US20200146259A1 - Swine activated feeder with actuation sensor - Google Patents
Swine activated feeder with actuation sensor Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- US20200146259A1 US20200146259A1 US16/678,031 US201916678031A US2020146259A1 US 20200146259 A1 US20200146259 A1 US 20200146259A1 US 201916678031 A US201916678031 A US 201916678031A US 2020146259 A1 US2020146259 A1 US 2020146259A1
- Authority
- US
- United States
- Prior art keywords
- feeder
- feed
- dispenser
- animal
- sensor
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Abandoned
Links
- 241000282898 Sus scrofa Species 0.000 title claims abstract description 23
- 241001465754 Metazoa Species 0.000 claims abstract description 43
- 230000003031 feeding effect Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 21
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 10
- 230000005355 Hall effect Effects 0.000 claims description 6
- 230000001815 facial effect Effects 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 claims description 2
- 238000012544 monitoring process Methods 0.000 abstract description 4
- 230000009471 action Effects 0.000 abstract description 2
- 230000004913 activation Effects 0.000 abstract 1
- 230000035935 pregnancy Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000003756 stirring Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000005484 gravity Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000036541 health Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000006872 improvement Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000002699 waste material Substances 0.000 description 3
- 241000282887 Suidae Species 0.000 description 2
- 238000009313 farming Methods 0.000 description 2
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000007792 addition Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004140 cleaning Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000151 deposition Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000011156 evaluation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012840 feeding operation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000002445 nipple Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 238000010079 rubber tapping Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000006467 substitution reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000011144 upstream manufacturing Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A01—AGRICULTURE; FORESTRY; ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; HUNTING; TRAPPING; FISHING
- A01K—ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; AVICULTURE; APICULTURE; PISCICULTURE; FISHING; REARING OR BREEDING ANIMALS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; NEW BREEDS OF ANIMALS
- A01K5/00—Feeding devices for stock or game ; Feeding wagons; Feeding stacks
- A01K5/02—Automatic devices
- A01K5/0225—Gravity replenishment from a reserve, e.g. a hopper
- A01K5/0241—Gravity replenishment from a reserve, e.g. a hopper dispensing by means of stirring mechanisms or agitators operated by the animal
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A01—AGRICULTURE; FORESTRY; ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; HUNTING; TRAPPING; FISHING
- A01K—ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; AVICULTURE; APICULTURE; PISCICULTURE; FISHING; REARING OR BREEDING ANIMALS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; NEW BREEDS OF ANIMALS
- A01K11/00—Marking of animals
- A01K11/006—Automatic identification systems for animals, e.g. electronic devices, transponders for animals
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A01—AGRICULTURE; FORESTRY; ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; HUNTING; TRAPPING; FISHING
- A01K—ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; AVICULTURE; APICULTURE; PISCICULTURE; FISHING; REARING OR BREEDING ANIMALS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; NEW BREEDS OF ANIMALS
- A01K29/00—Other apparatus for animal husbandry
- A01K29/005—Monitoring or measuring activity, e.g. detecting heat or mating
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A01—AGRICULTURE; FORESTRY; ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; HUNTING; TRAPPING; FISHING
- A01K—ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; AVICULTURE; APICULTURE; PISCICULTURE; FISHING; REARING OR BREEDING ANIMALS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; NEW BREEDS OF ANIMALS
- A01K5/00—Feeding devices for stock or game ; Feeding wagons; Feeding stacks
- A01K5/02—Automatic devices
- A01K5/0225—Gravity replenishment from a reserve, e.g. a hopper
- A01K5/0233—Gravity replenishment from a reserve, e.g. a hopper dispensing by dosing means actively operated by the animal
Definitions
- feeding systems include community self-feeding wherein numerous animals feed at a common station, or alternatively, individual stall feeders in the gestation barn. Transitioning from the group feeding to the individual feeder may be problematic or difficult for some animals, if they over-feed or under-feed. Therefore, to optimize the overall farming operation, it is important to monitor or track the feeding activity of the individual animals.
- a primary objective of the present invention is the provision of a sensor associated with a swine-powered self-feeder to monitor feeding activity of individual swine.
- Another objective of the present invention is a provision of a method of tracking feeding activity of individual swine, by sensing actuation of a swine-powered dispenser on a self-feeder so as to generate data for evaluation of the feeding activity for an individual animal.
- a further objective of the present invention is the provision of a feeding system to track individual animal feeding activities.
- Yet another objective of the present invention is a provision of an improvement to a swine-activated self-feeder utilizing a sensor to monitor an individual animal.
- a further objective of the present invention is the provision of a feeding activity sensor which tracks different animals via RFID technology, or by facial or body recognition.
- Still another objective of the present invention is a provision of an animal feeder having a feed dispenser movable by the animal to discharge feed from a feed supply line and a sensor operatively connected to the dispenser to generate a signal in response to movement of the dispenser by the animal, to thereby track the feeding activity and measure the amount of feed consumed by the animal.
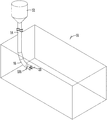
- FIG. 1 is a schematic sketch of a farrowing crate having a conventional feed hopper and drop tube, with the dispenser in the lower end of the tube for actuation by a swine, and a sensor on the dispenser, according to the present invention.
- FIG. 2 is an enlarged view of the lower end of the drop tube with a rotatable dispenser for actuation by the swine, and the sensor.
- FIG. 3A is an end view of the tube and dispenser with the spokes in a first position.
- FIG. 3B is a view similar to FIG. 3A with the spokes in a second rotated position.
- FIG. 4 is a sectional view of the dispenser taken along lines 4 - 4 of FIG. 3A .
- FIG. 5 is a sectional view of the dispenser taken along lines 5 - 5 of FIG. 2 .
- FIG. 6 is a front view of an individual feed station having a self-activated feed tube and sensor according to the present invention.
- FIG. 7 is a rear perspective view of the feed station of FIG. 6 .
- FIG. 8 is another view showing the sensor and circuit board, according to the present invention.
- FIG. 9 is an alternative view of the feed dispense with a vertical orientation.
- FIG. 10 is a close-up view showing the feed dispenser for the vertical feeding tube shown in FIG. 9 and having a magnet on the rotatable fin for sensing by a Hall-effect sensor.
- FIG. 11 is a schematic flow chart of one embodiment of the sensor and controls of the present invention.
- FIG. 12 is another schematic flow chart of a second embodiment of the invention for use with an RFID tag on an animal.
- the present invention is directed toward an improvement to Applicant's sow gestation and farrowing tube feeder shown and described in U.S. Pat. No. 9,220,236, which is incorporated herein by reference in its entirety.
- a conventional sow farrowing crate is schematically shown in FIG. 1 and designated by the reference numeral 10 .
- the stall 10 is one of many placed side-by-side in a gestation barn.
- a feeding system in the barn provides feed for each stall 10 .
- the feeding system for each stall 10 includes a hopper 12 with a gravity drop tube 14 having a lower end 16 adjacent the floor of the stall 10 .
- the hopper 12 can be loaded in a known manner, such as by an auger system or manual filling, so that feed fills the tube 14 .
- the feed system may be utilized with a feed station 11 ( FIGS. 6-8 ) with the tube 14 depositing feed into a pan or bowl 18 near the bottom or floor of the feed station.
- the feed station may also include a water line 15 to provide water into the bowl 18 via a hog-activated nipple in the end of the line 15 .
- the feed tube dispenser 20 is in the form of an insert which fits into the lower end 16 of the tube 14 so as to convert the tube 14 from a standard gravity drop system to a self-feeding or ad libitum system. More particularly, the dispenser 20 includes a cylindrical body or housing 22 which matingly fits inside the lower end 16 of the tube 14 , as best seen in FIG. 4 .
- the body 22 may be secured, latched, or fixed in the tube 14 by a set screw 24 , a self-tapping screw, or any other convenient means. Preferably, the screw 24 does not extend through the body 22 .
- the body 22 includes an upper plate 26 and a lower plate 28 fixed at the opposite ends of the body.
- the upper plate has a feed inlet 30 preferably located on a lower portion of the plate, for example, at the 6 o'clock position.
- the lower plate 28 has a feed outlet 32 on an upper portion of the plate, for example, at the 12 o'clock position.
- the inlet 30 and outlet 32 are offset with respect to one another.
- the plates 26 , 28 rotatably support an axle 34 extending through the plates.
- a plurality of fins 36 extends radially outwardly from the axle 34 and have outer edges in close proximity to the interior wall of the body 22 , as best seen in FIG. 5 .
- a washer 38 is mounted on the axle 34 adjacent the plates 26 , 28 , so as to space the upper and lower ends of the fins 36 from the plates 26 , 28 , as shown in FIG. 4 .
- a spinner or actuator comprising a plurality of spokes 40 extends radially outwardly from the lower end of the axle 34 , outside of the body 22 .
- the outer ends of the spokes 40 extend beyond the perimeter of the body 22 . While the drawings show four spokes 40 , it is understood that the number and shape of spokes 40 may vary from that shown in the drawings.
- a stirring device 42 such as a bar or finger, is fixed on the upper end of the axle 34 so as to rotate with the axle.
- the bar 42 resides upstream from the upper plate 26 so as to stir feed in the tube 14 , and thereby prevent clogging or bridging of the feed within the tube 14 .
- the stirring device 42 may be any shape, or size, or material to stir the feed in the tube 14 , including a rigid or flexible member.
- the feeding system has a vertical tube 14 A connected to the hopper, and the dispenser 20 A has an upper inlet 20 A and a lower outlet 32 A, shown in FIG. 10 .
- the dispenser 20 A functions similarly to the dispenser 20 to provide feed on demand when the animal spins the spokes 40 , so that feed drops from the tube outlet 15 A.
- the vertical orientation allows feed chambers in the dispenser to be filled completely for better feed flow and measuring of feed passing through the dispenser 20 A, as compared to the sloped dispenser 20 of FIGS. 1-8 .
- the dispenser 20 In use, when the dispenser 20 is installed in the tube 14 , the plates 26 , 28 effectively close the lower end of the tube 14 , which is normally open in a conventional drop tube feeder. Thus, the dispenser 20 prevents feed from being discharged from the tube 14 until a gilt or sow in the stall 10 nudges the spokes 40 to rotate the axle 34 . Such rotation of the axle 34 also rotates the attached fins 36 , such that feed which has entered the body 22 of the dispenser 20 through the inlet 30 in the upper plate 26 is carried upwardly by the fins 36 along the inner wall of the body 22 for discharge through the feed outlet 32 in the lower plate 28 . Since the tube 14 is angled downwardly, as seen in FIGS.
- feed carried by the fins 36 to the outlet 32 will discharge by gravity over the spokes 40 and onto the floor of the stall or feed pan or bowl 18 for consumption by the gilt or sow.
- the depth of the spokes 40 carries the feed beyond the lower plate 28 so as to deposit the feed further from the lower end 16 of the tube 14 , for easier access by the gilt or sow or growing market hog.
- the structure of the various components of the dispenser 20 can be modified without departing from the scope of the present invention.
- the upper end of the body 22 is shown to be cut at an angle of approximately 45° which facilitates assembly of the body 22 inside the tube 14 .
- This angle can be more or less than that shown in the drawings or can be eliminated.
- the shape of the fins 36 may be modified, such as a curved, cup-like surface, or maybe an auger flighting to carry feed from the inlet 30 to the outlet 32 .
- the device 20 can be quickly and easily retrofit into the feed tube 14 for each stall or crate 10 in a gestation or farrowing barn. While the volume of the feed provided to the gilt or sow is controlled by the volume in the hopper 12 , the gilt or sow controls the timing of the feed discharge into the bowl or pan 18 by actuation of the spokes 40 . Since the gilt or sow will actuate the self-feeder device 20 of the present invention when she is hungry, the animal will consume the discharged feed, substantially reducing or eliminating feed waste which occurs with a conventional drop feed system. Also, since there is no waste feed being washed out of the stall or crate 10 by the cleaning system, clogging of drain troughs by waste feed is eliminated, thereby saving labor costs and time.
- a sensor assembly 100 is provided on the feed tube 14 .
- the assembly 100 includes a Hall-effect sensor 102 mounted on the feed tube 14 , a magnet 104 mounted on one of the fins 36 , and a printed circuit board (PCB) 106 operatively connected to the sensor 102 via wires 102 or wirelessly.
- PCB printed circuit board
- the sensor assembly 100 is mounted on the rear end of the dispense 20 A, rather than on the tube 14 .
- the circuit board 106 logs the rotations of the spokes 40 and transmits this data wirelessly to a computer or microprocessor, such as CPU 108 , or to a website which can then provide feedback to the operator regarding the individual animal's feeding activity.
- a computer or microprocessor such as CPU 108
- a website which can then provide feedback to the operator regarding the individual animal's feeding activity.
- a website is www.thingspeak.com, which is an open IoT analytics platform which allows data to be collected for private or public use, via the cloud.
- the data is transmitted via the circuit board 106 to the processor or microprocessor 108 , which stores the data and generates reports 110 on demand.
- the reports can be a plot for each feeder, showing a timeline of when each sow or pig activated the spokes 40 of the specific feeder.
- the plots and other data generated by the sensor 102 and circuit board 106 can be used to evaluate whether individual animals are under-feeding or over-feeding, so that corrective action can be taken.
- the sensor assembly 100 can be used on a community feeding station in conjunction with an additional identification device 112 to identify specific sows or growing pigs for monitoring their respective individual feeding activity.
- the device 112 can be an RFID tag with each sow or pig can have a personalized RFID tag which is detected in a known manner when the animal activates the dispenser 20 .
- the device 112 can be a camera for individual animal recognition, such as facial and body recognition.
- the sensor assembly 100 can provide specific feeding activity information and data regarding each animal which uses a common feeder.
- the sensor assembly may also be used on each feeder station as shown in Applicant's co-pending application Ser. No. 16/415,407 filed on May 17, 2019, entitled Wet/Dry Feeder for Swine, and incorporated herein by reference in its entirety.
- the sensor assembly 100 of the present invention allows the farmer or operator to track or monitor individual feeding activity in both separate feeder stalls or community feeding environments. The individual feeding activity can be plotted or charted, and notifications can be sent to the operator to provide alerts for changes in feeding activity for specific animals.
- the feed system of the present invention can be used to report the amount of feed dispensed into individual feeder, pen, or whole barn which aids in feed inventory tracking, feed ordering, and evaluating health of the barn or individual pigs being tracked.
- the feed system can also be used to report the size of the individual pig being tracked based on how much feed has been consumed.
- feed monitoring system and method of the present invention can be used for similar feed systems used by animals other than swine, wherein the animal manually actuates dispensement of feed on an individual, ad lib basis, rather than a motorized or timed feed dispensing system.
Landscapes
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Environmental Sciences (AREA)
- Animal Husbandry (AREA)
- Biodiversity & Conservation Biology (AREA)
- Birds (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Feeding And Watering For Cattle Raising And Animal Husbandry (AREA)
- Zoology (AREA)
Abstract
A sensor assembly on a swine-activated self-feeder allows monitoring or tracking of individual animal feeding activity, thereby allowing corrective action to be taken in instances of under-feeding or over-feeding by an animal. The sensor assembly includes a sensor on the feed dispenser and, with a printed circuit board to generate a signal corresponding to activation of the dispenser by an animal. The signal can be sent to a computer or website which generates reports on the individual animal's feeding activity.
Description
- This application claims priority to Provisional Application U.S. Ser. No. 62/757,464, filed on Nov. 8, 2018, which is herein incorporated by reference in its entirety.
- In the hog industry, proper feeding of gilts and sows is important to the health of the animal, as well as the overall productivity and profitability of the farming operation. As described in Applicant's U.S. Pat. No. 9,220,236 issued on Dec. 29, 2015, feeding systems include community self-feeding wherein numerous animals feed at a common station, or alternatively, individual stall feeders in the gestation barn. Transitioning from the group feeding to the individual feeder may be problematic or difficult for some animals, if they over-feed or under-feed. Therefore, to optimize the overall farming operation, it is important to monitor or track the feeding activity of the individual animals.
- Accordingly, a primary objective of the present invention is the provision of a sensor associated with a swine-powered self-feeder to monitor feeding activity of individual swine.
- Another objective of the present invention is a provision of a method of tracking feeding activity of individual swine, by sensing actuation of a swine-powered dispenser on a self-feeder so as to generate data for evaluation of the feeding activity for an individual animal.
- A further objective of the present invention is the provision of a feeding system to track individual animal feeding activities.
- Yet another objective of the present invention is a provision of an improvement to a swine-activated self-feeder utilizing a sensor to monitor an individual animal.
- A further objective of the present invention is the provision of a feeding activity sensor which tracks different animals via RFID technology, or by facial or body recognition.
- Still another objective of the present invention is a provision of an animal feeder having a feed dispenser movable by the animal to discharge feed from a feed supply line and a sensor operatively connected to the dispenser to generate a signal in response to movement of the dispenser by the animal, to thereby track the feeding activity and measure the amount of feed consumed by the animal.
- These and other objectives become apparent from the following description of the invention.
-
FIG. 1 is a schematic sketch of a farrowing crate having a conventional feed hopper and drop tube, with the dispenser in the lower end of the tube for actuation by a swine, and a sensor on the dispenser, according to the present invention. -
FIG. 2 is an enlarged view of the lower end of the drop tube with a rotatable dispenser for actuation by the swine, and the sensor. -
FIG. 3A is an end view of the tube and dispenser with the spokes in a first position. -
FIG. 3B is a view similar toFIG. 3A with the spokes in a second rotated position. -
FIG. 4 is a sectional view of the dispenser taken along lines 4-4 ofFIG. 3A . -
FIG. 5 is a sectional view of the dispenser taken along lines 5-5 ofFIG. 2 . -
FIG. 6 is a front view of an individual feed station having a self-activated feed tube and sensor according to the present invention. -
FIG. 7 is a rear perspective view of the feed station ofFIG. 6 . -
FIG. 8 is another view showing the sensor and circuit board, according to the present invention. -
FIG. 9 is an alternative view of the feed dispense with a vertical orientation. -
FIG. 10 is a close-up view showing the feed dispenser for the vertical feeding tube shown inFIG. 9 and having a magnet on the rotatable fin for sensing by a Hall-effect sensor. -
FIG. 11 is a schematic flow chart of one embodiment of the sensor and controls of the present invention. -
FIG. 12 is another schematic flow chart of a second embodiment of the invention for use with an RFID tag on an animal. - The present invention is directed toward an improvement to Applicant's sow gestation and farrowing tube feeder shown and described in U.S. Pat. No. 9,220,236, which is incorporated herein by reference in its entirety.
- A conventional sow farrowing crate is schematically shown in
FIG. 1 and designated by thereference numeral 10. Thestall 10 is one of many placed side-by-side in a gestation barn. A feeding system in the barn provides feed for eachstall 10. More particularly, the feeding system for eachstall 10 includes ahopper 12 with agravity drop tube 14 having alower end 16 adjacent the floor of thestall 10. Thehopper 12 can be loaded in a known manner, such as by an auger system or manual filling, so that feed fills thetube 14. - As an alternative to the
crate 10, the feed system may be utilized with a feed station 11 (FIGS. 6-8 ) with thetube 14 depositing feed into a pan orbowl 18 near the bottom or floor of the feed station. The feed station may also include awater line 15 to provide water into thebowl 18 via a hog-activated nipple in the end of theline 15. - The
feed tube dispenser 20 is in the form of an insert which fits into thelower end 16 of thetube 14 so as to convert thetube 14 from a standard gravity drop system to a self-feeding or ad libitum system. More particularly, thedispenser 20 includes a cylindrical body orhousing 22 which matingly fits inside thelower end 16 of thetube 14, as best seen inFIG. 4 . Thebody 22 may be secured, latched, or fixed in thetube 14 by aset screw 24, a self-tapping screw, or any other convenient means. Preferably, thescrew 24 does not extend through thebody 22. - The
body 22 includes anupper plate 26 and alower plate 28 fixed at the opposite ends of the body. The upper plate has afeed inlet 30 preferably located on a lower portion of the plate, for example, at the 6 o'clock position. Thelower plate 28 has afeed outlet 32 on an upper portion of the plate, for example, at the 12 o'clock position. Thus, theinlet 30 andoutlet 32 are offset with respect to one another. Theplates axle 34 extending through the plates. A plurality offins 36 extends radially outwardly from theaxle 34 and have outer edges in close proximity to the interior wall of thebody 22, as best seen inFIG. 5 . Awasher 38 is mounted on theaxle 34 adjacent theplates fins 36 from theplates FIG. 4 . - A spinner or actuator comprising a plurality of
spokes 40 extends radially outwardly from the lower end of theaxle 34, outside of thebody 22. Preferably, the outer ends of thespokes 40 extend beyond the perimeter of thebody 22. While the drawings show fourspokes 40, it is understood that the number and shape ofspokes 40 may vary from that shown in the drawings. - A
stirring device 42, such as a bar or finger, is fixed on the upper end of theaxle 34 so as to rotate with the axle. Thebar 42 resides upstream from theupper plate 26 so as to stir feed in thetube 14, and thereby prevent clogging or bridging of the feed within thetube 14. The stirringdevice 42 may be any shape, or size, or material to stir the feed in thetube 14, including a rigid or flexible member. - In an alternative embodiment, shown in
FIG. 9 , the feeding system has avertical tube 14A connected to the hopper, and thedispenser 20A has anupper inlet 20A and alower outlet 32A, shown inFIG. 10 . Thedispenser 20A functions similarly to thedispenser 20 to provide feed on demand when the animal spins thespokes 40, so that feed drops from thetube outlet 15A. The vertical orientation allows feed chambers in the dispenser to be filled completely for better feed flow and measuring of feed passing through thedispenser 20A, as compared to thesloped dispenser 20 ofFIGS. 1-8 . - In use, when the
dispenser 20 is installed in thetube 14, theplates tube 14, which is normally open in a conventional drop tube feeder. Thus, thedispenser 20 prevents feed from being discharged from thetube 14 until a gilt or sow in thestall 10 nudges thespokes 40 to rotate theaxle 34. Such rotation of theaxle 34 also rotates the attachedfins 36, such that feed which has entered thebody 22 of thedispenser 20 through theinlet 30 in theupper plate 26 is carried upwardly by thefins 36 along the inner wall of thebody 22 for discharge through thefeed outlet 32 in thelower plate 28. Since thetube 14 is angled downwardly, as seen inFIGS. 1 and 4 , feed carried by thefins 36 to theoutlet 32 will discharge by gravity over thespokes 40 and onto the floor of the stall or feed pan orbowl 18 for consumption by the gilt or sow. Also, the depth of thespokes 40 carries the feed beyond thelower plate 28 so as to deposit the feed further from thelower end 16 of thetube 14, for easier access by the gilt or sow or growing market hog. - The structure of the various components of the
dispenser 20 can be modified without departing from the scope of the present invention. For example, as shown inFIG. 4 , the upper end of thebody 22 is shown to be cut at an angle of approximately 45° which facilitates assembly of thebody 22 inside thetube 14. This angle can be more or less than that shown in the drawings or can be eliminated. Also, the shape of thefins 36 may be modified, such as a curved, cup-like surface, or maybe an auger flighting to carry feed from theinlet 30 to theoutlet 32. - The
device 20 can be quickly and easily retrofit into thefeed tube 14 for each stall orcrate 10 in a gestation or farrowing barn. While the volume of the feed provided to the gilt or sow is controlled by the volume in thehopper 12, the gilt or sow controls the timing of the feed discharge into the bowl or pan 18 by actuation of thespokes 40. Since the gilt or sow will actuate the self-feeder device 20 of the present invention when she is hungry, the animal will consume the discharged feed, substantially reducing or eliminating feed waste which occurs with a conventional drop feed system. Also, since there is no waste feed being washed out of the stall orcrate 10 by the cleaning system, clogging of drain troughs by waste feed is eliminated, thereby saving labor costs and time. - The improvement to the tube feeder described above relates to a sensor and method for tracking or monitoring the feeding activity of individual sows or market hog. More particularly, as shown in
FIGS. 1-8 , asensor assembly 100 is provided on thefeed tube 14. In a preferred embodiment, theassembly 100 includes a Hall-effect sensor 102 mounted on thefeed tube 14, amagnet 104 mounted on one of thefins 36, and a printed circuit board (PCB) 106 operatively connected to thesensor 102 viawires 102 or wirelessly. One example of thesensor 102 which can be utilized in thesensor assembly 100 of the present invention, is the SR4 series Magneto Resistive Digital Position Sensor sold by Honeywell. See https://sensing.honeywell.com/SR4P3-A1-value-added-magnetic-sensors. - In the alternative vertical feed system of
FIG. 9 , thesensor assembly 100 is mounted on the rear end of the dispense 20A, rather than on thetube 14. - When the sow turns the
spokes 40 to dispense feed from thetube 14, themagnet 104 moves past thesensor 102 so as to generate a signal corresponding to the swine's actuation of the feeder system. Thecircuit board 106 logs the rotations of thespokes 40 and transmits this data wirelessly to a computer or microprocessor, such asCPU 108, or to a website which can then provide feedback to the operator regarding the individual animal's feeding activity. One example of such a website is www.thingspeak.com, which is an open IoT analytics platform which allows data to be collected for private or public use, via the cloud. The data is transmitted via thecircuit board 106 to the processor ormicroprocessor 108, which stores the data and generatesreports 110 on demand. For example, the reports can be a plot for each feeder, showing a timeline of when each sow or pig activated thespokes 40 of the specific feeder. The plots and other data generated by thesensor 102 andcircuit board 106 can be used to evaluate whether individual animals are under-feeding or over-feeding, so that corrective action can be taken. - In an alternative embodiment of the invention, the
sensor assembly 100 can be used on a community feeding station in conjunction with anadditional identification device 112 to identify specific sows or growing pigs for monitoring their respective individual feeding activity. For example, thedevice 112 can be an RFID tag with each sow or pig can have a personalized RFID tag which is detected in a known manner when the animal activates thedispenser 20. Another example is for thedevice 112 to be a camera for individual animal recognition, such as facial and body recognition. Thus, thesensor assembly 100 can provide specific feeding activity information and data regarding each animal which uses a common feeder. - For example, the sensor assembly may also be used on each feeder station as shown in Applicant's co-pending application Ser. No. 16/415,407 filed on May 17, 2019, entitled Wet/Dry Feeder for Swine, and incorporated herein by reference in its entirety. Thus, the
sensor assembly 100 of the present invention allows the farmer or operator to track or monitor individual feeding activity in both separate feeder stalls or community feeding environments. The individual feeding activity can be plotted or charted, and notifications can be sent to the operator to provide alerts for changes in feeding activity for specific animals. - It is understood that other types of motion sensors can be utilized, other than the Hall-
effect sensor 102 described above. Also, additional software can be developed to provide desired feedback regarding the sow feeding activity. Thus, the overall swine feeding operation can be closely monitored for improved animal health, productivity, and profitability. - The feed system of the present invention can be used to report the amount of feed dispensed into individual feeder, pen, or whole barn which aids in feed inventory tracking, feed ordering, and evaluating health of the barn or individual pigs being tracked. The feed system can also be used to report the size of the individual pig being tracked based on how much feed has been consumed.
- It is also understood that the feed monitoring system and method of the present invention can be used for similar feed systems used by animals other than swine, wherein the animal manually actuates dispensement of feed on an individual, ad lib basis, rather than a motorized or timed feed dispensing system.
- The invention has been shown and described above with the preferred embodiments, and it is understood that many modifications, substitutions, and additions may be made which are within the intended spirit and scope of the invention. From the foregoing, it can be seen that the present invention accomplishes at least all of its stated objectives.
Claims (22)
1. A swine-activated self-feeder, comprising:
a feed tube having a lower end;
a rotatable dispenser in the lower end of the feed tube to discharge feed from the tube when the dispenser is rotated by the swine;
a sensor associated with the dispenser to sense rotation of the dispenser so as to monitor feeding activity of the swine.
2. The self-feeder of claim 1 wherein the sensor includes a magnet on the dispenser and a counter on the feed tube.
3. The self-feeder of claim 1 further comprising a printed circuit board (PCB) mounted on the feed tube to gather dispenser rotation data.
4. The self-feeder of claim 3 further comprising a storage device operatively connected to the PCB to receive data from the PCB.
5. The self-feeder of claim 1 wherein the sensor is a Hall effect sensor.
6. The self-feeder of claim 1 further comprising an animal identification device to identify individual animals.
7. A method of tracking feeding activity of swine, comprising:
providing feed on demand from a self-feeder wherein the swing actuates discharge of feed from the self-feeder;
sensing swine actuation of the self-feeder;
generating data corresponding to the sensed swine actuation of the feeder; and
evaluating the data to track the swine feeding activity.
8. The method of claim 7 wherein the self-feeder is actuated by the swine rotating a dispenser in a lower end of the feed tube.
9. The method of claim 8 wherein the dispenser includes a magnet for sensing by a sensor to count rotations of the dispenser.
10. The method of claim 7 wherein the data includes time of day of actuation.
11. The method of claim 7 wherein the data includes frequency of actuation.
12. The method of claim 7 wherein the sensing step utilizes a Hall effect sensor.
13. The method of claim 7 further comprising identifying the swine with an RFID tag.
14. An animal feeder, comprising:
a food receptacle;
a feed supply line with an outlet to direct feed into the receptacle;
a dispenser in the outlet of the feed supply line;
the dispenser being movable by an animal to discharge feed from the feed supply line into the food receptacle; and
a sensor operatively connected to the dispenser to sense movement of the dispenser and generate a signal in response to the movement.
15. The animal feeder of claim 14 wherein the dispenser is rotatably mounted adjacent the outlet of the feed supply line.
16. The animal feeder of claim 14 wherein the signal represents feeding activity of the animal and the volume of feed dispensed.
17. The animal feeder of claim 14 further comprising a microprocessor to receive and store the signals from the sensor.
18. The animal feeder of claim 17 further comprising an identification device to identify each animal who uses the feeder.
19. The animal feeder of claim 18 wherein the identification device is an RFID tag on the animal.
20. The animal feeder of claim 18 wherein the identification device is a facial or body recognition camera.
21. The animal feeder of claim 14 wherein the sensor is a Hall effect sensor.
22. The animal feeder of claim 14 further comprising a PCB operatively connected to the sensor.
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US16/678,031 US20200146259A1 (en) | 2018-11-08 | 2019-11-08 | Swine activated feeder with actuation sensor |
| US17/655,264 US11684038B2 (en) | 2018-11-08 | 2022-03-17 | Swine activated feeder with actuation sensor |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US201862757464P | 2018-11-08 | 2018-11-08 | |
| US16/678,031 US20200146259A1 (en) | 2018-11-08 | 2019-11-08 | Swine activated feeder with actuation sensor |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US17/655,264 Division US11684038B2 (en) | 2018-11-08 | 2022-03-17 | Swine activated feeder with actuation sensor |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| US20200146259A1 true US20200146259A1 (en) | 2020-05-14 |
Family
ID=70552324
Family Applications (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US16/678,031 Abandoned US20200146259A1 (en) | 2018-11-08 | 2019-11-08 | Swine activated feeder with actuation sensor |
| US17/655,264 Active US11684038B2 (en) | 2018-11-08 | 2022-03-17 | Swine activated feeder with actuation sensor |
Family Applications After (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US17/655,264 Active US11684038B2 (en) | 2018-11-08 | 2022-03-17 | Swine activated feeder with actuation sensor |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (2) | US20200146259A1 (en) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US11039597B2 (en) * | 2018-12-18 | 2021-06-22 | Zaxe Technologies Inc. | Electronic animal feeding system |
| US11553690B2 (en) * | 2017-06-07 | 2023-01-17 | Delaval Holding Ab | Drop tube and a rotary parlour feeding provided with such a drop tube |
| US20230232784A1 (en) * | 2021-02-06 | 2023-07-27 | Shane D. Winn | Mounting and Adapting System for Animal Feeder Nozzle with Species-Selective Access |
Family Cites Families (40)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US1346784A (en) | 1919-04-08 | 1920-07-13 | Clayton R Hamilton | Self-feeder for swine |
| US2207395A (en) | 1938-07-11 | 1940-07-09 | George C Brown | Measuring and dispensing device |
| US2723783A (en) | 1952-06-11 | 1955-11-15 | Ewin Frank Ervin | Container and quantitative dispenser for soap powder and the like |
| US4270489A (en) | 1979-09-06 | 1981-06-02 | Joronen Osmo K | Fish-operated aquarium feeder |
| US4353329A (en) | 1980-07-17 | 1982-10-12 | Osborne Industries, Inc. | Rotary self-feeder |
| FR2563078B1 (en) | 1984-04-20 | 1987-02-06 | Nusse Bernard | SELF-CONDUCTIVE AUTOMATIC FEEDER |
| US4582023A (en) | 1984-11-14 | 1986-04-15 | Zumbahlen Equipment Company | Livestock self-feeder |
| DE4013008A1 (en) | 1990-04-24 | 1991-10-31 | Taschitzki Aratowerk | DEVICE FOR SELF-FEEDING FOR PETS, IN PARTICULAR PIGS |
| FR2689727B1 (en) | 1992-04-14 | 1994-07-08 | Legrain Michel A J | COMPUTER-SUPPORTED YOUNG ANIMAL FEEDING EQUIPMENT. |
| US5275130A (en) | 1992-09-08 | 1994-01-04 | Agri/$ense, Inc. | Animal feeder having animal actuated feed transport device between hopper and trough |
| US5335625A (en) * | 1993-04-29 | 1994-08-09 | Rawlings Richard T | Portable programmable liquid feed dispensing device |
| US5579719A (en) | 1995-04-06 | 1996-12-03 | Iowa State University Research Foundation, Inc. | Method and means for quasi ad-libitum feeding for gestation sows in loose housing |
| US5911195A (en) | 1997-04-28 | 1999-06-15 | The One Step Corporation | Apparatus for raising pigs including waste management and recycling |
| US5782201A (en) | 1997-07-01 | 1998-07-21 | Wells; John A. | Automated livestock feeding system |
| JP2004180543A (en) | 2002-11-29 | 2004-07-02 | Fujii Shokai:Kk | Feeder for livestock |
| US9802225B2 (en) | 2005-06-27 | 2017-10-31 | General Vibration Corporation | Differential haptic guidance for personal navigation |
| US20080252464A1 (en) * | 2007-04-13 | 2008-10-16 | Panasevich Michael R | Palatability monitoring system |
| GB0819220D0 (en) * | 2008-10-21 | 2008-11-26 | Laliberte Jean Charles | Automatic food dispenser |
| CN101861837A (en) | 2009-04-16 | 2010-10-20 | 杜骁释 | Automatic sow feeding management system |
| GB201000613D0 (en) | 2010-01-15 | 2010-03-03 | Pet Mate Ltd | Feeder |
| US20120116832A1 (en) | 2010-02-01 | 2012-05-10 | Dubinsky Ziv | Device, system and method for livestock feeding |
| EP2625664B1 (en) | 2010-10-07 | 2024-07-17 | Growsafe Systems Ltd. | Animal identification, measurement, monitoring and management system |
| US8453601B2 (en) | 2011-05-19 | 2013-06-04 | C-Lock Inc. | Vaccine and health-related applications for ruminant breath monitoring system |
| EP2876997B1 (en) | 2012-07-26 | 2016-09-07 | Powers, Kenneth | Automated animal feeding apparatus |
| US20150355003A1 (en) | 2013-01-11 | 2015-12-10 | Feedlogic Corporation | Accelerometer-based system for monitoring flow |
| US9220236B2 (en) * | 2013-03-20 | 2015-12-29 | Dave Klocke | Sow gestation tube feeder |
| GB201305725D0 (en) * | 2013-03-28 | 2013-05-15 | Univ Leuven Kath | Automated monitoring of animal nutriment ingestion |
| LT2983465T (en) | 2013-04-10 | 2021-02-10 | Viking Genetics Fmba | System for determining feed consumption of at least one animal |
| US20150373945A1 (en) * | 2014-06-26 | 2015-12-31 | Zillians Incorporated | Smart Animal Feeder |
| US11189368B2 (en) | 2014-12-24 | 2021-11-30 | Stephan HEATH | Systems, computer media, and methods for using electromagnetic frequency (EMF) identification (ID) devices for monitoring, collection, analysis, use and tracking of personal data, biometric data, medical data, transaction data, electronic payment data, and location data for one or more end user, pet, livestock, dairy cows, cattle or other animals, including use of unmanned surveillance vehicles, satellites or hand-held devices |
| CN204650323U (en) | 2015-04-02 | 2015-09-16 | 北京农学院 | Based on the intelligent pig raising system of wireless network |
| US10085419B2 (en) * | 2015-07-13 | 2018-10-02 | C-Lock Inc. | Modular livestock feed system for measuring animal intake and monitoring animal health |
| US11602281B2 (en) | 2015-11-02 | 2023-03-14 | North Carolina State University | Injectable sensors and methods of use |
| US10278363B2 (en) * | 2016-02-05 | 2019-05-07 | Lioness Feeding Technology Inc. | Method and system for providing controlled food portions to an animal and assessing the animal's health |
| US10674703B2 (en) * | 2016-03-23 | 2020-06-09 | Harold G. Monk | Species specific feeder |
| US10506793B2 (en) | 2016-09-30 | 2019-12-17 | Precisionzx Inc. | System and method for feeding animals |
| NZ752569A (en) | 2016-09-30 | 2022-01-28 | Prec Inc | System and method for feeding animals |
| CN206776432U (en) | 2017-05-08 | 2017-12-22 | 北京农业信息技术研究中心 | A kind of pig feeds system |
| US9848577B1 (en) | 2017-05-15 | 2017-12-26 | Herddogg, Inc. | Animal tag system |
| CN107331109A (en) | 2017-07-31 | 2017-11-07 | 重庆万建电子工程有限责任公司重庆第分公司 | A kind of intelligent monitor system and alarm method for animal feeding |
-
2019
- 2019-11-08 US US16/678,031 patent/US20200146259A1/en not_active Abandoned
-
2022
- 2022-03-17 US US17/655,264 patent/US11684038B2/en active Active
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US11553690B2 (en) * | 2017-06-07 | 2023-01-17 | Delaval Holding Ab | Drop tube and a rotary parlour feeding provided with such a drop tube |
| US11039597B2 (en) * | 2018-12-18 | 2021-06-22 | Zaxe Technologies Inc. | Electronic animal feeding system |
| US20230232784A1 (en) * | 2021-02-06 | 2023-07-27 | Shane D. Winn | Mounting and Adapting System for Animal Feeder Nozzle with Species-Selective Access |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US11684038B2 (en) | 2023-06-27 |
| US20220201974A1 (en) | 2022-06-30 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US11684038B2 (en) | Swine activated feeder with actuation sensor | |
| US10595507B2 (en) | Method and system for providing controlled food portions to an animal and assessing the animal's health | |
| EP3402323B1 (en) | Highly automated system and method of using the same to measure, monitor manage and control grazing environment and animals | |
| US6145472A (en) | Automatic feed distribution apparatus for animals | |
| AU2016214937B2 (en) | Automated method and system for feeding animals | |
| US6367417B1 (en) | Electronically controlled animal food dispenser | |
| US10631520B2 (en) | Automatic animal feeding system | |
| US20120325156A1 (en) | System and method for weight management of one or more pets | |
| US6615764B2 (en) | Device for automatically supplying a predetermined amount of feed to an animal in a period having a predetermined length | |
| EP3010333B1 (en) | Networked automatic animal feeding system | |
| KR101756360B1 (en) | Smart feeding device for pet and smart feeding system using the same | |
| US8245664B2 (en) | Animal monitoring method and apparatus | |
| US6619228B2 (en) | Device for automatically supplying a predetermined amount of at least one sort of feed to an animal in a predetermined period | |
| WO2010091686A1 (en) | An apparatus and method for surveillance of individual animals' liquid intake behaviour | |
| KR20120022035A (en) | Hog mix feeder | |
| KR20200091627A (en) | Automatic feeder for pets | |
| US6758163B1 (en) | Bird feeder | |
| WO2017080688A1 (en) | An animal drinking system | |
| US20170318779A1 (en) | Animal feed activity collection apparatuses, methods and systems | |
| US20150181837A1 (en) | Networked Automatic Animal Feeding System | |
| EP1527680B1 (en) | A device for and a method of automatically supplying feed to an animal | |
| Dawson | Equipment for feeding concentrates in and out of the parlour | |
| JP2002360097A (en) | Automatic feeder for small animal and feed therefor | |
| EP2898768B1 (en) | Feeding system for feeding piglets | |
| CA2933173A1 (en) | Method and system for providing controlled food portions to an animal and assessing the animal's health |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| STPP | Information on status: patent application and granting procedure in general |
Free format text: NON FINAL ACTION MAILED |
|
| STPP | Information on status: patent application and granting procedure in general |
Free format text: RESPONSE TO NON-FINAL OFFICE ACTION ENTERED AND FORWARDED TO EXAMINER |
|
| STPP | Information on status: patent application and granting procedure in general |
Free format text: NON FINAL ACTION MAILED |
|
| STPP | Information on status: patent application and granting procedure in general |
Free format text: RESPONSE TO NON-FINAL OFFICE ACTION ENTERED AND FORWARDED TO EXAMINER |
|
| STPP | Information on status: patent application and granting procedure in general |
Free format text: FINAL REJECTION MAILED |
|
| STCB | Information on status: application discontinuation |
Free format text: ABANDONED -- FAILURE TO RESPOND TO AN OFFICE ACTION |