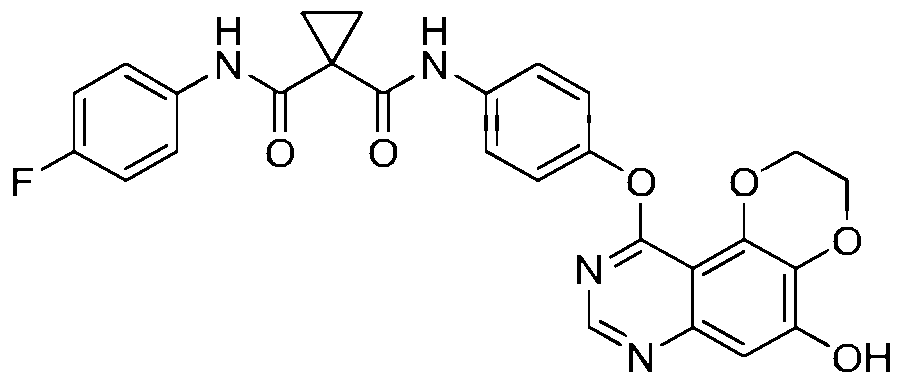
WO2018153293A1 - 二噁烷并喹唑啉与二噁烷并喹啉类化合物及其制备方法与应用 - Google Patents
二噁烷并喹唑啉与二噁烷并喹啉类化合物及其制备方法与应用 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2018153293A1 WO2018153293A1 PCT/CN2018/076233 CN2018076233W WO2018153293A1 WO 2018153293 A1 WO2018153293 A1 WO 2018153293A1 CN 2018076233 W CN2018076233 W CN 2018076233W WO 2018153293 A1 WO2018153293 A1 WO 2018153293A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- group
- acid
- compound
- fluorenyl
- fluorophenyl
- Prior art date
Links
- BEJWABWOVNHUNX-UHFFFAOYSA-N CC(C)(C(Nc(cc1)ccc1O)=O)C(Nc(cc1)ccc1F)=O Chemical compound CC(C)(C(Nc(cc1)ccc1O)=O)C(Nc(cc1)ccc1F)=O BEJWABWOVNHUNX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WBJXSVAZKDURCV-UHFFFAOYSA-N CCCCNc(ncnc1cc2OC)c1c(OC)c2OCC Chemical compound CCCCNc(ncnc1cc2OC)c1c(OC)c2OCC WBJXSVAZKDURCV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VJLAWCZHXKUJPU-UHFFFAOYSA-N CN(C)CCCOc1cc(nccc2Oc(ccc(NC(C3(CC3)C(Nc(cc3)ccc3F)=O)=O)c3)c3F)c2c2c1OCCO2 Chemical compound CN(C)CCCOc1cc(nccc2Oc(ccc(NC(C3(CC3)C(Nc(cc3)ccc3F)=O)=O)c3)c3F)c2c2c1OCCO2 VJLAWCZHXKUJPU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RGESWKWQKNLAFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N COCCOc1cc2ncnc(Nc(cc3)ccc3NC(C3(CC3)C(Nc(cc3)ccc3F)=O)=O)c2c2c1OCCO2 Chemical compound COCCOc1cc2ncnc(Nc(cc3)ccc3NC(C3(CC3)C(Nc(cc3)ccc3F)=O)=O)c2c2c1OCCO2 RGESWKWQKNLAFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XWDKUESIGCPJOY-UHFFFAOYSA-N CS(c(cc1)ccc1NC(C1(CC1)C(Nc(cc1)ccc1O)=O)=O)(=O)=O Chemical compound CS(c(cc1)ccc1NC(C1(CC1)C(Nc(cc1)ccc1O)=O)=O)(=O)=O XWDKUESIGCPJOY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FLEXLYCPDFDUOE-UHFFFAOYSA-N Clc(ncnc1cc2OC3CCOCC3)c1c1c2OCCO1 Chemical compound Clc(ncnc1cc2OC3CCOCC3)c1c1c2OCCO1 FLEXLYCPDFDUOE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RJMHEPGVICPLKM-UHFFFAOYSA-N Clc1ccnc(cc2OCCCN3CCOCC3)c1c1c2OCCO1 Chemical compound Clc1ccnc(cc2OCCCN3CCOCC3)c1c1c2OCCO1 RJMHEPGVICPLKM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WHTYLRLZUGABTR-UHFFFAOYSA-N NC(C1(CC1)C(Nc(cc1)ccc1F)=O)=O Chemical compound NC(C1(CC1)C(Nc(cc1)ccc1F)=O)=O WHTYLRLZUGABTR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KGSRNFVJZDGCCI-UHFFFAOYSA-N O=C(C1(CC1)C(Nc(cc1)cc(F)c1Oc1ncnc(cc2OC3COCC3)c1c1c2OCCO1)=O)Nc(cc1)ccc1F Chemical compound O=C(C1(CC1)C(Nc(cc1)cc(F)c1Oc1ncnc(cc2OC3COCC3)c1c1c2OCCO1)=O)Nc(cc1)ccc1F KGSRNFVJZDGCCI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PHLBKRHRFIVYBE-UHFFFAOYSA-N O=C(C1(CC1)C(Nc(ccc(Oc1ncnc(cc2OCCCN3CCOCC3)c1c1c2OCCO1)c1)c1F)=O)Nc(cc1)ccc1F Chemical compound O=C(C1(CC1)C(Nc(ccc(Oc1ncnc(cc2OCCCN3CCOCC3)c1c1c2OCCO1)c1)c1F)=O)Nc(cc1)ccc1F PHLBKRHRFIVYBE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- POCKVICBOUHQRH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Oc(c(F)c1)ccc1NC(C1(CC1)C(Nc(cccc1)c1F)=O)=O Chemical compound Oc(c(F)c1)ccc1NC(C1(CC1)C(Nc(cccc1)c1F)=O)=O POCKVICBOUHQRH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FSFMBVMXIPQPMJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Oc(cc1)ccc1NC(C1(CC1)C(Nc(cc1)ccc1F)=O)=O Chemical compound Oc(cc1)ccc1NC(C1(CC1)C(Nc(cc1)ccc1F)=O)=O FSFMBVMXIPQPMJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/395—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins
- A61K31/495—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having six-membered rings with two or more nitrogen atoms as the only ring heteroatoms, e.g. piperazine or tetrazines
- A61K31/505—Pyrimidines; Hydrogenated pyrimidines, e.g. trimethoprim
- A61K31/519—Pyrimidines; Hydrogenated pyrimidines, e.g. trimethoprim ortho- or peri-condensed with heterocyclic rings
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P35/00—Antineoplastic agents
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D491/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing in the condensed ring system both one or more rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms and one or more rings having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, not provided for by groups C07D451/00 - C07D459/00, C07D463/00, C07D477/00 or C07D489/00
- C07D491/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing in the condensed ring system both one or more rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms and one or more rings having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, not provided for by groups C07D451/00 - C07D459/00, C07D463/00, C07D477/00 or C07D489/00 in which the condensed system contains two hetero rings
- C07D491/04—Ortho-condensed systems
- C07D491/056—Ortho-condensed systems with two or more oxygen atoms as ring hetero atoms in the oxygen-containing ring
Definitions
- the present invention relates to dioxindinoquinazoline and dioxin and quinoline compounds, which are pharmaceutically acceptable a salt, an isomer, a hydrate, a solvate, or a prodrug, and a process for its preparation and use.
- RTKs Receptor tyrosine kinases
- the active intracellular domain consists of three parts.
- Binding of the ligand to the receptor stimulates receptor-associated tyrosine kinase activity, which leads to the acidification of tyrosine residues on the receptor and other intracellular molecules, leading to cascades that lead to various cellular responses. signal. Overexpression of tyrosine receptors activates downstream signal transduction pathways, which ultimately lead to abnormal cell transformation and proliferation, and promote tumorigenesis and development.
- Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor is a family of receptor tyrosine kinases that combines with its ligand vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) to produce a range of biochemical and vascular endothelial growth factor receptors (VEGFs). The physiological process eventually promotes the formation of new blood vessels.
- VEGF vascular endothelial growth factor receptor
- VEGF vascular endothelial growth factor
- VEGFR-1 vascular endometrial receptor 1
- VEGFR-2 vascular endometrial receptor 1
- VEGF vascular endometrial permeability
- VEGF is an important stimulator of normal and pathological angiogenesis and vascular permeability (Jakeman et al., 1993, Endocrinology 133: 848-859; Kolch et al., 1995, Breast Cancer Research and Treatment 36: 139-155; Connolly et al, 1989, J. Biol. Chem. 264: 20017-20024).
- Vascular endothelial growth factor induces a angiogenic phenotype by inducing endothelial cell proliferation, protease expression and migration, and subsequent formation of capillary cell tissue. Therefore, antagonism of VEGF by chelation of VEGF by antibodies can lead to inhibition of tumor growth (Kim et al., 1993, Nature 362: 841-844).
- VEGFR-2 Since VEGFR-2 is mainly distributed in vascular endothelial cells, it can bind to VEGF-A, VEGF-C, VEGF-D, and VEGF-E.
- the proliferation of VEGF, the increase of vascular permeability and the formation of new blood vessels by VEGF are mainly achieved by binding and activating VEGFR-2. If the activity of VEGFR-2 is blocked, tumor growth and metastasis can be inhibited by direct and indirect pathways, thereby achieving an ideal anti-tumor effect. Therefore, finding a small molecule inhibitor with high activity and high selectivity for VEGFR-2 has become a very promising tumor treatment strategy.
- Hepatocyte growth factor receptor (c-Met) is a kind of tyrosine kinase receptor, and its abnormal activation plays an important role in the occurrence and development of various malignant tumors including lung cancer.
- Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) is a specific ligand for c-Met, and c-Met binds to HGF and exerts a biological effect through the HGF/c-Met signaling pathway.
- HGF/c-Met signaling pathway can induce a series of biological effects such as cell proliferation, dispersion, migration, organ morphology, and angiogenesis.
- Abnormal activation of c-Met can be expressed as receptor overexpression, gene mutation, amplification, ectopic, rearrangement, and the like.
- c-Met plays an important role in cell proliferation, metabolism, tumor production, metastasis, and angiogenesis, and has become an important target for anti-tumor therapy.
- Targeted therapy targeting c-Met has become important in the treatment of a variety of malignancies, including lung cancer.
- the interaction of multiple signaling pathways may affect the effects of anti-tumor drugs.
- the interaction of HFG/c-Met signaling pathway with other pathways affects the therapeutic effect of anti-tumor drugs.
- Drug resistance Therefore, the combination of multi-kinase targets has become a new anti-tumor treatment, and the successful marketing of Crizotinib and Cabozantinib demonstrates the potential and application of multi-kinase target inhibitors.
- Cabozantinib is a small molecule inhibitor of protein kinase that inhibits various kinases such as c-Met, VEGFR-2, Ret, Kit, and AXL.
- Cabozantinib inhibits phosphorylation of c-Met and VEGFR-2 in tumor models and shows potent anti-tumor metastasis and anti-angiogenic activity in preclinical pharmacodynamic models.
- No increase in tumor burden was observed in the lung tumor metastasis model treated with Cabozantinib compared to inhibitors acting alone on the VEGFR target, suggesting that Cabozantinib is a tumor angiogenesis and metastasis in patients with dysregulated c-Met and VEGFR2 signaling pathways. Effective inhibitor.
- the FDA approved the listing of Cabozantinib for the treatment of progressive, metastatic medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) patients.
- MTC metastatic medullary thyroid carcinoma
- the present invention provides a compound represented by the formula (I), a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, isomer, hydrate, solvate, or prodrug thereof, which can be used for the treatment or prevention of a tyrosine kinase (for example) VEGFR-2 and
- Replacement page (Article 26) / or c-Met) causes diseases, including certain variants of the tyrosine kinase receptor.
- Q is N or CH
- G is 0 or NH
- Z is N or CH
- a linking group of a cyclononan hydrocarbon selected from the group consisting of
- X is H or a decyl group of dC 3 ;
- Y is a thiol group of H or dC 3 ;
- R 1 is H, CC 9 fluorenyl, C 3 -C 7 cyclodecyl, 4-7 membered heterocyclic, C 3 -C 7 cyclodecyl substituted dC 6 fluorenyl, 4-7 membered heterocyclic ring a substituted dC 6 fluorenyl group, a substituted dC 9 fluorenyl group, the substituent of the substituted C r C 9 alkyl group being a hydroxyl group, a decyloxy group of C r C 6 , a thiol group of dC 6 or -NR 6
- R 7 is H, CC 9 fluorenyl, C 3 -C 7 cyclodecyl, 4-7 membered heterocyclic, C 3 -C 7 cyclodecyl substituted dC 6 fluorenyl, 4-7 membered heterocyclic ring a substituted dC 6 fluorenyl group, a substituted d
- R 6 and R 7 are each independently H, CC 6 fluorenyl, hydroxy-substituted dC 6 alkyl, dC 3 methoxy-substituted 6 alkyl;
- the above 4-7 membered heterocyclic group is a 4-7 membered heterocyclic group having 1 to 2 atoms selected from N, 0, and S, and the 4-7 membered heterocyclic group is not substituted or dC 3 fluorenyl,
- the dC 3 acyl group is substituted or oxidized by one to two oxygen atoms.
- 1 2 is 11, decyl or halogen of dC 3 ;
- 1 3 is 11, decyl or halogen of dC 3 ;
- R 5 is H, CC 9 fluorenyl, C 3 -C 7 cyclodecyl, C 3 -C 7 cyclodecyl substituted CC 6 alkyl, aryl, aryl substituted dC 6 fluorenyl, heteroaryl Or a heteroaryl substituted - fluorenyl group;
- the aryl or heteroaryl group is an unsubstituted or substituted alkyl group, an alkoxy group of dC 3 , a replacement page of ⁇ -3 ⁇ 4 (Rule 26)
- the above heteroaryl group is a monocyclic or bicyclic group having 5 to 10 ring atoms; the heteroaryl group contains 1 to 3 hetero atoms selected from N, 0, and S.
- the R 1 is H, dC 6 alkyl, C 3 -C 6 cyclodecyl, 5-6 membered heterocyclic, C 3 -C 6 cycloalkyl substituted dC 3 alkyl, 5-6 a heterocyclic group-substituted C C3 alkyl group, a substituted dC 6 fluorenyl group, the substituent of the substituted dC 6 fluorenyl group being a hydroxyl group, a dC 3 decyloxy group, a dC 3 thiol group or -NR 6 R 7 ,
- R 6 and R 7 are each independently H, CC 3 fluorenyl, hydroxy-substituted dC 3 fluorenyl, C r C 3 alkoxy-substituted 3 fluorenyl.
- the above 5- to 6-membered heterocyclic group is a 5-6 membered heterocyclic group having 1 to 2 atoms selected from N, 0, and S, which is unsubstituted or substituted by dC 3 fluorenyl group, dC 3 acyl group or Two oxygen atoms are oxidized.
- the R 1 is selected from the group consisting of methyl, ethyl, propyl, isopropyl, methoxyethyl, methoxypropyl, methoxybutyl, methoxypentyl, methoxyhexyl, tetrahydrofuran- 3-yl, tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-yl, tetrahydropyrrole small ethyl, tetrahydropyrrole-1-propyl, morpholin-4-ethyl, morpholin-4-propyl, methyl Piperazine-4-ethyl, methylpiperazine-4-propyl, N-formylpiperazine-4-ethyl, N-formylpiperazine-4-propyl, N-acetylpiperazine-4 -ethyl, N-acetylpiperazine-4-propyl, (1,1-dioxothiomorpholinyl)-4-ethyl,
- the halogen described by R 2 , R 3 and R 4 is 0 or 1 ⁇ .
- R 5 is H, dC 6 fluorenyl, C 3 -C 6 cyclodecyl, C 3 -C 6 cyclodecyl substituted CC 3 fluorenyl, aryl, aryl substituted cc 3 fluorenyl, heteroaryl or -3 ⁇ 4 heteroaryl substituted alkyl with the aryl group, a substituted heteroaryl group is c r c 3 alkyl, dC embankment group 3, group 3 CC embankment, mono- or di ⁇ - 3 ⁇ 4 take
- the heteroaryl group is a monocyclic or bicyclic group having 5 to 10 ring atoms; the heteroaryl group contains 1-2 hetero atoms selected from N, 0, and S.
- R 5 is selected from the group consisting of H, methyl, ethyl, propyl, isopropyl, isopentyl, cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl, cyclohexyl, phenyl, 4-fluorophenyl, 3-fluoro Phenyl, 2-fluorophenyl, 4-chlorophenyl, 3-chlorophenyl, 2-chlorophenyl, 2,4-difluorophenyl, 2,5-difluorophenyl, 3,4-di Fluorophenyl, 2,4-dichlorophenyl, 2,5-dichlorophenyl, 3,4-dichlorophenyl, 2-fluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl, 2-fluoro- 5-(Trifluoromethyl)phenyl, 3-fluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl, 3-fluoro-5-(trifluoromethyl)phen
- the present invention provides a pharmaceutically acceptable salt of a compound of the formula (I), wherein the salt is an acidic/anionic salt or a basic/cationic salt; the pharmaceutically acceptable acidic/anionic salt is usually taken in a form Basic nitrogen is protonated by inorganic or organic acids, and representative organic or inorganic acids include hydrochloric acid, hydrobromic acid, hydroiodic acid, perchloric acid, sulfuric acid, nitric acid, citric acid, formic acid, acetic acid, propionic acid, glycolic acid, Lactic acid, succinic acid, maleic acid, tartaric acid, malic acid, citric acid, fumaric acid, gluconic acid benzoic acid, mandelic acid, methanesulfonic acid, isethionic acid, benzenesulfonic acid, oxalic acid, palmitic acid, 2- Naphthalenesulfonic acid, p-toluenesulfonic acid, cyclohexylaminesul
- the present invention provides a process for the preparation of the above compound or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, isomer, hydrate, solvate or prodrug thereof, which comprises the following steps, a compound of the formula (II) and a formula (III)
- the compound is prepared by a reaction to obtain a compound of the formula (I), Q is N, G, Z, L, RR 2 , R 3 , R 4 and R 5 are as defined above.
- the present invention provides a preparation of the above compound or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, isomer, hydrate, replacement page (Article 26)
- a method of solvating a solvate or a prodrug comprising the steps of: reacting a compound of the formula (II ') with a compound of the formula (III ') to obtain a compound of the formula (I), wherein Q, G, Z , L, RR 2 , 3 , R 4 and R 5 are as defined above,
- the present invention provides an intermediate for preparing the above compound, such as a compound represented by the formula ( ⁇ ), wherein G, Z, L, R 2 , R 3 , R 4 and R 5 are as before
- the present invention provides an intermediate for preparing the above compound, a compound represented by the formula ( ⁇ '), wherein
- substituted includes complex substituents (e.g., phenyl, aryl, heteroalkyl, heteroaryl), suitably 1 to 5 substituents, preferably 1 to 3
- substituents e.g., phenyl, aryl, heteroalkyl, heteroaryl
- 1 to 5 substituents preferably 1 to 3
- alkyl groups including saturated straight chain, branched chain hydrocarbon, carbon atoms, represents alkyl of 1-9 carbon atoms, empathy C r C 3 alkyl carbon atoms such as 1 a carbon atom of -3, for example, C C6 fluorenyl includes methyl, ethyl, propyl, isopropyl, n-butyl, isobutyl, sec-butyl, tert-butyl, n-pentyl, 3-(2-methyl)butyl, 2-pentyl, 2-methylbutyl, neopentyl, n-hexyl, 2-hexyl and 2-methylpentyl.
- a decyl ether consisting of a linear, branched chain as previously described.
- alkenyl and alkynyl groups include straight-chain, branched alkenyl or alkynyl groups.
- Cyclodecyl a cyclic group formed by a carbon atom.
- C 3 -C 7 represents a fluorenyl group having 3-7 carbon atoms.
- aryl refers to an unsubstituted or substituted aryl group, such as phenyl, naphthyl, anthracenyl.
- aroyl refers to -C(O)-aryl.
- Oxidation by one or two oxygen atoms means that a sulfur atom is oxidized by an oxygen atom to form a double bond between sulfur and oxygen, or is oxidized by two oxygen atoms to form sulfur and a double bond between two oxygen atoms.
- heterocyclyl represents an unsubstituted or substituted stable 3 to 8 membered monocyclic saturated ring system selected from carbon atoms and from N, 0, S.
- the heterocyclic ring can be combined with any hetero atom or carbon atom to form a stable structure.
- heterocyclic rings include, but are not limited to, azetidinyl, pyrrolidinyl, tetrahydrofuranyl, tetrahydrothiazolyl, tetrahydropyranyl, morpholinyl, thiomorpholinyl, piperidine Pyridyl, piperazinyl, piperazinyl, piperidinyl, dioxetolyl, dioxocyclohexyltetrahydroimidazolyl, tetrahydrooxazolyl, thiomorpholine sulfoxide, thio Morpholine sulfone and oxadiazolyl.
- heteroaryl represents a stable 5 or 6 membered monocyclic aromatic ring system which is unsubstituted or substituted, and may also represent unsubstituted or substituted 9 or a 10-ring atomic benzene fused heteroaromatic ring system or a bicyclic heteroaromatic ring system consisting of a carbon atom and one or three heteroatoms selected from N, 0, S, wherein the N, S heteroatoms can be Oxidation, N heteroatoms can also be quaternized.
- the heteroaryl group can be bonded to any hetero atom or carbon atom to form a stable structure.
- Heteroaryl includes, but is not limited to, thienyl, furyl, imidazolyl, pyrrolyl, thiazolyl, oxazolyl, isoxazolyl, pyranyl, pyridyl, piperazinyl, pyrimidinyl, pyrazine, Pyridazinyl, pyrazolyl, thiadiazolyl, triazolyl, fluorenyl, azaindolyl, carbazolyl, azacarbazolyl, benzimidazolyl, benzofuranyl, benzothiophene Benzoisoxazolyl, benzoxazolyl, benzopyrazolyl, benzothiazolyl, benzothiadiazolyl, benzotriazolyl, adenyl, quinolinyl or isoquinoline base.
- carbonyl refers to the C(0) group.
- alkyl or aryl or any of their prefix roots appear in the name of a substituent (eg, aryl fluorenyl, dimethylamino), it will be considered to contain the above " ⁇ Those limitations given by "and” aryl groups.
- the specified number of carbon atoms e.g., d-
- d- will independently represent the number of carbon atoms in a thiol moiety or an alkyl moiety in a larger substituent (where thiol is the prefix root).
- the invention also provides a process for the preparation of the corresponding compounds, which can be prepared using a variety of synthetic methods, including the methods described below, a compound of the invention or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, a heterogeneous replacement page (fine 26)
- the body or hydrate can be synthesized using the following methods and synthetic methods known in the art of organic chemical synthesis, or by variations of those methods as understood by those skilled in the art, and the preferred methods include, but are not limited to, the following methods.
- the compound of the formula (I) of the present invention is prepared by reacting a compound of the formula (II ') with the formula (III'), and Z, L, RR 2 , R 3 , R 4 and R 5 are as described above.
- the present invention further provides a compound of the formula (I), which is a compound of the formula (II '), wherein Q, G, Z, RR 2 , R 3 and R 4 are as defined above,
- the compound of formula (I) of the present invention is prepared by reacting a compound of formula (II) with a compound of formula ( ⁇ ) wherein Q is N, G, Z, L, R 1 , R 2 , R 3 , R 4 and R 5 are as defined above,
- the invention also provides an intermediate, a compound of formula (II), wherein G, Z, L, R 2 , R 3 , R 4 and R 5 are as defined above,
- the present invention provides a process for the preparation of a compound of formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, isomer or hydrate thereof,
- the compounds of the invention may be prepared by Schemes 1 through 4 or by technical schemes known to those skilled in the art.
- reaction conditions are:
- Step 1) The dicarboxylic acid starting material is reacted with thionyl chloride to remove the solvent, an organic base is added, and the aprotic organic solvent is reacted with the starting material VII to obtain a compound of the formula VI; wherein the organic base is preferably triethylamine or diisopropyl A combination of one or more of a base amine, pyridine.
- the aprotic organic solvent is selected from the group consisting of tetrahydrofuran, toluene, methylene chloride, dioxane, DMF, DMA or a combination of two or more thereof.
- Step 2 In a preferred embodiment, when a compound of the formula (VI) is reacted with a compound of the formula (V), wherein the formula (VI) is reacted with an acylating reagent, and then reacted with the formula (V).
- the acylating agent includes, but is not limited to, one or a combination of two or more of phosphorus oxychloride, thionyl chloride, oxalyl chloride, phosphorus trichloride or phosphorus pentachloride.
- a compound of formula (VI) is reacted with a compound of formula (V) in the presence of a condensing agent to provide a compound of formula (IV).
- the condensing agent includes, but not limited to, a carbodiimide type condensing agent, a gun salt type condensing agent, an organic condensing agent, and one or more kinds of other types of condensing agents, preferably ruthenium, osmium-bicyclic ring Hexyl carbodiimide (DCC), hydrazine, hydrazine-diisopropylcarbodiimide (DIC), hydroxybenzotriazole (HOBt), hydrazine, hydrazine-diisopropylethylamine (DIEA), 1- Hydroxy-7-azobenzotriazole (HOAt), 0-benzotriazole-N,N,N',N'-tetramethyluronium tetrafluoroborate (TBTU), benzotriazine Zin-1-yloxytris(dimethylamino) Phosphorus hexafluorodibenzoate (DCC),
- HBTU 6-chlorobenzotriazole-1,1,3,3-tetramethylurea hexafluorophosphate
- HCTU 6-chlorobenzotriazole-1,1,3,3-tetramethylurea hexafluorophosphate
- HATU 2-(7-oxidized benzotriazole)-N,NN' , N'-tetramethylurea hexafluorophosphate
- T3P propylphosphonic anhydride
- EDCI 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride
- EDC 1-ethyl(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide
- PyBOP hexafluoro-petic acid benzotriazol-1-yl-oxytripyrrolidine scale
- PyAOP (3H-1 a combination of one or more of 2,3 triazolo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-yloxy)
- this step can be carried out in an organic base including, but not limited to, triethylamine, diisopropylethylamine (DIEA), pyridine, 4-dimethylaminopyridine (DMAP), 2, One or a combination of two or more of 6-lutidine, 1,8-diazabicycloundec-7-ene (DBU) or N-methylmorpholine.
- organic base including, but not limited to, triethylamine, diisopropylethylamine (DIEA), pyridine, 4-dimethylaminopyridine (DMAP), 2, One or a combination of two or more of 6-lutidine, 1,8-diazabicycloundec-7-ene (DBU) or N-methylmorpholine.
- Step 3 conditions for the nitro reduction reaction include, but are not limited to, hydrogen and Raney nickel, hydrogen or ammonium formate with palladium carbon, iron powder, zinc powder, stannous chloride;
- Step 4) In a organic solvent, base-catalyzed reaction at room temperature to reflux temperature.
- the base is selected from one or a combination of two or more of sodium carbonate, potassium carbonate and cesium carbonate;
- the organic solvent is selected from the group consisting of tetrahydrofuran, dioxane, isopropanol, ethanol, DMF, DMA, acetonitrile or both The combination of the above.
- reaction conditions are:
- Step 1) when a compound of the formula (VI) is reacted with a compound of the formula (VIII), wherein the formula (VI) is reacted with an acylating reagent and then with the formula (VIII).
- the acylating agent includes, but is not limited to, one or a combination of two or more of phosphorus oxychloride, thionyl chloride, oxalyl chloride, phosphorus trichloride or phosphorus pentachloride.
- a compound of formula (VI) is reacted with a compound of formula (VIII) in the presence of a condensing agent to provide a compound of formula ( ⁇ - ⁇ ),
- the condensing agent includes, but not limited to, a carbodiimide type condensing agent, a gun salt type condensing agent, a organic condensing agent, and one or more kinds of other types of condensing agents, preferably ruthenium, osmium-dicyclohexyl carbon Diimine
- HBTU 6-chlorobenzotriazole-1,1,3,3-tetramethylurea hexafluorophosphate
- HCTU 6-chlorobenzotriazole-1,1,3,3-tetramethylurea hexafluorophosphate
- HATU 2-(7-benzotriazole)-N,NN' , N'-tetramethylurea hexafluorophosphate
- T3P propylphosphonic anhydride
- T3P 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride (EDCI) , 1-ethyl(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide (EDC), hexafluoro-petic acid benzotriazol-1-yl-oxytripyrrole scale (PyBOP), (3H-1 a combination of one or more of 2,3 triazolo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-oxy)tri-1-pyr
- this step can be carried out in an organic base including, but not limited to, triethylamine, diisopropylethylamine, pyridine, 4-dimethylaminopyridine, 2,6-lutidine One or a combination of two or more of 1,8-diazabicycloundec-7-ene or N-methylmorpholine.
- organic base including, but not limited to, triethylamine, diisopropylethylamine, pyridine, 4-dimethylaminopyridine, 2,6-lutidine One or a combination of two or more of 1,8-diazabicycloundec-7-ene or N-methylmorpholine.
- Step 2) Base-catalyzed the reaction in an organic solvent at room temperature to reflux temperature.
- the base is selected from one or a combination of two or more of sodium carbonate, potassium carbonate and cesium carbonate;
- the organic solvent is selected from the group consisting of tetrahydrofuran, dioxane, isopropanol, ethanol, DMF, DMA, acetonitrile or both. combination.
- the introduction of the substituents R 1 , R 2 , R 3 , R 4 and R 5 can also be introduced by other methods known to those skilled in the art, for example, the introduction of a substituent of -0-R 1 can be passed
- the benzyloxy intermediate is debenzyloxy protected, the phenolic hydroxyl group is prepared, and the compound of the formula (I) or the intermediate product X is obtained by substitution reaction, and the intermediate product X is further substituted with an amine compound (or Grignard reagent).
- reaction conditions of the above reaction are:
- the organic solvent is selected from the group consisting of one or more of methanol, ethanol, and isopropanol, or a mixture of one or more of methanol, ethanol, and isopropanol mixed with ethyl acetate or tetrahydrofuran;
- Step 2 Base-catalyzed reaction in an organic solvent at room temperature to reflux temperature.
- the base is selected from one or a combination of two or more of sodium carbonate, potassium carbonate, and cesium carbonate;
- the organic solvent is selected from the group consisting of tetrahydrofuran, dioxane, isopropanol, ethanol, DMF, DMA, acetonitrile, DMSO, or both. The combination above.
- Protection of the protecting group can be used during the preparation of the compounds of the invention.
- the substituent R 1 can be protected by a protecting group before or during the reaction, and the "protecting group" is used to temporarily block a chemical reaction at a potential reaction site (for example, an amine, a hydroxyl group, a thiol group, an aldehyde, etc.) Thereby achieving a selective reaction of the chemical reaction.
- a potential reaction site for example, an amine, a hydroxyl group, a thiol group, an aldehyde, etc.
- a highly selective reaction is achieved by introducing a protecting group; the protecting group is selectively removed in high yield by a rapidly available preferred reagent which does not unduly affect other functional groups of the invention;
- the protecting group preferably forms a readily separable derivative (more preferably does not produce a new stereocenter); and the protecting group preferably has minimal other functionality to avoid complicating other sites of the reaction.
- a variety of protecting groups and protocols, reagents, and conditions for using and removing such protecting groups are known in the art. See, for example, "Protective Groups in Organic Synthesis” Third Ed. Greene, TW. Wouts, PG., Eds "John Wiley & Sons, New York: 1999.
- Step 1) The nitration reaction is carried out.
- the nitration reaction conditions are nitric acid and acetic acid.
- Step 2) performing a nitro reduction reaction, and the nitro reduction is carried out by a person skilled in the art; preferably, the conditions of the nitro reduction reaction include, but are not limited to, hydrogen and Raney nickel, hydrogen and palladium carbon, and iron powder under acidic conditions. Or zinc powder or stannous chloride;
- Step 3) 1-(8-Methoxy-6-amino-2,3-ddihydrobenzo[b][l,4]dioxin-5-)ethan-1-one and methyl formate Or ethyl formate in an organic solvent, catalyzed by a base to give 10-hydroxy-5-methoxy-2,3-dihydro-[1,4]dioxin and [2,3-f]-quinoline
- the organic solvent includes, but is not limited to, one or a combination of two or more of dioxane, tetrahydrofuran, tert-butanol, ethanol, methanol
- the base includes, but is not limited to, sodium t-butoxide, tert-butyl Potassium alkoxide, sodium methoxide, sodium ethoxide; the reaction can also be carried out under heating, heating at room temperature to reflux.
- Step 4) Preparation of 10-hydroxy-5-methoxy-2,3-dihydro-[1,4]dioxamic [2,3-f]-quinoline and chlorinating reagent in organic solvent 10-chloro-5-methoxy-2,3-dihydro-[1,4]dioxaindolo[2,3-f]-quinoline, wherein the chlorinating reagent is phosphorus oxychloride;
- the organic solvent includes, but is not limited to, one or a combination of two or more of benzene, toluene, chlorobenzene, and xylene; the reaction can also be carried out in the presence of an organic base, which is triethylamine. Or diisopropylethylamine.
- Step 4b) wherein 5-hydroxy-10-chloro-2,3-dihydro-[1,4]dioxamic [2,3-f]-quinoline is prepared in an organic solvent.
- Step 5 The compound represented by the formula ⁇ - ⁇ is heated in an organic solvent and mixed with the formula V' to 100 ° C to 140 ° C to obtain a compound represented by IV';
- the organic solvent is selected from the group consisting of toluene, chlorobenzene, and Toluene, DMF,
- Step 6) performing a nitro reduction reaction, and the nitro reduction can be carried out by a person skilled in the art;
- the nitro reduction reaction conditions include, but are not limited to, hydrogen and Raney nickel, hydrogen and palladium carbon, iron powder under acidic conditions, zinc powder or stannous chloride;
- Step 7) the compound of the formula ( ⁇ ) is shown by the formula ( ⁇ ' -A)
- the formula ( ⁇ ) can be reacted with an acylating reagent and then reacted with the formula ( ⁇ '-A).
- the acylating agent includes, but is not limited to, one or a combination of two or more of phosphorus oxychloride, thionyl chloride, oxalyl chloride, phosphorus trichloride or phosphorus pentachloride.
- a compound of the formula (I') is reacted with a compound of the formula (II'-A) in the presence of a condensing agent to provide a compound of the formula (I-C).
- the condensing agent includes, but not limited to, a carbodiimide type condensing agent, a gun salt type condensing agent, an organic phosphorus type condensing agent, and one or more kinds of other types of condensing agents, preferably ruthenium, osmium-bicyclic ring Hexyl carbodiimide (DCC), hydrazine, hydrazine-diisopropylcarbodiimide (DIC), hydroxybenzotriazole (HOBt), hydrazine, hydrazine-diisopropylethylamine (DIEA), 1- Hydroxy-7-azobenzotriazole (HOAt), 0-benzotriazole-N,N,N',N'-tetramethyluronium tetrafluoroborate (TBTU), benzotriazine Zin-1-yloxytris(dimethylamino) Phosphorus hexafluorophosphat
- this step can be carried out in an organic base including, but not limited to, triethylamine, diisopropylethylamine, pyridine, 4-dimethylaminopyridine, 2,6-lutidine One or a combination of two or more of 1,8-diazabicycloundec-7-ene or N-methylmorpholine.
- organic base including, but not limited to, triethylamine, diisopropylethylamine, pyridine, 4-dimethylaminopyridine, 2,6-lutidine One or a combination of two or more of 1,8-diazabicycloundec-7-ene or N-methylmorpholine.
- step 4a and step 4b may be omitted, and after step 4), the operation of step 5) may be performed.
- the compounds, isomers, crystalline forms or prodrugs of formula I, and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof may exist in both solvated and unsolvated forms.
- the solvated form can be in a water soluble form.
- the invention includes all such solvated and unsolvated forms.
- the compounds of the invention may have asymmetric carbon atoms which, depending on their physicochemical differences, may be separated by known techniques, such as by chromatography or fractional crystallization. Into a single diastereomer. Separation of the enantiomers can be carried out by first reacting the appropriate optically active compound, converting the enantiomeric mixture into a diastereomeric mixture, separating the diastereomers, and then separating the individual The enantiomers are converted (hydrolyzed) to the corresponding pure enantiomers. All such isomers, including diastereomeric mixtures and pure enantiomers, are considered part of this invention.
- the compound of the present invention as an active ingredient, and a method of preparing the same are all the contents of the present invention.
- the crystalline form of some of the compounds may exist as polycrystals, and such forms may also be included in the current invention.
- some compounds can be combined with water (ie hydrates) or common organic solvents.
- the compounds of the invention may be used in the free form for treatment or, where appropriate, in the form of a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or other derivative for treatment.
- pharmaceutically acceptable salt refers to organic and inorganic salts of the compounds of the present invention which are suitable for use in humans and lower animals without undue toxicity, irritation, allergic response, etc., and have reasonable Benefit/risk ratio.
- Pharmaceutically acceptable salts of amines, carboxylic acids, phosphonates, and other types of compounds are well known in the art.
- the salt can be formed by reacting a compound of the invention with a suitable free base or acid.
- salts with inorganic acids such as hydrochloric acid, hydrobromic acid, phosphoric acid, sulfuric acid, perchloric acid or with organic acids such as acetic acid, oxalic acid, maleic acid, tartaric acid, citric acid, succinic acid, malonic acid,
- inorganic acids such as hydrochloric acid, hydrobromic acid, phosphoric acid, sulfuric acid, perchloric acid or with organic acids such as acetic acid, oxalic acid, maleic acid, tartaric acid, citric acid, succinic acid, malonic acid
- salts include adipate, alginate, ascorbate, aspartate, besylate, benzoate, hydrogen sulfate, borate, butyrate, camphoric acid Salt, camphor sulfonate, citrate, digluconate, dodecyl sulfate, ethanesulfonate, formate, fumarate, glucoheptonate, glycerol phosphate, gluconic acid Salt, hemisulfate, hexanoate, hydroiodide, 2-hydroxyethanesulfonate, lactobionate, lactate, laurate, lauryl sulfate, malate, maleate, A Anthracene sulfonate, 2-naphthalene sulfonate, nicotinate, nitrate, oleate, palmitate, pamoate, pectate, persulphate, per-3-phenylpropionate , pity salt
- Representative alkali or alkaline earth metal salts include sodium, lithium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, and the like.
- Other pharmaceutically acceptable salts include suitable non-toxic ammonium, quaternary ammonium, and the use of such as halides, hydroxides, carboxylates, sulfates, phosphates, nitrates, lower alkylsulfonates and arylsulfonates.
- prodrug as used herein means that a compound can be converted into a compound of the formula (I) of the present invention in vivo. This transformation is affected by hydrolysis of the prodrug in the blood or enzymatic conversion to the parent compound in the blood or tissue.
- the pharmaceutical composition of the present invention comprises a compound of the formula (I) described herein or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, a kinase inhibitor (small molecule, polypeptide, antibody, etc.), an immunosuppressant, an anticancer drug, an antiviral agent, an antibiotic An additional agent for an inflammatory, antifungal, antibiotic or anti-vascular hyperproliferative compound; and any pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, adjuvant or vehicle.
- a kinase inhibitor small molecule, polypeptide, antibody, etc.
- an immunosuppressant an anticancer drug
- an antiviral agent an antibiotic
- an additional agent for an inflammatory, antifungal, antibiotic or anti-vascular hyperproliferative compound an additional agent for an inflammatory, antifungal, antibiotic or anti-vascular hyperproliferative compound.
- the compounds of the invention may be used alone or in combination with one or more other compounds of the invention or with one or more other agents.
- the therapeutic agents can be formulated for simultaneous administration or sequentially at different times, or the therapeutic agents can be administered as a single composition.
- “combination therapy” is meant the use of a compound of the invention in combination with another agent in the form of co-administration of each agent or sequential administration of each agent, in either case, for the purpose Achieve the best results of the drug.
- Co-administration includes simultaneous delivery of the dosage form, as well as separate dosage forms for each compound.
- administration of the compounds of the invention can be used in conjunction with other therapies known in the art, for example,
- one or more compounds or salts of the formula (I) as an active ingredient thereof can be intimately mixed with a pharmaceutical carrier, which is carried out according to conventional pharmaceutical ingredient technology.
- the carrier can be used in a wide variety of forms depending on the form of preparation which is designed for different modes of administration (for example, oral or parenteral administration).
- Suitable pharmaceutically acceptable carriers are well known in the art. A description of some of these pharmaceutically acceptable carriers can be found in the Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients, published jointly by the American Pharmaceutical Association and the British Pharmaceutical Society.
- the pharmaceutical composition of the present invention may be in the form of, for example, a suitable oral administration such as a tablet, a capsule, a pill, a powder, a sustained release form, a solution or a suspension; for parenteral injection such as a clear liquid, a suspension, Emulsion; or for topical use such as creams, creams; or as a suppository for rectal administration.
- a suitable oral administration such as a tablet, a capsule, a pill, a powder, a sustained release form, a solution or a suspension
- parenteral injection such as a clear liquid, a suspension, Emulsion
- topical use such as creams, creams; or as a suppository for rectal administration.
- the medicinal ingredients can also be administered in unit dosage form for a single dose of precise dosage.
- the pharmaceutical ingredient will include a conventional pharmaceutical carrier or excipient and a compound as an active ingredient prepared according to the present invention, and may also include other medical or pharmaceutical preparations, carriers, adjuvants
- Therapeutic compounds can also be administered to mammals other than humans.
- the dosage of the drug to be administered to a mammal will depend on the species of the animal and its condition or the condition in which it is placed.
- the therapeutic compound can be administered to the animal in the form of a capsule, a bolus, or a tablet.
- the therapeutic compound can also be introduced into the animal by injection or infusion. We prepare these forms of the drug in a traditional manner that meets the standards of veterinary practice.
- the pharmaceutical synthetic drug can be mixed with the animal feed and fed to the animal, so that the concentrated feed additive or premix can be prepared by mixing ordinary animal feed.
- the invention also encompasses the use of a compound of the invention, or a pharmaceutically acceptable derivative thereof, for the manufacture of a cancer (including non-solid tumors, solid tumors, primary or metastatic cancer, as indicated elsewhere herein and including cancer)
- a cancer including non-solid tumors, solid tumors, primary or metastatic cancer, as indicated elsewhere herein and including cancer
- An agent that is resistant or refractory to one or more other treatments, as well as other diseases including, but not limited to, fundus diseases, psoriasis, atheroma, pulmonary fibrosis, liver fibrosis, myelofibrosis, and the like .
- Such cancers include, but are not limited to, non-small cell lung cancer, small cell lung cancer, breast cancer, pancreatic cancer, glioma, glioblastoma, ovarian cancer, cervical cancer, colorectal cancer, melanoma, intrauterine Membrane cancer, prostate cancer, bladder cancer, leukemia, gastric cancer, liver cancer, gastrointestinal stromal tumor, thyroid cancer, chronic myeloid leukemia, acute myeloid leukemia, non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, nasopharyngeal carcinoma, esophageal cancer, brain Any of tumor, B cell and T cell lymphoma, lymphoma, multiple myeloma, cholangiocarcinoma, and cholangiocarcinoma.
- the invention is better illustrated by the examples provided below, all temperatures being in degrees Celsius unless otherwise stated.
- FIG. 26 Replacement page (Article 26) 1 is a schematic diagram showing experimental results of inhibition of c-MET signaling pathway in Example 21 of the present invention; and FIG. 2 is a schematic diagram showing experimental results of inhibition of c-MET signaling pathway in Example 24 of the present invention.
- the intermediate involved in the compound of the present invention can be produced by the following method, but is not limited to the following method.
- a part of the intermediates of the present invention can be synthesized by referring to the method of the patent CN104530063, and a simple replacement of some functional groups, and those skilled in the art can obtain corresponding intermediates according to the knowledge of the chemical synthesis field.
- the following invention provides the preparation route of the intermediate, and the intermediate involved in the compound of the present invention can be produced by the following scheme, but is not limited to the following scheme.
- Method B 240 mg of 1-((4-fluorophenyl)carbamoyl)cyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid was dissolved in chlorosulfoxide (5 mL) and heated under reflux for 1 hour, cooled and concentrated to give a yellow oil.
- dichloromethane 2 mL
- 3-fluoro-4-nitroaniline 160 mg
- dichloromethane 1 mL
- Example 3 consisting of 10-chloro-5-(2-methoxyethoxy)-2,3-dihydro-[1,4]dioxamic [2,3;] quinazoline and Reaction of N-(3-fluoro-4-hydroxyphenyl)-N-(4-chlorophenyl)cyclopropane-1, 1-dimethylformamide gave a white solid (yield: 79%).
- Example 3 consisting of 10-chloro-5-(2-methoxyethoxy)-2,3-dihydro-[1,4]dioxane[2,3;]quinazoline and Reaction of N-(3-fluoro-4-hydroxyphenyl)-N-(3-chlorophenyl)cyclopropane-1,1-dimethylamide gave a white solid in a yield of 75%.
- Example 3 consisting of 10-chloro-5-(2-methoxyethoxy)-2,3-dihydro-[1,4]dioxane[2,3;]quinazoline and Reaction of fluorophenyl)-N-(3-fluoro-4-hydroxyphenyl)cyclopropane-1, 1-dimethylformamide gave a white solid in a yield of 68%.
- Example 20 N-(4-fluorophenyl)-N- (4-((5-(3-(tetrahydropyrrol-1-yl)propoxy)-2,3-dihydro-[1,4] dioxo[2,3-f
- Example 22 N-(3-fluoro-4-((5-(3-morpholinepropoxy)-2,3-dihydro-[1,4] Preparation of oxane-[2,3-f]quinazolin-10-yl)amino)phenyl)-N-(4-fluorophenyl)cyclopropyl-1,1-dimethylamide
- Example 25 N-(2-chloro-4-((5-(3-morpholinepropoxy)) 2,3-Dihydro-[1,4]dioxane[2,3-f]quinazolin-10-yl)oxy)phenyl)-N-(4-fluorophenyl)cyclopropane- Preparation of 1,1-dimethyl amide
- Example 34 N-(3-Fluoro-4-((5-(3-(methylthio)propoxy)-2,3-dihydro-[l,4j dioxane[2,3- Preparation of f]quinazolin-10-yl)oxy)phenyl)-N-(4-fluorophenyl)cyclopropane-1,1-dimethylamide
- Example 36 N-(4-((5-(3-(l,1-dithiomorpholino)propoxy)-2,3-dihydro-[1,41 dioxane[2, Preparation of 3-f
- Example 38 N-(3-fluoro-4-((5-(2-(tetrahydropyrrol-1-yl)ethoxy)) -2,3-dihydro-[1,4]dioxane [2,3-f
- Example 24 The compound obtained in Example 24 (660 mg, 1 mmol) was dissolved in 15 mL of acetone, and stirred at room temperature for 15 min, then 2 mL of aqueous solution of L-malic acid (134 mg, 1 mmol) was added, stirring was continued for 12 hours, and the reaction mixture was filtered to give a white solid (400 mg). The solid was dissolved in 15 mL of ethanol and heated under reflux. After completely dissolved, the mixture was cooled and allowed to stand to afford white crystal compound 260 mg, HPLC >99%.
- Step 2) N-(4-Fluorophenyl)-N-(4-((5-hydroxy-2,3-dihydro-[1,4]dioxin[2,3-quinazoline-10 - base)
- Example 53 N-(4-Fluorophenyl)-N-(4-((5-(3-((2-hydroxyethyl))amino)propoxy)-2,3-dihydro-[1 , 4] Preparation of dioxo[2,3-f
- Step 4) 7V-(4-Fluorophenyl)-N-(4-((5-(3-((2-methoxyethyl)amino)propoxy)-2,3-dihydro-[ 1,4] Preparation of dioxo[2,3:/]quinazolin-10-yl)oxy)phenyl)cyclopropyl-1,1-dimethylformamide
- Step 4 N-(4-Fluorophenyl)-N-(4-((5-(3-((2-hydroxyethyl)methyl)amino)propoxy)-2,3-dihydro- Preparation of [1,4]-]quinazolin-10-yl)oxy)phenyl)cyclopropyl-1,1-dimethylformamide
- Example 58 N-(3-Fluoro-4-((5-(3-hydroxypropoxy)-2,3-dihydro-[1,4]dioxane[2,3-f
- step 3 was carried out from N-(3-fluoro-4-((5-hydroxy-2,3-dihydro-[1,4]dioxin and [2,3;]
- Example 59 N-(3-Fluoro-4-((5-(2-hydroxy-2-methylpropoxy)-2,3-dihydro-[1,4]dioxane[2,3 -f] quinazolin-10-yloxy)phenyl)-N-(4-fluorophenyl)cyclopropyl-1,1-dimethylamide Preparation Step 1) 2) Operation as in Example 57 .
- EtOAc EtOAc (EtOAc)EtOAc. - ⁇ 6 ) ⁇ 10.30 (s, 1H), 10.02 (s, 1H), 8.43 (s, 1H), 7.79 (dd, J 12.9, 2.4 Hz, 1H), 7.68 ⁇ 7.58 (m, 2H), 7.49 - 7.40 (m, 1H), 7.36 - 7.25
- Example 60 N-(4-((5-(3-Aminopropoxy)-2,3-dihydro-[1,4]dioxane[2,3-f]quinazoline-10- Preparation of 3-fluorophenyl)-N-(4-fluorophenyl)cyclopropyl-1,1-dimethylamide Step 1) 2) Operation as in Example 57.
- Step 4) N-(4-((5-(3-Aminopropoxy)-2,3-dihydro-[1,4]dioxin[2,3-]quinazolin-10-yl) Preparation of oxy)-3-fluorophenyl)-N-(4-fluorophenyl)cyclopropyl-1,1-dimethylamide
- tert-Butyl (R)-(4-hydroxybutyl-2-yl)carbamate 400 mg, 2.11 mmol
- pyridine 3 mL
- a solution of benzenesulfonyl chloride (606 mg, 3.2 mmol) in dichloromethane (2 mL).
- the reaction mixture was diluted with chloroformic acid, and washed with EtOAc EtOAc EtOAc (EtOAc m. +H) + .
- step 1) from 5-benzyloxy-10-chloro-2,3-dihydro-[1,4]dioxime[2,3;]quinazoline and N-(2 -Fluoro-4-hydroxyphenyl)-N-(4-fluorophenyl)cyclopropane-1, 1-dimethylformamide is obtained as a brown solid.
- Step 2) Preparation of l-(8-methoxy-6-amino-2,3-dihydrobenzo[b][l,4]dioxin-5-yl)ethyl-1-one
- Steps 1 to 4 are the same as Steps 1 to 4 of the preparation of Example 66.
- Step 7) N-(3-Fluoro-4-((5-methoxy-2,3-dihydro-[1,4]dioxin[2,3-f]quinolin-10-yl) yloxy) phenyl) - N - (4- fluorophenyl) cycloalkyl
- Steps 1 through 4 are the same as steps 1 through 4 of the preparation of Example 66.
- Step 7) N-(2-Fluoro-4-((5-methoxy-2,3-dihydro-[1,4]dioxin[2,3-f]quinolin-10-yl) yloxy) phenyl) - N - (4- fluorophenyl) cyclopropane - preparation dicarboxamide - 1, 1
- Steps 1 to 4 are the same as Steps 1 to 4 of the preparation of Example 66.
- Steps 1 to 4b are the same as Steps 1 to 4b of the preparation of Example 69.
- Compound dilution a total of 12 concentrations after a 4-fold gradient dilution from the highest concentration of 10000 nM (the maximum final concentration of the drug used in this experiment is 10000 nM, the minimum final concentration is 0.002384 nM).
- Stop the enzymatic reaction Add 5 ⁇ 4 ⁇ Stop solution to the well of a 384-well plate, mix by centrifugation, and react at room temperature for 5 min.
- Inhibition rate (%) [1- (experimental well reading - negative control well reading) / (positive control well reading) - Negative control well reading)) ⁇ 100%.
- Using GraphPad Prism5 software deal with the corresponding IC 50 values (concentration of compound inhibition rate of enzyme up 50%).
- Table (1) lists the results of measurement of tyrosine kinase inhibitory activity by some of the compounds of the present invention, wherein A represents IC 5 o is less than or equal to 50 nM, and B represents IC 5 . Greater than 50 nM but less than or equal to 500 nM, C means IC 5Q is greater than 500 nM but less than or equal to 5000 nM, and D represents IC 5 . More than 5000 nM.
- Positive control Add 2.5 ⁇ ! well to the 384-well plate 4 ⁇ substrate / ATP Mix, 2.5 ⁇ ! 7 well IX Kinase Assay Buffer with 4% DMSO, 5 ⁇ ! well 2 ⁇ c-Met solution. The final concentration of DMSO in the reaction system is 4%.
- Stop the enzymatic reaction Add 5 ⁇ 4 ⁇ Stop solution to the well of a 384-well plate, mix by centrifugation, and react at room temperature for 5 min.
- Inhibition rate (%) [1 - (experimental well reading - negative control well reading) / (positive control well reading) - Negative control well reading)) ⁇ 100%.
- the corresponding IC 5 was obtained by processing with GraphPad Prism5 software. Value (concentration of compound at the highest inhibition rate of enzyme 50%).
- Table (b) lists the results of the determination of tyrosine kinase inhibitory activity by some of the compounds in this patent, wherein A represents IC 5 .
- B means IC 50 is greater than 50 nM but less than or equal to 500 nM, and C represents IC 5 . More than 500 nM but less than or equal to 5000 nM, D represents IC 5 . More than 5000 nM.
- test for cell survival of small molecule compounds is as follows:
- Table (3) lists the results of assays for the activity of representative compounds of the present invention against various cancer cells, wherein MHCC97H, HuH7, and HepG2 are liver cancer cell lines, A549 is a lung cancer cell line, and 8505C is a thyroid cancer cell line. NT indicates that the corresponding cell activity was not tested. Table (3) Results of measurement of cell activity of representative compounds of the present invention
- Electrophoresis First electrophoresis at 100V for 30 min, then increase the voltage by only 120 V until the electrophoresis is completed.
- Transfer film Transfer film by wet transfer method, constant pressure 100V, transfer film for 90min.
- the highly metastatic MHCC97H hepatoma cell line was selected as the experimental object, and the results showed that the cell itself highly expressed pERK and c-Met.
- pERK and c-Met replacement page fine 26
- the expression was significantly reduced and presented a dose-dependent response.
- the small molecule compounds of Examples 21 and 24 of this patent exhibited the same effects as cabozantinib, as shown in Figures 1 and 2.
- the experimental results of Examples 21 and 24 are only representative of a plurality of experiments.
- the biological data provided by the present invention indicate that the compounds of the present invention are useful for treating or preventing diseases caused by abnormalities of VEGFR-2 and c-Met kinase.
- Some of the compounds of the present invention have potent in vitro inhibitory activities against cancer cells, including liver cancer cells MHCC97, HuH7, HepG2, lung cancer cells A549, and thyroid cancer cells 8505C.
- the compounds of the invention are useful in the treatment of cancer, including primary and metastatic cancers, including solid tumors.
- Such cancers include, but are not limited to, non-small cell lung cancer, small cell lung cancer, breast cancer, pancreatic cancer, glioma, glioblastoma, ovarian cancer, cervical cancer, colorectal cancer, melanoma, intrauterine Membrane cancer, prostate cancer, bladder cancer, leukemia, gastric cancer, liver cancer, gastrointestinal stromal tumor, thyroid cancer, chronic myeloid leukemia, acute myeloid leukemia, non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, nasopharyngeal carcinoma, esophageal cancer, brain Tumor, B-cell and T-cell lymphoma, lymphoma, multiple myeloma, biliary sarcoma, cholangiocarcinoma.
- the compounds of the invention also include cancers that are resistant to one or more other therapeutic remedies.
- the compounds of the invention are also useful in diseases other than cancer associated with VEGFR-2 kinase and/or c-Met kinase, including but not limited to fundus diseases, psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, atheroma, lung Fibrosis, liver fibrosis.
- the compounds of the present invention may be administered as a monotherapy or a combination therapy, in combination with a plurality of compounds of the present invention or in combination with other drugs other than the present invention.
- the compounds of the invention are also useful as standards and reagents for characterizing various kinases, particularly but not limited to protein tyrosine kinases, and are useful for studying the role of such kinases in biological and pathological phenomena: Intracellular signal transduction pathways mediated by such kinases are studied for comparative evaluation of new kinase inhibitors; and in cell lines and animal models for studying different cancers.
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Pharmaceuticals Containing Other Organic And Inorganic Compounds (AREA)
Abstract
本发明涉及具有式(I)的二噁烷并喹唑啉以及二噁烷并喹啉类化合物或其可药用盐。本发明还提供了一种式(I)所述化合物及其可药用盐的制备和作为药物的应用,所述药物作为络氨酸激酶(例如VEGFR-2和c-Met)抑制剂用于治疗与络氨酸激酶相关的疾病。
Description
二噁烷并喹唑啉与二噁烷并喹啉类化合物及其制备方法与应用 技术领域 本发明涉及二噁垸并喹唑啉与二噁垸并喹啉类化合物,其药学上可接受的盐, 异构体, 水合物, 溶剂化物, 或前药, 及其制备方法和用途。 背景技术 受体酪氨酸激酶 (RTKs)横跨细胞膜,影响生物化学信号的跨细胞膜传输, 其 由含有配体结合位点的细胞外结构域、单次跨膜区、含有酪氨酸蛋白激酶活性的 细胞内结构域三部分组成。配体与受体的结合会刺激受体相关的酪氨酸激酶活性, 该活性导致受体和其他细胞内分子上的酪氨酸残基的憐酸化,进而引发导致各种 细胞反应的级联信号。酪氨酸受体的过度表达激活了下游信号转导通路, 最终导 致细胞的异常转化和增殖, 促进肿瘤的发生、 发展。
血管内皮生长因子受体 ( vascular endothelial growth factor receptor, VEGFR ) 是受体酪氨酸激酶家族中的一种, 通过与其配体血管内皮生长因子 ( vascular endothelial growth factor, VEGF ) 结合产生一系列生化和生理过程, 最终促使新 生血管形成。 肿瘤血管的生成和它们的通透性主要通过血管内皮细胞生长因子
(VEGF)调节,其通过至少两种不同的受体(VEGFR-1、 VEGFR-2)发挥作用。 根据 Jakeman、 Kolch、 Connolly等的研究显示: VEGF是正常和病理性血管生成 和血管渗透性的重要刺激物 (Jakeman 等, 1993, Endocrinology 133: 848-859; Kolch 等, 1995, Breast Cancer Research and Treatment, 36: 139-155; Connolly 等, 1989, J. Biol. Chem. 264: 20017-20024)。 血管内皮细胞生长因子通过诱导 内皮细胞增殖、蛋白酶表达和迁移及随后形成毛细管的细胞组织来诱发血管芽生 表型。 因此, 通过抗体对 VEGF的螯合作用产生的对 VEGF的拮抗作用可导致 肿瘤生长的抑制 (Kim等, 1993, Nature 362: 841-844)。
由于 VEGFR-2主要分布在血管内皮细胞内, 可以与 VEGF-A、 VEGF-C、 VEGF-D, VEGF-E结合。 而 VEGF刺激内皮细胞的增殖、 增加血管的通透性和 新血管的生成作用主要是通过结合和激活 VEGFR-2 来实现的。 如果阻断 VEGFR-2 的活性, 可以通过直接和间接途径抑制肿瘤的生长和转移, 进而达到 理想的抗肿瘤效果。 因此, 寻找对 VEGFR-2具有高活性、 高选择性的小分子抑 制剂成为非常有前景的肿瘤治疗策略。
1
替换页(细则第 26条)
肝细胞生长因子受体(hepatocyte growth factor receptor, c-Met)是酪氨酸激 酶受体的一种,其异常活化在多种恶性肿瘤包括肺癌的发生和发展中起着重要的 作用。 肝细胞生长因子 (HGF)为 c-Met的特异性配体, c-Met与 HGF结合后通过 HGF/c-Met信号通路发挥生物学作用。 HGF/c-Met信号通路能诱导细胞增殖、 分 散、 迁移、 器官形态形成、 血管发生等一系列生物效应。 c-Met的异常活化可表 现为受体过表达、 基因突变、 扩增、 异位、 重排等。 这些变化可导致下游信号通 路失调, 如丝氨酸 /苏氨酸蛋白激酶 (AKT)、 胞外信号激酶 (ERK )、 璘脂酰肌 醇 -3-羟基激酶、 视网膜母细胞瘤抑制蛋白 (Rb ) 通路等, 介导肿瘤发生、 侵袭 和转移、 血管新生、 上皮间质转化等过程。 c-Met在细胞的增殖、 代谢以及肿瘤 的产生、 转移、 血管生成中扮演着重要角色, 已成为抗肿瘤治疗的重要靶点。 以 c-Met为靶点的靶向治疗已在包括肺癌在内的多种恶性肿瘤的治疗中显现出其重 要意义。
在使用抗肿瘤药物的治疗过程中,多个信号通路的相互作用会影响抗肿瘤药 物的作用效果, 如 HFG/c-Met信号通路与其他通路的相互作用影响了抗肿瘤药 物的治疗效果, 产生药物耐药性。 因此, 多激酶靶点联合用药成为新的抗肿瘤治 疗手段, 而 Crizotinib 和 Cabozantinib 的成功上市说明了多激酶靶点抑制剂的 开发具有良好的潜力和应用价值。
Cabozantinib是一种蛋白激酶的小分子抑制剂, 对 c-Met、 VEGFR-2、 Ret、 Kit、 AXL等多种激酶有抑制作用。 Cabozantinib在肿瘤模型中能抑制 c-Met和 VEGFR-2 的磷酸化, 在临床前药效模型中显示出有效的抗肿瘤转移和抗血管生 成活性。 同单独作用于 VEGFR靶标的抑制剂相比, 在用 Cabozantinib治疗的肺 部肿瘤转移模型中并未发现肿瘤负荷增加, 说明 Cabozantinib 是 c-Met 和 VEGFR2信号通路失调肿瘤患者中肿瘤血管生成和转移的有效抑制剂。 FDA于 2012年 11月 29日批准 Cabozantinib上市用于进展性,转移甲状腺髓样癌 (MTC) 患者的治疗。
类似于 Cabozantinib这样作用于多靶标的抑制剂有许多优点,对于此种类型 抑制剂的研究也十分火热。 目前上市的药物很少, 获得的渠道有限, 并且已上市 的药物在使用中会出现耐药性和副作用等问题。因此,相比已经上市的单靶点抑 制剂而言, 多靶标的小分子抑制剂会有更好的治疗效果和应用前景。 发明内容 本发明所提供式 (I) 表示的化合物, 其药学上可接受的盐, 异构体, 水合 物, 溶剂化物, 或前药, 其可用作治疗或预防由酪氨酸激酶 (例如 VEGFR-2和
2
替换页(细则第 26条)
/或 c-Met) 引起的 病, 包括酪氨酸激酶受体的某些变种。
式 (I)
式 (I) 中,
Q为 N或者 CH;
G为 0或者 NH;
Z为 N或者 CH;
其中 X为 H或 d-C3的垸基; Y为 H或 d-C3的垸基; n=0-3,且当 n=0时, L表示为环丙垸的连接基团;
R1为 H, C C9垸基, C3-C7的环垸基, 4-7元杂环基, C3-C7的环垸基取代 的 d-C6垸基, 4-7元杂环基取代的 d-C6垸基, 取代的 d-C9垸基, 所述取代的 CrC9烷基的取代基为羟基、 CrC6的垸氧基、 d-C6的垸硫基或 -NR6R7中的一种 或一种以上,
R6和 R7分别独立地为 H、 C C6垸基、 羟基取代的 d-C6烷基、 d-C3垸氧 基取代的 6烷基;
上述 4-7元杂环基为含有 1-2个选自 N、 0、 S中的原子的 4-7元杂环基, 4-7 元杂环基不被取代或被 d-C3垸基、 d-C3酰基取代或被一至二个氧原子氧化。
1 2为11、 d-C3的垸基或卤素;
1 3为11、 d-C3的垸基或卤素;
1 4为 d-C3的垸基或卤素;
R5为 H, C C9垸基, C3-C7的环垸基, C3-C7环垸基取代的 C C6烷基, 芳 基, 芳基取代的 d-C6垸基, 杂芳基或杂芳基取代的 - 垸基;
所述芳基、 杂芳基为不被取代或被^-¾的烷基、 d-C3的烷氧基、 ^-¾的 替换页(细则第 26条)
烷硫基、 单或双 CrC3的氨基、 卤素、 三氟甲基、 芳氧基和甲砜基中的一种或一 种以上取代;
上述杂芳基为含有 5至 10个环原子的单环或双环基团; 杂芳基含有 1-3个 选自 N、 0、 S中的杂原子。
在优选的方案中,
所述 R1为 H, d-C6烷基, C3-C6的环垸基, 5-6元杂环基, C3-C6的环烷基 取代的 d-C3烷基, 5-6元杂环基取代的 C C3烷基, 取代的 d-C6垸基, 所述取 代的 d-C6垸基的取代基为羟基、 d-C3的垸氧基、 d-C3的垸硫基或 -NR6R7,
R6和 R7分别独立地为 H、 C C3垸基、 羟基取代的 d-C3垸基、 CrC3烷氧 基取代的 3垸基。
上述 5-6元杂环基为含有 1-2个选自 N、 0、 S中的原子的 5-6元杂环基、不 被取代或被 d-C3垸基、 d-C3酰基取代或被一至二个氧原子氧化。
在优选的方案中,
所述 R1选自甲基、 乙基、 丙基、 异丙基、 甲氧基乙基、 甲氧基丙基、 甲氧 基丁基、 甲氧基戊基、 甲氧基己基、 四氢呋喃 -3-基、 四氢 -2H-吡喃 -4-基、 四氢 吡咯小乙基、 四氢吡咯 -1-丙基、 吗啉 -4-乙基、 吗啉 -4-丙基、 甲基哌嗪 -4-乙基、 甲基哌嗪 -4-丙基、 N-甲酰基哌嗪 -4-乙基、 N-甲酰基哌嗪 -4-丙基、 N-乙酰基哌嗪 -4-乙基、 N-乙酰基哌嗪 -4-丙基、 (1,1-二氧硫代吗啉基) -4-乙基、 (1,1-二氧硫代吗 啉基) -4-丙基、 甲硫基乙基、 甲硫基丙基、 二甲氨基乙基、 二甲氨基丙基、 二甲 氨基丁基、 二甲氨基戊基、二甲氨基己基、 二乙氨基乙基、 二乙氨基丙基、 羟基 乙基、 羟基丙基、 羟乙基氨基乙基、 羟丙基氨基乙基、 羟乙基氨基丙基、 甲氧基 乙基氨基乙基、 甲氧基丙基氨基乙基、 甲氧基乙基氨基丙基、 氨基乙基、 氨基丙 基、 氨基丁基、 N-甲基 -N-羟乙基氨基乙基、 N-甲基 -N-羟丙基氨基乙基、 N-甲基 -N-羟乙基氨基丙基、 N-甲基 -N-甲氧基乙基氨基乙基、 N-甲基 -N-甲氧基丙基氨 基乙基、 N-甲基 -N-甲氧基乙基氨基丙基、 2-甲基 -2-羟基丙基、 3-甲基 -3-羟基丁 基、 (3S)-3-氨基丁基、 (3R)-3-氨基丁基、 (3S)-3-羟基丁基或 (3R)-3-羟基丁基中的 一种或一种以上。
在优选的方案中,
R2、 R3、 R4所述的卤素为 0或1^。
在优选的方案中,
R5为 H, d-C6垸基, C3-C6环垸基, C3-C6环垸基取代的 C C3垸基, 芳基, 芳基取代的 c c3垸基, 杂芳基或杂芳基取代的 -¾垸基, 所述的芳基、 杂芳 基的取代基为 crc3的烷基、 d-C3的垸氧基、 c c3的垸硫基、 单或双 ^-¾取
4
替换页(细则第 26条)
代的氨基、 卤素、 三氟甲基、 芳氧基和甲砜基中的一种或一种以上;
所述杂芳基为含有 5至 10个环原子的单环或双环基团; 杂芳基含有 1-2个 选自 N、 0、 S中的杂原子。
在优选的方案中,
R5选自 H、 甲基、 乙基、 丙基、 异丙基、 异戊基、 环丙基、 环丁基、 环戊 基、 环己基、 苯基、 4-氟苯基、 3-氟苯基、 2-氟苯基、 4-氯苯基、 3-氯苯基、 2- 氯苯基、 2,4-二氟苯基、 2,5-二氟苯基、 3,4-二氟苯基、 2,4-二氯苯基、 2,5-二氯苯 基、 3,4-二氯苯基、 2-氟 -4- (三氟甲基)苯基、 2-氟 -5- (三氟甲基)苯基、 3-氟 -4- (三 氟甲基)苯基、 3-氟 -5- (三氟甲基)苯基、 3-三氟甲基 -4氟苯基、 2-氟 -4-氯苯基、 2- 氟 -5-氯苯基、 3-氟 -4-氯苯基、 3-氟 -5-氯苯基、 3-氯 -4-氟苯基、 2-氯 -4- (三氟甲基) 苯基、 2-氯 -5- (三氟甲基)苯基、 3-氯 -4- (三氟甲基)苯基、 3-氯 -5- (三氟甲基)苯基、
3-三氟甲基 -4-氯苯基、 2-氯 -4-氟苯基、 2-氯 -5-氟苯基、 3-氯 -4-氟苯基、 苄基、 苯 乙基、 4-氟苄基、萘 -1-基、 3-甲基-异噁唑 -5-基、 4-苯氧基苯基、 3- (甲砜基)苯基、
4- (甲砜基)苯基、 吡啶 -2-基、 吡啶 -3-基、 吡啶 -4-基、 3-甲氧基苄基或 4-甲氧基苄 基。
本发明提供了的式 (I) 化合物可药用的盐, 其中所述的盐是酸性 /阴离子盐 或碱性 /阳离子盐; 药学上可接受的酸性 /阴离子盐通常采取的形式是让其中的碱 性氮被无机或有机酸质子化,代表性的有机或无机酸包括盐酸、氢溴酸、氢碘酸、 高氯酸、 硫酸、 硝酸、 璘酸、 甲酸、 乙酸、 丙酸、 羟基乙酸、 乳酸、 琥珀酸、 马 来酸、酒石酸、苹果酸、柠檬酸、富马酸、葡萄糖酸安息香酸、扁桃酸、 甲磺酸、 羟乙基磺酸、 苯磺酸、 草酸、 棕榈酸、 2-萘磺酸、 对甲苯磺酸、 环己胺基磺酸、 水杨酸、 己糖酸、 三氟乙酸。 药学上可接受的碱性 /阳离子盐类包括 (当然不仅限 于此)铝、 钙、 氯普鲁卡因、 胆碱、 二乙醇胺、 乙二胺、 锂、 镁、 钾、 钠和锌。
本发明提供一种制备上述化合物或者其药学上可接受的盐,异构体、水合物、 溶剂化物、或前药的方法,其特征在于,包括以下步骤,式(II)化合物与式(III) 化合物反应制备得到式 (I) 化合物, Q为 N, G、 Z、 L、 R R2、 R3、 R4和 R5 如前文 ,
本发明提供一种制备上述化合物或者其药学上可接受的盐,异构体、水合物、 替换页(细则第 26条)
溶剂化物、 或前药的方法, 其特征在于, 包括以下步骤, 由式 (II ' ) 所示化合 物与式(III ' )所示化合物反应制备得到式(I)化合物, 其中 Q、 G、 Z、 L、 R R2、 3、 R4和 R5如前文所定义,
(Π)
本发明提供制备上述化合物的中间体, 一种式(π ' )所示的化合物, 其中,
Q、 G、 Z、 R R2、 R3、 和 R4如前文所定义,
发明详述
在这里所指的术语"取代", 包括复杂取代基 (比如, 苯基, 芳基, 杂垸基, 杂芳基), 比较合适的是 1至 5个取代基,较好的是 1到 3个,最好是 1到 2个, 可从取代基列表上自由选择。
除非有特殊说明, 烷基, 包括饱和直链、 支链烃基, 9表示烷基的碳原 子数为 1-9的碳原子, 同理的 CrC3比如表示烷基的碳原子数为 1-3的碳原子, 比 如, C C6垸基包括甲基, 乙基, 丙基, 异丙基, n-丁基, 异丁基, 仲-丁基, 叔- 丁基, n-戊基, 3-(2-甲基)丁基, 2-戊基, 2-甲基丁基, 新戊基, n-己基, 2-己 基和 2-甲基戊基。 垸氧基由先前描述的直链, 分支链组成的垸基醚。类似的, 烯 基和炔基包括直链, 支链烯基或炔基。
环垸基, 指碳原子形成的环状基团, 例如, C3-C7表示垸基的碳原子数为 3-7
6
替换页(细则第 26条)
的碳原子, 环丙基、 环丁基、 环戊基、 环己基、 环庚基, 类似的, 同样包括环状 烁基。
在这里使用的术语"芳基", 除非有特别说明, 指的是未被取代的或已被取代 的芳香基, 例如苯基, 萘基, 蒽基。 术语"芳酰基 "指 -C(O)-芳基。
"被一至两个氧原子氧化"是指硫原子被一个氧原子氧化形成硫和氧之间以 双键连接, 或被两个氧原子氧化形成硫和两个氧之间以双键连接。
在这里使用的术语"杂环基", 除非有特殊说明, 代表未被取代的或已被取代 的稳定的 3至 8元单环饱和环体系, 它们由碳原子以及从 N, 0, S中选的 1至 3个杂原子组成, 其中 N, S杂原子可以被随意氧化, N杂原子还可以被随意季 铵化。杂环可以和任何杂原子或碳原子结合, 从而组成一个稳定的结构。这类杂 环的例子包括(但并不局限于)氮杂环丁烷基, 吡咯垸基, 四氢呋喃基, 四氢噻 唑基, 四氢吡喃基, 吗啉基, 硫代吗啉基, 哌啶基, 哌嗪基, 氧化哌嗪基, 氧化 哌啶基,二氧环戊烷基,二氧环己垸基四氢咪唑基,四氢噁唑基,硫代吗啉亚砜, 硫代吗啉砜以及噁二唑基。
在这里使用的术语"杂芳基", 除非有特别说明, 代表未被取代或已被取代的 稳定的 5或 6元单环芳香环体系, 也可以代表未被取代或已被取代的 9或 10个 环原子的苯稠杂芳环体系或二环杂芳环体系, 它们由碳原子和由 1至 3个从 N, 0, S中选择的杂原子组成, 其中 N、 S杂原子可以被氧化, N杂原子还可以被 季铵化。杂芳基可以和任何杂原子或碳原子连接组成一个稳定的结构。杂芳基包 括但并不局限于噻吩基,呋喃基, 咪唑基,吡咯基,噻唑基,噁唑基,异噁唑基, 吡喃基, 吡啶基, 哌嗪基, 嘧啶基, 吡嗪, 哒嗪基, 吡唑基, 噻二唑基, 三唑基, 吲哚基, 氮杂吲哚基, 吲唑基, 氮杂吲唑基, 苯并咪唑基, 苯并呋喃基, 苯并噻 吩基, 苯并异噁唑基, 苯并噁唑基, 苯并吡唑基, 苯并噻唑基, 苯并噻二唑基, 苯并三唑基, 腺嘌呤基, 喹啉基或异喹啉基。
术语"羰基"指的是 C(0)基。
无论何时术语 "烷基 "或"芳基"或任何它们的前缀词根出现在一个取代物的 名称中 (例如, 芳垸基, 二垸基氨), 它将被认为包含了以上为"垸基"和"芳基"而 给出的那些限制。碳原子的指定数量 (比如, d- )将独立的表示在一个垸基部分 或在一个更大的取代基中的烷基部分(其中垸基作为其前缀词根)中的碳原子的 数直。
在本发明的一个优选方案中提供式 (I) 化合物或其异构体、 互变异构体、 溶剂化物, 水合物及其药学上可接受的盐,
本发明还提供了制备相应化合物的方法,可以使用多种合成方法制备本文所 述的化合物, 包括下述的方法, 本发明的化合物或者其药学上可接受的盐, 异构 替换页(细 第 26条)
体或水合物可以使用下述方法与有机化学合成领域已知的合成方法,或通过本领 域技术人员理解对这些方法的变化方法合成, 优选方法包括但不限于下述方法。
在一个方案中, 本发明式(I)化合物由式(II ' )化合物与式(III' ) 反应制 备, Z、 L、 R R2、 R3、 R4和 R5如前文所述。
本发明进一步提供了制备式(I)化合物中间体, 即式(II ' )所示的化合物, 其中, Q、 G、 Z、 R R2、 R3和 R4如前文所定义,
(TT)
替换页(细则第 26条)
进一步地, 本发明提供制备式 (I) 化合物或者其药学上可接受的盐, 异构 体或水合物的方法,
本发明化合物可以通过方案 1至方案 4或本领域技术人员已知的技术方案制 备,
步骤 1 ) 二羧酸原料与二氯亚砜反应后除去溶剂, 加入有机碱, 非质子有机 溶剂和原料 VII反应得到式 VI所示化合物; 其中有机碱优选于三乙胺、 二异丙 基乙基胺、 吡啶之一或两者以上的组合。 非质子有机溶剂选自四氢呋喃、 甲苯、 二氯甲垸、 二氧六环、 DMF、 DMA之一或者两者以上的组合。
步骤 2) 在一个优选的方案中, 式 (VI) 所示化合物与式 (V) 所示化合物 反应时, 其中式 (VI) 可与酰化试剂反应, 再与式 (V) 进行反应。
优选地, 所述的酰化试剂包括但不限于三氯氧磷、 二氯亚砜、 草酰氯、 三氯 化磷或五氯化磷中一种或两种以上的组合。
在另一个实施方案中, 式 (VI) 所示化合物, 在缩合剂存在下, 与式 (V) 所示化合物反应, 得到式 (IV) 所示化合物,
优选地, 所述缩合剂包括但不限于碳二亚胺型缩合剂, 鎗盐类缩合剂, 有机 憐类缩合剂及其他类别缩合剂的一种或两种以上, 优选 Ν,Ν-二环己基碳二亚胺 (DCC ) , Ν,Ν-二异丙基碳二亚胺 (DIC ) , 羟基苯并三唑 (HOBt) , Ν,Ν-二 异丙基乙胺 (DIEA ) , 1-羟基 -7-偶氮苯并三氮唑 (HOAt) , 0-苯并三氮唑- N,N,N',N'-四甲基脲四氟硼酸酯 (TBTU) , 苯并三氮唑 -1-基氧基三 (二甲基氨基) 磷鎗六氟憐酸盐 (B0P), 2 -(7-氧化苯并三氮唑) -N,N,N',N'-四甲基脲六氟磷酸酯
9
替换页(细则第 26条)
(HBTU) 、 6-氯苯并三氮唑 -1,1,3,3-四甲基脲六氟磷酸酯 (HCTU) , 2-(7-氧化 苯并三氮唑) -N,NN',N'-四甲基脲六氟磷酸酯 (HATU) , 丙基磷酸酐 (T3P) , 1-(3-二甲氨基丙基 )-3-乙基碳二亚胺盐酸盐 (EDCI) , 1-乙基 (3-二甲基氨基丙基) 碳二亚胺(EDC ),六氟憐酸苯并三唑 -1-基-氧基三吡咯烷鳞(PyBOP), (3H-1,2,3 三唑并 [4,5-b]吡啶 -3-氧基)三 -1-吡咯垸基鳞六氟磷酸盐 (PyAOP) 中一种或两种 以上的组合;
优选地, 此步骤可在有机碱中进行, 所述的有机碱包含但不限于三乙胺、 二 异丙基乙基胺(DIEA),吡啶,4-二甲氨基吡啶(DMAP),2,6-二甲基吡啶(Lutidine), 1,8-二氮杂二环十一碳 -7-烯 (DBU) 或 N-甲基吗啉一种或两种以上的组合。
步骤 3 )硝基还原反应的条件包含但不限于氢气与雷尼镍, 氢气或甲酸铵与 钯碳, 铁粉, 锌粉, 氯化亚锡;
步骤 4) 在有机溶剂中, 室温至回流温度下, 碱催化反应。
优选地, 碱选自碳酸钠、 碳酸钾、 碳酸铯的其中一个或者两个以上的组合; 有机溶剂选自四氢呋喃、 二氧六环、 异丙醇、 乙醇、 DMF、 DMA, 乙腈之一或 者两者以上的组合。
方案 2, 当式 (I) 中 G为 0时,
反应条件为:
步骤 1 ) 在一个优选的方案中, 式 (VI) 所示化合物与式 (VIII) 所示化合 物反应时, 其中式 (VI) 可与酰化试剂反应, 再与式 (VIII) 进行反应。
优选地, 所述的酰化试剂包括但不限于三氯氧磷、 二氯亚砜、 草酰氯、 三氯 化磷或五氯化磷中一种或两种以上的组合。
在另一个实施方案中, 式(VI)所示化合物,在缩合剂存在下, 与式(VIII) 所示化合物反应, 得到式 (Π-Β) 所示化合物,
优选地, 缩合剂包括但不限于碳二亚胺型缩合剂, 鎗盐类缩合剂, 有机憐类 缩合剂及其他类别缩合剂的一种或两种以上, 优选 Ν,Ν-二环己基碳二亚胺
10
替换页(细则第 26条)
(DCC ) , Ν,Ν-二异丙基碳二亚胺 (DIC ) , 羟基苯并三唑 (HOBt) , Ν,Ν-二 异丙基乙胺 (DIEA ) , 1-羟基 -7-偶氮苯并三氮唑 (HOAt) , 0-苯并三氮唑- N,N,N',N'-四甲基脲四氟硼酸酯 (TBTU) , 苯并三氮唑 -1-基氧基三 (二甲基氨基) 憐鎗六氟憐酸盐 (BOP), 2 -(7-氧化苯并三氮唑) -N,NN',N'-四甲基脲六氟璘酸酯
(HBTU) 、 6-氯苯并三氮唑 -1,1,3,3-四甲基脲六氟磷酸酯 (HCTU) , 2-(7-氧化 苯并三氮唑 )-N,NN',N'-四甲基脲六氟磷酸酯 (HATU) , 丙基磷酸酐 (T3P) , 1-(3-二甲氨基丙基 )-3-乙基碳二亚胺盐酸盐 (EDCI) , 1-乙基 (3-二甲基氨基丙基) 碳二亚胺(EDC ),六氟憐酸苯并三唑 -1-基-氧基三吡咯垸鳞(PyBOP), (3H-1,2,3 三唑并 [4,5-b]吡啶 -3 氧基)三 -1-吡咯烷基鳞六氟磷酸盐 (PyAOP) 中一种或两种 以上的组合;
优选地, 此步骤可在有机碱中进行, 所述的有机碱包含但不限于三乙胺、 二 异丙基乙基胺, 吡啶, 4-二甲氨基吡啶, 2,6-二甲基吡啶, 1,8-二氮杂二环十一碳 -7-烯或 N-甲基吗啉一种或两种以上的组合。
步骤 2)在有机溶剂中, 室温至回流温度下碱催化反应。 碱选自碳酸钠、 碳 酸钾、碳酸铯的其中一个或者两个以上的组合; 有机溶剂选自四氢呋喃、二氧六 环、 异丙醇、 乙醇、 DMF、 DMA, 乙腈之一或者两者以上的组合。
除上述提供的方法外, R1, R2, R3, R4和 R5取代基的引入还可以通过本领 域技术人员知晓的其他方法引入, 例如 -0-R1取代基的引入可以通过苄氧基中间 体脱苄氧基保护反应, 制备酚羟基, 再与 经过取代反应得到式 (I)化合物 或中间产物 X, 中间产物 X进一步与胺类化合物 (或格氏试剂) 经取代反应获 得式(I)化合物,(M选自卤素或其他离去基团,所述离去基团选自 TsO-,MsO-, TfO-; 卤素优选 Cl-, Br-或 1-)。
方案 3 :
上述反应的反应条件为:
11
替换页(细则第 26条)
步骤 1 )在有机溶剂中的钯碳 /氢气脱保护基团反应。有机溶剂选自甲醇、 乙 醇、 异丙醇的其中一个或者两个以上的混用, 或者甲醇、 乙醇、 异丙醇的其中一 个或者两个以上的混和溶剂与乙酸乙酯或四氢呋喃的混用;
步骤 2) 在有机溶剂中, 室温至回流温度下的碱催化反应。 碱选自碳酸钠、 碳酸钾、碳酸铯的其中一个或者两个以上的组合; 有机溶剂选自四氢呋喃、 二氧 六环、 异丙醇、 乙醇、 DMF、 DMA, 乙腈、 DMSO之一或者两者以上的组合。
本发明化合物制备过程中, 可以使用保护基保护。 例如, 取代基 R1在接入 前, 或反应过程中, 可进行保护基保护, "保护基"用于暂时阻断潜在的反应位点 发生化学反应 ( 例如, 胺、 羟基、 巯基、 醛等)从而实现化学反应选择性进行。 在优选的实施方案中,通过引入保护基团实现高选择性反应; 所述保护基通过快 速可用的优选反应试剂以高产率选择性除去,所述反应试剂不会过度影响本发明 的其它官能团; 保护基优选形成可容易分离的衍生物(更优选不产生新的立构中 心); 且保护基优选具有最小的其它功能以避免使反应其他位点复杂化。 多种保 护基和使用和移除这些保护基的方案、试剂和条件是本领域已知的。 参见, 例如 "Protective Groups in Organic Synthesis "Third Ed .Greene ,T W . 禾口 Wuts ,P G .,Eds "John Wiley&Sons ,New York: 1999。
步骤 1)进行硝化反应, 优选的, 硝化反应条件为硝酸和醋酸。
步骤 2) 进行硝基还原反应, 硝基还原采用本领域技术人员常规操作进行; 优选的, 硝基还原反应的条件包含但不限于氢气与雷尼镍、氢气与钯碳、 酸 性条件下铁粉或锌粉或氯化亚锡;
步骤 3)中 1-(8-甲氧基 -6-氨基 -2,3-d二氢苯并 [b][l,4]二噁垸 -5-)乙 -1-酮与甲酸 甲酯或甲酸乙酯在有机溶剂中,碱的催化下得到 10-羟基 -5-甲氧基 -2,3-二氢 -[1,4] 二噁垸并 [2,3-f]-喹啉, 其中所述的有机溶剂包含但不限于二氧六环、 四氢呋喃、 叔丁醇、 乙醇、 甲醇的其中一个或者两个以上的组合; 所述的碱包含但不限于叔 丁醇钠、 叔丁醇钾、 甲醇钠、 乙醇钠; 该反应也可在加热条件下进行, 加热的温 度为室温至回流。
步骤 4)中 10-羟基 -5-甲氧基 -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3-f]-喹啉与氯化试剂 在有机溶剂中反应制备 10-氯 -5-甲氧基 -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3-f]-喹啉,其中 所述的氯化试剂为三氯氧磷; 所述的有机溶剂包含但不限于苯、 甲苯、 氯苯、 二 甲苯的其中一个或者两个以上的组合; 该反应也可在有机碱存在的条件下进行, 所述的有机碱为三乙胺或者二异丙基乙基胺。
步骤 4a)中 10-氯 -5-甲氧基 -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁烷并 [2,3-f]-喹啉在有机溶剂中, 路易斯酸的作用下得到 5-羟基 -10-氯 -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3-f]-喹啉,其中所 述的路易斯酸为三溴化硼或三氯化硼; 有机溶剂为二氯甲垸。
步骤 4b)中 5-羟基 -10-氯 -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3-f]-喹啉与 在有机溶 剂中制备式 ΙΠ-Α所示化合物, 其中 R1如前文所定义; 有机溶剂包含但不限于四 氢呋喃、 二氧六环、 DMF、 DMA, DMSO、 乙腈之一或者两者以上的组合; 中的 X为氯、 溴、 碘、 甲磺酸酯、 对甲苯磺酸酯或三氟甲磺酸酯。
步骤 5) 将式 ΠΙ-Α所示化合物在有机溶剂中, 与式 V' 混合加热至 100°C 至 140°C得到 IV'所示化合物;所述的有机溶剂选自甲苯、氯苯、二甲苯、 DMF、
DMA, DMSO的其中一个或者两个以上的组合。
步骤 6) 进行硝基还原反应, 硝基还原采用本领域技术人员可以常规进行操 作;
优选的, 硝基还原反应条件包含但不限于氢气与雷尼镍、氢气与钯碳、 酸性 条件下铁粉, 锌粉或氯化亚锡;
步骤 7) 在一个优选的方案中, 式 (Π ) 所示化合物与式 (Π' -A) 所示
13 替换页(细则第 26条)
化合物反应时, 其中式(Π )可与酰化试剂反应, 再与式(Π' -A)进行反应。 优选地, 所述的酰化试剂包括但不限于三氯氧磷、 二氯亚砜、 草酰氯、 三氯 化磷或五氯化磷中一种或两种以上的组合。
在另一个实施方案中, 式(ΠΙ' )所示化合物, 在缩合剂存在下, 与式(II' -A) 所示化合物反应, 得到式 (I-C) 所示化合物,
优选地, 所述缩合剂包括但不限于碳二亚胺型缩合剂, 鎗盐类缩合剂, 有机 磷类缩合剂及其他类别缩合剂的一种或两种以上, 优选 Ν,Ν-二环己基碳二亚胺 (DCC ) , Ν,Ν-二异丙基碳二亚胺 (DIC ) , 羟基苯并三唑 (HOBt) , Ν,Ν-二 异丙基乙胺 (DIEA ) , 1-羟基 -7-偶氮苯并三氮唑 (HOAt) , 0-苯并三氮唑- N,N,N',N'-四甲基脲四氟硼酸酯 (TBTU) , 苯并三氮唑 -1-基氧基三 (二甲基氨基) 磷鎗六氟磷酸盐 (B0P), 2 -(7-氧化苯并三氮唑) -N,N,N',N'-四甲基脲六氟磷酸酯 (HBTU) 、 6-氯苯并三氮唑 -1,1,3,3-四甲基脲六氟磷酸酯 (HCTU) , 2-(7-氧化 苯并三氮唑) -N,N,N',N'-四甲基脲六氟磷酸酯 (HATU) , 丙基磷酸酐 (T3P) , 1-(3-二甲氨基丙基 )-3-乙基碳二亚胺盐酸盐 (EDCI) , 1-乙基 (3-二甲基氨基丙基) 碳二亚胺盐酸盐( EDC ), 六氟磷酸苯并三唑 -1-基-氧基三吡咯垸鳞 (PyBOP) , (3H-1,2,3三唑并 [4,5-b]P比啶 -3氧基)三 -1-吡咯烷基鳞六氟磷酸盐 (PyAOP) 中一 种或两种以上的组合;
优选地, 此步骤可在有机碱中进行, 所述的有机碱包含但不限于三乙胺、 二 异丙基乙基胺, 吡啶, 4-二甲氨基吡啶, 2,6-二甲基吡啶, 1,8-二氮杂二环十一碳 -7-烯或 N-甲基吗啉一种或两种以上的组合。
当 R1为 -CH3时, 可省略步骤 4a和步骤 4b, 完成步骤 4)后进行步骤 5 ) 的 操作。
很清楚, 式 I的化合物、 异构体、 晶型或前药及其可药用盐可以存在溶剂化 形式和非溶剂化形式。例如溶剂化形式可以是水溶形式。本发明包括所有这些溶 剂化的和未溶剂化的形式。
本发明的化合物可能有不对称的碳原子,根据它们的理化差异,通过已知技 术上已成熟的方法, 比如, 通过色谱或分步结晶法, 这种非对映异构的混合物可 以被分离成单一的非对映异构体。对映异构体的分离可通过先用适当有旋光活性 的化合物进行反应,把对映异构的混合物转化成非对映异构的混合物, 分离非对 映异构体, 再把单一非对映异构体转化 (水解)成相应的纯的对映异构体。 所有这 样的异构体, 包括非对映异构体混合物和纯对映体被认为是该发明的一部分。
作为活性成分的本发明的化合物, 以及制备该化合物的方法, 都是本发明的 内容。而且, 一些化合物的晶型形式可以作为多晶体存在, 这种形式也可以被包 括在目前的发明里。 另外, 一些化合物可以和水(即水合物)或普通的有机溶剂
14
替换页(细则第 26条)
一起形成溶剂化物, 这种溶剂化物也被包括在此项发明的范畴内。
本发明的化合物可以以游离的形式用于治疗,或者在适当情况下以药学上可 接受的盐或其它衍生物的形式用于治疗。如本文所用, 术语"药学上可接受的盐" 是指本发明的化合物的有机盐及无机盐,此盐适用于人类和低等动物,无过度毒 性、 刺激性、 过敏反应等, 具有合理的利益 /风险比。 胺, 羧酸, 膦酸盐, 和其 它类型的化合物的药学上可接受的盐在所属领域中是众所周知的。该盐可以由本 发明的化合物与合适的游离碱或酸反应而成。 包括但不限于, 与无机酸如盐酸、 氢溴酸、 磷酸、 硫酸、 高氯酸或与有机酸如乙酸、 草酸、 马来酸、 酒石酸、 柠檬 酸、琥珀酸、丙二酸形成的盐,或通过使用本领域熟知的方法,例如离子交换法, 来得到这些盐。 其他药学上可接受的盐包括己二酸盐、 藻酸盐、 抗坏血酸盐、 天 冬氨酸盐、 苯磺酸盐、 苯甲酸盐、 硫酸氢盐、 硼酸盐、 丁酸盐、 樟脑酸盐、 樟脑 磺酸盐、 柠檬酸盐、 二葡糖酸盐、 十二垸基硫酸盐、 乙磺酸盐、 甲酸盐、 富马酸 盐、 葡庚糖酸盐、 甘油磷酸盐、 葡萄糖酸盐、 半硫酸盐、 己酸盐、 氢碘酸盐、 2 - 羟基乙磺酸盐、 乳糖酸盐、 乳酸盐、 月桂酸盐、 月桂基硫酸盐、 苹果酸盐、 马来 酸盐、 甲垸磺酸盐、 2-萘磺酸盐、 烟酸盐、 硝酸盐、 油酸盐、 棕榈酸盐、 双羟萘 酸盐、 果胶酸盐、 过硫酸盐、 过 3-苯基丙酸盐、 憐酸盐、 苦味酸盐、 丙酸盐、 硬 脂酸盐、 硫酸盐、 硫氰酸盐、 对甲苯磺酸盐、 十一烷酸盐等。 代表性的碱或碱土 金属盐包括钠、锂、钾、钙、镁等。其他药学上可接受的盐包括适当的无毒的铵、 季铵, 和使用诸如卤离子、 氢氧根、 羧酸根、 硫酸根、 磷酸根、 硝酸根, 低级垸 基磺酸盐和芳基磺酸盐形成的胺基阳离子。
另外,本文所用术语"前药"是指一个化合物在体内可以转化为本发明式( I) 所示的化合物。此转化受前体药物在血液中水解或在血液或组织中经酶转化为母 体化合物的影响。
本发明的药物组合物包含本文所述结构式 (I) 化合物或其药学上可接受的 盐、 激酶抑制剂 (小分子, 多肽, 抗体等) 、 免疫抑制剂、 抗癌药、 抗病毒剂、 抗炎剂、抗真菌剂、抗生素或抗血管过度增生化合物的另外的活性剂; 以及任何 药学上可接受的载体、 佐剂或赋形剂。
本发明的化合物可以作为单独使用,也可以与一种或多种其它本发明的化合 物或与一种或多种其它药剂联合使用。当联合给药时, 治疗剂可以配制成同时给 药或顺序地在不同的时间给药, 或者所述治疗剂可以作为单一组合物给药。所谓 "组合疗法", 指的是使用本发明的化合物与另一种药剂一起使用, 给药方式为每 种药剂同时共同给药或每种药剂顺序给药,无论哪种情况, 目的都是要达到药物 的最佳效果。共同给药包括同时递送剂型, 以及每种化合物分别的单独剂型。 因 此, 本发明的化合物的给药可以与已知的本领域的其他疗法同时使用, 例如, 在
15
替换页(细则第 26条)
癌症治疗中使用放射治疗或细胞生长抑制剂、细胞毒性剂、其它抗癌剂等附加疗 法来改善癌症状。 本发明并不限于给药的顺序;本发明的化合物可以先前施用, 同时施用, 或在其他抗癌剂或细胞毒性剂之后施用。
为了制备这一发明的药学成分, 作为其活性成分的分子式 (I) 的一种或多 种化合物或盐类可紧密的与药学载体混合在一起,这是根据传统的制药配料技术 而进行的, 其中的载体可根据按不同的给药方式(例如, 口服或肠外给药)设计 好的制备形式而采用多种多样的形式。适当的药学上可接受的载体在技术上是众 所周知的。对一些这类药学可接受的载体的描述可以在《药学赋形剂手册》里找 到, 该书由美国药学会和英国药学社联合出版。
本发明药物组合物可以有以下形式, 比如说, 适合口服给药, 例如药片, 胶 囊, 药丸, 药粉, 持续释放的形式, 溶液或悬浮液; 用于胃肠外注射如透明液, 悬浮液, 乳状液; 或者用于局部用药如膏, 霜; 亦或作为栓剂用于直肠给药。 药 学成分也可以单位剂量的形式适合用于精确剂量的一次性给药。该药学成分将包 括一种传统的药学载体或赋形剂以及根据目前的发明制成的作为活性成分的化 合物, 另外, 也可以包括其他的医学或药学制剂, 载体, 辅助剂, 等等。
治疗性化合物也可给于哺乳动物而非人类。给一个哺乳动物所用的药物剂量 将取决于该动物的种类以及它的疾病状况或其所处的失调状态。治疗性化合物可 以以胶囊, 大丸药, 药片药水的形式喂给动物。也可以通过注射或灌输的方式让 治疗性化合物进入动物体内。我们根据符合兽医实践标准的传统的方式制备好这 些药物形式。作为一种可选择的方式, 药学合成药可以同动物饲料混合在一起喂 给动物, 因此, 浓缩的饲料添加剂或预拌和料可以备以混合普通的动物饲料。
本发明的又一目的是在于提供一种用于治疗有需要的受试者中癌症的方法, 其包括给受试者施用含本发明的化合物的组合物的治疗有效量的一种方法。
本发明还包括本发明的化合物或其药学上可接受的衍生物的使用,制造用于 治疗癌症 (包括非实体瘤、 实体瘤、 原发性或转移性癌症, 如本文别处所指出和 包括癌症具有抗性或难治的一种或多种其它治疗)以及其它疾病 (包括但不限于 眼底疾病、银屑病、动脉粥样化、肺纤维化、肝纤维化、骨髓纤维化等)的药剂。 所述癌症包括但不限于: 非小细胞肺癌、 小细胞肺癌、 乳腺癌、 胰腺癌、 神经胶 质瘤、胶质母细胞瘤、卵巢癌、子宫颈癌、结肠直肠癌、黑色素瘤、子宫内膜癌、 前列腺癌、 膀胱癌、 白血病、 胃癌、 肝癌、 胃肠间质瘤、 甲状腺癌、 慢性粒细胞 白血病、 急性髓细胞性白血病、 非霍奇金淋巴瘤、 鼻咽癌、 食道癌、 脑瘤、 B 细 胞和 T细胞淋巴瘤、淋巴瘤、多发性骨髓瘤、胆道癌肉瘤、胆管癌中的任一种。 下面提供的实施例可以更好的说明本发明,除非特别说明,所有的温度为摄氏度。
附图说明
16
替换页(细则第 26条)
图 1为本发明实施例 21对 c-MET信号通路抑制的实验结果示意图; 图 2为本发明实施例 24对 c-MET信号通路抑制的实验结果示意图。
具体实施方式
本发明化合物涉及的中间体, 可以通过以下方法制备, 但不限于以下方法。 本发明的部分中间体合成可以参考专利 CN104530063 的方法, 一些官能团的简 单替换,本领域技术人员根据掌握的化学合成领域知识可以相应调整而获得相应 的中间体。 以下本发明提供中间体的制备路径, 本发明化合物涉及的中间体, 可 以通过以下方案制备, 但不限于以下方案。
中间体合成:
中间体 1: 1-((4-氟苯基廣基甲酰基)环丙烷 -1-羧酸的制备
将 1,1-环丙基二羧酸 (1.04克)加入无水四氢呋喃 (20mL)中, 在冰水浴条件下 向搅拌的悬浊液中缓慢滴加三乙胺 (0.84g)并搅拌半小时,随后在 0°C条件下逐滴 加入二氯亚砜 (l .lg), 加完继续搅拌 1小时, 随后分别加入三乙胺 (0.8g), 四氟苯 胺 (0.9g)的四氢呋喃 (10mL)溶液, 反应搅拌 2小时完毕; 浓缩, 溶于 1N的氢氧 化钠, 乙酸乙酯萃取, 取水相用 1N的稀盐酸溶液调节 pH至 2.0, 继续搅拌半小 时, 过滤得白色固体产物 l. lg, 收率 62%, MS: 224[M+H]+。 中间体 2: N-(4-氟苯基) -N-(4-羟基苯基)环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
将 1-((4-氟苯基)氨基甲酰基)环丙垸 -1-羧酸 250mg,4-胺基苯酚 150mg,EDCI lOOOmg, 二氯甲垸 2ml加入反应釜中, 室温反应 2h。 反应完毕, 过滤, 滤液浓 缩后由柱层析 (硅胶 200-300目, 石油醚与乙酸乙酯体积比 2: 1 ) 纯化, 得到黄 白色固体 270mg, 产率 77%。 MS: 315[M+H]+ 。 中间体 3: N-(3-氟 -4-羟苯基 )-N-(4-氟苯基)环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
替换页(细则第 26条)
将 l-((4-氟苯基)氨基甲酰基)环丙垸 -1-羧酸 250mg,4-氨基 -2-氟苯酚 175mg, EDCI lOOOmg, 二氯甲垸 2ml加入反应釜中, 室温反应 2h。 反应完毕, 过滤, 滤液浓缩后由柱层析 (硅胶 200-300目, 石油醚与乙酸乙酯体积比 2: 1 ) 纯化, 得到黄白色固体 295mg, 产率 80%。 MS: 333[M+H]+ 。 中间体 4: N-(2-氟 -4-羟基苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
将 1-((4-氟苯基)氨基甲酰基)环丙垸 -1-羧酸 250mg,4-氨基 -3-氟苯酚 175mg, EDCI lOOOmg, 二氯甲垸 2ml加入反 室温反应 2h。 反应完毕, 过滤, 滤液浓缩后由柱层析 (硅胶 200-300目, 石油醚与乙酸乙酯体积比 2: 1 ) 纯化, 得到黄白色固体 252mg, 产率 75%。
1H NMR (DMSO-i/e, 300 MHz) δ 10.21 (1Η, s), 9.98 (1H, s), 9.83 (1H, s), 7.62 (2H, dd, J=9.1, 5.0 Hz), 7.46 (1H, t, J=8.9 Hz), 7.15 (2H, t, J=8.7 Hz), 6.70-6.47 (2H, m), 1.54 (4H, d, J=4.8 Hz); MS: 333[M+H]+ 中间体 5: N-(2-氯 -4-羟苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙垸 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
与中间体 2相同操作, 由 1-((4-氟苯基)氨基甲酰基)环丙垸 -1-羧酸和 4-胺基 -3-氯苯酚反应得到白色固体, 收率 66%。 MS: 349[M+H]+ 中间体 6: N-(3-氯 -4-羟苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
与中间体 2相同操作, 由 1-((4-氟苯基)氨基甲酰基)环丙烷 -1-羧酸和 4-胺基 -2-氯苯酚反应得到白色固体, 收率 82%。
1H MR (DMSO-d6, 300 MHz) δ 10.13 (1Η, s), 9.98 (1H, s), 9.91 (1H, s), 7.78-7.54 (3H, m), 7.30 (1H, dd, J=9.0, 2.8 Hz), 7.14 (2H, t, J=8.7 Hz), 6.90 (1H, dd, J=8.7, 3.0 Hz), 1.44 (4H, s); MS: 349[M+H]+ 中间体 7: N-(4-氟苯基) -N- (4-羟基苯基)二甲基丙二酰胺的制备
18
与步骤 2相同操作, 由 3-((4-氟苯基)氨基) -2,2-二甲基 -3-氧代丙酸和 4-胺基 苯酚反应得到白色固体, 收率 75%。 MS: 317[M+H]+ 中间体 8: N-(3-氟 -4-轻基苯基) -N-(2-氟苯基)环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
与步骤 2相同操作, 由 1-((2-氟苯基)氨基甲酰基)环丙垸 -1-羧酸和 4-胺基 -2- 氟苯酚反应得到白色固体, 收率 52%。 MS: 333[M+H]+ 中间体 9: N-(4-氯苯基) -N-(3-氟 -4- ¾基苯基)环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
与步骤 2相同操作, 由 1-((4-氯苯基)氨基甲酰基)环丙烷 -1-羧酸和 4-胺基 -2- 氟苯酚反应得到白色固体, 收率 52%。 MS: 349[M+H]+ 步骤 10: N-(2-氟 -5- (三氟甲基)苯基) -N-(4-羟基苯基)环丙基 -1,1-二甲酰胺的 制备
与中间体 2相同操作, 由 1-((2-氟 -5-三氟甲基苯基)氨基甲酰基)环丙垸 -1-羧 酸和 4-胺基苯酚反应得到白色固体, 收率 65%。 MS: 383[M+H]+ 中间体 11: N-(4-氟苯基) -N-(4- 苯基)环丁烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
与中间体 2相同操作, 由 1-((4-氟苯基)氨基甲酰基)环丁烷 -1-羧酸和 4-胺基 苯酚反应得到白色固体, 收率 75%。 MS: 329[M+H]+
19
与中间体 2相同操作, 由 1- (苄基氨基甲酰基)环丙垸 -1-羧酸和 4-胺基 -2氟- 苯酚反应得到白色固体, 收率 77%。 MS: 329[M+H]+ 中间体 13: N-(3-氟 -4-羟基苯基) 苯乙基丽基 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
与中间体 2相同操作, 由 1- (苯乙基氨基甲酰基)环丙垸 -1-羧酸和 4-胺基 -2 氟 -苯酚反应得到白色固体, 收率 64%。 MS: 343[M+H]+ 中间体 14: N-(3-氟 -4-羟基苯基) -N-(4-氟苄基)环丙基 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
与中间体 2相同操作,由 1-(4-氟苄基氨基甲酰基)环丙垸 -1-羧酸和 4-胺基 -2- 氟苯酚反应得到白色固体, 收率 72%。 MS: 347[M+H]+ 中间体 15: N-(4- 基苯基) (萘 -1-基)环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
与中间体 2相同操作, 由 1- (萘 -1-氨甲酰基)环丙烷 -1-羧酸和 4-胺基苯酚反 应得到白色固体, 收率 68%。 MS:347[M+H]+ 中间体 16: N-(4-羟基苯基) -N-(3-甲基异恶唑 -5-基)环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制
20
与中间体 2相同操作, 由 1-《3-甲基异恶唑 -5-基)胺基甲酰基)环丙垸 -1-羧酸 和 4-胺基苯酚反应得到白色固体, 收率 61%。 MS:302[M+H]+
与中间体 2相同操作, 由 1- (吡啶 -2-基氨甲酰基)环丙烷 -1-羧酸和 4-胺基苯 酚反应得到白色固体, 收率 60%。 MS:298[M+H]+
与中间体 2相同操作, 由 1-((4-苯氧基苯基)氨基甲酰基)环丙烷 -1-羧酸和 4- 胺基苯酚反应得到浅黄色固体, 收率 52%。 MS:389[M+H]+
与中间体 2相同操作, 由 1-((4-甲砜基苯基)胺基甲酰基)环丙垸 -1-羧酸和 4- 胺基苯酚反应得到白色固体, 收率 67%。 MS:375[M+H]+
与中间体 2相同操作,由 1- (环己基氨基甲酰基)环丙垸 -1-羧酸和 4-胺基苯酚 反应得到白色固体, 收率 55%。 MS:303[M+H]+
21
与中间体 2相同操作,由 1- (异戊基氨甲酰基)环丙垸 -1-羧酸和 4-胺基苯酚反 应得到白色固体, 收率 55%。 MS:291[M+H]+ 中间体 22: N-(4-氟苯基) -N-(6-羟基吡啶 -3-基)环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
与中间体 2相同操作, 由 1-((4-氟苯基)氨基甲酰基)环丙烷 -1-羧酸和 5-氨基 -2-羟基吡啶反应得到白色固体产物, 收率 76%。 MS:316[M+H]+ 中间体 23: N-(4-氨基苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
与中间体 2相同操作, 由 1-((4-氟苯基)胺基甲酰基)环丙烷 -1-羧酸和 4-硝基 苯胺反应得到的浅黄色固体,然后由氢气钯碳还原得浅紫色目标产物,收率 72%。 MS:314[M+H]+ 中间体 24: N-(4-氨基 -3-氟苯基 )-N-(4-氟苯基)环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
方法 A: 与中间体 2相同操作, 由 1-((4-氟苯基)胺基甲酰基)环丙垸 -1-羧酸 和 4-硝基 -3-氟苯胺反应得到浅黄色固体, 由氢气钯碳还原得到浅紫色目标产物, 收率 77%。 MS:332[M+H]+
方法 B: 将 1-((4-氟苯基)氨基甲酰基)环丙烷 -1-羧酸 240mg溶于二氯亚砜 (5mL)中回流加热 1小时, 冷却, 浓缩得黄色油状物溶于二氯甲垸 (2mL)中; 在 冰水浴条件下向上述溶液滴加 3-氟 -4-硝基苯胺 (160mg)的二氯甲垸 (lmL)溶液, 随后缓慢滴加三乙胺 (300mg), 撤去冰水浴, 室温反应过夜, 加水淬灭, 有机相 干燥浓缩得到浅黄色固体产物; 将上述直接溶于甲醇 (20mL)中, 用钯碳 (20mg, 替换页(细则第 26条)
10%Pd) 催化氢化还原得到目标产物。 中间体 25: N-(2-氟 -5- (三氟甲基)苯基) -N-(4-羟基苯基)环丙基 -1,1-二甲酰胺 的制备
与中间体 2相同操作, 由 1-((2-氟 -5-三氟甲基苯基)胺基甲酰基)环丙垸 -1-羧酸 和 4-氨基苯酚反应得到白色固体, 收率 72%。 MS:383[M+H]+ 中间体 26: -(4-氨基苯基) -N3
同中间体 2操作, 由 3-((4-氟苯基)氨基) -3-氧代丙酸和 4-硝基苯胺反应得到 白色固体, 由氢气钯碳还原得到目标产物, 收率 71%。 MS:288[M+H]+ 中间体 27: N-(4- 基苯基) -N-(4-甲氧基节基)环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
同中间体 2操作, 由 1-((4-甲氧基苄基)氨基甲酰基)环丙垸 -1-羧酸和 4-胺基 苯酚反应得到白色固体, 收率 77%。 MS: 341 [M+H]+ 中间体 28, N-(4-氟苯基) -N-(4-羟基 -3-甲基苯基)环丙基 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备:
与中间体 2相同操作, 由 1-((4-氟苯基)氨基甲酰基)环丙垸 -1-羧酸和 4-胺基 -2- 甲基苯酚反应得白色固体产物, 收率 61%。 MS: 329[M+H]+ 中间体 29, N-(4-氟苯基 )-7V-(4-¾¾-2-甲基苯基)环丙基 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备:
23
与中间体 2相同操作, 由 1-((4-氟苯基)氨基甲酰基)环丙垸 -1-羧酸和 4-胺基 -3-甲基苯酚反应得白色固体产物, 收率 65%。 MS: 329[M+H]+ 中间体 30: 10-氯 -5-甲氧基 -2,3-二氢 -【1,4】二噁烷并 [2,3- 喹唑啉的制备 合成路线:
A5
详细合成步骤参见专利文献 CN104530063。化合物 A1与碘甲垸在碳酸钾的 N'N-二甲基甲酰溶液中加热到 80 °C反应 2小时, 加入到水中, 过滤干燥得白色 固体 A2; 将 A2溶于乙酸中, 在 0摄氏度条件下向其中滴加发烟硝酸与乙酸的 混酸, 滴加完毕后再在 0 °C反应一小时, 将反应液倒入碎冰中搅拌, 过滤干燥 得浅黄色固体 A3 ; A3溶于甲醇后在氢气钯碳条件下反应 1小时, 过滤, 滤液浓 缩得到浅紫色油状物 A4;化合物 A4和醋酸甲脒在乙醇中回流加热反应 10小时, 冷却过夜, 反应液过滤干燥, 得浅灰色固体 A5; 化合物 A5在三氯氧磷中回流 加热 10小时, 反应完毕, 浓缩, 分别向其中加入二氯甲垸、 碳酸钾和碎冰, 将 pH值调至 9, 分液, 有机相用饱和食盐水洗涤, 干燥, 浓缩得到黄色固体的目 标产物。 MS:253[M+H]+ 中间体 31 : 10-氯 -5- ((四氢 -2H-吡喃 -4-基 基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4】二噁烷并 [2,3-/] 喹唑啉的制备
同中间体 30合成方法, 由四氢 -2H-吡喃 -4-基 -4-甲磺酰苯酯替代 CH3I进行
24
替换页(细则第 26条)
上述反应, 得到黄色固体产物, 收率 45%, MS:323[M+H]+ 中间体 32: 10-氯 -5-(2-甲氧基乙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -【1,4】二噁烷并 [2,3-_ ]喹唑啉 的制备
同中间体 30合成方法, 由甲氧基溴代乙垸替代 CH3I进行上述反应,得到黄 色固体产物, 收率 60%, MS:297[M+H]+ 中间体 33: 10-氯 -5-(2-吗啉乙氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4】二噁烷并 [2,3-_ ]喹唑啉的 制备
同中间体 30合成方法, 由氯代乙基吗啉替代 CH3I进行上述反应,得到黄色固 体产物; 1H NMR (DMSO-i¾, 300 MHz) δ ppm: 3.16 (IH, d, J=5.0 Hz), 3.43 (4H, s), 3.71 (4H, d, J=5.1 Hz), 3.87 (IH, s), 4.29 - 4.55 (6H, m), 6.90 (IH, s), 8.38 (IH, d, J=2.9 Hz); MS:352[M+H]+。
中间体 34: 10-氯 -5-(2- (四氢吡咯 -1-基)乙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,41二噁烷并 [2,3-/] 喹唑啉的制备
同中间体 30合成方法, 由氯乙基四氢吡咯替代 CH3I进行上述反应,得到黄 色固体产物, MS:336[M+H]+ 中间体 35: 3-((10-氯 -2,3-二氢 -[1,4】二噁垸并【2,3-/]喹唑啉 -5-基)氧基) -N,N- 二甲基丙烷 -1-胺的制备
同中间体 30合成方法,由氯丙基二甲胺替代 CH3I进行上述反应得到黄色固 替换页(细则第 26条)
体产物, MS:324[M+H]+ 中间体 36 : 10-氯 -5-(3- (四氢吡咯 -1-基)丙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4】二噁烷并
[2,3-/]喹唑啉的制备
同中间体 30合成方法, 由氯丙基四氢吡咯替代 CH3I进行上述反应,得到黄 色固体产物, MS:350[M+H]+ 中间体 37: 10-氯 -5-(3-吗啉丙氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4】二噁烷并 [2,3- ]喹唑啉的 制备
同中间体 30合成方法, 由氯丙基吗啉替代 CH3I进行上述反应,得到黄色固 体产物, MS:366[M+H]+ 中间体 38: 10-氯 -5-(1-甲硫基丙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -【1,4】二噁 [2,3-_ ]喹唑啉 的制备
同中间体 30合成方法, 由氯丙基甲硫醚替代 CH3I进行上述反应,得到黄色 固体产物, MS:327[M+H]+ 中间体 39 : 10-氯 -5-(3-(4-甲基哌嗪 -1-基)丙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4】二噁烷并
[2,3-/1喹唑啉的制备
同中间体 30合成方法, 由 1-(3-氯丙基 )-4-甲基哌嗪替代 CH3I进行上述反应
26
替换页(细则第 26条)
得到黄色固体产物, MS:379[M+H]+
中间体 40: 10-氯 -5-(3- (哌啶 -1-基)丙 # ¾)-2,3-二氢 -[1,4】二噁烷并 [2,3-/]喹 唑啉的制备
同中间体 30合成方法, 由 1-氯 -3-哌啶基丙烷替代 CH3I进行上述反应, 得 到黄色固体产物, MS:364[M+H]+
中间体 41 : 4-(3-((10-氯-2,3-二氢-[1,4】二噁烷并【2,3-/]喹唑啉-5-基)氧基)丙 基)硫代吗啉 1,1-二氧化物的制备
同中间体 30合成方法, 由 4-(3氯丙基)硫代吗啉 -1, 1二氧化物替代 CH3I进 行上述反应,得到黄色固体产物, MS:414[M+H]+
同中间体 30合成方法, 由 1 -溴 -6-甲氧基己垸替代 CH3I进行上述反应, 得 到黄色固体产物, MS:353[M+H]+
同中间体 30合成方法, 由 6-氯 -Ν,Ν-二甲基 -1-己胺盐酸盐替代 CH3I进行上
27
替换页(细则第 26条)
述反应, 得到黄色固体产物, MS:366[M+H]+ 中间体 44: 10-氯 -5-异丙氧基 -2,3-二氢 -【1,4】二噁烷并 [2,3- ]喹唑啉的制备
同中间体 30合成方法, 由异丙基溴替代 CH3I进行上述反应,得到黄色固体 产物, MS:281 [M+H]+ 中间体 45: 10-氯 -5-(6-甲氧基己氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4】二噁烷并 [2,3-f|喹唑啉 的制备
同中间体 30合成方法, 得到黄色固体产物, MS:366[M+H]+ 中间体 47: 10^-5-异丙氧基 -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁烷并 [2,3-f|喹唑啉的制备
同中间体 30合成方法, 得到黄色固体产物, MS:281[M+H]
中间体 48: 10-氯 -5-苄氧基 -2,3-二氢 -[1,4】二噁烷并 [2,3-/]喹唑啉的制备
同中间体 30合成方法,由氯化苄替代 CH3I进行上述反应,得到淡黄色固体,
28
替换页(细则第 26条)
6Z 糊 ¾華 詾二 [ι^]-^τ-ε'ζ- ώ-5) )-ΛΚ 1Η)-Λ ·ε^m^
+[H+n]0£9 S :(s 'ΗΙ)ΠΌΙ '(s 'ΗθθΙΌΐ '(s ¾l)900l '(s 'Hl)9S'8 'O 'Η9)99ϋ9'乙 '(ZHO 'J 'HS)S1 . '(s 'Ηΐ)ε6'9 ' q 'HS)t9 '(-iq 'H )Wt7 '(s 'H )S6'e '(m 'Ht7)8t l-H I : idd ς (zHW00 9/ OSWa)¾RM Ht
+[H+W]W)S:SW
'(jq ¾)et7 '(s ¾ε)/.6 ' q 'ro)os ^dd? (zHwoot'9/ oswa)¾RN HT
齡邈激 ¾(louii¾ 0 '§ i8g)¾¾-¾l(g¾¾-t7)-£N-(¾¾g)i-t7)-iN
¾華 二〖 -^二 -ε'ζ- ώ-5) )-ετ -( 鸷 h^ ι m^
。+[H+W]H = Z/ I sn
££Z9L0m0ZSiD/lDd C6ZCSl/8T0Z OAV
-10-基)氧基)雜)环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
将 N-(4-氟苯基) -N-(4-羟苯基)环丙垸 -1, 1-二甲酰胺 (32mg, O. lmmol ) 溶解 在 lmLN,N-二甲基甲酰胺中,加入 10-氯 -5-甲氧基 -2,3-二氢 -[1,4] 二噁垸并 [2,3;/] 喹唑啉 (25mg, O. lmmol)和碳酸钾 (20mg, 0.15mmol), 80°C下反应 3小时。 冷却后 使用乙酸乙酯和饱和食盐水萃取, 有机相用无水硫酸钠干燥, 浓缩得黄色固体, 所得固体由柱层析 (硅胶 200-300目, 石油醚与乙酸乙酯体积比 1 : 1 ) 纯化, 得 到黄白色固体 33mg,产率 62%。 1H NMR (DMSO-i¾,400MHz) δ ppm: 1.47 (s, 4H), 3.96 (s, 3H), 4.38(2H, br), 4.45(2H, br), 7.05 (s, IH), 7.13-7.17 (m, 4H), 7.62-7.69 (m. 4H), 8.42(s, IH), 10.08(s, IH), 10.11(s, IH). MS : 531 [M+H]+. 实施例 4. N-(3-氟 -4-((5-甲氧基 -2,3-二氢 -[1,4】二噁垸并 [2,3-/]喹唑啉 -10-基) 氧基)苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙基 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
与实施例 3同样操作, 由 N-(3-氟 -4-羟苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙垸 -1, 1-二甲酰 胺和 10-氯 -5-甲氧基 -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3:] 喹唑啉获得紫色目标化合物, 产率 73%。 1H NMR (DMSO-i/6,400MHz) δ ppm: 1.47 (s, 4H), 3.96 (s, 3H), 4.40(2H, br), 4.47(2H, br), 7.08 (s, IH), 7.13-7.18 (m, 2H), 7.30-7.35 (m, IH), 7.43-7.44 (m, 1Η),7.62-7.66 (m, 2H), 7.82 (d, J = 4.0 Hz, IH), 8.44(s, IH), 10.03(s, IH), 10.31(s, IH). MS: 549[M+H] +. 实施例 5. ^-(4-氟苯基) -N3-(4-((5-甲氧基 -2,3-二氢 -[1,41二噁烷并 [2,3-/]喹唑 啉 -10-基)氧基)苯基) -2,2-二甲基丙二酰胺的制备
30
同实施例 3操作, 由 10-氯 -5-甲氧基 -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁烷并 [2,3;]喹唑啉和 N1-^-氟苯基) -N3-(4-羟基苯基) -2,2-二甲基丙二酰胺反应得到白色固体,产率 48%。 1H NMR(DMSO-i/6,400MHz) S ppm: 1.56(6H, s), 3.96(3H, s), 4.39(2H, br), 4.45(2H, br), 7.05(1H, s), 7.13-7.17(4H, m), 7.67-7.73(4H, m), 8.41(1H, s), 9.55(1H, s), 9.56(1H, s); MS:533[M+H]+. 实施例 6. N-(4-氟苯基) -N-(4-((5-甲氧基 -2,3-二氢 -[1,4】二噁烷并 [2,3-_ ]喹唑啉 -10-基)氧基)苯基) i T烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
同实施例 3操作, 由 10-氯 -5-甲氧基 -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3- 喹唑啉和 N-(4-氟苯基) -N-(4-羟基苯基)环丁基 -1, 1-丙二酰胺反应得到白色固体,产率 54%。 1H NMR(DMSO-i/6,400MHz) δ ppm: 1.86-2.01(2H, m), 2.67(4Η, t, J = 8.0Hz), 3.96(3H, s), 4.38(2H ,br), 4.45(2H, br), 7.04(1H, s), 7.13-7.17(4H, m), 7.68-7.74(4H, m), 8.40(1H, s), 9.68(2H, s); MS:545[M+H]+ . 实施例 7. -(4-氟苯基 )- V3-(4-((5-(2-甲氧基乙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4】二噁烷并
[2,3-/]喹唑啉 -10-基)氨基)苯基)丙二酰胺的制备
同实施例 1操作,由 10-氯 -5-(2-甲氧基乙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁烷并 [2,3-f] 喹唑啉和 ^-(4-氨基苯基) -N3-(4-氟苯基)丙二酰胺得到黄色固体, 收率 68%。
31
替换页(细则第 26条)
1H NMR(DMSO-d6,400MHz) δ ppm: 3.34(3H, s), 3.52(2H, br), 3.75(2H, br), 4.29(2H, br), 4.45(2H, br), 4.61(2H, br), 7.00(1H, s), 7.17(2H, t, J = lO.OHz), 7.58(2H, d, J = 8.0Hz), 7.64-7.67(2H, m), 7.72(2H, d, J = 8.0Hz), 8.67(1H, s), 10.41(1H, s), 10.48(2H, s); MS:548[M+H]+. 实施例 8. N-(4-氟苯基 )-N-(4-((5-(2-甲氧基乙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -【1,4】二噁烷并
[2,3-_ ]喹唑啉 -10-基)氨基)雜)环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
同实施例 1操作, 由化合物 N-(4-氨基苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙基 -1, 1-二甲酰 胺和 10-氯 -5-(2-甲氧基乙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3;/]喹唑啉反应得到白 色固体, 产率 66%。 1H NMR(DMSO-i/6,400MHz) δ ppm: 1.49(4H, s), 3.34(3H, s), 3.76(2H, br), 4.29(2H, br), 4.45(2H, br), 4.61(2H, br), 6.98(1H, s), 7.16(2H, t, J = lO.OHz), 7.58-7.71(6H, m), 8.65(1H, s), 10.05(1H, s), 10.22(1H, s), 10.41(1H, s); MS:574[M+H]+. 实施例 9. N-(4-氟苯基 )-N-(4-((5-(2-甲氧基乙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -【1,4】二噁烷并
[2,3-/]喹唑啉 -10-基)氧基)苯基)环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
同实施例 3操作, 由 N-(4-氟苯基) -N-(4-羟苯基)环丙垸 -1, 1-二甲酰胺和 10- 氯 -5-(2-甲氧基乙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3:/]喹唑啉反应得到浅黄色固体, 产率 65%。 1H NMR(DMSO-i/6,400MHz) δ ppm: 1.48(4H, s), 3.36(3H, s), 3.74(2H, br), 4.30(2H, br), 4.41(2H, br), 4.45(2H, br), 7.06(1H, s), 7.13-7.18(4H, m),
7.62-7.69(4H, m),8.41(lH, s), 10.08(1H, s), 10.12(1H, s); MS: 575[M+H]+. 实施例 10. N-(3-氟 -4-((5-(2-甲氧基乙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -【1,4】二噁烷并 [2,3-/]喹 唑啉 -10-基)氧基)苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙基 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
同实施例 3操作, 由 N-(3-氟 -4-羟基苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺 和 10-氯 -5-(2-甲氧基乙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁烷并 [2,3- ]喹唑啉反应得白色固 体, 产率 58%。 1H NMR(DMSO-i¾,400MHz) (5 ppm: 1.47(4H, s), 3.35(3H, s), 3.74-3.76(2H, m), 4.31(2H, br), 4.41(2H, br), 4.46(2H, br), 7.09(1H, s), 7.13-7.18(2H, m), 7.33(1H, t, J= 8.0Hz), 7.45(1H, d, J= 8.0Hz), 7.62-7.66(2H, m), 7.80(1H, d, J = 12.0Hz), 8.44(1H, s), 10.03(1H, s), 10.31(1H, s); MS:593[M+H]+ 实施例 11. -(4-氟苯基) -N3-(4-((5-(2-甲氧基乙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4】二噁烷并
[2,3-_ ]喹唑啉 -10-基)氧基)雜) -2,2-二甲基二酰胺的制备
同实施例 3操作,由 10-氯 -5-(2-甲氧基乙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3:/] 喹唑啉和 Λ^-(4-氟苯基) - -(4-羟基苯基) -2,2-二甲基丙二酰胺反应得白色固体, 产率 65%。
1H MR(DMSO-i/6,400MHz) δ ppm: 1.56(6H, s), 3.34(3 H, s), 3.75(2H, s), 4.31(2H, s), 4.40(2H, s), 4.45(2H, s), 7.06(1H, s), 7.12-7.17(4H, m), 7.66-7.73(4H, m): 8.40(1H, s), 9.53(1H, s), 9.54(1H, s); MS:577[M+H]+. 实施例 12. N-(4-氟苯基) -N-(4-((5-(2-甲氧基乙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4】二噁烷并
[2,3-/]喹唑啉 -10-基)氧基)苯基)环丁烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
33
替换页(细则第 26条)
同实施例 3操作,由 10-氯 -5-(2-甲氧基乙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3;] 喹唑啉和 N-(4-氟苯基) -N-(4-羟基苯基)环丁基 -1, 1-丙二酰胺反应得白色固体, 产 率 51%。 1H MR(DMSO-i/6,400MHz) δ ppm: 1.83-1.87(1H, m), 1.98-2.00(1H, m), 2.66-2.70(4H, m), 3.34(3H, s), 3.75(2H, s), 4.29(2H, s), 4.40(2H, s), 4.45(2H, s), 7.05(1H, s), 7.13-7.17(4H, m), 7.69-7.75(4H, m), 8.39(1H, s), 9.75(2H, s);
MS:589[M+H]+. 实施例 13. N-(3-氟 -4-((5-(2-甲氧基乙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -【1,4】二噁烷并 [2,3-/]喹 唑啉 -10-基)氧基)苯基) 苯基环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
同实施例 3操作,由 10-氯 -5-(2-甲氧基乙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3:/] 喹唑啉和 K3-氟 -4-羟基苯基) 苯基环丙垸 -1, 1-二甲酰胺反应得到白色固体产 物, 收率 81%。 1H NMR(DMSO-i¾,400MHz) δ ppm: 1.47(4H, s), 3.34(3H, s), 3.75(2H, br), 4.30(2H, br), 4.41(2H, br), 4.46(2H, br), 7.07-7.09(2H, m),
7.29-7.35(3H, m), 7.45(1H, d, J= 8.0Hz), 7.63 (2H, d, J = 8.0Hz), 7.80(1H, d, J = 8.8Hz), 8.44(1H, s), 10.02(1H, s), 10.28(1H, s); MS:575[M+H]+. 实施例 14. N-(4~m苯基) -N-(3-氟 -4-((5-(2-甲氧基乙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁 烷并 [2,3-/1喹唑啉 -10-基)氧基)苯基)环丙垸 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
同实施例 3操作,由 10-氯 -5-(2-甲氧基乙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3;] 喹唑啉和 N-(3-氟 -4羟基苯基) -N-(4-氯苯基)环丙垸 -1, 1-二甲酰胺反应得到白色固 体, 收率 79%。 1H NMR(DMSO-i/6,400MHz) δ ppm: 1.47(4H, s), 3.34(3H, s), 3.75(2H, br), 4.31(2H, br), 4.42(2H, br), 4.47(2H, br), 7.09(1H, s), 7.30-7.38(3H, m), 7.44(1H, d, J= 8.8Hz), 7.68(2H, d, J= 8.8Hz), 7.79(1H, d, J= 8.0Hz), 8.44(1H, s), 10.15(1H, s), 10.27(1H, s); MS:609[M+H]+. 替换页(细则第 26条)
实施例 15. N-(3-氯雜) -N-(3-氟 -4-((5-(2-甲氧基乙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4】二噁 垸并 [2,3-/1喹唑啉 -10-基)氧基)苯基)环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
同实施例 3操作,由 10-氯 -5-(2-甲氧基乙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁烷并 [2,3;] 喹唑啉和 N-(3-氟 -4羟基苯基) -N-(3-氯苯基)环丙垸 -1,1-二甲酰胺反应得到白色固 体, 收率 75%。 1H NMR(DMSO-i/6,400MHz) δ ppm: 1.47(4H, s), 3.34(3H, s), 3.75(2H, br), 4.31(2H, br), 4.41(2H, br), 4.46(2H, br), 7.09(1H, s), 7.13(1H, d, J = 8.0Hz), 7.31-7.36(2H, m), 7.44(1H, d, J= 8.0Hz), 7.53(1H, d, J= 8.0Hz), 7.80(1H, d, J= 8.0Hz), 7.87(1H, s), 8.44(1H, s), 10.21(1H, s), 10.25(1H, s); MS:609[M+H]+. 实施例 16. N-(3-氟 -4-((5-(2-甲氧基乙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -【1,4】二噁烷并 [2,3-/]喹 唑啉 -10-基)氧基)苯基) -N-(4-氟苄基)环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
同实施例 3操作,由 10-氯 -5-(2-甲氧基乙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3:/] 喹唑啉和 N-(3-氟 -4羟基苯基) -N-(4-氟苄基)环丙垸 -1,1-二甲酰胺反应得到白色固 体, 收率 71%。 1H NMR(DMSO-i/6,400MHz) δ ppm: 1.40(4H, s), 3.34(3H, s), 3.74(2H, br), 4.31(4H, br), 4.41(2H, br), 4.46(2H, br), 7.08(1H, s), 7.15(2H, t, J = 8.8Hz), 7.30-7.35(3H, m), 7.41(1H, d, J= 8.8Hz), 7.80(1H, d, J= 8.8Hz), 8.43(1H, s): 8.50(1H, t, J= 6.4Hz), 10.77(1H, s); MS:607[M+H]+. 实施例 17. N-(2-氟苯基 )-4-(3-氟 -4-((5-(2-甲氧基乙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4】二噁 烷并【2,3-/1喹唑啉 -10-基雍基)苯基)环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
35
替换页(细则第 26条)
〇.
I 1
同实施例 3操作,由 10-氯 -5-(2-甲氧基乙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁烷并 [2,3;] 喹唑啉和 氟苯基) -N-(3-氟 -4羟基苯基)环丙烷 -1, 1-二甲酰胺反应得到白色固 体, 收率 68%。 1H NMR(DM δ ppm: 1.59(4H, d, J= 14.0Hz), 3.34(3 H, s), 3.75(2H, br), 4.31(2H, br), 4.42(2H, br), 4.46(2H, br), 7.09(1H, s), 7.17-7.20(2H, m), 7.26-7.30(lH, m), 7.3 t, J= 8.8Hz), 7.45(1H, d, J= 8.8Hz), 7.76(1H, d, J= 12.8Hz), 7.86(1H, s), 8.44(1H, s), 10.18(1H, s), 10.43(1H, s);
MS:593[M+H]+. 实施例 18.N-苄基 -N-(3-氟 -4-((5-(2-甲氧基乙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4】二噁烷并
[2,3-f|喹唑啉 -10-基)氧基)苯基)环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
同实施例 3操作,由 10-氯 -5-(2-甲氧基乙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3-f] 喹唑啉和 N-(3-氟 -4羟基苯基) -N-苄基环丙垸 -1, 1-二甲酰胺反应得到白色固体, 收率 76%。 1H NMR(DMSO-i¾,400MHz) δ ppm: 1.41(4H, s), 3.34(3H, s), 3.75(2H, br), 4.31(2H, br), 4.34(2H, d, J = 6.4Hz), 4.41(2H, br), 4.46(2H, br), 7.08(1H, s), 7.22-7.35(6H, m), 7.41(1H, d, J = 8.8Hz), 7.81(1H, d, J = 8.8Hz), 8.43(1H, s), 8.50(1H, t, j = 6.4Hz), 10.81(1H, s); MS:589[M+H]+. 实施例 19. N-(4-氟苯基) -N-(6-((5-(2-甲氧基乙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4】二噁垸并
[2,3-f|喹唑啉 -10-基)氧基)吡啶 -3-基)环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
36
替换页(细则第 26条)
同实施例 3操作,由 10-氯 -5-(2-甲氧基乙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3-f] 喹唑啉和 N-(4-氟苯基) -N-(6-羟基吡啶 -3-基)环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺反应得到白色 固体, 收率 76% o 1H MR(DMSO-d6,300MHz) δ ppm: 1.47(4H, s), 3.36(3H, s), 3.74(2H, s), 4.30(2H, s), 4.40(4H, s), 7.08(1H, s), 7.16(2H, t, J = 9.0Hz), 7.27(1H, d, J = 9.0Hz), 7.65(2H, t, J = 9.0Hz), 8.17(1H, d, J = 9.0Hz), 8.45(1H, s), 8.57(1H, s), 10.14(1H, s), 10.33(1H, s); MS:576[M+H]+. 实施例 20. N-(4-氟苯基) -N-(4-((5-(3- (四氢吡咯 -1-基)丙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4】 二噁烷并 [2,3-f|喹唑啉 -10-基)氧基)苯基)环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
同实施例 3操作, 由化合物 Ν-(4-氟苯基) -Ν-(4-羟苯基)环丙垸 -1,1-二甲酰胺 和 10-氯 -5-(3- (吡咯烷 -1-基)丙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3-f]喹唑啉反应得 到白色固体, 产率 65%。 1H NMR(DMSO-d6,400MHz) δ ppm: 1.47(4H, s), 1.71-1.75(4H, m), 1.95-2.03(2H, m), 2.57(2H, br), 2.67(2H, br), 4.02(2H, d, J = 4.0Hz), 4.22(2H, t, J = 4.0Hz), 4.39-4.40(2H, m), 4.44-4.46(2H, m), 7.03(1H, s), 7.13-7.17(4H, m), 7.63-7.73(4H, m), 8.41(1H, s), 10.09(1H, s), 10.12(1H, s);
MS:628[M+H]+. 实施例 21. N-(3-氟 -4-((5-(3- (四氢吡咯 -1-基)丙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4】二噁烷并
[2,3-f|喹唑啉 -10-基庠基)苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
同实施例 3操作, 由化合物 N-(3-氟 -4羟基苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙垸 -1,1-二 甲酰胺和 10-氯 -5-(3- (:吡咯垸 -1-基)丙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3-f]喹唑啉 反应得到白色固体, 产率 61%。 1H NMR(DMSO-d6,400MHz) (5 ppm: 1.47(4H, s), 1.71(4H, br), 1.97-2.02(4H, m), 2.57(2H, br), 4.02(2H, d, J = 4.0Hz), 4.23(2H, t, J = 4.0Hz), 4.40-4.41(2H, m), 4.46-4.47(2H, m), 7.06(1H, s), 7.13-7.17(2H, m), 7.32(1H, 替换页(细则第 26条)
t, J -8.0Hz), 7.44(1H, d , J -8.0Hz), 7.63-7.81(3H, m), 8.43(1H, s), 10.03(1H, s), 10.30(1H, s); MS:646[M+H]+. 实施例 22. N-(3-氟 -4-((5-(3-吗啉丙氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4】二噁烷并【2,3-f]喹唑 啉 -10-基)氨基)苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙基 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
同实施例 1操作, 由化合物 N-(3-氟 -4-氨基苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙垸 -1,1-二 甲酰胺和 10-氯 -5- (吗啉丙基氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3-f]喹唑啉反应得白 色固体产率 61%。 1H MR(DMSO-d6,400MHz) 3 ppm: 1.46(4H, br), 1.91-2.01(2H, m), 2.38(4H, br), 2.44(2H, t, J = 8.0Hz), 3.57-3.60(4H, m), 4.18(2H, t, J = 6.0Hz), 4.40-4.42(2H, m), 4.55-4.56(2H, m), 6.88(1H, s), 7.15(2H, t, J = 8.0Hz), 7.38(1H, d, J = 12.0Hz), 7.62-7.65(2H, m), 7.77(1H, d, J = 8.0Hz), 8.20 (1H, t, J = lOHz), 8.36(1H, s), 9.55(1H, s), 10.02(1H, s), 10.25(1H, s); MS:661 [M+H]+. 实施例 23. N-(4-氟苯基) -N-(4-((5-(3-吗啉丙氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4】二噁烷并
[2,3-f|喹唑啉 -10-基 基)苯基)环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
同实施例 3操作, 由化合物 Ν-(4-氟苯基) -Ν-(4-羟苯基)环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺 和 10-氯 -5-(3- (吗啉丙基氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3-f]喹唑啉反应得到白色 固体, 产率 61%。 1H MR(DMSO-d6,400MHz) ^ ppm: 1.47(4H, br), 1.95-2.01(2H, m), 2.39(4H, br), 2.45(2H, t, J = 8.0Hz), 3.58-3.60(4H, m), 4.22(2H, t, J = 6.0Hz), 4.42(4H, d, J = 20.0Hz), 7.03(1H, s), 7.13-7.17(4H, m), 7.62-7.69(4H, m), 8.41(1H, s), 10.08(1H, s), 10.11(1H, s); MS:644[M+H]+ 实施例 24. N-(3-氟 -4-((5-(3-吗啉丙氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4】二噁烷并【2,3-f]喹唑 啉 -10-基)氧基)苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
替换页(细则第 26条)
同实施例 3操作, 由化合物 N-(3-氟 -4羟基苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙垸 -1,1-二 甲酰胺和 10-氯 -5-(3- (吗啉丙基氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3-f]喹唑啉反应得 到白色固体, 产率 69%。 1H NMR(DMSO-d6,400MHz) δ ppm: 1.47(4H, br), 1.95-1.99(2H, m), 2.38(4H, br), 2.44(2H, t, J = 8.0Hz), 3.58-3.60(4H, m), 4.23(2H, t, J = 6.0Hz), 4.43(4H, d, J = 20.0Hz), 7.07(1H, s), 7.16(2H, t, J = lO.OHz), 7.32(1H, t, J = 8.0Hz), 7.45(1H, d, J = 12.0Hz), 7.62-7.66(2H, m), 7.79(1H, d, J = 16.0Hz), 8.43(1H, s), 10.03(1H, s), 10.13(1H, s); MS:662[M+H]+. 实施例 25. N-(2-氯 -4-((5-(3-吗啉丙氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4】二噁烷并 [2,3-f]喹唑 啉 -10-基)氧基)苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
同实施例 3操作, 由化合物 N-(2-氯 -4羟基苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙垸 -1,1-二 甲酰胺和 10-氯 -5-(3- (吗啉丙基氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3-f]喹唑啉反应得 到白色固体,产率 66%。1H NMR(DMSO-d6,400MHz) δ ppm: 1.64(4H, d, J = 9.3Hz), 1.96-1.98(2H, m), 2.38-2.45(6H, m), 3.59(4H, br), 4.22(2H,br), 4.40(2H, br), 4.44(2R br), 7.05(1H, s), 7.16-7.26(3 H, m), 7.51(1H, s), 7.60(2H, br), 8.05(1H, d, J = 9.0Hz), 8.45(1H, s), 9.94(1H, s), 10.86(1H, s); MS:678[M+H]+. 实施例 26. N-(3-氯 -4-((5-(3-吗啉丙氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4】二噁烷并 [2,3-f]喹唑 啉 -10-基)氧基)苯基) -Ν-(4-氟苯基)环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
39
同实施例 3操作, 由化合物 N-(3-氯 -4羟基苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙垸 -1, 1-二 甲酰胺和 10-氯 -5-(3- (吗啉丙基氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3-f]喹唑啉反应得 到白色固体, 产率 69%。 1H NMR (DMSO-i 300 MHz) (5 ppm:, 1.45-1.47(4H, m), 1.97-1.98(2H, m), 2.39-2.46(6H, m), 3.59(4H, s), 4.22-4.24(2H, m), 4.41-4.46(4H, m),7.07(lH, s), 7.14-7.17(2H, s), 7.34-7.35(lH, m), 7.62-7.66(3H, m), 7.98-8.00(1H, m), 8.42(1H, s), 10.07(1H, s), 10.28(1H, s); MS:678[M+H]+. 实施例 27. N-(2-氟 -4-((5-(3-吗啉丙氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4】二噁烷并【2,3-f|喹唑 啉 -10-基)氧基)苯基) -Ν-(4-氟苯基)环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
同实施例 3操作, 由化合物 Ν-(2-氟 -4羟基苯基) -Ν-(4-氟苯基)环丙垸 -1, 1-二 甲酰胺和 10-氯 -5-(3- (吗啉丙基氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁烷并 [2,3-f]喹唑啉反应得 到白色固体, 产率 64%。
1H MR (DMSO-d6y 300 MHz) δ ppm: 1.51-1.70 (4H, m), 1.96 (2H, s), 2.39 (6H, s), 3.59 (4H, s), 4.22 (2H, s), 4.42 (4H, d, J=14.2 Hz), 7.06 (2H, s), 7.18 (2H, t, J = 8.5 Hz), 7.32 (IH, d, J=l l . l Hz), 7.62 (2H, s), 7.89 (IH, s), 8.45 (IH, s), 10.02 (IH, s), 10.54 (IH, s); MS:662[M+H]+. 实施例 28. N-(3-氟 -4-((5-(3-吗啉丙氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4】二噁烷并 [2,3-f]喹唑 啉 -10基)氧基)苯基) -Ν-苯乙基环丙垸 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
40
替换页(细则第 26条)
ίί-ε'ζ1#¾ίϋι二 [ί^】-¾=-ε'ζ-(¾¾ (耷" Ξ (聲篱 ώ二) -9)-S) )-N ·οε
Au+n\L09 sn s 'H ee oi '(s 'ΗΙ)90ΌΙ '(S
'ΗΙ)Μζ·8 '(ZHO'8 = Ρ 'Η1)18'Δ 'Ο ¾^)997.-£9 , '(ΖΗ0.8 = Γ 'Ρ c )5 L '(ΖΗ0·8 = Γ Ί 'Hl)e£7. '(ZH0.8 = Γ ¾ ¾Ζ)91 . '(s 'ΗΙ)90 ' '( 'Ηζ)8»9» '(ui 'UZ)ZV^-0V^ '(ZH08 = f Ί 'Η2)ε2 '(ZH08 = Γ Ί 'Η )1 '(s '(冚 )90 -£0'∑;
'(s 'Ht)9t7 : uidd (zHW00t7'9P"OSWa)¾ N Η 南^ ' 固 曰「1¾ ¾td¾id[i-e¾]^ 'd^[^i]-M-- ¾-(¾¾M¾¾i- )-s-B-oi
二 (耷 * ) -N-(g¾¾¾ t ^ -ε)-Ν呦 w申 m e m^M
+[u+n\zL9 sn '(s
£Hl)28'01 '(s 'ΗΙ)Μζ·8 '(ui 'Ηΐ) 0'8-00'8 '(ΖΗ 6 Zl=f 'P 'HI) 6 L 'HZ) 0VL-£Z L '(ui ¾)6^ .-617. '(S 'Hi) LQ'L 'TO)9^ ' q 'ΗΖ) tt7 '(ui 'uz Z -lZ '(s ¾17) 6S '(s ^Zi i-OZ t '("I 'HZ) '(^ 'H9)WZ-6rZ '(^ 'H2)86' -^6'l
;(ΖΗΑ'Π = f 'P 'H^e t :i"dd ς (ZHW OOe "OSl a) ¾RM Η^Ύο^^^ί'^Μ^^ i二 -I'I- -ε)-Ν呦 HEp e \ ^
同实施例 3操作, 由化合物 N-(3-氟 -4羟基苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙垸 -1,1-二 甲酰胺和 10-氯 -5-(6- (二甲胺基)己氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3-f]喹唑啉反应 得到白色固体, 产率 52%。 1H NMR(DMSO-d6,400MHz) (5 ppm: 1.34-1.40(2H, m), 1.46(4H, s), 1.49-1.55(2H, m), 1.76-1.85(2H, m), 1.93-2.00(2H, m), 2.38(6H, s), 2.55(2H, br), 4.18(2H, t, J = 6.4Hz), 4.40-4.41(2H, m), 4.46-4.47(2H, m), 7.07(1H, s), 7.16(2H, t, J = 8.8Hz), 7.32(1H, t, J = 8.8Hz), 7.44(1H, d, J = 8.8Hz), 7.63-7.66(2H, m), 7.80(1H, d, J = 8.8Hz), 8.43(1H, s), 10.06(1H, s), 10.34(1H, s); MS:662[M+H]+. 实施例 31. N-(3-氟 -4-((5-(6-甲氧基己基)氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4】二噁垸并 [2,3-f] 喹唑啉 -10-基)氧基)苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
同实施例 3操作, 由化合物 N-(3-氟 -4羟基苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙垸 -1,1-二 甲酰胺和 10-氯 -5-(6- (甲氧基)己氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3-f]喹唑啉反应得 到白色固体, 产率 52%。 1H MR(DMSO-d6,300MHz) δ ppm: 1.11(2H, br), 1.40-1.53(8H, m), 1.79(2H, s), 3.21(3H, s), 3.32-3.34(2H, m), 4.17(2H, s), 4.41(2H, s), 4.46(2H, s), 7.06(1H, s), 7.16(2H, t, J = 8.7Hz), 7.33(1H, t, J = 8.7Hz), 7.45(1H, d, J = 8.7Hz), 7.62-7.66(2H, m), 7.80(1H, d, J = 8.7Hz), 8.43(1H, s), 10.06(1H, s), 10.33(1H, s); MS:649[M+H]+ 实施例 32. N-(4-((5-(3- (二甲胺基)丙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4】二噁烷并 [2,3-f]喹唑 啉 -10-基)氧基) -3-氟苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
替换页(细则第 26条)
同实施例 3操作, 由化合物 N-(3-氟 -4羟基苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙垸 -1, 1-二 甲酰胺和 10-氯 -5-(3- (二甲氨基)丙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1 ,4]二噁垸并 [2,3-f]喹唑啉反应 得到白色固体, 产率 55%。 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-i¾) (5
1.37-1.54(4H, m), 1.88-2.03(2H, m), 2.13-2.26(6H, m), 2.37-2.47(2H, m), 4.14-4.27(2H, m), 4.35-4.61 (4H, m), 7.06(1H, s), 7.09-7.21 (2H, m), 7.26-7.40(lH, m), 7.45(1H, d, J = 9.2Hz), 7.65(2H, d, J = 8.7Hz), 7.81 (1H, d, J = 12.9Hz),8.44(lH, s), 10.07(1H, s), 10.34(1H, s); MS:620[M+H]+. 实施例 33. N-(3-氟 -4-((5-(3- (哌啶 -1-基)丙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4】二噁烷并 [2,3-f] 喹唑啉 -10-基)氧基)苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
同实施例 3操作, 由化合物 N-(3-氟 -4羟基苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙垸 -1, 1-二 甲酰胺和 10-氯 -5-P- (哌啶 -1 -基)丙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3-f]喹唑啉反 应得到白色固体, 产率 58%。 1H NMR (300 MHz, OMSO-d6) δ ppm:
1.29-1.48(6H, m), 1.48-1.64(4H, m), 1.84-2.06(2H, m), 2.25-2.45(6H, m), 4.08-4.30(2H, m), 4.40-4.62(4H, m), 7.06(1H, s), 7.10-7.24(2H, m), 7.32(1H, s), 7.42(1H, s), 7.56-7.73(2H, m), 7.81 (1H, d, J = 13.4Hz), 8.45(1H, d, J = 4.2Hz), 10.10(1H, s), 10.34(1H, s); MS:660[M+H]+.
实施例 34. N-(3-氟 -4-((5-(3- (甲硫基)丙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[l,4j二噁烷并 [2,3-f]喹 唑啉 -10-基)氧基)苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
同实施例 3操作, 由化合物 Ν-(3-氟 -4羟基苯基) -Ν-(4-氟苯基)环丙垸 -1,1-二 甲酰胺和 10-氯 -5-(3- (甲硫基)丙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3-f]喹唑啉反应得 到白色固体,产率 63%。 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO- ) (Η·46(4Η, s), 1.90-2.10(5H, m), 2.63-2.68(2H, m), 4.14-4.34(2H, m), 4.35-4.64(4H, m), 7.08(1H, s), 7.10-7.23(2H; m), 7.24-7.38(lH, m), 7.44(1H, d, J = 9.2Hz), 7.56-7.72(2H, m), 7.80(1H, d, J = 12.9Hz), 8.44(1H, s), 10.06(1H, s), 10.33(1H, s); MS:623[M+H]+.
实施例 35. N-(3-氟 -4-((5-(3-(4-甲基哌嗪 -1-基)丙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4】二噁烷 并 [2,3-f|喹唑啉 -10-基)氧基)苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
同实施例 3操作, 由化合物 N-(3-氟 -4羟基苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙垸 -1,1-二 甲酰胺和 10-氯 -5-(3-(4-甲基哌嗪 -1-基)丙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3-f]喹唑 啉反应得到白色固体, 产率 63%。 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-^6) S 1.40-1.55(4H, m), 1.82-2.01(2H, m), 2.15(3H, s), 2.23-2.48(10H, m), 4.07-4.31(2H, m),
4.31-4.59(4H, m), 7.06(1H, s), 7.09-7.23(2H, m), 7.25-7.39(lH, m), 7.44(1H, d, J = 9.1Hz), 7.58-7.73(2H, m), 7.81(1H, d, J = 13.2Hz), 8.44(1H, s), 10.10(1H, s),
10.36(1H, s); MS:675[M+H]+
实施例 36. N-(4-((5-(3-(l,l-二氧化硫代吗啉基)丙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,41二噁烷 并 [2,3-f|喹唑啉 -10-基 ^基 )-3-氟苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙焼 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
同实施例 3操作, 由化合物 N-(3-氟 -4羟基苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙烷 -1,1-二 甲酰胺和 10-氯 -5-(3-(1,1-二氧化硫代吗啉基)丙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并
[2,3-f]喹唑啉反应得到白色固体,产率 63%。 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-^6) δ ppm: 1.46(4H, br), 1.84-2.03(2H, m), 2.58-2.70(2H, m), 2.79-3.01(4H, m),
3.01-3.21(4H ,m), 4.06-4.31(2H, m), 4.31-4.62(4H, m), 7.09(1H, s), 7.11-7.26(2H, m): 7.26-7.39(lH, m), 7.44(1H, d, J = 9.0Hz), 7.55-7.73(2H, m), 7.80(1H, d, J = 12.9Hz), 8.44(1H, s), 10.06(1H, s), 10.33(1H, s); MS:710[M+H]+. 实施例 37. N-(4-((5- ((四氢呋喃 -3-基)氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4】二噁烷并【2,3-f]喹 唑啉 -10-基)氧基) -3-氟苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
同实施例 3操作, 由化合物 N-(3-氟 -4羟基苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙垸 -1,1-二 甲酰胺和 10-氯 -5- ((四氢呋喃 -3基)氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3-f]喹唑啉反 应得到白色固体, 产率 65%。 1H MR (300 MHz, DMSO-i/6) δ ppm: 1.46(4H, s), 1.94-1.97(2H, m), 2.26-2.31(1H, m), 2.39-2.45(2H, m), 4.17-4.23(2H, m), 4.41(2H, br), 4.46(2H, br), 7.05(1H, s), 7.15(2H, t, J = 8.4Hz), 7.32(1H, t, J = 8.4Hz), 7.44(1H, d, J = 8.4Hz), 7.62-7.68(2H, m), 7.80(1H, d, J = 12.3Hz), 8.43(1H, s), 10.06(1H, s), 10.33(1H, s); MS:605[M+H]+. 实施例 38. N-(3-氟 -4-((5-(2- (四氢吡咯 -1-基)乙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4】二噁烷并 【2,3-f|喹唑啉 -10-基)氧基)苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
45
同实施例 3操作, 由化合物 N-(3-氟 -4羟基苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙垸 -1,1-二 甲酰胺和 10-氯 -5-(2- (四氢吡咯 -1-基)乙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3-f]喹唑 啉反应得到白色固体, 产率 61%。 1H NMR (DMSO- , 300 MHz) δ ppm: 1.43 (4H, s), 1.80 (4H, s), 3.59 (4H, s), 4.28 - 4.51 (8H, m), 6.82 (IH, s), 7.07― 7.26 (3H, m), 7.27 - 7.41 (IH, m), 7.55 - 7.72 (3H, m), 8.18 (IH, d, J=3.0 Hz), 10.07 (2H, s);
MS:632[M+H]+. 实施例 39. N-(3-氟 -4-((5-(2-吗啉基乙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -|1,4】二噁烷并 [2,3-f]喹 唑啉 -10-基)氧基)苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
同实施例 3操作, 由化合物 N-(3-氟 -4-羟基苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙垸 -1,1-二 甲酰胺和 10-氯 -5-(2-吗啉基乙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3-f]喹唑啉反应得 到白色固体, 产率 68%。 1H NMR (DMSO-i¾, 300 MHz) ppm: 1.43 (4H, s), 3.43 (4H, s), 3.72 (4H, d, J=5.1 Hz), 4.40 (8H, t, J-18.5 Hz), 6.95 (IH, d, J=2.8 Hz), 7.15 (2H, t, J=8.8 Hz), 7.21 (IH, s), 7.30 (IH, s), 7.62 (2H, s), 7.66 (IH, s), 8.39 (IH, d, J=2.9 Hz), 10.07 (2H, s); MS:648[M+H]+. 实施例 40. N-(3-氟 -4-((5- ((四氢 -2H-吡喃 -4-基) t基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4】二噁烷并
[2,3-f]喹唑啉 -10-基)氧基)苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
同实施例 3操作, 由化合物 N-(3-氟 -4羟基苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙垸 -1,1-二
46
替换页(细则第 26条)
甲酰胺和 10-氯 -5- ((四氢 -2H-吡喃 -4-基)氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3-f]喹唑 啉反应得到白色固体, 产率 65%。 1H NMR (300 MHz, OMSO-d6) δ ppm: 1.46(4H, br), 1.65-1.69(2H, m), 2.05-2.09(2H, m), 3.52-3.59(2H, m), 3.87-3.91 (2H, m), 4.41 (2H, s), 4.47(2H, s), 4.91(1H, br), 7.07-7.25(3H, m), 7..25-7.39(lH, m), 7.44(1H, d, J = 9.0Hz), 7.57-7.73(2H, m), 7.78-7.83(lH, m), 8.43(1H, s), 10.06(1H, s),
10.33(1H, s); MS:619[M+H]+. 实施例 41. N-(4-((5-(3-吗啉丙氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4】二噁烷并 [2,3-f|喹唑啉 -10- 基)氧基)苯基) -Ν-(4-苯氧基苯基)环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
同实施例 3操作, 由化合物 Ν-(4-羟基苯基) -Ν-(4-苯氧基苯基)环丙垸 -1, 1 -二 甲酰胺和 10-氯 -5-(3-吗啉丙氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁烷并 [2,3-f]喹唑啉反应得到 白色固体,产率 55%。1H NMR(DMSO-d6,300MHz) (5 ppm: 1.46(4H, s), 1.96(2H, br), 2.39(4H, br), 3.58(4H, br), 3.68(2H, br), 4.21 (2H, br), 4.39(2H, br), 4.45(2H, br), 6.95-7.03(5H, m), 7.10-7.19(4H, m), 7.34-7.36(2H, m), 7.65-7.71 (4H, m), 8.41(1H, s): 10.38(1H, d, J = 12.9Hz); MS:718[M+H]+ 实施例 42. N-(4-((5-(3-吗啉丙氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4】二噁烷并 [2,3-f]喹唑啉 -10- 基)氧基)苯基) -N- -1-基)环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
同实施例 3操作,由化合物 N-(4-羟基苯基) -N- (萘胺 -1 -基)环丙院 -1, 1 -二甲酰 胺和 10-氯 -5-(3-吗啉丙氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3-f]喹唑啉反应得到白色 固体,产率 66%。 1H NMR(DMSO-d6,300MHz) δ ppm: 1.65(4H, s), 1.93-1.98(2H, m): 2.38-2.50(6H, m), 3.59(4H,br), 4.22(2H, br), 4.40(2H, br), 4.45(2H, br), 7.04(1H, s), 7.20(2H, d, J = 9.0Hz), 7.52-7.56(3H, m), 7.69-7.81 (4H, m), 7.96-8.04(2H, m), 8.42(1H, s), 10.30(1H, s), 10.69(1H, s); MS:676[M+H]+. 替换页(细则第 26条)
实施例 43. N-(3-氟 -4-((5- (异丙基氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4】二噁烷并 [2,3-f|喹唑啉 -10-基)氧基)苯基) -Ν-(4-氟苯基)环丙烷 -U-二甲酰胺的制备
同实施例 3操作, 由化合物 Ν-(3-氟 -4羟基苯基) -Ν-(4-氟苯基)环丙垸 -1, 1-二 甲酰胺和 10-氯 -5- (异丙基氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3-f]喹唑啉反应得到白 色固体, 产率 69%。 iH MR (300 MHz, OMSO-d6) δ ppm 1.37(6Η, d, J = 6.0Hz), 1.41-1.67(4H, m), 4.40(2H, s), 4.45(2H, s), 4.91 (1H, t, J = 6.0Hz), 7.07(1H, s), 7.15(2H, t, J = 8.7Hz), 7.33(1H, t, J = 8.7Hz), 7.45(1H, d, J = 8.7Hz), 7.63-7.67(2H, m), 7.78-7.82(lH, m), 8.42(1H, s), 10.06(1H, s), 10.33(1H, s); MS:577[M+H]+. 实施例 44. N-(4-((5-(3-吗啉丙氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,41二噁烷并 [2,3-f|喹唑啉 -10- 基)氧基)苯基) -Ν-(3-甲基异恶唑 -5-基)环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
同实施例 3操作, 由化合物 Ν-(4-羟基苯基) -Ν-(3-甲基异恶唑 -5-基)环丙烷 -1, 1-二甲酰胺和 10-氯 -5- (异丙基氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3-f]喹唑啉反应 得到白色固体, 产率 64%。 1H NMR(DMSO-d6,300MHz) ppm: 1.50(4H, s), 1.94-1.96(2H, m), 2.38-2.45(9H, m), 3.57-3.60(4H, m), 4.19-4.23(2H, m), 4.40(2H, br), 4.44(2H, br), 6.64(1H, s), 7.03(1H, s), 7.16(2H, d, J = 8.7Hz), 7.67(2H, d, J = 8.7Hz), 8.48(1H, s), 9.91(1H, s), 11.14(1H, s); MS:631 [M+H]+ 实施例 45. N-(4-((5-(3-吗啉丙氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4】二噁烷并 [2,3-f]喹唑啉 -10- 基) ft基)苯基) -N-(4-甲砜基苯基)环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
同实施例 3操作, 由化合物 N-(4-羟基苯基) -N-(4- (甲砜基)苯基)环丙烷 -1,1- 二甲酰胺和 10-氯 -5- (异丙基氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁烷并 [2,3-f]喹唑啉反应得到 白色固体, 产率 62%。
ppm: 1·49-1·50(4Η, m), 1.94-1.98(2H, m), 2.38-2.45(6H, m), 3.17(3H, s), 3.59(4H, br), 4.20-4.23(2H, m), 4.39(2H, br), 4.44(2H, br), 7.02(1H, s), 7.16(2H, d, J =8.7Hz), 7.68(2H, d, J = 8.7Hz), 7.84-7.93(4H, m), 8.41(1H, s), 10.05(1H, s), 10.59(1H, s); MS:704[M+H]+ 实施例 46. N-(4-((5-(3-吗啉丙氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4】二噁烷并 [2,3-f]喹唑啉 -10- 基)氧基)雜) -N-(2-氟 -5-三氟甲基雜)环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
同实施例 3操作, 由化合物 N-(2-氟 -5- (三氟甲基)苯基) -N-(4-羟基苯基)环丙 基 -1,1-二甲酰胺和 10-氯 -5- (异丙基氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3-f]喹唑啉反 应得到白色固体,产率 66%。 1H NMR(DMSO-d6,300MHz) S ppm: 1.61-1■ 67(4H, m), 1.97-1.99(2H, m), 2.35-2.42(6H, m), 3.59(4H, br), 4.20-4.23(2H, m), 4.40(2H, br), 4.44(2H, br), 7.04(1H, s), 7.19(2H, d, J = 8.1Hz), 7.55(2H, d, J = 8.7Hz), 7.65(2H, d, J = 8.1Hz), 8.43(2H, d, J = 8.7Hz), 9.87(1H, s), 11.14(1H, s); MS:712[M+H]+ 实施例 47. N-(4-((5-(3-吗啉丙氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4】二噁烷并 [2,3-f]喹唑啉 -10- 基)氧基)苯基) -N- (吡啶 -2-基)环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
替换页(细则第 26条)
同实施例 3操作,由化合物 N-(4-羟基苯基) -N- (吡啶 -2-基)环丙垸 -1,1-二甲酰 胺和 10-氯 -5- (异丙基氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁烷并 [2,3-f]喹唑啉反应得到白色固 体,产率 46%。 1HNMR(DMSO-d6,300MHz) δ ppm: 1.57-1.61(4H, m), 1.95-1.98(2H, m), 2.37-2.45(6H, m), 3.59(4H, br), 4.19-4.23(2H, m), 4.39(2H, br), 4.44(2H, br), 7.04(1H, s), 7.12-7.19(3H, m), 7.67(2H, d, J = 8.7Hz), 7.80(1H, t, J = 8.1Hz),
8.08(1H, d, J = 8.1Hz), 8.31-8.33(1H, m), 8.41(1H, m), 9.82(1H, s), 10.99(1H, s); MS:627[M+H]+. 实施例 48. N-环己基- N-(4-((5-(3-吗啉丙氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4】二噁烷并 [2,3-f] 喹唑啉 _10_基)氧基)苯基)环丙院 甲醜胺的制备
同实施例 3操作, 由化合物 N-环己基 -N-(4-羟基苯基)环丙垸 -1, 1-二酰胺和 10-氯 -5- (异丙基氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3-f]喹唑啉反应得到白色固体,产 率 46%。 1H NMR(DMSO-d6,300MHz) δ ppm: 1.09-1.23(6H, m), 1.36-1.39(4H, m), 1.54-1.72(6H, m), 1.98(2H, s), 2.38-2.42(4H, m), 3.58-3.62(5H, m), 4.22(2H, br), 4.39(2H, br), 4.44(2H, br), 7.03(1H, s), 7.16(2H, d, J = 8.7Hz), 7.65(2H, d, J = 8.7Hz). 7.82(1H, d, J = 8.7Hz), 8.41(1H, s), 10.60(1H, s); MS:632[M+H]+. 实施例 49. N-(4-((5-(3-吗啉丙氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4J二噁嫁并 [2,3-f]喹唑啉 -10- 基^基)苯基) -N-异戊基环丙烧 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
同实施例 3操作, 由化合物 N-(4-羟基苯基) -N-异戊基环丙垸 -1, 1-二酰胺和 10-氯 -5- (异丙基氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁烷并 [2,3-f]喹唑啉反应得到白色固体,产 率 57%。 1H NMR(DMSO-d6,300MHz) δ ppm: 0.88(6H, d, J = 6.6Hz), 1.33-1.38(6H, m), 1.51-1.58(1H, m), 1.97(2H, br), 2.34-2.43(6H, m), 3.10-3.17(2H, m), 3.60(4H, br);
替换页(细则第 26条)
4.23(2H, br), 4.39(2H, br) ,4.44(2H, br), 7.04(1H, s), 7.15(2H, d, J = 8.4Hz), 7.66(2H, d, J = 8.4Hz), 7.91(1H, s), 8.41(1H, s), 10.77(1H, s); MS:620[M+H]+. 实施例 50. N-(4-甲氧基苄基) -N-(4-((5-(3-吗啉丙氧基) -2,3-二氢 -【1,4】二噁烷 并 [2,3-f]喹唑啉 -10-基)氧基)苯基) - 1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
同实施例 3操作, 由化合物 N-(4-甲氧基苄基) -N-(4-羟基苯基)环丙垸 -1, 1- 二酰胺和 10-氯 -5- (异丙基氧基 2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3-f]喹唑啉反应得到白 色固体,产率 68%。 1HNMR(DMSO-d6,300MHz) δ ppm: 1.38-1.41(4H, m), 1.96(2H t, J = 8.7Hz), 2.35-2.43(4H, m), 3.17(2H, d, J = 8.7Hz), 3.59(4H, s), 3.72(3H, s), 4.21-4.27(4H, m), 4.39(2H, br), 4.44(2H, br), 6.89(2H, d, J = 8.1Hz), 7.03(1H, s), 7.14-7.22(4H, m), 7.65(2H, 8.1Hz), 8.40-8.45(2H, m), 10.70(1H, s); MS:670[M+H]+. 实施例 51. N-(3-氟 -4-((5-(3-吗啉丙氧基) -2,3-二氢 -【1,4】二噁烷 [2,3-f]喹唑啉 -10-基) «基)苯 -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的 L-苹果酸盐的制备
将实施例 24所得化合物 (660mg, lmmol)溶于 15mL丙酮中, 室温搅拌 15分 钟, 加入 L-苹果酸 (134mg, lmmol)水溶液 2mL,继续搅拌 12小时, 将反应液过滤 得到白色固体 400mg, 将此固体溶于 15mL乙醇中回流加热, 完全溶解后冷却静 置, 得白色晶体化合物 260mg, HPLC>99%. 1HNMR(DMSO-d6, 400ΜΗζ) δ ppm: 1.47(4H, s), 2.07-2.09(2H, s), 2.39-2.63 (4H, m), 2.67(3H, m), 3.68(4H, s), 4.19-4.24(0.5H, m), 4.25(2H, t, J = 8.0Hz), 4.40-4.42(2H, m), 4.46-4.48(2H, m), 7.08(1H, s), 7.16(2H, t, J = 8.8Hz), 7.33(1H, t, J = 8.8Hz), 7.45(1H, d, J = 8.8Hz), 7.63-7.67(2H, m), 7.81(1H, d, J = 8.8Hz), 8.44(1H, s), 10.07(1H, s), 10.35(1H, s)。 实施例 52 N-(4-氟苯基) -N-(4-((5-(2-羟基乙氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4】二噁烷并
[2,3-f|喹唑啉 -10-基)氧基)苯基)环丙基 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
51
替换页(细则第 26条)
步骤 1 ) N-(4-((5-苄氧基 -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3- 喹唑啉 -10-基)氧基)苯 基) -
同实施例 3操作, 由 5-苄氧基 -10-氯 -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3- 喹唑啉和 N-(4-羟基苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙垸 -1, 1-二甲酰胺反应得到棕色固体, MS: m/z = 607.2[M+H]+
步骤 2) N-(4-氟苯基) -N-(4-((5-羟基 -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3- 喹唑啉 -10- 基)
将 N-(4-((5-苄氧基 -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3:/]喹唑啉 -10-基)氧基)苯 基) -N—(4-氟苯基)环丙基 -1, 1-二甲酰胺 (330mg, 0.52mmol ) 溶于乙醇 ( 1.5mL) 和乙酸乙酯 (1.5mL ) 的混合溶剂中, 加入钯碳 (10%, 30mg), 氢气环境下, 反应 3小时。 反应液过滤, 蒸干滤液, 得粗产品 160mg, 产率 57%, MS: m/z = 517.1 [M+H]+ o
步骤 3 ) N-(4-氟苯基) -N-(4-( (5-(2-羟基乙氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁烷并 [2,3:/] 喹唑
将 N-(4-氟苯基) -N-(4-((5-羟基 -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3:/]喹唑啉 -10-基)氧 基)苯基)环丙基 -1, 1 -二甲酰胺(60mg, 0.12mmol ), 2-溴乙醇(30mg, 0.24mmol ) 和碳酸钾 (48mg, 0.35mmol ) 溶于 Ν,Ν-二甲基甲酰胺 (2mL) 中, 80°C反应 2 小时。反应液过滤,蒸干滤液,柱层析得白色固体 20mg,产率 31%, 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-i/g) S 10.22 - 9.98 (m, 2H), 8.40 (s, 1H), 7.74 - 7.56 (m, 4H), 7.26 - 7.10 (m, 4H), 7.04 (s, 1H), 4.96 (brs, 1H), 4.51 - 4.34 (m, 4H), 4.19 (t, J = 4.9 Hz,
52
替换页(细则第 26条)
2H), 3.80 (t, J= 4.7 Hz, 2H), 1.51 - 1.37 (m, 4H). LCMS: m/z = 561.2[M+H]+。
实施例 53. N-(4-氟苯基) -N-(4-((5-(3-((2-羟基乙基)氨基)丙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4】二噁烷并 [2,3-f|喹唑啉 -10-基)氧基)苯基)环丙基 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备 步骤 1 ) 2) 同实施例 52操作。
步骤 3 ) N-(4-((5-(3-溴丙氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3;/]喹唑啉 -10-基)氧 基)
同实施例 52 操作, 由 Λ 4-氟苯基) -N-(4- 5-羟基 -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3- ]喹唑啉 -10-基)氧基)苯基)环丙基 -1,1-二甲酰胺和 1,3-二溴丙垸反应得棕色 油状物, LCMS: m/z = 637.1[M+H]+。
步骤 4) N-(4-氟苯基) -N-(4-((5-(3-((2-羟基乙基)氨基)丙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4] 二噁 -10-基)氧基)苯基)环丙基 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
将 N-(4-((5-(3-溴丙氧基 2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3- 喹唑啉 -10-基)氧基)苯 基) -N—(4-氟苯基)环丙基 -1,1-二甲酰胺 (100mg, 0.16mmol ), 乙醇胺 ( 10mg, 0.16mmol )和 Ν,Ν-二异丙基乙胺(61mg, 0.47mmol )溶于乙腈 (2mL)中, 25°C 反应 16小时。 反应液乙酸乙酯稀释, 饱和食盐水洗, 无水硫酸钠干燥, 蒸干滤 液,柱层析得白色固体 5mg,产率 5%, 1H NMR (400 MHz, Methanol-^) δ 8.26 (s, 1H), 7.61 - 7.53 (m, 2H), 7.52 - 7.41 (m, 2H), 7.13 - 7.03 (m, 2H), 7.03 - 6.92 (m, 2H), 6.87 (s, 1H), 4.42 - 4.30 (m, 4H), 4.26 - 4.21 (m, 2H), 3.71 - 3.67 (m, 2H), 3.11 - 3.07 (m, 2H), 2.99 - 2.95 (m, 2H), 2.19 - 2.13 (m, 2H), 1.58 - 1.50 (m, 4H). LCMS: m/z = 618.2[M+H]+。
实施例 54 N-(4-氟苯基) -N-(4-((5-(3-((2-甲氧基乙基)氨基)丙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -【1,4】二噁烷并 [2,3-f|喹唑啉 -10-基)氧基)苯基)环丙基 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
53
替换页(细则第 26条)
步骤 1 ) 2) 3 ) 同实施例 53操作。
步骤 4)7V-(4-氟苯基) -N-(4-((5-(3-((2-甲氧基乙基)氨基)丙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4] 二噁 [2,3:/]喹唑啉 -10-基)氧基)苯基)环丙基 -1, 1-二甲酰胺的制备
同实施例 53操作, 由 N-(4-((5-(3-溴丙氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3- ]喹 唑啉 -10-基)氧基)苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙基 -1, 1-二甲酰胺和 2-甲氧基乙基 -1-胺反 应得白色固体, 1H NMR (400 MHz, Methanol -ί/4) δ 8.85 (s, IH), 7.70 - 7.79 (m, 2H); 7.52 - 7.62 (m, 2H), 7.22 - 7.35 (m, 2H), 7.72 - 7.12 (m, 2H), 6.80 - 6.72 (m, IH), 4.42 - 4.30 (m, 4H), 4.26― 4.21 (m, 2H), 3.71 - 3.67 (m, 2H), 3.11 - 3.07 (m, 2H), 2.95 (s, 3H), 2.99 - 2.95 (m, 2H), 2.19 - 2.13 (m, 2H), 1.58 - 1.50 (m, 4H). LCMS:
实施例 55 N-(4-氟苯基) -N-(4-((5-(3-((2-羟基乙基) (甲基)氨基)丙氧基 )-2,3-二 氢 -[1,4】二噁烷并 [2,3-f]喹唑啉 -10-基)氧基)苯基)环丙基 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备 步骤 1 ) 、 2) 、 3 ) 同实施例 53操作。
步骤 4) N-(4-氟苯基) -N-(4-((5-(3-((2-羟基乙基 X甲基)氨基)丙氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1,4] - ]喹唑啉 -10-基)氧基)苯基)环丙基 -1, 1-二甲酰胺的制备
同实施例 53操作, 由 N-(4-((5-(3-溴丙氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3- ]喹 唑啉 -10-基)氧基)苯基) -ΛΗ4-氟苯基)环丙基 -1, 1-二甲酰胺和 2- (甲基氨基)乙基 -1- 醇反应得白色固体, 1H NMR (400 MHz, Methanol-^) δ 8.25 (s, IH), 7.62 (dd, J = 5.7, 3.3 Hz, IH), 7.58 - 7.54 (m, IH), 7.53 - 7.50 (m, IH), 7.50 - 7.43 (m, 2H), 7.08 - 7.04 (m, IH), 7.01― 6.92 (m, 2H), 6.87 (s, IH), 4.43 - 4.27 (m, 4H), 4.20— 4.15 (m: 2H), 3.73 - 3.64 (m, 2H), 2.93 - 2.82 (m, 2H), 2.84 - 2.76 (m, 2H), 2.50 (s, 3H), 2.15 - 2.04 (m, 2H), 1.59― 1.49 (m, 4H). MS: m/z = 632.2[M+H]+。
54
同实施例 52步骤 2)操作, 由 N-(4-((5-苄氧基 -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁烷并 [2,3;] 喹唑啉 -10-基)氧基) -3-氟苯) -N-(4-氟苯)环丙基 -1,1-二甲酰胺反应得白色固体, MS: m/z = 535.1 [M+H]+。
步骤 3 ) N-(3-氟 -4-((5-(2-羟基乙氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3- ]喹唑啉 -10-基)氧基)苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙基 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
同实施例 52步骤 3 )操作,由 N-(3-氟 -4-((5-羟基 -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3:/] 喹唑啉 -10-基)氧基)苯基) -W-(4-氟苯基)环丙基 -1,1-二甲酰胺和 2-溴乙醇反应得白 色固体, 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-^6) δ 10.29 (s, IH), 10.02 (s, IH), 8.43 (s, IH), 7.79 (dd, J = 13.0, 2.3 Hz, IH), 7.70 - 7.57 (m, 2H), 7.44 (dd, J = 8.6, 2.2 Hz, IH), 7.36 - 7.27 (m, IH), 7.19 - 7.11 (m, 2H), 7.07 (s, IH), 4.96 (brs, IH), 4.52 - 4.44 (m, 2H), 4.44― 4.36 (m, 2H), 4.20 (t, J= 4.9 Hz, 2H), 3.85 - 3.76 (m, 2H), 1.53 - 1.39 (m. 4H). MS: m/z = 579.2[M+H]+。 实施例 58 N-(3-氟 -4-((5-(3-羟基丙氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4】二噁烷并 [2,3-f|喹唑啉 -10- 基)氧基)苯基) -Ν-(4-氟苯基)环丙基 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备 步骤 1 ) 2) 同实施例 57操作。
步骤 3 ) N-(3-氟 -4-((5-(3-羟基丙氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3:/]喹唑啉 -10-基)
同实施例 57步骤 3 )操作,由 N-(3-氟 -4-((5-羟基 -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3;]
56
替换页(细则第 26条)
喹唑啉 -10-基)氧基)苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙基 -1, 1-二甲酰胺和 3-溴丙基 -1-醇反应 白色固体, 1H NMR (400 MHz, OMSO-d6) δ 10.30 (s, 1H), 10.03 (s, 1H), 8.43 (s, 1H), 7.79 (dd, J = 13.0, 2.3 Hz, 1H), 7.73 - 7.58 (m, 2H), 7.44 (dd, J = 9.0, 2.3 Hz, 1H), 7.36 - 7.27 (m, 1H), 7.19 - 7.11 (m, 2H), 7.06 (s, 1H), 4.49 - 4.39 (m, 4H), 4.25 (t, J = 6.4 Hz, 2H), 3.60 (t, J = 6.2 Hz, 2H), 3.06 (brs, 1H), 2.00 - 1.92 (m, 2H), 1.52 - 1.41 (m, 4H). LCMS: m/z = 593.2[M+H]+。 实施例 59 N-(3-氟 -4-((5-(2-羟基 -2-甲基丙氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4】二噁烷并 [2,3-f]喹 唑啉 -10-基)氧基)苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙基 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备 步骤 1 ) 2) 同实施例 57操作。
步骤 3 ) 2-((10-(2-氟 -4-(1 -((4-氟苯基)氨基甲酰基)环丙基 -1-甲酰胺)苯氧基 )-2,3- 酯的制备
同实施例 57操作, 由 N-(3-氟 -4-((5-羟基 -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3- ]喹唑 啉 -10-基)氧基)苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙基 -1, 1-二甲酰胺和 2-溴乙酸甲酯反应得浅 黄色固体, MS: m/z = 607.2[M+H]+。
步骤 4 ) N-(3-氟 -4-((5-(2-羟基 -2-甲基丙氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3;] -10-基)氧基)苯基) -^-(4-氟苯基)环丙基 -1, 1-二甲酰胺的制备
将 2-((10-(2-氟 -4-(1-((4-氟苯基)氨基甲酰基)环丙基 -1-甲酰胺)苯氧基 )-2,3-二 氢 -[1,4]二噁烷并 [2,3:/]喹唑啉 -5-基)氧基)乙酸甲酯 (100mg, 0.16mmol ) 溶于无 水四氢呋喃(2mL)中, 氩气保护条件下, 0°C滴加甲基格氏试剂(1M, 0.5mL, 0.5mmol), 25°C反应 16小时。 饱和氯化铵水溶液淬灭反应, 乙酸乙酯萃取, 有 机相饱和食盐水洗, 无水硫酸钠干燥, 蒸干滤液, 柱层析得白色固体 20mg, 产 率 20%, 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-^6) δ 10.30 (s, 1H), 10.02 (s, 1H), 8.43 (s, 1H), 7.79 (dd, J = 12.9, 2.4 Hz, 1H), 7.68― 7.58 (m, 2H), 7.49 - 7.40 (m, 1H), 7.36 - 7.25
57
替换页(细则第 26条)
(m, IH), 7.21 - 7.10 (m, 2H), 7.05 (s, IH), 4.69 (s, IH), 4.56 - 4.29 (m, 4H), 3.93 (s, 2H), 1.53 - 1.42 (m, 4H), 1.26 (s, 6H). LCMS: m/z = 607.2[M+H]+。 实施例 60 N-(4-((5-(3-氨基丙氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4】二噁烷并 [2,3-f]喹唑啉 -10-基慮 基) -3-氟苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙基 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备 步骤 1 ) 2) 同实施例 57操作。
步骤 3 ) (3-((10-(2-氟 -4-(1-((4-氟苯基)氨甲酰基)环丙基 -1-甲酰胺基)苯氧基 )-2,3- 酸叔丁酯的制备
同实施例 57操作, 由 N-(3-氟 -4-((5-羟基 -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3- ]喹唑 啉 -10-基)氧基)苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙基 -1, 1 -二甲酰胺和 (3-溴丙基)氨基甲酸叔 丁酯反应得浅黄色固体, LCMS: m/z = 692.2 (M+H)+。
步骤 4) N-(4-((5-(3-氨基丙氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3- ]喹唑啉 -10-基)氧 基) -3-氟苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙基 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
将 (3 10-(2-氟 -4-(1- 4-氟苯基)氨甲酰基) 环丙基 -1-甲酰胺)苯氧基 )-2,3-二 氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3- ]喹唑啉 -5-基)氧基)丙基)氨基甲酸叔丁酯 (100mg, 0.14mmol ) 溶于二氯甲垸中, 加入三氟乙酸 (2mL), 25°C反应 1小时。 反应液 浓缩, 二氯甲垸稀释, 分别用饱和碳酸钠和饱和食盐水洗, 无水硫酸钠干燥, 滤 液蒸干, 柱层析得白色固体 15mg, 产率 18%, 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-^6) δ 10.59― 9.66 (m, 2H), 8.43 (s, IH), 7.84 - 7.73 (m, IH), 7.67 - 7.61 (m, 2H), 7.44 (d, J = 9.0 Hz, IH), 7.34 - 7.26 (m, IH), 7.20 - 7.12 (m, 2H), 7.06 (s, IH), 4.53 - 4.34 (m, 4H), 4.30 - 4.15 (m, 2H), 2.83 - 2.69 (m, 2H), 1.98 - 1.85 (m, 2H), 1.51 - 1.38 (m, 4H), 1.30 - 1.14 (m, 2H). MS: m/z = 592.2 (M+H)+。 实施例 61 (R)-N-(4-((5-(3-氨基丁氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4〗二噁垸并 [2,3-f]喹唑啉 -10- 基 基) -3-氟苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙基 -U-二甲酰胺的制备
58
替换页(细则第 26条)
步骤 1 ) 2 ) 同实施例 57操作。
将 (R)-(4-羟基丁基 -2-基)氨基甲酸叔丁酯(400mg, 2.11mmol )禾口吡啶(3mL ) 溶于二氯甲垸 (4mL ) 中, 滴加 4-甲基苯磺酰氯 (606mg, 3.2mmol ) 的二氯甲 烷(2mL )溶液, 25°C反应 16h。 反应液二氯甲垸稀释, 分别用 1M 盐酸和饱和 食盐水洗, 无水硫酸钠干燥, 滤液蒸干, 得粗产物黄色油状物 300mg, 粗产率 41%, MS: m/z = 344.1 (M+H)+。
步骤 4 ) (R)-(4-((10-(2-氟 -4-(1 -((4-氟苯基)氨甲酰基)环丙基 -1 -甲酰胺)苯氧基 )-2,3- 基甲酸叔丁酯的制备
同实施例 57操作, 由 N-(3-氟 -4-((5-羟基 -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3- ]喹唑 啉 -10-基)氧基)苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙基 -1 , 1-二甲酰胺和 (R)-4-甲基苯磺酸
-3- ((叔丁氧羰基)氨基)丁酯反应得浅黄色固体, MS: m/z = 706.3 (M+H)+。
步骤 5 ) (R)-N-(4-((5-(3-氨基丁氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3;/]喹唑啉 -10- 基)氧基) -3-氟苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙基- 1 , 1 -二甲酰胺的制备
同实施例 60步骤 4 )操作, 由 (R)-(4-((10-(2-氟 -4-(1 -((4-氟苯基)氨甲酰基)环 丙基 -1 -甲酰胺)苯氧基 )-2,3-二氢 -[1 ,4]二噁垸并 [2,3 /]喹唑啉 -5-基)氧基)丁基 -2-基) 氨基甲酸叔丁酯反应得浅黄色固体, 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-^6) δ 10.30 (s, 1H), 10.14 (s, 1H), 8.43 (s, 1H), 7.87 - 7.75 (m, 1H), 7.64 (dd, J = 8.8, 5.1 Hz, 2H), 7.49 - 7.38 (m, 1H), 7.37 - 7.26 (m, 1H), 7.21 - 7.11 (m, 2H), 7.09 (s, 1H), 4.51 - 4.37 (m, 4H), 4.32 - 4.21 (m, 2H), 3.18 - 3.05 (m, 1H), 1.86 - 1.79 (m, 4H), 1.51 - 1.43 (m, 3H), 1.27 - 1.20 (m, 2H), 1.12 (d, J = 6.4 Hz, 2H). MS: m/z = 606.2 (M+H)+。
59
替换页(细则第 26条)
#¾¾#®¾¾¾¾弒lJl!:lJu u)s)ol_£t ££(£)s)z( Z9 --- ------- ss^g叵 s (?l
实施例 63 N-(2-氟 -4-((5-(2-羟基乙氧基) -2,3-二氢 -|1,4】二噁^#[2,3- 喹唑 啉 -10-基)氧基)苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙基 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备 步骤 1 ) N-(4-((5-苄氧基 -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3:/]喹唑啉 -10-基)氧基) -2- 氟苯 -N-(4-氟苯)环丙基 -1, 1-二甲酰胺的制备
同实施例 52步骤 1 )操作, 由 5-苄氧基 -10-氯 -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3;] 喹唑啉和 N-(2-氟 -4-羟苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙垸 -1, 1-二甲酰胺反应得棕色固体, LCMS: m/z = 625·2[Μ+Η]+。
步骤 2 ) N-(2-氟 -4-((5-(2-羟基乙氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3;/]喹唑啉 -10- 酰胺的制备
同实施例 52步骤 2)操作, 由 N-(4-((5-苄氧基 -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3;] 喹唑啉 -10-基)氧基) -2-氟苯) -N-(4-氟苯)环丙基 -1, 1-二甲酰胺反应得白色固体, LCMS: m/z = 535.1 [M+H]+。
步骤 3 ) N-(2-氟 -4-((5-(2-羟基乙氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3- ]喹唑啉 -10- 制备
同实施例 52步骤 3 ) 操作, 由 N-(2-氟 -4-((5-(2-羟基乙氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4] 二噁垸并 [2,3- ]喹唑啉 -10-基)氧基)苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙基 -1, 1-二甲酰胺和 2- 溴乙醇反应得白色固体, 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-i¾) δ 10.51 (s, IH), 9.99 (s, IH), 8.45 (s, IH), 7.95 - 7.79 (m, IH), 7.72 - 7.55 (m, 2H), 7.31 (dd, J = 11.1, 2.5 Hz: IH), 7.22 - 7.10 (m, 2H), 7.13 - 6.98 (m, 2H), 4.95 (t, J= 5.4 Hz, IH), 4.53 - 4.33 (m. 4H), 4.19 (t, J = 4.8 Hz, 2H), 3.85 - 3.76 (m, 2H), 1.67 - 1.46 (m, 4H). MS: m/z = 替换页(细则第 26条)
Ζ9
+[H+W]8S9 :SYi (m 's) 9S 1 XllZ ' ) 961-861
'(H 's) zz z H9 'UI) Z Z- YZ Xm 'ZH L = r Ί) 6S XUZ 'ZH V9 = r ¾ \z Xm s£ - 8» Xuz 'ZH ι ε '/. ε = r 'b) εο· '( Z = r 'p) OIL XUZ
6.8 = f LVL L S = f 6S7. UZ 0'5 '0.6 = f \^9 L 's) ZY S) 866 '( S) ε θΐ s (9p-oswa 'z丽 oot^) -)&mmx °%69 i i¾? i¾iii[iH]^¾i fl二 [t i]-焉二 -rt- (聲 ¾ i½r -s-驚 -o〖 ¾ 賴二 -i
'i-聲 Mii (奪 *耷 ϋ-¾¾ ) -N- (聲 *篤寸) -N呦 w申 m ι m^M
]8 9 :sn (m 's) LV\ Xnz ¾i
S L = f 'P) 96' 1 '(H£ 'S) £0 Z '(H9 '^) τ +Σ; '(Ht 9 = f Ί) 09 XliZ Y9 = Γ Ό '(Ht7 'ui) t7 -8t '(HI 'S) W).乙 '(HI 'ZH乙 '8 = Γ 'Ρ) 607. '(Η2 '^) ZVL - 6VL '(HI ¾ 9 Z 8 = Γ 'ΡΡ) IS L '(HI ¾ SZ = f 'Ρ) '(HZ '^) 19 L- 9 L '(HI 's) 6 8 '(HZ 's) 60012 (9P-OSWa 'z謂 OOt^) ¾MMHT °%Z9 *^ '^園 曰
^ i¾itiLi-£t]^¾ ti: [t7'i]-蓄二 -rt- (耷 ¾M i¾r£)-s-驚 -οι w mi ^-i
'ΐ-耷 (耷 *¾*-ε-¾¾ ) 寸) -N呦^ w申 ι m^M
二【t^】-奪二 -ε'ζ-( Μ^¾τε)-5)) -耷 ώ-ε)-Ν-( ) -N 9 P ¾
££Z9L0/810Z 13/I3d C6ZCSl/8T0Z OAV
啉 -10-基)氧基)苯基)环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
1) 1-(8-甲氧基 -6-硝基 -2,3-二氢苯并 [b][l,4]二噁垸 -5-基)乙基 -1-酮的制
将 1-(8-甲氧基 -2,3-二氢苯并 [b][l,4]二噁烷 -5-基)乙基 -1-酮 (20.8 g, 100 mmol), 硝酸 (22 mL)和醋酸 (44 mL)置于圆底烧瓶搅拌至反应完毕, 倒入碎 冰中,抽滤,得黄色固体产品 16.5 克,产率 66%。 !HNMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 7.37 (s, 1Η), 4.43 (dd, J = 5.4, 2.7 Hz, 2H), 4.35 (dd, J = 5.3, 2.7 Hz, 2H), 3.98 (s, 3H), 2.57 (s, 3H); MS: 254[M+H]+。
将 1-(8-甲氧基 -6-硝基 -2,3-二氢苯并 [b][l,4]二噁垸 -5-基)乙基 -1-酮(16.5 g, 65 mmol ) 置于反应瓶中, 加入钯碳 (2 g) 在氢气环境下搅拌至反应完毕, 抽滤浓 缩得类白色固体产品 13.7克, 产率 95%。 iHNMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 6.90 (s, 2Η), 5.96 (s, 1H), 4.32 - 4.25 (m, 2H), 4.18 - 4.09 (m, 2H), 3.72 (s, 3H), 2.41 (s, 3H);
将 1-(6-氨基 -8-甲氧基 -2,3-二氢苯并 [b][l,4] 二噁垸 -5-基)乙基 -1-酮 (13.7 g, 62 mmol)与甲酸乙酯 (27.5 g, 372 mmol) 溶于二氧六环中, 加入叔丁醇钠 (17.8 g, 186 mmol)搅拌至原料消失, 加入甲醇 10毫升继续搅拌至反应完毕, 盐酸中和 反应液至中性后抽滤、 浓缩、 得类白色固体产品 14.4克, 产率 99%。 iHNMR OO 替换页(细则第 26条)
MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 11.26 (s, IH), 7.59 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, IH), 6.55 (s, IH), 5.77 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, IH), 4.34 - 4.13 (m, 4H), 3.82 (s, 3H); MS: 234[M+H]+。
将 10-羟基 -5-甲氧基 -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3-f]喹啉( 14.4 g, 61 mmol )置 于反应瓶中, 加入甲苯溶解, 之后加入三乙胺 (42 mL, 305 mmol) 、 三氯氧磷 ( 17 mL, 183 mmol ) 加热搅拌至反应完毕, 蒸去溶剂后所得固体用碳酸氢钠水 溶液洗涤后抽滤,得类白色固体 14.1克,产率 92%。 1HNMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.51 (d, J = 4.9 Hz, IH), 7.38 (d, J = 4.8 Hz, IH), 7.12 (s, IH), 4.49 - 4.29 (m, 4H), 3.93 (s, 3H); MS: 252[M+H]+。
步骤 5) 5-甲氧基 -10-(4-硝基苯氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4] 二噁垸并 [2,3-f]喹啉的 制备
将 10-氯 -5-甲氧基 -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁烷并 [2,3-f]喹啉 (251 mg, 1 mmol ) 与 对硝基苯酚 (139 mg, l mmol ) 置于反应瓶中, 加入氯苯, 加热至回流搅拌至反 应完毕。 冷却后抽滤, 所得固体用碳酸钾水溶液洗涤后得浅黄色固体 250毫克, 产率 71%。 MS: 355[M+H]+。
步骤 6) 4-((5-甲氧基 -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3-f]喹啉 -10-基)氧基)苯胺的 制备
将 5-甲氧基 -10-(4-硝基苯氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3-f]喹啉 (250 mg, 0.7 mmol )置于反应瓶中, 加入甲醇, 雷尼镍 (250 mg) , 在氢气环境下搅拌至 反应完毕,抽滤、浓缩得类白色固体产品 226毫克,产率 99%。 MS: 325[M+H]+o 步骤 7) N-(4-氟苯基) -N-(4-((5-甲氧基 -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3-f]喹啉 -10- 基)氧基)苯基)环丙垸 -1 , 1 -二甲酰胺的制备 替换页(细则第 26条)
将 4-((5-甲氧基 -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3-f]喹啉 -10-基)氧基)苯胺 (226 mg, 0.7 mmol ) 和 1-((4-氟苯基)氨基甲酰基)环丙烷 -1-羧酸置于反应瓶中, 加入 N, N- 二甲基甲酰胺溶解,随后加入 2-(7-氧化苯并三氮唑) -Ν,Ν,Ν',Ν'-四甲基脲六氟磷酸 酯 (HATU)(380 mg, 1 mmol)和二乙基异丙基胺 (0.25 mL, 1.5 mmol),搅拌至反应完 毕,加入碳酸钠水溶液洗涤、抽滤、柱层析得白色固体 296毫克,产率 80% HNMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.19 - 10.02 (m, 2H), 8.43 (d, J = 5.2 Hz, 1H), 7.78 - 7.67 (m, 2H), 7.67 - 7.56 (m, 2H), 7.22 - 7.01 (m, 5H), 6.42 (d, J = 5.3 Hz, 1H), 4.38 - 4.25 (m, 4H), 3.92 (s, 3H), 1.50 - 1.40 (m, 4H).MS: 530[M+H]+。 实施例 67 N-(3-氟 -4-((5-甲氧基 -2,3-二氢 -|1,4】二噁烷并 [2,3-fj-喹啉 -10-基) 氧基)雜) -N-(4-氟雜)环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
步骤 1至步骤 4与实施例 66的制备的步骤 1至步骤 4相同。
步骤 5) 10-(2-氟 -4-硝基苯氧基) -5-甲氧基 -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁烷并 [2,3-f]-喹 啉的制备
参考实施例 66步骤 5 ) 操作, 以相同摩尔当量的 2-氟 -4硝基苯酚替代对硝基 苯酚即可。 iHNMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.67 (d, J = 5.0 Hz, 1H), 8.44― 8.27 (m, 1H), 8.13 - 7.93 (m, 1H), 7.19 (s, 1H), 7.07 (d, J = 4.9 Hz, 1H), 6.98 (t, J = 8.7 Hz, 1H), 4.31 - 4.18 (m, 2H), 4.16 - 4.06 (m, 2H), 3.95 (s, 3H); MS: 373[M+H]+。
步骤 6) 3-氟 -4-((5-甲氧基 -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3-f]喹啉 -10-基)氧基)苯 胺的制备
65
参考实施例 66步骤 6) 操作, 以相同摩尔当量的 10-(2-氟 -4-硝基苯氧基) -5-甲 氧基 -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3-f]喹啉替代 5-甲氧基 -10-(4-硝基苯氧基) -2,3-二 氢 -[1,4] 二噁烷并 [2,3-f]-喹啉即可。 !HNMR (400 Hz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.38 (d, J = 5.2 Hz, 1H), 7.05 (s, 1H), 6.99 (t, J = 9.0 Hz, 1H), 6.61 - 6.49 (m, 1H), 6.49 - 6.38 (m, 1H), 6.33 (d, J = 5.3 Hz, 1H), 5.53 - 5.37 (m, 2H), 4.36 - 4.38 (m, 4H), 3.92 (s, 3H); MS: 343[M+H]+。
步骤 7) N-(3-氟 -4-((5-甲氧基 -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3-f]喹啉 -10-基)氧基) 苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环
参考实施例 66步骤 7) 操作, 以相同摩尔当量的 3-氟 -4-((5-甲氧基 -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3-f]喹啉 -10-基)氧基)苯胺替代 4-((5-甲氧基 -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁 垸并 [2,3-f]喹啉 -10-基)氧基)苯胺即可。 1HNMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.30 (s, 1H), 9.97 (s, 1H), 8.35 (d, J = 5.2 Hz, 1H), 7.94 - 7.69 (m, 1H), 7.64 - 7.52 (m, 2H), 7.48 - 7.32 (m, 1H), 7.19 (t, J = 9.0 Hz, 1H), 7.09 (t, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.01 (s, 1H), 6.32 (d, J = 5.2 Hz, 1H), 4.28 (s, 4H), 3.85 (s, 3H), 1.55 - 1.28 (m, 4H).MS: 548[M+H]+。
实施例 68 N-(2-氟 -4-((5-甲氧基 -2,3-二复 -[1,4]二噁烷并 [2,3-f|喹啉 -10-基) 氧基)苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
步骤 1至步骤 4与实施例 66的制备的步骤 1至步骤 4相同
66
替换页(细则第 26条)
步骤 5) 10-(3-氟 -4-硝基苯氧基) -5-甲氧基 -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3-f]喹啉 的制备
参考实施例 66步骤 5 ) 操作, 以相同摩尔当量的 3-氟 -4硝基苯酚替代对硝 基苯酚即可。 MS: 373[M+H]+。
步骤 6) 2-氟 -4-((5-甲氧基 -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3-f]喹啉 -10-基)氧基)苯 胺的制备
参考实施例 66步骤 6) 操作, 以相同摩尔当量的 10-(3-氟 -4-硝基苯氧基) -5-甲 氧基 -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3-f]喹啉替代 5-甲氧基 -10-(4-硝基苯氧基) -2,3-二 氢 -[1,4]二噁院并 [2,3-f]喹啉即可。 1HNMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.38 (d, J = 5.2 Hz, IH), 7.04 (s, IH), 6.98 - 6.91 (m, IH), 6.89― 6.79 (m, IH), 6.78 - 6.67 (m, IH), 6.37 (d, J = 5.2 Hz, IH), 5.14 (s, 2H), 4.43 - 4.30 (m, 4H), 3.91 (s, 3H); MS: 343[M+H]+。
步骤 7) N-(2-氟 -4-((5-甲氧基 -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3-f]喹啉 -10-基)氧基) 苯基) -N-(4-氟苯基)环丙烷- 1 , 1 -二甲酰胺的制备
参考实施例 66步骤 7 ) 操作, 以相同摩尔当量的 2-氟 -4-((5-甲氧基 -2,3-二氢 -[1,4] 二噁烷并 [2,3-f]喹啉 -10-基)氧基)苯胺替代 4-((5-甲氧基 -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3-f]喹 -10-¾)氧基)苯胺即可。 iHNMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.49 (s, IH), 9.97 (s, IH), 8.50 (d, J = 5.1 Hz, IH), 7.92 - 7.82 (m, IH), 7.65 - 7.57 (m, 2H), 7.25 - 7.06 (m, 4H), 6.89 - 6.84 (m, IH), 6.63 (d, J = 5.1 Hz, IH), 4.33 - 4.22 (m, 4H), 替换页(细则第 26条)
3.92 (s, 3H), 1.63 - 1.52 (m, 4H); MS: 548[M+H]+。
实施例 69 N-(4-氟苯基) -N-(4-((5-(3-吗啉丙氧基) -2,3-二复 -[1,4】二噁垸并
[2,3-f|喹啉 -10-基) *基)苯基)环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
步骤 1至步骤 4与实施例 66的制备的步骤 1至步骤 4相同。
将 10-氯 -5-甲氧基 -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3-f]喹啉(251 mg, 1 mmol )溶于 二氯甲垸中, 滴入 1摩尔每升的三溴化硼的二氯甲垸溶液 (3 mL, 3 mmol) , 搅 拌至反应完毕。 浓缩得浅黄色固体产品 236mg, 产率 99%。 MS: 238[M+H]+。
步骤 4b) 10-氯 -5-(3-吗 垸并 [2,3-f]-喹啉的制备
将 5-羟基 -10-氯 -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3-f]喹啉(236 mg, 1 mmol )溶于 N, N-二甲基甲酰胺, 加入 4-(3-氯丙基)吗啉(163 mg, 1 mmol)和碳酸钾(414 mg, 3 mmol ) , 加热搅拌至反应完毕。 加入水和乙酸乙酯萃取, 有机相浓缩后柱层析 得类白色固体 291mg, 产率 80%。 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) S 8.50 (d, J = 4.8 Hz, IH), 7.37 (d, J = 4.8 Hz, IH), 7.10 (s, IH), 4.47 - 4.30 (m, 4H), 4.17 (t, J = 6.4 Hz, 2H), 3.59 (t, J = 4.6 Hz, 4H), 2.45 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 2H), 2.39 (d, J = 4.5 Hz, 4H), 1.97-1.95 (m, 2H). MS: 365[M+H]+。
步骤 5) 5-(3-吗啉丙氧基) -10-(4-硝基苯氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3-f] 喹啉的制备
68
替换页(细则第 26条)
-ζ.ε '(HI 'zHs s = r 'Ρ) it79 '(He '^) εοζ,- ir乙 ΧΗΣ; '^) m '(HZ 'ZH I S
: (耷 r£)-s))-Hg畧^ 翕 ^ (^^99 ^»%
^P$^«i--i'i-¾iMi£(¾*(¾¾(¾-oi-tiiiii
Li-£¾^¾ifd^[t7'i]-¾^- ¾-(¾¾ ii¾D- )-s))-t7)-N-(g¾W-t7)-N 凝^
°+[H+W]8 t SW(H∑; 'ω) 161 - 0 Z '(Η9 '^) 9ί1 - ΥΖ
'(Ht7 ' ) 9S'e - Z9 £ UZ ' ) ll+t7 — OZ '(Ht 's) gs '(HZ; 'S) OfS '(HI 'ZH £'S = Γ 'P) 6Z 9 XUZ 'ZH = f 'P) S9.9 XllZ Γ8 = Γ 'P) t/8+9 '(HI 's) 007. '(HI £'S
= r 'p) ee s § (9P-oswa 'z丽 oot^)霸 N H〖 °l^¾#iid[i-£'d:^^ ti二 Ι 'Ϊ]- : T -ε'^¾¾¾¾¾-^)-οι-¾¾ώ-$^##ΰΐΰϋ-ε¾^^1¾^[^ι]-¾^-ε'^¾¾¾ 聲 ¾ ) -οι- (耷 ¾M
(¾¾(¾-oi-tdiii-[i- ¾^¾ifd^[t7't]-¾--£'z-(¾¾Mtii¾a- )-g)H (9凝^
££Z9L0/810Z 13/I3d C6ZCSl/8T0Z OAV
4.26 (m, 4H), 4.26 - 4.10 (m, 2H), 3.68 - 3.54 (m, 4H), 2.44 - 2.39 (m, 4H), 2.02 - 1.92 (m, 2H), 1.52 - 1.41 (m, 6H); 13C NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 168.6, 168.5, 161.3, 151.7, 151.1, 149.6, 146.7, 138.2, 136.0, 135.6, 132.28, 122.9, 122.8, 122.6, 120.7, 115.6, 115.3, 108.7, 105.7, 102.2, 67.1, 66.7, 64.4, 63.9, 55.3, 53.8, 31.9, 26.2, 15.8; MS: 643[M+H]+。
实施例 70 N-(3-氟 -4-((5-(3-吗啉丙氧基) -2,3-二氢 -【1,4】二噁烷并 [2,3-f]喹啉 -10-基)氧基)雜) -N-(4-氟雜)环丙烷 -1,1-二甲酰胺的制备
步骤 1至步骤 4b与实施例 69的制备的步骤 1至步骤 4b相同。
步骤 5) 10-(2-氟 -4-硝基苯氧基) -5-(3-吗啉丙氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3-f]喹啉的制备
参考实施例 69步骤 5 ) 操作, 以相同摩尔当量的 2-氟 -4硝基苯酚替代对硝 基苯酚即可。 MS: 486[M+H]+。
步骤 6) 3-氟 -4-((5-(3-吗啉丙氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3-f]喹啉 -10-基) 氧基)苯胺的制备
参考实施例 66步骤 6)操作,以相同摩尔当量的 10-(2-氟 -4-硝基苯氧基) -5-(3- 吗啉丙氧基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3-f]喹啉替代 5-甲氧基 -10-(4-硝基苯氧 基) -2,3-二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3-f]喹啉即可。 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.37 (d, J = 5.3 Hz, 1H), 7.08 - 6.88 (m, 2H), 6.60 - 6.49 (m, 1H), 6.48 - 6.40 (m, 1H),
70
替换页(细则第 26条)
\L
"urn ^ ^ w i t ^ 69 m^ ^ w〖凝^
°+[H+W]l99 SYi -LSI 'Z 9Z 'Z£ '/.6 9 9 ' '99 '17.9 ¾XOt
'67.01 V'Stt '9 S11 'βΖΖΙ iZl 'LLZX '8·6ΖΙ '8 i ' 8£Ι '99t l '96t7t '81S1 '6091 V89I 'Δ'89ΐ S (9P-OS匪 'z丽 lOl) W讓 Di\ m ί'Ζ = ί 'Ρ) Ζ 1 '(Η∑; 'UI) 6L I - SO Z m 'ZH 9 = Γ 'Ρ) 6ί Ζ XUZ VL = Γ '1) 9VZ \ 'ZH 9
= r ¾ 6s ΧΗΣ; V9 = r ¾ LY Xm ' ) ^Z ^-LZ ^ '(HI ' ) m - iV9 '(HI 'S)
907. '(HZ; 'UI) \YL- YL '(HI ¾i 0.6 = f Ό L '(HI '^) 6ZL - Z9L XliZ ' )
- L9 L '(HI 'ω) 6L.L - 6 L '(Ηΐ ¾ Ζ'ξ = Γ 'Ρ) '(HI 's) ΟΟΌΙ '(Ηΐ 's) ^e ot 2
(9P"OS ia 'ZHW OOt ΗΧ ° dg瑚 ¾(¾¾(¾-0I- liii[j-£ :^¾i ti:[t7'I]-焉
: m¾¾i-s))-t7 ^ ¾¾(¾¾(¾-oi-tditi-[i-£¾^^fd-[^£i]-¾^- '2-(¾ ¾ d¾- )-s)H-w-e 翁 凝^ 99 mm^
-ot-td i[i-e¾^¾ifd~[t7£i]-M^-£¾-(g¾ ii¾a- )-g))-t7-¾-£)-N 凝^
■(UZ L6 \ - S61 '(Ht7 's) 6Z Z XliZ O L = f 'P) 9VZ Xm 9 = f ¾ 6S '(HZ; 'ZH V9 = Γ ¾ 9t '(Ht7 'ui) 6C - Z.e '(iK 's) M^S '(HI 'ZH Ζ'ξ = f 'Ρ) ZZ 9
°+[H+W]9St : SW(H; 'UI) L6 1 - ς&Ι '(Ht7 'ZH 6 = f 'P) 6£ Z UZ 'ZH Z L = f Ί) LVZ m 'ZH 9 = f Ί) 6ζ ί XUZ
'ZH s'9 = r ¾ srt '(Ht7 's) s '(H∑; 'S) erg '(HI ζ'ς = r 'p) 9Z 9 '(HI OZ/9
- 8乙9 '(HI 'ui) 089 - 689 '(HI '^) Z69 - 869 '(HI 's) ZO L '(HI Ζ'ξ = f 'P)
/ 8 § (9P-oswa 'ZHW oot/) ¾MN H °ΐίί¾#ι1ΰ[ί-ε :^¾@ιι二 ΐ]-焉二 -ε'ζ-(¾ -ε - (耷 ¾¾耷¾卞篤 -ε)-οι 畧^ 翁 (9lf^?99^5g^%
(¾-oi-td [j-e¾^¾ifd^[^'i]-M^- '3-(¾¾M ii¾-e)-s)H-¾-3 (9
SW(H∑; zs i - ςοτ H9 '^) 9ζτ - LVZ Xm '^) ε - 59 ε '(ΗΣ; '^) 86.ε - ζι ^ X 9t - ee '(HI '^) ZL9 - L6.9 ΧΉΖ SOT. - ZZL '(HI '^) ςζ
- IS L '(HI '冚) 608― 6 8 '(HI 's) 69'82 (9P"OSWa ¾iW OOt) ¾RM HT ° M^ ^
££Z9L0/810Z 13/I3d C6ZCSl/8T0Z OAV
参考实施例 66步骤 7)操作,以相同摩尔当量的 2-氟 -4-((5-(3-吗啉丙氧基) -2,3- 二氢 -[1,4]二噁垸并 [2,3-f]喹啉 -10-基)氧基)苯胺替代 (5-甲氧基 -2,3-二氢 -[1,4] 二噁烷并 [2,3-f]喹啉 -10-基)氧基)苯胺即可。 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.48 (s, 1H), 9.97 (s, 1H), 8.50 (d, J = 5.1 Hz, 1H), 7.86 (s, 1H), 7.71 - 7.48 (m, 2H), 7.16 (dd, J = 9.9, 7.9 Hz, 2H), 7.10 (d, J = 10.5 Hz, 2H), 6.95 - 6.80 (m, 1H), 6.63 (d, J = 5.1 Hz, 1H), 4.34 - 4.28 (m, 2H), 4.27-4.24 (m, 2H), 4.17 (t, J = 6.4 Hz, 2H), 3.59 (t, J = 4.6 Hz, 4H), 2.46 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H), 2.38 (d, J = 4.8 Hz, 4H), 1.95 (q, J = 6.8 Hz, 2H), 1.56-1.58 (m, 4H).MS: 661[M+H]+。
实验例 1.
小分子化合物抑制 VEGFR-2激酶活性的测试, 测试方法如下:
1. 化合物稀释:从最高浓度 10000 nM 开始进行 4倍梯度稀释后共 12个浓 度 (本实验使用的药物的最大终浓度为 10000 nM,最低终浓度为 0.002384 nM),
2. 用排枪取 2.5μί经梯度稀释的化合物, 加入 384孔板中,
3. 加酶:用排枪取 5^ 2X VEGFR-2 激酶加入到 384孔板相应的反应孔中, 混匀后室温预反应 30min,
4. 排枪取 2.5μί 4Χ底物 /ATP Mix加入到 384孔板相应的反应孔中,
5. 阴性对照: 在 384孔板孔加入 2.5 μ!7孔 4X底物 /ATP Mix 禾 [Ί 7.5 L IX Kinase Assay Buffer
阳性对照: 在 384孔板中加入 2.5 μΙ 孔 4Χ底物 /ATP Mix, 2.5 μ!7孔 含 4%DMSO的 IX Kinase Assay Buffer, 5 μ!7孔 2Χ VEGFR-2 solution 反应体 系中 DMSO的终浓度为 4%,
6. 离心混匀, 避光室温反应 60 min,
7. 终止酶促反应: 用排枪取 5μί 4Χ Stop solution加入到 384孔板中孔中, 离心混匀, 室温反应 5 min,
8. 显色反应: 用排枪取 5μί 4Χ Detection Mix加入到 384孔板中孔中进行 显色, 离心混匀, 室温反应 60 min,
9. 将 384孔板放入 Envision读板仪读板, 调取相应的程序检测信号。
10.原始数据的分析和处理:
将药物浓度和相应抑制率输入 GraphPad Prism5计算处理, 化合物的抑制率 的计算方法如下: 抑制率(%)=[1- (实验孔读值- 阴性对照孔读值) / (阳性对照孔读 值- 阴性对照孔读值)] χ100%。 用 GraphPad Prism5 软件处理得出相应的 IC50值 (酶最高抑制率 50%时的化合物浓度)。 表 (一) 列出了本发明中部分化合物对 酪氨酸激酶抑制活性的测定结果, 其中 A表示 IC5o小于或等于 50 nM, B表示 IC5。大于 50 nM但小于或等于 500 nM, C表示 IC5Q大于 500 nM但小于或等于 5000 nM, D表示 IC5。大于 5000 nM。
73
替换页(细则第 26条)
表 (一;)、 本发明部分化合物对 VEGFR-2酪氨酸激酶抑制活性测定结:
实施例 VEGFR-2 实施例 VEGFR-2
编号 IC50 (nM) 编号 IC50 (nM)
1 D 37 A
2 B 38 D
3 A 39 D
4 A 40 A
5 B 41 D
6 B 42 B
7 C 43 B
8 B 44 B
9 A 45 C
10 A 46 B
1 1 B 47 C
12 B 48 A
13 A 49 B
14 B 50 C
15 A 51 A
16 B 52 A
17 A 53 A
18 A 54 B
19 C 55 A
20 A 56 A
21 A 57 A
22 A 58 A
23 A 59 A
24 A 60 A
25 B 61 A
26 A 62 B
27 A 63 A
28 B 64 A
29 A 65 A
30 A 66 A
31 B 67 A
32 A 68 A
33 A 69 A
34 A 70 A
35 A 71 A
36 A 实验例 2.
小分子化合物抑制 c-Met激酶活性的测试, 测试方法如下:
1. 化合物稀释:从最高浓度 10000 nM开始进行 4倍梯度稀释后共 12个浓
74
替换页(细则第 26条)
度 (本实验使用的药物的最大终浓度为 10000 nM,最低终浓度为 0.002384 nM),
2. 用排枪取 2.5μί经梯度稀释的化合物, 加入 384孔板中,
3. 加酶: 用排枪取 5 L 2X c-Met激酶加入到 384孔板相应的反应孔中, 混 匀后室温预反应 30min,
4. 排枪取 2.5 μί 4Χ底物 /ATP Mix加入到 384孔板相应的反应孔中,
5. 阴性对照: 在 384孔板孔加入 2.5 μ!7孔 4X底物 /ATP Mix 禾 [Ί 7.5 L IX Kinase Assay Buffer
阳性对照: 在 384孔板中加入 2.5 μ! 孔 4Χ底物 /ATP Mix, 2.5 μ!7孔 含 4%DMSO的 IX Kinase Assay Buffer, 5 μ! 孔 2Χ c-Met solution。 反应体系中 DMSO的终浓度为 4%,
6. 离心混匀, 避光室温反应 60 min,
7. 终止酶促反应: 用排枪取 5μί 4Χ Stop solution加入到 384孔板中孔中, 离心混匀, 室温反应 5 min,
8. 显色反应: 用排枪取 5 L 4X Detection Mix加入到 384孔板中孔中进行 显色, 离心混匀, 室温反应 60 min,
9. 将 384孔板放入 Envision读板仪读板, 调取相应的程序检测信号。
10.原始数据的分析和处理:
将药物浓度和相应抑制率输入 GraphPad Prism5计算处理, 化合物的抑制率 的计算方法如下: 抑制率(%)=[1 - (实验孔读值- 阴性对照孔读值) / (阳性对照孔读 值- 阴性对照孔读值)] χ100%。 用 GraphPad Prism5 软件处理得出相应的 IC5。值 (酶最高抑制率 50%时的化合物浓度)。 表 (二) 列出了本专利中部分化合物对 酪氨酸激酶抑制活性的测定结果, 其中 A表示 IC5。小于或等于 50 nM, B表示 IC50大于 50 nM但小于或等于 500 nM, C表示 IC5。大于 500 nM但小于或等于 5000 nM, D表示 IC5。大于 5000 nM。
表(二)、 本发明部分化合物对 c-Met酪氨酸激酶抑制活性测定结果
实施例 VEGFR-2 实施例 VEGFR-2
编号 IC50 (nM) 编号 IC50 (nM)
1 D 33 A
2 C 34 A
3 A 35 A
4 A 36 A
5 C 37 A
6 C 40 A
8 B 46 B
9 A 48 A
10 A 51 A
1 1 B 52 A
75
替换页(细则第 26条)
12 C 53 A
13 A 54 C
14 A 55 A
15 B 56 A
16 A 57 A
17 A 58 A
18 A 59 A
20 A 60 A
21 A 61 A
22 A 62 A
23 A 63 A
24 A 64 A
26 A 65 A
27 A 66 A
29 A 67 A
30 A 68 A
31 A 69 A
32 A 实验例 3.
小分子化合物细胞存活的测试, 具体方法如下:
1. 在 T75细胞培养瓶中加入 600 μί胰酶, 于 37°C培养箱中消化约 lmin, 随后加入 5mL DMEM 的完全培养液, 吹打均匀, 转移至 15 mL离心管中, 1000 rpm,4 min离心;
2. 弃去上清液, 加入 5mL DMEM完全培养液, 吹打均匀, 取 ΙΟ μί细胞 悬浮液和 10 0.4%胎盼蓝混匀, 在细胞计数仪下进行计数;
3. 分别将 6种不同细胞系 (MHCC97H、 HuH7、 HepG2、 A549、 8505C) 的细胞以 6000 Ce\υS0μL完全培养液 /孔的细胞密度接种于 96孔板中培养过夜, 96孔板外周 36孔不加细胞仅加无菌水, 仅里面 60孔用于细胞实验和对照;
4. 化合物稀释:化合物以 10mM为起始浓度进行 3倍稀释,共 10个浓度;
5. 在每孔中加入 20 μL不同种类不同浓度的化合物,其余孔加入 20μί完全 培养液摇匀, 每孔中 DMSO的中浓度为 0.25%;
6. 培养 72 h后每孔加入 10 CCK-8试剂, 37°C培养 1-2 h; 于 450 nm处 读其 OD值;
7. 细胞存活率 (%) -[(As-Ab)/(Ac-Ab)] * 100%
As: 实验孔 (含有细胞的培养基、 CCK-8、 compound)
Ac: 对照孔 (含有细胞的培养基、 CCK-8)
Ab: 空白孔 (不含细胞和 compound的培养基、 CCK-8)
76
替换页(细则第 26条)
8. 将数值导入 Graphpad Prism5软件进行 IC5。(最高存活率 50%时的化合物 浓度) 计算。
表(三)列出了本发明中代表性的化合物对各种癌细胞的活性测定结果, 其 中 MHCC97H、 HuH7、 HepG2为肝癌细胞系, A549为肺癌细胞系, 8505C为甲 状腺癌细胞系。 NT表示没有测试相对应的细胞活性。 表 (三) 、 本发明代表性的化合物对细胞活性的测定结果
蛋白印迹方法证实抑制肝癌细胞 c-Met 的表达, 具体方法如下:
为了证实肝癌细胞 c-Met的表达以及化合物对其的抑制作用,开展了以下实 验, 具体实验步骤如下-
1. 收集对数期的细胞, 以 2x l06/2 mL/孔的密度将细胞种于六孔板中,在 37°C 培养过夜。
2. 依次向上述 6孔板的各孔加入不同浓度的药物, 混匀后置于 37 °C培养 箱培养 1 h。 然后取出 6孔板, 用 PBS清洗后加入 250 的完全裂解液, 待细 胞完全裂解后离心, 收上清。
3. 用 BCA法测定收集的上清中的蛋白浓度。
4. 按比例向提取的蛋白样品中加入蛋白上样缓冲液, 100 °C金属浴加热 5 min, 使蛋白充分变性, 置于冰上冷却。
5. 电泳: 先低压 100V电泳 30 min, 然后将电压增只 120 V直到电泳完成。
6. 转膜: 采用湿转的方法进行转膜, 恒压 100V, 转膜 90min。
7. 转膜完成后用 5%的 BSA进行封闭, 然后依次结合一抗、 二抗, 最后通 过化学发光法用 ChemiDocTM MP Imaging System进行检测。
选用高度转移的 MHCC97H肝癌细胞系作为实验对象, 结果显示该细胞本 身高度表达 pERK和 c-Met, 经阳性对照药 cabozantinib 处理后, pERK和 c-Met 替换页(细 第 26条)
表达明显减低并呈现剂量依赖性反应。 本专利的小分子化合物实施例 21 和 24 表现出与 cabozantinib 相同的效果, 如图 1及图 2所示。实施例 21和 24的实验 结果仅为多个实验中的代表。
本发明所提供的生物学数据表明, 本发明的化合物有利于治疗或预防由于 VEGFR-2和 c-Met激酶异常而引起的疾病。 本发明的一些化合物对癌细胞具有 强效的体外抑制活性, 其中包括肝癌细胞 MHCC97、 HuH7、 HepG2, 肺癌细胞 A549, 以及甲状腺癌细胞 8505C。 因此, 本发明的化合物有利于治疗癌症, 包 括原发性和转移性癌症, 包括实体瘤。 此类癌症包括但不限于: 非小细胞肺癌、 小细胞肺癌、乳腺癌、胰腺癌、神经胶质瘤、胶质母细胞瘤、卵巢癌、子宫颈癌、 结肠直肠癌、黑色素瘤、子宫内膜癌、前列腺癌、膀胱癌、 白血病、 胃癌、肝癌、 胃肠间质瘤、 甲状腺癌、 慢性粒细胞白血病、 急性髓细胞性白血病、 非霍奇金淋 巴瘤、 鼻咽癌、 食道癌、 脑瘤、 B 细胞和 T细胞淋巴瘤、 淋巴瘤、 多发性骨髓 瘤、胆道癌肉瘤、胆管癌。本发明的化合物也包括治疗耐一种或多种其它治疗方 法的癌症。本发明的化合物还可用于与 VEGFR-2激酶和 /或 c-Met激酶有关的除 了癌症以外的其他疾病, 包括但不限于眼底疾病, 银屑病、 风湿性关节炎、 动脉 粥样化、 肺纤维化、 肝纤维化。 本发明的化合物可以作为单一疗法或联合疗法, 可以与多个本发明的化合物联合用药或与本发明以外的其他药物联合用药。
本发明的化合物也可作为标准品和试剂用于表征各种激酶,特别是但不限于 蛋白酪氨酸激酶,以及为研究这种激酶在生物学和病理学现象中的作用非常有用: 用于研究由这类激酶介导的胞内信号转导途径,对于新的激酶抑制剂的对比评价; 以及用于研究不同癌症的细胞系和动物模型中。
以上所述是本发明的优选实施方式,应当指出,对于本技术领域的普通技术 人员来说,在不脱离本发明所述原则的前提下,本发明的实施方式还可以作出若 干改进和修饰, 这些改进和修饰也应视为本发明的保护范围。
78
替换页(细则第 26条)
Claims
1、 式 (I) 表示的化合物、 其药学上可接受的盐、 异构体、 水合物、 溶剂化物、 或前药,
式 (I)
式 (I) 中,
Q为 N或者 CH;
G为 0或者 NH;
Z为 N或者 CH;
其中 X为 H或 CrC3的垸基; Y为 H或 CrC3的垸基; n=0-3,且当 n=0时, L表示为环丙垸的连接基团;
R1为 H, C C9垸基, C3-C7的环垸基, 4-7元杂环基, C3-C7的环垸基取代 的 CrC6垸基, 4-7元杂环基取代的 CrC6垸基, 取代的 d-C9垸基, 所述取代的 d-C9垸基的取代基为羟基、 d-C6的垸氧基、 C C6的垸硫基或 -NR6R7中的一种 或一种以上,
R6和 R7分别独立地为 H、 d-C6垸基、 羟基取代的 d-C6垸基、 d-C3垸氧 基取代的 CrC6垸基;
上述 4-7元杂环基为含有 1-2个选自 N、 0、 S中的原子的 4-7元杂环基, 4-7 元杂环基不被取代或被 d-C3垸基、 3酰基取代或被一至二个氧原子氧化。
1 2为11、 -C3的垸基或卤素;
1 3为11、 d-C3的垸基或卤素;
1 4为11、 -C3的垸基或卤素;
R5为 H, -C9垸基, C3-C7的环垸基, C3-C7环垸基取代的 -C6垸基, 芳
基, 芳基取代的 crc6垸基, 杂芳基或杂芳基取代的 d-C6垸基; 所述芳基、 杂芳基为不被取代或被 d-C3的垸基、 d-C3的垸氧基、 C C3的 垸硫基、 单或双 d-C3的氨基、 卤素、 三氟甲基、 芳氧基和甲砜基中的一种或一 种以上取代;
上述杂芳基为含有 5至 10个环原子的单环或双环基团; 杂芳基含有 1-3个 选自 N、 0、 S中的杂原子。
2、 根据权利要求 1所述化合物、 其药学上可接受的盐、 异构体、 水合物、 溶剂化物、 或前药,
R1为 H, C C6垸基, C3-C6的环垸基, 5-6元杂环基, C3-C6的环垸基取代 的 CrC3垸基, 5-6元杂环基取代的 CrC3垸基, 取代的 d-C6垸基, 所述取代的 d-C6垸基的取代基为羟基、 d-C3的垸氧基、 C C3的垸硫基或 -NR6R7,
R6和 R7分别独立地为 H、 CrC3垸基、 羟基取代的 CrC3垸基、 -C3垸氧 基取代的 d-C3垸基。
上述 5-6元杂环基为含有 1-2个选自 N、 0、 S中的原子的 5-6元杂环基、 不 被取代或被 d-C3垸基、 C C3酰基取代或被一至二个氧原子氧化。
3、根据权利要求 1所述的化合物、其药学上可接受的盐、异构体、水合物、 溶剂化物、 或前药,
R1选自甲基、 乙基、 丙基、 异丙基、 甲氧基乙基、 甲氧基丙基、 甲氧基丁 基、 甲氧基戊基、 甲氧基己基、 四氢呋喃 -3-基、 四氢 -2H-吡喃 -4-基、 四氢吡咯 -1- 乙基、 四氢吡咯 -1-丙基、 吗啉 -4-乙基、 吗啉 -4-丙基、 甲基哌嗪 -4-乙基、 甲基哌 嗪 -4-丙基、 N-甲酰基哌嗪 -4-乙基、 N-甲酰基哌嗪 -4-丙基、 N-乙酰基哌嗪 -4-乙基、 N-乙酰基哌嗪 -4-丙基、 (1,1-二氧硫代吗啉基) -4-乙基、 (1,1-二氧硫代吗啉基) -4- 丙基、甲硫基乙基、甲硫基丙基、二甲氨基乙基、二甲氨基丙基、二甲氨基丁基、 二甲氨基戊基、 二甲氨基己基、 二乙氨基乙基、 二乙氨基丙基、 羟基乙基、 羟基 丙基、 羟乙基氨基乙基、 羟丙基氨基乙基、 羟乙基氨基丙基、 甲氧基乙基氨基乙 基、 甲氧基丙基氨基乙基、 甲氧基乙基氨基丙基、 氨基乙基、 氨基丙基、 氨基丁 基、 N-甲基 -N-羟乙基氨基乙基、 N-甲基 -N-羟丙基氨基乙基、 N-甲基 -N-羟乙基 氨基丙基、 N-甲基 -N-甲氧基乙基氨基乙基、 N-甲基 -N-甲氧基丙基氨基乙基、 N-甲基 -N-甲氧基乙基氨基丙基、 2-甲基 -2-羟基丙基、 3-甲基 -3-羟基丁基、 (3S)-3- 氨基丁基、(3R)-3-氨基丁基、(3S)-3-羟基丁基或 (3R)-3-羟基丁基中的一种或一种 以上。
4、 根据权利要求 1所述化合物、 其药学上可接受的盐、 异构体、 水合物、 溶剂化物、 或前药, 其中 R2、 R3、 R4所述的卤素为 0或?。
5、 根据权利要求 1所述的所述化合物、 其药学上可接受的盐、 异构体、 水 合物、 溶剂化物、 或前药, R5为 H, C C6垸基, C3-C6环垸基, C3-C6环垸基取 代的 d-C3垸基, 芳基, 芳基取代的 -C3垸基, 杂芳基或杂芳基取代的 -C3 垸基, 所述的芳基、 杂芳基的取代基为 d-C3的垸基、 d-C3的垸氧基、 C C3的 垸硫基、 单或双 d-C3取代的氨基、 卤素、 三氟甲基、 芳氧基和甲砜基中的一种 或一种以上;
所述杂芳基为含有 5至 10个环原子的单环或双环基团; 杂芳基含有 1-2个 选自 N、 0、 S中的杂原子。
6、 根据权利要求 5所述化合物、 其药学上可接受的盐、 异构体、 水合物、 溶剂化物、 或前药, R5选自 H、 甲基、 乙基、 丙基、 异丙基、 异戊基、 环丙基、 环丁基、 环戊基、 环己基、 苯基、 4-氟苯基、 3-氟苯基、 2-氟苯基、 4-氯苯基、 3-氯苯基、 2-氯苯基、 2,4-二氟苯基、 2,5-二氟苯基、 3,4-二氟苯基、 2,4-二氯苯基、 2,5-二氯苯基、 3,4-二氯苯基、 2-氟 -4- (三氟甲基)苯基、 2-氟 -5- (三氟甲基)苯基、
3-氟 -4- (三氟甲基)苯基、 3-氟 -5- (三氟甲基)苯基、 3-三氟甲基 -4 氟苯基、 2-氟 -4- 氯苯基、 2-氟 -5-氯苯基、 3-氟 -4-氯苯基、 3-氟 -5-氯苯基、 3-氯 -4-氟苯基、 2-氯 -4- (三 氟甲基)苯基、 2-氯 -5- (三氟甲基)苯基、 3-氯 -4- (三氟甲基)苯基、 3-氯 -5- (三氟甲基) 苯基、 3-三氟甲基 -4-氯苯基、 2-氯 -4-氟苯基、 2-氯 -5-氟苯基、 3-氯 -4-氟苯基、 苄 基、 苯乙基、 4-氟苄基、 萘 -1-基、 3-甲基-异噁唑 -5-基、 4-苯氧基苯基、 3- (甲砜 基)苯基、 4- (甲砜基)苯基、 吡啶 -2-基、 吡啶 -3-基、 吡啶 -4-基、 3-甲氧基苄基或
4-甲氧基苄基。
7、 根据权利要求 1所述的式(I)化合物药学上可接受的盐, 其中所述的盐 是酸性 /阴离子盐或碱性 /阳离子盐;药学上可接受的酸性 /阴离子盐通常采取的形 式是让其中的碱性氮被无机或有机酸质子化, 代表性的有机或无机酸包括盐酸、 氢溴酸、 氢碘酸、 高氯酸、 硫酸、 硝酸、 磷酸、 甲酸、 乙酸、 丙酸、 羟基乙酸、 乳酸、琥珀酸、马来酸、酒石酸、苹果酸、柠檬酸、富马酸、葡萄糖酸安息香酸、 扁桃酸、 甲磺酸、羟乙基磺酸、苯磺酸、草酸、棕榈酸、 2-萘磺酸、对甲苯磺酸、 环己胺基磺酸、 水杨酸、 己糖酸、 三氟乙酸。 药学上可接受的碱性 /阳离子盐类 包括 (当然不仅限于此)铝、钙、氯普鲁卡因、胆碱、二乙醇胺、 乙二胺、锂、镁、
钾、 钠和锌。
8、 一种制备权利要求 1-6所述化合物、 其药学上可接受的盐、 异构体、 水 合物、 溶剂化物、 或前药的方法, 其特征在于, 包括以下步骤, 由式 (II) 化合 物与式(III化合物)反应制备得到式(I)化合物, Q为 N, G、 Z、 L、 R1, R2、 3、 R4和 R5如权利要求 1-6所定义,
9、 一种制备权利要求 1-6所述化合物、 其药学上可接受的盐、 异构体、 水 合物、 溶剂化物、 或前药的方法, 其特征在于, 包括以下步骤, 由式 (Ι ) 所 示化合物与式(III' )所示化合物反应制备得到式(I)化合物, 其中 Q、 G、 Z、
2、 R3、 R4和 R5如权利要求 1-6所定义,
10、 一种式 (II) 所示的化合物, 其中, G、 Z、 L、 R2、 R3、 R4和 R5如权 利要求 1-6所定义,
(Π)
12、 一种药用组合物, 其由权利要求 1-6所述的式 (I)化合物或其药学上可接 受的盐或其水合物或其前药与药学上可接受的载体或赋形剂组成。
13、 一种药用组合物, 其中包含权利要求 1-6所述的式 (I) 的化合物、 其 药学上可接受的盐、 水合物、 溶剂化物、 或前药作为活性成分, 一个或多个其它 的治疗剂, 以及一种或多种药学上可接受的载体或赋形剂。
14、 根据权利要求 1-6中任一项所述的式 (I) 的化合物、 其药学上可接受 的盐、水合物、溶剂化物、或前药在治疗与络氨酸激酶, 例如 VEGFR-2和 c-Met 相关疾病的药物中的应用, 其中所述疾病包括但不限于: 眼底疾病、 银屑病、 风 湿性关节炎、 动脉粥样化、 肺纤维化、 肝纤维化和 /或肿瘤。
15、 根据权利要求 14所述的应用, 其中所述肿瘤包括但不限于: 非小细胞 肺癌、 小细胞肺癌、 乳腺癌、 胰腺癌、 神经胶质瘤、 胶质母细胞瘤、 卵巢癌、 子 宫颈癌、 结肠直肠癌、 黑色素瘤、 子宫内膜癌、 前列腺癌、 膀胱癌、 白血病、 胃 癌、 肝癌、 胃肠间质瘤、 甲状腺癌、 慢性粒细胞白血病、 急性髓细胞性白血病、 非霍奇金淋巴瘤、 鼻咽癌、 食道癌、 脑瘤、 B 细胞和 T 细胞淋巴瘤、 淋巴瘤、 多发性骨髓瘤、 胆道癌肉瘤、 胆管癌中的任一种。
Priority Applications (13)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201810983341.3A CN110156803A (zh) | 2017-02-27 | 2018-08-27 | 二噁烷并喹啉类化合物及其制备方法与应用 |
| SG11202007554TA SG11202007554TA (en) | 2017-02-27 | 2019-01-25 | Dioxazoline compound, preparation method therefor, and uses thereof |
| PCT/CN2019/073260 WO2019154133A1 (zh) | 2018-02-11 | 2019-01-25 | 二噁烷并喹啉类化合物及其制备方法与应用 |
| ES19751025T ES2945573T3 (es) | 2017-02-27 | 2019-01-25 | Compuesto de dioxazolina, método de preparación y usos del mismo |
| US16/968,797 US11407760B2 (en) | 2018-02-11 | 2019-01-25 | Dioxinoquinoline compounds, preparation method and uses thereof |
| JP2020542958A JP7022454B2 (ja) | 2018-02-11 | 2019-01-25 | ジオキシノキノリン系化合物、その調製方法および使用 |
| KR1020207025607A KR102433023B1 (ko) | 2018-02-11 | 2019-01-25 | 디옥시노퀴놀린 화합물, 이의 제조방법 및 용도 |
| EP19751025.8A EP3750893B1 (en) | 2018-02-11 | 2019-01-25 | Dioxazoline compound, preparation method therefor, and uses thereof |
| DK19751025.8T DK3750893T3 (da) | 2017-02-27 | 2019-01-25 | Dioxazolinforbindelse, fremgangsmåde til fremstilling deraf og anvendelser deraf |
| PL19751025.8T PL3750893T3 (pl) | 2018-02-11 | 2019-01-25 | Związek dioksazoliny, sposób jego wytwarzania oraz jego zastosowania |
| CN201980012397.7A CN111788207B (zh) | 2017-02-27 | 2019-01-25 | 二噁烷并喹啉类化合物及其制备方法与应用 |
| AU2019218187A AU2019218187B2 (en) | 2017-02-27 | 2019-01-25 | Dioxinoquinoline compounds, preparation method and uses thereof |
| CA3090876A CA3090876C (en) | 2018-02-11 | 2019-01-25 | Dioxinoquinoline compounds, preparation method and uses thereof |
Applications Claiming Priority (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201710107756.X | 2017-02-27 | ||
| CN201710107756 | 2017-02-27 | ||
| CN201710161873.4 | 2017-03-17 | ||
| CN201710161873.4A CN108503650B (zh) | 2017-02-27 | 2017-03-17 | 二噁烷并喹唑啉类化合物或其药用盐或其水合物及其作为酪氨酸激酶抑制剂的应用 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2018153293A1 true WO2018153293A1 (zh) | 2018-08-30 |
Family
ID=63252387
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/CN2018/076233 WO2018153293A1 (zh) | 2017-02-27 | 2018-02-11 | 二噁烷并喹唑啉与二噁烷并喹啉类化合物及其制备方法与应用 |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| WO (1) | WO2018153293A1 (zh) |
Cited By (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2019154133A1 (zh) * | 2018-02-11 | 2019-08-15 | 北京赛特明强医药科技有限公司 | 二噁烷并喹啉类化合物及其制备方法与应用 |
| WO2020103769A1 (zh) * | 2018-11-19 | 2020-05-28 | 北京赛特明强医药科技有限公司 | 芳环连二噁烷并喹唑啉或喹啉类化合物、组合物及其应用 |
| CN111217821A (zh) * | 2020-03-13 | 2020-06-02 | 北京工业大学 | 系列二噁烷并喹唑啉衍生物的制备方法 |
| WO2020188015A1 (en) | 2019-03-21 | 2020-09-24 | Onxeo | A dbait molecule in combination with kinase inhibitor for the treatment of cancer |
| CN111788207A (zh) * | 2017-02-27 | 2020-10-16 | 北京赛特明强医药科技有限公司 | 二噁烷并喹啉类化合物及其制备方法与应用 |
| WO2021089791A1 (en) | 2019-11-08 | 2021-05-14 | INSERM (Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale) | Methods for the treatment of cancers that have acquired resistance to kinase inhibitors |
| WO2021148581A1 (en) | 2020-01-22 | 2021-07-29 | Onxeo | Novel dbait molecule and its use |
| US11731946B2 (en) | 2017-10-19 | 2023-08-22 | The General Hospital Corporation | Broad spectrum antivirulence, anti-persistence compounds |
| EP4103188A4 (en) * | 2020-02-10 | 2024-04-10 | StemSynergy Therapeutics, Inc. | MYC INHIBITORS AND THEIR USES |
| CN111936487B (zh) * | 2018-01-26 | 2024-07-09 | 埃克塞里艾克西斯公司 | 用于治疗激酶依赖性病症的化合物 |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104530063A (zh) * | 2015-01-13 | 2015-04-22 | 北京达立泰制药科技有限公司 | 喹唑啉并杂环类化合物及其制备方法和作为用于治疗癌症的表皮生长因子受体抑制剂的应用 |
| CN105837586A (zh) * | 2015-12-14 | 2016-08-10 | 北京赛特明强医药科技有限公司 | 二噁烷并喹唑啉胺类化合物及其制备方法和作为表皮生长因子受体抑制剂的应用 |
-
2018
- 2018-02-11 WO PCT/CN2018/076233 patent/WO2018153293A1/zh active Application Filing
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104530063A (zh) * | 2015-01-13 | 2015-04-22 | 北京达立泰制药科技有限公司 | 喹唑啉并杂环类化合物及其制备方法和作为用于治疗癌症的表皮生长因子受体抑制剂的应用 |
| CN105837586A (zh) * | 2015-12-14 | 2016-08-10 | 北京赛特明强医药科技有限公司 | 二噁烷并喹唑啉胺类化合物及其制备方法和作为表皮生长因子受体抑制剂的应用 |
Cited By (18)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN111788207B (zh) * | 2017-02-27 | 2021-03-23 | 北京赛特明强医药科技有限公司 | 二噁烷并喹啉类化合物及其制备方法与应用 |
| AU2019218187B2 (en) * | 2017-02-27 | 2021-10-14 | Beijing Scitech-Mq Pharmaceuticals Limited | Dioxinoquinoline compounds, preparation method and uses thereof |
| CN111788207A (zh) * | 2017-02-27 | 2020-10-16 | 北京赛特明强医药科技有限公司 | 二噁烷并喹啉类化合物及其制备方法与应用 |
| US11731946B2 (en) | 2017-10-19 | 2023-08-22 | The General Hospital Corporation | Broad spectrum antivirulence, anti-persistence compounds |
| CN111936487B (zh) * | 2018-01-26 | 2024-07-09 | 埃克塞里艾克西斯公司 | 用于治疗激酶依赖性病症的化合物 |
| US11407760B2 (en) | 2018-02-11 | 2022-08-09 | Beijing Scitech-Mq Pharmaceuticals Limited | Dioxinoquinoline compounds, preparation method and uses thereof |
| WO2019154133A1 (zh) * | 2018-02-11 | 2019-08-15 | 北京赛特明强医药科技有限公司 | 二噁烷并喹啉类化合物及其制备方法与应用 |
| TWI732344B (zh) * | 2018-11-19 | 2021-07-01 | 大陸商北京賽特明強醫藥科技有限公司 | 芳環連二噁烷並喹唑啉或喹啉類化合物、組合物及其應用 |
| JP2022509076A (ja) * | 2018-11-19 | 2022-01-20 | 北京賽特明強医薬科技有限公司 | 芳香環結合ジオキシノ-キナゾリンまたはジオキシノ-キノリン系化合物、組成物およびその使用 |
| AU2019383103B2 (en) * | 2018-11-19 | 2023-02-02 | Beijing Scitech-Mq Pharmaceuticals Limited | Aromatic ring-linked dioxane-quinazoline or -quinoline compounds, compositions and use thereof |
| JP7251841B2 (ja) | 2018-11-19 | 2023-04-04 | 北京賽特明強医薬科技有限公司 | 芳香環結合ジオキシノ-キナゾリンまたはジオキシノ-キノリン系化合物、組成物およびその使用 |
| WO2020103769A1 (zh) * | 2018-11-19 | 2020-05-28 | 北京赛特明强医药科技有限公司 | 芳环连二噁烷并喹唑啉或喹啉类化合物、组合物及其应用 |
| WO2020188015A1 (en) | 2019-03-21 | 2020-09-24 | Onxeo | A dbait molecule in combination with kinase inhibitor for the treatment of cancer |
| WO2021089791A1 (en) | 2019-11-08 | 2021-05-14 | INSERM (Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale) | Methods for the treatment of cancers that have acquired resistance to kinase inhibitors |
| WO2021148581A1 (en) | 2020-01-22 | 2021-07-29 | Onxeo | Novel dbait molecule and its use |
| EP4103188A4 (en) * | 2020-02-10 | 2024-04-10 | StemSynergy Therapeutics, Inc. | MYC INHIBITORS AND THEIR USES |
| CN111217821B (zh) * | 2020-03-13 | 2021-04-23 | 北京工业大学 | 系列二噁烷并喹唑啉衍生物的制备方法 |
| CN111217821A (zh) * | 2020-03-13 | 2020-06-02 | 北京工业大学 | 系列二噁烷并喹唑啉衍生物的制备方法 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2018153293A1 (zh) | 二噁烷并喹唑啉与二噁烷并喹啉类化合物及其制备方法与应用 | |
| US10435389B2 (en) | Octahydrocyclopenta[c]pyrrole allosteric inhibitors of SHP2 | |
| TWI324154B (zh) | ||
| WO2017167182A1 (zh) | 一种选择性的c-kit激酶抑制剂 | |
| US20200039974A1 (en) | Pyridine compound | |
| CN111093645A (zh) | Egfr酪氨酸激酶的临床上重要的突变体的选择性抑制剂 | |
| US10980809B2 (en) | Urea-substituted aromatic ring-linked dioxane-quinazoline and -linked dioxane-quinoline compounds, preparation method therefor and use thereof | |
| AU2019218187B2 (en) | Dioxinoquinoline compounds, preparation method and uses thereof | |
| CN113454081B (zh) | 咪唑并吡啶基化合物及其用于治疗增生性疾病的用途 | |
| US20230114195A1 (en) | Benzisoxazole compound | |
| ES2871673T3 (es) | Activador de los canales KCNQ2-5 | |
| TW201625620A (zh) | 作為蛋白去乙醯酶抑制劑及雙蛋白去乙醯酶蛋白激酶抑制劑之雜環氧肟酸及其使用方法 | |
| WO2017097216A1 (zh) | 五元杂环酰胺类wnt通路抑制剂 | |
| CA2990583A1 (en) | 1,4-disubstituted imidazole derivative | |
| JP7251841B2 (ja) | 芳香環結合ジオキシノ-キナゾリンまたはジオキシノ-キノリン系化合物、組成物およびその使用 | |
| WO2021079962A1 (ja) | 難聴の予防および/または治療用医薬組成物 | |
| WO2018157730A1 (zh) | 脲取代的芳环连二噁烷并喹唑啉与连二噁烷并喹啉类化合物及其制备方法与应用 | |
| JP7022454B2 (ja) | ジオキシノキノリン系化合物、その調製方法および使用 | |
| US11479559B2 (en) | Urea-substituted aromatic ring-linked dioxinoquinoline compounds, preparation method and uses thereof | |
| CN115515579A (zh) | 吡咯并[2,3-b]吡啶-3-甲酰胺组合物和改善听力损失的方法 | |
| WO2019170086A1 (zh) | 一种酰基取代的噁嗪并喹唑啉类化合物、制备方法及其应用 | |
| WO2017097215A1 (zh) | 内嵌脲类结构的wnt通路抑制剂 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 18756568 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 18756568 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |