供的一种具有滤波功能的跨阻放大器TIA的电路示意图;Figure 4 is a schematic circuit diagram of a transimpedance amplifier TIA with filtering function provided by an embodiment of the present application;
图5为本申请实施例提供的一种具有滤波功能的跨阻放大器TIA的电路示意图;Figure 5 is a schematic circuit diagram of a transimpedance amplifier TIA with filtering function provided by an embodiment of the present application;
图6为本申请实施例提供的一种具有滤波功能的TIA频响曲线示意图;Figure 6 is a schematic diagram of a TIA frequency response curve with filtering function provided by an embodiment of the present application;
图7为本申请实施例提供的一种2阶TIA电路示意图;Figure 7 is a schematic diagram of a 2-stage TIA circuit provided by an embodiment of the present application;
图8为本申请实施例提供的一种2阶TIA电路示意图;Figure 8 is a schematic diagram of a 2-stage TIA circuit provided by an embodiment of the present application;
图9为本申请实施例提供的一种2阶TIA电路示意图;Figure 9 is a schematic diagram of a 2-stage TIA circuit provided by an embodiment of the present application;
图10为本申请实施例提供的一种2阶TIA电路示意图;Figure 10 is a schematic diagram of a 2-stage TIA circuit provided by an embodiment of the present application;
图11为本申请实施例提供的一种系统芯片的结构示意图。FIG. 11 is a schematic structural diagram of a system chip provided by an embodiment of the present application.
为了便于理解,示例的给出了部分与本申请实施例相关概念的说明以供参考。如下所示:To facilitate understanding, some descriptions of concepts related to the embodiments of the present application are provided for reference. As follows:
LPF:去掉输入信号中不必要的高频成分,去除高频干扰。LPF: Remove unnecessary high-frequency components from the input signal and remove high-frequency interference.
TIA:是放大器类型的一种,放大器类型是根据其输入输出信号的类型来定义的。在电学范畴,假设放大器增益A=Y/X,Y为输出,X为输入。由于表征一个信号不是用电压就是电流,所以组合一下就有四种放大器。例如当输入X为电流信号时,输出Y为电压信号,A可理解为具有电阻的量纲。TIA: It is a type of amplifier. The amplifier type is defined according to the type of its input and output signals. In the electrical field, assume that the amplifier gain A=Y/X, Y is the output and X is the input. Since a signal is represented by either voltage or current, there are four types of amplifiers combined. For example, when the input X is a current signal and the output Y is a voltage signal, A can be understood as having the dimension of resistance.
VGA:是射频接收(ReceiveX,RX)链路中的一个关键模块,与反馈环路组成的自动增益控制电路为模数转换器(Analog to Digital Converter,ADC)提供恒定的信号功率。当模拟电路需要对信号进行放大或衰减时,这一功能可由VGA实现。VGA在无线通信的收/发信机模拟前端中,起着至关重要的作用。处于基波频率的VGA补偿射频模块和中频模块的增益衰减。且VGA将输出信号放大到ADC需要的幅度。VGA: It is a key module in the radio frequency reception (ReceiveX, RX) link. The automatic gain control circuit composed of a feedback loop provides constant signal power to the analog-to-digital converter (Analog to Digital Converter, ADC). When analog circuits need to amplify or attenuate signals, this function can be implemented by VGA. VGA plays a vital role in the analog front-end of the wireless communication receiver/transmitter. The VGA at the fundamental frequency compensates for the gain attenuation of the RF module and IF module. And the VGA amplifies the output signal to the amplitude required by the ADC.
LNA:在放大微弱信号的场合,放大器自身的噪声对信号的干扰可能很严重,因此希望减小这种噪声。而LNA是噪声系数很低的放大器。一般用作各类无线电接收机的高频或中频前置放大器(比如手机、电脑或者iPAD里面的WiFi模块),以及高灵敏度电子探测设备的放大电路。LNA: When a weak signal is amplified, the noise of the amplifier itself may seriously interfere with the signal, so it is hoped to reduce this noise. The LNA is an amplifier with a very low noise figure. It is generally used as a high-frequency or medium-frequency preamplifier for various types of radio receivers (such as WiFi modules in mobile phones, computers, or iPads), as well as amplification circuits for high-sensitivity electronic detection equipment.
放大器(Amplifier,AMP):尤指利用晶体管或电子管使电子信号放大的仪器。Amplifier (AMP): especially an instrument that uses transistors or tubes to amplify electronic signals.
下面将结合本申请实施例中的附图,对本申请实施例中的技术方案进行描述。其中,在本申请实施例的描述中,除非另有说明,“/”表示或的意思,例如,A/B可以表示A或B;本文中的“和/或”仅仅是一种描述关联对象的关联关系,表示可以存在三种关系,例如,A和/或B,可以表示:单独存在A,同时存在A和B,单独存在B这三种情况。另外,在本申请实施例的描述中,“多个”是指两个或多于两个。The technical solutions in the embodiments of the present application will be described below with reference to the drawings in the embodiments of the present application. Among them, in the description of the embodiments of this application, unless otherwise stated, "/" means or, for example, A/B can mean A or B; "and/or" in this article is only a way to describe related objects. The association relationship means that there can be three relationships. For example, A and/or B can mean: A alone exists, A and B exist simultaneously, and B alone exists. In addition, in the description of the embodiments of this application, "plurality" refers to two or more than two.
以下,术语“第一”、“第二”仅用于描述目的,而不能理解为指示或暗示相对重要性或者隐含指明所指示的技术特征的数量。由此,限定有“第一”、“第二”的特征可以明示或者隐含地包括一个或者更多个该特征。在本实施例的描述中,除非另有说明,“多个”的含义是两个或两个以上。Hereinafter, the terms “first” and “second” are used for descriptive purposes only and cannot be understood as indicating or implying relative importance or implicitly indicating the quantity of indicated technical features. Therefore, features defined as "first" and "second" may explicitly or implicitly include one or more of these features. In the description of this embodiment, unless otherwise specified, "plurality" means two or more.
如图1所示,传统的射频接收链路包括LNA、Mixer、LPF、VGA、本振(Local oscillator,LO)和ADC等电路。其中,LNA可将从天线接收到的信号进行低噪声放大后得到的射频信号和LO输出的混频信号叠加后输出给Mixer;Mixer将接收到的叠加后的信号下变频到中频后输出给LPF;LPF对接收到的中频信号进行滤波处理,去除高频干扰,将去除高频后的信号输出给VGA;VGA对接收到的信号进行放大,且提供恒定的信号功率给ADC;ADC对接收到的信号进行模数转换,将得到的数字信号输出给射频接收链路的其他模块进行处理,例如输出给处理模块进行处理。As shown in Figure 1, the traditional RF receiving chain includes circuits such as LNA, Mixer, LPF, VGA, local oscillator (LO) and ADC. Among them, the LNA can superimpose the RF signal obtained by low-noise amplification of the signal received from the antenna and the mixed signal output by the LO and output it to the Mixer; the Mixer down-converts the received superimposed signal to an intermediate frequency and outputs it to the LPF. ; LPF filters the received intermediate frequency signal, removes high-frequency interference, and outputs the high-frequency-removed signal to VGA; VGA amplifies the received signal and provides constant signal power to the ADC; ADC Perform analog-to-digital conversion on the signal, and output the resulting digital signal to other modules of the radio frequency receiving link for processing, such as output to the processing module for processing.
对于该射频接收链路,追求低功耗接收链路一直是研究的方向。常用的方法中,可通过降低滤波器的阶数,达到降低链路中放大器数量的目的。这里的放大器数量是 指LPF中的放大器数量。如图2所示的2阶TIA为LPF的一种设计。可理解,该2阶TIA中需要两个放大器,考虑到射频接收链路通常包括I路和Q路共两路,如果图1示出的是I路或Q路中的其中一路,两路的LPF中共有4个放大器,而放大器会消耗很大的静态功耗,不利于降低整个射频接收链路的功耗。而且,虽然该方案采用闭环结构,线性度较好,通过改变2阶TIA中的电阻,可实现一定的增益控制,但是实现较为复杂。此外,该方案中,LPF中的每个放大器的信号带宽由LPF中的电阻和电容决定,对于带宽低的射频接收链路,电阻和电容会占据相当大的面积,不利于降低成本。For this radio frequency receiving link, pursuing a low-power receiving link has always been a research direction. Among the commonly used methods, the number of amplifiers in the link can be reduced by reducing the order of the filter. The number of amplifiers here refers to the number of amplifiers in the LPF. The 2-stage TIA shown in Figure 2 is a design of LPF. It is understandable that two amplifiers are needed in this 2-stage TIA. Considering that the radio frequency receiving chain usually includes two channels, I and Q, if Figure 1 shows one of the I or Q, the two channels There are four amplifiers in the LPF, and the amplifiers consume a lot of static power, which is not conducive to reducing the power consumption of the entire radio frequency receiving link. Moreover, although this solution adopts a closed-loop structure and has good linearity, a certain gain control can be achieved by changing the resistance in the second-order TIA, but the implementation is more complicated. In addition, in this solution, the signal bandwidth of each amplifier in the LPF is determined by the resistors and capacitors in the LPF. For a low-bandwidth radio frequency receiving link, the resistors and capacitors will occupy a considerable area, which is not conducive to cost reduction.
如图3所示为另一种TIA的结构,采用开环结构,功耗相较于闭环结构的TIA有所降低。其中,inp和inn为两个电流输入端,outn和outp为两个电压输出端,Vref为参考电压输入端。图3所示的TIA可实现共模控制,同时增加了输出阻抗,且该TIA的功耗与信号带宽无关,可以设计较低的功耗。但是,该图3示出的TIA中,输入阻抗是输入端的NMOS管31和NMOS管32的跨导的倒数,输入阻抗如果设计的过低,需要加大TIA的输入电流,功耗会增加,因此,输入阻抗无法设计的过低。况且,该图3示出的TIA没有滤波功能,只有信号放大功能。如果没有滤波功能,使用图3示出的TIA时还需在该TIA的后级设计2阶以上的滤波器,射频接收链路的系统整体上功耗并未减少。此外,该方案需要一个共模稳定的放大器33,也会增加额外的功耗。Figure 3 shows the structure of another TIA, which adopts an open-loop structure, and the power consumption is reduced compared to the TIA with a closed-loop structure. Among them, inp and inn are two current input terminals, outn and outp are two voltage output terminals, and Vref is a reference voltage input terminal. The TIA shown in Figure 3 can achieve common mode control and increase the output impedance. The power consumption of the TIA has nothing to do with the signal bandwidth, and lower power consumption can be designed. However, in the TIA shown in Figure 3, the input impedance is the reciprocal of the transconductance of the NMOS transistor 31 and NMOS transistor 32 at the input end. If the input impedance is designed to be too low, the input current of the TIA needs to be increased, and the power consumption will increase. Therefore, the input impedance cannot be designed too low. Moreover, the TIA shown in Figure 3 has no filtering function but only a signal amplification function. If there is no filtering function, when using the TIA shown in Figure 3, it is necessary to design a second-order or higher filter in the subsequent stage of the TIA. The overall power consumption of the radio frequency receiving link system is not reduced. In addition, this solution requires a common-mode stable amplifier 33, which also adds additional power consumption.
由此,本申请针对射频接收链路中的LPF的设计中,功耗较大,成本较高、复杂度较高的问题,提出一种LPF的电路设计。本申请为LPF设计一种可同时实现2阶滤波器的TIA功能的电路,以达到降低LPF功耗、成本和面积的目的。Therefore, this application proposes an LPF circuit design to address the problems of large power consumption, high cost, and high complexity in the design of LPF in the radio frequency receiving link. This application designs a circuit for LPF that can simultaneously realize the TIA function of a second-order filter, in order to reduce the power consumption, cost and area of the LPF.
本申请提供的具有滤波功能的跨阻放大器,可应用于射频接收链路的LPF中。该射频接收链路包括I路和Q路并行的两个链路,I路和I路的相位差90度。I路和Q路的电路结构相同,本申请的实施例对其中一路电路结构进行介绍。The transimpedance amplifier with filtering function provided by this application can be applied to the LPF of the radio frequency receiving link. The radio frequency receiving link includes two parallel links, I and Q. The phase difference between I and I is 90 degrees. The circuit structures of the I path and the Q path are the same, and the embodiment of this application introduces the circuit structure of one of them.
需理解,射频接收链路可用于射频接收系统中,既适用于高带宽系统,例如WiFi中,也适用于低带宽低功耗的系统中,例如蓝牙(BlueTooth,BLE)系统中。It should be understood that the radio frequency receiving link can be used in radio frequency receiving systems, which is suitable for both high-bandwidth systems, such as WiFi, and low-bandwidth and low-power consumption systems, such as Bluetooth (BlueTooth, BLE) systems.
在一些实施例中,射频接收链路可用于射频收发芯片中,射频收发芯片例如可用于终端设备和网络设备中,还可以用于其他可收发信号的设备中,本申请不做限定。In some embodiments, the radio frequency receiving link can be used in a radio frequency transceiver chip. The radio frequency transceiver chip can be used in terminal equipment and network equipment, for example, and can also be used in other equipment that can transmit and receive signals. This application does not limit it.
本申请提供的具有滤波功能的跨阻放大器中,通过在正输入端和负输出端间耦合第一放大电路,和在负输入端和正输出端间耦合第二放大电路,可使得跨阻放大器的正输入端和负输入端的电流稳定,从而在跨阻放大器的增益等于电流乘以负载的电阻的情况下,可通过改变负载的阻值调整跨阻放大器的增益。In the transimpedance amplifier with filtering function provided by the present application, by coupling a first amplification circuit between the positive input terminal and the negative output terminal, and coupling a second amplification circuit between the negative input terminal and the positive output terminal, the transimpedance amplifier can be The currents at the positive and negative inputs are stable, so that the gain of the transimpedance amplifier can be adjusted by changing the resistance of the load in the case where the gain of the transimpedance amplifier is equal to the current times the resistance of the load.
在此过程中,通过第一放大电路、第二放大电路和第一放大器的耦合关系,可提升跨阻放大器的滤波特性,例如可呈现2阶滤波特性,从而实现具有滤波作用的跨阻放大器。本申请提供的具有滤波作用的跨阻放大器,占用面积较小,复杂度较低,功耗也较低。In this process, through the coupling relationship between the first amplification circuit, the second amplification circuit and the first amplifier, the filtering characteristics of the transimpedance amplifier can be improved, for example, it can exhibit second-order filtering characteristics, thereby realizing a transimpedance amplifier with filtering effect. The transimpedance amplifier with filtering function provided by this application occupies a smaller area, has lower complexity and lower power consumption.
下面对本申请提供的具有滤波作用的跨阻放大器进行介绍。The transimpedance amplifier with filtering function provided by this application is introduced below.
如图4所示,本申请提供一种具有滤波功能的跨阻放大器TIA,该TIA为开关结构,包括差分输入端和差分输出端,差分输入端包括正输入端inp和负输入端inn,差分输出端包括正输出端outp和负输出端outn。As shown in Figure 4, this application provides a transimpedance amplifier TIA with a filtering function. The TIA has a switching structure and includes a differential input terminal and a differential output terminal. The differential input terminal includes a positive input terminal inp and a negative input terminal inn. The output terminal includes a positive output terminal outp and a negative output terminal outn.
正输入端inp和负输出端outn所在的第一信号通路上耦合有第一放大电路和第一负载,负输入端inn和所述正输出端outp所在的第二信号通路上耦合有第二放大电路和第二负载,所述第一放大电路和所述第二放大电路间耦合有第一放大器AMP1;A first amplification circuit and a first load are coupled to the first signal path where the positive input terminal inp and the negative output terminal outn are located, and a second amplification circuit is coupled to the second signal path where the negative input terminal inn and the positive output terminal outp are located. circuit and a second load, a first amplifier AMP1 is coupled between the first amplification circuit and the second amplification circuit;
所述第一放大电路,用于控制流经所述第一负载的电流;The first amplifier circuit is used to control the current flowing through the first load;
所述第二放大电路,用于控制流经所述第二负载的电流;The second amplifier circuit is used to control the current flowing through the second load;
所述第一放大器AMP1,用于提升所述第一信号通路的滤波特性,以及提升所述第二信号通路的滤波特性。The first amplifier AMP1 is used to improve the filtering characteristics of the first signal path and to improve the filtering characteristics of the second signal path.
在一些实施例中,第一负载和第二负载为电阻。In some embodiments, the first load and the second load are resistors.
由此,本申请提供的具有滤波功能的跨阻放大器中,通过第一放大电路和第二放大电路,可使得跨阻放大器的正输入端和负输入端的电流稳定,从而在跨阻放大器的增益等于电流乘以第一负载(或第二负载)的电阻的基础上,通过改变第一负载的阻值调整跨阻放大器在第一信号通路上的增益,以及通过改变第二负载的阻值调整跨阻放大器在第二信号通路上的增益。而且,通过第一放大器,可提升跨阻放大器的滤波特性,例如呈现2阶滤波特性,从而实现具有滤波作用的跨阻放大器。Therefore, in the transimpedance amplifier with filtering function provided by the present application, the first amplification circuit and the second amplification circuit can stabilize the currents at the positive input terminal and the negative input terminal of the transimpedance amplifier, thereby increasing the gain of the transimpedance amplifier. Based on the current multiplied by the resistance of the first load (or the second load), the gain of the transimpedance amplifier on the first signal path is adjusted by changing the resistance of the first load, and the gain of the transimpedance amplifier on the first signal path is adjusted by changing the resistance of the second load. The gain of the transimpedance amplifier on the second signal path. Moreover, through the first amplifier, the filtering characteristics of the transimpedance amplifier can be improved, for example, to exhibit second-order filtering characteristics, thereby realizing a transimpedance amplifier with filtering effect.
这样一来,本申请提供的具有滤波作用的跨阻放大器,相较现有技术中滤波器的信号带宽由电阻和电容决定,对于带宽低的系统,电容和电阻占据相当大的面积,本申请通过第一放大电路、第二放大电路和第一放大器的耦合可实现具有滤波功能的跨阻放大器,占用面积较小,复杂度较低,功耗也较低。而且,单个I路或Q路中需要的放大器数量相较现有技术来说较少,例如图2的滤波电路中单个I路或Q路需要2个放大器,本申请提供的滤波器中单个I路或Q路需要1个放大器即可,功耗较低。In this way, compared with the transimpedance amplifier with filtering function provided by this application, the signal bandwidth of the filter is determined by resistors and capacitors in the prior art. For systems with low bandwidth, capacitors and resistors occupy a considerable area. This application Through the coupling of the first amplification circuit, the second amplification circuit and the first amplifier, a transimpedance amplifier with filtering function can be realized, which occupies a smaller area, has lower complexity and lower power consumption. Moreover, the number of amplifiers required in a single I or Q path is smaller than in the existing technology. For example, in the filter circuit of Figure 2, a single I or Q path requires two amplifiers. In the filter provided by this application, a single I Channel or Q channel only requires one amplifier, and the power consumption is low.
在一些实施例中,参考图5,正输入端inp和所述负输出端outn所在的第一信号通路上耦合有串联的所述第一放大电路和所述第一负载,第一负载以电阻R1示出;所述第一放大电路包括跨接在第一开关器件M1的第一电容C1和第二电容C2,以及与所述正输入端inp耦合的第一电流源S1;In some embodiments, referring to Figure 5, the first amplification circuit and the first load in series are coupled to the first signal path where the positive input terminal inp and the negative output terminal outn are located, and the first load is connected in series with a resistor. R1 shows; the first amplification circuit includes a first capacitor C1 and a second capacitor C2 connected across the first switching device M1, and a first current source S1 coupled with the positive input terminal inp;
所述负输入端inn和所述正输出端outp所在的第二信号通路上耦合有串联的所述第二放大电路和所述第二负载,第二负载以电阻R2示出;所述第二放大电路包括跨接在第二开关器件的第三电容C3和第四电容C4,以及与所述负输入端inn耦合的第二电流源S2。The second amplifier circuit and the second load in series are coupled to the second signal path where the negative input terminal inn and the positive output terminal outp are located. The second load is represented by a resistor R2; the second The amplifying circuit includes a third capacitor C3 and a fourth capacitor C4 connected across the second switching device, and a second current source S2 coupled to the negative input terminal inn.
下面以第一负载为第一电阻R1,第二负载为第二电阻R2进行说明。In the following description, the first load is the first resistor R1 and the second load is the second resistor R2.
参考图5,对于第一信号通路,第一开关器件M1的第一端a和第一电阻R1的第一端b耦合,第一开关器件M1的第二端c与正输入端inp耦合,第一开关器件的第一端a和第一开关器件M1的第二端c跨接有第一电容C1,第一开关器件M1的第二端c和第一开关器件M1的第三端d跨接有第二电容C2,第一放大器AMP1的第一输出端e耦合在第二电容C2的第一端f和第一开关器件M1的第三端d间,且第一放大器M1的第一输入端g耦合在正输入端inp和第一电流源S1的第一端A间。Referring to Figure 5, for the first signal path, the first terminal a of the first switching device M1 is coupled to the first terminal b of the first resistor R1, the second terminal c of the first switching device M1 is coupled to the positive input terminal inp, and the first terminal c of the first switching device M1 is coupled to the positive input terminal inp. The first terminal a of a switching device and the second terminal c of the first switching device M1 are connected across the first capacitor C1, and the second terminal c of the first switching device M1 and the third terminal d of the first switching device M1 are connected across There is a second capacitor C2, the first output terminal e of the first amplifier AMP1 is coupled between the first terminal f of the second capacitor C2 and the third terminal d of the first switching device M1, and the first input terminal of the first amplifier M1 g is coupled between the positive input terminal inp and the first terminal A of the first current source S1.
在第一信号通路和第二信号通路对称的情况下,参考图5,对于第二信号通路,第二开关器件M2的第一端h和第二电阻R2的第一端i耦合,第二开关器件M2的第二端j与负输入端inn耦合,第二开关器件M2的第一端h和第二开关器件M2的第二端j跨接有第三电容C3,第二开关器件M2的第二端j和第二开关器件M2的第三端k 跨接有第四电容C4,第一放大器AMP1的第二输出端l耦合在第四电容C4的第一端m和第二开关器件M2的第三端k间,且第一放大器AMP2的第二输入端n耦合在负输入端inn和第二电流源S2的第一端B间;When the first signal path and the second signal path are symmetrical, referring to Figure 5, for the second signal path, the first terminal h of the second switching device M2 and the first terminal i of the second resistor R2 are coupled, and the second switch The second terminal j of the device M2 is coupled to the negative input terminal inn. The first terminal h of the second switching device M2 and the second terminal j of the second switching device M2 are connected across a third capacitor C3. The second terminal j and the third terminal k of the second switching device M2 are connected across a fourth capacitor C4, and the second output terminal l of the first amplifier AMP1 is coupled between the first terminal m of the fourth capacitor C4 and the second switching device M2. between the third terminal k, and the second input terminal n of the first amplifier AMP2 is coupled between the negative input terminal inn and the first terminal B of the second current source S2;
第一电阻R1的第二端o和第二电阻R2的第二端p耦合;The second terminal o of the first resistor R1 is coupled to the second terminal p of the second resistor R2;
第一电流源S1的第二端C和第二电流源S2的第二端D耦合。The second terminal C of the first current source S1 and the second terminal D of the second current source S2 are coupled.
其中,在射频接收链路中,正输入端inp和负输入端inn与混频器Mixer的两个输出端耦合,用于接收Mixer的两个输出端输出的电流。Among them, in the radio frequency receiving chain, the positive input terminal inp and the negative input terminal inn are coupled with the two output terminals of the mixer Mixer, and are used to receive the current output by the two output terminals of the Mixer.
负输出端outn和正输出端outp用于与后级的VGA或ADC的连个输入端耦合。The negative output terminal outn and the positive output terminal outp are used to couple with the two input terminals of the VGA or ADC of the subsequent stage.
本申请中的开关器件,例如本申请中涉及的第一开关器件、第二开关器件、第三开关器件和第四开关器件等,可以为MOS管,具体可为PMOS或NMOS等。The switching devices in this application, such as the first switching device, the second switching device, the third switching device and the fourth switching device involved in this application, may be MOS transistors, specifically PMOS or NMOS, etc.
在图5的电路结构上,可理解,第一电流源S1和第二电流源S2都可提供稳定电流,该稳定电流可理解为具有滤波功能的TIA所需的静态电流。这样,可使得TIA的输入端呈现低阻。在正输入端inp和负输入端inn没有信号电流输入时,第一电流源S1产生的稳定电流流经第一电阻R1,第二电流源S2产生的稳定电流流经第二电阻R2,负输出端outn输出的增益为第一电流源S1产生的稳定电流乘以第一电阻R1,正输出端outp输出的增益为第二电流源S2产生的稳定电流乘以第二电阻R2。这样,可通过改变第一电阻R1和第二电阻R2的阻值,调整TIA的增益。From the circuit structure of FIG. 5 , it can be understood that both the first current source S1 and the second current source S2 can provide a stable current, and the stable current can be understood as the quiescent current required by the TIA with a filtering function. In this way, the input end of the TIA can be made to have low impedance. When there is no signal current input to the positive input terminal inp and the negative input terminal inn, the stable current generated by the first current source S1 flows through the first resistor R1, the stable current generated by the second current source S2 flows through the second resistor R2, and the negative output The gain output by the terminal outn is the stable current generated by the first current source S1 multiplied by the first resistor R1, and the gain output by the positive output terminal outp is the stable current generated by the second current source S2 multiplied by the second resistor R2. In this way, the gain of the TIA can be adjusted by changing the resistance values of the first resistor R1 and the second resistor R2.
换句话说,第一电流源S1用于产生稳定的第一静态电流,第一静态电流流经第一电阻R1,使负输出端outn的增益随第一电阻R1的阻值的变化而变化。第二电流源S2用于产生稳定的第二静态电流,第二静态电流流经第二电阻R2,使正输出端outp的增益随第二电阻R2的阻值的变化而变化。In other words, the first current source S1 is used to generate a stable first quiescent current, and the first quiescent current flows through the first resistor R1, so that the gain of the negative output terminal outn changes with the change of the resistance of the first resistor R1. The second current source S2 is used to generate a stable second quiescent current. The second quiescent current flows through the second resistor R2, so that the gain of the positive output terminal outp changes with the change of the resistance of the second resistor R2.
当正输入端inp和负输入端inn有信号电流时,由于第一放大器AMP1的负反馈作用,也会使得正输入端inp的电压和负输入端inn的电压稳定,这样流经第一信号通路的第一电阻R1的信号电流和流经第二信号通路的第二电阻R2的信号电流也会稳定。在稳定的第一静态电流、第二静态电流和稳定的信号电流下,流经第一信号通路的第一电阻R1的电流稳定,流经第二信号通路的第二电阻R2的电流稳定。本申请可通过改变第一电阻R1和第二电阻R2的阻值,调整TIA的增益。When there is a signal current at the positive input terminal inp and the negative input terminal inn, due to the negative feedback effect of the first amplifier AMP1, the voltage of the positive input terminal inp and the voltage of the negative input terminal inn will also be stabilized, so that they flow through the first signal path The signal current of the first resistor R1 and the signal current flowing through the second resistor R2 of the second signal path will also be stable. Under stable first quiescent current, second quiescent current and stable signal current, the current flowing through the first resistor R1 of the first signal path is stable, and the current flowing through the second resistor R2 of the second signal path is stable. This application can adjust the gain of the TIA by changing the resistance values of the first resistor R1 and the second resistor R2.
根据图5提供的具有滤波功能的TIA,从滤波功能来说,在第一信号通路上,第二电容C2和第一开关器件M1会产生第一极点,第一电阻R1和第一电容C1会产生第二极点,形成2阶滤波器。由于第一电容C1跨接在第一信号通路上,会形成一个前馈的零点。但是,由于第一放大器AMP1的反馈作用,可使得第一信号通路和第二信号通路上流经的电流保持不变,使得具有TIA始终存在增益,零点的位置始终在高频处。零点并不会抵消极点,TIA依然呈现2阶滤波特性。由此,具有滤波功能的TIA在改变增益的同时可很好的保持2阶滤波特性。According to the TIA with filtering function provided in Figure 5, in terms of filtering function, on the first signal path, the second capacitor C2 and the first switching device M1 will generate the first pole, and the first resistor R1 and the first capacitor C1 will A second pole is generated, forming a second-order filter. Since the first capacitor C1 is connected across the first signal path, a feedforward zero point will be formed. However, due to the feedback effect of the first amplifier AMP1, the current flowing through the first signal path and the second signal path can remain unchanged, so that there is always a gain with TIA, and the zero point is always at a high frequency. The zero points do not cancel the poles, and the TIA still exhibits second-order filtering characteristics. Therefore, a TIA with a filtering function can maintain the second-order filtering characteristics well while changing the gain.
其中,零点可理解为,当TIA的信号输入幅度不为零且输入频率使TIA输出为零时,此输入频率值即为零点。极点可理解为,当TIA的输入幅度不为零且输入频率使TIA的输出为无穷大(TIA稳定破坏,发生振荡)时,此频率值即为极点。极点可用于抑制噪声,零点可用于恶化噪声。极点和零点时成对的,一个零点可抵消一个极点。本申请利用第一放大器AMP1的控制,可将零点的位置推离,零点的抵消作用不会产生, 且在高频处,使得TIA依然呈现2阶滤波特性。Among them, the zero point can be understood as, when the signal input amplitude of the TIA is not zero and the input frequency causes the TIA output to be zero, the input frequency value is the zero point. The pole can be understood as, when the input amplitude of TIA is not zero and the input frequency makes the output of TIA infinite (TIA stability is destroyed and oscillation occurs), this frequency value is the pole. Poles can be used to suppress noise, and zeros can be used to worsen noise. The poles and zeros are in pairs, and a zero cancels a pole. This application uses the control of the first amplifier AMP1 to push the position of the zero point away, and the offset effect of the zero point will not occur, and at high frequencies, the TIA still exhibits second-order filter characteristics.
这里举例说明下,在一些实施例中,对于第一信号通路,当第一开关器件M1的跨导gm=100u,第二电容C2的容量C2=4pf时,图6示出了本申请的具有滤波功能的TIA频响曲线,包括曲线1、曲线2和曲线3。横轴表示具有滤波功能的TIA从混频器Mixer接收到的信号的频率,单位为Hz,纵轴表示滤波功能的TIA中第一信号通路上的增益,即第一信号通路上的电流值与第一电阻R1的阻值相乘得到的电压值,单位为V或dB,dB为增益分贝。Here is an example. In some embodiments, for the first signal path, when the transconductance gm of the first switching device M1=100u and the capacity C2 of the second capacitor C2=4pf, FIG. 6 shows the configuration of the present application. The TIA frequency response curve of the filter function includes curve 1, curve 2 and curve 3. The horizontal axis represents the frequency of the signal received by the TIA with filtering function from the mixer, in Hz, and the vertical axis represents the gain on the first signal path in the TIA with filtering function, that is, the current value on the first signal path and The voltage value obtained by multiplying the resistance of the first resistor R1 is in V or dB, and dB is the gain in decibels.
对照图6,曲线1对应:第一电容C1的容量C1=4pf,第一电阻R1=5K;曲线2对应:第一电容C1的容量C1=2pf,第一电阻R1=10K;曲线3对应:第一电容C1的容量C1=1pf,第一电阻R1=20K。其中,第一电阻R1=5K时,TIA接收信号时的增益约为74V;第一电阻R1=10K时,TIA接收信号时的增益约为80V;第一电阻R1=20K时,TIA接收信号时的增益约为86V。Referring to Figure 6, curve 1 corresponds to: the capacity C1 of the first capacitor C1 = 4pf, the first resistor R1 = 5K; curve 2 corresponds to: the capacity C1 of the first capacitor C1 = 2pf, the first resistor R1 = 10K; curve 3 corresponds to: The capacity of the first capacitor C1 is C1=1pf, and the first resistor R1=20K. Among them, when the first resistor R1=5K, the gain of TIA when receiving signals is about 74V; when the first resistor R1=10K, the gain of TIA when receiving signals is about 80V; when the first resistor R1=20K, when TIA receives signals The gain is approximately 86V.
可知,第一电阻R1的值越大,TIA的增益越大。通过改变第一电阻R1的值,可调整TIA在负输出端outn的增益。类似的,对于第二信号通路的增益调整与第一信号通路类似。It can be seen that the greater the value of the first resistor R1, the greater the gain of the TIA. By changing the value of the first resistor R1, the gain of the TIA at the negative output terminal outn can be adjusted. Similarly, the gain adjustment for the second signal path is similar to that for the first signal path.
此外,针对TIA的滤波特性,对于第一信号通路中的第一极点,第一极点的位置是由第二电容C2的容值C2和第一开关器件M1的跨导gm确定的,当gm值和C2值不变时,第一极点的位置不变。对于第二信号通路中的第二极点,第二极点的位置是由第一电阻R1的阻值和第一电容C1的容值确定的,当R1的值和C1的值不变时,第二极点的位置不变。In addition, for the filtering characteristics of TIA, for the first pole in the first signal path, the position of the first pole is determined by the capacitance C2 of the second capacitor C2 and the transconductance gm of the first switching device M1. When the value of gm When the values of C2 and C2 remain unchanged, the position of the first pole remains unchanged. For the second pole in the second signal path, the position of the second pole is determined by the resistance of the first resistor R1 and the capacitance of the first capacitor C1. When the values of R1 and C1 remain unchanged, the second pole The position of the pole remains unchanged.
当第一极点的位置和第二极点的位置不变时,TIA的带宽就不变。参考图6,当正输入端inp接收到的电流信号的频率不变时,例如频率为10
3Hz时,电流信号经过第一信号通路后,当增大第一电阻R1的阻值时,负输出端outn的增益从74V增大到84V。这样,可在改变TIA的增益的同时保持TIA的带宽不变。在电流信号的频率小于或等于10
6Hz时,曲线1、曲线2和曲线3为平向曲线,即在电流信号的频率小于或等于10
6Hz的频率范围内,可在改变TIA的增益的同时保持TIA的带宽不变,将频率小于或等于10
6Hz的频率范围的信号通过增益放大后输出给后级模块,例如输出给VGA。
When the position of the first pole and the position of the second pole remain unchanged, the bandwidth of the TIA remains unchanged. Referring to Figure 6, when the frequency of the current signal received by the positive input terminal inp remains unchanged, for example, when the frequency is 10 3 Hz, after the current signal passes through the first signal path, when the resistance of the first resistor R1 is increased, the negative The gain of the output terminal outn increases from 74V to 84V. In this way, the TIA's gain can be changed while keeping the TIA's bandwidth constant. When the frequency of the current signal is less than or equal to 10 6 Hz, curve 1, curve 2 and curve 3 are flat curves, that is, in the frequency range where the frequency of the current signal is less than or equal to 10 6 Hz, the gain of the TIA can be changed. At the same time, the bandwidth of the TIA remains unchanged, and the signals in the frequency range less than or equal to 10 6 Hz are amplified through the gain and output to the subsequent module, such as VGA.
当电流信号的频率大于10
6Hz时,TIA的增益急剧变小,频率大于10
6Hz的电流信号被衰减,频率大于10
6Hz的信号不能在实现增益放大的同时输出给TIA的后级模块。这样,本申请提供的具有滤波作用的TIA在改变TIA增益的同时保持了2阶滤波特性。
When the frequency of the current signal is greater than 10 6 Hz, the gain of the TIA decreases sharply. The current signal with a frequency greater than 10 6 Hz is attenuated. The signal with a frequency greater than 10 6 Hz cannot be output to the TIA's subsequent module while achieving gain amplification. . In this way, the TIA with filtering function provided by this application maintains the second-order filtering characteristics while changing the TIA gain.
相对图2提供的2阶TIA的方案,本申请的LPF采用具有2阶滤波特性的TIA时,在I路或Q路中的一路需要1个放大器,I路和Q路共需要2个放大器,放大器数量减少了,功耗较低。而且,电路实现上较为简单,电路占用面积较小。相对图3提供的TIA,不仅提供了信号放大功能,还存在2阶滤波特性,本申请不需要在后级额外设计2阶以上滤波器,而图3提供的TIA并不具有滤波特性,本申请减少射频接收电路的整体功耗。Compared with the 2-order TIA solution provided in Figure 2, when the LPF of this application uses a TIA with 2-order filtering characteristics, one amplifier is required in one of the I or Q channels, and a total of 2 amplifiers are required in the I and Q channels. The number of amplifiers is reduced and power consumption is lower. Moreover, the circuit implementation is relatively simple and the circuit occupies a small area. Compared with the TIA provided in Figure 3, it not only provides a signal amplification function, but also has second-order filtering characteristics. This application does not need to design an additional second-order or higher filter in the subsequent stage, and the TIA provided in Figure 3 does not have filtering characteristics. This application Reduce the overall power consumption of the RF receiving circuit.
对于本申请提供的可提供稳定电流的2阶TIA,第一电流源S1提供的稳定电流和 第二电流源S2提供的稳定电流可通过参考电压vref控制TIA的电流输入端(inn和inp)的电压实现,同时通过参考电压vref产生TIA所需要静态电流,即上文中的第一静态电流和第二静态电流。在利用第一放大器AMP1形成负反馈的情况下,可使得TIA的电流输入端呈现低阻。TIA的增益在等于小信号电流乘以负载电阻(R1和R2)的情况下,改变负载电阻的阻值即可调整TIA的增益。For the 2-stage TIA provided in this application that can provide stable current, the stable current provided by the first current source S1 and the stable current provided by the second current source S2 can control the current input terminals (inn and inp) of the TIA through the reference voltage vref. voltage, and at the same time generate the quiescent current required by the TIA through the reference voltage vref, that is, the first quiescent current and the second quiescent current mentioned above. When the first amplifier AMP1 is used to form negative feedback, the current input end of the TIA can be made to exhibit low resistance. When the gain of the TIA is equal to the small signal current multiplied by the load resistor (R1 and R2), the gain of the TIA can be adjusted by changing the value of the load resistor.
参考图7,图7提供的2阶TIA为本申请图5提供的2阶TIA电路的另一种实现方式。图7中示出了两个放大器AMP11和AMP12,以及电阻R11和电阻R12,放大器AMP11的一个输入端用于输入参考电压vref,一个输入端61和输出端62跨接在第一开关器件M1的一端d和正输入端inp间,放大器AMP12的一个输入端用于输入参考电压vref,一个输入端63和输出端64跨接在第二开关器件M2的一端k和负输入端inn间。电阻R11的一端与正输入端inp耦合,另一端与电阻R12耦合,电阻R12的另一端与负输入端inn耦合。在实际实现时,可通过图5中的AMP1、第一电流源S1和第二电流源S2代替图7中的放大器AMP11和AMP12,以及电阻R11和电阻R12即可。Referring to Figure 7, the 2-stage TIA provided in Figure 7 is another implementation of the 2-stage TIA circuit provided in Figure 5 of the present application. Figure 7 shows two amplifiers AMP11 and AMP12, as well as resistors R11 and R12. One input terminal of the amplifier AMP11 is used to input the reference voltage vref, and an input terminal 61 and an output terminal 62 are connected across the first switching device M1 An input terminal of the amplifier AMP12 is used to input the reference voltage vref between one terminal d and the positive input terminal inp. An input terminal 63 and an output terminal 64 are connected across one terminal k of the second switching device M2 and the negative input terminal inn. One end of the resistor R11 is coupled to the positive input terminal inp, the other end is coupled to the resistor R12, and the other end of the resistor R12 is coupled to the negative input terminal inn. In actual implementation, the amplifiers AMP11 and AMP12 in Figure 7 and the resistors R11 and R12 can be replaced by AMP1, the first current source S1 and the second current source S2 in Figure 5.
具体地,以第一信号通路来说,本申请可向放大器AMP11的一个输入端输入参考电压vref。该参考电压vref与电阻R11的阻值的比值,即为第一信号通路上的第一静态电流。在该参考电压vref的大小不变时,第一静态电流不变。当第一静态电流保持不变时,正输入端inp的共模电压可设计的较低,与正输入端inp耦合的混频器Mixer的开关尺寸可设计的较低,减小器件占用面积。Specifically, taking the first signal path as an example, the present application can input the reference voltage vref to an input terminal of the amplifier AMP11. The ratio of the reference voltage vref to the resistance of the resistor R11 is the first quiescent current on the first signal path. When the magnitude of the reference voltage vref remains unchanged, the first quiescent current remains unchanged. When the first quiescent current remains unchanged, the common mode voltage of the positive input terminal inp can be designed to be lower, and the switch size of the mixer Mixer coupled to the positive input terminal inp can be designed to be lower, thereby reducing the area occupied by the device.
当该2阶TIA从混频器Mixer接收到信号时,正输入端inp会接收到信号电流,正输入端inp产生电压,当正输入端inp的电压抬升时,放大器AMP11会将参考电压vref与正输入端inp的电压差值放大,放大之后的电压差值输入到第一开关器件M1的输入端时,第一开关器件M1会产生电压,用于抑制正输入端inp的电压抬升,使得参考电压vref和正输入端inp的电压差值减小,最终会使得参考电压vref和正输入端inp的电压相同,使得正输入端inp的信号电流固定。总之,第一开关器件M1会形成负反馈,使得正输入端inp呈现低阻,或者说,从正输入端inp端输入的信号电流流经第一信号通路至第一电阻R1时,第一信号通路为一条低阻通路。这样,就实现了通过控制放大器AMP11的参考电压vref的电压值,可达到控制正输入端inp的电压值的目的,使得正输入端inp的电压值稳定,从而使得流经第一信号通路至第一电阻R1的小信号电流稳定。进而,可通过改变第一信号通路上第一电阻R1的阻值达到调整2阶TIA增益的目的。When the 2-stage TIA receives a signal from the mixer Mixer, the positive input terminal inp will receive the signal current, and the positive input terminal inp will generate a voltage. When the voltage of the positive input terminal inp rises, the amplifier AMP11 will compare the reference voltage vref and The voltage difference at the positive input terminal inp is amplified. When the amplified voltage difference is input to the input terminal of the first switching device M1, the first switching device M1 will generate a voltage to suppress the voltage rise at the positive input terminal inp, so that the reference The voltage difference between the voltage vref and the positive input terminal inp decreases, which will eventually make the reference voltage vref and the voltage of the positive input terminal inp the same, making the signal current of the positive input terminal inp fixed. In short, the first switching device M1 will form negative feedback, causing the positive input terminal inp to exhibit low resistance. In other words, when the signal current input from the positive input terminal inp flows through the first signal path to the first resistor R1, the first signal The path is a low resistance path. In this way, by controlling the voltage value of the reference voltage vref of the amplifier AMP11, the voltage value of the positive input terminal inp can be controlled, so that the voltage value of the positive input terminal inp is stabilized, so that the voltage value flowing through the first signal path to the third signal path is stabilized. A small signal current in resistor R1 is stable. Furthermore, the gain of the second-order TIA can be adjusted by changing the resistance of the first resistor R1 on the first signal path.
类似的,通过向第二信号通路上放大器AMP12输入参考电压vref,也可以达到控制负输入端inn的电压,使得第二信号通路上的第二电阻R2的小信号电流稳定的目的,从而达到调整第二电阻R2的阻值调整2阶TIA增益的目的。Similarly, by inputting the reference voltage vref to the amplifier AMP12 on the second signal path, the voltage of the negative input terminal inn can also be controlled to stabilize the small signal current of the second resistor R2 on the second signal path, thereby achieving adjustment. The resistance of the second resistor R2 is used to adjust the gain of the second-order TIA.
与阐述图5给出的滤波特性类似的,图7示出的2阶TIA也具有2阶滤波特性。Similar to the explanation of the filter characteristics given in Figure 5, the 2-order TIA shown in Figure 7 also has 2-order filter characteristics.
此外,在图5示出的2阶TIA中,在2阶TIA的电路未从混频器Mixer接收到信号时,如果人为因素或芯片生产时的偏差使得第一电阻R1的阻值变化时,该2阶TIA的链路共模点(负输出端outn)的电压会随R1的阻值发生变化。但是,一旦确定电路需要的增益时,目的是要保持负输出端outn的电压值保持不变的。此时,可通过调 整第一信号通路上的第一静态电流使得负输出端outn的电压保持不变。一旦负输出端outn或者正输出端outp的电压变化,会影响到2阶TIA电路的工作范围,当2阶TIA接收到大信号,例如正输入端outp接收到大电流的信号时,该信号会被压缩或不能被正常处理。但是,调整第一静态电流的同时,第一开关器件M1的跨导gm也会随第一静态电流而变化。In addition, in the 2-stage TIA shown in Figure 5, when the circuit of the 2-stage TIA does not receive a signal from the mixer, if human factors or deviations during chip production cause the resistance of the first resistor R1 to change, The voltage at the link common mode point (negative output terminal outn) of the second-order TIA will change with the resistance of R1. However, once the gain required for the circuit is determined, the goal is to keep the voltage value at the negative output terminal outn unchanged. At this time, the voltage of the negative output terminal outn can be kept constant by adjusting the first quiescent current on the first signal path. Once the voltage of the negative output terminal outn or the positive output terminal outp changes, it will affect the working range of the second-order TIA circuit. When the second-order TIA receives a large signal, for example, when the positive input terminal outp receives a large current signal, the signal will are compressed or cannot be processed normally. However, while adjusting the first quiescent current, the transconductance gm of the first switching device M1 will also change with the first quiescent current.
因此,本申请还提供一种2阶TIA的电路架构,如图8所示。本申请在图4的电路基础上进行改进。Therefore, this application also provides a circuit architecture of a 2-stage TIA, as shown in Figure 8. This application improves on the circuit of Figure 4.
在图4的电路架构的基础上,跨阻放大器还包括稳压电路,所述稳压电路用于形成负反馈,控制所述正输出端outp的电压和所述负输出端outn的电压与基准电压vcom保持一致。Based on the circuit architecture of Figure 4, the transimpedance amplifier also includes a voltage stabilizing circuit, which is used to form negative feedback and control the voltage of the positive output terminal outp and the voltage of the negative output terminal outn to be consistent with the reference The voltage vcom remains consistent.
在一些实施例中,如图9所示,稳压电路包括串联耦合的第三开关器件M3和第四开关器件M4,还包括第二放大器AMP2;In some embodiments, as shown in Figure 9, the voltage stabilizing circuit includes a third switching device M3 and a fourth switching device M4 coupled in series, and also includes a second amplifier AMP2;
所述第三开关器件M3和所述第四开关器件M4所在的信号通路与所述第一负载R1和所述第二负载R2所在的信号通路,并联耦合在所述正输出端outp和所述负输出端outn间;The signal path where the third switching device M3 and the fourth switching device M4 are located and the signal path where the first load R1 and the second load R2 are located are coupled in parallel between the positive output terminal outp and the Between the negative output terminal outn;
所述第二放大器AMP2的输出端q耦合在所述第三开关器件M3的栅极,和所述第四开关器件M4的栅极间;所述第二放大器AMP2的第一输入端t耦合在串联耦合的所述第一负载R1和所述第二负载R2间,所述第二放大器AMP2的第二输入端用于输入所述基准电压vcom。The output terminal q of the second amplifier AMP2 is coupled between the gate of the third switching device M3 and the gate of the fourth switching device M4; the first input terminal t of the second amplifier AMP2 is coupled between Between the first load R1 and the second load R2 coupled in series, the second input terminal of the second amplifier AMP2 is used to input the reference voltage vcom.
具体说来,参考图9,第二放大器AMP2的输出端q耦合在第三开关器件M3的第一端r和第四开关器件M4的第一端s间,第二放大器AMP2的第一输入端耦合t在第一电阻R1的第二端o和第二电阻R2的第二端p间,第二放大器AMP2的第二输入端输入基准电压vcom;Specifically, referring to Figure 9, the output terminal q of the second amplifier AMP2 is coupled between the first terminal r of the third switching device M3 and the first terminal s of the fourth switching device M4, and the first input terminal of the second amplifier AMP2 The coupling t is between the second terminal o of the first resistor R1 and the second terminal p of the second resistor R2, and the second input terminal of the second amplifier AMP2 inputs the reference voltage vcom;
第三开关器件M3的第二端u与第四开关器件M4的第二端v耦合;第三开关器件M3的第三端w与第一电阻R1的第一端b耦合,第四开关器件M4的第三端x与第二电阻R2的第一端i耦合。The second terminal u of the third switching device M3 is coupled to the second terminal v of the fourth switching device M4; the third terminal w of the third switching device M3 is coupled to the first terminal b of the first resistor R1. The fourth switching device M4 The third terminal x is coupled to the first terminal i of the second resistor R2.
由图9示出的2阶TIA可知,第二放大器AMP2、第三开关器件M3和第四开关器件M4组成负反馈电路,用于使得负输出端outn、正输出端outp的输出电压与基准电压vcom保持一致。It can be seen from the 2-stage TIA shown in Figure 9 that the second amplifier AMP2, the third switching device M3 and the fourth switching device M4 form a negative feedback circuit, which is used to make the output voltage of the negative output terminal outn and the positive output terminal outp equal to the reference voltage. vcom remains consistent.
具体来说,第一电阻R1和第二电阻R2并联接入了电路,通过第二放大器AMP2以及第三开关器件M3和第四开关器件M4可形成负反馈,使得TIA的输出共模电压始终保持在vcom,或者说使得TIA的负输出端outn和正输出端outp的电压始终保持在vcom。这样,即使切换第一电阻R1或第二电阻R2,或者说改变第一电阻R1的阻值或改变第二电阻R2的阻值时,TIA的输出共模电压依然保持不变。Specifically, the first resistor R1 and the second resistor R2 are connected in parallel to the circuit, and negative feedback can be formed through the second amplifier AMP2 and the third switching device M3 and the fourth switching device M4, so that the output common mode voltage of the TIA is always maintained. At vcom, or in other words, the voltages of the negative output terminal outn and the positive output terminal outp of the TIA are always maintained at vcom. In this way, even if the first resistor R1 or the second resistor R2 is switched, or the resistance value of the first resistor R1 or the second resistor R2 is changed, the output common mode voltage of the TIA remains unchanged.
当负输出端outn和正输出端outp与基准电压vcom不一致时,第二放大器AMP2可将电压误差放大,第二放大器AMP2的输出端输出电流到第三开关管M3和第四开关管M4,第三开关管M3导通后的电流流经第一电阻R1,第四开关管M4导通后的电流流经第二电阻R2,第一电阻R1的第二端o的电压会和基准电压vcom进行比较,第二电阻R2的第二端p的电压也会和基准电压进行比较。当比较后确定存在电压误 差时,第二放大器AMP2会继续将电压误差放大并输出。这样,在第二放大器AMP2的这种负反馈的作用下,会使得第一电阻R1的第二端o的电压和第二电阻R2的第二端p的电压与基准电压vcom保持一致。或者说,使得负输出端outn和正输出端outp的电压与基准电压vcom保持一致。When the negative output terminal outn and the positive output terminal outp are inconsistent with the reference voltage vcom, the second amplifier AMP2 can amplify the voltage error. The output terminal of the second amplifier AMP2 outputs current to the third switching tube M3 and the fourth switching tube M4. After the switch M3 is turned on, the current flows through the first resistor R1. After the fourth switch M4 is turned on, the current flows through the second resistor R2. The voltage at the second terminal o of the first resistor R1 is compared with the reference voltage vcom. , the voltage at the second terminal p of the second resistor R2 will also be compared with the reference voltage. When it is determined that there is a voltage error after comparison, the second amplifier AMP2 will continue to amplify the voltage error and output it. In this way, under the action of the negative feedback of the second amplifier AMP2, the voltage of the second terminal o of the first resistor R1 and the voltage of the second terminal p of the second resistor R2 will be consistent with the reference voltage vcom. In other words, the voltages of the negative output terminal outn and the positive output terminal outp are consistent with the reference voltage vcom.
此外,由于第一电阻R1和第二电阻R2是并联在2阶TIA电路中的,第一电阻R1的两端并未流入第一静态电流,第二电阻R2的两端并未流入第二静态电流,第一电阻R1和第二电阻R2上没有压降,没有压降就不会抵消电压裕度。In addition, since the first resistor R1 and the second resistor R2 are connected in parallel in the 2-stage TIA circuit, the first quiescent current does not flow into both ends of the first resistor R1, and the second quiescent current does not flow into both ends of the second resistor R2. current, there is no voltage drop across the first resistor R1 and the second resistor R2, and no voltage drop will offset the voltage margin.
而图5提供的2阶TIA电路中,第一电阻R1和第二电阻R2上都有静态电流流过,会存在压降,减小2阶TIA电路的工作范围。In the second-order TIA circuit provided in Figure 5, both the first resistor R1 and the second resistor R2 have static current flowing through them, and there will be a voltage drop, which reduces the working range of the second-order TIA circuit.
按照图7对图5的进一步解释,本申请还提供一种2阶TIA电路如图10所示。图10可理解为将图7和图9结合得到的2阶TIA电路。According to the further explanation of Figure 7 to Figure 5, this application also provides a 2-stage TIA circuit as shown in Figure 10. Figure 10 can be understood as a 2-stage TIA circuit obtained by combining Figures 7 and 9.
由此,通过本申请提供的2阶TIA,相对图2提供的2阶TIA需要的放大器数量,本申请提供的2阶TIA需要的放大器数量减少,链路上的功耗减小。且带宽控制由纯粹的电阻电容控制变为了由跨导gm(例如M1)和电容(例如电容C1和C2)控制,相对电阻电容占用的面积来说,开关器件例如MOS管和电容的占用面积较小。况且,本申请提供的2阶TIA相对图3提供的TIA来说,还具有滤波功能,且复杂度较低。Therefore, through the second-order TIA provided by this application, compared with the number of amplifiers required by the second-order TIA provided in Figure 2, the number of amplifiers required by the second-order TIA provided by this application is reduced, and the power consumption on the link is reduced. And the bandwidth control has changed from pure resistance and capacitance control to transconductance gm (such as M1) and capacitance (such as capacitance C1 and C2). Compared with the area occupied by resistors and capacitors, switching devices such as MOS tubes and capacitors occupy a smaller area. Small. Moreover, compared with the TIA provided in Figure 3, the second-order TIA provided by this application also has a filtering function and is less complex.
本申请实施例还提供了一种系统芯片,如图11所示,该系统芯片110包括:处理器和收发器,该收发器例如可以包括输入/输出接口、管脚或电路等,该电路可包括本申请中的射频接收链路,射频接收链路包括本申请中的具有滤波功能的跨阻放大器。该处理器可执行计算机指令。可选地,上述本申请实施例中提供的任意一种射频接收链路中的跨阻放大器可包括在收发器中。The embodiment of the present application also provides a system chip. As shown in Figure 11, the system chip 110 includes: a processor and a transceiver. The transceiver may include, for example, an input/output interface, pins or circuits. The circuit may It includes the radio frequency receiving link in this application, and the radio frequency receiving link includes the transimpedance amplifier with filtering function in this application. The processor executes computer instructions. Optionally, the transimpedance amplifier in any of the radio frequency receiving links provided in the above embodiments of the present application may be included in the transceiver.
可选地,该系统芯片还可以包括存储器。Optionally, the system chip may also include memory.
可选地,该存储器为该芯片内的存储单元,如寄存器、缓存等,该存储器还可以是通信装置(例如终端设备或网络设备)内的位于该芯片外部的存储单元,如只读存储器(read only memory,ROM)或可存储静态信息和指令的其他类型的静态存储设备,随机存取存储器(random access memory,RAM)等。其中,上述任一处提到的处理器,可以是一个CPU,微处理器,ASIC等。该处理器和该存储器可以解耦,分别设置在不同的物理设备上,通过有线或者无线的方式连接来实现该处理单元和该存储器的各自的功能,以支持该系统芯片实现上述实施例中的各种功能。或者,该处理器和该存储器也可以耦合在同一个设备上。应理解,在本申请实施例中的处理器可以是中央处理器(central processing unit,简称CPU),该处理器还可以是其他通用处理器、数字信号处理(Digital Signal Processing,简称DSP)、专用集成电路(Application Specific Integrated Circuit、ASIC)、现场可编程门阵列(Field-Programmable Gate Array,FPGA)或者其他可编程逻辑器件、分立门或者晶体管逻辑器件、分立硬件组件等。通用处理器可以是微处理器或者该处理器也可以是任何常规的处理器等。Optionally, the memory is a storage unit within the chip, such as a register, cache, etc. The memory may also be a storage unit located outside the chip in a communication device (such as a terminal device or network device), such as a read-only memory ( read only memory (ROM) or other types of static storage devices that can store static information and instructions, random access memory (random access memory, RAM), etc. Among them, the processor mentioned in any of the above places can be a CPU, microprocessor, ASIC, etc. The processor and the memory can be decoupled, respectively arranged on different physical devices, and connected through wired or wireless means to realize the respective functions of the processing unit and the memory, so as to support the system chip to implement the above embodiments. Various functions. Alternatively, the processor and memory may be coupled on the same device. It should be understood that the processor in the embodiment of the present application can be a central processing unit (CPU for short), and the processor can also be other general-purpose processors, digital signal processing (Digital Signal Processing, DSP for short), dedicated Integrated circuits (Application Specific Integrated Circuit, ASIC), field-programmable gate array (Field-Programmable Gate Array, FPGA) or other programmable logic devices, discrete gate or transistor logic devices, discrete hardware components, etc. A general-purpose processor may be a microprocessor or the processor may be any conventional processor, etc.
所属领域的技术人员可以清楚地了解到,为描述的方便和简洁,上述描述的系统、装置的具体工作过程,可以参考前述方法实施例中的对应过程,在此不再赘述。Those skilled in the art can clearly understand that for the convenience and simplicity of description, the specific working processes of the systems and devices described above can be referred to the corresponding processes in the foregoing method embodiments, and will not be described again here.
需理解,本申请提供的系统芯片可应用于多种终端设备和网络设备中。It should be understood that the system chip provided by this application can be applied to a variety of terminal equipment and network equipment.
通过以上实施方式的描述,所属领域的技术人员可以了解到,为描述的方便和简 洁,仅以上述各功能模块的划分进行举例说明,实际应用中,可以根据需要而将上述功能分配由不同的功能模块完成,即将装置的内部结构划分成不同的功能模块,以完成以上描述的全部或者部分功能。Through the description of the above embodiments, those skilled in the art can understand that for the convenience and simplicity of description, only the division of the above functional modules is used as an example. In practical applications, the above functions can be allocated to different modules according to needs. The functional module is completed, that is, the internal structure of the device is divided into different functional modules to complete all or part of the functions described above.
在本申请所提供的几个实施例中,应该理解到,所揭露的装置和方法,可以通过其它的方式实现。例如,以上所描述的装置实施例仅仅是示意性的,例如,所述模块或单元的划分,仅仅为一种逻辑功能划分,实际实现时可以有另外的划分方式,例如多个单元或组件可以结合或者可以集成到另一个装置,或一些特征可以忽略,或不执行。另一点,所显示或讨论的相互之间的耦合或直接耦合或通信连接可以是通过一些接口,装置或单元的间接耦合或通信连接,可以是电性,机械或其它的形式。In the several embodiments provided in this application, it should be understood that the disclosed devices and methods can be implemented in other ways. For example, the device embodiments described above are only illustrative. For example, the division of modules or units is only a logical function division. In actual implementation, there may be other division methods, for example, multiple units or components may be The combination can either be integrated into another device, or some features can be omitted, or not implemented. On the other hand, the coupling or direct coupling or communication connection between each other shown or discussed may be through some interfaces, and the indirect coupling or communication connection of the devices or units may be in electrical, mechanical or other forms.
所述作为分离部件说明的单元可以是或者也可以不是物理上分开的,作为单元显示的部件可以是一个物理单元或多个物理单元,即可以位于一个地方,或者也可以分布到多个不同地方。可以根据实际的需要选择其中的部分或者全部单元来实现本实施例方案的目的。The units described as separate components may or may not be physically separated. The components shown as units may be one physical unit or multiple physical units, that is, they may be located in one place, or they may be distributed to multiple different places. . Some or all of the units can be selected according to actual needs to achieve the purpose of the solution of this embodiment.
另外,在本申请各个实施例中的各功能单元可以集成在一个处理单元中,也可以是各个单元单独物理存在,也可以两个或两个以上单元集成在一个单元中。上述集成的单元既可以采用硬件的形式实现,也可以采用软件功能单元的形式实现。In addition, each functional unit in each embodiment of the present application can be integrated into one processing unit, each unit can exist physically alone, or two or more units can be integrated into one unit. The above integrated units can be implemented in the form of hardware or software functional units.
所述集成的单元如果以软件功能单元的形式实现并作为独立的产品销售或使用时,可以存储在一个可读取存储介质中。基于这样的理解,本申请实施例的技术方案本质上或者说对现有技术做出贡献的部分或者该技术方案的全部或部分可以以软件产品的形式体现出来,该软件产品存储在一个存储介质中,包括若干指令用以使得一个设备(可以是单片机,芯片等)或处理器(processor)执行本申请各个实施例所述方法的全部或部分步骤。而前述的存储介质包括:U盘、移动硬盘、ROM、RAM、磁碟或者光盘等各种可以存储程序代码的介质。If the integrated unit is implemented in the form of a software functional unit and sold or used as an independent product, it may be stored in a readable storage medium. Based on this understanding, the technical solutions of the embodiments of the present application are essentially or contribute to the existing technology, or all or part of the technical solution can be embodied in the form of a software product, and the software product is stored in a storage medium , including several instructions to cause a device (which can be a microcontroller, a chip, etc.) or a processor to execute all or part of the steps of the methods described in various embodiments of this application. The aforementioned storage media include: U disk, mobile hard disk, ROM, RAM, magnetic disk or optical disk and other media that can store program codes.
以上内容,仅为本申请的具体实施方式,但本申请的保护范围并不局限于此,任何熟悉本技术领域的技术人员在本申请揭露的技术范围内,可轻易想到变化或替换,都应涵盖在本申请的保护范围之内。因此,本申请的保护范围应以所述权利要求的保护范围为准。The above contents are only specific embodiments of the present application, but the protection scope of the present application is not limited thereto. Any person familiar with the technical field can easily think of changes or replacements within the technical scope disclosed in the present application, and should are covered by the protection scope of this application. Therefore, the protection scope of this application should be subject to the protection scope of the claims.
Claims (10)
- 一种具有滤波功能的跨阻放大器,其特征在于,所述跨阻放大器为开环结构,包括差分输入端和差分输出端,所述差分输入端包括正输入端和负输入端,所述差分输出端包括正输出端和负输出端;A transimpedance amplifier with filtering function, characterized in that the transimpedance amplifier has an open-loop structure and includes a differential input terminal and a differential output terminal. The differential input terminal includes a positive input terminal and a negative input terminal. The differential input terminal includes a positive input terminal and a negative input terminal. The output terminal includes a positive output terminal and a negative output terminal;所述正输入端和所述负输出端所在的第一信号通路上耦合有第一放大电路和第一负载,所述负输入端和所述正输出端所在的第二信号通路上耦合有第二放大电路和第二负载,所述第一放大电路和所述第二放大电路间耦合有第一放大器;A first amplification circuit and a first load are coupled to the first signal path where the positive input terminal and the negative output terminal are located, and a third signal path is coupled to the second signal path where the negative input terminal and the positive output terminal are located. two amplification circuits and a second load, a first amplifier coupled between the first amplification circuit and the second amplification circuit;所述第一放大电路,用于控制流经所述第一负载的电流;The first amplifier circuit is used to control the current flowing through the first load;所述第二放大电路,用于控制流经所述第二负载的电流;The second amplifier circuit is used to control the current flowing through the second load;所述第一放大器,用于提升所述第一信号通路的滤波特性,以及提升所述第二信号通路的滤波特性。The first amplifier is used to improve the filtering characteristics of the first signal path and to improve the filtering characteristics of the second signal path.
- 根据权利要求1所述的跨阻放大器,其特征在于,The transimpedance amplifier according to claim 1, characterized in that:所述正输入端和所述负输出端所在的第一信号通路上耦合有串联的所述第一放大电路和所述第一负载;所述第一放大电路包括跨接在第一开关器件的第一电容和第二电容,以及与所述正输入端耦合的第一电流源;The first amplification circuit and the first load connected in series are coupled to the first signal path where the positive input terminal and the negative output terminal are located; the first amplification circuit includes a circuit connected across the first switching device. a first capacitor and a second capacitor, and a first current source coupled to the positive input terminal;所述负输入端和所述正输出端所在的第二信号通路上耦合有串联的所述第二放大电路和所述第二负载;所述第二放大电路包括跨接在第二开关器件的第三电容和第四电容,以及与所述负输入端耦合的第二电流源。The second signal path where the negative input terminal and the positive output terminal are located is coupled with the second amplification circuit and the second load in series; the second amplification circuit includes a second signal path connected across the second switching device. a third capacitor and a fourth capacitor, and a second current source coupled to the negative input terminal.
- 根据权利要求2所述的跨阻放大器,其特征在于,The transimpedance amplifier according to claim 2, characterized in that:所述第一开关器件的第一端和所述第一负载的第一端耦合,所述第一开关器件的第二端与所述正输入端耦合,所述第一开关器件的第一端和所述第一开关器件的第二端跨接有所述第一电容,所述第一开关器件的第二端和所述第一开关器件的第三端跨接有所述第二电容,所述第一放大器的第一输出端耦合在所述第二电容的第一端和所述第一开关器件的第三端间,且所述第一放大器的第一输入端耦合在所述正输入端和所述第一电流源的第一端间;The first terminal of the first switching device is coupled to the first terminal of the first load, the second terminal of the first switching device is coupled to the positive input terminal, and the first terminal of the first switching device is coupled to the first terminal of the first load. The first capacitor is connected across the second end of the first switching device, and the second capacitor is connected across the second end of the first switching device and the third end of the first switching device, The first output terminal of the first amplifier is coupled between the first terminal of the second capacitor and the third terminal of the first switching device, and the first input terminal of the first amplifier is coupled between the positive terminal and the first terminal of the first switching device. between the input terminal and the first terminal of the first current source;所述第二开关器件的第一端和第二负载的第一端耦合,所述第二开关器件的第二端与所述负输入端耦合,所述第二开关器件的第一端和所述第二开关器件的第二端跨接有所述第三电容,所述第二开关器件的第二端和所述第二开关器件的第三端跨接有所述第四电容,所述第一放大器的第二输出端耦合在所述第四电容的第一端和所述第二开关器件的第三端间,且所述第一放大器的第二输入端耦合在所述负输入端和所述第二电流源的第一端间;The first terminal of the second switching device is coupled to the first terminal of the second load, the second terminal of the second switching device is coupled to the negative input terminal, and the first terminal of the second switching device is coupled to the first terminal of the second load. The third capacitor is connected across the second end of the second switching device, the fourth capacitor is connected across the second end of the second switching device and the third end of the second switching device, and The second output terminal of the first amplifier is coupled between the first terminal of the fourth capacitor and the third terminal of the second switching device, and the second input terminal of the first amplifier is coupled to the negative input terminal. and between the first terminal of the second current source;所述第一负载的第二端和所述第二负载的第二端耦合;The second end of the first load is coupled to the second end of the second load;所述第一电流源的第二端和所述第二电流源的第二端耦合。The second terminal of the first current source is coupled to the second terminal of the second current source.
- 根据权利要求2或3所述的跨阻放大器,其特征在于,所述第一电流源用于产生第一静态电流,所述第一静态电流流经所述第一负载,使所述负输出端的增益随所述第一负载的阻值的变化而变化;The transimpedance amplifier according to claim 2 or 3, characterized in that the first current source is used to generate a first quiescent current, and the first quiescent current flows through the first load so that the negative output The gain of the terminal changes with the change of the resistance of the first load;所述第二电流源用于产生第二静态电流,所述第二静态电流流经所述第二负载,使所述正输出端的增益随所述第二负载的阻值的变化而变化。The second current source is used to generate a second quiescent current, and the second quiescent current flows through the second load, so that the gain of the positive output terminal changes as the resistance of the second load changes.
- 根据权利要求2-4任一项所述的跨阻放大器,其特征在于,The transimpedance amplifier according to any one of claims 2-4, characterized in that,所述第二电容和所述第一开关器件产生第一极点,所述第一负载和所述第一电容产生第二极点;The second capacitor and the first switching device generate a first pole, and the first load and the first capacitor generate a second pole;所述第四电容和所述第二开关器件产生第三极点,所述第二负载和所述第三电容产生第四极点。The fourth capacitor and the second switching device generate a third pole, and the second load and the third capacitor generate a fourth pole.
- 根据权利要求5所述的跨阻放大器,其特征在于,The transimpedance amplifier according to claim 5, characterized in that:所述第一电容跨接在所述第一开关器件的第一端和所述第一开关器件的第二端间时,产生前馈的第一零点;所述第一放大器用于控制所述第一零点的位置在高频处,使所述第一信号通路为2阶滤波特性;When the first capacitor is connected across the first end of the first switching device and the second end of the first switching device, a first zero point of feedforward is generated; the first amplifier is used to control the The position of the first zero point is at a high frequency, so that the first signal path has a second-order filter characteristic;所述第三电容跨接在所述第二开关器件的第一端和所述第二开关器件的第二端间时,产生前馈的第二零点;所述第二放大器用于控制所述第二零点的位置在高频处,使所述第二信号通路为2阶滤波特性。When the third capacitor is connected across the first end of the second switching device and the second end of the second switching device, a feedforward second zero point is generated; the second amplifier is used to control the The position of the second zero point is at a high frequency, so that the second signal path has a second-order filter characteristic.
- 根据权利要求根据权利要求1所述的跨阻放大器,其特征在于,所述跨阻放大器还包括稳压电路,所述稳压电路用于形成负反馈,控制所述正输出端的电压和所述负输出端的电压与基准电压保持一致。The transimpedance amplifier according to claim 1, characterized in that the transimpedance amplifier further includes a voltage stabilizing circuit, the voltage stabilizing circuit is used to form negative feedback and control the voltage of the positive output terminal and the voltage of the positive output terminal. The voltage at the negative output remains consistent with the reference voltage.
- 根据权利要求7所述的跨阻放大器,其特征在于,The transimpedance amplifier according to claim 7, characterized in that:所述稳压电路包括串联耦合的第三开关器件和第四开关器件,还包括第二放大器;The voltage stabilizing circuit includes a third switching device and a fourth switching device coupled in series, and also includes a second amplifier;所述第三开关器件和所述第四开关器件所在的信号通路与所述第一负载和所述第二负载所在的信号通路,并联耦合在所述正输出端和所述负输出端间;The signal path where the third switching device and the fourth switching device are located and the signal path where the first load and the second load are located are coupled in parallel between the positive output terminal and the negative output terminal;所述第二放大器的输出端耦合在所述第三开关器件的栅极和所述第四开关器件的栅极间;所述第二放大器的第一输入端耦合在串联耦合的所述第一负载和所述第二负载间,所述第二放大器的第二输入端用于输入所述基准电压。The output terminal of the second amplifier is coupled between the gate electrode of the third switching device and the gate electrode of the fourth switching device; the first input terminal of the second amplifier is coupled between the first input terminal coupled in series. Between the load and the second load, the second input terminal of the second amplifier is used to input the reference voltage.
- 一种射频接收装置,其特征在于,所述射频接收装置包括如权利要求1-8任一项所述的具有滤波功能的跨阻放大器。A radio frequency receiving device, characterized in that the radio frequency receiving device includes a transimpedance amplifier with a filtering function according to any one of claims 1 to 8.
- 一种芯片,其特征在于,所述芯片包括如权利要求9所述的射频接收装置。A chip, characterized in that the chip includes the radio frequency receiving device according to claim 9.
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202280093960.XA CN118891822A (en) | 2022-03-31 | 2022-03-31 | Transimpedance amplifier with filtering function |
| PCT/CN2022/084603 WO2023184415A1 (en) | 2022-03-31 | 2022-03-31 | Transimpedance amplifier having filtering function |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/CN2022/084603 WO2023184415A1 (en) | 2022-03-31 | 2022-03-31 | Transimpedance amplifier having filtering function |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2023184415A1 true WO2023184415A1 (en) | 2023-10-05 |
Family
ID=88198747
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/CN2022/084603 WO2023184415A1 (en) | 2022-03-31 | 2022-03-31 | Transimpedance amplifier having filtering function |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN118891822A (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2023184415A1 (en) |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2002087071A2 (en) * | 2001-04-20 | 2002-10-31 | Semiconductor Ideas To The Market (Itom) B.V. | Tunable resonance amplifier |
| US20100007424A1 (en) * | 2008-07-08 | 2010-01-14 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Method of achieving high selectivity in receiver rf front-ends |
| JP2019036839A (en) * | 2017-08-15 | 2019-03-07 | 日本電信電話株式会社 | Transimpedance amplifier |
| CN111384902A (en) * | 2020-03-05 | 2020-07-07 | 深圳市纽瑞芯科技有限公司 | Broadband receiver circuit with adjustable impedance matching frequency |
| CN111900945A (en) * | 2020-06-22 | 2020-11-06 | 东南大学 | Transimpedance amplifier applied to current mode passive mixer |
| CN113193840A (en) * | 2021-05-10 | 2021-07-30 | 东南大学 | High-linearity trans-impedance amplifier applied to silent surface filter receiver |
-
2022
- 2022-03-31 WO PCT/CN2022/084603 patent/WO2023184415A1/en unknown
- 2022-03-31 CN CN202280093960.XA patent/CN118891822A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2002087071A2 (en) * | 2001-04-20 | 2002-10-31 | Semiconductor Ideas To The Market (Itom) B.V. | Tunable resonance amplifier |
| US20100007424A1 (en) * | 2008-07-08 | 2010-01-14 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Method of achieving high selectivity in receiver rf front-ends |
| JP2019036839A (en) * | 2017-08-15 | 2019-03-07 | 日本電信電話株式会社 | Transimpedance amplifier |
| CN111384902A (en) * | 2020-03-05 | 2020-07-07 | 深圳市纽瑞芯科技有限公司 | Broadband receiver circuit with adjustable impedance matching frequency |
| CN111900945A (en) * | 2020-06-22 | 2020-11-06 | 东南大学 | Transimpedance amplifier applied to current mode passive mixer |
| CN113193840A (en) * | 2021-05-10 | 2021-07-30 | 东南大学 | High-linearity trans-impedance amplifier applied to silent surface filter receiver |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN118891822A (en) | 2024-11-01 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US9054648B1 (en) | Wideband active balun LNA topology with narrow-band filtering and noise cancelling | |
| US7697915B2 (en) | Gain boosting RF gain stage with cross-coupled capacitors | |
| CN102790596B (en) | Automatic gain control amplifier for canceling direct current offset | |
| US7633341B2 (en) | Wideband circuits and methods | |
| Rasekh et al. | Design of low-power low-area tunable active RC filters | |
| US9154170B2 (en) | TIA-to-ADC interface with low-noise and a wide-range of passive gain control | |
| JP4095398B2 (en) | Amplifier and radio communication apparatus using the same | |
| CA2559169A1 (en) | Highly linear variable gain amplifier | |
| US7113016B2 (en) | Device for DC offset cancellation | |
| CN108988883B (en) | Apparatus, and associated method, for radio frequency receiver with reduced power consumption | |
| WO2023184415A1 (en) | Transimpedance amplifier having filtering function | |
| US8538367B2 (en) | Buffer circuit with integrated loss canceling | |
| CN107809220B (en) | Low noise amplifier, radio frequency integrated circuit, signal receiving module and radio frequency transceiver chip | |
| CN114696855A (en) | Novel zero intermediate frequency receiver | |
| Bai et al. | A review of CMOS variable gain amplifiers and programmable gain amplifiers | |
| Kumar et al. | A 35 mW 30 dB gain control range current mode programmable gain amplifier with DC offset cancellation | |
| Zhang et al. | A 250MHz 60dB gain control range 1dB gain step programmable gain amplifier with DC-offset calibration | |
| JP2000134046A (en) | Current amplifier | |
| Ye et al. | A 2.3 mA 240-to-500MHz 6 th-order active-RC low-pass filter for ultra-wideband transceiver | |
| Fary et al. | A 28nm bulk-cmos 50MHz 18 dbm-IIP3 Active-RC analog filter based on 7 GHz UGB OTA | |
| Miral et al. | A 17 mW 33 dBm IB-OIP3 0.5-1.5 GHz bandwidth TIA based on an inductor-stabilized OTA | |
| Ye et al. | A 0.47 mW 6 th-order 20MHz active filter using highly power-efficient Opamp | |
| Qin et al. | A 0–35dB wideband variable gain amplifier in 0.13 μm CMOS | |
| Huang et al. | A 20-Gb/s wideband AGC amplifier with 26-dB dynamic range in 0.18-μm SiGe BiCMOS | |
| CN216565125U (en) | Multimode RXFE circuit |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 22934252 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |