WO2020145711A1 - Dna polymerase for egfr mutation detection and kit comprising same - Google Patents
Dna polymerase for egfr mutation detection and kit comprising same Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2020145711A1 WO2020145711A1 PCT/KR2020/000448 KR2020000448W WO2020145711A1 WO 2020145711 A1 WO2020145711 A1 WO 2020145711A1 KR 2020000448 W KR2020000448 W KR 2020000448W WO 2020145711 A1 WO2020145711 A1 WO 2020145711A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- egfr gene
- pcr
- amino acid
- gene mutation
- egfr
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12Q—MEASURING OR TESTING PROCESSES INVOLVING ENZYMES, NUCLEIC ACIDS OR MICROORGANISMS; COMPOSITIONS OR TEST PAPERS THEREFOR; PROCESSES OF PREPARING SUCH COMPOSITIONS; CONDITION-RESPONSIVE CONTROL IN MICROBIOLOGICAL OR ENZYMOLOGICAL PROCESSES
- C12Q1/00—Measuring or testing processes involving enzymes, nucleic acids or microorganisms; Compositions therefor; Processes of preparing such compositions
- C12Q1/68—Measuring or testing processes involving enzymes, nucleic acids or microorganisms; Compositions therefor; Processes of preparing such compositions involving nucleic acids
- C12Q1/6844—Nucleic acid amplification reactions
- C12Q1/686—Polymerase chain reaction [PCR]
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12N—MICROORGANISMS OR ENZYMES; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF; PROPAGATING, PRESERVING, OR MAINTAINING MICROORGANISMS; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING; CULTURE MEDIA
- C12N9/00—Enzymes; Proenzymes; Compositions thereof; Processes for preparing, activating, inhibiting, separating or purifying enzymes
- C12N9/10—Transferases (2.)
- C12N9/12—Transferases (2.) transferring phosphorus containing groups, e.g. kinases (2.7)
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12N—MICROORGANISMS OR ENZYMES; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF; PROPAGATING, PRESERVING, OR MAINTAINING MICROORGANISMS; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING; CULTURE MEDIA
- C12N9/00—Enzymes; Proenzymes; Compositions thereof; Processes for preparing, activating, inhibiting, separating or purifying enzymes
- C12N9/10—Transferases (2.)
- C12N9/12—Transferases (2.) transferring phosphorus containing groups, e.g. kinases (2.7)
- C12N9/1241—Nucleotidyltransferases (2.7.7)
- C12N9/1252—DNA-directed DNA polymerase (2.7.7.7), i.e. DNA replicase
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12Q—MEASURING OR TESTING PROCESSES INVOLVING ENZYMES, NUCLEIC ACIDS OR MICROORGANISMS; COMPOSITIONS OR TEST PAPERS THEREFOR; PROCESSES OF PREPARING SUCH COMPOSITIONS; CONDITION-RESPONSIVE CONTROL IN MICROBIOLOGICAL OR ENZYMOLOGICAL PROCESSES
- C12Q1/00—Measuring or testing processes involving enzymes, nucleic acids or microorganisms; Compositions therefor; Processes of preparing such compositions
- C12Q1/68—Measuring or testing processes involving enzymes, nucleic acids or microorganisms; Compositions therefor; Processes of preparing such compositions involving nucleic acids
- C12Q1/6876—Nucleic acid products used in the analysis of nucleic acids, e.g. primers or probes
- C12Q1/6883—Nucleic acid products used in the analysis of nucleic acids, e.g. primers or probes for diseases caused by alterations of genetic material
- C12Q1/6886—Nucleic acid products used in the analysis of nucleic acids, e.g. primers or probes for diseases caused by alterations of genetic material for cancer
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12Y—ENZYMES
- C12Y207/00—Transferases transferring phosphorus-containing groups (2.7)
- C12Y207/07—Nucleotidyltransferases (2.7.7)
- C12Y207/07007—DNA-directed DNA polymerase (2.7.7.7), i.e. DNA replicase
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12Q—MEASURING OR TESTING PROCESSES INVOLVING ENZYMES, NUCLEIC ACIDS OR MICROORGANISMS; COMPOSITIONS OR TEST PAPERS THEREFOR; PROCESSES OF PREPARING SUCH COMPOSITIONS; CONDITION-RESPONSIVE CONTROL IN MICROBIOLOGICAL OR ENZYMOLOGICAL PROCESSES
- C12Q2521/00—Reaction characterised by the enzymatic activity
- C12Q2521/10—Nucleotidyl transfering
- C12Q2521/101—DNA polymerase
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12Q—MEASURING OR TESTING PROCESSES INVOLVING ENZYMES, NUCLEIC ACIDS OR MICROORGANISMS; COMPOSITIONS OR TEST PAPERS THEREFOR; PROCESSES OF PREPARING SUCH COMPOSITIONS; CONDITION-RESPONSIVE CONTROL IN MICROBIOLOGICAL OR ENZYMOLOGICAL PROCESSES
- C12Q2527/00—Reactions demanding special reaction conditions
- C12Q2527/125—Specific component of sample, medium or buffer
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12Q—MEASURING OR TESTING PROCESSES INVOLVING ENZYMES, NUCLEIC ACIDS OR MICROORGANISMS; COMPOSITIONS OR TEST PAPERS THEREFOR; PROCESSES OF PREPARING SUCH COMPOSITIONS; CONDITION-RESPONSIVE CONTROL IN MICROBIOLOGICAL OR ENZYMOLOGICAL PROCESSES
- C12Q2561/00—Nucleic acid detection characterised by assay method
- C12Q2561/101—Taqman
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12Q—MEASURING OR TESTING PROCESSES INVOLVING ENZYMES, NUCLEIC ACIDS OR MICROORGANISMS; COMPOSITIONS OR TEST PAPERS THEREFOR; PROCESSES OF PREPARING SUCH COMPOSITIONS; CONDITION-RESPONSIVE CONTROL IN MICROBIOLOGICAL OR ENZYMOLOGICAL PROCESSES
- C12Q2561/00—Nucleic acid detection characterised by assay method
- C12Q2561/113—Real time assay
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12Q—MEASURING OR TESTING PROCESSES INVOLVING ENZYMES, NUCLEIC ACIDS OR MICROORGANISMS; COMPOSITIONS OR TEST PAPERS THEREFOR; PROCESSES OF PREPARING SUCH COMPOSITIONS; CONDITION-RESPONSIVE CONTROL IN MICROBIOLOGICAL OR ENZYMOLOGICAL PROCESSES
- C12Q2600/00—Oligonucleotides characterized by their use
- C12Q2600/106—Pharmacogenomics, i.e. genetic variability in individual responses to drugs and drug metabolism
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12Q—MEASURING OR TESTING PROCESSES INVOLVING ENZYMES, NUCLEIC ACIDS OR MICROORGANISMS; COMPOSITIONS OR TEST PAPERS THEREFOR; PROCESSES OF PREPARING SUCH COMPOSITIONS; CONDITION-RESPONSIVE CONTROL IN MICROBIOLOGICAL OR ENZYMOLOGICAL PROCESSES
- C12Q2600/00—Oligonucleotides characterized by their use
- C12Q2600/118—Prognosis of disease development
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12Q—MEASURING OR TESTING PROCESSES INVOLVING ENZYMES, NUCLEIC ACIDS OR MICROORGANISMS; COMPOSITIONS OR TEST PAPERS THEREFOR; PROCESSES OF PREPARING SUCH COMPOSITIONS; CONDITION-RESPONSIVE CONTROL IN MICROBIOLOGICAL OR ENZYMOLOGICAL PROCESSES
- C12Q2600/00—Oligonucleotides characterized by their use
- C12Q2600/158—Expression markers
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a DNA polymerase for detecting EGFR mutations and a kit comprising the same, and more specifically, a DNA polymerase and primer set capable of detecting 44 somatic mutations in exons 18 to 21 of the EGFR gene with high sensitivity.
- Probes, kits and methods for detecting EGFR gene mutations using the kits are provided.
- G719X, S768I, Ex19 deletion, L858R and L861Q mutations are associated with susceptibility to EGFR TKI, whereas T790M and most Ex20 insertion mutations are associated with reduced EGFR TKI response.
- Early detection of EGFR gene mutations in lung cancer patients allows predicting drug response before treatment.
- Korean Patent Publication No. 10-2015-0102468 discloses a kit for diagnosing lung cancer, which includes a primer set for amplifying a lung cancer-related mutation and a probe complementary to the mutation, but a polymerase for detecting a mutation in the EGFR gene and There is no known reaction buffer to increase its activity.
- the present inventors have developed a kit comprising a DNA polymerase capable of detecting 44 somatic mutations in exons 18, 19, 20 and 21 of the EGFR gene with high sensitivity and a reaction buffer for increasing its activity.
- the invention was completed.
- An object of the present invention is to provide a DNA polymerase for detecting EGFR gene mutation.
- Another object of the present invention is to provide a primer set for detecting EGFR gene mutations.
- Another object of the present invention is to provide a probe for detecting an EGFR gene mutation.
- the present invention is a 507th amino acid residue glutamic acid (E) in the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1 is substituted with lysine (K), the 536th amino acid residue arginine (R) is lysine (K)
- a DNA polymerase for detecting EGFR gene mutations including Taq polymerase substituted with valine (V), wherein arginine (R), the 660th amino acid residue, is substituted with
- the present invention also provides a primer set for EGFR gene mutation detection, comprising at least one primer selected from the group consisting of SEQ ID NOs: 3 to 54.
- the present invention also provides a probe for detecting an EGFR gene mutation, comprising a nucleotide sequence selected from the group consisting of SEQ ID NOs: 55 to 63.
- the 507th amino acid residue glutamic acid (E) is substituted with lysine (K)
- the 536th amino acid residue arginine (R) is substituted with lysine (K)
- the 660th Taq polymerase in which the amino acid residue arginine (R) is substituted with valine (V);
- And / or at least one primer selected from the group consisting of SEQ ID NO: 3 to 54; provides a kit for detecting EGFR gene mutation.
- the nucleotide sequences of SEQ ID NOs: 55 to 63 are each selected from the group consisting of FAM, CAL Fluor Orange 560, VIC, HEX, JOE, Quasar 670 and CY5 at the 5'-end.
- One fluorophore may be labeled, and one quencher selected from the group consisting of BHQ-1 BHQ1 nova and BHQ-2 may be labeled at the 3'-end.
- the kit comprises 25 to 100 mM KCl; And 1 to 7 mM (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 ; and may further include a PCR buffer composition having a final pH of 8.0 to 9.5.
- the kit comprises 25 to 100 mM KCl; 1 to 7 mM (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 ; And 5 to 50 mM of TMAC (Tetra methyl ammonium chloride), and may further include a PCR buffer composition having a final pH of 8.0 to 9.5.
- the present invention also provides a method for detecting an EGFR gene mutation comprising the following steps: (a) extracting a nucleic acid from an isolated biological sample; (b) processing the kit of the present invention on the extracted nucleic acid to perform PCR (polymerase chain reaction); And (c) confirming the amplification result by the PCR with fluorescence.
- the PCR may be allele-specific PCR or real-time PCR.
- (d) may further include the step of confirming the amplification result by the PCR by measuring the Ct (cycle threshold) value.
- the EGFR gene mutation includes at least one selected from the group consisting of deletion, substitution and insertion mutations in exons 18, 19, 20 and 21 of the EGFR gene. can do.
- the EGFR gene mutation is a 719th amino acid glycine substitution in exon 18 of EGFR, a deletion in exon 19, a 768th amino acid in exon 20.
- the EGFR gene mutation detection method may be for predicting responsiveness to drugs of lung cancer patients.
- the lung cancer may be non-small cell lung cancer.
- the drug may be a tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
- the tyrosine kinase inhibitor may be gefitinib, erlotinib or osimitinib.
- the nucleic acid of step (a) may be extracted from a formalin-fixed paraffin embedded sample or a liquid biopsy of a tissue biopsy.
- the kit of the present invention shows high detection sensitivity (up to 0.01%, 3 mutant copies in 30,000 wild-type copies), high specificity and reproducibility, and is applicable to both liquid biopsy and tissue biopsy.
- high detection sensitivity up to 0.01%, 3 mutant copies in 30,000 wild-type copies
- high specificity and reproducibility high specificity and reproducibility
- Figure 1 shows the production process of Taq DNA polymerase containing each of the R536K, R660V and R536K/R660V mutations, (a) schematically shows fragment PCR and overlap PCR, (b) is amplified in fragment PCR The result of confirming the product by electrophoresis, and (c) shows the result of confirming the amplified product by electrophoresis by amplifying the entire length by overlap PCR.
- Figure 2 is a result of confirming the overlap PCR product of FIG. 1(c) purified by digestion with the restriction enzyme EcoRI/XbaI and then the SAP-treated pUC19 vector for gel extraction.
- Figure 3 is a schematic diagram showing fragment PCR and overlap PCR during the preparation of Taq DNA polymerase containing E507K, E507K/R536K, E507K/R660V and E507K/R536K/R660V mutations, respectively.
- FIG. 4 shows the results of confirming by electrophoresis the overlap PCR product of FIG. 3 purified with the pUC19 vector digested with the restriction enzyme EcoRI/XbaI for gel extraction, and then with SAP.
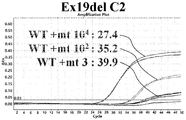
- 5A to 5L show the results of detecting mutations with AS-qPCR in the Ex19del C1 to Ex19del C12 mutant plasmid (3, 10 2 and 10 4 copies) template.
- 7A to 7G show the results of detecting mutations with AS-qPCR in the Ex19del C25 to Ex19del C31 mutant plasmid (3, 10 2 and 10 4 copies) template
- 7h is S768I mutant plasmid (3, 10 2 and 10 4 Copy) shows the result of detecting the mutation with AS-qPCR in the template
- 7i shows the result of detecting the mutation with AS-qPCR in WT.
- Figure 9a shows the results of detecting the mutation in the G719S mutant plasmid (3, 10 1 , 30, 10 2 and 10 4 copies) template with AS-qPCR.
- Figure 9b shows the results of detecting the mutation in the G719C mutant plasmid (3, 10 1 , 30, 10 2 and 10 4 copies) template with AS-qPCR.
- Figure 9c shows the results of detecting the mutation in the G719A mutant plasmid (3, 10 1 , 30, 10 2 and 10 4 copies) template with AS-qPCR.
- Figure 9d shows the results of detecting the mutation in WT AS-qPCR.
- 9E shows the results of detecting mutations with AS-qPCR in the L861Q mutant plasmid (0, 3, 10 2 and 10 4 copies) template.
- 10A to 10E show the results of detecting mutations with AS-qPCR in the Ex20Ins C1 to Ex20Ins C5 mutant plasmid (3, 10 2 and 10 4 copies) template
- 10f is the result of detecting mutations from WT to AS-qPCR
- 10g shows the results of detecting mutations with AS-qPCR in the L858R mutant plasmid (3, 10 2 and 10 4 copies) template
- 10h shows the results of detecting mutations in WT with AS-qPCR. will be.
- kits for more accurately predicting drug reactivity of lung cancer patients by improving the sensitivity of detecting EGFR mutations there is a continuous need to develop a kit for more accurately predicting drug reactivity of lung cancer patients by improving the sensitivity of detecting EGFR mutations.
- the present inventors provide an optimized kit comprising a DNA polymerase capable of detecting 44 somatic mutations in exons 18, 19, 20 and 21 of the EGFR gene with high sensitivity and a reaction buffer to increase its activity.
- the solution to the above problem was sought.
- the kit of the present invention exhibits high detection sensitivity, high specificity and reproducibility, and is applicable to both liquid biopsy and tissue biopsy.
- amino acid refers to any monomeric unit that can be incorporated into a peptide, polypeptide, or protein.
- amino acid includes the following 20 natural or genetically encoded alpha-amino acids: alanine (Ala or A), arginine (Arg or R), asparagine (Asn or N), aspart Acid (Asp or D), cysteine (Cys or C), glutamine (Gln or Q), glutamic acid (Glu or E), glycine (Gly or G), histidine (His or H), isoleucine (Ile or I), leucine (Leu or L), lysine (Lys or K), methionine (Met or M), phenylalanine (Phe or F), proline (Pro or P), serine (Ser or S), threonine (Thr or T), tryptophan ( Trp or W), tyrosine (Tyr or Y), and valine (Val
- Amino acids are typically organic acids, which include substituted or unsubstituted amino groups, substituted or unsubstituted carboxy groups, and one or more side chains or groups, or any analogue of these groups.
- exemplary side chains include, for example, thiol, seleno, sulfonyl, alkyl, aryl, acyl, keto, azido, hydroxyl, hydrazine, cyano, halo, hydrazide, alkenyl, alkynyl, ether, Borate, boronate, phospho, phosphono, phosphine, heterocyclic, enone, imine, aldehyde, ester, thio acid, hydroxylamine, or any combination of these groups.
- mutant refers to a recombinant polypeptide comprising one or more amino acid substitutions compared to the corresponding naturally occurring or unmodified DNA polymerase.
- thermo stable polymerase (referring to a heat stable enzyme) is heat resistant, retains sufficient activity to achieve subsequent polynucleotide elongation reactions and is treated with elevated temperature for the time required to achieve denaturation of the double-stranded nucleic acid Does not irreversibly denature (deactivate) when As used herein, it is suitable for use at temperatures cycling reactions such as PCR. Irreversible denaturation herein refers to permanent and complete loss of enzyme activity.
- enzymatic activity refers to catalyzing a combination of nucleotides in a suitable way to form a polynucleotide extension product complementary to the template nucleic acid strand.
- thermophilic bacteria include, for example: Thermomoto maritima, thermos aquaticus, thermos thermophilus, thermos flavus, thermomod philipformis, thermos species DNA polymerase derived from Sps17, Thermos species Z05, Thermos Caldophyllus, Bacillus caldotenax, Thermomoto Neopolitana, and Thermosippo africanus.
- thermoactivity refers to an enzyme that maintains catalytic properties at temperatures (ie 45-80° C.) commonly used for reverse transcription or annealing/extension steps in RT-PCR and/or PCR reactions.
- Thermostable enzymes are those that are not irreversibly inactivated or denatured when treated at elevated temperatures required for nucleic acid denaturation.
- the thermoactive enzyme may or may not be thermostable.
- the thermally active DNA polymerase can be DNA or RNA dependent from thermophilic or mesophilic species, including but not limited to:
- nucleotide is a deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) or ribonucleic acid (RNA) that exists in the form of a single strand or a double strand, and is not specifically mentioned otherwise. Unless it can contain analogs of natural nucleotides.
- nucleic acid or “polynucleotide” refers to a polymer that can correspond to a DNA or RNA polymer, or analogs thereof.
- Nucleic acids can be, for example, chromosomal or chromosomal segments, vectors (eg, expression vectors), expression cassettes, naked DNA or RNA polymers, products of polymerase chain reaction (PCR), oligonucleotides, probes, and primers. Or may include it.
- Nucleic acids can be, for example, single-stranded, double-stranded, or triple-stranded, but are not limited to any particular length. Unless otherwise stated, certain nucleic acid sequences include or encode complementary sequences in addition to any sequence specified.
- primer refers to a polynucleotide that can serve as a starting point for nucleic acid synthesis in the template-direction when placed under conditions where polynucleotide elongation is initiated. Primers can also be used in a variety of other oligonucleotide-mediated synthesis processes, including as initiators of de novo RNA synthesis and in vitro transcription-related processes. Primers are typically single-stranded oligonucleotides (eg, oligodeoxyribonucleotides). The appropriate length of the primer will typically depend on the intended use in the range of 6 to 40 nucleotides, more typically in the range of 15 to 35 nucleotides.
- Primers are not required to reflect the exact sequence of the template, but must be sufficiently complementary to hybridize with the template for elongation of the primer.
- the term “primer pair” includes a 5′-sense primer that hybridizes complementarily to the 5′-end of the amplified nucleic acid sequence, and a 3′-antisense primer that hybridizes to the 3′ end of the amplified sequence.
- Means a set of primers comprising Primers can be labeled, if necessary, by incorporating a label that can be detected by spectroscopic, photochemical, biochemical, immunochemical or chemical means.
- useful labels include: 32 P, fluorescent dyes, electron-dense reagents, enzymes (usually used in ELISA assays), biotin, or haptens and proteins in which antiserum or monoclonal antibodies can be used. .
- 5′-nuclease probe refers to an oligonucleotide comprising at least one luminescent label moiety used in a 5′-nuclease reaction to target nucleic acid detection.
- the 5'-nuclease hydrolyzate probe comprises only a single luminescent moiety (eg, fluorescent dye, etc.).
- the 5'-nuclease probe contains a self-complementary region so that the probe can form a hairpin structure under selective conditions.
- the 5'-nuclease hydrolyzate probe comprises two or more labeling moieties, and one of the two labels is released from the oligonucleotide after being separated or degraded to increase the emission intensity.
- the 5'-nuclease hydrolase probe is labeled with two different fluorescent dyes, for example a 5'-terminal reporter dye and a 3'-terminal quencher dye or moiety.
- the 5'-nuclease probe is labeled in addition to, or at one or more positions other than the terminal position. When the probe is intact, energy transfer typically occurs between the two phosphors such that the fluorescence emission from the reporter dye is partially extinguished.
- a 5'-nucleic acid hydrolase probe bound to the template nucleic acid has an activity such that the fluorescence of the reporter dye is no longer quenched, for example, Taq polymerase or other Degraded by the 5'to 3'-nucleic acid hydrolase activity of the polymerase.
- a 5'-nuclease probe can be labeled with two or more different reporter dyes and a 3'-terminal quencher dye or moiety.
- FRET fluorescence resonance energy transfer
- poster resonance energy transfer refers to the transfer of energy between two or more chromophores, donor chromophores and receptor chromophores (referred to as quenchers).
- the donor typically transfers energy to the receptor when the donor is excited by emitting light of a suitable wavelength.
- Receptors typically re-emit energy transferred in the form of light emitted at different wavelengths.
- the receptor is a “cancer” matting agent, it disperses the energy transferred in a form other than light. Whether a particular fluorescent substance acts as a donor or a receptor depends on the properties of other members of the FRET pair. Commonly used donor-receptor pairs include FAM-TAMRA pairs.
- Commonly used matting agents are DABCYL and TAMRA.
- Commonly used cancer matting agents include: BlackHole QuenchersTM (BHQ), (Biosearch Technologies, Inc., Novato, Cal.), Iowa BlackTM (Integrated DNA Tech., Inc., Coralville, Iowa), And BlackBerryTM Quencher 650 (BBQ-650) (Berry & Assoc., Dexter, Mich.).
- nucleic acid base nucleoside triphosphate, or nucleotide refers to naturally occurring polynucleotides described (ie, for DNA, they are dATP, dGTP, dCTP and dTTP).
- dATP dGTP
- dCTP dCTP
- dTTP dTTP
- dITP, and 7-deaza-dGTP are frequently used instead of dGTP and can be used instead of dATP in in vitro DNA synthesis reactions such as sequencing.
- nucleic acid base nucleotide, or nucleotide
- nucleotide is a conventional base, nucleotide, or modification, derivative, or nucleotide that occurs naturally in a particular polynucleotide, or Analogs.
- Certain unusual nucleotides are modified at the 2'position of the ribose sugar compared to conventional dNTP.
- nucleotides for RNA are ribonucleotides (i.e., ATP, GTP, CTP, UTP, collective rNTP), since nucleotides have hydroxyl groups at the 2'position of the sugar, this is compared to the absence of dNTP,
- ribonucleotides are unusual nucleotides as substrates for DNA polymerases.
- unusual nucleotides include, but are not limited to, compounds used as terminators for nucleic acid sequencing.
- Exemplary terminator compounds include, but are not limited to, compounds having a 2',3'- dideoxy structure, referred to as dideoxynucleoside triphosphate.
- Dideoxynucleoside triphosphate ddATP, ddTTP, ddCTP and ddGTP are collectively referred to as ddNTP.
- Additional examples of terminator compounds include 2'-PO 4 analogues of ribonucleotides.
- Other unusual nucleotides are phosphorothioate dNTP ([[ ⁇ ]-S]dNTP), 5'-[ ⁇ ]-borano-dNTP, [ ⁇ ]-methyl-phosphonate dNTP, and ribonucleosides Triphosphate (rNTP).
- Uncommon bases include radioactive isotopes such as 32 P, 33 P, or 35 S; Fluorescent labels; A label for chemiluminescence; Bioluminescent markers; Hapten labels such as biotin; Or it can be labeled with an enzyme label such as streptavidin or avidin.
- Fluorescent labels can include negatively charged dyes, such as the dyes of the fluorescein family, or neutrally charged dyes, such as the dyes of the rhodamine family, or positively charged dyes, such as the dyes of the cyanine family. Dyes of the fluorescein family include, for example, FAM, HEX, TET, JOE, NAN and ZOE.
- Rhodamine family dyes include Texas Red, ROX, R110, R6G, and TAMRA.
- Various dyes or nucleotides labeled FAM, HEX, TET, JOE, NAN, ZOE, ROX, R110, R6G, Texas Red and TAMRA are Perkin-Elmer (Boston, MA), Applied Biosystems (Foster City, CA), or Invitrogen /Molecular Probes (Eugene, OR).
- the cyanine family dyes include Cy2, Cy3, Cy5, and Cy7, and are marketed by GE Healthcare UK Limited (Amersham Place, Little Chalfont, Buckinghamshire, England).
- the 507th amino acid residue, glutamic acid (E), is substituted with lysine (K), the 536th amino acid residue, arginine (R), is replaced with lysine (K), and the 660th amino acid residue.
- a DNA polymerase for detecting EGFR gene mutations including Taq polymerase in which phosphorus arginine (R) is substituted with valine (V).
- the "Taq polymerase” was a thermophilic DNA polymerase named after the thermophilic bacterium Thermus aquaticus and was first isolated from the bacteria.
- Thermos Aquaticus is a bacterium inhabiting hot springs and hot water jets, and Taq polymerase has been identified as an enzyme capable of withstanding the protein denaturation conditions (high temperature) required in PCR.
- the optimum activity temperature of Taq polymerase is 75-80 °C, has a half-life of 9 hours at 22.5 hours at 92.5 °C, 40 minutes at 95 °C, 9 minutes at 97.5 °C, and replicates 1000 base pair DNA within 10 seconds at 72 °C Can.
- PCR can be performed at high temperatures (above 60°C).
- the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 for Taq polymerase is used as a reference sequence.
- the 507th amino acid residue in the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1 is substituted with lysine (K) in glutamic acid (E)
- the 536th amino acid residue is substituted with lysine (K) in arginine (R)
- the 660th amino acid The Taq polymerase in which the residue is substituted with arginine (R) to valine (V) was designated as “E507K/R536K/R660V”, and its amino acid sequence and nucleotide sequence are shown in SEQ ID NO: 2 and SEQ ID NO: 72, respectively.
- the present invention also provides a primer set for detecting EGFR gene mutations comprising one or more primers selected from the group consisting of SEQ ID NOs: 3 to 54.
- the primer set for detecting EGFR gene mutation of the present invention may be, for example, those described in Tables 16 to 19 of Example 3, but is not limited thereto.
- the polymerase according to the present invention is particularly excellent in EGFR mutation detection sensitivity when used with the primer sequences of Tables 16 to 19.
- the present invention also provides a kit for detecting EGFR gene mutations, which includes the DNA polymerase and/or primer set described above.
- the kit of the present invention can be used for research (Research Use Only, RUO) or in-vitro diagnostic (IVD).
- the kit of the present invention may be a PCR kit, and may contain any reagents or other elements recognized by those skilled in the art as being used in the primer extension process.
- the PCR kit of the present invention includes (a) nucleoside triphosphate; (b) a reagent for quantification that binds double-stranded DNA; (c) polymerase blocking antibodies; (d) one or more control values or control sequences; And (e) one or more templates; may further include one or more selected from the group consisting of.
- the kit comprises 25 to 100 mM KCl; And 1 to 7 mM (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 ; and may further include a PCR buffer composition having a final pH of 8.0 to 9.5.
- the kit comprises 40 to 90 mM KCl; And 1 to 5 mM (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 ; and may further include a PCR buffer composition having a final pH of 8.0 to 9.0.
- the kit comprises 25 to 100 mM KCl; 1 to 7 mM (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 ; And 5 to 50 mM of TMAC (Tetra methyl ammonium chloride), and may further include a PCR buffer composition having a final pH of 8.0 to 9.5.
- the kit comprises 40 to 90 mM KCl; 1 to 5 mM (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 ; And 10 to 40 mM of TMAC (Tetra methyl ammonium chloride), and may further include a PCR buffer composition having a final pH of 8.0 to 9.0.
- the PCR buffer composition as described above enables reliable gene mutation-specific amplification by remarkably improving the activity of the DNA polymerase of the present invention.
- the PCR kit may be applied to general PCR (1st generation PCR), real-time PCR (2nd generation PCR), digital PCR (3rd generation PCR) or mass array (MassARRAY).
- the “cast PCR” is a method for detecting and quantifying rare mutations in a sample containing a large amount of normal wild type gDNA, allele-specific TaqMan ® qPCR to inhibit non-specific amplification from wild type alleles. Combination with gene-specific MGB blockers can produce specificity superior to traditional allele-specific PCR.
- the “Droplet digital PCR” is a system for counting target DNA by splitting and amplifying a PCR reaction of 20 ⁇ l into 20,000 droplets, and depending on whether or not the target DNA is amplified in the droplet, positive droplets (1) It is counted as a digital signal with a negative drop (0), counts the copy number of the target DNA through Poisson distribution, and finally, the result can be confirmed by the number of copies per ⁇ l of the sample. Rare mutation detection, very small amount of gene It can be used when amplification, mutation type, etc. are to be simultaneously confirmed.
- the “mass array” is a multiplexing analysis method applicable to various genomic studies such as genotyping using a MALDI-TOF mass spectrometer, and rapidly analyzes multiple samples and targets at a low cost. It can be used when you want to do it, or if you want to do customized analysis only for a specific target.
- the EGFR gene mutation detection kit of the present invention may further include a probe, a fluorophore, and/or a quencher.
- the fluorophore may be VIC, HEX, JOE, FAM, CAL Flour Orange 560, Quasar 670, CY5 EverGreen dye, etc., but is not limited thereto.
- the probe sequence, the type of the fluorophore and the quencher may be the same as in Table 18 of Example 5, but is not limited thereto.
- the kit of the present invention employs AS-PCR (Allele-specific PCR) and real-time PCR technology, and includes a specific primer and a fluorescent probe for detecting EGFR mutation of cfDNA in human plasma samples.
- AS-PCR Allele-specific PCR
- the targeted mutant DNA matches the base at the 3'end of the primer, is selectively and efficiently amplified, and then the mutant amplicon is detected by a fluorescent probe labeled with FAM or CAL Fluor Orange 560 (CFO560). Wild-type DNA cannot match specific primers, and no amplification occurs.
- the kit of the present invention may be composed of EGFR Master Mixture 1-4, ADPS TM smart DNA polymerase, EGFR positive control and nuclease-free distilled water.
- the EGFR gene mutation detection kit of the present invention may be configured as shown in Table 1, for example, but is not limited thereto.
- Table 2 Exemplary configuration of each EGFR Master Mix in Table 1 is shown in Table 2.
- Table 3 shows the detection information of EGFR Master Mix 1-4.
- the present invention also provides a method for detecting an EGFR gene mutation comprising the following steps:
- the PCR may be allele-specific PCR or real-time PCR.
- the EGFR gene mutation detection method of the present invention may further include (d) confirming the amplification result by the PCR by measuring a Ct (cycle threshold) value.
- the cycle threshold (Ct) value means the number of cycles in which the fluorescence generated in the reaction exceeds a threshold, which is inversely proportional to the logarithm of the initial copy number. Therefore, the Ct value assigned to a particular well reflects the number of cycles in which a sufficient number of amplicons have accumulated in the reaction.
- the Ct value is the cycle in which the increase in ⁇ Rn was first detected.
- Rn means the magnitude of the fluorescence signal generated during PCR at each time point
- ⁇ Rn means the fluorescence emission intensity (standardized reporter signal) of the reporter dye divided by the fluorescence emission intensity of the reference dye.
- the Ct value is also referred to as a crossing point (Cp) in LightCycler.
- the Ct value represents the point in time at which the system begins to detect an increase in the fluorescence signal associated with the exponential growth of the PCR product in the log-linear phase. This period provides the most useful information about the reaction.
- the slope of the log-linear phase represents the amplification efficiency (Eff) (https://www.appliedbiosystems.co.kr/).
- FRET Frster or fluorescence resonance energy transfer
- the TaqMan probe specifically hybridizes to the template DNA in the annealing step, but fluorescence is inhibited by quenching on the probe.
- the TaqMan probe hybridized to the template is decomposed by the 5'to 3'nuclease activity of the Taq DNA polymerase, and the fluorescent dye is released from the probe.
- the 5'-end of the TaqMan probe should be located downstream of the 3'-end of the extension primer. That is, when the 3'-end of the extension primer is extended by a template-dependent nucleic acid polymerase, the 5'to 3'nuclease activity of this polymerase cuts the 5'-end of the TaqMan probe, thereby Fluorescence signal is generated.
- the non-fluorescent material used in the reporter molecule and the quencher molecule bound to the TaqMan probe may include a minor groove binding (MGB) moiety.
- MGB minor groove binding
- TaqMan MGB-conjugate probe refers to a TaqMan probe conjugated with MGB at the 3'-end of the probe.
- MGB is a substance that binds to the minor groove of DNA with high affinity, such as netropsin, distamicin, lexitropsin, mitramycin, chromomycin A3, and olibo. Olivomycin, anthramycin, sibiromycin, pentamidine, stilbamidine, berenil, CC-1065, Hoechst 33258, DAPI (4-6- diamidino-2-phenylindole), CDPI dimers, trimers, tetramers and pentamers, MPC (N-methylpyrrole-4-carbox-2-amide) and dimers thereof, trimers, tetramers and pentamers It does not work.
- Conjugation of the probe and MGB significantly increases the stability of the hybrid formed between the probe and its target. More specifically, increased stability (ie, increased degree of hybridization) results in increased melting temperature (Tm) of the hybrid duplex formed by MGB-conjugated probes compared to normal probes.
- Tm melting temperature
- MGB stabilizes the van der Waals force, thereby increasing the melting temperature (Tm) of the MGB-conjugate probe without increasing the probe length, resulting in shorter probes (e.g. no more than 21 nucleotides) in Taqman real-time PCR under more stringent conditions. Enables the use of.
- the EGFR gene mutation is selected from the group consisting of deletion, substitution and insertion mutations in exons 18, 19, 20 and 21 of the EGFR gene. It may contain one or more.
- the EGFR gene mutation is the substitution of the 719th amino acid glycine in exon 18 of EGFR, the deletion in exon 19, the 768th amino acid serine in exon 20, the 790th amino acid threonine, It may include one or more selected from the group consisting of substitution of the cysteine, the 797th amino acid, insertion in exon 20, leucine, which is the 858th amino acid in exon 21, and the replacement of the 861th amino acid, leucine.
- the EGFR gene mutation detection method of the present invention can simultaneously detect one or more of the 44 mutations listed in Table 4 below in exons 18, 19, 20 and 21 of EGFR.
- the target sequence may be present in the sample of step (a), and includes DNA, cDNA or RNA, preferably genomic DNA.
- the test sample may be included in an animal, preferably a vertebrate, more preferably a human subject.
- the biological sample in step (a) may be sputum, blood, saliva, or urine
- the nucleic acid in step (a) is a formalin-fixed paraffin embedded sample or a liquid biopsy of a tissue biopsy.
- the EGFR gene mutation detection method of the present invention may include melting temperature analysis using a double-strand specific dye.
- Melt temperature curve analysis can be performed in real-time PCR devices such as ABI 5700/7000 (96 well format) or ABI 7900 (384 well format) devices with onboard software (SDS 2.1). Alternatively, melt temperature curve analysis can be performed as an endpoint analysis.
- Double binding to double-stranded DNA or “double-strand specific dye” can be used when it has a higher fluorescence when bound to double-stranded DNA than to the unbound state.
- dyes are SOYTO-9, SOYTO-13, SOYTO-16, SOYTO-60, SOYTO-64, SYTO-82, Etidium Bromide (EtBr), SYTOX Orange, TO-PRO-1, SYBR Green I, TO-PRO-3 or EvaGreen. These dyes, except EtBr and EvaGreen (Quiagen), have been tested in real-time applications.
- the EGFR gene mutation detection method of the present invention includes real-time PCR (RT-PCR) or quantitative PCR (qPCR), analysis on agarose gel after standard PCR, gene mutation specific amplification or allele-specific amplification through real-time PCR, Tetra-primer amplification-refractory mutant systems can be performed by PCR or isothermal amplification.
- RT-PCR real-time PCR
- qPCR quantitative PCR
- the "standard PCR” is a technique for amplifying single or several copies of DNA or cDNA known to those skilled in the art. Almost all PCR uses thermostable DNA polymerases such as Taq polymerase or Klen Taq. DNA polymerases use single-stranded DNA as a template and enzymatically assemble new DNA strands from nucleotides by using oligonucleotides (primers). The amplicon generated by PCR can be analyzed, for example, on an agarose gel.
- the "real-time PCR” can monitor the process in real time when performing PCR. Therefore, data is collected throughout the PCR process, not when the PCR ends.
- the reaction is characterized by a time point during the cycle when amplification is first detected, rather than the target amount accumulated after a fixed number of cycles.
- Two methods mainly dye-based detection and probe-based detection, are used to perform quantitative PCR.
- ASA allele specific amplification
- the "gene mutation specific amplification or allele-specific amplification through real-time PCR” detects gene mutation or SNP in a very efficient manner. Unlike most other methods for detecting gene mutations or SNPs, preliminary amplification of the target genetic material is not required.
- ASA combines amplification and detection in a single reaction based on the distinction of matched and mismatched primer/target sequence complexes.
- the increase in DNA amplified during the reaction can be monitored in real time with an increase in the fluorescence signal caused by dyes such as SYBR Green I, which emit light upon binding to double-stranded DNA.
- Gene mutation-specific amplification or allele-specific amplification through real-time PCR shows delay or absence of a fluorescent signal for mismatched cases. In detecting genetic variation or SNP, it provides information on the presence or absence of genetic variation or SNP.
- the "tetra-primer amplification-refractory mutation system PCR” amplifies both wild type and mutant alleles with control fragments in a single tube PCR reaction.
- Non-allele specific control amplicons are amplified by two common (outer) primers flanking the mutation region.
- the two allele specific (inner) primers are designed in the opposite direction to the common primer, and can be amplified both wild-type and mutant amplicons simultaneously with the common primer. Consequently, the two allele-specific amplicons have different lengths and can be easily separated by standard gel electrophoresis because the mutations are located asymmetrically with respect to the common (outer) primer.
- the control amplicon provides internal control for false negatives as well as amplification failures, and at least one of the two allele-specific amplicons is always present in the tetra-primer amplification-refractory mutation system PCR.
- the "isothermal amplification” does not depend on the thermocycler, and preferably means that the amplification of the nucleic acid takes place at a lower temperature without the need to change the temperature during amplification.
- the temperature used in isothermal amplification can be between room temperature (22-24 °C) to about 65 °C, or at room temperature of about 60-65 °C, 45-50 °C, 37-42 °C or 22-24 °C.
- the products of the isothermal amplification results are gel electrophoresis, ELISA, ELOSA (Enzyme linked oligosorbent assay), real-time PCR, ECL (improved chemiluminescence), RNA, DNA, and chip-based capillary electrophoresis devices that analyze protein or turbidity It can be detected with an analyzer (bioanalyzer).
- ELOSA Enzyme linked oligosorbent assay
- ECL improved chemiluminescence
- RNA DNA
- chip-based capillary electrophoresis devices that analyze protein or turbidity It can be detected with an analyzer (bioanalyzer).
- the EGFR gene mutation detection method of the present invention is performed with qPCR, for example, it may be performed under the conditions of Tables 22 to 24 below.
- the DNA polymerase, primer set, probe, and/or kit for detecting EGFR gene mutations of the present invention can be used for predicting reactivity to drugs of lung cancer patients.
- the present invention can provide a DNA polymerase, primer set, probe, and/or kit for detecting EGFR gene mutation to predict responsiveness to drugs of lung cancer patients.
- the present invention can also provide a method for predicting the reactivity of a lung cancer patient to a drug using the aforementioned DNA polymerase, primer set, probe, and/or kit.
- the cancer may be non-small cell lung cancer.
- the EGFR gene mutation detection method of the present invention provides information to diagnose cancer early and establish a treatment strategy for each patient by detecting a known EGFR mutation of Table 4 above, thereby more effectively treating patients Contribute.
- prognosis refers to the act of predicting the course and outcome of a disease in advance. More specifically, the prognosis prediction can be interpreted to mean any action that predicts the course of the disease after treatment by comprehensively taking into account the patient's physiological or environmental conditions. Can be.
- the prognosis prediction may be interpreted as an action of predicting the disease-free survival rate or survival rate of a patient in advance by predicting the progress and complete cure of the disease after treatment of a specific disease. For example, predicting that "the prognosis is good” means that the patient has a high probability of being treated without disease or having a high survival rate after treatment of the disease, and predicting that the "prognosis is bad” is a disease After treatment, the patient's disease-free survival rate or survival rate is low, indicating that the disease is likely to recur or die from the disease.
- no disease survival rate of the present invention means the possibility that a patient can survive without recurrence of the disease after treatment of the specific disease.
- survival rate of the present invention means the possibility that a patient can survive regardless of whether or not the disease recurs after treatment of a specific disease.
- Taq DNA polymerase in which the 536th amino acid residue in the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1 is substituted with arginine to lysine (hereinafter referred to as "R536K”), Taq DNA polymerase in which the 660th amino acid residue is substituted with valine in arginine. (Hereinafter referred to as “R660V”) and Taq DNA polymerase (hereinafter referred to as “R536K/R660V”) in which the 536th amino acid residue is substituted from arginine to lysine and the 660th amino acid residue is substituted from arginine to valine is prepared as follows. Did.
- Taq DNA polymerase fragments (F1 to F5) were amplified by PCR using the mutant specific primers listed in Table 5, as shown in Figure 1(a). The reaction conditions are shown in Table 6.
- Each fragment amplified in 1-1 was used as a template to amplify the full length using primers at both ends (Eco-F and Xba-R primers).
- the reaction conditions are shown in Tables 7 and 8.
- pUC19 was digested with the restriction enzyme EcoRI/XbaI at 37°C for 4 hours under the conditions of Table 9 below, and then the DNA was purified and the purified DNA was treated with SAP for 1 hour at 37°C under the conditions of Table 10 to prepare a vector. .
- the overlap PCR product of Example 1-2 was purified, digested with restriction enzyme EcoRI/XbaI at 37°C for 3 hours under the conditions of Table 11, and then gel extracted with the prepared vector (FIG. 2 ). ).
- E. coli DH5 ⁇ was transformed to select from the medium containing ampicillin.
- the plasmid prepared from the obtained colonies was sequenced to obtain Taq DNA polymerase mutants ("R536K”, “R660V” and “R536K/R660V”) into which the desired mutation was introduced.
- Taq polymerase activity of "R536K”, “R660V” and “R536K/R660V” prepared in Example 1 was tested to confirm that the activity was poor (data not shown), R536K, R660V, R536K/R660V, respectively
- an E507K mutation substituted the 507th amino acid residue in the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1 with glutamic acid for lysine
- WT wild-type Taq DNA polymerase
- Taq DNA polymerase fragments (F6 to F7) were amplified by PCR using the mutant specific primers listed in Table 13. The reaction conditions are shown in Table 14.
- Each fragment amplified in 2-1 was used as a template, and the full length was amplified using primers (Eco-F and Xba-R primers) at both ends.
- the reaction conditions are shown in Table 15.
- pUC19 was digested with the restriction enzyme EcoRI/XbaI at 37°C for 4 hours under the conditions of Table 9, and then the DNA was purified, and the purified DNA was treated with SAP for 1 hour at 37°C under the conditions of Table 10 to prepare a vector. .
- the overlap PCR product of Example 2-2 was purified, digested with restriction enzyme EcoRI/XbaI at 37° C. for 3 hours under the conditions of Table 11, and then gel extracted with the prepared vector (FIG. 4 ). ).
- E. coli was transformed into DH5 ⁇ or DH10 ⁇ , and was selected in a medium containing ampicillin.
- the plasmid prepared from the obtained colonies was sequenced to obtain Taq DNA polymerase mutants introduced with E507K mutations (“E507K/R536K”, “E507K/R660V” and “E507K/R536K/R660V”).
- Primer size and Tm value using the OligoAnalyzer Tool https://sg.idtdna.com/calc/analyzer) program to design primers that generate PCR products for mutations in the EGFR gene but not for the wild-type EGFR gene
- a primer set capable of amplifying the periphery of the target mutation in Table 4 was applied to prepare wild-type clones at exon 18, 19, 20, and 21 sites. Mutagenesis was performed on 44 target mutations using the prepared wild-type DNA, and transformed into E.Coli DH5 ⁇ cells to obtain each mutant clone. Wild type clones and mutant clones were identified by direct sequencing. Wild-type DNA and mutant DNA for each exon extracted through clones were used as standards to evaluate the performance of the EGFR mutation detection kit.
- samples were prepared by adding 10,000 copies, 100 copies, 30 copies, 10 copies, or 3 copies of each mutant plasmid described in Table 4 per 30,000 copies of HEK293T cell genomic DNA. The group was used as a control.
- MMX Neon Mutant group EGFR nucleic acid sequence (COSMIC ID) MMX1 FAM S768I 2303G>T (6241) CFO560 Ex19Del 2240_2251del12 (6210), 2239_2247del9 (6218), 2238_2255del18 (6220), 2235_2249del15 (6223), 2236_2250del15 (6225), 2239_2253del15 (6254), 2239_2256del18 (6255), 2237_2254del18 (12367), 2240_2254del15 (370) 2239_2248TTAAGAGAAG>C (12382), 2239_2251>C (12383), 2237_2255>T (12384), 2235_2255>AAT (12385), 2237_2252>T (12386), 2239_2258>CA (12387), 2239_2256>CAA (12403), 2237_2253 >TTGCT (12416), 2238_2252
- EGFR reaction mixtures containing each of the components listed in Table 22 were each prepared in separate sterile centrifuge tubes, and the reaction Master Mixture was vortexed for 3 seconds to thoroughly mix and centrifuge briefly.
- Two PCR tubes were prepared for each sample as follows: 10.0 ⁇ L of EGFR reaction mixture was divided for each PCR tube, and 5.0 ⁇ L of each sample DNA was added to each sample tube, and then the PCR tube was covered. Nuclease-free distilled water was added to all PCR tubes to 20.0 ⁇ L, and PCR strips were briefly centrifuged to collect all liquids at the bottom of each PCR tube.
- PCR strip tube was placed in a real-time PCR (real-time PCR) instrument, and PCR was performed after setting the PCR protocol using the cycling parameters in Table 24. After the PCR was completed, FAM/CAL Fluor Orange 560/Quasar 670 Ct values of each sample were recorded to analyze the data, and ⁇ Ct values per well were calculated as follows:
- ⁇ Ct value sample Ct value (FAM of each MMX)-positive control Ct value (FAM of each MMX)
- ⁇ Ct value sample Ct value (each MMX CFO560)-positive control Ct value (CFO560 of each MMX)
- the kit of the present invention shows high detection sensitivity (up to 0.01%, 3 mutant copies in 30,000 wild-type copies), high specificity and reproducibility, and is applicable to both liquid biopsy and tissue biopsy.
- high detection sensitivity up to 0.01%, 3 mutant copies in 30,000 wild-type copies
- high specificity and reproducibility high specificity and reproducibility
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Zoology (AREA)
- Wood Science & Technology (AREA)
- Genetics & Genomics (AREA)
- Proteomics, Peptides & Aminoacids (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Biochemistry (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Biotechnology (AREA)
- Analytical Chemistry (AREA)
- Immunology (AREA)
- Microbiology (AREA)
- Pathology (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Oncology (AREA)
- Hospice & Palliative Care (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Measuring Or Testing Involving Enzymes Or Micro-Organisms (AREA)
Abstract
The present invention relates to a DNA polymerase for EGFR mutation detection and a kit comprising same and, more specifically, to a DNA polymerase capable of detecting 44 somatic mutations in exons 18 to 21 of EGFR gene with high sensitivity, a primer set, a probe, a kit, and a method for detecting an EGFR gene mutation by using the kit.
Description
본 발명은 EGFR 돌연변이 검출을 위한 DNA 중합효소 및 이를 포함하는 키트에 관한 것으로, 보다 상세하게는 EGFR 유전자의 엑손 18 내지 21에서 44개의 체세포 돌연변이를 높은 민감도로 검출할 수 있는 DNA 중합효소, 프라이머 세트, 프로브, 키트 및 상기 상기 키트를 이용한 EGFR 유전자 돌연변이 검출방법에 관한 것이다.The present invention relates to a DNA polymerase for detecting EGFR mutations and a kit comprising the same, and more specifically, a DNA polymerase and primer set capable of detecting 44 somatic mutations in exons 18 to 21 of the EGFR gene with high sensitivity. , Probes, kits and methods for detecting EGFR gene mutations using the kits.
비소세포폐암(NSCLC)은 모든 폐암 진단의 80-85%를 차지하는 가장 일반적인 유형의 폐암이다. 상피 성장인자 수용체 (EGFR) 돌연변이를 갖는 환자는 게피티닙 (Iressa, AstraZeneca), 에를로티닙 (Tarceba, Roche) 및 오시머티닙 (Tagrisso, AstraZeneca)과 같은 EGFR 티로신 키나아제 억제제 (TKI)에 대한 높은 약물 반응 또는 내성을 나타내는 것으로 알려져 있다. G719X, S768I, Ex19 결실, L858R 및 L861Q 돌연변이는 EGFR TKI에 대한 감수성과 연관된 반면, T790M과 대부분의 Ex20 삽입 돌연변이는 감소된 EGFR TKI 반응과 연관되어 있다. 폐암 환자에서 EGFR 유전자 돌연변이의 조기 검출은 치료 전 약물 반응을 예측할 수 있도록 한다.Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the most common type of lung cancer, accounting for 80-85% of all lung cancer diagnoses. Patients with epithelial growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations have high levels of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) such as gefitinib (Iressa, AstraZeneca), erlotinib (Tarceba, Roche), and osimmertinib (Tagrisso, AstraZeneca). It is known to exhibit drug response or resistance. G719X, S768I, Ex19 deletion, L858R and L861Q mutations are associated with susceptibility to EGFR TKI, whereas T790M and most Ex20 insertion mutations are associated with reduced EGFR TKI response. Early detection of EGFR gene mutations in lung cancer patients allows predicting drug response before treatment.
지금까지 EGFR 돌연변이의 검출을 위하여 가장 많이 사용되는 방법 중 하나는 직접 염기서열분석법으로, EGFR의 엑손 18번 내지 21번에 해당하는 유전자의 염기서열을 직접 확인하는 것이다. 이 방법은 실시간 중합효소연쇄반응(realtime- polymerase chain reaction)이나 DNA 칩 분석에 비하여 시간은 많이 소요되는 단점이 있으나, 특정 염기만이 아니라 표적부위 전체의 염기분석이 가능하다는 점에서 가장 정확한 분석이 가능하다는 장점을 가진다. 따라서, EGFR 돌연변이 검출 민감도를 향상시킴으로써 폐암 환자의 약물 반응성을 보다 정확하게 예측하기 위한 키트의 개발이 지속적으로 요구되고 있다. So far, one of the most used methods for the detection of EGFR mutations is direct sequencing, which directly identifies the nucleotide sequence of the gene corresponding to exons 18 to 21 of EGFR. This method has the disadvantage that it takes a lot of time compared to real-time polymerase chain reaction or DNA chip analysis, but it is the most accurate analysis in that it is possible to analyze the base of the target site as well as a specific base. It has the advantage of being possible. Accordingly, there is a continuous need for a kit for more accurately predicting drug reactivity of lung cancer patients by improving the sensitivity of detecting EGFR mutations.
한편, 대한민국 공개특허 제10-2015-0102468호에는 폐암 관련 돌연변이 증폭용 프라이머 세트, 및 상기 돌연변이에 상보적인 프로브를 포함하는 폐암 진단용 키트가 개시된 바 있으나, EGFR 유전자의 돌연변이를 검출하기 위한 중합효소 및 이의 활성을 증가시키기 위한 반응 버퍼에 대해서는 알려진 바가 없다.On the other hand, Korean Patent Publication No. 10-2015-0102468 discloses a kit for diagnosing lung cancer, which includes a primer set for amplifying a lung cancer-related mutation and a probe complementary to the mutation, but a polymerase for detecting a mutation in the EGFR gene and There is no known reaction buffer to increase its activity.
이에, 본 발명자들은 EGFR 유전자의 엑손 18, 19, 20 및 21에서 44개의 체세포 돌연변이를 높은 민감도로 검출할 수 있는 DNA 중합효소 및 이의 활성을 증가시키기 위한 반응 버퍼를 포함하는 키트를 개발하고, 본 발명을 완성하였다.Accordingly, the present inventors have developed a kit comprising a DNA polymerase capable of detecting 44 somatic mutations in exons 18, 19, 20 and 21 of the EGFR gene with high sensitivity and a reaction buffer for increasing its activity. The invention was completed.
본 발명의 목적은 EGFR 유전자 돌연변이 검출용 DNA 중합효소를 제공하는 것이다.An object of the present invention is to provide a DNA polymerase for detecting EGFR gene mutation.
본 발명의 다른 목적은 EGFR 유전자 돌연변이 검출용 프라이머 세트를 제공하는 것이다.Another object of the present invention is to provide a primer set for detecting EGFR gene mutations.
본 발명의 다른 목적은 EGFR 유전자 돌연변이 검출용 프로브를 제공하는 것이다.Another object of the present invention is to provide a probe for detecting an EGFR gene mutation.
본 발명의 또 다른 목적은 전술한 DNA 중합효소 및/또는 프라이머 세트를 포함하는, EGFR 유전자 돌연변이 검출용 키트를 제공하는 것이다.Another object of the present invention is to provide a kit for detecting EGFR gene mutations, which includes the DNA polymerase and/or primer set described above.
본 발명의 또 다른 목적은 전술한 키트를 이용한, EGFR 유전자 돌연변이 검출방법을 제공하는 것이다.Another object of the present invention is to provide a method for detecting EGFR gene mutations using the aforementioned kit.
상술한 과제를 해결하기 위해, 본 발명은 서열번호 1의 아미노산 서열에서 507번째 아미노산 잔기인 글루탐산(E)이 리신(K)으로 치환되고, 536번째 아미노산 잔기인 아르기닌(R)이 리신(K)으로 치환되며, 660번째 아미노산 잔기인 아르기닌(R)이 발린(V)으로 치환된 Taq 중합효소를 포함하는, EGFR 유전자 돌연변이 검출용 DNA 중합효소를 제공한다,In order to solve the above-described problem, the present invention is a 507th amino acid residue glutamic acid (E) in the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1 is substituted with lysine (K), the 536th amino acid residue arginine (R) is lysine (K) Provided is a DNA polymerase for detecting EGFR gene mutations, including Taq polymerase substituted with valine (V), wherein arginine (R), the 660th amino acid residue, is substituted with
본 발명은 또한, 서열번호 3 내지 54로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택되는 1종 이상의 프라이머를 포함하는, EGFR 유전자 돌연변이 검출용 프라이머 세트를 제공한다.The present invention also provides a primer set for EGFR gene mutation detection, comprising at least one primer selected from the group consisting of SEQ ID NOs: 3 to 54.
본 발명은 또한, 서열번호 55 내지 63으로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택되는 뉴클레오티드 서열을 포함하는, EGFR 유전자 돌연변이 검출용 프로브를 제공한다.The present invention also provides a probe for detecting an EGFR gene mutation, comprising a nucleotide sequence selected from the group consisting of SEQ ID NOs: 55 to 63.
본 발명의 바람직한 일실시예에 따르면, 상기 서열번호 55 내지 63의 뉴클레오티드 서열은 각각 5'-말단에 FAM, CAL Fluor Orange 560, VIC, HEX, JOE, Quasar 670 및 CY5로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택되는 1종의 형광물질 (fluorophore)이 표지될 수 있고, 3'-말단에 BHQ-1 BHQ1 nova 및 BHQ-2로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택되는 1종의 소광물질이 표지될 수 있다.According to one preferred embodiment of the present invention, the nucleotide sequences of SEQ ID NOs: 55 to 63 are each selected from the group consisting of FAM, CAL Fluor Orange 560, VIC, HEX, JOE, Quasar 670 and CY5 at the 5'-end. Fluorophores of the species may be labeled, and one quencher selected from the group consisting of BHQ-1 BHQ1 nova and BHQ-2 may be labeled at the 3'-end.
본 발명은 또한, 서열번호 1의 아미노산 서열에서 507번째 아미노산 잔기인 글루탐산(E)이 리신(K)으로 치환되고, 536번째 아미노산 잔기인 아르기닌(R)이 리신(K)으로 치환되며, 660번째 아미노산 잔기인 아르기닌(R)이 발린(V)으로 치환된 Taq 중합효소; 및/또는 서열번호 3 내지 54로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택되는 1종 이상의 프라이머;를 포함하는, EGFR 유전자 돌연변이 검출용 키트를 제공한다.In the present invention, in the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1, the 507th amino acid residue glutamic acid (E) is substituted with lysine (K), the 536th amino acid residue arginine (R) is substituted with lysine (K), and the 660th Taq polymerase in which the amino acid residue arginine (R) is substituted with valine (V); And / or at least one primer selected from the group consisting of SEQ ID NO: 3 to 54; provides a kit for detecting EGFR gene mutation.
본 발명의 바람직한 일실시예에 따르면, 상기 키트는 서열번호 55 내지 63으로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택되는 뉴클레오티드 서열을 포함하는 프로브를 추가로 포함할 수 있다.According to one preferred embodiment of the present invention, the kit may further include a probe comprising a nucleotide sequence selected from the group consisting of SEQ ID NOs: 55 to 63.
본 발명의 바람직한 다른 일실시예에 따르면, 상기 서열번호 55 내지 63의 뉴클레오티드 서열은 각각 5'-말단에 FAM, CAL Fluor Orange 560, VIC, HEX, JOE, Quasar 670 및 CY5로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택되는 1종의 형광물질 (fluorophore)이 표지될 수 있고, 3'-말단에 BHQ-1 BHQ1 nova 및 BHQ-2로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택되는 1종의 소광물질이 표지될 수 있다.According to another preferred embodiment of the present invention, the nucleotide sequences of SEQ ID NOs: 55 to 63 are each selected from the group consisting of FAM, CAL Fluor Orange 560, VIC, HEX, JOE, Quasar 670 and CY5 at the 5'-end. One fluorophore may be labeled, and one quencher selected from the group consisting of BHQ-1 BHQ1 nova and BHQ-2 may be labeled at the 3'-end.
본 발명의 바람직한 일실시예에 따르면, 상기 키트는 25 내지 100 mM의 KCl; 및 1 내지 7 mM의 (NH4)2SO4;를 포함하고, 최종 pH가 8.0 내지 9.5인 PCR 버퍼 조성물을 추가로 포함할 수 있다.According to a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the kit comprises 25 to 100 mM KCl; And 1 to 7 mM (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 ; and may further include a PCR buffer composition having a final pH of 8.0 to 9.5.
본 발명의 바람직한 다른 일실시예에 따르면, 상기 키트는 25 내지 100 mM의 KCl; 1 내지 7 mM의 (NH4)2SO4; 및 5 내지 50 mM의 TMAC(Tetra methyl ammonium chloride)를 포함하고, 최종 pH가 8.0 내지 9.5인 PCR 버퍼 조성물을 추가로 포함할 수 있다.According to another preferred embodiment of the present invention, the kit comprises 25 to 100 mM KCl; 1 to 7 mM (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 ; And 5 to 50 mM of TMAC (Tetra methyl ammonium chloride), and may further include a PCR buffer composition having a final pH of 8.0 to 9.5.
본 발명은 또한, 다음의 단계를 포함하는 EGFR 유전자 돌연변이 검출방법을 제공한다: (a) 분리된 생물학적 시료로부터 핵산을 추출하는 단계; (b) 상기 추출한 핵산에 본 발명의 키트를 처리하여 PCR (polymerase chain reaction)을 수행하는 단계; 및 (c) 상기 PCR에 의한 증폭 결과를 형광으로 확인하는 단계.The present invention also provides a method for detecting an EGFR gene mutation comprising the following steps: (a) extracting a nucleic acid from an isolated biological sample; (b) processing the kit of the present invention on the extracted nucleic acid to perform PCR (polymerase chain reaction); And (c) confirming the amplification result by the PCR with fluorescence.
본 발명의 바람직한 일실시예에 따르면, 상기 PCR은 대립유전자 특이적 (allele-specific) PCR 또는 실시간 (real-time) PCR일 수 있다.According to a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the PCR may be allele-specific PCR or real-time PCR.
본 발명의 바람직한 다른 일실시예에 따르면, (d) 상기 PCR에 의한 증폭 결과를 Ct (cycle threshold) 값을 측정하여 확인하는 단계를 추가로 포함할 수 있다.According to another preferred embodiment of the present invention, (d) may further include the step of confirming the amplification result by the PCR by measuring the Ct (cycle threshold) value.
본 발명의 바람직한 일실시예에 따르면, 상기 EGFR 유전자 돌연변이는 EGFR 유전자의 엑손 18번, 19번, 20번 및 21번 내에서의 결실, 치환 및 삽입 돌연변이로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택되는 1종 이상을 포함할 수 있다.According to a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the EGFR gene mutation includes at least one selected from the group consisting of deletion, substitution and insertion mutations in exons 18, 19, 20 and 21 of the EGFR gene. can do.
본 발명의 바람직한 다른 일실시예에 따르면, 상기 EGFR 유전자 돌연변이는 EGFR의 엑손 18번 내에서의 719번째 아미노산인 글리신의 치환, 엑손 19번 내에서의 결손, 엑손 20번 내에서의 768번째 아미노산인 세린, 790번째 아미노산인 트레오닌, 797번째 아미노산인 시스테인의 치환, 엑손 20번 내에서의 삽입, 엑손 21번 내에서의 858번째 아미노산인 류신 및 861번째 아미노산인 류신의 치환으로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택된 1종 이상을 포함할 수 있다.According to another preferred embodiment of the present invention, the EGFR gene mutation is a 719th amino acid glycine substitution in exon 18 of EGFR, a deletion in exon 19, a 768th amino acid in exon 20. Serine, 790th amino acid threonine, 797th amino acid cysteine substitution, exon 20 insertion, exon 21 858 amino acid leucine and 861 amino acid leucine substitution. It may include the above.
본 발명의 바람직한 또 다른 일실시예에 따르면, EGFR 유전자 돌연변이 검출방법은 폐암 환자의 약물에 대한 반응성을 예측하기 위한 것일 수 있다.According to another preferred embodiment of the present invention, the EGFR gene mutation detection method may be for predicting responsiveness to drugs of lung cancer patients.
본 발명의 바람직한 다른 일실시예에 따르면, 상기 폐암은 비소세포폐암일 수 있다.According to another preferred embodiment of the present invention, the lung cancer may be non-small cell lung cancer.
본 발명의 바람직한 또 다른 일실시예에 따르면, 상기 약물은 티로신 키나아제 억제제(tyrosine kinase inhibitor)일 수 있다.According to another preferred embodiment of the present invention, the drug may be a tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
본 발명의 바람직한 다른 일실시예에 따르면, 상기 티로신 키나아제 억제제는 게피티닙, 에를로티닙 또는 오시머티닙인일 수 있다.According to another preferred embodiment of the present invention, the tyrosine kinase inhibitor may be gefitinib, erlotinib or osimitinib.
본 발명의 바람직한 또 다른 일실시예에 따르면, 상기 (a) 단계의 핵산은 조직 생검의 포르말린 고정 파라핀 포매 시료(formalin-fixed paraffin embedded sample) 또는 액체 생검으로부터 추출된 것일 수 있다.According to another preferred embodiment of the present invention, the nucleic acid of step (a) may be extracted from a formalin-fixed paraffin embedded sample or a liquid biopsy of a tissue biopsy.
본 발명의 키트는 높은 검출 민감도 (최대 0.01%, 30,000 야생형 카피에서 3개의 돌연변이 카피), 높은 특이성 및 재현성을 나타내며, 액체 생검 및 조직 생검에 모두 적용 가능하다. 또한, EGFR 유전자의 엑손 18번 내지 21번 내에서 44개의 돌연변이를 동시 다발적으로 검출함으로써 폐암 환자의 티로신 키나아제 억제제에 대한 약물 반응성을 정확하게 예측할 수 있다.The kit of the present invention shows high detection sensitivity (up to 0.01%, 3 mutant copies in 30,000 wild-type copies), high specificity and reproducibility, and is applicable to both liquid biopsy and tissue biopsy. In addition, by simultaneously detecting 44 mutations within exons 18 to 21 of the EGFR gene, it is possible to accurately predict drug reactivity to lung cancer patients against tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
도 1은 R536K, R660V 및 R536K/R660V 변이를 각각 포함하는 Taq DNA 중합효소의 제조과정을 나타낸 것으로, (a)는 단편 PCR 및 오버랩 PCR을 도식화하여 나타낸 것이고, (b)는 단편 PCR에서 증폭된 산물을 전기영동으로 확인한 결과를 나타낸 것이며, (c)는 오버랩 PCR로 전장을 증폭하여 증폭된 산물을 전기영동으로 확인한 결과를 나타낸 것이다.Figure 1 shows the production process of Taq DNA polymerase containing each of the R536K, R660V and R536K/R660V mutations, (a) schematically shows fragment PCR and overlap PCR, (b) is amplified in fragment PCR The result of confirming the product by electrophoresis, and (c) shows the result of confirming the amplified product by electrophoresis by amplifying the entire length by overlap PCR.
도 2는 겔 추출을 위해, 제한효소 EcoRI/XbaI로 분해한 다음 SAP를 처리한 pUC19 벡터와 정제한 도 1(c)의 오버랩 PCR 산물을 전기영동으로 확인한 결과이다.Figure 2 is a result of confirming the overlap PCR product of FIG. 1(c) purified by digestion with the restriction enzyme EcoRI/XbaI and then the SAP-treated pUC19 vector for gel extraction.
도 3은 E507K, E507K/R536K, E507K/R660V 및 E507K/R536K/R660V 변이를 각각 포함하는 Taq DNA 중합효소의 제조과정 중 단편 PCR 및 오버랩 PCR을 도식화하여 나타낸 것이다. Figure 3 is a schematic diagram showing fragment PCR and overlap PCR during the preparation of Taq DNA polymerase containing E507K, E507K/R536K, E507K/R660V and E507K/R536K/R660V mutations, respectively.
도 4는 겔 추출을 위해, 제한효소 EcoRI/XbaI로 분해한 다음 SAP를 처리한 pUC19 벡터와 정제한 도 3의 오버랩 PCR 산물을 전기영동으로 확인한 결과이다.FIG. 4 shows the results of confirming by electrophoresis the overlap PCR product of FIG. 3 purified with the pUC19 vector digested with the restriction enzyme EcoRI/XbaI for gel extraction, and then with SAP.
도 5a 내지 5l은 Ex19del C1 내지 Ex19del C12 돌연변이 플라스미드 (3, 102 및 104 카피) 주형에서 AS-qPCR로 돌연변이를 검출한 결과를 나타낸 것이다.5A to 5L show the results of detecting mutations with AS-qPCR in the Ex19del C1 to Ex19del C12 mutant plasmid (3, 10 2 and 10 4 copies) template.
도 6a 내지 6l은 Ex19del C13 내지 Ex19del C24 돌연변이 플라스미드 (3, 102 및 104 카피) 주형에서 AS-qPCR로 돌연변이를 검출한 결과를 나타낸 것이다.6A to 6L show the results of detecting mutations with AS-qPCR in the Ex19del C13 to Ex19del C24 mutant plasmid (3, 10 2 and 10 4 copies) template.
도 7a 내지 7g는 Ex19del C25 내지 Ex19del C31 돌연변이 플라스미드 (3, 102 및 104 카피) 주형에서 AS-qPCR로 돌연변이를 검출한 결과를 나타낸 것이고, 7h는 S768I 돌연변이 플라스미드 (3, 102 및 104 카피) 주형에서 AS-qPCR로 돌연변이를 검출한 결과를 나타낸 것이고, 7i는 WT에서 AS-qPCR로 돌연변이를 검출한 결과를 나타낸 것이다.7A to 7G show the results of detecting mutations with AS-qPCR in the Ex19del C25 to Ex19del C31 mutant plasmid (3, 10 2 and 10 4 copies) template, and 7h is S768I mutant plasmid (3, 10 2 and 10 4 Copy) shows the result of detecting the mutation with AS-qPCR in the template, and 7i shows the result of detecting the mutation with AS-qPCR in WT.
도 8은 T790M 돌연변이 플라스미드 (0, 3, 101, 30, 102 및 104 카피) 주형에서 AS-qPCR로 돌연변이를 검출한 결과를 나타낸 것이다.8 shows the results of detecting mutations with AS-qPCR in the T790M mutant plasmid (0, 3, 10 1 , 30, 10 2 and 10 4 copies) template.
도 9a는 G719S 돌연변이 플라스미드 (3, 101, 30, 102 및 104 카피) 주형에서 AS-qPCR로 돌연변이를 검출한 결과를 나타낸 것이다.Figure 9a shows the results of detecting the mutation in the G719S mutant plasmid (3, 10 1 , 30, 10 2 and 10 4 copies) template with AS-qPCR.
도 9b는 G719C 돌연변이 플라스미드 (3, 101, 30, 102 및 104 카피) 주형에서 AS-qPCR로 돌연변이를 검출한 결과를 나타낸 것이다.Figure 9b shows the results of detecting the mutation in the G719C mutant plasmid (3, 10 1 , 30, 10 2 and 10 4 copies) template with AS-qPCR.
도 9c는 G719A 돌연변이 플라스미드 (3, 101, 30, 102 및 104 카피) 주형에서 AS-qPCR로 돌연변이를 검출한 결과를 나타낸 것이다.Figure 9c shows the results of detecting the mutation in the G719A mutant plasmid (3, 10 1 , 30, 10 2 and 10 4 copies) template with AS-qPCR.
도 9d는 WT에서 AS-qPCR로 돌연변이를 검출한 결과를 나타낸 것이다.Figure 9d shows the results of detecting the mutation in WT AS-qPCR.
도 9e는 L861Q 돌연변이 플라스미드 (0, 3, 102 및 104 카피) 주형에서 AS-qPCR로 돌연변이를 검출한 결과를 나타낸 것이다.9E shows the results of detecting mutations with AS-qPCR in the L861Q mutant plasmid (0, 3, 10 2 and 10 4 copies) template.
도 10a 내지 10e는 Ex20Ins C1 내지 Ex20Ins C5 돌연변이 플라스미드 (3, 102 및 104 카피) 주형에서 AS-qPCR로 돌연변이를 검출한 결과를 나타낸 것이고, 10f는 WT에서 AS-qPCR로 돌연변이를 검출한 결과를 나타낸 것이며, 도 10g는 L858R 돌연변이 플라스미드 (3, 102 및 104 카피) 주형에서 AS-qPCR로 돌연변이를 검출한 결과를 나타낸 것이고, 10h는 WT에서 AS-qPCR로 돌연변이를 검출한 결과를 나타낸 것이다.10A to 10E show the results of detecting mutations with AS-qPCR in the Ex20Ins C1 to Ex20Ins C5 mutant plasmid (3, 10 2 and 10 4 copies) template, and 10f is the result of detecting mutations from WT to AS-qPCR. 10g shows the results of detecting mutations with AS-qPCR in the L858R mutant plasmid (3, 10 2 and 10 4 copies) template, and 10h shows the results of detecting mutations in WT with AS-qPCR. will be.
상술한 바와 같이, EGFR 돌연변이 검출 민감도를 향상시킴으로써 폐암 환자의 약물 반응성을 보다 정확하게 예측하기 위한 키트의 개발이 지속적으로 요구되고 있다. 이에, 본 발명자들은 EGFR 유전자의 엑손 18, 19, 20 및 21에서 44개의 체세포 돌연변이를 높은 민감도로 검출할 수 있는 DNA 중합효소 및 이의 활성을 증가시키기 위한 반응 버퍼를 포함하는 최적화된 키트를 제공함으로써 상술한 문제의 해결방안을 모색하였다. 본 발명의 키트는 높은 검출 민감도, 높은 특이성 및 재현성을 나타내며, 액체 생검 및 조직 생검에 모두 적용 가능하다. 또한, 반-정량적 분석(Semi-quantitative analysis)을 특징으로 하며, 4개의 채널로 모든 qPCR 기기에서 분석이 가능하다.As described above, there is a continuous need to develop a kit for more accurately predicting drug reactivity of lung cancer patients by improving the sensitivity of detecting EGFR mutations. Thus, the present inventors provide an optimized kit comprising a DNA polymerase capable of detecting 44 somatic mutations in exons 18, 19, 20 and 21 of the EGFR gene with high sensitivity and a reaction buffer to increase its activity. The solution to the above problem was sought. The kit of the present invention exhibits high detection sensitivity, high specificity and reproducibility, and is applicable to both liquid biopsy and tissue biopsy. In addition, it features a semi-quantitative analysis, and analysis is possible on all qPCR devices with 4 channels.
이하, 본원에 사용되는 용어를 설명한다.Hereinafter, terms used in the present application will be described.
"아미노산" 은 펩타이드, 폴리펩타이드, 또는 단백질에 혼입될 수 있는 임의의 단량체 단위를 지칭한다. 본원에 사용되는 바와 같이, 용어 "아미노산" 은 하기 20 개의 천연 또는 유전적으로 인코딩된 알파-아미노산을 포함한다: 알라닌 (Ala 또는 A), 아르기닌 (Arg 또는 R), 아스파라긴 (Asn 또는 N), 아스파르트산 (Asp 또는 D), 시스테인 (Cys 또는 C), 글루타민 (Gln 또는 Q), 글루탐산 (Glu 또는 E), 글리신 (Gly 또는 G), 히스티딘 (His 또는 H), 이소류신 (Ile 또는 I), 류신 (Leu 또는 L), 라이신 (Lys 또는 K), 메티오닌 (Met 또는 M), 페닐알라닌 (Phe 또는 F), 프롤린 (Pro 또는 P), 세린 (Ser 또는 S), 트레오닌 (Thr 또는 T), 트립토판 (Trp 또는 W), 티로신 (Tyr 또는 Y), 및 발린 (Val 또는 V). "Amino acid" refers to any monomeric unit that can be incorporated into a peptide, polypeptide, or protein. As used herein, the term "amino acid" includes the following 20 natural or genetically encoded alpha-amino acids: alanine (Ala or A), arginine (Arg or R), asparagine (Asn or N), aspart Acid (Asp or D), cysteine (Cys or C), glutamine (Gln or Q), glutamic acid (Glu or E), glycine (Gly or G), histidine (His or H), isoleucine (Ile or I), leucine (Leu or L), lysine (Lys or K), methionine (Met or M), phenylalanine (Phe or F), proline (Pro or P), serine (Ser or S), threonine (Thr or T), tryptophan ( Trp or W), tyrosine (Tyr or Y), and valine (Val or V).
아미노산은 전형적으로 유기산이며, 이는 치환되거나 치환되지 않은 아미노기, 치환되거나 치환되지 않은 카르복시기, 및 하나 이상의 측사슬(side chain) 또는 기(group), 또는 이들 기의 임의의 유사체를 포함한다. 예시적인 측사슬은, 예를 들어, 티올, 셀레노, 술포닐, 알킬, 아릴, 아실, 케토, 아지도, 히드록실, 히드라진, 시아노, 할로, 히드라지드, 알케닐, 알키닐, 에테르, 보레이트, 보로네이트, 포스포, 포스포노, 포시핀, 헤테로시클릭, 에논, 이민, 알데히드, 에스테르, 티오산, 히드록실아민, 또는 이들 기의 임의의 조합을 포함한다.Amino acids are typically organic acids, which include substituted or unsubstituted amino groups, substituted or unsubstituted carboxy groups, and one or more side chains or groups, or any analogue of these groups. Exemplary side chains include, for example, thiol, seleno, sulfonyl, alkyl, aryl, acyl, keto, azido, hydroxyl, hydrazine, cyano, halo, hydrazide, alkenyl, alkynyl, ether, Borate, boronate, phospho, phosphono, phosphine, heterocyclic, enone, imine, aldehyde, ester, thio acid, hydroxylamine, or any combination of these groups.
본 발명의 DNA 중합효소에서, 용어 "돌연변이체"는 상응하는 자연 발생 또는 변형되지 않은 DNA 중합효소에 비해 하나 이상의 아미노산 치환을 포함하는 재조합 폴리펩타이드를 의미한다.In the DNA polymerase of the present invention, the term "mutant" refers to a recombinant polypeptide comprising one or more amino acid substitutions compared to the corresponding naturally occurring or unmodified DNA polymerase.
용어 "열안정성 중합효소" (열에 안정한 효소를 지칭함)는 열 저항성이 있으며, 후속 폴리뉴클레오타이드 신장 반응을 달성하기에 충분한 활성을 보유하고 이중가닥 핵산의 변성을 달성하기 위해 요구되는 시간 동안 승온으로 처리될 때 비가역적으로 변성 (불활성화) 되지 않는다. 본원에 사용되는 바와 같이, PCR 과 같은 반응을 사이클링하는 온도에 사용되기에 적합하다. 본원에서 비가역성 변성은 영구하고 효소 활성의 완전한 손실을 지칭한다. 열안정성 중합효소에 대해, 효소 활성은 주형 핵산 가닥에 대해 상보적인 폴리뉴클레오타이드 신장 생성물을 형성하기 위한 적절한 방식으로 뉴클레오타이드의 조합을 촉매작용하는 것을 지칭한다. 호열성 박테리아 유래 열안정성 DNA 중합효소는 예를 들어 하기를 포함한다: 써모토가 마리티마, 써무스 아쿠아티쿠스, 써무스써모필루스, 써무스 플라부스, 써모드 필리포르미스, 써무스 종 Sps17, 써무스 종 Z05, 써무스 칼도필루스, 바실러스 칼도테낙스, 써모토가 네오폴리타나, 및 써모시포 아프리카누스 유래 DNA 중합효소.The term “thermal stable polymerase” (referring to a heat stable enzyme) is heat resistant, retains sufficient activity to achieve subsequent polynucleotide elongation reactions and is treated with elevated temperature for the time required to achieve denaturation of the double-stranded nucleic acid Does not irreversibly denature (deactivate) when As used herein, it is suitable for use at temperatures cycling reactions such as PCR. Irreversible denaturation herein refers to permanent and complete loss of enzyme activity. For thermostable polymerases, enzymatic activity refers to catalyzing a combination of nucleotides in a suitable way to form a polynucleotide extension product complementary to the template nucleic acid strand. Thermostable DNA polymerases derived from thermophilic bacteria include, for example: Thermomoto maritima, thermos aquaticus, thermos thermophilus, thermos flavus, thermomod philipformis, thermos species DNA polymerase derived from Sps17, Thermos species Z05, Thermos Caldophyllus, Bacillus caldotenax, Thermomoto Neopolitana, and Thermosippo africanus.
용어 "열활성" 은 RT-PCR 및/또는 PCR 반응에서 역전사 또는 어닐링/신장 단계에 통상적으로 사용되는 온도 (즉, 45-80℃)에서 촉매 특성을 유지하는 효소를 지칭한다. 열안정성 효소는 핵산 변성에 요구되는 상승된 온도로 처리될 때 비가역적으로 불활성화되거나 변성되지 않는 것이다. 열활성 효소는 열안정성일 수 있거나 열안정성일 수 없다. 열활성 DNA 중합효소는 하기를 포함하나 이에 한정되지 않는 호열성 종 또는 중온성 종으로부터 의존적인 DNA 또는 RNA 일 수 있다.The term “thermal activity” refers to an enzyme that maintains catalytic properties at temperatures (ie 45-80° C.) commonly used for reverse transcription or annealing/extension steps in RT-PCR and/or PCR reactions. Thermostable enzymes are those that are not irreversibly inactivated or denatured when treated at elevated temperatures required for nucleic acid denaturation. The thermoactive enzyme may or may not be thermostable. The thermally active DNA polymerase can be DNA or RNA dependent from thermophilic or mesophilic species, including but not limited to:
용어 “뉴클레오타이드(nucleotide)”는 단일가닥(single strand) 또는 이중가닥(double strand) 형태로 존재하는 디옥시리보뉴클레오타이드(deoxyribonucleic acid; DNA) 또는 리보뉴클레오타이드(ribonucleic acid; RNA)이며, 다르게 특별하게 언급되어 있지 않은 한 자연의 뉴클레오타이드의 유사체를 포함할 수 있다. The term “nucleotide” is a deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) or ribonucleic acid (RNA) that exists in the form of a single strand or a double strand, and is not specifically mentioned otherwise. Unless it can contain analogs of natural nucleotides.
용어 "핵산"은 또는 "폴리뉴클레오타이드"는 DNA 또는 RNA 중합체, 또는 이의 유사체에 상응할 수 있는 중합체를 지칭한다. 핵산은, 예를 들어, 염색체 또는 염색체 분절, 벡터 (예를 들어, 발현 벡터), 발현 카세트, 네이키드 DNA 또는 RNA 중합체, 중합효소 사슬 반응 (PCR) 의 생성물, 올리고뉴클레오타이드, 탐침, 및 프라이머일 수 있거나 이를 포함할 수 있다. 핵산은 예를 들어, 단일-가닥, 이중-가닥, 또는 삼중-가닥일 수 있으나 임의의 특정 길이에 한정되지 않는다. 달리 언급되지 않는 한, 특정 핵산 서열은 명시되는 임의의 서열 외에도 상보 서열을 포함하거나 이를 코딩한다.The term “nucleic acid” or “polynucleotide” refers to a polymer that can correspond to a DNA or RNA polymer, or analogs thereof. Nucleic acids can be, for example, chromosomal or chromosomal segments, vectors (eg, expression vectors), expression cassettes, naked DNA or RNA polymers, products of polymerase chain reaction (PCR), oligonucleotides, probes, and primers. Or may include it. Nucleic acids can be, for example, single-stranded, double-stranded, or triple-stranded, but are not limited to any particular length. Unless otherwise stated, certain nucleic acid sequences include or encode complementary sequences in addition to any sequence specified.
용어 "프라이머" 는 폴리뉴클레오타이드 신장이 개시되는 조건 하에 놓일 때 주형-방향으로 핵산 합성의 개시점으로서 작용할 수 있는 폴리뉴클레오타이드를 지칭한다. 프라이머는 또한 de novo RNA 합성 및 시험관내 전사-관련 공정의 개시제로서 포함되는, 다양한 기타 올리고뉴클레오타이드-중재 합성 공정에서 사용될 수 있다. 프라이머는 전형적으로는, 단일-가닥 올리고뉴클레오타이드 (예를 들어, 올리고데옥시리보뉴클레오타이드)이다. 프라이머의 적절한 길이는 전형적으로는 6 내지 40 개의 뉴클레오타이드 범위, 보다 전형적으로는 15 내지 35 개의 뉴클레오타이드 범위에서 의도되는 사용에 따라 달라진다. 짧은 프라이머 분자는 일반적으로 주형과 충분히 안정적인 혼성화 착물을 형성하기 위해 보다 저온의 온도를 요구한다. 프라이머는 주형의 정확한 서열을 반영하는데 요구되지 않으나, 프라이머가 신장되기 위한 주형과 혼성화되기 위해 충분히 상보적이어야만 한다. 특정 구현예에서, 용어 "프라이머 쌍"은 증폭되는 핵산 서열의 5'-말단에 상보적으로 혼성화되는 5'-센스 프라이머를 포함하고, 증폭되는 서열의 3' 말단에 혼성화되는 3'-안티센스 프라이머를 포함하는 프라이머의 세트를 의미한다. 프라이머는, 필요한 경우, 분광학적, 광화학적, 생화학적, 면역화학적 또는 화학적 수단에 의해 검출될 수 있는 표지를 혼입함으로써 표지될 수 있다. 예를 들어, 유용한 표지는 하기를 포함한다: 32P, 형광 염료, 전자-덴스 시약, 효소 (ELISA 분석에서 통상적으로 사용됨), 비오틴, 또는 합텐 및 항혈청 또는 모노클로날 항체가 이용될 수 있는 단백질.The term “primer” refers to a polynucleotide that can serve as a starting point for nucleic acid synthesis in the template-direction when placed under conditions where polynucleotide elongation is initiated. Primers can also be used in a variety of other oligonucleotide-mediated synthesis processes, including as initiators of de novo RNA synthesis and in vitro transcription-related processes. Primers are typically single-stranded oligonucleotides (eg, oligodeoxyribonucleotides). The appropriate length of the primer will typically depend on the intended use in the range of 6 to 40 nucleotides, more typically in the range of 15 to 35 nucleotides. Short primer molecules generally require a lower temperature to form a sufficiently stable hybridization complex with the template. Primers are not required to reflect the exact sequence of the template, but must be sufficiently complementary to hybridize with the template for elongation of the primer. In certain embodiments, the term “primer pair” includes a 5′-sense primer that hybridizes complementarily to the 5′-end of the amplified nucleic acid sequence, and a 3′-antisense primer that hybridizes to the 3′ end of the amplified sequence. Means a set of primers comprising Primers can be labeled, if necessary, by incorporating a label that can be detected by spectroscopic, photochemical, biochemical, immunochemical or chemical means. For example, useful labels include: 32 P, fluorescent dyes, electron-dense reagents, enzymes (usually used in ELISA assays), biotin, or haptens and proteins in which antiserum or monoclonal antibodies can be used. .
용어 "5'-핵산가수분해효소(nuclease) 프로브"는 핵산 검출을 표적화하기 위해 5'-핵산가수분해효소 반응에서 사용되는 하나 이상의 발광 표지 부분을 포함하는 올리고뉴클레오타이드를 지칭한다. 몇몇 구현예에서, 예를 들어, 5'-핵산가수분해효소 프로브는 오직 단일 발광 부분 (예를 들어, 형광 염료, 등)을 포함한다. 특정 구현예에서, 5'-핵산가수분해효소 프로브는, 프로브가 선택 조건 하에서 헤어핀 구조를 형성할 수 있도록 자가-상보적 영역을 포함한다. 몇몇 구현예에서, 5'-핵산가수분해효소 프로브는, 2개 이상의 표지 부분을 포함하고, 2개 중 하나의 표지가 올리고뉴클레오타이드로부터 분리되거나 분해된 후 방사 강도가 증가하여 방출된다. 특정 구현예에서, 5'-핵산가수분해효소 프로브는 2개의 상이한 형광 염료, 예를 들어 5'-말단 리포터 염료 및 3'-말단 소광제 염료 또는 부분과 표지된다. 몇몇 구현예에서, 5'-뉴클레아제 탐침은, 말단 위에 더하여, 또는 말단 위치 이외의 하나 이상의 위치에서 표지된다. 프로브가 원래대로인 경우, 전형적으로, 리포터 염료로부터 형광 방출이 부분 이상 소광되도록 2 개의 형광물질 사이에서 에너지 이동이 발생한다. 중합효소 사슬 반응의 신장 단계동안, 예를 들어 주형 핵산에 결합되는 5'-핵산가수분해효소 프로브가 리포터 염료의 형광 발광이 더 이상 소광되지 않도록 하는 활성을 갖는 예를 들어, Taq 중합효소 또는 다른 중합효소의 5' 내지 3'-핵산가수분해효소 활성에 의해 분해된다. 몇몇 구현예에서, 5'-핵산가수분해효소 프로브가 둘 이상의 상이한 리포터 염료 및 3'-말단 소광제 염료 또는 부분과 표지될 수 있다.The term “5′-nuclease probe” refers to an oligonucleotide comprising at least one luminescent label moiety used in a 5′-nuclease reaction to target nucleic acid detection. In some embodiments, for example, the 5'-nuclease hydrolyzate probe comprises only a single luminescent moiety (eg, fluorescent dye, etc.). In certain embodiments, the 5'-nuclease probe contains a self-complementary region so that the probe can form a hairpin structure under selective conditions. In some embodiments, the 5'-nuclease hydrolyzate probe comprises two or more labeling moieties, and one of the two labels is released from the oligonucleotide after being separated or degraded to increase the emission intensity. In certain embodiments, the 5'-nuclease hydrolase probe is labeled with two different fluorescent dyes, for example a 5'-terminal reporter dye and a 3'-terminal quencher dye or moiety. In some embodiments, the 5'-nuclease probe is labeled in addition to, or at one or more positions other than the terminal position. When the probe is intact, energy transfer typically occurs between the two phosphors such that the fluorescence emission from the reporter dye is partially extinguished. During the elongation phase of the polymerase chain reaction, for example, a 5'-nucleic acid hydrolase probe bound to the template nucleic acid has an activity such that the fluorescence of the reporter dye is no longer quenched, for example, Taq polymerase or other Degraded by the 5'to 3'-nucleic acid hydrolase activity of the polymerase. In some embodiments, a 5'-nuclease probe can be labeled with two or more different reporter dyes and a 3'-terminal quencher dye or moiety.
용어 "FRET" 또는 "형광 공명 에너지 이동" 또는 "포에스터 공명 에너지 이동" 은 둘 이상의 발색단, 공여체 발색단 및 수용체 발색단 (소광제로서 지칭됨) 사이의 에너지의 이동을 지칭한다. 공여체는 전형적으로는, 공여체가 적합한 파장의 빛이 방사됨으로써 여기될 때 에너지를 수용체에 이동시킨다. 수용체는 전형적으로는 상이한 파장으로 방사되는 빛의 형태로 이동된 에너지를 재방사한다. 수용체가 "암" 소광제인 경우, 이는 빛 이외의 형태로 이동된 에너지를 분산시킨다. 특정 형광물질이 공여체 또는 수용체로서 작용하는지 여부는 FRET 쌍의 다른 멤버의 특성에 의존적이다. 통상적으로 사용되는 공여체-수용체 쌍은 FAM-TAMRA 쌍을 포함한다. 통상적으로 사용되는 소광제는 DABCYL 및 TAMRA 이다. 통상적으로 사용되는 암 소광제는 하기를 포함한다: BlackHole Quenchers™ (BHQ), (Biosearch Technologies, Inc., Novato, Cal.), Iowa Black™ (Integrated DNA Tech., Inc., Coralville, Iowa), 및 BlackBerry™ Quencher 650 (BBQ-650) (Berry & Assoc., Dexter, Mich.).The terms "FRET" or "fluorescence resonance energy transfer" or "poster resonance energy transfer" refer to the transfer of energy between two or more chromophores, donor chromophores and receptor chromophores (referred to as quenchers). The donor typically transfers energy to the receptor when the donor is excited by emitting light of a suitable wavelength. Receptors typically re-emit energy transferred in the form of light emitted at different wavelengths. When the receptor is a “cancer” matting agent, it disperses the energy transferred in a form other than light. Whether a particular fluorescent substance acts as a donor or a receptor depends on the properties of other members of the FRET pair. Commonly used donor-receptor pairs include FAM-TAMRA pairs. Commonly used matting agents are DABCYL and TAMRA. Commonly used cancer matting agents include: BlackHole Quenchers™ (BHQ), (Biosearch Technologies, Inc., Novato, Cal.), Iowa Black™ (Integrated DNA Tech., Inc., Coralville, Iowa), And BlackBerry™ Quencher 650 (BBQ-650) (Berry & Assoc., Dexter, Mich.).
핵산 염기, 뉴클레오시드 트리포스페이트, 또는 뉴클레오타이드를 지칭할 때 용어 "통상적인" 또는 "천연"은, 기술되는 폴리뉴클레오타이드에서 천연 발생하는 것을 지칭한다 (즉, DNA 에 대해 이들은 dATP, dGTP, dCTP 및 dTTP임). 또한, dITP, 및 7-데아자-dGTP 는 dGTP 대신 빈번히 이용되며 서열화와 같은 시험관내 DNA 합성 반응에서 dATP 대신 이용될 수 있다.The term “conventional” or “natural” when referring to a nucleic acid base, nucleoside triphosphate, or nucleotide refers to naturally occurring polynucleotides described (ie, for DNA, they are dATP, dGTP, dCTP and dTTP). In addition, dITP, and 7-deaza-dGTP are frequently used instead of dGTP and can be used instead of dATP in in vitro DNA synthesis reactions such as sequencing.
핵산 염기, 뉴클레오시드, 또는 뉴클레오타이드를 지칭할 때 용어 "통상적이지 않은" 또는 "변형된" 은, 특정 폴리뉴클레오타이드에서 천연적으로 발생하는 통상적인 염기, 뉴클레오시드, 또는 뉴클레오타이드의 변형, 유도체 또는 유사체를 포함한다. 특정한 통상적이지 않은 뉴클레오타이드는 통상적인 dNTP 와 비교하여 리보오스 당의 2' 위치에서 변형된다. 따라서, RNA 에 대해 자연 발생 뉴클레오타이드가 리보뉴클레오타이드 (즉, ATP, GTP, CTP, UTP, 집합적 rNTP)이더라도, 뉴클레오타이드가 당의 2' 위치에서 히드록실기를 갖기 때문에, 이는 비교하여 dNTP가 부재하고, 본원에 사용되는 바와 같이, 리보뉴클레오타이드는 DNA 중합효소에 대한 기질로서 통상적이지 않은 뉴클레오타이드다. 본원에 사용되는 바와 같이, 통상적이지 않은 뉴클레오타이드는 핵산 서열화에 대한 종결자로서 사용되는 화합물을 포함하나 이에 한정되지 않는다. 예시적인 종결자 화합물은 2',3'-디데옥시 구조를 갖는 화합물을 포함하나 이에 한정되지 않으며, 이는 디데옥시뉴클레오시드 트리포스페이트로서 지칭된다. 디데옥시뉴클레오시드 트리포스페이트 ddATP, ddTTP, ddCTP 및 ddGTP 는 ddNTP 로서 집합적으로 지칭된다. 종결자 화합물의 추가의 예는 리보뉴클레오타이드의 2'-PO4 유사체를 포함한다. 다른 통상적이지 않은 뉴클레오타이드는 포스포로티오에이트 dNTP ([[α]-S]dNTP), 5'-[α]-보라노-dNTP, [α]-메틸-포스포네이트 dNTP, 및 리보뉴클레오시드 트리포스페이트 (rNTP) 를 포함한다. 통상적이지 않은 염기는 방사성 동위원소, 예컨대 32P, 33P, 또는 35S; 형광 표지; 화학발광의 표지; 생물발광의 표지; 합텐 표지 예컨대 비오틴; 또는 효소 표지 예컨대 스트렙타비딘 또는 아비딘으로 표지될 수 있다. 형광 표지는, 음성으로 하전된 염료, 예컨대 플루오세인 패밀리의 염료, 또는 중성으로 하전된 염료, 예컨대 로다민 패밀리의 염료, 또는 양성으로 하전된 염료, 예컨대 시아닌 패밀리의 염료를 포함할 수 있다. 플루오세인 패밀리의 염료는, 예를 들어, FAM, HEX, TET, JOE, NAN 및 ZOE를 포함한다. 로다민 패밀리의 염료는 Texas Red, ROX, R110, R6G, 및 TAMRA를 포함한다. FAM, HEX, TET, JOE, NAN, ZOE, ROX, R110, R6G, Texas Red 및 TAMRA로 라벨링된 다양한 염료 또는 뉴클레오타이드는 Perkin-Elmer (Boston, MA), Applied Biosystems (Foster City, CA), 또는 Invitrogen/Molecular Probes (Eugene, OR) 에 의해 시판된다. 시아닌 패밀리의 염료는 Cy2, Cy3, Cy5, 및 Cy7 을 포함하고, GE Healthcare UK Limited (Amersham Place, Little Chalfont, Buckinghamshire, England)에 의해 시판된다.The term “unconventional” or “modified” when referring to a nucleic acid base, nucleotide, or nucleotide, is a conventional base, nucleotide, or modification, derivative, or nucleotide that occurs naturally in a particular polynucleotide, or Analogs. Certain unusual nucleotides are modified at the 2'position of the ribose sugar compared to conventional dNTP. Thus, even though naturally occurring nucleotides for RNA are ribonucleotides (i.e., ATP, GTP, CTP, UTP, collective rNTP), since nucleotides have hydroxyl groups at the 2'position of the sugar, this is compared to the absence of dNTP, As used herein, ribonucleotides are unusual nucleotides as substrates for DNA polymerases. As used herein, unusual nucleotides include, but are not limited to, compounds used as terminators for nucleic acid sequencing. Exemplary terminator compounds include, but are not limited to, compounds having a 2',3'- dideoxy structure, referred to as dideoxynucleoside triphosphate. Dideoxynucleoside triphosphate ddATP, ddTTP, ddCTP and ddGTP are collectively referred to as ddNTP. Additional examples of terminator compounds include 2'-PO 4 analogues of ribonucleotides. Other unusual nucleotides are phosphorothioate dNTP ([[α]-S]dNTP), 5'-[α]-borano-dNTP, [α]-methyl-phosphonate dNTP, and ribonucleosides Triphosphate (rNTP). Uncommon bases include radioactive isotopes such as 32 P, 33 P, or 35 S; Fluorescent labels; A label for chemiluminescence; Bioluminescent markers; Hapten labels such as biotin; Or it can be labeled with an enzyme label such as streptavidin or avidin. Fluorescent labels can include negatively charged dyes, such as the dyes of the fluorescein family, or neutrally charged dyes, such as the dyes of the rhodamine family, or positively charged dyes, such as the dyes of the cyanine family. Dyes of the fluorescein family include, for example, FAM, HEX, TET, JOE, NAN and ZOE. Rhodamine family dyes include Texas Red, ROX, R110, R6G, and TAMRA. Various dyes or nucleotides labeled FAM, HEX, TET, JOE, NAN, ZOE, ROX, R110, R6G, Texas Red and TAMRA are Perkin-Elmer (Boston, MA), Applied Biosystems (Foster City, CA), or Invitrogen /Molecular Probes (Eugene, OR). The cyanine family dyes include Cy2, Cy3, Cy5, and Cy7, and are marketed by GE Healthcare UK Limited (Amersham Place, Little Chalfont, Buckinghamshire, England).
달리 정의되지 않는 한, 본원에 사용되는 모든 기술적 및 과학적 용어는 당업자에 의해 통상적으로 이해되는 바와 동일한 의미를 갖는다. Unless defined otherwise, all technical and scientific terms used herein have the same meaning as commonly understood by one of ordinary skill in the art.
이하, 본 발명을 보다 상세히 설명한다.Hereinafter, the present invention will be described in more detail.
본 발명은 서열번호 1의 아미노산 서열에서 507번째 아미노산 잔기인 글루탐산(E)이 리신(K)으로 치환되고, 536번째 아미노산 잔기인 아르기닌(R)이 리신(K)으로 치환되며, 660번째 아미노산 잔기인 아르기닌(R)이 발린(V)으로 치환된 Taq 중합효소를 포함하는, EGFR 유전자 돌연변이 검출용 DNA 중합효소를 제공한다.In the present invention, in the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1, the 507th amino acid residue, glutamic acid (E), is substituted with lysine (K), the 536th amino acid residue, arginine (R), is replaced with lysine (K), and the 660th amino acid residue. Provided is a DNA polymerase for detecting EGFR gene mutations, including Taq polymerase in which phosphorus arginine (R) is substituted with valine (V).
상기 "Taq 중합효소"는 고온성 세균인 써모스 아쿠아티쿠스(Thermus aquaticus)의 이름을 따서 명명된 내열성 DNA 중합효소로 상기 세균으로부터 최초로 분리되었다. 써모스 아쿠아티쿠스는 온천 및 열수 분출공에 서식하는 세균으로, Taq 중합효소는 PCR 과정에서 요구되는 단백질 변성 조건 (고온)을 견딜 수 있는 효소로 확인되었다. Taq 중합효소의 최적 활성온도는 75-80 ℃이고, 92.5 ℃에서 2시간 이상, 95 ℃에서 40분, 97.5 ℃에서 9분의 반감기를 가지며, 72 ℃에서 10초 이내에 1000개의 염기쌍 DNA를 복제할 수 있다. 이는 3'→5' 핵산말단가수분해효소(exonuclease) 교정 활성이 결여되어 있으며, 9,000개의 뉴클레오타이드 중 약 1개에서 오류율이 측정된다. 예를 들어 내열성 Taq를 사용하면 고온(60 ℃ 이상)에서 PCR을 실행할 수 있다. Taq 중합효소에 대하여 서열번호 1에 나타낸 아미노산 서열이 기준 서열로 사용된다.The "Taq polymerase" was a thermophilic DNA polymerase named after the thermophilic bacterium Thermus aquaticus and was first isolated from the bacteria. Thermos Aquaticus is a bacterium inhabiting hot springs and hot water jets, and Taq polymerase has been identified as an enzyme capable of withstanding the protein denaturation conditions (high temperature) required in PCR. The optimum activity temperature of Taq polymerase is 75-80 ℃, has a half-life of 9 hours at 22.5 hours at 92.5 ℃, 40 minutes at 95 ℃, 9 minutes at 97.5 ℃, and replicates 1000 base pair DNA within 10 seconds at 72 ℃ Can. It lacks 3'→5' nucleic acid endonuclease correcting activity, and the error rate is measured in about 1 out of 9,000 nucleotides. For example, using the heat-resistant Taq, PCR can be performed at high temperatures (above 60°C). The amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 for Taq polymerase is used as a reference sequence.
본 발명에서, 서열번호 1의 아미노산 서열에서 507번째 아미노산 잔기가 글루탐산(E)에서 리신(K)으로 치환되고, 536번째 아미노산 잔기가 아르기닌(R)에서 리신(K)으로 치환되며, 660번째 아미노산 잔기가 아르기닌(R)에서 발린(V)으로 치환된 Taq 중합효소는 "E507K/R536K/R660V"로 명명하였고, 이의 아미노산 서열 및 뉴클레오티드 서열을 각각 서열번호 2와 서열번호 72에 나타내었다.In the present invention, the 507th amino acid residue in the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1 is substituted with lysine (K) in glutamic acid (E), the 536th amino acid residue is substituted with lysine (K) in arginine (R), and the 660th amino acid The Taq polymerase in which the residue is substituted with arginine (R) to valine (V) was designated as “E507K/R536K/R660V”, and its amino acid sequence and nucleotide sequence are shown in SEQ ID NO: 2 and SEQ ID NO: 72, respectively.
본 발명은 또한, 서열번호 3 내지 54로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택되는 1종 이상의 프라이머를 포함하는 EGFR 유전자 돌연변이 검출용 프라이머 세트를 제공한다.The present invention also provides a primer set for detecting EGFR gene mutations comprising one or more primers selected from the group consisting of SEQ ID NOs: 3 to 54.
본 발명의 EGFR 유전자 돌연변이 검출용 프라이머 세트는 예를 들어 실시예 3의 표 16 내지 19에 기재된 것일 수 있으나, 이로 제한되는 것은 아니다.The primer set for detecting EGFR gene mutation of the present invention may be, for example, those described in Tables 16 to 19 of Example 3, but is not limited thereto.
바람직하게는, 본 발명에 따른 중합효소는 표 16 내지 19의 프라이머 서열과 함께 사용하였을 때 특히 EGFR 돌연변이 검출 민감도가 우수하다.Preferably, the polymerase according to the present invention is particularly excellent in EGFR mutation detection sensitivity when used with the primer sequences of Tables 16 to 19.
본 발명은 또한, 전술한 DNA 중합효소 및/또는 프라이머 세트를 포함하는, EGFR 유전자 돌연변이 검출용 키트를 제공한다.The present invention also provides a kit for detecting EGFR gene mutations, which includes the DNA polymerase and/or primer set described above.
본 발명의 키트는 연구용(Research Use Only, RUO) 또는 생체 외 진단용 (In-Vitro Diagnostic, IVD)으로 사용될 수 있다.The kit of the present invention can be used for research (Research Use Only, RUO) or in-vitro diagnostic (IVD).
본 발명의 키트는 PCR 키트일 수 있으며, 통상의 기술자에게 프라이머 신장 과정에 사용되는 것으로 인지되는 임의의 시약 또는 다른 요소를 포함할 수 있다.The kit of the present invention may be a PCR kit, and may contain any reagents or other elements recognized by those skilled in the art as being used in the primer extension process.
예를 들어, 본 발명의 PCR 키트는 (a) 뉴클레오사이드 트리포스페이트; (b) 이중가닥 DNA에 결합하는 정량화를 위한 시약; (c) 중합효소 차단 항체; (d) 하나 이상의 대조값 또는 대조서열; 및 (e) 하나 이상의 주형;으로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택되는 1종 이상을 추가로 포함할 수 있다.For example, the PCR kit of the present invention includes (a) nucleoside triphosphate; (b) a reagent for quantification that binds double-stranded DNA; (c) polymerase blocking antibodies; (d) one or more control values or control sequences; And (e) one or more templates; may further include one or more selected from the group consisting of.
본 발명의 바람직한 일실시예에 따르면, 상기 키트는 25 내지 100 mM의 KCl; 및 1 내지 7 mM의 (NH4)2SO4;를 포함하고, 최종 pH가 8.0 내지 9.5인 PCR 버퍼 조성물을 추가로 포함할 수 있다.According to a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the kit comprises 25 to 100 mM KCl; And 1 to 7 mM (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 ; and may further include a PCR buffer composition having a final pH of 8.0 to 9.5.
보다 바람직하게, 상기 키트는 40 내지 90 mM의 KCl; 및 1 내지 5 mM의 (NH4)2SO4;를 포함하고, 최종 pH가 8.0 내지 9.0인 PCR 버퍼 조성물을 추가로 포함할 수 있다.More preferably, the kit comprises 40 to 90 mM KCl; And 1 to 5 mM (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 ; and may further include a PCR buffer composition having a final pH of 8.0 to 9.0.
본 발명의 바람직한 다른 일실시예에 따르면, 상기 키트는 25 내지 100 mM의 KCl; 1 내지 7 mM의 (NH4)2SO4; 및 5 내지 50 mM의 TMAC(Tetra methyl ammonium chloride)를 포함하고, 최종 pH가 8.0 내지 9.5인 PCR 버퍼 조성물을 추가로 포함할 수 있다.According to another preferred embodiment of the present invention, the kit comprises 25 to 100 mM KCl; 1 to 7 mM (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 ; And 5 to 50 mM of TMAC (Tetra methyl ammonium chloride), and may further include a PCR buffer composition having a final pH of 8.0 to 9.5.
보다 바람직하게, 상기 키트는 40 내지 90 mM의 KCl; 1 내지 5 mM의 (NH4)2SO4; 및 10 내지 40 mM의 TMAC(Tetra methyl ammonium chloride)를 포함하고, 최종 pH가 8.0 내지 9.0인 PCR 버퍼 조성물을 추가로 포함할 수 있다.More preferably, the kit comprises 40 to 90 mM KCl; 1 to 5 mM (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 ; And 10 to 40 mM of TMAC (Tetra methyl ammonium chloride), and may further include a PCR buffer composition having a final pH of 8.0 to 9.0.
본 발명의 키트는 KCl, (NH4)2SO4, 및 TMAC 이외에도 Tris·Cl (pH 8.0 내지 9.5), MaCl2, Tween 20, 및 BSA (Bovine serum albumin)을 더 포함할 수 있으며, 이들 구성의 농도는 통상의 기술자가 적절한 범위로 조절하여 사용할 수 있다.The kit of the present invention may further include TrisCl (pH 8.0 to 9.5), MaCl 2 , Tween 20, and Bovine serum albumin (BSA) in addition to KCl, (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 , and TMAC, and these components The concentration of can be used by a person skilled in the art to adjust to an appropriate range.
상기와 같은 PCR 버퍼 조성물은 본 발명의 DNA 중합효소의 활성을 현저하게 향상시킴으로써 신뢰성 있는 유전자 변이-특이적 증폭을 가능하게 한다.The PCR buffer composition as described above enables reliable gene mutation-specific amplification by remarkably improving the activity of the DNA polymerase of the present invention.
본 발명의 바람직한 일실시예에 따르면, 상기 PCR 키트는 일반 PCR(1 세대 PCR), 실시간 PCR(2 세대 PCR), 디지털 PCR(3세대 PCR) 또는 매스 어레이(MassARRAY)에 적용하여 사용할 수 있다.According to a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the PCR kit may be applied to general PCR (1st generation PCR), real-time PCR (2nd generation PCR), digital PCR (3rd generation PCR) or mass array (MassARRAY).
본 발명의 PCR 키트에 있어서, 상기 디지털 PCR은 캐스트 PCR(Competitive allele-specific TaqMan PCR) 또는 드랍렛 디지털 PCR(Droplet digital PCR; ddPCR)일 수 있고, 보다 구체적으로 대립유전자 특이적 캐스트 PCR 또는 대립유전자 특이적 드랍렛 디지털 PCR일 수 있으나, 이에 한정되지 않는다.In the PCR kit of the present invention, the digital PCR may be cast PCR (Competitive allele-specific TaqMan PCR) or Droplet digital PCR (ddPCR), and more specifically, allele specific cast PCR or allele It may be a specific droplet digital PCR, but is not limited thereto.
상기 “캐스트 PCR”은 다량의 정상적인 야생형 gDNA를 함유하는 샘플에서 희귀 돌연변이를 검출하고 수량화하는 방법으로, 야생형 대립유전자로부터의 비-특이적 증폭을 억제하기 위해 대립유전자-특이적 TaqMan® qPCR을 대립유전자-특이적 MGB 차단제와 조합하여 전통적인 대립유전자-특이적 PCR보다 우수한 특이성을 생성할 수 있다.The “cast PCR” is a method for detecting and quantifying rare mutations in a sample containing a large amount of normal wild type gDNA, allele-specific TaqMan ® qPCR to inhibit non-specific amplification from wild type alleles. Combination with gene-specific MGB blockers can produce specificity superior to traditional allele-specific PCR.
상기 “드랍렛 디지털 PCR”은 20 ㎕의 PCR 반응을 2 만개의 드랍렛으로 쪼개어 증폭시킨 후, 표적 DNA를 계수하는 시스템으로, 드랍렛에서의 표적 DNA의 증폭 여부에 따라 양성 드랍렛 (1)과 음성 드랍렛 (0)으로 디지털 신호처럼 받아들여 계수하고, 프아송 분포를 통해 표적 DNA의 카피수를 계산해 최종적으로 샘플 ㎕ 당 카피수로 결과값을 확인할 수 있고, 희귀 돌연변이 검출, 극소량의 유전자 증폭, 돌연변이 유형을 동시에 확인하고자 하는 경우 등에 사용될 수 있다.The “Droplet digital PCR” is a system for counting target DNA by splitting and amplifying a PCR reaction of 20 μl into 20,000 droplets, and depending on whether or not the target DNA is amplified in the droplet, positive droplets (1) It is counted as a digital signal with a negative drop (0), counts the copy number of the target DNA through Poisson distribution, and finally, the result can be confirmed by the number of copies per µl of the sample. Rare mutation detection, very small amount of gene It can be used when amplification, mutation type, etc. are to be simultaneously confirmed.
상기 “매스 어레이”는 MALDI-TOF 질량 분석법(MALDI-TOF mass spectrometer)을 이용하여 유전형질분석(genotyping) 등 다양한 유전체 연구에 적용가능한 멀티플렉싱 분석방법으로, 적은 비용으로 다수의 샘플과 타겟을 빠르게 분석하고자 하는 경우 또는 특정 표적에 대해서만 맞춤형(customized) 분석을 하고자 하는 경우 등에 사용될 수 있다.The “mass array” is a multiplexing analysis method applicable to various genomic studies such as genotyping using a MALDI-TOF mass spectrometer, and rapidly analyzes multiple samples and targets at a low cost. It can be used when you want to do it, or if you want to do customized analysis only for a specific target.
본 발명의 EGFR 유전자 돌연변이 검출용 키트는 프로브, 형광단(Fluorophore) 및/또는 소광물질(quencher)을 추가로 포함할 수 있다. 상기 형광단은 VIC, HEX, JOE, FAM, CAL Flour Orange 560, Quasar 670, CY5 EverGreen dye 등일 수 있으나, 이로 제한되는 것은 아니다. 상기 프로브 서열, 형광단 및 소광물질의 종류는 예를 들어 실시예 5의 표 18과 같을 수 있으나, 이로 제한되는 것은 아니다.The EGFR gene mutation detection kit of the present invention may further include a probe, a fluorophore, and/or a quencher. The fluorophore may be VIC, HEX, JOE, FAM, CAL Flour Orange 560, Quasar 670, CY5 EverGreen dye, etc., but is not limited thereto. The probe sequence, the type of the fluorophore and the quencher may be the same as in Table 18 of Example 5, but is not limited thereto.
본 발명의 키트는 AS-PCR (Allele-specific PCR) 및 실시간 PCR 기술을 채용하며, 인간 혈장 시료에서 cfDNA의 EGFR 돌연변이를 검출하기 위한 특정 프라이머와 형광 프로브를 포함한다. 핵산 증폭 동안, 표적화된 돌연변이 DNA는 프라이머의 3' 말단에서 염기와 매치되고, 선택적이고 효율적으로 증폭된 다음 돌연변이 앰플리콘은 FAM 또는 CAL Fluor Orange 560 (CFO560)으로 표지된 형광 프로브에 의해 검출된다. 야생형 DNA는 특정 프라이머와 매치될 수 없으며, 증폭이 발생하지 않는다. 본 발명의 키트는 EGFR Master Mixture 1-4, ADPSTM smart DNA 중합효소, EGFR 양성 대조군 및 뉴클레아제 무첨가 증류수로 구성될 수 있다.The kit of the present invention employs AS-PCR (Allele-specific PCR) and real-time PCR technology, and includes a specific primer and a fluorescent probe for detecting EGFR mutation of cfDNA in human plasma samples. During nucleic acid amplification, the targeted mutant DNA matches the base at the 3'end of the primer, is selectively and efficiently amplified, and then the mutant amplicon is detected by a fluorescent probe labeled with FAM or CAL Fluor Orange 560 (CFO560). Wild-type DNA cannot match specific primers, and no amplification occurs. The kit of the present invention may be composed of EGFR Master Mixture 1-4, ADPS TM smart DNA polymerase, EGFR positive control and nuclease-free distilled water.
본 발명의 EGFR 유전자 돌연변이 검출용 키트는, 예를 들어, 표 1과 같이 구성될 수 있으나, 이로 제한되는 것은 아니다.The EGFR gene mutation detection kit of the present invention may be configured as shown in Table 1, for example, but is not limited thereto.
| 구성Configuration | 주요 성분main ingredient | 양amount |
| EGFR Master Mixture 1EGFR Master Mixture 1 | dNTP를 포함하는 버퍼, EGFR 표적 및 IC에 대한 프라이머/프로브Primers/probes for buffers, EGFR targets and ICs containing dNTPs | 240 μL/튜브 Х1240 μL/tube Х1 |
|
EGFR Master Mixture 2 |
dNTP를 포함하는 버퍼, EGFR 표적 및 IC에 대한 프라이머/프로브Primers/probes for buffers, EGFR targets and ICs containing dNTPs | 240 μL/튜브 Х1240 μL/tube Х1 |
|
EGFR Master Mixture 3 |
dNTP를 포함하는 버퍼, EGFR 표적 및 IC에 대한 프라이머/프로브Primers/probes for buffers, EGFR targets and ICs containing dNTPs | 240 μL/튜브 Х1240 μL/tube Х1 |
|
EGFR Master Mixture 4 |
dNTP를 포함하는 버퍼, EGFR 표적 및 IC에 대한 프라이머/프로브Primers/probes for buffers, EGFR targets and ICs containing dNTPs | 240 μL/튜브 Х1240 μL/tube Х1 |
| ADPSTM 스마트 DNA 중합효소ADPS TM Smart DNA Polymerase | ADPSTM 스마트 DNA 중합효소ADPS TM Smart DNA Polymerase | 60 μL/튜브 Х160 μL/tube Х1 |
| EGFR 양성 대조군EGFR positive control | 각 EGFR돌연변이를 포함하는 재조합 플라스미드 블렌드Recombinant plasmid blend containing each EGFR mutation | 160 μL/튜브 Х1160 μL/tube Х1 |
| 뉴클레아제 무첨가 증류수Nuclease-free distilled water | PCR 등급의 증류수PCR grade distilled water | 1.0 mL/튜브 Х11.0 mL/tube Х1 |
상기 표 1의 각 EGFR Master Mix의 예시적인 구성은 표 2와 같다.Exemplary configuration of each EGFR Master Mix in Table 1 is shown in Table 2.
| 최종농도Final concentration | |||
| MMX 1~4MMX 1-4 | ADPS 버퍼ADPS buffer | Tris·Cl (pH 8.8)TrisCl (pH 8.8) | 50 mM50 mM |
| MgCl2 MgCl 2 | 2.5 mM2.5 mM | ||
| KClKCl | 60 mM60 mM | ||
| (NH4)2SO4 (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 | 2.5 mM2.5 mM | ||
| TMACTMAC |
25 mM25 | ||
| Tween 20Tween 20 | 0.1%0.1% | ||
| BSABSA | 0.01%0.01% | ||
| dNTPdNTP | 각 0.25 mM0.25 mM each | ||
| 프라이머/프로브Primer/Probe | 특정 농도Specific concentration | ||
| ROX 표준 염료ROX standard dye | 1X1X | ||
EGFR Master Mix 1-4의 검출 정보는 표 3과 같다.Table 3 shows the detection information of EGFR Master Mix 1-4.
| 시약reagent | 형광 신호Fluorescent signal | ||
| FAMFAM | CAL Fluor Orange 560* CAL Fluor Orange 560 * | Quasar 670* Quasar 670 * | |
| EGFR Master Mixture 1EGFR Master Mixture 1 | S768IS768I | Ex19DelEx19Del | IC** IC ** |
|
EGFR Master Mixture 2 |
T790MT790M | -- | ICIC |
|
EGFR Master Mixture 3 |
L861QL861Q | G719XG719X | ICIC |
|
EGFR Master Mixture 4 |
Ex20InsEx20Ins | L858RL858R | ICIC |
*대체 가능한 염료: CAL Fluor Orange 560 (VIC/HEX/JOE), Quasar 670 (CY5)**IC: PCR을 위한 내부 대조군*Alternative dye: CAL Fluor Orange 560 (VIC/HEX/JOE), Quasar 670 (CY5)**IC: Internal control for PCR
본 발명은 또한, 다음의 단계를 포함하는 EGFR 유전자 돌연변이 검출방법을 제공한다:The present invention also provides a method for detecting an EGFR gene mutation comprising the following steps:
(a) 분리된 생물학적 시료로부터 핵산을 추출하는 단계;(A) extracting the nucleic acid from the isolated biological sample;
(b) 상기 추출한 핵산에 본 발명의 키트를 처리하여 중합효소연쇄반응을 수행하는 단계; 및(B) processing the kit of the present invention to the extracted nucleic acid to perform a polymerase chain reaction; And
(c) 상기 중합효소연쇄반응 결과 증폭 산물의 크기 또는 염기서열을 분석하는 단계.(c) analyzing the size or base sequence of the amplification product as a result of the polymerase chain reaction.
본 발명의 바람직한 일실시예에 따르면, 상기 PCR은 대립유전자 특이적 (allele-specific) PCR 또는 실시간 (real-time) PCR일 수 있다.According to a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the PCR may be allele-specific PCR or real-time PCR.
본 발명의 EGFR 유전자 돌연변이 검출방법은 (d) 상기 PCR에 의한 증폭 결과를 Ct (cycle threshold) 값을 측정하여 확인하는 단계를 추가로 포함할 수 있다.The EGFR gene mutation detection method of the present invention may further include (d) confirming the amplification result by the PCR by measuring a Ct (cycle threshold) value.
Ct(cycle threshold) 값은 반응에서 발생된 형광이 역치(threshold)를 넘어서는 사이클 수를 의미하며, 이는 초기 카피 수의 대수에 반비례한다. 그러므로, 특정 웰에 할당된 Ct 값은 반응에서 앰플리콘의 충분한 수가 축적된 사이클의 수를 반영한다. Ct 값은 ΔRn의 증가가 처음으로 검출된 사이클이다. Rn은 각 시점에서 PCR 동안 발생된 형광 시그널의 크기를 의미하며, ΔRn은 레퍼런스 염료의 형광 방출 강도로 나뉘어진 리포터 염료의 형광방출 강도(표준화된 리포터 시그널)를 의미한다. Ct 값은 LightCycler에서는 Cp(crossing point)로도 명명된다. Ct 값은 시스템이 로그-선형 단계(log-linear phase)에서 PCR 생산물의 지수성장과 관련된 형광 시그널의 증가를 검출하기 시작하는 시점을 나타낸다. 이 시기는 반응에 대한 가장 유용한 정보를 제공한다. 로그-선형 단계의 기울기는 증폭 효율(amplification efficiency, Eff)을 나타낸다 (https://www.appliedbiosystems.co.kr/).The cycle threshold (Ct) value means the number of cycles in which the fluorescence generated in the reaction exceeds a threshold, which is inversely proportional to the logarithm of the initial copy number. Therefore, the Ct value assigned to a particular well reflects the number of cycles in which a sufficient number of amplicons have accumulated in the reaction. The Ct value is the cycle in which the increase in ΔRn was first detected. Rn means the magnitude of the fluorescence signal generated during PCR at each time point, and ΔRn means the fluorescence emission intensity (standardized reporter signal) of the reporter dye divided by the fluorescence emission intensity of the reference dye. The Ct value is also referred to as a crossing point (Cp) in LightCycler. The Ct value represents the point in time at which the system begins to detect an increase in the fluorescence signal associated with the exponential growth of the PCR product in the log-linear phase. This period provides the most useful information about the reaction. The slope of the log-linear phase represents the amplification efficiency (Eff) (https://www.appliedbiosystems.co.kr/).
한편, TaqMan 프로브는 전형적으로 5'-말단에 형광물질(fluorophore) 및 3'-말단에 소광물질(quencher; 예컨대, TAMRA 또는 비-형광 소광물질(NFQ))을 포함하는 프라이머(예컨대, 20-30 뉴클레오타이드) 보다 더 긴 올리고뉴클레오타이드이다. 여기된 형광물질은 형광을 내기 보다는 근처의 소광물질에 에너지를 전달한다(FRET = Frster or fluorescence resonance energy transfer; Chen, X., et al., Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 94(20): 10756-61(1997)). 그러므로, 프로브가 정상인 경우, 어떠한 형광도 발생되지 않는다. TaqMan 프로브는 PCR 생산물의 내부 부위에 어닐링할 수 있도록 고안된다.On the other hand, TaqMan probes typically include a 5'-terminal fluorophore and a 3'-terminal quencher (e.g., TAMRA or non-fluorescent quencher (NFQ)) primers (e.g., 20- 30 nucleotides). Excited phosphors transfer energy to nearby quenchers rather than fluorescence (FRET = Frster or fluorescence resonance energy transfer; Chen, X., et al., Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 94(20): 10756- 61 (1997)). Therefore, when the probe is normal, no fluorescence is generated. TaqMan probes are designed to anneal to the inner part of the PCR product.
TaqMan 프로브는 어닐링 단계에서 주형 DNA에 특이적으로 혼성화하지만, 프로브 상에 소광물질에 의해 형광 발색이 억제된다. 연장 반응 시에 Taq DNA 폴리머라제가 갖는 5' 내지 3' 뉴클레아제 활성에 의해 주형에 혼성화한 TaqMan 프로브가 분해되어 형광 색소가 프로브로부터 유리되면서 소광물질에 의한 억제가 해제되어 형광은 나타낸다. 이 때, TaqMan 프로브의 5'-말단은 상기 연장 프라이머의 3'-말단의 다운스트림에 위치하여야 한다. 즉, 연장 프라이머의 3'-말단이 주형-의존성 핵산 중합효소에 의해 연장되는 경우, 이 중합효소의 5' 내지 3' 뉴클레아제 활성에 의해 TaqMan 프로브의 5'-말단이 절단되어 리포터 분자의 형광 시그널이 발생하게 된다.The TaqMan probe specifically hybridizes to the template DNA in the annealing step, but fluorescence is inhibited by quenching on the probe. During the extension reaction, the TaqMan probe hybridized to the template is decomposed by the 5'to 3'nuclease activity of the Taq DNA polymerase, and the fluorescent dye is released from the probe. At this time, the 5'-end of the TaqMan probe should be located downstream of the 3'-end of the extension primer. That is, when the 3'-end of the extension primer is extended by a template-dependent nucleic acid polymerase, the 5'to 3'nuclease activity of this polymerase cuts the 5'-end of the TaqMan probe, thereby Fluorescence signal is generated.
TaqMan 프로브에 결합되어 있는 상기 리포터 분자 및 소광물질 분자는 형광성 물질 및 비형광성 물질을 포함한다. 본 발명에 이용될 수 있는 형광성 리포터 분자 및 소광물질 분자는 당업계에 공지되어 있는 어떠한 것도 이용할 수 있으며, 그 예는 다음과 같다(괄호의 숫자는 나노미터 단위로 표시한 발광 최대 파장이다): Cy2TM (506), YOPRO TM-1 (509), YOYO TM-1 (509), Calcein (517), FITC (518), FluorX TM (519), AlexaTM (520), Rhodamine 110 (520), 5-FAM (522), Oregon Green TM 500 (522), Oregon GreenTM 488 (524), RiboGreenTM (525), Rhodamine GreenTM (527), Rhodamine 123 (529), Magnesium GreenTM (531), Calcium GreenTM (533), TO-PROTM-1 (533), TOTO1 (533), JOE (548), BODIPY530/550 (550), Dil (565), BODIPY TMR (568), BODIPY558/568 (568), BODIPY564/570 (570), Cy3TM (570), AlexaTM 546 (570), TRITC (572), Magnesium OrangeTM (575), Phycoerythrin R&B (575), Rhodamine Phalloidin (575), Calcium OrangeTM (576), Pyronin Y (580), Rhodamine B (580), TAMRA (582), Rhodamine RedTM (590), Cy3.5TM (596), ROX (608), Calcium CrimsonTM (615), AlexaTM 594 (615), Texas Red(615), Nile Red (628), YO-PROTM-3 (631), YOYOTM-3 (631), R-phycocyanin (642), CPhycocyanin(648), TO-PROTM-3 (660), TOTO3 (660), DiD DilC(5) (665), Cy5TM (670), Thiadicarbocyanine (671), Cy5.5 (694), HEX (556), TET (536), VIC (546), BHQ-1 (534), BHQ-2 (579), BHQ-3 (672), Biosearch Blue (447), CAL Fluor Gold 540 (544), CAL Fluor Orange 560 (559), CAL Fluor Red 590 (591), CAL Fluor Red 610 (610), CAL Fluor Red 635 (637), FAM (520), Fluorescein (520), Fluorescein-C3 (520), Pulsar 650 (566), Quasar 570 (667), Quasar 670 (705) 및 Quasar 705 (610). 괄호의 숫자는 나노미터 단위로 표시한 발광 최대 파장이다.The reporter molecule and quencher molecule bound to the TaqMan probe include fluorescent and non-fluorescent materials. Fluorescent reporter molecules and quencher molecules that can be used in the present invention can use any of those known in the art, and examples thereof are as follows (numbers in parentheses are the maximum emission wavelength in nanometers): Cy2 TM 506, YOPRO TM -1 (509), YOYO TM -1 (509), Calcein (517), FITC (518), FluorX TM (519), Alexa TM (520), Rhodamine 110 (520), 5-FAM (522), Oregon Green TM 500 (522), Oregon Green TM 488 (524), RiboGreen TM (525), Rhodamine Green TM (527), Rhodamine 123 (529), Magnesium Green TM (531), Calcium Green TM (533), TO-PRO TM -1 (533), TOTO1 (533), JOE (548), BODIPY530/550 (550), Dil (565), BODIPY TMR (568), BODIPY558/568 (568) , BODIPY564/570 (570), Cy3 TM (570), Alexa TM 546 (570), TRITC (572), Magnesium Orange TM (575), Phycoerythrin R&B (575), Rhodamine Phalloidin (575), Calcium Orange TM (576) ), Pyronin Y (580), Rhodamine B (580), TAMRA (582), Rhodamine Red TM (590), Cy3.5 TM (596), ROX (608), Calcium Crimson TM (615), Alexa TM 594 ( 615), Texas Red (615) , Nile Red (628), YO-PRO TM -3 (631), YOYO TM -3 (631), R-phycocyanin (642), CPhycocyanin (648), TO-PRO TM - 3 (660), TOTO3 (660), DiD DilC(5) (665), Cy5 TM (670), Thiadicarbocyanine (671), Cy5.5 (694), HEX (556), TET (536), VIC (546), BHQ-1 ( 534), BHQ-2 (579), BHQ-3 (672), Biosearch Blue (447), CAL Fluor Gold 540 (544), CAL Fluor Orange 560 (559), CAL Fluor Red 590 (591), CAL Fluor Red 610 (610), CAL Fluor Red 635 (637), FAM (520), Fluorescein (520), Fluorescein-C3 (520), Pulsar 650 (566), Quasar 570 (667), Quasar 670 (705) and Quasar 705 (610). The number in parentheses is the maximum wavelength of light emitted in nanometers.
적합한 리포터-소광물질 쌍(pairs)은 많은 문헌에 개시되어 있다: Pesce et al., editors, FLUORESCENCE SPECTROSCOPY(Marcel Dekker, New York, 1971); White et al., FLUORESCENCE ANALYSIS: A PRACTICAL APPROACH (Marcel Dekker, New York, 1970); Berlman, HANDBOOK OF FLUORESCENCE SPECTRA OF AROMATIC MOLECULES, 2nd EDITION (Academic Press, New York, 1971); Griffiths, COLOUR AND CONSTITUTION OF ORGANIC MOLECULES(Academic Press, New York, 1976); Bishop, editor, INDICATORS(Pergamon Press, Oxford, 1972); Haugland, HANDBOOK OF FLUORESCENT PROBES AND RESEARCH CHEMICALS(Molecular Probes, Eugene, 1992); Pringsheim, FLUORESCENCE AND PHOSPHORESCENCE(Interscience Publishers, New York, 1949); Haugland, R. P., HANDBOOK OF FLUORESCENT PROBES AND RESEARCH CHEMICALS, Sixth Edition, Molecular Probes, Eugene, Oreg., 1996; U.S. Pat. Nos. 3,996,345 and 4,351,760.Suitable reporter-quencher pairs have been described in many documents: Pesce et al., editors, FLUORESCENCE SPECTROSCOPY (Marcel Dekker, New York, 1971); White et al., FLUORESCENCE ANALYSIS: A PRACTICAL APPROACH (Marcel Dekker, New York, 1970); Berlman, HANDBOOK OF FLUORESCENCE SPECTRA OF AROMATIC MOLECULES, 2 nd EDITION (Academic Press, New York, 1971); Griffiths, COLOUR AND CONSTITUTION OF ORGANIC MOLECULES (Academic Press, New York, 1976); Bishop, editor, INDICATORS (Pergamon Press, Oxford, 1972); Haugland, HANDBOOK OF FLUORESCENT PROBES AND RESEARCH CHEMICALS (Molecular Probes, Eugene, 1992); Pringsheim, FLUORESCENCE AND PHOSPHORESCENCE (Interscience Publishers, New York, 1949); Haugland, RP, HANDBOOK OF FLUORESCENT PROBES AND RESEARCH CHEMICALS, Sixth Edition, Molecular Probes, Eugene, Oreg., 1996; US Pat. Nos. 3,996,345 and 4,351,760.
또한, TaqMan 프로브에 결합되어 있는 상기 리포터 분자 및 소광물질 분자에 이용되는 비형광성 물질은 마이너 그루브 결합 모이어티(minor groove binding(MGB) moiety)를 포함할 수 있다. 본 명세서의 용어 "TaqMan MGB-컨쥬게이트 프로브(MGB-conjugate probe)"는 프로브의 3'-말단에 MGB와 컨쥬게이션된 TaqMan 프로브를 의미한다.In addition, the non-fluorescent material used in the reporter molecule and the quencher molecule bound to the TaqMan probe may include a minor groove binding (MGB) moiety. The term "TaqMan MGB-conjugate probe" herein refers to a TaqMan probe conjugated with MGB at the 3'-end of the probe.
MGB는 높은 친화도로 DNA의 마이너 그루브에 결합하는 물질로서, 네트롭신(netropsin), 디스타마이신 (distamycin), 렉시트롭신 (lexitropsin), 미트라마이신 (mithramycin), 크로모마이신 (chromomycin) A3, 올리보마이신 (olivomycin), 안트라마이신 (anthramycin), 시비로마이신 (sibiromycin), 펜타미딘 (pentamidine), 스틸바미딘 (stilbamidine), 베레닐 (berenil), CC-1065, Hoechst 33258, DAPI (4-6-diamidino-2-phenylindole), CDPI의 다이머, 트리머, 테트라머 및 펜타머, MPC (N-methylpyrrole-4-carbox-2-amide) 및 이의 다이머, 트리머, 테트라머 및 펜타머를 포함하지만, 이에 한정되는 것은 아니다.MGB is a substance that binds to the minor groove of DNA with high affinity, such as netropsin, distamicin, lexitropsin, mitramycin, chromomycin A3, and olibo. Olivomycin, anthramycin, sibiromycin, pentamidine, stilbamidine, berenil, CC-1065, Hoechst 33258, DAPI (4-6- diamidino-2-phenylindole), CDPI dimers, trimers, tetramers and pentamers, MPC (N-methylpyrrole-4-carbox-2-amide) and dimers thereof, trimers, tetramers and pentamers It does not work.
프로브와 MGB의 컨쥬게이션(conjugation)은 프로브와 이의 타겟 간에 형성되는 하이브리드의 안정성을 현저하게 증가시킨다. 보다 상세하게는, 증가된 안정성(즉, 혼성화 정도의 증가)는 정상 프로브와 비교하여 MGB-컨쥬게이트 프로브에 의해 형성된 하이브리드 듀플렉스의 증가된 Tm(melting temperature)을 유발한다. 따라서, MGB는 반데르발스 힘을 안정화시켜 프로브 길이의 증가 없이 MGB-컨쥬게이트 프로브의 Tm(melting temperature)를 증가시킴으로써 보다 엄격 조건 하의 Taqman 실시간 PCR에서 더 짧은 프로브(예컨대, 21개 이하의 뉴클레오타이드)의 이용을 가능하게 해준다.Conjugation of the probe and MGB significantly increases the stability of the hybrid formed between the probe and its target. More specifically, increased stability (ie, increased degree of hybridization) results in increased melting temperature (Tm) of the hybrid duplex formed by MGB-conjugated probes compared to normal probes. Thus, MGB stabilizes the van der Waals force, thereby increasing the melting temperature (Tm) of the MGB-conjugate probe without increasing the probe length, resulting in shorter probes (e.g. no more than 21 nucleotides) in Taqman real-time PCR under more stringent conditions. Enables the use of.
또한, MGB-컨쥬게이트 프로브는 백그라운드 형광을 보다 효율적으로 제거시켜 준다. 따라서, 본 발명의 프로브는 TaqMan MGB-컨쥬게이트 형태일 수도 있으며, 이때 프로브의 길이는 15-21 뉴클레오타이드를 포함하지만, 이에 한정되는 것은 아니다.In addition, the MGB-conjugated probe removes background fluorescence more efficiently. Therefore, the probe of the present invention may be in the form of a TaqMan MGB-conjugate, wherein the length of the probe includes 15-21 nucleotides, but is not limited thereto.
본 발명의 바람직한 일실시예에 따르면, 상기 EGFR 유전자 돌연변이는 상기 EGFR 유전자 돌연변이는 EGFR 유전자의 엑손 18번, 19번, 20번 및 21번 내에서의 결실, 치환 및 삽입 돌연변이로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택되는 1종 이상을 포함할 수 있다.According to a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the EGFR gene mutation is selected from the group consisting of deletion, substitution and insertion mutations in exons 18, 19, 20 and 21 of the EGFR gene. It may contain one or more.
구체적으로, 상기 EGFR 유전자 돌연변이는 EGFR의 엑손 18번 내에서의 719번째 아미노산인 글리신의 치환, 엑손 19번 내에서의 결손, 엑손 20번 내에서의 768번째 아미노산인 세린, 790번째 아미노산인 트레오닌, 797번째 아미노산인 시스테인의 치환, 엑손 20번 내에서의 삽입, 엑손 21번 내에서의 858번째 아미노산인 류신 및 861번째 아미노산인 류신의 치환으로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택된 1종 이상을 포함할 수 있다.Specifically, the EGFR gene mutation is the substitution of the 719th amino acid glycine in exon 18 of EGFR, the deletion in exon 19, the 768th amino acid serine in exon 20, the 790th amino acid threonine, It may include one or more selected from the group consisting of substitution of the cysteine, the 797th amino acid, insertion in exon 20, leucine, which is the 858th amino acid in exon 21, and the replacement of the 861th amino acid, leucine.
예를 들어, 본 발명의 EGFR 유전자 돌연변이 검출방법은 EGFR의 엑손 18번, 19번, 20번 및 21번에서 하기 표 4에 기재된 44개의 돌연변이 중 1종 이상을 동시 다발적으로 검출할 수 있다.For example, the EGFR gene mutation detection method of the present invention can simultaneously detect one or more of the 44 mutations listed in Table 4 below in exons 18, 19, 20 and 21 of EGFR.
| 엑손Exxon | 돌연변이Mutation | EGFR 핵산서열EGFR nucleic acid sequence |
COSMIC ID |
| 엑손 18Exon 18 | G719XG719X | 2155G>A2155G>A | 62526252 |
| 2155G>T2155G>T | 62536253 | ||
| 2156G>C2156G>C | 62396239 | ||
| 엑손 19Exon 19 | Ex19DelEx19Del | 2240_2251del122240_2251del12 | 62106210 |
| 2239_2247del92239_2247del9 | 62186218 | ||
| 2238_2255del182238_2255del18 | 62206220 | ||
| 2235_2249del152235_2249del15 | 62236223 | ||
| 2236_2250del152236_2250del15 | 62256225 | ||
| 2239_2253del152239_2253del15 | 62546254 | ||
| 2239_2256del182239_2256del18 | 62556255 | ||
| 2237_2254del182237_2254del18 | 1236712367 | ||
| 2240_2254del152240_2254del15 | 1236912369 | ||
| 2240_2257del182240_2257del18 | 1237012370 | ||
| 2239_2248TTAAGAGAAG>C2239_2248TTAAGAGAAG>C | 1238212382 | ||
| 2239_2251>C2239_2251>C | 1238312383 | ||
| 2237_2255>T2237_2255>T | 1238412384 | ||
| 2235_2255>AAT2235_2255>AAT | 1238512385 | ||
| 2237_2252>T2237_2252>T | 1238612386 | ||
| 2239_2258>CA2239_2258>CA | 1238712387 | ||
| 2239_2256>CAA2239_2256>CAA | 1240312403 | ||
| 2237_2253>TTGCT2237_2253>TTGCT | 1241612416 | ||
| 2238_2252>GCA2238_2252>GCA | 1241912419 | ||
| 2238_2248>GC2238_2248>GC | 1242212422 | ||
| 2237_2251del152237_2251del15 | 1267812678 | ||
| 2236_2253del182236_2253del18 | 1272812728 | ||
| 2235_2248>AATTC2235_2248>AATTC | 1355013550 | ||
| 2235_2252>AAT2235_2252>AAT | 1355113551 | ||
| 2235_2251>AATTC2235_2251>AATTC | 1355213552 | ||
| 2253_2276del242253_2276del24 | 1355613556 | ||
| 2237_2257>TCT2237_2257>TCT | 1842718427 | ||
| 2238_2252del152238_2252del15 | 2357123571 | ||
| 2233_2247del152233_2247del15 | 2603826038 | ||
| 2232_2249del152232_2249del15 | 221565221565 | ||
| 2234_2248del152234_2248del15 | 11907911190791 | ||
|
엑손 20 |
S768IS768I | 2303G>T2303G>T | 62416241 |
| T790MT790M | 2369C>T2369C>T | 62406240 | |
| Ex20InsEx20Ins | 2307_2308ins9GCCAGCGTG2307_2308ins9GCCAGCGTG | 1237612376 | |
| 2319_2320insCAC2319_2320insCAC | 1237712377 | ||
| 2310_2311insGGT2310_2311insGGT | 1237812378 | ||
| 2311_2312ins9GCGTGGACA2311_2312ins9GCGTGGACA | 1342813428 | ||
| 2309_2310AC>CCAGCGTGGAT2309_2310AC>CCAGCGTGGAT | 1355813558 | ||
| 엑손 21Exon 21 | L858RL858R | 2573T>G2573T>G | 62246224 |
| 2573_2574TG>GT2573_2574TG>GT | 1242912429 | ||
| L861QL861Q | 2582T>A2582T>A | 62136213 |
본 발명의 EGFR 유전자 돌연변이 검출방법에 있어서, 표적서열은 상기 (a) 단계의 시료에 존재할 수 있으며, DNA, cDNA 또는 RNA, 바람직하게는 유전체 DNA를 포함한다. 테스트 시료는 동물, 바람직하게는 척추동물, 보다 바람직하게는 인간 대상체에 포함된 것일 수 있다. 예를 들어, 상기 (a) 단계의 생물학적 시료는 객담, 혈액, 타액 또는 소변일 수 있고, (a) 단계의 핵산은 조직 생검의 포르말린 고정 파라핀 포매 시료(formalin-fixed paraffin embedded sample) 또는 액체 생검으로부터 추출될 수 있다.본 발명의 EGFR 유전자 돌연변이 검출방법은 이중 가닥 특이적 염료를 이용한 용융 온도 분석을 포함할 수 있다.In the EGFR gene mutation detection method of the present invention, the target sequence may be present in the sample of step (a), and includes DNA, cDNA or RNA, preferably genomic DNA. The test sample may be included in an animal, preferably a vertebrate, more preferably a human subject. For example, the biological sample in step (a) may be sputum, blood, saliva, or urine, and the nucleic acid in step (a) is a formalin-fixed paraffin embedded sample or a liquid biopsy of a tissue biopsy. The EGFR gene mutation detection method of the present invention may include melting temperature analysis using a double-strand specific dye.
용융 온도 곡선 분석은, 온보드 소프트웨어 (SDS 2.1)를 포함하는 ABI 5700/7000 (96 웰 포맷) 또는 ABI 7900 (384 웰 포맷) 장치와 같은 실시간 PCR 장치에서 수행될 수 있다. 대안적으로는, 용융 온도 곡선 분석은 종결점 분석으로서 수행될 수 있다.Melt temperature curve analysis can be performed in real-time PCR devices such as ABI 5700/7000 (96 well format) or ABI 7900 (384 well format) devices with onboard software (SDS 2.1). Alternatively, melt temperature curve analysis can be performed as an endpoint analysis.
"이중 가닥 DNA에 결합하는 염료" 또는 "이중 가닥 특이적 염료"는 결합되지 않은 상태보다 이중 가닥 DNA에 결합하였을 때 높은 형광을 가지는 경우 사용될 수 있다. 이러한 염료의 예로는, SOYTO-9, SOYTO-13, SOYTO-16, SOYTO-60, SOYTO-64, SYTO-82, 브롬화 에티듐(EtBr), SYTOX Orange, TO-PRO-1, SYBR Green I, TO-PRO-3 또는 EvaGreen이 있다. EtBr 및 EvaGreen (Quiagen)을 제외한 이들 염료는 실시간 응용에 시험되어 왔다.“Dye binding to double-stranded DNA” or “double-strand specific dye” can be used when it has a higher fluorescence when bound to double-stranded DNA than to the unbound state. Examples of such dyes are SOYTO-9, SOYTO-13, SOYTO-16, SOYTO-60, SOYTO-64, SYTO-82, Etidium Bromide (EtBr), SYTOX Orange, TO-PRO-1, SYBR Green I, TO-PRO-3 or EvaGreen. These dyes, except EtBr and EvaGreen (Quiagen), have been tested in real-time applications.
본 발명의 EGFR 유전자 돌연변이 검출방법은 실시간 PCR(RT-PCR) 또는 정량적 PCR(qPCR), 표준 PCR 후 아가로스 겔에서의 분석, 실시간 PCR을 통한 유전자 변이 특이적 증폭 또는 대립 유전자-특이적 증폭, 테트라-프라이머 증폭-불응성 돌연변이 시스템 PCR 또는 등온 증폭에 의해 수행될 수 있다.The EGFR gene mutation detection method of the present invention includes real-time PCR (RT-PCR) or quantitative PCR (qPCR), analysis on agarose gel after standard PCR, gene mutation specific amplification or allele-specific amplification through real-time PCR, Tetra-primer amplification-refractory mutant systems can be performed by PCR or isothermal amplification.
상기 "표준 PCR"은 통상의 기술자에게 알려진 DNA 또는 cDNA의 단일 또는 수 개의 복제를 증폭시키는 기술이다. 거의 대부분의 PCR은 Taq 중합효소 또는 Klen Taq와 같은 열안정성 DNA 중합효소를 사용한다. DNA 중합 효소는 주형으로 단일 가닥 DNA를 사용하고, 올리고뉴클레오타드 (프라이머)를 사용함으로써 뉴클레오타이드로부터 새로운 DNA 가닥을 효소적으로 조립한다. PCR에 의해 생성 된 앰플리콘은 예를 들어, 아가로오스 겔에서 분석될 수 있다.The "standard PCR" is a technique for amplifying single or several copies of DNA or cDNA known to those skilled in the art. Almost all PCR uses thermostable DNA polymerases such as Taq polymerase or Klen Taq. DNA polymerases use single-stranded DNA as a template and enzymatically assemble new DNA strands from nucleotides by using oligonucleotides (primers). The amplicon generated by PCR can be analyzed, for example, on an agarose gel.
상기 "실시간 PCR"은 PCR을 할 때 실시간으로 그 과정을 모니터링할 수 있다. 따라서, 데이터는 PCR이 종료되는 시점이 아니라, PCR 과정 전반에 걸쳐 수집된다. 실시간 PCR에서, 반응은 고정된 사이클 수 후에 축적된 표적 양보다는 증폭이 처음으로 검출될 때의 사이클 동안의 시점을 특징으로 한다. 주로 염료 기반 검출 및 프로브 기반 검출의 두 가지 방법이 정량적 PCR을 수행하는데 사용된다.The "real-time PCR" can monitor the process in real time when performing PCR. Therefore, data is collected throughout the PCR process, not when the PCR ends. In real-time PCR, the reaction is characterized by a time point during the cycle when amplification is first detected, rather than the target amount accumulated after a fixed number of cycles. Two methods, mainly dye-based detection and probe-based detection, are used to perform quantitative PCR.
상기 "대립 유전자-특이적 증폭(Allele Specific Amplification, ASA)"은 PCR 프라이머를 단일 뉴클레오타이드 잔기가 다른 주형들을 구별할 수 있도록 고안한 증폭 기술이다.The “allele specific amplification (ASA)” is an amplification technique designed to distinguish PCR primers from different templates with a single nucleotide residue.
상기 "실시간 PCR을 통한 유전자 변이 특이적 증폭 또는 대립 유전자-특이적 증폭"은 매우 효율적인 방법으로 유전자 변이 또는 SNP를 검출한다. 유전자 변이 또는 SNP를 검출하기 위한 다른 대부분의 방법과는 달리, 표적 유전자 물질의 예비 증폭이 필요하지 않다. ASA는 매치 및 미스매치된 프라이머/표적서열 복합체의 구별을 바탕으로 단일 반응에서 증폭 및 검출을 결합한다. 반응동안 증폭된 DNA의 증가는 이중 가닥 DNA에 결합하는 것에 따라 발광하는 SYBR Green I과 같은 염료에 의해 야기되는 형광 신호의 증가로 실시간 모니터링될 수 있다. 실시간 PCR을 통한 유전자 변이 특이적 증폭 또는 대립 유전자-특이적 증폭은 미스매치된 경우에 대한 형광 신호의 지연 또는 부재가 나타난다. 유전자 변이 또는 SNP 검출에서, 이는 유전자 변이 또는 SNP 존재 유무에 대한 정보를 제공한다.The "gene mutation specific amplification or allele-specific amplification through real-time PCR" detects gene mutation or SNP in a very efficient manner. Unlike most other methods for detecting gene mutations or SNPs, preliminary amplification of the target genetic material is not required. ASA combines amplification and detection in a single reaction based on the distinction of matched and mismatched primer/target sequence complexes. The increase in DNA amplified during the reaction can be monitored in real time with an increase in the fluorescence signal caused by dyes such as SYBR Green I, which emit light upon binding to double-stranded DNA. Gene mutation-specific amplification or allele-specific amplification through real-time PCR shows delay or absence of a fluorescent signal for mismatched cases. In detecting genetic variation or SNP, it provides information on the presence or absence of genetic variation or SNP.
상기 "테트라-프라이머 증폭-불응성 돌연변이 시스템 PCR"은 단일 튜브 PCR 반응에서 대조 단편과 함께 야생형 및 돌연변이 대립 유전자를 모두 증폭한다. 비 대립 유전자 특이적 대조 앰플리콘은 돌연변이 영역 측면의 2개의 공통적인 (바깥쪽) 프라이머에 의해 증폭된다. 2개의 대립 유전자 특이적 (안쪽) 프라이머는 공통 프라이머와 반대 방향으로 설계되며, 공통 프라이머와 함께 야생형 및 돌연변이 앰플리콘 둘 다를 동시에 증폭시킬 수 있다. 결과적으로, 2개의 대립 유전자-특이적 앰플리콘은 돌연변이가 공통 (바깥쪽) 프라이머에 대해 비대칭으로 위치하기 때문에 다른 길이를 가지며 표준 겔 전기영동으로 쉽게 분리할 수 있다. 상기 대조 앰플리콘은 증폭 실패뿐만 아니라 위음성에 대한 내부 대조를 제공하며 2개의 대립 유전자-특이적 앰플리콘 중 적어도 하나는 테트라-프라이머 증폭-불응성 돌연변이 시스템 PCR에 항상 존재한다.The "tetra-primer amplification-refractory mutation system PCR" amplifies both wild type and mutant alleles with control fragments in a single tube PCR reaction. Non-allele specific control amplicons are amplified by two common (outer) primers flanking the mutation region. The two allele specific (inner) primers are designed in the opposite direction to the common primer, and can be amplified both wild-type and mutant amplicons simultaneously with the common primer. Consequently, the two allele-specific amplicons have different lengths and can be easily separated by standard gel electrophoresis because the mutations are located asymmetrically with respect to the common (outer) primer. The control amplicon provides internal control for false negatives as well as amplification failures, and at least one of the two allele-specific amplicons is always present in the tetra-primer amplification-refractory mutation system PCR.
상기 "등온 증폭"은 써모사이클러에 의존하지 않고, 바람직하게는 증폭하는 동안 온도가 변화할 필요없이 핵산의 증폭이 더 낮은 온도에서 이루어짐을 의미한다. 등온 증폭에서 사용되는 온도는 실온 (22-24 ℃) 내지 약 65 ℃ 사이, 또는 약 60-65 ℃, 45-50 ℃, 37-42 ℃ 또는 22-24 ℃의 상온일 수 있다. 등온 증폭 결과의 생성물은 겔 전기 영동, ELISA, ELOSA (Enzyme linked oligosorbent assay), 실시간 PCR, ECL (개선된 화학 발광), RNA, DNA 및 단백질 또는 탁도를 분석하는 칩 기반의 모세관 전기 영동 기기인 생물분석기 (bioanalyzer)로 검출될 수 있다.The "isothermal amplification" does not depend on the thermocycler, and preferably means that the amplification of the nucleic acid takes place at a lower temperature without the need to change the temperature during amplification. The temperature used in isothermal amplification can be between room temperature (22-24 °C) to about 65 °C, or at room temperature of about 60-65 °C, 45-50 °C, 37-42 °C or 22-24 °C. The products of the isothermal amplification results are gel electrophoresis, ELISA, ELOSA (Enzyme linked oligosorbent assay), real-time PCR, ECL (improved chemiluminescence), RNA, DNA, and chip-based capillary electrophoresis devices that analyze protein or turbidity It can be detected with an analyzer (bioanalyzer).
본 발명의 EGFR 유전자 돌연변이 검출방법이 qPCR로 수행되는 경우, 예를 들어, 하기 표 22 내지 24의 조건으로 수행될 수 있다.When the EGFR gene mutation detection method of the present invention is performed with qPCR, for example, it may be performed under the conditions of Tables 22 to 24 below.
본 발명의 EGFR 유전자 돌연변이 검출용 DNA 중합효소, 프라이머 세트, 프로브, 및/또는 키트를 폐암 환자의 약물에 대한 반응성을 예측하기 위한 용도로 사용할 수 있다.The DNA polymerase, primer set, probe, and/or kit for detecting EGFR gene mutations of the present invention can be used for predicting reactivity to drugs of lung cancer patients.
따라서, 본 발명은 폐암 환자의 약물에 대한 반응성을 예측하기 위한 EGFR 유전자 돌연변이 검출용 DNA 중합효소, 프라이머 세트, 프로브 및/또는 키트를 제공할 수 있다.Accordingly, the present invention can provide a DNA polymerase, primer set, probe, and/or kit for detecting EGFR gene mutation to predict responsiveness to drugs of lung cancer patients.
본 발명은 또한, 전술한 DNA 중합효소, 프라이머 세트, 프로브 및/또는 키트를 이용한, 폐암 환자의 약물에 대한 반응성을 예측하는 방법을 제공할 수 있다.The present invention can also provide a method for predicting the reactivity of a lung cancer patient to a drug using the aforementioned DNA polymerase, primer set, probe, and/or kit.
본 발명의 바람직한 또 다른 일실시예에 따르면, 상기 암은 비소세포폐암일 수 있다.According to another preferred embodiment of the present invention, the cancer may be non-small cell lung cancer.
본 발명의 EGFR 유전자 돌연변이 검출방법은, 상기 표 4의 공지된 EGFR 돌연변이를 검출함으로써 암을 조기에 진단하고 환자 맞춤별로 치료전략을 수립할 수 있는 정보를 제공하고, 이를 통해 환자를 보다 효과적으로 치료하는데 기여한다.The EGFR gene mutation detection method of the present invention provides information to diagnose cancer early and establish a treatment strategy for each patient by detecting a known EGFR mutation of Table 4 above, thereby more effectively treating patients Contribute.
본 발명의 EGFR 유전자 돌연변이 검출용 DNA 중합효소, 프라이머 세트 및/또는 키트는 상기 표 4에 기재된 돌연변이를 검출함으로써 적용할 수 있는 모든 질환의 진단, 예후 및 약물 반응성 예측방법에 사용될 수 있다.The DNA polymerase, primer set and/or kit for detecting EGFR gene mutations of the present invention can be used in the diagnosis, prognosis and drug reactivity prediction methods of all diseases applicable by detecting the mutations listed in Table 4 above.
본 발명에서, 용어 "예후"란, 질환의 경과 및 결과를 미리 예측하는 행위를 의미한다. 보다 구체적으로, 예후 예측이란 질환의 치료 후 경과는 환자의 생리적 또는 환경적 상태에 따라 달라질 수 있으며, 이러한 환자의 상태를 종합적으로 고려하여 치료 후 병의 경과를 예측하는 모든 행위를 의미하는 것으로 해석될 수 있다.In the present invention, the term "prognosis" refers to the act of predicting the course and outcome of a disease in advance. More specifically, the prognosis prediction can be interpreted to mean any action that predicts the course of the disease after treatment by comprehensively taking into account the patient's physiological or environmental conditions. Can be.
상기 예후 예측은 특정 질환의 치료 후, 해당 질환의 경과 및 완치여부를 미리 예상하여 환자의 무병생존율 또는 생존율을 예측하는 행위로 해석될 수 있다. 예를 들어, "예후가 좋다"라고 예측하는 것은 질환의 치료 후 환자의 무병생존율 또는 생존율이 높은 수준을 나타내어, 환자가 치료될 가능성이 높다는 것을 의미하고, "예후가 나쁘다"라고 예측하는 것은 질환의 치료 후 환자의 무병생존율 또는 생존율이 낮은 수준을 나타내어, 질환이 재발하거나 또는 해당 질환으로 인하여 사망할 가능성이 높다는 것을 의미한다.The prognosis prediction may be interpreted as an action of predicting the disease-free survival rate or survival rate of a patient in advance by predicting the progress and complete cure of the disease after treatment of a specific disease. For example, predicting that "the prognosis is good" means that the patient has a high probability of being treated without disease or having a high survival rate after treatment of the disease, and predicting that the "prognosis is bad" is a disease After treatment, the patient's disease-free survival rate or survival rate is low, indicating that the disease is likely to recur or die from the disease.
본 발명의 용어 "무병생존율"이란, 특정 질환의 치료 후, 환자가 해당 질환의 재발 없이 생존할 수 있는 가능성을 의미한다.The term "no disease survival rate" of the present invention means the possibility that a patient can survive without recurrence of the disease after treatment of the specific disease.
본 발명의 용어 "생존율"이란, 특정 질환의 치료 후, 환자가 해당 질환의 재발여부에 관계 없이 생존할 수 있는 가능성을 의미한다.The term "survival rate" of the present invention means the possibility that a patient can survive regardless of whether or not the disease recurs after treatment of a specific disease.
본 발명의 EGFR 유전자 돌연변이 검출방법을 폐암 환자의 약물에 대한 반응성을 예측하기 위한 용도로 사용하는 경우, 상기 약물은 티로신 키나아제 억제제 (tyrosine kinase inhibitor)일 수 있고, 티로신 키나아제 억제제의 종류는 예를 들어, 게피티닙, 에를로티닙 또는 오시머티닙일 수 있다.When the EGFR gene mutation detection method of the present invention is used for the purpose of predicting the reactivity to a drug in a lung cancer patient, the drug may be a tyrosine kinase inhibitor, and the type of the tyrosine kinase inhibitor is, for example , Gefitinib, erlotinib or osimmertinib.
이하 본 발명을 실시예에 의하여 더욱 상세히 설명한다. 이들 실시예는 단지 본 발명을 보다 구체적으로 설명하기 위한 것으로, 이에 의해 본 발명의 기술적 범위가 이들 실시예에 국한되지 않는다는 것은 당업계에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자에게 있어서 자명 할 것이다.Hereinafter, the present invention will be described in more detail by examples. These examples are only for explaining the present invention in more detail, whereby it will be apparent to those skilled in the art that the technical scope of the present invention is not limited to these examples.
[실시예 1][Example 1]
Taq 중합효소의 돌연변이유발Mutagenesis of Taq polymerase
1-1. 단편 PCR1-1. Fragment PCR
본 실시예에서는 서열번호 1의 아미노산 서열에서 536번째 아미노산 잔기를 아르기닌에서 리신으로 치환된 Taq DNA 중합효소 (이하 "R536K"라 함), 660번째 아미노산 잔기를 아르기닌에서 발린으로 치환된 Taq DNA 중합효소 (이하 "R660V"라 함) 및 536번째 아미노산 잔기를 아르기닌에서 리신으로 치환되고 660번째 아미노산 잔기를 아르기닌에서 발린으로 치환된 Taq DNA 중합효소 (이하 "R536K/R660V"라 함)를 하기와 같이 제조하였다.In this embodiment, Taq DNA polymerase in which the 536th amino acid residue in the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1 is substituted with arginine to lysine (hereinafter referred to as "R536K"), Taq DNA polymerase in which the 660th amino acid residue is substituted with valine in arginine. (Hereinafter referred to as “R660V”) and Taq DNA polymerase (hereinafter referred to as “R536K/R660V”) in which the 536th amino acid residue is substituted from arginine to lysine and the 660th amino acid residue is substituted from arginine to valine is prepared as follows. Did.
먼저, 표 5에 기재된 돌연변이 특이적 프라이머를 이용하여 도 1의 (a)에 나타난 바와 같이 Taq DNA 중합효소 단편들(F1 내지 F5)을 PCR로 증폭하였다. 반응조건은 표 6과 같다.First, Taq DNA polymerase fragments (F1 to F5) were amplified by PCR using the mutant specific primers listed in Table 5, as shown in Figure 1(a). The reaction conditions are shown in Table 6.
| 프라이머primer | 서열 (5'→3')Sequence (5'→3') | 서열번호Sequence number |
| Eco-FEco-F | GG GGTACC TCA TCA CCC CGGGG GGTACC TCA TCA CCC CGG | 6464 |
| R536K-RR536K-R | CTT GGT GAG CTC CTT GTA CTG CAG GATCTT GGT GAG CTC CTT GTA CTG CAG GAT | 6565 |
| R536K-FR536K-F | ATC CTG CAG TAC AAG GAG CTC ACC AAGATC CTG CAG TAC AAG GAG CTC ACC AAG | 6666 |
| R660V-RR660V-R | GAT GGT CTT GGC CGC CAC GCG CAT CAG GGGGAT GGT CTT GGC CGC CAC GCG CAT CAG GGG | 6767 |
| R660V-FR660V-F | CCC CTG ATG CGC GTG GCG GCC AAG ACC ATCCCC CTG ATG CGC GTG GCG GCC AAG ACC ATC | 6868 |
| Xba-RXba-R | GC TCTAGA CTA TCA CTC CTT GGC GGA GAG CCAGC TCTAGA CTA TCA CTC CTT GGC GGA GAG CCA | 6969 |
| 10xpfu 버퍼 (솔젠트)10xpfu buffer (solvent) | 2.5 μl2.5 μl |
| dNTP (각 10 mM)dNTP (10 mM each) | 1 μl1 μl |
| F 프라이머F primer | 1 μl1 μl |
| R 프라이머R primer | 1 μl1 μl |
|
증류수Distilled |
18 μl18 μl |
| pUC19-Taq (10 ng/ μl)pUC19-Taq (10 ng/μl) | 1 μl1 μl |
| Pfu 중합효소Pfu polymerase |
0.5 μl0.5 |
| 30 사이클 (Ta=60℃)30 cycles (Ta=60℃) | 25 μl25 μl |
PCR 산물을 전기영동 상에서 확인해본 결과, 도 1의 (b)에 나타난 바와 같이 각 단편에 대한 밴드가 확인되어 목적하는 단편이 증폭되었음을 확인하였다.As a result of confirming the PCR product on the electrophoresis, as shown in Fig. 1 (b), it was confirmed that the band for each fragment was confirmed and the desired fragment was amplified.
1-2. 오버랩 (overlap) PCR1-2. Overlap PCR
상기 1-1에서 증폭한 각 단편을 주형으로 하여 양 말단의 프라이머(Eco-F 및 Xba-R 프라이머)를 이용하여 전장을 증폭하였다. 반응조건은 표 7 및 8과 같다.Each fragment amplified in 1-1 was used as a template to amplify the full length using primers at both ends (Eco-F and Xba-R primers). The reaction conditions are shown in Tables 7 and 8.
| 10xpfu 버퍼 (솔젠트)10xpfu buffer (solvent) | 5 μl5 μl |
| 5x인핸서 (솔젠트)5x Enhancer (Solent) | 10 μl10 μl |
| dNTP (각 10 mM)dNTP (10 mM each) | 1 μl1 μl |
| Eco-F 프라이머 (10 pmol/μl)Eco-F primer (10 pmol/μl) | 2 μl2 μl |
| Xba-R 프라이머 (10 pmol/μl)Xba-R primer (10 pmol/μl) | 2 μl2 μl |
| 증류수Distilled water | 27 μl27 μl |
| 단편 1 (또는 단편 3)Fragment 1 (or Fragment 3) | 1 μl1 μl |
| 단편 2 (또는 단편 4)Short 2 (or Short 4) | 1 μl1 μl |
| Pfu 중합효소Pfu polymerase |
1 μl1 |
| 40 사이클 (Ta=62℃)40 cycles (Ta=62℃) | 50 μl50 μl |
| 10xpfu 버퍼 (솔젠트)10xpfu buffer (solvent) | 5 μl5 μl |
| 5x인핸서 (솔젠트)5x Enhancer (Solent) | 10 μl10 μl |
| dNTP (각 10 mM)dNTP (10 mM each) | 1 μl1 μl |
| Eco-F 프라이머 (10 pmol/μl)Eco-F primer (10 pmol/μl) | 2 μl2 μl |
| Xba-R 프라이머 (10 pmol/μl)Xba-R primer (10 pmol/μl) | 2 μl2 μl |
|
증류수Distilled |
26 μl26 |
| 단편 2Short 2 |
1 μl1 |
| 단편 3Short 3 | 1 μl1 μl |
| 단편 5Short 5 | 1 μl1 μl |
| Pfu 중합효소Pfu polymerase |
1 μl1 |
| 40 사이클 (Ta=62℃)40 cycles (Ta=62℃) | 50 μl50 μl |
그 결과, 도 1의 (c)에 나타난 바와 같이 "R536K", "R660V" 및 "R536K/R660V"의 Taq 중합효소가 증폭되었음을 확인하였다.As a result, it was confirmed that Taq polymerases of "R536K", "R660V" and "R536K/R660V" were amplified as shown in FIG. 1(c).
1-3. 라이게이션1-3. Ligation
pUC19을 하기 표 9의 조건으로 37℃에서 4시간 동안 제한효소 EcoRI/XbaI로 분해한 다음 DNA를 정제하고 정제된 DNA를 표 10의 조건으로 37℃에서 1시간 동안 SAP를 처리하여 벡터를 준비하였다.pUC19 was digested with the restriction enzyme EcoRI/XbaI at 37°C for 4 hours under the conditions of Table 9 below, and then the DNA was purified and the purified DNA was treated with SAP for 1 hour at 37°C under the conditions of Table 10 to prepare a vector. .
| 10xCutSmart 버퍼 (NEB)10xCutSmart buffer (NEB) | 2.5 μl2.5 μl |
| pUC19 (500 ng/μl)pUC19 (500 ng/μl) | 21.5 μl21.5 μl |
| EcoRI-HF (NEB)EcoRI-HF (NEB) | 0.5 μl0.5 μl |
| XbaI (NEB)XbaI (NEB) | 0.5 μl0.5 μl |
| 25 μl25 μl |
| 10xSAP 버퍼 (로슈)10xSAP buffer (Roche) | 2 μl2 μl |
| 정제된 DNAPurified DNA | 17 μl17 μl |
| SAP (로슈)SAP (Roche) |
1 μl1 |
| 20 μl20 μl |
인서트(insert)의 경우, 상기 실시예 1-2의 오버랩 PCR 산물을 정제하여 표 11의 조건으로 37℃에서 3시간 동안 제한효소 EcoRI/XbaI로 분해한 다음 준비된 벡터와 함께 겔 추출하였다 (도 2).In the case of inserts, the overlap PCR product of Example 1-2 was purified, digested with restriction enzyme EcoRI/XbaI at 37°C for 3 hours under the conditions of Table 11, and then gel extracted with the prepared vector (FIG. 2 ). ).
| 10xCutSmart 버퍼 (NEB)10xCutSmart buffer (NEB) | 2 μl2 μl |
| 정제된 PCR 산물Purified PCR product | 17 μl17 μl |
| EcoRI-HF (NEB)EcoRI-HF (NEB) | 0.5 μl0.5 μl |
| XbaI (NEB)XbaI (NEB) |
0.5 μl0.5 |
| 20 μl20 μl |
표 12의 조건으로 실온(RT)에서 2시간 동안 라이게이션한 후, E. coli DH5α에 형질전환하여 암피실린이 포함된 배지에서 선별하였다. 수득된 콜로니들로부터 준비된 플라스미드를 시퀀싱하여 원하는 변이가 도입된 Taq DNA 중합효소 돌연변이체 ("R536K", "R660V" 및 "R536K/R660V")를 수득하였다.After ligation at room temperature (RT) for 2 hours under the conditions of Table 12, E. coli DH5α was transformed to select from the medium containing ampicillin. The plasmid prepared from the obtained colonies was sequenced to obtain Taq DNA polymerase mutants ("R536K", "R660V" and "R536K/R660V") into which the desired mutation was introduced.
| 벡터 단독Vector sole | 벡터+인서트Vector + insert | |
| 10x연결효소 버퍼 (솔젠트)10x ligase buffer (solvent) | 1 μl1 μl | 1 μl1 μl |
| 벡터vector | 1 μl1 μl | 1 μl1 μl |
| 인서트insert | -- | 3 μl3 μl |
| 증류수Distilled water |
7 μl7 |
4 μl4 μl |
| T4 DNA 연결효소 (솔젠트)T4 DNA ligase (solvent) | 1 μl1 μl |
1 μl1 |
|
10 μl10 |
10 μl10 μl |
[실시예 2][Example 2]
E507K 변이의 도입Introduction of E507K mutation
2-1. 단편 PCR2-1. Fragment PCR
상기 실시예 1에서 제조된 "R536K", "R660V" 및 "R536K/R660V"의 Taq 중합효소 활성을 테스트해 본 결과 활성이 떨어지는 것을 확인하고(데이터 미도시), R536K, R660V, R536K/R660V 각각에 추가로 E507K 변이(서열번호 1의 아미노산 서열에서 507번째 아미노산 잔기를 글루탐산에서 리신으로 치환)를 도입하였으며, 대조군으로 사용하기 위해 야생형 Taq DNA 중합효소(WT)에도 E507K 변이를 도입하였다. E507K 변이가 도입된 Taq DNA 중합효소의 제조방법은 실시예 1과 동일하다.Taq polymerase activity of "R536K", "R660V" and "R536K/R660V" prepared in Example 1 was tested to confirm that the activity was poor (data not shown), R536K, R660V, R536K/R660V, respectively In addition, an E507K mutation (substituting the 507th amino acid residue in the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1 with glutamic acid for lysine) was introduced, and an E507K mutation was also introduced into the wild-type Taq DNA polymerase (WT) for use as a control. The production method of Taq DNA polymerase introduced with the E507K mutation is the same as in Example 1.
표 13에 기재된 돌연변이 특이적 프라이머를 이용하여 도 3에 나타난 바와 같이 Taq DNA 중합효소 단편들(F6 내지 F7)을 PCR로 증폭하였다. 반응조건은 표 14와 같다.Taq DNA polymerase fragments (F6 to F7) were amplified by PCR using the mutant specific primers listed in Table 13. The reaction conditions are shown in Table 14.
| 프라이머primer | 서열 (5'→3')Sequence (5'→3') | 서열번호Sequence number |
| Eco-FEco-F | GG GGTACC TCA TCA CCC CGGGG GGTACC TCA TCA CCC CGG | 6464 |
| E507K-RE507K-R | CTT GCC GGT CTT TTT CGT CTT GCC GATCTT GCC GGT CTT TTT CGT CTT GCC GAT | 7070 |
| E507K-FE507K-F | ATC GGC AAG ACG AAA AAG ACC GGC AAGATC GGC AAG ACG AAA AAG ACC GGC AAG | 7171 |
| Xba-RXba-R | GC TCTAGA CTA TCA CTC CTT GGC GGA GAG CCAGC TCTAGA CTA TCA CTC CTT GGC GGA GAG CCA | 6969 |
| 10xpfu 버퍼 (솔젠트)10xpfu buffer (solvent) | 2.5 μl2.5 μl |
| dNTP (각 10 mM)dNTP (10 mM each) | 1 μl1 μl |
| F 프라이머 (10 pmol/μl)F primer (10 pmol/μl) | 1 μl1 μl |
| R 프라이머 (10 pmol/μl)R primer (10 pmol/μl) | 1 μl1 μl |
|
증류수Distilled |
18 μl18 μl |
| 주형 플라스미드 (10 ng/μl)Template plasmid (10 ng/μl) | 1 μl1 μl |
| Pfu 중합효소Pfu polymerase |
0.5 μl0.5 |
| 30 사이클 (Ta=60℃)30 cycles (Ta=60℃) | 25 μl25 μl |
*주형 플라스미드: pUC19-Taq (WT)pUC19-Taq (R536K)pUC19-Taq (R660V)* Template plasmid: pUC19-Taq (WT) pUC19-Taq (R536K) pUC19-Taq (R660V)
pUC19-Taq (R536K/R660V)pUC19-Taq (R536K/R660V)
2-2. 오버랩 (overlap) PCR2-2. Overlap PCR
상기 2-1에서 증폭한 각 단편을 주형으로 하여 양 말단의 프라이머(Eco-F 및 Xba-R 프라이머)를 이용하여 전장을 증폭하였다. 반응조건은 표 15와 같다.Each fragment amplified in 2-1 was used as a template, and the full length was amplified using primers (Eco-F and Xba-R primers) at both ends. The reaction conditions are shown in Table 15.
| 10xpfu 버퍼 (솔젠트)10xpfu buffer (solvent) | 5 μl5 μl |
| 5x인핸서 (솔젠트)5x Enhancer (Solent) | 10 μl10 μl |
| dNTP (각 10 mM)dNTP (10 mM each) | 1 μl1 μl |
| Eco-F 프라이머 (10 pmol/μl)Eco-F primer (10 pmol/μl) | 2 μl2 μl |
| Xba-R 프라이머 (10 pmol/μl)Xba-R primer (10 pmol/μl) | 2 μl2 μl |
| 증류수Distilled water |
27 μl27 |
| 단편 6Short 6 | 1 μl1 μl |
| 단편 7Short 7 | 1 μl1 μl |
| Pfu 중합효소Pfu polymerase |
1 μl1 |
| 40 사이클 (Ta=62℃)40 cycles (Ta=62℃) | 50 μl50 μl |
2-3. 라이게이션2-3. Ligation
pUC19을 표 9의 조건으로 37℃에서 4시간 동안 제한효소 EcoRI/XbaI로 분해한 다음 DNA를 정제하고, 정제된 DNA를 표 10의 조건으로 37℃에서 1시간 동안 SAP를 처리하여 벡터를 준비하였다.pUC19 was digested with the restriction enzyme EcoRI/XbaI at 37°C for 4 hours under the conditions of Table 9, and then the DNA was purified, and the purified DNA was treated with SAP for 1 hour at 37°C under the conditions of Table 10 to prepare a vector. .
인서트(insert)의 경우, 상기 실시예 2-2의 오버랩 PCR 산물을 정제하여 표 11의 조건으로 37℃에서 3시간 동안 제한효소 EcoRI/XbaI로 분해한 다음 준비된 벡터와 함께 겔 추출하였다 (도 4).In the case of inserts, the overlap PCR product of Example 2-2 was purified, digested with restriction enzyme EcoRI/XbaI at 37° C. for 3 hours under the conditions of Table 11, and then gel extracted with the prepared vector (FIG. 4 ). ).
표 12의 조건으로 실온(RT)에서 2시간 동안 라이게이션한 후, E. coli DH5α 또는 DH10β에 형질전환하여 암피실린이 포함된 배지에서 선별하였다. 수득된 콜로니들로부터 준비된 플라스미드를 시퀀싱하여 E507K 변이가 도입된 Taq DNA 중합효소 돌연변이체 ("E507K/R536K", "E507K/R660V" 및 "E507K/R536K/R660V")를 수득하였다.After ligation at room temperature (RT) for 2 hours under the conditions of Table 12, E. coli was transformed into DH5α or DH10β, and was selected in a medium containing ampicillin. The plasmid prepared from the obtained colonies was sequenced to obtain Taq DNA polymerase mutants introduced with E507K mutations (“E507K/R536K”, “E507K/R660V” and “E507K/R536K/R660V”).
[실시예 3][Example 3]
프라이머 세트의 제작Production of primer sets
EGFR 유전자의 돌연변이에 대해서는 PCR 산물을 생성하지만 야생형 EGFR 유전자에 대해서는 생성하지 않는 프라이머를 디자인하기 위해 OligoAnalyzer Tool (https://sg.idtdna.com/calc/analyzer) 프로그램을 이용하여 프라이머 크기, Tm값, 프라이머 GC 함량, 프라이머 내에 자가-상보적 서열(self-complementary sequence)이 있는지의 여부 등을 확인하여 2차 구조(secondary structure)의 형성 가능성을 배제한 후 표 16 내지 19에 나타난 바와 같이 프라이머를 디자인하였다.Primer size and Tm value using the OligoAnalyzer Tool (https://sg.idtdna.com/calc/analyzer) program to design primers that generate PCR products for mutations in the EGFR gene but not for the wild-type EGFR gene After designing primers as shown in Tables 16 to 19 after excluding the possibility of formation of a secondary structure by checking whether the primer GC content, whether there is a self-complementary sequence in the primer, etc. Did.
| 돌연변이 그룹Mutant group | 프라이머primer | 서열 (5'-3')Sequence (5'-3') | 서열번호Sequence number | 최종농도 (nM)Final concentration (nM) |
| S768IS768I | S768I Rmt14+CS768I Rmt14+C | CGG GGT TGT CCA CGA CGG GGT TGT CCA CGA | 33 | 200200 |
| S768I SF2S768I SF2 | ACA CTG ACG TGC CTC TCC CACA CTG ACG TGC CTC TCC C | 44 | 200200 | |
| Ex19delEx19del | Ex19del C1 Rmt20Ex19del C1 Rmt20 | TGT TGG CTT TCG GAG ATG CCTGT TGG CTT TCG GAG ATG CC | 55 | 5050 |
| Ex19del C2 Rmt21Ex19del C2 Rmt21 | TTG GCT TTC GGA GAT GAT TCCTTG GCT TTC GGA GAT GAT TCC | 66 | 5050 | |
| Ex19del C3 Rmt20Ex19del C3 Rmt20 | GTT GGC TTT CGG AGA TTC CTGTT GGC TTT CGG AGA TTC CT | 77 | 4040 | |
| Ex19del C4 Rmt24Ex19del C4 Rmt24 | GCT TTC GGA GAT GTT GCT TCC TTGGCT TTC GGA GAT GTT GCT TCC TTG | 88 | 150150 | |
| Ex19del C5 Rmt21Ex19del C5 Rmt21 | CCT TGT TGG CTT TCT GTT CCT CCT TGT TGG CTT TCT GTT CCT | 99 | 4040 | |
| Ex19del C6 Rmt21Ex19del C6 Rmt21 | CCT TGT TGG CTT TCG GAT CCTCCT TGT TGG CTT TCG GAT CCT | 1010 | 4040 | |
| Ex19del C7 Rmt21Ex19del C7 Rmt21 | TGG CTT TCG GAG ATG TTT TGATGG CTT TCG GAG ATG TTT TGA | 1111 | 5050 | |
| Ex19del C8 Rmt20Ex19del C8 Rmt20 | TGG CTT TCG GAG ATG TCT TGTGG CTT TCG GAG ATG TCT TG | 1212 | 5050 | |
| Ex19del C9 Rmt21Ex19del C9 Rmt21 | TCC TTG TTG GCT TTC GGT TCCTCC TTG TTG GCT TTC GGT TCC | 1313 | 4040 | |
| Ex19del C10 Rmt2(20)Ex19del C10 Rmt2(20) | TGT TGG CTT TCG GAG CCT TGTGT TGG CTT TCG GAG CCT TG | 1414 | 5050 | |
| Ex19del C11 Rmt20Ex19del C11 Rmt20 | TTG TTG GCT TTC GGA GAT TC TTG TTG GCT TTC GGA GAT TC | 1515 | 5050 | |
| Ex19del C12 Rmt21Ex19del C12 Rmt21 | TTC CTT GTT GGC TTT CGA TTCTTC CTT GTT GGC TTT CGA TTC | 1616 | 5050 | |
| Ex19del C13 Rmt21Ex19del C13 Rmt21 | GCT TTC GGA GAT GTT GGT TCC GCT TTC GGA GAT GTT GGT TCC | 1717 | 100100 | |
| Ex19del C14 Rmt20Ex19del C14 Rmt20 | GTT GGC TTT CGG AGA TGG TT GTT GGC TTT CGG AGA TGG TT | 1818 | 100100 | |
| Ex19del C15 Rmt20Ex19del C15 Rmt20 | CTT GTT GGC TTT CGG AAC CTCTT GTT GGC TTT CGG AAC CT | 1919 | 5050 | |
| Ex19del C16 Rmt23Ex19del C16 Rmt23 | TTC CTT GTT GGC TTT CGG AAT TT TTC CTT GTT GGC TTT CGG AAT TT | 2020 | 7575 | |
| Ex19del C17 Rmt20Ex19del C17 Rmt20 | GTT GGC TTT CGG AGA TAC CTGTT GGC TTT CGG AGA TAC CT | 2121 | 5050 | |
| Ex19del C18 Rmt3(21)Ex19del C18 Rmt3(21) | TTT CCT TGT TGG CTT TCG GTTTTT CCT TGT TGG CTT TCG GTT | 2222 | 7575 | |
| Ex19del C19 Rmt21Ex19del C19 Rmt21 | TGT TGG CTT TCG GAG AAG CAATGT TGG CTT TCG GAG AAG CAA | 2323 | 7575 | |
| Ex19del C20 Rmt21Ex19del C20 Rmt21 | TGT TGG CTT TCG GAG ATT GCTTGT TGG CTT TCG GAG ATT GCT | 2424 | 5050 | |
| Ex19del C21 Rmt21Ex19del C21 Rmt21 | TTG GCT TTC GGA GAT GTT GGCTTG GCT TTC GGA GAT GTT GGC | 2525 | 7575 | |
| Ex19del C22 Rmt20Ex19del C22 Rmt20 | TGT TGG CTT TCG GAG ACT TGTGT TGG CTT TCG GAG ACT TG | 2626 | 5050 | |
| Ex19del C23 Rmt22Ex19del C23 Rmt22 | TGG CTT TCG GAG ATG TTG GAA T TGG CTT TCG GAG ATG TTG GAA T | 2727 | 100100 | |
| Ex19del C24 Rmt22Ex19del C24 Rmt22 | GTT GGC TTT CGG AGA TAT TTT GGTT GGC TTT CGG AGA TAT TTT G | 2828 | 5050 | |
| Ex19del C25 Rmt22Ex19del C25 Rmt22 | TGT TGG CTT TCG GAG ATG GAA TTGT TGG CTT TCG GAG ATG GAA T | 2929 | 100100 | |
| Ex19del C26 Rmt19+FLEx19del C26 Rmt19+FL | AAT AAA TCA TAA AAA CTC ACA TCG AGG GTT GAAT AAA TCA TAA AAA CTC ACA TCG AGG GTT G | 3030 | 100100 | |
| Ex19del C27 Rmt20Ex19del C27 Rmt20 | TCC TTG TTG GCT TTC GAG ACTCC TTG TTG GCT TTC GAG AC | 3131 | 5050 | |
| Ex19del C28 Rmt2(20)Ex19del C28 Rmt2(20) | TTG TTG GCT TTC GGA GAT TCTTG TTG GCT TTC GGA GAT TC | 3232 | 4040 | |
| Ex19del C29 Rmt21Ex19del C29 Rmt21 | GCT TTC GGA GAT GTT GCG ATAGCT TTC GGA GAT GTT GCG ATA | 3333 | 5050 | |
| Ex19del C30 Rmt23Ex19del C30 Rmt23 | GTT GGC TTT CGG AGA TGT TAT AGGTT GGC TTT CGG AGA TGT TAT AG | 3434 | 7575 | |
| Ex19del C31 Rmt20Ex19del C31 Rmt20 | GCT TTC GGA GAT GTT GTG ATGCT TTC GGA GAT GTT GTG AT | 3535 | 100100 | |
| 19del SF219del SF2 | TCC TTC TCT CTC TGT CAT AGG GTCC TTC TCT CTC TGT CAT AGG G | 3636 | 200200 | |
| EGFR ICEGFR IC | EGFR IC Ex2FEGFR IC Ex2F | CAG TTG GGC ACT TTT GAA GAT CCAG TTG GGC ACT TTT GAA GAT C | 3737 | 100100 |
| EGFR IC Ex2REGFR IC Ex2R | TCC AAA TTC CCA AGG ACC ACTCC AAA TTC CCA AGG ACC AC | 3838 | 100100 |
| 돌연변이 그룹Mutant group | 프라이머primer | 서열 (5'-3')Sequence (5'-3') | 서열번호Sequence number | 최종 농도 (nM)Final concentration (nM) |
| T790MT790M | T790M Rmt(15)T790M Rmt(15) | AGG GCA TGA GCT GCAAGG GCA TGA GCT GCA | 3939 | 240240 |
| T790M SF5T790M SF5 |
ACC CCC ACG TGT GCC GACC CCC ACG |
4040 | 150150 | |
| EGFR ICEGFR IC | EGFR IC Ex2FEGFR IC Ex2F | CAG TTG GGC ACT TTT GAA GAT CCAG TTG GGC ACT TTT GAA GAT C | 3737 | 100100 |
| EGFR IC Ex2REGFR IC Ex2R |
TCC AAA TTC CCA AGG ACC ACTCC AAA TTC CCA |
3838 | 100100 |
| 돌연변이 그룹Mutant group | 프라이머primer | 서열 (5'-3')Sequence (5'-3') | 서열번호Sequence number | 최종 농도 (nM)Final concentration (nM) |
| G719XG719X | G719S Rmt17G719S Rmt17 | CCG AAC GCA CCG GAG CTCCG AAC GCA CCG GAG CT | 4141 | 200200 |
| G719C Rmt16G719C Rmt16 |
CGA ACG CAC CGG AGC ACGA ACG CAC |
4242 | 200200 | |
| G719A Rmt18(-3T)G719A Rmt18(-3T) | TGC CGA ACG CAC CGT AGGTGC CGA ACG CAC CGT AGG | 4343 | 200200 | |
| G719X SF4G719X SF4 |
GCC TCT TAC ACC CAG TGG AGA AGCC TCT TAC ACC CAG |
4444 | 200200 | |
| L861QL861Q | L861Q Rmt17L861Q Rmt17 | CTC TTC CGC ACC CAG CTCTC TTC CGC ACC CAG CT | 4545 | 200200 |
| L861Q SF1L861Q SF1 |
CGT ACT GGT GAA AAC ACC GCGT ACT GGT GAA |
4646 | 200200 | |
| EGFR ICEGFR IC | EGFR IC Ex2FEGFR IC Ex2F | CAG TTG GGC ACT TTT GAA GAT CCAG TTG GGC ACT TTT GAA GAT C | 3737 | 100100 |
| EGFR IC Ex2REGFR IC Ex2R |
TCC AAA TTC CCA AGG ACC ACTCC AAA TTC CCA |
3838 | 100100 |
| 돌연변이 그룹Mutant group | 프라이머primer | 서열 (5'-3')Sequence (5'-3') | 서열번호Sequence number | 최종 농도 (nM)Final concentration (nM) |
| Ex20InsEx20Ins | 20Ins C1 Rmt2(15)-4A20Ins C1 Rmt2(15)-4A | CCA CGC TGG CAA CGC CCA CGC TGG CAA CGC | 4747 | 400400 |
| 20Ins C2 Rmt3(15)20Ins C2 Rmt3(15) |
GGC ACA CGT GGT GGG GGC ACA |
4848 | 200200 | |
| 20Ins C3 Rmt2(16)20Ins C3 Rmt2(16) | CAC ACG TGG GGG TTA CCAC ACG TGG GGG TTA C | 4949 | 300300 | |
| 20Ins C4 Rmt2(16)-3T20Ins C4 Rmt2(16)-3T |
TGT CCA CGC TGT TCA CTGT CCA CGC |
5050 | 200200 | |
| 20Ins C5 Rmt2(16)-3T20Ins C5 Rmt2(16)-3T |
ATC CAC GCT GGC TAC GATC CAC GCT |
5151 | 100100 | |
| 20Ins SF420Ins SF4 | GAA GCC ACA CTG ACG TGC CGAA GCC ACA CTG ACG TGC C | 5252 | 200200 | |
| L858RL858R | L858R Fmt21-2AL858R Fmt21-2A | CAA GAT CAC AGA TTT TGG ACGCAA GAT CAC AGA TTT TGG ACG | 5353 | 400400 |
| L858R OR2L858R OR2 | TGA CCT AAA GCC ACC TCC TTA CTTGA CCT AAA GCC ACC TCC TTA CT | 5454 | 400400 | |
| EGFR ICEGFR IC | EGFR IC Ex2FEGFR IC Ex2F | CAG TTG GGC ACT TTT GAA GAT CCAG TTG GGC ACT TTT GAA GAT C | 3737 | 100100 |
| EGFR IC Ex2REGFR IC Ex2R |
TCC AAA TTC CCA AGG ACC ACTCC AAA TTC CCA |
3838 | 100100 |
[실시예 4][Example 4]
시료의 준비Sample preparation
돌연변이 플라스미드 준비Mutant plasmid preparation
EGFR의 야생형 DNA인 HEK293T 세포주의 gDNA를 이용하여 표 4의 표적 돌연변이의 주변부위를 증폭할 수 있는 프라이머 세트를 적용하여 엑손 18, 19, 20, 21 부위의 야생형 클론을 제작하였다. 제작한 야생형 DNA를 이용하여 타겟변이 44개에 대해 돌연변이 유발 (mutagenesis)을 진행하여 E.Coli DH5α 세포에 형질전환하여 각 돌연변이형 클론을 확보하였다. 야생형 클론과 돌연변이형 클론의 확인은 직접 염기서열분석법에 의해 확인하였다. 클론을 통해 추출된 각 엑손별 야생형 DNA와 돌연변이형 DNA는 EGFR 돌연변이 검출 키트의 성능을 평가하기 위한 표준물질로 사용하였다.Using the gDNA of the HEK293T cell line, the wild-type DNA of EGFR, a primer set capable of amplifying the periphery of the target mutation in Table 4 was applied to prepare wild-type clones at exon 18, 19, 20, and 21 sites. Mutagenesis was performed on 44 target mutations using the prepared wild-type DNA, and transformed into E.Coli DH5α cells to obtain each mutant clone. Wild type clones and mutant clones were identified by direct sequencing. Wild-type DNA and mutant DNA for each exon extracted through clones were used as standards to evaluate the performance of the EGFR mutation detection kit.
표 20에 나타낸 바와 같이, HEK293T 세포 유전체 DNA 30,000 카피 당 표 4에 기재된 각 돌연변이 플라스미드를 10,000 카피, 100 카피, 30 카피, 10 카피 또는 3 카피를 첨가하여 시료를 준비하였고, 돌연변이 플라스미드를 첨가하지 않은 그룹을 대조군으로 사용하였다.As shown in Table 20, samples were prepared by adding 10,000 copies, 100 copies, 30 copies, 10 copies, or 3 copies of each mutant plasmid described in Table 4 per 30,000 copies of HEK293T cell genomic DNA. The group was used as a control.
| 그룹group | 시료sample |
| WTWT | HEK293T 세포 유전체 DNA 30,000 카피HEK293T cell genomic DNA 30,000 copies |
|
WT+mt 104
WT+ |
HEK293T 세포 유전체 DNA 30,000 카피 + 해당 돌연변이 플라스미드 10,000 카피HEK293T cell genomic DNA 30,000 copies + corresponding mutant plasmid 10,000 copies |
|
WT+mt 102
WT+ |
HEK293T 세포 유전체 DNA 30,000 카피 + 해당 돌연변이 플라스미드 100 카피HEK293T cell genomic DNA 30,000 copies + corresponding mutant plasmid 100 copies |
|
WT+mt 30WT+ |
HEK293T 세포 유전체 DNA 30,000 카피 + 해당 돌연변이 플라스미드 30 카피HEK293T cell genomic DNA 30,000 copies + corresponding |
|
WT+mt 10WT+ |
HEK293T 세포 유전체 DNA 30,000 카피 + 해당 돌연변이 플라스미드 10 카피HEK293T cell genomic DNA 30,000 copies + corresponding |
|
WT+mt 3WT+ |
HEK293T 세포 유전체 DNA 30,000 카피 + 해당 돌연변이 플라스미드 3 카피HEK293T cell genomic DNA 30,000 copies + corresponding |
[실시예 5][Example 5]
EGFR 돌연변이 검출EGFR mutation detection
상기 실시예 2에서 수득한 "E507K/R536K/R660V"변이를 각각 포함하는 Taq 중합효소 (서열번호 2) 및 실시예 3의 프라이머 세트를 사용하여 표 20의 각 그룹으로부터 표 4의 EGFR 유전자 돌연변이를 검출하였다. 표 21에는 EGFR Master Mixture 1-4가 각각 표적하는 돌연변이 정보를 나타내었다.Using the Taq polymerase (SEQ ID NO: 2) and the primer set of Example 3, each containing the "E507K/R536K/R660V" mutation obtained in Example 2 above, the EGFR gene mutations of Table 4 from each group of Table 20 were obtained. Detected. Table 21 shows mutant information targeted by EGFR Master Mixture 1-4, respectively.
| MMXMMX | 형광Neon | 돌연변이 그룹Mutant group | EGFR 핵산서열 (COSMIC ID)EGFR nucleic acid sequence (COSMIC ID) |
| MMX1MMX1 | FAMFAM | S768IS768I | 2303G>T (6241)2303G>T (6241) |
| CFO560CFO560 | Ex19DelEx19Del | 2240_2251del12 (6210), 2239_2247del9 (6218), 2238_2255del18 (6220), 2235_2249del15 (6223), 2236_2250del15 (6225), 2239_2253del15 (6254), 2239_2256del18 (6255), 2237_2254del18 (12367), 2240_2254del15 (12369), 2240_2257del18 (12370), 2239_2248TTAAGAGAAG>C (12382) , 2239_2251>C (12383), 2237_2255>T (12384), 2235_2255>AAT (12385), 2237_2252>T (12386), 2239_2258>CA (12387), 2239_2256>CAA (12403), 2237_2253>TTGCT (12416), 2238_2252>GCA (12419), 2238_2248>GC (12422), 2237_2251del15 (12678), 2236_2253del18 (12728), 2235_2248>AATTC (13550), 2235_2252>AAT (13551), 2235_2251>AATTC (13552), 2253_2276del24 (13556), 2237_2257>TCT (18427), 2238_2252del15 (23571), 2233_2247del15 (26038), 2232_2249del15 (221565), 2234_2248del15 (1190791)2240_2251del12 (6210), 2239_2247del9 (6218), 2238_2255del18 (6220), 2235_2249del15 (6223), 2236_2250del15 (6225), 2239_2253del15 (6254), 2239_2256del18 (6255), 2237_2254del18 (12367), 2240_2254del15 (370) 2239_2248TTAAGAGAAG>C (12382), 2239_2251>C (12383), 2237_2255>T (12384), 2235_2255>AAT (12385), 2237_2252>T (12386), 2239_2258>CA (12387), 2239_2256>CAA (12403), 2237_2253 >TTGCT (12416), 2238_2252>GCA (12419), 2238_2248>GC (12422), 2237_2251del15 (12678), 2236_2253del18 (12728), 2235_2248>AATTC (13550), 2235_2252>AAT (13551), 2235_2251>AATTC (13552) , 2253_2276del24 (13556), 2237_2257>TCT (18427), 2238_2252del15 (23571), 2233_2247del15 (26038), 2232_2249del15 (221565), 2234_2248del15 (1190791) | |
| MMX2MMX2 | FAMFAM | T790MT790M | 2369C>T (6240)2369C>T (6240) |
| MMX3MMX3 | FAMFAM | L861QL861Q | 2582T>A (6213)2582T>A (6213) |
| CFO560CFO560 | G719XG719X | 2155G>A (6252), 2155G>T (6253), 2156G>C (6239) 2155G>A (6252), 2155G>T (6253), 2156G>C (6239) | |
| MMX4MMX4 | FAMFAM | Ex20InsEx20Ins | 2307_2308ins9GCCAGCGTG (12376), 2319_2320insCAC (12377), 2310_2311insGGT (12378), 2311_2312ins9GCGTGGACA (13428), 2309_2310AC>CCAGCGTGGAT (13558)2307_2308ins9GCCAGCGTG (12376), 2319_2320insCAC (12377), 2310_2311insGGT (12378), 2311_2312ins9GCGTGGACA (13428), 2309_2310AC>CCAGCGTGGAT (13558) |
| CFO560CFO560 | L858RL858R | 2573T>G (6224), 2573_2574TG>GT (12429)2573T>G (6224), 2573_2574TG>GT (12429) |
구체적인 qPCR (Applied Biosystems 7500 Fast) 실험 조건은 하기 표 22 내지24와 같고, 프로브는 표 23과 같이 이중으로 표지하였다.Specific qPCR (Applied Biosystems 7500 Fast) experimental conditions are shown in Tables 22 to 24, and the probes were double-labeled as in Table 23.
|
2X EGFR MMX |
10 μl10 |
| 시료sample | 2 μl2 μl |
| 뉴클레아제 무첨가 증류수Nuclease-free distilled water | 7.5 μl7.5 μl |
| ADPS Smart DNA 중합효소 (1 U/ul)ADPS Smart DNA polymerase (1 U/ul) |
0.5 μl0.5 |
| 총gun | 20 μl20 μl |
| 돌연변이 그룹Mutant group | 프로브Probe | 서열 (5'-3')Sequence (5'-3') | 서열번호Sequence number | 5' 형광단5'fluorophore | 3' 소광물질3'matting material | 최종 농도 (nM)Final concentration (nM) | |
| S768IS768I | S768I FAM_RS768I FAM_R | TCA CGT AGG CTT CCT GGA GGG ATCA CGT AGG CTT CCT GGA GGG A | 5555 | FAMFAM | BHQ1BHQ1 | 400400 | |
| Ex19delEx19del | 19del CFO_R219del CFO_R2 | CTC TGG ATC CCA GAA GGT GAG AAA GCTC TGG ATC CCA GAA GGT GAG AAA G | 5656 | CAL Fluor Orange 560CAL Fluor Orange 560 | BHQ1BHQ1 | 400400 | |
| T790MT790M | T790M IR4T790M IR4 | GTG ATG AGC TGC ACG GGTG ATG AGC TGC ACG G | 5757 | FAMFAM | BHQ1BHQ1 | 125125 | |
| T790M IR2(-8T)T790M IR2(-8T) | GTG ATG AGT TGC ACG GTG GGTG ATG AGT TGC ACG GTG G | 5858 | FAMFAM | BHQ1BHQ1 | 130130 | ||
| G719XG719X | G719X CFO_R2_novaG719X CFO_R2_nova | AAA CTG AAT TCA AAA AGA TCA AAG TGC TGAAA CTG AAT TCA AAA AGA TCA AAG TGC TG | 5959 | CAL Fluor Orange 560CAL Fluor Orange 560 | BHQ1 novaBHQ1 nova | 400400 | |
| L861QL861Q | L858R FAM_RL858R FAM_R | AAA CTG AAT TCA AAA AGA TCA AAG TGC TGAAA CTG AAT TCA AAA AGA TCA AAG TGC TG | 6060 |
FAM | BHQ1BHQ1 | 5050 | |
| Ex20InsEx20Ins | Ex20Ins FAM_REx20Ins FAM_R | TCA CGT AGG CTT CCT GGA GGG ATCA CGT AGG CTT CCT GGA GGG A | 6161 | FAMFAM | BHQ1BHQ1 | 400400 | |
| L858RL858R | L858R CFO560_FL858R CFO560_F | CCA AAC TGC TGG GTG CGG AAG AGCCA AAC TGC TGG GTG CGG AAG AG | 6262 | CAL Fluor Orange 560CAL Fluor Orange 560 | BHQ1BHQ1 | 400400 | |
| EGFR ICEGFR IC | EGFR IC Ex2 QS670EGFR IC Ex2 QS670 | TCT CAG CCT CCA GAG GAT GTT CAA TCT CAG CCT CCA GAG GAT GTT CAA | 6363 | Quasar 670Quasar 670 |
BHQ2 |
200200 |
| 단계step | 사이클cycle | 온도Temperature | 시간time | 데이터 수집Data collection |
| 1One | 1One | 95℃95℃ | 5 분5 minutes | -- |
| 95℃95℃ | 10 초10 seconds | -- | ||
| 22 | 5050 | 60℃60℃ | 30 초30 seconds | FAM /FAM / |
| CAL Fluor Orange 560 (VIC/HEX/JOE) /CAL Fluor Orange 560 (VIC/HEX/JOE) / | ||||
| Quasar670 (CY5)Quasar670 (CY5) | ||||
| 72℃72℃ | 10 초10 seconds | -- |
표 22에 기재된 각 구성물질을 포함하는 충분한 EGFR 반응 혼합물을 별도의 멸균 원심분리 튜브에 각각 준비하고 반응 Master Mixture를 3초 동안 볼텍싱하여 완전히 혼합하고 짧게 원심분리하였다. 각 시료에 대해 다음과 같이 2개의 PCR 튜브를 준비하였다: 각 PCR 튜브에 대해 10.0 μL의 EGFR 반응 혼합물을 나누고, 5.0 μL의 각 시료 DNA를 각 시료 튜브에 첨가한 다음 PCR 튜브의 뚜껑을 덮었다. 뉴클레아제 무첨가 증류수를 모든 PCR 튜브에 20.0 μL까지 추가하고, PCR 스트립 (strips)을 짧게 원심분리하여 각 PCR 튜브의 바닥에 모든 액체를 수집하였다. PCR 스트립 튜브를 실시간 PCR (real-time PCR) 기기에 두고, 표 24의 사이클링 파라미터를 이용하여 PCR 프로토콜을 설정한 후 PCR을 수행하였다. PCR 종료 후, 데이터를 분석하기 위해 각 시료의 FAM/CAL Fluor Orange 560/Quasar 670 Ct 값을 기록하고, 각 웰 당 ΔCt 값을 다음과 같이 계산하였다:Sufficient EGFR reaction mixtures containing each of the components listed in Table 22 were each prepared in separate sterile centrifuge tubes, and the reaction Master Mixture was vortexed for 3 seconds to thoroughly mix and centrifuge briefly. Two PCR tubes were prepared for each sample as follows: 10.0 μL of EGFR reaction mixture was divided for each PCR tube, and 5.0 μL of each sample DNA was added to each sample tube, and then the PCR tube was covered. Nuclease-free distilled water was added to all PCR tubes to 20.0 μL, and PCR strips were briefly centrifuged to collect all liquids at the bottom of each PCR tube. The PCR strip tube was placed in a real-time PCR (real-time PCR) instrument, and PCR was performed after setting the PCR protocol using the cycling parameters in Table 24. After the PCR was completed, FAM/CAL Fluor Orange 560/Quasar 670 Ct values of each sample were recorded to analyze the data, and ΔCt values per well were calculated as follows:
ΔCt 값 = 시료 Ct 값 (각 MMX의 FAM) - 양성 대조군 Ct 값 (각 MMX의 FAM)ΔCt value = sample Ct value (FAM of each MMX)-positive control Ct value (FAM of each MMX)
ΔCt 값 = 시료 Ct 값 (각 MMX CFO560) - 양성 대조군 Ct 값 (각 MMX의 CFO560)ΔCt value = sample Ct value (each MMX CFO560)-positive control Ct value (CFO560 of each MMX)
표 25 및 26의 컷오프 ΔCt 값에 따라 각 튜브에 대한 결과를 해석하였다. ΔCt 값이 < 컷오프 ΔCt 값인 경우, 시료는 양성인 것으로 판단하고, 형광 신호가 없고 내부 대조군의 Ct 값이 21.5 < Ct < 40인 경우, 시료는 음성이거나 검출 한계 (LoD) 미만인 것으로 판단한다.The results for each tube were analyzed according to the cutoff ΔCt values in Tables 25 and 26. If the ΔCt value is <cutoff ΔCt value, the sample is judged to be positive, and if there is no fluorescence signal and the Ct value of the internal control is 21.5 <Ct <40, the sample is judged to be negative or below the detection limit (LoD).
| EGFR MMXsEGFR MMXs | 결정decision | |
| 내부 대조군 Ct 값Internal control Ct value | 21.5 ≤ Ct ≤ 4021.5 ≤ Ct ≤ 40 | 유효available |
| Ct < 21.5 또는 Ct > 40Ct <21.5 or Ct> 40 | 무효invalidity | |
| 시료 Ct 값Sample Ct value | Ct < 23.5Ct <23.5 | 무효invalidity |
| Ct > 45 또는 신호 없음Ct> 45 or no signal | 음성voice | |
| 유효 결과 결정Determining valid results | 컷오프 ΔCt 값Cutoff ΔCt value | 범위range | 결정decision | |
| ΔCt 컷오프 값ΔCt cutoff value | S768I-FAMS768I-FAM | 10.010.0 | ΔCt≤10.0ΔCt≤10.0 | 양성positivity |
| ΔCt > 10.0ΔCt> 10.0 | 음성voice | |||
| Ex19Del-CFO560Ex19Del-CFO560 | 14.514.5 | ΔCt≤14.5ΔCt≤14.5 | 양성positivity | |
| ΔCt > 14.5ΔCt> 14.5 | 음성voice | |||
| T790M-FAMT790M-FAM | 14.514.5 | ΔCt≤14.5ΔCt≤14.5 | 양성positivity | |
| ΔCt > 14.5ΔCt> 14.5 | 음성voice | |||
| L861Q-FAML861Q-FAM | 13.013.0 | ΔCt≤13.0ΔCt≤13.0 | 양성positivity | |
| ΔCt > 13.0ΔCt> 13.0 | 음성voice | |||
| G719X-CFO560G719X-CFO560 | 8.58.5 | ΔCt≤8.5ΔCt≤8.5 | 양성positivity | |
| ΔCt≤8.5ΔCt≤8.5 | 음성voice | |||
| Ex20Ins-FAMEx20Ins-FAM | 16.016.0 | ΔCt≤16.0ΔCt≤16.0 | 양성positivity | |
| ΔCt > 16.0ΔCt> 16.0 | 음성voice | |||
| L858R-CFO560L858R-CFO560 | 10.010.0 | ΔCt≤10.0ΔCt≤10.0 | 양성positivity | |
| ΔCt > 10.0ΔCt> 10.0 | 음성voice | |||
상기와 같이 데이터를 분석한 결과, 도 5a 내지 5l, 6a 내지 6l, 7a 내지 7i, 8, 9a 내지 9e 및 10a 내지 10h에 나타난 바와 같이 WT에서는 형광 신호가 검출되지 않았으나, 표 4의 EGFR 유전자 돌연변이를 포함하는 시료에서는 형광 신호가 검출되었으며, 표 27에 나타난 바와 같이 최대 0.01% (30,000 야생형 카피에서 3개의 돌연변이 카피)의 높은 민감도로 EGFR 유전자 돌연변이를 검출할 수 있는 것으로 확인되었다.As a result of analyzing the data as described above, as shown in FIGS. 5A to 5L, 6A to 6L, 7A to 7I, 8, 9A to 9E, and 10A to 10H, fluorescence signals were not detected in WT, but the EGFR gene mutation of Table 4 Fluorescence signal was detected in the sample containing, and it was confirmed that EGFR gene mutation can be detected with a high sensitivity of up to 0.01% (3 mutant copies in 30,000 wild-type copies) as shown in Table 27.
| 엑손Exxon | 돌연변이Mutation | EGFR 핵산 서열EGFR nucleic acid sequence | COSMIC IDCOSMIC ID | LoD (카피)LoD (copy) | 검출 민감도 (%)Detection sensitivity (%) |
| Exon 18Exon 18 | G719XG719X | 2155G>A2155G>A | 62526252 | 1515 | 0.050.05 |
| 2155G>T2155G>T | 62536253 | 1010 | 0.030.03 | ||
| 2156G>C2156G>C | 62396239 | 33 | 0.010.01 | ||
| Exon 19Exon 19 | Ex19DelEx19Del | 2240_2251del122240_2251del12 | 62106210 | 33 | 0.010.01 |
| 2239_2247del92239_2247del9 | 62186218 | 33 | 0.010.01 | ||
| 2238_2255del182238_2255del18 | 62206220 | 33 | 0.010.01 | ||
| 2235_2249del152235_2249del15 | 62236223 | 33 | 0.010.01 | ||
| 2236_2250del152236_2250del15 | 62256225 | 33 | 0.010.01 | ||
| 2239_2253del152239_2253del15 | 62546254 | 33 | 0.010.01 | ||
| 2239_2256del182239_2256del18 | 62556255 | 33 | 0.010.01 | ||
| 2237_2254del182237_2254del18 | 1236712367 | 33 | 0.010.01 | ||
| 2240_2254del152240_2254del15 | 1236912369 | 33 | 0.010.01 | ||
| 2240_2257del182240_2257del18 | 1237012370 | 33 | 0.010.01 | ||
| 2239_2248TTAAGAGAAG>C2239_2248TTAAGAGAAG>C | 1238212382 | 33 | 0.010.01 | ||
| 2239_2251>C2239_2251>C | 1238312383 | 33 | 0.010.01 | ||
| 2237_2255>T2237_2255>T | 1238412384 | 33 | 0.010.01 | ||
| 2235_2255>AAT2235_2255>AAT | 1238512385 | 33 | 0.010.01 | ||
| 2237_2252>T2237_2252>T | 1238612386 | 33 | 0.010.01 | ||
| 2239_2258>CA2239_2258>CA | 1238712387 | 33 | 0.010.01 | ||
| 2239_2256>CAA2239_2256>CAA | 1240312403 | 33 | 0.010.01 | ||
| 2237_2253>TTGCT2237_2253>TTGCT | 1241612416 | 33 | 0.010.01 | ||
| 2238_2252>GCA2238_2252>GCA | 1241912419 | 33 | 0.010.01 | ||
| 2238_2248>GC2238_2248>GC | 1242212422 | 33 | 0.010.01 | ||
| 2237_2251del152237_2251del15 | 1267812678 | 33 | 0.010.01 | ||
| 2236_2253del182236_2253del18 | 1272812728 | 33 | 0.010.01 | ||
| 2235_2248>AATTC2235_2248>AATTC | 1355013550 | 33 | 0.010.01 | ||
| 2235_2252>AAT2235_2252>AAT | 1355113551 | 33 | 0.010.01 | ||
| 2235_2251>AATTC2235_2251>AATTC | 1355213552 | 33 | 0.010.01 | ||
| 2253_2276del242253_2276del24 | 1355613556 | 33 | 0.010.01 | ||
| 2237_2257>TCT2237_2257>TCT | 1842718427 | 33 | 0.010.01 | ||
| 2238_2252del152238_2252del15 | 2357123571 | 33 | 0.010.01 | ||
| 2233_2247del152233_2247del15 | 2603826038 | 33 | 0.010.01 | ||
| 2232_2249del152232_2249del15 | 221565221565 | 33 | 0.010.01 | ||
| 2234_2248del152234_2248del15 | 11907911190791 | 33 | 0.010.01 | ||
| Exon 20Exon 20 | S768IS768I | 2303G>T2303G>T | 62416241 | 33 | 0.010.01 |
| T790MT790M | 2369C>T2369C>T | 62406240 | 1010 | 0.030.03 | |
| Ex20InsEx20Ins | 2307_2308ins9GCCAGCGTG2307_2308ins9GCCAGCGTG | 1237612376 | 33 | 0.010.01 | |
| 2319_2320insCAC2319_2320insCAC | 1237712377 | 33 | 0.010.01 | ||
| 2310_2311insGGT2310_2311insGGT | 1237812378 | 33 | 0.010.01 | ||
| 2311_2312ins9GCGTGGACA2311_2312ins9GCGTGGACA | 1342813428 | 33 | 0.010.01 | ||
| 2309_2310AC>CCAGCGTGGAT2309_2310AC>CCAGCGTGGAT | 1355813558 | 33 | 0.010.01 | ||
| Exon 21Exon 21 | L858RL858R | 2573T>G2573T>G | 62246224 | 33 | 0.010.01 |
| 2573_2574TG>GT2573_2574TG>GT | 1242912429 | 33 | 0.010.01 | ||
| L861QL861Q | 2582T>A2582T>A | 62136213 | 33 | 0.010.01 |
본 발명의 키트는 높은 검출 민감도 (최대 0.01%, 30,000 야생형 카피에서 3개의 돌연변이 카피), 높은 특이성 및 재현성을 나타내며, 액체 생검 및 조직 생검에 모두 적용 가능하다. 또한, EGFR 유전자의 엑손 18번 내지 21번 내에서 44개의 돌연변이를 동시 다발적으로 검출함으로써 폐암 환자의 티로신 키나아제 억제제에 대한 약물 반응성을 정확하게 예측할 수 있다.The kit of the present invention shows high detection sensitivity (up to 0.01%, 3 mutant copies in 30,000 wild-type copies), high specificity and reproducibility, and is applicable to both liquid biopsy and tissue biopsy. In addition, by simultaneously detecting 44 mutations within exons 18 to 21 of the EGFR gene, it is possible to accurately predict drug reactivity to lung cancer patients against tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
Claims (19)
- 서열번호 1의 아미노산 서열에서 507번째 아미노산 잔기인 글루탐산(E)이 리신(K)으로 치환되고, 536번째 아미노산 잔기인 아르기닌(R)이 리신(K)으로 치환되며, 660번째 아미노산 잔기인 아르기닌(R)이 발린(V)으로 치환된 Taq 중합효소를 포함하는, EGFR 유전자 돌연변이 검출용 DNA 중합효소.In the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1, the 507th amino acid residue glutamic acid (E) is replaced with lysine (K), the 536th amino acid residue arginine (R) is replaced with lysine (K), and the 660th amino acid residue arginine ( R) DNA polymerase for detecting EGFR gene mutations, including Taq polymerase substituted with valine (V).
- 서열번호 3 내지 54로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택되는 1종 이상의 프라이머를 포함하는, EGFR 유전자 돌연변이 검출용 프라이머 세트.A primer set for EGFR gene mutation detection, comprising at least one primer selected from the group consisting of SEQ ID NOs: 3 to 54.
- 서열번호 55 내지 63으로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택되는 뉴클레오티드 서열을 포함하는, EGFR 유전자 돌연변이 검출용 프로브.A probe for detecting an EGFR gene mutation, comprising a nucleotide sequence selected from the group consisting of SEQ ID NOs: 55 to 63.
- 제3항에 있어서, 상기 서열번호 55 내지 63의 뉴클레오티드 서열은 각각 5'-말단에 FAM, CAL Fluor Orange 560, VIC, HEX, JOE, Quasar 670 및 CY5로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택되는 1종의 형광물질 (fluorophore)이 표지되고, 3'-말단에 BHQ-1 BHQ1 nova 및 BHQ-2로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택되는 1종의 소광물질이 표지되는, EGFR 유전자 돌연변이 검출용 프로브.The method of claim 3, wherein the nucleotide sequence of SEQ ID NO: 55 to 63, each of the 5'- terminal FAM, CAL Fluor Orange 560, VIC, HEX, JOE, Quasar 670 and CY5 is selected from the group consisting of one fluorescent material (fluorophore) is labeled, a probe for detecting the EGFR gene mutation, which is labeled with one quencher selected from the group consisting of BHQ-1 BHQ1 nova and BHQ-2 at the 3'-end.
- 서열번호 1의 아미노산 서열에서 507번째 아미노산 잔기인 글루탐산(E)이 리신(K)으로 치환되고, 536번째 아미노산 잔기인 아르기닌(R)이 리신(K)으로 치환되며, 660번째 아미노산 잔기인 아르기닌(R)이 발린(V)으로 치환된 Taq 중합효소; 및/또는In the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1, the 507th amino acid residue glutamic acid (E) is replaced with lysine (K), the 536th amino acid residue arginine (R) is replaced with lysine (K), and the 660th amino acid residue arginine ( R) Taq polymerase substituted with valine (V); And/or서열번호 3 내지 54로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택되는 1종 이상의 프라이머;At least one primer selected from the group consisting of SEQ ID NOs: 3 to 54;를 포함하는, EGFR 유전자 돌연변이 검출용 키트.Containing, EGFR gene mutation detection kit.
- 제5항에 있어서, 서열번호 55 내지 63으로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택되는 뉴클레오티드 서열을 포함하는 프로브를 추가로 포함하는, EGFR 유전자 돌연변이 검출용 키트.The kit for detecting an EGFR gene mutation according to claim 5, further comprising a probe comprising a nucleotide sequence selected from the group consisting of SEQ ID NOs: 55 to 63.
- 제6항에 있어서, 상기 서열번호 55 내지 63의 뉴클레오티드 서열은 각각 5'-말단에 FAM, CAL Fluor Orange 560, VIC, HEX, JOE, Quasar 670 및 CY5로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택되는 1종의 형광물질 (fluorophore)이 표지되고, 3'-말단에 BHQ-1 BHQ1 nova 및 BHQ-2로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택되는 1종의 소광물질이 표지되는, EGFR 유전자 돌연변이 검출용 키트.The method of claim 6, wherein the nucleotide sequence of SEQ ID NO: 55 to 63 is a fluorescent substance of one selected from the group consisting of FAM, CAL Fluor Orange 560, VIC, HEX, JOE, Quasar 670 and CY5 at the 5'-terminal, respectively. A kit for detecting EGFR gene mutation, wherein (fluorophore) is labeled, and one quencher selected from the group consisting of BHQ-1 BHQ1 nova and BHQ-2 is labeled at the 3'-end.
- 제5항에 있어서,The method of claim 5,25 내지 100 mM의 KCl; 및25 to 100 mM KCl; And1 내지 7 mM의 (NH4)2SO4;1 to 7 mM (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 ;를 포함하고, 최종 pH가 8.0 내지 9.5인 PCR 버퍼 조성물을 추가로 포함하는, EGFR 유전자 돌연변이 검출용 키트.Included, the final pH is 8.0 to 9.5, further comprising a PCR buffer composition, EGFR gene mutation detection kit.
- 제5항에 있어서,The method of claim 5,25 내지 100 mM의 KCl;25 to 100 mM KCl;1 내지 7 mM의 (NH4)2SO4; 및1 to 7 mM (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 ; And5 내지 50 mM의 TMAC(Tetra methyl ammonium chloride)를 포함하고, 최종 pH가 8.0 내지 9.5인 PCR 버퍼 조성물을 추가로 포함하는, EGFR 유전자 돌연변이 검출용 키트.A kit for detecting EGFR gene mutations, comprising 5-50 mM of TMAC (Tetra methyl ammonium chloride), and further comprising a PCR buffer composition having a final pH of 8.0 to 9.5.
- 다음의 단계를 포함하는 EGFR 유전자 돌연변이 검출방법:EGFR gene mutation detection method comprising the following steps:(a) 분리된 생물학적 시료로부터 핵산을 추출하는 단계;(A) extracting the nucleic acid from the isolated biological sample;(b) 상기 추출한 핵산에 제5항 내지 제9항 중 어느 한 항의 키트를 처리하여 PCR (polymerase chain reaction)을 수행하는 단계; 및(b) performing a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) by treating the kit of any one of claims 5 to 9 with the extracted nucleic acid; And(c) 상기 PCR에 의한 증폭 결과를 형광으로 확인하는 단계.(c) confirming the amplification result by the PCR with fluorescence.
- 제10항에 있어서, 상기 PCR은 대립유전자 특이적 (allele-specific) PCR 또는 실시간 (real-time) PCR인, EGFR 유전자 돌연변이 검출방법.The method according to claim 10, wherein the PCR is allele-specific PCR or real-time PCR.
- 제10항에 있어서, (d) 상기 PCR에 의한 증폭 결과를 Ct (cycle threshold) 값을 측정하여 확인하는 단계를 추가로 포함하는, EGFR 유전자 돌연변이 검출방법.11. The method of claim 10, (d) EGFR gene mutation detection method further comprising the step of confirming the amplification result by the PCR by measuring the Ct (cycle threshold) value.
- 제10항에 있어서, 상기 EGFR 유전자 돌연변이는 상기 EGFR 유전자 돌연변이는 EGFR 유전자의 엑손 18번, 19번, 20번 및 21번 내에서의 결실, 치환 및 삽입 돌연변이로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택되는 1종 이상을 포함하는, EGFR 유전자 돌연변이 검출방법.The method of claim 10, wherein the EGFR gene mutation is EGFR gene mutation is at least one selected from the group consisting of deletion, substitution and insertion mutations in exons 18, 19, 20 and 21 of the EGFR gene. Including, EGFR gene mutation detection method.
- 제13항에 있어서, 상기 EGFR 유전자 돌연변이는 EGFR의 엑손 18번 내에서의 719번째 아미노산인 글리신의 치환, 엑손 19번 내에서의 결손, 엑손 20번 내에서의 768번째 아미노산인 세린, 790번째 아미노산인 트레오닌, 797번째 아미노산인 시스테인의 치환, 엑손 20번 내에서의 삽입, 엑손 21번 내에서의 858번째 아미노산인 류신 및 861번째 아미노산인 류신의 치환으로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택된 1종 이상을 포함하는, EGFR 유전자 돌연변이 검출방법.14. The method of claim 13, wherein the EGFR gene mutation is a substitution of the 719th amino acid glycine in exon 18 of EGFR, a deletion in exon 19, the 768th amino acid serine in exon 20, the 790th amino acid. An threonine, a substitution of cysteine at the 797th amino acid, insertion in exon 20, leucine at 858th amino acid in exon 21, and leucine at 861th amino acid; EGFR gene mutation detection method.
- 제10항에 있어서, EGFR 유전자 돌연변이 검출방법은 폐암 환자의 약물에 대한 반응성을 예측하기 위한 것인, EGFR 유전자 돌연변이 검출방법.The method of claim 10, wherein the EGFR gene mutation detection method is for predicting responsiveness to drugs of lung cancer patients.
- 제15항에 있어서, 상기 폐암은 비소세포폐암인, EGFR 유전자 돌연변이 검출방법.16. The method of claim 15, wherein the lung cancer is non-small cell lung cancer.
- 제15항에 있어서, 상기 약물은 티로신 키나아제 억제제(tyrosine kinase inhibitor)인, EGFR 유전자 돌연변이 검출방법.16. The method of claim 15, wherein the drug is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
- 제17항에 있어서, 상기 티로신 키나아제 억제제는 게피티닙, 에를로티닙 또는 오시머티닙인, EGFR 유전자 돌연변이 검출방법.18. The method of claim 17, wherein the tyrosine kinase inhibitor is gefitinib, erlotinib, or osimmertinib.
- 제10항에 있어서, 상기 (a) 단계의 핵산은 조직 생검의 포르말린 고정 파라핀 포매 시료(formalin-fixed paraffin embedded sample) 또는 액체 생검으로부터 추출된 것인, EGFR 유전자 돌연변이 검출방법.The method of claim 10, wherein the nucleic acid of step (a) is extracted from a formalin-fixed paraffin embedded sample or a liquid biopsy of a tissue biopsy.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR10-2019-0004216 | 2019-01-11 | ||
| KR20190004216 | 2019-01-11 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2020145711A1 true WO2020145711A1 (en) | 2020-07-16 |
Family
ID=71520556
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/KR2020/000448 WO2020145711A1 (en) | 2019-01-11 | 2020-01-10 | Dna polymerase for egfr mutation detection and kit comprising same |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR102370550B1 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2020145711A1 (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN113755590A (en) * | 2021-09-13 | 2021-12-07 | 北京乐土医学检验实验室有限公司 | Reagent and kit for combined detection of EGFR gene mutation |
| WO2024000270A1 (en) * | 2022-06-29 | 2024-01-04 | 京东方科技集团股份有限公司 | Primer-probe composition for detecting egfr gene mutation and kit |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101967525A (en) * | 2010-11-18 | 2011-02-09 | 重庆医科大学 | Real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection kit for BDV (Borna Disease Virus) p24 segment |
| EP2554665A2 (en) * | 2011-08-03 | 2013-02-06 | Fermentas UAB | DNA polymerases |
| KR20140033854A (en) * | 2012-09-11 | 2014-03-19 | 주식회사 디앤피바이오텍 | Multiplex pcr primer set for detecting egfr mutant and kit comprising the same |
| WO2015082449A2 (en) * | 2013-12-02 | 2015-06-11 | Universitaet Konstanz | Mutated dna polymerases with high selectivity and activity |
| CN108504725A (en) * | 2018-06-12 | 2018-09-07 | 上海浦美生物医药科技有限公司 | A kind of primer and probe for detecting EGFR TKI sensitizing mutations |
| CN109251907A (en) * | 2017-07-12 | 2019-01-22 | 基因凯斯特有限公司 | The archaeal dna polymerase that gene mutation specific amplification efficiency improves |
Family Cites Families (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101208354A (en) * | 2005-02-24 | 2008-06-25 | 安姆根有限公司 | Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations |
| JP5859274B2 (en) * | 2010-10-29 | 2016-02-10 | アークレイ株式会社 | EGFR gene polymorphism detection probe, amplification primer and use thereof |
| KR101958660B1 (en) * | 2017-07-12 | 2019-03-18 | 주식회사 진캐스트 | Pcr buffer compositions for increasing activity of dna polymerases with increased mutation specificity |
-
2020
- 2020-01-10 WO PCT/KR2020/000448 patent/WO2020145711A1/en active Application Filing
- 2020-01-10 KR KR1020200003939A patent/KR102370550B1/en active IP Right Grant
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101967525A (en) * | 2010-11-18 | 2011-02-09 | 重庆医科大学 | Real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection kit for BDV (Borna Disease Virus) p24 segment |
| EP2554665A2 (en) * | 2011-08-03 | 2013-02-06 | Fermentas UAB | DNA polymerases |
| KR20140033854A (en) * | 2012-09-11 | 2014-03-19 | 주식회사 디앤피바이오텍 | Multiplex pcr primer set for detecting egfr mutant and kit comprising the same |
| WO2015082449A2 (en) * | 2013-12-02 | 2015-06-11 | Universitaet Konstanz | Mutated dna polymerases with high selectivity and activity |
| CN109251907A (en) * | 2017-07-12 | 2019-01-22 | 基因凯斯特有限公司 | The archaeal dna polymerase that gene mutation specific amplification efficiency improves |
| CN108504725A (en) * | 2018-06-12 | 2018-09-07 | 上海浦美生物医药科技有限公司 | A kind of primer and probe for detecting EGFR TKI sensitizing mutations |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN113755590A (en) * | 2021-09-13 | 2021-12-07 | 北京乐土医学检验实验室有限公司 | Reagent and kit for combined detection of EGFR gene mutation |
| CN113755590B (en) * | 2021-09-13 | 2023-09-22 | 北京乐土医学检验实验室有限公司 | Reagent and kit for combined detection of EGFR gene mutation |
| WO2024000270A1 (en) * | 2022-06-29 | 2024-01-04 | 京东方科技集团股份有限公司 | Primer-probe composition for detecting egfr gene mutation and kit |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR20200087723A (en) | 2020-07-21 |
| KR102370550B1 (en) | 2022-03-08 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2017122896A1 (en) | Genetic marker for discriminating and detecting causative virus of marine creature infectious disease, and causative virus discrimination and detection method using same | |
| WO2012046981A2 (en) | Real time pcr detection of single nucleotide polymorphisms | |
| JP2003528626A (en) | Hybridization beacons and methods for rapid sequence detection and discrimination | |
| JP2001057892A (en) | Method for detecting mutation in nucleic acid sequence and oligonucleotide | |
| US20240076633A1 (en) | Pcr buffer composition for increasing activity of dna polymerase with increased gene mutation specificity | |
| TW201908482A (en) | DNA polymerase with improved mutation-specific amplification efficiency | |
| US20100143901A1 (en) | Nuclease-Free Real-Time Detection of Nucleic Acids | |
| WO2017122897A1 (en) | Genetic marker for detecting causative virus of red sea bream iridoviral disease, and causative virus detection method using same | |
| US20120045747A1 (en) | Kit for detecting hepatitis b virus and method for detecting hepatitis b virus using the same | |
| WO2020145711A1 (en) | Dna polymerase for egfr mutation detection and kit comprising same | |
| WO2020145715A1 (en) | Dna polymerase for detecting tert mutation and kit comprising same | |
| US20160369330A1 (en) | Compositions for improved allele-specific pcr | |
| WO2020145734A1 (en) | Dna polymerase for detecting braf mutations, and kit comprising same | |
| US10907203B1 (en) | DNA methylation assays for body fluid identification | |
| Aldape et al. | Real‐time quantitative polymerase chain reaction: a potential tool for genetic analysis in neuropathology | |
| WO2022203297A1 (en) | Target nucleic acid amplification method using guide probe and clamping probe and composition for amplifying target nucleic acid comprising same | |
| WO2020145762A1 (en) | Dna polymerase for jak2 mutation detection, and kit comprising same | |
| WO2021172653A1 (en) | Single nucleic acid for real-time detection of genetic variation of single target gene, and detection method using same | |
| WO2021118288A1 (en) | Pcr method and pcr kit for increasing allelic discrimination | |
| WO2020209522A1 (en) | Primer for dengue virus detection using lamp | |
| WO2022114720A1 (en) | Target nucleic acid amplification method with high specificity and target nucleic acid amplifying composition using same | |
| WO2020145754A1 (en) | Mass spectrometry using dna polymerase with increased genetic mutation specificity | |
| WO2024167289A1 (en) | Method for detecting target oligonucleotide by using detection oligonucleotide | |
| WO2013081200A1 (en) | Kit for detecting hiv-2, and method for detecting hiv-2 using same | |
| WO2024186140A1 (en) | Method for detecting target nucleic acid using artificial nucleic acid |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 20739016 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 32PN | Ep: public notification in the ep bulletin as address of the adressee cannot be established |
Free format text: NOTING OF LOSS OF RIGHTS PURSUANT TO RULE 112(1) EPC (EPO FORM 1205A DATED 18/11/2021) |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 20739016 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |