WO2013137190A1 - Charging management system, charging management method, and vehicle-mounted device - Google Patents
Charging management system, charging management method, and vehicle-mounted device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2013137190A1 WO2013137190A1 PCT/JP2013/056629 JP2013056629W WO2013137190A1 WO 2013137190 A1 WO2013137190 A1 WO 2013137190A1 JP 2013056629 W JP2013056629 W JP 2013056629W WO 2013137190 A1 WO2013137190 A1 WO 2013137190A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- vehicle
- use reservation
- reservation
- parking
- time
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60L—PROPULSION OF ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES; SUPPLYING ELECTRIC POWER FOR AUXILIARY EQUIPMENT OF ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES; ELECTRODYNAMIC BRAKE SYSTEMS FOR VEHICLES IN GENERAL; MAGNETIC SUSPENSION OR LEVITATION FOR VEHICLES; MONITORING OPERATING VARIABLES OF ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES; ELECTRIC SAFETY DEVICES FOR ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES
- B60L58/00—Methods or circuit arrangements for monitoring or controlling batteries or fuel cells, specially adapted for electric vehicles
- B60L58/10—Methods or circuit arrangements for monitoring or controlling batteries or fuel cells, specially adapted for electric vehicles for monitoring or controlling batteries
- B60L58/12—Methods or circuit arrangements for monitoring or controlling batteries or fuel cells, specially adapted for electric vehicles for monitoring or controlling batteries responding to state of charge [SoC]
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60L—PROPULSION OF ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES; SUPPLYING ELECTRIC POWER FOR AUXILIARY EQUIPMENT OF ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES; ELECTRODYNAMIC BRAKE SYSTEMS FOR VEHICLES IN GENERAL; MAGNETIC SUSPENSION OR LEVITATION FOR VEHICLES; MONITORING OPERATING VARIABLES OF ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES; ELECTRIC SAFETY DEVICES FOR ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES
- B60L53/00—Methods of charging batteries, specially adapted for electric vehicles; Charging stations or on-board charging equipment therefor; Exchange of energy storage elements in electric vehicles
- B60L53/30—Constructional details of charging stations
- B60L53/305—Communication interfaces
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60L—PROPULSION OF ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES; SUPPLYING ELECTRIC POWER FOR AUXILIARY EQUIPMENT OF ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES; ELECTRODYNAMIC BRAKE SYSTEMS FOR VEHICLES IN GENERAL; MAGNETIC SUSPENSION OR LEVITATION FOR VEHICLES; MONITORING OPERATING VARIABLES OF ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES; ELECTRIC SAFETY DEVICES FOR ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES
- B60L53/00—Methods of charging batteries, specially adapted for electric vehicles; Charging stations or on-board charging equipment therefor; Exchange of energy storage elements in electric vehicles
- B60L53/60—Monitoring or controlling charging stations
- B60L53/68—Off-site monitoring or control, e.g. remote control
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60L—PROPULSION OF ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES; SUPPLYING ELECTRIC POWER FOR AUXILIARY EQUIPMENT OF ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES; ELECTRODYNAMIC BRAKE SYSTEMS FOR VEHICLES IN GENERAL; MAGNETIC SUSPENSION OR LEVITATION FOR VEHICLES; MONITORING OPERATING VARIABLES OF ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES; ELECTRIC SAFETY DEVICES FOR ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES
- B60L2240/00—Control parameters of input or output; Target parameters
- B60L2240/70—Interactions with external data bases, e.g. traffic centres
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60L—PROPULSION OF ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES; SUPPLYING ELECTRIC POWER FOR AUXILIARY EQUIPMENT OF ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES; ELECTRODYNAMIC BRAKE SYSTEMS FOR VEHICLES IN GENERAL; MAGNETIC SUSPENSION OR LEVITATION FOR VEHICLES; MONITORING OPERATING VARIABLES OF ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES; ELECTRIC SAFETY DEVICES FOR ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES
- B60L2260/00—Operating Modes
- B60L2260/40—Control modes
- B60L2260/50—Control modes by future state prediction
- B60L2260/54—Energy consumption estimation
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60L—PROPULSION OF ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES; SUPPLYING ELECTRIC POWER FOR AUXILIARY EQUIPMENT OF ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES; ELECTRODYNAMIC BRAKE SYSTEMS FOR VEHICLES IN GENERAL; MAGNETIC SUSPENSION OR LEVITATION FOR VEHICLES; MONITORING OPERATING VARIABLES OF ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES; ELECTRIC SAFETY DEVICES FOR ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES
- B60L2260/00—Operating Modes
- B60L2260/40—Control modes
- B60L2260/50—Control modes by future state prediction
- B60L2260/58—Departure time prediction
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02T—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES RELATED TO TRANSPORTATION
- Y02T10/00—Road transport of goods or passengers
- Y02T10/60—Other road transportation technologies with climate change mitigation effect
- Y02T10/70—Energy storage systems for electromobility, e.g. batteries
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02T—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES RELATED TO TRANSPORTATION
- Y02T10/00—Road transport of goods or passengers
- Y02T10/60—Other road transportation technologies with climate change mitigation effect
- Y02T10/7072—Electromobility specific charging systems or methods for batteries, ultracapacitors, supercapacitors or double-layer capacitors
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02T—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES RELATED TO TRANSPORTATION
- Y02T10/00—Road transport of goods or passengers
- Y02T10/60—Other road transportation technologies with climate change mitigation effect
- Y02T10/72—Electric energy management in electromobility
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02T—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES RELATED TO TRANSPORTATION
- Y02T90/00—Enabling technologies or technologies with a potential or indirect contribution to GHG emissions mitigation
- Y02T90/10—Technologies relating to charging of electric vehicles
- Y02T90/12—Electric charging stations
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02T—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES RELATED TO TRANSPORTATION
- Y02T90/00—Enabling technologies or technologies with a potential or indirect contribution to GHG emissions mitigation
- Y02T90/10—Technologies relating to charging of electric vehicles
- Y02T90/16—Information or communication technologies improving the operation of electric vehicles
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02T—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES RELATED TO TRANSPORTATION
- Y02T90/00—Enabling technologies or technologies with a potential or indirect contribution to GHG emissions mitigation
- Y02T90/10—Technologies relating to charging of electric vehicles
- Y02T90/16—Information or communication technologies improving the operation of electric vehicles
- Y02T90/167—Systems integrating technologies related to power network operation and communication or information technologies for supporting the interoperability of electric or hybrid vehicles, i.e. smartgrids as interface for battery charging of electric vehicles [EV] or hybrid vehicles [HEV]
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y04—INFORMATION OR COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES HAVING AN IMPACT ON OTHER TECHNOLOGY AREAS
- Y04S—SYSTEMS INTEGRATING TECHNOLOGIES RELATED TO POWER NETWORK OPERATION, COMMUNICATION OR INFORMATION TECHNOLOGIES FOR IMPROVING THE ELECTRICAL POWER GENERATION, TRANSMISSION, DISTRIBUTION, MANAGEMENT OR USAGE, i.e. SMART GRIDS
- Y04S30/00—Systems supporting specific end-user applications in the sector of transportation
- Y04S30/10—Systems supporting the interoperability of electric or hybrid vehicles
- Y04S30/12—Remote or cooperative charging
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a charge management system that manages charging of a vehicle, a charge management method, and an in-vehicle device.
- Patent Document 1 a charging device for an electric vehicle that reliably charges a shared vehicle is known.
- Patent Document 1 describes that even when a vehicle is present and the vehicle is not connected to a charging device even during a predetermined charging time period, a warning is issued to prevent forgetting to charge.
- the present invention has been proposed in view of the above-described circumstances, and an object thereof is to provide a charge management system, a charge management method, and an in-vehicle device that can suppress insufficient charging of a vehicle.
- a charge management system, a charge management method, and an in-vehicle device store a scheduled use start time of a vehicle, a scheduled use end time, a use reservation in which a destination is set, and a chargeable time of the vehicle. Then, it is determined whether or not the amount of power for the first use reservation is insufficient. When the amount of power of the first use reservation is insufficient, information recommending charging of the in-vehicle battery is presented during a period in which the vehicle is used by the second use reservation prior to the first use reservation.
- FIG. 1 is a block diagram of a charge management system shown as the present embodiment.
- FIG. 2 is a flowchart showing an operation in the charge management system shown as the present embodiment.
- FIG. 3 is a flowchart showing an example of parking detection processing in the charge management system shown as the present embodiment.
- FIG. 4 is a flowchart showing another example of the parking detection process in the charge management system shown as the present embodiment.
- FIG. 5 is a flowchart showing another example of the parking detection process in the charge management system shown as the present embodiment.
- FIG. 6 is a flowchart showing another example of the parking detection process in the charge management system shown as the present embodiment.
- FIG. 7 is a flowchart showing an example of a determination process of whether or not charging is necessary in the charge management system shown as the present embodiment.
- FIG. 1 is a block diagram of a charge management system shown as the present embodiment.
- FIG. 2 is a flowchart showing an operation in the charge management system shown as the present embodiment.
- FIG. 3 is
- FIG. 8 is a flowchart showing another example of the determination process of whether or not charging is necessary in the charge management system shown as the present embodiment.
- FIG. 9 is a diagram for explaining the operation of the charge management system shown as the present embodiment, where (a) shows the transition of the remaining charge of the comparative example, and (b) shows the transition of the remaining charge of the present embodiment.
- Show. 10A and 10B are diagrams for explaining the operation of the charge management system shown as the present embodiment.
- FIG. 10A shows a scene where charging is not recommended
- FIG. 10B shows a scene where charging is recommended.
- FIG. 10A shows a scene where charging is not recommended.
- FIG. 11 is a diagram illustrating that in the charge management system shown as the present embodiment, information that recommends charging when parking for a long time is presented, and information that recommends charging is not presented when charging with an insufficient amount of power is completed. It is.
- FIG. 12 is another diagram showing that in the charge management system shown as the present embodiment, information that recommends charging when parking for a long stay time is presented and information that recommends charging is not presented when parking for a short stay time. is there.
- the charge management system shown as an embodiment of the present invention is configured as shown in FIG.
- This charge management system manages charging of a vehicle so that a plurality of users can use the vehicle jointly.
- This charging management system is configured by connecting a vehicle-mounted system (vehicle-mounted device) 1, a center device 2, a user terminal 3, and a schedule table database 4 to a network NW.
- the vehicle in this charge management system is an electric vehicle (EV).
- EV electric vehicle
- a destination such as a destination is set for this electric vehicle when a user makes a reservation for use.
- This electric vehicle is connected to a return (return) port provided in a predetermined parking area.
- This return port is a charging station for an electric vehicle. The electric vehicle is removed from the return port when the vehicle is rented, and is connected to the return port when the vehicle is returned.
- the user terminal 3 is a personal computer, a mobile terminal, a mobile phone or the like.
- the user terminal 3 is connected to the center device 2 and the schedule table database 4 via a network NW such as the Internet.
- NW such as the Internet.
- the user terminal 3 displays a reservation screen on a display (not shown) according to the control of the center device 2.
- the user terminal 3 accepts various types of information according to user operations.
- the user terminal 3 receives a user ID, a desired vehicle type, a destination, a scheduled use start date / time (scheduled use start time), and a scheduled use end date / time (scheduled use end time).
- the user terminal 3 transmits the user ID, the desired vehicle type, the destination, the scheduled use start date and time, and the scheduled use end date and time to the center device 2 together with the electric vehicle use request. Moreover, the staying time in the destination may be set to the use reservation.
- the center device 2 manages use reservations by a plurality of users for a plurality of electric vehicles.
- Center device 2 includes a vehicle reservation management unit 21 and a communication unit 22.
- the vehicle reservation management unit 21 is actually composed of a ROM, a RAM, a CPU, and the like, but functions that can be realized by the CPU performing processing according to a charge management program stored in the ROM will be described as blocks. To do.
- the communication unit 22 is a communication interface or the like that can communicate via the network NW.
- the vehicle reservation management unit 21 transmits usage reservation information in which a user ID, a desired vehicle type, a destination, a scheduled usage start date and time, and a scheduled usage end date and time are set together with a request for using an electric vehicle from the user terminal 3. .
- the center device 2 determines whether or not there is an electric vehicle that meets the use conditions of the destination related to the use request, the scheduled use start date and time, and the scheduled use end date and time. When there is an electric vehicle that meets the usage conditions, the usage reservation is registered by storing the usage reservation. Thereby, in the center apparatus 2, a schedule including a plurality of use reservations arranged in time series is constructed for each vehicle.
- the center device 2 stores a scheduled use start time, a scheduled use end time, a use reservation in which a destination is set, and a vehicle chargeable time.
- the chargeable time of the electric vehicle is a period during which the electric vehicle is connected to the charger of the return port between use reservations that change in time. This chargeable time is approximately the value obtained by multiplying the chargeable amount per unit time by the period between the scheduled use end date and time set in the previous use reservation and the scheduled use start date and time set in the subsequent use reservation. It is.
- the center device 2 calculates the amount of power for recommending charging of the on-vehicle battery. Based on the expected power consumption based on the destination set in the first (rear) use reservation and the chargeable time until the scheduled use start time set in the first use reservation, the center device 2 It is determined whether or not the amount of power for the first use reservation is insufficient. Further, the center device 2 is based on the estimated power consumption based on the destination set in the first (rear) use reservation and the chargeable time until the scheduled use start time set in the first use reservation. Then, the insufficient power amount of the first use reservation is calculated. This insufficient power amount is transmitted to the in-vehicle system 1 and stored by the scheduled use start date and time in the second use reservation before the first use reservation. Further, the insufficient power amount may be transmitted to the schedule table database 4 and stored as a recommended charge amount in the second (previous) use reservation.
- the schedule table database 4 is constructed by a cloud service in which a user uses computer processing as a service via a network.
- the schedule table database 4 stores a schedule table constructed by the center device 2.
- the schedule database 4 transmits the schedule to the requesting device in response to a request from the center device 2, the user terminal 3, or the in-vehicle system 1. Further, the schedule table database 4 may store a recommended charge amount corresponding to the insufficient power amount calculated by the center device 2 for each use reservation.
- the in-vehicle system 1 is in a period when the vehicle is used by the second (rear) use reservation in which the planned use end time is set before the planned use start time set in the first (rear) use reservation. Presents information that recommends charging the vehicle battery. Moreover, the vehicle-mounted system 1 may present the information recommending charging the insufficient electric energy of a vehicle-mounted battery.
- the in-vehicle system 1 includes a communication unit 11, a vehicle sensor 12, a charger database 13, a parking lot database 14, a map database 15, a position acquisition unit 16, a position search unit 17, a route search unit 18, and a notification unit 19.
- the communication unit 11 includes a communication interface that communicates with the center device 2 and the schedule table database 4 via the network NW.
- the vehicle sensor 12 detects the remaining charge amount of the in-vehicle battery mounted on the electric vehicle.
- the charger database 13 stores latitude and longitude information where a charger capable of charging an electric vehicle is installed.
- the parking lot database 14 stores latitude and longitude information of parking lots where electric vehicles can be parked.
- the map database 15 stores road link information indicating a road on which an electric vehicle can travel, road node information indicating an intersection, facility information indicating a type of a point, and the like.
- the charger database 13, the parking lot database 14, and the map database 15 are stored in a server (not shown) connected to the in-vehicle system 1 via the network NW if the in-vehicle system 1 is accessible. It may be.
- the position acquisition unit 16 includes, for example, a GPS receiver and the like, calculates current position information, and further acquires current time information.
- the position search unit 17 receives a user operation and detects a position corresponding to the operation.
- the position search unit 17 refers to the map database 15 and searches for the position of the destination of the electric vehicle.
- the position search unit 17 refers to the parking lot database 14 and searches for a position of the parking lot close to the current position information of the electric vehicle.
- the route search unit 18 receives a destination setting operation by the user, and refers to the map database 15 to search for a recommended route from the current position of the electric vehicle to the destination.
- the notification unit 19 includes a display that presents various information, a speaker, and the like.
- the notification unit 19 presents information that recommends charging the in-vehicle battery for a subsequent use reservation subsequent to the current use (presentation means).
- the notification unit 19 also provides insufficient power for the subsequent use reservation.
- Information that recommends charging the amount can also be presented (presentation means).
- the in-vehicle system 1 may store a use reservation (storage means), as with the center device 2. Furthermore, the in-vehicle system 1, similarly to the center device 2, expects power consumption based on the destination set in the first (rear) use reservation and the scheduled use start time set in the first use reservation. It may be determined whether or not the amount of power required for the first use reservation is insufficient based on the available charging time. Furthermore, the in-vehicle system 1 may calculate an insufficient power amount of the first usage reservation (calculation means).
- reservation information is transmitted from the center device 2 via the network NW.
- This reservation information includes a user ID, a scheduled use start date and time, and a scheduled use end date and time.
- the user of the electric vehicle places the IC card on an IC card reader (not shown) mounted on the vehicle after the scheduled use start date and time.
- the IC card reader reads the user ID stored in the IC card, and when it matches the user ID included in the reservation information, controls the key device to open the key.
- the in-vehicle system 1 is connected (returned) to the port (return position) by the scheduled end date of use of the electric vehicle. After the use is completed, the IC card is put on the IC card reader. The in-vehicle system 1 recognizes that the electric vehicle has been returned to the port from the current position information, and notifies the center device 2 that it has been returned.
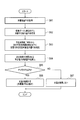
- step S1 the in-vehicle system 1 detects whether the electric vehicle is about to stop to park in the parking lot.
- the details of the electric vehicle parking detection process will be described later with reference to FIGS.
- step S2 the in-vehicle system 1 determines whether or not the electric vehicle is about to stop at the parking lot based on the result of the parking detection process in step S1. If the electric vehicle is about to stop at the parking lot, the process proceeds to step S3. If not, the process returns to step S1.
- step S3 the in-vehicle system 1 determines whether charging by an electric vehicle is necessary. The details of the determination process of whether or not charging is necessary will be described later with reference to FIGS.
- step S4 the in-vehicle system 1 determines whether or not the electric vehicle needs to be charged based on the result of the determination process of whether or not charging is required in step S3. If the electric vehicle needs to be charged, the process proceeds to step S5, and if not, the process returns to step S1.
- step S5 the in-vehicle system 1 uses the notification unit 19 to present information that recommends charging to the user of the electric vehicle.
- you may show required recommended charge amount to the information which recommends this charge.
- the vehicle-mounted system 1 may present the information which recommends charge, for example, when the parking brake which stops an electric vehicle is operated.
- the presentation method may be displayed on a vehicle-mounted display, or sound may be output from a speaker.
- step S1 the parking detection process in step S1 described above will be described.
- step S11 the position acquisition unit 16 acquires current position information of the electric vehicle.
- the position search unit 17 of the in-vehicle system 1 refers to the map database 15 and collates the type of the current position acquired in step S11. This type is information such as a parking lot.
- step S13 the in-vehicle system 1 determines whether or not the type of the current position is a parking lot as a result of the process in step S12. If the type of the current position is a parking lot, the process proceeds to step S14; otherwise, the process returns to step S11.
- step S14 the in-vehicle system 1 determines that the electric vehicle is currently parked in the parking lot.
- step S ⁇ b> 21 the in-vehicle system 1 determines whether or not a destination for route search is input by the route search unit 18. At this time, the in-vehicle system 1 determines whether or not the destination information is stored by the route search unit 18. If it is determined that the destination has been input, the process proceeds to step S22. If not, the process ends.
- step S ⁇ b> 22 the in-vehicle system 1 acquires the current position information of the electric vehicle by the position acquisition unit 16.
- step S23 the in-vehicle system 1 determines whether or not the current position acquired in step S22 by the position search unit 17 is around the destination determined to have been input in step S21. For example, the position search unit 17 determines that the electric vehicle is located around the destination when the current position is within a range of several tens of meters from the destination. Further, the position search unit 17 may determine that the current position of the electric vehicle is around the destination that the electric vehicle is traveling toward the destination. If it is determined that the current position of the electric vehicle is around the destination, the process proceeds to step S24, and if not, the process ends.
- step S24 the in-vehicle system 1 determines that the electric vehicle is parked after arrival at the destination.
- this in-vehicle system when it is detected that the acquired current position is around the destination set in the use reservation, parking of the vehicle is detected. Thereby, according to the in-vehicle system 1, it is possible to recommend charging of the in-vehicle battery to the user only when the electric vehicle is parked. When charging is necessary, for example, frequent recommendation of charging during traveling can be suppressed.
- the parking detection process shown in FIG. 5 first determines in step S31 whether or not the parking lot has been searched by the route search unit 18 of the in-vehicle system 1. At this time, the in-vehicle system 1 accepts a user's operation such as a button, and determines whether or not a parking lot has been searched as a peripheral facility. If it is determined that a parking lot has been searched, the process proceeds to step S32. If not, the process ends.
- step S32 the in-vehicle system 1 determines that the electric vehicle is parked after that because the user is about to park the electric vehicle in the parking lot.
- the in-vehicle system when an operation for searching for a parking lot by a user is detected, parking of the vehicle is detected. Thereby, according to the vehicle-mounted system 1, charging can be recommended to the user only when the electric vehicle is parked. When charging is necessary, for example, frequent recommendation of charging during traveling can be suppressed.
- the parking detection process shown in FIG. 6 first accesses the schedule table database 4 by the communication unit 11 of the in-vehicle system 1 in step S41. At this time, the in-vehicle system 1 transmits a schedule download request including the ID of the electric vehicle, the user ID, and the like to the schedule table database 4.
- step S42 the in-vehicle system 1 acquires from the schedule table database 4 a schedule table that matches the electric vehicle ID and user ID.
- the in-vehicle system 1 determines whether or not the current destination has been acquired from the use reservation included in the acquired schedule. If it is determined that the current destination has been acquired, the process proceeds to step S43. If not, the process ends.
- step S43 the position acquisition unit 16 of the in-vehicle system 1 acquires current position information of the electric vehicle.
- the in-vehicle system 1 determines whether or not the current position acquired in step S43 by the position search unit 17 is near the destination acquired in step S42. For example, the position search unit 17 determines that the electric vehicle is located near the destination when the current position is within a range of several tens of meters from the destination. Further, the position search unit 17 may determine that there is a high possibility of arrival at the destination at the scheduled time as scheduled. If it is determined that the current position of the electric vehicle is near the destination, the process proceeds to step S45, and if not, the process returns to step S43.
- step S45 the in-vehicle system 1 determines that the electric vehicle is parked after arrival at the destination. In addition, the in-vehicle system 1 determines that parking is performed thereafter when the scheduled time approaches the scheduled time.
- this in-vehicle system when it is detected that the acquired current position is around the destination set in the use reservation, parking of the vehicle is detected. Thereby, according to the vehicle-mounted system 1, charging can be recommended to the user only when the electric vehicle is parked. When charging is necessary, for example, frequent recommendation of charging during traveling can be suppressed.
- step S3 the process for determining whether or not charging is necessary in step S3 will be described.
- step S51 the vehicle sensor 12 of the in-vehicle system 1 acquires the remaining charge amount of the in-vehicle battery.
- the in-vehicle system 1 determines whether or not the remaining charge amount of the in-vehicle battery acquired in step S51 is less than a threshold value.
- This threshold value may be a preset value (for example, SOC is 20%), and varies based on the distance from the current position of the electric vehicle to the destination or the distance from the current position of the electric vehicle to the return position. You may let them. If it is determined that the remaining charge is less than the threshold, the process proceeds to step S53, and if not, the process proceeds to step S54.
- step S53 the in-vehicle system 1 presents information recommending charging of the electric vehicle to the user by the notification unit 19.
- the in-vehicle system 1 does not recommend charging by the notification unit 19.
- this charge management system it is possible to present information that recommends charging of an electric vehicle when the remaining charge of the on-vehicle battery is low, and it is necessary without frequently bothering because charging is recommended frequently. Charging can be recommended depending on Although it is possible to tell to always charge when parking is detected, the in-vehicle system 1 can suppress the recommended number of times.
- the determination process for determining whether charging is necessary presents information that recommends charging when there is a charger around the position to be parked obtained by the parking detection process.
- the in-vehicle system 1 acquires the current position of the electric vehicle by the position acquisition unit 16 and refers to the charger database 13 in which the position of the charger is stored. Then, when the current position of the electric vehicle is around the charger stored in the charger database 13, information recommending charging of the in-vehicle battery or information recommending charging the insufficient power amount of the subsequent use reservation is provided. Present. Thereby, according to this in-vehicle system 1, it is necessary to detect the parking of the electric vehicle, and the electric vehicle needs to be charged.
- the charging can be recommended, and the vehicle is moved to the charger for parking. Can be made.
- the vehicle-mounted system 1 may change the parking position of the electric vehicle to a position where the charger exists by the route search unit 18. For example, when there is a charger on the third floor of the multilevel parking lot, information such as “Please connect to the charger on the third floor” can be included in the information that recommends charging.
- step S61 the vehicle sensor 12 of the in-vehicle system 1 acquires the remaining charge P1 of the in-vehicle battery.
- the in-vehicle system 1 determines whether or not the amount of power necessary for the first (rear) use reservation is insufficient. In the next step S62, the in-vehicle system 1 estimates the power consumption P2 that the electric vehicle consumes to travel to the return port. At this time, the in-vehicle system 1 estimates the power consumption P2 based on the distance from the current position to the destination, the average travel speed, the power consumption per unit distance, and the like.
- the in-vehicle system 1 estimates the chargeable power amount P3 that can be charged from the scheduled use end date / time in the current use reservation to the scheduled use start date / time in the next use reservation.
- This chargeable power amount P3 is calculated by calculating the amount of charge per unit time of the charger from the scheduled use end date / time in the current use reservation to the scheduled use start date / time in the next use reservation. Estimate by multiplying.
- the in-vehicle system 1 calculates an expected power consumption P4 consumed by the next use reservation. At this time, the in-vehicle system 1 calculates the predicted power consumption P4 based on the destination information set for the next use reservation. For example, the predicted power consumption P4 is calculated based on the moving distance according to the position of the return port or the destination and the power consumption per unit distance.
- the in-vehicle system 1 determines whether or not the insufficient power amount obtained by subtracting the power consumption amount P2 and the chargeable power amount P3 from the remaining charge amount P1 acquired in step S61 is equal to or less than the predicted power consumption amount P4. Determine whether. This insufficient power amount is a shortage of the power amount necessary for the next use reservation. If it is determined that the insufficient power amount is equal to or less than the predicted power consumption P4, the process proceeds to step S66, and if not, the process returns to step S67.
- step S66 the in-vehicle system 1 presents information recommending charging of the electric vehicle to the user by the notification unit 19.
- the in-vehicle system 1 charges the in-vehicle battery during a period in which the vehicle is used by the current use reservation in which the scheduled use end time is set before the scheduled use start time set in the subsequent use reservation.
- Information recommending charging, or information recommending charging the amount of insufficient power can be presented.
- step S ⁇ b> 67 the in-vehicle system 1 does not recommend charging by the notification unit 19.
- the in-vehicle system 1 acquires the current position of the electric vehicle by the position acquisition unit 16 and refers to the charger database 13 in which the position of the charger is stored. Then, when the current position of the electric vehicle is around the charger stored in the charger database 13, information recommending charging of the in-vehicle battery or information recommending charging the insufficient power amount of the subsequent use reservation is provided. Present. Thereby, according to this in-vehicle system 1, it is necessary to detect the parking of the electric vehicle, and the electric vehicle needs to be charged.
- the charging can be recommended, and the vehicle is moved to the charger for parking. Can be made.
- the vehicle-mounted system 1 may change the parking position of the electric vehicle to a position where the charger exists by the route search unit 18. For example, when there is a charger on the third floor of the multilevel parking lot, information such as “Please connect to the charger on the third floor” can be included in the information that recommends charging.
- this in-vehicle system 1 may present in the information recommending charging that there is a possibility that insufficient power may occur in the next usage reservation, and it is desirable to charge in the current usage.
- charging can be performed for the next use reservation.
- the remaining charge of the in-vehicle battery for the next use reservation needs to be 90% or more.
- FIG. 9A shows a comparative example in which charging is not recommended for the next usage reservation in the previous usage reservation.
- the remaining charge amount at the start of use of the previous use reservation is 100%, and the remaining charge amount is reduced by 30% by traveling (going) to the destination, and traveling from the destination to the return port. (Return) further reduces the remaining charge by 30%. Further, only 30% of the remaining charge can be charged depending on the chargeable power amount from the scheduled use end date and time of the previous use reservation to the scheduled use start date and time of the next use reservation. Therefore, in the comparative example, a power shortage of 20% occurs in the remaining charge for the next use reservation.
- the charge management system shown as this embodiment detects parking by the parking detection process when the remaining charge is reduced by 30% due to traveling (going) to the destination, and determines whether or not charging is necessary in FIG. By processing, it is possible to present information that recommends charging with a remaining charge of 20% or more. As a result, the charger installed in the parking lot at the destination can charge 21% with the remaining charge. After that, even if the remaining charge level further decreases by 30% and the remaining charge level reaches 61% due to travel from the destination to the return port (return), the next use reservation will be started from the scheduled use end date and time of the previous use reservation.
- the remaining charge can be increased to 91% by the scheduled use start date and time of the next use reservation.
- the charge management system can suppress the power shortage due to the travel of the next use reservation.
- this charging management system does not present information that recommends charging even if charging can be performed when a sufficient amount of power is charged in the in-vehicle battery by the next use reservation.
- the remaining charge at the time of parking is 8 kwh
- the power consumption up to the return port is 3 kwh
- the chargeable power is 3 kwh.
- the power consumption of the next usage reservation n + 1 is 5 kwh.
- the remaining charge amount of 8 kwh can be secured at the scheduled use start date and time of the next use reservation n + 1. Therefore, even if the vehicle-mounted system 1 detects parking in the use reservation n, it does not present information that recommends charging.
- the charge management system has a remaining charge of 9 kwh at the time of parking in the use reservation n, a power consumption of 3 kwh up to the return port, and a chargeable power Let the amount be 3 kwh.
- the power consumption of the next usage reservation n + 1 is 10 kwh. In this case, there is only a remaining charge of 9 kwh at the scheduled use start date and time of the next use reservation n + 1. Therefore, when the in-vehicle system 1 detects parking in the use reservation n, it presents information that recommends charging.
- this charging management system may switch whether or not to present information recommending charging according to the stay time at the destination.
- the use reservation n includes two destinations and the stay times at the destinations are different.
- the in-vehicle system 1 downloads the schedule for use reservation n from the schedule table database 4 and acquires the stay time at each destination.
- the in-vehicle system 1 refers to the stay time in the parking P ⁇ b> 1 and the stay time in the parking P ⁇ b> 2, and determines that the insufficient power amount can be charged by the stay time in the parking P ⁇ b> 1.
- the in-vehicle system 1 presents information recommending charging when detecting parking corresponding to the staying time in the parking P1. Thereby, the vehicle-mounted system 1 charges the insufficient power amount with the stay time in the parking P1.
- the in-vehicle system 1 does not present information that recommends charging even when parking is detected when the stay time in the next parking P2 is reached.
- the information recommending that the in-vehicle battery be charged during the period in which the vehicle is used by the second usage reservation before the first usage reservation is used for the insufficient power amount of the first usage reservation is used for the insufficient power amount of the first usage reservation. Therefore, insufficient charging of the vehicle can be suppressed.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Transportation (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Sustainable Development (AREA)
- Sustainable Energy (AREA)
- Electric Propulsion And Braking For Vehicles (AREA)
Abstract
A vehicle-mounted system (1), a center device (2), or a schedule database (4) store the time that a vehicle can be charged, and a usage booking for which the scheduled usage start time for the vehicle, the scheduled usage finish time, and the destination are set. A charging management system: determines whether or not there is sufficient power for a first usage booking requirement, on the basis of an estimated power consumption amount on the basis of a destination set for a subsequent usage booking, and the time that the vehicle can be changed until the scheduled usage start time set to the first usage booking; and presents information recommending that the vehicle be charged by a vehicle-mounted battery during the period that the vehicle is being used by usage bookings before the subsequent usage booking.
Description
本発明は、車両への充電を管理する充電管理システム、充電管理方法、及び、車載装置に関する。
The present invention relates to a charge management system that manages charging of a vehicle, a charge management method, and an in-vehicle device.
従来より、下記の特許文献1に記載されているように、共用車両の充電を確実に行うようにする電気車両用の充電装置が知られている。この特許文献1には、車両があり充電の所定の時間帯であっても車両が充電装置に接続されていない場合にはウォーニングを出し、充電忘れを防止できることが記載されている。
Conventionally, as described in Patent Document 1 below, a charging device for an electric vehicle that reliably charges a shared vehicle is known. Patent Document 1 describes that even when a vehicle is present and the vehicle is not connected to a charging device even during a predetermined charging time period, a warning is issued to prevent forgetting to charge.
しかしながら、車両を複数の利用者で共同して利用する場合、所定の帰着位置に設置された充電器により車載バッテリの充電を行うだけでは充電残量が不足することがあった。
However, when the vehicle is shared by a plurality of users, there is a case where the remaining charge amount is insufficient only by charging the in-vehicle battery with the charger installed at the predetermined return position.
そこで、本発明は、上述した実情に鑑みて提案されたものであり、車両の充電不足を抑制することができる充電管理システム、充電管理方法、及び、車載装置を提供することを目的とする。
Therefore, the present invention has been proposed in view of the above-described circumstances, and an object thereof is to provide a charge management system, a charge management method, and an in-vehicle device that can suppress insufficient charging of a vehicle.
本発明の態様に係る充電管理システム、充電管理方法、及び、車載装置は、車両の予定利用開始時刻、予定利用終了時刻及び目的地が設定された利用予約、車両の充電可能時間を記憶しておき、第1の利用予約の電力量が不足するかを判断する。第1の利用予約の電力量が不足する場合、第1の利用予約より以前の第2の利用予約によって車両を利用している期間に、車載バッテリに充電することを推奨する情報を提示する。
A charge management system, a charge management method, and an in-vehicle device according to an aspect of the present invention store a scheduled use start time of a vehicle, a scheduled use end time, a use reservation in which a destination is set, and a chargeable time of the vehicle. Then, it is determined whether or not the amount of power for the first use reservation is insufficient. When the amount of power of the first use reservation is insufficient, information recommending charging of the in-vehicle battery is presented during a period in which the vehicle is used by the second use reservation prior to the first use reservation.
以下、本発明の実施の形態について図面を参照して説明する。
Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
本発明の実施形態として示す充電管理システムは、例えば図1に示すように構成される。この充電管理システムは、複数の利用者が車両を共同して利用するために車両の充電を管理する。この充電管理システムは、ネットワークNWに、車載システム(車載装置)1、センター装置2、利用者端末3、及び、予定表データベース4が接続されて構成されている。
The charge management system shown as an embodiment of the present invention is configured as shown in FIG. This charge management system manages charging of a vehicle so that a plurality of users can use the vehicle jointly. This charging management system is configured by connecting a vehicle-mounted system (vehicle-mounted device) 1, a center device 2, a user terminal 3, and a schedule table database 4 to a network NW.
この充電管理システムにおける車両は、この実施形態において、電気自動車(EV)とする。この電気自動車は、走行前に充電を行うために車載バッテリの充電時間の確保が必要となる。また、この電気自動車は、利用者の利用予約時に、訪問先等の目的地が設定される。この電気自動車は、所定の駐車エリアに設けられた帰着(返却)ポートに接続される。この帰着ポートは、電気自動車のための充電スタンド等である。電気自動車は、車両の貸し出し時には帰着ポートから取り外され、車両の返却時には帰着ポートに接続される。
In this embodiment, the vehicle in this charge management system is an electric vehicle (EV). In order to charge this electric vehicle before traveling, it is necessary to secure the charging time of the in-vehicle battery. In addition, a destination such as a destination is set for this electric vehicle when a user makes a reservation for use. This electric vehicle is connected to a return (return) port provided in a predetermined parking area. This return port is a charging station for an electric vehicle. The electric vehicle is removed from the return port when the vehicle is rented, and is connected to the return port when the vehicle is returned.
利用者端末3は、パーソナルコンピュータや、携帯端末、携帯電話等である。利用者端末3は、インターネット等のネットワークNWを介して、センター装置2、予定表データベース4に接続する。利用者端末3は、センター装置2への接続時に、センター装置2の制御に従って、図示しないディスプレイに予約画面を表示させる。利用者端末3は、利用者の操作に従って、各種の情報を受け付ける。利用者端末3は、利用者ID、希望車種、目的地、予定利用開始日時(予定利用開始時刻)、予定利用終了日時(予定利用終了時刻)が入力される。利用者端末3は、電気自動車の利用要求と共に、利用者ID、希望車種、目的地、予定利用開始日時、予定利用終了日時をセンター装置2に送信する。また、利用予約には、目的地における滞在時間が設定されていてもよい。
The user terminal 3 is a personal computer, a mobile terminal, a mobile phone or the like. The user terminal 3 is connected to the center device 2 and the schedule table database 4 via a network NW such as the Internet. When connecting to the center device 2, the user terminal 3 displays a reservation screen on a display (not shown) according to the control of the center device 2. The user terminal 3 accepts various types of information according to user operations. The user terminal 3 receives a user ID, a desired vehicle type, a destination, a scheduled use start date / time (scheduled use start time), and a scheduled use end date / time (scheduled use end time). The user terminal 3 transmits the user ID, the desired vehicle type, the destination, the scheduled use start date and time, and the scheduled use end date and time to the center device 2 together with the electric vehicle use request. Moreover, the staying time in the destination may be set to the use reservation.
センター装置2は、複数の電気自動車について、複数の利用者による利用予約を管理する。センター装置2は、車両予約管理部21と通信部22とを含む。車両予約管理部21は、実際にはROM、RAM、CPU等にて構成されているが、当該CPUがROMに格納された充電管理用のプログラムに従って処理をすることによって実現できる機能をブロックとして説明する。通信部22は、ネットワークNWを介して通信可能な通信インターフェース等である。
The center device 2 manages use reservations by a plurality of users for a plurality of electric vehicles. Center device 2 includes a vehicle reservation management unit 21 and a communication unit 22. The vehicle reservation management unit 21 is actually composed of a ROM, a RAM, a CPU, and the like, but functions that can be realized by the CPU performing processing according to a charge management program stored in the ROM will be described as blocks. To do. The communication unit 22 is a communication interface or the like that can communicate via the network NW.
車両予約管理部21は、利用者端末3から、電気自動車の利用要求と共に、利用者ID、希望車種、目的地、予定利用開始日時、予定利用終了日時が設定された利用予約情報が送信される。センター装置2は、利用要求に係る目的地、予定利用開始日時、予定利用終了日時という利用条件に該当する電気自動車があるか否かを判断する。利用条件に合致する電気自動車がある場合に、利用予約を記憶することによって、利用予約を登録する。これにより、センター装置2には、車両毎に、時系列に配置された複数の利用予約を含む予定表が構築される。
The vehicle reservation management unit 21 transmits usage reservation information in which a user ID, a desired vehicle type, a destination, a scheduled usage start date and time, and a scheduled usage end date and time are set together with a request for using an electric vehicle from the user terminal 3. . The center device 2 determines whether or not there is an electric vehicle that meets the use conditions of the destination related to the use request, the scheduled use start date and time, and the scheduled use end date and time. When there is an electric vehicle that meets the usage conditions, the usage reservation is registered by storing the usage reservation. Thereby, in the center apparatus 2, a schedule including a plurality of use reservations arranged in time series is constructed for each vehicle.
また、センター装置2は、電気自動車の予定利用開始時刻、予定利用終了時刻及び目的地が設定された利用予約、車両の充電可能時間を記憶する。この電気自動車の充電可能時間は、時間的に前後する利用予約間において、電気自動車が帰着ポートの充電器に接続されている期間である。この充電可能時間は、概ね前の利用予約に設定された予定利用終了日時と後の利用予約に設定された予定利用開始日時との間の期間に、単位時間あたりの充電可能量を乗算した値である。
Further, the center device 2 stores a scheduled use start time, a scheduled use end time, a use reservation in which a destination is set, and a vehicle chargeable time. The chargeable time of the electric vehicle is a period during which the electric vehicle is connected to the charger of the return port between use reservations that change in time. This chargeable time is approximately the value obtained by multiplying the chargeable amount per unit time by the period between the scheduled use end date and time set in the previous use reservation and the scheduled use start date and time set in the subsequent use reservation. It is.
センター装置2は、車載バッテリの充電を推奨するための電力量の演算を行う。センター装置2は、第1(後)の利用予約に設定された目的地に基づく予想電力消費量及び当該第1の利用予約に設定された予定利用開始時刻までの充電可能時間に基づいて、当該第1の利用予約の電力量が不足するかどうかを判断する。また、センター装置2は、第1(後)の利用予約に設定された目的地に基づく予想電力消費量及び当該第1の利用予約に設定された予定利用開始時刻までの充電可能時間に基づいて、当該第1の利用予約の不足電力量を算出する。この不足電力量は、第1の利用予約の前の第2の利用予約における予定利用開始日時までに、車載システム1に送信されて、記憶される。また、この不足電力量は、予定表データベース4に送信され、第2(前)の利用予約における推奨充電量として記憶されていてもよい。
The center device 2 calculates the amount of power for recommending charging of the on-vehicle battery. Based on the expected power consumption based on the destination set in the first (rear) use reservation and the chargeable time until the scheduled use start time set in the first use reservation, the center device 2 It is determined whether or not the amount of power for the first use reservation is insufficient. Further, the center device 2 is based on the estimated power consumption based on the destination set in the first (rear) use reservation and the chargeable time until the scheduled use start time set in the first use reservation. Then, the insufficient power amount of the first use reservation is calculated. This insufficient power amount is transmitted to the in-vehicle system 1 and stored by the scheduled use start date and time in the second use reservation before the first use reservation. Further, the insufficient power amount may be transmitted to the schedule table database 4 and stored as a recommended charge amount in the second (previous) use reservation.
予定表データベース4は、利用者がコンピュータ処理をネットワーク経由で、サービスとして利用するクラウドサービスによって構築されている。予定表データベース4は、センター装置2により構築された予定表を記憶する。予定表データベース4は、センター装置2、利用者端末3、又は、車載システム1からの要求に応じて、予定表を要求元の装置に送信する。また、予定表データベース4は、センター装置2によって算出された不足電力量に応じた推奨充電量を利用予約ごとに記憶してもよい。
The schedule table database 4 is constructed by a cloud service in which a user uses computer processing as a service via a network. The schedule table database 4 stores a schedule table constructed by the center device 2. The schedule database 4 transmits the schedule to the requesting device in response to a request from the center device 2, the user terminal 3, or the in-vehicle system 1. Further, the schedule table database 4 may store a recommended charge amount corresponding to the insufficient power amount calculated by the center device 2 for each use reservation.
車載システム1は、第1(後)の利用予約に設定された予定利用開始時刻より以前に予定利用終了時刻が設定されている第2(後)の利用予約によって車両を利用している期間に、車載バッテリに充電をすることを推奨する情報を提示する。また、車載システム1は、車載バッテリの不足電力量を充電することを推奨する情報を提示してもよい。
The in-vehicle system 1 is in a period when the vehicle is used by the second (rear) use reservation in which the planned use end time is set before the planned use start time set in the first (rear) use reservation. Presents information that recommends charging the vehicle battery. Moreover, the vehicle-mounted system 1 may present the information recommending charging the insufficient electric energy of a vehicle-mounted battery.
車載システム1は、通信部11、車両センサー12、充電器データベース13、駐車場データベース14、地図データベース15、位置取得部16、位置検索部17、経路探索部18、及び、通知部19を含む。
The in-vehicle system 1 includes a communication unit 11, a vehicle sensor 12, a charger database 13, a parking lot database 14, a map database 15, a position acquisition unit 16, a position search unit 17, a route search unit 18, and a notification unit 19.
通信部11は、ネットワークNWを介して、センター装置2、予定表データベース4と通信を行う通信インターフェース等からなる。
The communication unit 11 includes a communication interface that communicates with the center device 2 and the schedule table database 4 via the network NW.
車両センサー12は、電気自動車に搭載された車載バッテリの充電残量を検出する。
The vehicle sensor 12 detects the remaining charge amount of the in-vehicle battery mounted on the electric vehicle.
充電器データベース13は、電気自動車の充電が可能な充電器が設置されている緯度経度情報を蓄積している。
The charger database 13 stores latitude and longitude information where a charger capable of charging an electric vehicle is installed.
駐車場データベース14は、電気自動車の駐車が可能な駐車場の緯度経度情報を蓄積している。
The parking lot database 14 stores latitude and longitude information of parking lots where electric vehicles can be parked.
地図データベース15は、電気自動車が走行可能な道路を示す道路リンク情報、交差点を示す道路ノード情報、地点の種別を示す施設情報等を記憶している。
The map database 15 stores road link information indicating a road on which an electric vehicle can travel, road node information indicating an intersection, facility information indicating a type of a point, and the like.
なお、充電器データベース13、駐車場データベース14、地図データベース15は、車載システム1がアクセス可能であれば、車載システム1とネットワークNWを介して接続されたサーバ(図示せず)に記憶されたものであってもよい。
The charger database 13, the parking lot database 14, and the map database 15 are stored in a server (not shown) connected to the in-vehicle system 1 via the network NW if the in-vehicle system 1 is accessible. It may be.
位置取得部16は、例えばGPS受信機等からなり、現在位置情報を演算し、更に、現在時刻情報を取得する。
The position acquisition unit 16 includes, for example, a GPS receiver and the like, calculates current position information, and further acquires current time information.
位置検索部17は、利用者の操作を受け付け、当該操作に応じた位置を検出する。電気自動車の目的地を検索する操作を受け付けた場合、位置検索部17は、地図データベース15を参照して、電気自動車の目的地の位置を検索する。電気自動車の近隣の駐車場を検索する操作を受け付けた場合、位置検索部17は、駐車場データベース14を参照して、電気自動車の現在位置情報に近い駐車場の位置を検索する。
The position search unit 17 receives a user operation and detects a position corresponding to the operation. When the operation of searching for the destination of the electric vehicle is received, the position search unit 17 refers to the map database 15 and searches for the position of the destination of the electric vehicle. When an operation for searching for a parking lot in the vicinity of the electric vehicle is received, the position search unit 17 refers to the parking lot database 14 and searches for a position of the parking lot close to the current position information of the electric vehicle.
経路探索部18は、利用者による目的地の設定操作を受け付け、地図データベース15を参照して、電気自動車の現在位置から目的地までの推奨経路を探索する。
The route search unit 18 receives a destination setting operation by the user, and refers to the map database 15 to search for a recommended route from the current position of the electric vehicle to the destination.
通知部19は、各種の情報を提示するディスプレイ、スピーカ等を含む。特に、通知部19は、現在の利用に後続する後続利用予約のため、車載バッテリに充電することを推奨する情報を提示する(提示手段)また、通知部19は、当該後続利用予約の不足電力量を充電することを推奨する情報を提示することもできる(提示手段)。
The notification unit 19 includes a display that presents various information, a speaker, and the like. In particular, the notification unit 19 presents information that recommends charging the in-vehicle battery for a subsequent use reservation subsequent to the current use (presentation means). The notification unit 19 also provides insufficient power for the subsequent use reservation. Information that recommends charging the amount can also be presented (presentation means).
また、この車載システム1は、センター装置2と同様に、利用予約を記憶してもよい(記憶手段)。更に、車載システム1は、センター装置2と同様に、第1(後)の利用予約に設定された目的地に基づく予想電力消費量及び当該第1の利用予約に設定された予定利用開始時刻までの充電可能時間に基づいて、第1の利用予約に必要な電力量が不足するかどうかを判断してもよい。さらに車載システム1は、当該第1の利用予約の不足電力量を算出してもよい(演算手段)。
In addition, the in-vehicle system 1 may store a use reservation (storage means), as with the center device 2. Furthermore, the in-vehicle system 1, similarly to the center device 2, expects power consumption based on the destination set in the first (rear) use reservation and the scheduled use start time set in the first use reservation. It may be determined whether or not the amount of power required for the first use reservation is insufficient based on the available charging time. Furthermore, the in-vehicle system 1 may calculate an insufficient power amount of the first usage reservation (calculation means).
このような車載システム1は、センター装置2からネットワークNWを介して、予約情報が送信される。この予約情報には、利用者ID、予定利用開始日時、予定利用終了日時が含まれている。電気自動車の利用者は、予定利用開始日時後に、ICカードを、車両に搭載されたICカードリーダ(図示せず)に翳す。ICカードリーダは、ICカードに記憶された利用者IDを読み取り、予約情報に含まれる利用者IDと合致する場合に、鍵装置を制御して、鍵を開状態にする。
In such an in-vehicle system 1, reservation information is transmitted from the center device 2 via the network NW. This reservation information includes a user ID, a scheduled use start date and time, and a scheduled use end date and time. The user of the electric vehicle places the IC card on an IC card reader (not shown) mounted on the vehicle after the scheduled use start date and time. The IC card reader reads the user ID stored in the IC card, and when it matches the user ID included in the reservation information, controls the key device to open the key.
また、車載システム1は、電気自動車が予定利用終了日時までにポート(帰着位置)に接続(返却)される。利用終了後において、ICカードがICカードリーダに翳される。車載システム1は、電気自動車がポートに返却されたことを現在位置情報により認識し、センター装置2に返却されたことを通知する。
In addition, the in-vehicle system 1 is connected (returned) to the port (return position) by the scheduled end date of use of the electric vehicle. After the use is completed, the IC card is put on the IC card reader. The in-vehicle system 1 recognizes that the electric vehicle has been returned to the port from the current position information, and notifies the center device 2 that it has been returned.
つぎに、上述した充電管理システムにより、電気自動車の利用者に充電を行うことを推奨する動作について図2を参照して説明する。
Next, with reference to FIG. 2, an explanation will be given of the operation recommended to charge the user of the electric vehicle by the above-described charging management system.
先ずステップS1において、車載システム1は、電気自動車が駐車場に駐車するために停まろうとしているかを検出する。なお、この電気自動車の駐車検出処理の詳細は、図3乃至図6を参照して後述する。
First, in step S1, the in-vehicle system 1 detects whether the electric vehicle is about to stop to park in the parking lot. The details of the electric vehicle parking detection process will be described later with reference to FIGS.
次のステップS2において、車載システム1は、ステップS1の駐車検出処理の結果に基づいて、電気自動車が駐車場に停まろうとしているか否かを判定する。電気自動車が駐車場に停まろうとしている場合にはステップS3に処理を進め、そうでない場合にはステップS1に処理を戻す。
In the next step S2, the in-vehicle system 1 determines whether or not the electric vehicle is about to stop at the parking lot based on the result of the parking detection process in step S1. If the electric vehicle is about to stop at the parking lot, the process proceeds to step S3. If not, the process returns to step S1.
ステップS3において、車載システム1は、電気自動車による充電の要否を判断する。なお、この充電要否の判断処理の詳細については、図7及び図8を参照して後述する。
In step S3, the in-vehicle system 1 determines whether charging by an electric vehicle is necessary. The details of the determination process of whether or not charging is necessary will be described later with reference to FIGS.
次のステップS4において、車載システム1は、ステップS3の充電要否の判断処理の結果に基づいて、電気自動車に対する充電が必要か否かを判定する。電気自動車に対する充電が必要である場合にはステップS5に処理を進め、そうでない場合にはステップS1に処理を戻す。
In the next step S4, the in-vehicle system 1 determines whether or not the electric vehicle needs to be charged based on the result of the determination process of whether or not charging is required in step S3. If the electric vehicle needs to be charged, the process proceeds to step S5, and if not, the process returns to step S1.
ステップS5において、車載システム1は、通知部19によって、電気自動車の利用者に充電を推奨する情報を提示する。なお、この充電を推奨する情報には、必要な推奨充電量を提示してもよい。また、車載システム1は、例えば電気自動車を停止するパーキングブレーキが操作された時に、充電を推奨する情報を提示してもよい。また、提示の方法は、車載ディスプレイに表示してもよく、スピーカから音声を出力してもよい。
In step S5, the in-vehicle system 1 uses the notification unit 19 to present information that recommends charging to the user of the electric vehicle. In addition, you may show required recommended charge amount to the information which recommends this charge. Moreover, the vehicle-mounted system 1 may present the information which recommends charge, for example, when the parking brake which stops an electric vehicle is operated. In addition, the presentation method may be displayed on a vehicle-mounted display, or sound may be output from a speaker.
つぎに、上述したステップS1における駐車検出処理について説明する。
Next, the parking detection process in step S1 described above will be described.
図3に示す駐車検出処理は、先ずステップS11において、位置取得部16によって電気自動車の現在位置情報を取得する。
3, first, in step S11, the position acquisition unit 16 acquires current position information of the electric vehicle.
次のステップS12において、車載システム1の位置検索部17は、地図データベース15を参照して、ステップS11により取得された現在位置の種別を照合する。この種別は、例えば駐車場といった情報である。
In the next step S12, the position search unit 17 of the in-vehicle system 1 refers to the map database 15 and collates the type of the current position acquired in step S11. This type is information such as a parking lot.
次のステップS13において、車載システム1は、ステップS12の処理の結果、現在位置の種別が駐車場か否かを判定する。現在位置の種別が駐車場である場合にはステップS14に処理を進め、そうでない場合にはステップS11に処理を戻す。
In the next step S13, the in-vehicle system 1 determines whether or not the type of the current position is a parking lot as a result of the process in step S12. If the type of the current position is a parking lot, the process proceeds to step S14; otherwise, the process returns to step S11.
ステップS14において、車載システム1は、電気自動車が現在、駐車場に駐車している最中であると判断する。
In step S14, the in-vehicle system 1 determines that the electric vehicle is currently parked in the parking lot.
以上のように、この車載システム1によれば、取得した現在位置が駐車場データベース14に記憶された駐車場である場合に、車両の駐車を検出する。これによって、車載システム1によれば、電気自動車が駐車する場合にのみ利用者に充電を推奨できる。充電が必要な場合に、例えば走行中等に頻繁に充電の推奨をすることを抑制できる。
As described above, according to this in-vehicle system 1, when the acquired current position is a parking lot stored in the parking lot database 14, parking of the vehicle is detected. Thereby, according to the vehicle-mounted system 1, charging can be recommended to the user only when the electric vehicle is parked. When charging is necessary, for example, frequent recommendation of charging during traveling can be suppressed.
図4に示す駐車検出処理は、先ずステップS21において、車載システム1は、経路探索部18により経路探索するための目的地が入力されているか否かを判定する。このとき、車載システム1は、経路探索部18によって目的地情報を記憶しているか否かを判定する。目的地が入力されていると判定した場合にはステップS22に処理を進め、そうでない場合には処理を終了する。
In the parking detection process shown in FIG. 4, first, in step S <b> 21, the in-vehicle system 1 determines whether or not a destination for route search is input by the route search unit 18. At this time, the in-vehicle system 1 determines whether or not the destination information is stored by the route search unit 18. If it is determined that the destination has been input, the process proceeds to step S22. If not, the process ends.
ステップS22において、車載システム1は、位置取得部16によって電気自動車の現在位置情報を取得する。
In step S <b> 22, the in-vehicle system 1 acquires the current position information of the electric vehicle by the position acquisition unit 16.
ステップS23において、車載システム1は、位置検索部17によってステップS22にて取得した現在位置が、ステップS21にて入力されていると判定された目的地の周辺か否かを判定する。例えば、位置検索部17は、現在位置が目的地から数10メートルの範囲内である場合に、電気自動車が目的地周辺に位置していると判定する。また、位置検索部17は、電気自動車が目的地に向かって走行していることを、電気自動車の現在位置が目的地周辺であると判定する条件にしてもよい。電気自動車の現在位置が目的地周辺であると判定した場合にはステップS24に処理を進め、そうでない場合には処理を終了する。
In step S23, the in-vehicle system 1 determines whether or not the current position acquired in step S22 by the position search unit 17 is around the destination determined to have been input in step S21. For example, the position search unit 17 determines that the electric vehicle is located around the destination when the current position is within a range of several tens of meters from the destination. Further, the position search unit 17 may determine that the current position of the electric vehicle is around the destination that the electric vehicle is traveling toward the destination. If it is determined that the current position of the electric vehicle is around the destination, the process proceeds to step S24, and if not, the process ends.
ステップS24において、車載システム1は、目的地に到着して以降に電気自動車が駐車すると判断する。
In step S24, the in-vehicle system 1 determines that the electric vehicle is parked after arrival at the destination.
以上のように、この車載システム1によれば、取得された現在位置が利用予約に設定された目的地周辺であることを検出した場合に、車両の駐車を検出する。これによって、車載システム1によれば、電気自動車が駐車する場合にのみ利用者に車載バッテリの充電を推奨できる。充電が必要な場合に、例えば走行中等に頻繁に充電の推奨をすることを抑制できる。
As described above, according to this in-vehicle system 1, when it is detected that the acquired current position is around the destination set in the use reservation, parking of the vehicle is detected. Thereby, according to the in-vehicle system 1, it is possible to recommend charging of the in-vehicle battery to the user only when the electric vehicle is parked. When charging is necessary, for example, frequent recommendation of charging during traveling can be suppressed.
図5に示す駐車検出処理は、先ずステップS31において、車載システム1の経路探索部18によって、駐車場が検索されたか否かを判定する。このとき、車載システム1は、利用者のボタン等の操作を受け付けて、周辺施設として駐車場が検索されたか否かを判定する。駐車場が検索されたと判定した場合にはステップS32に処理を進め、そうでない場合には処理を終了する。
The parking detection process shown in FIG. 5 first determines in step S31 whether or not the parking lot has been searched by the route search unit 18 of the in-vehicle system 1. At this time, the in-vehicle system 1 accepts a user's operation such as a button, and determines whether or not a parking lot has been searched as a peripheral facility. If it is determined that a parking lot has been searched, the process proceeds to step S32. If not, the process ends.
ステップS32において、車載システム1は、利用者が電気自動車を駐車場に駐車しようとしているため、以降に電気自動車が駐車すると判断する。
In step S32, the in-vehicle system 1 determines that the electric vehicle is parked after that because the user is about to park the electric vehicle in the parking lot.
以上のように、この車載システム1によれば、利用者による駐車場を検索する操作を検出した場合に、車両の駐車を検出する。これによって、車載システム1によれば、電気自動車が駐車する場合にのみ利用者に充電を推奨できる。充電が必要な場合に、例えば走行中等に頻繁に充電の推奨をすることを抑制できる。
As described above, according to the in-vehicle system 1, when an operation for searching for a parking lot by a user is detected, parking of the vehicle is detected. Thereby, according to the vehicle-mounted system 1, charging can be recommended to the user only when the electric vehicle is parked. When charging is necessary, for example, frequent recommendation of charging during traveling can be suppressed.
図6に示す駐車検出処理は、先ずステップS41において、車載システム1の通信部11によって、予定表データベース4にアクセスする。このとき、車載システム1は、電気自動車のID、利用者ID等を含む予定表のダウンロード要求を予定表データベース4に送信する。
The parking detection process shown in FIG. 6 first accesses the schedule table database 4 by the communication unit 11 of the in-vehicle system 1 in step S41. At this time, the in-vehicle system 1 transmits a schedule download request including the ID of the electric vehicle, the user ID, and the like to the schedule table database 4.
次のステップS42において、車載システム1は、予定表データベース4から、電気自動車のID、利用者IDに合致した予定表を取得する。車載システム1は、取得した予定表に含まれる利用予約から、現在の目的地の取得ができたか否かを判定する。現在の目的地が取得できたと判定した場合にはステップS43に処理を進め、そうでない場合には処理を終了する。
In the next step S42, the in-vehicle system 1 acquires from the schedule table database 4 a schedule table that matches the electric vehicle ID and user ID. The in-vehicle system 1 determines whether or not the current destination has been acquired from the use reservation included in the acquired schedule. If it is determined that the current destination has been acquired, the process proceeds to step S43. If not, the process ends.
ステップS43において、車載システム1の位置取得部16は、電気自動車の現在位置情報を取得する。
In step S43, the position acquisition unit 16 of the in-vehicle system 1 acquires current position information of the electric vehicle.
次のステップS44において、車載システム1は、位置検索部17によってステップS43にて取得した現在位置が、ステップS42にて取得できた目的地の付近か否かを判定する。例えば、位置検索部17は、現在位置が目的地から数10メートルの範囲内である場合に、電気自動車が目的地の付近に位置していると判定する。また、位置検索部17は、予定通りの予定時刻に、目的地に到着する可能性が高いことを判定してもよい。電気自動車の現在位置が目的地付近であると判定した場合にはステップS45に処理を進め、そうでない場合にはステップS43に処理を戻す。
In the next step S44, the in-vehicle system 1 determines whether or not the current position acquired in step S43 by the position search unit 17 is near the destination acquired in step S42. For example, the position search unit 17 determines that the electric vehicle is located near the destination when the current position is within a range of several tens of meters from the destination. Further, the position search unit 17 may determine that there is a high possibility of arrival at the destination at the scheduled time as scheduled. If it is determined that the current position of the electric vehicle is near the destination, the process proceeds to step S45, and if not, the process returns to step S43.
ステップS45において、車載システム1は、目的地に到着して以降に電気自動車が駐車すると判断する。また、車載システム1は、予定された目的地に予定時刻に近づいた時に、以降に駐車が行われると判断する。
In step S45, the in-vehicle system 1 determines that the electric vehicle is parked after arrival at the destination. In addition, the in-vehicle system 1 determines that parking is performed thereafter when the scheduled time approaches the scheduled time.
以上のように、この車載システム1によれば、取得された現在位置が利用予約に設定された目的地周辺であることを検出した場合に、車両の駐車を検出する。これによって、車載システム1によれば、電気自動車が駐車する場合にのみ利用者に充電を推奨できる。充電が必要な場合に、例えば走行中等に頻繁に充電の推奨をすることを抑制できる。
As described above, according to this in-vehicle system 1, when it is detected that the acquired current position is around the destination set in the use reservation, parking of the vehicle is detected. Thereby, according to the vehicle-mounted system 1, charging can be recommended to the user only when the electric vehicle is parked. When charging is necessary, for example, frequent recommendation of charging during traveling can be suppressed.
つぎに、上述したステップS3の充電要否の判断処理について説明する。
Next, the process for determining whether or not charging is necessary in step S3 will be described.
図7に示す充電要否の判断処理は、先ずステップS51において、車載システム1の車両センサー12によって、車載バッテリの充電残量を取得する。
7, first, in step S51, the vehicle sensor 12 of the in-vehicle system 1 acquires the remaining charge amount of the in-vehicle battery.
次のステップS52において、車載システム1は、ステップS51で取得した車載バッテリの充電残量が、閾値よりも少ないか否かを判定する。この閾値は、予め設定された値(例えばSOCが20%)であってもよく、電気自動車の現在位置の目的地までの距離や、電気自動車の現在位置から帰着位置までの距離に基づいて変動させてもよい。充電残量が閾値よりも少ないと判定した場合にはステップS53に処理を進め、そうでない場合にはステップS54に処理を進める。
In the next step S52, the in-vehicle system 1 determines whether or not the remaining charge amount of the in-vehicle battery acquired in step S51 is less than a threshold value. This threshold value may be a preset value (for example, SOC is 20%), and varies based on the distance from the current position of the electric vehicle to the destination or the distance from the current position of the electric vehicle to the return position. You may let them. If it is determined that the remaining charge is less than the threshold, the process proceeds to step S53, and if not, the process proceeds to step S54.
ステップS53において、車載システム1は、通知部19によって電気自動車の充電を推奨する情報を利用者に提示する。一方、ステップS54において、車載システム1は、通知部19によって充電を推奨しない。
In step S53, the in-vehicle system 1 presents information recommending charging of the electric vehicle to the user by the notification unit 19. On the other hand, in step S54, the in-vehicle system 1 does not recommend charging by the notification unit 19.
これにより、この充電管理システムによれば、車載バッテリの充電残量が少なくなった場合に電気自動車の充電を推奨する情報を提示でき、頻繁に充電が推奨されて煩わしさを与えることなく、必要に応じて充電を推奨できる。また、駐車を検出した場合に常に充電するように伝えることも可能であるが、この車載システム1によれば推奨回数を抑制できる。
As a result, according to this charge management system, it is possible to present information that recommends charging of an electric vehicle when the remaining charge of the on-vehicle battery is low, and it is necessary without frequently bothering because charging is recommended frequently. Charging can be recommended depending on Although it is possible to tell to always charge when parking is detected, the in-vehicle system 1 can suppress the recommended number of times.
また、この充電要否の判断処理は、駐車検出処理によって得られた駐車しようとする位置周辺に充電器が存在する場合に、充電を推奨する情報を提示することが望ましい。このために、車載システム1は、位置取得部16によって電気自動車の現在位置を取得し、充電器の位置を記憶した充電器データベース13を参照する。そして、電気自動車の現在位置が充電器データベース13に記憶された充電器の周辺である場合に、車載バッテリの充電を推奨する情報又は後続利用予約の不足電力量を充電することを推奨する情報を提示する。これにより、この車載システム1によれば、電気自動車の駐車を検出し、電気自動車の充電が必要であり、更に、充電器が存在する場合に充電を推奨でき、駐車するために充電器まで移動させることができる。また、この車載システム1によれば、充電を推奨する情報中に充電器の位置を含めてもよい。更に、車載システム1は、経路探索部18によって、電気自動車の駐車位置を充電器が存在する位置に変更してもよい。例えば、立体駐車場の3階に充電器がある場合、充電を推奨する情報に「3階の充電器に接続してください」といった情報を含めることができる。
Further, it is desirable that the determination process for determining whether charging is necessary presents information that recommends charging when there is a charger around the position to be parked obtained by the parking detection process. For this purpose, the in-vehicle system 1 acquires the current position of the electric vehicle by the position acquisition unit 16 and refers to the charger database 13 in which the position of the charger is stored. Then, when the current position of the electric vehicle is around the charger stored in the charger database 13, information recommending charging of the in-vehicle battery or information recommending charging the insufficient power amount of the subsequent use reservation is provided. Present. Thereby, according to this in-vehicle system 1, it is necessary to detect the parking of the electric vehicle, and the electric vehicle needs to be charged. Further, when the charger exists, the charging can be recommended, and the vehicle is moved to the charger for parking. Can be made. Moreover, according to this vehicle-mounted system 1, you may include the position of a charger in the information which recommends charging. Furthermore, the vehicle-mounted system 1 may change the parking position of the electric vehicle to a position where the charger exists by the route search unit 18. For example, when there is a charger on the third floor of the multilevel parking lot, information such as “Please connect to the charger on the third floor” can be included in the information that recommends charging.
図8に示す充電要否の判断処理は、先ずステップS61において、車載システム1の車両センサー12によって、車載バッテリの充電残量P1を取得する。
8, first, in step S61, the vehicle sensor 12 of the in-vehicle system 1 acquires the remaining charge P1 of the in-vehicle battery.
次のステップS62乃至ステップS65において、車載システム1は、第1(後)の利用予約に必要な電力量が不足するかどうかを判断する。次のステップS62において、車載システム1は、電気自動車が帰着ポートまで走行するために消費する消費電力量P2を推定する。このとき、車載システム1は、現在位置から目的地までの距離、平均走行速度、単位距離あたりの電力消費量等に基づいて、消費電力量P2を推定する。
In the next step S62 to step S65, the in-vehicle system 1 determines whether or not the amount of power necessary for the first (rear) use reservation is insufficient. In the next step S62, the in-vehicle system 1 estimates the power consumption P2 that the electric vehicle consumes to travel to the return port. At this time, the in-vehicle system 1 estimates the power consumption P2 based on the distance from the current position to the destination, the average travel speed, the power consumption per unit distance, and the like.
次のステップS63において、車載システム1は、現在の利用予約における予定利用終了日時から、次の利用予約における予定利用開始日時までに充電できる充電可能電力量P3を推定する。この充電可能電力量P3は、現在の利用予約における現在の利用予約における予定利用終了日時から、次の利用予約における予定利用開始日時までの充電可能時間に、充電器の単位時間あたりの充電量を乗算することによって推定する。
In the next step S63, the in-vehicle system 1 estimates the chargeable power amount P3 that can be charged from the scheduled use end date / time in the current use reservation to the scheduled use start date / time in the next use reservation. This chargeable power amount P3 is calculated by calculating the amount of charge per unit time of the charger from the scheduled use end date / time in the current use reservation to the scheduled use start date / time in the next use reservation. Estimate by multiplying.
次のステップS64において、車載システム1は、次の利用予約によって消費される予想電力消費量P4を算出する。このとき、車載システム1は、次の利用予約に設定された目的地情報に基づいて、予想電力消費量P4を算出する。例えば、帰着ポートの位置や目的地の位置に応じた移動距離と単位距離あたりの消費電力量とに基づいて予想電力消費量P4を算出する。
In the next step S64, the in-vehicle system 1 calculates an expected power consumption P4 consumed by the next use reservation. At this time, the in-vehicle system 1 calculates the predicted power consumption P4 based on the destination information set for the next use reservation. For example, the predicted power consumption P4 is calculated based on the moving distance according to the position of the return port or the destination and the power consumption per unit distance.
次のステップS65において、車載システム1は、ステップS61にて取得した充電残量P1から消費電力量P2及び充電可能電力量P3を差し引いた不足電力量が、予想電力消費量P4以下であるか否かを判定する。この不足電力量は、次の利用予約で必要な電力量の不足分である。不足電力量が予想電力消費量P4以下であると判定した場合にはステップS66に処理を進め、そうでない場合にはステップS67に処理を戻す。
In the next step S65, the in-vehicle system 1 determines whether or not the insufficient power amount obtained by subtracting the power consumption amount P2 and the chargeable power amount P3 from the remaining charge amount P1 acquired in step S61 is equal to or less than the predicted power consumption amount P4. Determine whether. This insufficient power amount is a shortage of the power amount necessary for the next use reservation. If it is determined that the insufficient power amount is equal to or less than the predicted power consumption P4, the process proceeds to step S66, and if not, the process returns to step S67.
ステップS66において、車載システム1は、通知部19によって電気自動車の充電を推奨する情報を利用者に提示する。これにより、車載システム1は、以降の利用予約に設定された予定利用開始時刻より以前に予定利用終了時刻が設定されている現在の利用予約によって車両を利用している期間に、車載バッテリの充電を推奨する情報又は不足電力量を充電することを推奨する情報を提示できる。一方、ステップS67において、車載システム1は、通知部19によって充電を推奨しない。
In step S66, the in-vehicle system 1 presents information recommending charging of the electric vehicle to the user by the notification unit 19. As a result, the in-vehicle system 1 charges the in-vehicle battery during a period in which the vehicle is used by the current use reservation in which the scheduled use end time is set before the scheduled use start time set in the subsequent use reservation. Information recommending charging, or information recommending charging the amount of insufficient power can be presented. On the other hand, in step S <b> 67, the in-vehicle system 1 does not recommend charging by the notification unit 19.
また、この充電要否の判断処理は、図7と同様に、駐車検出処理によって得られた駐車しようとする位置周辺に充電器が存在する場合に、充電を推奨する情報を提示することが望ましい。このために、車載システム1は、位置取得部16によって電気自動車の現在位置を取得し、充電器の位置を記憶した充電器データベース13を参照する。そして、電気自動車の現在位置が充電器データベース13に記憶された充電器の周辺である場合に、車載バッテリの充電を推奨する情報又は後続利用予約の不足電力量を充電することを推奨する情報を提示する。これにより、この車載システム1によれば、電気自動車の駐車を検出し、電気自動車の充電が必要であり、更に、充電器が存在する場合に充電を推奨でき、駐車するために充電器まで移動させることができる。また、この車載システム1によれば、充電を推奨する情報中に充電器の位置を含めてもよい。更に、車載システム1は、経路探索部18によって、電気自動車の駐車位置を充電器が存在する位置に変更してもよい。例えば、立体駐車場の3階に充電器がある場合、充電を推奨する情報に「3階の充電器に接続してください」といった情報を含めることができる。
In addition, in the determination process of whether or not charging is necessary, it is desirable to present information recommending charging when there is a charger around the position to be parked obtained by the parking detection process, as in FIG. . For this purpose, the in-vehicle system 1 acquires the current position of the electric vehicle by the position acquisition unit 16 and refers to the charger database 13 in which the position of the charger is stored. Then, when the current position of the electric vehicle is around the charger stored in the charger database 13, information recommending charging of the in-vehicle battery or information recommending charging the insufficient power amount of the subsequent use reservation is provided. Present. Thereby, according to this in-vehicle system 1, it is necessary to detect the parking of the electric vehicle, and the electric vehicle needs to be charged. Further, when the charger exists, the charging can be recommended, and the vehicle is moved to the charger for parking. Can be made. Moreover, according to this vehicle-mounted system 1, you may include the position of a charger in the information which recommends charging. Furthermore, the vehicle-mounted system 1 may change the parking position of the electric vehicle to a position where the charger exists by the route search unit 18. For example, when there is a charger on the third floor of the multilevel parking lot, information such as “Please connect to the charger on the third floor” can be included in the information that recommends charging.
更に、この車載システム1は、充電を推奨する情報中に、次の利用予約において不足電力が発生する可能性があり、現在の利用において充電することが望ましいことを提示してもよい。
Furthermore, this in-vehicle system 1 may present in the information recommending charging that there is a possibility that insufficient power may occur in the next usage reservation, and it is desirable to charge in the current usage.
以上のように、この充電管理システムによれば、例えば図9に示すように、次の利用予約のために充電を実施できる。例えば、次の利用予約のための車載バッテリの充電残量が90%以上必要であるとする。
As described above, according to this charging management system, for example, as shown in FIG. 9, charging can be performed for the next use reservation. For example, it is assumed that the remaining charge of the in-vehicle battery for the next use reservation needs to be 90% or more.
前の利用予約において次の利用予約のために充電を推奨しない比較例を図9(a)に示す。この比較例では、前の利用予約の利用開始時の充電残量は、100%であり、目的地までの走行(行き)によって充電残量が30%減少し、目的地から帰着ポートまでの走行(帰り)によって更に充電残量が30%減少してしまう。また、前の利用予約の予定利用終了日時から次の利用予約の予定利用開始日時までの充電可能電力量によって、30%の充電残量しか充電できない。したがって、比較例では、次の利用予約のために充電残量で20%の電力不足が発生してしまう。
9A shows a comparative example in which charging is not recommended for the next usage reservation in the previous usage reservation. In this comparative example, the remaining charge amount at the start of use of the previous use reservation is 100%, and the remaining charge amount is reduced by 30% by traveling (going) to the destination, and traveling from the destination to the return port. (Return) further reduces the remaining charge by 30%. Further, only 30% of the remaining charge can be charged depending on the chargeable power amount from the scheduled use end date and time of the previous use reservation to the scheduled use start date and time of the next use reservation. Therefore, in the comparative example, a power shortage of 20% occurs in the remaining charge for the next use reservation.
一方、本実施形態として示した充電管理システムは、目的地までの走行(行き)によって充電残量が30%減少した時に、駐車検出処理によって駐車を検出して、図8の充電要否の判断処理によって、充電残量で20%以上の充電を推奨する情報を提示できる。この結果、出先の駐車場に設置された充電器によって、充電残量で21%の充電ができる。その後、目的地から帰着ポートまでの走行(帰り)によって更に充電残量が30%減少して充電残量が61%となっても、前の利用予約の予定利用終了日時から次の利用予約の予定利用開始日時までの充電可能電力量によって、次の利用予約の予定利用開始日時までに充電残量を91%まで上昇させることができる。これによって、充電管理システムは、次の利用予約の走行によって電力不足となることを抑制できる。
On the other hand, the charge management system shown as this embodiment detects parking by the parking detection process when the remaining charge is reduced by 30% due to traveling (going) to the destination, and determines whether or not charging is necessary in FIG. By processing, it is possible to present information that recommends charging with a remaining charge of 20% or more. As a result, the charger installed in the parking lot at the destination can charge 21% with the remaining charge. After that, even if the remaining charge level further decreases by 30% and the remaining charge level reaches 61% due to travel from the destination to the return port (return), the next use reservation will be started from the scheduled use end date and time of the previous use reservation. Depending on the amount of chargeable power up to the scheduled use start date and time, the remaining charge can be increased to 91% by the scheduled use start date and time of the next use reservation. Thereby, the charge management system can suppress the power shortage due to the travel of the next use reservation.
更に、この充電管理システムは、次の利用予約によって十分な電力量が車載バッテリに充電されている場合には、充電を行うことができても、充電を推奨する情報の提示を行わない。例えば図10(a)に示すように、利用予約nにおいて、駐車する時点での充電残量が8kwhであり、帰着ポートまでの消費電力量が3kwhであり、充電可能電力量が3kwhであるとする。これに対し、次の利用予約n+1の消費電力量が5kwhであったする。この場合、次の利用予約n+1の予定利用開始日時において8kwhの充電残量が確保できる。したがって、車載システム1は、利用予約nにおいて駐車を検出しても、充電を推奨する情報を提示しない。
Furthermore, this charging management system does not present information that recommends charging even if charging can be performed when a sufficient amount of power is charged in the in-vehicle battery by the next use reservation. For example, as shown in FIG. 10A, in the use reservation n, the remaining charge at the time of parking is 8 kwh, the power consumption up to the return port is 3 kwh, and the chargeable power is 3 kwh. To do. On the other hand, the power consumption of the next usage reservation n + 1 is 5 kwh. In this case, the remaining charge amount of 8 kwh can be secured at the scheduled use start date and time of the next use reservation n + 1. Therefore, even if the vehicle-mounted system 1 detects parking in the use reservation n, it does not present information that recommends charging.
一方、充電管理システムは、図10(b)に示すように、利用予約nにおいて、駐車する時点での充電残量が9kwhであり、帰着ポートまでの消費電力量が3kwhであり、充電可能電力量が3kwhであるとする。これに対し、次の利用予約n+1の消費電力量が10kwhであったする。この場合、次の利用予約n+1の予定利用開始日時において9kwhの充電残量しかない。したがって、車載システム1は、利用予約nにおいて駐車を検出した場合に、充電を推奨する情報を提示する。
On the other hand, as shown in FIG. 10 (b), the charge management system has a remaining charge of 9 kwh at the time of parking in the use reservation n, a power consumption of 3 kwh up to the return port, and a chargeable power Let the amount be 3 kwh. On the other hand, the power consumption of the next usage reservation n + 1 is 10 kwh. In this case, there is only a remaining charge of 9 kwh at the scheduled use start date and time of the next use reservation n + 1. Therefore, when the in-vehicle system 1 detects parking in the use reservation n, it presents information that recommends charging.
更に、この充電管理システムは、目的地における滞在時間に応じて充電を推奨する情報を提示するか否かを切り換えてもよい。例えば図11に示すように、利用予約nに2つの目的地が含まれ、当該目的地の滞在時間が異なっていたとする。この場合、車載システム1は、予定表データベース4から利用予約nの予定表をダウンロードして、各目的地の滞在時間を取得する。車載システム1は、駐車P1における滞在時間と、駐車P2における滞在時間とを参照して、駐車P1における滞在時間によって不足電力量の充電が可能であると判定する。車載システム1は、駐車P1における滞在時間に対応した駐車を検出した場合に、充電を推奨する情報を提示する。これにより、車載システム1は、駐車P1における滞在時間で不足電力量を充電させる。車載システム1は、次の駐車P2における滞在時間となった場合には、駐車を検出しても充電を推奨する情報を提示しない。
Furthermore, this charging management system may switch whether or not to present information recommending charging according to the stay time at the destination. For example, as shown in FIG. 11, it is assumed that the use reservation n includes two destinations and the stay times at the destinations are different. In this case, the in-vehicle system 1 downloads the schedule for use reservation n from the schedule table database 4 and acquires the stay time at each destination. The in-vehicle system 1 refers to the stay time in the parking P <b> 1 and the stay time in the parking P <b> 2, and determines that the insufficient power amount can be charged by the stay time in the parking P <b> 1. The in-vehicle system 1 presents information recommending charging when detecting parking corresponding to the staying time in the parking P1. Thereby, the vehicle-mounted system 1 charges the insufficient power amount with the stay time in the parking P1. The in-vehicle system 1 does not present information that recommends charging even when parking is detected when the stay time in the next parking P2 is reached.
図11とは逆に、先に不足電力量の充電ができない短い滞在時間の駐車P1があり、次に不足電力量の充電が可能な長い駐車P2がある場合であっても、図12に示すように、先の駐車P1では充電を推奨せず、次の駐車P2を検出した場合に充電を推奨する情報を提示する。
Contrary to FIG. 11, even when there is a parking period P <b> 1 of a short stay time that cannot be charged with an insufficient amount of electric power first, and then there is a long parking period P <b> 2 that can be charged with an insufficient electric power amount, FIG. Thus, in the previous parking P1, charging is not recommended, and information that recommends charging is presented when the next parking P2 is detected.
以上のように、この充電管理システムによれば、前の利用予約の滞在時間に応じて、不足電力量の充電が可能な場合にのみ、充電を推奨する情報を提示する。
As described above, according to this charge management system, information that recommends charging is presented only when charging with an insufficient amount of power is possible according to the stay time of the previous use reservation.
なお、上述の実施の形態は本発明の一例である。このため、本発明は、上述の実施形態に限定されることはなく、この実施の形態以外であっても、本発明に係る技術的思想を逸脱しない範囲であれば、設計等に応じて種々の変更が可能であることは勿論である。
The above embodiment is an example of the present invention. For this reason, the present invention is not limited to the above-described embodiment, and various modifications can be made depending on the design and the like as long as the technical idea according to the present invention is not deviated from this embodiment. Of course, it is possible to change.
特願2012-054598号(出願日:2012年03月12日)の全内容は、ここに援用される。
The entire contents of Japanese Patent Application No. 2012-054598 (filing date: March 12, 2012) are incorporated herein by reference.
本発明によれば、第1の利用予約の不足電力量を、第1の利用予約より以前の第2の利用予約によって車両を利用している期間に、車載バッテリに充電することを推奨する情報を提示するので、車両の充電不足を抑制することができる。
According to the present invention, the information recommending that the in-vehicle battery be charged during the period in which the vehicle is used by the second usage reservation before the first usage reservation is used for the insufficient power amount of the first usage reservation. Therefore, insufficient charging of the vehicle can be suppressed.
1 車載システム
2 センター装置
3 利用者端末
4 予定表データベース
11 通信部
12 車両センサー
13 充電器データベース
14 駐車場データベース
15 地図データベース
16 位置取得部
17 位置検索部
18 経路探索部
19 通知部
21 車両予約管理部
22 通信部 DESCRIPTION OF SYMBOLS 1 In-vehicle system 2 Center apparatus 3 User terminal 4 Schedule table 11 Communication part 12 Vehicle sensor 13 Charger database 14 Parking lot database 15 Map database 16 Location acquisition part 17 Position search part 18 Route search part 19 Notification part 21 Vehicle reservation management Part 22 Communication Department
2 センター装置
3 利用者端末
4 予定表データベース
11 通信部
12 車両センサー
13 充電器データベース
14 駐車場データベース
15 地図データベース
16 位置取得部
17 位置検索部
18 経路探索部
19 通知部
21 車両予約管理部
22 通信部 DESCRIPTION OF SYMBOLS 1 In-
Claims (10)
- 車両の予定利用開始時刻、予定利用終了時刻及び目的地が設定された利用予約、車両の充電可能時間を記憶し、第1の利用予約に設定された目的地に基づく予想電力消費量及び当該第1の利用予約に設定された予定利用開始時刻までの充電可能時間に基づいて、当該第1の利用予約に必要な電力量が不足するかどうかを判断する充電管理装置と、
前記充電管理装置によって前記第1の利用予約に必要な電力量が不足する場合に、前記第1の利用予約に設定された予定利用開始時刻より以前に予定利用終了時刻が設定されている第2の利用予約によって車両を利用している期間に車載バッテリに充電することを推奨する情報を提示する車載装置と
を備えることを特徴とする充電管理システム。 The scheduled use start time of the vehicle, the scheduled use end time, the use reservation in which the destination is set, the chargeable time of the vehicle are stored, the expected power consumption based on the destination set in the first use reservation, and the first A charge management device that determines whether or not the amount of power required for the first use reservation is insufficient based on the chargeable time until the scheduled use start time set in the one use reservation;
The scheduled use end time is set before the scheduled use start time set in the first use reservation when the power management apparatus has insufficient power amount for the first use reservation. And a vehicle-mounted device that presents information recommending that the vehicle-mounted battery be charged during a period in which the vehicle is being used according to the use reservation. - 前記充電管理装置は、前記第1の利用予約に設定された目的地に基づく予想電力消費量及び当該第1の利用予約に設定された予定利用開始時刻までの充電可能時間に基づいて、当該第1の利用予約の不足電力量を算出し、
前記車載装置は、前記第2の利用予約によって車両を利用している期間に、前記不足電力量を充電することを推奨する情報を提示すること
を備えることを特徴とする請求項1に記載の充電管理システム。 The charge management device is configured based on the estimated power consumption based on the destination set in the first use reservation and the chargeable time until the scheduled use start time set in the first use reservation. Calculate the power shortage of 1 usage reservation,
The said in-vehicle apparatus is provided with the information which recommends charging the said insufficient electric energy in the period using the vehicle by the said 2nd use reservation. Charge management system. - 前記車載装置は、車両の現在位置を取得する位置取得手段と、充電器の位置を記憶した充電器位置記憶手段とを含み、
前記位置取得手段によって取得した現在位置が前記充電器位置記憶手段に記憶された充電器の周辺である場合に、前記車載バッテリに充電することを推奨する情報を提示することを特徴とする請求項1に記載の充電管理システム。 The in-vehicle device includes position acquisition means for acquiring the current position of the vehicle, and charger position storage means for storing the position of the charger,
The present invention presents information that recommends charging the in-vehicle battery when the current position acquired by the position acquisition means is around the charger stored in the charger position storage means. The charge management system according to 1. - 前記車載装置は、車両の駐車を検出する駐車検出手段を備え、前記駐車検出手段によって駐車を検出した場合に、前記車載バッテリに充電することを推奨する情報を提示することを特徴とする請求項3に記載の充電管理システム。 The said in-vehicle device is provided with parking detection means for detecting parking of a vehicle, and presents information recommending that the in-vehicle battery is charged when parking is detected by the parking detection means. 3. The charge management system according to 3.
- 前記車載装置は、車両の現在位置を取得する位置取得手段と、駐車場の位置を記憶した駐車場位置記憶手段とを含み、
前記駐車検出手段は、前記位置取得手段によって取得した現在位置が前記駐車場位置記憶手段に記憶された駐車場である場合に、車両の駐車を検出することを特徴とする請求項4に記載の充電管理システム。 The in-vehicle device includes position acquisition means for acquiring the current position of the vehicle, and parking lot position storage means for storing the position of the parking lot,
The said parking detection means detects parking of a vehicle, when the present position acquired by the said position acquisition means is a parking lot memorize | stored in the said parking lot position storage means. Charge management system. - 前記車載装置は、車両の利用者の操作に応じて駐車場を検索する検索手段を含み、
前記駐車検出手段は、前記検索手段により車両の利用者による駐車場を検索する操作を検出した場合に、車両の駐車を検出することを特徴とする請求項4に記載の充電管理システム。 The in-vehicle device includes search means for searching for a parking lot in response to an operation of a vehicle user,
The charge management system according to claim 4, wherein the parking detection unit detects parking of the vehicle when the search unit detects an operation of searching for a parking lot by a user of the vehicle. - 前記車載装置は、車両の現在位置を取得する位置取得手段を含み、
前記駐車検出手段は、前記位置取得手段によって取得された現在位置が前記利用予約に設定された目的地周辺であることを検出した場合に、車両の駐車を検出することを特徴とする請求項4に記載の充電管理システム。 The in-vehicle device includes position acquisition means for acquiring a current position of the vehicle,
5. The parking detection unit detects parking of a vehicle when detecting that the current position acquired by the position acquisition unit is around a destination set in the use reservation. Charge management system as described in. - 前記利用予約に目的地における滞在時間を設定し、
前記車載装置は、前記滞在時間によって前記不足電力量の充電が可能な場合に前記不足電力量を充電することを推奨する情報を提示し、前記滞在時間によって前記不足電力量の充電が可能な場合に前記不足電力量を充電することを推奨する情報を提示しないことを特徴とする請求項7に記載の充電管理システム。 Set the stay time at the destination in the use reservation,
The in-vehicle device presents information recommending that the insufficient power amount is charged when the insufficient power amount can be charged according to the stay time, and the insufficient power amount can be charged according to the stay time. The charging management system according to claim 7, wherein information recommending that the amount of insufficient power is charged is not presented. - 車両の予定利用開始時刻、予定利用終了時刻及び目的地に設定された利用予約、車両の充電可能時間を記憶するステップと、
第1の利用予約に設定された目的地に基づく予想電力消費量及び当該第1の利用予約に設定された予定利用開始時刻までの充電可能時間に基づいて、第1の利用予約に必要な電力量が不足するかどうかを判断するステップと、
前記第1の利用予約に必要な電力量が不足する場合に、前記第1の利用予約に設定された予定利用開始時刻より以前に予定利用終了時刻が設定されている第2の利用予約によって車両を利用している期間に、前記車載バッテリに充電することを推奨する情報を提示するステップと
を含むことを特徴とする充電管理方法。 Storing the scheduled use start time of the vehicle, the scheduled use end time, the use reservation set at the destination, and the chargeable time of the vehicle;
Electric power required for the first use reservation based on the expected power consumption based on the destination set in the first use reservation and the chargeable time until the scheduled use start time set in the first use reservation Determining whether the amount is insufficient,
When the amount of power required for the first use reservation is insufficient, the vehicle is set by the second use reservation in which the scheduled use end time is set before the scheduled use start time set in the first use reservation. And a step of presenting information recommending that the in-vehicle battery be charged during a period in which the battery is used. - 車両の予定利用開始時刻、予定利用終了時刻及び目的地が設定された利用予約、車両の充電可能時間を記憶する記憶手段と、
第1の利用予約に設定された目的地に基づく予想電力消費量及び当該第1の利用予約に設定された予定利用開始時刻までの充電可能時間に基づいて、当該第1の利用予約に必要な電力量が不足するかどうかを判断する演算手段と、
前記第1の利用予約に必要な電力量が不足する場合に、前記第1の利用予約に設定された予定利用開始時刻より以前に予定利用終了時刻が設定されている第2の利用予約によって車両を利用している期間に、車載バッテリに充電することを推奨する情報を提示する提示手段と
を備えることを特徴とする車載装置。 Storage means for storing the scheduled use start time of the vehicle, the scheduled use end time and the use reservation set with the destination, and the chargeable time of the vehicle;
Necessary for the first use reservation based on the expected power consumption based on the destination set in the first use reservation and the chargeable time until the scheduled use start time set in the first use reservation. A calculation means for determining whether the amount of electric power is insufficient,
When the amount of power required for the first use reservation is insufficient, the vehicle is set by the second use reservation in which the scheduled use end time is set before the scheduled use start time set in the first use reservation. An in-vehicle device comprising: presentation means for presenting information that recommends charging the in-vehicle battery during a period of using the in-vehicle battery.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012054598 | 2012-03-12 | ||
| JP2012-054598 | 2012-03-12 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2013137190A1 true WO2013137190A1 (en) | 2013-09-19 |
Family
ID=49161099
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2013/056629 WO2013137190A1 (en) | 2012-03-12 | 2013-03-11 | Charging management system, charging management method, and vehicle-mounted device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| WO (1) | WO2013137190A1 (en) |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN106991484A (en) * | 2016-11-14 | 2017-07-28 | 蔚来汽车有限公司 | Predetermined secondary resource reserving method is repeated based on intelligence |
| CN109858650A (en) * | 2019-01-08 | 2019-06-07 | 恒大智慧科技有限公司 | Charge reserving method, computer equipment and storage medium |
| US10599301B2 (en) | 2015-03-04 | 2020-03-24 | Bang & Olufsen A/S | Panel with a two-hand operated user interface for a multi-room media player |
| CN114254889A (en) * | 2021-12-08 | 2022-03-29 | 深圳易加油信息科技有限公司 | Method and system for queuing and scheduling vehicles in charging station, electronic equipment and storage medium |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009136109A (en) * | 2007-11-30 | 2009-06-18 | Toyota Motor Corp | Charge control device and method |
| JP2011147283A (en) * | 2010-01-15 | 2011-07-28 | Alpine Electronics Inc | Charging support system |
-
2013
- 2013-03-11 WO PCT/JP2013/056629 patent/WO2013137190A1/en active Application Filing
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009136109A (en) * | 2007-11-30 | 2009-06-18 | Toyota Motor Corp | Charge control device and method |
| JP2011147283A (en) * | 2010-01-15 | 2011-07-28 | Alpine Electronics Inc | Charging support system |
Cited By (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US10599301B2 (en) | 2015-03-04 | 2020-03-24 | Bang & Olufsen A/S | Panel with a two-hand operated user interface for a multi-room media player |
| CN106991484A (en) * | 2016-11-14 | 2017-07-28 | 蔚来汽车有限公司 | Predetermined secondary resource reserving method is repeated based on intelligence |
| WO2018086386A1 (en) * | 2016-11-14 | 2018-05-17 | 蔚来汽车有限公司 | Secondary resource reservation method based on intelligent repeated reservation |
| CN106991484B (en) * | 2016-11-14 | 2021-07-23 | 蔚来(安徽)控股有限公司 | Secondary resource reservation method based on intelligent repeated reservation |
| CN109858650A (en) * | 2019-01-08 | 2019-06-07 | 恒大智慧科技有限公司 | Charge reserving method, computer equipment and storage medium |
| CN114254889A (en) * | 2021-12-08 | 2022-03-29 | 深圳易加油信息科技有限公司 | Method and system for queuing and scheduling vehicles in charging station, electronic equipment and storage medium |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN106574843B (en) | Charging at a charging station to extend range | |
| JP5553106B2 (en) | Power supply control device | |
| EP2645062B1 (en) | Route search system and method for electric automobile | |
| JP5693856B2 (en) | Server apparatus and power supply reservation reception method | |
| EP2592383B1 (en) | Information providing apparatus | |
| JP6218269B2 (en) | Electric vehicle charging station guidance system | |
| JP5238792B2 (en) | On-vehicle navigation device and server device | |
| JP6394790B2 (en) | Shared vehicle management apparatus and shared vehicle management method | |
| CN102906540A (en) | Information providing device and information providing method | |
| JP2013115873A (en) | Vehicle-to-vehicle power transmitting/receiving system and in-vehicle power transmitting/receiving controller | |
| JP6375676B2 (en) | Vehicle management system and vehicle management method for shared vehicle | |
| JP5601008B2 (en) | Information providing apparatus and information providing method | |
| JP2011158322A (en) | Information processor and destination search method | |
| JP6428190B2 (en) | Shared vehicle management apparatus and shared vehicle management method | |
| JP2019095196A (en) | System, method, and program for guiding charging facility | |
| JP6439251B2 (en) | Vehicle management system and vehicle management method | |
| WO2013137190A1 (en) | Charging management system, charging management method, and vehicle-mounted device | |
| JP2021015087A (en) | Traveling assistance device and computer program | |
| JP2013213799A (en) | Information providing system, terminal device, and server | |
| JP2013055731A (en) | Charging system and charging method | |
| JP2014155351A (en) | Information provision system | |
| JP6428185B2 (en) | Shared vehicle management apparatus and shared vehicle management method | |
| JP6519339B2 (en) | Shared vehicle management apparatus and shared vehicle management method | |
| JP6464847B2 (en) | Shared vehicle management apparatus and shared vehicle management method | |
| WO2016009508A1 (en) | Information supply device and information presentation device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 13761014 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| DPE2 | Request for preliminary examination filed before expiration of 19th month from priority date (pct application filed from 20040101) | ||
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 13761014 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: JP |