WO2019030841A1 - Compressor and refrigeration cycle device - Google Patents
Compressor and refrigeration cycle device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2019030841A1 WO2019030841A1 PCT/JP2017/028883 JP2017028883W WO2019030841A1 WO 2019030841 A1 WO2019030841 A1 WO 2019030841A1 JP 2017028883 W JP2017028883 W JP 2017028883W WO 2019030841 A1 WO2019030841 A1 WO 2019030841A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- container
- terminal
- terminals
- compressor
- center
- Prior art date
Links
- 238000005057 refrigeration Methods 0.000 title claims description 20
- 239000003507 refrigerant Substances 0.000 claims description 71
- 230000006835 compression Effects 0.000 claims description 43
- 238000007906 compression Methods 0.000 claims description 43
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 claims description 39
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 claims description 8
- 239000003921 oil Substances 0.000 description 33
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 21
- 238000003466 welding Methods 0.000 description 21
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 17
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 description 17
- 238000004804 winding Methods 0.000 description 17
- 238000005096 rolling process Methods 0.000 description 16
- 230000000052 comparative effect Effects 0.000 description 11
- XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N Iron Chemical compound [Fe] XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 8
- 229910000831 Steel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 8
- 239000010959 steel Substances 0.000 description 8
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 4
- 229910052742 iron Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- WABPQHHGFIMREM-UHFFFAOYSA-N lead(0) Chemical compound [Pb] WABPQHHGFIMREM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 239000004812 Fluorinated ethylene propylene Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229920000106 Liquid crystal polymer Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 239000004977 Liquid-crystal polymers (LCPs) Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000004813 Perfluoroalkoxy alkane Substances 0.000 description 3
- -1 Polyethylene Terephthalate Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 239000004734 Polyphenylene sulfide Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000007599 discharging Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000000605 extraction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000004907 flux Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000010721 machine oil Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229920009441 perflouroethylene propylene Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 229920011301 perfluoro alkoxyl alkane Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 229920001707 polybutylene terephthalate Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 229920000139 polyethylene terephthalate Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 239000005020 polyethylene terephthalate Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229920000069 polyphenylene sulfide Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 229920001343 polytetrafluoroethylene Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 239000004810 polytetrafluoroethylene Substances 0.000 description 3
- CURLTUGMZLYLDI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Carbon dioxide Chemical compound O=C=O CURLTUGMZLYLDI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910000975 Carbon steel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Copper Chemical group [Cu] RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910001060 Gray iron Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Nickel Chemical compound [Ni] PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- ATUOYWHBWRKTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Propane Chemical compound CCC ATUOYWHBWRKTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium Chemical compound [Al] XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000010962 carbon steel Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000004020 conductor Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000010949 copper Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000013461 design Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000012530 fluid Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000006698 induction Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000009413 insulation Methods 0.000 description 2
- NNPPMTNAJDCUHE-UHFFFAOYSA-N isobutane Chemical compound CC(C)C NNPPMTNAJDCUHE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000010030 laminating Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000005461 lubrication Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000003825 pressing Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000004080 punching Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910000851 Alloy steel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ammonia Chemical compound N QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VYZAMTAEIAYCRO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Chromium Chemical compound [Cr] VYZAMTAEIAYCRO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZOKXTWBITQBERF-UHFFFAOYSA-N Molybdenum Chemical compound [Mo] ZOKXTWBITQBERF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000007977 PBT buffer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910001315 Tool steel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000009471 action Effects 0.000 description 1
- 150000004996 alkyl benzenes Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000005219 brazing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910002092 carbon dioxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000001569 carbon dioxide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052804 chromium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011651 chromium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011248 coating agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007547 defect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- HQQADJVZYDDRJT-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethene;prop-1-ene Chemical group C=C.CC=C HQQADJVZYDDRJT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000005484 gravity Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000012447 hatching Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000003780 insertion Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000037431 insertion Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000001282 iso-butane Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052750 molybdenum Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011733 molybdenum Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052759 nickel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000000149 penetrating effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000005011 phenolic resin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920001289 polyvinyl ether Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000001294 propane Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052761 rare earth metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000002910 rare earth metals Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 230000000630 rising effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010792 warming Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910000859 α-Fe Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F04—POSITIVE - DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; PUMPS FOR LIQUIDS OR ELASTIC FLUIDS
- F04C—ROTARY-PISTON, OR OSCILLATING-PISTON, POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; ROTARY-PISTON, OR OSCILLATING-PISTON, POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT PUMPS
- F04C23/00—Combinations of two or more pumps, each being of rotary-piston or oscillating-piston type, specially adapted for elastic fluids; Pumping installations specially adapted for elastic fluids; Multi-stage pumps specially adapted for elastic fluids
- F04C23/02—Pumps characterised by combination with, or adaptation to, specific driving engines or motors
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F04—POSITIVE - DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; PUMPS FOR LIQUIDS OR ELASTIC FLUIDS
- F04B—POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; PUMPS
- F04B35/00—Piston pumps specially adapted for elastic fluids and characterised by the driving means to their working members, or by combination with, or adaptation to, specific driving engines or motors, not otherwise provided for
- F04B35/04—Piston pumps specially adapted for elastic fluids and characterised by the driving means to their working members, or by combination with, or adaptation to, specific driving engines or motors, not otherwise provided for the means being electric
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F04—POSITIVE - DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; PUMPS FOR LIQUIDS OR ELASTIC FLUIDS
- F04B—POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; PUMPS
- F04B39/00—Component parts, details, or accessories, of pumps or pumping systems specially adapted for elastic fluids, not otherwise provided for in, or of interest apart from, groups F04B25/00 - F04B37/00
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F04—POSITIVE - DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; PUMPS FOR LIQUIDS OR ELASTIC FLUIDS
- F04B—POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; PUMPS
- F04B39/00—Component parts, details, or accessories, of pumps or pumping systems specially adapted for elastic fluids, not otherwise provided for in, or of interest apart from, groups F04B25/00 - F04B37/00
- F04B39/12—Casings; Cylinders; Cylinder heads; Fluid connections
- F04B39/123—Fluid connections
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F04—POSITIVE - DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; PUMPS FOR LIQUIDS OR ELASTIC FLUIDS
- F04C—ROTARY-PISTON, OR OSCILLATING-PISTON, POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; ROTARY-PISTON, OR OSCILLATING-PISTON, POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT PUMPS
- F04C29/00—Component parts, details or accessories of pumps or pumping installations, not provided for in groups F04C18/00 - F04C28/00
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F04—POSITIVE - DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; PUMPS FOR LIQUIDS OR ELASTIC FLUIDS
- F04C—ROTARY-PISTON, OR OSCILLATING-PISTON, POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; ROTARY-PISTON, OR OSCILLATING-PISTON, POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT PUMPS
- F04C29/00—Component parts, details or accessories of pumps or pumping installations, not provided for in groups F04C18/00 - F04C28/00
- F04C29/0042—Driving elements, brakes, couplings, transmissions specially adapted for pumps
- F04C29/0085—Prime movers
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F04—POSITIVE - DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; PUMPS FOR LIQUIDS OR ELASTIC FLUIDS
- F04C—ROTARY-PISTON, OR OSCILLATING-PISTON, POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; ROTARY-PISTON, OR OSCILLATING-PISTON, POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT PUMPS
- F04C29/00—Component parts, details or accessories of pumps or pumping installations, not provided for in groups F04C18/00 - F04C28/00
- F04C29/12—Arrangements for admission or discharge of the working fluid, e.g. constructional features of the inlet or outlet
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25B—REFRIGERATION MACHINES, PLANTS OR SYSTEMS; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS
- F25B13/00—Compression machines, plants or systems, with reversible cycle
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02K—DYNAMO-ELECTRIC MACHINES
- H02K5/00—Casings; Enclosures; Supports
- H02K5/04—Casings or enclosures characterised by the shape, form or construction thereof
- H02K5/22—Auxiliary parts of casings not covered by groups H02K5/06-H02K5/20, e.g. shaped to form connection boxes or terminal boxes
- H02K5/225—Terminal boxes or connection arrangements
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F04—POSITIVE - DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; PUMPS FOR LIQUIDS OR ELASTIC FLUIDS
- F04C—ROTARY-PISTON, OR OSCILLATING-PISTON, POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; ROTARY-PISTON, OR OSCILLATING-PISTON, POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT PUMPS
- F04C2210/00—Fluid
- F04C2210/26—Refrigerants with particular properties, e.g. HFC-134a
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F04—POSITIVE - DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; PUMPS FOR LIQUIDS OR ELASTIC FLUIDS
- F04C—ROTARY-PISTON, OR OSCILLATING-PISTON, POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; ROTARY-PISTON, OR OSCILLATING-PISTON, POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT PUMPS
- F04C2240/00—Components
- F04C2240/40—Electric motor
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F04—POSITIVE - DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; PUMPS FOR LIQUIDS OR ELASTIC FLUIDS
- F04C—ROTARY-PISTON, OR OSCILLATING-PISTON, POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; ROTARY-PISTON, OR OSCILLATING-PISTON, POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT PUMPS
- F04C2240/00—Components
- F04C2240/80—Other components
- F04C2240/803—Electric connectors or cables; Fittings therefor
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F05—INDEXING SCHEMES RELATING TO ENGINES OR PUMPS IN VARIOUS SUBCLASSES OF CLASSES F01-F04
- F05B—INDEXING SCHEME RELATING TO WIND, SPRING, WEIGHT, INERTIA OR LIKE MOTORS, TO MACHINES OR ENGINES FOR LIQUIDS COVERED BY SUBCLASSES F03B, F03D AND F03G
- F05B2210/00—Working fluid
- F05B2210/10—Kind or type
- F05B2210/14—Refrigerants with particular properties, e.g. HFC-134a
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a compressor and a refrigeration cycle apparatus.
- a hermetic rotary compressor which is an example of a rotary compressor
- internal components such as a motor and a compression mechanism are accommodated in a welded integrated hermetic container.
- a discharge pipe for discharging the refrigerant and an airtight terminal connected to the internal stator via a lead wire are provided on the upper part of the sealed container.
- a hermetic container of a rotary compressor is provided with one airtight terminal.
- two airtight terminals it is possible to reduce the current flowing to the airtight terminals and the lead wire, and to switch the wire connection method of the motor winding.
- Patent Document 1 describes a technique in which a first lead wire is drawn in a counterclockwise direction and connected to a first terminal, and a second lead wire is drawn in a clockwise direction and connected to a second terminal. ing.
- An object of the present invention is to shorten a length of a plurality of connection lines for electrically connecting a plurality of terminals attached to a container of a compressor and an electric motor stored in the container of the compressor.
- a compressor is A compression mechanism for compressing a refrigerant; An electric motor for driving the compression mechanism; A container for containing the compression mechanism and the motor; A first straight line including a first terminal and a second terminal and attached to one axial end of the container, the first straight line having a center passing through a center of the container and a center of the first terminal in plan view; A plurality of terminals located within an angle range of 180 ° or less formed by a second straight line passing through the center of the second terminal and the center of the second terminal; The plurality of terminals and the motor are electrically connected in the container, and a plurality of connection lines extracted from the plurality of terminals in the angle range in plan view are provided.
- each connecting wire electrically connecting each terminal and the motor is, in plan view, a first straight line passing through the center of the container and the center of the first terminal, the center of the container and the center of the second terminal It is taken out within an angle range of 180 ° or less formed by the passing second straight line. Therefore, the length of each connection line can be shortened.
- FIG. 1 is a circuit diagram of a refrigeration cycle apparatus according to Embodiment 1.
- FIG. 1 is a circuit diagram of a refrigeration cycle apparatus according to Embodiment 1.
- FIG. 1 is a longitudinal sectional view of a compressor according to Embodiment 1.
- FIG. Fig. 2 is a cross-sectional view of a part of the compressor according to the first embodiment.
- FIG. 2 is a plan view of a part of the compressor according to Embodiment 1.
- FIG. 2 is a longitudinal sectional view of part of the compressor according to Embodiment 1;
- FIG. 2 is a partial vertical cross-sectional view of a part of the compressor according to Embodiment 1.
- FIG. 2 is a side view of part of the compressor according to Embodiment 1;
- FIG. 1 is a circuit diagram of a refrigeration cycle apparatus according to Embodiment 1.
- FIG. 1 is a circuit diagram of a refrigeration cycle apparatus according to Embodiment 1.
- FIG. 1 is a longitudinal sectional
- FIG. 2 is a bottom view of a part of the compressor according to Embodiment 1.
- FIG. 2 is a diagram showing a connection method of connection lines at the time of assembly of a compressor according to Embodiment 1. The figure which shows the connection method of the connecting wire at the time of the assembly of the compressor concerning a comparative example.
- FIG. 2 is a plan view of a part of the compressor according to Embodiment 1. The top view of a part of compressor concerning a comparative example. The graph which shows the comparison result of the deformation with respect to the internal pressure of the container upper part of the compressor which concerns on Embodiment 1 and a comparative example.
- FIG. 7 is a plan view of a portion of a compressor according to a second embodiment.
- FIG. 9 is a longitudinal sectional view of a compressor according to a third embodiment.
- FIG. 10 is a longitudinal sectional view of a compressor according to a fourth embodiment.
- Embodiment 1 The present embodiment will be described with reference to FIGS. 1 to 14.
- FIG. 1 shows the refrigerant circuit 11 in the cooling operation.
- FIG. 2 shows the refrigerant circuit 11 in the heating operation.
- the refrigeration cycle apparatus 10 is an air conditioner in the present embodiment, but may be an apparatus other than an air conditioner such as a refrigerator or a heat pump cycle apparatus.
- the refrigeration cycle apparatus 10 includes a refrigerant circuit 11 in which a refrigerant circulates.
- the refrigeration cycle apparatus 10 includes a compressor 12, a four-way valve 13, a first heat exchanger 14 which is an outdoor heat exchanger, an expansion mechanism 15 which is an expansion valve, and a second heat exchanger which is an indoor heat exchanger. And 16.
- the compressor 12, the four-way valve 13, the first heat exchanger 14, the expansion mechanism 15, and the second heat exchanger 16 are connected to the refrigerant circuit 11.
- the compressor 12 compresses the refrigerant.
- the four-way valve 13 switches the flow direction of the refrigerant between the cooling operation and the heating operation.
- the first heat exchanger 14 operates as a condenser during the cooling operation, and dissipates the refrigerant compressed by the compressor 12. That is, the first heat exchanger 14 performs heat exchange using the refrigerant compressed by the compressor 12.
- the first heat exchanger 14 operates as an evaporator at the time of heating operation, performs heat exchange between outdoor air and the refrigerant expanded by the expansion mechanism 15, and heats the refrigerant.
- the expansion mechanism 15 expands the refrigerant that has dissipated heat in the condenser.
- the second heat exchanger 16 operates as a condenser during heating operation, and dissipates the refrigerant compressed by the compressor 12. That is, the second heat exchanger 16 performs heat exchange using the refrigerant compressed by the compressor 12.
- the second heat exchanger 16 operates as an evaporator during the cooling operation, performs heat exchange between room air and the refrigerant expanded by the expansion mechanism 15, and heats the refrigerant.
- the refrigeration cycle apparatus 10 further includes a controller 17.
- the control device 17 is, for example, a microcomputer. Although only the connection between the control device 17 and the compressor 12 is shown in FIGS. 1 and 2, the control device 17 includes not only the compressor 12 but also components other than the compressor 12 connected to the refrigerant circuit 11. It may be connected. The controller 17 monitors and controls the state of each component connected to the controller 17.
- an HFC refrigerant such as R32, R125, R134a, R407C or R410A is used.
- HFO-based refrigerants such as R1123, R1132 (E), R1132 (Z), R1132 a, R1141, R1234yf, R1234ze (E) or R1234ze (Z) are used.
- natural refrigerants such as R290 (propane), R600a (isobutane), R744 (carbon dioxide) or R717 (ammonia) are used.
- other refrigerants are used.
- a mixture of two or more of these refrigerants is used.
- HFC is an abbreviation of Hydrofluorocarbon.
- HFO is an abbreviation of Hydrofluoroolefin.
- FIG. 3 shows a longitudinal cross section of the compressor 12.
- the compressor 12 is a hermetic compressor in the present embodiment.
- the compressor 12 is specifically a multi-cylinder rotary compressor, but may be a single-cylinder rotary compressor, a scroll compressor or a reciprocating compressor.
- the compressor 12 includes a container 20, a compression mechanism 30, an electric motor 40, and a crankshaft 50.
- the container 20 is a closed container. At the bottom of the container 20, refrigeration oil 25 is stored. A suction pipe 21 for suctioning the refrigerant into the container 20 and a discharge pipe 22 for discharging the refrigerant to the outside of the container 20 are attached to the container 20.
- the motor 40 is housed in the container 20. Specifically, the motor 40 is installed at the upper inside of the container 20.
- the motor 40 is a concentrated winding motor in the present embodiment, but may be a distributed winding motor.
- the compression mechanism 30 is housed in the container 20. Specifically, the compression mechanism 30 is installed at the lower inside of the container 20. That is, the compression mechanism 30 is disposed below the motor 40 in the container 20.
- the crankshaft 50 connects the motor 40 and the compression mechanism 30.
- the crankshaft 50 forms an oil supply passage of the refrigerator oil 25 and a rotation shaft of the electric motor 40.
- the refrigeration oil 25 is pumped up by the oil supply mechanism such as an oil pump provided at the lower part of the crankshaft 50 as the crankshaft 50 rotates.
- the refrigeration oil 25 is supplied to the sliding parts of the compression mechanism 30 to lubricate the sliding parts of the compression mechanism 30.
- POE is an abbreviation of Polyolester.
- PVE is an abbreviation for Polyvinyl Ether.
- AB is an abbreviation of Alkylbenzene.
- the motor 40 rotates the crankshaft 50.
- the compression mechanism 30 is driven by the rotation of the crankshaft 50 to compress the refrigerant. That is, the compression mechanism 30 compresses the refrigerant by being driven by the rotational force of the electric motor 40 transmitted through the crankshaft 50. Specifically, this refrigerant is a low-pressure gas refrigerant sucked into the suction pipe 21. The high temperature and high pressure gas refrigerant compressed by the compression mechanism 30 is discharged from the compression mechanism 30 into the space in the container 20.
- the crankshaft 50 has an eccentric shaft 51, a main shaft 52, and a countershaft 53. These are provided in the order of the main shaft portion 52, the eccentric shaft portion 51, and the sub shaft portion 53 in the axial direction D0. That is, the main shaft portion 52 is provided on one end side in the axial direction of the eccentric shaft portion 51, and the sub shaft portion 53 is provided on the other end side in the axial direction of the eccentric shaft portion 51.
- the eccentric shaft portion 51, the main shaft portion 52, and the sub shaft portion 53 each have a cylindrical shape.
- the main shaft portion 52 and the sub shaft portion 53 are provided such that the central axes thereof coincide with each other, that is, coaxially.
- the eccentric shaft portion 51 is provided such that the central axis thereof is offset from the central axes of the main shaft portion 52 and the auxiliary shaft portion 53.
- the eccentric shaft portion 51 eccentrically rotates.
- the container 20 has a body portion 20a, a container upper portion 20b, and a container lower portion 20c.
- the body 20a is cylindrical.
- the container upper part 20b is closing the upper opening of the trunk
- the container upper portion 20 b corresponds to one axial end of the container 20.
- the lower part 20c of the container is closing the lower opening of the body 20a.
- the container lower portion 20 c corresponds to the other axial end of the container 20.
- the body 20a and the container upper portion 20b are connected by welding, and the body 20a and the container lower portion 20c are connected by welding, whereby the container 20 is sealed.
- the body 20 a is provided with a suction pipe 21 connected to the suction muffler 23.
- a discharge pipe 22 is provided in the container upper portion 20b.
- the motor 40 is a brushless DC motor in the present embodiment, but may be a motor other than a brushless DC motor such as an induction motor.
- DC is an abbreviation of Direct Current.
- the motor 40 has a stator 41 and a rotor 42.
- the stator 41 is cylindrical and fixed so as to be in contact with the inner circumferential surface of the container 20.
- the rotor 42 has a cylindrical shape, and is installed inside the stator 41 with an air gap.
- the width of the air gap is, for example, 0.3 mm or more and 1.0 mm or less.
- the stator 41 has a stator core 43 and windings 44.
- the stator core 43 is manufactured by punching a plurality of magnetic steel sheets containing iron as a main component into a predetermined shape, laminating them in the axial direction D0, and fixing them by caulking.
- the thickness of each electromagnetic steel sheet is, for example, 0.1 mm or more and 1.5 mm or less.
- the stator core 43 has an outer diameter larger than the inner diameter of the body 20 a of the container 20, and is fixed to the inside of the body 20 a of the container 20 by shrink fitting.
- the windings 44 are wound around a stator core 43. Specifically, the winding 44 is wound in a concentrated manner around the stator core 43 via an insulating member.
- the winding 44 comprises a core wire and at least one layer of coating covering the core wire.
- the material of the core wire is copper.
- the material of the film is AI / EI.
- AI is an abbreviation of Amide-Imide.
- EI is an abbreviation of Ester-Imide.
- the material of the insulating member is PET.
- PET is an abbreviation for Polyethylene Terephthalate.
- the method of fixing the electromagnetic steel plates of the stator core 43 is not limited to caulking, and other methods such as welding may be used.
- the method of fixing the stator core 43 to the inside of the body portion 20a of the container 20 is not limited to shrink fitting, and may be another method such as press fitting or welding.
- the material of the core wire of the winding 44 may be aluminum.
- the material of the insulating member may be PBT, FEP, PFA, PTFE, LCP, PPS or a phenol resin.
- PBT is an abbreviation for Polybutylene Terephthalate.
- FEP is an abbreviation for Fluorinated Ethylene Propylene.
- PFA is an abbreviation of Perfluoroalkoxy Alkane.
- PTFE is an abbreviation of Polytetrafluoroethylene.
- LCP is an abbreviation for Liquid Crystal Polymer.
- PPS is an abbreviation of Polyphenylene Sulfide.
- the rotor 42 has a rotor core 45 and permanent magnets 46. Similar to the stator core 43, the rotor core 45 is manufactured by punching a plurality of magnetic steel sheets containing iron as a main component into a predetermined shape, laminating them in the axial direction D0, and fixing them by caulking. The thickness of each electromagnetic steel sheet is, for example, 0.1 mm or more and 1.5 mm or less.
- the permanent magnets 46 are inserted into a plurality of insertion holes formed in the rotor core 45.
- the permanent magnet 46 forms a magnetic pole.
- As the permanent magnet 46 a ferrite magnet or a rare earth magnet is used.
- the method of fixing the electromagnetic steel plates of the rotor core 45 is not limited to caulking, and other methods such as welding may be used.
- an axial hole is formed in which the main shaft portion 52 of the crankshaft 50 is shrink-fit or press-fitted. That is, the inner diameter of the rotor core 45 is smaller than the outer diameter of the main shaft portion 52.
- a plurality of through holes penetrating in the axial direction D0 are formed around the shaft hole of the rotor core 45.
- Each through hole is one of the passages of the gas refrigerant discharged from the discharge muffler 35 described later to the space in the container 20.
- Each through hole also serves as one of the passages for dropping the refrigerator oil 25 led to the upper part of the container 20 to the lower part of the container 20.
- the motor 40 when configured as an induction motor, a plurality of slots formed in the rotor core 45 are filled or inserted with a conductor formed of aluminum or copper or the like. Then, a cage winding in which both ends of the conductor are shorted by the end ring is formed.
- the container upper portion 20b is provided with a terminal 24 connected to an external power supply such as an inverter device, and a rod 28 to which a cover for protecting the terminal 24 is attached.
- the terminal 24 is an airtight terminal such as a glass terminal.
- the terminal 24 is fixed to the container 20 by welding.
- the terminal 24 is connected to a connecting wire 26 extended from the winding 44 of the motor 40.
- the terminal 24 and the motor 40 are electrically connected.
- the discharge pipe 22 which the axial direction both ends opened is provided in the container upper part 20b.
- the gas refrigerant discharged from the compression mechanism 30 sequentially passes through the rotor 42 and the oil separation plate 29 above the rotor 42, and from the space in the container 20 to the external refrigerant circuit 11 through the discharge pipe 22. It is discharged.
- the oil separating plate 29 separates the refrigerating machine oil 25 in the container 20 pumped up with the refrigerant.
- the oil separation plate 29 is fixed to the crankshaft 50 by press-fitting, and rotates as the crankshaft 50 rotates.
- the oil separation plate 29 is fixed to the rotor 42 using a fixing tool such as a rivet, and rotates at high speed as the rotor 42 rotates.
- the refrigeration oil 25 has a specific gravity larger than that of the refrigerant. Therefore, the oil separation plate 29 can separate the refrigerator oil 25 by flying it in the outer peripheral direction by centrifugal force.
- the discharge pipe 22 may be installed at the outer peripheral portion of the container upper portion 20b, but in the present embodiment, it is installed at the center of the container upper portion 20b just above the crankshaft 50. Assuming that the discharge pipe 22 is installed on the outer peripheral portion of the container upper portion 20b, the refrigerator oil 25 separated by the oil separating plate 29 enters the discharge pipe 22 and is discharged to the outside of the container 20. The amount of refrigeration oil 25 may be reduced, and the lubricity of the compression mechanism 30 may be reduced. In order to prevent such a decrease in lubricity, it is desirable that the discharge pipe 22 be installed at the center of the upper portion 20b of the container.
- FIG. 4 shows a cross section of a portion of the compressor 12 as viewed along the axial direction D0.
- hatching representing a cross section is omitted.
- the compression mechanism 30 has a cylinder 31, a rolling piston 32, a main bearing 33, an auxiliary bearing 34, and a discharge muffler 35.
- the inner periphery of the cylinder 31 is circular in plan view. Inside the cylinder 31, a cylinder chamber 61 which is a circular space in plan view is formed. A suction port for suctioning the gas refrigerant from the refrigerant circuit 11 is provided on the outer peripheral surface of the cylinder 31. The refrigerant drawn from the suction port is compressed in the cylinder chamber 61. Both ends in the axial direction of the cylinder 31 are open.
- the rolling piston 32 is ring-shaped. Therefore, the inner circumference and the outer circumference of the rolling piston 32 are circular in plan view.
- the rolling piston 32 rotates eccentrically in the cylinder chamber 61.
- the rolling piston 32 is slidably fitted on an eccentric shaft portion 51 of a crankshaft 50 which is a rotation shaft of the rolling piston 32.
- the cylinder 31 is provided with vane grooves 62 connected to the cylinder chamber 61 and extending in the radial direction.
- a back pressure chamber 63 which is a circular space in plan view connected to the vane groove 62 is formed.
- a vane 64 for separating the cylinder chamber 61 into a suction chamber, which is a low pressure operating chamber, and a compression chamber, which is a high pressure operating chamber is installed in the vane groove 62.
- the vanes 64 are in the form of a plate whose tip is rounded.
- the vanes 64 reciprocate while sliding in the vane grooves 62.
- the vanes 64 are always pressed against the rolling piston 32 by vane springs provided in the back pressure chamber 63.
- the vane spring is mainly used for the purpose of pressing the vane 64 against the rolling piston 32 when the compressor 12 starts with no difference in pressure in the container 20 and in the cylinder chamber 61.
- the main bearing 33 is a reverse T-shaped bearing in a side view.
- the main bearing 33 is slidably fitted on a main shaft portion 52 which is a portion above the eccentric shaft portion 51 of the crankshaft 50.
- a through hole 54 serving as an oil supply passage is provided along the axial direction D0 inside the crankshaft 50, and is sucked through the through hole 54 between the main bearing 33 and the main shaft portion 52.
- An oil film is formed by the supply of the refrigerating machine oil 25.
- the main bearing 33 closes the upper side of the cylinder chamber 61 and the vane groove 62 of the cylinder 31. That is, the main bearing 33 closes the upper side of the two working chambers in the cylinder 31.
- the auxiliary bearing 34 is a T-shaped bearing in a side view.
- the sub bearing 34 is slidably fitted in a sub shaft portion 53 which is a portion below the eccentric shaft portion 51 of the crankshaft 50.
- An oil film is formed between the sub bearing 34 and the sub shaft portion 53 by supplying the refrigerating machine oil 25 sucked up through the through hole 54 of the crankshaft 50.
- the sub bearing 34 closes the lower side of the cylinder chamber 61 and the vane groove 62 of the cylinder 31. That is, the sub bearing 34 closes the lower side of the two working chambers in the cylinder 31.
- the main bearing 33 and the sub bearing 34 are fixed to the cylinder 31 by fasteners 36 such as bolts, respectively, and support a crankshaft 50 which is a rotation shaft of the rolling piston 32.
- the main bearing 33 supports the main shaft 52 without contacting the main shaft 52 by fluid lubrication of the oil film between the main bearing 33 and the main shaft 52.
- the secondary bearing 34 supports the secondary shaft 53 without contacting the secondary shaft 53 by fluid lubrication of the oil film between the secondary bearing 34 and the secondary shaft 53 as the main bearing 33 does.
- the main bearing 33 is provided with a discharge port for discharging the refrigerant compressed in the cylinder chamber 61 to the refrigerant circuit 11.
- the discharge port is at a position where it is connected to the compression chamber when the cylinder chamber 61 is divided by the vane 64 into a suction chamber and a compression chamber.
- the main bearing 33 is attached with a discharge valve that closes the discharge port so as to open and close. The discharge valve is closed until the gas refrigerant in the compression chamber reaches a desired pressure, and is opened when the gas refrigerant in the compression chamber reaches a desired pressure. Thereby, the discharge timing of the gas refrigerant from the cylinder 31 is controlled.
- the discharge muffler 35 is attached to the outside of the main bearing 33.
- the high-temperature, high-pressure gas refrigerant discharged when the discharge valve is opened enters the discharge muffler 35 and is then discharged from the discharge muffler 35 into the space in the container 20.
- the discharge port and the discharge valve may be provided in the sub bearing 34 or both the main bearing 33 and the sub bearing 34.
- the discharge muffler 35 is attached to the outside of the bearing on which the discharge port and the discharge valve are provided.
- An intake muffler 23 is provided beside the container 20.
- the suction muffler 23 sucks the low-pressure gas refrigerant from the refrigerant circuit 11.
- the suction muffler 23 prevents the liquid refrigerant from directly entering the cylinder chamber 61 of the cylinder 31 when the liquid refrigerant returns.
- the suction muffler 23 is connected to a suction port provided on the outer peripheral surface of the cylinder 31 via a suction pipe 21.
- the suction port is in a position to be connected to the suction chamber when the cylinder chamber 61 is divided by the vane 64 into the suction chamber and the compression chamber.
- the main body of the suction muffler 23 is fixed to the side surface of the body 20 a of the container 20 by welding or the like.
- the material of the eccentric shaft portion 51, the main shaft portion 52 and the countershaft portion 53 of the crankshaft 50 is a cast material or a forged material.
- the material of the main bearing 33 and the auxiliary bearing 34 is a cast material or a sintered material, and specifically, sintered steel, gray cast iron or carbon steel.
- the material of the cylinder 31 is also sintered steel, gray cast iron or carbon steel.
- the material of the rolling piston 32 is a cast material, and specifically, an alloy steel containing molybdenum, nickel and chromium, or an iron-based cast material.
- the material of the vanes 64 is high speed tool steel.
- the vanes 64 are provided integrally with the rolling piston 32.
- the vanes 64 reciprocate along the grooves of a support rotatably mounted on the rolling piston 32.
- the vanes 64 radially advance and retract while oscillating as the rolling piston 32 rotates, thereby dividing the inside of the cylinder chamber 61 into a compression chamber and a suction chamber.
- the support is constituted by two columnar members having a semicircular cross section. The support is rotatably fitted in a circular holding hole formed at an intermediate portion between the suction port and the discharge port of the cylinder 31.
- Electric power is supplied from the terminal 24 to the stator 41 of the motor 40 via the connection line 26.
- current flows through the windings 44 of the stator 41, and magnetic flux is generated from the windings 44.
- the rotor 42 of the motor 40 is rotated by the action of the magnetic flux generated from the winding 44 and the magnetic flux generated from the permanent magnet 46 of the rotor 42.
- the rotor 42 is rotated by the attraction and repulsion between the rotating magnetic field generated by the flow of current through the winding 44 of the stator 41 and the magnetic field of the permanent magnet 46 of the rotor 42.
- the rotation of the rotor 42 causes the crankshaft 50 fixed to the rotor 42 to rotate.
- the rolling piston 32 of the compression mechanism 30 eccentrically rotates in the cylinder chamber 61 of the cylinder 31 of the compression mechanism 30.
- a cylinder chamber 61 which is a space between the cylinder 31 and the rolling piston 32 is divided by a vane 64 into a suction chamber and a compression chamber.
- the volume of the suction chamber and the volume of the compression chamber change.
- the low-pressure gas refrigerant is sucked from the suction muffler 23 through the suction pipe 21 by gradually expanding the volume.
- the volume of the gas refrigerant is gradually reduced by gradually reducing the volume.
- the compressed, high-pressure and high-temperature gas refrigerant is discharged from the discharge muffler 35 into the space in the container 20.
- the discharged gas refrigerant further passes through the electric motor 40 and is discharged from the discharge pipe 22 in the container upper portion 20 b to the outside of the container 20.
- the refrigerant discharged out of the container 20 returns to the suction muffler 23 again through the refrigerant circuit 11.
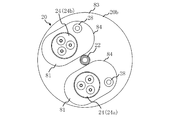
- FIG. 5 shows a top view of a portion of the compressor 12 as viewed along the axial direction D0.
- FIG. 6 shows a cross section of a portion of the compressor 12 as viewed along a first direction D1 orthogonal to the axial direction D0.
- FIG. 7 shows a front view and a cross section of a portion of the compressor 12 as viewed along a second direction D2 orthogonal to the axial direction D0 and the first direction D1.
- FIG. 8 shows a side view of a portion of the compressor 12 as viewed along the first direction D1. In FIG. 8, the terminal 24 is omitted.
- drum 20a is circular shape in planar view.
- a discharge pipe 22 is provided at the center of the container upper portion 20b.
- a first flat surface portion 81, a second flat surface portion 82, and a curved surface portion 83 are formed on the surface of the container upper portion 20b.
- the first flat portion 81 is provided with a plurality of terminals 24. Each terminal 24 is electrically connected to the motor 40 in the container 20. Each terminal 24 is fitted in a through hole provided in the first flat portion 81. The outermost shell of each terminal 24 is in contact with the inner peripheral edge of the through hole.
- the second flat portion 82 is provided with a rod 28 perpendicular to the second flat portion 82.
- the outer diameter of the discharge pipe 22 provided at the central portion of the container upper portion 20b is desirably 0.1 times or more the outer diameter of the container upper portion 20b.
- the outer diameter of the discharge pipe 22 is preferably 0.2 or less times the outer diameter of the container upper portion 20b.
- the surface of the curved surface portion 83 is composed of a plurality of curved surfaces.
- the curved surface portion 83 has a shape similar to a partially missing hemisphere.
- the edges of the first flat surface portion 81 and the second flat surface portion 82 are connected to the curved surface portion 83 by the concave portion 84 which is smoothly curved. That is, portions between the first flat surface portion 81 and the second flat surface portion 82 and the curved surface portion 83 are recessed.
- the recess 84 is formed thick and has a function as a rib for improving the strength.
- the first flat surface portion 81 is inclined at a first inclination angle ⁇ 1 in a direction away from the virtual vertical plane with respect to a virtual vertical surface formed in the upper end or upper opening of the cylindrical body portion 20a and orthogonal to the axial direction D0. ing.
- the first inclination angle ⁇ 1 is desirably 5 ° or more and 30 ° or less, and is 5 ° in the present embodiment.
- One end 81 a of the first flat surface 81 protrudes outward beyond the curved surface 83.
- the distance from one end 81 a of the first flat surface 81 to the imaginary vertical plane is longer than the distance from the other end 81 b of the first flat surface 81 to the imaginary vertical plane.
- the first plane portion 81 is inclined with respect to the virtual vertical plane.
- the first flat surface portion 81 is smoothly connected to the curved surface portion 83 by the concave portion 84. Therefore, even when the distance between the terminal 24 and the discharge pipe 22 is maintained in plan view, the distance along the shape of the container upper portion 20b between the outermost shell of the terminal 24 and the outer peripheral wall of the discharge pipe 22 And, the distance along the shape of the container upper portion 20b between the outermost shell of the terminal 24 and the inner peripheral wall of the container upper portion 20b is extended.
- one end 81a of the first flat surface 81 is further separated from the curved surface 83, and one end 81a of the first flat surface 81 is It protrudes beyond the curved surface portion 83, and the distance to the virtual vertical surface is increased. Therefore, the distance along the surface of the container upper portion 20b from the terminal 24 to the discharge pipe 22 is further extended.
- the container upper portion 20b has a diameter of 100 mm, the distance between the outermost shell of the terminal 24 and the outer peripheral wall of the discharge pipe 22 is less than 3 mm, and the outermost shell of the terminal 24 between the inner peripheral wall of the container upper 20b Distance of less than 5 mm.
- the first flat portion 81 is not inclined, the distance between the outermost shell of the terminal 24 and the outer peripheral wall of the discharge pipe 22, and the outermost shell of the terminal 24 and the inner peripheral wall of the container upper portion 20b The distance between the two can not be secured enough. That is, it is not possible to design according to the specification of the insulation distance.
- the distance between the outermost shell of the terminal 24 and the outer peripheral wall of the discharge pipe 22 is 3 mm or more, and the outermost shell of the terminal 24 and the container upper portion 20b 5 mm or more can be secured between the inner circumferential wall of That is, the design according to the specification of the insulation distance is possible.
- the first inclination angle ⁇ 1 of the first flat portion 81 is within the range of 5 ° to 30 ° with respect to the virtual vertical plane, the distance between the outermost shell of the terminal 24 and the outer peripheral wall of the discharge pipe 22; And, the distance between the outermost shell of the terminal 24 and the inner peripheral wall of the container upper portion 20b is secured.
- the discharge pipe 22 is provided at a position overlapping the central axis of the container 20 at one end in the axial direction of the container 20.
- the container 20 has a curved surface portion 83 in which the discharge pipe 22 is disposed, and a first flat portion 81 in which the plurality of terminals 24 are disposed at one axial end of the container 20.
- the first flat portion 81 is virtually perpendicular to the central axis of the container 20 along at least one direction with respect to a virtual vertical plane perpendicular to the axial direction D0, which is located between the plurality of terminals 24 and the motor 40. Inclined at an inclination angle away from the surface.
- the first flat portion 81 is inclined at an inclination angle away from the virtual vertical plane as approaching the central axis of the container 20 along the two directions with respect to the virtual vertical plane.
- the first flat portion 81 including one end of the first direction D1 orthogonal to the axial direction D0 is the central axis of the container 20 along the first direction D1 with respect to the virtual vertical plane. As it approaches, it inclines at the 1st inclination angle (theta) 1 which leaves
- the entire first flat surface portion 81 is inclined at the first inclination angle ⁇ 1 with respect to the virtual vertical plane along the first direction D1.
- a part of the first flat portion 81 including one end in the first direction D1 is farther from the virtual vertical plane as it approaches the central axis of the container 20 along the first direction D1.
- the remaining portion of the first flat portion 81 including the other end in the first direction D1 is farther from the virtual vertical plane as it goes away from the central axis of the container 20 along the first direction D1.
- the first inclination angle ⁇ 1 is desirably 5 ° or more and 30 ° or less, and is 5 ° in the present embodiment.
- the first flat portion 81 including one end of the second direction D2 orthogonal to the axial direction D0 and the first direction D1 is the center of the container 20 along the second direction D2 with respect to the virtual vertical plane. As it approaches the axis, it inclines at a second inclination angle ⁇ 2 that is away from the virtual vertical plane. In the present embodiment, the entire first flat surface portion 81 is inclined at a second inclination angle ⁇ 2 with respect to the virtual vertical plane along the second direction D2. Thus, a part of the first flat portion 81 including one end in the second direction D2 is farther from the virtual vertical plane as it approaches the central axis of the container 20 along the second direction D2.
- the remaining portion of the first flat portion 81 including the other end in the second direction D2 is farther from the virtual vertical plane as it goes away from the central axis of the container 20 along the second direction D2.
- the second tilt angle ⁇ 2 is different from the first tilt angle ⁇ 1. Is desirable. That is, if the distance from one end to the other end of first flat portion 81 in the second direction D2 is larger than the distance from one end to the other end in first direction D1 of first flat portion 81, the second inclination angle ⁇ 2 Is desirably smaller than the first inclination angle ⁇ 1.
- the second inclination angle ⁇ 2 is It is desirable to be larger than the first inclination angle ⁇ 1. This is because the steeper the slope, the shorter the distance can be obtained. If the height can be obtained, it will be easier to secure the distance and the area.
- the second inclination angle ⁇ 2 is desirably 5 ° or more and 30 ° or less, and is 10 ° in the present embodiment.
- At least one of the first inclination angle ⁇ 1 and the second inclination angle ⁇ 2 of the first flat surface portion 81 may be different in each region where the terminal 24 is provided. That is, the inclination angle of the first flat portion 81 may be different for each of the terminals 24.
- the container 20 When the refrigerant compressed in the compression mechanism 30 is discharged into the space in the container 20, the container 20 receives an outward force by the high temperature and high pressure gas refrigerant.
- the cylindrical portion of the body portion 20a can reduce stress concentration due to the outward force.
- the hemispherical or dome-shaped lower container portion 20c can reduce stress concentration due to an outward force.
- the first flat portion 81 In the container upper portion 20b, the first flat portion 81 is inclined, and one end 81a of the first flat portion 81 protrudes outward beyond the curved surface portion 83 and extends to a position higher than the center of the container upper portion 20b There is.
- first flat surface portion 81 and the curved surface portion 83 are connected by the concave portion 84 which is smoothly curved. Therefore, when the distance between the plurality of terminals 24 provided in the first flat portion 81 and the discharge pipe 22 provided in the center of the container upper portion 20b is that the surface of the container upper portion 20b is flat, and the container upper portion 20b This is more than if the surface of the is hemispherical.
- the recess 84 is formed thick and has a function as a rib. Therefore, even if the pressure in the container 20 rises, the stress is not easily concentrated, and the deformation of the container upper portion 20b is suppressed.
- the first flat surface portion 81 is flat, and the curved surface portion 83 approximates to a hemispherical shape partially missing, and the concave portion 84 connecting the first flat surface portion 81 and the curved surface portion 83. Is formed thick and smoothly curved, stress concentration due to outward force can be reduced.
- one axial end of the container 20 is circular in plan view.
- the outer diameter of the discharge pipe 22 is at least 0.1 times the outer diameter of one axial end of the container 20.
- the first flat surface portion 81 is inclined, and the distance between the terminal 24 provided on the first flat surface portion 81 and the discharge pipe 22 provided on the curved surface portion 83 is extended. Therefore, even when the discharge pipe 22 having a large diameter of 0.1 times or more of the outer diameter of the container upper portion 20b is used, the terminal 24 and the discharge pipe 22 can be disposed sufficiently apart from each other.
- the rod 28 to which the cover for covering the terminal 24 is attached may be disposed in the first flat portion 81, it is disposed in the second flat portion 82 in the present embodiment.
- the rod 28 is extended to a position higher than the curved portion 83 of the container upper portion 20b. Therefore, the arrangement and mounting operation of the terminal 24 and the rod 28 are easy. The attachment of the cover to the rod 28 is also facilitated.
- Accessories such as a temperature sensor may be attached to the second flat portion 82.
- the second flat portion 82 is lower than the top of the first flat portion 81 by the distance H1. Therefore, when the temperature sensor is attached to the second flat portion 82, the temperature sensor can be disposed at a position near the compression mechanism 30. As the temperature sensor is closer to the compression mechanism 30, the temperature change of the refrigerant discharged from the compression mechanism 30 can be detected earlier, even when the circulation flow rate of the refrigerant is small.
- the container 20 has the second flat portion 82 in which the rod 28 is disposed at one axial end of the container 20.
- a cover for covering the plurality of terminals 24 is attached to the rod 28.
- the second flat portion 82 may be inclined with respect to the virtual vertical plane, but in the present embodiment, is parallel to the virtual vertical plane.
- the rod 28 is provided perpendicularly to the second flat portion 82. That is, the rod 28 is provided to extend along the axial direction D0.
- accessories different from the plurality of terminals 24 and the rod 28 may be disposed.
- an accessory such as a temperature sensor is disposed in the second flat portion 82, it is desirable that the maximum distance from the virtual vertical plane of the second flat portion 82 be closer than the first flat portion 81.
- resistance welding is used as a method of attaching the discharge pipe 22 to the container upper portion 20b.
- the discharge pipe 22 is joined to the curved surface portion 83 via the ring member 85.
- the material of the ring member 85 is iron.
- the method of attaching the discharge pipe 22 to the container upper portion 20b is not limited to resistance welding, and may be other methods such as gas welding using a brazing material or laser welding.
- gas welding has a large heat input and a wide heat input range. Therefore, when the plurality of terminals 24 are attached by resistance welding after the discharge pipe 22 is attached by gas welding, distortion may occur on the surface of the portion of the container upper portion 20b to which the terminals 24 are attached. If distortion occurs, the surface of the container upper portion 20b and the surface of the terminal 24 do not come in contact with each other, which may cause welding defects during resistance welding. Therefore, also in the welding of the discharge pipe 22, it is desirable to reduce the heat input and the heat input range by using resistance welding or laser welding.
- FIG. 9 shows the underside of a portion of the compressor 12 as viewed from inside the vessel 20 along the axial direction D0.
- the plurality of terminals 24 includes a first terminal 24 a and a second terminal 24 b.
- the plurality of terminals 24 may include terminals 24 different from the first terminals 24 a and the second terminals 24 b.
- the plurality of terminals 24 have a first straight line L1 whose center passes through the center P0 of the container 20 and the center P1 of the first terminal 24a, and the center P0 of the container 20 and the center P2 of the second terminal 24b in plan view. It is attached to one axial direction end of the container 20 so as to be located within an angle range R1 of 180 ° or less formed by the second straight line L2 passing through.
- the plurality of terminals 24 are collectively arranged on the first flat portion 81 of the container upper portion 20b.
- the plurality of connection lines 26 electrically connect the plurality of terminals 24 and the motor 40 in the container 20.
- the plurality of connection lines 26 include a first connection line 26 a electrically connecting the first terminal 24 a and the motor 40, and a second connection line 26 b electrically connecting the second terminal 24 b and the motor 40.
- first connection line 26 a electrically connecting the first terminal 24 a and the motor 40
- second connection line 26 b electrically connecting the second terminal 24 b and the motor 40.
- another plurality of connecting wires 26 may be used to electrically connect the other terminal 24 to the motor 40.
- Connecting lines 26 may be included.
- the plurality of connection lines 26 are extracted from the plurality of terminals 24 into the angular range R1 in plan view. Specifically, the portion of each connecting wire 26 following the end connected to each terminal 24 is taken out of the existing range R2 of each terminal 24 at a position within the angular range R1 in plan view.
- the existence range R2 of each terminal 24 is a region surrounded by an outline formed by the outermost shell of each terminal 24 in a plan view. Although the presence range R2 of each terminal 24 may be an area of any shape, it is a circular area in the present embodiment.
- the connecting wire 26 extends from the end of the connecting wire 26 connected to the certain terminal 24 and the connecting wire 26 extends from the end of the connection range 26 of the terminal 24 in plan view. It is the position being taken out.
- the plurality of connection lines 26 are routed such that this position falls within the angular range R1 for all the connection lines 26. Therefore, the lengths of the plurality of connection lines 26 can be shortened. Also, the wiring space can be reduced. In order to reduce the wiring space as much as possible, it is desirable that the plurality of connection lines 26 be disposed within the angular range R1 in plan view. That is, it is desirable that the plurality of connection lines 26 be routed so that the whole of all the connection lines 26 falls within the angle range R1.
- each connecting wire 26 is taken out toward the center of the angle range R1. That is, the first connection line 26a and the second connection line 26b are on the third straight line L3 passing through the center P0 of the container 20 and the midpoint P3 of the center P1 of the first terminal 24a and the center P2 of the second terminal 24b. It is taken out in the approaching direction. Therefore, the wiring space can be made smaller.
- the angular range R1 formed by a straight line passing the center of the container upper portion 20b and the centers of the plurality of terminals 24 is 180 ° or less.
- the range of the extraction direction of each connection line 26 connected to each terminal 24 corresponds to the angle range R1.
- the connection line 26 extended from the stator 41 is connected to the terminal 24 via the cluster 72 inside the container upper portion 20b.
- the point P4 of the body 20a in the angle range R1 and the point P5 of the container upper portion 20b are aligned, and the point P6 of the body 20a and the point P7 of the container upper portion 20b on the opposite side are aligned.
- the container upper portion 20b is fixed to the body 20a by welding so as to cover the opening of the body 20a.
- each connecting line 26 is extended from the stator 41 The point is also on the point P4 side, that is, within the angle range R1. Therefore, each connection line 26 can be connected to each terminal 24 at the shortest.
- the compressor 12 can be assembled without causing the connecting wire 26 to extend in the container 20 without extending the connecting wire 26 more than necessary.
- the connecting line 26 is fixed when the take-out direction of the connecting line 26 connected to a certain terminal 24 is out of the angle range R1 and the body 20a and the container upper portion 20b are aligned.
- the connecting wire 26 or the other connecting wire 26 is extended more than necessary, and a slack occurs in the container 20.
- the second connection line 26b connected to the second terminal 24b is more than necessary because the extraction direction of the first connection line 26a connected to the first terminal 24a is outside the angle range R1.
- connection line 26 passes near the discharge pipe 22, the refrigeration oil 25 pumped up in the upper space of the container 20 is trapped in the connection line 26, enters the discharge pipe 22, and is discharged to the outside of the container 20 It becomes easy to be done.
- the refrigeration oil 25 is trapped in the band, and the refrigeration oil 25 is easily discharged out of the container 20.
- the first terminal 24 a and the second terminal 24 b each have three pins 71. It is desirable that the three pins 71 of the first terminal 24a and the second terminal 24b be disposed symmetrically with respect to the third straight line L3.
- At least one connection line 26 included in the plurality of connection lines 26 is connected to one terminal 24 included in the plurality of terminals 24 via the cluster 72.
- the first connection line 26 a and the second connection line 26 b are connected to each of the first terminal 24 a and the second terminal 24 b via the cluster 72.
- a cluster 72 configured by covering a metal connection terminal with a resin cover is used for connection between the connection wire 26 and the terminal 24 inside the container upper portion 20b. Since connection to the three pins 71 can be performed at one time, workability is improved. In order to prevent erroneous connection between the terminals 24, the cluster 72 may be used for some of the terminals 24 and only metal connection terminals may be used for the remaining terminals 24.
- the three pins 71 of the two terminals 24 are arranged symmetrically with respect to a straight line passing through the center of the discharge pipe 22 and the middle point of the terminal 24.
- the connection lines 26 connected to the three pins 71 of the terminal 24 are taken out in the direction approaching this straight line. Therefore, the connection line 26 can be taken out collectively in the vicinity of the point P4 of the trunk portion 20a and the point P5 of the container upper portion 20b. Therefore, the lengths of the connection lines 26 can be set to be uniform and minimum.
- Some connection wires 26 do not sag in the container 20, and the wire connection workability is improved. Parts sharing of the connection line 26 can also be achieved, reducing the cost of parts and increasing the part management efficiency.
- FIG. 12 shows the top of a portion of the compressor 12 as viewed in the axial direction D0, as in FIG.
- the plurality of power supply lines 27 are connected to the plurality of terminals 24 outside the container 20.
- the plurality of power supply lines 27 electrically connect the plurality of terminals 24 to the external power supply.
- the plurality of power supply lines 27 include a first power supply line 27a connected to the first terminal 24a and a second power supply line 27b connected to the second terminal 24b.
- a first power supply line 27a connected to the first terminal 24a
- a second power supply line 27b connected to the second terminal 24b.
- another power supply line 27 connected to the other terminal 24 is connected to the plurality of power supply lines 27. It may be included.
- each power supply line 27 following the end connected to each terminal 24 is taken out of the existing range R2 of each terminal 24 in plan view.
- the power supply line 27 extends from the end of a certain power supply line 27 connected to a certain terminal 24, and the power supply line 27 extends from the end of the existence range R2 of the terminal 24 in plan view. It is the position being taken out.
- each power supply line 27 is taken out from each terminal 24 may be any direction, but in the present embodiment, the first power supply line 27a is taken out in the direction away from the third straight line L3 in plan view.
- the line 27b is taken out in a direction approaching the third straight line L3. That is, the first power supply line 27a is taken out in the direction away from the third straight line L3 in plan view.
- the second power supply line 27b is extracted in a direction away from the third straight line L3 in plan view.
- the first power supply line 27a may be extracted in a direction approaching the third straight line L3 and the second power supply line 27b may be extracted in a direction away from the third straight line L3 in plan view.
- the first power supply line 27a and the second power supply line 27b may be taken out in a direction away from the third straight line L3.
- the power supply line 27 for supplying power is connected to the terminal 24 outside the container upper portion 20b.
- a plurality of power supply lines 27 are integrated as in the comparative example shown in FIG. It is desirable that the power supply lines 27 be separated and clearly distinguished even after the cover is attached. As shown in FIG. 12, erroneous connection can be prevented by extracting one of the power supply lines 27 in a direction away from the straight line passing through the center of the discharge pipe 22 and the middle points of the plurality of terminals 24.
- the angle range R1 is a second straight line passing through the center P0 of the container 20 and the center P1 of the first terminal 24a and the center P0 of the container 20 and the center P2 of the second terminal 24b in plan view. It is the range of 180 degrees or less which L2 makes.
- the connection wires 26 electrically connecting the terminals 24 and the motor 40 are taken out of the existing range R2 of the terminals 24 at a position within the angle range R1 in plan view. Therefore, the length of each connection line 26 can be shortened.
- the present embodiment even if there are more places where the terminal 24 provided in the container upper portion 20b and the discharge pipe 22 are close, when the inside of the container 20 becomes high in pressure, the space between the terminal 24 and the discharge pipe The stress is less likely to be concentrated in the region of (b), so deformation of the container 20 is less likely to occur. Leakage of refrigerant gas and breakage of the terminal 24 due to deformation of the container 20 can be prevented.
- the risk of disconnection due to contact with a structure rotating at high speed with the rotor 42 in the container 20 is reduced.
- the efficiency of the work of connecting the connecting wire 26 to the terminal 24 is increased.
- the first flat portion 81 where the terminal 24 is disposed is inclined with respect to a virtual vertical plane orthogonal to the axial direction D0.
- the distance between the discharge pipe 22 and the terminal 24 and the distance between the terminal 24 and the peripheral wall of the container 20 are extended. Therefore, even if the plurality of terminals 24 are provided while maintaining the outer diameter of the container 20, concentration of stress between the discharge pipe 22 and the terminals 24 is suppressed, and the container 20 is less likely to be deformed. That is, the strength of the container 20 can be secured.
- angle range R1 which connected the center of the container 20 and the center of the some terminal 24 in planar view is 180 degrees or less.
- the extraction direction of the connection line 26 is within the angle range R1.
- FIG. 14 shows a comparison result of the amount of deformation relative to the internal pressure of the container upper portion 20b of the present embodiment and the container upper portion of the comparative example.
- the load pressure was set to 5 MPa, the numerical analysis conditions were set, and the amount of deformation under load was calculated.
- the black bar graph is the variation of the present embodiment, and the white bar graph is the comparison of the comparative example.
- the amount of deformation of the upper portion of the container of the comparative example was 100%.
- the amount of deformation between the discharge pipe 22 and the terminal 24 of the container upper portion 20b is reduced to about 50% of that of the comparative example.
- the amount of deformation of the central portion of the terminal 24 is reduced to about 80% of that of the comparative example. It is considered that this is because the distance between the discharge pipe 22 and the terminal 24 is sufficiently maintained.
- one of the factors is that the first flat portion 81 in which the terminal 24 is disposed and the curved surface portion 83 in which the discharge pipe 22 is disposed are connected by the smooth concave portion 84.
- stress applied to the terminal 24 can be reduced, and refrigerant leakage due to a micro crack or the like of the glass portion of the terminal 24 can be suppressed. Even if a flammable refrigerant having a low global warming potential, including R290, is sealed in the container 20, the flammable refrigerant does not leak from the container 20, and safety is maintained.
- the container 20 is sufficiently strong, so safety can be maintained.
- the wedge-shaped hermetic container is press-fit into the release portion of the cylindrical hermetic container, and a discharge pipe is provided at the center It can be applied to cases.
- FIG. 15 shows a top view of a portion of the compressor 12 as viewed along the axial direction D0.
- the plurality of terminals 24 are collectively disposed in one first flat portion 81, but in the present embodiment, the plurality of terminals 24 are disposed in two or more first flat portions 81. It is divided and arranged.
- each first flat portion 81 has an oval shape such as an oval or a rounded rectangle.
- the edge of each first flat section 81 is connected to the curved section 83 by a smoothly curved recess 84. That is, the portion between the first flat surface portion 81 and the curved surface portion 83 is recessed.
- the recess 84 is formed thick and has a function as a rib for improving the strength.
- each first flat surface portion 81 is inclined at an inclination angle away from the virtual vertical plane as approaching the central axis of the container 20 along the two directions with respect to the virtual vertical plane.
- the entire first flat surface portion 81 is inclined at a first inclination angle ⁇ 1 with respect to the virtual vertical plane.
- a part including the end of the 1st direction D1 of each 1st plane part 81 is separated from an imaginary perpendicular plane as the central axis of container 20 is approached along with the 1st direction D1.
- the remaining portion including the other end of the first flat portion 81 in the first direction D1 is farther from the virtual vertical plane as it goes away from the central axis of the container 20 along the first direction D1.
- the first inclination angle ⁇ 1 is desirably 5 ° or more and 30 ° or less, and is 5 ° in the present embodiment.
- each first flat surface portion 81 including one end in the second direction D2 is farther from the virtual vertical plane as it approaches the central axis of the container 20 along the second direction D2.
- the remaining portion of each first flat portion 81 including the other end in the second direction D2 is farther from the virtual vertical plane as it goes away from the central axis of the container 20 along the second direction D2.
- the second inclination angle ⁇ 2 is desirably 5 ° or more and 30 ° or less, and is 10 ° in the present embodiment.
- At least one of the first inclination angle ⁇ 1 and the second inclination angle ⁇ 2 of the first flat surface portion 81 may be different for each first flat surface portion 81. That is, the inclination angle of the first flat portion 81 may be different for each of the terminals 24.
- the rods 28 are disposed on the lower side of the respective first flat portions 81.
- the rod 28 is provided to extend along the axial direction D0.
- the connecting wire 26 is integrated with the winding 44 of the motor 40. However, as shown in FIG. 16, the connecting wire 26 is connected to the winding 44 of the motor 40 via the connection terminal 47. It may be
- the body 20a and the container lower portion 20c of the container 20 are connected by welding, but as shown in FIG. 17, the body 20a and the container lower portion 20c of the container 20 are integrally formed. It is also good.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Thermal Sciences (AREA)
- Compressor (AREA)
- Applications Or Details Of Rotary Compressors (AREA)
Abstract
Description
冷媒を圧縮する圧縮機構と、
前記圧縮機構を駆動する電動機と、
前記圧縮機構と前記電動機とを収容する容器と、
第1端子および第2端子を含み、前記容器の軸方向一端に取り付けられ、平面視で、それぞれの中心が、前記容器の中心と前記第1端子の中心とを通る第1直線と、前記容器の中心と前記第2端子の中心とを通る第2直線とがなす180°以下の角度範囲内に位置する複数の端子と、
前記容器の中で前記複数の端子と前記電動機とを電気接続し、平面視で、前記複数の端子から前記角度範囲内に取り出されている複数の接続線とを備える。 A compressor according to one aspect of the present invention is
A compression mechanism for compressing a refrigerant;
An electric motor for driving the compression mechanism;
A container for containing the compression mechanism and the motor;
A first straight line including a first terminal and a second terminal and attached to one axial end of the container, the first straight line having a center passing through a center of the container and a center of the first terminal in plan view; A plurality of terminals located within an angle range of 180 ° or less formed by a second straight line passing through the center of the second terminal and the center of the second terminal;
The plurality of terminals and the motor are electrically connected in the container, and a plurality of connection lines extracted from the plurality of terminals in the angle range in plan view are provided.
本実施の形態について、図1から図14を用いて説明する。 Embodiment 1
The present embodiment will be described with reference to FIGS. 1 to 14.
図1および図2を参照して、本実施の形態に係る冷凍サイクル装置10の構成を説明する。 *** Description of the configuration ***
The configuration of a
図3および図4を参照して、本実施の形態に係る圧縮機12の動作を説明する。圧縮機12の動作は、本実施の形態に係る冷媒圧縮方法に相当する。 *** Description of operation ***
The operation of the
図3のほかに、図5から図13を参照して、本実施の形態に係る圧縮機12の構成の詳細を説明する。 *** Description of configuration details ***
The details of the configuration of the
角度範囲R1は、平面視で、容器20の中心P0と第1端子24aの中心P1とを通る第1直線L1と、容器20の中心P0と第2端子24bの中心P2とを通る第2直線L2とがなす180°以下の範囲である。本実施の形態では、各端子24と電動機40とを電気接続する各接続線26が、平面視で、角度範囲R1内の位置で各端子24の存在範囲R2外に取り出されている。そのため、各接続線26の長さを短くすることができる。 *** Description of the effects of the embodiment ***
The angle range R1 is a second straight line passing through the center P0 of the
本実施の形態は、縦置き型の圧縮機12だけでなく、横置き型の圧縮機において、椀形密閉容器が円筒型密閉容器の解放部に圧入され、中心に吐出管が設けられている場合に適用することができる。 *** Other configuration ***
In the present embodiment, not only the vertical-
本実施の形態について、主に実施の形態1との差異を、図15を用いて説明する。 Second Embodiment
The difference between this embodiment and the first embodiment will be mainly described with reference to FIG.
実施の形態1では、接続線26が電動機40の巻線44と一体になっているが、図16に示すように、接続線26が電動機40の巻線44に接続端子47を介して接続されていてもよい。 Third Embodiment
In the first embodiment, the connecting
実施の形態1では、容器20の胴部20aと容器下部20cとが溶接により連結されているが、図17に示すように、容器20の胴部20aと容器下部20cとが一体成形されていてもよい。 Fourth Embodiment
In the first embodiment, the
Claims (18)
- 冷媒を圧縮する圧縮機構と、
前記圧縮機構を駆動する電動機と、
前記圧縮機構と前記電動機とを収容する容器と、
第1端子および第2端子を含み、前記容器の軸方向一端に取り付けられ、平面視で、それぞれの中心が、前記容器の中心と前記第1端子の中心とを通る第1直線と、前記容器の中心と前記第2端子の中心とを通る第2直線とがなす180°以下の角度範囲内に位置する複数の端子と、
前記容器の中で前記複数の端子と前記電動機とを電気接続し、平面視で、前記複数の端子から前記角度範囲内に取り出されている複数の接続線とを備える圧縮機。 A compression mechanism for compressing a refrigerant;
An electric motor for driving the compression mechanism;
A container for containing the compression mechanism and the motor;
A first straight line including a first terminal and a second terminal and attached to one axial end of the container, the first straight line having a center passing through a center of the container and a center of the first terminal in plan view; A plurality of terminals located within an angle range of 180 ° or less formed by a second straight line passing through the center of the second terminal and the center of the second terminal;
The compressor electrically connects the plurality of terminals and the electric motor in the container, and includes a plurality of connection lines extracted from the plurality of terminals into the angular range in a plan view. - 前記複数の接続線は、平面視で、前記角度範囲内に配置されている請求項1に記載の圧縮機。 The compressor according to claim 1, wherein the plurality of connection lines are disposed within the angular range in a plan view.
- 前記複数の接続線には、前記第1端子と前記電動機とを電気接続する第1接続線と、前記第2端子と前記電動機とを電気接続する第2接続線とが含まれ、
前記第1接続線および前記第2接続線は、平面視で、前記容器の中心と、前記第1端子の中心と前記第2端子の中心との中点とを通る第3直線に近づく方向に取り出されている請求項1または2に記載の圧縮機。 The plurality of connection lines include a first connection line electrically connecting the first terminal and the motor, and a second connection line electrically connecting the second terminal and the motor.
The first connection line and the second connection line approach a third straight line passing through the center of the container, and the midpoint between the center of the first terminal and the center of the second terminal in plan view The compressor according to claim 1 or 2, which has been taken out. - 前記容器の外で前記複数の端子と接続されている複数の電源線をさらに備え、
前記複数の電源線には、前記第1端子と接続されている第1電源線と、前記第2端子と接続されている第2電源線とが含まれ、
前記第1電源線および前記第2電源線の少なくともいずれかは、平面視で、前記容器の中心と、前記第1端子の中心と前記第2端子の中心との中点とを通る第3直線から離れる方向に取り出されている請求項1または2に記載の圧縮機。 It further comprises a plurality of power supply lines connected to the plurality of terminals outside the container,
The plurality of power supply lines include a first power supply line connected to the first terminal and a second power supply line connected to the second terminal,
At least one of the first power supply line and the second power supply line is a third straight line passing through a center of the container, and a midpoint between the center of the first terminal and the center of the second terminal in plan view The compressor according to claim 1, wherein the compressor is taken out in the direction away from. - 前記第1端子および前記第2端子は、3本のピンをそれぞれ有し、
前記第1端子および前記第2端子の3本のピンは、前記第3直線に対して対称に配置されている請求項3または4に記載の圧縮機。 The first terminal and the second terminal each have three pins,
The compressor according to claim 3 or 4, wherein three pins of the first terminal and the second terminal are arranged symmetrically with respect to the third straight line. - 前記複数の接続線に含まれる少なくとも1つの接続線は、クラスタを介して前記複数の端子に含まれる1つの端子と接続されている請求項1から5のいずれか1項に記載の圧縮機。 The compressor according to any one of claims 1 to 5, wherein at least one connection line included in the plurality of connection lines is connected to one terminal included in the plurality of terminals via a cluster.
- 前記冷媒を前記容器の外に吐出するために、前記容器の軸方向一端で前記容器の中心軸と重なる位置に設けられている吐出管をさらに備え、
前記容器は、前記吐出管が配置されている曲面部と、前記複数の端子と前記電動機との間に位置する、前記容器の軸方向に垂直な仮想垂直面に対し、少なくとも1つの方向に沿って前記容器の中心軸に近づくにつれて前記仮想垂直面から離れる傾斜角度で傾斜し、前記複数の端子が配置されている1つ以上の平面部とを前記容器の軸方向一端に有する請求項1から6のいずれか1項に記載の圧縮機。 In order to discharge the refrigerant to the outside of the container, the container further includes a discharge pipe provided at a position overlapping with the central axis of the container at one axial end of the container,
The container extends in at least one direction with respect to a virtual vertical plane perpendicular to the axial direction of the container, which is located between the curved surface portion in which the discharge pipe is disposed, and the plurality of terminals and the motor. From one end in the axial direction of the container, with one or more flat portions inclined at an inclination angle away from the virtual vertical plane as the central axis of the container is approached, and one or more flat portions on which the plurality of terminals are disposed The compressor according to any one of 6. - 前記傾斜角度は、前記仮想垂直面に対して5°以上30°以下である請求項7に記載の圧縮機。 The compressor according to claim 7, wherein the inclination angle is 5 ° or more and 30 ° or less with respect to the virtual vertical plane.
- 前記1つ以上の平面部の、軸方向と直交する第1方向の一端を含む少なくとも一部は、前記仮想垂直面に対し、前記第1方向に沿って前記容器の中心軸に近づくにつれて前記仮想垂直面から離れる第1傾斜角度で傾斜し、
前記1つ以上の平面部の、軸方向および前記第1方向と直交する第2方向の一端を含む少なくとも一部は、前記仮想垂直面に対し、前記第2方向に沿って前記容器の中心軸に近づくにつれて前記仮想垂直面から離れる第2傾斜角度で傾斜している請求項7または8に記載の圧縮機。 At least a portion of the one or more flat portions including one end in a first direction orthogonal to the axial direction with respect to the virtual vertical plane, as the virtual axis approaches the central axis of the container along the first direction Tilt at a first tilt angle away from the vertical plane,
At least a portion of the one or more flat portions, including one end in the second direction orthogonal to the first direction and the axial direction, is a central axis of the container along the second direction with respect to the virtual vertical plane. The compressor according to claim 7 or 8, wherein the compressor is inclined at a second inclination angle away from the virtual vertical plane as it approaches. - 前記第2傾斜角度は、前記第1傾斜角度とは異なる請求項9に記載の圧縮機。 The compressor according to claim 9, wherein the second tilt angle is different from the first tilt angle.
- 前記複数の端子は、1つの平面部に纏めて配置されている請求項7から10のいずれか1項に記載の圧縮機。 The compressor according to any one of claims 7 to 10, wherein the plurality of terminals are arranged in one flat portion.
- 前記複数の端子は、2つ以上の平面部に分けて配置されている請求項7から10のいずれか1項に記載の圧縮機。 The compressor according to any one of claims 7 to 10, wherein the plurality of terminals are divided into two or more flat portions.
- 前記容器は、前記仮想垂直面からの最大距離が前記1つ以上の平面部よりも近く、前記複数の端子とは別の付属品が配置されている別の平面部を前記容器の軸方向一端に有する請求項7から12のいずれか1項に記載の圧縮機。 The container may have another flat surface located at the maximum distance from the virtual vertical plane closer to the one or more flat surface portions and an accessory different from the plurality of terminals disposed, the one axial direction end of the container The compressor according to any one of claims 7 to 12, wherein
- 前記複数の端子を覆うためのカバーが取り付けられるロッドをさらに備え、
前記容器は、前記ロッドが配置されている別の平面部を前記容器の軸方向一端に有する請求項7から12のいずれか1項に記載の圧縮機。 It further comprises a rod to which a cover for covering the plurality of terminals is attached,
The compressor according to any one of claims 7 to 12, wherein the container has another flat portion in which the rod is disposed at one axial end of the container. - 前記吐出管は、リング材を介して前記曲面部に接合され、前記容器の中で前記リング材よりも前記圧縮機構に近い位置まで延びている請求項7から14のいずれか1項に記載の圧縮機。 The discharge pipe according to any one of claims 7 to 14, wherein the discharge pipe is joined to the curved surface portion via a ring member and extends to a position closer to the compression mechanism than the ring member in the container. Compressor.
- 前記容器の軸方向一端は、平面視円形状であり、
前記吐出管の外径は、前記容器の軸方向一端の外径の0.1倍以上である請求項7から15のいずれか1項に記載の圧縮機。 One axial end of the container is circular in plan view,
The compressor according to any one of claims 7 to 15, wherein an outer diameter of the discharge pipe is equal to or greater than 0.1 times an outer diameter of one axial end of the container. - 各接続線の、各端子と接続されている端に続く部分は、平面視で、前記角度範囲内の位置で各端子の存在範囲外に取り出されている請求項1から16のいずれか1項に記載の圧縮機。 The part following each end of each connecting wire connected to each terminal is taken out of the existing range of each terminal at a position within the angle range in a plan view. The compressor as described in.
- 請求項1から17のいずれか1項に記載の圧縮機を備える冷凍サイクル装置。 A refrigeration cycle apparatus comprising the compressor according to any one of claims 1 to 17.
Priority Applications (5)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CZ202011A CZ309325B6 (en) | 2017-08-09 | 2017-08-09 | Compressor and refrigeration cycle equipment |
| PCT/JP2017/028883 WO2019030841A1 (en) | 2017-08-09 | 2017-08-09 | Compressor and refrigeration cycle device |
| KR1020207001824A KR102320908B1 (en) | 2017-08-09 | 2017-08-09 | Compressors and refrigeration cycle units |
| CN201780093649.4A CN111033052B (en) | 2017-08-09 | 2017-08-09 | Compressor and refrigeration cycle device |
| JP2019535491A JP6746000B2 (en) | 2017-08-09 | 2017-08-09 | Compressor and refrigeration cycle device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2017/028883 WO2019030841A1 (en) | 2017-08-09 | 2017-08-09 | Compressor and refrigeration cycle device |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2019030841A1 true WO2019030841A1 (en) | 2019-02-14 |
Family
ID=65272144
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2017/028883 WO2019030841A1 (en) | 2017-08-09 | 2017-08-09 | Compressor and refrigeration cycle device |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6746000B2 (en) |
| KR (1) | KR102320908B1 (en) |
| CN (1) | CN111033052B (en) |
| CZ (1) | CZ309325B6 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2019030841A1 (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPWO2021181463A1 (en) * | 2020-03-09 | 2021-09-16 | ||
| US20220127507A1 (en) * | 2019-02-11 | 2022-04-28 | Mexichem Fluor S.A. De C.V. | Compositions |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20020075665A1 (en) * | 2000-12-07 | 2002-06-20 | Kwang-Woo Jang | Shielding cover for terminal device of electric appliance and compressor assembly having the same |
| JP2009108837A (en) * | 2007-11-01 | 2009-05-21 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | Compressor |
| JP2012082776A (en) * | 2010-10-13 | 2012-04-26 | Toshiba Carrier Corp | Hermetic compressor and refrigeration cycle device |
| JP2012237266A (en) * | 2011-05-13 | 2012-12-06 | Hitachi Appliances Inc | Hermetic electric compressor |
Family Cites Families (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5117218B2 (en) * | 2008-02-18 | 2013-01-16 | 東芝キヤリア株式会社 | Hermetic compressor and refrigeration cycle apparatus |
| JP2010053786A (en) | 2008-08-28 | 2010-03-11 | Toshiba Carrier Corp | Hermetic compressor and refrigerating cycle device |
| JP4964288B2 (en) * | 2009-11-18 | 2012-06-27 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Compressor |
| CN201621038U (en) * | 2010-02-25 | 2010-11-03 | 东芝开利株式会社 | Compressor and refrigeration circulation apparatus employing the same |
| JP2011229221A (en) * | 2010-04-16 | 2011-11-10 | Hitachi Appliances Inc | Hermetic type electric compressor and refrigeration cycle device |
| CN102352830B (en) * | 2011-10-28 | 2014-06-18 | 黄石东贝电器股份有限公司 | Sealed compressor shell |
| JP6109063B2 (en) * | 2013-12-26 | 2017-04-05 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Hermetic compressor |
-
2017
- 2017-08-09 CN CN201780093649.4A patent/CN111033052B/en active Active
- 2017-08-09 WO PCT/JP2017/028883 patent/WO2019030841A1/en active Application Filing
- 2017-08-09 KR KR1020207001824A patent/KR102320908B1/en active IP Right Grant
- 2017-08-09 CZ CZ202011A patent/CZ309325B6/en unknown
- 2017-08-09 JP JP2019535491A patent/JP6746000B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20020075665A1 (en) * | 2000-12-07 | 2002-06-20 | Kwang-Woo Jang | Shielding cover for terminal device of electric appliance and compressor assembly having the same |
| JP2009108837A (en) * | 2007-11-01 | 2009-05-21 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | Compressor |
| JP2012082776A (en) * | 2010-10-13 | 2012-04-26 | Toshiba Carrier Corp | Hermetic compressor and refrigeration cycle device |
| JP2012237266A (en) * | 2011-05-13 | 2012-12-06 | Hitachi Appliances Inc | Hermetic electric compressor |
Cited By (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20220127507A1 (en) * | 2019-02-11 | 2022-04-28 | Mexichem Fluor S.A. De C.V. | Compositions |
| US12018203B2 (en) * | 2019-02-11 | 2024-06-25 | Mexichem Fluor S.A. De C.V. | Heat transfer compositions |
| JPWO2021181463A1 (en) * | 2020-03-09 | 2021-09-16 | ||
| WO2021181463A1 (en) * | 2020-03-09 | 2021-09-16 | 東芝キヤリア株式会社 | Compressor and refrigeration cycle device |
| CN115103962A (en) * | 2020-03-09 | 2022-09-23 | 东芝开利株式会社 | Compressor and refrigeration cycle device |
| EP4119796A4 (en) * | 2020-03-09 | 2023-10-11 | Toshiba Carrier Corporation | Compressor and refrigeration cycle device |
| JP7405946B2 (en) | 2020-03-09 | 2023-12-26 | 東芝キヤリア株式会社 | Compressor and refrigeration cycle equipment |
| CN115103962B (en) * | 2020-03-09 | 2024-07-02 | 东芝开利株式会社 | Compressor and refrigeration cycle device |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR102320908B1 (en) | 2021-11-03 |
| CZ309325B6 (en) | 2022-08-24 |
| CN111033052A (en) | 2020-04-17 |
| CZ202011A3 (en) | 2020-06-17 |
| JP6746000B2 (en) | 2020-08-26 |
| JPWO2019030841A1 (en) | 2019-11-07 |
| KR20200020860A (en) | 2020-02-26 |
| CN111033052B (en) | 2021-12-10 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP2199615B1 (en) | Motor for compressor, compressor, and refrigerating cycle apparatus | |
| WO2019102574A1 (en) | Electric motor, compressor, and refrigeration cycle device | |
| CN105545746A (en) | Compressor manufacturing device and compression manufacturing method | |
| JP6746000B2 (en) | Compressor and refrigeration cycle device | |
| JP6752376B2 (en) | Compressor and refrigeration cycle equipment | |
| JP6407432B2 (en) | Compressor and refrigeration cycle apparatus | |
| CN108475955B (en) | Motor, compressor, refrigeration cycle device, and method for manufacturing motor | |
| CN207039313U (en) | Stator, motor, compressor and refrigerating circulatory device | |
| CN106981935B (en) | Stator core, compressor, and refrigeration cycle device | |
| WO2017098567A1 (en) | Compressor and refrigeration cycle device | |
| WO2021229742A1 (en) | Electric motor, compressor, and refrigeration cycle device | |
| US11378080B2 (en) | Compressor | |
| WO2022137492A1 (en) | Rotor, electric motor, compressor, refrigeration cycle device, and air conditioning device | |
| JP6878443B2 (en) | Rotary compressor and refrigeration cycle equipment | |
| JP2016021837A (en) | Motor and compressor |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 17920875 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2019535491 Country of ref document: JP Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 20207001824 Country of ref document: KR Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 17920875 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |