WO2019003340A1 - Position detection system - Google Patents
Position detection system Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2019003340A1 WO2019003340A1 PCT/JP2017/023738 JP2017023738W WO2019003340A1 WO 2019003340 A1 WO2019003340 A1 WO 2019003340A1 JP 2017023738 W JP2017023738 W JP 2017023738W WO 2019003340 A1 WO2019003340 A1 WO 2019003340A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- vibration
- detection unit
- work
- signal
- unit
- Prior art date
Links
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 238
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 claims description 27
- 238000010801 machine learning Methods 0.000 claims description 7
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 37
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 20
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 10
- 230000001133 acceleration Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000969 carrier Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000007796 conventional method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000006073 displacement reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W4/00—Services specially adapted for wireless communication networks; Facilities therefor
- H04W4/70—Services for machine-to-machine communication [M2M] or machine type communication [MTC]
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G05—CONTROLLING; REGULATING
- G05B—CONTROL OR REGULATING SYSTEMS IN GENERAL; FUNCTIONAL ELEMENTS OF SUCH SYSTEMS; MONITORING OR TESTING ARRANGEMENTS FOR SUCH SYSTEMS OR ELEMENTS
- G05B19/00—Programme-control systems
- G05B19/02—Programme-control systems electric
- G05B19/418—Total factory control, i.e. centrally controlling a plurality of machines, e.g. direct or distributed numerical control [DNC], flexible manufacturing systems [FMS], integrated manufacturing systems [IMS] or computer integrated manufacturing [CIM]
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06Q—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES; SYSTEMS OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G06Q10/00—Administration; Management
- G06Q10/06—Resources, workflows, human or project management; Enterprise or organisation planning; Enterprise or organisation modelling
- G06Q10/063—Operations research, analysis or management
- G06Q10/0631—Resource planning, allocation, distributing or scheduling for enterprises or organisations
- G06Q10/06311—Scheduling, planning or task assignment for a person or group
- G06Q10/063114—Status monitoring or status determination for a person or group
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W4/00—Services specially adapted for wireless communication networks; Facilities therefor
- H04W4/02—Services making use of location information
- H04W4/029—Location-based management or tracking services
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a position detection system that detects the position of a movable body on which a work object is placed and the work state of the movable body or the work object placed on the movable body.
- Patent Document 1 As a device for detecting the position of a worker, for example, a device disclosed in Patent Document 1 is known.
- the position of the worker is detected using an ultrasonic transmitter mounted on a helmet of the worker and an ultrasonic receiver installed on an industrial vehicle.
- the present invention has been made to solve the above-described problems, and an object of the present invention is to provide a position detection system capable of detecting an operation state without putting a burden on the operator.
- a position detection system is attached to a movable body on which a work object is placed, detects a vibration, and transmits a signal having vibration information indicating the detected vibration and identification information;
- the transmitter of the signal is attached from a transmitter attached to the mobile body and periodically transmitting a signal having identification information, a plurality of receivers receiving the signal, and identification information of the signal received by the receiver.
- a position detection unit that detects the position of a transmitter that is a transmission source of the signal from the identification unit that identifies, the reception strength of the signal received by the receiver, and the identification result by the identification unit, and the signal received by the receiver From the vibration information possessed by the identification unit, the identification result by the identification unit and the detection result by the position detection unit, the mobile unit attached with the vibration detection unit that is the transmission source of the signal or the work object mounted on the mobile unit Characterized in that a work state detection unit that detects a working state that.
- the position detection system which concerns on Embodiment 1 of this invention WHEREIN It is a figure explaining the case where a working state is detected by a vibration pattern.
- the position detection system which concerns on Embodiment 1 of this invention WHEREIN It is a figure explaining the case where a working state is detected by a vibration pattern, and is a figure which shows the case where a vibration pattern is registered for every process.
- the position detection system which concerns on Embodiment 1 of this invention WHEREIN It is a figure explaining the case where a working state is detected by a vibration pattern, and is a figure which shows the case where the vibration pattern for every process is changed.
- FIGS. 15A and 15B are diagrams showing an example of a hardware configuration of a control device according to Embodiment 1-4 of the present invention.
- FIG. 1 is a view showing a configuration example of a position detection system according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention.
- the position detection system detects the position of a carriage (mobile body) 12 on which a work object 11 (see FIG. 6 etc.) such as a product is placed at a production site, and places the carriage 12 or the carriage 12 on it. The work state of the worker with respect to the work object 11 thus detected is detected.
- one or more carriages 12 are used at a production site.
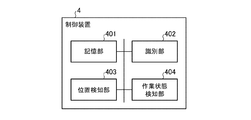
- the position detection system includes a vibration detection unit 1, a transmitter 2, a plurality of receivers 3, and a control device 4. In the example of FIG. 1, two receivers 3 are shown.
- the vibration detection unit 1 is attached to the carriage 12 and detects vibration. Then, each time the vibration detection unit 1 detects a vibration, the vibration detection unit 1 transmits a signal including vibration information indicating the detected vibration and identification information for identifying itself (the vibration detection unit 1) to the outside.
- the signal transmitted from the vibration detection unit 1 is set to have a high radio wave intensity so that the receiver 3 does not miss it.
- a vibration sensor is mentioned, for example.
- the transmitter 2 is attached to the carriage 12 and periodically (for example, every 0.5 seconds) transmits a signal having identification information for identifying itself (the transmitter 2) to the outside.
- the receiver 3 receives a signal.
- the receiver 3 is disposed, for example, for each process at a production site.
- the control device 4 processes the reception result by the receiver 3.
- the control device 4 includes a storage unit 401, an identification unit 402, a position detection unit 403, and a work state detection unit 404.
- the storage unit 401 stores identification information of the vibration detection unit 1 and the transmitter 2.
- the storage unit 401 also stores the correspondence between the vibration detection unit 1 and the transmitter 2.
- the storage unit 401 is, for example, a nonvolatile or volatile semiconductor memory such as a random access memory (RAM), a read only memory (ROM), a flash memory, an EPROM (erasable programmable ROM), an EEPROM (electrically EPROM), or the like.
- RAM random access memory
- ROM read only memory
- flash memory an EPROM (erasable programmable ROM), an EEPROM (electrically EPROM), or the like.
- Magnetic disks flexible disks, optical disks, compact disks, mini disks, DVDs (Digital Versatile Disc), etc.
- the identification unit 402 identifies the transmission source of the signal from the identification information included in the signal received by the receiver 3. At this time, the identification unit 402 identifies the transmission source of the signal by collating the identification information of the signal received by the receiver 3 with the identification information stored in the storage unit 401.
- the position detection unit 403 detects the position of the transmitter 2 that is the transmission source of the signal from the reception strength of the signal received by the receiver 3 and the identification result by the identification unit 402. At this time, the position detection unit 403 first specifies the receiver 3 with the highest reception strength of the signal from the transmitter 2 that is the detection target identified by the identification unit 402 among the plurality of receivers 3. Then, the position detection unit 403 detects an area (for example, a process) in which the specified receiver 3 is arranged as the position of the transmitter 2.
- the work state detection unit 404 is attached with the vibration detection unit 1 that is a transmission source of the signal from the vibration information included in the signal received by the receiver 3, the identification result by the identification unit 402, and the detection result by the position detection unit 403.
- the working condition of the work vehicle 11 or the work object 11 placed on the work vehicle 12 is detected by the worker.
- the work state detection unit 404 includes vibration information included in the signal from the vibration detection unit 1 as a detection target identified by the identification unit 402 and a transmitter attached to the same carriage 12 as the vibration detection unit 1.
- the work state is detected from the position 2.
- the production line method at the production site is the cell production method.
- a plurality of processes are provided.
- one or a plurality of workers are arranged for one or a plurality of processes, and the workers perform the work on the work object 11 placed on the carriage 12.
- bogie 12 is decided for every process.
- the dolly 12 may be moved to the next process by the worker who has performed the work in the previous process, or may be withdrawn from the previous process by the worker who performs the work in the next process.
- the operator sets the parts if necessary to mount the parts, and then takes a tool to perform work. The worker may work without moving and may work while moving around the carriage 12.
- the storage unit 401 stores in advance identification information of the vibration detection unit 1 and the transmitter 2 and the correspondence between the vibration detection unit 1 and the transmitter 2. Further, one set of the vibration detection unit 1 and the transmitter 2 are attached to the carriage 12. For example, two vibration sensors having the functions of vibration detection and position beacon can be used as one set of the vibration detection unit 1 and the transmitter 2. Then, the vibration detection unit 1 detects a vibration and transmits a signal including vibration information and identification information indicating the detected vibration to the outside. The transmitter 2 periodically transmits a signal having identification information to the outside. Also, a plurality of receivers 3 are arranged for each process and receive signals.
- the identification unit 402 first identifies the transmission source of the signal from the identification information possessed by the signal received by the receiver 3 (step ST401). At this time, the identification unit 402 identifies the transmission source of the signal by collating the identification information of the signal received by the receiver 3 with the identification information stored in the storage unit 401.
- the position detection unit 403 detects the position of the transmitter 2 that is the transmission source of the signal from the reception strength of the signal received by the receiver 3 and the identification result by the identification unit 402 (step ST402). At this time, the position detection unit 403 first specifies the receiver 3 with the highest reception strength of the signal from the transmitter 2 that is the detection target identified by the identification unit 402 among the plurality of receivers 3. Then, the position detection unit 403 detects, as the position of the transmitter 2, the process in which the specified receiver 3 is arranged. As described above, the transmitter 2 periodically transmitting a signal is attached to the carriage 12 and the plurality of receivers 3 are arranged at the production site, so that the control device 4 receives the signal of the signal received by the receiver 3.
- the position of the transmitter 2 can be detected from the reception intensity. Therefore, the control device 4 can detect the position of the carriage 12 to which the transmitter 2 is attached. In addition, when the control device 4 determines that the bogie 12 has stopped at the stop position of the process, the control device 4 can instruct the operator to start the operation by displaying (screen display or light) or by voice.
- the work state detection unit 404 also receives the vibration information of the signal received by the receiver 3, the identification result by the identification unit 402, and the detection result by the position detection unit 403, the vibration detection unit 1 that is the transmission source of the signal.
- the work condition by the worker with respect to the mounted carriage 12 or the work object 11 placed on the carriage 12 is detected (step ST403).
- the work state detection unit 404 includes vibration information included in the signal from the vibration detection unit 1 as a detection target identified by the identification unit 402 and a transmitter attached to the same carriage 12 as the vibration detection unit 1.
- the work state is detected from the position 2.
- the vibration detection unit 1 for detecting the vibration is attached to the carriage 12, so that the control device 4 detects the vibration detected by the vibration detection unit 1 and the detection result by the position detection unit 403.
- the presence or absence of movement or the presence or absence of work on the work object 11 placed on the carriage 12 can be detected.
- FIG. 5 shows the result of reception of signals by the receiver 3 arranged in a specific process.
- the horizontal axis indicates time, and the vertical axis indicates reception intensity.
- reference numeral 501 indicates a signal transmitted by the transmitter 2 attached to the specific carriage 12.
- Reference numeral 502 denotes vibration (acceleration) in the x-axis direction detected by the vibration detection unit 1 attached to the specific carriage 12, and reference numeral 503 denotes vibration in the y-axis direction detected by the vibration detection unit 1.
- the (acceleration) is shown, and reference numeral 504 indicates the vibration (acceleration) in the z-axis direction detected by the vibration detection unit 1.
- the position detection unit 403 determines that the specific carriage 12 is not positioned in the specific process. In the time zone 505, the vibrations 502 to 504 are detected by the vibration detection unit 1. Therefore, the work state detection unit 404 determines that the cart 12 is moving from the detection result of the position detection unit 403 and the vibrations 502 to 504. On the other hand, in the time zone 506, since the reception intensity of the signal 501 by the receiver 3 is high, the position detection unit 403 determines that the specific truck 12 is located in the specific process. Further, in the time zone 506, the vibrations 502 to 504 are detected by the vibration detection unit 1. Therefore, the work state detection unit 404 determines from the detection result of the position detection unit 403 and the vibrations 502 to 504 that the work on the work object 11 placed on the carriage 12 is being performed.
- the work state detection unit 404 may detect the work state in consideration of the displacement of the reception intensity of the signal 501.
- the control device 4 manage progress at the production site.
- the control device 4 uses three receivers 12-1 to 12-3 or corresponding carriers 12-1 using the receivers 3-1 to 3-4 respectively disposed in the first to fourth steps.
- a case of detecting the work state of the work object 11 placed on the positions .about.12-3 is shown.
- the upper part in FIG. 6 is mounted on the positional relationship between the receivers 3-1 to 3-4 and the carriages 12-1 to 12-3 and the carriages 12-1 to 12-3 or the carriages 12-1 to 12-3.
- the work state for the work object 11 is shown.
- the lower part in FIG. 6 shows the reception results of the signals by the receivers 3-1 to 3-4.
- the receiver 3-1 disposed in the first step and the receiver 3-2 disposed in the second step indicate the vibrations detected by the vibration detection unit 1 attached to the carriage 12-1.
- a signal including vibration information and a signal transmitted by the transmitter 2 are received.
- the reception strength of the signal from the transmitter 2 gradually decreases, and in the receiver 3-2, the reception strength of the signal from the transmitter 2 gradually increases. That is, from the reception result by the receiver 3-1 and the receiver 3-2, vibration is detected by the vibration detection unit 1 attached to the carriage 12-1, and the carriage 12-1 is separated from the receiver 3-1. Also, it can be seen that the receiver 3-2 is approaching. Therefore, the control device 4 determines that the carriage 12-1 is moving from the first process side to the second process side.
- the receiver 3-3 arranged in the third step and the receiver 3-4 arranged in the fourth step detect the vibration detected by the vibration detection unit 1 attached to the carriage 12-2.
- a signal including vibration information shown and a signal transmitted by the transmitter 2 are received.
- the reception strength of the signal in the receiver 3-3 is the same as that in the receiver 3-4.
- High for received signal strength That is, from the reception result by the receiver 3-3 and the receiver 3-4, the vibration is detected by the vibration detection unit 1 attached to the truck 12-2, and the truck 12-2 is close to the receiver 3-3 And it can be seen that it is far from the receiver 3-4. Therefore, the control device 4 determines that work is being performed on the work object 11 placed on the carriage 12-2 in the third step.
- the receiver 3-4 disposed in the fourth step receives a signal transmitted by the transmitter 2 attached to the carriage 12-3, and the reception intensity is high.
- the receiver 3-4 does not receive the signal from the vibration detection unit 1 attached to the carriage 12-3. That is, from the reception result by the receiver 3-4, it is understood that the vibration is not detected by the vibration detection unit 1 attached to the carriage 12-3, and the carriage 12-3 is close to the receiver 3-4. Therefore, the control device 4 determines that the dolly 12-3 is stopped in the fourth step.
- the vibration detection unit 1 is attached to the carriage 12 to detect vibration and transmits a signal having vibration information and identification information indicating the detected vibration, and the carriage 12 From the transmitter 2 for transmitting a signal having identification information periodically, the plurality of receivers 3 for receiving the signal, and the identification information of the signal received by the receiver 3, the transmission source of the signal And a position detection unit 403 for detecting the position of the transmitter 2 that is the transmission source of the signal from the reception strength of the signal received by the receiver 3 and the identification result by the identification unit 402; From the vibration information possessed by the signal received by the machine 3, the identification result by the identification unit 402 and the detection result by the position detection unit 403, the carriage 12 to which the vibration detection unit 1 as the transmission source of the signal is attached Since a work state detection unit 404 for detecting the working state for the work object 11 placed on ⁇ wheel 12, and can detect the work state. Further, since the vibration detection unit 1 and the transmitter 2 are attached to the carriage 12, the burden on the worker is reduced compared to the prior
- the production line system in a production field is a cell production system, and the trolley
- the present invention is not limited to this, as long as the mobile object is one on which the work object 11 is placed.
- the production line system is the line production system and a belt conveyor is used as the movable body, the position detection system according to the first embodiment can be applied.
- the position detection unit 403 identifies the receiver 3 having the highest reception strength of the signal from the transmitter 2 which is the detection target identified by the identification unit 402 among the plurality of receivers 3, and identifies the receiver 3 The case where the area where the receiver 3 is placed is detected as the position of the transmitter 2 is shown. However, not limited to this, the position detection unit 403 may detect the position of the transmitter 2 based on the difference in the reception intensity of the signal from the transmitter 2 in the plurality of receivers 3. As described above, position detection using the plurality of receivers 3 enables more detailed position detection in the area.
- the work state detection unit 404 may detect the work state by machine learning using a vibration pattern indicated by vibration information included in the signal received by the receiver 3. In this case, the work state detection unit 404 machine-learns a vibration pattern from the vibration detected by the vibration detection unit 1 in advance when the corresponding work is performed by the manager (the length of the work place or the like). . As a result, the work state detection unit 404 can detect the contents of the work on the work object 11.
- the work state detection unit 404 performs work state detection using a vast number of vibration patterns.
- FIG. 7 shows a case where a plurality of steps (first to ninth) exist and 45 operations are performed in total, and the operation state detection unit 404 uses 45 vibration patterns in each step. It shows the case where the operation state detection is performed. In this case, the process in the work state detection unit 404 takes time.
- the work content to be performed for each process and the corresponding vibration pattern are associated and registered.
- the number of vibration patterns used in each process can be reduced, and the processing in the work state detection unit 404 can be shortened.
- FIG. 8 shows the case where, in the work state detection unit 404, the three work contents performed in the first step and the corresponding vibration patterns are linked and registered.
- the work content and vibration pattern for each process registered in the work state detection unit 404 may be changed. This makes it possible to change the work performed in a certain process to the work in another process according to the work load on the current day.
- the example shown in FIG. 9 shows a case where the 45th operation (compressor screw tightening) performed in the first step is changed as performed in the second step.
- FIG. 10 is a diagram showing an example of a configuration of the transmission side (functional units excluding the receiver 3 and the control device 4) in the position detection system according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention, and FIG. It is a figure which shows the structural example of the control apparatus 4 in.
- a plurality of vibration detection units (second vibration detection units) 1b are provided to the position detection system according to the first embodiment shown in FIGS. , And a work position determination unit 405 is added.
- the other configurations are the same, the same reference numerals are given, and only different portions will be described.
- a plurality of vibration detection units 1b are attached to the work object 11, and detect vibrations. Then, each time the vibration detection unit 1 b detects a vibration, the vibration detection unit 1 b transmits a signal including vibration information indicating the detected vibration and identification information for identifying itself (the vibration detection unit 1 b) to the outside.
- the signal transmitted by the vibration detection unit 1 b is set to have a high radio wave intensity so that the receiver 3 does not miss it.
- a vibration sensor is mentioned, for example. In the example of FIG. 10, two vibration detection units 1b are shown.
- the storage unit 401 stores the identification information of the vibration detection unit 1, the vibration detection unit 1b, and the transmitter 2, and the correspondence between the vibration detection unit 1, the vibration detection unit 1b, and the transmitter 2.
- the work position determination unit 405 is attached with the vibration detection unit 1b that is a transmission source of the signal from the vibration information included in the signal received by the receiver 3, the identification result by the identification unit 402, and the detection result by the position detection unit 403. It is determined whether the work position for the work target 11 is correct.
- the work position determination unit 405 performs the above determination by machine learning.
- the work position determination unit 405 includes vibration information included in the signal from the vibration detection unit 1b which is the determination target identified by the identification unit 402, and a transmitter attached to the same carriage 12 as the vibration detection unit 1b. From the position of 2, it is determined whether the work position for the work object 11 is correct.
- the work position determination unit 405 detects the vibration detection unit 1b in advance when work is performed at a correct work position by a manager (the length of a production site, etc.) and when work is performed at a wrong work position. Machine learning the vibration pattern from the detected vibration.
- control device 4 detects an operation on work object 11 based on the signal received by receiver 3 (step ST1201). ).
- the process in step ST1201 is realized by the process shown in FIG.
- the work position determination unit 405 transmits the vibration detection unit 1b that is the transmission source of the signal.
- a work position for the attached work object 11 is specified (step ST1202).
- step ST1203 determines whether the work position is correct (step ST1203).
- step ST1203 when the work position determination unit 405 determines that the work position is correct, the sequence ends. Thereafter, the work position determination unit 405 shifts to work position determination for the next work.
- the work position determination unit 405 determines that the work position is incorrect in step ST1203, the fact is notified to the outside by display or voice.
- the plurality of vibration detection units 1b for detecting vibrations can determine whether the screw tightening position is correct or not based on the combination of the vibration patterns detected by the vibration detection unit 1 b.
- the work is repeated a plurality of times in advance, and the work position determination unit 405 performs machine learning of the vibration pattern, so that the vibration pattern can be standardized.
- the vibration detection unit 1b is attached to the work object 11, detects vibration, and transmits a signal having vibration information indicating the detected vibration and identification information; From the vibration information included in the signal received by the receiver 3, the identification result by the identification unit 402, and the detection result by the position detection unit 403, the operation for the work object 11 to which the vibration detection unit 1b as the transmission source of the signal is attached Since the work position determination unit 405 that determines whether the position is correct or not is provided, in addition to the effects of the first embodiment, it is possible to detect whether the worker is working at the correct work position.
- the work position determination unit 405 shows the case of determining whether the work position is correct.
- the present invention is not limited to this, and in addition to the above, the work position determination unit 405 may determine whether the number or order of work is correct.
- the transmitter 2 is attached to the carriage 12, the plurality of receivers 3 are disposed at the production site, and the position detection unit 403 transmits the transmitter based on the reception intensity of the signals received by the plurality of receivers 3. The case of detecting the position of 2 was shown.
- the sheet-like uneven portion 5 is provided on the ground on which the carriage 12 moves, and the position detection unit 403 b detects the vibration pattern generated when the carriage 12 moves over the uneven portion 5. A method of detecting the position of the carriage 12 will be described. FIG.
- FIG. 13 is a diagram showing an example of a configuration of the transmitting side (functional units excluding the receiver 3 and the control device 4) in the position detection system according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention, and FIG. It is a figure which shows the structural example of the control apparatus 4 in.
- the transmitter 2 is removed from the position detection system according to the first embodiment shown in FIGS.
- the position detection unit 403 is changed to a position detection unit 403b.
- a plurality of receivers 3 may be used as a single receiver 3.
- the other configuration is the same, and the same reference numerals are given and the description thereof is omitted.
- the uneven portion 5 is a sheet-like member having an uneven pattern and disposed on the ground on which the carriage 12 moves.
- the uneven pattern is configured in a pattern that can identify the position of the carriage 12.
- the position detection unit 403 b detects the position of the vibration detection unit 1 that is the transmission source of the signal from the vibration information included in the signal received by the receiver 3 and the identification result by the identification unit 402.
- the position detection unit 403 b performs the above detection by machine learning.
- the position detection unit 403 b detects the position of the vibration detection unit 1 from the vibration information included in the signal from the vibration detection unit 1 that is the detection target identified by the identification unit 402.
- the position detection unit 403 b performs machine learning of the vibration pattern from the vibration detected by the vibration detection unit 1 in advance when the bogie 12 moves on the uneven portion 5 by the manager (the length of the production site or the like).
- the uneven portion 5 is provided on the ground on which the carriage 12 moves, and the position detection unit 403 b uses the pattern of vibration detected by the vibration detection unit 1 when the carriage 12 moves on the uneven portion 5.
- the present embodiment is configured to detect the position of 12, the position of the carriage 12 and the working condition of the carriage 12 or the work object 11 with the single vibration detection unit 1 with respect to the first embodiment without using the transmitter 2 And can be detected. This also improves the maintainability of the position detection system. That is, in the sensors such as the vibration detection unit 1 and the transmitter 2, a button battery may be used. In this case, battery replacement is required. In particular, the transmitter 2 used as a position beacon tends to be depleted in battery.
- parameter setting for functioning as vibration detection or a position beacon is required, respectively. Therefore, by using only the single vibration detection unit 1 without using the transmitter 2, the frequency of battery replacement and the number of setting parameters can be suppressed, and the maintainability is improved.
- the vibration detection unit 1 is attached to the carriage 12, and in the second embodiment, the vibration detection unit 1 b is attached to the work object 11.
- a vibration detection unit similar to the vibration detection units 1 and 1b may be attached to a worker or a tool to perform progress management at a production site.
- the vibration detection unit when the vibration detection unit is attached to the arm of the worker and parts are insufficient in the assembly process, the vibration detection unit detects the vibration by causing the worker to perform a predetermined operation (such as shaking) of the arm. Then, the control device 4 recognizes the shortage of parts from the pattern of the vibration and notifies the outside by display or voice. Further, for example, the vibration detection unit is attached to the driver, and the vibration detection unit detects the vibration of screw tightening by the driver.
- a predetermined operation such as shaking
- control device 4 calculates the screw tightening time and the number of rotations by the driver from the pattern of vibration (amplitude, period, etc.), and when the screw tightening is completed within a predetermined time or less or less than the predetermined rotation number It is determined that the information is displayed or notified to the outside by voice or the like.
- FIG. 15A a hardware configuration example of the control device 4 in the embodiment 1-4
- FIG. 15B a hardware configuration example of the control device 4 in the first embodiment
- a CPU Central Processing Unit, central processing unit, processing device
- a microprocessor a microcomputer, a processor, or a DSP (Digital Signal Processor) 52.
- DSP Digital Signal Processor
- the processing circuit 51 may be, for example, a single circuit, a complex circuit, a programmed processor, a parallel programmed processor, an application specific integrated circuit (ASIC), an FPGA (field programmable gate) Array) or a combination thereof.
- ASIC application specific integrated circuit
- FPGA field programmable gate
- the processing circuit 51 When the processing circuit 51 is the CPU 52, the functions of the identification unit 402, the position detection unit 403, and the work state detection unit 404 are realized by software, firmware, or a combination of software and firmware.
- Software and firmware are described as a program and stored in the memory 53.
- the processing circuit 51 reads out and executes the program stored in the memory 53 to realize the function of each part.
- these programs cause a computer to execute the procedures and methods of the identification unit 402, the position detection unit 403, and the work state detection unit 404.
- the memory 53 is, for example, nonvolatile or volatile semiconductor memory such as RAM, ROM, flash memory, EPROM, EEPROM, etc., magnetic disk, flexible disk, optical disk, optical disk, compact disk, mini disk, DVD, etc. Applicable
- the functions of the identification unit 402, the position detection unit 403, and the work state detection unit 404 may be partially realized by dedicated hardware and partially realized by software or firmware.
- the function of the identification unit 402 is realized by the processing circuit 51 as dedicated hardware, and for the position detection unit 403 and the work state detection unit 404, the processing circuit 51 reads and executes the program stored in the memory 53. It is possible to realize the function by doing.
- the processing circuit 51 can implement the above-described functions by hardware, software, firmware, or a combination thereof.
- the present invention allows free combination of each embodiment, or modification of any component of each embodiment, or omission of any component in each embodiment. .
- the position detection system can detect the work state, and detects the position of the movable body on which the work object is placed and the work state on the movable body or the work object placed on the movable body It is suitable for use in position detection systems and the like.
Landscapes
- Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Human Resources & Organizations (AREA)
- Economics (AREA)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Quality & Reliability (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Strategic Management (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Educational Administration (AREA)
- Game Theory and Decision Science (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Marketing (AREA)
- Operations Research (AREA)
- Tourism & Hospitality (AREA)
- General Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Development Economics (AREA)
- Automation & Control Theory (AREA)
- General Factory Administration (AREA)
Abstract
Description
実施の形態1.
図1はこの発明の実施の形態1に係る位置検知システムの構成例を示す図である。
位置検知システムは、生産現場において、製品等の作業対象物11(図6等参照)が載置される台車(移動体)12の位置を検知し、且つ、台車12又は当該台車12に載置された作業対象物11に対する作業者による作業状態を検知する。なお、台車12は、生産現場において、1台以上用いられる。この位置検知システムは、図1に示すように、振動検知部1、発信機2、複数の受信機3、及び制御装置4を備えている。図1の例では、受信機3を2台示している。 Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings.
FIG. 1 is a view showing a configuration example of a position detection system according to
The position detection system detects the position of a carriage (mobile body) 12 on which a work object 11 (see FIG. 6 etc.) such as a product is placed at a production site, and places the
以下では、生産現場における生産ライン方式がセル生産方式であるとする。この生産現場では、例えば図3に示すように、複数の工程(セル)が設けられている。そして、一つ又は複数の工程に対して一人又は複数人の作業者が配置され、作業者は台車12に載置された作業対象物11に対する作業を行う。なお、作業者が配置されず、作業が行われない工程も存在する。また、台車12は工程毎に停止位置が決まっている。また、台車12は、前工程で作業を行った作業者により次工程へ移動される場合もあるし、次工程で作業を行う作業者により前工程から引取られる場合もある。台車12が停止位置に停止した後、作業者は、部品を取付ける必要がある場合には部品をセットした上で、工具を取って作業を行う。作業者は、移動せずに作業を行う場合もあるし、台車12の周りを移動しながら作業を行う場合もある。 Next, an operation example of the position detection system according to the first embodiment will be described with reference to FIGS. 3 to 5.
In the following, it is assumed that the production line method at the production site is the cell production method. At this production site, for example, as shown in FIG. 3, a plurality of processes (cells) are provided. Then, one or a plurality of workers are arranged for one or a plurality of processes, and the workers perform the work on the
このように、定期的に信号を発信する発信機2が台車12に取付けられ、生産現場に複数の受信機3が配置されることで、制御装置4は、受信機3により受信された信号の受信強度から、発信機2の位置を検知できる。よって、制御装置4は、この発信機2が取付けられた台車12の位置を検知できる。また、制御装置4は、台車12が工程の停車位置に停車したと判定した場合に、作業者に対して作業開始を表示(画面表示又は光等)又は音声等で指示することもできる。 Next, the
As described above, the
このように、振動を検知する振動検知部1が台車12に取付けられることで、制御装置4は、振動検知部1により検知された振動及び位置検知部403による検知結果から、作業状態(台車12の移動有無又は台車12に載置された作業対象物11への作業有無)を検知できる。 The work
As described above, the
一方、時間帯506では、受信機3による信号501の受信強度が高いため、位置検知部403は、上記特定の台車12が上記特定の工程に位置していると判定する。また、時間帯506では、振動検知部1により振動502~504が検知されている。よって、作業状態検知部404は、位置検知部403による検知結果及び上記振動502~504から、台車12に載置された作業対象物11に対する作業が行われていると判定する。 In FIG. 5, since the reception intensity of the
On the other hand, in the
図6では、第1工程に配置された受信機3-1及び第2工程に配置された受信機3-2が、台車12-1に取付けられた振動検知部1により検知された振動を示す振動情報を含む信号及び発信機2により発信された信号を受信している。また、受信機3-1では発信機2からの信号の受信強度が徐々に低くなり、受信機3-2では発信機2からの信号の受信強度が徐々に高くなっている。すなわち、受信機3-1及び受信機3-2による受信結果から、台車12-1に取付けられた振動検知部1で振動が検知され、また、台車12-1は受信機3-1から離れ且つ受信機3-2に近づいていることがわかる。よって、制御装置4は、台車12-1が第1工程側から第2工程側へ移動中であると判定する。 In FIG. 6, the
In FIG. 6, the receiver 3-1 disposed in the first step and the receiver 3-2 disposed in the second step indicate the vibrations detected by the
実施の形態1では、1組の振動検知部1及び発信機2が台車12に取付けられることで、位置検知部403が台車12の位置を検知し、作業状態検知部404が台車12又は当該台車12に載置された作業対象物11に対する作業状態を検知する場合を示した。
一方、従来から、振動検知部を工具に取付け、作業が正常に行われたか否かを検知する方法が知られている(例えば特許文献2,3参照)。しかしながら、これらの従来技術では、作業者が正しい作業位置で作業しているか否かは検知できない。そこで、以下では、これを解決する方法について説明する。
In the first embodiment, by attaching one set of the
On the other hand, conventionally, there is known a method of attaching a vibration detection unit to a tool and detecting whether or not an operation has been performed normally (see, for example,
実施の形態2に係る位置検知システムでは、図12に示すように、まず、制御装置4は、受信機3により受信された信号に基づいて、作業対象物11への作業を検知する(ステップST1201)。このステップST1201における処理は、図4に示す処理により実現される。 Next, an operation example of the position detection system according to the second embodiment will be described with reference to FIG.
In the position detection system according to the second embodiment, as shown in FIG. 12, first,
一方、ステップST1203において、作業位置判定部405が作業位置が誤っていると判定した場合には、その旨を外部に表示又は音声等で報知する。 Next, the work
On the other hand, when the work
また、精度が求められる作業に対しては事前に複数回作業を繰り返し、作業位置判定部405がその振動パターンを機械学習することで、振動パターンの標準化が可能となる。 As described above, by attaching the plurality of
In addition, with respect to the work for which the accuracy is required, the work is repeated a plurality of times in advance, and the work
実施の形態1では、発信機2が台車12に取付けられ、複数の受信機3が生産現場に配置され、位置検知部403が、複数の受信機3により受信された信号の受信強度から発信機2の位置を検知する場合を示した。それに対し、実施の形態3では、台車12が移動する地面にシート状の凹凸部5を設け、位置検知部403bが、台車12がその凹凸部5上を移動した際に発生する振動のパターンから台車12の位置を検知する方法について説明する。
図13はこの発明の実施の形態3に係る位置検知システムにおける発信側(受信機3及び制御装置4を除く機能部)の構成例を示す図であり、図14はこの発明の実施の形態3における制御装置4の構成例を示す図である。この図13,14に示す実施の形態3に係る位置検知システムでは、図1,2に示す実施の形態1に係る位置検知システムに対し、発信機2を取除き、凹凸部5を追加し、位置検知部403を位置検知部403bに変更している。また、複数の受信機3を単一の受信機3としてもよい。その他の構成は同様であり、同一の符号を付してその説明を省略する。 Third Embodiment
In the first embodiment, the
FIG. 13 is a diagram showing an example of a configuration of the transmitting side (functional units excluding the receiver 3 and the control device 4) in the position detection system according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention, and FIG. It is a figure which shows the structural example of the
また、これにより、位置検知システムのメンテナンス性が向上する。すなわち、振動検知部1及び発信機2等のセンサでは、ボタン電池が用いられている場合があり、この場合には電池交換が必要となる。特に位置ビーコンとして用いられる発信機2は電池が消耗し易い。また、上記センサでは、振動検知又は位置ビーコンとして機能させるためのパラメータ設定がそれぞれ必要となる。そのため、発信機2を用いずに、単一の振動検知部1のみを用いることで、電池交換の頻度及びパラメータの設定数を抑制でき、メンテナンス性が向上する。 As described above, the
This also improves the maintainability of the position detection system. That is, in the sensors such as the
実施の形態1,3では振動検知部1が台車12に取付けられ、実施の形態2では振動検知部1bが作業対象物11に取付けられた場合を示した。それに対し、更に、これらの振動検知部1,1bと同様の振動検知部を作業者又は工具にも取付けて生産現場における進捗管理を行ってもよい。 Fourth Embodiment
In the first and third embodiments, the
また、例えば、ドライバに振動検知部を取付け、振動検知部がドライバによるネジ締めの振動を検知する。そして、制御装置4は、その振動のパターン(振幅及び周期等)から、ドライバによるネジ締め時間及び回転数を算出し、所定時間以下又は所定回転数以下でネジ締めが終了した場合には不締りと判定して外部に表示又は音声等で報知する。 For example, when the vibration detection unit is attached to the arm of the worker and parts are insufficient in the assembly process, the vibration detection unit detects the vibration by causing the worker to perform a predetermined operation (such as shaking) of the arm. Then, the
Further, for example, the vibration detection unit is attached to the driver, and the vibration detection unit detects the vibration of screw tightening by the driver. Then, the
制御装置4における識別部402、位置検知部403及び作業状態検知部404の各機能は、処理回路51により実現される。処理回路51は、図15Aに示すように、専用のハードウェアであっても、図15Bに示すように、メモリ53に格納されるプログラムを実行するCPU(Central Processing Unit、中央処理装置、処理装置、演算装置、マイクロプロセッサ、マイクロコンピュータ、プロセッサ、DSP(Digital Signal Processor)ともいう)52であってもよい。 Finally, a hardware configuration example of the
Each function of the
Claims (5)
- 作業対象物が載置される移動体に取付けられ、振動の検知を行い、検知した振動を示す振動情報及び識別情報を有する信号を発信する振動検知部と、
前記移動体に取付けられ、定期的に識別情報を有する信号を発信する発信機と、
信号を受信する複数の受信機と、
前記受信機により受信された信号が有する識別情報から、当該信号の送信元を識別する識別部と、
前記受信機により受信された信号の受信強度及び前記識別部による識別結果から、当該信号の送信元である前記発信機の位置を検知する位置検知部と、
前記受信機により受信された信号が有する振動情報、前記識別部による識別結果及び前記位置検知部による検知結果から、当該信号の送信元である前記振動検知部が取付けられた前記移動体又は当該移動体に載置された前記作業対象物に対する作業状態を検知する作業状態検知部と
を備えた位置検知システム。 A vibration detection unit attached to a movable body on which the work object is mounted, detecting a vibration, and transmitting a signal having vibration information indicating the detected vibration and identification information;
A transmitter attached to the mobile unit and periodically transmitting a signal having identification information;
Multiple receivers receiving the signal,
An identification unit for identifying a transmission source of the signal from identification information of the signal received by the receiver;
A position detection unit that detects the position of the transmitter that is the transmission source of the signal from the reception strength of the signal received by the receiver and the identification result by the identification unit;
From the vibration information included in the signal received by the receiver, the identification result by the identification unit, and the detection result by the position detection unit, the movable body attached with the vibration detection unit as the transmission source of the signal or the movement A position detection system comprising: a work state detection unit that detects a work state of the work object placed on a body. - 作業対象物が載置される移動体に取付けられ、振動の検知を行い、検知した振動を示す振動情報及び識別情報を有する信号を発信する振動検知部と、
前記移動体が移動する地面に配置されたシート状の凹凸部と、
信号を受信する受信機と、
前記受信機により受信された信号が有する識別情報から、当該信号の送信元を識別する識別部と、
前記受信機により受信された信号が有する振動情報及び前記識別部による識別結果から、当該信号の送信元である前記振動検知部の位置を検知する位置検知部と、
前記受信機により受信された信号が有する振動情報、前記識別部による識別結果及び前記位置検知部による検知結果から、当該信号の送信元である前記振動検知部が取付けられた前記移動体又は当該移動体に載置された前記作業対象物に対する作業状態を検知する作業状態検知部と
を備えた位置検知システム。 A vibration detection unit attached to a movable body on which the work object is mounted, detecting a vibration, and transmitting a signal having vibration information indicating the detected vibration and identification information;
A sheet-like uneven portion disposed on the ground on which the movable body moves;
A receiver that receives the signal;
An identification unit for identifying a transmission source of the signal from identification information of the signal received by the receiver;
A position detection unit that detects the position of the vibration detection unit that is the transmission source of the signal from the vibration information included in the signal received by the receiver and the identification result by the identification unit;
From the vibration information included in the signal received by the receiver, the identification result by the identification unit, and the detection result by the position detection unit, the movable body attached with the vibration detection unit as the transmission source of the signal or the movement A position detection system comprising: a work state detection unit that detects a work state of the work object placed on a body. - 前記位置検知部は、予め、前記移動体が前記凹凸部上を移動した際に前記振動検知部で検知された振動から、振動パターンを機械学習する
ことを特徴とする請求項2記載の位置検知システム。 The position detection unit according to claim 2, wherein the position detection unit performs machine learning of a vibration pattern from the vibration detected by the vibration detection unit in advance when the movable body moves on the uneven portion. system. - 前記作業対象物に取付けられ、振動の検知を行い、検知した振動を示す振動情報及び識別情報を有する信号を発信する複数の第2の振動検知部と、
前記受信機により受信された信号が有する振動情報、前記識別部による識別結果及び前記位置検知部による検知結果から、当該信号の送信元である前記第2の振動検知部が取付けられた前記作業対象物に対する作業位置の正否を判定する作業位置判定部と
を備えた請求項1から請求項3のうちの何れか1項記載の位置検知システム。 A plurality of second vibration detection units attached to the work object, detecting a vibration, and transmitting a signal having vibration information and identification information indicating the detected vibration;
From the vibration information included in the signal received by the receiver, the identification result by the identification unit, and the detection result by the position detection unit, the work target to which the second vibration detection unit as the transmission source of the signal is attached The position detection system according to any one of claims 1 to 3, further comprising: a work position determination unit that determines whether a work position with respect to an object is correct. - 前記作業位置判定部は、予め、正しい作業位置で作業が行われた際及び誤った作業位置で作業が行われた際に前記第2の振動検知部で検知された振動から、振動パターンを機械学習する
ことを特徴とする請求項4記載の位置検知システム。 The work position determination unit is configured to generate a vibration pattern from the vibration detected by the second vibration detection unit in advance when the work is performed at the correct work position and when the work is performed at the incorrect work position. The position detection system according to claim 4, wherein learning is performed.
Priority Applications (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| GB1918547.9A GB2578031A (en) | 2017-06-28 | 2017-06-28 | Position detection system |
| PCT/JP2017/023738 WO2019003340A1 (en) | 2017-06-28 | 2017-06-28 | Position detection system |
| CN201780092565.9A CN110832413A (en) | 2017-06-28 | 2017-06-28 | Position detection system |
| JP2019526030A JPWO2019003340A1 (en) | 2017-06-28 | 2017-06-28 | Position detection system |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2017/023738 WO2019003340A1 (en) | 2017-06-28 | 2017-06-28 | Position detection system |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2019003340A1 true WO2019003340A1 (en) | 2019-01-03 |
Family
ID=64740475
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2017/023738 WO2019003340A1 (en) | 2017-06-28 | 2017-06-28 | Position detection system |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JPWO2019003340A1 (en) |
| CN (1) | CN110832413A (en) |
| GB (1) | GB2578031A (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2019003340A1 (en) |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2020222342A1 (en) * | 2019-05-02 | 2020-11-05 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | Method, learning module, and cart robot for identifying driving space by using artificial intelligence |
| WO2021002511A1 (en) * | 2019-07-03 | 2021-01-07 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | Marker, method for moving in marker-tracking mode, and cart robot implementing same |
| CN112675449A (en) * | 2019-10-17 | 2021-04-20 | 黄炜皓 | Safety shackle and fall protection system |
| CN113874798A (en) * | 2019-05-23 | 2021-12-31 | 三菱电机株式会社 | Numerical control device |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN117192524B (en) * | 2023-09-27 | 2024-07-05 | 广东星云开物科技股份有限公司 | Helmet wearing sensing method and device and shared electric vehicle system |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008123184A (en) * | 2006-11-10 | 2008-05-29 | Pentax Corp | Process management system, method and program |
| JP2009075941A (en) * | 2007-09-21 | 2009-04-09 | Hitachi Ltd | Process management method, system, and device |
| JP2010146202A (en) * | 2008-12-17 | 2010-07-01 | Toyota Central R&D Labs Inc | Moving object and position estimation method for moving object |
| JP2012243037A (en) * | 2011-05-18 | 2012-12-10 | Mitsubishi Heavy Ind Ltd | Operation process management system and operation process management method |
| JP2014215231A (en) * | 2013-04-26 | 2014-11-17 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | Vehicle position detection apparatus |
Family Cites Families (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102350732B (en) * | 2010-11-12 | 2013-08-14 | 浙江广天构件股份有限公司 | Duct piece production control system and duct piece production system |
-
2017
- 2017-06-28 WO PCT/JP2017/023738 patent/WO2019003340A1/en active Application Filing
- 2017-06-28 CN CN201780092565.9A patent/CN110832413A/en not_active Withdrawn
- 2017-06-28 JP JP2019526030A patent/JPWO2019003340A1/en active Pending
- 2017-06-28 GB GB1918547.9A patent/GB2578031A/en not_active Withdrawn
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008123184A (en) * | 2006-11-10 | 2008-05-29 | Pentax Corp | Process management system, method and program |
| JP2009075941A (en) * | 2007-09-21 | 2009-04-09 | Hitachi Ltd | Process management method, system, and device |
| JP2010146202A (en) * | 2008-12-17 | 2010-07-01 | Toyota Central R&D Labs Inc | Moving object and position estimation method for moving object |
| JP2012243037A (en) * | 2011-05-18 | 2012-12-10 | Mitsubishi Heavy Ind Ltd | Operation process management system and operation process management method |
| JP2014215231A (en) * | 2013-04-26 | 2014-11-17 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | Vehicle position detection apparatus |
Cited By (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2020222342A1 (en) * | 2019-05-02 | 2020-11-05 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | Method, learning module, and cart robot for identifying driving space by using artificial intelligence |
| CN113874798A (en) * | 2019-05-23 | 2021-12-31 | 三菱电机株式会社 | Numerical control device |
| CN113874798B (en) * | 2019-05-23 | 2023-12-05 | 三菱电机株式会社 | Numerical control device |
| WO2021002511A1 (en) * | 2019-07-03 | 2021-01-07 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | Marker, method for moving in marker-tracking mode, and cart robot implementing same |
| US20210405646A1 (en) * | 2019-07-03 | 2021-12-30 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Marker, method of moving in marker following mode, and cart-robot implementing method |
| CN112675449A (en) * | 2019-10-17 | 2021-04-20 | 黄炜皓 | Safety shackle and fall protection system |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| GB2578031A (en) | 2020-04-15 |
| CN110832413A (en) | 2020-02-21 |
| JPWO2019003340A1 (en) | 2019-11-07 |
| GB201918547D0 (en) | 2020-01-29 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2019003340A1 (en) | Position detection system | |
| US8342223B2 (en) | Method of and apparatus for fitting or removing a motor vehicle tyre | |
| CN102126405B (en) | For method and apparatus tire is installed on wheel rim and pull down from wheel rim | |
| CN101788389B (en) | Wheel diagnosis system | |
| CN104044141B (en) | The control method of robot system and robot system | |
| US9302859B2 (en) | Vehicle loading and unloading detection | |
| US7715024B2 (en) | Method of and apparatus for determining geometrical dimensions of a wheel rim, in particular when fitting and/or removing a motor vehicle tyre | |
| JP7091324B2 (en) | Methods and systems for detecting the position of a vehicle with respect to the truck on which the vehicle is traveling. | |
| US20180045536A1 (en) | On-Line Calibration Testing During The Operation Of An Autonomous Vehicle | |
| JP2015016854A (en) | Fastening guarantee system for vehicle assembly and control method of the same | |
| JP2005350046A (en) | Position detection device and tire air pressure detection device provided with position detection function | |
| EP2335874B1 (en) | Eyeglass frame shape measurement apparatus | |
| US10365091B2 (en) | Electronic angle measuring device for a bending machine for measuring the bending angle between the limbs of a sheet | |
| US20210268849A1 (en) | A method for detecting wheel units of a vehicle and wheel mounting positions belonging to the wheel units, and a wheel information system | |
| TW201536660A (en) | Conveying vehicle system, method of inspecting conveying vehicle system, and inspection truck | |
| JP2018062241A (en) | Rail inspection device and rail inspection system | |
| CN104668312A (en) | Method for detecting overall dimension of platelike workpiece | |
| CN105008150A (en) | Method for associating tire positions on vehicle having tire-pressure monitoring system | |
| WO2020163194A1 (en) | System and method for tracking a reference laser | |
| CN102818547A (en) | Tool for measuring travel of vehicular clutch pedal | |
| WO2020139524A1 (en) | Method of vehicle localization using passive roadway detection during a minimum risk maneuver | |
| KR102189908B1 (en) | System for transferring product | |
| EP3360652B1 (en) | Detection of engagement of robot with object | |
| US20230194331A1 (en) | Weight-based item detection | |
| CN105722691A (en) | Spoked wheel aligners and method for aligning spoked wheels using said aligner |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 17915532 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2019526030 Country of ref document: JP Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 201918547 Country of ref document: GB Kind code of ref document: A Free format text: PCT FILING DATE = 20170628 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 17915532 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |