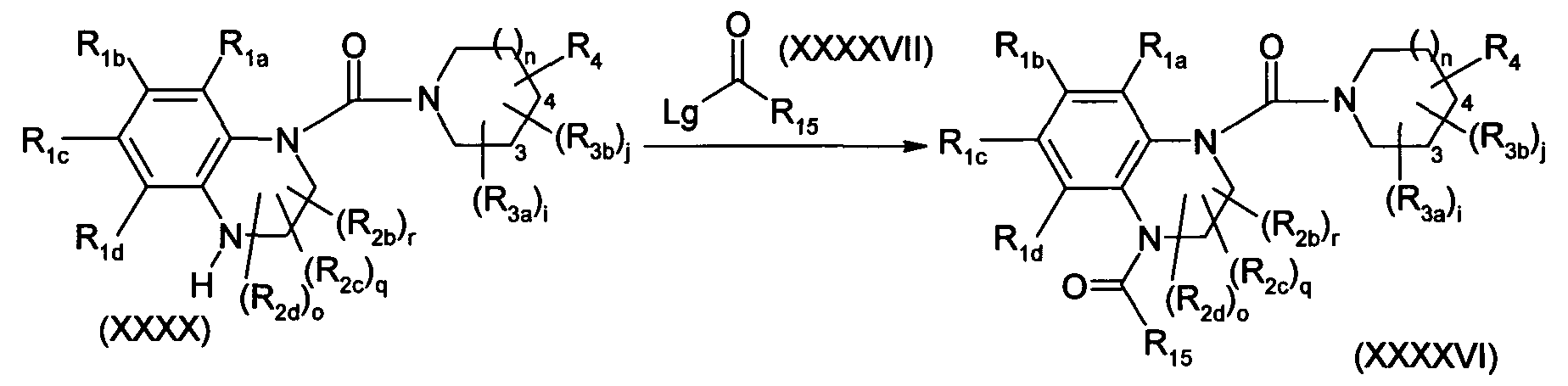WO2008000950A2 - Dérivés d'urées de piperidine ou pyrrolidine, leur préparation et leur application en thérapeutique - Google Patents
Dérivés d'urées de piperidine ou pyrrolidine, leur préparation et leur application en thérapeutique Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2008000950A2 WO2008000950A2 PCT/FR2007/001069 FR2007001069W WO2008000950A2 WO 2008000950 A2 WO2008000950 A2 WO 2008000950A2 FR 2007001069 W FR2007001069 W FR 2007001069W WO 2008000950 A2 WO2008000950 A2 WO 2008000950A2
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- group
- alkyl
- formula
- atom
- optionally substituted
- Prior art date
Links
- 0 CC(C)(CC(C)(C)*1C(CC*)=O)CC(C)(*)*(C*)c(c(C#C)c2C)c1c(*)c2O Chemical compound CC(C)(CC(C)(C)*1C(CC*)=O)CC(C)(*)*(C*)c(c(C#C)c2C)c1c(*)c2O 0.000 description 3
- GDOPTJXRTPNYNR-UHFFFAOYSA-N CC1CCCC1 Chemical compound CC1CCCC1 GDOPTJXRTPNYNR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D401/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with only one nitrogen atom
- C07D401/14—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with only one nitrogen atom containing three or more hetero rings
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/395—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins
- A61K31/435—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having six-membered rings with one nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom
- A61K31/47—Quinolines; Isoquinolines
- A61K31/4709—Non-condensed quinolines and containing further heterocyclic rings
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P19/00—Drugs for skeletal disorders
- A61P19/08—Drugs for skeletal disorders for bone diseases, e.g. rachitism, Paget's disease
- A61P19/10—Drugs for skeletal disorders for bone diseases, e.g. rachitism, Paget's disease for osteoporosis
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P25/00—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system
- A61P25/28—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system for treating neurodegenerative disorders of the central nervous system, e.g. nootropic agents, cognition enhancers, drugs for treating Alzheimer's disease or other forms of dementia
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P27/00—Drugs for disorders of the senses
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P27/00—Drugs for disorders of the senses
- A61P27/02—Ophthalmic agents
- A61P27/06—Antiglaucoma agents or miotics
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P3/00—Drugs for disorders of the metabolism
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P3/00—Drugs for disorders of the metabolism
- A61P3/04—Anorexiants; Antiobesity agents
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P3/00—Drugs for disorders of the metabolism
- A61P3/08—Drugs for disorders of the metabolism for glucose homeostasis
- A61P3/10—Drugs for disorders of the metabolism for glucose homeostasis for hyperglycaemia, e.g. antidiabetics
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P37/00—Drugs for immunological or allergic disorders
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P37/00—Drugs for immunological or allergic disorders
- A61P37/02—Immunomodulators
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P5/00—Drugs for disorders of the endocrine system
- A61P5/48—Drugs for disorders of the endocrine system of the pancreatic hormones
- A61P5/50—Drugs for disorders of the endocrine system of the pancreatic hormones for increasing or potentiating the activity of insulin
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P9/00—Drugs for disorders of the cardiovascular system
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P9/00—Drugs for disorders of the cardiovascular system
- A61P9/10—Drugs for disorders of the cardiovascular system for treating ischaemic or atherosclerotic diseases, e.g. antianginal drugs, coronary vasodilators, drugs for myocardial infarction, retinopathy, cerebrovascula insufficiency, renal arteriosclerosis
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P9/00—Drugs for disorders of the cardiovascular system
- A61P9/12—Antihypertensives
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D401/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with only one nitrogen atom
- C07D401/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with only one nitrogen atom containing two hetero rings
- C07D401/06—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with only one nitrogen atom containing two hetero rings linked by a carbon chain containing only aliphatic carbon atoms
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D403/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, not provided for by group C07D401/00
- C07D403/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, not provided for by group C07D401/00 containing two hetero rings
- C07D403/06—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, not provided for by group C07D401/00 containing two hetero rings linked by a carbon chain containing only aliphatic carbon atoms
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D403/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, not provided for by group C07D401/00
- C07D403/14—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, not provided for by group C07D401/00 containing three or more hetero rings
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D409/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having sulfur atoms as the only ring hetero atoms
- C07D409/14—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having sulfur atoms as the only ring hetero atoms containing three or more hetero rings
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D413/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having nitrogen and oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms
- C07D413/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having nitrogen and oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms containing two hetero rings
- C07D413/06—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having nitrogen and oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms containing two hetero rings linked by a carbon chain containing only aliphatic carbon atoms
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D413/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having nitrogen and oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms
- C07D413/14—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having nitrogen and oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms containing three or more hetero rings
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D417/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having nitrogen and sulfur atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, not provided for by group C07D415/00
- C07D417/14—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having nitrogen and sulfur atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, not provided for by group C07D415/00 containing three or more hetero rings
Definitions
- the present invention relates to piperidine or pyrrolidine urea derivatives, to their preparation and to their therapeutic application.
- the present compounds modulate the activity of 11 ⁇ -hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 (11 ⁇ HSD1) and are useful for the treatment of pathologies in which such modulation is beneficial, as in the case of metabolic syndrome or type 2 diabetes. insulin dependent.
- 11 ⁇ HSD1 11 ⁇ -hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1
- 11 ⁇ -hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 (11 ⁇ HSD1) locally catalyzes the conversion of inactive glucocorticoids (cortisone in humans) into active glucocorticoids (cortisol in humans) in various tissues and organs, mainly the liver and adipose tissue, but also in muscles, bones, pancreas, endothelium, ocular tissue and in some parts of the central nervous system.
- 11 ⁇ HSD1 acts as a regulator of the action of glucocorticoids in the tissues and organs where it is expressed (Tomlinson et al., Endocrine Reviews 25 (5), 831-866 (2004), Davani et al., J.
- 11 ⁇ HSD1 in obesity, type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome (also known as syndrome X or insulin resistance syndrome) where symptoms include visceral obesity, intolerance glucose, insulin resistance, hypertension, type 2 diabetes and hyperlipidemia ⁇ Reaven Ann. Rev. Med 44, 121 (1993)) is described in numerous publications. In humans, treatment with carbenoxolone (a nonspecific inhibitor of 11 ⁇ HSD1) improves insulin sensitivity in thin volunteers and in type 2 diabetics (Andrews et al., J. Clin Endocrinol Metab 88, 285 (2003)).
- mice whose 11 ⁇ HSD1 gene has been extinguished are resistant to hyperglycemia induced by stress and obesity, show an attenuation of the induction of hepatic gluconeogenesis enzymes (PEPCK and G6P) and show an increase in insulin sensitivity in adipose tissue (Kotelevstev et al., Proc Nat Acad Sci 94, 14924 (1997) Morton et al., J. Biol Chem 276, 41293 (2001)). )).
- arylsulfonamidothiazoles have been shown to improve insulin sensitivity and to reduce blood glucose levels in mice with hyperglycemia (Barf et al., J. Med Chem 45, 3813 (2002)). In addition, in a recent study, it has been shown that these compounds reduce food intake and weight gain in obese mice (Wang et al., Diabetologia 49, 1333 (2006)). triazoles showed that they improved the metabolic syndrome and slowed the progression of atherosclerosis in mice (Hermanowski-Vosatka et al., J. Exp Med 202, 517 (2005)).
- 11 ⁇ HSD1 is abundant in the brain and is expressed in many subregions including the hypothalamus, frontal cortex and cerebellum (Sandeep et al., Proc Natl Acad Sci 101, 6734 (2004)). Mice deficient in 11 ⁇ HSD1 are protected against glucocorticoid-associated hypothalamus dysfunctions that are associated with old age (Yau et al., Proc Natl Acad Sci 98, 4716, (2001)).
- Glucocorticoids can be used topically or systemically for a wide variety of clinical ophthalmology pathologies. A particular complication of these treatments is glaucoma induced by the use of corticosteroids. This pathology is characterized by the increase of intraocular pressure (IOP). In the most severe cases and for untreated forms, IOP may lead to a loss of partial field of vision and possibly a complete loss of vision. IOP is the result of an imbalance between the production of aqueous humor and its drainage. Aqueous humor is produced in non-pigmented epithelial cells and drainage is achieved through trabecular meshwork cells.
- IOP intraocular pressure
- 11 ⁇ HSD1 is localized in unpigmented epithelial cells and its function is clearly the amplification of glucocorticoid activity in these cells (Stokes et al., Invest Ophthalmol, Vis, Sci 41, 1629 (2000)). . This notion is confirmed by the observation that the concentration of free cortisol is strongly excess compared with cortisone in the aqueous humor (ratio 14/1).
- the functional activity of 11 ⁇ HSD1 in the eyes was evaluated by studying the action of carbenoxolone in healthy volunteers. After seven days of treatment with carbenoxolone, the IOP is reduced by 18% (Rauz et al., Invest Ophtamol, Vis, Sci 42, 2037 (2001)). Inhibition of 11 ⁇ HSD1 in the eyes is therefore predicted to reduce local glucocorticoid and IOP levels, producing a beneficial effect in the treatment of glaucoma and other vision disorders.
- Angiotensinogen which is produced in the liver and adipose tissue, is a key substrate for renin and is responsible for activating RAS.
- the angiotensiogenic plasma level is significantly elevated in transgenic aP2-11 ⁇ HSD1 mice, as are those of angiotensin II and aldosterone (Masuzaki et al., J. Clinical Invest 112, 83 (2003)); these elements lead to elevation of blood pressure. Treatment of these mice with low doses of an angiotensin II receptor antagonist abolishes this hypertension (Masuzaki et al., J. Clinical Invest 112, 83 (2003)).
- X represents either a carbon, oxygen, sulfur or nitrogen atom or the group
- Ria, b, c, d and R ⁇ abcd which may be identical or different, each represent a hydrogen or halogen atom, a (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl or (C 1 -C 5 ) alkoxy group, C 1 -C 5 ) haloalkyl, hydroxy, hydroxy- (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl, cyano, a group -COOR 5 , a group -NR 6 R 7 , a group COOR 5 - (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl, a group NR 6 R 7 - (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl, a group -CONR 6 R 7 , a group CONR 6 R 7 - (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl, a group - SO 2 NR 6 R 7 , a group -COR 5 , an aryl or heteroaryl group, aryl (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl,
- the dotted line is a single bond or a double bond; - s is an integer equal to 0, 1, 2 or 3;
- t is an integer equal to 0, 1, 2 or 3, s and t can not be equal at the same time to 0;
- R 8 represents a hydrogen or halogen atom, a (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl, (C 1 -C 5 ) alkoxy, trifluoromethyl, hydroxyl, hydroxymethyl, cyano, a group -COOR 5 , a group -NR 6 R 7 ;
- R 9 represents a hydrogen atom or a (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl or hydroxy group
- Y represents a bond or a carbon or nitrogen atom
- n is an integer equal to 0 or 1; o, p, q and r, identical or different, are integers equal to 0, 1 or 2;
- - i and j are integers equal to 0, 1, 2, 3 or 4;
- R 5 represents a hydrogen atom, a (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl group, a (C 3 -C 6 ) cycloalkyl, halo (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl group.
- the compounds of formula (I) may comprise one or more asymmetric carbon atoms. They can therefore exist as enantiomers or diastereoisomers. These enantiomers, diastereoisomers, as well as their mixtures, including the racemic mixtures, form part of the invention.
- the compounds of formula (I) may exist in the form of bases or salified by acids or bases, in particular pharmaceutically acceptable acids or bases. Such addition salts are part of the invention. These salts are advantageously prepared with pharmaceutically acceptable acids, but the salts of other acids that are useful, for example, for the purification or the isolation of the compounds of formula (I), also form part of the invention.
- the compounds of formula (I) may also exist in the form of hydrates or solvates, namely in the form of associations or combinations with one or more molecules of water or with a solvent. Such hydrates and solvates are also part of the invention.
- halogen atom a fluorine, a chlorine, a bromine or an iodine
- a (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl group a linear or branched saturated aliphatic group having from 1 to 5 successive carbon atoms.
- a (C 3 -C 6 ) cycloalkyl group a cyclic alkyl group having from 3 to 6 carbon atoms.
- cyclopropyl methylcyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl and cyclohexyl groups, and the like;
- a (C 1 -C 5 ) alkoxy group a -O- (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl radical in which the (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl group is as previously defined;
- aryl group a mono or bicyclic aromatic group comprising between 5 and 10 carbon atoms.
- aryl groups mention may be made of the phenyl group, the thiophene group, the furan group or the naphthalene group;
- heteroaryl group a mono or bicyclic aromatic group comprising between 5 and 9 carbon atoms and comprising between 1 and 3 heteroatoms, such as nitrogen, oxygen or sulfur.
- heteroaryl groups mention may be made of the groups: pyridine
- a (C 1 -C 5 ) haloalkyl group a (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl group as defined above substituted with 1 to 5 halogen atoms.
- Examples include fluoromethyl, difluoromethyl, trifluoromethyl, trichloromethyl or pentafluoroethyl; a heterocycloalkyl group: an optionally fused or bridged ring comprising from 4 to 9 atoms, at least one of which is chosen from oxygen, nitrogen or sulfur atoms.
- morpholine, piperidine, pyrrolidine and piperazine groups are examples of morpholine, piperidine, pyrrolidine and piperazine groups;
- an “optionally substituted phenyl”, “optionally substituted benzyl” group a phenyl or benzyl group which is optionally substituted by one or more of the following groups: halogen atoms, (C 1 -C 5) alkyl groups ,
- R 2a , Rb, Rc and R 2d ; 3a, b refers to the groups R 33, R 3b,
- R 2a p denotes a number p of R 2a groups carried by the same atom or by different atoms
- R 2b r denotes a number r of R 2b groups carried by the same atom or by different atoms
- R 2c ) q denotes a number q of R 2c groups carried by the same atom or by different atoms
- R 2c ⁇ ) o denotes a number o of R 2d groups carried by the same atom or by different atoms
- R 3a ) ⁇ denotes a number i of groups R 33 carried by the same atom or by different atoms
- R 3b ) j denotes a number j of R 3b groups carried by the same atom or by different atoms, - a group of type "functional group (C 1 -C 5) alkyl" such as alkoxy
- CONR 6 R 7 (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl or aryl (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl, heteroaryl (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl, heterocycloalkyl- (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl means a group having an alkylene group linear or branched having from 1 to 5 times in succession carbon atoms is respectively - (CH ⁇ k - ⁇ rCsJalcoxy, - (CH 2) k -OH, - (CH 2) k -COOR 5, - (CH 2) k -COOR 5 , - (CH 2 ) k -NR 6 R 7 , - (CH 2 ) k -CONR 6 R 7 , - (CH 2 ) n - aryl, - (CH 2 ) k -heteroaryl, - (CH 2 ) k -heterocycloalkyl with k is an integer from 1 to 5.
- X represents either a carbon, oxygen, sulfur or nitrogen atom or the group
- Ria, b, c, d and R2a, b, c, d which may be identical or different, each represent a hydrogen or halogen atom, a (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl or (C 1 -C 5 ) alkoxy group; , (C 1 -
- C 5 haloalkyl, hydroxy, hydroxy- (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl, cyano, a group -COOR 5 , a group -NR 6 R 7 , a group -COOR 5 - (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl, a -NR 6 R 7 - (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl group, -CONR 6 R 7 group, -CONR 6 R 7 - (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl group, - SO 2 NR 6 R 7 group , -COR 5, aryl or heteroaryl, aryl (C 1 -C 5) alkyl, heteroaryl (C 1 -C 5) alkyl, heterocycloalkyl (C r C 5) alkyl, any aryl, heteroaryl may optionally substituted with cyano groups, COOR 5 CONR 6 R 7 , or (R 2a ) or (R 2I 5 ) can also form, with
- the dotted line is a single bond or a double bond
- - s is an integer equal to 0, 1, 2 or 3;
- t is an integer equal to 0, 1, 2 or 3, s and t can not be equal at the same time to 0;
- R 8 represents a hydrogen or halogen atom, a (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl, (C 1 -C 5 ) alkoxy, trifluoromethyl, hydroxyl, hydroxymethyl, cyano, a group -COOR 5 , a group -NR 6 R 7 ;
- R 9 represents a hydrogen atom or a (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl or hydroxy group
- Y represents a bond or a carbon or nitrogen atom
- n is an integer equal to 0 or 1
- o, p, q and r, identical or different, are integers equal to 0, 1 or 2
- i and j are integers equal to 0, 1, 2, 3 or 4;
- R 5 represents a hydrogen atom, a (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl group, a (C 3 -C 6 ) cycloalkyl group;
- X represents either a carbon, oxygen, sulfur or nitrogen atom
- the dotted line is a single bond or a double bond
- - s is an integer equal to 0, 1;
- t is an integer equal to 0, 1, s and t can not be equal at the same time to 0;
- R 8 represents a hydrogen atom or a hydroxyl group
- R 9 represents a hydrogen atom or a (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl group
- Y represents a bond or a carbon or nitrogen atom
- n is an integer equal to 0 or 1;
- o, p, q and r are integers equal to 0 or 1;
- - i and j are integers equal to 0 or 1;
- R 5 represents a hydrogen atom, a (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl group, a (C 3 -C 6 ) cycloalkyl, halo (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl, optionally substituted phenyl;
- formula (Ia) in which:
- X represents either a carbon, oxygen, sulfur or nitrogen atom, or
- R 1a and R 2a, b, c, d are identical or different, each represent a hydrogen or halogen atom, a (C 1 -C 5) alkyl, (C 1 -C 5) alkoxy, ( C 1 -C 5 ) haloalkyl, hydroxy, hydroxy- (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl, cyano, a group -COOR 5 , a group -NR 6 R 7 , a group COOR 5 - (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl , a group NR 6 R 7 - (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl, a group -CONR 6 R 7 , a group CONReR 1 -C 5 alkyl, a group -
- R 3a, R b and R 4 are carried by different carbon atoms; n is an integer equal to 0 or 1;
- o, p, q and r are integers equal to 0, 1 or 2;
- - i and j are integers equal to 0, 1, 2, 3 or 4;
- R 5 represents a hydrogen atom, a (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl group, a (C 3 -C 6 ) cycloalkyl, halo (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl, optionally substituted phenyl;
- R 6 and R 7 which are identical or different, each represent a hydrogen atom, a (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl group, a (C 3 -C 6 ) cycloalkyl or (C 1 -C 5 ) alkylcarbonyl, hydroxymethyl group;
- X represents either a carbon, oxygen, sulfur or nitrogen atom or the group s
- Ria, b, c, d and R 2a , b, c, d which may be identical or different, each represent a hydrogen or halogen atom, a (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl or (C 1 -C 5 ) alkoxy group; (C r -C 5) haloalkyl, hydroxy, hydroxy- (C r C 5) alkyl, cyano, -COOR 5, -NR 6 R 7, COOR 5 - (Ci-C 5) alkyl, a group NR 6 R 7 - (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl, a group -CONR 6 R 7 , a group CONR 6 R 7 - (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl, a group -
- R 3a, b are each a hydrogen atom, a fluorine atom or a (C 1 -C 5) alkyl, (C 1 -C 5) alkoxy, alkoxy- (C 1 -C 5) alkyl, hydroxy, hydroxy- (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl, (C 1 -C 5 ) haloalkyl, cyano, a group -COOR 5 , a group -NR 6 R 7 , a group COOR 5 - (C 1 -C 5) 5 ) alkyl, a group NR 6 R 7 - (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl, a group -CONR 6 R 7 , a group CONR 6 R 7 - (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl, R 4 represents: o a (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl group; a (C 3 -C 6 ) cycloalkyl group; a heterocyclo
- R 3a b and R 4 are carried by the same carbon atom, but do not form a spiro group
- n is an integer equal to 0 or 1; o, p, q and r, identical or different, are integers equal to 0, 1 or 2;
- - i and j are integers equal to 0, 1, 2, 3 or 4;
- Ria, b , c, d and R 2a , b, c, d are identical or different, each represent a hydrogen or halogen atom, a (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl, (C 1 -C 5 ) alkoxy, (C 1 -C 5 ) haloalkyl, hydroxy, hydroxy- (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl, a group -COOR 5 , a group -CONR 6 R 7 , a group -SO 2 NR 6 R 7 , a -COR 5 group, an aryl or heteroaryl group, aryl (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl group, heteroaryl (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl group, heterocycloalkyl- (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl group, any aryl group, heteroaryl group being optionally substituted with 1 to 3 substituents selected
- R 3a b each represent a hydrogen atom
- R 4 represents: a (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl group; a (C 3 -C 6 ) cycloalkyl group; a heterocycloalkyl group, a monocyclic aryl group having from 5 to 6 carbon atoms; a monocyclic heteroaryl group having from 2 to 5 carbon atoms; when R 4 is an aryl or heteroaryl or heterocycloalkyl group, it may be optionally substituted with 1 to 2 substituents selected from halogen atoms, (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl, (C 1 -C 5 ) alkoxy groups, (C 1 -C 5 ) haloalkyl, hydroxy, cyano, optionally substituted phenyl, benzyl, -CONR 6 R 7 group ,
- n is an integer equal to 0 or 1; o, p, q and r, identical or different, are integers equal to 0 or 1;
- - i and j are integers equal to 0 or 1;
- R 5 represents a hydrogen atom, a (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl, optionally substituted phenyl;
- X represents either a carbon, oxygen, sulfur or nitrogen atom;
- R 1a , b, c, d and R 2 a, b, c, d which may be identical or different, each represent a hydrogen or halogen atom, a (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl group, (C 1 - C 5 ) alkoxy, (C 1 -C 5 ) haloalkyl, hydroxy, hydroxy- (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl, -COOR 5 group, -CONR 6 R 7 group, -SO 2 NR 6 group R 7 , -COR 5 , aryl or heteroaryl, aryl (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl, heteroaryl (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl, heterocycloalkyl (C 5 -C 5 ) alkyl, any aryl, heteroaryl may be optionally substituted with 1 to 3 substituents selected from cyano, COOR 5 ,
- n is an integer equal to 0 or 1;
- o, p, q and r are integers equal to 0 or 1;
- - i and j are integers equal to 0 or 1;
- - R 5 represents a hydrogen atom, a (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl, optionally substituted phenyl;
- compounds of the invention are compounds of formula (I), (Ia) or (Ib) in which: p and r are 1; o and q represent 0; i and j represent 1 or 2 n represents O or 1;
- Ria, b, c, d represent hydrogen, or one of the groups Ri a , b, c, d is halogen and the others are hydrogen;
- R 2a , b are hydrogen or one of R 2a , b is (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl, preferably methyl and the other R 2a, b is hydrogen;
- R 3a , b represent hydrogen
- R 4 in position 4 is selected from the following heteroaryls:
- Another group of compounds within the meaning of the invention corresponds to the derivatives of formulas (I) 1 (la) or (Ib) in which X represents the carbon or oxygen atom, n represents 1 and R 4 in the 4-position.
- X represents the carbon or oxygen atom
- n represents 1 and R 4 in the 4-position.
- Another group of compounds within the meaning of the invention corresponds to the derivatives of formulas (I), (Ia) or (Ib) in which X represents the carbon or oxygen atom, n represents 0 and R 4 in the 4-position.
- X represents the carbon or oxygen atom
- n represents 0 and R 4 in the 4-position.
- Ri a , b , c , d> R ⁇ abcd, R3a, b, Rs to R 7 , i, j, o, p, q and r being as defined above .
- Another group of compounds within the meaning of the invention corresponds to the derivatives of formulas (I), (Ia) or (Ib) in which X represents the nitrogen atom, n represents 0 and R 4 in position 4 is a pyrazole or a pyridine, Ri a , b, c, d, R ⁇ abcd, R3a, b, Rs to R 7 , i, j, o, p, q and r being as defined above.
- Another group of compounds within the meaning of the invention corresponds to the derivatives of formulas (I), (Ia) or (Ib) in which X represents the carbon atom or the oxygen atom, n represents 0, p represents 1, r represents 1, the two groups R 2a and R 2b carried by the same carbon atom forming a spiro group and R 4 in the 4-position is a pyrazole or a pyridine, Ri aib , c, d, R 2c , d. R 3a, R b, R to R 7, i, j, o, and q are as defined above.
- Another group of compounds according to the invention correspond to the compounds of formula (I) or (Ib) in which X represents the carbon, oxygen or nitrogen atom, n represents 0 or 1, i represents 1, R 33 and R 4 are attached to the same carbon atom in the 4-position and R 3a is a cyano or (C 1 -C 5 ) alkoxy group, Ri a , b, c, d, R 2a, b, c, d, R ⁇ b, Rs to R 7 , wherein o, p, q and r are as defined above.
- Another group of compounds of the invention consists of the compounds of formula (I) in which:
- X is a carbon, oxygen or nitrogen atom, Ria, b, c , d. R ⁇ abcd are hydrogen;
- i 1;
- Another group of compounds of the invention consists of the compounds of formula (I) in which:
- X is carbon
- Ria, b, c, d, R 2 ab, c, d are hydrogen;
- i 1;
- R 3D R 3D , Rs to R 7 , where n, o, p, q and r are defined as in formula (I) above.
- Another group of compounds of the invention consists of the compounds of formula (I) or (Ic) in which:
- X is oxygen
- Ria, b, c, d, R2a, b, c, d are hydrogen;
- i 1;
- R 3b R 3b , Rs to R 7 , wherein n, o, p, q and r are defined as in formula (I) above.
- Another group of compounds within the meaning of the invention corresponds to the derivatives of formulas (I), (Ia) or (Ib) in which X represents the nitrogen atom, n represents 0, p represents 1, r, q, o represent 0, R 2a carried by X is an aryl group optionally substituted by a CONR 6 R 7 group or an OCH 2 CONR 6 R 7 group , R 4 in the 4-position is a pyrazole or a pyridine, Ri a , b, c , d > R2b, c, d. 3a, b> Rs to R 7, i and j are as defined above.
- the above compounds may be optionally substituted by one or more of the following groups: halogen atoms, groups (Ci-C 5) alkyl, (C 1 - C 5) alkoxy, (C r C 5) haloalkyl, hydroxy, hydroxy - ⁇ Cs) alkyl, (C 1 -C 5) alkoxy (C r
- C 5 ) alkyl cyano, optionally substituted phenyl, optionally substituted benzyl, COOR 5 , -NR 6 R 7 , a group - COOR 5 - (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl, a group - NR 6 R 7 - (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl, a group -CONR 6 R 7 , a group-CONR 6 R 7 - (CrC 5 ) alkyl, a group - SO 2 NR 6 R 7 .
- a protective group is understood to mean a group which makes it possible, on the one hand, to protect a reactive function such as a hydroxyl or an amine during a synthesis and, on the other hand, to regenerate the function reactive intact at the end of synthesis.
- protecting groups and methods of protection and deprotection are given in "Protective Groups in Organic Synthesis", Green et al., 3 rd Edition (John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York).
- leaving group (Lg) is meant, in what follows, a group that can be easily cleaved from a molecule by breaking a heterolytic bond, with the departure of an electronic pair. This group can thus be easily replaced by another group during a substitution reaction, for example.
- Such leaving groups are, for example, halogens or an activated hydroxy group such as mesyl, tosyl, triflate, acetyl, paranitrophenyl, etc. Examples of leaving groups as well as methods for their preparation are given in Advances in Organic Chemistry, J. March, 3rd Edition, Wiley Interscience, p. 310-316.
- the compounds of general formula (I) can be prepared according to the following methods.
- X represents a nitrogen atom, it must be substituted either by a group R 2 a. b , c, d (different from H) or with a protective group Pg as defined above.
- the compounds of formula (IV) can be prepared by reaction between the intermediates of formula (II) and a carbonyl of formula (III) having two leaving groups Lg (for example a chlorine atom, a trichloromethoxy group, a para-nitrophenyl group, an imidazole group, or methylimidazolium) in the presence of a base such as triethylamine or diisopropylamine in a solvent such as dichlomethane, tetrahydrofuran at a temperature ranging from room temperature to 80 ° C.
- a base such as triethylamine or diisopropylamine
- a solvent such as dichlomethane, tetrahydrofuran
- the compounds of formula (I) are obtained by coupling between the activated derivatives (IV) and the amines (V) in the presence or absence of a base such as triethylamine or potassium carbonate in a solvent such as tetrahydrofuran or dichloromethane. , acetonitrile or water, at a temperature ranging from room temperature to 100 ° C.
- heterocycles of the general formula (II) are commercially available or can be prepared by methods described in the literature ( "Comprehensive Heterocyclic Chemistry", Katritzky et al, 2 rd Edition (Pergamon Press). Kuwabe, S .; Torraca, KE Buchwald, SL JACS (2001) 123 (49), 12202-12206); Coudert, G .; Nicolast, G .; Loubinoux, B. Synthesis 7, 541-543. Hoffman, WW; Kraska, AR Eur. Pat. Appl. (1985), EP 130795 A2.
- heterocycles of general formula (V) are commercially available or may be prepared by methods described in the literature ("Comprehensive heterocyclic chemistry", Katritzky et al., 2 ed Edition (Pergamon press), Buffat, Maxime GP Tetrahedron (2004) , 60 (8), 1701-1729, Laschat, S., Dickner, T. Synthesis (2000), (13), 1781-1813, Y. Terao, H. Kotaki, N. Imai, K. Achiwa Chem Pharm Bull (1985) 33 (7), 2762-2766, K.Shankaran et al., Bioorg.Med.Chem.Lett (2004), (14), 3419-3424.
- Scheme 2 details a synthesis of the compounds of formula (I) in which R 4 is placed in position 4 of the carbon ring and represents an aryl or heteroaryl group as defined above, these compounds are hereinafter called compounds of formula (VI) .
- the heterocycles (VIII) whose amino function is protected by a protective group Pg for example a Boc or Fmoc group
- a protective group Pg for example a Boc or Fmoc group
- A may be a trifluoromethyl group or a nonafluorobutyl group
- ketones (VII) can be prepared by converting the ketones (VII) with a sulfonating agent such as trifluoromethanesulfonic anhydride or N-phenyltrifluoromethanesulfonimide in the presence of a base such as lithium diisopropyl amide or lithium hexamethyl disilazane in a solvent such as that tetrahydrofuran or ethylene glycol dimethyl ether at a temperature ranging from -78 ° C to room temperature.
- a sulfonating agent such as trifluoromethanesulfonic anhydride or N-phenyltrifluoromethanesulfonimide
- a base such as lithium diisopropyl amide or lithium hexamethyl disilazane
- solvent such as that tetrahydrofuran or ethylene glycol dimethyl ether at a temperature ranging from -78 ° C to room temperature.
- the heterocycles (X) are obtained by organometallic coupling between a compound (VIII) and a compound (IX) where Y is a boron derivative (for example a boronic acid or a boronic ester), tin (for example a group tri-n-butyl tin) or a halogen atom (for example bromine or iodine) in the presence of a suitable metal derivative (for example palladium, zinc or copper derivatives) in the presence of a base or not such as potassium carbonate, potassium fluoride or sodium phosphate in a solvent or solvent mixture such as dioxane, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, toluene, water at a temperature varying from room temperature at 120 ° C.
- a boron derivative for example a boronic acid or a boronic ester
- tin for example a group tri-n-butyl tin
- a halogen atom for example bromine or iod
- the double bond of the heterocycles (X) is then hydrogenated with a suitable metal catalyst in methanol or ethanol to give the derivatives (XI).
- the amines of formula (VI) are obtained by deprotection of the amine function of the compounds of formula (XI) by methods known to those skilled in the art. They include inter alia the use of trifluoroacetic acid or hydrochloric acid in dichloromethane, dioxane, tetrahydrofuran or diethyl ether in the case of protection by a Boc group, and piperidine for a Fmoc group, to temperatures ranging from -10 0 C to 100 ° C.
- Scheme 3 shows an alternative preparation route of the compounds of formula (I) in which R 4 is placed in position 4 of the carbon ring and represents an aryl or heteroaryl group as defined above, these compounds are hereinafter called compounds of formula (XII).
- X represents a nitrogen atom, it must be substituted either with a group R 2a , b (other than H) or with a protective group Pg as defined above.
- the amines (XIII) are obtained by deprotection of the amine function of the compounds of formula (VIII), by methods chosen from those known to those skilled in the art. They include inter alia the use of trifluoroacetic acid or hydrochloric acid in dichloromethane, dioxane, tetrahydrofuran or diethyl ether in the case of protection by a Boc group, and piperidine for a Fmoc group, to temperatures ranging from -10 to 100 ° C.
- the compounds of formula (XIV) are obtained by coupling between the activated derivatives (IV) and the amines (XIII) in the presence or absence of a base such as triethylamine or potassium carbonate in a solvent such as tetrahydrofuran, dichloromethane, acetonitrile or water, at a temperature ranging between room temperature and 100 ° C. in the following step, the heterocycles (XV) are obtained by organometallic coupling between a compound (XIV) and a compound (IX) wherein Y is a boron derivative (e.g. boronic acid or boronic ester), tin (e.g.
- a n-butyl tin group or a halogen atom (for example bromine or iodine) in the presence of a suitable metal derivative (for example palladium, zinc or copper derivatives) and in the presence of base or not such as potassium carbonate, potassium fluoride or sodium phosphate in a solvent or solvent mixture such as dioxane, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, toluene, water at a temperature varying from the ambient temperature at 120 ° C.
- a suitable metal derivative for example palladium, zinc or copper derivatives
- base or not such as potassium carbonate, potassium fluoride or sodium phosphate in a solvent or solvent mixture such as dioxane, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, toluene, water at a temperature varying from the ambient temperature at 120 ° C.
- the double bond of heterocycles (XV) is then hydrogenated with a suitable metal in methanol or ethanol to give derivatives (XII).
- Scheme 4 shows a route of synthesis of the compounds of formula (I) in which i represents 1 and R 3a is a CN group placed in position 4, R 4 is placed in position 4 of the carbon ring and represents an aryl or heteroaryl group such as defined above, these compounds are hereinafter called compounds of formula (XVI).
- X represents a nitrogen atom, it must be substituted either by a group R 2 a, b, c, d (other than H) or by a protective group Pg as defined above.
- Scheme 4 (Method 3):
- the compounds (XVI) are obtained by the reaction of the nitriles (XIX) with the derivatives (XVIII) in the presence of a base such as sodium hydride, diisopropyl lithium amide or hexamethyl disilazane in a solvent such as tetrahydrofuran at a temperature ranging from -50 ° C. to 80 ° C.
- Scheme 5 shows an alternative synthetic route of the compounds of formula (I) in which i represents 1, R 33 is a CN group placed in position 4, R 4 is placed in position 4 of the carbon ring and represents an alkyl or cycloalkyl group as defined above, these compounds are hereinafter referred to as compounds of formula (XVI) '.
- X represents a nitrogen atom, it must be substituted either with a group R 2a , b , c , d (other than H) or with a protective group Pg as defined above.
- Scheme 5 (Method 4):
- the compounds of formulas (XVI) ' are obtained by alkylation of compounds (XX) with compounds (XXI) having a leaving group Lg (for example a chlorine atom, a mesyl or tosyl group), in the presence a base such as sodium hydride, lithium diisopropyl amide, lithium hexamethyldisilazane or lithium amide in a solvent such as tetrahydrofuran at a temperature ranging from -78 ° C. to room temperature.
- a base such as sodium hydride, lithium diisopropyl amide, lithium hexamethyldisilazane or lithium amide
- Scheme 6 shows a route of preparation of the compounds of formula (I) in which R 4 is a thiazole group substituted with a group R 10 where R 10 represents a hydrogen atom, a (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl or aryl group optionally substituted, these compounds are hereinafter called compounds of formula (XXII).
- X represents a nitrogen atom, it must be substituted either by a group R 2a , b , c , c i (different from H) or by a protective group Pg as defined above.
- Scheme 6 (Method 5): In Scheme 6, the compounds of formulas (XXIV) are obtained by coupling between the activated derivatives (IV) and the amines (XXIII) having a primary thioamide group, in the presence or absence of a base such as triethylamine or sodium carbonate. potassium in a solvent such as tetrahydrofuran, dichloromethane, or acetonitrile, at a temperature ranging from room temperature to 100 ° C.
- a base such as triethylamine or sodium carbonate.
- the compounds (XXII) are obtained by the reaction of thioamides (XXIV) with the oxo derivatives (XXV) having, in alpha, a leaving group Lg (for example a chlorine or bromine atom) in which R 10 represents a hydrogen atom, an alkyl or aryl group optionally substituted in the presence of a base such as triethylamine, diisopropylethylamine in a solvent such as tetrahydrofuran or acetonitrile at a temperature ranging from room temperature to 80 ° C.
- a base such as triethylamine, diisopropylethylamine in a solvent such as tetrahydrofuran or acetonitrile
- Scheme 7 shows a route of preparation of the compounds of formula (I) in which R 4 is a 1,2,4-oxadiazole group substituted by a group R 11 where R 11 represents a (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl group or optionally substituted aryl, these compounds are hereinafter referred to as compounds of formula (XXVI).
- X represents a nitrogen atom, it must be substituted either by a group R ⁇ abcd (other than H) or by a protective group Pg as defined above.
- the compounds of formulas (XXVIII) are obtained by coupling between the activated derivatives (IV) and the amines (XXVII) having an ester group, in the presence or absence of a base such as triethylamine or potassium carbonate. in a solvent such as tetrahydrofuran, dichloromethane or acetonitrile, at a temperature ranging from room temperature to 100 ° C.
- the next step consists of saponification of the ester function of the compounds (XXVIII) in an acid group by means of soda, potash or lithium hydroxide in a solvent such as an alcohol or water at a temperature ranging from room temperature to 100 ° C to yield acids (XXIX).
- the compounds (XXIX) are obtained by the reaction of the acids (XXVI) with the hydroxyamidine derivatives (XXX) where Rn represents an optionally substituted alkyl or aryl group in the presence of a coupling agent such as O- benzotriazol-1-yl-N, N, N ', N'-tetramethyluronium tetrafluoroborate, in the presence or absence of 1-hydroxybenzotriazole, a base such as triethylamine, diisopropylethylamine in a solvent such as dimethylformamide, tetrahydrofuran or acetonitrile at a temperature ranging from room temperature to 100 ° C.
- a coupling agent such as O- benzotriazol-1-yl-N, N, N ', N'-tetramethyluronium tetrafluoroborate
- 1-hydroxybenzotriazole a base such as triethylamine, diisopropylethy
- Scheme 8 shows a route of synthesis of the compounds of formula (I) wherein R 4 is a 1,2,4-oxadiazole group, these compounds are hereinafter referred to as compounds of formula (XXXI).
- X represents a nitrogen atom, it must be substituted either by a group R 2 a, b , c, d (other than H) or by a protective group Pg as defined above.
- the hydroxyamidines (XXXIII) are obtained by reaction of the nitriles (XXXII) with hydroxylamine in the presence or absence of a base such as triethylamine in a solvent such as methanol or ethanol, at a temperature varying between ambient temperature and 100 ° C.
- the oxadiazoles (XXXI) are obtained by condensation of hydroxyamidines (XXXIII) with a formic acid derivative such as triethylorthoformate in the presence or absence of a solvent such as ethanol at a temperature of between room temperature and 100 ° C.
- Scheme 9 shows a route of synthesis of the compounds of formula (I) in which R 4 is an imidazole group substituted with a group Rn, where R 11 represents a (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl or optionally substituted benzyl group, these compounds are hereinafter referred to as compounds of formula (XXXIV) and (XXXV).
- X represents a nitrogen atom, it must be substituted either by a group R ⁇ a . b .c d (other than H) or by a protective group Pg as defined above.
- the mixture of the substituted imidazoles (XXXIV) and (XXXV) are obtained by alkylation of the imidazoles (XXXVI) with alkylating agents (XXXVII) having a leaving group Lg (for example an iodine atom, an atom of bromine, a mesyl or tosyl group) wherein Rn represents a (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl or optionally substituted benzyl group, in the presence of a base such as triethylamine or potassium carbonate in a solvent such as dimethylformamide or tetrahydrofuran , at a temperature ranging from 0 0 C to 80 ° C.
- a base such as triethylamine or potassium carbonate
- a solvent such as dimethylformamide or tetrahydrofuran
- Scheme 10 shows a route of synthesis of the compounds of formula (I) in which p represents 1, X is a nitrogen atom substituted by the R 2a group, these compounds are hereinafter called compounds of formula (XXXVIII).
- Scheme 10 (Method 9):
- the substituted quinoxalines of formula (XXXVIII) are obtained by reductive amination, carried out by bringing the compounds of formula (XXXX) in the presence of a derivative of the group R 2a of the aldehyde or ketone type, using a reducing agent such as sodium borohydride, sodium triacetoxyborohydride or sodium cyanoborohydride, in the presence or absence of a Brönsted acid (such as hydrochloric acid) or Lewis acid (such as titanium tetraisopropoxide) in a solvent such as dichloroethane, dichloromethane, acetic acid or methanol, at temperatures of between -10 ° C. and 30 ° C.
- a reducing agent such as sodium borohydride, sodium triacetoxyborohydride or sodium cyanoborohydride
- a Brönsted acid such as hydrochloric acid
- Lewis acid such as titanium tetraisopropoxide
- Scheme 11 shows a route of synthesis of the compounds of formula (I) in which X is a nitrogen atom, p represents 1, R 2a is a CO-N group (R 12 , R 13 ) which substitutes X, Ri 2 and R 13 represent R 6 and R 7 as defined in formula (I), these compounds are hereinafter called compounds of formula (XXXXII).
- Scheme 11 (Method 10):
- the ureas (XXXXII) are obtained by reacting with the amines (XXXXIII) in the presence or absence of a base such as triethylamine or potassium carbonate in a solvent such as tetrahydrofuran, dichloromethane, acetonitrile or water, at a temperature ranging from room temperature to 100 ° C.
- a base such as triethylamine or potassium carbonate
- a solvent such as tetrahydrofuran, dichloromethane, acetonitrile or water
- Scheme 12 shows a route of synthesis of the compounds of formula (I) in which X is a nitrogen atom, p represents 1, R 2a is a CO-OR 14 group which substitutes X, R 14 represents R 5 as defined in formula (I), these compounds are hereinafter referred to as compounds of formula (XXXXIV).
- Scheme 12 (Method 11):
- (XXXX) react first with a carbonyl of formula (III) having two leaving groups Lg (for example a chlorine atom, a trichloromethoxy group, a para-nitrophenyl group, an imidazole group, or methyl-imidazolium) in the presence of a base such as triethylamine or diisopropylamine in a solvent such as dichlomethane, tetrahydrofuran at a temperature ranging from room temperature to 80 0 C; then, in a second step, with the alcohols (XXXXV) in the presence or absence of a base such as triethylamine or potassium carbonate in a solvent such as tetrahydrofuran, dichloromethane, acetonitrile or water, at a temperature ranging from room temperature to 100 0 C, to lead to carbamates (XXXXIV).
- a base such as triethylamine or diisopropylamine
- a solvent
- Scheme 13 shows a route of synthesis of the compounds of formula (I) in which X is a nitrogen atom, p represents 1, R 2a is a COR 15 group which substitutes X, R 15 represents R 5 as defined in formula (I), these compounds are hereinafter called compounds of formula (XXXXVI).
- Scheme 14 shows a route of synthesis of the compounds of formula (I) in which one of the groups R 1 is a -COOH group (for example placed hereinafter, in position R 1c ) as well as to the compounds of formula (IC ) in which one of the groups R 1 is a group -CH 2 OH, these compounds are hereinafter called compounds of formula (XXXXVIII).
- the compounds of formula (XXXXVIII) can be synthesized by saponification of the esters of formula (XXXXVI), for example in the presence of sodium hydroxide or of lithium hydroxide in a solvent such as methanol, tetrahydrofuran or water, or a mixture of these solvents.
- the compounds of formula (IC) are obtained by reduction of acids (XXXXVIII) or of esters of formula (XXXXVI) using reducing agents such as lithium aluminum hydride or, after formation of a mixed anhydride in the presence of isobutyl chloroformate and triethylamine in tetrahydrofuran or dioxane, sodium borohydride in methanol or ethanol at temperatures ranging from -40 0 C to 10 0 C.
- reducing agents such as lithium aluminum hydride or, after formation of a mixed anhydride in the presence of isobutyl chloroformate and triethylamine in tetrahydrofuran or dioxane, sodium borohydride in methanol or ethanol at temperatures ranging from -40 0 C to 10 0 C.
- Figure 15 shows two ways of access to synthesis intermediates of formula (C) wherein R 17 is a hydrogen atom or a (Ci-C 5) alkoxy, or (C 1 -C 5) haloalkyl and L a linker (single bond, (C 1 -C 5 ) alkoxy group, (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl group) and R 16 is defined as above.
- CII having a group X (for example a halogen, a tosylate, triflate or nanoflate group) in the presence of an organometallic species such as a palladium derivative, in the presence or absence of a phosphine such as triterbutylphosphine or triphenylphosphine, in the presence of a base such as potassium carbonate, potassium fluoride, potassium tertbutylate or potassium phosphate in a solvent or solvent mixture such as dioxane, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, toluene, tetrahydrofuran, the water at a temperature ranging from room temperature to 100 ° C.
- group X for example a halogen, a tosylate, triflate or nanoflate group
- an organometallic species such as a palladium derivative
- a phosphine such as triterbutylphosphine or triphenylphosphine
- a base such as potassium
- the amines (C) are obtained by deprotection of the amine function of the compounds of formula (CIII), by methods chosen from those known to those skilled in the art. They include inter alia the use of trifluoroacetic acid or hydrochloric acid in dichloromethane, dioxane, tetrahydrofuran or diethyl ether in the case of protection by a Boc group, and piperidine for a Fmoc group, to temperatures ranging from -10 to 100 ° C.
- An alternative approach to the synthesis of intermediates (C) consists in carrying out a nucleophilic aromatic substitution reaction between the monoprotected tetrahydroquinoxaline (Cl) or the protective group is a "boc" group and a derivative aromatic cyano (CIV) in which Y is a halogen atom (for example fluorine) in the presence of a base such as potassium tert-butoxide or sodium hexamethyldisilazane in a solvent such as ⁇ / -methyl pyrrolidinone or dimethylformamide, at a temperature ranging from room temperature to 100 ° C.
- a base such as potassium tert-butoxide or sodium hexamethyldisilazane
- solvent such as ⁇ / -methyl pyrrolidinone or dimethylformamide
- the cyano function of the compounds (CV) is then hydrolysed in an acidic medium using, for example, mple of a solution of concentrated hydrochloric acid in a solvent such as water at a temperature ranging from room temperature to 100 0 C to lead to acids (CVI) in which the protective group "boc" was simultaneously removed.
- a solvent such as water
- ester (C) is obtained by esterification of the acid derivative (CVI) with an alcohol HOR 16 under conventional peptide coupling conditions, using for example as coupling agent dicyclohexylcarbodiimide, the hydrochloride of 1- (3-dimethylaminopropyl) ) -3-ethylcarbodiimide or bromo-tris-pyrrolidino-phosphonium hexafluorophosphate, in the presence or absence of hydroxybenzo-triazole, and using as organic base triethylamine or diisopropyl-ethylamine in a solvent such as dioxane, dichloromethane or acetonitrile.
- dicyclohexylcarbodiimide the hydrochloride of 1- (3-dimethylaminopropyl) ) -3-ethylcarbodiimide or bromo-tris-pyrrolidino-phosphonium hexafluorophosphate
- Scheme 16 shows a route of synthesis of the compounds of formula (CVII), which correspond to compounds of formula (I) in which R 2 ( j comprises L 2 which is a linker (single bond or group (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl), L and R 17 are defined as above.
- the compounds of formula (CVIII) can be prepared by reaction between the intermediates of formula (C) and a carbonyl of formula (III) having two leaving groups Lg (for example a chlorine atom, a trichloromethoxy group, a para-nitrophenyl group, an imidazole group, or methylimidazolium) in the presence of a base such as triethylamine or diisopropylamine in a solvent such as dichlomethane, tetrahydrofuran at a temperature ranging from room temperature to 80 ° C.
- a base such as triethylamine or diisopropylamine
- a solvent such as dichlomethane, tetrahydrofuran
- the compounds of formula (CIX) are obtained by coupling between the activated derivatives (CVIII) and the amines (V) in the presence or absence of a base such as triethylamine or potassium carbonate in a solvent such as tetrahydrofuran or dichloromethane. , acetonitrile or water, at a temperature ranging from room temperature to 100 ° C.
- a base such as triethylamine or potassium carbonate
- a solvent such as tetrahydrofuran or dichloromethane.
- acetonitrile or water at a temperature ranging from room temperature to 100 ° C.
- the ester function of the compounds (CIX) is then saponified in an acidic function using soda, potassium hydroxide or lithium hydroxide in a solvent or solvent mixture such as an alcohol, water or tetrahydrofuran at a temperature ranging from room temperature to 100 0 C to lead to acids (CX).
- the compounds (CVII) can be prepared by condensation between the acidic intermediates of formula (CX) and an amine (CXI) under conventional peptide coupling conditions, using for example as coupling agent dicyclohexylcarbodiimide, the hydrochloride 1- (3-dimethylaminopropyl) -3-ethylcarbodiimide or bromo-tris-pyrrolidino-phosphonium hexafluorophosphate, in the presence or absence of hydroxybenzo-triazole, and using as an organic base triethylamine or diisopropyl-ethylamine in a solvent or solvent mixture such as dioxane, dichloromethane or acetonitrile.
- coupling agent dicyclohexylcarbodiimide the hydrochloride 1- (3-dimethylaminopropyl) -3-ethylcarbodiimide or bromo-tris-pyrrolidino-phosphonium hex
- Scheme 17 shows an alternative synthetic route of the intermediates of formula (XV) as defined above.
- the compounds of formula (CXI) can be prepared by converting the sulfonic ester function of compounds (XIV) to a boronic ester derivative (CXI) by reaction with bispinacolatodiborane in the presence of a palladium such as 1,1'-bis (diphenylphosphino) ferrocedichloropalladium (II) in the presence of a base such as potassium acetate, lithium chloride in a solvent or solvent mixture such as dichloromethane, dioxane, dimethylsulfoxide at a temperature ranging from ambient temperature to 100 ° C.
- a palladium such as 1,1'-bis (diphenylphosphino) ferrocedichloropalladium (II)
- a base such as potassium acetate
- lithium chloride in a solvent or solvent mixture
- dichloromethane dioxane, dimethylsulfoxide at a temperature ranging from ambient temperature to 100 ° C.
- the derivatives (XV) can be obtained by a coupling reaction between the derivative (CXI) and a compound (CXII) having a group V (by a halogen, a triflate, a nonaflate) in the presence of an organometallic species such as a palladium derivative, in the presence or absence of a phosphine such as tricyclohexylphosphine or triphenylphosphine, in the presence of a base such as sodium or potassium carbonate, potassium fluoride in a solvent or solvent mixture such as dioxane, dimethylformamide, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, tetrahydrofuran, water at a temperature ranging from room temperature to 100 0 C.
- Scheme 18 shows an alternative synthetic route of the compounds of formula (XXXVIII) in which R 2d is a (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl, aryl (C 1 -C 5 ) alkyl or heteroaryl (C 1 -C 5 ) group alkyl, (the aryl, heteroaryl groups may be optionally substituted).
- the substituted tetrahydroquinoxalines of formula (CXIII) are obtained by reductive amination, carried out by bringing the compounds of formula (Cl) in the presence of a derivative of the R 2d group of the aldehyde or ketone type (CXIV), using a reducing agent such as sodium borohydride, sodium triacetoxyborohydride or sodium cyanoborohydride, in the presence or absence of a Bronsted acid (such as hydrochloric acid) or Lewis acid (such as titanium tetraisopropoxide) in a solvent such as dichloromethane, dichloromethane, acetic acid or methanol, at temperatures between -10 ° C. and 30 ° C.
- a Bronsted acid such as hydrochloric acid
- Lewis acid such as titanium tetraisopropoxide
- the amines (CXV) are obtained by deprotection of the amine function of the compounds of formula (CXIII), by methods selected from those known to those skilled in the art. They include inter alia the use of trifluoroacetic acid or hydrochloric acid in dichloromethane, dioxane, tetrahydrofuran or diethyl ether in the case of protection by a Boc group, and piperidine for a Fmoc group, to temperatures ranging from -10 to 100 ° C.
- the compounds of formula (CXVI) can be prepared by reaction between the intermediates of formula (CXV) and a carbonyl of formula (III) having two leaving groups Lg (by a chlorine atom, a trichloromethoxy group, a para-nitrophenyl group, an imidazole group, or methyl-imidazolium) in the presence of a base such as triethylamine or diisopropylamine in a solvent such as dichlomethane, tetrahydrofuran at a temperature ranging from room temperature to 80 ° C.
- a base such as triethylamine or diisopropylamine
- a solvent such as dichlomethane, tetrahydrofuran
- the compounds of formula (XXXVIII) are obtained by coupling between the activated derivatives (CXVI) and the amines (V) in the presence or absence of a base such as triethylamine or potassium carbonate in a solvent such as tetrahydrofuran or dichloromethane. , acetonitrile or water, at a temperature ranging from room temperature to 100 ° C.
- Scheme 19 shows a synthesis route of the intermediates of formula (CXVII), wherein the carbon atom carrying the spiro cyclopropyl group is not adjacent to the nitrogen atom of tetrahydroquinoline.
- the compounds (CXIX) can be obtained by converting the ketone function of the intermediate (CXVIII) to an ethylenic derivative, for example by means of a Wittig reaction with methyltriphenylphosphonium bromide, in the presence of a base such as potassium tert-butoxide, in a solvent such as ether.
- the spirocyclorponaic derivatives (CXXI) can then be obtained by the use of trimethylsilyl fluorosulfonydifluoroacetate (CXX), in the presence of a fluorine source such as sodium fluoride, in a solvent such as toluene, at a temperature varying from at room temperature at 100 ° C.
- the amines (CXVII) are obtained by deprotection of the amine function of the compounds of formula (CXXI), by methods chosen from those known to those skilled in the art. They include inter alia the use of trifluoroacetic acid or hydrochloric acid in dichloromethane, dioxane, tetrahydrofuran or diethyl ether in the case of protection by a Boc group, and piperidine for a Fmoc group, to temperatures ranging from -10 to 100 ° C.
- Scheme 20 shows a route of synthesis of the intermediates of formula (CXXIII) wherein the difluorovinyl group is not adjacent to the nitrogen atom of tetrahydroquinoline.
- the compounds (CXXIII) can be obtained by conversion of the ketone function of the intermediate (CXVIII) to a difluoroethylene derivative, for example by means of a Wittig reaction with tri-n-butylphosphine and sodium chlorodifluoroacetate, in a a solvent such as ⁇ -methylpyrrolidinone at a temperature ranging from room temperature to 160 ° C.
- the amines (CXVII) are obtained by deprotection of the amine function of the compounds of formula (CXXI), by methods chosen from those known from the art. skilled person.
- the heterocycles (CXXVII) whose amino function is protected by a protective group Pg (for example a Boc or Fmoc group) having a vinyl sulfonate-W group (for example W may be a trifluoromethyl group, a nonafluorobutyl group ) can be prepared by conversion of the ketones (CXXVI) with a sulfonating agent such as trifluoromethanesulfonic anhydride or ⁇ -phenyltrifluoromethanesulfonimide in the presence of a base such as lithium diisopropyl amide or lithium hexamethyl disilazane in a solvent such as tetrahydrofuran or ethylene glycol dimethyl ether at a temperature ranging from -78 ° C to room temperature.
- a sulfonating agent such as trifluoromethanesulfonic anhydride or ⁇ -phenyltrifluoromethanesulfonimide
- the heterocycles (CXXIX) are obtained by organometallic coupling between a derivative (CXXVII) and a compound (CXXVIII) where D is a boron derivative (for example a boronic acid or a boronic ester), tin (for example a group tri-n-butyl tin) or a halogen atom (for example bromine or iodine) in the presence of a suitable metal derivative (for example palladium, zinc or copper derivatives) in the presence of a base or not such as potassium carbonate, potassium fluoride or sodium phosphate in a solvent or solvent mixture such as dioxane, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, toluene, water at a temperature varying from room temperature at 120 ° C.
- D is a boron derivative (for example a boronic acid or a boronic ester), tin (for example a group tri-n-butyl tin) or a hal
- the Ar group is a pyrazole
- the free NH function of the heterocycle may optionally be protected by a protecting group (for example a Boc group), before carrying out the coupling reaction catalyze by a organometallic species.
- a protecting group for example a Boc group
- the protecting group especially if it is a Boc group
- the heterocycle double bond (CXXIX) is then hydrogenated with a suitable metal catalyst in methanol or ethanol to give the derivatives (CXXX).
- the amines of formula (CXXXI) are obtained by deprotection of the amine function of the compounds of formula (CXXX) by methods known to those skilled in the art. They include inter alia the use of trifluoroacetic acid or hydrochloric acid in dichloromethane, dioxane, tetrahydrofuran or diethyl ether in the case of protection by a Boc group, and piperidine for a Fmoc group, to temperatures ranging from -10 0 C to 100 0 C.
- the mixture of the two enantiomers (CXXIV) and (CXXV) can be separated using methods known to those skilled in the art. In particular by high-pressure or supercritical chiral stationary phase chromatography such as a tris (3,5-dimethylphenylcarbamate) amylose derivative deposited on a spherical silica support, or by recrystallization in the presence of an optically active acid such as than tartaric acid or camphorsulfonic acid.
- an optically active acid such as than tartaric acid or camphorsulfonic acid.
- the invention also relates to the compounds of formulas (XIV), (XV), (XVIII), (XXIV), (XXIX) 1 (XXVIII), (XXXIII), (C) , (CIX), (CX), (CXVII) and (CXXII). These compounds are useful as synthesis intermediates for the compounds of formula (I).
- Example 3 4 - [(3-Pyridin-3-ylpyrrolidin-1-yl) carbonyl] -3,4-dihydro-2H-1,4-benzoxazine Hydrochloride (Compound No. 26) 3.1: 4-nitrophenyl 2,3-dihydro-4H-1,4-benzoxazine-4-carboxylate
- Example 4 1 - ( ⁇ 4- [3- (2,6-dichlorophenyl) -1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl] -piperidine-1 yl ⁇ carbonyl) -1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoline (compound no. 25)
- tert-butyl 4-pyridin-4-ylpiperidine-1-carboxylate In a high pressure reactor, under nitrogen, 0.336 g of 5% Pd / C is added to 0.821 g of tert-butyl 3,6-dihydro-4, 4'-bipyridine-1 (2 / - /) - carboxylate solubilized in 65 ml of methanol. The reaction mixture is pressurized with 3 atmospheres of hydrogen at 25 ° C and stirred mechanically for 1 hour. The palladium is filtered on Whatman (trademark) paper and is washed with methanol.
- Example 7 N, N-Dimethyl-4 - [(3-pyridin-3-ylpyrrolidin-1-yl) carbonyl] -3,4-dihydroquinoxaline-1 (2-yl) carboxamide hydrochloride (compound no. 110) Z 1 I: N, N - dimethyl-4 - [(3-pyridin-3-ylpyrrolidin-1-yl) carbonyl] -3,4-dihydroquinoxaline-1 (2H) -carboxamide
- Example 8 Methyl 4 - [(3-pyridin-3-ylpyrrolidin-1-yl) carbonyl] -3,4-dihydroquinoxaline-1 (2W) -carboxylate (Compound No. 118) In a 50 ml flask under a d nitrogen are placed 0.25 g of 1-
- Example 9 1-Acetyl-4 - [(3-pyridin-3-ylpyrrolidin-1-yl) carbonyl] -1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoxaline hydrochloride (Compound No. 120) 9J. : 1-Acetyl-4 - [(3-pyridin-3-ylpyrrolidin-1-yl) carbonyl] -1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoxaline
- Example 10 ⁇ 4 - [(3-Pyridin-3-ylpyrrolidin-1-yl) carbonyl] -3,4-dihydro-2H-1,4-benzoxazin-6-yl ⁇ methanol hydrochloride (Compound No. 82)
- aqueous phase is extracted three times with dichloromethane.
- the organic phases are combined, washed with water and with saturated aqueous sodium chloride solution, dried over sodium sulfate, and the solvent is evaporated off under reduced pressure.
- the reaction mixture is hydrolyzed by methanol, then an aqueous sodium hydroxide solution and then with a saturated aqueous solution of sodium hydrogencarbonate.
- the aqueous phase is extracted three times with dichloromethane.
- the organic phases are combined, washed with water and with saturated aqueous sodium chloride solution, dried over sodium sulfate, and the solvent is evaporated off under reduced pressure.
- the residue is chromatographed on silica gel with a mixture of dichloromethane / methanol 90/10.
- Example 11 Sodium salt of 1 - [(3-pyridin-3-ylpyrrolidin-1-yl) carbonyl]
- the reaction mixture is then poured onto 8 g of DOWEX 50WX8 resin and the heterogeneous mixture is stirred until the product of the liquid phase disappears (monitored by TLC).
- the resin is filtered and then washed successively with water, tetrahydrofuran and acetonitrile.
- the compound is removed by means of a 2N ammonia solution in methanol, and the solvent is evaporated off under reduced pressure. The residue is taken up in methanol and 0.95 ml of a 0.5M solution of sodium methoxide in methanol is added.
- Example 13 N-Piperidin-1-yl-4- ⁇ 4- [3- (1H-pyrazol-4-yl) -pyrrolidin-1-carbonyl] -3,4-dihydro-2H-quinoxalin-1-yl ⁇ -benzamide (Example 172)
- Example 14 N-Cyclopropyl-2-methoxy-4- ⁇ 4- [3- (1H-pyrazol-4-yl) -pyrrolidine-1-carbonyl] -3,4-dihydro-2H-quinoxalin-1-yl ⁇ Benzamide (Example No. 78)
- the reaction medium is again degassed and then placed under a nitrogen atmosphere and stirred at 100 ° C. for 18 h. It is poured into ice water, neutralized by the addition of solid ammonium chloride and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic phase is washed with water and saturated sodium chloride solution, dried over magnesium sulfate and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue is purified by chromatography on a silica column eluted with a heptane-ethyl acetate gradient from 96/4 to 60/40.
- Example 15 (4-Difluoromethylene-3,4-dihydro-2H-quinolin-1-yl) - (3-pyridin-3-yl-pyrrolidin-1-yl) -methanone (Example 163)
- reaction medium is washed with a 1N solution of sodium hydroxide; the sentence organic is dried over sodium sulfate and concentrated under reduced pressure.
- the residue is chromatographed on silica gel eluted with a 98/2 dichloromethane-methanol mixture.
- 0.05 g of (4-difluoromethylene-3,4-dihydro-2H-quinolin-1-yl) - (3-pyridin-3-yl-pyrrolidin-1-yl) -methanone are obtained which are treated with fumaric acid in an ethanol - diisopropyl ether mixture to give the fumarate.
- reaction medium is refluxed for 14 h and then concentrated under reduced pressure. Water and ethyl acetate are added, and the heterogeneous mixture is filtered through celite. The organic phase is washed with water and dried over sodium sulfate and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue is chromatographed on silica gel eluted with a gradient of 30% to 50% ethyl acetate in heptane. 1.22 g of (2,3-Dihydro-benzo [1,4] oxazin-4-yl) - [3- (4,4,5,5-tetramethyl- [1, 3,2] dioxaborolan) are obtained.
- Example 17 2,2-difluoro-i '- ⁇ [3- (1H-pyrazol-4-yl) pyrrolidin-1 -yllcarbonyl ⁇ ⁇ 1 ⁇ 1 - 1 ⁇ -dihydro-spiro [cyclopropane-1,4'- quinoline] (example 183)
- Me and Et respectively represent methyl and ethyl groups
- the compounds according to the invention have been the subject of pharmacological tests to determine their inhibitory effect of the enzyme 11beta-HSD1 which is an enzyme that is involved in lipid metabolism or glucose metabolism. These tests consisted in measuring the in vitro inhibitory activity of the compounds of the invention by means of a SPA (Scintillation Proximity Assay) test in 384-well format.
- the recombinant 11beta-HSD1 protein was produced in S. cerevisiae yeast.
- the reaction was performed by incubating the enzyme in the presence of 3 H-cortisone and NADPH, in the absence or presence of increasing inhibitor concentration.
- the inhibitory activity with respect to the 11 beta-HSD1 enzyme is given by the concentration which inhibits 50% of the activity of 11beta-HSD1 (Cl 50 ).
- Cl 50 of the compounds according to the invention are less than 1 ⁇ M.
- the Cl 50's of Compounds Nos. 4, 7, 18, 78, 101, 162 and 188 are respectively 0.115 ⁇ M, 0.230 ⁇ M, 0.043 ⁇ M, 0.039 ⁇ M, 0.09 ⁇ M, 0.057 ⁇ M and 0.130 ⁇ M.
- the compounds according to the invention have an inhibitory activity of the 11beta-HSD1 enzyme.
- the compounds according to the invention can therefore be used for the preparation of medicaments, in particular drugs which inhibit the 11beta-HSD1 enzyme.
- the subject of the invention is medicaments which comprise a compound of formula (I), or an addition salt thereof to a pharmaceutically acceptable acid, or a hydrate or a solvate of compound of formula (I).
- the present invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising, as active principle, a compound according to the invention.
- These pharmaceutical compositions contain an effective dose of at least one compound according to the invention or a salt pharmaceutically acceptable, a hydrate or solvate of said compound, as well as at least one pharmaceutically acceptable excipient.
- Said excipients are chosen according to the pharmaceutical form and the desired mode of administration, from the usual excipients which are known to those skilled in the art.
- compositions of the present invention for oral, sublingual, subcutaneous, intramuscular, intravenous, topical, local, intratracheal, intranasal, transdermal or rectal administration the active ingredient of formula (I) above, or its salt, solvate or hydrate, may be administered in unit dosage form, in admixture with conventional pharmaceutical excipients, to animals and humans for the prophylaxis or treatment of the above disorders or diseases.
- Suitable unit dosage forms include oral forms, such as tablets, soft or hard capsules, powders, granules and oral solutions or suspensions, sublingual, oral, intratracheal, intraocular, Intranasal, inhalation, topical, transdermal, subcutaneous, intramuscular or intravenous administration forms, rectal administration forms and implants.
- oral forms such as tablets, soft or hard capsules, powders, granules and oral solutions or suspensions
- sublingual, oral, intratracheal intraocular, Intranasal, inhalation
- topical, transdermal, subcutaneous, intramuscular or intravenous administration forms rectal administration forms and implants.
- the compounds according to the invention can be used in creams, gels, ointments or lotions.
- a unitary form of administration of a compound according to the invention in tablet form may comprise the following components: Compound according to the invention 50.0 mg
- the present invention also relates to a method of treatment of the pathologies indicated above which comprises the administration to a patient of an effective dose of a compound according to the invention, or one of its pharmaceutically acceptable salts or hydrates or solvates.
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Diabetes (AREA)
- Obesity (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Cardiology (AREA)
- Hematology (AREA)
- Physical Education & Sports Medicine (AREA)
- Immunology (AREA)
- Endocrinology (AREA)
- Neurosurgery (AREA)
- Rheumatology (AREA)
- Orthopedic Medicine & Surgery (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Ophthalmology & Optometry (AREA)
- Neurology (AREA)
- Emergency Medicine (AREA)
- Psychiatry (AREA)
- Hospice & Palliative Care (AREA)
- Vascular Medicine (AREA)
- Urology & Nephrology (AREA)
- Child & Adolescent Psychology (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Pharmaceuticals Containing Other Organic And Inorganic Compounds (AREA)
- Plural Heterocyclic Compounds (AREA)
- Hydrogenated Pyridines (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Claims
Priority Applications (8)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CA002652852A CA2652852A1 (fr) | 2006-06-27 | 2007-06-26 | Derives d'urees de piperidine ou pyrrolidine, leur preparation et leur application en therapeutique |
| AU2007264791A AU2007264791A1 (en) | 2006-06-27 | 2007-06-26 | Derivatives of ureas of piperidine or pyrrolidine, their preparation and their therapeutical use |
| EP07803781A EP2044057A2 (fr) | 2006-06-27 | 2007-06-26 | Dérivés d'urées de piperidine ou pyrrolidine, leur préparation et leur application en thérapeutique |
| MX2008016563A MX2008016563A (es) | 2006-06-27 | 2007-06-26 | Derivados de ureas de piperidina o pirrolidina, su preparación y su aplicación en terapeutica. |
| BRPI0713042-2A BRPI0713042A2 (pt) | 2006-06-27 | 2007-06-26 | derivados de urÉias de piperidina ou pirrolidina, o respectivo preparo e a respectiva aplicaÇço em terapÊutica |
| JP2009517318A JP2009541463A (ja) | 2006-06-27 | 2007-06-26 | ピペリジンまたはピロリジンの尿素誘導体、これらの調製およびこれらの治療的使用 |
| IL195820A IL195820A0 (en) | 2006-06-27 | 2008-12-09 | Derivatives of ureas of piperidine or pyrrolidine, their preparation and their therapeutical use |
| US12/337,967 US7947834B2 (en) | 2006-06-27 | 2008-12-18 | Substituted quinoxalines, their preparation and their therapeutical use as 11βHSD1 modulators |
Applications Claiming Priority (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| FR0605786 | 2006-06-27 | ||
| FR0605786A FR2902790A1 (fr) | 2006-06-27 | 2006-06-27 | Derives d'urees de piperidine ou pyrrolidine,leur preparation et leur application en therapeutique |
| FR0611239 | 2006-12-22 | ||
| FR0611239 | 2006-12-22 |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US12/337,967 Continuation US7947834B2 (en) | 2006-06-27 | 2008-12-18 | Substituted quinoxalines, their preparation and their therapeutical use as 11βHSD1 modulators |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2008000950A2 true WO2008000950A2 (fr) | 2008-01-03 |
| WO2008000950A3 WO2008000950A3 (fr) | 2008-02-14 |
Family
ID=38692075
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/FR2007/001069 WO2008000950A2 (fr) | 2006-06-27 | 2007-06-26 | Dérivés d'urées de piperidine ou pyrrolidine, leur préparation et leur application en thérapeutique |
Country Status (16)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US7947834B2 (fr) |
| EP (1) | EP2044057A2 (fr) |
| JP (1) | JP2009541463A (fr) |
| KR (1) | KR20090021192A (fr) |
| AR (1) | AR061643A1 (fr) |
| AU (1) | AU2007264791A1 (fr) |
| BR (1) | BRPI0713042A2 (fr) |
| CA (1) | CA2652852A1 (fr) |
| CL (1) | CL2007001886A1 (fr) |
| IL (1) | IL195820A0 (fr) |
| MX (1) | MX2008016563A (fr) |
| PE (1) | PE20080212A1 (fr) |
| RU (1) | RU2009102527A (fr) |
| TW (1) | TW200811158A (fr) |
| UY (1) | UY30448A1 (fr) |
| WO (1) | WO2008000950A2 (fr) |
Cited By (15)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2009021740A2 (fr) | 2007-08-15 | 2009-02-19 | Sanofis-Aventis | Nouvelles tétrahydronaphtalines substituées, leurs procédés de préparation et leur utilisation comme médicaments |
| FR2948369A1 (fr) * | 2009-07-27 | 2011-01-28 | Sanofi Aventis | Derives d'uree de tetrahydroquinoxaline, leur preparation et leur application en therapeutique |
| FR2948370A1 (fr) * | 2009-07-27 | 2011-01-28 | Sanofi Aventis | Derives d'uree de tetrahydroquinoxaline, leur preparation et leur application en therapeutique |
| JP2011510919A (ja) * | 2008-01-28 | 2011-04-07 | サノフイ−アベンテイス | テトラヒドロキノキサリン尿素誘導体、これらの調製、および治療的適用 |
| WO2011107494A1 (fr) | 2010-03-03 | 2011-09-09 | Sanofi | Nouveaux dérivés aromatiques de glycoside, médicaments contenants ces composés, et leur utilisation |
| WO2011157827A1 (fr) | 2010-06-18 | 2011-12-22 | Sanofi | Dérivés d'azolopyridin-3-one en tant qu'inhibiteurs de lipases et de phospholipases |
| WO2011161030A1 (fr) | 2010-06-21 | 2011-12-29 | Sanofi | Dérivés de méthoxyphényle à substitution hétérocyclique par un groupe oxo, leur procédé de production et leur utilisation comme modulateurs du récepteur gpr40 |
| WO2012004270A1 (fr) | 2010-07-05 | 2012-01-12 | Sanofi | Dérivés 1,3-propanedioxyde à substitution spirocyclique, procédé de préparation et utilisation comme médicament |
| WO2012004269A1 (fr) | 2010-07-05 | 2012-01-12 | Sanofi | Dérivés d'acide ( 2 -aryloxy -acétylamino) - phényl - propionique, procédé de production et utilisation comme médicament |
| WO2012010413A1 (fr) | 2010-07-05 | 2012-01-26 | Sanofi | Acides hydroxy-phényl-hexiniques substitués par aryloxy-alkylène, procédé de production et utilisation comme médicament |
| WO2013037390A1 (fr) | 2011-09-12 | 2013-03-21 | Sanofi | Dérivés amides d'acide 6-(4-hydroxyphényl)-3-styryl-1h-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridine-4-carboxylique en tant qu'inhibiteurs de kinase |
| WO2013045413A1 (fr) | 2011-09-27 | 2013-04-04 | Sanofi | Dérivés d'amide d'acide 6-(4-hydroxyphényl)-3-alkyl-1h-pyrazolo[3,4-b] pyridine-4-carboxylique utilisés comme inhibiteurs de kinase |
| US8524894B2 (en) | 2009-06-04 | 2013-09-03 | Laboratorios Salvat, S.A. | Inhibitor compounds of 11-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 |
| WO2022234193A1 (fr) * | 2021-05-07 | 2022-11-10 | Forendo Pharma Ltd | Nouveaux composés hétérocycliques, compositions, procédés de préparation et utilisations de ceux-ci |
| KR20230171398A (ko) * | 2022-06-10 | 2023-12-20 | 주식회사 사피엔스바이오 | 신규한 화합물 및 이를 유효성분으로 포함하는 약학적 조성물 |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DK2248812T5 (da) * | 2006-06-27 | 2015-01-26 | Takeda Pharmaceutical | Kondenserede cykliske forbindelser som GPR40-receptormodulatorer |
| US9388161B2 (en) | 2013-11-18 | 2016-07-12 | Forma Therapeutics, Inc. | Tetrahydroquinoline compositions as BET bromodomain inhibitors |
| EP3071205B1 (fr) | 2013-11-18 | 2020-02-05 | Forma Therapeutics, Inc. | Compositions de benzopipérazine en tant qu'inhibiteurs de bromodomaines bet |
Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO1992022552A1 (fr) * | 1991-06-14 | 1992-12-23 | The Upjohn Company | IMIDAZO[1,5-a]QUINOXALINES |
| EP1283199A1 (fr) * | 2000-05-16 | 2003-02-12 | Takeda Chemical Industries, Ltd. | Antagoniste de l'hormone de concentration de la melanine |
| WO2003031436A1 (fr) * | 2001-10-05 | 2003-04-17 | Recordati S.A. | Composes heterocycliques utilises pour traiter des troubles de la voie urinaire |
| WO2004033427A1 (fr) * | 2002-10-11 | 2004-04-22 | Astrazeneca Ab | Derives de piperidine 1,4 disubstituee et leur utilisation en tant qu'inhibiteurs de 11-betahsd1 |
| WO2005047250A1 (fr) * | 2003-11-05 | 2005-05-26 | Astrazeneca Ab | Utilisation de 3-(benzoyl)-pyrrolidines n-acylees comme inhibiteurs de 11-beta-hsdi pour le traitement de troubles metaboliques |
| WO2006053024A2 (fr) * | 2004-11-10 | 2006-05-18 | Incyte Corporation | Composes de lactame et leur utilisation en temps que substances pharmaceutiques |
| WO2006055752A2 (fr) * | 2004-11-18 | 2006-05-26 | Incyte Corporation | INHIBITEURS DE LA 11-β-HYDROXYSTEROIDE DEHYDROGENASE DE TYPE 1 ET PROCEDES D’UTILISATION |
| WO2006105127A2 (fr) * | 2005-03-31 | 2006-10-05 | Takeda San Diego, Inc. | Inhibiteurs de l'hydroxysteroide deshydrogenase |
| WO2006132436A1 (fr) * | 2005-06-08 | 2006-12-14 | Japan Tobacco Inc. | Composé hétérocyclique |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATE38835T1 (de) | 1983-07-05 | 1988-12-15 | Pfizer | Karbonsaeure-derivate verwendbar bei der verhuetung der zersetzung von knorpeln. |
| US6369057B1 (en) * | 1991-04-15 | 2002-04-09 | Aventis Pharma Deutschland Gmbh | Quinoxalines, processes for their preparation and their use |
| HUP0202001A2 (hu) | 2002-06-14 | 2005-08-29 | Sanofi-Aventis | DDP-IV gátló hatású azabiciklooktán- és nonánszármazékok |
| EP2239012A3 (fr) | 2003-04-11 | 2011-06-15 | High Point Pharmaceuticals, LLC | Dérivés amidés substitués et leurs utilisations pharmaceutiques |
-
2007
- 2007-06-25 TW TW096122887A patent/TW200811158A/zh unknown
- 2007-06-25 PE PE2007000809A patent/PE20080212A1/es not_active Application Discontinuation
- 2007-06-26 AU AU2007264791A patent/AU2007264791A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2007-06-26 EP EP07803781A patent/EP2044057A2/fr not_active Withdrawn
- 2007-06-26 RU RU2009102527/04A patent/RU2009102527A/ru not_active Application Discontinuation
- 2007-06-26 MX MX2008016563A patent/MX2008016563A/es unknown
- 2007-06-26 BR BRPI0713042-2A patent/BRPI0713042A2/pt not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2007-06-26 CL CL2007001886A patent/CL2007001886A1/es unknown
- 2007-06-26 AR ARP070102822A patent/AR061643A1/es not_active Application Discontinuation
- 2007-06-26 CA CA002652852A patent/CA2652852A1/fr not_active Abandoned
- 2007-06-26 KR KR1020087031622A patent/KR20090021192A/ko not_active Application Discontinuation
- 2007-06-26 JP JP2009517318A patent/JP2009541463A/ja not_active Withdrawn
- 2007-06-26 WO PCT/FR2007/001069 patent/WO2008000950A2/fr active Application Filing
- 2007-06-27 UY UY30448A patent/UY30448A1/es not_active Application Discontinuation
-
2008
- 2008-12-09 IL IL195820A patent/IL195820A0/en unknown
- 2008-12-18 US US12/337,967 patent/US7947834B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO1992022552A1 (fr) * | 1991-06-14 | 1992-12-23 | The Upjohn Company | IMIDAZO[1,5-a]QUINOXALINES |
| EP1283199A1 (fr) * | 2000-05-16 | 2003-02-12 | Takeda Chemical Industries, Ltd. | Antagoniste de l'hormone de concentration de la melanine |
| WO2003031436A1 (fr) * | 2001-10-05 | 2003-04-17 | Recordati S.A. | Composes heterocycliques utilises pour traiter des troubles de la voie urinaire |
| WO2004033427A1 (fr) * | 2002-10-11 | 2004-04-22 | Astrazeneca Ab | Derives de piperidine 1,4 disubstituee et leur utilisation en tant qu'inhibiteurs de 11-betahsd1 |
| WO2005047250A1 (fr) * | 2003-11-05 | 2005-05-26 | Astrazeneca Ab | Utilisation de 3-(benzoyl)-pyrrolidines n-acylees comme inhibiteurs de 11-beta-hsdi pour le traitement de troubles metaboliques |
| WO2006053024A2 (fr) * | 2004-11-10 | 2006-05-18 | Incyte Corporation | Composes de lactame et leur utilisation en temps que substances pharmaceutiques |
| WO2006055752A2 (fr) * | 2004-11-18 | 2006-05-26 | Incyte Corporation | INHIBITEURS DE LA 11-β-HYDROXYSTEROIDE DEHYDROGENASE DE TYPE 1 ET PROCEDES D’UTILISATION |
| WO2006105127A2 (fr) * | 2005-03-31 | 2006-10-05 | Takeda San Diego, Inc. | Inhibiteurs de l'hydroxysteroide deshydrogenase |
| WO2006132436A1 (fr) * | 2005-06-08 | 2006-12-14 | Japan Tobacco Inc. | Composé hétérocyclique |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| GRZYB J A ET AL: "Carbamoylimidazolium and thiocarbamoylimidazolium salts: novel reagents for the synthesis of ureas, thioureas, carbamates, thiocarbamates and amides" TETRAHEDRON, ELSEVIER SCIENCE PUBLISHERS, AMSTERDAM, NL, vol. 61, no. 30, 25 juillet 2005 (2005-07-25), pages 7153-7175, XP004970475 ISSN: 0040-4020 * |
| See also references of EP2044057A2 * |
Cited By (21)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2009021740A2 (fr) | 2007-08-15 | 2009-02-19 | Sanofis-Aventis | Nouvelles tétrahydronaphtalines substituées, leurs procédés de préparation et leur utilisation comme médicaments |
| JP2011510919A (ja) * | 2008-01-28 | 2011-04-07 | サノフイ−アベンテイス | テトラヒドロキノキサリン尿素誘導体、これらの調製、および治療的適用 |
| US8822452B2 (en) | 2009-06-04 | 2014-09-02 | Laboratorios Salvat, S.A. | Inhibitor compounds of 11-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 |
| US8524894B2 (en) | 2009-06-04 | 2013-09-03 | Laboratorios Salvat, S.A. | Inhibitor compounds of 11-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 |
| US8530473B2 (en) | 2009-07-27 | 2013-09-10 | Sanofi | Tetrahydroquinoxaline urea derivatives as modulators of 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 |
| WO2011012801A1 (fr) * | 2009-07-27 | 2011-02-03 | Sanofi-Aventis | Dérivés d'urée de tetrahydroquinoxaline, leur préparation et leur application en thérapeutique |
| WO2011012800A1 (fr) * | 2009-07-27 | 2011-02-03 | Sanofi-Aventis | Dérivés d'urée de tetrahydroquinoxaline, leur préparation et leur application en thérapeutique |
| FR2948369A1 (fr) * | 2009-07-27 | 2011-01-28 | Sanofi Aventis | Derives d'uree de tetrahydroquinoxaline, leur preparation et leur application en therapeutique |
| US8536173B2 (en) | 2009-07-27 | 2013-09-17 | Sanofi | Tetrahydroquinoxaline urea derivatives as modulators of 11-B-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type I |
| FR2948370A1 (fr) * | 2009-07-27 | 2011-01-28 | Sanofi Aventis | Derives d'uree de tetrahydroquinoxaline, leur preparation et leur application en therapeutique |
| WO2011107494A1 (fr) | 2010-03-03 | 2011-09-09 | Sanofi | Nouveaux dérivés aromatiques de glycoside, médicaments contenants ces composés, et leur utilisation |
| WO2011157827A1 (fr) | 2010-06-18 | 2011-12-22 | Sanofi | Dérivés d'azolopyridin-3-one en tant qu'inhibiteurs de lipases et de phospholipases |
| WO2011161030A1 (fr) | 2010-06-21 | 2011-12-29 | Sanofi | Dérivés de méthoxyphényle à substitution hétérocyclique par un groupe oxo, leur procédé de production et leur utilisation comme modulateurs du récepteur gpr40 |
| WO2012004270A1 (fr) | 2010-07-05 | 2012-01-12 | Sanofi | Dérivés 1,3-propanedioxyde à substitution spirocyclique, procédé de préparation et utilisation comme médicament |
| WO2012010413A1 (fr) | 2010-07-05 | 2012-01-26 | Sanofi | Acides hydroxy-phényl-hexiniques substitués par aryloxy-alkylène, procédé de production et utilisation comme médicament |
| WO2012004269A1 (fr) | 2010-07-05 | 2012-01-12 | Sanofi | Dérivés d'acide ( 2 -aryloxy -acétylamino) - phényl - propionique, procédé de production et utilisation comme médicament |
| WO2013037390A1 (fr) | 2011-09-12 | 2013-03-21 | Sanofi | Dérivés amides d'acide 6-(4-hydroxyphényl)-3-styryl-1h-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridine-4-carboxylique en tant qu'inhibiteurs de kinase |
| WO2013045413A1 (fr) | 2011-09-27 | 2013-04-04 | Sanofi | Dérivés d'amide d'acide 6-(4-hydroxyphényl)-3-alkyl-1h-pyrazolo[3,4-b] pyridine-4-carboxylique utilisés comme inhibiteurs de kinase |
| WO2022234193A1 (fr) * | 2021-05-07 | 2022-11-10 | Forendo Pharma Ltd | Nouveaux composés hétérocycliques, compositions, procédés de préparation et utilisations de ceux-ci |
| KR20230171398A (ko) * | 2022-06-10 | 2023-12-20 | 주식회사 사피엔스바이오 | 신규한 화합물 및 이를 유효성분으로 포함하는 약학적 조성물 |
| KR102715926B1 (ko) | 2022-06-10 | 2024-10-15 | 주식회사 사피엔스바이오 | 신규한 화합물 및 이를 유효성분으로 포함하는 약학적 조성물 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US20090176775A1 (en) | 2009-07-09 |
| KR20090021192A (ko) | 2009-02-27 |
| MX2008016563A (es) | 2009-03-02 |
| AU2007264791A1 (en) | 2008-01-03 |
| UY30448A1 (es) | 2008-01-31 |
| JP2009541463A (ja) | 2009-11-26 |
| RU2009102527A (ru) | 2010-08-10 |
| WO2008000950A3 (fr) | 2008-02-14 |
| IL195820A0 (en) | 2009-09-01 |
| TW200811158A (en) | 2008-03-01 |
| EP2044057A2 (fr) | 2009-04-08 |
| US7947834B2 (en) | 2011-05-24 |
| CA2652852A1 (fr) | 2008-01-03 |
| CL2007001886A1 (es) | 2009-11-10 |
| PE20080212A1 (es) | 2008-04-25 |
| BRPI0713042A2 (pt) | 2013-01-08 |
| AR061643A1 (es) | 2008-09-10 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2008000950A2 (fr) | Dérivés d'urées de piperidine ou pyrrolidine, leur préparation et leur application en thérapeutique | |
| EP2046791B1 (fr) | Dérivés d'urees de tropane, leur préparation et leur application en thérapeutique | |
| EP2238126B1 (fr) | Dérivés d'urée de tetrahydroquinoxaline, leur préparation et leur application en thérapeutique | |
| EP2528901B9 (fr) | Composés de pyrazole en tant qu'antagonistes de crth2 | |
| EP1989196B1 (fr) | Pipéridinoylpyrrolidines en tant qu'agonistes du récepteur de la mélanocortine de type 4 | |
| CA2701150C (fr) | Derives de quinazolinedione, leur preparation et leurs applications therapeutiques | |
| TW201132642A (en) | Diaza-spiro[5.5]undecanes | |
| US20040162278A1 (en) | Triazole compounds useful in therapy | |
| WO2019089664A1 (fr) | Composés multicycliques en tant que modulateurs du récepteur farnésoïde x | |
| TWI826406B (zh) | 作為血管升壓素V1a受體拮抗劑之三唑並苯並吖呯 | |
| US10889569B2 (en) | Condensed ring group azacyclobutyl triazole derivative, preparation method therefor and use thereof in medicine | |
| CN109689656B (zh) | 7-取代的1-芳基二氮杂萘-3-羧酰胺及其用途 | |
| EP2459549B1 (fr) | Dérivés d'urée de tetrahydroquinoxaline, leur préparation et leur application en thérapeutique | |
| FR2902791A1 (fr) | Derives d'urees de tropane,leur preparation et leur application en therapeutique | |
| AU2008307576A1 (en) | N-substituted oxindoline derivatives as calcium channel blockers | |
| FR2902790A1 (fr) | Derives d'urees de piperidine ou pyrrolidine,leur preparation et leur application en therapeutique | |
| EP3227282B1 (fr) | Nouveaux dérivés de pipéridine | |
| JP5243274B2 (ja) | 4型メラノコルチン受容体アゴニストのピペリジノイルピロリジン | |
| RU2409582C2 (ru) | Конденсированные трициклические производные для лечения психотических расстройств | |
| FR2934858A1 (fr) | Derives d'uree de tetrahydroquinoxaline, leur preparation et leur application en therapeutique | |
| FR2911874A1 (fr) | Derives d'urees de tropane, leur preparation et leur application en therapeutique |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 200780024556.2 Country of ref document: CN |
|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 07803781 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A2 |
|
| DPE1 | Request for preliminary examination filed after expiration of 19th month from priority date (pct application filed from 20040101) | ||
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2652852 Country of ref document: CA |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 195820 Country of ref document: IL |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 5196/KOLNP/2008 Country of ref document: IN Ref document number: MX/A/2008/016563 Country of ref document: MX |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2007803781 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2009517318 Country of ref document: JP Ref document number: 1020087031622 Country of ref document: KR |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2007264791 Country of ref document: AU |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2009102527 Country of ref document: RU Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2007264791 Country of ref document: AU Date of ref document: 20070626 Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: PI0713042 Country of ref document: BR Kind code of ref document: A2 Effective date: 20081229 |