US3482294A - Apparatus for fluid treating filamentary materials - Google Patents
Apparatus for fluid treating filamentary materials Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- US3482294A US3482294A US695511A US3482294DA US3482294A US 3482294 A US3482294 A US 3482294A US 695511 A US695511 A US 695511A US 3482294D A US3482294D A US 3482294DA US 3482294 A US3482294 A US 3482294A
- Authority
- US
- United States
- Prior art keywords
- orifices
- fluid
- chamber
- yarn
- injector
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
- 239000012530 fluid Substances 0.000 title description 32
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 title description 4
- 238000002788 crimping Methods 0.000 description 22
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000012856 packing Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000004753 textile Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000004677 Nylon Substances 0.000 description 1
- 208000003028 Stuttering Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 239000000835 fiber Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920001778 nylon Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000013589 supplement Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920001169 thermoplastic Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004416 thermosoftening plastic Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000011144 upstream manufacturing Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D02—YARNS; MECHANICAL FINISHING OF YARNS OR ROPES; WARPING OR BEAMING
- D02G—CRIMPING OR CURLING FIBRES, FILAMENTS, THREADS, OR YARNS; YARNS OR THREADS
- D02G1/00—Producing crimped or curled fibres, filaments, yarns, or threads, giving them latent characteristics
- D02G1/12—Producing crimped or curled fibres, filaments, yarns, or threads, giving them latent characteristics using stuffer boxes
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D02—YARNS; MECHANICAL FINISHING OF YARNS OR ROPES; WARPING OR BEAMING
- D02G—CRIMPING OR CURLING FIBRES, FILAMENTS, THREADS, OR YARNS; YARNS OR THREADS
- D02G1/00—Producing crimped or curled fibres, filaments, yarns, or threads, giving them latent characteristics
- D02G1/16—Producing crimped or curled fibres, filaments, yarns, or threads, giving them latent characteristics using jets or streams of turbulent gases, e.g. air, steam
Definitions
- the invention relates to an apparatus for the treatment of textile yarns, and more particularly to an apparatus for the stuffer crimping of yarns, comprising an elongated tubular chamber provided at one end with a pneumatic device for the introduction of a yarn and having between its two ends means for partially evacuating the fluid introduced by the pneumatic device.
- thermoplastics textile yarns consists in accumulating them under pressure in a crimping chamber provided at its outlet with a wall capable of maintaining the pressure at a predetermined value, the deformations obtained being set by heat treatment, usually within the crimping chamber.
- the yarn is fed by means of rollers into the crimping chamber wherein it accumulates until its pressure is sufiicient to pivot counter-pressure devices opposing emergence of the crimped material from the chamber.
- this apparatus comprises a number of mechanical, moving members, and this is always a disadvantage when it is desirable to operate at high speed.
- a simpler known apparatus comprises a pneumatic device for feeding the yarn into the crimping chamber, the wall of such chamber being constituted by a moving belt which maintains the pressure within the chamber and also provides for the advance of the packed yarn.
- the present invention relates to apparatus which is even simpler still and does not comprise any moving mechanical elements.
- the apparatus of this invention comprises a tubular member defining an elongated laterally confined space, means operative to produce a current of fluid under pressure through said space from one end thereof to the other for introducing filaments to be treated into said one end thereof, and means on said member spaced from said other end of said space effective to controllably release part of said fluid laterally of said space.
- the tubular member preferably has the shape of a cylinder and in particular a right circular cylinder, but it may also have the shape of a parallelepipedon.
- a tubular member the zone of which near the outlet end is inwardly curved. It is also possible to adjust the packing of the yarn by appropriate selection of the material of the inner surface of the tubular member, since the coefficient of friction between the packed yarn and the tubular member varies in accordance with such material, or by modifying the structure of the said inner surface, for example by means of grooves extending perpendicular to the axis.
- the said co-efficient of friction may also be influenced by the nature of the fluid utilised.
- the length and the cross-section of the enclosed space delimited by the tubular member may vary depending on the count of the yarn to be processed, the effect on the yarn desired, etc.
- the tubular member may be rigid or deformable.
- any pneumatic injector of known type may be employed.
- such injector is adapted to introduce the yarn and the fluid axially simultaneously into the tubular member. It may be constituted by a simple tube the cross-section of which is smaller than that of the tubular member, such as for example the apparatus described in French Patent No. 674,578 of Oct. 22, 1929.
- the means for laterally evacuating the fluid in a controlled manner may be orifices formed in the wall of the enclosed space and preferably distributed over the entire periphery of a zone of the enclosed space. They may have a surface which is fixed or adjustable, such surface being selected as a function of the rate of flow of the fluid passing through the apparatus. Preferably small-dimension orifices will be utilised, and, if necessary, there will be a large number of such orifices, in order to prevent the fluid laterally entraining the yarn to an excessive degree; if the apparatus is intended for the treatment of tows, the said orifices may, however, have relatively large dimensions.
- the zone of the tubular member in which the orifices are formed is preferably located a short distance from the inlet end of the tubular member.
- the orifices may establish communication between the enclosed space delimited by the tubular member and an atmosphere at atmospheric pressure or at a pressure differing from atmospheric pressure.
- the essential feature in order that the device may function is that the pressure of the said atmosphere shall be less than the pressure of the fluid feeding the injector and equal to or higher than the pressure obtaining at the outlet end.
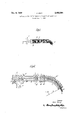
- FIGURE 1 is a diagrammatic sectional view of one embodiment of apparatus according to this invention wherein the tubular member is straight;
- FIGURE 2 is a diagrammatic sectional view of a second embodiment of apparatus according to this invention wherein the tubular member is curved.
- the apparatus illustrated comprises a pneumatic injector which has a fluid-feeding means 1 and a passage for the yarn 2 and is fitted at the end of a tube 3 formed with orifices 4 arranged in a number of annular rows, only two of which are illustrated in the drawing.
- the tube 3 may be a cylindrical tube which is 12 cm. long and 0.8 cm. in diameter and is provided in a zone extending from a position 1 cm. from the inlet end to a position 2 ems. from the inlet end with four annular rows of orifices, the orifices being 0.1 cm. in diameter and there being twelve orifices in each row.
- This apparatus may be utilised for example for crimping a nylon yarn (50 denier, 17-filaments) introduced into the enclosed space provided by tube 3 at a rate of 40 metres per minute by means of the injector fed with steam at a pressure of 4 kg./cm. and at a temperature of 151 C.
- the greater part of the steam escapes violently in a radial direction.
- the fluid entrains the yarn which no longer follows a substantially rectilinear path but is strongly nndulated until it forms a compact mass 6 which is accumulated and packed and progresses in the enclosed space, being recovered in the form of a wad 7.
- the violence with which the fluid escapes through the first row of orifices may be such that it will sometimes entrain the yarn through such orifices; then, however, the pressure of the fluid on the packed yarn increases and causes the yarn to advance, thus once again freeing the orifices.
- FIGURE 2 shows a further embodiment of apparatus according to the invention.
- reference numeral 8 designates the injector which comprises a nozzle 10 having therethrough a passage 10' and a pipe 11 having an end 11 into which the nozzle is screwed and surrounding the outlet of the passage 10'.
- a conduit 12 having a passage 12' there through and an enlarged extension 13 provided with a permeable wall.
- Fitted within the extension 13 is a metal spring 14 having gaps 14 between the convolutions thereof.
- the spring 14 is curved at its outlet end to an arc of radius R, length l and having an angle a at the centre.
- the tubular member is constituted by the combination of the conduit 12 and the spring 14.
- the passage Ill has an inner diameter which is 10 mm. at the inlet and 2 mm. in its downstream portion where the outer wall of the nozzle 10 has the shape of a frustum of a cone, the apex angle of which is 53.
- the outlet orifice of the injector has an inner diameter of 3 mm. and the inner wall of the injector has, in its downstream portion, the shape of a frustum of a cone, the apex angle of which is 66".
- the length of the conduit 12 is 10 mm.,. and the diameter is 10 mm.
- the spring 14 has an internal diameter of 10 mm. and a length of 110 mm.
- the angle a, as shown in FIGURE 2, is approximately 40 and Z is approximately 80 mm.
- the wall 7 which is diametrally and longitudinally permeable canalises the vapour escaping through the first convolutions of the spring, thus contributing to increasing the temperature of the packed yarn.
- Fiber stufling apparatus comprising a tubular member defining an elongated laterally confined space, means operative to produce a current of fluid under pressure through said space from one end thereof to the other for introducing filaments to be treated into said one end thereof, and means on said member spaced from said other end of said space effective to controllably release part of said fluid laterally of said space.
- Stuffer crimping apparatus comprising a tubular member defining an elongate laterally confined space, means operative to produce a current of heated fluid under pressure through said space from one end thereof to the other for introducing filaments to be crimped into said one end thereof, and means on said member spaced from said other end of said space effective to controllably release part of said fluid laterally of said space.
- Stuffer crimping apparatus comprising an injector having therethrough a passage for filaments; a tubular Wall defining an elongate confining crimping chamber having an inlet end communicating with said injector and having an outlet end; a central portion at least of said wall spaced from said outlet end of the chamber having orifices therein constructed such that fluid passing into said inlet end of the chamber will be released through said orifices; and means for supplying heated fluid under pressure to said injector and in a direction to entrain filaments in said passage and cause such filaments to pass into the inlet end of said chamber and be packed therein by lateral release of fluid through said orifices and the packed filaments forced through the chamber to the outlet end thereof.
- Stuffer crimping apparatus comprising a pipe having a bore therethrough; an enlargement of said pipe having an outlet orifice communicating with said bore; a nozzle mounted in said pipe enlargement and having an outlet Within and aligned with said outlet orifice of the pipe enlargement; a tube mounted adjacent said pipe enlargement and having a passage therethrough; a permeable extension to said tube; a coil spring mounted within said extension and projecting outwardly thereof, coils of said spring with- .in said extension being spaced apart; and means for supplying heated fluid under pressure through said pipe.
- Stuffer crimping apparatus comprising an injector having therethrough a passage for filaments; a tubular wall defining an elongate confining crimping chamber having an inlet end communicating with said injector and having a curved outlet end; a central portion at least of said wall spaced from said outlet end of the chamber having orifices therein constructed such that fluid passing into said inlet end of the chamber will be released through said orifices; and means for supplying heated fluid under pressure to said injector and in a direction to entrain filaments in said passage and cause such filaments to pass into the inlet end of said chamber and be packed therein by lateral release of fluid through said orifices and the packed filaments forced through the chamber to the outlet end thereof.
- Stuifer crimping apparatus comprising an injector having therethrough a passage for filaments; a tubular wall defining an elongate confining crimping chamber having an inlet end communicating with said injector and having an outlet end; a coil spring forming at least the outlet end of said crimping chamber; a central portion at least of said wall spaced from said outlet end of the chamber having orifices therein constructed such that fluid passing into said inlet end of the chamber will be released through said orifices; and means for supplying heated fluid under pressure to said injector and in a direction to entrain filaments in said passage and cause such filaments to pass into the inlet end of said chamber and be packed therein by lateral release of fluid through said orifices and the packed filaments forced through the chamber to the outlet end thereof.
- Stuffer crimping apparatus comprising an injector having therethrough a passage for filaments; a tubular wall defining an elongate confining crimping chamber having an inlet end communicating with said injector, an outlet section and a central section between said inlet end and outlet section, a coil spring forming at least the central section and outlet section of said chamber, the coil spring at least at the central section being extended to open the coils of the spring to provide orifices such that fluid passing into said inlet end of the chamber will be released through said orifices; and means for supplying heated fluid under pressure to said injector and in a direction to entrain filaments in said passage and cause such filaments to pass into the inlet end of said chamber and be packed therein by lateral release of fluid through said orifices and the packed UNITED STATES PATENTS 3,296,677 1/1967 Chase.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Textile Engineering (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Fluid Mechanics (AREA)
- Yarns And Mechanical Finishing Of Yarns Or Ropes (AREA)
- Compositions Of Macromolecular Compounds (AREA)
- Treatment Of Fiber Materials (AREA)
Description
J. JOLY Dec. 9, 1969 APPARATUS FOR FLUID TREATING FILAMENTARY MATERIALS Filed Jan. 5, 1968 Inventor J'EHN J'DLLy -m,%
A Home y 5 United States Patent 3,482,294 APPARATUS FOR FLUID TREATING FILAMENTARY MATERIALS Jean Joly, Brindas, France, assignor to Societe Rhodiaceta, Paris, France, a French body corporate Continuation-impart of application Ser. No. 355,379, Mar. 27, 1964. This application Jan. 3, 1968, Ser. No. 695,511 Claims priority, application France, Feb. 8, 1961, 852,055; Dec. 21, 1961, 882,739, 882,740; Mar. 25, 1963, 929,113, 929,115
Int. Cl. D02g 1/16 US. Cl. 281 8 Claims ABSTRACT OF THE DISCLOSURE The invention relates to an apparatus for the treatment of textile yarns, and more particularly to an apparatus for the stuffer crimping of yarns, comprising an elongated tubular chamber provided at one end with a pneumatic device for the introduction of a yarn and having between its two ends means for partially evacuating the fluid introduced by the pneumatic device.
Cross-reference to related applications This application is a continuation-in-part of application Ser. No. 355,379 filed on Mar. 27, 1964, now US. Patent 3,373,470, granted Mar. 19, 1968, itself a continuation-inpart of application Ser. No. 171,521 filed Feb. 6, 1962, now abandoned.
Background of the invention A known process for the crimping of thermoplastics textile yarns consists in accumulating them under pressure in a crimping chamber provided at its outlet with a wall capable of maintaining the pressure at a predetermined value, the deformations obtained being set by heat treatment, usually within the crimping chamber.
Various types of apparatus may be employed for the practical carrying into effect of such process. In the best known type, the yarn is fed by means of rollers into the crimping chamber wherein it accumulates until its pressure is sufiicient to pivot counter-pressure devices opposing emergence of the crimped material from the chamber. As will be appreciated, this apparatus comprises a number of mechanical, moving members, and this is always a disadvantage when it is desirable to operate at high speed.
A simpler known apparatus comprises a pneumatic device for feeding the yarn into the crimping chamber, the wall of such chamber being constituted by a moving belt which maintains the pressure within the chamber and also provides for the advance of the packed yarn.
Summary of the invention The present invention relates to apparatus which is even simpler still and does not comprise any moving mechanical elements.
The apparatus of this invention comprises a tubular member defining an elongated laterally confined space, means operative to produce a current of fluid under pressure through said space from one end thereof to the other for introducing filaments to be treated into said one end thereof, and means on said member spaced from said other end of said space effective to controllably release part of said fluid laterally of said space.
The tubular member preferably has the shape of a cylinder and in particular a right circular cylinder, but it may also have the shape of a parallelepipedon. In some cases, and particularly when it is desired to supplement resistance to the passage of the yarn and in this way to 3,482,294 Patented Dec. 9, 1969 increase the packing effect, it is appropriate to employ a tubular member, the zone of which near the outlet end is inwardly curved. It is also possible to adjust the packing of the yarn by appropriate selection of the material of the inner surface of the tubular member, since the coefficient of friction between the packed yarn and the tubular member varies in accordance with such material, or by modifying the structure of the said inner surface, for example by means of grooves extending perpendicular to the axis. The said co-efficient of friction may also be influenced by the nature of the fluid utilised.
Furthermore, the length and the cross-section of the enclosed space delimited by the tubular member may vary depending on the count of the yarn to be processed, the effect on the yarn desired, etc. By way of example, it is possible to employ for the crimping of 70 denier yarns a cylindrical tubular member which is 4 cm. long and 0.4 cm. in diameter, and for the crimping of 240,000 deniers roving a tubular member 1 m. long and 5 cm. in diameter. The tubular member may be rigid or deformable.
In order to produce the flow of fluid through the confined space, any pneumatic injector of known type may be employed. Preferably such injector is adapted to introduce the yarn and the fluid axially simultaneously into the tubular member. It may be constituted by a simple tube the cross-section of which is smaller than that of the tubular member, such as for example the apparatus described in French Patent No. 674,578 of Oct. 22, 1929.
The means for laterally evacuating the fluid in a controlled manner may be orifices formed in the wall of the enclosed space and preferably distributed over the entire periphery of a zone of the enclosed space. They may have a surface which is fixed or adjustable, such surface being selected as a function of the rate of flow of the fluid passing through the apparatus. Preferably small-dimension orifices will be utilised, and, if necessary, there will be a large number of such orifices, in order to prevent the fluid laterally entraining the yarn to an excessive degree; if the apparatus is intended for the treatment of tows, the said orifices may, however, have relatively large dimensions.
The zone of the tubular member in which the orifices are formed, is preferably located a short distance from the inlet end of the tubular member.
The orifices may establish communication between the enclosed space delimited by the tubular member and an atmosphere at atmospheric pressure or at a pressure differing from atmospheric pressure. The essential feature in order that the device may function is that the pressure of the said atmosphere shall be less than the pressure of the fluid feeding the injector and equal to or higher than the pressure obtaining at the outlet end.
In order that the invention may more readily be understood, reference will now be made to the accompanying drawings which illustrate, by way of non-limitative example, two forms of apparatus according to the invention. In the drawings:
FIGURE 1 is a diagrammatic sectional view of one embodiment of apparatus according to this invention wherein the tubular member is straight; and
FIGURE 2 is a diagrammatic sectional view of a second embodiment of apparatus according to this invention wherein the tubular member is curved.
Referring to FIGURE 1, the apparatus illustrated comprises a pneumatic injector which has a fluid-feeding means 1 and a passage for the yarn 2 and is fitted at the end of a tube 3 formed with orifices 4 arranged in a number of annular rows, only two of which are illustrated in the drawing.
In one suitable embodiment of the apparatus of FIG- URE 1, the tube 3 may be a cylindrical tube which is 12 cm. long and 0.8 cm. in diameter and is provided in a zone extending from a position 1 cm. from the inlet end to a position 2 ems. from the inlet end with four annular rows of orifices, the orifices being 0.1 cm. in diameter and there being twelve orifices in each row.
This apparatus may be utilised for example for crimping a nylon yarn (50 denier, 17-filaments) introduced into the enclosed space provided by tube 3 at a rate of 40 metres per minute by means of the injector fed with steam at a pressure of 4 kg./cm. and at a temperature of 151 C.
In the zone of the enclosed space upstream of the orifices 4, the fluid is canalised, the flow thereof taking place only with extremely little perturbation which undulates the yarn only to a slight degree.
At the level of the orifices, the greater part of the steam escapes violently in a radial direction. In its lateral movement, the fluid entrains the yarn which no longer follows a substantially rectilinear path but is strongly nndulated until it forms a compact mass 6 which is accumulated and packed and progresses in the enclosed space, being recovered in the form of a wad 7.
The violence with which the fluid escapes through the first row of orifices may be such that it will sometimes entrain the yarn through such orifices; then, however, the pressure of the fluid on the packed yarn increases and causes the yarn to advance, thus once again freeing the orifices.
FIGURE 2 shows a further embodiment of apparatus according to the invention. In this figure, reference numeral 8 designates the injector which comprises a nozzle 10 having therethrough a passage 10' and a pipe 11 having an end 11 into which the nozzle is screwed and surrounding the outlet of the passage 10'. At the outlet of the pipe 11 is located a conduit 12 having a passage 12' there through and an enlarged extension 13 provided with a permeable wall. Fitted within the extension 13 is a metal spring 14 having gaps 14 between the convolutions thereof. The spring 14 is curved at its outlet end to an arc of radius R, length l and having an angle a at the centre. In this device, the tubular member is constituted by the combination of the conduit 12 and the spring 14.
In a suitable embodiment of the apparatus of FIGURE 2 for crimping an 840 denier, 60-filaments yarn 9 introduced at 200 metres per minute into the conduit 12 by steam fed to the injector at a rate of 2 kg./cm. and at a temperature of 165 C., the passage Ill has an inner diameter which is 10 mm. at the inlet and 2 mm. in its downstream portion where the outer wall of the nozzle 10 has the shape of a frustum of a cone, the apex angle of which is 53. The outlet orifice of the injector has an inner diameter of 3 mm. and the inner wall of the injector has, in its downstream portion, the shape of a frustum of a cone, the apex angle of which is 66".
The length of the conduit 12 is 10 mm.,. and the diameter is 10 mm. The spring 14 has an internal diameter of 10 mm. and a length of 110 mm. The angle a, as shown in FIGURE 2, is approximately 40 and Z is approximately 80 mm.
The wall 7 which is diametrally and longitudinally permeable canalises the vapour escaping through the first convolutions of the spring, thus contributing to increasing the temperature of the packed yarn.
The mode of functioning of this apparatus is identical with that previously described and the packed yarn is recovered in the form of a wad 15 from which the crimped yarn is extracted.
I claim:
1. Fiber stufling apparatus comprising a tubular member defining an elongated laterally confined space, means operative to produce a current of fluid under pressure through said space from one end thereof to the other for introducing filaments to be treated into said one end thereof, and means on said member spaced from said other end of said space effective to controllably release part of said fluid laterally of said space.
2. Stuffer crimping apparatus comprising a tubular member defining an elongate laterally confined space, means operative to produce a current of heated fluid under pressure through said space from one end thereof to the other for introducing filaments to be crimped into said one end thereof, and means on said member spaced from said other end of said space effective to controllably release part of said fluid laterally of said space.
3. Stuffer crimping apparatus comprising an injector having therethrough a passage for filaments; a tubular Wall defining an elongate confining crimping chamber having an inlet end communicating with said injector and having an outlet end; a central portion at least of said wall spaced from said outlet end of the chamber having orifices therein constructed such that fluid passing into said inlet end of the chamber will be released through said orifices; and means for supplying heated fluid under pressure to said injector and in a direction to entrain filaments in said passage and cause such filaments to pass into the inlet end of said chamber and be packed therein by lateral release of fluid through said orifices and the packed filaments forced through the chamber to the outlet end thereof.
4. Stuffer crimping apparatus comprising a pipe having a bore therethrough; an enlargement of said pipe having an outlet orifice communicating with said bore; a nozzle mounted in said pipe enlargement and having an outlet Within and aligned with said outlet orifice of the pipe enlargement; a tube mounted adjacent said pipe enlargement and having a passage therethrough; a permeable extension to said tube; a coil spring mounted within said extension and projecting outwardly thereof, coils of said spring with- .in said extension being spaced apart; and means for supplying heated fluid under pressure through said pipe.
5. The stutter crimping apparatus specified in claim 4, in which the said coil spring has a part projecting from said tube extension of curved form.
6. Stuffer crimping apparatus comprising an injector having therethrough a passage for filaments; a tubular wall defining an elongate confining crimping chamber having an inlet end communicating with said injector and having a curved outlet end; a central portion at least of said wall spaced from said outlet end of the chamber having orifices therein constructed such that fluid passing into said inlet end of the chamber will be released through said orifices; and means for supplying heated fluid under pressure to said injector and in a direction to entrain filaments in said passage and cause such filaments to pass into the inlet end of said chamber and be packed therein by lateral release of fluid through said orifices and the packed filaments forced through the chamber to the outlet end thereof.
7. Stuifer crimping apparatus comprising an injector having therethrough a passage for filaments; a tubular wall defining an elongate confining crimping chamber having an inlet end communicating with said injector and having an outlet end; a coil spring forming at least the outlet end of said crimping chamber; a central portion at least of said wall spaced from said outlet end of the chamber having orifices therein constructed such that fluid passing into said inlet end of the chamber will be released through said orifices; and means for supplying heated fluid under pressure to said injector and in a direction to entrain filaments in said passage and cause such filaments to pass into the inlet end of said chamber and be packed therein by lateral release of fluid through said orifices and the packed filaments forced through the chamber to the outlet end thereof.
8. Stuffer crimping apparatus comprising an injector having therethrough a passage for filaments; a tubular wall defining an elongate confining crimping chamber having an inlet end communicating with said injector, an outlet section and a central section between said inlet end and outlet section, a coil spring forming at least the central section and outlet section of said chamber, the coil spring at least at the central section being extended to open the coils of the spring to provide orifices such that fluid passing into said inlet end of the chamber will be released through said orifices; and means for supplying heated fluid under pressure to said injector and in a direction to entrain filaments in said passage and cause such filaments to pass into the inlet end of said chamber and be packed therein by lateral release of fluid through said orifices and the packed UNITED STATES PATENTS 3,296,677 1/1967 Chase.
LOUIS K. RIMRODT, Primary Examiner
Applications Claiming Priority (5)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| FR852055A FR1289491A (en) | 1961-02-08 | 1961-02-08 | Process for crimping thermoplastic yarns, device for its implementation and new yarns obtained |
| FR882740A FR80843E (en) | 1961-12-21 | 1961-12-21 | Process for crimping thermoplastic yarns, device for its implementation and new yarns obtained |
| FR882739A FR80842E (en) | 1961-12-21 | 1961-12-21 | Process for crimping thermoplastic yarns, device for its implementation and new yarns obtained |
| FR929115A FR83329E (en) | 1963-03-25 | 1963-03-25 | Process for crimping thermoplastic yarns, device for its implementation and new yarns obtained |
| FR929113A FR83328E (en) | 1963-03-25 | 1963-03-25 | Process for crimping thermoplastic yarns, device for its implementation and new yarns obtained |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| US3482294A true US3482294A (en) | 1969-12-09 |
Family
ID=27515049
Family Applications (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US355379A Expired - Lifetime US3373470A (en) | 1961-02-08 | 1964-03-27 | Process for crimping yarn |
| US695511A Expired - Lifetime US3482294A (en) | 1961-02-08 | 1968-01-03 | Apparatus for fluid treating filamentary materials |
Family Applications Before (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US355379A Expired - Lifetime US3373470A (en) | 1961-02-08 | 1964-03-27 | Process for crimping yarn |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (2) | US3373470A (en) |
| BE (3) | BE645601A (en) |
| CH (3) | CH378459A (en) |
| DE (3) | DE1435653C2 (en) |
| GB (3) | GB953782A (en) |
| NL (3) | NL6402767A (en) |
Cited By (14)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3707745A (en) * | 1970-12-16 | 1973-01-02 | Phillips Petroleum Co | Yarn texturing |
| US3712526A (en) * | 1970-09-18 | 1973-01-23 | Elitex Z Textilniko Strojirens | Device for storing a transported weft thread |
| US3729831A (en) * | 1970-12-07 | 1973-05-01 | Mitsubishi Rayon Co | Process and apparatus for continuously relaxing textile yarns |
| US3832759A (en) * | 1970-05-01 | 1974-09-03 | Akzona Inc | Process and apparatus for texturizing yarn |
| US3840950A (en) * | 1973-03-22 | 1974-10-15 | Textured Yarn Co | Strand treatment apparatus |
| US3879821A (en) * | 1973-03-22 | 1975-04-29 | Textured Yarn Co | Strand treatment apparatus |
| US3911538A (en) * | 1970-10-15 | 1975-10-14 | Rhone Poulenc Textile | Apparatus for texturizing a plurality of yarns simultaneously |
| US4083208A (en) * | 1975-07-10 | 1978-04-11 | Carl Lennart Ekstroem | Apparatus for the wet treatment of textiles |
| DE2116274C3 (en) | 1970-04-06 | 1979-06-21 | John Heathcoat & Co. Ltd., Tiverton, Devon (Grossbritannien) | Device for the production of a loosened, crimped multifilament yarn |
| EP0049052A1 (en) * | 1980-09-04 | 1982-04-07 | Plasticisers Limited | Yarn crimping by means of a stuffer-box |
| US4691947A (en) * | 1985-01-19 | 1987-09-08 | Barmag Ag | Yarn texturing nozzle |
| US4724588A (en) * | 1985-07-20 | 1988-02-16 | Barmag Ag | Yarn texturing nozzle |
| US5054173A (en) * | 1989-05-18 | 1991-10-08 | Barmag Ag | Method and apparatus for the enhanced crimping of multifilament yarn |
| US20160319469A1 (en) * | 2014-01-02 | 2016-11-03 | American Linc Corp. | Textile stuffer box and method for texturing yarn |
Families Citing this family (29)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3296677A (en) * | 1963-05-20 | 1967-01-10 | Eastman Kodak Co | Crimping apparatus and process |
| US3952385A (en) * | 1973-03-22 | 1976-04-27 | Textured Yarn Co., Inc. | Strand treatment apparatus |
| GB1193625A (en) * | 1966-07-21 | 1970-06-03 | Courtaulds Ltd | Textile Crimping Process. |
| GB1077520A (en) * | 1963-12-27 | 1967-08-02 | Snia Viscosa | Improved process and apparatus for use in the crimping of filaments |
| US3303546A (en) * | 1964-07-22 | 1967-02-14 | British Nylon Spinners Ltd | Apparatus for treating filamentary material in a fluid |
| GB1165672A (en) * | 1966-03-25 | 1969-10-01 | Scragg & Sons | Yarn Bulking Process and Apparatus. |
| US3438105A (en) * | 1966-09-23 | 1969-04-15 | Rhodiaceta | Process for crimping thermoplastic yarns |
| US3435497A (en) * | 1967-09-25 | 1969-04-01 | Techniservice Corp | Strand treatment |
| US3499194A (en) * | 1968-03-20 | 1970-03-10 | Phillips Petroleum Co | Method of glass texturizing |
| US3483691A (en) * | 1968-03-26 | 1969-12-16 | Monsanto Co | Bulky yarn having snarled filaments |
| DE1760168B2 (en) * | 1968-04-11 | 1978-08-10 | Enka Ag, 5600 Wuppertal | Process for the continuous compression crimping of thread bundles consisting of endless thermoplastic threads |
| US3594878A (en) * | 1969-08-11 | 1971-07-27 | Northrop Carolina Inc | Process and apparatus for texturizing yarn |
| US3650431A (en) * | 1969-12-19 | 1972-03-21 | Phillips Petroleum Co | Safety container |
| DE2006022C3 (en) * | 1970-02-11 | 1981-10-15 | Basf Ag, 6700 Ludwigshafen | Device for the production of textured threads |
| USRE29774E (en) * | 1970-10-15 | 1978-09-19 | Rhone-Poulenc-Textile | Elongated textile product |
| US3946133A (en) * | 1971-10-13 | 1976-03-23 | Rhone-Poulenc-Textile Sa | Elongated textile product |
| US3678547A (en) * | 1970-11-06 | 1972-07-25 | Phillips Petroleum Co | Yarn texturing |
| US3724037A (en) * | 1971-05-10 | 1973-04-03 | Tmm Research Ltd | Processes and apparatus for crimping synthetic filamentary materials |
| DE2217109C3 (en) * | 1972-04-10 | 1979-04-12 | Hoechst Ag, 6000 Frankfurt | Method and device for crimping threads and yarns |
| FR2217441B1 (en) * | 1973-02-08 | 1975-03-07 | Rhone Poulenc Textile | |
| FR2288800A1 (en) * | 1974-03-22 | 1976-05-21 | Rhone Poulenc Textile | POLYESTER YARN AND YARN TEXTURING PROCESS OBTAINED BY THIS PROCESS |
| FR2278808A1 (en) * | 1974-06-10 | 1976-02-13 | Rhone Poulenc Textile | PROCESS AND DEVICE FOR CONTINUOUS CRIMPING AND CUTTING OF FILAMENT TEXTILE MATERIAL |
| FR2368211A1 (en) * | 1976-10-21 | 1978-05-19 | Rhone Poulenc Textile | PROCEDURE FOR FIXING SANDY GROUNDS |
| DE2709680C2 (en) * | 1977-03-05 | 1985-07-18 | Basf Farben + Fasern Ag, 2000 Hamburg | Process for the removal of textured yarns |
| DE2722257C2 (en) * | 1977-05-17 | 1983-04-14 | Neumünstersche Maschinen- und Apparatebau GmbH (Neumag), 2350 Neumünster | Shirring chamber for texturing several artificial threads at the same time |
| DE3538871A1 (en) * | 1985-11-02 | 1987-05-07 | Bayer Ag | METHOD FOR TREATING AN ENDLESS FIBER CABLE |
| DE4236514C2 (en) † | 1992-10-26 | 1997-03-27 | Fischer Karl Ind Gmbh | Method and device for conveying and depositing sheets of endless threads by means of air forces |
| DE4320303C1 (en) * | 1993-06-18 | 1995-02-16 | Rhodia Ag Rhone Poulenc | Multi-wide fiber strips and a method and an apparatus for the production thereof |
| US20070137166A1 (en) * | 2005-12-20 | 2007-06-21 | Bobby Carter | Devices and methods for heat-setting yarns |
Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3296677A (en) * | 1963-05-20 | 1967-01-10 | Eastman Kodak Co | Crimping apparatus and process |
Family Cites Families (21)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CA636054A (en) * | 1962-02-06 | Weiss Ernst | Method and apparatus for producing crimped yarn | |
| DD17786A (en) * | ||||
| DD20597A (en) * | ||||
| DE1004337B (en) * | 1943-03-06 | 1957-03-14 | Du Pont | Method for opening an endless, running strand of artificial thread |
| US2569700A (en) * | 1947-06-14 | 1951-10-02 | Owens Corning Fiberglass Corp | Method of making colored glass fibers |
| DE971078C (en) * | 1949-10-09 | 1959-01-15 | Hoechst Ag | Process for the production of crimped fibers from a tow made of polymeric ªŠ-caprolactam |
| NL79301C (en) * | 1950-10-04 | |||
| US2914835A (en) * | 1954-03-04 | 1959-12-01 | Owens Corning Fiberglass Corp | Method of crimping fibrous glass strand |
| US2854729A (en) * | 1955-04-21 | 1958-10-07 | Bancroft & Sons Co J | Crimping apparatus |
| BE555458A (en) * | 1956-03-07 | |||
| NL207405A (en) * | 1956-05-24 | |||
| NL228434A (en) * | 1957-06-05 | |||
| GB873368A (en) * | 1957-07-16 | 1961-07-26 | British Celanese | Improvements relating to the crimping of textile fibres |
| NL112601C (en) * | 1959-03-04 | |||
| FR1279122A (en) * | 1960-03-04 | 1961-12-15 | Glanzstoff Ag | Method and apparatus for continuous drying and fixing of crimped tapes of endless synthetic yarns |
| FR1264506A (en) * | 1960-04-27 | 1961-06-23 | Rhodiaceta | Process for crimping yarns based on thermoplastic polymers and new yarns obtained |
| US3099594A (en) * | 1960-05-05 | 1963-07-30 | Eastman Kodak Co | Method for blooming filter tow |
| US3055080A (en) * | 1960-07-19 | 1962-09-25 | Du Pont | Apparatus for fluid treatment of tow and yarn bundles |
| NL273433A (en) * | 1961-01-12 | |||
| US3099064A (en) * | 1961-04-13 | 1963-07-30 | Eastman Kodak Co | Method and apparatus for making rug yarn |
| US3103731A (en) * | 1961-09-18 | 1963-09-17 | Eastman Kodak Co | Textile apparatus for bulking yarns and process |
-
0
- BE BE613495D patent/BE613495A/xx unknown
- BE BE632803D patent/BE632803A/xx unknown
- NL NL292987D patent/NL292987A/xx unknown
-
1962
- 1962-02-08 GB GB4957/62A patent/GB953782A/en not_active Expired
- 1962-02-08 CH CH157262A patent/CH378459A/en unknown
- 1962-02-08 CH CH1070162A patent/CH387868A/en unknown
- 1962-02-08 DE DE1435653A patent/DE1435653C2/en not_active Expired
-
1963
- 1963-05-24 GB GB20941/63A patent/GB977937A/en not_active Expired
-
1964
- 1964-03-16 NL NL6402767A patent/NL6402767A/xx unknown
- 1964-03-16 NL NL646402768A patent/NL141588B/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1964-03-23 BE BE645601D patent/BE645601A/xx unknown
- 1964-03-24 DE DE19641435679 patent/DE1435679A1/en active Pending
- 1964-03-24 GB GB12463/64A patent/GB988140A/en not_active Expired
- 1964-03-24 DE DE1964S0090186 patent/DE1435678A1/en active Pending
- 1964-03-25 CH CH383664A patent/CH461696A/en unknown
- 1964-03-27 US US355379A patent/US3373470A/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
-
1968
- 1968-01-03 US US695511A patent/US3482294A/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
Patent Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3296677A (en) * | 1963-05-20 | 1967-01-10 | Eastman Kodak Co | Crimping apparatus and process |
Cited By (16)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE2116274C3 (en) | 1970-04-06 | 1979-06-21 | John Heathcoat & Co. Ltd., Tiverton, Devon (Grossbritannien) | Device for the production of a loosened, crimped multifilament yarn |
| DE2167095C2 (en) * | 1970-04-06 | 1984-12-13 | John Heathcoat & Co. Ltd., Tiverton, Devon | Process for the production of a loosened, crimped multi-ply yarn |
| US3832759A (en) * | 1970-05-01 | 1974-09-03 | Akzona Inc | Process and apparatus for texturizing yarn |
| US3712526A (en) * | 1970-09-18 | 1973-01-23 | Elitex Z Textilniko Strojirens | Device for storing a transported weft thread |
| US3911538A (en) * | 1970-10-15 | 1975-10-14 | Rhone Poulenc Textile | Apparatus for texturizing a plurality of yarns simultaneously |
| US3729831A (en) * | 1970-12-07 | 1973-05-01 | Mitsubishi Rayon Co | Process and apparatus for continuously relaxing textile yarns |
| US3707745A (en) * | 1970-12-16 | 1973-01-02 | Phillips Petroleum Co | Yarn texturing |
| US3840950A (en) * | 1973-03-22 | 1974-10-15 | Textured Yarn Co | Strand treatment apparatus |
| US3879821A (en) * | 1973-03-22 | 1975-04-29 | Textured Yarn Co | Strand treatment apparatus |
| US4083208A (en) * | 1975-07-10 | 1978-04-11 | Carl Lennart Ekstroem | Apparatus for the wet treatment of textiles |
| EP0049052A1 (en) * | 1980-09-04 | 1982-04-07 | Plasticisers Limited | Yarn crimping by means of a stuffer-box |
| US4691947A (en) * | 1985-01-19 | 1987-09-08 | Barmag Ag | Yarn texturing nozzle |
| US4724588A (en) * | 1985-07-20 | 1988-02-16 | Barmag Ag | Yarn texturing nozzle |
| US5054173A (en) * | 1989-05-18 | 1991-10-08 | Barmag Ag | Method and apparatus for the enhanced crimping of multifilament yarn |
| US20160319469A1 (en) * | 2014-01-02 | 2016-11-03 | American Linc Corp. | Textile stuffer box and method for texturing yarn |
| US10214837B2 (en) * | 2014-01-02 | 2019-02-26 | American Linc, Llc | Textile stuffer box and method for texturing yarn |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| NL6402768A (en) | 1964-09-28 |
| DE1435653C2 (en) | 1980-02-07 |
| BE632803A (en) | |
| DE1435678A1 (en) | 1976-06-24 |
| GB977937A (en) | 1964-12-16 |
| BE613495A (en) | |
| DE1435679A1 (en) | 1969-04-10 |
| CH461696A (en) | 1968-10-31 |
| CH378459A (en) | 1964-02-28 |
| BE645601A (en) | 1964-09-23 |
| NL141588B (en) | 1974-03-15 |
| NL292987A (en) | |
| NL6402767A (en) | 1964-09-28 |
| CH387868A (en) | 1965-02-15 |
| CH383664A4 (en) | 1968-05-15 |
| US3373470A (en) | 1968-03-19 |
| GB988140A (en) | 1965-04-07 |
| GB953782A (en) | 1964-04-02 |
| DE1435653B1 (en) | 1973-12-06 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US3482294A (en) | Apparatus for fluid treating filamentary materials | |
| US3343240A (en) | Method and apparatus for bulking synthetic fibers | |
| US2584043A (en) | Method and apparatus for processing filamentary materials | |
| US3417445A (en) | Method and apparatus for producing a voluminous yarn with uniformly spaced bindings | |
| US3545057A (en) | Yarn treating apparatus | |
| US3810285A (en) | Method of producing bulked yarns | |
| US5579566A (en) | Apparatus and method for stuffer box crimping synthetic filament yarns | |
| GB941931A (en) | Manufacture of bulked yarn from synthetic continuous thermoplastic filaments | |
| US3778872A (en) | Method and apparatus for texturing yarn | |
| US3703753A (en) | Method for producing a bulked yarn and apparatus therefor | |
| US3303546A (en) | Apparatus for treating filamentary material in a fluid | |
| US4059068A (en) | Apparatus for treating filamentary products | |
| US2994938A (en) | Yarn-treating apparatus | |
| US3363041A (en) | Method of jet crimping for texturing thermoplastic yarn | |
| US3389445A (en) | Moving side wall crimping process and apparatus therefor | |
| US3576058A (en) | Process and apparatus for the continuous compression crimping and setting of a multifilament yarn | |
| US4020196A (en) | Process for treating filamentary products | |
| US3831231A (en) | Method for producing a yarn having latent bulking characteristics | |
| US4141121A (en) | Apparatus for producing fluid jet teased yarns from short/medium staple multifiber spun yarns | |
| US3413697A (en) | Apparatus for production of high-shrink yarn | |
| US3478401A (en) | Method and apparatus for treating textile yarn | |
| US3895420A (en) | Process for crimping filaments and yarns | |
| GB1242758A (en) | Continuously fixing and shrinking tows | |
| US3678549A (en) | Process for the manufacture of high-bulk yarn | |
| US2997771A (en) | Apparatus for the production of bulky yarns |